- 1Department of Digestive Surgery, Xijing Hospital of Digestive Diseases, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Holistic Integrative Management of Gastrointestinal Cancers and National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases, Xijing Hospital of Digestive Diseases, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, China
- 3Faculty of Arts, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is the most common mesenchymal tumor. Imatinib, as a receptor-type tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), becomes a first-line drug for adjuvant therapy and prognosis. However, patients are facing with the problem of primary and secondary drug resistance when using imatinib, which affects the effect of imatinib. Thus, it is particularly important to explore the mechanism of drug resistance. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination process have been proofed to performance as posttranslational modifications (PTMs) to influence the occurrence and progression of most tumors. Hence, we attach importance to these mechanisms and found that GIST resistance may be related to ubiquitination and deubiquitination in regulating exosome secretion, autophagy, apoptosis and ferroptosis. Through clarifying these connections, this review aims to offers insights and hope for therapeutic advancements of imatinib-resistant GIST patients and the use of specific ubiquitin modifications as markers in the future.
1 Introduction
GISTs is a type of tumor that originates from the stromal cells of Cajal. The most common driver mutations in GISTs occur in kinase insert domain receptor (KIT) (60-70%) and platelet—derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) (10-15%) (1). In the case of KIT, the binding of KIT ligands and stem cell factors (SCFs) to the extracellular domain of the receptor leads to its dimerization and activation of the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain and receptor through autophosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues (2). As for PDGFRA, activation of this type is intrinsically driven by acquired mutations causing conformational changes. Especially for mutations which cluster in critical domains (exons 12/14/18) that disrupt auto-inhibition and stabilize active states (1).
Currently, surgical resection is the most common treatment for resectable GISTs, and about 60% of patients can be cured by surgery (3). However, for patients with advanced metastatic GISTs and locally advanced unresectable GISTs, imatinib plays an important role. Imatinib was originally designed for breakpoint cluster region-Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene (BCR-ABL) translocation in chronic myeloid leukemia and has subsequently shown to be effective against KIT and PDGFRA tyrosine kinases in GIST (4).Although more than 80% of patients with GIST can benefit from imatinib, many patients develop imatinib resistance after treatment. Universally acknowledged mechanisms include: decreased drug consuming, metabolism and degradation of drugs, evasion of apoptosis, mutations in the drug target proteins (5). Resistance to imatinib in GIST patients can be divided into primary resistance and secondary resistance. Primary drug resistance is that GIST has no effect on imatinib at the beginning, which is mainly related to GIST genotype. For example: the mutation of PDGFRA exon 18 D842V can mediate primary imatinib resistance (6). About 50% advanced GISTs developed tumor progression after the initial efficacy of imatinib after 2 years of medication which is defined as secondary resistance (7). Ubiquitination is an important posttranslational modification (PTMs) in eukaryotes that begins with the attachment of a single ubiquitin molecule to a substrate lysine residue to mediate biochemical reactions such as organelle recognition and protein degradation (8). In contrast, deubiquitination is mediated by a family of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), which specifically recognize ubiquitin chains for deubiquitination (9, 10). This review focuses on the current status of treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and sorts out the relationship between ubiquitination or deubiquitination modifications and GIST progression as well as imatinib resistance.
2 Current treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
2.1 Surgical management strategies for GISTs
From a surgical perspective, the goal of resection is to ensure surgical margins are negative and prevent the rupture of tumors to avoid recurrence (11, 12). For patients with large tumors (>5 cm), those with invasion of adjacent organs, or metastatic patients, tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) targeted therapy (such as imatinib) is preferred over immediate surgery. Proper surgical treatments can be applied after reaching the maximum response at 6 to 12 months (1). For micro/small GISTs (<2 cm), endoscopic ultrasound surveillance (annually) is recommended for gastric/duodenal lesions, while rectal lesions mandate resection regardless of size. In wild-type GISTs, SDH-deficient cases require resection of visible lesions with frequent lymph node dissection, whereas NF1-associated GISTs, given their indolent biology, only require surgery for symptomatic lesions without radical intent (3). Notably, all postoperative intermediate-to-high-risk GIST patients—excluding those harboring the PDGFRA D842V mutation—should undergo prolonged adjuvant TKI therapy (imatinib 400 mg/day for 3 years).
2.2 Pharmacological interventions for GISTs
Patients with metastatic disease should not be operated on earlier but being treated with TKIs first. Over the past 20 years, TKIs have been recognized as the preferred first-line treatment based on a series of clinical trials. Additionally, several active therapies corresponding to different symptoms have been identified, and imatinib as the main drug have been developed (1). Acting as TKIs, imatinib revokes the KIT signaling mainly through binding onto the ATP-binding site. Prior to imatinib treatment, 50 percent of patients who underwent surgical resection of GIST relapsed within five years, with a 50 percent five-year survival rate (13, 14). Additionally, the partiality of imatinib to this site depends on the mutation of receptor, which explains why imatinib improves prognosis and survival outcomes, but rarely directly cured due to the emergence of resistant cells within the tumor (15). However, the molecular mechanisms of imatinib resistance have not been elucidated. Despite from playing a significant role in the prognostic level of patients and controlling the progression of the disease, imatinib appears to be feasible and safe when used during preoperative treatment, as it does not lead to an increase in postoperative complications (16). Other TKIs used in treating GISTs includes sunitinib (a second-line drug against KIT exon 9 mutations (17)) and regorafenib (demonstrate significant efficacy in GISTs which had progressed after failure of both imatinib and sunitinib (18)).
2.3 Summary of changes in the way of managing GISTs
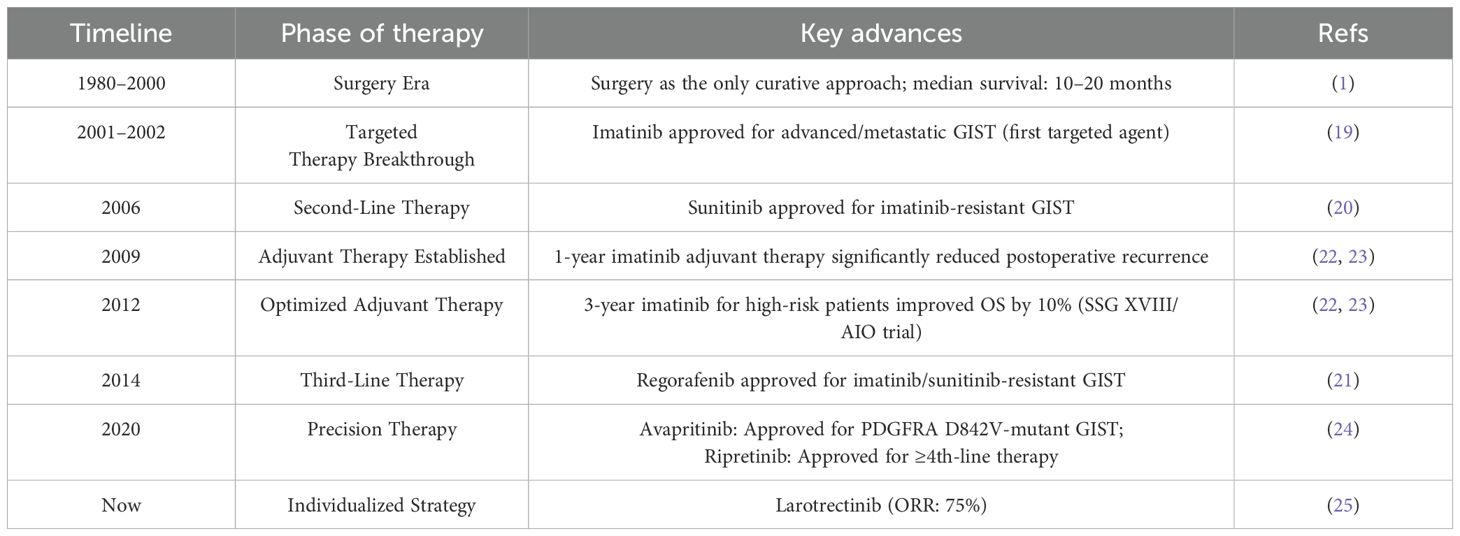
The timeline highlights pivotal transitions from surgical monotherapy (1980–2000) to molecularly targeted strategies (Table 1). Key milestones begin with the introduction of imatinib (2001–2002), which revolutionized metastatic GIST treatment (19). This was followed by the sequential approval of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for resistant disease—sunitinib in 2006 (20) and regorafenib in 2014 (21). Concurrently, optimization of adjuvant imatinib duration evolved from 1-year (2009) to 3-year regimens (2012), significantly improving survival in high-risk resected GIST (22, 23). The precision therapy era emerged in 2020 with mutation-specific agents, including avapritinib for PDGFRA D842V-mutant tumors and ripretinib for ≥fourth-line therapy (24). Further advancing individualized management, molecular subtype-directed approaches such as larotrectinib for NTRK fusion-positive GIST demonstrate targeted efficacy (25). Collectively, these advances transformed survival outcomes from a median of 10–20 months in the surgery era to multi-year survival with contemporary targeted regimens.
