- 1Department of Urology, Yunnan Dehong People’s Hospital, Dehong, China
- 2Department of Anesthesia, Yunnan Dehong People’s Hospital, Dehong, China
- 3Department of Urology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chendu, China
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy is the standard treatment for muscle invasive bladder cancer. For patients who are intolerant or unwilling to receive radical surgery and chemotherapy, the use of immune therapy combined with bladder preservation treatment has gradually become a viable treatment option. In this article, We aimed to present a case of cT2N0M0 Bladder cancer patient who was intolerant to chemotherapy and was treated with Toripalimab as a single-agent bladder preservation therapy for three cycles. After 15 months of treatment, a clinical complete response(cCR) was achieved, thus retaining the bladder. In this report, the safety profile of Toripalimab was favorable, with no severe or uncontrollable adverse events. The patient’s pathological IHC showed PD-L1 negative (TPS <1%, CPS <1%) and did not undergo mTURBT, which is a rare phenomenon. Our report suggests that Patients with PD-L1 negative but CD8+ T cell positive tumor infiltration can also benefit from PD-L1 inhibitor treatment and even achieve cCR to preserve the bladder.
1 Introduction
Bladder cancer is one of the most common malignancies in the urinary system, ranking as the 10th most prevalent new malignancy in the world (1). Based on the depth of tumor invasion, it can be classified into non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). MIBC accounts for approximately 25% of all bladder cancers and has a poor clinical prognosis (2). The current standard treatment for MIBC involves neoadjuvant chemotherapy, radical cystectomy (RC), and pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) (2, 3). However, RC is a highly morbid procedure, especially for elderly patients with poor performance status, with a perioperative complication and 90-d mortality rates of 47.2% and 9.35-10.6%, respectively (4). Studies have shown that approximately 49% of MIBC patients opt for bladder preservation therapies (BPT) due to decreased post-surgical quality of life and reluctance to change the mode of urination (5). Therefore, BPT is an important treatment in clinical practice, especialy in those with high risk of perioperative complication and mortality, or unwilling to receive RC.
