- 1Clinical Laboratory, Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Changxing County, Huzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Clinical Laboratory, Lishui People’s Hospital, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Lishui, Zhejiang, China
Background: Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR) has been widely studied for its prognostic value in gynecological cancers, but the results remain inconsistent. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the precise prognostic significance of FAR in gynecological cancers.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases up to 12 May 2025. The prognostic value of FAR for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in gynecological cancers was examined using pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: A total of 10 articles comprising 1,902 patients were included in this meta-analysis. Pooled results indicated that elevated FAR was significantly associated with poor OS (HR = 2.75, 95% CI: 2.26–3.36, p < 0.001) and shorter PFS (HR = 1.60, 95% CI: 1.20–2.12, p = 0.001) in patients with gynecological cancers. Subgroup analyses confirmed that FAR predicted OS regardless of sample size, cancer type, FIGO stage, treatment modality, FAR threshold, threshold determination method, or type of survival analysis (p < 0.05). Additionally, FAR remained a significant predictor of poor PFS across different cancer types.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed that a high FAR is significantly associated with worse OS and PFS in patients with gynecological cancers. FAR may serve as a promising prognostic biomarker in clinical practice.
Systematic review registration: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2025-5-0036/, identifier INPLASY202550036.
Introduction
Gynecological cancers, the most prevalent female malignancies globally, affect the reproductive system and significantly impact the quality of life (1). These cancers typically include endometrial, cervical, vulvar, ovarian, and vaginal cancers (2). They can impair reproductive organ function, leading to negative effects on sexual health, self-concept, self-esteem, and physical fitness (3). According to GLOBOCAN, 1,471,803 new cases of gynecological cancers and 679,549 cancer-related deaths were recorded in 2022 globally (2). Despite major advancements in surgical, radiation, and chemotherapy treatments, the prognosis for advanced-stage gynecological cancers remains poor due to limited treatment options. The 5-year survival rates for cervical, endometrial, and ovarian cancers are only 17.2%, 16.3%, and 29.2%, respectively (4, 5). Prognostic markers play a crucial role in improving survival outcomes in patients with gynecological cancers (6). Therefore, identifying reliable and effective prognostic markers is essential.
Increasing data show that deficiencies in nutrition, hemostatic elements, and inflammation are key contributors to the development of human cancers (7). Previous studies have identified several hematological parameters that are crucial biomarkers for cancer prognosis, including platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (8), prognostic nutritional index (9), systemic immune inflammation index (10), and albumin-to-globulin ratio (11). The fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR), obtained based on routine blood test results as FAR = fibrinogen/albumin, has also demonstrated significant potential in predicting cancer prognosis. FAR has been linked to outcomes in various cancers, including laryngeal cancer (12), non-small-cell lung cancer (13), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (14), pancreatic cancer (15), and hepatocellular carcinoma (16). Although many studies have explored the prognostic value of FAR in patients with gynecological cancers, the findings remain inconsistent (17–26). Some studies reported that elevated FAR is markedly associated with poor prognosis in gynecological cancers (17, 19, 22, 23), while others suggest that a higher FAR is linked to improved survival outcomes (24). Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to identify the accurate prognostic value of FAR in gynecological cancers.
Materials and methods
Study guideline
The study was conducted in strict accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (27). The research protocol was registered in INPLASY (registration number: INPLASY202550036), and the protocol is accessible at https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2025-5-0036/.
Search strategy
We systematically searched PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) up to 12 May 2025. The search strategy included the following terms: (albumin-to-fibrinogen OR albumin/fibrinogen OR fibrinogen-to-albumin OR fibrinogen/albumin) AND (cervical cancer OR gynecological cancer OR ovarian cancer OR endometrial cancer OR gynecological carcinoma OR cervical carcinoma OR ovarian carcinoma OR endometrial carcinoma OR gynecological neoplasm OR vulvar cancer OR vaginal cancer). No publication language restriction was applied. Detailed search strategies for each database are provided in Supplementary File 1. Moreover, reference lists of relevant studies were manually screened to identify any further eligible articles.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies were included based on the following criteria (1): pathological diagnosis of gynecological cancers, including cervical, endometrial, ovarian, vulvar, and vaginal cancers (2); investigation of the association between FAR and survival outcomes in gynecological cancers (3); reporting of hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) (4); identification of a FAR threshold; and (5) publication in any language. The exclusion criteria were (1): meeting abstracts, reviews, comments, letters, or case reports (2); studies with duplicate data; and (3) animal studies.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two investigators (Y.C. and J.Z.) independently extracted data from eligible articles, and any disagreements were settled through discussion. The following information was collected: author, year, country, sample size, age, study period, study design, study center, cancer type, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage, treatment, FAR threshold, threshold determination method, follow-up duration, survival outcomes, survival analysis, HRs, and 95% CIs. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were considered the primary and secondary outcomes, respectively. Moreover, the quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Newcastle–Ottawa scale (NOS; range: 0–9 points) (28), with a score of ≥ 6 indicating high quality.
