- 1Department of Thoracic Surgery, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a rare pathological type of lung cancer, frequently associated with neuroendocrine symptoms such as hyponatremia. This article presents a case involving a 59-year-old male patient admitted to the hospital with neurological symptoms and severe hyponatremia. He was diagnosed with SCLC accompanied by syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) upon admission. Following oral and intravenous sodium supplementation, along with the administration of tolvaptan, the patient’s serum sodium levels increased. However, upon initiating chemotherapy, the patient’s hyponatremia worsened, leading to seizures and the need for ventilator support therapy. Despite normalization of serum sodium levels, the patient’s symptoms did not improve. Ultimately, due to the severity of the patient’s condition, the family elected to discontinue further medical intervention and proceeded with hospital discharge. Thus, in clinical practice, when encountering unexplained refractory hyponatremia with lung lesions, clinicians should consider the possibility of lung cancer with SIADH to ensure timely and precise treatment.
Introduction
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a distinct type of lung cancer known for its rapid growth, early metastasis, ectopic hormone secretion, and extrathoracic manifestations, with a notably poor prognosis. The release of endocrine-active substances by cancer cells often results in paraneoplastic syndromes, one of which is the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Clinically, a significant number of patients present with hyponatremia as the initial symptom, which can easily lead to misdiagnosis. We report a case involving a 59-year-old male who exhibited neuropsychiatric symptoms and developed severe hyponatremia due to SIADH. Pathological examination confirmed a diagnosis of SCLC. Based on our patient’s case, in patients with severe hyponatremia, it is crucial to consider whether the condition is caused by lung cancer-associated SIADH. Due to the rarity of this condition, clinicians should enhance their awareness to achieve early diagnosis and treatment.
Case presentation
A 59-year-old man was admitted to our hospital due to generalized weakness for 20 days, predominantly affecting the lower limbs, described as a sensation of walking on cotton. This condition worsened with nausea and vomiting for one day. The patient had a five-year history of hypertension, treated with oral irbesartan (75 mg daily), and diabetes, managed with oral metformin (0.85 mg bid). The patient denied any history of smoking. On physical examination, his pulse rate was 80 beats per minute, blood pressure was 120/80 mmHg, and body temperature was 36.4 °C. Neurologic examination was normal, and lung auscultation was unremarkable.
