- 1Division of Pediatric Nephrology, Department of Pediatrics, LeBonheur Children’s Hospital, Memphis, TN, United States
- 2Department of Biostatistics, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, United States
- 3Division of Critical Care Medicine, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, United States
Introduction: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious complication encountered often in critically ill children with cancer. Hypoalbuminemia, commonly present in this population, has been associated with poor outcomes, including a higher rate of AKI. Studies examining the impact of hypoalbuminemia on outcomes in critically ill children with cancer are lacking. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the impact of low serum albumin levels (SAL) on outcomes, including mortality and AKI, in critically ill children with oncologic/hematologic diseases. We also sought to examine the risk factors of AKI in this population.
Methods: Retrospective review of all children with hematologic/oncologic disease admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) from December 2020 to April 2021.
Results: A total of 82 patients were included in this study cohort. The median age in our cohort was 10.3 y (0.8, 22.3), and the most common diagnosis was hematologic malignancy (41%). Thirty percent of the cohort experienced AKI; 30% of these cases were severe. Risk factors for AKI included sepsis, antiviral medications, higher nephrotoxicity index, and a higher number of nephrotoxic drugs. The rate of AKI was higher in children with SAL <2.5 g/dL (55% vs 27% in children with SAL ≥2.5 g/dL, P=0.09). SAL <3 g/dL was associated with higher rate of invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) (15% vs 2% in children with SAL≥3 g/dL, P=0.038) and a longer duration of ICU stay (4 days vs 2, P=0.028).
Conclusion: Hypoalbuminemia is associated with adverse outcomes in children with oncologic/hematologic disease. Particularly, SAL < 3 g/dL are associated with higher need for IMV and longer ICU duration. Future studies are required to investigate the impact of hypoalbuminemia in this population and whether correcting hypoalbuminemia improves outcomes.
1 Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common in children with cancer, worsening outcomes in this population. Pediatric cancer patients are at heightened risk for AKI due to nephrotoxic therapies, tumor lysis syndrome, treatments such as chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, bone marrow transplantation, and multi-organ failure, adding significant cumulative nephrotoxic stress (1, 2). In a cohort of 1868 pediatric cancer patients, 52.6% developed AKI during treatment, highlighting the necessity of monitoring kidney function throughout the treatment process (3). Moreover, cancer therapies often require dose adjustments due to AKI, which can impair cancer treatment outcomes and overall patient prognosis. Higher risk of AKI is also observed in children admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with a reported prevalence of 10% to 30% (4). Previous studies have reported a correlation of hypoalbuminemia with prolonged ICU stays, higher rates of infection, and increased mortality (5). This underscores the importance of monitoring serum albumin levels as part of the clinical assessment in pediatric patients with AKI. In children with malignancies, hypoalbuminemia is common and can reflect a compromised nutritional status and systemic inflammation, which can exacerbate the course of kidney injury and lead to further complications. Studies examining the impact of hypoalbuminemia on outcomes in critically ill children with cancer are lacking. Therefore, the primary objective of our study was to investigate the impact of low serum albumin level (SAL) on outcomes, including mortality, AKI, and duration of ICU stay, in critically ill children with oncologic/hematologic diseases. The secondary objective was to examine the risk factors of AKI in this population.
2 Patients and methods
2.1 Patient population
All patients who were admitted to the ICU at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (SJCRH), a specialized pediatric hematologic-oncology hospital, from December 2020 to April 2021 were considered for this retrospective study. Patients were included if they met the inferred criteria of having a hematologic or oncologic diagnosis and were admitted to the ICU during the study period. Patients were excluded if they (1) were admitted to the ICU for less than 24 hours (2), were admitted solely for post-surgical recovery (3), had a pre-existing diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD), or (4) lacked serum creatinine data or had substantially incomplete records.
2.2 Data collection
A list of all ICU admissions during the study period was obtained from institutional database queries and duplicate entries and inter-hospital transfers were removed. Comprehensive data from the EPIC electronic health record (EHR) of the patients was collected, including demographic details (age, sex, race, ethnicity, type of malignancy, history of hematopoietic cell transplant [HCT], viral infections, sepsis, graft-versus-host disease [GVHD], and thrombotic microangiopathy). Measurements of weight, length/height, and body mass index (BMI) were also recorded. In addition, the use of medications known to be nephrotoxic was recorded (Supplementary Table 1). The medications administered encompassed a wide range, including chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., cisplatin, carboplatin, methotrexate), antivirals (e.g., acyclovir, foscarnet), CAR-T therapy, antifungals (e.g., amphotericin B), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics (e.g., aminoglycosides, vancomycin), antihypertensives, vasopressors (e.g., epinephrine, norepinephrine), and contrast agents. In addition, Pediatric Risk of Mortality (PRISM) III and Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM)2 data were recorded.
