- 1Department of Breast Center, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 2Hebei Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer Molecular Medicine, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 3Gland Surgery, The Hebei Province People’s Hospital, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 4Department of Imaging, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 5Research Center and Tumor Research Institute, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
Background: The introduction of novel strategies for neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) has significantly enhanced the rate of pathological complete response (pCR) in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). However, due to tumor heterogeneity, some patients continue to experience poor treatment efficacy, early recurrence, metastasis, and even mortality. Therefore, it is crucial to identify new molecular targets for precise treatment and to develop predictive models for pCR to facilitate tailored therapeutic approaches.
Methods: We conducted a study involving a cohort of TNBC patients who underwent NAT, collecting data on clinicopathological indicators, MRI parameters, and pathological remission outcomes. The expression levels of baseline circular RNA WWC3 (circWWC3) in breast cancer tissue were assessed, and the relationship between its expression and clinicopathological indicators as well as pathological response was analyzed. A nomogram for predicting pCR in TNBC was developed and subsequently validated.
Results: From January 2020 to December 2023, a total of 205 patients were included in the final analysis. The rate of total pathological complete response (tpCR), defined as ypT0/is and ypN0, was observed to be 51.7%. CircWWC3 was found to be highly expressed in the cytoplasm, with an expression rate of 79% among all analyzed cancerous tissues. The elevated expression of circWWC3 was positively correlated with T2 stage, N1 status, Ki-67 levels greater than 30%, and moderate to high infiltration of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) (p < 0.05). Additionally, a change rate in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of breast MRI after two cycles of neoadjuvant therapy (ΔADC 0-2%) greater than 24.53% was significantly associated (p < 0.05). Patients exhibiting high levels of circWWC3 expression were more likely to achieve pCR. Univariate and multivariate regression analyses identified TILs, ΔADC 0-2%, and circWWC3 as key variables for constructing a predictive nomogram for pCR. This model demonstrated strong discrimination, calibration, and clinical applicability.
Conclusion: Elevated expression levels of circWWC3 serve as an independent risk factor influencing the likelihood of achieving a pCR. A predictive model that integrates circWWC3 expression alongside pathological and imaging parameters demonstrates a robust capacity to accurately forecast the probability of pCR in patients diagnosed with TNBC.
Introduction
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a subtype of breast cancer characterized by the absence of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression. Although TNBC has the lowest incidence among breast cancer (BC) subtypes, it presents significant treatment challenges due to limited therapeutic options and its aggressive nature (1, 2). Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) is commonly employed for patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer to facilitate tumor downstaging, enable breast-conserving surgery, and guide subsequent adjuvant therapy based on pathological response (3, 4). Evidence has established a correlation between complete pathological response (pCR) following NAT and improved survival outcomes in TNBC patients (5). However, the pCR rates achieved with chemotherapy alone remain suboptimal (6). While the incorporation of immunotherapy has been shown to enhance pCR rates (7), some patients still experience early disease recurrence and poor prognosis, attributed to the high heterogeneity of the tumor (8). Therefore, it is crucial to investigate new therapeutic targets for the treatment of TNBC.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs), which are noncoding RNAs generated from precursor (pre)-mRNA through back splicing, are characterized by their covalently closed structure and enhanced stability compared to linear RNAs (9, 10). Evidence suggests that circRNAs play significant roles in tumorigenesis and progression, functioning as either oncogenes or tumor suppressors through various mechanisms (11). Our previous research demonstrated that Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) upregulates circular RNA WWC3 (circWWC3), thereby promoting BC progression via the activation of the Ras signaling pathway (12). Furthermore, circWWC3 may facilitate BC progression by inducing M2 macrophage polarization and tumor immune evasion through the upregulation of interleukin-4 (IL-4) expression and secretion (13). Elevated levels of circWWC3 have been associated with poor disease-free survival (DFS) (13) and overall survival (OS) (12, 13). However, the role of circWWC3 in the context of NAT for TNBC remains unexplored.
In this study, we examined the expression of circWWC3 in patients with newly diagnosed TNBC and explored its association with various clinicopathological parameters, as well as its relationship with pCR following NAT. Additionally, we developed a nomogram to predict the likelihood of achieving pCR in TNBC patients. Our findings provided new therapeutic targets for TNBC, laid the foundation for earlier assessment of the efficacy of NAT for TNBC, and further provided a basis for individualized therapy.
Materials and methods
Patients
Patients who received NAT at the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University from January 2020 to December 2023 were included in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) Female, 2) Newly diagnosed and previously untreated TNBC, 3) Unilateral breast cancer without evidence of metastasis to internal mammary or supraclavicular lymph nodes, 4) Completion of the full course of NAT followed by radical breast surgery, 5) Regular breast MRI examinations conducted prior to and during NAT (every two cycles) and before surgery, 6) Availability of comprehensive clinicopathological and follow-up data. The exclusion criteria included: 1) Bilateral or occult breast cancer, 2) A history of other malignancies, 3) Insufficient clinicopathological data, 4) Loss to follow-up.
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University. No identifiable or private patient information was involved; furthermore, as this study did not involve any interventions, the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Tumor specimens
All cancerous specimens were obtained through puncture biopsy from patients diagnosed with TNBC. The samples were subsequently preserved and embedded in paraffin blocks, which were then sectioned into slides for the detection of circWWC3.
Chromogenic in situ hybridization
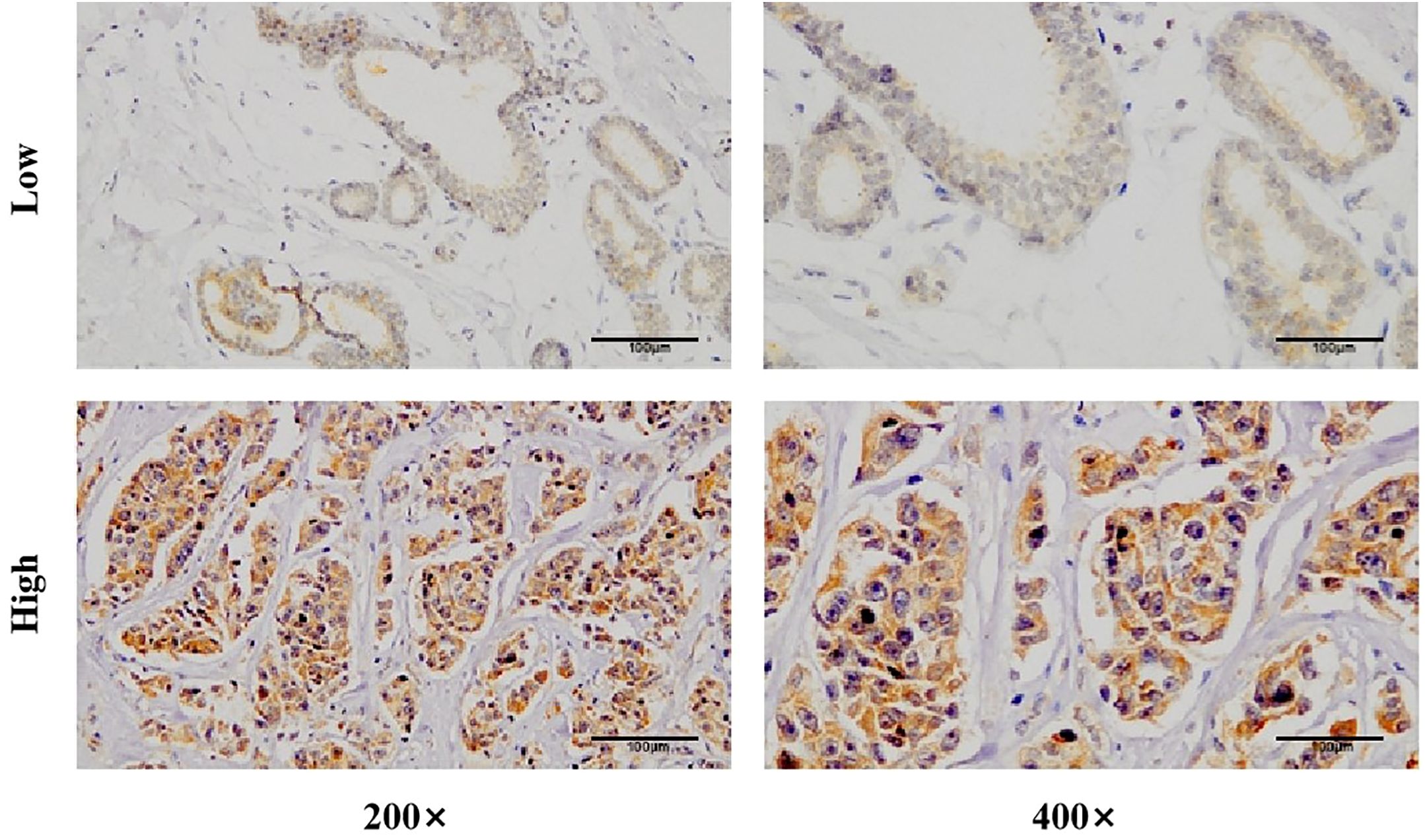
Slides were dewaxed using xylene and ethanol solutions of varying concentrations. Following a prehybridization step at 37°C for one hour, the slides were hybridized overnight at 37°C with probes targeting circWWC3. The expression of circWWC3 was assessed using a 3, 3’-diaminobenzidine (DAB) color development agent, and the nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin. Images were captured at different magnifications. The expression of circWWC3 was evaluated based on the intensity of cytoplasmic staining and the percentage of stained tumor cells (14). Moderate to strong staining intensity observed in the majority of cells was classified as high expression, while all other cases were categorized as low expression.