A head CT scan revealed multiple lacunar cerebral infarctions. An MRI showed multiple lacunar infarctions, softening foci, leukoaraiosis, and brain atrophy. A chest CT revealed a malignant lesion at the left pulmonary hilum, about 6 cm in diameter, invading the left pulmonary vessels, with multiple enlarged lymph nodes in both pulmonary hilums and the mediastinal space (Figure 1a). PET-CT indicated increased FDG metabolism in the mass near the left lung hilum, suggestive of malignancy with surrounding inflammation, and enlarged lymph nodes in the left hilum and mediastinum, suggestive of metastasis (Figure 1c).

Figure 1. (a) Patient’s chest CT after the admission showed the pulmonary consolidation in the left lung, enlarged lymph nodes in the hilum and mediastinum. (b) Patient’s chest CT after the treatment showed an increased pulmonary mass and lymph nodes. (c) Patient’s Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET CT) showed the pulmonary hypermetabolic consolidation (SUVmax=5.69), suggesting malignancy, and there are multiple high metabolic lymph nodes in the mediastinum and pulmonary hilum, indicating metastasis.
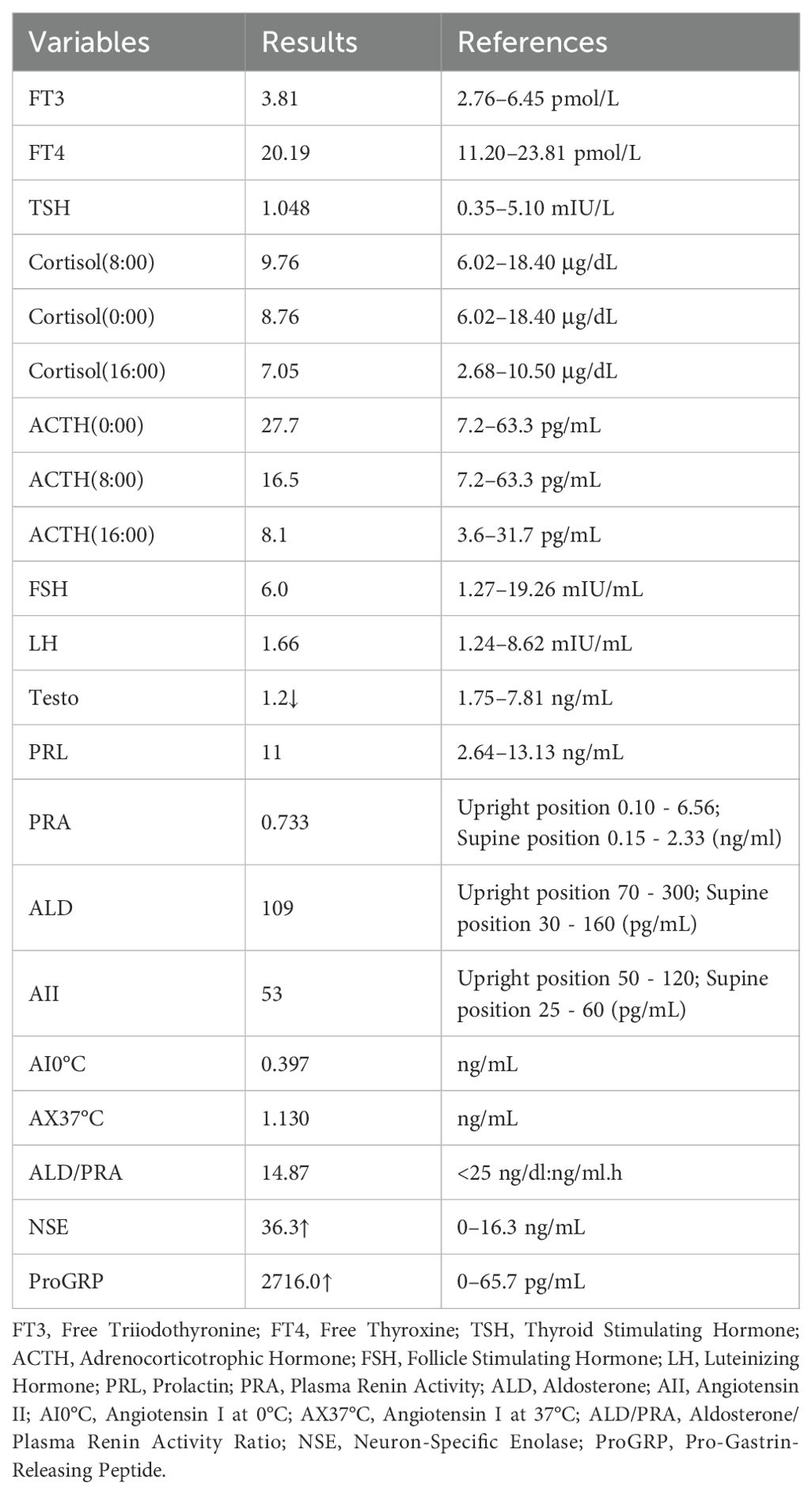
A blood ion assay revealed sodium at 123 mmol/L and chloride at 88.4 mmol/L. Lung cancer tumor markers showed a significant elevation in neuron-specific enolase level to 36.30 ng/mL. We considered the patient to have severe hyponatremia and initiated sodium supplementation to correct the electrolyte imbalance. Despite treatments, including a high-salt diet and intravenous hypertonic saline supplementation, blood sodium levels did not significantly increase. The patient’s 24-hour urinary sodium concentration was 251.2 mmol/L alongside severe hyponatremia. Some laboratory test results during treatment are shown in Table 1. Considering the patient’s condition, a pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor with SIADH was suspected.
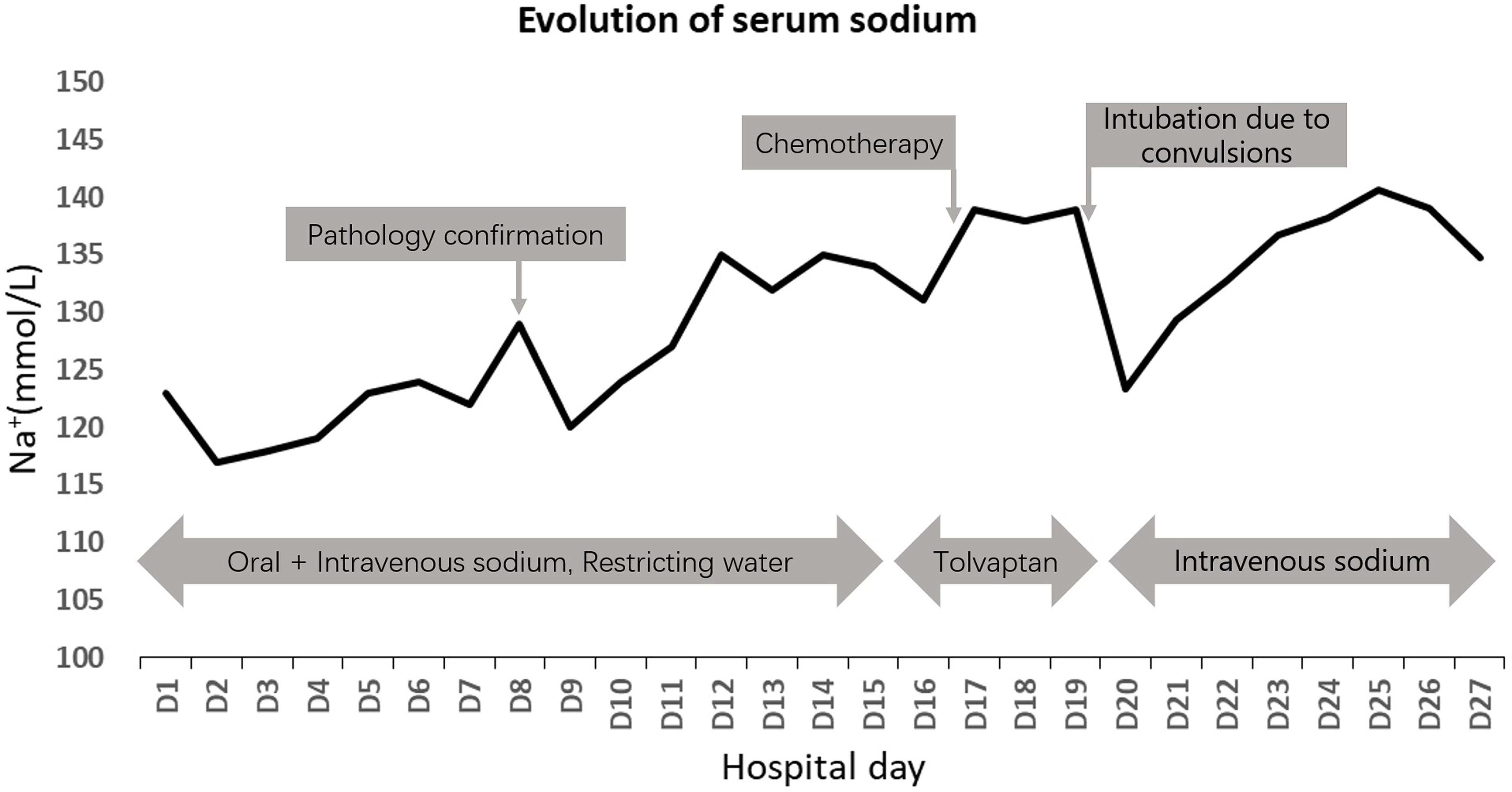
Subsequently, bronchoscopic biopsy confirmed SCLC in the bronchial mucosa and lymph nodes of the left upper lobe (Figures 2a, b). Oral tolvaptan (15 mg daily) was administered, normalizing serum sodium to 138.9 mmol/L. Soon after, the patient commenced the first chemotherapy cycle with Etoposide (70 mg daily), Lobaplatin (100 mg daily), and Adebrelimab (1200 mg single treatment). On the third day of chemotherapy, the patient suffered persistent seizures, accompanied by a drop in blood pressure and oxygen saturation, requiring intubation and transfer to the intensive care unit. A blood ion assay indicated sodium at 123 mmol/L compared to 138.9 mmol/L before chemotherapy. The patient’s comorbidities included severe hyponatremia, respiratory failure, acidosis, and hypoproteinemia. Intravenous hyperalimentation, sodium supplementation, and sodium valproate for seizure control and symptomatic treatment were administered.