Statistical analysis
We evaluated the prognostic value of FAR for predicting OS and PFS in gynecological cancers by computing pooled HRs and 95% CIs. Between-study heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and I-squared (I2) statistic. A random-effects model was employed when significant heterogeneity was present (I2 > 50%); otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used. Subgroup analyses were conducted to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially excluding individual studies to evaluate the robustness of the pooled results. Publication bias was assessed using Begg’s and Egger’s tests. All statistical analyses were conducted using Stata software version 12.0 (Stata Corp, College Station, TX, USA). A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Process of literature search
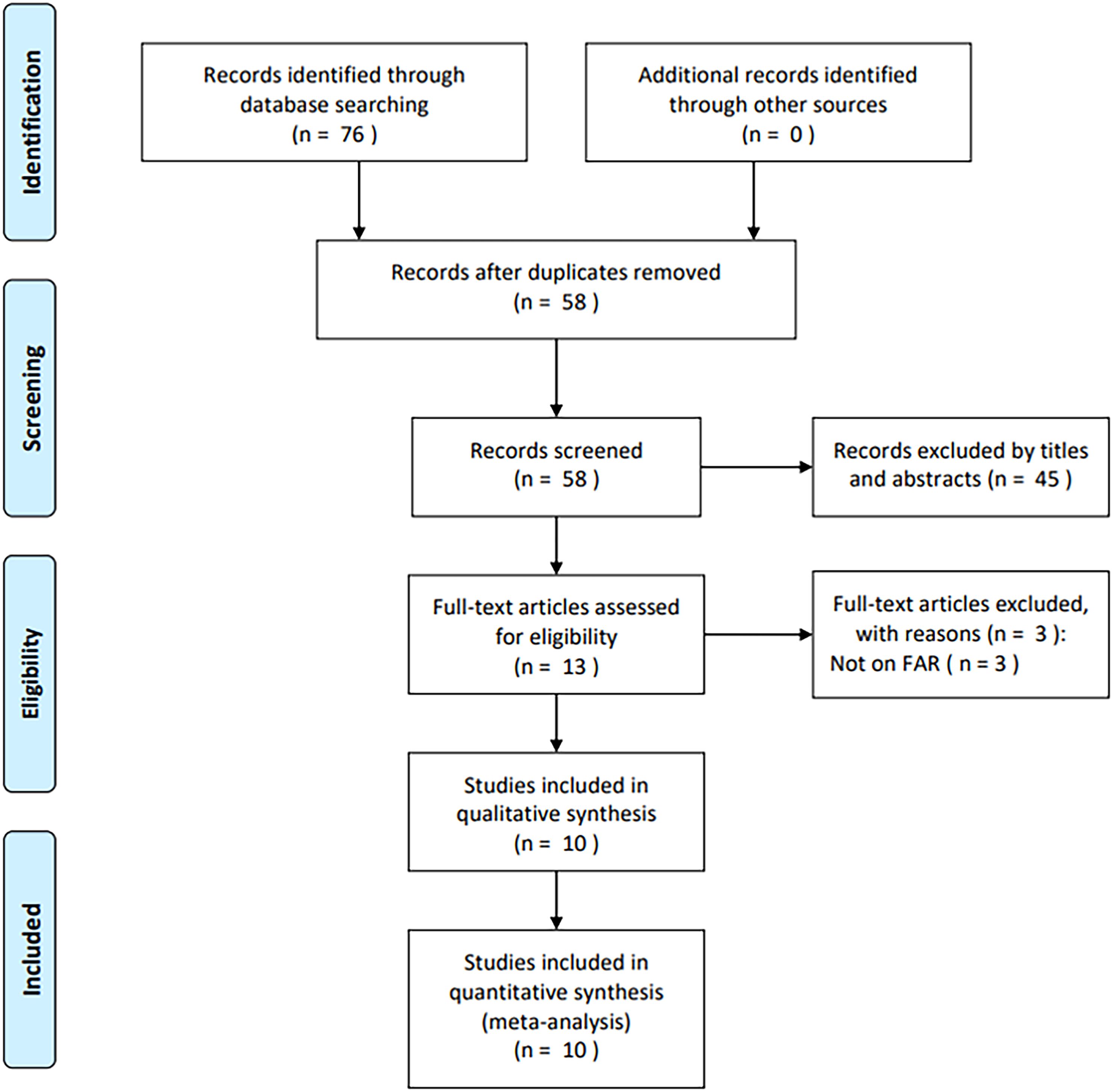
A total of 76 studies were initially identified through primary database searches (PubMed, n = 18; Web of Science, n = 15; Embase, n = 29; Cochrane Library, n = 1; and CNKI, n = 13). After removing duplicates, 58 studies remained (Figure 1). Following a review of titles and abstracts, 45 records were excluded due to irrelevance. The full texts of the remaining 13 articles were then assessed, with three excluded for not reporting FAR (n = 3). Eventually, 10 articles comprising 1,902 cases (17–26) were included in the final analysis (Figure 1).
Characteristics of included studies
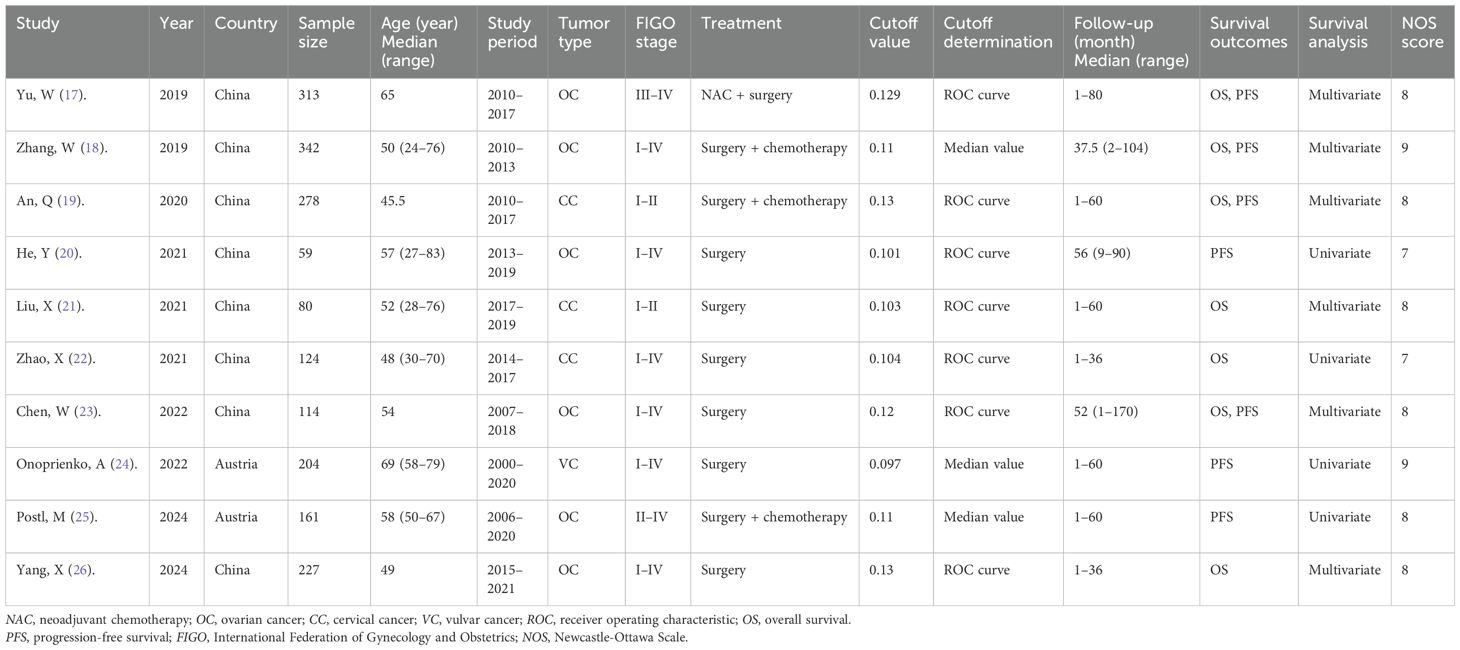
The included articles were published between 2019 and 2024 (Table 1) and were retrospective in design (17–26). Eight studies were performed in China (17–23, 26), while two were carried out in Austria (24, 25). Sample sizes ranged from 59 to 342, with a median of 182.5. Five articles were published in English (17, 19, 23–25) and five in Chinese (18, 20–22, 26). Six studies involved patients with ovarian cancer (17, 18, 20, 23, 25, 26), three included patients with cervical cancer (19, 21, 22), and one focused on vulvar cancer (24). Regarding treatment modalities, six studies evaluated surgical cases (20–24, 26), three involved surgery followed by chemotherapy (18, 19, 25), and one study assessed neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery (17). The FAR thresholds ranged from 0.097 to 0.13, with a median of 0.11. Seven studies examined the prognostic value of FAR for OS (17–19, 21–23, 26), while another seven reported the association between FAR and PFS (17–20, 23–25) in gynecological cancers. Six articles reported HRs with 95% CIs from multivariate analyses (17–19, 21, 23, 26), while four employed univariate regression (20, 22, 24, 25). The NOS scores ranged from 7 to 9, indicating high study quality (17–26) (Table 1).