Clinicopathologic information and variable definitions
Clinicopathologic data were collected from eligible patients, including age, menstrual status, tumor size, axillary lymph node staging, TNM stage, hormone receptor (HR) status, HER2 expression, Ki-67 index, infiltration status of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), change rate in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of breast MRI after two cycles of neoadjuvant therapy (ΔADC 0-2%), NAT regimens, surgical methods, Miller-Payne (MP) classification (15), and the condition of residual cancer burden (RCB). The ER, PR, HER2, and Ki-67 were assessed using immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. HR-negative status was defined as ER and PR expression of less than 1% (16). Given the similar biological behavior of negative and weak HR expression (ER and PR: 1 - 10%), TNBC was defined as HR expression of 0-10% along with HER2 negativity. The infiltration status of TILs was evaluated through hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and categorized as low (0% - 10%), moderate (11% - 59%), and high (> 60%) (17). The ΔADC 0-2% was calculated using the formula: (ADC value after two cycles of NAT - ADC value at baseline)/ADC value at baseline × 100%. Based on our previous research, ΔADC 0-2% was classified into two groups: ΔADC 0-2% > 24.53% and ΔADC 0-2% ≤ 24.53% (18).
Assessment and endpoints
Imaging assessments of the breast and the lymph nodes within the drainage area were conducted at baseline, every two cycles of NAT, and prior to surgery, utilizing breast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound. The pathological response was evaluated according to the MP grading system and the RCB scoring system. The primary endpoint of the study was the rate of total pCR (tpCR, defined as ypT0/is and ypN0). The secondary endpoint was the rate of breast pathological complete response (bpCR, defined as ypT0/is).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 27.0, with categorical data presented as n (%). The Chi-square test was employed to assess differences between the two groups. Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis was performed to identify independent predictors of pCR. A nomogram for predicting pCR was developed using the ‘rms’ package in R software, based on the identified independent predictors. The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve was generated using the ‘proc’ and ‘ggplot2’ packages to calculate the area under the curve (AUC), as well as to determine the optimal cutoff value, specificity, and sensitivity. The accuracy of the model was evaluated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow Calibration Curve. Additionally, Decision Curve Analysis (DCA) was performed using the ‘rmda’ package to assess the clinical applicability of the model. Internal validation of the model was conducted through the Bootstrap self-sampling method. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Demographic characteristics
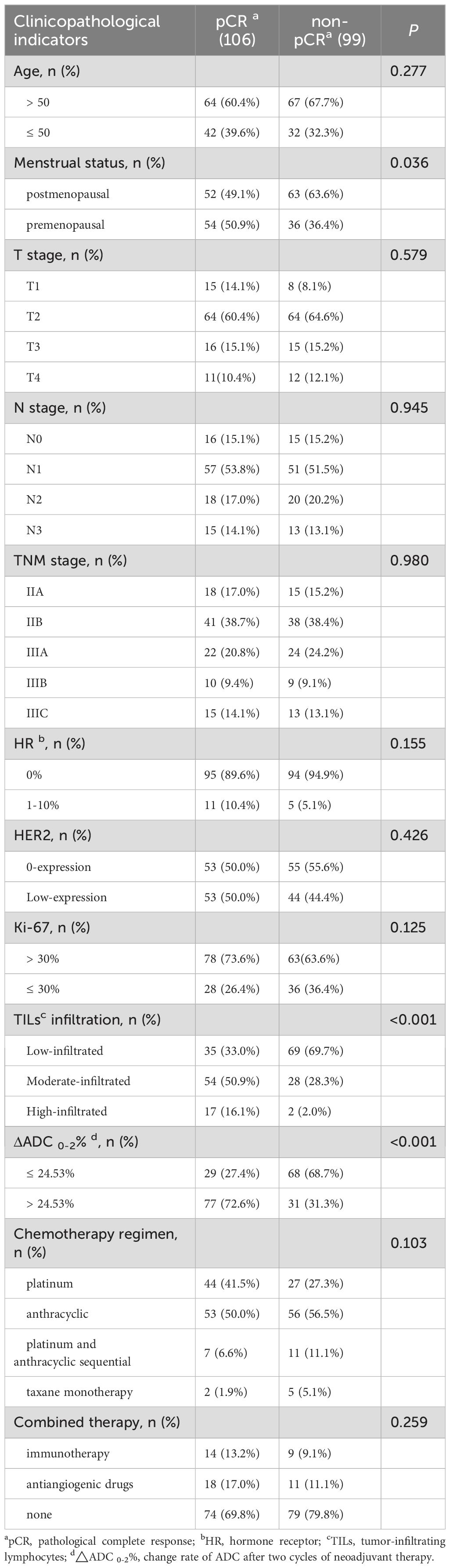
A total of 469 patients with TNBC received NAT between January 2020 and December 2023, of which 205 patients met the inclusion criteria for the final analysis. Patient demographics are summarized in Table 1. The majority of patients were over 50 years of age and postmenopausal. At initial diagnosis, 62.5% of patients presented with T2 tumors. Only 15.1% of patients exhibited no lymph node metastasis, while the majority were found to have lymph node involvement. All patients were staged at II-III, with a similar distribution between the two stages. Negative ER was observed in 92.2% of patients. The incidence of HER2 ‘0 expression’ was comparable to that of HER2 ‘low expression’. High Ki-67 expression (greater than 30%) was noted in 68.8% of patients, and the infiltration of TILs was predominantly low (50.7%) and moderate (40.0%). The proportions of patients with ΔADC 0-2% greater than 24.53% (52.7%) and those with ΔADC 0-2% less than or equal to 24.53% (47.3%) were comparable. Among the NAT regimens administered, those containing anthracyclines were the most prevalent (53.2%), followed by regimens incorporating platinum drugs (34.6%), anthracycline/platinum sequential regimens, and taxane monotherapy. A minority of patients (25.3%) received combined therapies, including immunotherapy or antiangiogenic agents.