The trimodality therapy (TMT) is currently the most evidence-based bladder-preserving treatment regimen with the strongest backing from clinical studies. This regimen includes three components: maximal transurethral resection of bladder tumor (mTURBT), systemic chemotherapy, and local radiation therapy. In recent years, immune therapy has achieved satisfactory results in clinical trials for tumor treatment, and it has gradually become a second-line or even first-line treatment option for bladder cancer (3). For MIBC patients who are intolerant or unwilling to receive RC, the use of immune therapy combined with bladder preservation treatment has gradually become a viable treatment option. In this article, we report on a case of a cT2N0M0 Bladder cancer patient who was intolerant to chemotherapy and was treated with toripalimab as a single-agent bladder preservation therapy for three cycles. After 15 months of treatment, a clinical complete response(cCR) was achieved.
2 Case report
2.1 Medical history and diagnosis
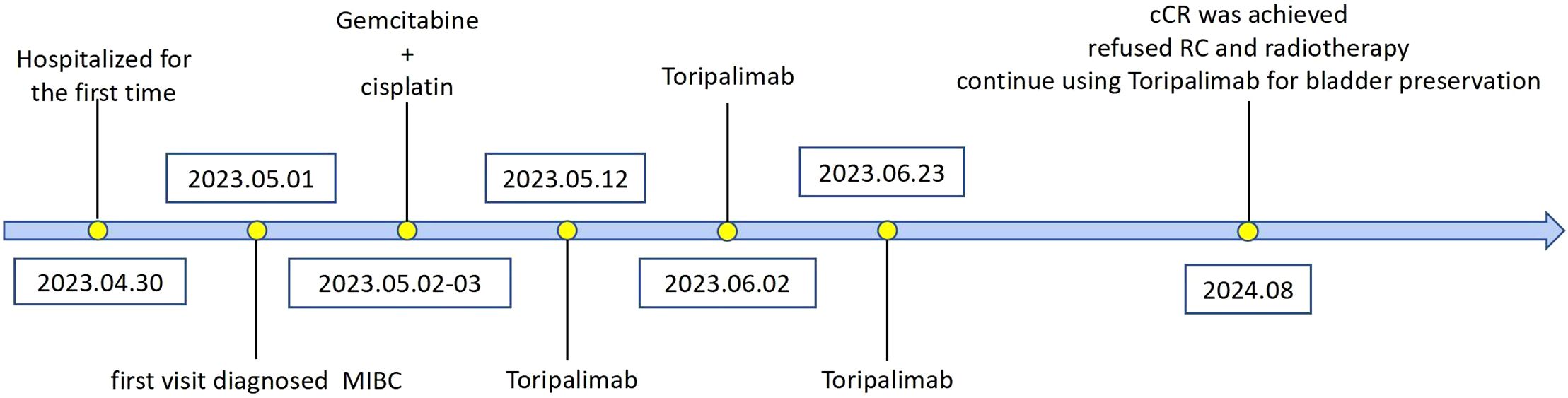
A 71-year-old male patient, with a history of smoking but currently quit, has no family history of cancer, a history of hypertension, and is without a history of diabetes or heart disease. He presented to our hospital with intermittent gross hematuria lasting over a year on April 30th, 2023. Initial physical examination upon admission showed no significant abnormalities.Urine routine examination revealed a red blood cell count of 211.2/ul; serum creatinine was 86umol/L; peripheral blood lymphocyte examination showed a percentage of 30.3% for the helper/inducer T-lymphocyte CD4+ and 53.1% for the suppressor/T-toxic T-lymphocyte CD8+. ECG, cardiac ultrasound, and head and lung CT scans showed no significant abnormalities. Enhanced abdominal CT (Figures 1A, B) revealed thickening of the posterior bladder wall with multiple irregular masses, approximately 4.4*2.6cm in size, suggestive of bladder malignancy. There were also multiple kidney stones and multiple liver cysts. Cystoscopy showed multiple cauliflower-like lesions on the left posterior bladder wall, with the largest tumor measuring approximately 4.5cm, accompanied by surface necrosis and bleeding. The left ureteral opening could not be explored. Pathological biopsy of the tumor revealed low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma. Immunohistochemical (IHC)staining (Figures 2A–C) showed PD-L1 (TPS<1%, CPS<1), CD8+ T (60% positive). The clinical diagnosis was bladder cancer at stage T2N0M0.
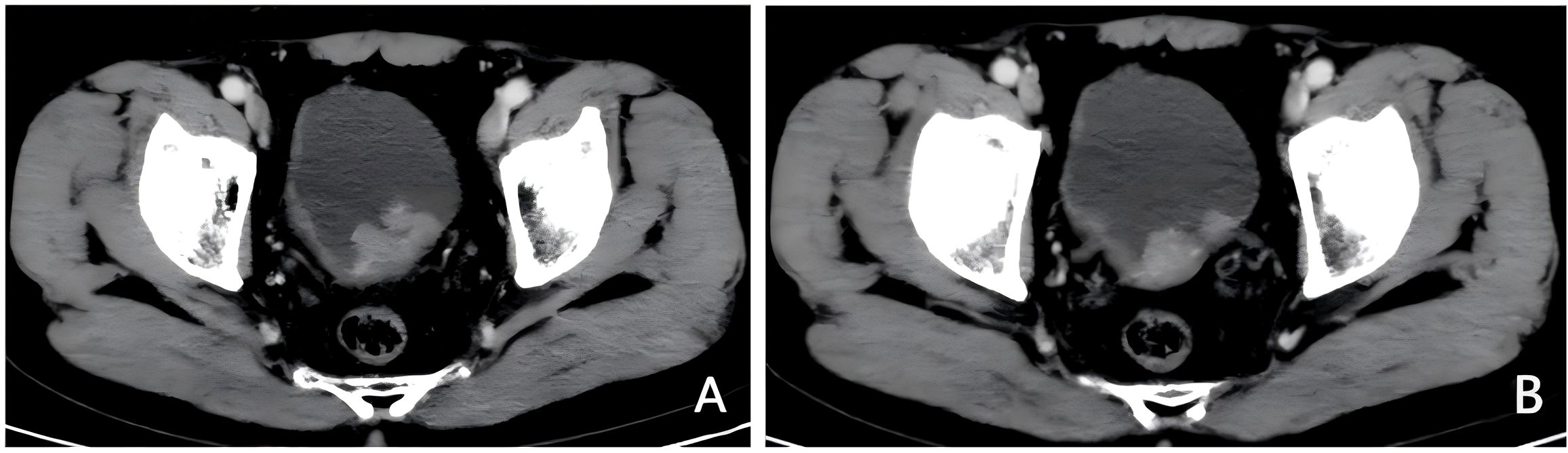
Figure 1. Imaging examination before treatment. (A, B) Pre-treatment enhanced CT, bladder posterior wall thickening with multiple irregular masses, approximately 4.4*2.6cm in size.
