- 1Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 2Xinxiang Engineering Technology Research Center of Digestive Tumor Molecular Diagnosis, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 3Department of Abdominal Surgical Oncology Ward 2, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang, China
- 4Henan Province Engineering Technology Research Center of Tumor Diagnostic Biomarkers and RNA Interference Drugs, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDAC inhibitors, HDACi) have garnered considerable attention due to their potential in treating various types of malignant tumors. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) not only influence chromatin structure and gene transcription by regulating histone acetylation status but also acetylate various non-histone proteins. They are widely involved in several key biological processes, such as cell cycle regulation, apoptosis induction, and immune responses. HDACi exert their effects by inhibiting HDAC activity; however, these effects are highly concentration-dependent and non-selective. HDACi inevitably disrupt both gene expression and signaling networks, leading to multi-target, non-specific biological effects. This article focuses on the immunomodulatory mechanisms of HDACi, including their role in remodeling the tumor extracellular matrix and their impact on various immune cell populations. The synergistic potential of combining HDACi with other therapeutic approaches is also discussed. This review examines the application of HDACi across different tumor types, highlighting preclinical and clinical evidence that demonstrates the multifunctionality and efficacy of HDACi. By leveraging their unique mechanism of action, HDACi opens new avenues for enhancing antitumor immunity and achieving durable therapeutic responses. Future research and clinical trials will play a crucial role in optimizing the use of HDACi, elucidating resistance mechanisms, and identifying the most effective combinations to maximize patient benefit.
1 Introduction
HDACs are a crucial class of enzymes that can be categorized into four distinct classes according to homology to yeast proteins. Class I includes HDAC1, 2, 3, and 8, which are usually localized in the nucleus, have deacetylase activity, and contain zinc-dependent active sites (1, 2). Class II is further divided into class IIa (HDAC4, 5, 7 and 9) and class IIb (HDAC6 and 10), which have tissue-specific expression and can shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, and class III sirtuins (SIRT1-7) are not dependent on zinc but on NAD+ as a cofactor (3, 4). The only Class IV HDAC is HDAC11, which exhibits characteristics similar to those of Class I and Class II HDACs (Table 1) (5–7). HDACs play a central regulatory role in cellular processes by dynamically modulating the acetylation of both histones and non-histones. In the nucleus, HDACs remove acetyl groups from histones, which in turn alter chromatin structure and regulate crucial processes like gene expression, cell cycle progression, and cellular differentiation (8, 9). In the cytoplasm, HDACs also target various non-histone substrates, including transcription factors, DNA repair proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, and molecular chaperones. They regulate the function, stability, and subcellular localization of these proteins through deacetylation modifications (10–12). HDACs catalyze histone deacetylation, which increases the positive charge on histones and enhances electrostatic interactions with negatively charged DNA molecules. This epigenetic modification can cause chromatin to compact, creating a transcriptionally repressive chromatin environment (Figure 1) (13–15). In certain genomic regions, epigenetic reprogramming can work synergistically with regulatory elements like DNA methylation or transcription factor complexes, ultimately resulting in the transcriptional silencing of functional genes (16, 17). The range of target genes silenced by this mechanism is broad, including, but not limited to, tumor suppressor genes and pro-apoptotic genes (18, 19).
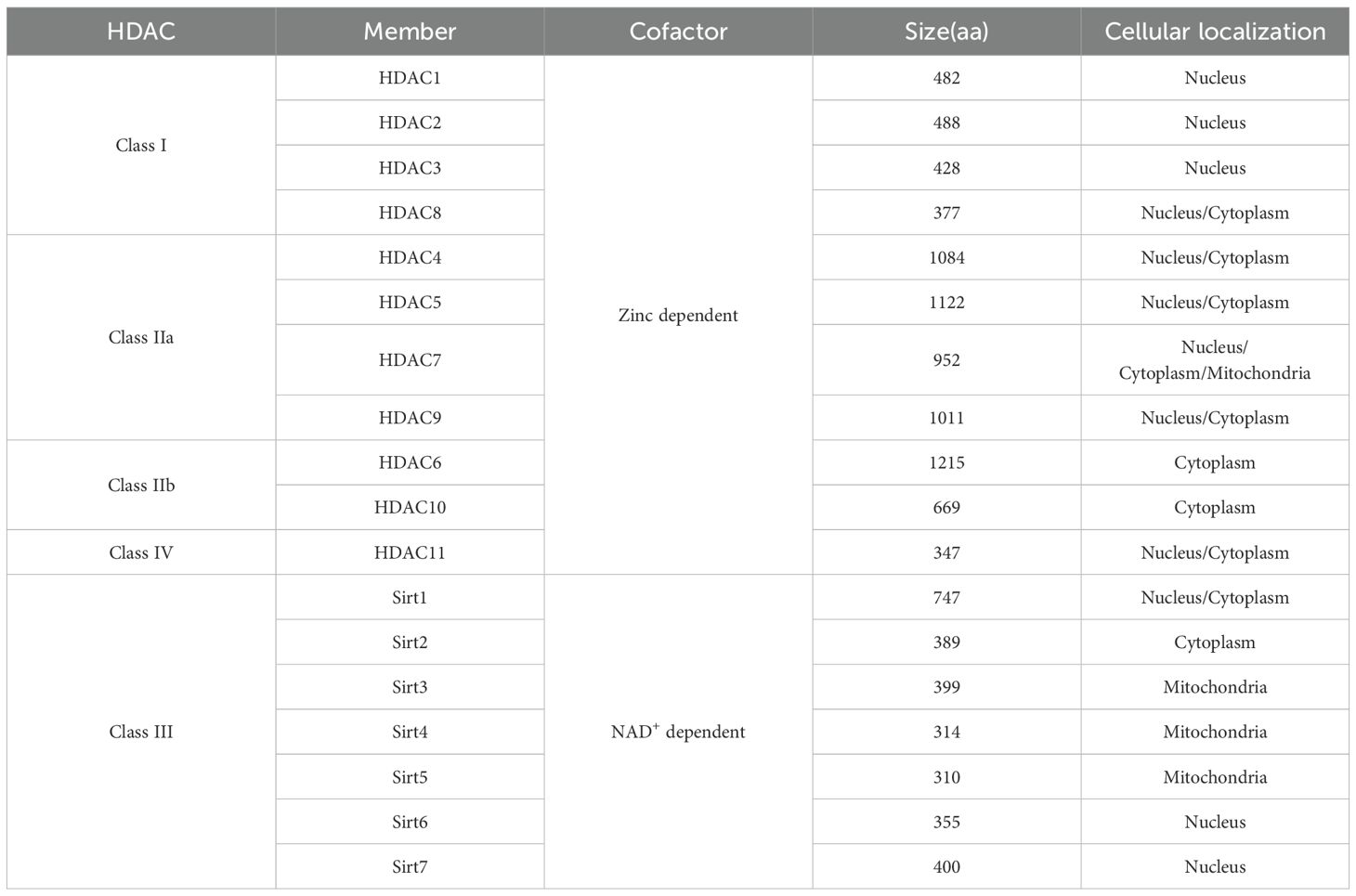
Table 1. Classification of HDACs based on homology to human yeast homologs and generalization of their cofactor, size, and cellular localization.
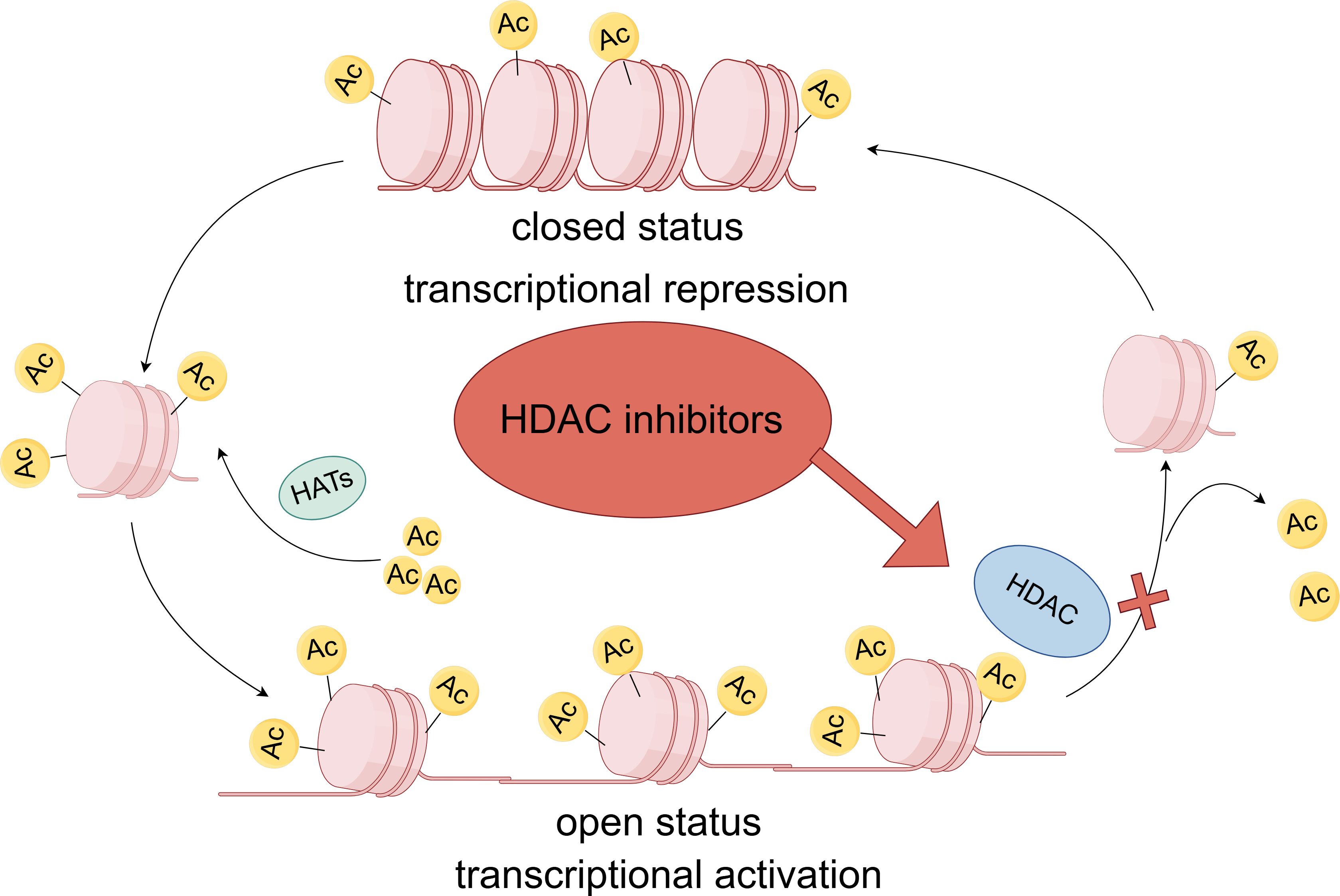
Figure 1. Dynamic regulatory processes of HDAC and HDACi. Chromatin consists of an association of DNA and proteins assembled in the nucleosome, the functional unit of genetic material. Nucleosomes are octamers composed of individual histone proteins. DNA is negatively charged, and histones are positively charged; therefore, the two are attracted to each other. Histone acetyltransferases(HATs) add an acetyl group to histone lysine residues. The positively charged acetyl group can neutralize the charge interaction between DNA and histones, thereby loosening the chromatin structure and facilitating transcription. In contrast, histone deacetylase removes the acetyl group from histones, reducing the degree of histone acetylation and inhibiting transcription. Inhibitors of histone deacetylase block the action of histone deacetylase, thereby increasing the degree of histone acetylation and loosening the chromatin structure, which promotes transcription.