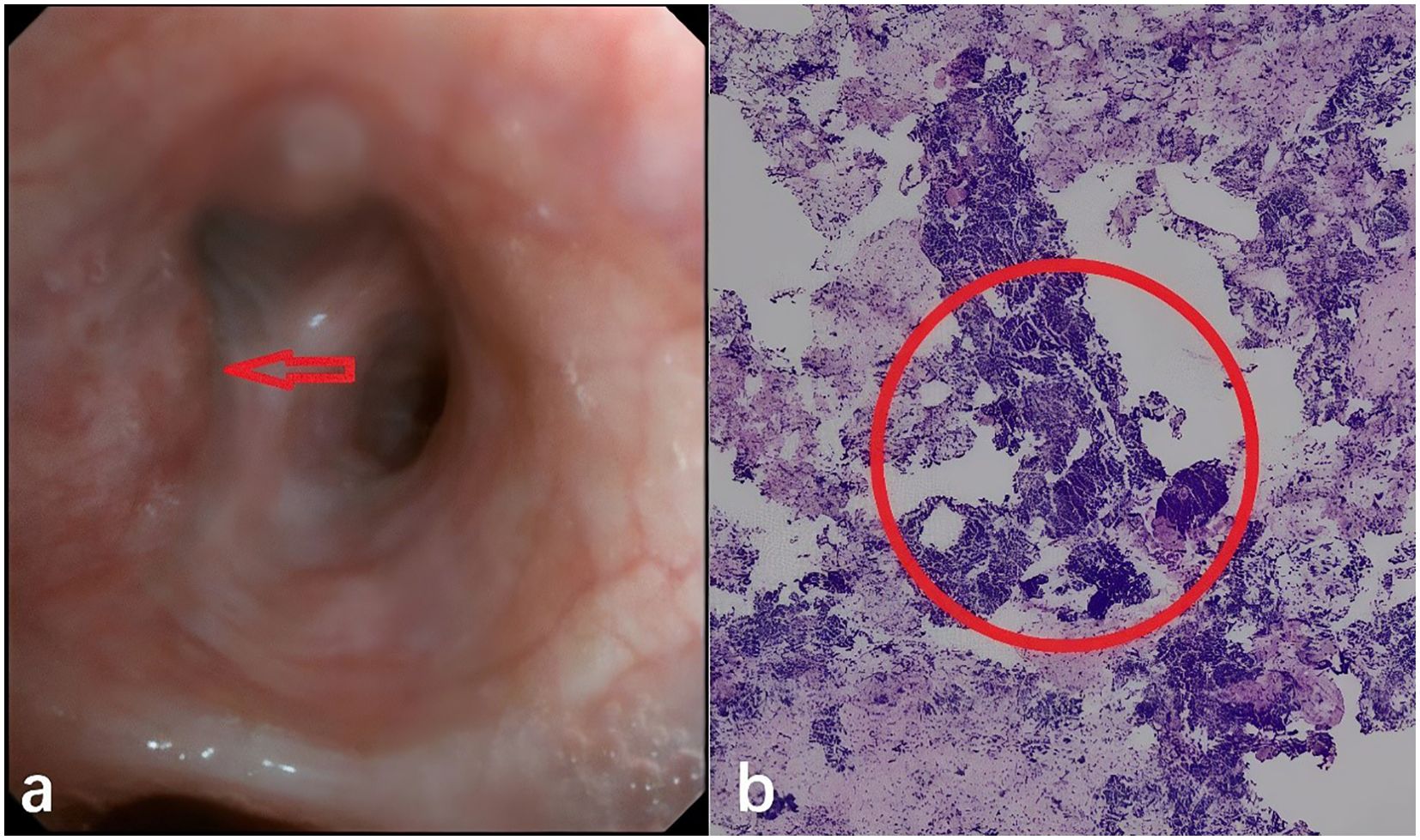
Figure 2. (a) Patient’s tracheoscopy picture at the trachea opening in the upper lobe of the left lung, the arrow indicates tumor invasion into the mucosal layer of the bronchus. (b) Patient’s pathological slides of seven groups of lymph node puncture biopsies performed by ultrasound tracheoscopy. Within the red circles, it’s shown that small, round, nest-like, and hyperchromatic neuroendocrine tumor cells.
