- 1Medical School, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 2Oncology Medical Center, The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
In recent years, with the advancement of RNA analysis techniques, such as single-cell RNA sequencing, noncoding RNAs have demonstrated substantial potential in regulating gene expression, encoding peptides and proteins, constructing the cellular microenvironment, and modulating cell function. They can serve as potential therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for various diseases, offering novel avenues for diagnosis and treatment. Among them, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent a principal component. Through the competing endogenous RNA mechanism, lncRNAs sequester microRNAs (miRNAs), interact with metabolic enzymes or transcription factors, regulate gene expression, and participate in the metabolic communication network within the tumor microenvironment. This process significantly promotes the growth, proliferation, and metastasis of lung cancer cells by reprogramming core metabolic pathways—including glucose utilization, lipid homeostasis, and amino acid flux. This article reviews the key roles of lncRNAs and miRNAs in the metabolic reprogramming of patients with lung cancer, elucidates the complex lncRNA–miRNA network involved, and provides mechanistic insights into metabolic vulnerabilities and translational opportunities for targeted interventions in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer remains the most prevalent malignant neoplasm worldwide and presents substantial public health challenges, as evidenced by its disproportionate mortality burden. According to statistics, lung cancer accounts for approximately 18.4% of total cancer-related deaths. Despite advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic technologies, the 5-year survival rate for patients with primary lung cancer remains below 16%, posing a persistent global public health concern (1, 2). As research delves deeper into the biological characteristics of tumors, the hallmark framework proposed by Hanahan and Weinberg has been continually refined, with metabolic reprogramming emerging as a key feature enabling tumor cells to adapt to microenvironmental stress and sustain malignant phenotypes (3). This metabolic remodeling extends beyond the classical Warburg effect (enhanced aerobic glycolysis) to encompass multidimensional regulatory networks, including the dynamic balance of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), lipid metabolic reprogramming, and amino acid metabolic dysregulation (4–13).
As a vital member of the noncoding RNA family, research on long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) has undergone a paradigm shift from being considered “transcriptional noise” to being recognized as “functional regulators.” Since their discovery in 1976, the biological functions of lncRNAs have gradually become clearer (14). By the early 21st century, high-throughput sequencing technologies revealed numerous lncRNA expression profiles (14). Since then, their roles have been systematically analyzed and characterized (14–20), gradually unveiling the complexities of lncRNA biology. LncRNAs are extensively involved in constructing tumor metabolic networks through multiple mechanisms, including the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism, protein binding, and transcriptional or posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. For example, LINC01123 enhances glycolytic flux by stabilizing c-Myc transcripts; AC020978 binds to pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) to simultaneously drive glycolysis and metastasis; and ADPGK-AS1 modulates M2 macrophage polarization via exosomes, thereby reshaping the tumor microenvironment (TME) (21–25). These findings highlight the pivotal role of lncRNAs in tumor metabolic reprogramming and introduce novel molecular targets and research paradigms for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with lung cancer.
Here, we systematically review the lncRNA–miRNA regulatory networks involved in the metabolic reprogramming of patients with lung cancer, focusing on their molecular mechanisms in glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism. In addition, we integrate relevant research from the past decade to explore: (i) how lncRNAs regulate rate-limiting metabolic enzymes through the ceRNA mechanism; (ii) the dynamic influence of lncRNA–protein interactions on metabolic pathways; and (iii) the interplay between metabolic microenvironment remodeling and tumor progression. Furthermore, individualized diagnostic and therapeutic strategies based on lncRNA expression profiles have progressed to phase II clinical trials (NCT04808362) (26), suggesting substantial translational potential. The objective of this review is to provide a theoretical foundation for understanding metabolic heterogeneity in patients with lung cancer and for developing precise, targeted intervention strategies.
2 Overview and development of lncRNA
LncRNAs are noncoding transcripts greater than 200 nucleotides in length. In 1976, research on lncRNAs was first documented, and early investigations predominantly characterized their universality and basic features. In the early 21st century, the ENCODE project employed systematic mapping technologies to identify numerous previously unknown lncRNAs and to establish their critical roles in gene regulation (14). Subsequently, various studies have been conducted to deepen our understanding of lncRNAs through data analysis and feature profiling (1–5, 14–19). LncRNAs are not restricted to the nucleus; they are also widely found in the cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes (where they affect protein translation), the cell periphery (associated with cell adhesion and connectivity), and exosomes (which influence cancer cell growth, metastasis, or innate immune activation) (27). LncRNAs exhibit high tissue and cell specificity, and their functions are modulated by subcellular localization, abundance, and interacting molecules (27–29). The growing body of knowledge surrounding lncRNAs has deepened the scope of related research, leading to increasing recognition of their roles in cell proliferation, migration, DNA repair, chromatin organization, and the pathogenesis of numerous diseases (29–38), thereby addressing critical gaps in prior research.
Since 2020, lncRNA-focused research has expanded rapidly, with more than 50% of studies concentrating on cancer. Other investigated areas include autophagy, subcellular localization and function, fibrosis, aging, immunity to COVID-19 infection, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, mental illness, and ischemia–reperfusion injury (27, 39–45). In recent years, many researchers have integrated multi-omics networks and machine learning to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of predicting lncRNA–disease associations using big data (46–49). The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence technology and its integration into medical research have revitalized modern scientific inquiry.
3 Significance of metabolic reprogramming in tumor progression
In the human body, cells primarily generate energy through several metabolic pathways: OXPHOS, glycolysis, lipid oxidation, and amino acid metabolism. In tumor cells, these metabolic processes undergo phenotypic transformation. In recent years, dynamic shifts between glycolytic reprogramming (Warburg effect) and OXPHOS activation in cancer cells have spurred a surge of research. Warburg first identified abnormal energy metabolism in tumor cells in 1930, referring to the phenomenon whereby tumor cells preferentially undergo glycolysis even in the presence of adequate oxygen. This shift satisfies their rapid energy and biosynthetic demands by enhancing glucose uptake and lactic acid production (8). Although subsequent studies have confirmed this observation (50, 51), several questions remain. These include the limited effectiveness of glycolysis-targeted therapies (52), high OXPHOS levels in some tumors (7, 53), and the presence of metabolic heterogeneity in tumors (54). Additionally, the reverse Warburg effect describes how stromal cells within the TME support tumor growth by secreting metabolites and promoting angiogenesis (52).
Over decades of study, the metabolic characteristics of tumor cells have gradually become clearer. Hanahan and Weinberg’s seminal 2000 (3) framework outlining six hallmarks of cancer was later expanded in 2011 to include two enabling characteristics (genomic instability and tumor-promoting inflammation) and two new hallmarks: energy metabolism reprogramming and immune evasion. Metabolic reprogramming refers to the capacity of tumor cells to reconfigure their energy networks—particularly glycolysis and lipid metabolism—to adapt to microenvironmental stress and sustain malignant phenotypes (8).
OXPHOS is the cellular process whereby reduced equivalents (NADH and FADH2) generated from the oxidation of organic substrates (including glucose and fatty acids) are converted into ATP through the synergistic action of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase (55). OXPHOS can support rapid tumor proliferation by efficiently producing ATP. Additionally, intermediates from the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, such as α-ketoglutarate and oxaloacetate, provide carbon backbones for synthesizing lipids, nucleic acids, and amino acids—thereby fulfilling the biosynthetic demands of proliferating tumor cells (56). While the Warburg effect dominates many solid tumors, OXPHOS plays an essential role in leukemia, drug-resistant tumor cells, and cancer stem cells (57). Metabolic plasticity allows tumors to adapt to microenvironmental stressors, such as hypoxia or nutrient deprivation. For example, under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α promotes glycolysis by upregulating GLUT1 and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), while suppressing OXPHOS (58). Conversely, cancer stem cells often rely on OXPHOS for self-renewal, driven by PGC-1α and mitochondrial biogenesis (59). Which metabolic process—OXPHOS or the Warburg effect—plays a more crucial role in tumor progression (including invasion, proliferation, and drug resistance) remains unknown. Interestingly, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells exhibit a mixed metabolic phenotype, simultaneously employing glycolysis and OXPHOS via glutamine-driven TCA cycle activity (60). In addition, metabolism in lung tumor cells does not shift from OXPHOS to glycolysis but instead involves enhancement of both pathways (54). In light of this, Liu et al. demonstrated that OXPHOS is upregulated during the dissemination of breast cancer and remains active during colonization, while aerobic glycolysis persists—indicating that the metabolic landscape of tumor cells exhibits complex spatial and temporal heterogeneity that warrants further investigation.
The metabolic pattern transition of tumor cells is dynamically regulated by various molecular networks, involving many processes, such as carcinogenic signals, epigenetic modifications, and microenvironment interactions. For instance, BRAF inhibitors abnormally activate OXPHOS in melanoma through the MITF–PGC1α axis, thereby promoting drug resistance (61). Dual inhibition strategies targeting these adaptive mechanisms, such as combining the glycolysis inhibitor 2-DG with the OXPHOS inhibitor metformin, have shown synergistic therapeutic potential (62). In addition, Hu et al. found that Sirt5 knockout enhances glutamine and glutathione metabolism through acetylation-mediated GOT1 activation, thereby promoting the progression of KRAS mutant pancreatic cancer, and metabolic competition within the TME also shapes metabolic phenotypes. For instance, tumor cells can overtake glucose by overexpressing the glucose transporter GLUT1, resulting in glucose deprivation in the microenvironment and forcing adjacent immune cells (such as T cells) to become dysfunctional owing to insufficient energy, thus avoiding immune surveillance (63). In addition, lactic acid, as a major byproduct of glycolysis, is secreted extracellularly through monocarboxylate transporters (MCT1/MCT4), taken up by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and used for OXPHOS to form a ‘lactic acid shuttle’ that sustains tumor growth (64). The competitive consumption of glutamine also significantly affects the metabolic phenotype. Tumor cells deplete glutamine in the microenvironment by upregulating the glutamine enzyme (GLS1), inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization, and promoting the tumor-promoting M2 phenotype (65). Exosome-mediated metabolite delivery, such as succinic acid, can activate HIF-1α signaling and induce chemotherapy resistance (62).
In summary, metabolic reprogramming endows malignant cells with unique abilities, including cell growth and proliferation at multiple levels (9–11), metastasis (12, 13), drug resistance (4, 5), immune regulation (6), and TME remodeling (7). For example, KRAS and LKB1 mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells synthesize pyrimidines by upregulating CPS1 to provide raw materials for proliferation (9); lipid metabolism reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma alters cell membrane fluidity and mediates migration activity (12); when chemotherapy-sensitive lung adenocarcinoma cells are transformed into drug-tolerant persister cells, this transformation is closely related to PINK1-mediated mitophagy, enhanced OXPHOS, and cellular redox imbalance (5).
4 LncRNA, miRNA, and lung tumor metabolic reprogramming
Lung cancer is the most common malignant tumor worldwide, accounting for 18.4% of total cancer mortality. Despite advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic technologies, the 5-year survival rate of primary lung cancer is less than 16%, representing a considerable global health challenge (1, 2). Lung cancer is mainly divided into small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and NSCLC. NSCLC accounts for 85% of all cases, including lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell lung cancer. Although the incidence of SCLC is lower than that of NSCLC, it increases rapidly and carries a high risk of metastasis (5). Aberrant expression of certain lncRNAs in lung cancer cells, such as HOTAIR, MALAT1, and HOTTIP (66–70), is closely related to TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, and survival rate. Conversely, other lncRNAs, including MEG3, LINC01537, and MIR17HG, are downregulated in tumor tissues, suggesting that they may inhibit tumor development (71–73). Current research on lncRNAs in cancer has primarily focused on their roles in reprogramming cancer cell metabolism (21), regulating the tumor immune microenvironment (22), promoting cancer cell invasion and metastasis (23, 24), and interacting with proteins (25). This article discusses the regulation of lncRNAs in the metabolic reprogramming of lung tumor cells.
The ceRNA hypothesis was originally proposed by Leonardo et al. (74), which posits that the interaction between RNAs is based on microRNA binding sites (microRNA response elements) and constructs a ceRNA network with potential effects on diseases. Emerging tools, such as CRISPR-based screening and multi-omics integration, are decoding ceRNA interactions in specific contexts, providing new directions for biomarkers (such as serum lncRNA HOTAIR) and therapeutic targets.
In most cases, cells use glucose and other carbohydrates to produce energy. Therefore, studies on lncRNA-mediated metabolic reprogramming of lung tumors have predominantly focused on modulating cell glucose metabolism. By summarizing existing research findings, we conclude that the mechanism of lncRNA regulating metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells mainly includes (1): acting as a ceRNA ‘sponge’ to adsorb miRNAs, thereby protecting mRNA translation from miRNA interference (2); combining with key enzymes to improve their stability and adjust the content of metabolic enzymes; (3) interacting with transcription factors to indirectly regulate gene expression; (4) participating in metabolic remodeling of the TME; and (5) regulating gene expression at the posttranscriptional level (as shown in Figure 1).