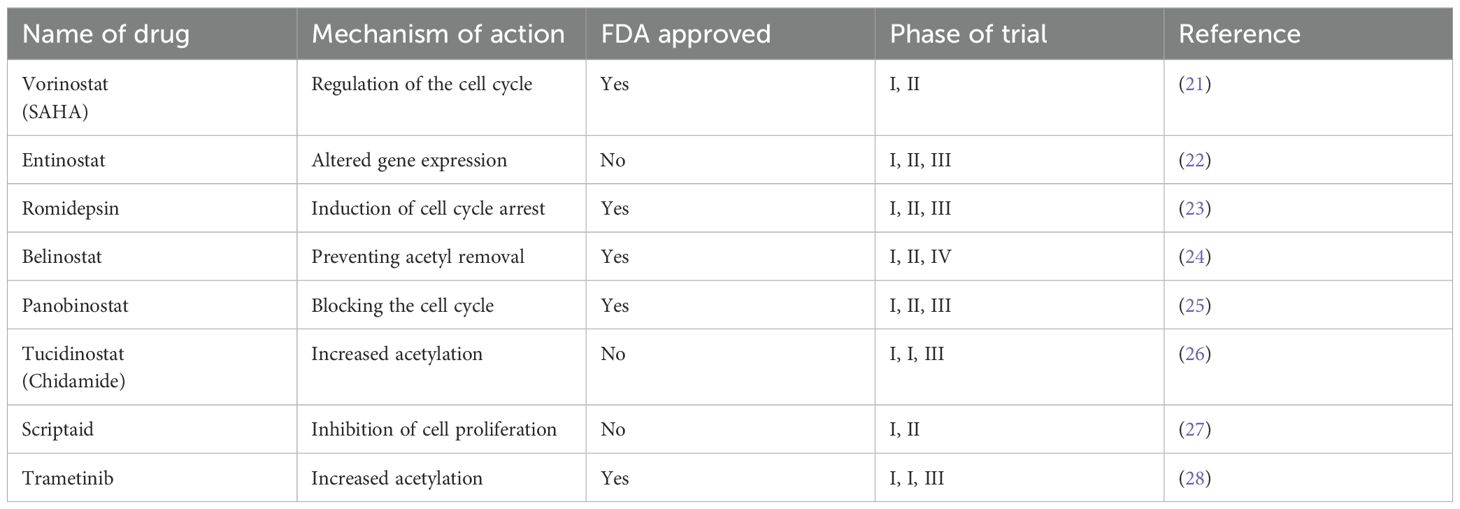
HDAC inhibitors are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of histone deacetylases, thereby regulating gene expression and affecting processes such as the cell cycle, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. HDAC inhibitors can be classified based on their synthetic or natural composition, subclass specificity, and chemical structure type. In general, they are divided into two categories: pan-inhibitors of HDACs and HDAC-specific inhibitors. HDAC inhibitors are classified into four main subgroups based on their chemical composition: hydroxamic acids, benzamides, cyclic tetrapeptides, and short-chain fatty acids (20). Several HDAC inhibitors, including Vorinostat, Romidepsin, Panobinostat, and Belinostat, have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. In addition, China and Japan have approved Tucidinostat, a novel subtype-selective HDAC inhibitor that targets class I HDACs (HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC3) as well as class IIb HDAC10 (Table 2) (26). HDAC inhibitors are considered novel epigenetic drugs whose therapeutic potential has been extensively tested in various disease models. For example, Vorinostat has shown efficacy in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, particularly by inhibiting the activity of class I and class II HDACs. Romidepsin is capable of disrupting the G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis (29). Panobinostat acts as a general inhibitor of tumor cell growth by affecting misfolded protein aggregation through the inhibition of HDAC6 and the upregulation of p21 (30). Belinostat, a hydroxy acid pan-HDAC, for the treatment of multiple cancers (31). Tucidinostat acts as a selective HDAC inhibitor and affects tumor cell growth and death through the inhibition of specific HDAC subtypes (32). These drugs have shown encouraging results in the treatment of multiple myeloma, Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, and many other cancers.
2 Mechanism of action of HDACi in immunotherapy
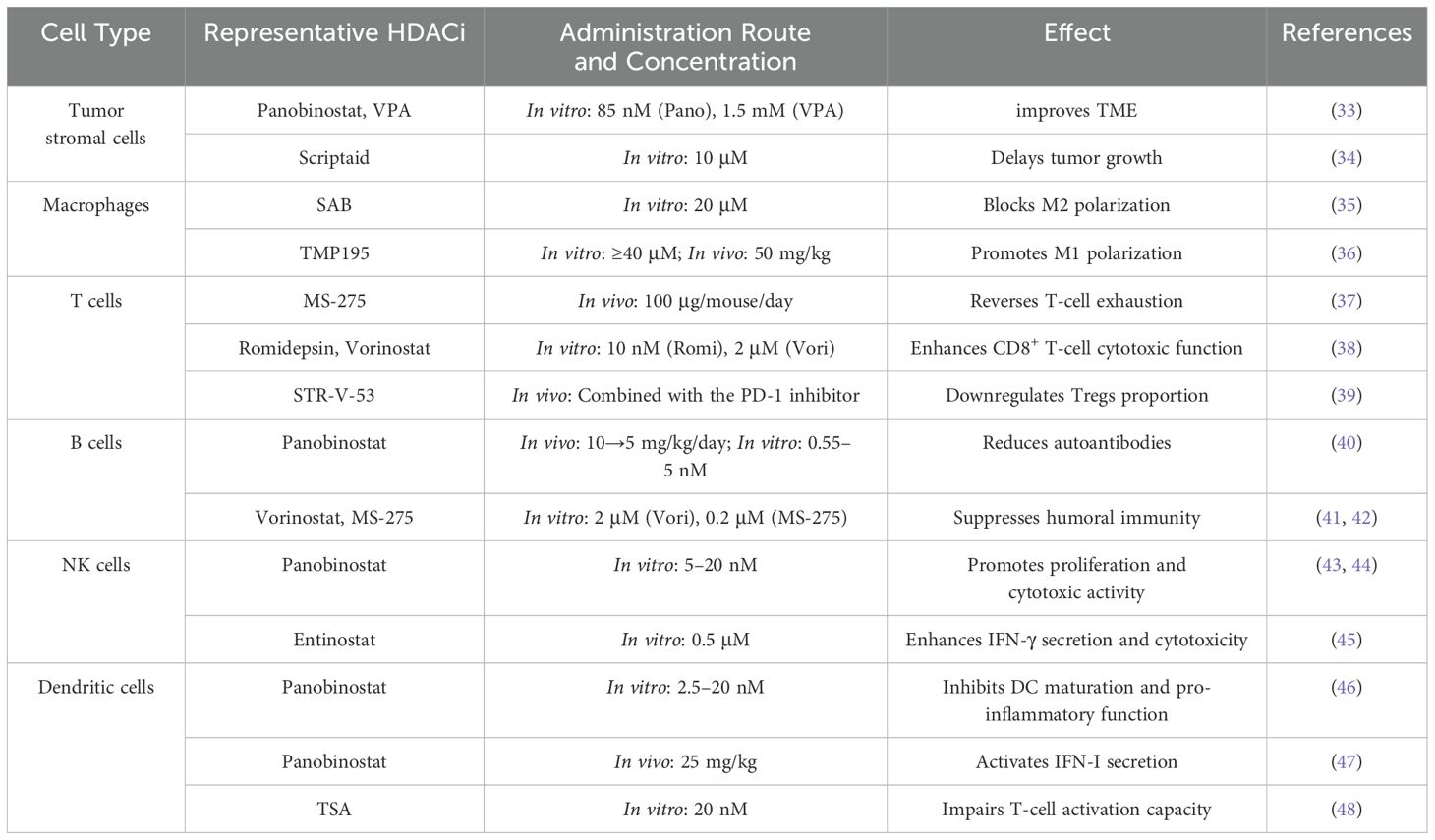
HDAC inhibitors exert complex and multifaceted immunomodulatory effects in a concentration-dependent manner by targeting key immune components in the tumor microenvironment (TME), including the extracellular matrix (ECM), macrophages, T cells, B cells, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells (Figure 2). These effects help reshape the tumor microenvironment (TME) and influence anti-tumor immune responses, offering new strategies for cancer immunotherapy (Table 3).
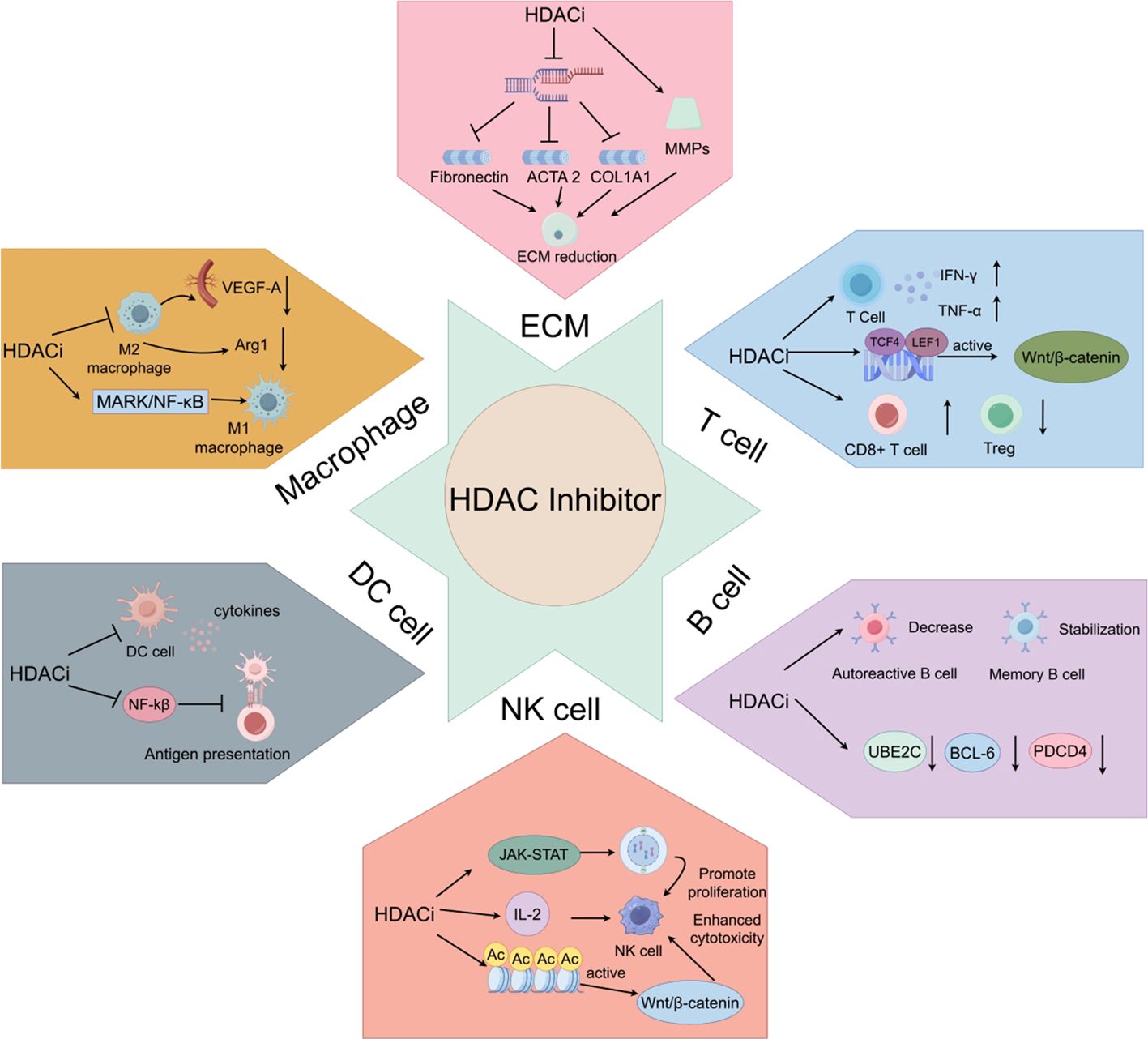
Figure 2. Mechanism of action of HDACi on immune cells. ECM: HDACi promotes ECM reduction. Macrophage: HDACi promotes M1 macrophage polarization and inhibits M2 macrophage polarization. T cell: HDACi activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, promotes cytokine release, and reduces the number of Tregs. B cell: HDACi promotes the reduction of autoreactive B cells, maintains the number of memory B cells, and promotes apoptosis of malignant B cells in B-cell lymphoma. NK cell, HDACi enhances cytotoxicity and promotes cell proliferation. DC, HDACi inhibits the release of cytokines by dendritic cells and suppresses their antigen-presenting capacity by downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.