Laboratory data, including results of serum albumin, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, cystatin C, hemoglobin, complete blood count, and liver function tests, were extracted from electronic medical records during each encounter. Laboratory values were collected on the basis of specific criteria to ensure comprehensive data analysis. The analysis included ICU preadmission laboratory results, the laboratory values associated with the highest creatinine or cystatin C levels during their ICU admission, and a value just prior to hospital discharge. If AKI occurred during the ICU admission, two additional laboratory results from the two days preceding the AKI were recorded.
AKI was diagnosed and staged according to the KDIGO criteria, which provides standardized definitions and staging for assessing the severity of kidney dysfunction (6). Stage 2 or 3 AKI was defined as severe AKI.
The nephrotoxicity index was utilized to evaluate the risk of kidney injury associated with specific drugs or drug combinations used during the study period. As part of the Nephrotoxic Injury Negated by Just-in-time Action (NINJA) framework, nephrotoxic drugs were identified and monitored to assess their impact on renal function in the study population (7, 8). NINJA’s nephrotoxic list currently contains 57 agents, whereas nephrotoxic drug score has 197 agents listed. We compared the nephrotoxic drugs administered to our patients and scored them based on these indices to evaluate patients’ cumulative risk of nephrotoxicity. The data were captured by using REDCap.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics of patient demographics, baseline measures, and treatment outcomes are presented by whole group and by albumin cut-off values: <2.5 g/dL, <3 g/dL, <3.5 g/dL, as well as by AKI. For this analysis, the lowest SAL during the ICU admission was used. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to compare differences in groups and group summaries are presented as median (min, max). The exact chi-squared test was used to examine differences in proportions by groups of interest and are presented as N (%). Simple and multiple logistic regression models were evaluated to determine the effect of albumin cut-off points on survival milestones after ICU discharge and AKI. Multivariable models controlled for serum albumin, cancer diagnosis, mechanical ventilation, BMT, vasopressor use, nephrotoxicity index, and length of ICU stay. An alpha of 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant for all statistical tests. Multiple hypothesis testing was accounted for using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure to control the false discovery rate (FDR) at 20%, resulting in an adjusted significance threshold of alpha = 0.0381 (results presented in Supplementary Table 2). All analyses were performed in SAS Studio 3.83, Cary, NC, USA and FDR control was performed in RStudio 4.4.1.
3 Results
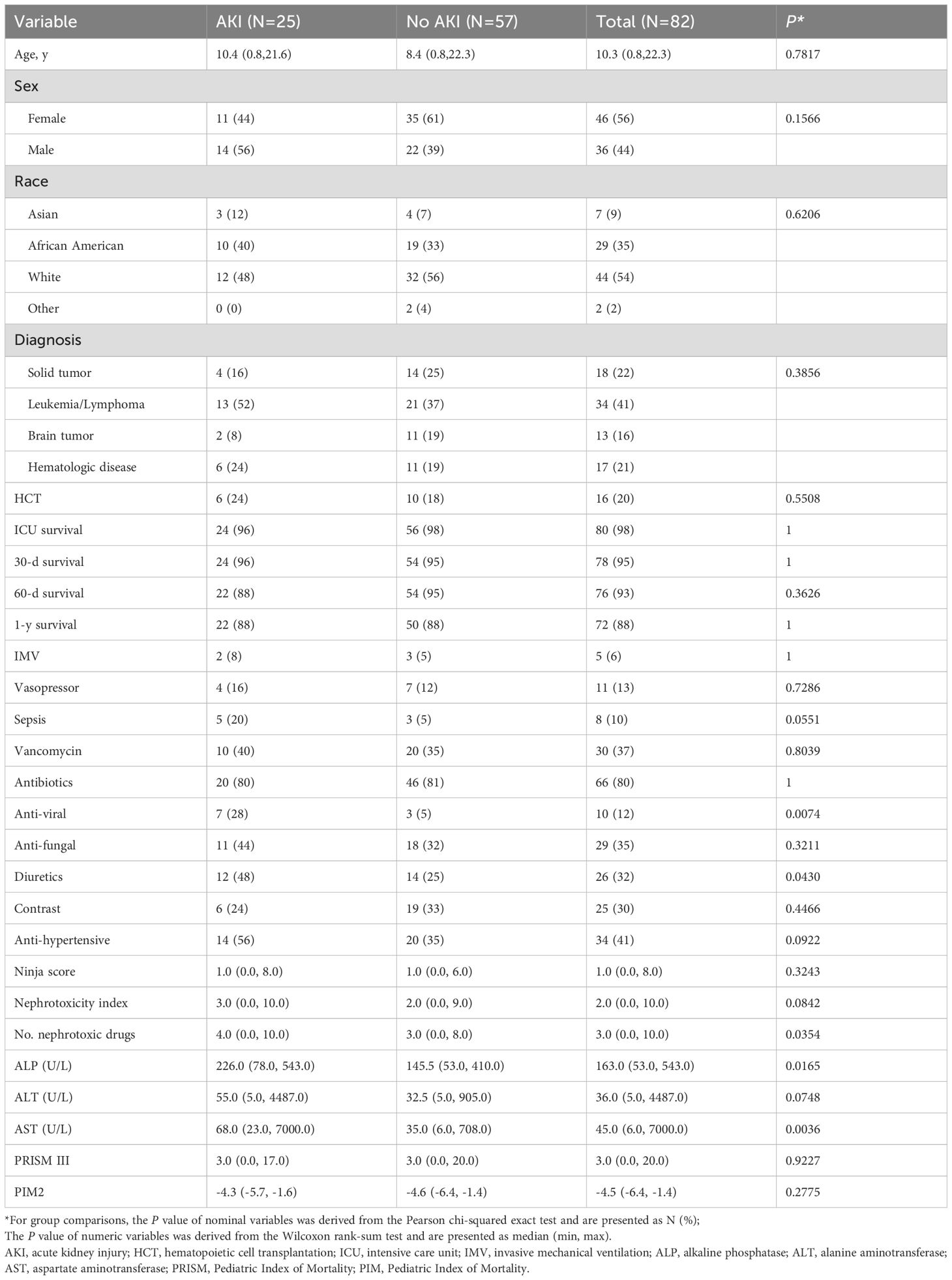
A total of 103 ICU admissions were initially identified. After applying exclusion criteria, 21 patients were excluded, and a final cohort of 82 patients with a diagnosed malignancy or hematologic condition were included (Supplementary Figure 1). The median age in our cohort was 10.3 y (0.8, 22.3), and the most common diagnosis was hematologic malignancy (41%) (Table 1). Sixteen patients (20%) were recipients of HCT. Nearly all patients (98%) survived beyond their ICU discharge, with 30-day, 60-day, and 1 year after discharge survival rates of 95%, 93%, and 88%, respectively. Of the 82 patients, 6% received invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), and 13% needed vasopressor support.
3.1 Acute kidney injury