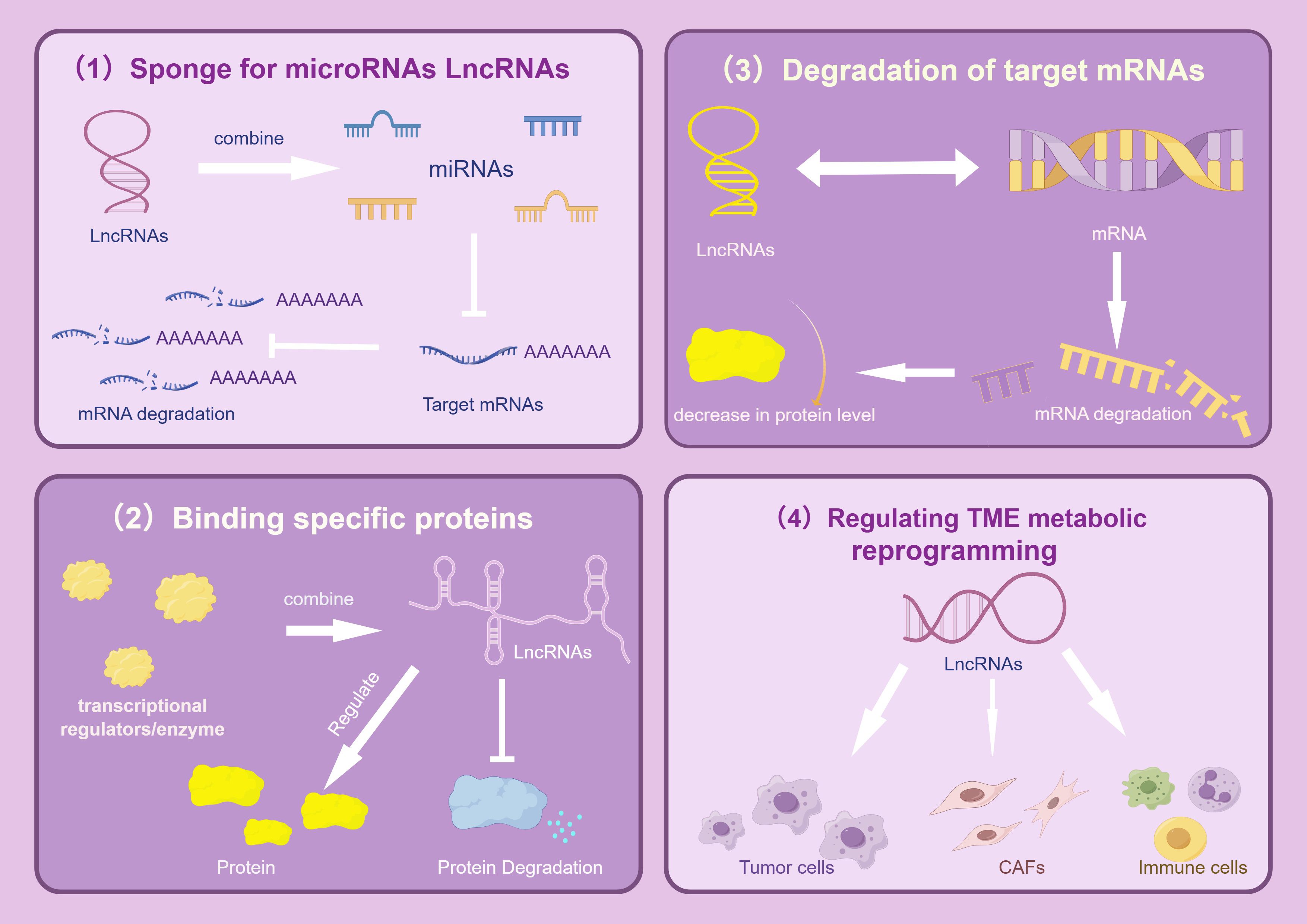
Figure 1. Regulatory mechanism of LncRNAs. The picture mainly describes the four main gene expression regulation mechanisms of LncRNAs in tumors, which are: As a ceRNAs “molecular sponge”, it adsorbs miRNAs, affects the enrichment level of specific proteins, promotes the degradation of target mRNAs, and regulates TME metabolic reprogramming, thereby mediating complex and accurate regulatory mechanisms and significantly promoting the growth, proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cells. The image is created with Figdraw.
4.1 Glucose metabolism
Glucose metabolism is the key transformation in tumor metabolic reprogramming. Tumor cells need to ingest and metabolize carbon sources, such as glucose, to meet the needs of rapid growth, metastasis, and immune escape. This process involves adjustments in the type, distribution, and abundance of cellular metabolic enzymes, indicating the presence of complex and precise regulatory mechanisms at the genetic level (as shown in Figure 2 and Table 1).
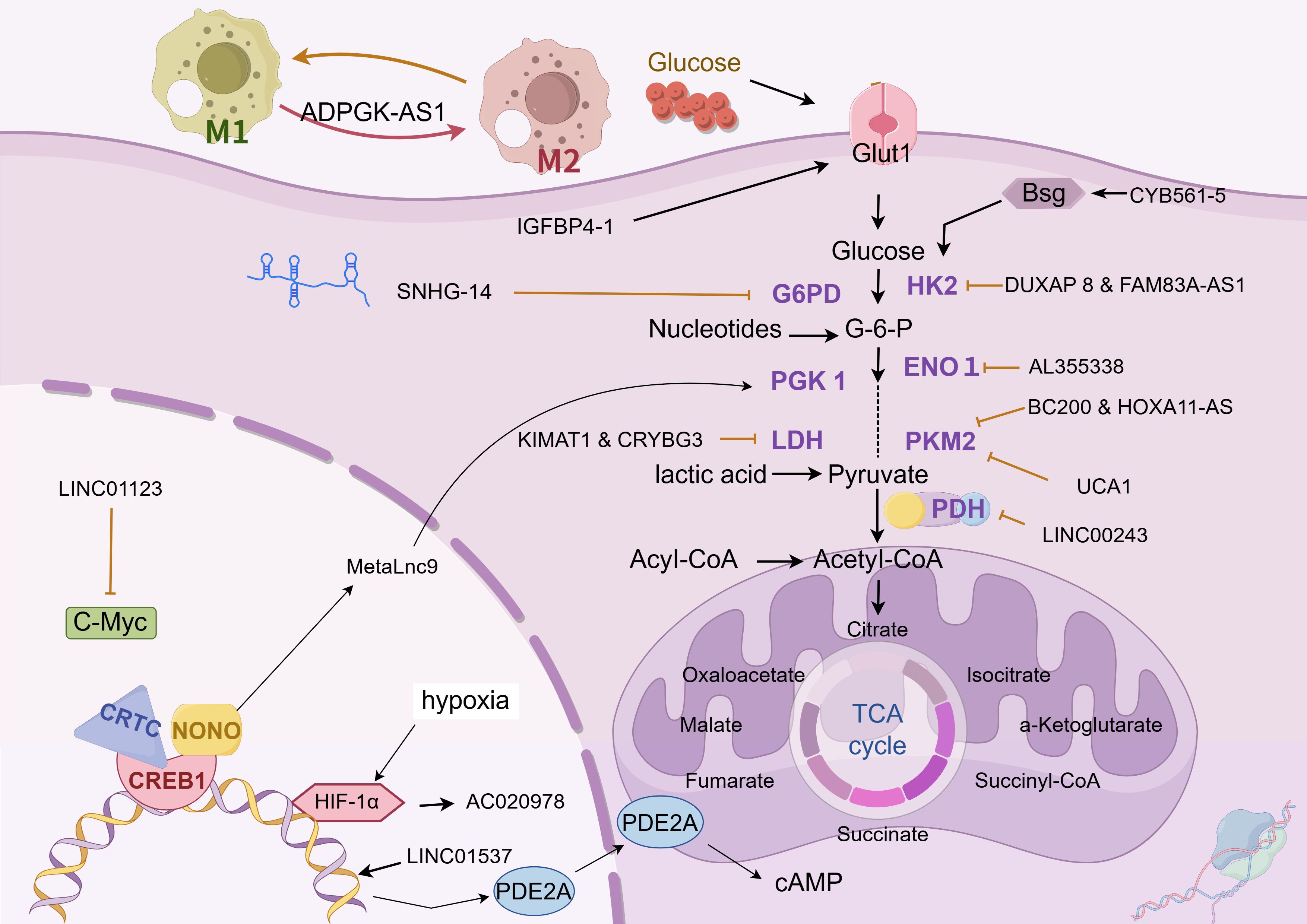
Figure 2. Glucose metabolism. The chart illustrates the regulation mechanism of different LncRNAs on glucose metabolism in lung cancer cells. These lncRNAs influence the abundance of glucose metabolic enzymes, glucose uptake, and the expression of related transcription factors through various pathways, in order to adapt to their rapid growth, metastasis and immune escape. The following is a supplement to the specific mechanisms in the figures: CYB561-5: Interacts with Bsg protein and stimulates the expression of HK2 and PFK1; DUXAP8 & FAM83A-AS1: Upregulate HIF-1α and glycolysis-related enzymes, and target miR-203-3p to boost HK2 expression; AL355338: Binds with ENO1 to enhance cellular glycolysis and drive malignant evolution of NSCLC via EGFR - AKT.; BC200 & HOXA11-AS: Function as a molecular sponge for miR-148b-3p to promote PKM2 expression; LINC00243: Sequesters miR-507 to enhance PDK4 expression; lnc-IGFBP4-1: Mainly localizes in the nucleus, regulates the transcription of glycolysis - related genes like GLUT1, PKM2, and HK2, and increases the expression of glycolysis - associated enzymes; SNHG14: Acts as a molecular sponge for miR-206, upregulates G6PD expression, and helps tumor cells combat oxidative stress, participate in antioxidant synthesis, and generate free radicals; KIMAT1 & LncCRYBG3: Activate mTOR to promote MYC transcription, and bind with LDH; LINC01123 competes with miR-199a-5p to relieve the suppression of c-Myc mRNA, and also participates in the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via the ZEB1/LINC01123/miR-499b-5p/NOTCH1 axis; MetaLnc9: Forms a NONO/CRTC/CREB1 complex in the nucleus to interfere with transcription, and binds with PGK1 in the cytoplasm to prevent its degradation and activate the Akt/mTOR pathway; AC020978: Under the regulation of HIF-1α binding site in the upstream region, it is inversely regulated by hypoxic conditions and HIF-1α . It binds to and stabilizes PKM2, modulates the interaction between PKM2 and HIF-1α to enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1α , and also binds to MDH2 to activate the PI3K-AKT pathway; LINC01537, mainly located in the cytoplasm, stabilizes PDE2A mRNA, enhancing its expression, and thus inhibits mitochondrial respiration and the Warburg effect. When its expression is down - regulated in lung cancer cell mitochondria, PDE2A expression decreases correspondingly, regulating mitochondrial biological activity and the Warburg effect. The image is created with Figdraw.
4.1.1 LncRNA acts as a molecular sponge to regulate miRNA
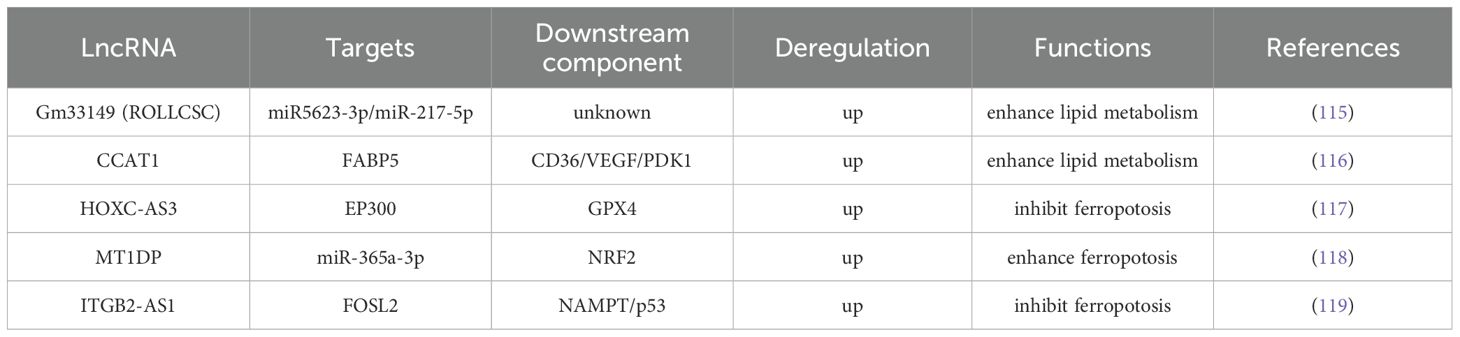
LncRNAs, such as LINC01123, DUXAP8, BCYRN1, LINC00243, HOXA11-AS, MALAT1, SNHG14, and FAM83A-AS1, are significantly upregulated in lung cancer tissues and are closely associated with tumor stage, lymph node metastasis risk, and poor prognosis (66, 69, 75, 77, 78, 85, 102, 103). These lncRNAs regulate glucose metabolism in lung cancer cells through diverse mechanisms and promote tumor progression. LINC01123 induces abnormal proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells, increases the expression and activity of key glycolytic enzymes, and enhances glucose uptake, lactate production, oxygen consumption, and ATP generation (75). Mechanistically, LINC01123 removes the inhibition of c-Myc mRNA by miR-199a-5p through competitive binding, creating a positive feedback loop and participating in lung adenocarcinoma progression via the ZEB1/LINC01123/miR-499b-5p/NOTCH1 axis (76). DUXAP8 upregulates the expression of key glycolytic enzymes by binding to miR-409-3p (77); BCYRN1 is mainly expressed in actively proliferating cells and enhances glycolysis and lactate secretion through the c-Myc/BCYRN1/miR-149/PKM2 axis (78); LINC00243 captures miR-507 and promotes the expression of PDK4 (79); HOXA11-AS, highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma cells, acts as a molecular sponge for miR-148b-3p, upregulates PKM2 expression, and regulates glucose metabolism reprogramming (79); MALAT1 targets miR-613 in NSCLC, downregulates COMMD8 expression, and enhances cell proliferation and glycolysis (84); as a molecular sponge for miR-206, SNHG14 upregulates G6PD expression, helping tumor cells resist oxidation and participate in reductive synthesis (86); FAM83A-AS1 promotes tumor cell metastasis and invasion in hypoxic environments by upregulating HIF-1α and glycolysis-related enzymes (92). Additionally, lncRNAs can target miR-203-3p to increase HK2 expression, thereby enhancing glycolysis and exacerbating the progression of lung adenocarcinoma (93).