A lumbar puncture found no tumor cells in cerebrospinal fluid pathology. A head CT scan review showed no new abnormalities. A chest CT scan revealed a slight tumor increase, with bronchial stenosis in the left lower lobe, pulmonary consolidation, and increased lymph node size in the hilar and mediastinal areas compared to previous scans (Figure 1b).
The patient continued to experience unexplained recurrent seizures despite hyponatremia correction and developed multiple complications such as pulmonary infection and respiratory failure. A comprehensive hospital consultation determined the patient was not an eligible candidate for chemotherapy. After family discussions, they decided to discontinue treatment and discharge the patient. Changes in blood sodium levels during treatment are shown in Figure 3.
Literature review
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and the Web of Science (WOS) databases for articles published up to July 2025. The search strategy utilized the following keywords: “small cell lung cancer”, “hyponatremia”, and “syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion”. Inclusion criteria were defined as follows: (1) Patients diagnosed with SCLC during a medical consultation. (2) Comprehensive clinical date. (3) Article type limited to case reports. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Articles published in languages other than English. (2) Duplicate publications.
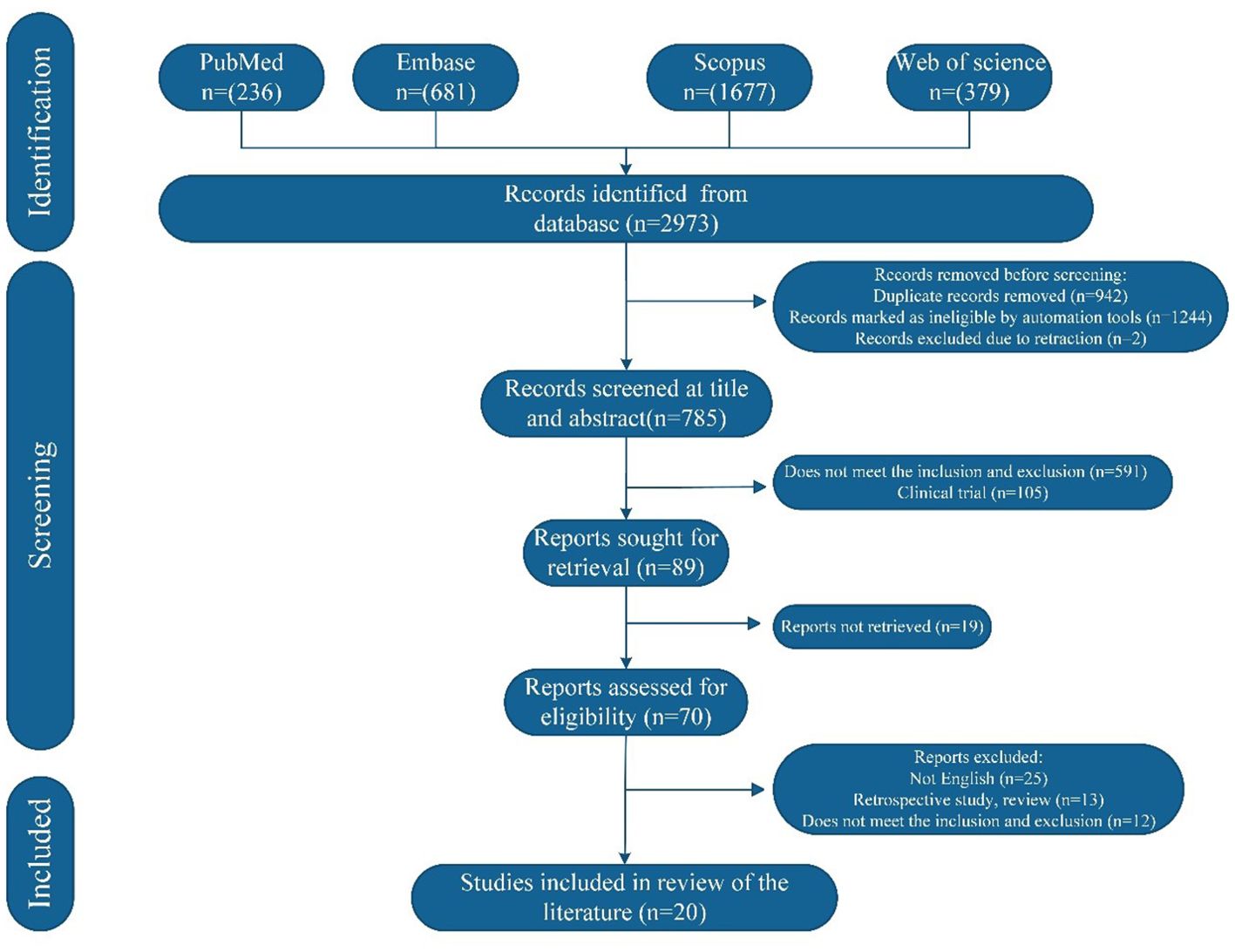
The initial search identified 2973 studies, of which 2188 were excluded before screening. After title and abstract screening, 89 studies were deemed potentially relevant and underwent full-text review. Following eligibility assessment, 20 studies met the inclusion criteria and a total of 23 cases were analyzed. The study selection process is summarized in Figure 4 and the demographic and clinical characteristics of the included patients are detailed in Table 2.