FAR and OS
Seven studies involving 1,478 patients (17–19, 21–23, 26) reported the association between FAR and OS in gynecological cancers. Heterogeneity among the studies was not significant (I2 = 0, p = 0.549); therefore, a fixed-effects model was applied (Table 2). The pooled analysis revealed that a high FAR was a significant prognostic biomarker for poor OS in gynecological cancers (HR = 2.75, 95% CI: 2.26–3.36, p < 0.001; Table 2; Figure 2). Subgroup analyses further demonstrated that the prognostic value of FAR for OS remained consistent regardless of sample size, cancer type, FIGO stage, treatment modality, threshold, threshold determination method, or type of survival analysis (p < 0.05; Table 2).
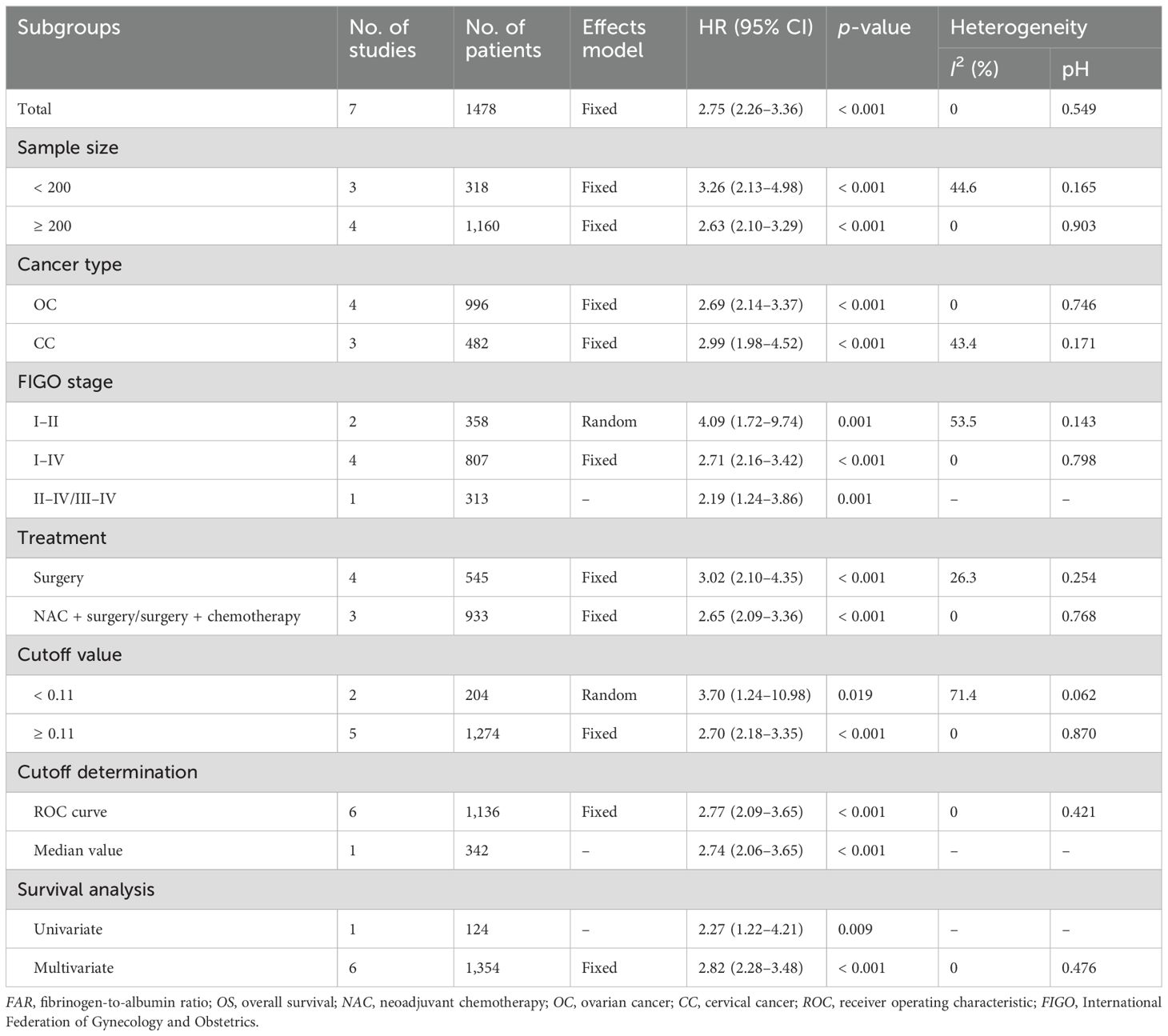
Table 2. Subgroup analysis of the prognostic value of FAR for OS in patients with gynecological cancers.