4.1.2 LncRNA binding protein
LncRNAs, such as AC020978, CYB561-5, LncCRYBG3, AL355338, KIMAT1, and MetaLnc9, are highly expressed in lung cancer tissues and are closely associated with tumor stage and poor prognosis (87–89, 91, 104, 105). These lncRNAs alter the metabolic pattern of lung cancer cells and promote tumor progression through multilevel regulation. AC020978 is reversibly regulated by hypoxic conditions and HIF-1α because of a HIF-1α binding site in its upstream region. It binds to and stabilizes PKM2, prolongs its functional activity, regulates its interaction with HIF-1α, enhances HIF-1α transcriptional activity, affects the expression of glucose metabolism-related proteins, and promotes cell proliferation and glycolysis (87). AC020978 also binds to malate dehydrogenase 2 (a mitochondrial enzyme involved in the TCA cycle and the malate–aspartate shuttle, MDH2), activates the PI3K–AKT pathway, and promotes lung cancer cell metastasis (106). CYB561-5 interacts with basigin to stimulate the expression of hexokinase 2 (the first rate-limiting enzyme in glycolysis, HK2) and phosphofructokinase-1 (the second rate-limiting enzyme in glycolysis, PFK1), thereby affecting glycolysis (88). LncCRYBG3 binds specifically to LDHA, a key glycolytic enzyme, and promotes glycolysis (107). AL355338 enhances glycolysis by binding to enolase 1( ENO1 ) and promotes the malignant evolution of NSCLC via the EGFR–AKT pathway (89). KIMAT1 promotes MYC transcription by activating mTOR; together with LDHB, it enhances glycolysis and the TCA cycle, thereby promoting tumor growth (90). MetaLnc9 forms a NONO/CRTC/CREB1 complex in the nucleus, interfering with transcription; in the cytoplasm, it binds to phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and prevents its degradation, thereby enhancing glycolysis and activating the Akt/mTOR pathway to promote cell metastasis (91).
4.1.3 LncRNA regulates gene expression at transcriptional or posttranscriptional levels
Some lncRNAs regulate gene expression via transcriptional or posttranscriptional mechanisms. The different binding targets determine the distinct modes of action between the two: transcriptional mechanism refers to the regulation of target gene activity at the transcriptional initiation stage by directly binding to chromatin modification complexes or transcription factors, whereas posttranscriptional mechanism refers to the regulation of RNA stability, splicing, or translation efficiency through binding to mRNA or miRNA. The expression of lnc-IGFBP4-1 and ABHD11-AS1 is upregulated in lung cancer tissues, whereas LINC01537 is downregulated; these expression patterns are associated with tumor stage and poor prognosis (92, 94, 95, 97, 108). These lncRNAs regulate the metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells through various mechanisms and contribute to tumor progression. Among them, ABHD11-AS1 inhibits KLF4 transcription by recruiting the histone methyltransferase EZH2 to its promoter region, contributing to epigenetic regulation (108). Lnc-IGFBP4-1, which is predominantly localized in the nucleus, promotes cell growth, proliferation, and glycolytic metabolism by regulating the transcription of glycolytic genes, such as GLUT1, PKM2, and HK2 (94). This lncRNA increases the expression of glycolysis-related enzymes, including GLUT1, PKM2, G6PDH, HK2, PDK1, and LDHA, at the transcriptional level, thereby increasing intracellular ATP production (94). However, the specific regulatory mechanisms remain poorly understood. The increased expression of ABHD11-AS1 in NSCLC tissues is mainly attributed to methylation modification by METTL3 (108). ABHD11-AS1 is enriched in the nucleus and functions as a transcriptional cofactor to regulate gene expression (108). LncRNAs can also recruit EZH2 to the promoter region of KLF4 and inhibit its expression (108). In addition, ABHD11-AS1 can interact with SART3 to alter its subcellular localization, thereby indirectly regulating RNA splicing and promoting malignant transformation and tumor stem cell growth (96). LINC01537, primarily located in the cytoplasm, stabilizes phosphodiesterase 2A mRNA, thereby increasing its expression and inhibiting both mitochondrial respiration and the Warburg effect (97). Downregulation of LINC01537 in the mitochondria of lung cancer cells leads to a corresponding decrease in phosphodiesterase 2A expression, impaired mitochondrial function, and alterations in the Warburg effect, thereby inhibiting cell death (97).
4.1.4 Metabolic communication network involved in the regulation of the TME
The TME refers to the local tissue environment established by tumor cells to facilitate their growth, proliferation, and migration. Its cellular components include non-immune cells (such as tumor cells, CAFs, and endothelial cells) and immune cells (such as tumor-associated macrophages, tumor-associated neutrophils, and natural killer cells) (109). ADPGK-AS1, Mir100hg, and OIP5-AS1 are lncRNAs that are highly expressed in lung cancer samples and are closely associated with disease stage and poor prognosis, suggesting their involvement in metabolic remodeling, immune regulation, and tumor progression (98–100). Within the TME, M2 macrophages—associated with glycolysis—promote tumor growth, whereas M1 macrophages—primarily dependent on OXPHOS—mediate inflammation control (110). ADPGK-AS1 is highly expressed in M2 macrophages and regulates their metabolism and function by interacting with mitochondrial ribosomes, thereby contributing to macrophage phenotypic transformation (98). Simultaneously, the lncRNA Mir100hg, which is found in exosomes released by lung cancer stem cells, alleviates the inhibitory effects of miR-15a-5p and miR-31-5p on glycolysis in tumor cells, thereby enhancing their metastatic potential (99). In addition, OIP5-AS1, present in exosomes in the hypoxic TME of lung adenocarcinoma, affects tumor cell glycolysis via the miR-200c-3p axis, thereby promoting cell proliferation, growth, and metastasis (100). Notably, lncRNAs are also present in exosomes secreted by CAFs. These lncRNAs can downregulate miR-142-5p expression in lung cancer cells and upregulate Programmed cell death ligand 1(PD-L1) on the cell surface, thereby inhibiting the cytotoxic activity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and facilitating tumor progression (101). Cellular interactions within the TME are not limited to tumor cell-centered regulatory networks. Recent findings reveal an lncRNA-mediated communication axis between CAFs and macrophages: CAF-derived exosomal LINC01833 promotes M2 macrophage polarization in the TME by inhibiting miR-335-5p and modulating VAPA activity (111). Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α also plays a crucial role in the lung cancer TME. Downregulation of miR-214 and upregulation of miR-31-5p lead to increased HIF-1α expression, which subsequently enhances the production of vascular endothelial growth factor. This, in turn, promotes glycolytic metabolic reprogramming (i.e., the Warburg effect) in both cancer cells and TME components, facilitating tumor angiogenesis and proliferation (112).
4.2 Lipid metabolism
Lipids perform numerous essential biological functions, including membrane construction, signal transduction, hormone and vitamin synthesis, and energy storage and mobilization during energy deficits (113). In malignant tumor cells, lipid metabolism is reprogrammed primarily to favor endogenous lipid synthesis pathways that utilize glucose and glutamine as substrates to generate citrate through the TCA cycle (114). This process is regulated by central metabolic proteins, such as SREBPs, ACC, FASN, and FABP (114). Aberrations in this pathway may disrupt membrane integrity and permeability, activate apoptosis-related enzymes, and lead to ferroptosis and coproptosis.
Various lncRNAs participate in the regulation of lipid metabolism in lung cancer cells (as shown in Figure 3 and Table 2). Gm33149, localized in the cytoplasm of lung cancer stem cells, is transported to the metastatic microenvironment via microvesicles. As a ceRNA, it binds to miR-5623-3p and miR-217-5p, thereby increasing lipid metabolism in tumor cells with low metastatic potential (115). CCAT1, highly expressed in NSCLC, interacts with FABP5 to enhance fatty acid metabolism (116). It also upregulates BMI-1 expression by targeting miR-218, thereby promoting tumor progression or inducing resistance to gefitinib (120). Ferroptosis contributes to tumor regulation in NSCLC and is orchestrated through key components, including the XC–GSH–GPX4 system and lipid peroxide (PLOOH) synthesis (121). The histone methyltransferase SETD1A and EP300 are co-enriched in the HOXC-AS3 promoter region, promoting the expression of HOXC-AS3 and improving its stability after binding to EP300, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (117). Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is a transcription factor that protects cells from oxidative stress and promotes malignant transformation (122). MT1DP binds to and stabilizes miR-365a-3p, amplifying its transcriptional inhibitory effect on NRF2, aggravating oxidative damage, and promoting ferroptosis (118). Ye et al. (123) explored the correlation between 13 lncRNAs related to gefitinib metabolism and prognosis, TME, and drug sensitivity in patients with NSCLC. GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses suggests that the functions of these lncRNAs are strongly correlated with fat digestion and absorption, as well as α-linolenic acid metabolism, although the specific mechanisms remain to be elucidated.
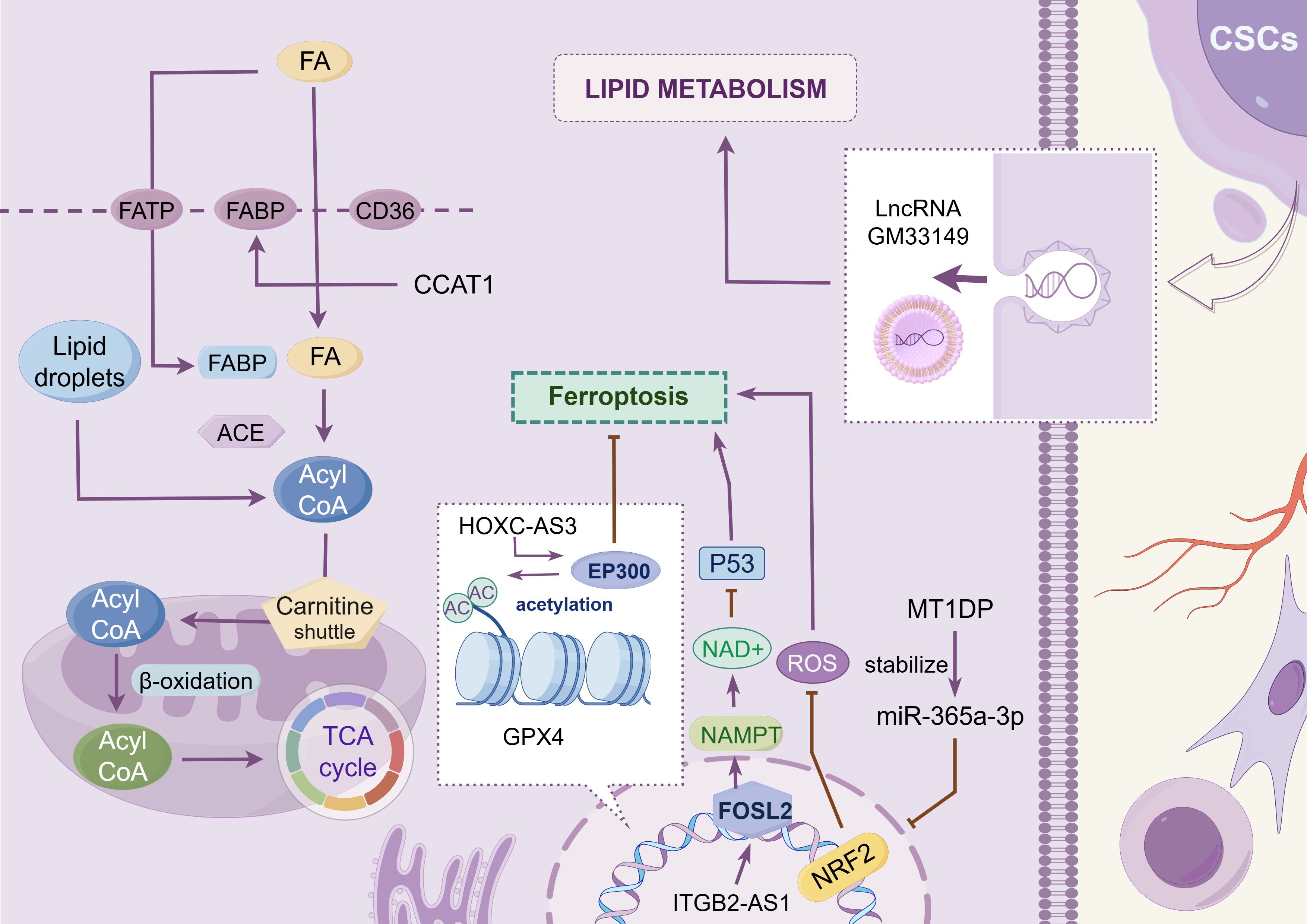
Figure 3. Lipid metabolism. This chart shows the regulatory mechanism of different LncRNAs in the reprogramming of lipid metabolism in tumor cells. These lncRNAs promote the progression of lung cancer by modulating lipid metabolism-related proteins such as FABP5, regulating the expression levels of ferroptosis-related transcription factors such as FOSL2 and NRF2, or facilitating intercellular interactions among tumor cells. The image is created with Figdraw.