2.1 Remodeling of tumor extracellular matrix by HDACi
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a key component of TME. HDACi has been reported to alter the structure of TEM and reduce the invasiveness of tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) by inhibiting the expression of fibronectin (FN) and collagen. According to Martina Korfei et al. (33), treatments with Panobinostat (85 nM) and Valproic acid (VPA, a class I HDACi, 1.5 mM) decreased the mRNA expression of genes related to fibronectin, ACTA2 (actin), and COL1A1 (collagen). CAFs support tumor progression and invasion by secreting an abundant extracellular matrix that protects tumor cells from immune checkpoints or kinase inhibitors. According to Dae Joong Kim et al. (34), Scriptaid (a selective inhibitor of HDACs 1/3/8, 10 μM) inhibits ECM secretion, reduces cell contraction and rigidity, and impairs collective cell invasion in CAF and tumor cell spheroid co-cultures. Scriptaid reduces CAF abundance and delays tumor growth in vivo. In addition, HDACi promotes the degradation of ECM by regulating the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), thereby attenuating the interaction between tumor cells and the stroma and further inhibiting tumor metastasis (49). These effects not only help inhibit tumor growth but also provide new strategies for immunotherapy of tumors. However, clinical trials remain indispensable for translating this strategy into clinical applications.
2.2 Effect of HDACi on macrophages
The role of HDACi in regulating the tumor microenvironment is receiving increasing attention, particularly its impact on tumor-associated macrophages. Macrophages can be classified into M1-type (classically activated macrophages) and M2-type(alternatively activated macrophages). IFN-γ can differentiate macrophages into pro-inflammatory M1-type macrophages (50). Unlike IFN-γ, IL-4 can convert macrophages into M2-type macrophages, which are associated with anti-inflammatory functions (51). M2-type macrophages exert synergistic effects in reducing inflammatory responses, promoting tissue repair, enhancing immune suppression, and supporting tumor growth by secreting anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β) and highly expressing arginase-1 (Arg1) (52). Trametinib (HDACi) inhibits M2-type polarization of macrophages, leading to a reduction in the expression of pro-angiogenic growth factors VEGF-A and Arg1 in these cells (53). SAB (20 μM, HDAC10 inhibitor) significantly inhibits the gene expression of M2 macrophage polarization markers (Arg1, Fizz1, Ym1) in both in vitro models (35). Yicheng Han et al. (36) found that TMP195 (HDACi) can reprogram macrophages into an M1 phenotype at specific concentrations (50 mg/kg in vivo and ≥40 μM in vitro), thereby enhancing the antitumor immune response. In addition, TMP195 continuously activates MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway phosphorylation, suggesting that it promotes M1 polarization through the synergistic action of epigenetic modification and inflammatory signaling pathways (54). In summary, HDAC inhibitors exert immune regulatory effects by modulating the polarization balance of macrophages.
2.3 Regulation of T cell function by HDACi
HDAC inhibitors play an important role in regulating T cell function. Exhausted T cells exhibit high expression of inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1 and TIM-3, and a loss of effector function (55, 56). To overcome this bottleneck, Andrew Nguyen’s team (37) conducted a study using Class I HDAC inhibitor MS-275 (100 μg/mouse/day) and found that MS-275 downregulated the expression of the exhaustion marker PD-1, thereby relieving its functional inhibition, while upregulating TIM-3. However, its expression exhibited dynamic decoupling from exhaustion characteristics. In contrast, terminal effector differentiation markers (KLRG1 and granzyme B) were significantly enriched. The viral activator Tax plays a crucial role in HTLV-1 reactivation and the initiation of new infections. Annika P. Schnell et al. (57) demonstrated that Panobinostat (100 nM) and Romidepsin (10 nM) significantly increased Tax transcription levels in CD4+ Jurkat T cells. Mohammed L. Ibrahim et al. (38) conducted a study in vitro with HDAC inhibitors at specific concentrations (10 nM Romidepsin or 2 μM Vorinostat). They observed a dose-dependent increase in TNF-α and IFN-γ secretion. Real-time cytotoxicity analysis confirmed that HDACi significantly enhances the cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells against tumor target cells. HDACi can also activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by upregulating the expression of specific transcription factors, such as TCF4 and LEF1, thereby enhancing the antitumor activity of T cells (58). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that the novel hepatocellular carcinoma-selective HDAC inhibitor STR-V-53 not only inhibits HDAC activity and upregulates PD-L1 expression in tumor cells but also significantly enhances CD8+ T cell infiltration. Notably, the combination of STR-V-53 with a PD-1 inhibitor synergistically reduces the proportion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) (39). This contrasts with the mechanism of HDACi (SAHA) found in previous studies. SAHA can induce the generation of Tregs in the thymus of mice, promote the conversion of peripheral T cells to Tregs (59). We speculate that this apparent contradiction may stem from differences in the subtype selectivity and effective concentrations of HDAC inhibitors. This suggests a significant association between HDAC subtype-specific inhibition and immune regulatory effects.
2.4 Regulation of B cell function by HDACi
The primary function of B cells is to produce antibodies and mediate humoral immune responses. They can also present soluble antigens and produce cytokines, participating in immune regulation (60). When administered via intraperitoneal injection to lupus-prone mice, the HDAC inhibitor Panobinostat significantly reduced the number of autoreactive plasma cells and serum antinuclear antibody levels. Importantly, this treatment did not affect the number of CD4+/CD8+ T cells or spleen weight. Further in vitro experiments confirmed that Panobinostat, within the low nanomolar concentration range (0.55–5.00 nM), selectively inhibited B cell proliferation and differentiation. However, it did not impair the activity of memory B cells (40). Depletion of certain key immune cell types during the early inflammatory phase has been shown to prevent sodium sulfate-induced colitis (DSS colitis). Studies have found that the HDAC6 inhibitor BML-281 does not affect the infiltration of neutrophils, macrophages, or T lymphocytes in DSS-treated mice. Still, it does inhibit the infiltration of CD191+ B lymphocytes into the inflamed lamina propria (61). B-cell antibody class-switch recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM) depend on the functional activity of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG2) (62). Studies have shown that HDACi affects CSR and SHM by reducing UNG2 expression levels. Following HDACi treatment, the expression levels of the cell cycle-related protein UBE2C and the anti-apoptotic protein BCL6 significantly decreased, while the expression level of the pro-apoptotic protein PDCD4 significantly increased. HDACi directly induces apoptosis of malignant B cells in B-cell lymphoma by increasing pro-apoptotic proteins (41). René Winkler et al. (42) found that HDACi (0.2 μM MS-275, 1.5 mM Valproic acid) increased H3/H4 acetylation levels by inhibiting histone deacetylase activity, interfering with chromatin openness and DNA repair complex recruitment, thereby significantly inhibiting B cell CSR and reducing the expression of IgG subclasses (IgG1, IgG2a) and IgA. HDAC inhibitors regulate B cell function through epigenetic reprogramming, exhibiting dual antitumor effects. Further exploration is needed to optimize dosage and precisely regulate combination therapy strategies.
2.5 Role of HDACi in enhancing natural killer cell activity
Natural killer (NK) cells are crucial immune effector cells that can limit the expansion and spread of cancer cells. Studies have shown that HDACi can enhance the killing ability of NK cells against tumor cells by promoting their proliferation and activation. Low concentrations (5 nM) of HDACi Dactinostat and Panobinostat can significantly enhance the proliferation of primary natural killer cells (pNK cells) induced by IL-2 through the JAK-STAT signaling pathway (43). Panobinostat (10–20 nM) activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by increasing the level of histone H3K27 acetylation in the β-catenin promoter region, thereby significantly upregulating the expression of NKG2D ligands MICA and MICB on the surface of soft tissue sarcoma cells, and subsequently enhancing the killing efficiency of NK92 cells and pNK cells against tumor cells (44). The treatment with 0.5 μM Entinostat for 24 hours significantly upregulates the expression of NKG2D, simultaneously inducing increased chromatin accessibility to activate IFIT1 gene transcription and its downstream STING-STAT4-IRF1 signaling pathway. Functional experiments confirmed that Entinostat pre-treatment of NK cells enhances their cytotoxic activity against tumors and IFN-γ secretion capacity (45). However, Lucas E. Rossi et al.’s findings contrast sharply with the previous view. They studied peripheral blood NK cells from healthy donors and NK cells from the spleens of C57BL/6 mice. Their results showed that HDAC inhibitors (0.1–1 μM Trichostatin A (TSA); 2–10 mM Valproic acid) significantly inhibited IL-12/IL-15/IL-18-induced IFN-γ secretion and the cytotoxic activity of NK cells (63). This contradictory effect may be related to the dose gradient, treatment duration, and cell type specificity of HDACi, suggesting that the administration regimen of HDACi needs to be precisely optimized in clinical applications to achieve positive regulation of NK cell function.
2.6 Effect of HDACi on dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are key antigen-presenting cells in the immune system, playing a critical role in antitumor immunity (64). It was assessed whether HDACi could modulate cytokine production by DCs. During the maturation process induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or poly (I: C) (polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid), DCs were treated with or without Panobinostat at concentrations of 2.5, 10, and 20 nM for 24 hours. Compared to the control, Panobinostat treatment significantly inhibited the production of a range of cytokines by DCs, including IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-23, and TNF-α (46). The HDAC inhibitor Panobinostat (25 mg/kg) activates IFN-I secretion by increasing H3K27 acetylation of type I interferon genes in pDCs (plasma cell-like dendritic cells) (47). HDACi was shown to inhibit the maturation process of dendritic cells, thereby affecting their ability to present antigens. Trichostatin A (HDACi, 20 nM) was found to inhibit the maturation of dendritic cells by down-regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby decreasing their ability to stimulate T cells (48). Additionally, HDACi may also influence the role of DCs in the tumor microenvironment by altering their cellular phenotype and secretory profile. This inhibitory effect may lead to increased immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment, which in turn affects the effectiveness of the overall immune response (65, 66). Based on the above, we find that the effect of HDACi on DCs appears to be more harmful than beneficial.
3 Joint application of HDACi
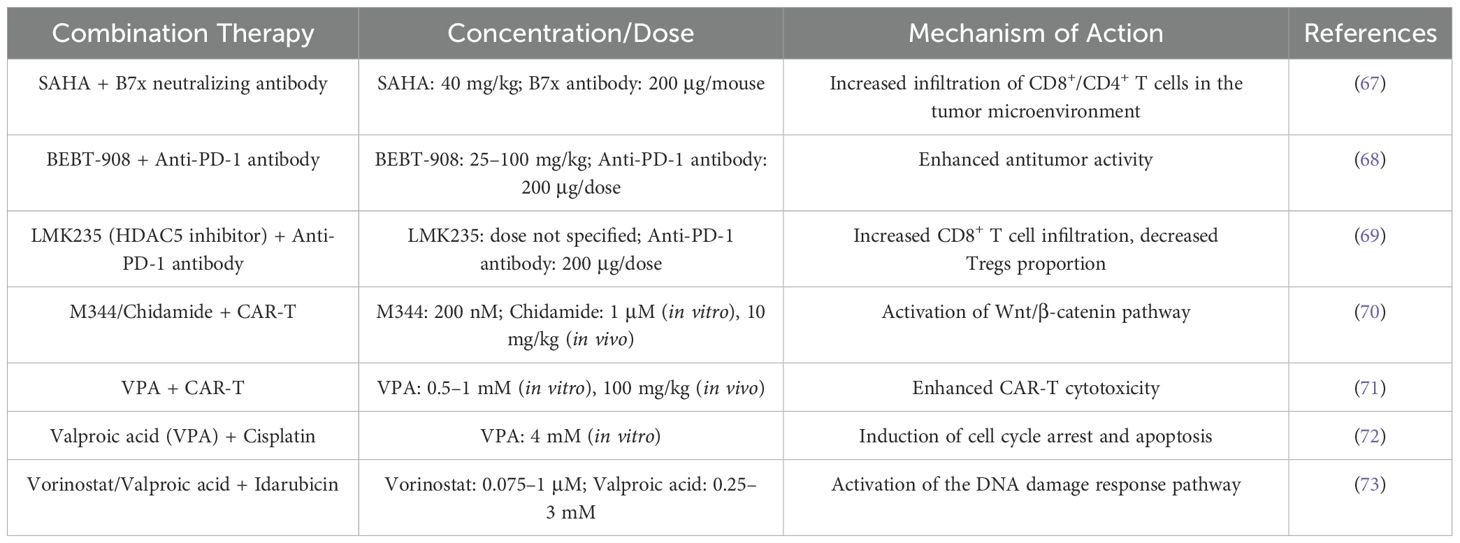
HDAC inhibitors significantly enhance the antitumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T therapy, and chemotherapy through epigenetic remodeling. Specifically, they synergistically activate antitumor immune responses, enhance the long-term functionality of CAR-T cells, promote chemotherapy drug sensitivity, and mitigate treatment toxicity (Table 4). Future research should focus on exploring subtype-specific mechanisms, clinical translation pathways, and combination strategies for expanding their application in solid tumors.