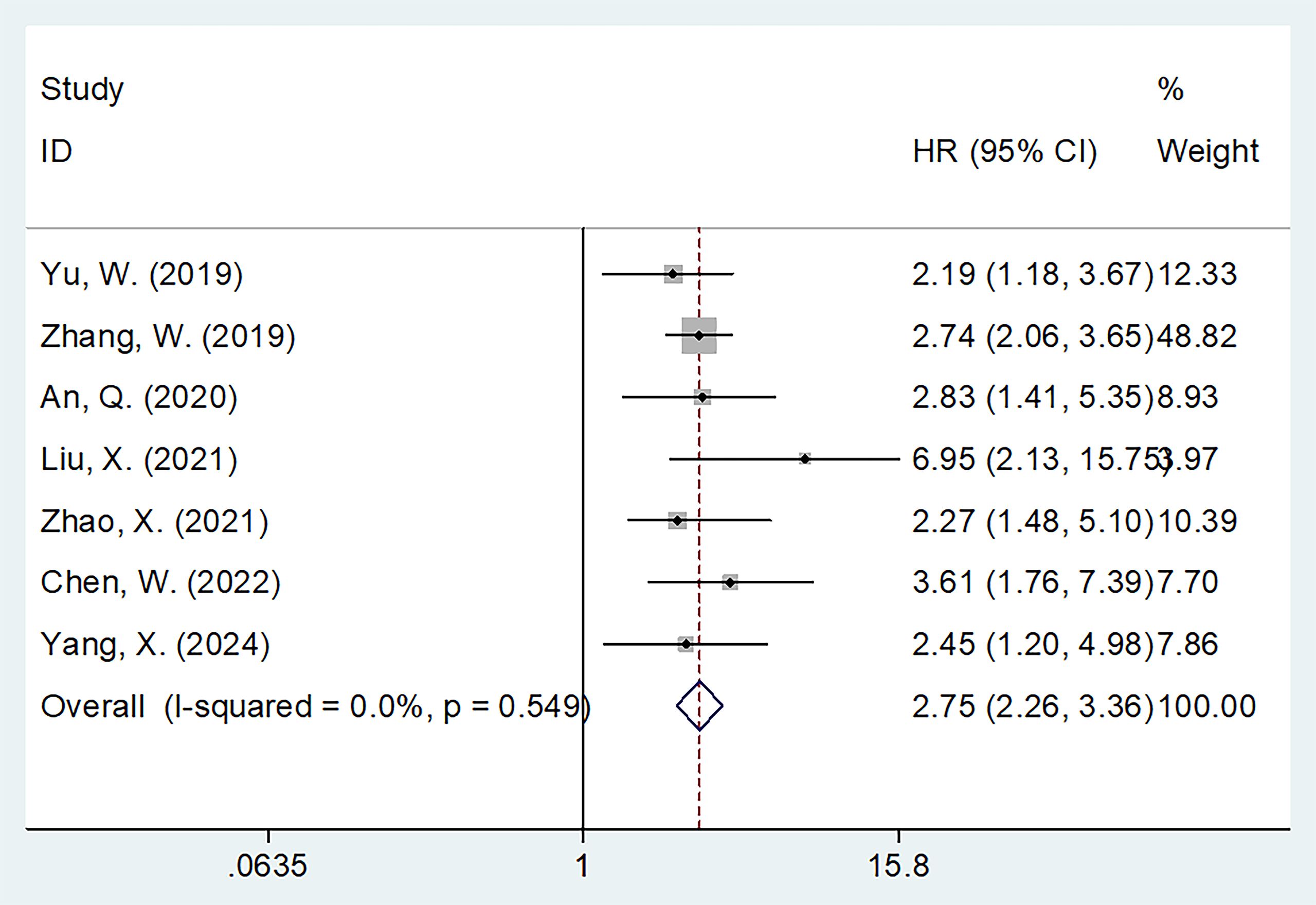
Figure 2. Forest plots showing the prognostic value of FAR for OS in patients with gynecological cancers.
FAR and PFS
Seven studies comprising 1,471 patients (17–20, 23–25) evaluated the correction between FAR and PFS. Due to significant heterogeneity (I2 = 93.3%, p < 0.001), a random-effects model was applied. The pooled results showed that a higher FAR was significantly associated with poorer PFS in gynecological cancers (HR = 1.60, 95% CI: 1.20–2.12, p = 0.001; Table 3; Figure 3). Subgroup analyses confirmed that FAR consistently predicted worse PFS across different cancer types (Table 3).
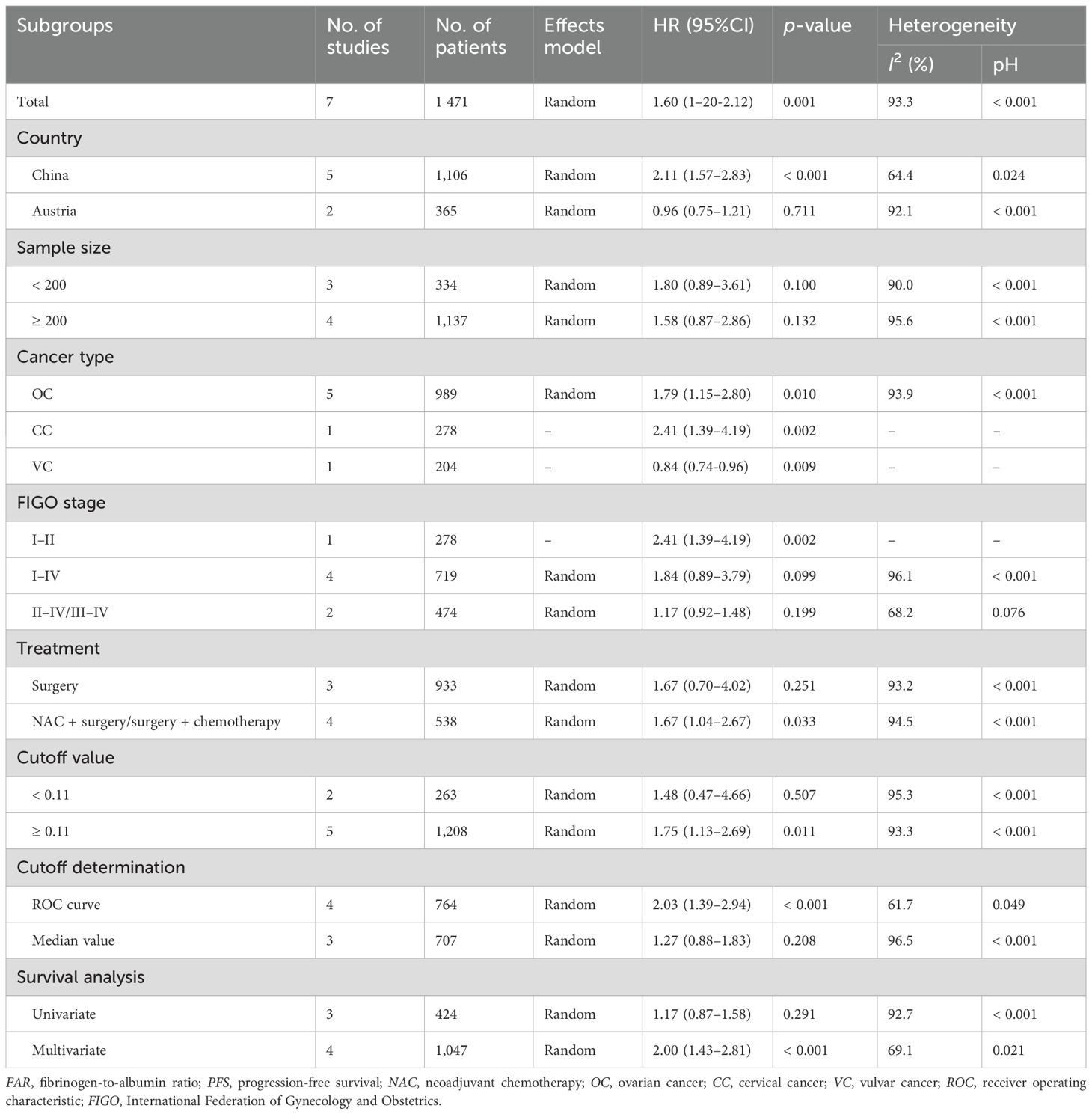
Table 3. Subgroup analysis showing the prognostic value of FAR for PFS in patients with gynecological cancers.