4.3 Amino acid metabolism
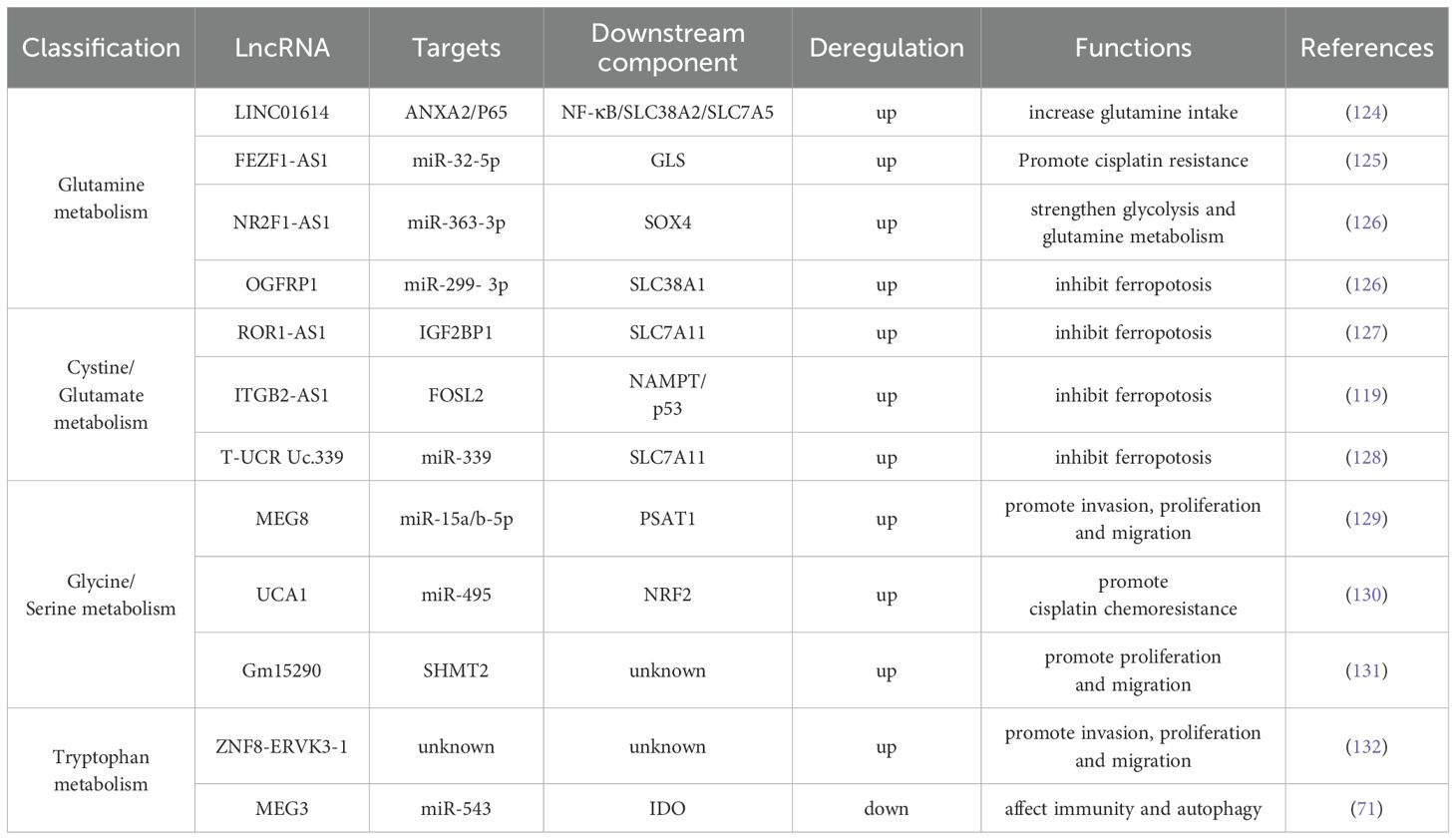
4.3.1 Glutamine metabolism
Glutamine, a non-essential amino acid in humans, is synthesized from glucose. However, tumor tissues exhibit a high propensity for glutamine uptake. This phenomenon underscores the significance of glutamine in mammals and its pivotal role in tumor cell proliferation (as shown in Figure 4 and Table 3) (133). In the metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer, the roles of different metabolic axes vary owing to their contributions to tumor growth, drug resistance, and microenvironmental adaptation. Based on existing research, glutamine metabolism may represent the most critical metabolic axis for lung cancer progression, second only to glucose metabolism. Glutamine serves as both a nitrogen and carbon source, supporting intracellular biosynthesis and enhancing the uptake of essential amino acids (134). After entering the cell, glutamine is hydrolyzed by glutaminase (GLS) into glutamic acid, which is then converted into α-ketoglutarate and ammonia by mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase (GLUD1) (124); α-ketoglutarate enters the TCA cycle to generate ATP and maintain redox stability, whereas ammonia helps regulate intracellular pH (124).
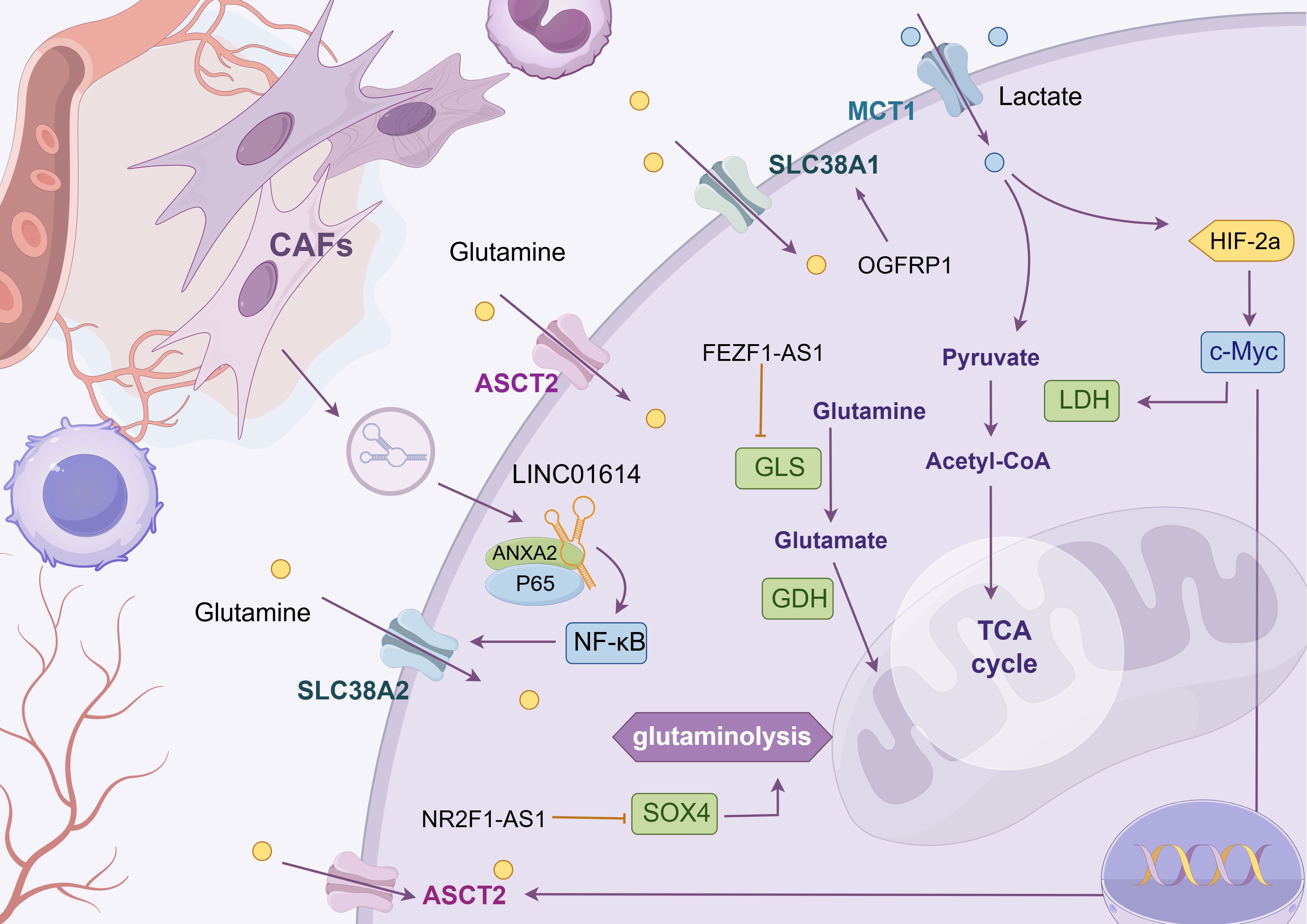
Figure 4. Glutamine metabolism. The chart shows the regulatory mechanism of different LncRNAs in glutamine metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells. LncRNAs can mediate mesenchymal-tumor cell interaction in TME, up-regulate glutamine uptake by cells, or affect the enrichment level of metabolic enzyme GLS to meet the high addiction tendency of lung cancer cells to glutamine. The following is a supplement to the specific mechanisms in the figures: OGFRP1: Indirectly promotes SLC38A1 expression by inhibiting miR-299-3p, alleviating intracellular lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis; FEZF1-AS1: Functions as a “ molecular sponge” to sequester miR-32-5p, enrich GLS, and promote cisplatin resistance in cells; LINC01614: Released from cancer - associated fibroblast exosomes, it interacts with ANXA2 and P65 to activate NF - κ B signaling and initiate the transcription of the glutamine transporters SLC38A2 and SLC7A5; NR2F1-AS1: Highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer, its silencing reduces HK2 and GLS expression, suppressing glycolysis and glutamine metabolism. Mechanistically, it binds with miR-363-3p to enrich SOX4, promoting glycolysis and glutamine metabolism, and accelerating tumor malignancy. The image is created with Figdraw.
In recent years, numerous studies have demonstrated that lncRNAs regulate glutamine metabolic reprogramming through various mechanisms that promote tumor cell growth and invasion. For example, LINC01614, released from exosomes of CAFs, acts on lung adenocarcinoma cells to activate the NF-κB signaling pathway through interaction with annexin A2 and P65. This activation initiates the transcription of glutamine transporters SLC38A2 and SLC7A5, increasing glutamine uptake by tumor cells (124). In addition, the oncogenic transcription factor c-Myc promotes glutamine catabolism by activating glutamine metabolism genes SLC1A5 and GLS1 (135). PCGEM1, a prostate-induced lncRNA, directly interacts with and acts as a coactivator of c-Myc (135). Consequently, we hypothesize that PCGEM1 indirectly regulates glutamine metabolism. FEZF1-AS1, which is upregulated in various tumors, acts as a “molecular sponge” to sequester miR-32-5p, thereby enriching GLS and promoting cisplatin resistance, although the specific mechanism remains unclear (125). In addition, NR2F1-AS1 is highly expressed in NSCLC, and its silencing reduces the expression of HK2 and GLS, thereby inhibiting glycolysis and glutamine metabolic activity (126). Mechanistically, NR2F1-AS1 binds to miR-363-3p to enrich SOX4, promoting glycolysis and glutamine metabolism and accelerating malignant tumor progression (126). Liu et al. demonstrated that the lncRNA OGFRP1 is upregulated in lung cancer cells and indirectly promotes the expression of the glutamine transporter SLC38A1 by inhibiting miR-299-3p, thereby reducing intracellular lipid peroxidation and ultimately suppressing ferroptosis (136). In general, lncRNAs influence glutamine metabolism in tumor cells by regulating the expression of key metabolic enzymes and transporters, thereby supplying the materials and energy required for tumor growth and invasion. Therefore, an in-depth investigation of lncRNA-mediated glutamine metabolic reprogramming may aid in identifying novel tumor biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Thean abundances of glucose and glutamine in the TME are also crucial for the development and activation of effector T cells. As early as 2018, it was demonstrated that glutamine inhibitors enhance the cytotoxic effect of CD8+ T cells (137). Saran et al. (138) further confirmed that the glutamine inhibitor CB-839 inhibits clonal expansion of CD8+ T cells in lung adenocarcinoma tissues. They found that activated CD8+ T cells depend on glutamine to maintain their antitumor activity and that glutamine inhibitors are currently at the forefront of drug development (139). Their combination with other therapeutic strategies (including radiotherapy and immunotherapy (140)) can amplify antitumor efficacy. CB-839 has advanced to phase I/II clinical trials (141). The application of glutamine inhibitors is not limited to these uses. At present, some researchers (142) have initiated phase I clinical trials in patients with advanced NSCLC, combining the mTOR inhibitor sapanisertib with the glutamine enzyme inhibitor CB-839 to assess drug safety, tolerability, and the recommended dose. However, the current article only reports preliminary findings, such as the scientific rationale, dose-escalation protocols, and cohort stratification criteria. Efficacy results remain pending and require further publication following long-term follow-up.