3 GISTs disease progression with ubiquitination and deubiquitination modifications
Previous studies have found the unique and definitive role that ubiquitin0061tion and deubiquitination have attended in the progression of many diseases as well as tumors. It is well acknowledged that through competing ubiquitin conjugation and deubiquitination that controls both proteasomal degradation and signaling complex formation, this system can control many classic pathways, for example TNF signaling pathway (26). In this way, it participates in various disease progression thus arising huge concern on targeting specific proteins working with UB molecule to seek for a better therapy. Among E1, E2, E3 and DUBs, the DUBs appear to be more misregulated in many tumors and play critical roles in tumorigenesis as well as progression (27). Among tumors, osteosarcoma who origins from mesenchymal tissues have been proofed to relate tightly with E3 ligases, containing high amounts of cellular processes and signaling pathways (28). Additionally, UCHL1, part of the DUBs, can promote osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion while leading to the development of other mesenchymal tumors like uterine leiomyoma (29, 30). There have already been varieties of treatments targeting ubiquitination and deubiquitination modifications (Table 2). Such as PARP inhibitors (PARPi) in germline BRCA mutated (gBRCAm) breast cancer (31). Combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapy special protein inhibitors have received good results on improving overall survival rate while kind of avoiding facing the stage of TKI resistance of lung cancer patients (32). When it comes to the progression of GISTs, ubiquitination and deubiquitination modifications can control apoptotic and ferroptosis through different proteins and cause GIST to develop and deteriorate.
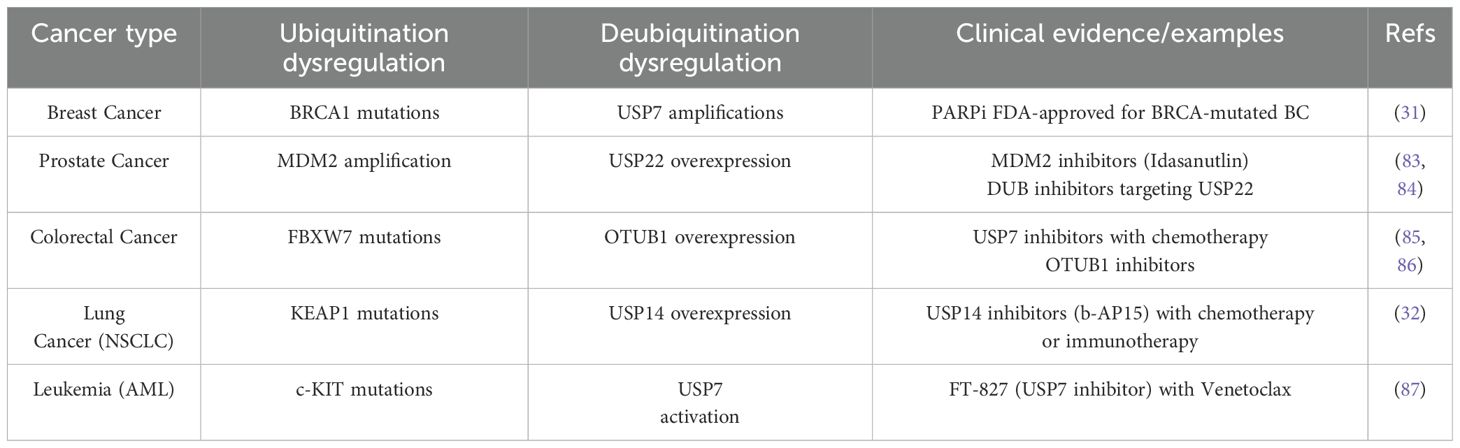
Table 2. Dysregulation of ubiquitination/deubiquitination in major cancer types and therapeutic implications.
3.1 General mechanisms of ubiquitination and deubiquitination modifications
Ubiquitination is the covalent attachment of ubiquitin as a small molecule protein modifier to substrate proteins, which is involved in almost all cellular processes by mediating the degradation of proteins. The ubiquitin molecule is characterized by seven lysine residues that can continue to be used to link the ubiquitin molecule or to phosphorylation and acetylation, and to deliver more complex intracellular signals through the modification of the ubiquitin molecule (33). During ubiquitination process, ubiquitin molecules (Ub) are expressed as head-tail fusions with ribosomal proteins (RPs), which are then processed into free Ub by deubiquitinating enzyme (DUBs), exposing their characteristic diglycine C-terminus.
Subsequently, the ubiquitin protein is processed by E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme, E2 ubiquitin-conjugated enzyme and E3 ubiquitin ligase to be gradually transferred from E1 to the target protein (Figure 1) (34). At the same time, the E4 molecule, a persistent synthesis factor that is itself E3 but has activity that helps and shapes the formation of the chain can synergize with another E3 molecule to promote the formation of the Ub chain (35).