Discussion
SCLC accounts for 10%-15% of all primary bronchial lung cancers (21). It predominantly affects the large bronchi and is characterized by poor differentiation, rapid proliferation, high malignancy, and early hematogenous metastasis (22). Paraneoplastic syndromes affect approximately 10% of patients with lung cancer. Among the most frequently observed are humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy (HHM), commonly associated with squamous cell carcinoma, and the SIADH, frequently seen in SCLC (23). SCLC is the most common malignant tumor associated with paraneoplastic syndromes, with hyponatremia being one of the most frequent syndromes due to ectopic hormone secretion. A cohort study in Denmark, which included 6,995 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and 1,171 patients with SCLC, found that the incidence of hyponatremia was 16% in patients with NSCLC and 26% in patients with SCLC, with a significant association between hyponatremia and low survival rates (24). In NSCLC, the possibility of radical resection can play a pivotal role in resolving paraneoplastic syndromes, particularly when the underlying tumor is the primary driver of systemic manifestations. Surgical removal of the tumor often leads to rapid improvement or complete resolution of symptoms such as hypercalcemia or ectopic hormone production. However, paraneoplastic syndromes associated with SCLC are common but rarely amenable to surgical resolution due to the disease’s aggressive nature and frequent metastatic spread at diagnosis. Instead, systemic therapies—particularly chemotherapy—are typically required to control both the primary tumor and associated paraneoplastic manifestations such as SIADH or ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) production.
Causes of hyponatremia
Hyponatremia is common during cancer treatment and related to factors such as primary tumors, brain metastases, pituitary-thyroid-adrenal insufficiency, pneumonia and other lung diseases, SIADH, as well as chemotherapeutic, immunotherapeutic, and targeted drugs. The most severe and malignant cause of hyponatremia is primary malignant tumors, especially SCLC. Ezoe et al. analyzed 29 clinical trial reports and found that the incidence of hyponatremia after platinum-based chemotherapy regimens was 11.9% (25, 26). A case reported by Meena et al. described a 65-year-old patient with NSCLC who developed drowsiness after three weeks of gefitinib treatment and was diagnosed with severe hyponatremia, attributed to gefitinib-induced effects (27). Some studies have reported that immunotherapy may increase the risk of hyponatremia in lung cancer; for example, Nivolumab can induce adrenal insufficiency and hyponatremia (28).
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion
SIADH refers to excessive secretion or hyperactive function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or ADH-like substances, unregulated by negative feedback mechanisms, causing retention of water and sodium, resulting in dilutional hyponatremia. It can occur due to medications, malignant tumors, pulmonary diseases, infections, and central nervous system disorders (29). ADH is synthesized in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis). It plays a central role in maintaining fluid homeostasis by binding to receptors in the kidneys and promoting water reabsorption, thereby reducing free water excretion. Under normal physiological conditions, an increase in plasma osmolality beyond approximately 280 mOsm/kg stimulates ADH secretion, which facilitates water retention in the renal collecting ducts to maintain osmotic equilibrium. In SCLC, tumor cells aberrantly express ADH mRNA and ectopically secrete ADH, disrupting normal feedback control and leading to elevated circulating ADH levels. The resulting impaired free water clearance in the distal nephron contributes to dilutional hyponatremia. Interestingly, not all patients with SCLC-associated hyponatremia exhibit elevated plasma ADH levels. In some cases, tumor cells may instead express atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) mRNA and secrete ANP, which promotes natriuresis and contributes to hyponatremia via an alternative pathophysiological pathway (30, 31). In 1957, Schwartz et al. identified SIADH as primarily causing hyponatremia in pulmonary malignancies, with approximately 70% of related cases being SCLC. It results from tumor-induced ADH secretion, enhancing water reabsorption (32). Literature indicates SIADH complicating SCLC in 10-16% of cases, and 2-4% in NSCLC{sp} (4, 33, 34){/sp}. SIADH symptoms may precede, coincide with, or follow lung cancer symptoms, often leading to misdiagnosis due to their atypical nature. The diagnosis of SIADH is based on specific laboratory findings, including: 1) Serum sodium <130 mmol/L, plasma osmolality <275 mOsm/kg; 2) Urine osmolality >100 mOsm/kg; 3) Normal blood volume; 4) Urinary sodium concentration >30 mmol/L with normal salt intake; 5) Normal thyroid, adrenal, and kidney function (35).
SIADH represents the most prevalent neuroendocrine paraneoplastic syndromes associated with SCLC, with up to 15% of SCLC exhibiting SIADH, which contributes to a poorer prognosis for SCLC (36). In patients with SCLC, hyponatremia frequently arises from the ectopic secretion of ADH, a hallmark of SIADH in malignancies. Beyond paraneoplastic ADH production, pharmacologic agents used in cancer therapy represent a major contributing factor. These agents may induce or exacerbate hyponatremia by stimulating ADH release, enhancing ADH binding to type 2 vasopressin receptors (AVPR2), or via combined mechanisms (37, 38). Notable offenders include several chemotherapeutic drugs—such as cyclophosphamide, vincristine, vinblastine, melphalan, and cisplatin (which more commonly causes salt-wasting nephropathy). In our study, lobaplatin—a third-generation platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent—and adebrelimab—a monoclonal antibody targeting programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)—were utilized as part of the treatment regimen. Both agents have been associated with an increased risk of hyponatremia. In a pooled analysis of 29 clinical trials, Ezoe et al. reported that the incidence of grade 3/4 hyponatremia was 11.9% among patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy, significantly higher than those treated with non–platinum-based regimens (25). Moreover, emerging cancer therapies, particularly molecularly targeted agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), warrant careful consideration regarding electrolyte disturbances. A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials conducted by Moraes et al. demonstrated a significantly higher incidence of hyponatremia—of any grade—in patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors compared to control groups (39, 40). The underlying mechanism may involve ACTH deficiency, which can lead to secondary adrenal insufficiency and, consequently, hyponatremia due to reduced cortisol production. In addition, non-pharmacologic factors commonly encountered in oncology practice may worsen hyponatremia. These include nausea, vomiting, pain, emotional stress, fluid overload related to chemotherapy administration, diarrhea, and comorbid heart or renal failure (41).
