- 1Department of Clinical Oncology, Kansai Medical University Hospital, Osaka, Japan
- 2Department of Medical Oncology, Kochi Medical School, Kochi, Japan
- 3Department of Medical Oncology, Kindai University Faculty of Medicine, Osaka, Japan
- 4Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan
- 5Department of Medical Oncology, Osaka International Cancer Institute, Osaka, Japan
- 6Cancer Chemotherapy Center, Osaka Medical and Pharmaceutical University, Osaka, Japan
- 7Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan
- 8Department of Clinical Oncology, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Miyagi, Japan
Introduction: Preclinical studies have demonstrated the potential of Lentinula edodes mycelium (L.E.M.) extract for managing oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN). The efficacy and optimal dosage of L.E.M. for OIPN remain uncertain. We evaluated the efficacy and safety as well as the optimal dosage of L.E.M. extract for OIPN in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC).
Methods: After curative resection, we used a 1:1:1 ratio to randomly assign patients with CRC with persistent OIPN (defined by a visual analogue scale [VAS] numbness score ≥40 mm) to the low-dose (L.E.M. 300 mg twice daily [bid]), high-dose (L.E.M. 900 mg bid), and placebo groups. The primary endpoint of this double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial was the reduction in the VAS numbness score in the low-dose group compared with that in the placebo group at 12 weeks. Adverse events (AEs) and quality of life were evaluated.
Results: Forty-five patients were randomly assigned to the placebo (n = 15), low-dose (n = 15), and high-dose (n = 15) groups. At 12 weeks, no significant difference in the reduction of the VAS numbness score was observed when the low-dose and placebo groups were compared (−12.20 [95% confidence interval {CI}; −34.54 to 10.14] vs. −10.69 [95% CI; −27.07 to 5.69]; p = 0.83); however, the high-dose group showed a favorable trend compared with the placebo group (−12.20 vs. −29.32 [95% CI; −53.4 to −5.2]; p = 0.06). Grade 3 or higher AEs related to the intervention were not observed.
Discussion: High-dose L.E.M. extract resulted in a clinically meaningful improvement in VAS numbness scores without severe toxicity.
Clinical Trial Registration: https://jrct.mhlw.go.jp/en-latest-detail/jRCTs051210085, identifier jRCTs051210085.
1 Introduction
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common and cumulative side effect of anticancer drugs such as oxaliplatin, paclitaxel, vincristine, and bortezomib (1). Symptoms include extremity numbness, sensory ataxia, decreased deep tendon reflexes, and muscle weakness (2). These symptoms can severely impact patients’ quality of life (QoL) by causing gait disturbances and hindering daily activities as well as limiting the continuation of chemotherapy. Currently, the combination of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and oxaliplatin is the standard adjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced colorectal cancer (high-risk stage II or stage III), as supported by multiple phase III trials (3–5). Although this regimen improves survival, it is associated with cumulative peripheral neuropathy, which is a well-known adverse event associated with oxaliplatin. Prolonged oxaliplatin use progressively worsens neuropathy. Studies have reported that persistent oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN) was observed in up to 15% of patients at 4 years post-treatment (6). Because no effective agents other than duloxetine for the treatment of oxaliplatin-induced numbness have been identified (7, 8), reducing the chemotherapy duration from 6 months to 3 months is a viable option for patients with high-risk stage II or low-risk stage III disease (9). However, for patients with high-risk disease, 6 months of therapy remains the standard; therefore, OIPN is an ongoing clinical challenge.
Lentinula edodes mycelium (L.E.M.) extract is produced by inoculating shiitake mushroom fungi into a solid medium primarily composed of bagasse and rice bran, cultivating the fungi for several months until just before mushroom development, and subsequently extracting the fungi with boiling water (10). Previous studies suggested that L.E.M. extract may help maintain patients’ QoL, primarily by preventing chemotherapy-related taste disorders. Thus, L.E.M. extract has shown potential benefits for patients with cancer (11, 12). However, although L.E.M. may improve the QoL of patients with cancer and is safe for long-term use at high doses, its efficacy and optimal dosage for OIPN remained uncertain (10, 11, 13). To address this uncertainty, we conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of L.E.M. extract for OIPN in patients undergoing postoperative chemotherapy for colorectal cancer (CRC) (10).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study enrolment
Participants were recruited from six institutes in Japan. Eligible individuals were 20 years of age or older, were diagnosed with grade 1 or higher peripheral sensory neuropathy (according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events [CTCAE] version 4.0) and had a visual analogue scale (VAS) numbness score of 40/100 mm or higher at least 3 months after completing oxaliplatin treatment. Participants were required to have pathologically confirmed CRC following curative resection, an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 to 2, adequate major organ function, and the ability to use oral medications. Additionally, participants were required to write with their dominant hand during the VAS assessment. Patients using gabapentin were excluded because L.E.M. extract may affect blood levels. Concomitant use of anti-CIPN medications other than gabapentin was allowed if the patient had been using stable doses for at least 2 weeks prior to randomization. Specifically, no new anti-CIPN agents could be initiated, existing anti-CIPN medications could not be discontinued, and the total dose of anti-CIPN medication could not increase or decrease by more than 10% during the 2 weeks prior to study enrolment.
This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and the Japanese Clinical Trials Act. Approval was granted by the Clinical Research Review Board of Nara Medical University (CRB5200002), and this study was registered in the Japanese Clinical Trials Registry (jRCTs051210085). All patients provided written informed consent before participation.