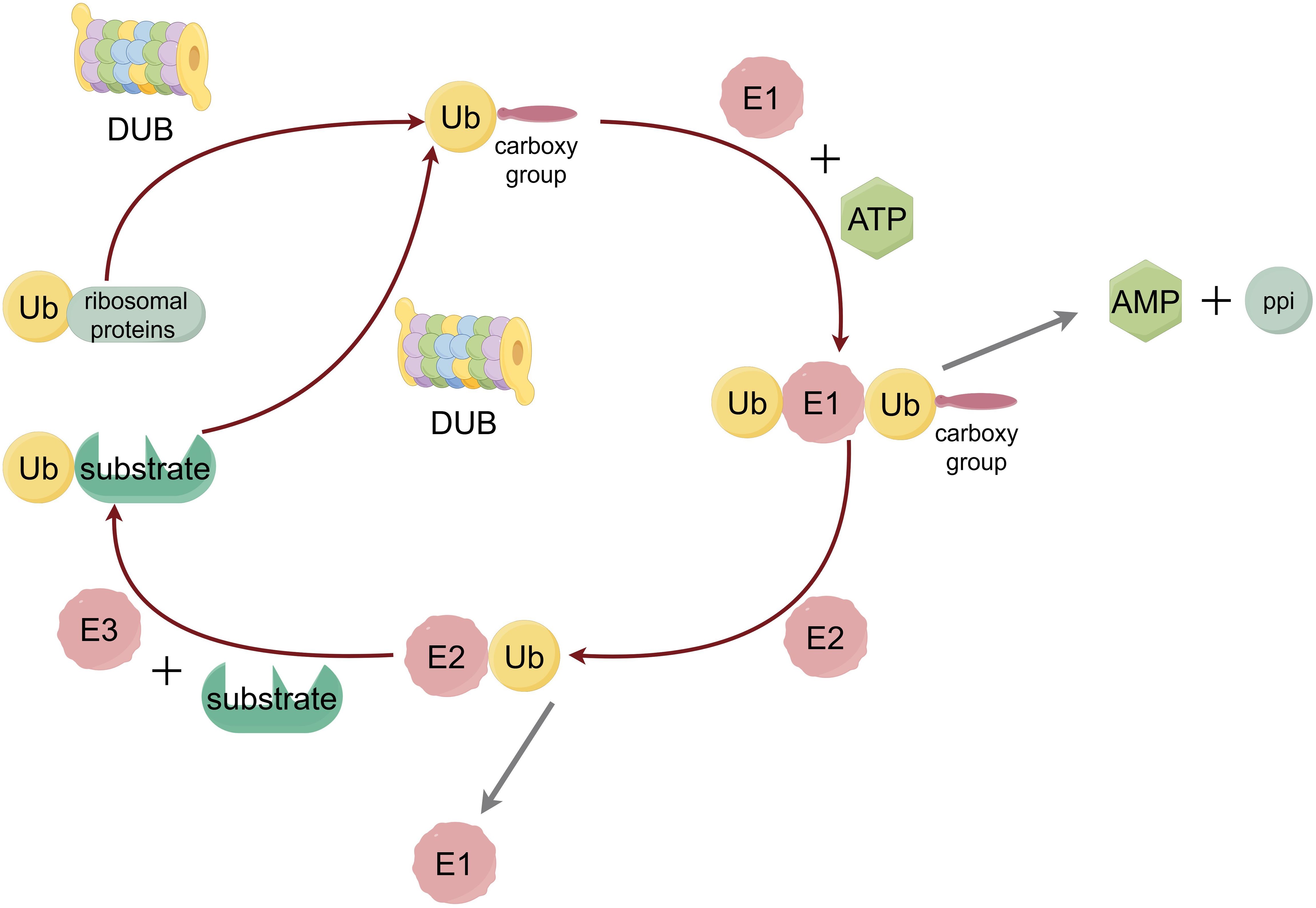
Figure 1. The process of ubiquitination. Ubiquitin protein is adenylytized at the C-terminal by E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme, and then transferred from the cysteine residue at the active site of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugated enzyme to the lysine residue of the substrate protein, which is linked to the isopeptide bond between the lysine residue in the substrate protein by the action of E3 ubiquitin ligase.
The process of deubiquitination of proteins is mediated by DUBs, which represent a large class of proteases that are specific for Ub, Ub conjugates, and Ub chains (36). There are five main types of deubiquitinating enzymes, namely: JAMM (JAB 1/MPN/Mov 34) domain DUB, UCH (Ub C-terminal hydrolase), USP (Ub-specific protease), OTU (ovarian tumor associated proteinase) and Josephin domain DUB (34). Inside the cell, the ubiquitination system regulates and participates in numerous biochemical reactions. Short-lived and soluble misfolded/unfolded proteins can be targeted and eliminated by the ubiquitin proteasome system (37). Acting as the key to the dynamic regulation of programmed cell death, ubiquitination can modulate autophagy. Such as reversible ubiquitination of core autophagy-inducible factors as subunits of the ULK1 and PI3K complexes, and has shown to be a common mechanism which turns on and off the autophagy process (38). Through participate into programmed cell death ubiquitination and deubiquitination may affect the TKI resistance which play roles by controlling certain mechanisms.
3.2 Elevated ubiquitination level of pro-apoptotic protein BIM in GIST suggests that it can affect disease progression
In most GISTs, c-KIT receptor tyrosine kinase is carcinogenic and being constitutively activated (1). Within this type of GISTs, tumors can evade apoptosis by upregulating the ubiquitination and phosphorylation levels of bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death (BIM) through transcriptional and post-translational mechanisms, which can lead to its degradation. Studies have shown that after imatinib treatment with the GIST 882 cell line, imatinib induces BIM transcription, while the mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway reduces the ubiquitination and phosphorylation levels of BIM through post-translational levels. The effect of imatinib ultimately leads to a rapid and sustained upregulation of the expression of the BIM molecule (Figure 2A), while other apoptotic factors do not show significant perturbation (39). This suggests that BIM upregulation can be used to trigger apoptosis through alternative therapies that inhibit c-KIT signaling. Such as frapine (40) which inhibits c-KIT transcription, and the heat shock protein 90 (HSP 90) inhibitor that targets c-KIT protein stability.
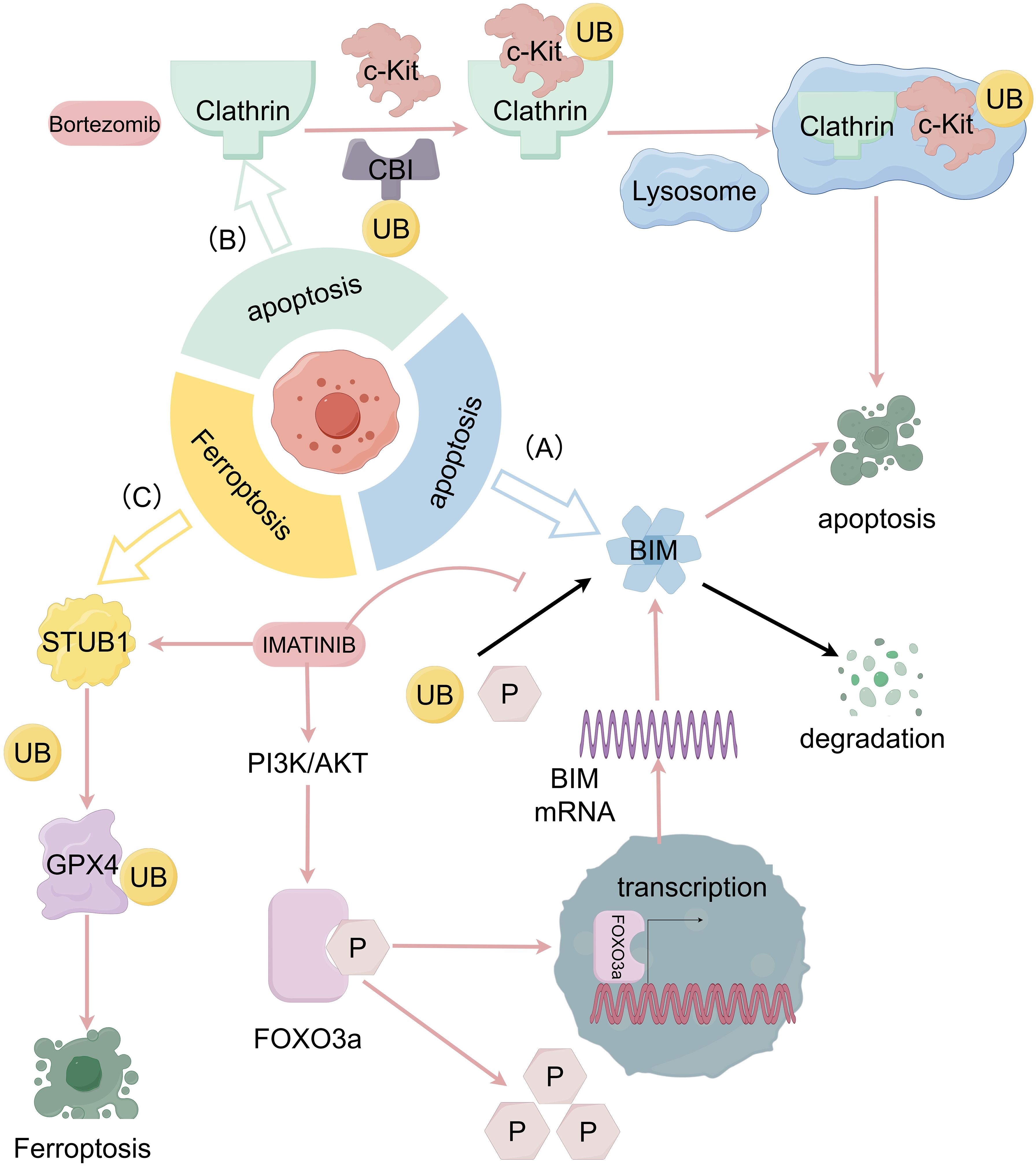
Figure 2. The relationship between GIST progression and ubiquitination and deubiquitination system. (A) Imatinib induces BIM transcription through the PI3K-AKT-FOXO 3a pathway and the ubiquitination and phosphorylation levels of BIM are also reduced through MAPK signaling pathway which prevent the degradation of BIM then cause the apoptosis of tumor cells. (B) With internalization of c-KIT engulfed by clathrin, Cbl can modify c-KIT which result in the c-KIT degradation in lysosomes and causes apoptosis of tumor cells as well. (C) Imatinib, in GIST can promote ubiquitination of the K191 site of GPX 4 by promoting the expression of STIP1 homology and u-box containing protein 1 (STUB 1), leading to degradation of GPX 4 protein and inducing ferroptosis.