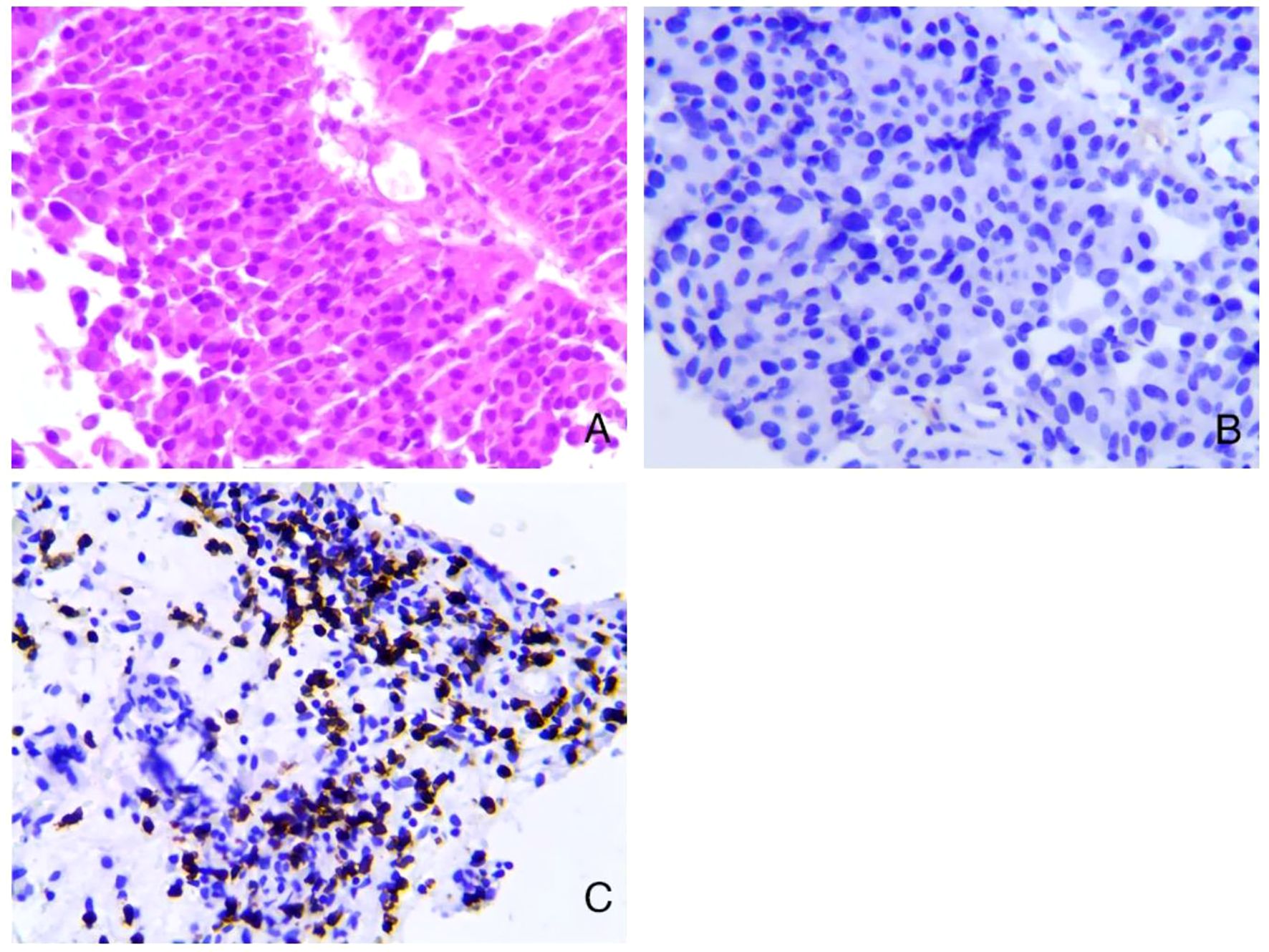
Figure 2. Pathological results before treatment. (A) Low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma (HE staining, 200X). (B) PD-L1 negative control (E1L3N, 200X). (C) CD8+ T 60% positive (IHC, 200X).