2.2 Intervention
Participants were randomized using a 1:1:1 ratio to the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups. Randomization was performed using dynamic allocation (minimization method). A list of study product numbers corresponding to the target sample size was generated using an Excel-based random number table. These numbers were randomly assigned to three groups. A study product manager who was not involved in the conduct of the study attached the study product numbers to each product package. The assignment table linking the study product numbers and groups was securely stored and accessed only at the time of unblinding. At the time of subject registration, investigators communicated the subject’s allocation factors (age, gender, and numbness score assessed by VAS) to the allocation center. Based on these factors and the already registered subjects’ allocations, the allocation center performed dynamic allocation. The center then reported the assigned study product numbers to the investigators, who administered the assigned treatment to the subjects. The low-dose group received 600 mg/day (300 mg twice daily) and the high-dose group received 1800 mg/day (900 mg twice daily) of L.E.M. extract-containing compounds for 12 weeks. The protocol treatment was discontinued if a causal relationship with L.E.M. could not be denied or if deemed necessary by the participant or investigator.
2.3 Measurements
The VAS score was rated using a 100-mm horizontal line. Participants were informed that the left end of the scale represented ‘no pain’ and that the right end represented ‘the most intense pain imaginable’. They were asked to mark the intensity of their current pain on the scale (14). Patient-reported OIPN-related QoL was assessed using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity (FACT/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire, which was designed to assess CIPN severity, including sensory, motor, and functional impairment, and its impact on QoL (15, 16). One systematic review found evidence supporting the use of the FACT/GOG-Ntx to assess CIPN in the research setting (17). The FACT/GOG-Ntx comprises 11 items related to neurotoxicity, with each rated using a 5-point scale (range, 0–4). FACT/GOG-Ntx scores range from 0 to 44, with lower scores indicating lower neurotoxicity. Any adverse events, including sensory neuropathy, were evaluated based on the criteria of CTCAE version 4.0.
2.4 Study design and endpoints
This study was a three-arm, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial that evaluated the efficacy of low-dose and high-dose L.E.M. extract to reduce OIPN severity in patients with CRC. The primary endpoint was the magnitude of change in the VAS numbness score in the low-dose group compared with that in the placebo group after 12 weeks of treatment. Secondary endpoints were the magnitude of change in VAS score for pain in the placebo group compared with that in the low-dose group at 12 weeks, that for numbness and pain in the placebo compared with that in the high-dose group at 12 weeks, and that for numbness among all groups at 4 weeks and 8 weeks; CTCAE grades of peripheral sensory neuropathy of all groups at 4 weeks; QoL scores of all groups according to the FACT/GOG-Ntx; and the incidence of adverse events of all groups.