3.3 E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl induces apoptosis in GIST cells by ubiquitination and degradation of internalized and engulfed c-KIT
The ubiquitin molecule with E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase and its mediated lysosomal pathways are generally involved in the degradation of membrane receptor proteins in the cell body (41). The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BOR) has shown to modulate the c-KIT-associated apoptosis cascade in leukemia cells by directly inducing c-KIT internalization and lysosome-induced degradation (42). This mechanism is also effective in GIST cells. By using dynasore (DY), an initiator protein inhibitor, to interfere with the formation of clathrin-mediated internalized coated vesicles, Ying Dong et al. demonstrated that KIT can be engulfed by clathrin-mediated internalization, followed by c-KIT degradation in lysosomes as a target protein modified by casitas B lymphoma-b (Cbl) (Figure 2B). PDGFRβ-dependent cell cycle arrest achieved with dasatinib and c-KIT internalization facilitated by bortezomib can be used in a coordinated combination to efficiently induce apoptosis in GIST cells (43).
3.4 Ubiquitination of GPX 4 inhabits the growth of tumor through inducing ferroptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent, non-apoptotic form of regulated cell death driven by lipid peroxidation (44). The main mechanism of ferroptosis lies on the inability to detoxify lipid hydroperoxides that leads to membrane rupture and cell death (45). Specifically, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX 4) is the only cellular enzyme capable of reducing lipid peroxides to lipids and has been used as a target for various ferroptosis inducers (46). Xiangfei Sun et al. found that imatinib in GISTs can promote ubiquitination of GPX 4, leading to degradation of GPX 4 protein and inducing ferroptosis (47) (Figure 2C). Among them, RAS-selective lethal 3 (RSL3)is an FDA-approved GPX 4-specific inhibitor that has shown to inhibit the growth, invasion, and metastasis of a variety of tumors (48). The combination of RSL3 and imatinib may also become a new therapeutic strategy.
4 Imatinib resistance with ubiquitination and deubiquitination of GISTs
As mentioned previously, the mechanism of GISTs imatinib resistance is quite complex, which in general can be divided into primary and secondary resistance. Primary resistance refers to the progression of tumors during the first six months of treatment, mainly seen in KIT exon 9 mutant GIST and PDGFRA exon 18 D842 V mutant GIST treated with 400 mg of imatinib per day, as well as wild-type (mainly SDH-deficient) GIST, accounting for 10%-14%. Secondary mutation acquired during treatment is secondary resistance, accounting for 40%-50% (49, 50). For primary resistance, mutations in KIT exon 9 lead to receptor dimerization, which may hinder the binding of tyrosine kinase receptors to imatinib (51). Acquired cis-mutations in the ATP-binding domain (encoded by exon 13 or 14 of KIT and exon 14 of PDGFRA) or activation loop (encoded by exon 17 of KIT and exon 18 of PDGFRA) are the main causes of secondary resistance to KIT-mutant and PDGFRA-mutant GIST (52).
For tumor cells with different exon mutations, even if the binding strength of imatinib and KIT receptors is excluded, differences in signaling pathways of their downstream effects are also related to imatinib resistance, resulting in very different therapeutic effects and drug resistance (53, 54). In the progression of GIST, downstream signal transduction pathways of KIT molecule include MAPK, phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase (PI3K), and Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathways. Activation of KIT and PDGFRA mutations results in ligand-independent dimerization, constitutive activation, and subsequent uncontrolled intracellular signaling and cell growth (55, 56). Among them, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways have been shown to play an important role in KIT signaling in GIST resistance (57). Bosbach et al. found that in a mouse model the inactivate of PI3K kinase binding site pY719 had a longer survival and did not develop GIST, suggesting this locus may recruit PI3K upon phosphorylation, and that GIST progression in mice can be reversed by inactivating it (58). Through a review of existing studies, we found that ubiquitination modification also plays an important role in GIST imatinib resistance by affecting the transmission of downstream signaling pathways, and may affect further adjuvant therapy of GIST by becoming a target of action drugs and tumor markers.
4.1 Ubiquitination system regulates exosome secretion leading to the transmission of imatinib resistance
In normal humans, the Ras-associated protein (Rab) controls vesicle trafficking by promoting organelle dynamics and the fusion of vesicles with receptor membranes (59). In GISTs, the Ras-related protein Rab-35 (RAB35) is also involved in regulating exosome secretion, thereby transporting special membrane pieces with imatinib resistance mutations through the GIST cells (60). In general, RAB35 is regulated by degradation in a ubiquitin-β proteasome system dependent manner (61), and further analysis of the type of demulti-ubiquitination on RAB35 protein shows that USP 32 (ubiquitin-specific protease 32) can effectively reduce the polyubiquitination of Lys 48 (K48) linkage of RAB35, but has no significant effect on the non-degradable Lys 63 (K63) linked polyubiquitination of RAB35. Finally, ETS variant transcription factor 1 (ETV 1), as a lineage-specific survival factor, can promote polycystic transport by regulating the expression and localization of RAB35 by USP32, thereby upregulating exosome secretion in GIST cells (Figure 3A) (60). As a result, exosomes secreted by imatinib resistance cells can enhance the ability for imatinib sensitive cells to resist imatinib (60, 62). Additionally, the severity of resistance transmission can depend on the amounts of exosomes and internalization by GISTs cells.