4.3.2 Cystine and glutamic acid metabolism
The balance of cysteine in cells directly affects the development of ferroptosis (as shown in Figure 4 and Table 3). For example, Jun Deng et al. revealed through experiments that SPTBN2 can increase the expression of the SLC7A11 subunit in the xc(−) system, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis in NSCLC cells and enabling abnormal cell viability (143). The xc(−) system is composed of two important subunits, SLC7A11 and SLC3A2, which are responsible for cystine absorption and glutamate release (11). Extracellular Glu has also been shown to affect the malignant behavior of tumor cells. For instance, Glu promotes the invasion and growth of malignant cells in glioma (144). In the field of cystine and glutamate metabolism in lung cancer, researchers have found that lncRNA ROR1-AS1 is present in the exosomes of CAFs. Its interaction with the N6-methyladenosine reader IGF2BP1 can increase the mRNA stability of SLC7A11, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (127). Chen et al. were the first to report that ITGB2-AS1, an lncRNA, is abnormally expressed in tumor tissues and cisplatin-resistant tissues of patients with NSCLC. They confirmed that ITGB2-AS1 regulates the expression of NAMPT by interacting with the transcription factor FOSL2, thereby affecting the production of ferroptosis-related proteins, including GPX4 and SLC7A11, with p53 as a downstream target (119). In addition, the lncT-UCRUc.339/miR-339/SLC7A11 axis can serve as a regulatory factor of ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma, promoting the proliferation, migration, and invasion of tumor cells (128). Although studies have shown that ITGB2-AS1 can inhibit ferroptosis by regulating SLC7A11, there is no direct evidence that these lncRNA-mediated ferroptosis phenotypes can be reversed in vivo by ferroptosis inducers (such as erastin and RSL3). Future research in this direction will help reveal the plasticity of lncRNA–metabolism interactions and provide new avenues for targeted ferroptosis combination therapy.
4.3.3 Glycine and serine metabolism
Glycine in cells can be converted from an intermediate product of glucose glycolysis, 3-phosphoglycerate. This pathway is also involved in serine synthesis. Following transamination and dephosphorylation, serine is synthesized by transferring a one-carbon unit to the folate pool (145). Gene set enrichment analysis has revealed that the transcription factor NRF2 may play a key regulatory role in the PHGDH and serine biosynthesis pathways (146). Based on this finding, researchers also discovered that NRF2 can induce the expression of proteins required for serine biosynthesis in an ATF4-dependent manner, such as PHGDH, phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1), PSPH, serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) 1, and SHMT2 (146). The lncRNA MEG8 promotes NSCLC progression through the miR-15a/b-5p/PSAT1 axis in vivo, further corroborating the key role of PSAT1 in NSCLC development (129). SHMT2 mediates the conversion of serine to glycine in lung cancer cells, and it can be regulated by lncRNA Gm15290 as its downstream target (131) (as shown in Figure 5 and Table 3).
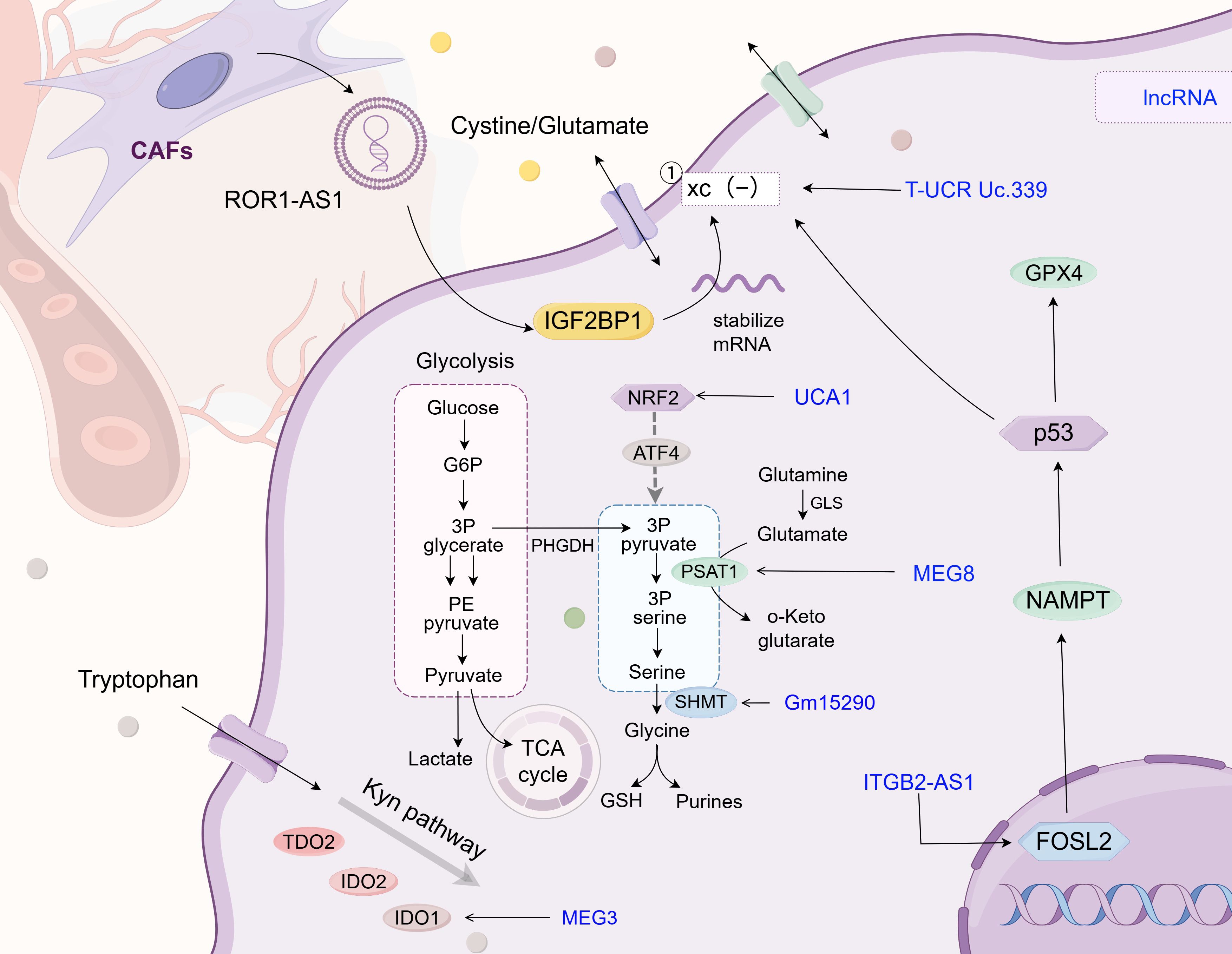
Figure 5. Glycine/serine/tryptophan metabolism. This chart describes the regulatory mechanism of different LncRNAs in the reprogramming of glycine/serine/tryptophan metabolism in tumor cells. Similar to its role in glutamine metabolism, lncRNA also affects the expression level of metabolic enzymes in glycine/serine/tryptophan, maintains the balance of glycine/serine concentration inside and outside the cell, and mediates fibroblast-tumor cell interaction in TME, which also provides novel insights for clinical diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer. The following is a supplement to the specific mechanism shown in the figure: the xc(-) system comprises the SLC3A2 and SLC7A11 subunits; The lnc T-UCR Uc.339/miR-339/SLC7A11 axis serves as a factor influencing ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma and promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of tumor cells; LncRNA UCA1 targets miR-495 to indirectly regulate NRF2 expression in cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells; LncRNA MEG8 drives NSCLC progression in vivo via the miR-15a/b-5p/PSAT1 axis; In lung cancer cells, lncRNA Gm15290 mediates serine - to - glycine conversion via SHMT2 and is regulated by lncRNA Gm15290 as a downstream target; ITGB2-AS1 is aberrantly expressed in the tumor tissue and cisplatin-resistant tissue of NSCLC patients. It regulates NAMPT expression by interacting with transcription factor FOSL2 and affects the production of ferroptosis - related proteins, including GPX4 and SLC7A11, by targeting p53 downstream; In NSCLC, LncRNA MEG3 is low - expressed. It can bind miR - 543 as a ceRNA and affects autophagy of lung cancer cells by regulating the IDO pathway; LncRNA ROR1-AS1 exists in cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) exosomes, interacts with the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) reader IGF2BP1 to enhance SLC7A11 mRNA stability, and suppresses ferroptosis. The image is created with Figdraw.
In cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells, UCA1 targets miR-495 to indirectly modulate NRF2 expression, although this process does not involve direct detection of serine/glycine metabolism (130). Shi et al. revealed that UCA1 regulates HO1 expression through NRF2 to enhance chemotherapy resistance in lung adenocarcinoma cells; however, the effect of lncRNA UCA1 on serine/glycine metabolism requires further verification (147).
4.3.4 Tryptophan metabolism
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid for humans, and its metabolites have been shown to be closely associated with the progression of various tumors (as shown in Figure 5; Table 3) (148). Tryptophan is catalyzed by the IDO1, IDO2, and TDO2 enzyme families in the kynurenine pathway to produce ATP, the redox cofactor NAD+, and metabolites, such as nicotinic acid, palmitate, quinolinic acid, and serotonin. IDO1 degrades tryptophan to generate the immunosuppressive metabolite kynurenine, which induces T-cell depletion and promotes the differentiation of regulatory T cells, thereby establishing an immunosuppressive microenvironment (149). Moreover, PD-1 can inhibit regulatory T cell activation by targeting CD28 costimulatory signals (150). These findings suggest that targeting the lncRNA-mediated IDO1 pathway may synergize with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. However, this hypothesis remains to be confirmed by further experimental data.
In lung cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and other malignancies, circulating tryptophan levels are generally reduced, potentially because of increased expression and activity of metabolic enzymes, as well as the nutritional status and dyspepsia of patients in advanced stages (148). In addition, Gao et al. used bioinformatic approaches to identify that the lncRNA ZNF8-ERVK3-1 in lung adenocarcinoma cells is closely associated with tryptophan metabolism and confirmed that it can promote the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells (132). However, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Lu et al. further confirmed that lncRNA MEG3 is expressed at low levels in NSCLC and that MEG3 can act as a ceRNA to bind miR-543 and affect autophagy in lung cancer cells by regulating the IDO pathway (71). Collectively, these findings suggest that targeting lncRNAs involved in the IDO pathway of tryptophan metabolism may offer a novel immunotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of lung cancer.
5 Discussion
The lncRNA family constructs a complex regulatory network by adsorbing miRNAs and regulating cellular behavior at the transcriptional, posttranscriptional, and protein levels, providing important guidance for the development of targeted therapeutic drugs. Recent studies have revealed remarkable survival characteristics of cancer cells. Fundamental tumor characteristics, including metabolic reprogramming, are involved in various biological processes, such as drug resistance, cell proliferation, cell death, and oxidative stress homeostasis. These findings highlight the need to consider the influence of multiple factors on malignant behavior during diagnosis and treatment and offer potential explanations and coping strategies for individual differences in clinical efficacy.
Currently, the primary methods of lung cancer treatment include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. However, each modality has its own strengths and limitations and is often used in combination. With the discovery and validation of novel oncogenic lncRNAs, biomarkers for the early diagnosis of lung cancer have been continuously enriched. Some lncRNAs also serve as potential therapeutic targets for NSCLC. For example, lncLCETRL3/4 drives resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant NSCLC by activating the AKT signaling pathway. Combined targeting of lncLCETRL3/4 and tyrosine kinase inhibitors may significantly reverse drug resistance and improve therapeutic efficacy (151). Targeted protein degradation strategies based on lncRNAs are highly effective in reducing the malignant phenotype of cancer cells. Cao et al. (152) developed artificial “alncRNAs” that can target and promote the degradation of carcinogenic transcription factors, such as c-MYC, NF-κB, and EGFR. This approach has demonstrated therapeutic effects, including inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion and promotion of apoptosis in bladder cancer cells.
