- 1Breast Tumor Center, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
- 2Anesthesiology Department, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
Background: Postoperative chest wall seroma is a common complication following modified radical mastectomy. When persistent, it can lead to the formation of a dense fibrous capsule (pseudobursa), resulting in a refractory seroma that is unresponsive to conventional treatments and may delay essential adjuvant therapies. Surgical excision of the capsule carries significant risks. This study introduces a less invasive surgical technique to manage this challenging condition.
Methods: From 2018 to 2021, 20 patients with refractory seroma after modified radical mastectomy were included in this retrospective study. Inclusion required seroma persistence for over one month despite repeated aspirations, with the presence of a fibrous capsule confirmed by ultrasonography. A minimally traumatic, four-step technique was employed under local anesthesia, involving capsule scraping, “cross-hatch” scoring, and flap fixation. A drainage tube was inserted post-procedure. Color Doppler ultrasound was used for pre- and post-procedural assessment.
Results: The study included 20 female patients with a median age of 57.5 years. All patients had node-positive breast cancer. The “cross-hatch” capsular scoring technique was successfully performed in all cases. The median postoperative drainage time was 7 days (range 6–12 days). During a median follow-up of 3 months, no seroma recurrence was observed. The procedure was well-tolerated with minimal pain, and no significant complications such as hematoma or infection occurred.
Conclusion: The “cross-hatch” capsular scoring technique is a safe, effective, and less invasive method for managing refractory post-mastectomy seroma. This approach minimizes patient trauma, reduces recovery time, and helps maintain the continuity of adjuvant therapies, thereby offering a valuable alternative to more aggressive surgical interventions.
Introduction
Postoperative chest wall seroma is one of the most common complications after modified radical mastectomy for breast cancer, characterized by the abnormal subcutaneous accumulation of plasma and lymphatic fluid in a dead space (1–3). Its incidence ranges from 15% to 85%, varying by diagnostic criteria and detection methods (4, 5). In some cases, the seroma persists or recurs despite conservative treatments like repeated aspiration or compression, evolving into a refractory seroma. This condition can impede recovery by causing skin necrosis, wound infection, and delays in crucial adjuvant therapies (6), thereby impacting patient outcomes and quality of life.
A key pathological feature of a refractory seroma is the formation of a dense, smooth-walled fibrous capsule, known as a pseudobursa, around the fluid collection (7). This capsule’s avascular, secretory inner lining prevents the adherence of the skin flap to the chest wall, perpetuating the fluid accumulation and rendering conventional treatments ineffective. While complete surgical excision of the capsule (capsulectomy) combined with negative pressure suction has been shown to be effective (8–10), this procedure presents significant challenges. For patients who have undergone axillary lymph node dissection, the capsule often extends into the axilla, in close proximity to vital nerves and vessels. A formal capsulectomy in this region requires extensive dissection, often under general anesthesia, and carries substantial risks of neurovascular injury, intraoperative bleeding, and significant postoperative pain.
Given these risks, there is a clear clinical need for a safer, less invasive alternative. In this study, we developed and evaluated a minimally traumatic surgical technique performed under local anesthesia. The procedure involves scraping and scoring the capsule (“cross-hatch” capsulotomy) without removing it, followed by flap fixation to obliterate the dead space. We herein report our experience, demonstrating the effectiveness and safety of this novel approach in a series of 20 patients.
Patients and methods
Patient selection
Between 2018 and 2021, 20 consecutive female patients with refractory seroma following modified radical mastectomy at our institution were included in this retrospective study. The inclusion criteria were: 1) persistence of seroma for over one month despite conventional management (including repeated percutaneous aspirations); and 2) the presence of a distinct, organized fibrous capsule confirmed by preoperative ultrasound examination. All patients had been pathologically diagnosed with breast cancer and had undergone axillary lymph node dissection as part of their initial surgery. Of these 20 patients, 10 underwent a standard Level I and II axillary lymph node dissection, while the remaining 10, who presented with clinically enlarged Level III lymph nodes, underwent a complete Level I-III dissection. The refractory seromas in this cohort developed after the removal of the initial surgical drains, which were typically kept in place for a period of 7 to 14 days.
The choice of modified radical mastectomy (MRM) for the initial surgery was based on clinical indications at the time of diagnosis, such as multicentric disease, large tumor-to-breast ratio, or patient preference, reflecting the clinical practice at our institution during the study period. Patients were excluded if they had an active infection, severe coagulation disorders, or declined the procedure. Since this study was conducted retrospectively based on a modification of an established clinical technique, formal ethical committee approval was not required by our institutional guidelines.