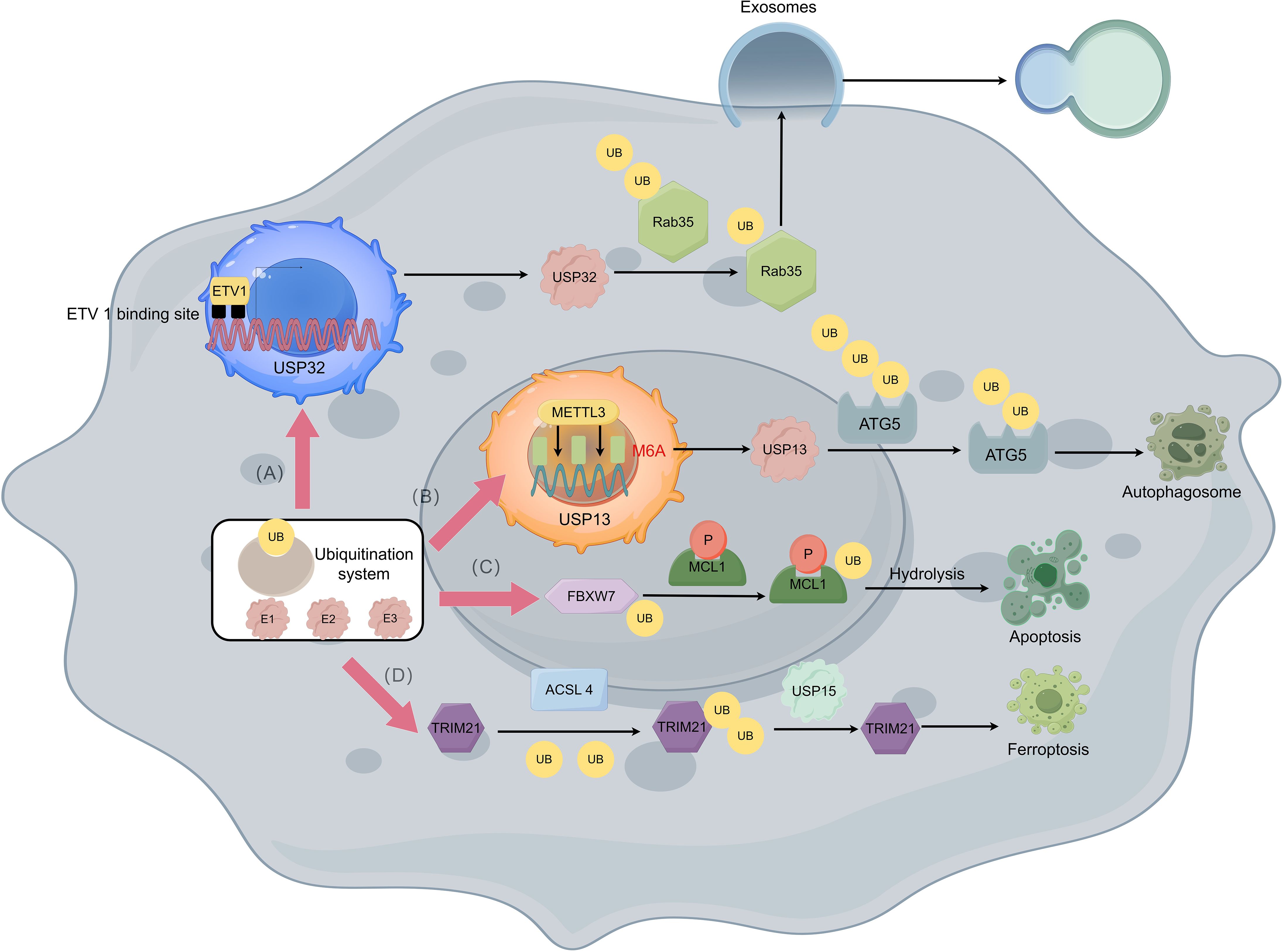
Figure 3. Imatinib resistance with the ubiquitination and deubiquitination of GISTs. (A) ETV1 can bind to two potential ETV 1 binding site upstream the USP32 promoter thus promoting polycystic transport by regulating the expression and localization of Rab35 through USP32 which can reduce the polyubiquitination of Rab35. With the help of Rab35, exosome secretion in GIST cells is upregulated which causes the resistance of imatinib in GIST cells to be transmitted. (B) Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) can read METTL3-mediated m6A modification thus stabilizing USP13 mRNA, while USP13 can work as a deubiquitination protein that deubiquitinate UB molecules attached to ATG5 and causes protective autophagy of GIST cells. (C) FBXW7 can target the phosphorylated MCL1 molecule which leads to the degradation of MCL1, thereby relieving the inhibition of apoptosis and showing increased sensitivity to imatinib. (D) TRIM21 promotes the degradation of ACSL 4 by using a K48-linked polyubiquitin chain to lead to drug resistance, while ubiquitin-specific protease 15 (USP 15) upregulates the stability of ACSL 4 molecules through its deubiquitination activity and promotes ferroptosis in GIST cells to against resistance.
4.2 Ubiquitination system regulates autophagy and imatinib resistance
USP 13 can affect imatinib resistance in GISTs by modulating the stability of autophagy-associated protein 5 (ATG5). USP 13 is an important member of the USP ubiquitin-specific processing enzyme subfamily, which controls the ubiquitination state of different substrates involved in multiple processes, thereby regulating cell cycle, autophagy, and metabolism (63, 64). This molecule and ATG5 are highly expressed in IM-resistant GIST cell lines, and USP13 has been found to potentially stabilize ATG5 by removing the K48-linked polyubiquitin chain at residue K5 (65). METTL3-mediated m6A modification maintains USP13 expression (66) thereby increasing the degree of imatinib resistance (67) (Figure 3B). By regulating the above links in the mechanism of action, the degree of protective autophagy of GIST cells can be attenuated by reducing the expression or effect of USP13, and the combination of imatinib on this basis may lead to better therapeutic effects.
4.3 Ubiquitination system regulates the cell cycle and imatinib resistance
F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 (FBXW7) can enhance the sensitivity of GIST-T1 cells to imatinib through inhibition of MCL1 (68). FBXW7 is a key tumor suppressor and cell cycle regulator, and proteasomal degradation is triggered in human cells through ubiquitination of proteins (69). Xiyu Wu et al. (68) found in GIST-T1 cells that MCL1 is involved in regulating the sensitivity of GIST-T1 cells to imatinib by inhibiting apoptosis. More specifically, FBXW7 can target the phosphorylated MCL1 molecule and perform ubiquitination modification, which leads to the degradation of MCL1, thereby relieving the inhibition of apoptosis and showing increased sensitivity to imatinib (Figure 3C).
In addition, similar studies suggest that bortezomib may also improve imatinib resistance through cell cycle regulation. Previous studies have shown that bortezomib induces KIT internalization and degradation by binding KIT to the ubiquitin protein ligase casitas B-cell lymphoma protein (CBL) in KIT-dependent GIST cells, thereby inducing apoptosis in GIST cells (43). The expression of cyclin D1 and the activity of Hippo/YAP signaling pathway were significantly increased in KIT-independent GIST cells (70).
4.4 Ubiquitination system regulates ferroptosis and imatinib resistance
As mentioned earlier, ferroptosis plays an important role in GIST disease progression, and ferroptosis has shown to play a key role in GIST resistance as well (71, 72). Acyl-CoA synthase 4 (ACSL 4), as a key enzyme in inducing ferroptosis can regulate lipid biosynthesis (73). By using the GPX4 inhibitor RSL3 as an inducer of ferroptosis, Zhiwei Cui et al. found that ACSL 4 expression was upregulated and GIST resistance was inhibited after the use of RSL3 in the GIST-T1 and GIST-882 cell lines (74). Further, in GIST-resistant cells, tripartite-motif protein 21 (TRIM21) promotes the degradation of ACSL 4. On the contrary, USP 15 can upregulate the stability of ACSL 4 molecules to promote ferroptosis in GIST cells (Figure 3D), thereby reducing drug resistance (74). Therefore, the activity of ACSL 4 molecule and its mediated ferroptosis show its potential as a future therapeutic target for GIST, whether by inhibiting the ubiquitination of TRIM21 or promoting the deubiquitination of USP 15.