2.2 Treatment and results
The patient was presented with the following treatment options during initial counseling: 1. Maximal TURBT followed by adjuvant therapy, 2. Radical cystectomy (RC) or 3. Neoadjuvant therapy followed by reassessment for bladder preservation (with maximal TURBT or RC based on response). The patient initially opted for neoadjuvant therapy followed by radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Therefore, the patient’s initial plan was to undergo GC protocol neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy. The first cycle of GC protocol chemotherapy began on May 2nd, 2023. However, due to severe gastrointestinal reactions including frequent vomiting and loss of appetite after cisplatin use (Grade 3 according to CTCAE 5.0), the patient’s chemotherapy was discontinued. We recommended that the patient undergo radical surgery or switch to neoadjuvant immunotherapy. After discussing the treatment plan and associated risks with the patient, the patient opted for neoadjuvant immunotherapy. On May 12th, the neoadjuvant treatment plan was changed to immune therapy with Toripalimab (produced by Shanghai Junshi Biosciences Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., with a drug approval number of S20191003). The treatment involved a 240mg dose of Toripalimab diluted in 100ml of normal saline, administered as a slow intravenous infusion once every 3 weeks. The patient showed no special adverse reactions during the observation period.
After receiving Toripalimab for three cycles, the patient’s hematuria symptoms disappeared, and the patient did not return to the hospital for further treatment. The patient returned to our hospital for a review on August 4th, 2024. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the chest and abdomen (Figures 3A, B) showed that multiple masses on the posterior wall of the bladder had disappeared compared to previous images. On August 6th, under anesthesia, the patient underwent cystoscopy and multiple mucosal biopsies, which revealed that the bladder tumor had disappeared. The pathological results showed chronic inflammation of the bladder mucosa with focal calcification. The patient achieved cCR after immunotherapy. We recommended that the patient could subsequently undergo either radical surgery or bladder-preserving therapy. Given the satisfactory response to immunotherapy and the patient’s strong preference for maintaining a high quality of life, he opted for bladder-preserving treatment. It was recommended that the patient undergo radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy. However, the patient was unable to accept radiotherapy. The treatment plan was therefore adjusted to continue using Toripalimab for bladder preservation, with cystoscopy and CT scans to be performed every three months for follow-up. Evolution of these different treatments is represented in Figure 4.
Figure 3. Enhanced CT examination after 15 months of immunotherapy. (A, B) Multiple masses on the posterior wall of the bladder have disappeared compared to previous images.
3 Discussion
MIBC is a fatal malignancy with a 5-year survival rate of 50% (6). The currently recommended standard treatment by major guidelines involves neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on cisplatin, followed by RC. Due to the decreased quality of life after RC surgery, some patients have a strong desire for BPT. According to data from the National Cancer Database of the United States, out of 28,691 patients diagnosed with MIBC between 2004 and 2008, only less than half of the MIBC patients received RC, while nearly half of them opted for BPT treatment (5). A crucial focus in the implementation of BPT is whether it can achieve a survival rate comparable to or matching the current RC scheme. Studies have shown that there is no significant difference in long-term survival between the TMT scheme and RC (7, 8). Hu’s study suggests that patients who achieve pathological complete response after neoadjuvant treatments plus maximal transurethral resection of the bladder tumor may be safe to receive bladder preservation therapy (9). These studies provide evidence support for the clinical application of comprehensive bladder-preserving treatment, at the same time, it also emphasizes the important role of maximum TURBT in bladder preservation therapy.