The regulatory mechanisms of lncRNAs provide a foundation for the development of clinically targeted drugs. Efforts are underway to develop lncRNA-targeted therapies or to employ RNA interference techniques, such as siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), to downregulate oncogenic lncRNAs (153, 154). Some lncRNAs have already entered preclinical research or early clinical trials. For instance, preclinical studies have shown that targeted inhibition of lncRNA MALAT1 by ASOs can effectively reduce lung cancer metastasis in mouse models (155). LncRNA PVT1 is upregulated in NSCLC tissues, and its knockout significantly inhibits cancer cell viability and invasion in xenograft mouse models while inducing apoptosis (156). In clinical trials, downregulation of HOTAIR has been shown to reduce the expression of DNA methyltransferases and increase the sensitivity of SCLC cells to cisplatin, adriamycin, and etoposide (156). Additionally, H19-DTA (BC-819), a therapeutic strategy targeting lncRNA H19, offers a promising new option for the treatment of breast, lung, and other malignancies. Phase I/II clinical trials (NCT04691739) for bladder and ovarian cancers are currently underway, with plans to extend this approach to lung cancer treatment in the future (157). These advancements offer substantial insights for the clinical translation of lncRNA-based therapies. From a technical perspective, ASOs and siRNAs targeting oncogenic lncRNAs have demonstrated potent antitumor effects. CRISPR-based gene editing technologies have shown unique advantages in preclinical models, offering high specificity, long-term silencing, and lower off-target risks (158). For example, the CRISPR-Cas9 system has been used to inhibit the expression of ΔNp63 in lung cancer, significantly suppressing the proliferation of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells, inducing apoptosis, and effectively blocking tumor growth in xenograft mouse models (159). CRISPR interference has demonstrated a more durable silencing effect than that of traditional ASO/siRNA approaches, although its delivery system still requires optimization. Therefore, the combined application of CRISPR and ASO/siRNA may become a key strategy to overcome therapeutic bottlenecks in future tumor treatments. Moreover, with the advent of big data, new personalized therapies based on patients’ lncRNA expression profiles have begun to emerge, aiming to predict prognosis and identify therapeutic targets (26).
Although lncRNAs have shown great promise in the regulation of lung cancer metabolism, several challenges continue to hinder their clinical translation: (1) Current research on lncRNA- and miRNA-mediated metabolic reprogramming in lung cancer is primarily based on in vitro cell lines (such as A549 and H1299), which cannot fully replicate the complexity of the TME in vivo (160). (2) Only a limited number of lncRNA-targeted therapies have advanced to phase I clinical trials, suggesting a substantial gap between laboratory findings and clinical application (161). (3) The development of both animals and plants relies on lncRNAs to regulate epigenetics through dynamic modular structures and target specificity. However, challenges remain because of the complexity of protein interaction networks and accuracy of target recognition. These issues must be addressed using multi-omics techniques, such as iCLIP 422, RAP-MS 423, ChIRP-MS 388, and iDRiP (162). (4) Despite the utility of current methods, comprehensive analyses of lncRNA subcellular localization, structural characteristics, and dynamic interaction networks remain technically challenging. For example, while RNA-FISH technology enables the localization of lncRNAs, its resolution is limited (163). Similarly, although CLIP-seq can capture lncRNA–protein interactions, it is susceptible to interference from RNA secondary structures and low-abundance transcripts (164).
The clinical translation of lncRNA-targeted therapies is particularly constrained because lncRNAs, as large, negatively charged molecules, are inherently difficult to transport across cell membranes. Existing delivery systems, such as lipid nanoparticles, struggle to achieve efficient and targeted intracellular delivery, and it is difficult to accurately direct them to specific tissues or organs, which limits the therapeutic efficacy of lncRNAs in vivo. Zhang et al. (165) used lentiviral vectors to achieve stable overexpression of lncRNAs. However, lncRNAs overexpressed in cell lines often contain additional sequences that alter their secondary structures, impair RNA-protein interactions, prevent them from exerting their intended functions, and may also be recognized by the patient’s immune system as exogenous molecules, activating immune receptors, such as TLRs, inducing inflammatory responses or immunotoxicity, and thereby affecting the safety and tolerability of treatment (166). Additionally, lncRNA therapy may lead to off-target effects because of sequence similarity or excessive administration, resulting in unintended actions on non-target cells or tissues, which can compromise therapeutic efficacy and increase potential risks (152, 166). It is evident that lncRNA-targeted therapy faces severe challenges in clinical translation, fundamentally stemming from the contradiction between the molecular characteristics of lncRNAs and complex physiological environment in vivo, and further research is needed to bridge these gaps. In addition to the lncRNAs discussed in this article, research on other noncoding RNAs, such as circRNAs, is also progressing and is expected to further expand the frontiers of disease diagnosis and treatment (167). Looking ahead, with the continued advancement of ncRNA research, more accurate and efficient strategies for cancer diagnosis and therapy are anticipated.
In summary, studies of the lncRNA family have elucidated the core mechanisms underlying cancer cell survival and development, providing novel insights for personalized and precise treatment. In the future, with the advancement of technology and a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of ncRNAs, further breakthroughs in the field of cancer therapy are expected, bringing renewed hope to patients.
Author contributions
ML: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. LD: Literature Search, Writing – original draft. SC: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Translation. MD: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Translation. LW: Writing – review & editing, Funding Acquisition, Supervision. YS: Writing – review & editing, Funding Acquisition, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The present study was supported by Hunan Provincial Clinical Medicine Research Center Project for Traditional Chinese Medicine in Oncology (2021SK4023) and Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Program (2023JJ40486).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rodak O, Peris-Díaz MD, Olbromski M, Podhorska-Okołów M, and Dzięgiel P. Current landscape of non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, histological classification, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184705
2. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. (2015) 136:E359–86. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210
3. Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. (2000) 100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9
4. Lin Z, Li J, Zhang J, Feng W, Lu J, Ma X, et al. Metabolic reprogramming driven by IGF2BP3 promotes acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:2187–207. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3059
5. Li Y, Chen H, Xie X, Yang B, Wang X, Zhang J, et al. PINK1-mediated mitophagy promotes oxidative phosphorylation and redox homeostasis to induce drug-tolerant persister cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:398–413. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-2370
6. Li Z, Chen S, He X, Gong S, Sun L, and Weng L. SLC3A2 promotes tumor-associated macrophage polarization through metabolic reprogramming in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:2306–17. doi: 10.1111/cas.15760
7. Nenkov M, Ma Y, Gaßler N, and Chen Y. Metabolic reprogramming of colorectal cancer cells and the microenvironment: implication for therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126262
8. Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
9. Kim J, Hu Z, Cai L, Li K, Choi E, Faubert B, et al. Author Correction: CPS1 maintains pyrimidine pools and DNA synthesis in KRAS/LKB1-mutant lung cancer cells. Nature. (2019) 569:E4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1133-3
10. Chen Y, Liu L, Xia L, Wu N, Wang Y, Li H, et al. TRPM7 silencing modulates glucose metabolic reprogramming to inhibit the growth of ovarian cancer by enhancing AMPK activation to promote HIF-1α degradation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 41:44. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02252-1
11. Ji X, Qian J, Rahman SMJ, Siska PJ, Zou Y, Harris BK, et al. xCT (SLC7A11)-mediated metabolic reprogramming promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression. Oncogene. (2018) 37:5007–19. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0307-z
12. Liu HH, Xu Y, Li CJ, Hsu SJ, Lin XH, Zhang R, et al. An SCD1-dependent mechanoresponsive pathway promotes HCC invasion and metastasis through lipid metabolic reprogramming. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:2554–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.03.015
13. Zhao H, Yan G, Zheng L, Zhou Y, Sheng H, Wu L, et al. STIM1 is a metabolic checkpoint regulating the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics. (2020) 10:6483–99. doi: 10.7150/thno.44025
14. Dunham I, Kundaje A, Aldred SF, Collins PJ, Davis CA, Doyle F, et al. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. (2012) 489(7414):57–74. doi: 10.1038/nature11247
15. Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer A, Djebali S, Tilgner H, et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. (2012) 22:1775–89. doi: 10.1101/gr.132159.111
16. Hangauer MJ, Vaughn IW, and McManus MT. Pervasive transcription of the human genome produces thousands of previously unidentified long intergenic noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. (2013) 9:e1003569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003569
17. Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. (2012) 7:562–78. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016
18. Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U, Sahu A, Hosono Y, et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:199–208. doi: 10.1038/ng.3192
19. St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C, and Kapranov P. The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet. (2015) 31:239–51. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.03.007
20. Kopp F and Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. (2018) 172:393–407. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011
21. Tan YT, Lin JF, Li T, Li JJ, Xu RH, and Ju HQ. LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2021) 41:109–20. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12108
22. Park EG, Pyo SJ, Cui Y, Yoon SH, and Nam JW. Tumor immune microenvironment lncRNAs. Brief Bioinform. (2022) 23. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab504
23. Cao HL, Liu ZJ, Huang PL, Yue YL, and Xi JN. lncRNA-RMRP promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer via miR-206. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:1012–21. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201902_16988
24. Malakoti F, Targhazeh N, Karimzadeh H, Mohammadi E, Asadi M, Asemi Z, et al. Multiple function of lncRNA MALAT1 in cancer occurrence and progression. Chem Biol Drug Des. (2023) 101:1113–37. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14006
25. Yao ZT, Yang YM, Sun MM, He Y, Liao L, Chen KS, et al. New insights into the interplay between long non-coding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2022) 42:117–40. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12254
26. Yin X, Liao H, Yun H, Lin N, Li S, Xiang Y, et al. Artificial intelligence-based prediction of clinical outcome in immunotherapy and targeted therapy of lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:146–59. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.08.002
27. Bridges MC, Daulagala AC, and Kourtidis A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol. (2021) 220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202009045
28. Herman AB, Tsitsipatis D, and Gorospe M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:2252–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.027
29. Lee S, Kopp F, Chang TC, Sataluri A, Chen B, Sivakumar S, et al. Noncoding RNA NORAD regulates genomic stability by sequestering PUMILIO proteins. Cell. (2016) 164:69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.017
30. Yap KL, Li S, Muñoz-Cabello AM, Raguz S, Zeng L, Mujtaba S, et al. Molecular interplay of the noncoding RNA ANRIL and methylated histone H3 lysine 27 by polycomb CBX7 in transcriptional silencing of INK4a. Mol Cell. (2010) 38:662–74. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.021
31. Lin A, Li C, Xing Z, Hu Q, Liang K, Han L, et al. The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Cell Biol. (2016) 18:213–24. doi: 10.1038/ncb3295
32. Chen L, Liu H, Sun C, Pei J, Li J, Li Y, et al. A novel lncRNA SNHG3 promotes osteoblast differentiation through BMP2 upregulation in aortic valve calcification. JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2022) 7:899–914. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.06.009
33. Liang R, Xiao G, Wang M, Li X, Li Y, Hui Z, et al. SNHG6 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate E2F7 expression by sponging miR-26a-5p in lung adenocarcinoma. BioMed Pharmacother. (2018) 107:1434–46. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.099
34. Leung A, Trac C, Jin W, Lanting L, Akbany A, Sætrom P, et al. Novel long noncoding RNAs are regulated by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. (2013) 113:266–78. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300849
35. Ulrich V, Rotllan N, Araldi E, Luciano A, Skroblin P, Abonnenc M, et al. Chronic miR-29 antagonism promotes favorable plaque remodeling in atherosclerotic mice. EMBO Mol Med. (2016) 8:643–53. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201506031
36. Wang K, Liu F, Zhou LY, Long B, Yuan SM, Wang Y, et al. The long noncoding RNA CHRF regulates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting miR-489. Circ Res. (2014) 114:1377–88. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302476
37. Chen T, Xue H, Lin R, and Huang Z. MiR-34c and PlncRNA1 mediated the function of intestinal epithelial barrier by regulating tight junction proteins in inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 486:6–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.115
38. Gu S, Li G, Zhang X, Yan J, Gao J, An X, et al. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 11:2631–43. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.3102
39. Lei HT, Wang JH, Yang HJ, Wu HJ, Nian FH, Jin FM, et al. LncRNA-mediated cell autophagy: An emerging field in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 168:115716. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115716
40. Savary G, Dewaeles E, Diazzi S, Buscot M, Nottet N, Fassy J, et al. The long noncoding RNA DNM3OS is a reservoir of fibromiRs with major functions in lung fibroblast response to TGF-β and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2019) 200:184–98. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201807-1237OC
41. Tayel SI, El-Masry EA, Abdelaal GA, Shehab-Eldeen S, Essa A, and Muharram NM. Interplay of LncRNAs NEAT1 and TUG1 in incidence of cytokine storm in appraisal of COVID-19 infection. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:4901–13. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.72318