5 Discussion
The existing mainstream treatment methods for gastrointestinal stromal tumors include conventional surgery and targeted drug therapy, among which tyrosine kinase inhibitors represented by imatinib are the most commonly used treatment strategies (1). Although new therapeutic ideas, have shown some therapeutic efficacy (75–78), the current focus of clinical and scientific research is still to deal with the drug resistance problem caused by the long-term use of imatinib. Imatinib has shown to be effective against KIT and PDGFRA tyrosine kinases in GISTs, and patients treated with imatinib are associated with primary resistance and secondary resistance. In exploring the treatment of GISTs, we found that ubiquitination and deubiquitination modifications play an important role in GIST progression and drug resistance by influencing the transmission of downstream signaling pathways.
In general, ubiquitination and deubiquitination, as important modification methods, have critical significance for the stability of protein molecules at the post-transcriptional level, and this mechanism can also regulate cell translation and transcription by affecting the stability of specific molecules. In gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), dysregulated ubiquitination drives pathogenesis: Elevated ubiquitination of pro-apoptotic protein BIM promotes its degradation, enabling apoptosis evasion. Imatinib counteracts this by suppressing MAPK signaling, reducing BIM ubiquitination and restoring its pro-apoptotic function. E3 ligase Cbl ubiquitinates internalized c-KIT receptors (activated oncogenic drivers in GIST), targeting them for lysosomal degradation. Combining proteasome inhibitor bortezomib with dasatinib enhances c-KIT degradation and apoptosis. Imatinib-induced GPX4 ubiquitination triggers ferroptosis (iron-dependent cell death via lipid peroxide accumulation) by degrading this key antioxidant enzyme. GPX4 inhibitors (RSL3) synergize with imatinib to amplify ferroptosis death. Collectively, targeting ubiquitination pathways (BIM stabilization, Cbl-mediated c-KIT degradation, and GPX4-driven ferroptosis) reveals promising therapeutic strategies against GIST.
Considering imatinib resistance, apoptosis and ferroptosis and abnormal autophagy cause the generation of imatinib resistance in GIST cells, and the regulation of these three mechanisms is expected to affect the drug resistance caused by mutations. Unlike apoptosis and ferroptosis, the inhibition of protective autophagy in GIST cells corresponds to a certain degree of controlling of drug resistance, while the promotion of apoptosis and ferroptosis through ubiquitination and deubiquitination pathways can reverse the increase of imatinib resistance in tumor cells caused by mutations (79, 80).
The intricate regulation of imatinib resistance in GISTs by ubiquitination pathways highlights several promising clinical strategies. Targeting USP32 or ETV1 could disrupt resistance-conferring exosome secretion, limiting its spread. USP13 inhibitors offer a direct route to block protective autophagy by destabilizing ATG5, sensitizing resistant cells. Enhancing FBXW7 activity or mimicking its effect could degrade MCL1, restoring apoptosis and imatinib sensitivity. Promoting ferroptosis by inhibiting TRIM21-mediated degradation or activating USP15 to stabilize ACSL4 represents a novel approach to kill resistant cells (74, 81). Critically, combining imatinib with agents targeting these specific ubiquitination nodes (deubiquitinase inhibitors, ferroptosis inducers like RSL3, or FBXW7 modulators) is a rational, multi-pronged strategy to overcome resistance and improve GIST treatment outcomes (68, 71, 82). It should be noted here that Ras-associated protein-mediated exosome secretion promotes the transmission of drug resistance between GIST cells, resulting in stubborn drug resistance that is more difficult to treat with (60). Considering a variety of benefit, this system still has lots to overcome to finally serve patients. Ubiquitin-related enzymes (USP32, USP13, TRIM21) typically regulate multiple substrates. Targeted inhibition may disrupt normal cellular functions, leading to unpredictable toxicity. Additionally, Ubiquitination pathways could intersect with other resistance mechanisms (BCL6-p53 axis). Isolated targeting of ubiquitination may be compromised by bypass signaling (p53 inactivation or KIT mutations), reducing efficacy. Most importantly, most studies remain confined to cell/animal models, lacking clinical verification. Real-time monitoring of dynamic ubiquitination modifications (dose-dependent effects of USP15 stabilizing ACSL4) is impractical, obscuring the therapeutic window. Furthermore, future studies can focus the ubiquitin–proteasome system of GIST to predict the progression of disease as well as the level of resistance to imatinib while trying to intercept the resistance to better help patients to restrict this tumor.
Author contributions
HH: Visualization, Writing – original draft. HL: Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing. SW: Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. JY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172973), Air Force Medical University clinical research program (No.2022LC2212), and the Innovative exploratory project of the State key Laboratory of Tumor Biology (CBSKL2022ZZ41).
Acknowledgments
Figure support was provided by Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Blay JY, Kang YK, Nishida T, and von Mehren M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:22. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00254-5
2. Antonescu CR. The gist paradigm: lessons for other kinase-driven cancers. J Pathol. (2011) 223:251–61. doi: 10.1002/path.2798
3. Joensuu H, Hohenberger P, and Corless CL. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet (London England). (2013) 382:973–83. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(13)60106-3
4. Al-Share B, Alloghbi A, Al Hallak MN, Uddin H, Azmi A, Mohammad RM, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: A review of current and emerging therapies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2021) 40:625–41. doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-09961-7
5. Narayanan S, Cai CY, Assaraf YG, Guo HQ, Cui Q, Wei L, et al. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to overcome anti-cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist Update. (2020) 48:100663. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2019.100663
6. Napolitano A and Vincenzi B. Secondary kit mutations: the gist of drug resistance and sensitivity. Br J Cancer. (2019) 120:577–8. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0388-7
7. Casali PG, Zalcberg J, Le Cesne A, Reichardt P, Blay JY, Lindner LH, et al. Ten-year progression-free and overall survival in patients with unresectable or metastatic gi stromal tumors: long-term analysis of the european organisation for research and treatment of cancer, italian sarcoma group, and australasian gastrointestinal trials group intergroup phase iii randomized trial on imatinib at two dose levels. J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:1713–20. doi: 10.1200/jco.2016.71.0228
8. Kaiser SE, Riley BE, Shaler TA, Trevino RS, Becker CH, Schulman H, et al. Protein standard absolute quantification (Psaq) method for the measurement of cellular ubiquitin pools. Nat Methods. (2011) 8:691–6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1649
9. Clague MJ, Barsukov I, Coulson JM, Liu H, Rigden DJ, and Urbé S. Deubiquitylases from genes to organism. Physiol Rev. (2013) 93:1289–315. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00002.2013
10. Komander D, Clague MJ, and Urbé S. Breaking the chains: structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2009) 10:550–63. doi: 10.1038/nrm2731
11. DeMatteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Mudan SS, Woodruff JM, and Brennan MF. Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg. (2000) 231:51–8. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200001000-00008
12. Demetri GD, Benjamin RS, Blanke CD, Blay JY, Casali P, Choi H, et al. Nccn task force report: management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor (Gist)–update of the nccn clinical practice guidelines. J Natl Compr Cancer Network. (2007) 5 Suppl 2:S1–29. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2007.2002
13. Eisenberg BL and Judson I. Surgery and imatinib in the management of gist: emerging approaches to adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. (2004) 11:465–75. doi: 10.1245/aso.2004.09.011
14. Gold JS and Dematteo RP. Combined surgical and molecular therapy: the gastrointestinal stromal tumor model. Ann Surg. (2006) 244:176–84. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000218080.94145.cf
15. Balachandran VP and DeMatteo RP. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: who should get imatinib and for how long? Adv Surg. (2014) 48:165–83. doi: 10.1016/j.yasu.2014.05.014
16. Cassier PA, Fumagalli E, Rutkowski P, Schöffski P, Van Glabbeke M, Debiec-Rychter M, et al. Outcome of patients with platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha-mutated gastrointestinal stromal tumors in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:4458–64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-11-3025