3.1 HDACi and immune checkpoints
Immune checkpoints are a group of key factors expressed on immune cells that regulate the level of immune activation. A key function of immune checkpoint molecules is similar to a car’s “braking system.” They can quickly intervene when the immune system is activated, acting as a timely brake. This helps ensure that immune system activation remains within moderate limits, thereby preventing excessive activation (74). Tumor cells can evade immune system surveillance by exploiting immune checkpoints, thereby allowing them to survive and proliferate. Research indicates that HDACi can enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors by modulating the tumor microenvironment and amplifying antitumor immune responses (75, 76). B7x is an immune checkpoint modulator. The combination therapy of SAHA (40 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection every 3 days) and B7x neutralizing antibody (200 μg/mouse, intraperitoneal injection every 2 days) significantly delayed tumor growth, with a tumor inhibition rate of 80.6%, and significantly increased the infiltration of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment (67). The large amount of butyrate produced by Clostridium difficile nucleic acid in tumors inhibits HDAC3/8 in CD8+ T cells, inducing acetylation and expression of H3K27 in the Tbx21 promoter, thereby inhibiting PD-1, alleviating CD8+ T cell exhaustion, and promoting effector function (77). Tumor growth experiments conducted in syngeneic mice inoculated with MC38 cells using PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors demonstrated that while BEBT-908 (a dual HDAC/PI3K inhibitor) alone could delay the growth of MC38 tumors, its efficacy was significantly enhanced when combined with anti-PD-1 antibodies, with some host mice surviving for extended periods. In fact, after combination therapy, 5 out of 8 mice achieved a durable cure (68). Researchers utilized the KPC genetically engineered mouse PDAC model (a pancreatic cancer model expressing mutant KRAS and p53 under the Pdx1-Cre drive) to investigate the combined therapy of HDAC5 inhibitor LMK235 (administered intraperitoneally) and anti-PD-1 antibody (200 μg per dose, administered intraperitoneally). The results showed that inhibiting HDAC5 significantly increased CD8+ T cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment, reduced the proportion of Tregs, and exhibited synergistic effects with anti-PD-1 antibodies, jointly inhibiting tumor growth (69). Combination therapy with HDACi and immune checkpoint inhibitors has shown promise in multiple clinical trials, particularly in patients with refractory tumors, where the combination therapy regimen can significantly improve patient survival rates and disease control rates (78–80).
3.2 Combination of HDACi and CAR-T cell therapy
In recent years, HDAC inhibitors have emerged as a promising adjuvant therapy with the potential to enhance CAR-T cell function (81). In vitro experiments showed that CAR-T cells pretreated with HDAC inhibitors (200 nM M344 or 1 μM Chidamide) exhibited reduced HDAC1 expression and significantly increased histone H3K27 acetylation. In in vivo experiments, using a leukemia mouse model, it was confirmed that HDACi pretreatment or oral administration of Citarabine (10 mg/kg) after infusion significantly reduced tumor burden and prolonged survival. The experiment also demonstrated through multi-omics analysis that HDACi activates the classical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, jointly driving CAR-T cell differentiation toward a central memory phenotype and inhibiting the expression of exhaustion-related receptors (70). Valproic acid enhances CAR-T cell recognition of tumor targets and cytotoxic effects by upregulating the expression of NKG2D ligands (ULBP1-3) on tumor cell surfaces and activating the NKG2D-NKG2DL immune recognition axis (71). Additionally, HDACi can promote the secretion of cytokines such as IL-2 and IFN-γ, thereby enhancing T cell proliferation and effector functions (82, 83). However, these findings are based on preclinical experiments, and further clinical trials are necessary for future applications.
3.3 HDACi and chemotherapy
The application of HDACi in chemotherapy is gaining increasing attention, particularly due to their potential to enhance antitumor activity. HDACi can improve the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents by altering the epigenetic state of tumor cells, thereby promoting cell cycle arrest and inducing apoptosis (84). For example, following Valproic acid treatment, the levels of p16, p21, and p27 were observed to increase by twofold, indicating that tumor suppressor-mediated cell cycle arrest and the observed cell death effects are involved. The Valproic acid pretreatment regimen opens chromatin, increases the expression of tumor suppressor genes, and enhances the binding of cisplatin to chromatin, ultimately leading to increased cell death (72). In gastric cancer cells, pretreatment with HDACi significantly increases the amount of DNA-binding drugs, promotes histone acetylation, and leads to cell cycle arrest and cell death (20). Studies have shown that the anthracycline drug idarubicin, when used in combination with histone deacetylase inhibitors (such as Vorinostat 0.075–1 μM or Valproic acid 0.25–3 mM), significantly enhances synergistic antitumor activity against MOLT4 and HL60 leukemia cell lines and primary acute leukemia patient cells. The mechanism of action involves the simultaneous activation of histone H3/H4 acetylation modifications and the γH2AX-mediated DNA damage response pathway, and this synergistic effect is not affected by the timing of administration (73). However, further in vivo experiments and toxicity assessments of normal hematopoietic stem cells are needed to determine their clinical translational value. Although chemotherapy is an important means of treating cancer, it is often accompanied by severe side effects. Research has shown that HDACi can alleviate patients suffering by improving gastrointestinal toxicity caused by chemotherapy (85). In addition, the study also found that HDACi, such as Curcumin, can alleviate chemotherapy-induced nephrotoxicity and cardiotoxicity, which may be related to their antioxidant properties (86). By combining HDACi with chemotherapy drugs, it may be possible to significantly improve patients’ quality of life and reduce the overall toxicity burden of chemotherapy without compromising antitumor efficacy (87). Therefore, the use of HDACi helps enhance the safety of chemotherapy, making it an important adjuvant drug in cancer treatment.
4 HDAC inhibitors in oncology
Histone deacetylase inhibitors demonstrate significant potential in the treatment of various hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. They exert their antitumor effects through multiple mechanisms, including epigenetic modification, inhibition of key signaling pathways, and modulation of the tumor microenvironment (Figure 3). Clinical studies across different phases have provided preliminary evidence supporting their clinical therapeutic value (Table 5). Future research efforts should focus on optimizing therapeutic strategies, exploring combination regimens, and developing precision biomarkers aimed at enhancing efficacy and reducing toxicity.
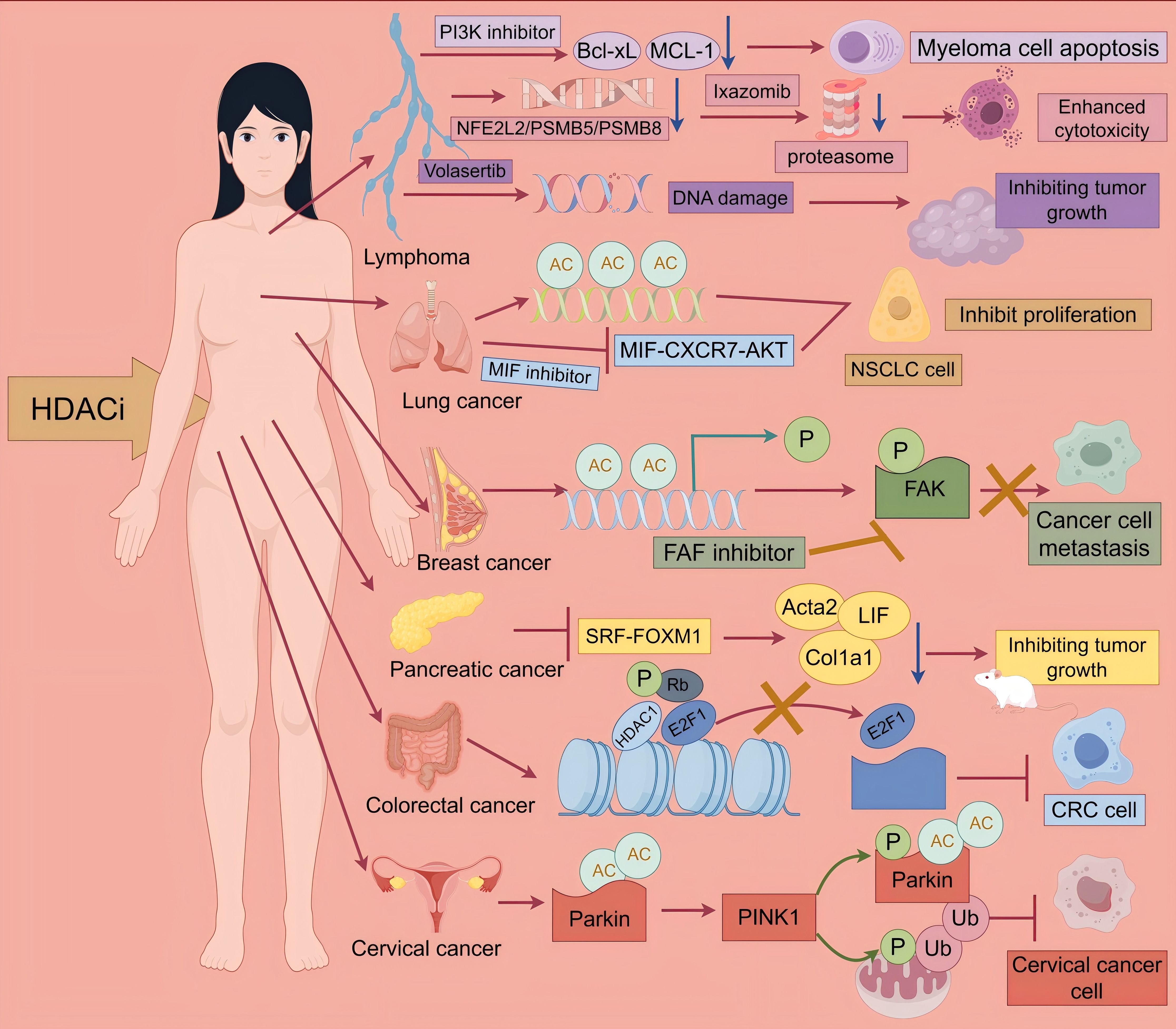
Figure 3. Antitumor effects of HDACi. multiple myeloma: Multiple myeloma: CUDC-907 simultaneously targets HDAC and PI3K, reducing the expression of Bcl-xL and MCL-1, thereby inhibiting myeloma cell growth. Hodgkin lymphoma: Ixazomib combined with Belinostat can synergistically inhibit the NFE2L2 pathway, suppress proteasome activity, and thereby enhance cytotoxicity. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Volasertib combined with HDACi induces DNA damage, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. Lung cancer: 6a simultaneously targets HDAC and MIF, inducing histone acetylation and blocking the MIF-CXCR7-AKT pathway, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of NSCLC cells. Breast cancer: HDACi can promote metastasis by enhancing H3K9 acetylation of the NEDD9 gene promoter, upregulating NEDD9 expression, and activating FAK phosphorylation. FAK inhibitors can reverse this process. Pancreatic cancer: HDACi inhibits the SRF-FOXM1 transcriptional axis, downregulating the pro-fibrotic genes Acta2 and Col1a1 and the pro-inflammatory factor LIF, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. Colorectal cancer: HDACi reduces the phosphorylation level of Rb, preventing E2F1 from being released from the E2F1/Rb/HDAC1 complex. The retention of E2F1 prevents it from activating downstream target genes that drive the cell cycle process, ultimately inhibiting the growth of CRC cells. Cervical cancer, HDACi activates PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy, thereby inhibiting the growth of cervical cancer cells.