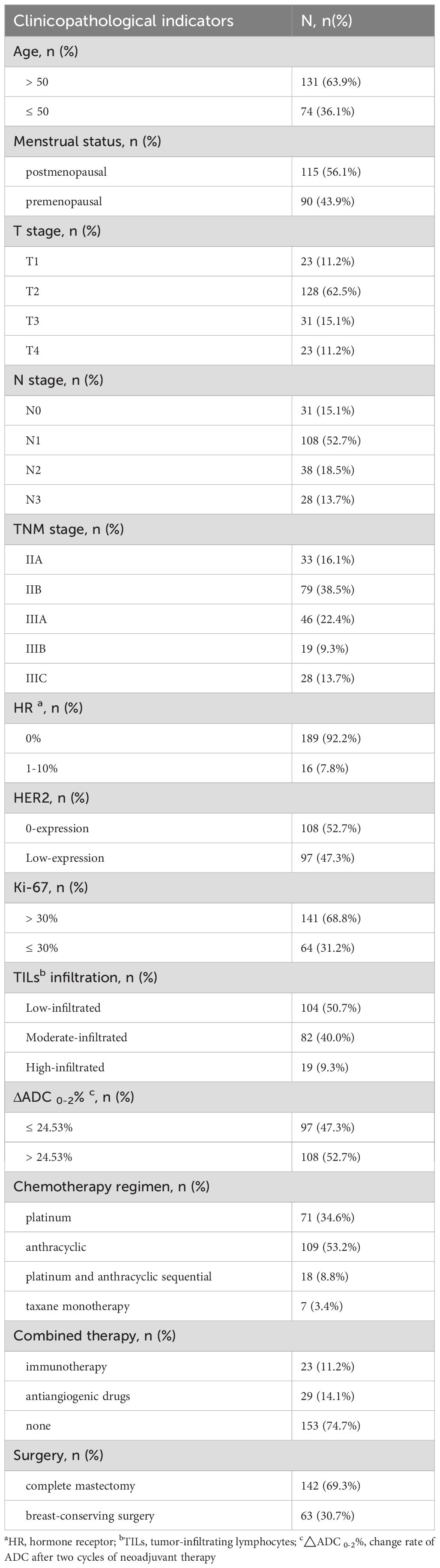
Table 1. Demographic and clinicopathological parameters of patients with triple-negative breast cancer.
Efficacy
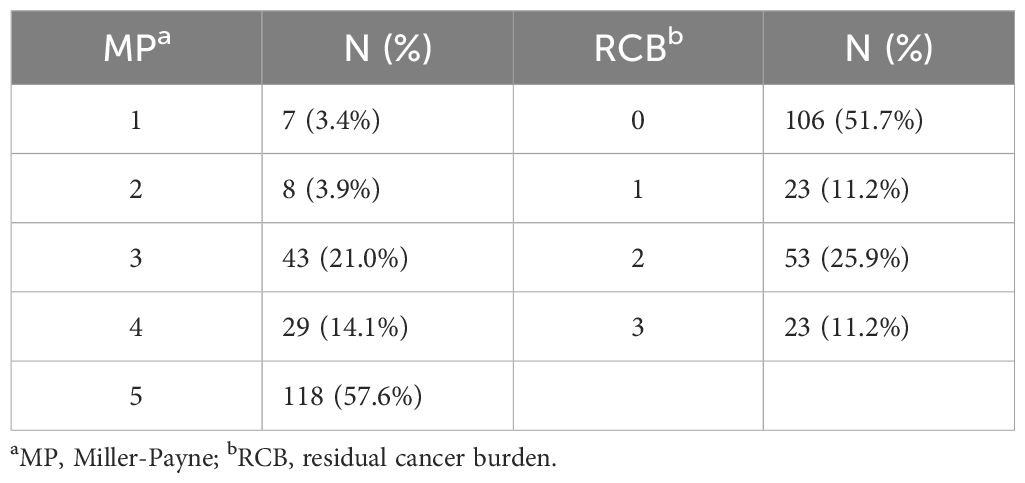
All patients underwent radical mastectomy following a complete course of NAT. Among these patients, 30.7% underwent breast-conserving surgery (BCS), while 69.3% received total mastectomy. A total of 106 patients achieved a tpCR following NAT, resulting in an overall pCR rate of 51.7%. Additionally, 57.6% of the patients attained a bpCR. The details regarding the pathological remission outcomes for the patients are presented in Table 2.
Expression of circWWC3 in TNBC tissue and its effect on the efficacy of NAT
CISH detection revealed that circWWC3 was predominantly localized in the cytoplasm. Among the analyzed samples, 162 out of 205 cases (79.0%) exhibited high levels of circWWC3 expression, while 43 cases (21.0%) demonstrated low expression levels. A representative image illustrating the varying levels of circWWC3 expression as assessed by CISH is presented in Figure 1. Following NAT, a tpCR was observed in 63.5% (103/162) of patients exhibiting high circWWC3 expression. In contrast only 3 patients (3/43, 6.9%) with low circWWC3 expression achieved tpCR (p < 0.001). High levels of circWWC3 expression were predominantly identified in patients classified as MP 4–5 and RCB 0-I, whereas low circWWC3 expression was more frequently observed in patients categorized as MP 1–3 and RCB II-III (p < 0.001) (Table 3).
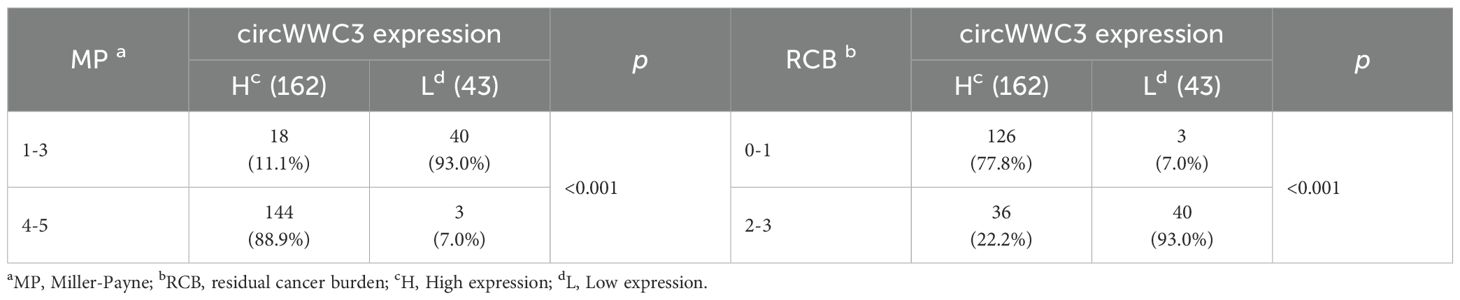
Table 3. Relationship between circWWC3 expression and pathological remission after neoadjuvant therapy.