2.5 Sample size
Previous clinical trial reports of the efficacy of duloxetine for Japanese patients with anticancer drug-induced peripheral neuropathy showed a mean VAS score change of -26.0 in the duloxetine group compared with -8.0 in the control group administered vitamin B12 after 4 weeks of treatment (18). Based on these results, the expected mean change in the VAS score for peripheral neuropathy after 12 weeks for the placebo group was set at -8.0, and the target mean change in the low-dose group was set at -36.0 with a standard deviation of 25.0. Using these parameters, we calculated that a sample size of 14 patients per group was necessary to detect a statistically significant difference in VAS score changes between the groups with a power of 80% and significance level of 5%. To account for potential dropouts and ineligible cases, we increased the target number of patients to 15 per group, which ensured that the study would remain adequately powered even if some participants did not complete the study or were excluded from the final analysis.
2.6 Statistical analysis
VAS scores and CTCAE grades in the low-dose, high-dose, and placebo groups were compared using two-tailed t-tests. Changes in FACT/GOG-Ntx QoL scores were evaluated using the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test. The incidence of adverse events was compared using Fisher’s exact test. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS (IBM version 26).
3 Results
3.1 Participant characteristics
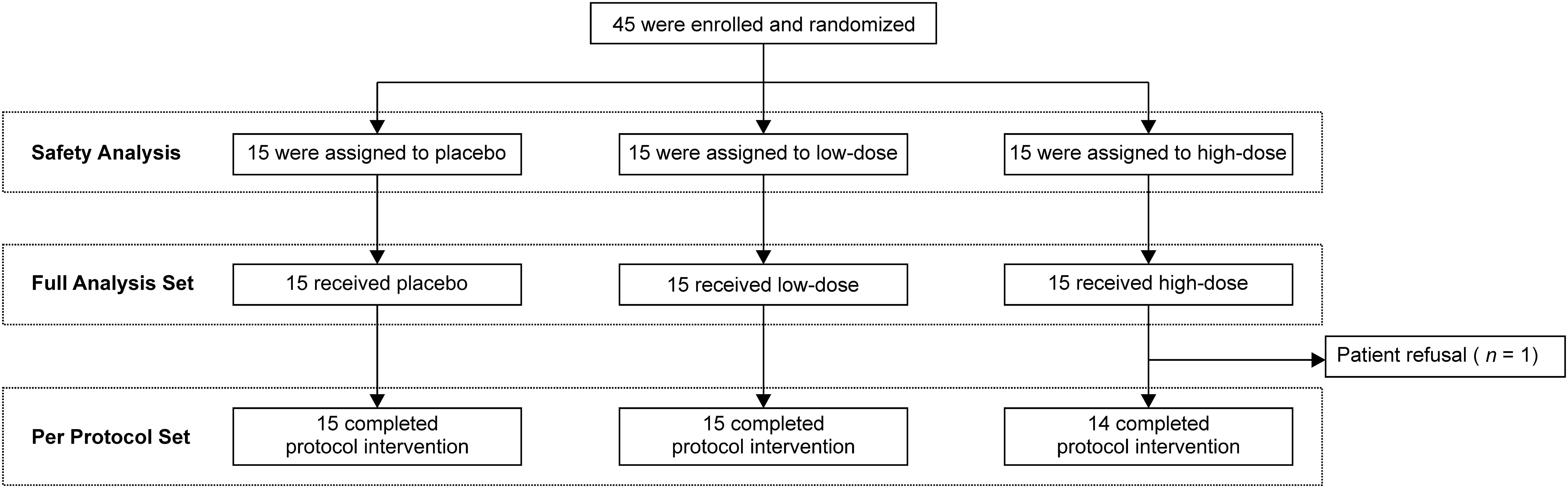
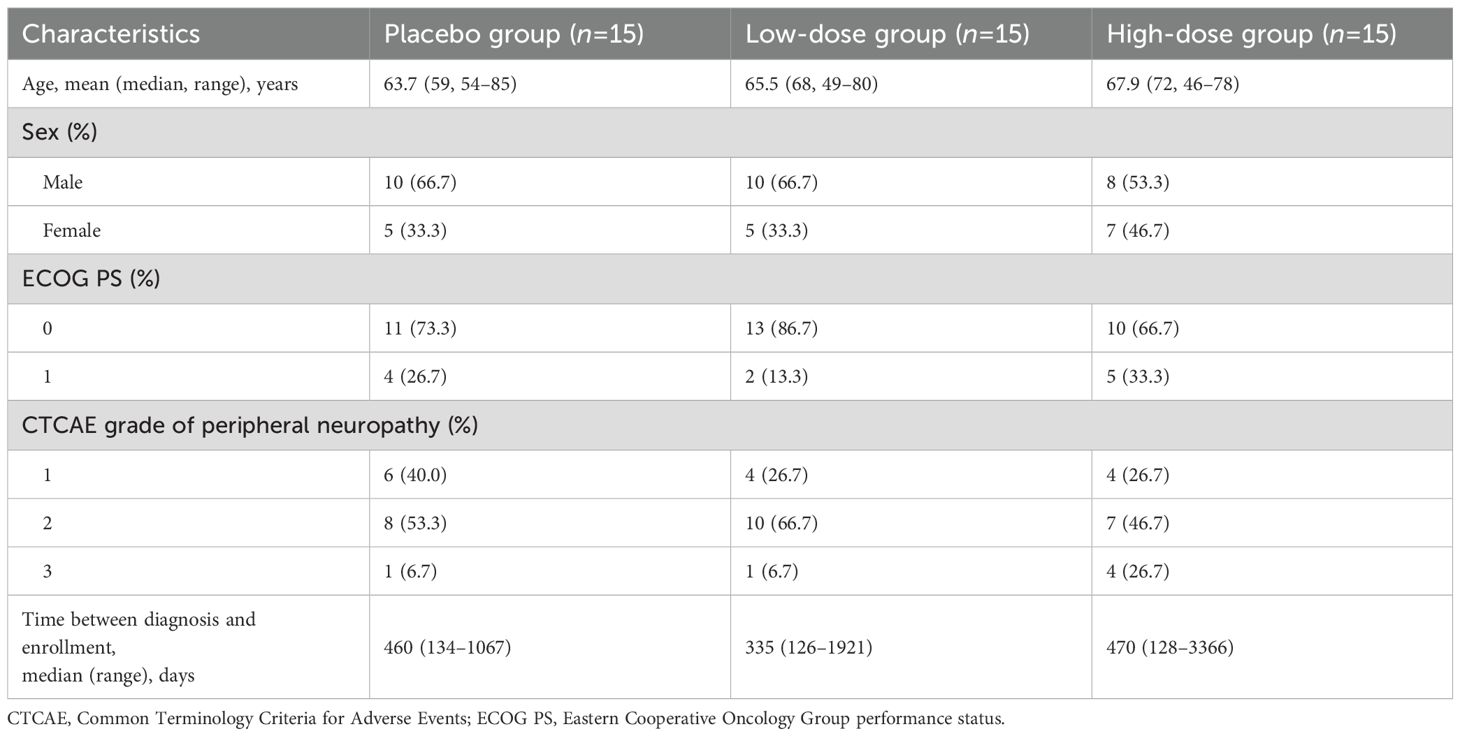
A total of 45 patients were enrolled between September 2021 and June 2023 (Figure 1). Patients were randomly assigned to the placebo (n = 15), low-dose (n = 15), and high-dose (n = 15) groups. One patient in the high-dose group discontinued treatment at week 3 because of personal reasons for refusal; therefore, that patient was excluded from the per-protocol analysis. The baseline characteristics of each group were broadly similar to those of the overall population (Table 1). The mean ages in the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups were 63.7 years, 65.5 years, and 67.9 years, respectively. The proportions of male patients in the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups were 66.7%, 66.7%, and 53.3%, respectively. The proportion of patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 was 73.3%, 86.7%, and 66.7% in the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups, respectively. CTCAE grade of peripheral neuropathy 1 was observed in 40.0%, 26.7%, and 26.7% of patients in the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups, respectively. The median times from diagnosis to enrolment in the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups were 460 days (range, 134–1067), 335 days (range, 126–1921), and 470 days (range, 128–3366).