Prognosis of hyponatremia
As a highly malignant tumor, SCLC is typically treated with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Patients with tumors accompanied by hyponatremia often have poor health; thus, sodium levels are considered a marker of disease severity. A retrospective study analyzing 999 patients with SCLC found that the overall survival (OS) of 226 hyponatremia patients was shorter compared to those with normal sodium levels (11.7 vs. 10.0 months, P=0.039). The OS of 119 untreated patients with hyponatremia was also shorter (6.8 vs. 5.2 months, P=0.009) (42). Other studies indicate hyponatremia as an independent adverse prognostic factor, irrespective of other prognostic variables (43). After chemotherapy, hyponatremia may resolve due to drug effects, yet tumor cell destruction might lead to increased ADH secretion, exacerbating hyponatremia. Persistent or recurrent hyponatremia often signals ineffective chemotherapy and disease progression (44).
Treatment of SIADH
Early detection and correction are essential for improving quality of life and reducing mortality (45). For patients with SCLC who had mild to moderate hyponatremia, daily water intake restriction to 800–1000 mL may provide relief, though progression can be slow. For serum sodium <120 mmol/L, 3% concentrated sodium chloride intravenous infusion, coupled with oral salt capsules, is recommended to increase sodium levels. Emergency treatment with hypertonic saline is warranted if neurological symptoms are present (46). For non-responsive patients, antidiuretic hormone V2 receptor antagonists can facilitate water excretion and correct hyponatremia. Tolvaptan has demonstrated stable corrective effects on hyponatremia in advanced SCLC with SIADH, outperforming diets and fluid restriction (47). Various drugs such as Conivaptan, Tolvaptan, and Mozavaptan are currently in clinical use, with Tolvaptan being widely employed (48, 49). Other treatments include urea, demeclocycline, and fludrocortisone (50, 51).
In conclusion
In clinical practice, when unexplained refractory hyponatremia coexists with pulmonary lesions, the possibility of pulmonary malignant tumors with SIADH should be considered. Prompt diagnosis based on SIADH criteria is crucial to determine its cause. When correcting hyponatremia, clinicians should limit fluids, supplement sodium ions, and possibly use antidiuretic hormone antagonists to improve prognosis. Hyponatremia during chemotherapy requires careful management. More clinical research is needed to ascertain whether hyponatremia independently affects the prognosis of patients with SCLC.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study is a single case report. According to the regulations of the Ethics Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, no ethics approval number is required for such case reports. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient (or the patient’s legal guardian) for participation and for publication of any potentially identifiable data or images.
Author contributions
XL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Visualization. TX: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Data curation. XJ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Data curation, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University for its support and the patient for permitting us to use her case to complete this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
This article has been corrected with minor changes. These changes do not impact the scientific content of the article.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Taskaldiran I. Case of hyponatremia due to pituitary metastasis of lung cancer. Acta Endo (Buc). (2023) 19:501–4. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2023.501, PMID: 38933238
2. Tyre JA, Nahr-Martey P, and Tyre NM. Pre-operative labs for left hemicolectomy reveals hyponatremia that leads to lung mass finding. Cureus. (2023) 15:e43865. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43865, PMID: 37608902
3. Kai K, Tominaga N, Koitabashi K, Ichikawa D, and Shibagaki Y. Tolvaptan corrects hyponatremia and relieves the burden of fluid/dietary restriction and hospitalization in hyponatremic patients with terminal lung cancer: a report of two cases. CEN Case Rep. (2019) 8:112–8. doi: 10.1007/s13730-019-00375-7, PMID: 30637666
4. Agarwal KA and Soe MH. Beyond the dual paraneoplastic syndromes of small-cell lung cancer with ADH and ACTH secretion: A case report with literature review and future implications. Case Rep Oncological Med. (2018) 2018:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2018/4038397, PMID: 30498610
5. Peri A, Grohé C, Berardi R, and Runkle I. SIADH: differential diagnosis and clinical management. Endocrine. (2017) 55:311–9. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0936-3, PMID: 27025948
6. John V, Evans P, and Kalhan A. Delayed dyskinesia and prolonged psychosis in a patient presenting with profound hyponatraemia. Endocrinology Diabetes Metab Case Rep. (2017) 2017. doi: 10.1530/edm-16-0147, PMID: 28458906
7. Jaal J, Jõgi T, and Altraja A. Small cell lung cancer patient with profound hyponatremia and acute neurological symptoms: an effective treatment with fludrocortisone. Case Rep Oncological Med. (2015) 2015:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2015/286029, PMID: 26240768
8. Bordi P, Tiseo M, Buti S, Regolisti G, and Ardizzoni A. Efficacy and safety of long-term tolvaptan treatment in a patient with SCLC and SIADH. Tumori. (2015) 101:e51–3. doi: 10.5301/tj.5000249, PMID: 25702667
9. Rossow CF and Luks AM. A 68-year-old woman with hoarseness and upper airway edema. Ann ATS. (2014) 11:668–70. doi: 10.1513/annalsats.201312-434cc, PMID: 24828805
10. Wakil A, Ng JM, and Atkin SL. Investigating hyponatraemia. BMJ. (2011) 342:d1118–8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d1118, PMID: 21382929