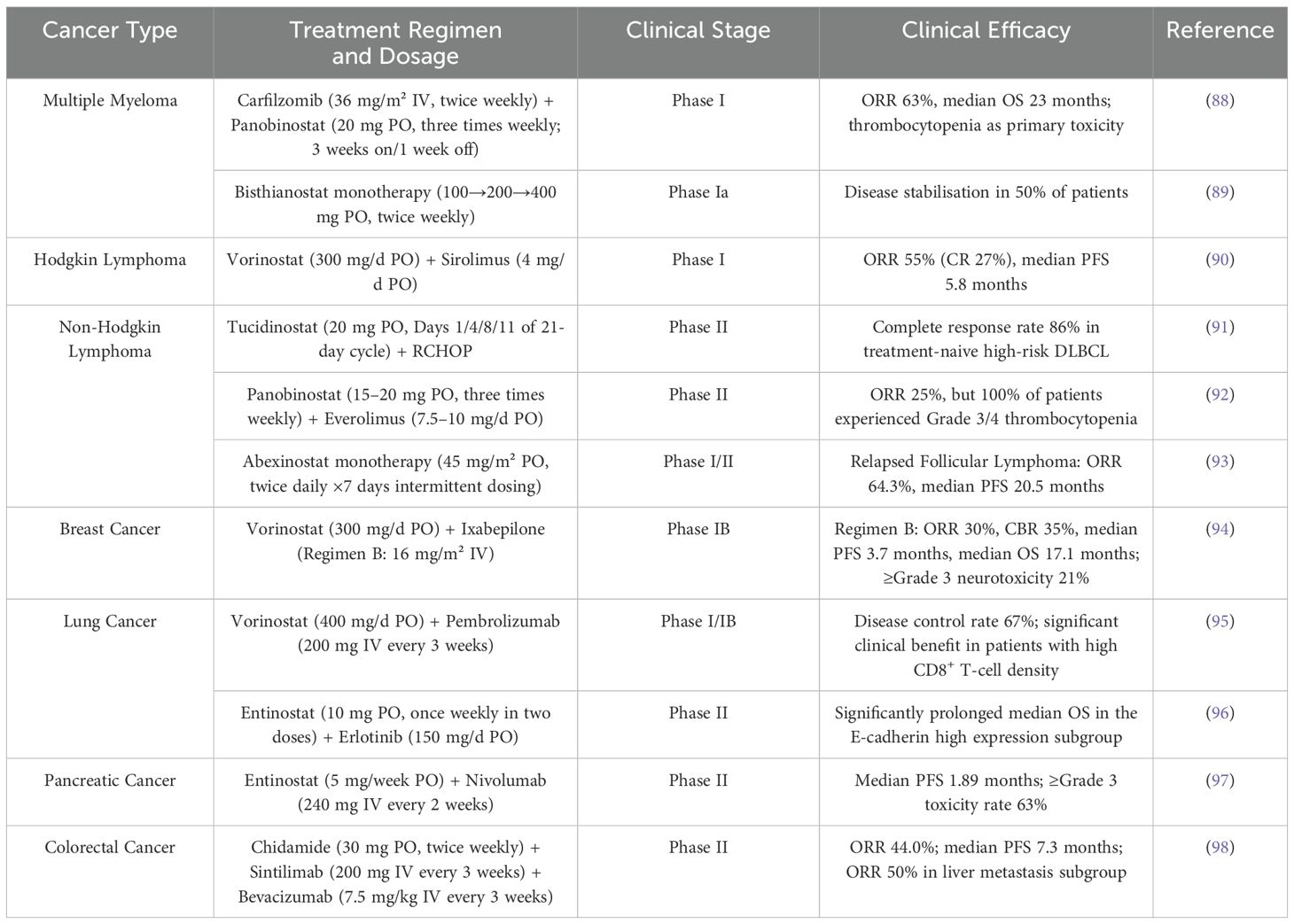
Table 5. Summary of the efficacy of HDACi in clinical trials for various tumors. PO indicates oral administration, IV indicates intravenous injection.
4.1 Multiple myeloma
In recent years, HDACi has shown significant potential in the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM) through epigenetic regulation, induction of apoptosis, and inhibition of key pathways (PI3K/Akt/mTOR and NF-κB). Studies have shown that the dual inhibitor CUDC-907 (10 nM) effectively inhibits myeloma cell growth and downregulates anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-xL, MCL-1) at lower concentrations by simultaneously targeting HDAC and PI3K. Its efficacy is significantly superior to that of Vorinostat (HDAC inhibitor) or Pictilisib (PI3K inhibitor) at 1 μM (99, 100). In a clinical study, a phase I trial of carfilzomib (intravenous infusion, dose range 27–45 mg/m²) in combination with palbociclib (oral, dose range 15–20 mg) confirmed the feasibility of the non-glucocorticoid combination regimen. This dose group achieved an objective response rate (ORR) of 63% and a median overall survival (OS) of 23 months; however, hematological toxicities, such as thrombocytopenia, were observed (88). The Phase I trial of the novel HDAC inhibitor Bisthianostat (BIS, oral tablets, starting dose of 100 mg, escalated to 200/400 mg, administered twice weekly) demonstrated good safety as a monotherapy, with no Grade 3/4 non-hematologic toxicities. Fifty percent of patients achieved stable disease (SD), including one case in the 200 mg group that maintained SD for nearly seven months, providing a solid foundation for future therapies (89).
4.2 Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a specific type of lymphoma that is typically treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy, but HL cells often develop resistance to traditional treatments. Frank C. Passero Jr. et al. (101) found that in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines, the proteasome inhibitor Ixazomib (25–75 nM) transiently inhibits proteasome activity, but subsequent functional recovery occurs due to NFE2L2 (NRF2)-dependent upregulation of proteasome gene expression. In contrast, the HDAC inhibitor Belinostat (250 nmol/l) blocked this adaptive response by downregulating NFE2L2 and proteasome genes (PSMB5, PSMB8). A phase I trial involving 40 patients with relapsed/refractory HL that the combination of Vorinostat (300 mg/day orally) with sirolimus (4 mg/day orally, n=22) or Everolimus (5-10 mg/day dose escalation, n=18) yielded ORR of 55% and 33%, respectively, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 5.8 months, suggesting synergistic efficacy of HDACi combined with mTOR inhibitors (90). Although current data support the notion that HDACi overcomes resistance through epigenetic regulation and inhibition of pro-survival pathways, the limitations of small sample sizes and non-randomized designs necessitate validation through larger-scale studies (102). Future research should explore precision combination strategies based on biomarkers, such as NFE2L2, to optimize treatment for relapsed/refractory HL (103).
4.3 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Multiple studies have demonstrated that the efficacy and toxicity of HDACi in treating non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are highly dependent on the administration strategy and disease subtype. In preclinical studies, the combination of PLK1 inhibitor Volasertib (intravenous injection, 30 mg/kg) and HDACi Belinostat (intraperitoneal injection, 50 mg/kg) significantly inhibited tumor growth in a DLBCL/MCL mouse model by synergistically inducing DNA damage and downregulating c-Myc (104). Clinical translational research shows that in a Phase II clinical trial of newly diagnosed high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (n=100), oral HDAC inhibitor Tucidinostat (20 mg per dose) in combination with the R-CHOP regimen achieved an 86% complete response rate (91). A phase II clinical trial in relapsed/refractory DLBCL evaluating the combination of the oral HDAC inhibitor palbociclib (40 mg three times weekly) with the oral mTOR inhibitor Everolimus showed an objective response rate of 25%. However, the regimen demonstrated limited clinical utility due to universal grade 3/4 hematologic toxicity, with thrombocytopenia occurring in 83% of patients (92). A multicenter phase I/II trial showed significant efficacy of oral pan-HDAC inhibitor Abexinostat (45 mg/m² twice daily, 7 days on/intermittent dosing) in relapsed follicular lymphoma, with a 64.3% ORR and 20.5-month median PFS. However, the response rate is limited in mantle cell lymphoma (ORR 27.3%) (93). The above results highlight the need for a comprehensive evaluation of the clinical value of HDACi in combination with specific disease subtypes and precise dosing regimens (route, dose, and cycle).
4.4 Breast cancer
In breast cancer, combination therapy strategies demonstrate considerable potential for overcoming the limitations associated with single-agent therapy. HDAC inhibitors can enhance H3K9 acetylation at the NEDD9 gene promoter, upregulate NEDD9 expression, and activate FAK phosphorylation, thereby promoting metastasis. Notably, preclinical evidence suggests that FAK inhibitors can reverse HDAC inhibitor-induced NEDD9-dependent metastasis, implying the feasibility of a targeted combination strategy (105). The HDAC inhibitor (SAHA) suppresses the proliferation, invasion, and migration of breast cancer cells by upregulating miR-200c to inhibit CRKL protein expression (106, 107). A randomized Phase IB clinical trial evaluated the feasibility of combining the HDAC inhibitor Vorinostat with the microtubule stabilizer ixabepilone for the treatment of previously treated metastatic breast cancer (94). Comparing two combination regimens (A and B), Regimen B, which employed a 28-day cycle with split-dose oral Vorinostat (days 1–7 and 15–21) and dose-dense, lower-dose ixabepilone (days 2, 9, and 16), demonstrated superior clinical efficacy compared to Regimen A (21-day cycle). Regimen B showed advantages in ORR, clinical benefit rate (CBR), and OS over Regimen A. While PFS was similar between the two regimens, Regimen B significantly improved patient survival. Regarding safety, the incidence of ≥ grade 3 peripheral sensory neuropathy for both regimens was significantly lower than historically reported rates for ixabepilone monotherapy or its combination with capecitabine. In summary, HDAC inhibitors demonstrate multiple mechanisms of action in breast cancer treatment. Future studies should focus on optimizing their use in combination therapy to enhance clinical efficacy (108).
4.5 Lung cancer
In the treatment of lung cancer, HDAC inhibitors have also shown promising application prospects. A novel HDAC/MIF dual-target inhibitor (6a) at a concentration of 12.5 μM promotes apoptosis by inhibiting HDAC activity and inducing histone acetylation (H3K27ac), while simultaneously blocking the MIF-CXCR7-AKT signaling pathway, thereby synergistically inhibiting the survival and proliferation of NSCLC cells (especially EGFR-mutant/TKI-resistant strains). Combination with TKI drugs further enhances efficacy, offering a potential dual-targeted therapeutic strategy to overcome NSCLC resistance (109). In addition, when used in combination with other chemotherapy drugs, Chidamide can effectively inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells and induce their apoptosis (110). Although HDACi face challenges in clinical application, such as poor water solubility, rapid clearance, and high systemic toxicity, their effectiveness in inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis has been supported by numerous studies (111). In a Phase 1/1b trial, oral HDAC inhibitor Vorinostat (400 mg/day) combined with intravenous PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab (200 mg every 3 weeks) was administered to 33 patients, with good tolerability and no dose-limiting toxicity. The disease control rate reached 67%, demonstrating antitumor activity in 58% of patients who had failed prior ICI therapy (95). Another Phase II randomized controlled trial evaluated the combination of oral HDAC inhibitor Entinostat (10 mg once weekly, administered in two divided doses) with Erlotinib (150 mg daily) in 132 patients with advanced NSCLC who had failed chemotherapy. Although overall efficacy did not improve, the median overall survival (OS) was significantly prolonged in the subgroup with high E-cadherin expression. The above studies screened potential beneficiary populations through biomarkers (CD8+ T cells or E-cadherin), providing a basis for overcoming drug resistance and developing precision treatment strategies (96).