Associations between circWWC3 expression and clinicopathological parameters
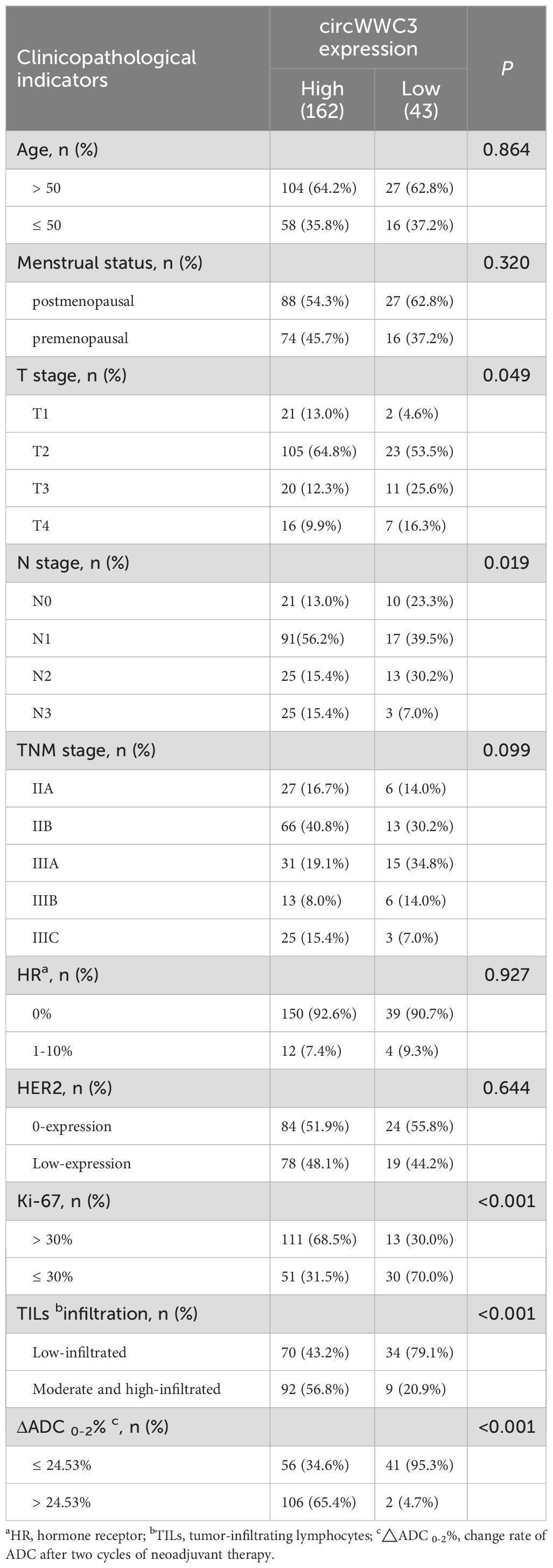
As presented in Table 4, the expression levels of circWWC3 demonstrated a significant correlation with tumor size, lymph node metastasis status, Ki-67 expression, TILs infiltration, and ΔADC 0-2% (p < 0.05). High expression of circWWC3 were predominantly observed in patients classified as T2N1, exhibiting elevated Ki-67 expression, and demonstrating moderate to high levels of TILs. Additionally, a ΔADC 0-2% greater than 24.53% was associated with increased circWWC3 expression. However, circWWC3 expression did not show a significant correlation with other clinical pathological parameters (p > 0.05).
Clinicopathological indicators affecting pCR
Patients in the premenopausal state with highly infiltrated TILs, and ΔADC 0-2% greater than 24.53% were more likely to achieve a tpCR (p < 0.001). Additionally, the rate of tpCR was higher among individuals exhibiting low HER2 expression, those treated with platinum-containing regimens or combination therapies, and patients with high Ki-67 expression, in spite of no statistical difference (p > 0.05) (Table 5).
Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis for affecting pCR
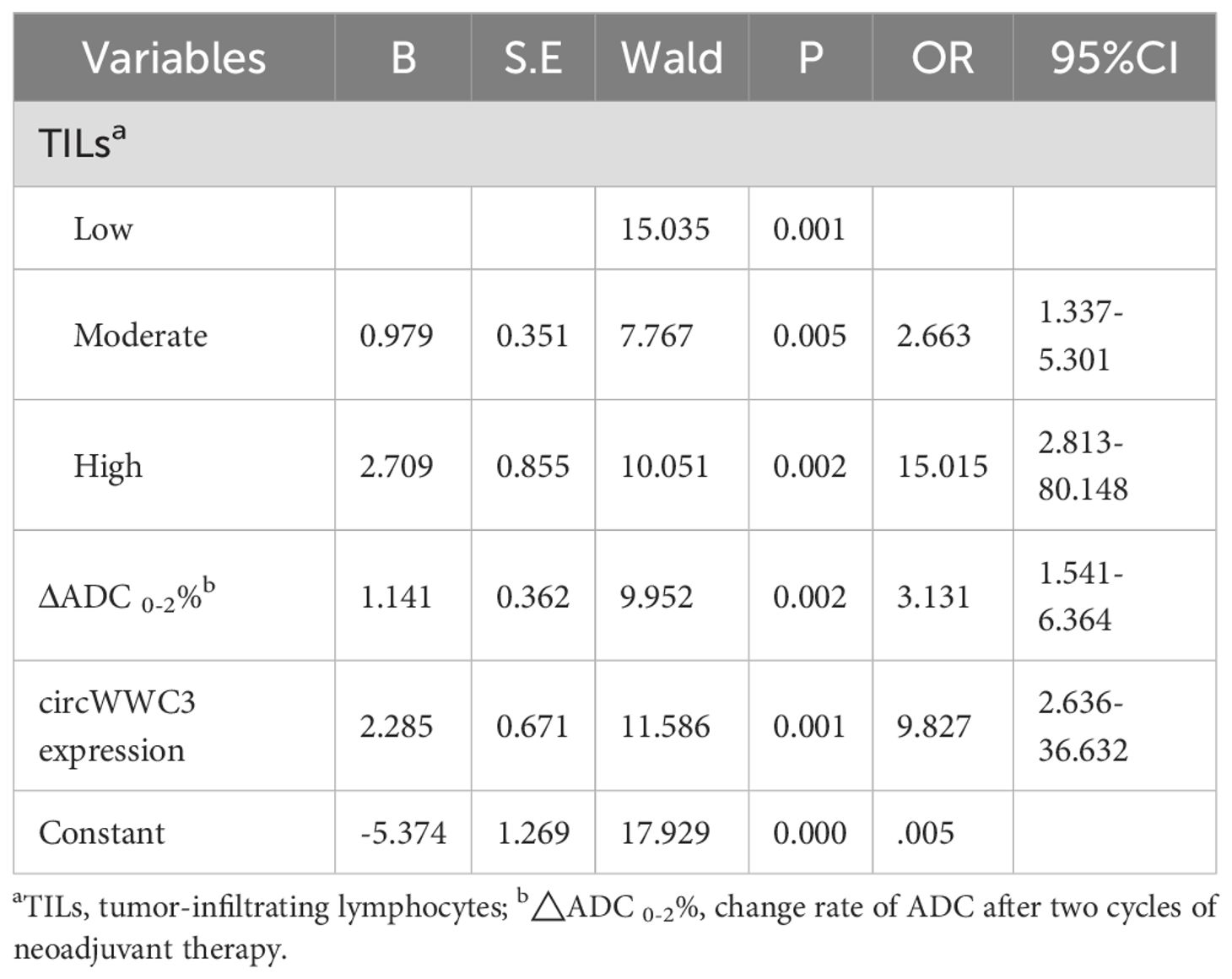
Further multivariate analysis revealed that TILs infiltration was an independent predictor of tpCR, with odds ratios (OR) of 2.663 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.337 - 5.301) for moderate infiltration and 15.015 (95% CI = 2.813 - 80.148) for high infiltration. Additionally, ΔADC 0-2% was associated with an OR of 3.131 (95% CI = 1.541 - 6.364). Furthermore, circWWC3 expression emerged as a significant independent factor, with an OR of 9.827 (95% CI = 2.636 - 36.632) for predicting tpCR (Table 6).