AKI was encountered in 25 patients (30%) (Table 1). Diagnosis, age, BMI, weight, and HCT were not associated with any stage of AKI. However, sepsis was associated with a higher prevalence of AKI (62% in septic patients vs. 27% in non-septic patients, P=0.055). Additionally, those receiving antiviral medications were more likely to have an AKI. Other risk factors of AKI included diuretics, higher aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, higher nephrotoxicity index, and a higher number of nephrotoxic drugs.
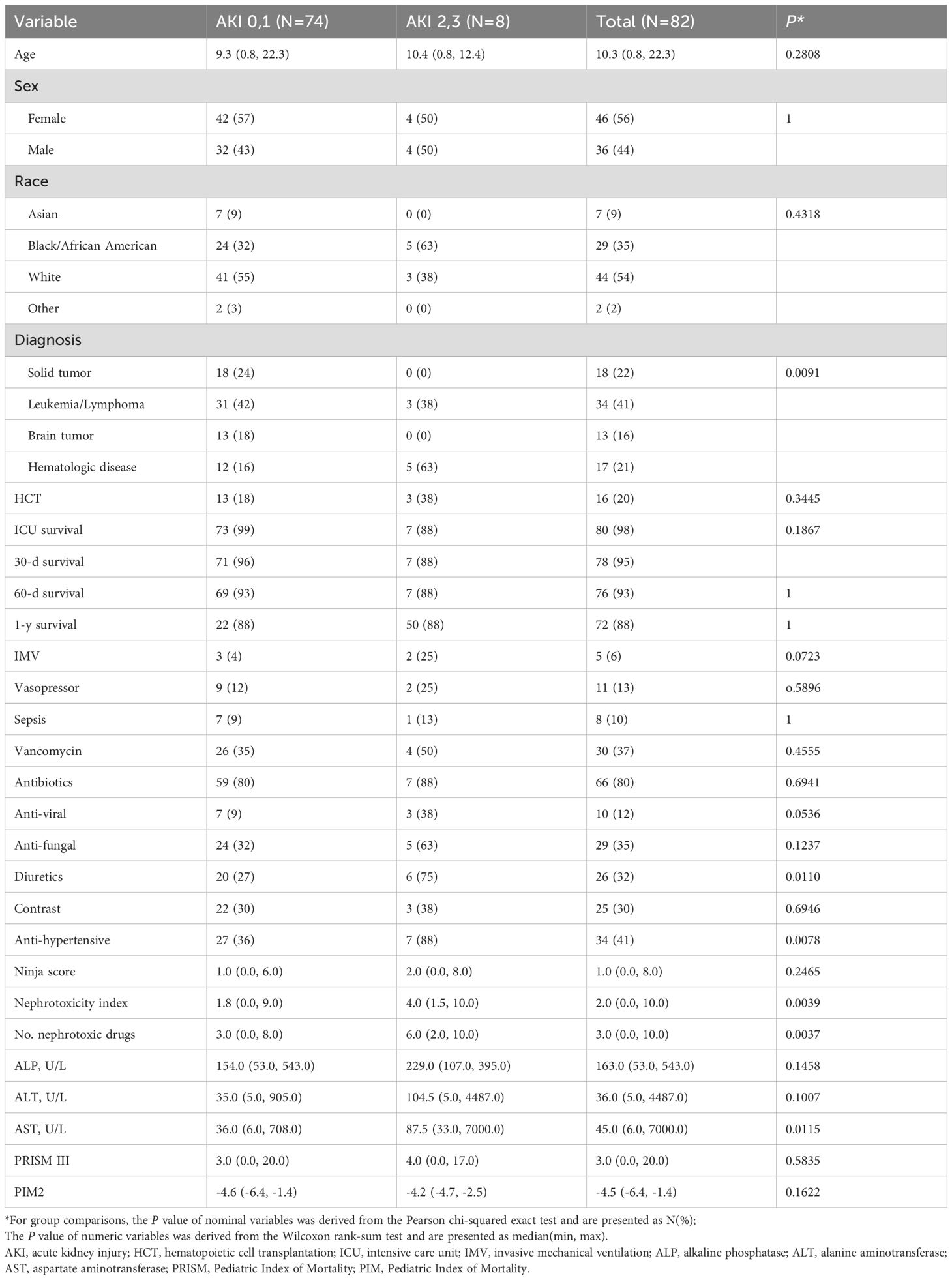
Of the 25 children with AKI, 8 (32%) had severe AKI, which comprised 10% of the total cohort (Table 2). Risk factors for severe AKI included IMV, higher AST, antiviral medications, diuretics use, higher nephrotoxicity index, and a higher number of nephrotoxic drugs. Most children (88%) with severe AKI required antihypertensive medications, whereas 36% of patients with mild/no AKI required such treatments.
3.2 Hypoalbuminemia and outcome
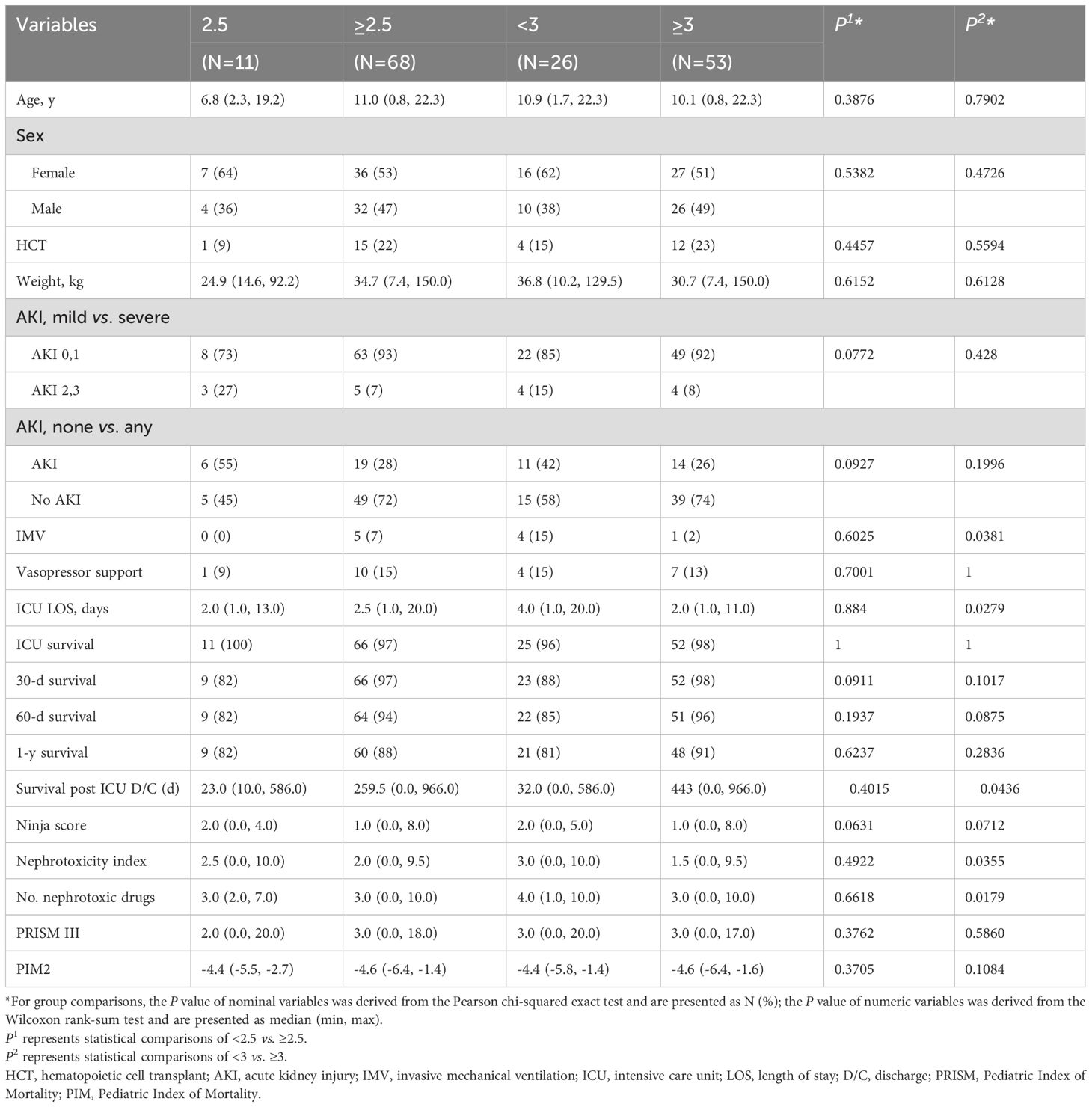
Out of the 82 patients, 3 lacked SAL data and were therefore excluded from this analysis. Three categories of SAL (all in g/dL) were analyzed: <2.5 vs. ≥2.5, <3 vs. ≥3, and <3.5 vs. ≥3.5. Fourteen percent had SAL <2.5 g/dL, whereas 33% and 65% had SAL <3 and <3.5 g/dL, respectively. Survival rate did not differ with SAL level at the time of ICU discharge. However, in children with SAL<2.5 g/dL, there was a non-statistically significant trend of lower survival rate at 30 days after ICU discharge (82% vs 97% in children with SAL ≥2.5 g/dL, P=0.09). Additionally, children with SAL < 3 g/dL had a non-statistically significant trend of lower 60-day survival rates (85% vs 96% in children with SAL ≥3 g/dL, P=0.088).
Severe AKI was diagnosed in 27% of patients with SAL <2.5 g/dL and 7% of those with SAL ≥2.5 g/dL (P=0.077) (Table 3). In addition, a non-statistically significant trend of higher any stage AKI was observed in children with SAL <2.5 g/dL (55% vs. 27% in children with SAL ≥2.5 g/dL, P=0.09). For patients with SAL <3 g/dL, severe AKI was diagnosed in 15% of the cohort vs 7.5% in children with SAL ≥3 g/dL. Although the prevalence of AKI was not significantly higher in patients with SAL <3 g/dL compared to those with ≥ 3 g/dL, other ICU outcome measures were impacted with these SAL (Table 3). Five patients received IMV, 4 of whom (80%) had SAL <3 g/dL (P=0.038): these patients experienced a longer duration of ICU admission (median, 4 days vs 2 days, P=0.028).