The cross-hatch capsular scoring technique
The surgical procedure was performed in an outpatient setting and comprises four essential steps (Figure 1).
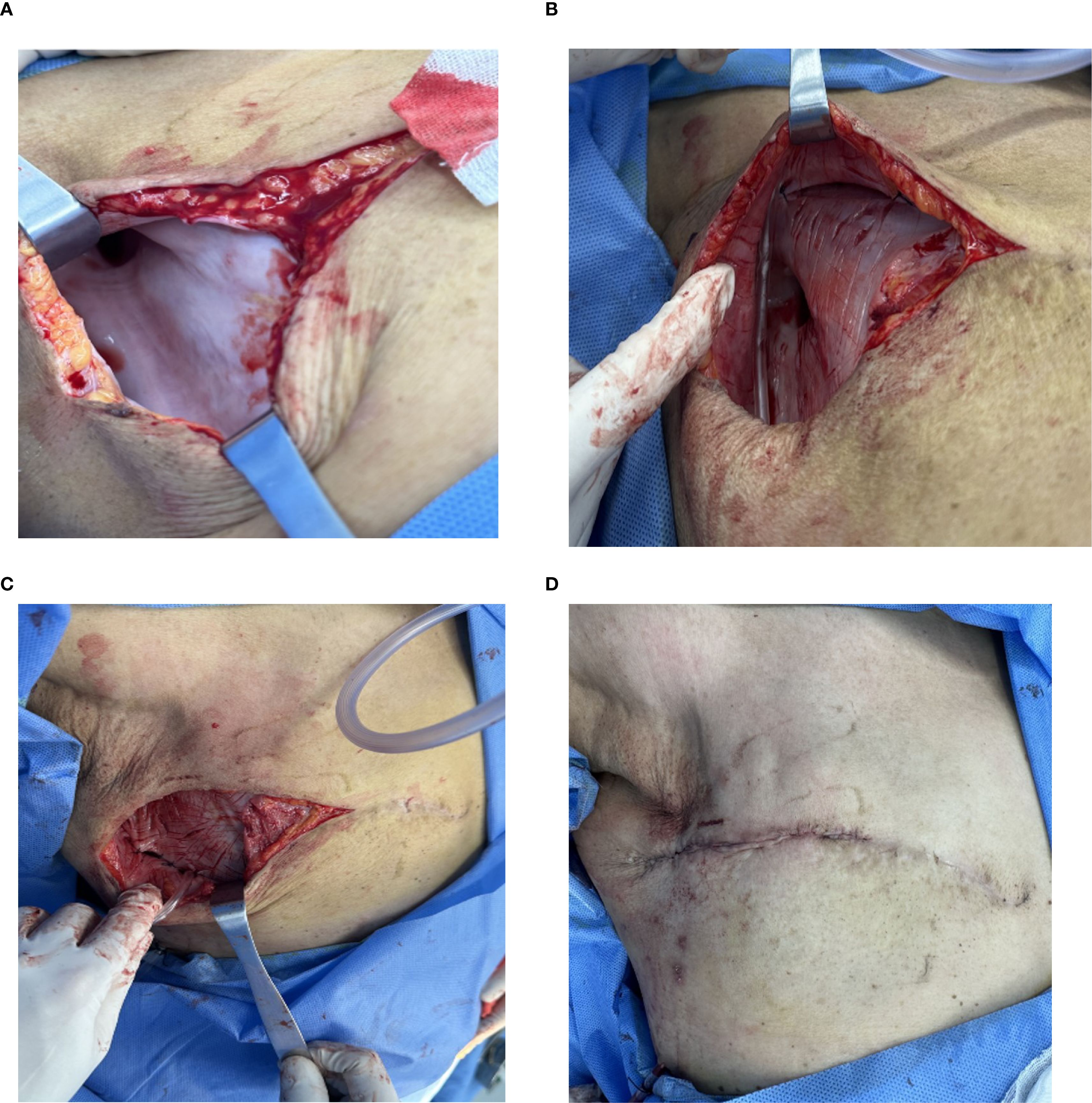
Figure 1. Key Steps of the Minimally Traumatic Surgical Procedure. (A) Exposure of the Pseudobursa: Following incision and complete fluid aspiration, the characteristic smooth, white fibrous capsule is visualized covering the chest wall and extending into the axilla. (B) Capsular Scoring: A scalpel is used to create multiple shallow, crisscrossing incisions (“cross-hatch” pattern) across the entire inner surface of the capsule, promoting an inflammatory healing response. The capsule itself is preserved. (C) Flap Fixation and Drainage: To ensure apposition, the skin flap is sutured to the underlying muscle fascia using 2–0 absorbable sutures. A drainage tube is placed to manage initial exudate. (D) Wound Closure: The incision is re-approximated with absorbable sutures, completing the procedure before compression bandaging is applied.