4.6 Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive solid tumors, and its treatment poses significant challenges. HDAC inhibitors have shown potential in pancreatic cancer research. Entinostat (Ent), as a Class I HDAC inhibitor, downregulates pro-fibrotic genes Acta2 and Col1a1, as well as the pro-inflammatory factor LIF, by inhibiting the SRF-FOXM1 transcriptional axis at concentrations of 5–10 μM in vitro, thereby blocking CAF activation and weakening the STAT3 pathway in tumor cells (112). In a mouse model, oral administration of the drug alone (5–10 mg/kg/day) reduced tumor burden by 41%. Combination therapy with gemcitabine further enhanced efficacy, with the mechanism involving increased lipogenic fibroblasts and reduced myofibroblasts to achieve “dual-chamber targeting.” Ent also attenuates the effects of TGF-β and TGF-α and antagonizes transcriptional activation (113). Another study proposed a triple epigenetic therapy combining subtoxic doses of HDAC inhibitors (Panobinostat: 7–15 nM; Vorinostat: 0.5–2 μM), a PARP inhibitor, and the demethylating agent Decitabine. The therapy overcame the traditional reliance of PARP inhibitors on BRCA gene status for inducing resistance by synergistically activating apoptotic pathways, exacerbating DNA damage responses, and dually inhibiting the DNA repair system (114). The novel HDAC inhibitor AES-135 can selectively kill pancreatic cancer cells in vitro without causing significant toxicity to surrounding cancer-associated fibroblasts. Additionally, AES-135 significantly prolongs survival time in mouse models, indicating its broad potential for application in the treatment of pancreatic cancer (115). In a Phase II trial of patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) refractory to prior therapy, combination therapy with oral Entinostat (5 mg weekly) and intravenous Nivolumab (240 mg every 2 weeks) yielded partial responses in 11.1% (3/27) of patients, with response durations reaching 10.2 months. However, the regimen demonstrated a median PFS of only 1.89 months, indicating rapid disease progression in most patients. Treatment-related adverse events of grade ≥3 occurred in 63% of participants, predominantly lymphocytopenia and anemia (97). HDAC inhibitors demonstrate multi-dimensional antitumor mechanisms in pancreatic cancer, but clinical efficacy is limited by tumor heterogeneity and treatment toxicity.
4.7 Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer, one of the most common malignant tumors among women worldwide, has limited efficacy with current treatment strategies, necessitating the development of novel therapies. Research revealed that SAHA (Vorinostat; 1.0, 2.5, 5.0 μM) activates PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. It upregulates full-length PINK1 protein expression and enhances Parkin Ser65 phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner in Parkin-expressing HeLa cells. This indicates that SAHA promotes ubiquitination and clearance of damaged mitochondria via the PINK1-Parkin axis, thereby suppressing tumor growth (116). SAHA directly forms hydrogen bonds with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2C, enabling it to target and regulate the ubiquitination pathway. More importantly, in a cervical cancer mouse model, administration of SAHA significantly inhibited tumor growth without causing significant toxicity. This study reveals that by targeting the UBE2C-ubiquitination axis, SAHA coordinates the regulation of protein degradation and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process (117). Class I histone deacetylase inhibitor 4SC-202 exerts its anti-cervical cancer effects by targeting the prolactin receptor (PRLR) signaling pathway, thereby suppressing cancer cell proliferation and promoting cancer cell apoptosis. Importantly, in vivo studies confirm that oral administration of 4SC-202 significantly inhibits tumor growth and reduces PRLR pathway activity within the tumor tissue, with no observed significant hepatotoxicity or organ pathological damage, highlighting its excellent in vivo safety profile (118). Although research demonstrates that HDAC inhibitors effectively suppress the development and progression of cervical cancer, relevant clinical studies are still lacking. Therefore, future efforts must prioritize advancing clinical translation studies to validate their therapeutic value and optimize treatment strategies.
4.8 Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide, with its incidence and mortality rates gradually increasing in recent years. According to statistics, in many countries, the incidence of colorectal cancer ranks second only to breast cancer and lung cancer (119). In vitro studies of colorectal cancer have demonstrated that HDACi effectively inhibits cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis. For example, the novel HDACi KH16 exhibits significant cell cycle arrest and apoptotic effects in colorectal cancer cells (120). Researchers found that HR488B (HDACi) induces cell cycle G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and accumulation of DNA damage, thereby specifically inhibiting the growth of CRC cells. Mechanistically, HR488B significantly reduces the phosphorylation level of the retinoblastoma protein (Rb). This prevents the release of E2F1 from the E2F1/Rb/HDAC1 complex. By sequestering E2F1 within the complex, HR488B blocks its ability to activate downstream target genes that drive cell cycle progression. Ultimately, this inhibits the growth of CRC cells (121). HDAC inhibitors have a significant regulatory effect on the characteristics of cancer stem cells (CSCs) in CRC. Research indicates that tumor stem cells possess self-renewal capacity and differentiation potential, which are key factors contributing to tumor recurrence and drug resistance. HDACi inhibit CSC proliferation and self-renewal capacity by altering histone acetylation status and influencing the expression of CSC-related genes (122). A randomized Phase II clinical trial confirmed that the triple therapy combination of an anti-PD-1 antibody (Sintilimab), an HDAC inhibitor (Citarinostat), and an anti-VEGF antibody (Bevacizumab) demonstrated significant clinical efficacy in colorectal cancer. The triple therapy group showed significantly higher objective response rates (44.0% vs. 13.0%), 18-week progression-free survival rates (64.0% vs. 21.7%), and longer median progression-free survival (7.3 vs. 1.5 months) compared to the control group. Notably, this regimen represents a breakthrough in treating patients with liver metastases, achieving a 50.0% objective response rate in this subgroup (98). HDACi monotherapy and combination immunotherapy represent a breakthrough for CRC. Future efforts should focus on optimizing combination regimens, unravelling resistance mechanisms, and developing precise biomarkers to advance the clinical translation of epigenetic therapy in the CRC field.
5 Conclusions and outlook
Conventional HDACi is associated with drug resistance, toxicity, and limited efficacy in clinical applications, making the development of novel HDACi an urgent issue. In recent years, researchers have begun to explore new strategies such as dual-acting HDAC inhibitors, selective HDAC inhibitors, and covalent inhibitors with the aim of overcoming the limitations of existing HDACi. For example, hydroxamic acid mixtures such as Fimepinostat and Tinostamustine have shown promising antitumor effects (123). In addition, inhibitors targeting specific subtypes, such as HDAC11, are being discovered. And the selectivity of these inhibitors may lead to fewer side effects and higher therapeutic efficacy (124). The development of novel HDACi is not limited to cancer treatment, but also extends to neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, and other fields, showing a wide range of application prospects (125). Although this review summarizes the mechanisms of action of HDAC inhibitors in antitumor immunity and their significant achievements in laboratory and early clinical studies, substantial challenges and uncertainties persist in the clinical setting. These challenges primarily include selectivity variations among different HDAC inhibitors, determination of optimal dosing regimens, and exploration of optimal combination strategies. Current research evidence indicates that distinct types of HDAC inhibitors may demonstrate differential therapeutic effects across various cancer types. Therefore, future research must urgently focus on elucidating the mechanisms of action of HDAC inhibitors and establishing their optimal clinical application strategies.
Author contributions
JT: Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MH: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation, Visualization. FS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YS: Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Henan province young and middle-aged health science and technology innovation talent project (No. YXKC2021044), College Students' innovation and entrepreneurship training program (No.202410472005), Henan Province University Science and Technology Innovation Team (No. 25IRTSTHN035).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Shi M-Q, Xu Y, Fu X, Pan D-S, Lu X-P, Xiao Y, et al. Advances in targeting histone deacetylase for treatment of solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. (2024) 17:37. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01551-8
2. Lisek M, Tomczak J, Swiatek J, Kaluza A, and Boczek T. Histone deacetylases in retinoblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6910. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136910
3. Yi M, Zheng X, Niu M, Zhu S, Ge H, and Wu K. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: current advances and future directions. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01489-2
4. Wang P, Wang Z, and Liu J. Role of HDACs in normal and Malignant hematopoiesis. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:5. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1127-7
5. Gonneaud A, Gagné JM, Turgeon N, and Asselin C. The histone deacetylase Hdac1 regulates inflammatory signalling in intestinal epithelial cells. J Inflammation (Lond). (2014) 11:43. doi: 10.1186/s12950-014-0043-2
6. Moreno-Yruela C, Galleano I, Madsen AS, and Olsen CA. Histone deacetylase 11 is an ϵ-N-myristoyllysine hydrolase. Cell Chem Biol. (2018) 25:849–856.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.04.007
7. Li J, Arnold J, Sima M, Al Faruque H, Galang J, Hu-Lieskovan S, et al. Combination of multivalent DR5 receptor clustering agonists and histone deacetylase inhibitors for treatment of colon cancer. J Controlled Release. (2024) 376:1014–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.10.062
8. Moreno-Yruela C and Fierz B. Revealing chromatin-specific functions of histone deacylases. Biochem Soc Trans. (2024) 52:353–65. doi: 10.1042/BST20230693
9. Asmamaw MD, He A, Zhang L-R, Liu H-M, and Gao Y. Histone deacetylase complexes: structure, regulation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Rev Cancer. (2024) 1879:189150. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189150
10. Kim E H, Bisson W, Löhr C V, Williams D E, Ho E, Dashwood R H, et al. Histone and non-histone targets of dietary deacetylase inhibitors. CTMC. (2015) 16:714–31. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150825125857
11. Demyanenko S and Sharifulina S. The role of post-translational acetylation and deacetylation of signaling proteins and transcription factors after cerebral ischemia: facts and hypotheses. IJMS. (2021) 22:7947. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157947
12. Li Z and Zhu W-G. Targeting histone deacetylases for cancer therapy: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. Int J Biol Sci. (2014) 10:757–70. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.9067
13. Chen WY and Townes TM. Molecular mechanism for silencing virally transduced genes involves histone deacetylation and chromatin condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2000) 97:377–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.1.377
14. Knoche SM, Brumfield GL, Goetz BT, Sliker BH, Larson AC, Olson MT, et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor M344 as a multifaceted therapy for pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0273518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273518
15. Marin-Husstege M, Muggironi M, Liu A, and Casaccia-Bonnefil P. Histone deacetylase activity is necessary for oligodendrocyte lineage progression. J Neurosci. (2002) 22:10333–45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10333.2002
16. Jia H, Morris CD, Williams RM, Loring JF, and Thomas EA. HDAC inhibition imparts beneficial transgenerational effects in huntington’s disease mice via altered DNA and histone methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:E56–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415195112
17. Goodman SJ, Luperchio TR, Ellegood J, Chater-Diehl E, Lerch JP, Bjornsson HT, et al. Peripheral blood DNA methylation and neuroanatomical responses to HDACi treatment that rescues neurological deficits in a kabuki syndrome mouse model. Clin Epigenet. (2023) 15:172. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01582-x
18. Zuo X, Qin Y, Zhang X, Ning Q, Shao S, Luo M, et al. Breast cancer cells are arrested at different phases of the cell cycle following the re-expression of ARHI. Oncol Rep. (2014) 31:2358–64. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3107
19. Foltz G, Ryu G-Y, Yoon J-G, Nelson T, Fahey J, Frakes A, et al. Genome-wide analysis of epigenetic silencing identifies BEX1 and BEX2 as candidate tumor suppressor genes in Malignant glioma. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:6665–74. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4453
20. Parveen R, Harihar D, and Chatterji BP. Recent histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer. (2023) 129:3372–80. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34974
21. Su JM, Kilburn LB, Mansur DB, Krailo M, Buxton A, Adekunle A, et al. Phase I/II trial of vorinostat and radiation and maintenance vorinostat in children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: a children’s oncology group report. Neuro-oncol. (2022) 24:655–64. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab188
22. Xu B, Zhang Q, Hu X, Li Q, Sun T, Li W, et al. Entinostat, a class I selective histone deacetylase inhibitor, plus exemestane for chinese patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:2250–8. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.001
23. Bachy E, Camus V, Thieblemont C, Sibon D, Casasnovas R-O, Ysebaert L, et al. Romidepsin plus CHOP versus CHOP in patients with previously untreated peripheral T-cell lymphoma: results of the ro-CHOP phase III study (conducted by LYSA). J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:242–51. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01815
24. Hainsworth JD, Daugaard G, Lesimple T, Hübner G, Greco FA, Stahl MJ, et al. Paclitaxel/carboplatin with or without belinostat as empiric first-line treatment for patients with carcinoma of unknown primary site: a randomized, phase 2 trial. Cancer. (2015) 121:1654–61. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29229
25. Panobinostat. Livertox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-induced Liver Injury. Bethesda (MD: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2012).