4 Discussion
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a significant and common complication in pediatric patients with malignancies and hematological conditions, particularly those requiring admission to the ICU. AKI developed in one-third of our cohort, with 10% experiencing severe AKI. The etiology of AKI in these patients is often multifactorial, arising from factors such as renal hypoperfusion, nephrotoxicity from medications, and complications related to the underlying disease. In our cohort, sepsis contributed to a higher occurrence of AKI (62%). The rate of AKI observed in septic patients in our cohort is similar to that reported by Bagshaw et al. (64.4%) in a large cohort of 4,532 critically ill adult patients with septic shock (9). Additionally, nephrotoxic drug exposure was significantly associated with AKI in our cohort. Both nephrotoxicity index and the number of nephrotoxic drugs were higher in children with any AKI as well as in those with severe AKI. Indeed, previous studies have demonstrated that the odds of developing AKI are 1.5 times more likely for patients who receive nephrotoxic medication and are increased with the use of more than one nephrotoxin (7, 10). Nephrotoxic drug exposure continues to be a challenging problem in an immune-compromised population that is at higher risk of infection. The use of medications such as antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals is inevitable with suspected infection. It is prudent to monitor renal function closely and use early prediction systems such as electronic medical record alerts to reduce the risk of AKI, especially when patients are receiving more than one nephrotoxic drug.