Construction of a nomogram for predicting pCR after NAT for TNBC
Based on the aforementioned analysis, the TILs, ΔADC 0-2%, and the expression levels of circWWC3 were utilized to construct a nomogram for predicting pCR following NAT (Figure 2). The points assigned to each predictor correspond to their respective scores for tpCR. Among the predictors evaluated, a high level of TIL infiltration emerged as the most significant indicator of pCR. The cumulative scores for each predictor were summed, with the resulting risk value at the bottom reflecting the likelihood of achieving tpCR.
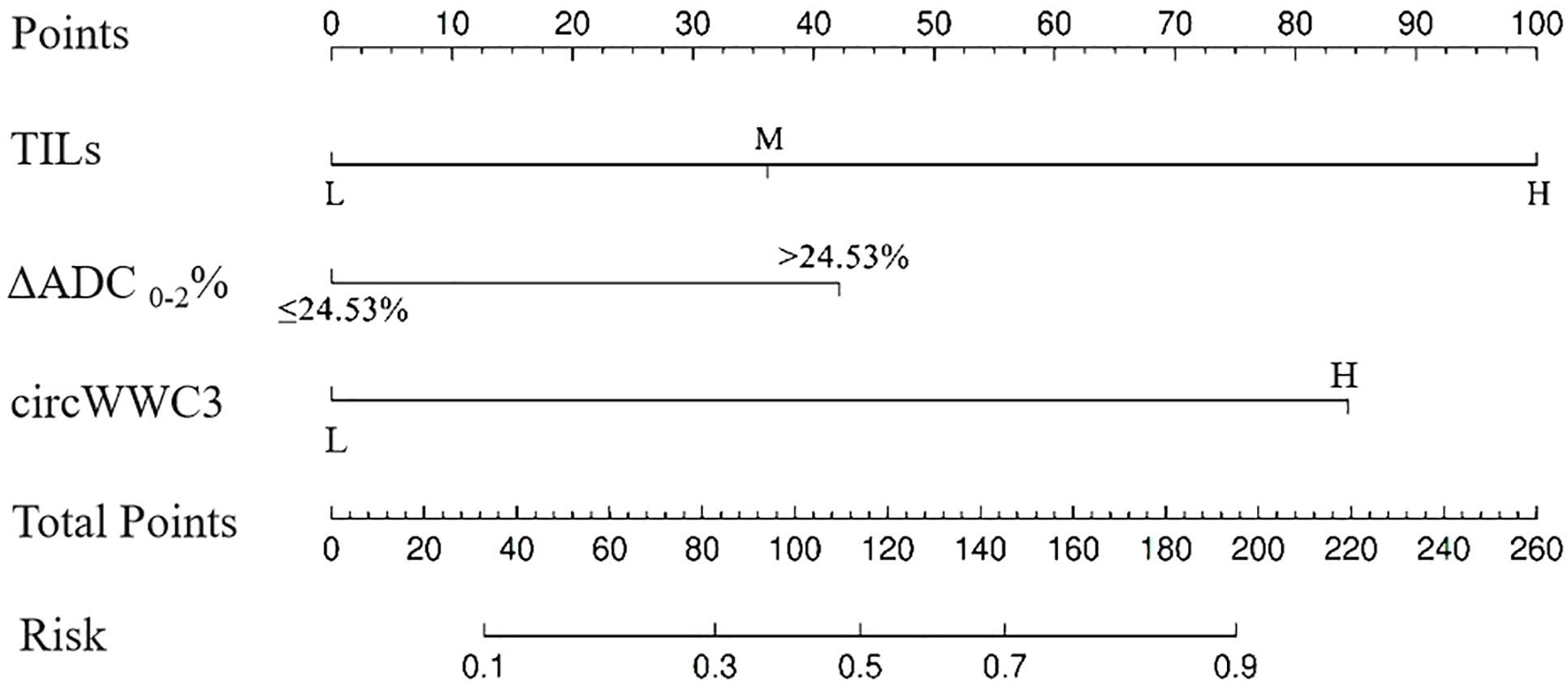
Figure 2. The nomogram for predicting pathological complete response after neoadjuvant therapy in patients with triple negative breast cancer.
Discrimination analysis of the nomogram model
The discrimination capability of the nomogram model was assessed using ROC curve analysis, yielding an AUC value of 0.815 (95% CI: 0.758 - 0.871; p < 0.001). At the optimal threshold of 0.358, the model demonstrated a sensitivity of 0.567 and a specificity of 0.877. Additionally, internal validation was conducted through bootstrap resampling, performed 1,000 times, which resulted in an AUC value of 0.821, further corroborating the model’s robust discriminatory performance (Figure 3).
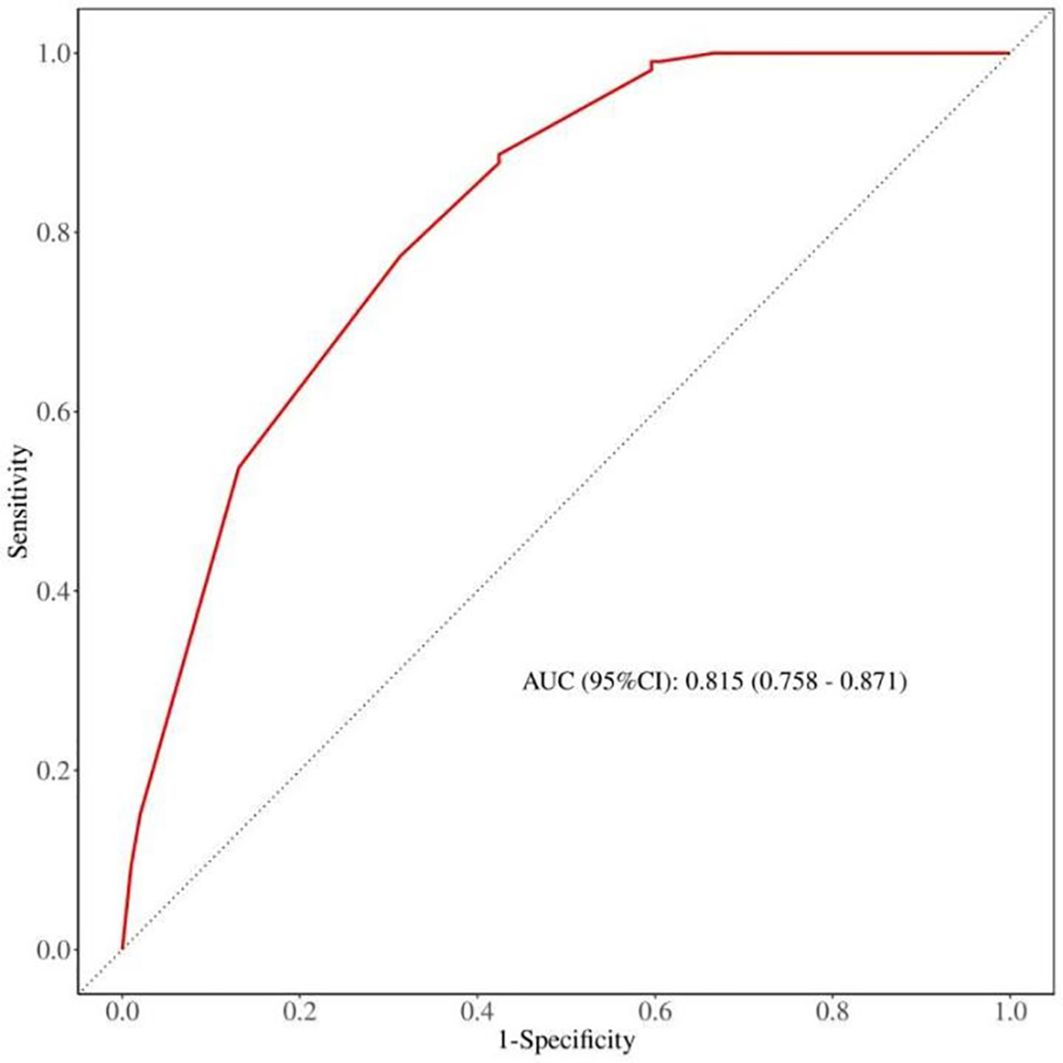
Figure 3. The expression of circWWC3 in triple negative breast cancer tissues by chromogenicin situ hybridization (CISH).