On the other hand, the proportion of neoadjuvant treatment is continuously increasing in patients undergoing RC (10). Approximately 10%-40% of patients can achieve cCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Studies have shown that the 5-year survival rate of patients with cCR who proceed with RC can exceed 90% (11). However, some cCR patients, whose tumors are no longer visible, refuse to proceed with the original plan of RC and opt for bladder-preserving treatment. Mazza found that even with close follow-up after cCR from neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the 5-year survival rate can still reach 86%, and the recurrence-free survival rate exceeds 60% (12). Preoperative neoadjuvant treatment with immune drugs alone or in combination with other agents increases the pathological complete response (pCR) rate and pathological downstaging rate in MIBC. Compared to chemotherapy, most immune treatment-related adverse reactions are grade 1-2, providing a safer and more effective treatment option for MIBC patients who are elderly, weak, or intolerant to chemotherapy. To benefit chemotherapy-intolerant MIBC patients from neoadjuvant treatment, a multicenter phase II clinical trial on Atezolizumab (ABACUS study) showed that the overall pCR rate was 31%, with a 1-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) rate of 79%. In PD-L1-positive patients, the pCR rate reached 37%, with 54% of patients having a pathological stage downgraded to NMIBC, and a 1-year RFS rate of 75%. The expression of PD-LI does not have a statistically significant difference in prognosis. Additionally, researchers found that high expression of CD8 before treatment is associated with 40% CRP and an 85% 1-year survival rate in the CD8+ population (13). Another single-arm phase II clinical trial on Pembrolizumab (PURE-01 study) showed that the overall pCR rate was 37%, with 55% of patients achieving tumor downstaging. In multivariate logistic regression, PD-LI CPS is an independent risk factor for achieving PT0 and PT ≤ 1 after immunotherapy for MIBC (14). Additionally, it is noteworthy that in this study, two patients refused RC after the achievement of a radiological complete response. They did not receive further treatment at +6 and +3 months of follow-up, yet showed no disease recurrence or progression. This observation suggests the potential feasibility of bladder-preserving therapy for bladder cancer patients who achieve pCR or cCR following PD-L1 therapy.
Our study reports on a case of a MIBC patient who was intolerant to chemotherapy and was treated with a single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitor for three cycles, the safety profile of Toripalimab was favorable, with no grade 3-4 adverse events. After 15 months of treatment, the patient achieved cCR with satisfactory treatment results and was then switched to bladder-preserving treatment. The patient’s pathological IHC showed PD-L1 negative (TPS <1%, CPS <1%) and did not undergo mTURBT, which is a rare phenomenon. There are several possibilities that may explain this phenomenon:
First, various solid tumors can suppress the tumor microenvironment and avoid being lysed by lymphocytes through the expression of PD-L1 binding to PD1 on the surface of T cells. However, current PD-L1 detection based on IHC has problems not only in determining which tumor tissues respond to immune therapy based on anti-PD-1/PD-L1 but also in determining which individual patients may benefit from treatment (15). Hu’s study suggests that there was no significant difference between response and resistance samples regarding the infiltration level of tumor-associated immune cells and the expression of PD-L1 and PD-1 (9). PD-L1 as a biomarker remains controversial mainly because it cannot accurately predict individual treatment responses (15, 16).