1. Incision and Exposure: After routine ultrasonography to map the extent of the seroma, the area was sterilized. Using 0.5% lidocaine for local anesthesia, an incision of 7–10 cm was made along the original mastectomy scar to access the seroma cavity. The seroma fluid was completely aspirated with a suction device, revealing the dense, smooth-walled fibrous capsule (pseudobursa) lining the cavity (Figure 1A). The aspirated fluid was visually inspected; as all cases presented with clear, serous fluid without signs of infection (e.g., purulence or turbidity), routine microbiological cultures were not performed.
2. Capsular Scoring: The key step involves altering the capsule surface. Using a No. 22 scalpel blade, the entire inner surface of the capsule on the skin flap and chest wall was methodically scraped to de-epithelialize the secretory lining. Following this, multiple “cross-hatch” scores or shallow incisions were made through the capsule down to the subcutaneous tissue or muscle layer (Figure 1B). Care was taken in the axillary region to avoid deep incisions that could injure the axillary vein or surrounding nerves. The fibrous capsule itself was left in situ.
3. Flap Fixation and Drainage: To obliterate the dead space, the skin flap was anchored to the underlying pectoral or serratus anterior muscle fascia using multiple interrupted 2–0 absorbable sutures (Figure 1C). A single closed-suction drainage tube was then placed within the cavity.
4. Closure and Compression: The skin incision was closed in layers. A sterile dressing and a multi-layer elastic compression bandage were applied to the chest wall to ensure firm apposition of the flaps (Figure 1D). The drain was connected to a low-pressure suction bottle. A single dose of a first-generation cephalosporin was administered preoperatively for surgical prophylaxis in all cases.
Post-procedure management and follow-up
The drainage tube was removed when the daily output was consistently less than 20 ml for two consecutive days. The compression dressing remained in place until after drain removal. All patients underwent a color Doppler ultrasound examination one week after drain removal to confirm the absence of fluid re-accumulation. Follow-up was conducted at 1 and 3 months post-procedure to assess for seroma recurrence and any late complications.
Results
Patient and tumor characteristics
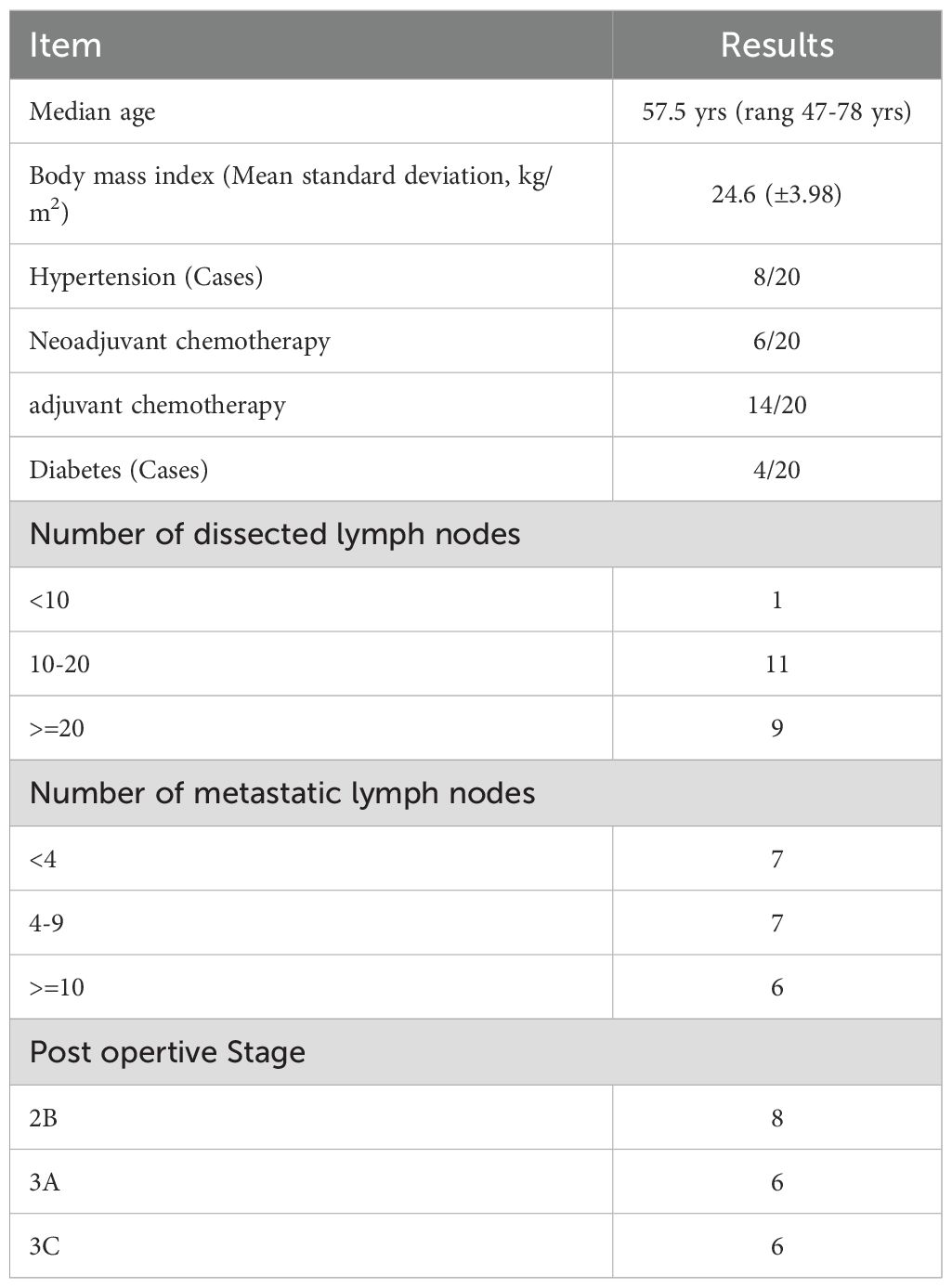
A total of 20 female breast cancer patients with refractory seroma were included. The median age was 57.5 years (range: 47-78), and the mean Body Mass Index (BMI) was 24.6 kg/m ² (range: 19.4-35.5 kg/m ²). Comorbidities included diabetes mellitus in 4 patients (20%) and hypertension in 8 patients (35%). Six patients (30%) had received neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Postoperative histopathology from the initial mastectomy revealed stage IIB in 8 patients (40%), IIIA in 6 patients (30%), and IIIC in 6 patients (30%). The median number of total lymph nodes removed was 17 (range: 7-30). All 20 patients had positive lymph nodes, with a median of 3 affected nodes (range: 1-25). Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Procedural outcomes