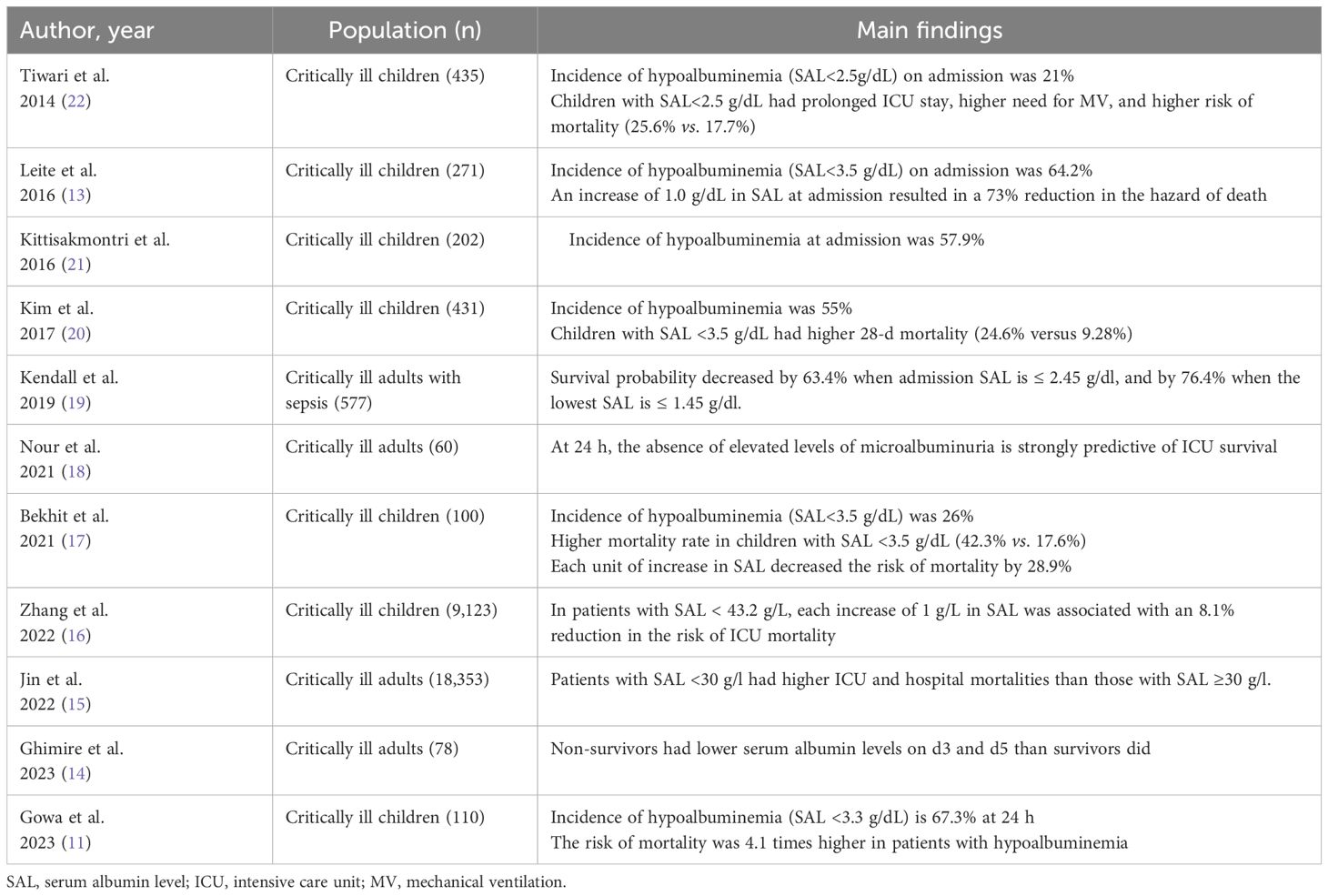
Hypoalbuminemia is highly prevalent in critically ill children (up to 67%) (11). After infancy, normal serum albumin levels rise to 3.4–5.6 g/dL, and values below 3.3 g/dL at any age are considered hypoalbuminemia. In our cohort, hypoalbuminemia was common and SAL <3.5 g/dL was present in 65%. Importantly, low SAL correlates with increased morbidity and mortality across hospitalized populations (12). Albumin, a protein synthesized by the liver, is critical for maintaining oncotic pressure and vascular integrity. Hypoalbuminemia occurs in children with malignancy secondary to poor nutritional status, impaired hepatic synthesis, increased catabolism, or increased loss due to capillary leak or proteinuria. Importantly, hypoalbuminemia increases the risk of mortality in critically ill patients and an increase of 1.0 g/dL in SAL at admission can result in a 73% reduction in the risk of mortality (13). Table 4 depicts a summary of studies that examined the effect of hypoalbuminemia on survival in critically ill patients (11, 13–22). In our cohort, children with SAL <2.5 g/dl were less likely to survive for 30 days after ICU discharge and those with SAL <3 g/dl were less likely to survive for 60 days after ICU discharge.