3.2 VAS-based outcome measures
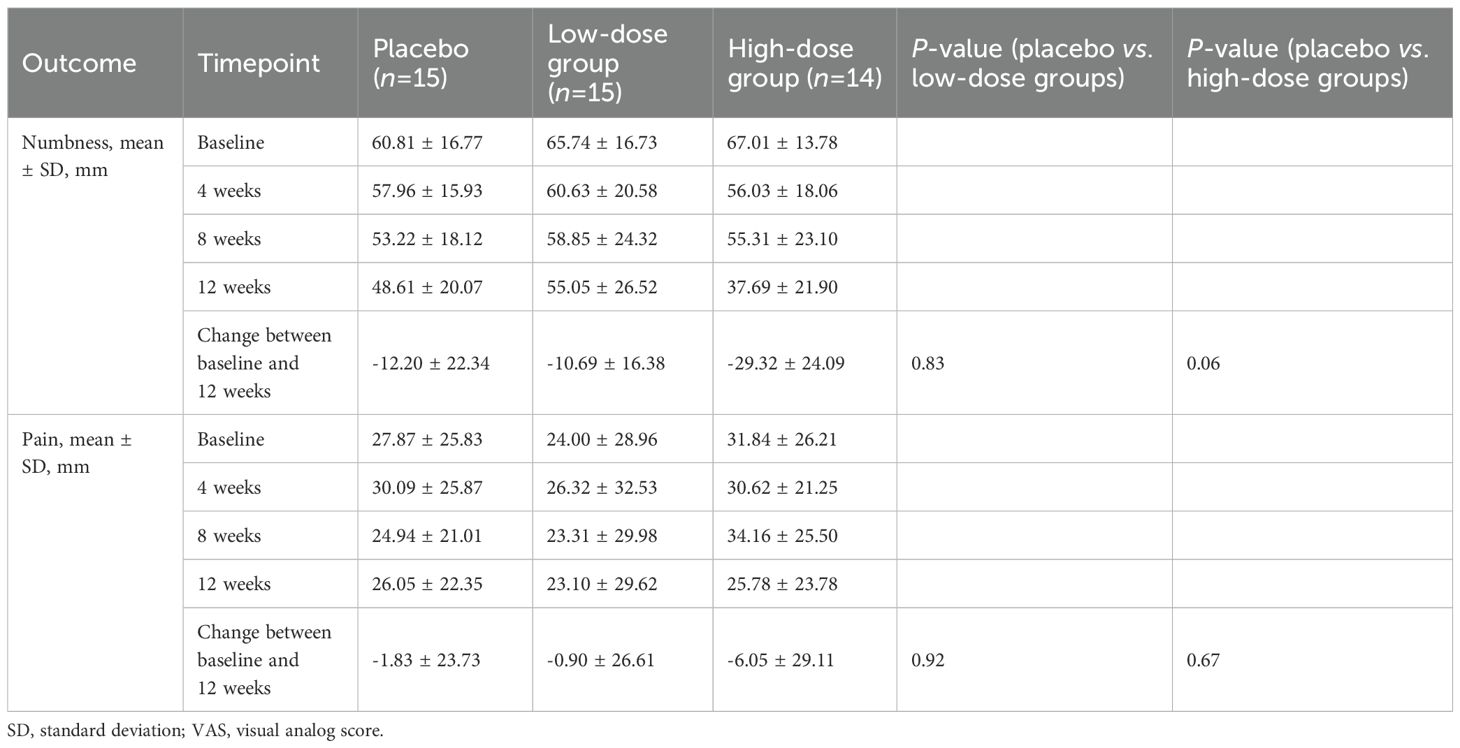
A significant difference in the reduction of the VAS numbness scores in the low-dose and placebo groups at 12 weeks was not observed (−12.20 [95% confidence interval {CI}, −34.54 to 10.14] vs. −10.69 [95% CI, −27.07 to 5.69]; p = 0.83) (Figure 2A). Detailed changes in VAS scores are summarized in Table 2. However, the high-dose group showed a greater, albeit not statistically significant, improvement in the VAS numbness score than the placebo group (−12.20 vs. −29.32 [95% CI, −53.35 to −5.29]; p = 0.06) (Figure 2B). No significant differences were observed when the VAS pain scores in the low-dose and placebo groups were compared (−1.83 [95% CI, −25.56 to 21.90] vs. −0.90 [95% CI, −27.51 to 25.71]; p = 0.92), or when comparing the high-dose and placebo groups (−6.05 [95% CI, −23.06 to 10.96]; p = 0.67).