The “cross-hatch” capsular scoring technique was successfully performed on all 20 patients under local anesthesia.
The median postoperative drainage time was 7 days (range 6–12 days). No major perioperative complications such as hematoma, surgical site infection, or flap necrosis were observed. Patients reported minimal postoperative pain, which was well-managed with oral analgesics.
During a median follow-up of 3 months, no recurrence of seroma was observed in any patient. Post-procedural ultrasound examinations confirmed complete resolution of the fluid collection and adherence of the skin flaps to the chest wall.
Discussion
Managing postoperative refractory seroma in breast cancer surgery remains a significant clinical challenge. Our study demonstrates that the “cross-hatch” capsular scoring technique is a highly effective and safe method for treating this condition.
The rationale behind our technique is not merely to drain fluid but to fundamentally alter the pathophysiology of the non-healing seroma cavity. The pseudobursa’s smooth, avascular inner lining prevents natural tissue adherence and perpetuates fluid secretion. By mechanically scraping and scoring this surface, we create a controlled inflammatory response. This, combined with meticulous flap fixation and external compression, promotes fibrin deposition and granulation, leading to the permanent obliteration of the dead space. The temporary drain serves only to manage the initial reactive exudate while this crucial adherence process occurs. Our results, showing no recurrences in 20 consecutive patients, provide strong preliminary evidence that this method offers a durable solution.
The standard surgical alternative for an encapsulated seroma is a formal capsulectomy. Unlike this procedure, which requires extensive and often high-risk dissection under general anesthesia, our technique is minimally traumatic. By leaving the capsule’s outer layer intact and avoiding deep dissection, especially in the axilla, we minimize the risk of bleeding and neurovascular injury. Other innovative approaches, such as ultrasound-guided scraping with Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), have been described (11). Our method, however, offers distinct advantages in its simplicity and accessibility, as it utilizes standard surgical instruments and does not require specialized equipment. The limited incision allows for direct visualization, ensuring thorough treatment of the capsule surface while protecting vital structures.