Calibration analysis of nomogram model
The calibration curve was employed to assess the calibration performance of the nomogram. The results indicated no significant difference between the predicted and actual probabilities (χ² = 2.118, df = 4, p = 0.714). Following internal validation via Bootstrap repeated sampling, the absolute error was determined to be 0.017. As illustrated in Figure 4, the calibration curve closely approximated the ideal curve, with the original curve also showing a slope near 1, indicating a strong concordance between the actual and predicted probabilities of pCR occurrence.
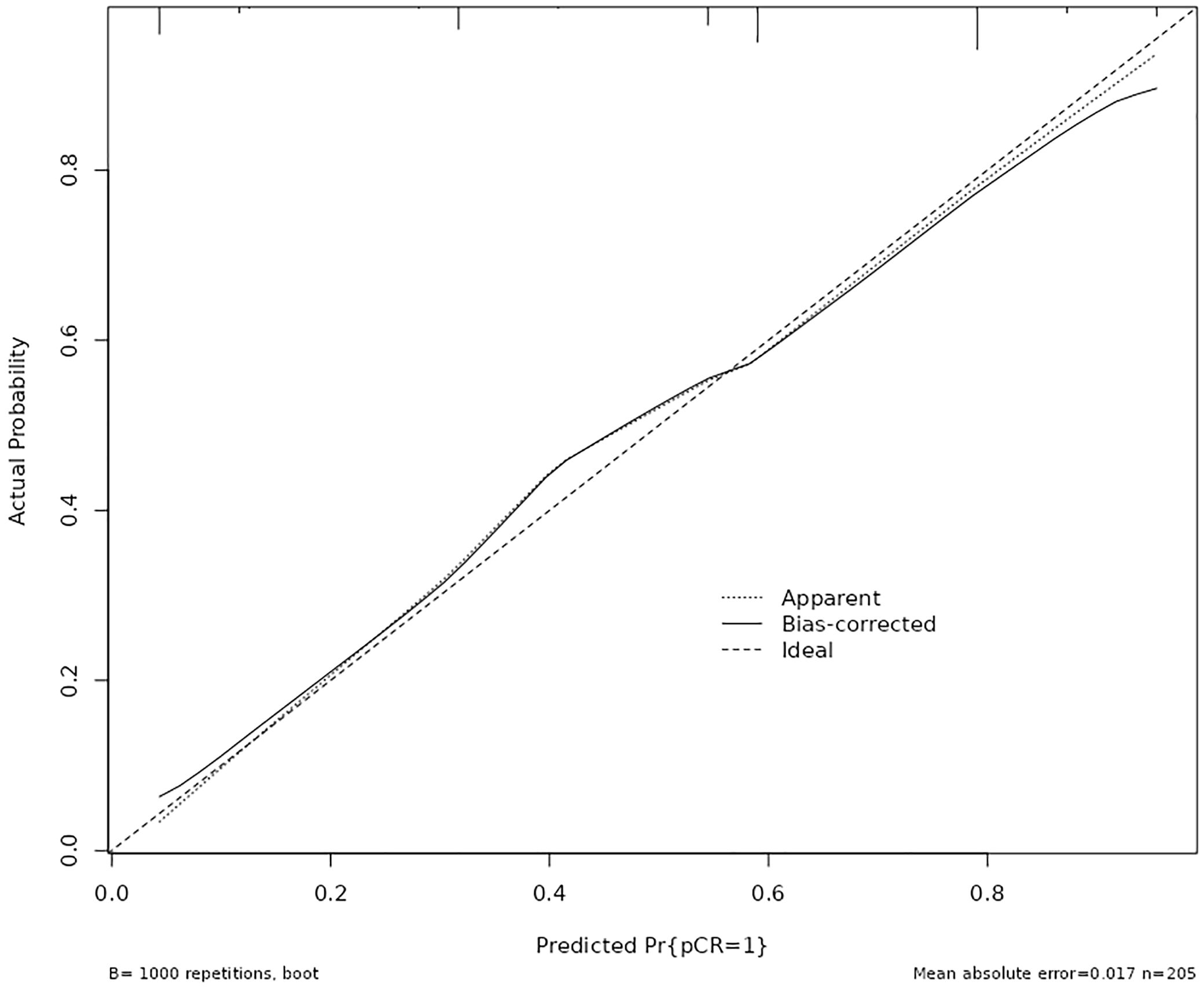
Figure 4. Calibration plots for the nomogram to predict pathological complete response after neoadjuvant therapy.