11. Tantisattamo E and Ng RCK. Dual paraneoplastic syndromes: small cell lung carcinoma-related oncogenic osteomalacia, and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion: report of a case and review of the literature. Hawaii Med J. (2011) 70:139–43., PMID: 21886301
12. Dasanu CA, Clark BA, Lahiri B, Ichim TE, and Alexandrescu DT. Small cell lung cancer with paraneoplastic lipase production. South Med J. (2010) 103:819–22. doi: 10.1097/smj.0b013e3181e6369e, PMID: 20622741
13. Kleinig TJ, Thompson PD, and Kneebone CS. Chorea, transverse myelitis, neuropathy and a distinctive MRI: Paraneoplastic manifestations of probable small cell lung cancer. J Clin Neurosci. (2009) 16:964–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2008.08.041, PMID: 19329321
14. Yang C-C, Lee H-S, Chen C-C, Cheng C-J, and Lin S-H. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in a patient with cryptococcal meningoencephalitis: A hidden mediastinal small cell carcinoma. Am J Med Sci. (2006) 331:288–91. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200605000-00012, PMID: 16702802
15. Kamoi K, Kurokawa I, Kasai H, Mizusawa A, Ebe T, Sasaki H, et al. Asymptomatic hyponatremia due to inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone as the first sign of a small cell lung cancer in an elderly man. Intern Med. (1998) 37:950–4. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.37.950, PMID: 9868958
16. Robin N, Gill G, Van Heyningen C, and Fraser W. A small cell bronchogenic carcinoma associated with tumoral hypophosphataemia and inappropriate antidiuresis. Postgraduate Med J. (1994) 70:746–8. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.70.828.746, PMID: 7831175
17. Pierce ST, Metcalfe M, Banks ER, O’Daniel ME, and Desimone P. Small cell carcinoma with two paraendocrine syndromes. Cancer. (1992) 69:2258–61. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920501)69:9<2258::aid-cncr2820690908>3.0.co;2-5, PMID: 1314126
18. Kamoi K, Ebe T, Hasegawa A, Sato F, Takato H, Iwamoto H, et al. Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer. Mech not involving inappropriate ADH secretion. Cancer. (1987) 60:1089–93. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870901)60:5<1089::aid-cncr2820600528>3.0.co;2-u
19. Suzuki H, Tsutsumi Y, Yamaguchi K, Abe K, and Yokoyama T. Small cell lung carcinoma with ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone and antidiuretic hormone syndromes: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (1984) 14:129–37., PMID: 6323789
20. Hirata Y, Matsukura S, Imura H, Yakura T, Ihjima S, Nagase C, et al. Two cases of multiple hormone-producing small cell carcinoma of the lung.Coexistence of tumor ADH, ACTH, and β-MSH. Cancer. (1976) 38:2575–82. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197612)38:6<2575::aid-cncr2820380651>3.0.co;2-b, PMID: 187319
21. Nooreldeen R and Bach H. Current and future development in lung cancer diagnosis. IJMS. (2021) 22:8661. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168661, PMID: 34445366
22. Megyesfalvi Z, Gay CM, Popper H, Pirker R, Ostoros G, Heeke S, et al. Clinical insights into small cell lung cancer: Tumor heterogeneity, diagnosis, therapy, and future directions. CA A Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:620–52. doi: 10.3322/caac.21785, PMID: 37329269
23. Spiro SG, Gould MK, and Colice GL. Initial evaluation of the patient with lung cancer: symptoms, signs, laboratory tests, and paraneoplastic syndromes. Chest. (2007) 132:149S–60S. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-1358, PMID: 17873166
24. Sandfeld-Paulsen B, Aggerholm-Pedersen N, and Winther-Larsen A. Hyponatremia in lung cancer: Incidence and prognostic value in a Danish population-based cohort study. Lung Cancer. (2021) 153:42–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.12.038, PMID: 33454516
25. Ezoe Y, Mizusawa J, Katayama H, Kataoka K, and Muto M. An integrated analysis of hyponatremia in cancer patients receiving platinum-based or nonplatinum-based chemotherapy in clinical trials (JCOG1405-A). Oncotarget. (2018) 9:6595–606. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23536, PMID: 29464095
26. Tian L, He L-Y, and Zhang H-Z. Nedaplatin-induced syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone: A case report and review of the literature. WJCC. (2021) 9:6810–5. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i23.6810, PMID: 34447829
27. Meena DS, Kumar D, Bohra GK, and Midha N. Gefitinib induced severe hyponatremia: A case report. J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2021) 27:711–5. doi: 10.1177/1078155220942302, PMID: 32686614
28. Cantini L, Merloni F, Rinaldi S, Lenci E, Marcantognini G, Meletani T, et al. Electrolyte disorders in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune check-point inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncology/Hematology. (2020) 151:102974. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.102974, PMID: 32416348
29. Wu R, Li C, Wang Z, Fan H, Song Y, and Liu H. A narrative review of progress in diagnosis and treatment of small cell lung cancer patients with hyponatremia. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2020) 9:2469–78. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1147, PMID: 33489807
30. Adrogué HJ, Tucker BM, and Madias NE. Diagnosis and management of hyponatremia: A review. JAMA. (2022) 328:280. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.11176, PMID: 35852524
31. Sun N-H, Wang S-H, Liu J-N, Liu A, Gong W-J, Liu Y, et al. The productions of atrial natriuretic peptide and arginine vasopressin in small cell lung cancer with brain metastases and their associations with hyponatremia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2017) 21:4104–12., PMID: 29028089
32. Schwartz WB, Bennett W, Curelop S, and Bartter FC. A syndrome of renal sodium loss and hyponatremia probably resulting from inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. (1957) 23:529–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90224-3, PMID: 13469824