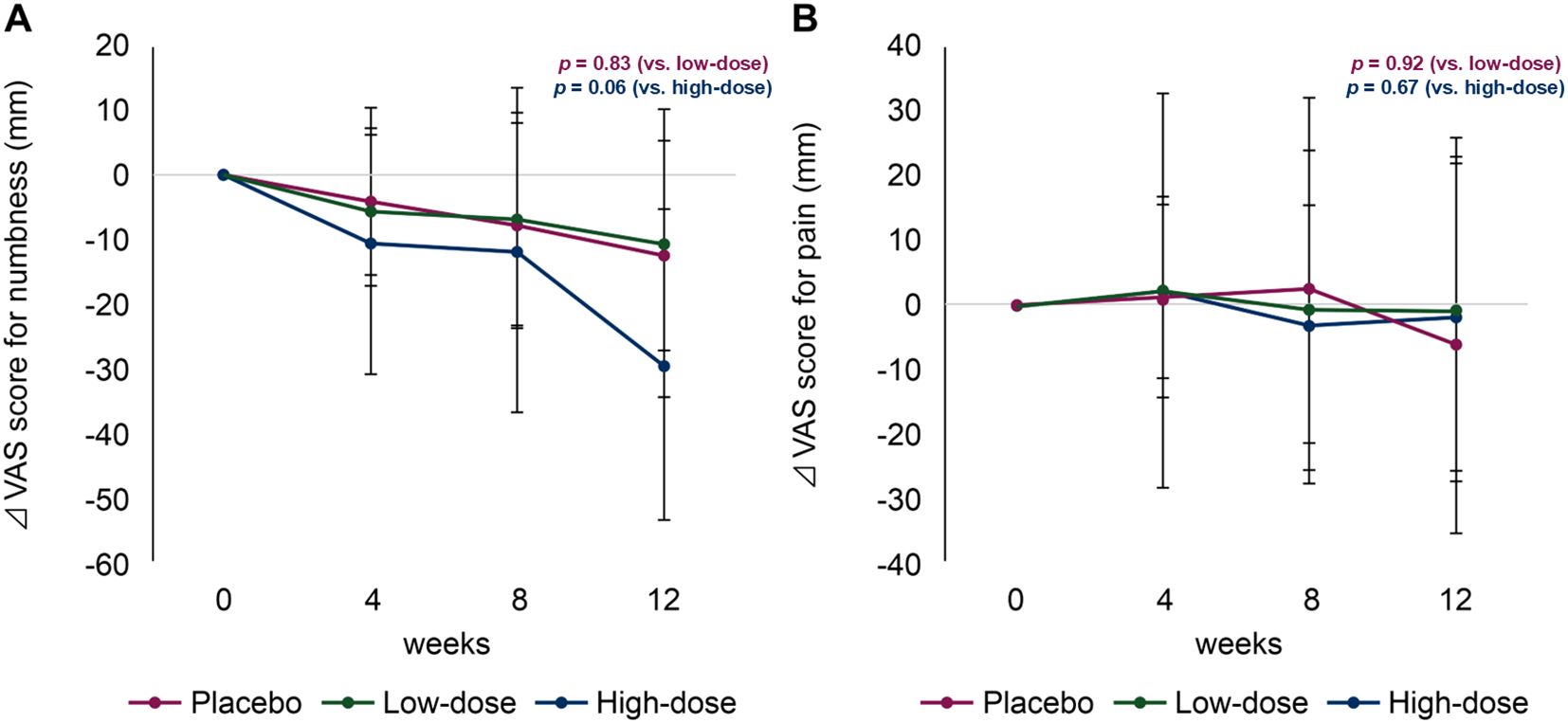
Figure 2. Changes in visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for numbness (A) and pain (B). Magenta line, placebo group; green line, low-dose group; blue line, high-dose group.
3.3 CTCAE
Peripheral neuropathy severity was assessed using CTCAE grades at baseline and at 4 and 12 weeks. Baseline scores in the placebo, low-dose, and high-dose groups were 1.7 ± 0.6, 1.8 ± 0.6, and 2.0 ± 0.8, respectively. At 12 weeks, the magnitude of change did not differ significantly between the placebo and low-dose groups (−0.1 ± 0.8 vs. −0.3 ± 0.6, p = 0.32) or between the placebo and high-dose groups (−0.1 ± 0.8 vs. −0.4 ± 0.7, p = 0.32) (Supplementary Table S1).
3.4 QoL
Among the 40 items of the FACT-GOG/Ntx questionnaire, the An6 (‘difficulty walking’) score in the high-dose group significantly improved compared with that in the placebo group at 12 weeks (−0.14 [95% CI, −1.24 to 0.96] vs. −1.00 [95% CI, 0.00 to 2.00]; p = 0.02) (Figure 3A). Similarly, the Ntx6 (‘I have trouble hearing’) score in the high-dose group was improved compared with that in the placebo group at 12 weeks (−0.29 [95% CI, −0.32 to 0.90] vs. −0.62 [95% CI, −1.66 to 0.42]; p = 0.01) (Figure 3B). A summary of changes in the FACT-GOG/Ntx questionnaire scores is shown in Supplementary Table S2.
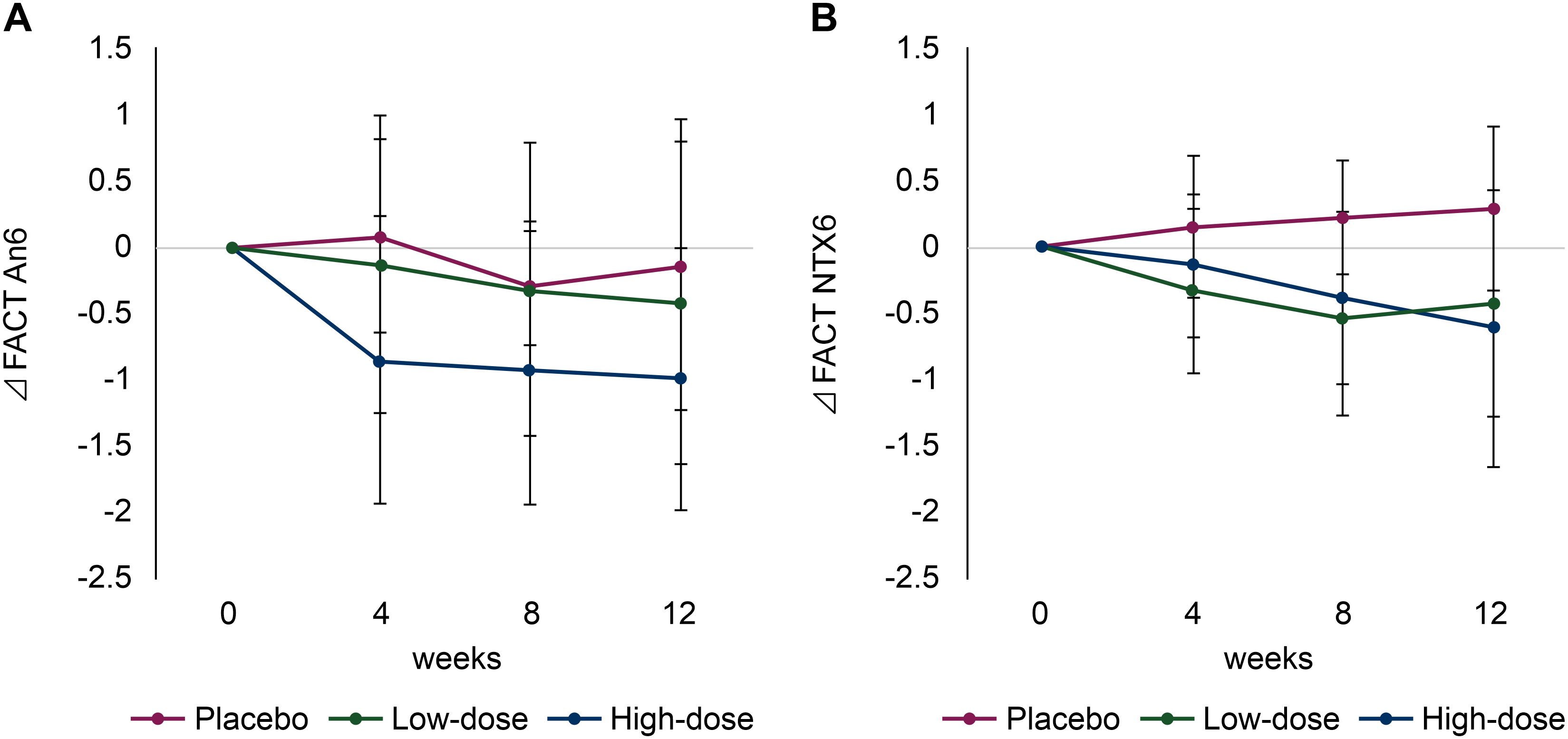
Figure 3. Changes in quality of life (QoL) scores using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity (FACT/GOG-Ntx). (A) Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) An6 (‘difficulty walking’) and (B) FACT Ntx6 (‘I have trouble hearing’). Red line: placebo group; green line: low-dose group; blue line: high-dose group.
3.5 Adverse events
Serious adverse events directly related to the intervention were not observed. One case of grade 1 anorexia in the low-dose group and one case of grade 2 shiitake dermatitis in the high-dose group were considered causally related but mild; therefore, the patients were allowed to continue treatment. One patient in the placebo group experienced a grade 4 small intestinal obstruction. Adverse events for which a causal relationship with the intervention could not be ruled out included abdominal distention (6.7%), abdominal pain (6.7%), anorexia (6.7%), and skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders (6.7%) in the low-dose group and nausea (6.7%) in the high-dose group (Supplementary Table S3).
3.6 Adherence to treatment
The median treatment adherence rates were 98.9% (range: 67.0%–100.0%) for the placebo group, 97.7% (range: 75.6%–100.0%) for the low-dose group, and 99.4% (range, 29.1%–100.0%) for the high-dose group.
4 Discussion
We explored whether low-dose and high-dose L.E.M. could reduce oxaliplatin-induced numbness experienced by patients undergoing postoperative chemotherapy for CRC. Although no significant difference in the reduction of the VAS numbness scores in the low-dose and placebo groups was observed at 12 weeks—the primary endpoint—a numerical decrease in the VAS numbness score in the high-dose group compared with that in the placebo group was observed. Although no clinically important minimum difference in VAS numbness scores has been established, we observed a change of 17 mm in the high-dose group, which aligned with the findings of a previous systematic review of acute pain that integrated 37 trials and reported a median clinically important minimum difference of 17 mm (8–40 mm) (19). These findings indicate that high-dose L.E.M. extract may have clinical relevance, and that further investigations are warranted.