A key strength of our approach is its performance under local anesthesia. This makes it suitable for a wider range of patients, including the elderly or those with comorbidities who may be poor candidates for general anesthesia. The minimal postoperative pain reported by our patients, combined with the outpatient nature of the procedure, enhances patient comfort, reduces healthcare costs, and lessens the psychological burden associated with recurrent clinic visits.
This study has several limitations. Firstly, it is a retrospective, single-arm study with a relatively small sample size. Therefore, it should be considered a proof-of-concept series demonstrating the technique’s feasibility and initial efficacy. Secondly, the follow-up period is limited to three months, although this is generally sufficient to detect early seroma recurrence. Future research should focus on larger, prospective, and potentially comparative studies to further validate these findings and assess long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
The “cross-hatch” capsular scoring technique represents a significant advancement in the management of postoperative refractory seroma. Its minimally traumatic nature, high efficacy, and excellent safety profile make it a valuable option for surgeons and patients alike. By adopting this method, clinicians can effectively resolve a challenging postoperative complication, improve recovery times, reduce morbidity, and ensure the timely continuation of essential adjuvant therapies, ultimately enhancing the quality of care in breast cancer surgery.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology, Validation. JZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Resources, Software, Validation. AS: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Project administration. HB: Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization. ZH: Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Agrawal A, Ayantunde AA, and Cheung KL. Concepts of seroma formation and prevention in breast cancer surgery. ANZ J Surg. (2006) 76:1088–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2006.03949.x
2. Kuroi K, Shimozuma K, Taguchi T, Imai H, Yamashiro H, Ohsumi S, et al. Effect of mechanical closure of dead space on seroma formation after breast surgery. Breast Cancer (Tokyo Japan). (2006) 13:260–5. doi: 10.2325/jbcs.13.260
3. van Bemmel AJ, van de Velde CJ, Schmitz RF, and Liefers GJ. Prevention of seroma formation after axillary dissection in breast cancer: a systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol: J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol. (2011) 37:829–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2011.04.012
4. Kuroi K, Shimozuma K, Taguchi T, Imai H, Yamashiro H, Ohsumi S, et al. Evidence-based risk factors for seroma formation in breast surgery. Japanese J Clin Oncol. (2006) 36:197–206. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyl019
5. Vinton AL, Traverso LW, and Jolly PC. Wound complications after modified radical mastectomy compared with tylectomy with axillary lymph node dissection. Am J Surg. (1991) 161:584–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(91)90905-s
6. Tejler G and Aspegren K. Complications and hospital stay after surgery for breast cancer: a prospective study of 385 patients. Br J Surg. (1985) 72:542–4. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720714
7. Fosheim K, Bojesen S, Troestrup H, and Laenkholm AV. Capsulectomy can successfully treat chronic encapsulated breast seroma: A case report. Cureus. (2022) 14:e21677. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21677
8. Bi H, Fang S, Jiang D, Xing X, Zhu J, Wang X, et al. Ultrasound-guided scraping of fibrous capsule plus bilayered negative pressure wound therapy for treatment of refractory postmastectomy seroma. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg: JPRAS. (2015) 68:403–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2014.11.007
9. Marangi GF, Segreto F, Morelli Coppola M, Arcari L, Gratteri M, and Persichetti P. Management of chronic seromas: A novel surgical approach with the use of vacuum assisted closure therapy. Int Wound J. (2020) 17:1153–8. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13447
10. Esen E, Saydam M, Guler S, Akinci M, Bahcecioglu IB, Gulcelik MA, et al. Successful use of minimal invasive debridement plus negative pressure wound therapy under skin flap and axillary region for refractory postmastectomy seroma: A STROBE-compliant retrospective study. Medicine. (2022) 101:e31634. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000031634
Keywords: breast cancer, refractory seroma, fibrous capsule, minimally traumatic surgery, flap fixation, local anesthesia
Citation: Cao R, Zhang J, Su A, Bao H, He Z and Wu J (2025) An effective four-step approach in treating refractory seroma after mastectomy for breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1577591. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1577591
Received: 16 February 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 10 September 2025.
Edited by:
Raquel Diaz, University of Genova, ItalyReviewed by:
Giovanni Tazzioli, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, ItalyMatteo Bardelli, Pisana University Hospital, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Zhang, Su, Bao, He and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiannan Wu, a2luZzg3MDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Rui Cao
Rui Cao Jing Zhang2†
Jing Zhang2† An Su
An Su Zhou He
Zhou He Jiannan Wu
Jiannan Wu