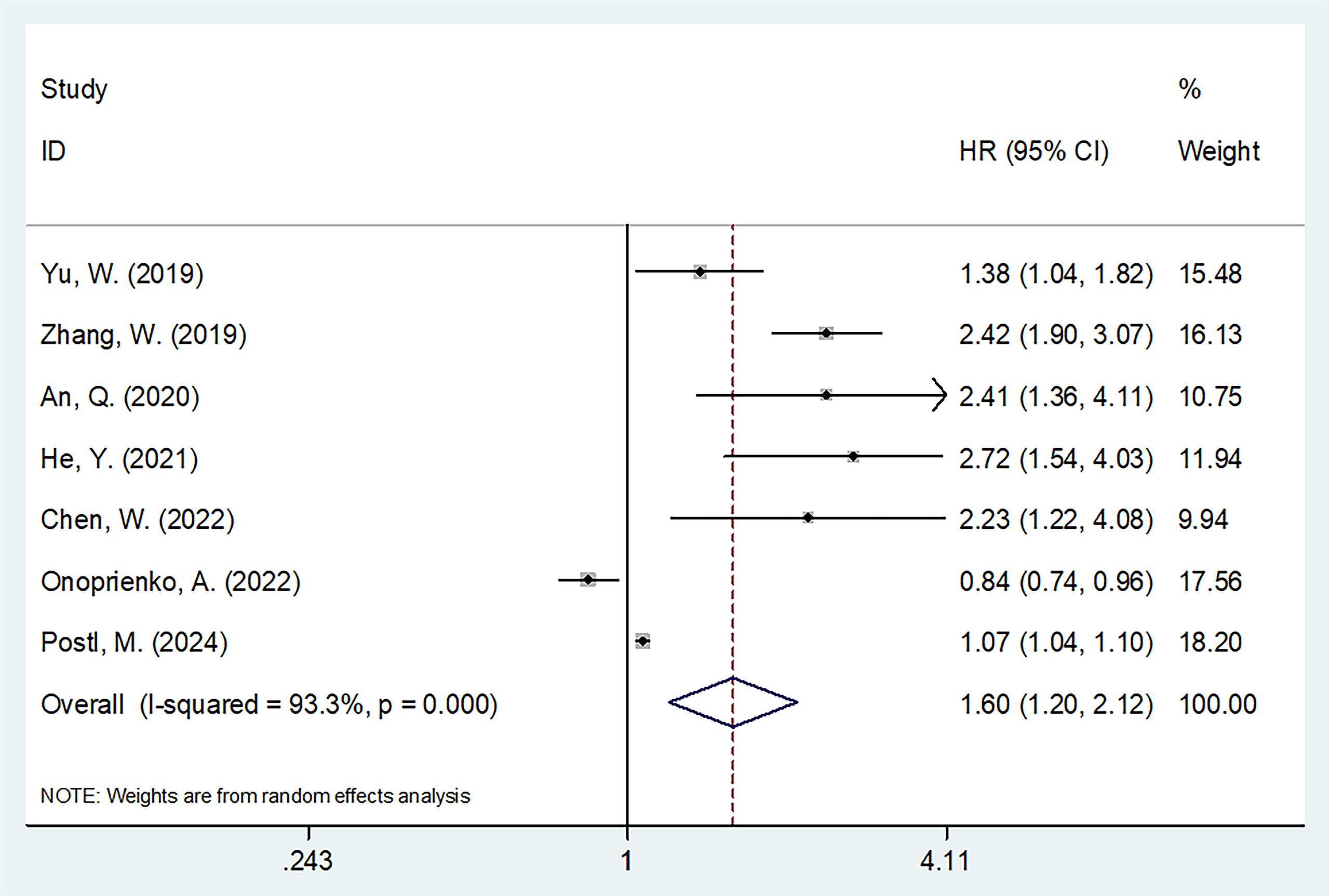
Figure 3. Forest plots showing the prognostic value of FAR for PFS in patients with gynecologic cancers.