26. Sun Y, Hong JH, Ning Z, Pan D, Fu X, Lu X, et al. Therapeutic potential of tucidinostat, a subtype-selective HDAC inhibitor, in cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:932914. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.932914
27. Dai W, Qiao X, Fang Y, Guo R, Bai P, Liu S, et al. Epigenetics-targeted drugs: current paradigms and future challenges. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2024) 9:332. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02039-0
28. Long GV, Hauschild A, Santinami M, Atkinson V, Mandalà M, Chiarion-Sileni V, et al. Adjuvant dabrafenib plus trametinib in stage III BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:1813–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1708539
29. Yang X, Cui X, Wang G, Zhou M, Wu Y, Du Y, et al. HDAC inhibitor regulates the tumor immune microenvironment via pyroptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. (2024) 63:1800–13. doi: 10.1002/mc.23773
30. Vuletić A, Mirjačić Martinović K, and Spasić J. Role of histone deacetylase 6 and histone deacetylase 6 inhibition in colorectal cancer. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 16:54. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010054
31. Marampon F, Di Nisio V, Pietrantoni I, Petragnano F, Fasciani I, Scicchitano BM, et al. Pro-differentiating and radiosensitizing effects of inhibiting HDACs by PXD-101 (Belinostat) in in vitro and in vivo models of human rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. (2019) 461:90–101. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.07.009
32. Zhang P, Du Y, Bai H, Wang Z, Duan J, Wang X, et al. Optimized dose-selective HDAC inhibitor tucidinostat overcomes anti-PD-L1 antibody resistance in experimental solid tumors. BMC Med. (2022) 20:435. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02598-5
33. Korfei M, Skwarna S, Henneke I, MacKenzie B, Klymenko O, Saito S, et al. Aberrant expression and activity of histone deacetylases in sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. (2015) 70:1022–32. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206411
34. Kim DJ, Dunleavey JM, Xiao L, Ollila DW, Troester MA, Otey CA, et al. Suppression of TGFβ-mediated conversion of endothelial cells and fibroblasts into cancer associated (myo)fibroblasts via HDAC inhibition. Br J Cancer. (2018) 118:1359–68. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0072-3
35. Zhong Y, Huang T, Huang J, Quan J, Su G, Xiong Z, et al. The HDAC10 instructs macrophage M2 program via deacetylation of STAT3 and promotes allergic airway inflammation. Theranostics. (2023) 13:3568–81. doi: 10.7150/thno.82535
36. Han Y, Sun J, Yang Y, Liu Y, Lou J, Pan H, et al. TMP195 exerts antitumor effects on colorectal cancer by promoting M1 macrophages polarization. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:5653–66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.73264
37. Nguyen A, Brown D, Krishnan R, Bastin D, Deng L, Chen L, et al. HDACi-dependent microenvironmental normalization overcomes tumor burden–induced T-cell exhaustion. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:4289–305. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2181
38. Ibrahim ML, Zheng H, Barlow ML, Latif Y, Chen Z, Yu X, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors directly modulate T cell gene expression and signaling and promote development of effector-exhausted T cells in murine tumors. J Immunol. (2024) 212:737–47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300475
39. Wu B, Tapadar S, Ruan Z, Sun CQ, Arnold RS, Johnston A, et al. A novel liver cancer-selective histone deacetylase inhibitor is effective against hepatocellular carcinoma and induces durable responses with immunotherapy. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. (2024) 7:3155–69. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00358
40. Waibel M, Christiansen AJ, Hibbs ML, Shortt J, Jones SA, Simpson I, et al. Manipulation of B-cell responses with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:6838. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7838
41. Iveland TS, Hagen L, Sharma A, Sousa MML, Sarno A, Wollen KL, et al. HDACi mediate UNG2 depletion, dysregulated genomic uracil and altered expression of oncoproteins and tumor suppressors in B- and T-cell lines. J Transl Med. (2020) 18:159. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02318-8
42. Winkler R and Kosan C. Effects of HDACi on immunological functions. In: Krämer OH, editor. HDAC/HAT Function Assessment and Inhibitor Development. Methods in Molecular Biology. Springer New York, New York, NY (2017). p. 93–101. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6527-4_7
43. Zheng J, Lu Y, Xiao J, Duan Y, Zong S, Chen X, et al. Pan-HDAC inhibitors augment IL2-induced proliferation of NK cells via the JAK2-STAT5B signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 116:109753. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109753
44. Lu X, Liu M, Yang J, Que Y, and Zhang X. Panobinostat enhances NK cell cytotoxicity in soft tissue sarcoma. Clin Exp Immunol. (2022) 209:127–39. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac068
45. Idso JM, Lao S, Schloemer NJ, Knipstein J, Burns R, Thakar MS, et al. Entinostat augments NK cell functions via epigenetic upregulation of IFIT1-STING-STAT4 pathway. Oncotarget. (2020) 11:1799–815. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27546
46. Song W, Tai Y-T, Tian Z, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Nanjappa P, et al. HDAC inhibition by LBH589 affects the phenotype and function of human myeloid dendritic cells. Leukemia. (2011) 25:161–8. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.244
47. Salmon JM, Todorovski I, Stanley KL, Bruedigam C, Kearney CJ, Martelotto LG, et al. Epigenetic activation of plasmacytoid DCs drives IFNAR-dependent therapeutic differentiation of AML. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:1560–79. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1145
48. Yu Y, Liu B, Chen S, Wang J, Chen F, Liu T, et al. Trichostatin A inhibits dendritic cell maturation through down-regulating NF—κ B (p65) pathway. Mol Biol Rep. (2022) 49:2619–27. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-07065-7
49. Berezin V, Walmod PS, Filippov M, and Dityatev A. Targeting of ECM molecules and their metabolizing enzymes and receptors for the treatment of CNS diseases. Prog Brain Res. (2014). p. 353–88. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63486-3.00015-3
50. Spiller KL, Nassiri S, Witherel CE, Anfang RR, Ng J, Nakazawa KR, et al. Sequential delivery of immunomodulatory cytokines to facilitate the M1-to-M2 transition of macrophages and enhance vascularization of bone scaffolds. Biomaterials. (2015) 37:194–207. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.017
51. Chow L, Soontararak S, Wheat W, Ammons D, and Dow S. Canine polarized macrophages express distinct functional and transcriptomic profiles. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:988981. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.988981
52. Kondoh N, Mizuno-Kamiya M, Umemura N, Takayama E, Kawaki H, Mitsudo K, et al. Immunomodulatory aspects in the progression and treatment of oral Malignancy. Japanese Dental Sci Rev. (2019) 55:113–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2019.09.001
53. Lee JE, Kim J-Y, and Leem J. Efficacy of trametinib in alleviating cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury: inhibition of inflammation, oxidative stress, and tubular cell death in a mouse model. Mol (basel Switz). (2024) 29(12):2881. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122881
54. Cui Y, Cai J, Wang W, and Wang S. Regulatory effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:690207. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.690207
55. Yang R, Sun L, Li C-F, Wang Y-H, Yao J, Li H, et al. Galectin-9 interacts with PD-1 and TIM-3 to regulate T cell death and is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:832. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21099-2
56. Zhao L, Cheng S, Fan L, Zhang B, and Xu S. TIM-3: an update on immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 99:107933. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107933
57. Schnell AP, Kohrt S, Aristodemou A, Taylor GP, Bangham CRM, and Thoma-Kress AK. HDAC inhibitors panobinostat and romidepsin enhance tax transcription in HTLV-1-infected cell lines and freshly isolated patients’ T-cells. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:978800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.978800
58. Boateng AT, Abaidoo-Myles A, Bonney EY, and Kyei GB. Isoform-selective versus nonselective histone deacetylase inhibitors in HIV latency reversal. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. (2022) 38:615–21. doi: 10.1089/aid.2021.0195
59. Akimova T, Beier UH, Liu Y, Wang L, and Hancock WW. Histone/protein deacetylases and T-cell immune responses. Blood. (2012) 119:2443–51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-292003
60. FranChina DG, Grusdat M, and Brenner D. B-cell metabolic remodeling and cancer. Trends Cancer. (2018) 4:138–50. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.12.006
61. Do A, Reid RC, Lohman R-J, Sweet MJ, Fairlie DP, and Iyer A. An HDAC6 inhibitor confers protection and selectively inhibits B-cell infiltration in DSS-induced colitis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2017) 360:140–51. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.236711
62. Chi W, Kang N, Sheng L, Liu S, Tao L, Cao X, et al. MCT1-governed pyruvate metabolism is essential for antibody class-switch recombination through H3K27 acetylation. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:163. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44540-0
63. Rossi LE, Avila DE, Spallanzani RG, Ziblat A, Fuertes MB, Lapyckyj L, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors impair NK cell viability and effector functions through inhibition of activation and receptor expression. J Leukocyte Biol. (2011) 91:321–31. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0711339
64. Palucka K and Banchereau J. Cancer immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:265–77. doi: 10.1038/nrc3258
65. Nguyen A, Ho L, Hogg R, Chen L, Walsh SR, and Wan Y. HDACi promotes inflammatory remodeling of the tumor microenvironment to enhance epitope spreading and antitumor immunity. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(19):e159283. doi: 10.1172/JCI159283
66. Kim Y-H and Lee JK. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress immature dendritic cell’s migration by regulating CC chemokine receptor 1 expression. Cell Immunol. (2017) 316:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.02.006
67. John P, Wei Y, Liu W, Du M, Guan F, and Zang X. The B7x immune checkpoint pathway: from discovery to clinical trial. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 40:883–96. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.09.008
68. Fan F, Liu P, Bao R, Chen J, Zhou M, Mo Z, et al. A dual PI3K/HDAC inhibitor induces immunogenic ferroptosis to potentiate cancer immune checkpoint therapy. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:6233–45. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1547
69. Zhou Y, Jin X, Yu H, Qin G, Pan P, Zhao J, et al. HDAC5 modulates PD-L1 expression and cancer immunity via p65 deacetylation in pancreatic cancer. Theranostics. (2022) 12:2080–94. doi: 10.7150/thno.69444
70. Zhu M, Han Y, Gu T, Wang R, Si X, Kong D, et al. Class I HDAC inhibitors enhance antitumor efficacy and persistence of CAR-T cells by activation of the wnt pathway. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114065. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114065
71. Wen J, Chen Y, Yang J, Dai C, Yu S, Zhong W, et al. Valproic acid increases CAR T cell cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006857. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006857
72. Amnekar RV, Khan SA, Rashi M, Khade B, Thorat R, Gera P, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor pre-treatment enhances the efficacy of DNA-interacting chemotherapeutic drugs in gastric cancer. WJG. (2020) 26:598–613. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.598
73. Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Hoshino K, Quintas-Cardama A, Richon VM, et al. Antileukemia activity of the combination of an anthracycline with a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Blood. (2006) 108:1174–82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-008086
74. Galluzzi L, Humeau J, Buqué A, Zitvogel L, and Kroemer G. Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2020) 17:725–41. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0413-z
75. Banik D, NooNepalle S, Hadley M, Palmer E, Gracia-Hernandez M, Zevallos-Delgado C, et al. HDAC6 plays a noncanonical role in the regulation of antitumor immune responses, dissemination, and invasiveness of breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:3649–62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3738
76. Sim W, Lim W-M, Hii L-W, Leong C-O, and Mai C-W. Targeting pancreatic cancer immune evasion by inhibiting histone deacetylases. WJG. (2022) 28:1934–45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i18.1934
77. Wang X, Fang Y, Liang W, Wong CC, Qin H, Gao Y, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum facilitates anti-PD-1 therapy in microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell. (2024) 42:1729–1746.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.08.019