Evaluation for clinical practicability of nomogram model
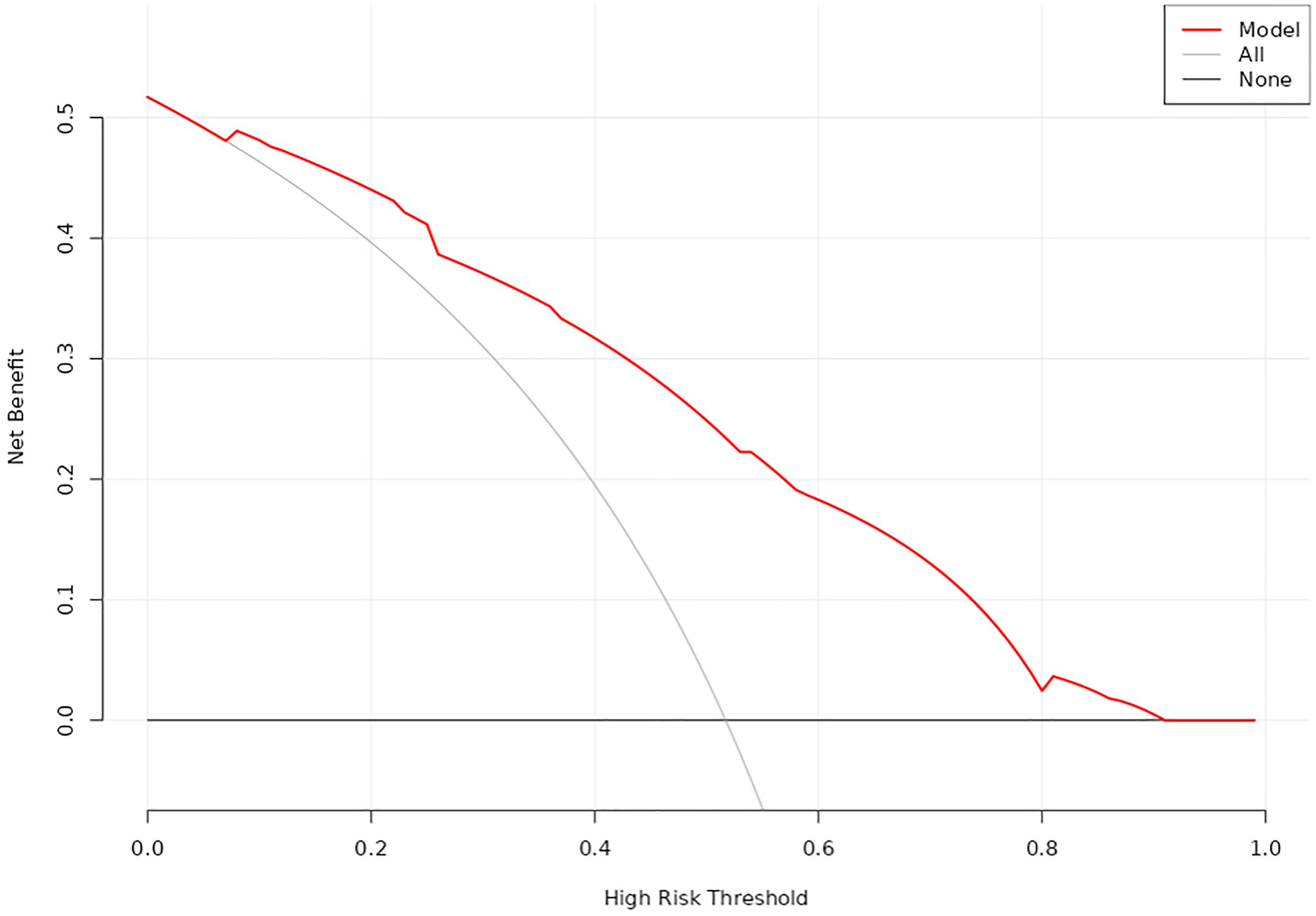
DCA was utilized to evaluate the clinical utility of the nomogram model (Figure 5). The analysis revealed that when the threshold probability ranged from 7% to 92%, the application of this model yielded a higher clinical net benefit, significantly surpassing the net benefit levels of the None line and All line. This finding underscores the model’s substantial clinical applicability.
Discussion
TNBC remains one of the most challenging subtypes to treat due to its high heterogeneity, aggressiveness, and limited therapeutic options. Consequently, precision typing and tailored treatment strategies are essential in contemporary clinical practice. Jiang et al. (19) classified TNBC into four distinct subtypes by analyzing clinical, genomic, and transcriptomic data from 465 patients diagnosed with primary TNBC. These subtypes include luminal androgen receptor (LAR), immunomodulatory, basal-like immune-suppressed, and mesenchymal-like. Based on the identified potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers for each subtype, several clinical trials have been initiated, with preliminary results reported (20–22). While the refinement of treatment protocols informed by precision typing has led to a modest improvement in the survival of TNBC patients, these advancements primarily focus on patients in the advanced stage, with limited studies addressing early-stage or locally advanced patients. Achieving a cure for early locally advanced breast cancer is critical for enhancing overall prognosis. Given the correlation between pCR and long-term survival, the current standard of care in NAT for TNBC involves chemotherapy combined with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy (23). However, some patients continue to exhibit suboptimal responses and may experience immune-related adverse events (7, 8). Therefore, exploring new therapeutic targets within the context of NAT to facilitate precision typing and therapy holds significant clinical value.
CircWWC3 has been established as a factor implicated in tumor progression, albeit with limited conflicting evidence documented in the literature. Liu et al. (24) demonstrated that circWWC3 inhibits cell growth, migration, and invasion while promoting apoptosis in osteosarcoma through the regulation of the miR-421/PDE7B axis, thereby reducing tumorigenicity in murine xenograft models. Conversely, circWWC3 is found to be highly expressed in renal carcinoma tissues compared to normal tissues, and its elevated expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with renal carcinoma (14). In the context of breast cancer, our findings indicate that circWWC3 functions as an oncogene, enhancing tumor cell aggressiveness and influencing the tumor microenvironment (TME) (12, 13). Notably, high levels of circWWC3 are associated with unfavorable OS and DFS outcomes (13). To our knowledge, this study represents the first investigation into the impact of circWWC3 expression on the efficacy of NAT in patients with TNBC. Our results suggest that elevated circWWC3 levels are significantly associated with tumors classified as T2 or N1, likely due to the relatively high proportion of such tumors. Additionally, high circWWC3 expression is more prevalent in cases exhibiting markers indicative of a propensity to achieve pCR, including elevated Ki-67 expression (25), moderate to high levels of TILs (26), and ΔADC 0-2% > 24.53% (18). Furthermore, it has been confirmed that patients with high circWWC3 expression are more likely to attain tpCR. Therefore, exploring new therapeutic targets in the context of NAT holds significant clinical value for achieving precision typing and therapy.
A series of studies have sought to develop predictive models for pCR following NAT in TNBC by utilizing various indicators. In addition to clinicopathological factors, most documented nomograms have incorporated radiomic signatures derived from imaging modalities such as ultrasound (27–29), contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) (30, 31), and MRI (32, 33). Notably, only two predictive models have integrated laboratory indicators (34) or employed a novel biomarker-based predictive response score (pRS) system (35). In the MRI-based nomogram, parameters such as tumor volume measured via dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), time to peak (TTP), and a radiomics score derived from contrast agent plasma-to-interstitial transfer (Ktrans), volume fraction of extravascular and extracellular space (Ve), and maximum contrast agent uptake rate (Slopemax) were included. These parameters were analyzed using unsupervised correlation and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) methodology (30, 31). In our previous research, we established a predictive nomogram for pCR in patients with various breast cancer subtypes by incorporating the change rate of ADC in enhanced MRI after two cycles of NAT. This model demonstrated strong discrimination, calibration, and clinical applicability (18). According to our findings, TILs infiltration, circWWC3 expression prior to NAT, and ΔADC 0-2% were identified as independent predictors of pCR. These factors were utilized to construct a prediction nomogram for pCR, which exhibited significant predictive power and clinical relevance. To our knowledge, this represents the first nomogram that predicts pCR by integrating pathological indicators, biomarkers, and imaging parameters.