Sensitivity analysis
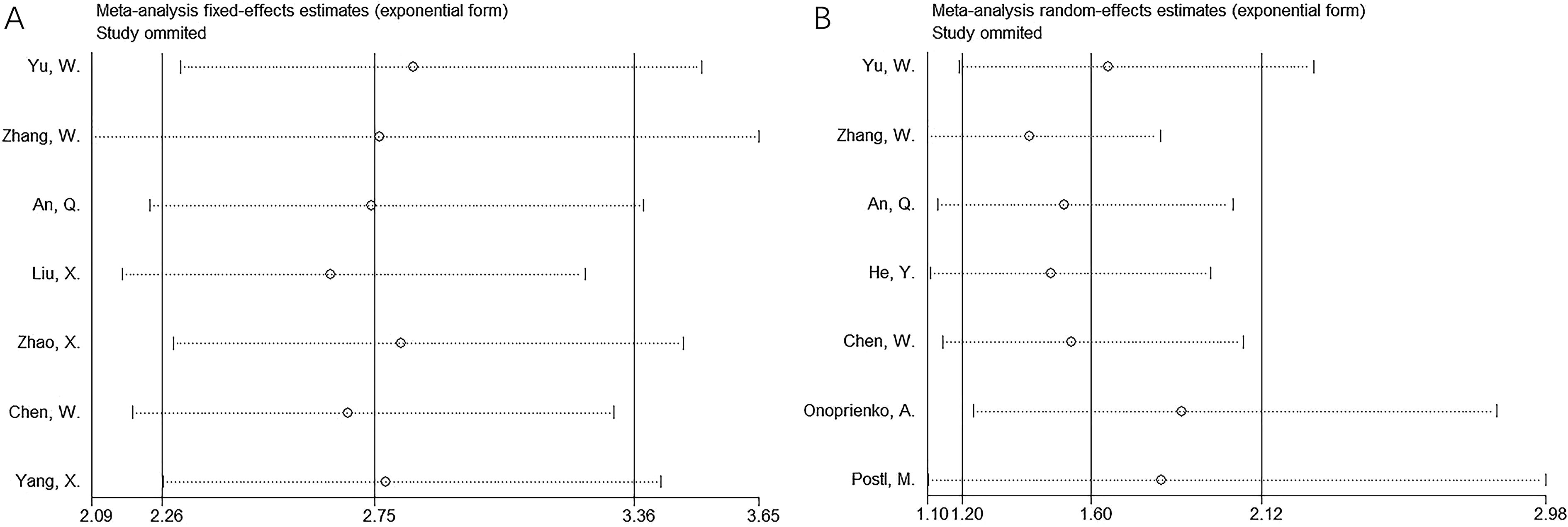
Sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially removing each study, and no significant changes were observed in the pooled results for OS and PFS (Figure 4).
Publication bias
Begg’s and Egger’s tests were used to assess publication bias. Forest plots were symmetrical, revealing no apparent publication bias for OS (p = 0.072 and 0.415 for Begg’s and Egger’s tests, respectively) or PFS (p = 0.548 and 0.126 for Begg’s and Egger’s tests, respectively) in this meta-analysis (Figure 5).
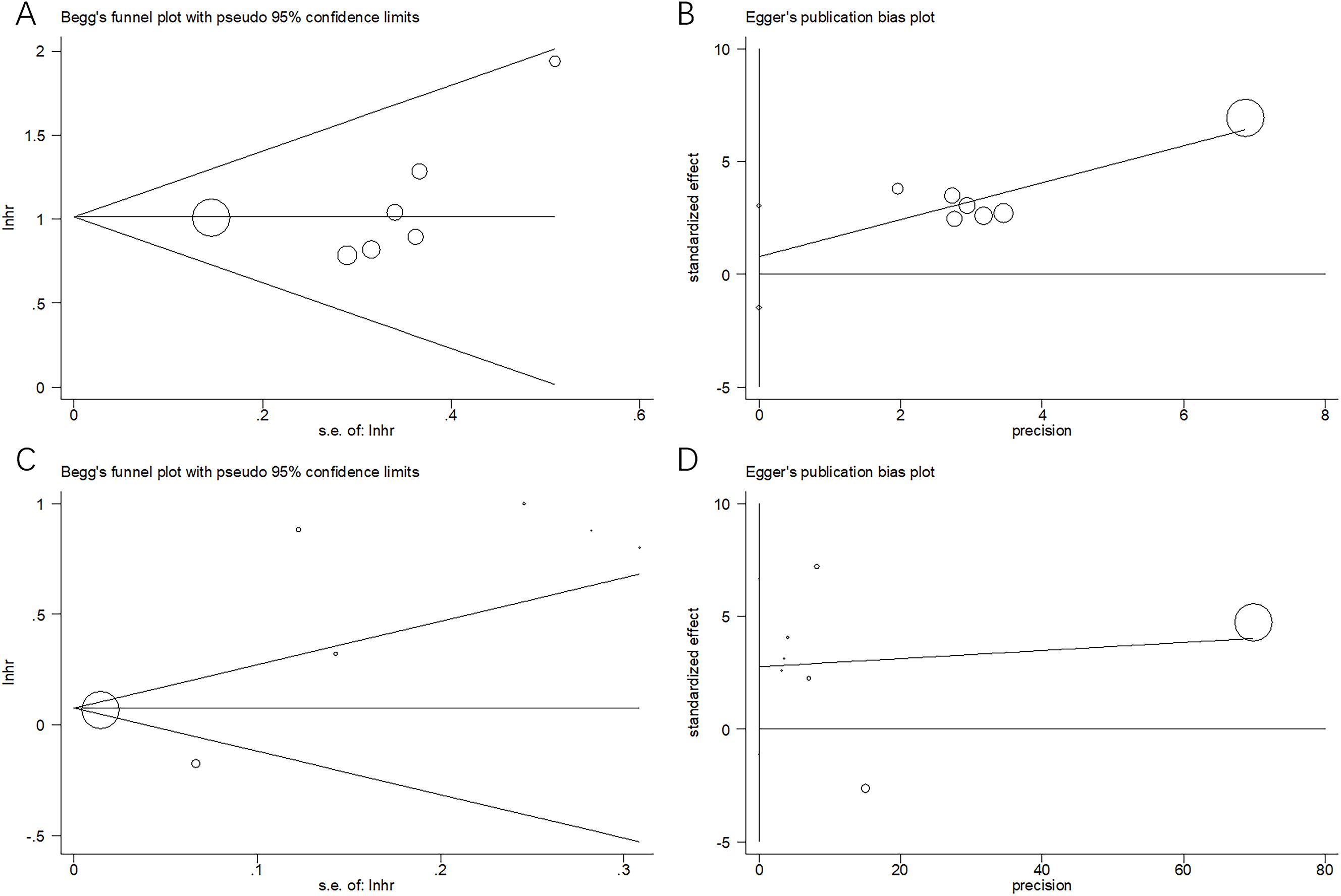
Figure 5. Assessment of publication bias: (A) Begg’s test for OS, p = 0.072; (B) Egger’s test for OS, p = 0.415; (C) Begg’s test for PFS, p = 0.548; and (D) Egger’s test for PFS, p = 0.126.
Discussion
FAR has been widely studied for its prognostic value in gynecological cancers, although previous findings have been inconsistent. This meta-analysis incorporated data from 10 studies involving 1,902 patients (17–26) to clarify the prognostic significance of FAR in gynecological cancers. Our results revealed a significant correlation between elevated FAR and poorer OS and PFS. Moreover, the prognostic value of FAR remained consistent across various subgroup analyses. Sensitivity and publication bias analyses supported the credibility of these findings. Overall, elevated FAR appears to be a strong predictor of both short- and long-term survival outcomes in gynecological cancers. To our knowledge, this meta-analysis is the first to comprehensively evaluate the prognostic value of FAR in this context.