Oxaliplatin-induced physical damage impairs neuronal function through mechanisms such as DNA damage, voltage-gated ion-channel dysfunction, neuroinflammation, altered transporter function, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis (20). Although oxaliplatin is less neurotoxic than cisplatin to dorsal root ganglion neurons because of fewer platinum–DNA adducts, it still induces apoptosis. For oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain, the efficacy of duloxetine, which is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, has been demonstrated in several randomized trials (18, 21), and a small randomized trial suggested that venlafaxine reduces both acute and chronic neuropathic pain in patients treated with oxaliplatin (22). These agents offer temporary relief from pain associated with CIPN and may enable patients to receive higher cumulative doses of oxaliplatin. However, although options for managing neuropathic pain exist, effective treatments that specifically target numbness in CIPN have not been identified. Moreover, the current agents lack neuroprotective effects and may paradoxically exacerbate OIPN, potentially contributing to motor dysfunction. Consequently, strategies that protect or repair nerve function that can replace analgesic or palliative treatments for OIPN are critically necessary. L.E.M. extract has shown antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in preclinical studies, suggesting potential neuroprotective effects (23, 24). Therefore, we focused our investigation on L.E.M. extract as a potential therapeutic agent.
In the high-dose and low-dose groups, adherence to L.E.M. extract treatment was high, and tolerability was acceptable. Serious adverse events causally related to the product were not observed, suggesting minimal safety concerns. Shiitake dermatitis is associated with a toxic or hypersensitivity reaction to lentinan, which is a polysaccharide component of the mushroom cell walls. Lentinan is heat-labile; therefore, inadequately cooked mushrooms often cause such reactions (25). Because L.E.M. extract is prepared via hot water extraction, the incidence of dermatitis may be decreased; however, attention should be focused on skin reactions during ingestion because the exact prevalence of shiitake dermatitis is unknown. In this study, dermatitis was observed in one (6.7%) patient in the low-dose group and one (6.7%) patient in the high-dose group. Participants who were using gabapentin were excluded because shiitake mushroom consumption can increase plasma ergothioneine levels, which stimulates OCTN1-mediated gabapentin secretion, thus potentially reducing blood levels (26). Caution is warranted when using L.E.M. for patients who require prophylactic gabapentin for epilepsy.