Our study has several limitations. Firstly, the sample size was constrained, although we employed the bootstrap repeated sampling method for internal validation of the model, further large-scale validation is essential. Secondly, the model was developed using data from a single center, necessitating verification and application across multiple centers. Thirdly, the follow-up period was relatively short, and there was a lack of data on the correlation between circWWC3 expression and long-term survival. In the future, we will report on this topic. Nevertheless, our study still holds certain clinical value: we have, for the first time, reported that the positive expression of circWWC3 is associated with pCR following NAT for TNBC. Based on multi-dimensional indicators (circWWC3 and clinical pathological indicators), we have constructed an early prediction model for pCR after NAT for TNBC. This model can assist clinicians in assessing the efficacy of NAT earlier, thereby allowing for timely adjustment of treatment plans and avoiding ineffective treatments and potential adverse reactions.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we found that high expression levels of circWWC3 in TNBC are significantly associated with an increased likelihood of achieving a pCR. An integrative predictive model for pCR incorporating pathological indicators, biomarkers, and imaging parameters has been developed, which holds promise for facilitating tailored clinical decision-making. This model requires further validation and application in larger cohorts.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from primarily isolated as part of your previous study for which ethical approval was obtained. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
HW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. SG: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZB: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – original draft. YZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. PZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. FL: Formal analysis, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. CG: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by S&T Program of Hebei (number 236Z7755G).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Howlader N, Cronin KA, Kurian AW, and Andridge R. Differences in breast cancer survival by molecular subtypes in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2018) 27:619–26. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0627
2. Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU, and Polyak K. Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast cancer: improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov. (2019) 9:176–98. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1177
3. Korde LA, Somerfield MR, Carey LA, Crews JR, Denduluri N, Hwang ES, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and targeted therapy for breast cancer: ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:1485–505. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03399
4. Pusztai L, Foldi J, Dhawan A, Digiovanna MP, and Mamounas EP. Changing frameworks in treatment sequencing of triple-negative and HER2-positive, early-stage breast cancers. Lancet Oncol. (2019) 20:e390–6. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30158-5
5. Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, Mehta K, Costantino JP, Wolmark N, et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. (2014) 384:164–72. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62422-8
6. Karim AM, Kwon JE, Ali T, Jang J, Ullah I, Lee YG, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: epidemiology, molecular mechanisms, and modern vaccine-based treatment strategies. Biochem Pharmacol. (2023) 212:115545. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115545
7. Schmid P, Cortes J, Pusztai L, Mcarthur H, Kümmel S, Bergh J, et al. Pembrolizumab for early triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:810–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910549
8. Pusztai L, Denkert C, O’Shaughnessy J, Cortes J, Dent R, Mcarthur H, et al. Event-free survival by residual cancer burden with pembrolizumab in early-stage TNBC: exploratory analysis from KEYNOTE-522. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:429–36. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.02.002
9. Jeck WR and Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. (2014) 32:453–61. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2890
10. Lasda E and Parker R. Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA. (2014) 20:1829–42. doi: 10.1261/rna.047126.114
11. Zhang C, Ding R, Sun Y, Huo ST, He A, Wen C, et al. Circular RNA in tumor metastasis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2021) 23:1243–57. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.01.032
12. Meng L, Liu S, Liu F, Sang M, Ju Y, Fan X, et al. ZEB1-mediated transcriptional upregulation of circWWC3 promotes breast cancer progression through activating ras signaling pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 22:124–37. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.08.015
13. Zheng Y, Ren S, Zhang Y, Liu S, Meng L, Liu F, et al. Circular RNA circWWC3 augments breast cancer progression through promoting M2 macrophage polarization and tumor immune escape via regulating the expression and secretion of IL-4. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:264. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02686-9
14. Wang H, Ma X, Li S, and Ni X. Prognostic value of circWWC3 as a novel survival-related biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. (2023) 25:196. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13782
15. Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2000) 92:205–16. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.3.205
16. Allison KH, Hammond MEH, Dowsett M, Mckernin SE, Carey LA, Fitzgibbons PL, et al. Estrogen and progesterone receptor testing in breast cancer: ASCO/CAP guideline update. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:1346–66. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02309
17. Denkert C, Von Minckwitz G, Darb-Esfahani S, Lederer B, Heppner BI, Weber KE, et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: a pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:40–50. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30904-X
18. Wang H, Lu Y, Li Y, Li S, Zhang X, and Geng C. Nomogram for early prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer combining both clinicopathological and imaging indicators. Curr Probl Cancer. (2022) 46:100914. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2022.100914
19. Jiang YZ, Ma D, Suo C, Shi J, Xue M, Hu X, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic landscape of triple-negative breast cancers: subtypes and treatment strategies. Cancer Cell. (2019) 35:428–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.02.001
20. Chen L, Jiang YZ, Wu SY, Wu J, Di GH, Liu GY, et al. Famitinib with camrelizumab and nab-paclitaxel for advanced immunomodulatory triple-negative breast cancer (FUTURE-C-Plus): an open-label, single-arm, phase II trial. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28:2807–17. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-4313
21. Fan L, Wang ZH, Ma LX, Wu SY, Wu J, Yu KD, et al. Optimising first-line subtyping-based therapy in triple-negative breast cancer (FUTURE-SUPER): a multi-cohort, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2024) 25:184–97. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00579-X
22. Liu Y, Zhu XZ, Xiao Y, Wu SY, Zuo WJ, Yu Q, et al. Subtyping-based platform guides precision medicine for heavily pretreated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: the FUTURE phase II umbrella clinical trial. Cell Res. (2023) 33:389–402. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00795-2
23. Gradishar WJ, Moran MS, Abraham J, Abramson V, Aft R, Agnese D, et al. Breast cancer, version 3.2024, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2024) 22:331–57. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2024.0035
24. Liu S, Zhang J, Zheng T, Mou X, and Xin W. Circ_WWC3 overexpression decelerates the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating miR-421/PDE7B axis. Open Life Sci. (2021) 16:229–41. doi: 10.1515/biol-2021-0021
25. Chen X, He C, Han D, Zhou M, Wang Q, Tian J, et al. The predictive value of Ki-67 before neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncol. (2017) 13:843–57. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0420
26. Denkert C, Von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:983–91. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.1967
27. Jiang M, Li CL, Luo XM, Chuan ZR, Lv WZ, Li X, et al. Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics in the assessment of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 147:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.028
28. Chung WS, Chen SC, Ko TM, Lin YC, Lin SH, Lo YF, et al. An integrative clinical model for the prediction of pathological complete response in patients with operable stage II and stage III triple-negative breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancers. (2022) 14:4170. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174170
29. Wang KN, Meng YJ, Yu Y, Cai WR, Wang X, Cao XC, et al. Predicting pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a nomogram combining clinical features and ultrasound semantics in patients with invasive breast cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1117538. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1117538
30. Huang X, Mai J, Huang Y, He L, Chen X, Wu X, et al. Radiomic nomogram for pretreatment prediction of pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: predictive value of staging contrast-enhanced CT. Clin Breast Cancer. (2021) 21:e388–401. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.12.004
31. Wang J, Tian C, Zheng BJ, Zhang J, Jiao DC, Qu JR, et al. The use of longitudinal CT-based radiomics and clinicopathological features predicts the pathological complete response of metastasized axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:549. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12257-y
32. Ramtohul T, Lepagney V, Bonneau C, Jin M, Menet E, Sauge J, et al. Use of pretreatment perfusion MRI-based intratumoral heterogeneity to predict pathologic response of triple-negative breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy. Radiology. (2024) 312:e240575. doi: 10.1148/radiol.240575
33. Li Y, Chen Y, Zhao R, Ji Y, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram based on pretreatment dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for the prediction of pathologic response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:1676–87. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08291-0
34. Zhang F, Huang M, Zhou H, Chen K, Jin J, Wu Y, et al. A nomogram to predict the pathologic complete response of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer based on simple laboratory indicators. Ann Surg Oncol. (2019) 26:3912–9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07655-7
Keywords: triple-negative breast cancer, circWWC3, neoadjuvant therapy, pathological complete response, nomogram
Citation: Wang H, Liu H, Gao S, Wang L, Bai Z, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Liu F and Geng C (2025) The impact of circWWC3 on neoadjuvant therapy for triple-negative breast cancer and the construction of a nomogram for predicting pathological complete response after neoadjuvant therapy. Front. Oncol. 15:1564693. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1564693
Received: 22 January 2025; Accepted: 25 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Somsubhra Nath, Presidency University, IndiaReviewed by:
Chandrama Mukherjee, Presidency University, IndiaChangzai Li, North China University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Liu, Gao, Wang, Bai, Zhang, Zhang, Liu and Geng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cuizhi Geng, NDYzMDAzNDlAaGVibXUuZWR1LmNu
 Haoqi Wang
Haoqi Wang Hongbo Liu1,2
Hongbo Liu1,2 Cuizhi Geng
Cuizhi Geng