17. Janeway KA, Albritton KH, Van Den Abbeele AD, D’Amato GZ, Pedrazzoli P, Siena S, et al. Sunitinib treatment in pediatric patients with advanced gist following failure of imatinib. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2009) 52:767–71. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21909
18. Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, Siena S, Falcone A, Ychou M, et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (Correct): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). (2013) 381:303–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)61900-x
19. Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, Roberts PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. New Engl J Med. (2002) 347:472–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020461
20. Demetri GD, van Oosterom AT, Garrett CR, Blackstein ME, Shah MH, Verweij J, et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London England). (2006) 368:1329–38. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(06)69446-4
21. Demetri GD, Reichardt P, Kang YK, Blay JY, Rutkowski P, Gelderblom H, et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (Grid): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). (2013) 381:295–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)61857-1
22. Dematteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, Maki RG, Pisters PW, Demetri GD, et al. Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of localised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London England). (2009) 373:1097–104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(09)60500-6
23. Joensuu H, Eriksson M, Sundby Hall K, Reichardt A, Hermes B, Schütte J, et al. Survival outcomes associated with 3 years vs 1 year of adjuvant imatinib for patients with high-risk gastrointestinal stromal tumors: an analysis of a randomized clinical trial after 10-year follow-up. JAMA Oncol. (2020) 6:1241–6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2091
24. Heinrich MC, Jones RL, von Mehren M, Schöffski P, Serrano C, Kang YK, et al. Avapritinib in advanced pdgfra D842v-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (Navigator): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:935–46. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(20)30269-2
25. Hong DS, DuBois SG, Kummar S, Farago AF, Albert CM, Rohrberg KS, et al. Larotrectinib in patients with trk fusion-positive solid tumours: A pooled analysis of three phase 1/2 clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:531–40. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30856-3
26. Cockram PE, Kist M, Prakash S, Chen SH, Wertz IE, and Vucic D. Ubiquitination in the regulation of inflammatory cell death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. (2021) 28:591–605. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-00708-5
27. Pal A, Young MA, and Donato NJ. Emerging potential of therapeutic targeting of ubiquitin-specific proteases in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:4955–66. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-1211
28. Mao P, Feng Z, Liu Y, Zhang K, Zhao G, Lei Z, et al. The role of ubiquitination in osteosarcoma development and therapies. Biomolecules. (2024) 14. doi: 10.3390/biom14070791
29. Suzuki T, Dai Y, Ono M, Kojima J, Sasaki T, Fujiwara H, et al. Pivotal role of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 (Uchl1) in uterine leiomyoma. Biomolecules. (2023) 13. doi: 10.3390/biom13020193
30. Zheng S, Qiao G, Min D, Zhang Z, Lin F, Yang Q, et al. Heterogeneous expression and biological function of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase-L1 in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. (2015) 359:36–46. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.12.001
31. Zimmer AS, Gillard M, Lipkowitz S, and Lee JM. Update on parp inhibitors in breast cancer. Curr Treat options Oncol. (2018) 19:21. doi: 10.1007/s11864-018-0540-2
32. Wang S, Wang T, Yang Q, Cheng S, Liu F, Yang G, et al. Proteasomal deubiquitylase activity enhances cell surface recycling of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordrecht Netherlands). (2022) 45:951–65. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00699-0
33. Swatek KN and Komander D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res. (2016) 26:399–422. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.39
34. Neutzner M and Neutzner A. Enzymes of ubiquitination and deubiquitination. Essays Biochem. (2012) 52:37–50. doi: 10.1042/bse0520037
35. Metzger MB and Weissman AM. Working on a chain: E3s ganging up for ubiquitylation. Nat Cell Biol. (2010) 12:1124–6. doi: 10.1038/ncb1210-1124
36. Reyes-Turcu FE, Ventii KH, and Wilkinson KD. Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. (2009) 78:363–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.082307.091526
37. Groll M and Huber R. Substrate access and processing by the 20s proteasome core particle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2003) 35:606–16. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00390-4
38. Chen RH, Chen YH, and Huang TY. Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of autophagy. J BioMed Sci. (2019) 26:80. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0569-y
39. Gordon PM and Fisher DE. Role for the proapoptotic factor bim in mediating imatinib-induced apoptosis in a C-kit-dependent gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell line. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:14109–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.078592
40. Bauer S, Yu LK, Demetri GD, and Fletcher JA. Heat shock protein 90 inhibition in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:9153–61. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-0165
41. Fang HT, Zhang B, Pan XF, Gao L, Zhen T, Zhao HX, et al. Bortezomib interferes with C-kit processing and transforms the T(8;21)-generated fusion proteins into tumor-suppressing fragments in leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2012) 109:2521–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121341109
42. Macia E, Ehrlich M, Massol R, Boucrot E, Brunner C, and Kirchhausen T. Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev Cell. (2006) 10:839–50. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.04.002
43. Dong Y, Liang C, Zhang B, Ma J, He X, Chen S, et al. Bortezomib enhances the therapeutic efficacy of dasatinib by promoting C-kit internalization-induced apoptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells. Cancer Lett. (2015) 361:137–46. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.02.044
44. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
45. Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by gpx4. Cell. (2014) 156:317–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
46. Seibt TM, Proneth B, and Conrad M. Role of gpx4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radical Biol Med. (2019) 133:144–52. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.014
47. Sun X, Zhang Q, Lin X, Shu P, Gao X, and Shen K. Imatinib induces ferroptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors by promoting stub1-mediated gpx4 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:839. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06300-2
48. Wang C, Zheng C, Wang H, Shui S, Jin H, Liu G, et al. Dual degradation mechanism of gpx4 degrader in induction of ferroptosis exerting anti-resistant tumor effect. Eur J medicinal Chem. (2023) 247:115072. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.115072
49. Boilève A, Dufresne A, Chamseddine A, Nassif E, Dumont S, Brahmi M, et al. Outcomes of patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (Gist) treated with multi-kinase inhibitors other than imatinib as first-line treatment. ESMO Open. (2020) 5:e001082. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2020-001082
50. Serex CA and Dulguerov N. Rapidly progressive stridor in a case of gist. BMJ Case Rep. (2021) 14. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-237360
51. Gounder MM and Maki RG. Molecular basis for primary and secondary tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer chemotherapy Pharmacol. (2011) 67 Suppl 1:S25–43. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1526-3
52. Serrano C, Mariño-Enríquez A, Tao DL, Ketzer J, Eilers G, Zhu M, et al. Complementary activity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors against secondary kit mutations in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J Cancer. (2019) 120:612–20. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0389-6
53. Noma K, Naomoto Y, Gunduz M, Matsuoka J, Yamatsuji T, Shirakawa Y, et al. Effects of imatinib vary with the types of kit-mutation in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell lines. Oncol Rep. (2005) 14:645–50. doi: 10.3892/or.14.3.645
54. Tarn C, Skorobogatko YV, Taguchi T, Eisenberg B, von Mehren M, and Godwin AK. Therapeutic effect of imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: akt signaling dependent and independent mechanisms. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:5477–86. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-3906
55. Corless CL, Barnett CM, and Heinrich MC. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: origin and molecular oncology. Nat Rev Cancer. (2011) 11:865–78. doi: 10.1038/nrc3143