These findings indicate that L.E.M. extract may help prevent hearing impairment progression. Common adverse effects of platinum-based drugs include nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. These drugs interact with DNA, resulting in irreversible changes that prevent tumor cell division. Although oxaliplatin is less ototoxic than cisplatin, sudden hearing loss has occurred during oxaliplatin treatment (27, 28). Both oxaliplatin and cisplatin are toxic to extracochlear hair cells and target thioredoxin reductase in the organ of Corti (29). Oxaliplatin can induce degeneration of hair cells in mouse cochlear tissue fragments through reactive oxygen species accumulation via ferroptosis; however, activation of Nrf2 by resveratrol can reduce cytotoxicity. Future studies should elucidate how L.E.M. extract attenuates these effects.
This study has several limitations. First, the limited follow-up period precluded a thorough evaluation of the long-term effects of L.E.M. extract. Second, the data were obtained exclusively from a Japanese population, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Therefore, larger studies with longer follow-up periods and more diverse populations are needed to fully elucidate the long-term effects of this agent.
In conclusion, although statistical significance was not observed, high doses of L.E.M. produced a numerically meaningful improvement in numbness scores, suggesting its potential clinical relevance. L.E.M. extract could be a potential neuroprotective agent for managing OIPN and other neurotoxicities. Further studies are necessary to establish its efficacy and explore its use as a neuroprotective agent for patients with cancer and chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Clinical Research Review Board of Nara Medical University (CRB5200002). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. HS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. KM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. TT: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. HK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Kobayashi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the patients who participated in this study and their families, as well as Oneness support for data management services.
Conflict of interest
SB has received research funding from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Amgen Inc., MSD Co. Ltd., AstraZeneca PLC, Bayer Co. Ltd., and honoraria from MSD Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. HS has received research funding from Asahi Kasei, Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Sanofi, and honoraria from Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca PLC, Bayer Co. Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan Co. Ltd., Merck Bio Pharma Co. Ltd., MSD Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Sanofi Co. Ltd., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. HS has received research funding from Asahi Kasei, Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Sanofi, and honoraria from Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca PLC, Bayer Co. Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan Co. Ltd., Merck Bio Pharma Co. Ltd., MSD Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Sanofi Co. Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Takeda Co. Ltd., and Yakult Honsha Co. Ltd. Takata Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.. SM has received consulting or advisory fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., research funding from Caris Life Science, and honoraria from Merck Bio Pharma Co. Ltd., MSD Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Takeda Co. Ltd., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. TK has received research funding from Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca PLC, Amgen Inc., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Incyte Biosciences Japan G.K., MSD Co. Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer Inc., and honoraria from MSD Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb K.K., and Merck Biopharma Co. Ltd. TY has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., MSD K.K., Daiichi-Sankyo Co., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. TT has received consulting or advisory fees from Fujimoto Pharmaceutical Corporation and research funding from Meister Guild Inc. HK has received consulting or advisory fees from Astellas Pharma Inc. and Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd. and honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., MSD K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., Merck Biopharma Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Yakult Pharmaceutical Industry Takata Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Novartis International AG, Bayer Yakuhin Ltd., and Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd.
The remaining author declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1577848/full#supplementary-material
Glossary
AE: adverse event
CI: confidence interval
CIPN: chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
CRC: colorectal cancer
CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events
FACT/GOG-Ntx: Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity
L.E.M.: Lentinula edodes mycelium
OIPN: oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy
QoL: quality of life
VAS: visual analog scale
References
1. Zajączkowska R, Kocot-Kępska M, Leppert W, Wrzosek A, Mika J, and Wordliczek J. Mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1451. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061451
2. Miltenburg NC and Boogerd W. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy: a comprehensive survey. Cancer Treat Rev. (2014) 40:872–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.04.004
3. Kuebler JP, Wieand HS, O’Connell MJ, Smith RE, Colangelo LH, Yothers G, et al. Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol. (2007) 25:2198–204. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.08.2974
4. André T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, et al. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the Mosaic trial. J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:3109–16. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.6771
5. Schmoll H-J, Tabernero J, Maroun J, de Braud F, Price T, Van Cutsem E, et al. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer: final results of the NO16968 randomized controlled Phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:3733–40. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.60.9107
6. Seretny M, Currie GL, Sena ES, Ramnarine S, Grant R, MacLeod MR, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. (2014) 155:2461–70. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.09.020
7. Loprinzi CL, Lacchetti C, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Hertz DL, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO Guideline update. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:3325–48. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01399
8. Jordan B, Margulies A, Cardoso F, Cavaletti G, Haugnes HS, Jahn P, et al. Systemic anticancer therapy-induced peripheral and central neurotoxicity: ESMO–EONS–EANO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, prevention, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1306–19. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.003
9. Grothey A, Sobrero AF, Shields AF, Yoshino T, Paul J, Taieb J, et al. Duration of adjuvant chemotherapy for Stage III colon cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:1177–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1713709
10. Okuno K and Uno K. Efficacy of orally administered Lentinula edodes mycelia extract for advanced gastrointestinal cancer patients undergoing cancer chemotherapy: a pilot study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2011) 12:1671–4.