Secondly, CD8+ T cells (cytotoxic T lymphocytes, CTL) are the preferred immune cells targeting tumors (17). They kill tumor cells by releasing granules or inducing FasL-mediated apoptosis and release interferon-γ (IFNγ) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) to induce tumor cell cytotoxicity (18). Naito’s study showed that the aggregation of CD8+ T cells in colon cancer predicts improved patient survival (19). Follow-up studies on ovarian cancer, melanoma, and colon cancer have further shown that the proportion and distribution of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and Treg cells are critical determinants of prognosis (20–23). Robert’s study suggests that the type and density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are better predictors of patient outcome compared to pathological stage and oncogene expression (24). Recent study shows that the number of T/NK cells of neoadjuvant ICB(NICB) resistance group was smaller than that of NICB response group. Especially, the proportions of CD8+ T cells and NK cells were lower in NICB resistance group, which highlighted the critical role of CD8+ T cells and NK cells for NICB response (9). In addition, lower clinical stage (T2N0M0), pure urothelial carcinoma (UC) histology, cell cycle subtype were, combine immunotherapy with targeted therapy significantly associated with higher pathological response rates (9, 25).
Although the case reported in this study was negative for PD-L1 expression, it exhibited strong CD8+ T lymphocyte infiltration, the clinical stage was T2N0M0, and the tumor was a pure UC. These factors may be the primary reasons for the satisfactory therapeutic response to PD-1 inhibitor in this case.
However, although this patient achieved satisfactory therapeutic outcomes with neoadjuvant treatment, clinical practice demonstrates that not all patients respond equally to this regimen. A significant proportion of patients fail to derive clinical benefit from such treatment approaches. Therefore, when making therapeutic decisions, clinicians should carefully consider cost-effectiveness implications, particularly given the substantial financial burden associated with immunotherapy. As highlighted by Contieri, the high cost of these treatments often not covered by health insurance in various countries and regions poses considerable challenges for patients. More comprehensive cost-effectiveness analyses are warranted to establish optimal and sustainable treatment strategies for future clinical applications (26).
4 Conclusion
In summary, for MIBC patients who are intolerant to chemotherapy, immunotherapy for bladder preservation is a viable treatment option. Patients with PD-L1 negative but CD8+ T cell positive tumor infiltration can also benefit from PD-L1 inhibitor treatment and even achieve cCR to preserve the bladder. Although this treatment regimen demonstrated good safety and effectiveness in this case, as a single-case report, we cannot rule out accidental and individual differences. Further studies are needed to explore the efficacy and indications of immunotherapy in bladder-preserving treatment for MIBC, providing better treatment options for patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The requirement of ethical approval was waived by Medical Ethics Review Committee of Dehong People’s Hospital, Dehong, Yunnan, China for the studies involving humans because Medical Ethics Review Committee of Dehong People’s Hospital, Dehong, Yunnan, China. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
ZY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing. JL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. XW: Writing – review & editing. JJ: Writing – review & editing. JP: Writing – review & editing. XZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/CAAC.21660
2. Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Compérat EM, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Eur urol. (2017) 71:447–61. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.041
3. Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, Compérat EM, Cowan NC, Gakis G, et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur urol. (2021) 79:82–104. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.055
4. Ramani VA, Maddineni SB, Grey BR, and Clarke NW. Differential complication rates following radical cystectomy in the irradiated and nonirradiated pelvis. Eur urol. (2010) 57:1058–63. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.12.002
5. Gray PJ, Fedewa SA, Shipley WU, Efstathiou JA, Lin CC, Zietman AL, et al. Use of potentially curative therapies for muscle-invasive bladder cancer in the United States: results from the National Cancer Data Base. Eur urol. (2013) 63:823–9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.11.015
6. Stein JP and Skinner DG. Radical cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer: long-term results of a standard procedure. World J urol. (2006) 24:296–304. doi: 10.1007/s00345-006-0061-7
7. Giacalone NJ, Shipley WU, Clayman RH, Niemierko A, Drumm M, Heney NM, et al. Long-term outcomes after bladder-preserving tri-modality therapy for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer: an updated analysis of the Massachusetts General Hospital experience. Eur urol. (2017) 71:952–60. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.12.020