42. Tang X, Luo Y, Yuan D, Calandrelli R, Malhi NK, Sriram K, et al. Long noncoding RNA LEENE promotes angiogenesis and ischemic recovery in diabetes models. J Clin Invest. (2023) 133. doi: 10.1172/JCI161759
43. Guo WH, Guo Q, Liu YL, Yan DD, Jin L, Zhang R, et al. Correction: Mutated lncRNA increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by promoting β cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:1013. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05467-4
44. Jovčevska I and Videtič Paska A. Neuroepigenetics of psychiatric disorders: Focus on lncRNA. Neurochem Int. (2021) 149:105140. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105140
45. Zhu SF, Yuan W, Du YL, and Wang BL. Research progress of lncRNA and miRNA in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. (2023) 22:45–53. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2022.07.008
46. Zhao BW, Su XR, Yang Y, Li DX, Li GD, Hu PW, et al. A heterogeneous information network learning model with neighborhood-level structural representation for predicting lncRNA-miRNA interactions. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2024) 23:2924–33. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.06.032
47. Wang J, Feng J, Kang Y, Pan P, Ge J, Wang Y, et al. Discovery of antimicrobial peptides with notable antibacterial potency by an LLM-based foundation model. Sci Adv. (2025) 11:eads8932. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads8932
48. Zhao BW, Su XR, Hu PW, Ma YP, Zhou X, and Hu L. A geometric deep learning framework for drug repositioning over heterogeneous information networks. Brief Bioinform. (2022) 23. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac384
49. Wang J, Luo H, Qin R, Wang M, Wan X, Fang M, et al. 3DSMILES-GPT: 3D molecular pocket-based generation with token-only large language model. Chem Sci. (2025) 16:637–48. doi: 10.1039/D4SC06864E
50. Semenza GL. HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2010) 20:51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.10.009
51. Semenza GL. Tumor metabolism: cancer cells give and take lactate. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:3835–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI37373
52. Fu Y, Liu S, Yin S, Niu W, Xiong W, Tan M, et al. The reverse Warburg effect is likely to be an Achilles’ heel of cancer that can be exploited for cancer therapy. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:57813–25. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18175
53. Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Carreño-Fuentes L, Gallardo-Pérez JC, Saavedra E, Quezada H, Vega A, et al. Oxidative phosphorylation is impaired by prolonged hypoxia in breast and possibly in cervix carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2010) 42:1744–51. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.07.010
54. Hensley CT, Faubert B, Yuan Q, Lev-Cohain N, Jin E, Kim J, et al. Metabolic heterogeneity in human lung tumors. Cell. (2016) 164:681–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.034
55. Greene J, Segaran A, and Lord S. Targeting OXPHOS and the electron transport chain in cancer; Molecular and therapeutic implications. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:851–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.02.002
56. Vasan K, Werner M, and Chandel NS. Mitochondrial metabolism as a target for cancer therapy. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:341–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.019
57. Vander Heiden MG and DeBerardinis RJ. Understanding the intersections between metabolism and cancer biology. Cell. (2017) 168:657–69. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.039
58. Lu CW, Lin SC, Chen KF, Lai YY, and Tsai SJ. Induction of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-3 by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes metabolic switch and drug resistance. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:28106–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803508200
59. Viale A, Pettazzoni P, Lyssiotis CA, Ying H, Sánchez N, Marchesini M, et al. Oncogene ablation-resistant pancreatic cancer cells depend on mitochondrial function. Nature. (2014) 514:628–32. doi: 10.1038/nature13611
60. Son J, Lyssiotis CA, Ying H, Wang X, Hua S, Ligorio M, et al. Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature. (2013) 496:101–5. doi: 10.1038/nature12040
61. Haq R, Shoag J, Andreu-Perez P, Yokoyama S, Edelman H, Rowe GC, et al. Oncogenic BRAF regulates oxidative metabolism via PGC1α and MITF. Cancer Cell. (2013) 23:302–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.02.003
62. Faubert B, Solmonson A, and DeBerardinis RJ. Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression. Science. (2020) 368. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw5473
63. Chang CH, Qiu J, O’Sullivan D, Buck MD, Noguchi T, Curtis JD, et al. Metabolic competition in the tumor microenvironment is a driver of cancer progression. Cell. (2015) 162:1229–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.016
64. Zhang Y, Peng Q, Zheng J, Yang Y, Zhang X, Ma A, et al. The function and mechanism of lactate and lactylation in tumor metabolism and microenvironment. Genes Dis. (2023) 10:2029–37. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.006
65. Leone RD, Zhao L, Englert JM, Sun IM, Oh MH, Sun IH, et al. Glutamine blockade induces divergent metabolic programs to overcome tumor immune evasion. Science. (2019) 366:1013–21. doi: 10.1126/science.aav2588
66. Loewen G, Jayawickramarajah J, Zhuo Y, and Shan B. Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2014) 7:90. doi: 10.1186/s13045-014-0090-4
67. Zhang J, Zhang B, Wang T, and Wang H. LncRNA MALAT1 overexpression is an unfavorable prognostic factor in human cancer: evidence from a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2015) 8:5499–505.
68. Deng HP, Chen L, Fan T, Zhang B, Xu Y, and Geng Q. Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes tumor growth and inhibits cell apoptosis in lung cancer. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). (2015) 61:34–40.
69. Nie FQ, Sun M, Yang JS, Xie M, Xu TP, Xia R, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by silencing KLF2 and P21 expression. Mol Cancer Ther. (2015) 14:268–77. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0492
70. Yang ZT, Li Z, Wang XG, Tan T, Yi F, Zhu H, et al. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA ZXF2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression through c-Myc pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 35:2360–70. doi: 10.1159/000374038
71. Lu KH, Li W, Liu XH, Sun M, Zhang ML, Wu WQ, et al. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits NSCLC cells proliferation and induces apoptosis by affecting p53 expression. BMC Cancer. (2013) 13:461. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-461
72. Pickard MR, Mourtada-Maarabouni M, and Williams GT. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 regulates apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2013) 1832:1613–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.005
73. Zhang EB, Yin DD, Sun M, Kong R, Liu XH, You LH, et al. P53-regulated long non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation in human non-small cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically regulating HOXB7 expression. Cell Death Dis. (2014) 5:e1243. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.201
74. Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, and Pandolfi PP. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. (2011) 146:353–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
75. Hua Q, Jin M, Mi B, Xu F, Li T, Zhao L, et al. Correction: LINC01123, a c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA, promotes proliferation and aerobic glycolysis of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-199a-5p/c-Myc axis. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:12. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01412-w
76. Zhang M, Han Y, Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Gao Z, et al. ZEB1-activated LINC01123 accelerates the Malignancy in lung adenocarcinoma through NOTCH signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:981. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03166-6
77. Yin D, Hua L, Wang J, Liu Y, and Li X. Long Non-Coding RNA DUXAP8 Facilitates Cell Viability, Migration, and Glycolysis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer via Regulating HK2 and LDHA by Inhibition of miR-409-3p. Onco Targets Ther. (2020) 13:7111–23. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S243542
78. Lang N, Wang C, Zhao J, Shi F, Wu T, and Cao H. Long non−coding RNA BCYRN1 promotes glycolysis and tumor progression by regulating the miR−149/PKM2 axis in non−small−cell lung cancer. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 21:1509–16. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10944
79. Feng X and Yang S. Long non-coding RNA LINC00243 promotes proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by positively regulating PDK4 through sponging miR-507. Mol Cell Biochem. (2020) 463:127–36. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03635-3
80. Zhang CW, Zhou B, Liu YC, Su LW, Meng J, Li SL, et al. LINC00365 inhibited lung adenocarcinoma progression and glycolysis via sponging miR-429/KCTD12 axis. Environ Toxicol. (2022) 37:1853–66. doi: 10.1002/tox.23532
81. Xu S, Cheng Z, Du B, Diao Y, Li Y, and Li X. LncRNA AP000695.2 promotes glycolysis of lung adenocarcinoma via the miR-335-3p/TEAD1 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2023) 55:1592–605. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023227
82. Zhang L, Liang J, Qin H, Lv Y, Liu X, Li Z, et al. Lnc AC016727.1/BACH1/HIF-1 α signal loop promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:296. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02875-y
83. Cheng Y, Wang S, and Mu X. Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting miR-625-5p/GSPT1. Transl Cancer Res. (2021) 10:5159–73. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1468
84. Wang S, Wang T, Liu D, and Kong H. LncRNA MALAT1 Aggravates the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Stimulating the Expression of COMMD8 via Targeting miR-613. Cancer Manag Res. (2020) 12:10735–47. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S263538
85. Chen W, Li X, Du B, Cui Y, Ma Y, and Li Y. The long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation and glycolysis via the microRNA-148b-3p/PKM2 axis. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:4421–33. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5103
86. Zhao L, Zhang X, Shi Y, and Teng T. LncRNA SNHG14 contributes to the progression of NSCLC through miR-206/G6PD pathway. Thorac Cancer. (2020) 11:1202–10. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13374
87. Hua Q, Mi B, Xu F, Wen J, Zhao L, Liu J, et al. Hypoxia-induced lncRNA-AC020978 promotes proliferation and glycolytic metabolism of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis. Theranostics. (2020) 10:4762–78. doi: 10.7150/thno.43839
88. Li L, Li Z, Qu J, Wei X, Suo F, Xu J, et al. Novel long non-coding RNA CYB561-5 promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenesis by interacting with basigin in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med. (2022) 26:1402–12. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17057
89. Hua Q, Wang D, Zhao L, Hong Z, Ni K, Shi Y, et al. AL355338 acts as an oncogenic lncRNA by interacting with protein ENO1 to regulate EGFR/AKT pathway in NSCLC. Cancer Cell Int. (2021) 21:525. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02232-z
90. La Montagna M, Shi L, Magee P, Sahoo S, Fassan M, and Garofalo M. AMPKα loss promotes KRAS-mediated lung tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. (2021) 28:2673–89. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00777-0
91. Yu T, Zhao Y, Hu Z, Li J, Chu D, Zhang J, et al. MetaLnc9 facilitates lung cancer metastasis via a PGK1-activated AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:5782–94. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0671
92. Chen Z, Hu Z, Sui Q, Huang Y, Zhao M, Li M, et al. LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 facilitates tumor proliferation and the migration via the HIF-1α/glycolysis axis in lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:522–35. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67556
93. Xiong X, Zhang L, Zang B, Xu D, Chen C, Dong G, et al. High−risk pathological subtype associated FAM83A−AS1 promotes Malignancy and glycolysis of lung adenocarcinoma via miR−202−3p/HK2 axis. Oncol Rep. (2023) 49. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8532
94. Yang B, Zhang L, Cao Y, Chen S, Cao J, Wu D, et al. Overexpression of lncRNA IGFBP4-1 reprograms energy metabolism to promote lung cancer progression. Mol Cancer. (2017) 16:154. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0722-8
95. Li Z, Li X, Wu S, Xue M, and Chen W. Long non-coding RNA UCA1 promotes glycolysis by upregulating hexokinase 2 through the mTOR-STAT3/microRNA143 pathway. Cancer Sci. (2014) 105:951–5. doi: 10.1111/cas.12461
96. Wang PS, Liu Z, Sweef O, Xie J, Chen J, Zhu H, et al. Long noncoding RNA ABHD11-AS1 interacts with SART3 and regulates CD44 RNA alternative splicing to promote lung carcinogenesis. Environ Int. (2024) 185:108494. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108494
97. Gong W, Yang L, Wang Y, Xian J, Qiu F, Liu L, et al. Analysis of survival-related lncRNA landscape identifies A role for LINC01537 in energy metabolism and lung cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153713
98. Karger A, Mansouri S, Leisegang MS, Weigert A, Günther S, Kuenne C, et al. ADPGK-AS1 long noncoding RNA switches macrophage metabolic and phenotypic state to promote lung cancer growth. EMBO J. (2023) 42:e111620. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022111620
99. Shi L, Li B, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Tan J, Chen Y, et al. Exosomal lncRNA Mir100hg derived from cancer stem cells enhance glycolysis and promote metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma through mircroRNA-15a-5p/31-5p. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:248. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01281-3
100. Ji X, Zhu R, Gao C, Xie H, Gong X, and Luo J. Hypoxia-derived exosomes promote lung adenocarcinoma by regulating HS3ST1-GPC4-mediated glycolysis. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040695
101. Jiang Y, Wang K, Lu X, Wang Y, and Chen J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomes promote lung cancer progression by OIP5-AS1/miR-142-5p/PD-L1 axis. Mol Immunol. (2021) 140:47–58. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.10.002
102. Chen D, Li Y, Wang Y, and Xu J. LncRNA HOTAIRM1 knockdown inhibits cell glycolysis metabolism and tumor progression by miR-498/ABCE1 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Genes Genomics. (2021) 43:183–94. doi: 10.1007/s13258-021-01052-9
103. Booy EP, McRae EK, Koul A, Lin F, and McKenna SA. The long non-coding RNA BC200 (BCYRN1) is critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation. Mol Cancer. (2017) 16:109. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0679-7
104. Rouchka EC, Flight RM, Fasciotto BH, Estrada R, Eaton JW, Patibandla PK, et al. Transcriptional profile of immediate response to ionizing radiation exposure. Genom Data. (2016) 7:82–5. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2015.11.027
105. Yun J, Rago C, Cheong I, Pagliarini R, Angenendt P, Rajagopalan H, et al. Glucose deprivation contributes to the development of KRAS pathway mutations in tumor cells. Science. (2009) 325:1555–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1174229