11. Yanagimoto H, Hirooka S, Yamamoto T, Yamaki S, and Sekimoto M. Efficacy of Lentinula edodes mycelia extract on chemotherapy-related tasted disorders in pancreatic cancer patients. Nutr Cancer. (2023) 75:236–46. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2022.2107226
12. Nagashima Y, Yoshino S, Yamamoto S, Maeda N, Azumi T, Komoike Y, et al. Lentinula edodes mycelia extract plus adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer patients: results of a randomized study on host quality of life and immune function improvement. Mol Clin Oncol. (2017) 7:359–66. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1346
13. Kajiyama S, Nagatake T, Ishikawa S, Hosomi K, Shimada Y, Matsui Y, et al. Lentinula edodes mycelia extract regulates the function of antigen-presenting cells to activate immune cells and prevent tumor-induced deterioration of immune function. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2023) 23:281. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04106-5
14. Bielewicz J, Daniluk B, and Kamieniak P. VAS and NRS, same or different? Are visual analog scale values and numerical rating scale equally viable tools for assessing patients after microdiscectomy? Pain Res Manag. (2022) 2022:5337483. doi: 10.1155/2022/5337483
15. Calhoun EA, Welshman EE, Chang CH, Lurain JR, Fishman DA, Hunt TL, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity (Fact/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire for patients receiving systemic chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2003) 13:741–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2003.13603.x
16. Huang HQ, Brady MF, Cella D, and Fleming G. Validation and reduction of FACT/GOG-Ntx subscale for platinum/paclitaxel-induced neurologic symptoms: a gynecologic oncology group study. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2007) 17:387–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2007.00794.x
17. Li T, Park SB, Battaglini E, King MT, Kiernan MC, Goldstein D, et al. Assessing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy with patient reported outcome measures: a systematic review of measurement properties and considerations for future use. Qual Life Res. (2022) 31:3091–107. doi: 10.1007/s11136-022-03154-7
18. Hirayama Y, Ishitani K, Sato Y, Iyama S, Takada K, Murase K, et al. Effect of duloxetine in Japanese patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a pilot randomized trial. Int J Clin Oncol. (2015) 20:866–71. doi: 10.1007/s10147-015-0810-y
19. Cheng F, Zhang R, Sun C, Ran Q, Zhang C, Shen C, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in colorectal cancer patients: mechanisms, pharmacokinetics and strategies. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1231401. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1231401
20. Matsuoka H, Iwase S, Miyaji T, Kawaguchi T, Ariyoshi K, Oyamada S, et al. Additive duloxetine for cancer-related neuropathic pain nonresponsive or intolerant to opioid-pregabalin therapy: a randomized controlled trial (JORTC-PAL08). J Pain Symptom Manage. (2019) 58:645–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2019.06.020
21. Durand JP, Deplanque G, Montheil V, Gornet JM, Scotte F, Mir O, et al. Efficacy of venlafaxine for the prevention and relief of oxaliplatin-induced acute neurotoxicity: results of EFFOX, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Ann Oncol. (2012) 23:200–5. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr045
22. Jiang T, Luo Z, and Ying T. Fumigation with essential oils improves sensory quality and enhanced antioxidant ability of shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes). Food Chem. (2015) 172:692–8. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.130
23. Ren Z, Liu W, Song X, Qi Y, Zhang C, Gao Z, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammation of enzymatic-hydrolysis residue polysaccharides by Lentinula edodes. Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 120:811–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.114
24. Olsen MF, Bjerre E, Hansen MD, Hilden J, Landler NE, Tendal B, et al. Pain relief that matters to patients: systematic review of empirical studies assessing the minimum clinically important difference in acute pain. BMC Med. (2017) 15:35. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0775-3
25. Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, Handler NS, Handler GA, and Schwartz RA. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2016) 17:485–9. doi: 10.1007/s40257-016-0212-6
26. Toh DSL, Limenta LMG, Yee JY, Wang L-Z, Goh B-C, Murray M, et al. Effect of mushroom diet on pharmacokinetics of gabapentin in healthy Chinese subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2014) 78:129–34. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12273
27. Güvenç MG, Dizdar D, Dizdar SK, Okutur SK, and Demir G. Sudden hearing loss due to oxaliplatin use in a patient with colon cancer. J Chemother. (2016) 28:341–2. doi: 10.1179/1973947815Y.0000000023
28. Kim SB, Kim SY, Kim KH, and Kim TN. Oxaliplatin-induced sudden hearing loss in a patient with pancreatic cancer. Korean J Gastroenterol. (2020) 76:261–4. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.121
Keywords: chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, colorectal cancer, Lentinula edodes mycelia, L.E.M., oxaliplatin
Citation: Boku S, Satake H, Mitani S, Maeda K, Kudo T, Yamaguchi T, Takagi T and Kawakami H (2025) A placebo-controlled study of the doses and efficacy of Lentinula edodes mycelia for oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1577848. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1577848
Received: 16 February 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 11 August 2025.
Edited by:
Ebenezer Idowu Olatunbosun Ajayi, Osun State University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Qingbin Cui, University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, United StatesAshaolu Victoria Oladimeji, Loyola College, India
Copyright © 2025 Boku, Satake, Mitani, Maeda, Kudo, Yamaguchi, Takagi and Kawakami. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hisato Kawakami, a2F3YWthbWlfaEB0b2hva3UuYWMuanA=
 Shogen Boku
Shogen Boku Hironaga Satake
Hironaga Satake Seiichiro Mitani
Seiichiro Mitani Kiyoshi Maeda4
Kiyoshi Maeda4 Toshihiro Kudo
Toshihiro Kudo Toshifumi Yamaguchi
Toshifumi Yamaguchi Tatsuya Takagi
Tatsuya Takagi Hisato Kawakami
Hisato Kawakami