FAR is calculated based on the levels of fibrinogen and albumin. An elevated FAR may result from increased fibrinogen levels, decreased albumin levels, or both. Although the precise mechanisms underlying FAR’s prognostic value in gynecological cancers remain to be fully elucidated, several explanations have been proposed. First, studies have shown that fibrinogen levels can rise under various pathophysiological conditions, including tumors, surgeries, infections, inflammations, or trauma (29). Fibrinogen is primarily produced by the liver and, in some cases, by malignant tumor cells. It is released into the bloodstream, with this release being amplified by systemic inflammatory responses (30). Moreover, fibrinogen promotes the production of inflammatory cytokines and is regarded as a reliable indicator of systemic inflammation (31). It also contributes to tumor cell coagulation, enhancing cancer cell survival and adhesion, thereby facilitating metastasis (32). Second, serum albumin is widely considered a marker of immune and nutritional status, with low albumin levels linked to poorer postoperative outcomes and cachexia in patients with cancer (33). Albumin, synthesized by liver parenchyma cells, serves as an indicator of liver reserve function and is essential for antioxidant defense, endothelial stability, and immune regulation (34). Serum albumin levels are positively correlated to body mass index and nutritional status, independent of systemic inflammation and liver function (35). Low albumin levels are linked to an increased risk of malnutrition, reduced OS, and elevated inflammatory markers such as interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein (36). Therefore, FAR represents a rational prognostic marker based on the biological roles of fibrinogen and albumin.
Notably, significant heterogeneity was observed in the PFS analysis (Table 3). This heterogeneity may be attributed to several factors. First, the results of the included studies on PFS were inconsistent. For instance, the study by Onoprienko (24) reported results that contradicted those of other studies (17–23, 25, 26) (Figure 3), which may be a major source of the heterogeneity. Second, despite this variability, sensitivity analysis and publication bias tests confirmed the reliability of the overall PFS results (Figures 4, 5).
The cutoff values reported in the included studies ranged from 0.097 to 0.13, with a median of 0.11. Therefore, we applied 0.11 as the cutoff value in the subgroup analyses for OS and PFS. The results indicated that FAR ≥ 0.11 consistently demonstrated significant prognostic value for both outcomes (Tables 2, 3). Based on these findings, we recommend 0.11 as the standard cutoff value for FAR in future studies on gynecological cancers.
Notably, literature assessment and decision-making in systematic reviews are crucial processes (37). Typically, three reviewers are involved in such studies, with decisions made by majority vote. In the present meta-analysis, two independent investigators were involved in data extraction. Two investigators (Y.C. and J.Z.) independently collected data from eligible articles following the PRISMA guidelines, and any disagreements were resolved through discussion until a consensus was reached. Although the PRISMA guidelines were strictly followed, the involvement of only two reviewers is considered a limitation of this study.
Recently, many studies reported that FAR can serve as a prognostic indicator for various cancers based on meta-analyses (38–40). In a meta-analysis by Zhang et al. involving 5,088 cases, a high FAR was significantly associated with poor OS and worse disease-free survival (DFS) in malignant tumors (38). Similarly, a meta-analysis by Wang et al. indicated that elevated FAR was linked to poor OS and DFS in breast cancer and was closely related to multiple indicators of tumor progression (39). Li et al. conducted a meta-analysis of 19 studies and concluded that a higher FAR was markedly associated with worse survival outcomes in patients with cancer (40). The findings of our study are consistent with these results, further supporting the prognostic significance of FAR in various cancer types.
This study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, many of the included studies were conducted in China, which may limit the generalizability of our findings to Chinese patients with gynecological cancers. Second, all eligible studies were retrospective in design, and the possibility of selection bias cannot be excluded. Third, the threshold for FAR varied across studies, leading to potential inconsistency in prognostic evaluation. Therefore, large-scale, multicenter prospective clinical studies are needed to validate these findings.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis demonstrates that elevated FAR is significantly associated with poorer OS and inferior in patients with gynecological cancers. FAR may serve as a promising prognostic biomarker in clinical settings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1580940/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
FAR, fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; CC, cervical cancer; EC, endometrial cancer; OC, ovarian cancer; VC, vulvar cancer; PNI, prognostic nutritional index; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; FIGO, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics; NOS, Newcastle–Ottawa scale; NAC, neoadjuvant chemotherapy; DFS, disease-free survival.
References
1. Keyvani V, Kheradmand N, Navaei ZN, Mollazadeh S, and Esmaeili SA. Epidemiological trends and risk factors of gynecological cancers: an update. Med Oncol (Northwood London England). (2023) 40:93. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01957-3
2. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
3. Reis N, Beji NK, and Coskun A. Quality of life and sexual functioning in gynecological cancer patients: results from quantitative and qualitative data. Eur J Oncol nursing: Off J Eur Oncol Nurs Soc. (2010) 14:137–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2009.09.004
4. Gardner AB, Charo LM, Mann AK, Kapp DS, Eskander RN, and Chan JK. Ovarian, uterine, and cervical cancer patients with distant metastases at diagnosis: most common locations and outcomes. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2020) 37:107–13. doi: 10.1007/s10585-019-10007-0
5. D’Augè TG, Giannini A, Bogani G, Di Dio C, Laganà AS, Di Donato V, et al. Prevention, screening, treatment and follow-up of gynecological cancers: state of art and future perspectives. Clin Exp Obstetrics Gynecology. (2023) 50:1–8. doi: 10.31083/j.ceog5008160
6. Xu C, Xu P, Zhang J, He S, Hua T, and Huang A. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in gynecological cancers: implications for therapy resistance and biomarkers. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1349474. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1349474
7. Feliciano EMC, Kroenke CH, Meyerhardt JA, Prado CM, Bradshaw PT, Kwan ML, et al. Association of systemic inflammation and sarcopenia with survival in nonmetastatic colorectal cancer: results from the C SCANS study. JAMA Oncol. (2017) 3:e172319. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.2319
8. Ohe Y, Fushida S, Yamaguchi T, Kinoshita J, Saito H, Okamoto K, et al. Peripheral blood platelet-lymphocyte ratio is good predictor of chemosensitivity and prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Manage Res. (2020) 12:1303–11. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S241069
9. Abe A, Hayashi H, Ishihama T, and Furuta H. Prognostic impact of the prognostic nutritional index in cases of resected oral squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health. (2021) 21:40. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01394-6
10. Ozbek E, Besiroglu H, Ozer K, Horsanali MO, and Gorgel SN. Systemic immune inflammation index is a promising non-invasive marker for the prognosis of the patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. (2020) 52:1455–63. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02440-y