56. Venkataraman V, George S, and Cote GM. Molecular advances in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Oncologist. (2023) 28:671–81. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad167
57. Di Vito A, Ravegnini G, Gorini F, Aasen T, Serrano C, Benuzzi E, et al. The multifaceted landscape behind imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (Gists): A lesson from ripretinib. Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 248:108475. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108475
58. Bosbach B, Rossi F, Yozgat Y, Loo J, Zhang JQ, Berrozpe G, et al. Direct engagement of the pi3k pathway by mutant kit dominates oncogenic signaling in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:E8448–e57. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711449114
59. Klinkert K and Echard A. Rab35 gtpase: A central regulator of phosphoinositides and F-actin in endocytic recycling and beyond. Traffic (Copenhagen Denmark). (2016) 17:1063–77. doi: 10.1111/tra.12422
60. Li C, Gao Z, Cui Z, Liu Z, Bian Y, Sun H, et al. Deubiquitylation of rab35 by usp32 promotes the transmission of imatinib resistance by enhancing exosome secretion in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Oncogene. (2023) 42:894–910. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02600-1
61. Villarroel-Campos D, Henríquez DR, Bodaleo FJ, Oguchi ME, Bronfman FC, Fukuda M, et al. Rab35 functions in axon elongation are regulated by P53-related protein kinase in a mechanism that involves rab35 protein degradation and the microtubule-associated protein 1b. J Neurosci. (2016) 36:7298–313. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.4064-15.2016
62. Chi P, Chen Y, Zhang L, Guo X, Wongvipat J, Shamu T, et al. Etv1 is a lineage survival factor that cooperates with kit in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nature. (2010) 467:849–53. doi: 10.1038/nature09409
63. Han C, Yang L, Choi HH, Baddour J, Achreja A, Liu Y, et al. Amplification of usp13 drives ovarian cancer metabolism. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:13525. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13525
64. Liu J, Xia H, Kim M, Xu L, Li Y, Zhang L, et al. Beclin1 controls the levels of P53 by regulating the deubiquitination activity of usp10 and usp13. Cell. (2011) 147:223–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.037
65. Gao Z, Li C, Sun H, Bian Y, Cui Z, Wang N, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-modified usp13 induces pro-survival autophagy and imatinib resistance via regulating the stabilization of autophagy-related protein 5 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cell Death Differ. (2023) 30:544–59. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01107-8
66. Cui T, Wang Y, Song P, Yi X, Chen J, Yang Y, et al. Hsf1-dependent autophagy activation contributes to the survival of melanocytes under oxidative stress in vitiligo. J Invest Dermatol. (2022) 142:1659–69.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.11.007
67. Ni B, Li Q, Zhuang C, Huang P, Xia X, Yang L, et al. The nerve-tumour regulatory axis gdnf-gfra1 promotes tumour dormancy, imatinib resistance and local recurrence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours by achieving autophagic flux. Cancer Lett. (2022) 535:215639. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215639
68. Wu X, Iwatsuki M, Takaki M, Saito T, Hayashi T, Kondo M, et al. Fbxw7 regulates the sensitivity of imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors by targeting mcl1. Gastric Cancer. (2024) 27:235–47. doi: 10.1007/s10120-023-01454-6
69. Nakayama KI and Nakayama K. Ubiquitin ligases: cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2006) 6:369–81. doi: 10.1038/nrc1881
70. Chen T, Ni N, Yuan L, Xu L, Bahri N, Sun B, et al. Proteasome inhibition suppresses kit-independent gastrointestinal stromal tumors via targeting hippo/yap/cyclin D1 signaling. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:686874. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.686874
71. Ishida T, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nishida T, Hirota S, Serada S, et al. Targeted therapy for drug-tolerant persister cells after imatinib treatment for gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J Cancer. (2021) 125:1511–22. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01566-9
72. Wang H, Zhao W, Wang D, and Chen J. Ano6 (Tmem16f) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis. Open Med (Warsaw Poland). (2024) 19:20240941. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0941
73. Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, et al. Acsl4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. (2017) 13:91–8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2239
74. Cui Z, Sun H, Gao Z, Li C, Xiao T, Bian Y, et al. Trim21/usp15 balances acsl4 stability and the imatinib resistance of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Br J Cancer. (2024) 130:526–41. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02562-x
75. D’Angelo SP, Mahoney MR, Van Tine BA, Atkins J, Milhem MM, Jahagirdar BN, et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab treatment for metastatic sarcoma (Alliance A091401): two open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trials. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:416–26. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(18)30006-8
76. Iida K, Abdelhamid Ahmed AH, Nagatsuma AK, Shibutani T, Yasuda S, Kitamura M, et al. Identification and therapeutic targeting of gpr20, selectively expressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors, with ds-6157a, a first-in-class antibody-drug conjugate. Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:1508–23. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-20-1434
77. Schumacher D, Hackenberger CP, Leonhardt H, and Helma J. Current status: site-specific antibody drug conjugates. J Clin Immunol. (2016) 36 Suppl 1:100–7. doi: 10.1007/s10875-016-0265-6
78. Seifert AM, Zeng S, Zhang JQ, Kim TS, Cohen NA, Beckman MJ, et al. Pd-1/pd-L1 blockade enhances T-cell activity and antitumor efficacy of imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:454–65. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-16-1163
79. Xie Q, Lin Q, Li D, and Chen J. Imatinib induces autophagy via upregulating xiap in gist882 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 488:584–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.096
80. Zeng X, Zhao F, Jia J, Ma X, Jiang Q, Zhang R, et al. Targeting bcl6 in gastrointestinal stromal tumor promotes P53-mediated apoptosis to enhance the antitumor activity of imatinib. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:3624–35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-23-0082
81. Sun H, Cui Z, Li C, Gao Z, Xu J, Bian Y, et al. Usp5 promotes ripretinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors by mdh2 deubiquition. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2024) 11:e2401171. doi: 10.1002/advs.202401171
82. Wu X, Yamashita K, Matsumoto C, Zhang W, Ding M, Harada K, et al. Yap acts as an independent prognostic marker and regulates growth and metastasis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors via fbxw7-yap pathway. J Gastroenterol. (2025) 60:275–84. doi: 10.1007/s00535-024-02180-1
83. Natarajan U, Venkatesan T, Radhakrishnan V, Samuel S, Rasappan P, and Rathinavelu A. Cell cycle arrest and cytotoxic effects of saha and rg7388 mediated through P21(Waf1/cip1) and P27(Kip1) in cancer cells. Medicina (Kaunas Lithuania). (2019) 55. doi: 10.3390/medicina55020030
84. Zhang B, Zhang M, Shen C, Liu G, Zhang F, Hou J, et al. Lncrna pcbp1-as1-mediated ar/ar-V7 deubiquitination enhances prostate cancer enzalutamide resistance. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:856. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04144-2
85. Zhu Y, Gu L, Lin X, Cui K, Liu C, Lu B, et al. Linc00265 promotes colorectal tumorigenesis via zmiz2 and usp7-mediated stabilization of Β-catenin. Cell Death Differ. (2020) 27:1316–27. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0417-3
86. Zhu Y, Wu W, Hou D, Zhao Y, Ye J, Shen L, et al. Mechanism of curcumol targeting the otub1/tgfbi ubiquitination pathway in the inhibition of angiogenesis in colon cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104899
Keywords: gastrointestinal stromal tumors, imatinib, drug resistance, ubiquitination modifications, deubiquitination modification
Citation: Huo H, Li H, Yang X, Wang S, Zhao Y and Yang J (2025) The effect of ubiquitination and deubiquitination to imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Front. Oncol. 15:1581920. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1581920
Received: 23 February 2025; Accepted: 02 July 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Jie Li, Peking Union Medical College Hospital (CAMS), ChinaReviewed by:
Anna M. Eiring, The University of Texas at El Paso, United StatesEmna Fehri, Pasteur Institute of Tunis, Tunisia
Copyright © 2025 Huo, Li, Yang, Wang, Zhao and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianjun Yang, eWFuZ2pqQGZtbXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Huade Huo
Huade Huo Haolin Li
Haolin Li Xinlin Yang3†
Xinlin Yang3† Jianjun Yang
Jianjun Yang