106. Xu F, Hua Q, Zhang A, Di Z, Wang Y, Zhao L, et al. LncRNA AC020978 facilitates non-small cell lung cancer progression by interacting with malate dehydrogenase 2 and activating the AKT pathway. Cancer Sci. (2021) 112:4501–14. doi: 10.1111/cas.15116
107. Chen H, Pei H, Hu W, Ma J, Zhang J, Mao W, et al. Long non-coding RNA CRYBG3 regulates glycolysis of lung cancer cells by interacting with lactate dehydrogenase A. J Cancer. (2018) 9:2580–8. doi: 10.7150/jca.24896
108. Xue L, Li J, Lin Y, Liu D, Yang Q, Jian J, et al. m(6) A transferase METTL3-induced lncRNA ABHD11-AS1 promotes the Warburg effect of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:2649–58. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30023
109. Tiwari A, Trivedi R, and Lin SY. Tumor microenvironment: barrier or opportunity towards effective cancer therapy. J BioMed Sci. (2022) 29:83. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00866-3
110. Li M, Yang Y, Xiong L, Jiang P, Wang J, and Li C. Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:80. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01478-6
111. Chen J, Sun JJ, Ma YW, Zhu MQ, Hu J, Lu QJ, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts derived exosomal LINC01833 promotes the occurrence of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-335-5p -VAPA axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2024) 38:e23769. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23769
112. Pirlog R, Cismaru A, Nutu A, and Berindan-Neagoe I. Field cancerization in NSCLC: A new perspective on microRNAs in macrophage polarization. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020746
113. Martin-Perez M, Urdiroz-Urricelqui U, Bigas C, and Benitah SA. The role of lipids in cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:1675–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.023
114. Cheng C, Geng F, Cheng X, and Guo D. Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2018) 38:27. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0301-4
115. Zhang YH, Chen Y, Shi L, Han X, Xie JC, Chen Y, et al. A novel lung cancer stem cell extracellular vesicles lncRNA ROLLCSC modulate non-stemness cancer cell plasticity through miR-5623-3p and miR-217-5p targeting lipid metabolism. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 256:128412. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128412
116. Chen J, Alduais Y, Zhang K, Zhu X, and Chen B. CCAT1/FABP5 promotes tumour progression through mediating fatty acid metabolism and stabilizing PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:9199–213. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16815
117. Shi Z, Zhang H, Shen Y, Zhang S, Zhang X, Xu Y, et al. SETD1A-mediated H3K4me3 methylation upregulates lncRNA HOXC-AS3 and the binding of HOXC-AS3 to EP300 and increases EP300 stability to suppress the ferroptosis of NSCLC cells. Thorac Cancer. (2023) 14:2579–90. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15037
118. Gai C, Liu C, Wu X, Yu M, Zheng J, Zhang W, et al. MT1DP loaded by folate-modified liposomes sensitizes erastin-induced ferroptosis via regulating miR-365a-3p/NRF2 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:751. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02939-3
119. Chen H, Wang L, Liu J, Wan Z, Zhou L, Liao H, et al. LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 promotes cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting ferroptosis via activating the FOSL2/NAMPT axis. Cancer Biol Ther. (2023) 24:2223377. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2223377
120. Jin X, Liu X, Zhang Z, and Guan Y. lncRNA CCAT1 acts as a microRNA-218 sponge to increase gefitinib resistance in NSCLC by targeting HOXA1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 19:1266–75. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.006
121. Jiang X, Stockwell BR, and Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:266–82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
122. He F, Ru X, and Wen T. NRF2, a transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134777
123. Ye W, Wu Z, Gao P, Kang J, Xu Y, Wei C, et al. Identified Gefitinib Metabolism-Related lncRNAs can be Applied to Predict Prognosis, Tumor Microenvironment, and Drug Sensitivity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:939021. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939021
124. Kovacević Z. The pathway of glutamine and glutamate oxidation in isolated mitochondria from mammalian cells. Biochem J. (1971) 125:757–63. doi: 10.1042/bj1250757
125. Lin W, Wu WC, Liang Z, Zhang JH, and Fang SP. LncRNA FEZF1-AS1 facilitates cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer through modulating the miR-32-5p-glutaminase axis. Am J Cancer Res. (2024) 14:3153–70. doi: 10.62347/WUKN6549
126. Jin L, Chen C, Huang L, Sun Q, and Bu L. Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4. Open Med (Wars). (2022) 17:87–95. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0403
127. Yao F, Zhao Y, Wang G, Zhao M, Hong X, Ye Z, et al. Exosomal lncRNA ROR1-AS1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits ferroptosis of lung cancer cells through the IGF2BP1/SLC7A11 signal axis. Cell Signal. (2024) 120:111221. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111221
128. Zhang N, Huang J, Xu M, and Wang Y. LncRNA T-UCR uc.339/miR-339/SLC7A11 axis regulates the metastasis of ferroptosis-induced lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer. (2022) 13:1945–57. doi: 10.7150/jca.65017
129. Guo K, Qi D, and Huang B. LncRNA MEG8 promotes NSCLC progression by modulating the miR-15a-5p-miR-15b-5p/PSAT1 axis. Cancer Cell Int. (2021) 21:84. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01772-8
130. Li C, Fan K, Qu Y, Zhai W, Huang A, Sun X, et al. Deregulation of UCA1 expression may be involved in the development of chemoresistance to cisplatin in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer via regulating the signaling pathway of microRNA-495/NRF2. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:3721–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29266
131. Dong Y, Huo X, Sun R, Liu Z, Huang M, and Yang S. lncRNA Gm15290 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in lung cancer through directly interacting with and suppressing the tumor suppressor miR-615-5p. Biosci Rep. (2018) 38. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29266
132. Gao M, Wang M, Chen Y, Wu J, Zhou S, He W, et al. Identification and validation of tryptophan metabolism-related lncRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma prognosis and immune response. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:171. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05665-x
133. Pavlova NN and Thompson CB. The emerging hallmarks of cancer metabolism. Cell Metab. (2016) 23:27–47. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.12.006
134. Zhu L, Zhu X, and Wu Y. Effects of glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and glutamine metabolism on tumor microenvironment and clinical implications. Biomolecules. (2022) 12. doi: 10.3390/biom12040580
135. Liu H, Luo J, Luan S, He C, and Li Z. Long non-coding RNAs involved in cancer metabolic reprogramming. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2019) 76:495–504. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2946-1
136. Liu L, Su S, Ye D, Yu Z, Lu W, and Li X. Long non-coding RNA OGFRP1 regulates cell proliferation and ferroptosis by miR-299-3p/SLC38A1 axis in lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs. (2022) 33:826–39. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001328
137. Johnson MO, Wolf MM, Madden MZ, Andrejeva G, Sugiura A, Contreras DC, et al. Distinct regulation of Th17 and Th1 cell differentiation by glutaminase-dependent metabolism. Cell. (2018) 175:1780–95.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.001
138. Best SA, Gubser PM, Sethumadhavan S, Kersbergen A, Negrón Abril YL, Goldford J, et al. Glutaminase inhibition impairs CD8 T cell activation in STK11-/Lkb1-deficient lung cancer. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:874–87.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.04.003
139. Zhou L, Zhang Q, Zhu Q, Zhan Y, Li Y, and Huang X. Role and therapeutic targeting of glutamine metabolism in non−small cell lung cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. (2023) 25:159. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13745
140. Binkley MS, Jeon YJ, Nesselbush M, Moding EJ, Nabet BY, Almanza D, et al. KEAP1/NFE2L2 mutations predict lung cancer radiation resistance that can be targeted by glutaminase inhibition. Cancer Discov. (2020) 10:1826–41. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0282
141. Jo M, Koizumi K, Suzuki M, Kanayama D, Watanabe Y, Gouda H, et al. Design, synthesis, structure-activity relationship studies, and evaluation of novel GLS1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. (2023) 87:129266. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129266
142. Riess JW, Frankel P, Shackelford D, Dunphy M, Badawi RD, Nardo L, et al. Phase 1 trial of MLN0128 (Sapanisertib) and CB-839 HCl (Telaglenastat) in patients with advanced NSCLC (NCI 10327): rationale and study design. Clin Lung Cancer. (2021) 22:67–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.10.006
143. Deng J, Lin X, Qin J, Li Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, et al. SPTBN2 suppresses ferroptosis in NSCLC cells by facilitating SLC7A11 membrane trafficking and localization. Redox Biol. (2024) 70:103039. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103039
144. Ye ZC and Sontheimer H. Glioma cells release excitotoxic concentrations of glutamate. Cancer Res. (1999) 59:4383–91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-99-1000
145. Amelio I, Cutruzzolá F, Antonov A, Agostini M, and Melino G. Serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. (2014) 39:191–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.004
146. DeNicola GM, Chen PH, Mullarky E, Sudderth JA, Hu Z, Wu D, et al. Erratum: NRF2 regulates serine biosynthesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. (2016) 48:473. doi: 10.1038/ng0329-473a
147. Shi W, Ling L, Li C, Wu R, Zhang M, Shao F, et al. LncRNA UCA1 promoted cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma with HO1 targets NRF2/HO1 pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:1295–311. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04152-5
148. Platten M, Nollen EAA, Röhrig UF, Fallarino F, and Opitz CA. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2019) 18:379–401. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0016-5
149. Zhai L, Spranger S, Binder DC, Gritsina G, Lauing KL, Giles FJ, et al. Molecular pathways: targeting IDO1 and other tryptophan dioxygenases for cancer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2015) 21:5427–33. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0420
150. Hui E, Cheung J, Zhu J, Su X, Taylor MJ, Wallweber HA, et al. T cell costimulatory receptor CD28 is a primary target for PD-1-mediated inhibition. Science. (2017) 355:1428–33. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1292
151. Li Y, Shen Y, Xie M, Wang B, Wang T, Zeng J, et al. LncRNAs LCETRL3 and LCETRL4 at chromosome 4q12 diminish EGFR-TKIs efficiency in NSCLC through stabilizing TDP43 and EIF2S1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:30. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00847-2
152. Cao C, Li A, Xu C, Wu B, Yao L, and Liu Y. Engineering artificial non-coding RNAs for targeted protein degradation. Nat Chem Biol. (2025) 21:393–401. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01719-w
153. Yang H, Liu Y, Chen L, Zhao J, Guo M, Zhao X, et al. MiRNA-based therapies for lung cancer: opportunities and challenges? Biomolecules. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3390/biom13060877
154. Nicolescu C, Vaidya A, Schilb A, and Lu ZR. Regulating oncogenic lncRNA DANCR with targeted ECO/siRNA nanoparticles for non-small cell lung cancer therapy. ACS Omega. (2022) 7:22743–53. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02260
155. Gutschner T, Hämmerle M, Eissmann M, Hsu J, Kim Y, Hung G, et al. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:1180–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2850
156. Guo D, Wang Y, Ren K, and Han X. Knockdown of LncRNA PVT1 inhibits tumorigenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer by regulating miR-497 expression. Exp Cell Res. (2018) 362:172–9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.11.014
157. Xia Y, Pei T, Zhao J, Wang Z, Shen Y, Yang Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19: functions and mechanisms in regulating programmed cell death in cancer. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:76. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01832-8
158. Gencel-Augusto J, Wu W, and Bivona TG. Long non-coding RNAs as emerging targets in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123135
159. Akbari Kordkheyli V, Rashidi M, Shokri Y, Fallahpour S, Variji A, Nabipour Ghara E, et al. CRISPER/CAS system, a novel tool of targeted therapy of drug-resistant lung cancer. Adv Pharm Bull. (2022) 12:262–73. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.027
160. Ao YQ, Gao J, Jiang JH, Wang HK, Wang S, and Ding JY. Comprehensive landscape and future perspective of long noncoding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer: it takes a village. Mol Ther. (2023) 31:3389–413. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.09.015
161. Chandra Gupta S and Nandan Tripathi Y. Potential of long non-coding RNAs in cancer patients: From biomarkers to therapeutic targets. Int J Cancer. (2017) 140:1955–67. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30546
162. Mattick JS, Amaral PP, Carninci P, Carpenter S, Chang HY, Chen LL, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:430–47. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00566-8
163. Schertzer MD, Murvin MM, and Calabrese JM. Using RNA Sequencing and Spike-in RNAs to Measure Intracellular Abundance of lncRNAs and mRNAs. Bio Protoc. (2020) 10. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3772
164. Li X, Liang QX, Lin JR, Peng J, Yang JH, Yi C, et al. Epitranscriptomic technologies and analyses. Sci China Life Sci. (2020) 63:501–15. doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-1658-x
165. Zhang Y, Huang YX, Jin X, Chen J, Peng L, Wang DL, et al. Overexpression of lncRNAs with endogenous lengths and functions using a lncRNA delivery system based on transposon. J Nanobiotechnol. (2021) 19:303. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01044-7
166. Winkle M, El-Daly SM, Fabbri M, and Calin GA. Noncoding RNA therapeutics - challenges and potential solutions. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:629–51. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00219-z
Keywords: lncRNA, miRNA, metabolic reprogramming, NSCLC, lung cancer
Citation: Li M, Dai L, Chen S, Deng M, Wang L and Sun Y (2025) “Molecular pigeon” network of lncRNA and miRNA: decoding metabolic reprogramming in patients with lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1578927. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1578927
Received: 18 February 2025; Accepted: 20 June 2025;
Published: 17 July 2025.
Edited by:
Matthew J. Marton, MSD, United StatesReviewed by:
Bo-Wei Zhao, Zhejiang University, ChinaChicca Lo Sardo, Hospital Physiotherapy Institutes (IRCCS), Italy
Abeer A.I. Hassanin, Texas A&M University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, Dai, Chen, Deng, Wang and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yinhui Sun, czMzNDY4MDg4QDE2My5jb20=; Lihua Wang, MzEwNjAwQGhudWNtLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors share first authorship
 Mingxiao Li
Mingxiao Li Ling Dai1†
Ling Dai1†