8. Arcangeli G, Strigari L, and Arcangeli S. Radical cystectomy versus organ-sparing trimodality treatment in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review of clinical trials. Crit Rev oncology/hematol. (2015) 95:387–96. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.04.006
9. Hu J, Chen J, Ou Z, Chen H, Liu Z, Chen M, et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and combination therapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A multi-center real-world retrospective study. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3:100785. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100785
10. Hermans TJ, van de Putte EE, Horenblas S, Lemmens V, Aben K, van der Heijden MS, et al. Perioperative treatment and radical cystectomy for bladder cancer—a population based trend analysis of 10,338 patients in the Netherlands. Eur J Cancer. (2016) 54:18–26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.11.006
11. Peyton CC, Tang D, Reich RR, Azizi M, Chipollini J, Pow-Sang JM, et al. Downstaging and survival outcomes associated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens among patients treated with cystectomy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2018) 4:1535–42. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3542
12. Mazza P, Moran GW, Li G, Robins DJ, Matulay JT, Herr HW, et al. Conservative management following complete clinical response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy of muscle invasive bladder cancer: contemporary outcomes of a multi-institutional cohort study. J urol. (2018) 200:1005–13. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.05.078
13. Powles T, Kockx M, Rodriguez-Vida A, Duran I, Crabb SJ, van der Heijden MS, et al. Clinical efficacy and biomarker analysis of neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial. Nat Med. (2019) 25:1706–14. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0628-7
14. Necchi A, Raggi D, Gallina A, Madison R, Colecchia M, Luciano R, et al. Updated results of PURE-01 with preliminary activity of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in patients with muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma with variant histologies. Eur urol. (2020) 4):439–46. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.10.026
15. Patel SP and Kurzrock R. PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. (2015) 14:847–56. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0983
16. Postow MA, Cardona DM, Taube JM, Anders RA, Taylor CR, Wolchok JD, et al. Peripheral and tumor immune correlates in patients with advanced melanoma treated with nivolumab (anti-PD-1, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) monotherapy or in combination with ipilimumab. J Trans Med. (2014) 12:2443–54. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-S1-O8
17. Waldman AD, Fritz JM, and Lenardo MJ. A guide to cancer immunotherapy: from T cell basic science to clinical practice. Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:651–68. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0306-5
18. Hoekstra ME, Vijver SV, and Schumacher TN. Modulation of the tumor micro-environment by CD8+ T cell-derived cytokines. Curr Opin Immunol. (2021) 69:65–71. doi: 10.1016/J.COI.2021.03.016
19. Naito Y, Saito K, Shiiba K, Ohuchi A, Saigenji K, Nagura H, et al. CD8+ T cells infiltrated within cancer cell nests as a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. (1998) 58:3491–4.
20. Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, et al. Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2005) 102:18538–43. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.0509182102
21. van Houdt IS, Sluijter BJ, Moesbergen LM, Vos WM, de Gruijl TD, Molenkamp BG, et al. Favorable outcome in clinically stage II melanoma patients is associated with the presence of activated tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes and preserved MHC class I antigen expression. Int J cancer. (2008) 123:609–15. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23543
22. Pagès F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R, et al. Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. (2005) 353:2654–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa051424
23. Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. (2006) 313:1960–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1129139
24. Schreiber RD, Old LJ, and Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. (2011) 331:1565–70. doi: 10.1126/science.1203486
25. Hu J, Yan L, Liu J, Chen M, Liu P, Deng D, et al. Efficacy and biomarker analysis of neoadjuvant disitamab vedotin (RC48-ADC) combined immunotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A multi-center real-world study. iMeta. (2025) 4:e70033. doi: 10.1002/imt2.70033
Keywords: muscle-invasive bladder cancer, bladder-preserving therapy, immune therapy, Toripalimab, PD-L1, CD8+ T lymphocytes
Citation: Yang Z, Liu Y, Li J, Wang X, Pan J, Jiang J and Zhang X (2025) Toripalimab treatment of bladder-preserving therapy for locally advanced bladder cancer: a case report. Front. Oncol. 15:1581452. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1581452
Received: 22 February 2025; Accepted: 30 May 2025;
Published: 17 June 2025.
Edited by:
Sanja Stifter-Vretenar, Skejby Sygehus, DenmarkCopyright © 2025 Yang, Liu, Li, Wang, Pan, Jiang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xingming Zhang, amFybWluQHNjdS5lZHUuY24=
 Zhiyun Yang
Zhiyun Yang Yidao Liu1
Yidao Liu1 Ji Li
Ji Li