78. Pili R, Quinn DI, Adra N, Logan T, Colligan S, Burney HN, et al. A phase I/IB, open label, dose finding study to evaluate safety, pharmacodynamics and efficacy of pembrolizumab in combination with vorinostat in patients with advanced prostate, renal or urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2025) 14:e70725. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70725
79. van Tilburg CM, Witt R, Heiss M, Pajtler KW, Plass C, Poschke I, et al. INFORM2 NivEnt: the first trial of the INFORM2 biomarker driven phase I/II trial series: the combination of nivolumab and entinostat in children and adolescents with refractory high-risk Malignancies. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:523. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07008-8
80. Johnson ML, Strauss J, Patel MR, Garon EB, Eaton KD, Neskorik T, et al. Mocetinostat in combination with durvalumab for patients with advanced NSCLC: results from a phase I/II study. Clin Lung Cancer. (2023) 24:218–27. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2023.01.013
81. Gomez S, Tabernacki T, Kobyra J, Roberts P, and Chiappinelli KB. Combining epigenetic and immune therapy to overcome cancer resistance. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 65:99–113. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.019
82. Shen C, Li M, Duan Y, Jiang X, Hou X, Xue F, et al. HDAC inhibitors enhance the anti-tumor effect of immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1170207. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1170207
83. Zhou M, Yuan M, Zhang M, Lei C, Aras O, Zhang X, et al. Combining histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) with other therapies for cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem. (2021) 226:113825. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113825
84. Bots M and Johnstone RW. Rational combinations using HDAC inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:3970–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2786
85. Akbarali HI, Muchhala KH, Jessup DK, and Cheatham S. Chemotherapy induced gastrointestinal toxicities. Adv Cancer Res. (2022) 155:131–66. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2022.02.007
86. Wang L, Li P, and Feng K. EGCG adjuvant chemotherapy: Current status and future perspectives. Eur J Medicinal Chem. (2023) 250:115197. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115197
87. Lu G, Jin S, Lin S, Gong Y, Zhang L, Yang J, et al. Update on histone deacetylase inhibitors in peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). Clin Epigenet. (2023) 15:124. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01531-8
88. Kaufman JL, Mina R, Jakubowiak AJ, Zimmerman TL, Wolf JJ, Lewis C, et al. Combining carfilzomib and panobinostat to treat relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: results of a multiple myeloma research consortium phase I study. Blood Cancer J. (2019) 9:3. doi: 10.1038/s41408-018-0154-8
89. Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Huang H, Shen L, Han X, Hu X, et al. Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic, and phase 1a study of bisthianostat, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2022) 43:1091–9. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00728-y
90. Janku F, Park H, Call SG, Madwani K, Oki Y, Subbiah V, et al. Safety and efficacy of vorinostat plus sirolimus or everolimus in patients with relapsed refractory hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:5579–87. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1215
91. Zhang M-C, Fang Y, Wang L, Cheng S, Fu D, He Y, et al. Clinical efficacy and molecular biomarkers in a phase II study of tucidinostat plus R-CHOP in elderly patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Epigenet. (2020) 12:160. doi: 10.1186/s13148-020-00948-9
92. Islam P, Rizzieri D, Lin C, De Castro C, Diehl L, Li Z, et al. Phase II study of single-agent and combination everolimus and panobinostat in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Invest. (2021) 39:871–9. doi: 10.1080/07357907.2021.1983584
93. Evens AM, Balasubramanian S, Vose JM, Harb W, Gordon LI, Langdon R, et al. A phase I/II multicenter, open-label study of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat in relapsed/refractory lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:1059–66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0624
94. Luu T, Kim K, Blanchard S, Anyang B, Hurria A, Yang L, et al. Phase IB trial of ixabepilone and vorinostat in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2018) 167:469–78. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4516-x
95. Gray JE, Saltos A, Tanvetyanon T, Haura EB, Creelan B, Antonia SJ, et al. Phase I/ib study of pembrolizumab plus vorinostat in advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:6623–32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1305
96. Witta SE, Jotte RM, Konduri K, Neubauer MA, Spira AI, Ruxer RL, et al. Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib with and without entinostat in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer who progressed on prior chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:2248–55. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.9411
97. Baretti M, Danilova L, Durham JN, Betts CB, Cope L, Sidiropoulos DN, et al. Entinostat in combination with nivolumab in metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a phase 2 clinical trial. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:9801. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52528-7
98. Wang F, Jin Y, Wang M, Luo H-Y, Fang W-J, Wang Y-N, et al. Combined anti-PD-1, HDAC inhibitor and anti-VEGF for MSS/pMMR colorectal cancer: a randomized phase 2 trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:1035–43. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02813-1
99. Okabe S, Tanaka Y, and Gotoh A. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinases and histone deacetylases in multiple myeloma. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2021) 10:19. doi: 10.1186/s40164-021-00213-6
100. Imai Y, Hirano M, Kobayashi M, Futami M, and Tojo A. HDAC inhibitors exert anti-myeloma effects through multiple modes of action. Cancers. (2019) 11(4):475. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040475
101. Passero FCJ, Ravi D, McDonald JT, Beheshti A, David KA, and Evens AM. Combinatorial ixazomib and belinostat therapy induces NFE2L2-dependent apoptosis in hodgkin and T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. (2020) 188:295–308. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16160
102. Sun W, Yi Y, Xia G, Zhao Y, Yu Y, Li L, et al. Nrf2-miR-129-3p-mTOR axis controls an miRNA regulatory network involved in HDACi-induced autophagy. Mol Ther. (2019) 27:1039–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.02.010
103. Ho T, Coleman C, Shah P, and Yazbeck V. Advances in hodgkin’s lymphoma pharmacotherapy: a focus on histone deacetylase inhibitors. Expert Opin Pharmacother. (2023) 24:1427–38. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2023.2219392
104. Nguyen T, Parker R, Hawkins E, Holkova B, Yazbeck V, Kolluri A, et al. Synergistic interactions between PLK1 and HDAC inhibitors in non-hodgkin’s lymphoma cells occur in vitro and in vivo and proceed through multiple mechanisms. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:31478–93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15649
105. Hu Z, Wei F, Su Y, Wang Y, Shen Y, Fang Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote breast cancer metastasis by elevating NEDD9 expression. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2023) 8:11. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01221-6
106. Bian X, Liang Z, Feng A, Salgado E, and Shim H. HDAC inhibitor suppresses proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells through regulation of miR-200c targeting CRKL. Biochem Pharmacol. (2018) 147:30–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.11.008
107. Liang T, Wang F, Elhassan RM, Cheng Y, Tang X, Chen W, et al. Targeting histone deacetylases for cancer therapy: trends and challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:2425–63. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.007
108. Zhu Q, Dai Q, Zhao L, Zheng C, Li Q, Yuan Z, et al. Novel dual inhibitors of PARP and HDAC induce intratumoral STING-mediated antitumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:10. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06303-z
109. Cao F, Xiao Z, Chen S, Zhao C, Chen D, Haisma HJ, et al. HDAC/MIF dual inhibitor inhibits NSCLC cell survival and proliferation by blocking the AKT pathway. Bioorg Chem. (2021) 117:105396. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105396
110. Gu S, Hou Y, Dovat K, Dovat S, Song C, and Ge Z. Synergistic effect of HDAC inhibitor Chidamide with Cladribine on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by targeting HDAC2/c-Myc/RCC1 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2023) 12:23. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00383-5
111. Chen G, Zhu X, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhang R, et al. Celastrol inhibits lung cancer growth by triggering histone acetylation and acting synergically with HDAC inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 185:106487. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106487
112. Trapani D, Esposito A, Criscitiello C, Mazzarella L, Locatelli M, Minchella I, et al. Entinostat for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin Invest Drugs. (2017) 26:965–71. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1353077
113. Liang G, Oh TG, Hah N, Tiriac H, Shi Y, Truitt ML, et al. Inhibiting stromal Class I HDACs curbs pancreatic cancer progression. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:7791. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42178-6
114. Valdez BC, Tsimberidou AM, Yuan B, Nieto Y, Baysal MA, Chakraborty A, et al. Synergistic cytotoxicity of histone deacetylase and poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors and decitabine in pancreatic cancer cells: implications for novel therapy. Oncotarget. (2024) 15:361–73. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28588
115. Shouksmith AE, Shah F, Grimard ML, Gawel JM, Raouf YS, Geletu M, et al. Identification and characterization of AES-135, a hydroxamic acid-based HDAC inhibitor that prolongs survival in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. J Med Chem. (2019) 62:2651–65. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01957
116. Sun X, Shu Y, Ye G, Wu C, Xu M, Gao R, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit cervical cancer growth through parkin acetylation-mediated mitophagy. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:838–52. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.003
117. Pan B, Yin S, Peng F, Liu C, Liang H, Su J, et al. Vorinostat targets UBE2C to reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition and control cervical cancer growth through the ubiquitination pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. (2021) 908:174399. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174399
118. Zhang H, Li M, Sun H, Yang W, Ye M, Li H, et al. 4SC-202 exerts an anti-tumor effect in cervical cancer by targeting PRLR signaling pathway. J Mol Histol. (2022) 53:891–902. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10105-6
119. Suraju MO, Freischlag K, Jacob D, Thompson D, Mckeen A, Tran C, et al. Epidemiology and survival outcomes of colorectal mixed neuroendocrine–non-neuroendocrine neoplasms and neuroendocrine carcinoma. Surgery. (2024) 175:735–42. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2023.09.019
120. Ashry R, Mustafa A-H, Hausmann K, Linnebacher M, Strand S, Sippl W, et al. NOXA accentuates apoptosis induction by a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Cancers. (2023) 15:3650. doi: 10.3390/cancers15143650
121. Duan N. Targeting the E2F1/Rb/HDAC1 axis with the small molecule HR488B effectively inhibits colorectal cancer growth. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14(12):801. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06205-0
122. Fiorentino F, Fabbrizi E, Raucci A, Noce B, Fioravanti R, Valente S, et al. Uracil- and pyridine-containing HDAC inhibitors displayed cytotoxicity in colorectal and glioblastoma cancer stem cells. ChemMedChem. (2024) 19:e202300655. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300655
123. Pan Y, Hou H, Zhou B, Gao J, and Gao F. Hydroxamic acid hybrids: Histone deacetylase inhibitors with anticancer therapeutic potency. Eur J Medicinal Chem. (2023) 262:115879. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115879
124. Jia G. Biological function and small molecule inhibitors of histone deacetylase 11. Eur J Medicinal Chem. (2024) 276:116634. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116634
Keywords: HDACi, tumor therapy, immunotherapy, tumor microenvironment, combination therapy
Citation: Tian J, Han M, Song F, Liu Y, Shen Y and Zhong J (2025) Advances of HDAC inhibitors in tumor therapy: potential applications through immune modulation. Front. Oncol. 15:1576781. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1576781
Received: 14 February 2025; Accepted: 16 June 2025;
Published: 27 June 2025.
Edited by:
Sandip Patil, Shenzhen Children’s Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Francesco Grignani, University of Perugia, ItalyBarbara A Osborne, University of Massachusetts Amherst, United States
Katia Carneiro, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Madduri Srinivasarao, Purdue University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Han, Song, Liu, Shen and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuhou Shen, c2h5MTIzNDU2QDEyNi5jb20=; Jiateng Zhong, anR6aG9uZ0B4eG11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiaqi Tian
Jiaqi Tian Miaomiao Han1†
Miaomiao Han1† Jiateng Zhong
Jiateng Zhong