33. Cuesta M and Thompson CJ. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD). Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 30:175–87. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2016.02.009, PMID: 27156757
34. Miyashita K, Matsuura S, Naoi H, Tsukui M, Koshimizu N, and Suda T. Successful treatment by tolvaptan of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion that may be associated with chemotherapy-induced tumour lysis in a patient with small-cell lung carcinoma. Respirology Case Rep. (2018) 6. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.296, PMID: 29796276
35. Berardi R, Rinaldi S, Caramanti M, Grohè C, Santoni M, Morgese F, et al. Hyponatremia in cancer patients: Time for a new approach. Crit Rev Oncology/Hematology. (2016) 102:15–25. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.03.010, PMID: 27066939
36. Iyer P, Ibrahim M, Siddiqui W, and Dirweesh A. Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH) as an initial presenting sign of non small cell lung cancer-case report and literature review. Respir Med Case Rep. (2017) 22:164–7. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2017.08.004, PMID: 28856088
37. Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Korzelius C, Schrier RW, Sterns RH, et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of hyponatremia: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. (2013) 126:S1–S42. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.07.006, PMID: 24074529
38. Liamis G, Milionis H, and Elisaf M. A review of drug-induced hyponatremia. Am J Kidney Dis. (2008) 52:144–53. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.03.004, PMID: 18468754
39. Berardi R, Santoni M, Rinaldi S, Nunzi E, Smerilli A, Caramanti M, et al. Risk of hyponatraemia in cancer patients treated with targeted therapies: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0152079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152079, PMID: 27167519
40. Cho KY, Miyoshi H, Nakamura A, Kurita T, and Atsumi T. Hyponatremia can be a powerful predictor of the development of isolated ACTH deficiency associated with nivolumab treatment [Letter to the Editor. Endocr J. (2017) 64:235–6. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej16-0596, PMID: 28070057
41. Castillo JJ, Vincent M, and Justice E. Diagnosis and management of hyponatremia in cancer patients. Oncologist. (2012) 17:756–65. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0400, PMID: 22618570
42. Hong X, Xu Q, Yang Z, Wang M, Yang F, Gao Y, et al. The value of prognostic factors in Chinese patients with small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study of 999 patients. Clin Respir J. (2018) 12:433–47. doi: 10.1111/crj.12534, PMID: 27460525
43. Sandfeld-Paulsen B, Aggerholm-Pedersen N, and Winther-Larsen A. Hyponatremia as a prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2021) 10:651–61. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-877, PMID: 33718011
44. Bartalis E, Gergics M, Tinusz B, Földi M, Kiss S, Németh D, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of hyponatremia in patients with lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med. (2021) 8:671951. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.671951, PMID: 34950676
45. Chewcharat A, Thongprayoon C, Cheungpasitporn W, Mao MA, Thirunavukkarasu S, and Kashani KB. Trajectories of serum sodium on in-hospital and 1-year survival among hospitalized patients. CJASN. (2020) 15:600–7. doi: 10.2215/cjn.12281019, PMID: 32213501
46. Decaux G and Gankam Kengne F. Hypertonic saline, isotonic saline, water restriction, long loops diuretics, urea or vaptans to treat hyponatremia. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 15:195–214. doi: 10.1080/17446651.2020.1755259, PMID: 32401559
47. Ren P and Yang Q. The role of tolvaptan in managing hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer patients with SIADH: a retrospective study of 23 cases. Transl Cancer Res TCR. (2021) 10:1229–37. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-2123, PMID: 35116450
48. Arecco A, Demontis D, Della Sala L, Musso N, Gay S, Boschetti M, et al. Case report: Twice-daily tolvaptan dosing regimen in a challenging case of hyponatremia due to SIAD. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 14:1309657. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1309657, PMID: 38288467
49. Der-Nigoghossian C, Lesch C, and Berger K. Effectiveness and tolerability of conivaptan and tolvaptan for the treatment of hyponatremia in neurocritically ill patients. Pharmacotherapy. (2017) 37:528–34. doi: 10.1002/phar.1926, PMID: 28295447
50. Imran R, Zia Z, Siddiqi AI, Shafiq W, and Irfan H. Overcoming challenges: doxycycline as an alternative treatment for hyponatremia in managing syndrome of inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH) in small cell lung cancer (SCLC): A case report. Cureus. (2023) 15:e42102. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42102, PMID: 37602064
Keywords: small cell lung cancer, hyponatremia, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, neuroendocrine tumor, lung cancer
Citation: Li X, Xu T and Jian X (2025) Advanced small cell lung cancer with severe hyponatremia: a case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 15:1558986. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1558986
Received: 11 January 2025; Accepted: 20 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025; Corrected: 12 September 2025.
Edited by:
Jules Louis Derks, Erasmus Medical Center, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Andrea De Vico, Azienda Usl Teramo, ItalyLindsey Sloan, University of Minnesota, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, Xu and Jian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tongtong Xu, MTM5NDA1MjQ2MzZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Xian Jian, amlhbnhpYW4wNDAzQDE2My5jb20=
 Xu Li
Xu Li Tongtong Xu
Tongtong Xu Xian Jian2*
Xian Jian2*