In our cohort, patients with SAL <2.5 g/dL were observed to have a trend of increased risk of any stage AKI and of severe AKI (stage 2,3). In the context of AKI, low albumin levels can exacerbate fluid shifts and lead to further renal damage. Low SAL may not only signify poor nutritional status but also contribute to the development of AKI by impairing renal perfusion and increasing the risk of nephrotoxicity. Monitoring SAL in this patient population could provide an early indication of AKI risk. Several studies, including those by Yu et al. (2017) and Wiedermann et al. (2010), have linked hypoalbuminemia to an increased risk of AKI, particularly in patients undergoing treatment with contrast media or during intensive care (23, 24). For instance, Yu et al. found that low serum albumin levels at hospital admission were predictive of AKI development in cancer patients undergoing CT with contrast (24). A meta-analysis by Wiedermann et al. (2010) that included 3,917 patients found that lower SAL was an independent predictor both of AKI and of death after AKI development. Each 1g/dL decrease in SAL increased the odds of AKI by 134% and the odds of mortality by 147% (pooled OR, 2.47) (23). Another meta-analysis of 39 studies in adult patients (n=168,740) found that each 1.0 g/dL decrease in SAL was significantly associated with an increased risk of AKI (OR,1.685) and a higher mortality in AKI patients with hypoalbuminemia (OR, 1.183) (25).
As in other studies (13, 14, 22), in our cohort, a higher requirement for IMV and longer ICU duration were observed in children with SAL <3 g/dL. In a cohort of 435 critically ill children, patients with SAL<2.5 g/dL had longer ICU stay (13.8 vs. 6.7 days, P < 0.001) and higher likelihood of respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilator (OR, 13.7) (22).
It is unclear whether hypoalbuminemia is causally related to poor prognosis or is just a marker of disease severity. However, it is biologically plausible that it contributes to worse outcomes in critically ill children with oncologic/hematologic diseases. In addition to its role in regulating osmotic pressure and capillary membrane permeability, albumin helps to preserve endothelial cell function from oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals (26). This is particularly important in the oncological population as endothelial injury occurs often. Additionally, capillary leaks are encountered in this population in the context of sepsis or as a complication of post-hematopoietic cell transplant therapy.
This study has several limitations that warrant careful consideration. First, selection bias may limit the generalizability of our findings. As the study was conducted at a highly specialized pediatric hematologic-oncology center with advanced resources and subspecialty care; the patient population, clinical decision-making, and access to interventions may not reflect those in general or community-based pediatric ICUs. Therefore, extrapolation of results to broader settings should be done cautiously. Second, measurement bias may have influenced our findings. Serum albumin levels were collected as part of routine clinical care, and variability in timing of measurement, assay methods could have introduced inconsistencies. Third, although an association between hypoalbuminemia and adverse outcomes was observed, we caution against inferring a causal relationship, given the observational design of our study, which limits the ability to control unmeasured confounders and establish temporality or causality. Although we recognize the study’s limitation, it is important to highlight that this is the first study to investigate the effects of hypoalbuminemia in critically ill children with oncologic or hematologic conditions. Future prospective, multicenter research is needed to confirm our findings, further explore this association in such a vulnerable population, and determine whether correcting hypoalbuminemia improves outcome.
5 Conclusion
To conclude, hypoalbuminemia is common in critically ill children with oncologic or hematologic conditions. Hypoalbuminemia was associated with adverse outcomes such as the need for IMV and longer ICU duration. Future studies are needed to confirm these risks and to investigate whether correction by exogenous albumin infusions improves outcomes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by St Jude Children’s Research hospital IRB. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Retrospective chart review with no intervention and no risk.
Author contributions
VJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EA: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CC: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities (ALSAC).
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Cherise Guess, PhD, ELS, for editing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1576639/full#supplementary-material
References
1. James V, Angelo J, and Elbahlawan L. Kidney injury in children after hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:3329–43. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30030253
2. Liu S, Zhao J, and Wang F. Acute kidney injury in cancer patients. Clin Exp Nephrol. (2022) 26:103–12. doi: 10.1007/s10157-021-02131-7
3. Park PG, Hong CR, Kang E, Park M, Lee H, Kang HJ, et al. Acute kidney injury in pediatric cancer patients. J Pediatr. (2019) 208:243–50.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.12.023
4. Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, and Goldstein SL. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N. Engl J Med. (2017) 376:11–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611391
5. Vincent JL, Dubois MJ, Navickis RJ, and Wilkes MM. Hypoalbuminemia in acute illness: is there a rationale for intervention? A meta-analysis of cohort studies and controlled trials. Ann Surg. (2003) 237:319–34. doi: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000055547.93484.87
6. Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. (2012) 120:c179–84. doi: 10.1159/000339789
7. Rivosecchi RM, Kellum JA, Dasta JF, Armahizer MJ, Bolesta S, Buckley MS, et al. Drug class combination-associated acute kidney injury. Ann Pharmacother. (2016) 50:953–72. doi: 10.1177/1060028016657839
8. Goldstein SL, Kirkendall E, Nguyen H, Schaffzin JK, Bucuvalas J, Bracke T, et al. Electronic health record identification of nephrotoxin exposure and associated acute kidney injury. Pediatrics. (2013) 132:e756–67. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-0794
9. Bagshaw SM, Lapinsky S, Dial S, Arabi Y, Dodek P, Wood G, et al. Acute kidney injury in septic shock: clinical outcomes and impact of duration of hypotension prior to initiation of antimicrobial therapy. Intensive Care Med. (2009) 35:871–81. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1367-2
10. Cartin-Ceba R, Kashiouris M, Plataki M, Kor DJ, Gajic O, and Casey ET. Risk factors for development of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Crit Care Res Pract. (2012) 2012:691013. doi: 10.1155/2012/691013
11. Gowa MA, Tauseef U, and Ahmed SH. A relation between serum albumin level and prognosis of critically ill children admitted to the paediatric Intensive Care Unit. J Pak Med Assoc. (2023) 73:1034–42. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.7465
12. Akirov A, Masri-Iraqi H, Atamna A, and Shimon I. Low albumin levels are associated with mortality risk in hospitalized patients. Am J Med. (2017) 130:1465.e11–.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.07.020
13. Leite HP, Rodrigues da Silva AV, de Oliveira Iglesias SB, and Koch Nogueira PC. Serum albumin is an independent predictor of clinical outcomes in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2016) 17:e50–7. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000596
14. Ghimire B, Shah S, Paudyal MB, Bhattarai M, Pangeni PM, Kharel A, et al. Serial estimations of serum albumin levels as a prognostic marker in critically ill patients admitted in ICU in tertiary center: An observational study. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e35979. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035979
15. Jin X, Li J, Sun L, Zhang J, Gao Y, Li R, et al. Prognostic value of serum albumin level in critically ill patients: observational data from large intensive care unit databases. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:770674. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.770674
16. Zhang X, Zhang L, Wei C, Feng L, Yang J, Zhang G, et al. U-shaped association between serum albumin and pediatric intensive care unit mortality in critically ill children. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:931599. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.931599
17. Bekhit OE, Yousef RM, Abdelrasol HA, and Mohammed MA. Serum albumin level as a predictor of outcome in patients admitted to pediatric intensive care units. Pediatr Emerg Care. (2021) 37:e855–e60. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000002567
18. Nour M, Hegazy A, Mosbah A, Abdelaziz A, and Fawzy M. Role of microalbuminuria and hypoalbuminemia as outcome predictors in critically ill patients. Crit Care Res Pract. (2021) 2021:6670642. doi: 10.1155/2021/6670642
19. Kendall H, Abreu E, and Cheng AL. Serum albumin trend is a predictor of mortality in ICU patients with sepsis. Biol Res Nurs. (2019) 21:237–44. doi: 10.1177/1099800419827600
20. Kim YS, Sol IS, Kim MJ, Kim SY, Kim JD, Kim YH, et al. Serum albumin as a biomarker of poor prognosis in the pediatric patients in intensive care unit. Korean. J Crit Care Med. (2017) 32:347–55. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2017.00437
21. Kittisakmontri K, Reungrongrat S, and Lao-Araya M. Hypoalbuminaemia at admission predicts the poor outcomes in critically ill children. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. (2016) 48:158–61. doi: 10.5603/AIT.a2016.0028
22. Tiwari LK, Singhi S, Jayashree M, Baranwal AK, and Bansal A. Hypoalbuminemia in critically sick children. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2014) 18:565–9. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.140143
23. Wiedermann CJ, Wiedermann W, and Joannidis M. Hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis of observational clinical studies. Intensive Care Med. (2010) 36:1657–65. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1928-z
24. Yu MY, Lee SW, Baek SH, Na KY, Chae DW, Chin HJ, et al. Hypoalbuminemia at admission predicts the development of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients: A retrospective cohort study. PloS One. (2017) 12:e0180750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180750
25. Wiedermann CJ, Wiedermann W, and Joannidis M. Causal relationship between hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury. World J Nephrol. (2017) 6:176–87. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v6.i4.176
Keywords: intensive care unit, acute kidney injury, children with cancer, hypoalbuminemia, survival, mechanical ventilation
Citation: James V, Ashcraft E, Cheng C and Elbahlawan L (2025) Hypoalbuminemia is associated with adverse outcomes in critically ill children with cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1576639. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1576639
Received: 14 February 2025; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 11 June 2025.
Edited by:
Dristhi Ragoonanan, Cure 4 The Kids, United StatesReviewed by:
Luz María Torres-Espindola, National Institute of Pediatrics, MexicoThomas McLean, Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 James, Ashcraft, Cheng and Elbahlawan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lama Elbahlawan, bGFtYS5lbGJhaGxhd2FuQHN0anVkZS5vcmc=
 Vinson James
Vinson James Emily Ashcraft
Emily Ashcraft Cheng Cheng
Cheng Cheng Lama Elbahlawan
Lama Elbahlawan