11. Kawata A, Taguchi A, Baba S, Miyamoto Y, Tanikawa M, Sone K, et al. A low preoperative albumin-to-globulin ratio is a negative prognostic factor in patients with surgically treated cervical cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. (2021) 26:980–5. doi: 10.1007/s10147-021-01861-8
12. Zhang Y, Meng Z, Lu M, Ruan S, Zhou J, Zhang M, et al. Study of the significance of the combination of the fibrinogen-albumin ratio and sarcopenia in predicting the prognosis of laryngeal cancer patients undergoing radical surgery. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:1265. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13039-2
13. Ma S and Wang L. Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR) is the best biomarker for the overall survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1396843. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1396843
14. Shi X, Wu C, Deng W, and Wu J. Prognostic value of lactate dehydrogenase to absolute lymphocyte count ratio and albumin to fibrinogen ratio in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e39097. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000039097
15. Cheng H, Lu D, Yin C, and Fang Y. Prognostic value of peripheral blood fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Am J Transl Res. (2024) 16:7165–75. doi: 10.62347/zohp7650
16. Sun H, Ma J, Lu J, Yao ZH, Ran HL, Zhou H, et al. Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio predicts overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2023) 15:1662–72. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1662
17. Yu W, Ye Z, Fang X, Jiang X, and Jiang Y. Preoperative albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio predicts chemotherapy resistance and prognosis in patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. (2019) 12:88. doi: 10.1186/s13048-019-0563-8
18. Zhang W, Zhang Z, and He L. Prognosis analysis of 342 ovarian cancer patients after surgery therapy. Chin J Cancer Prev Trea. (2019) 26:1288–95. doi: 10.16073/j.cnki.cjcpt.2019.17.11
19. An Q, Liu W, Yang Y, and Yang B. Preoperative fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio, a potential prognostic factor for patients with stage IB-IIA cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:691. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07191-8
20. He Y, Jin H, Chen S, Wen J, Wang S, and Guo C. Evaluation of the prognosis of ovarian cancer by the ratio of peripheral blood fibrinogen to albumin. Chin J Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2021) 22:413–5. doi: 10.13390/j.issn.1672-1861.2021.04.022
21. Liu X and Huang H. The predictive effect of FAR on the prognosis of patients with stage IB-IIA cervical cancer. China Continuing Med Educ. (2021) 13:163–7.
22. Zhao X, Jin L, Chang C, and Wei H. The value of preoperative albumin to fibrinogen ratio and systemic inflammation response index in evaluating the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer. Trauma Crit Care Med. (2021) 9:21–4. doi: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2021.01.05
23. Chen W, Shan B, Zhou S, Yang H, and Ye S. Fibrinogen/albumin ratio as a promising predictor of platinum response and survival in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:92. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09204-0
24. Onoprienko A, Hofstetter G, Dorittke T, Bekos C, Grimm C, Polterauer M, et al. The prognostic value of the fibrinogen-albumin-ratio index (FARI) in patients with advanced vulvar cancer. J Pers Med. (2022) 12(11):1882. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111882
25. Postl M, Danisch M, Schrott F, Kofler P, Petrov P, Aust S, et al. The predictive value of the fibrinogen-albumin-ratio index on surgical outcomes in patients with advanced high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16(19):3295. doi: 10.3390/cancers16193295
26. Yang X, Zhao T, and Wang R. Predictive value of the transvaginal color Doppler flow imaging combined with the fibrinogen/albumin ratio and the D-dimer IeveI of patients for their prognosis after ovarian cancer surgery. Chin J Fam Plann. (2024) 32:2901–5. doi: 10.3969/i.issn.1004-8189.2024.12.038
27. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, and Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg (London England). (2010) 8:336–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
28. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
29. Pieters M and Wolberg AS. Fibrinogen and fibrin: An illustrated review. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. (2019) 3:161–72. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12191
30. Li C, Fan Z, Guo W, Liang F, Mao X, Wu J, et al. Fibrinogen-to-prealbumin ratio: A new prognostic marker of resectable pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1149942. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1149942
31. Jensen T, Kierulf P, Sandset PM, Klingenberg O, Joø GB, Godal HC, et al. Fibrinogen and fibrin induce synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines from isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Thromb haemostasis. (2007) 97:822–9. doi: 10.1160/th07-01-0039
32. Palumbo JS, Kombrinck KW, Drew AF, Grimes TS, Kiser JH, Degen JL, et al. Fibrinogen is an important determinant of the metastatic potential of circulating tumor cells. Blood. (2000) 96:3302–9. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.10.3302
33. Haskins IN, Baginsky M, Amdur RL, and Agarwal S. Preoperative hypoalbuminemia is associated with worse outcomes in colon cancer patients. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh Scotland). (2017) 36:1333–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.08.023
34. Spinella R, Sawhney R, and Jalan R. Albumin in chronic liver disease: structure, functions and therapeutic implications. Hepatol Int. (2016) 10:124–32. doi: 10.1007/s12072-015-9665-6
35. Eckart A, Struja T, Kutz A, Baumgartner A, Baumgartner T, Zurfluh S, et al. Relationship of nutritional status, inflammation, and serum albumin levels during acute illness: A prospective study. Am J Med. (2020) 133:713–22.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.031
36. Almasaudi AS, Dolan RD, Edwards CA, and McMillan DC. Hypoalbuminemia reflects nutritional risk, body composition and systemic inflammation and is independently associated with survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12(7):1986. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071986
37. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev. (2021) 10:89. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
38. Zhang Y and Xiao G. Prognostic significance of the ratio of fibrinogen and albumin in human Malignancies: a meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res. (2019) 11:3381–93. doi: 10.2147/cmar.S198419
39. Wang Z and Shen X. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR) in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22:220. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03506-2
Keywords: fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio, meta-analysis, gynecological cancers, prognosis, evidence-based medicine
Citation: Chen Y and Zhang J (2025) Prognostic role of fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio in patients with gynecological cancers: a meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1580940. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1580940
Received: 21 February 2025; Accepted: 16 June 2025;
Published: 03 July 2025.
Edited by:
Sharon R Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesReviewed by:
Thomas Bartl, Medical University of Vienna, AustriaJie Hao, Southeast Colorado Hospital, United States
Copyright © 2025 Chen and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiliang Zhang, bXpoYW5namlsaWFuZ0AxMjYuY29t
 Yaping Chen1
Yaping Chen1 Jiliang Zhang
Jiliang Zhang