- 1Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, United States
- 2Ahmanson Translational Theranostics Division, Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States
- 3Department of Theranostics and Nuclear Medicine, St Vincent’s Hospital Sydney, St Vincent’s Clinical School, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 4Department of Radiology, City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA, United States
- 5Department of Genitourinary Medical Oncology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, United States
Although the recently approved prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radioligand therapy (RLT) [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 has improved outcomes for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), not all patients respond optimally to this treatment; even measuring response accurately can be difficult. Moreover, there is currently a lack of validated prognostic and predictive biomarkers for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment in this patient population. There is, therefore, a growing need to identify biomarkers to help optimize patient selection for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and guide therapy decision-making. This review explores the landscape of emerging clinical, molecular, and imaging biomarkers, and their potential utility as prognostic and/or predictive biomarkers in the context of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment for patients with mCRPC.
1 Introduction
In the United States, prostate cancer (PC) represents nearly 15% of all new cancer diagnoses (1) and is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in people assigned as male at birth (2). Numerous life-prolonging agents have been approved for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant PC (mCRPC), notably novel precision medicine approaches including radioligand therapy (RLT) (3). A review of established and novel therapies is beyond the scope of this manuscript, but the current clinical data, including overall survival (OS) rate, is comprehensively reviewed in the 2025 article by Poon et al. (3). Despite these advances in treatment approaches, PC remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality (4). Patients diagnosed with mCRPC have a median OS rate of less than 2 years (5, 6). Furthermore, among those who initiate first-line treatment, there is an approximate 50% reduction in the rate of progression to each subsequent line of therapy due to mortality (7), highlighting the urgent need for improved patient outcomes. As such, understanding factors for disease progression is crucial in this regard; identification and validation of new markers of progression may help to inform treatment selection.
In addition to identifying the likelihood of disease progression, biomarkers may also help predict treatment response and identify patients who are suitable for treatment with specific therapeutic targets. Precision medicine uses prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-directed radioligand imaging (RLI) to identify patients for treatment with RLT, which binds radioactive molecules directly to the targeted cancer cells (8, 9). PSMA is a transmembrane protein highly expressed at the cell surface of the majority of PCs (10–13) and its expression level is dependent on the disease state, with progressively greater expression reported in mCRPC (14). PSMA has numerous functions within the normal prostate and in PC and is an accessible cell surface target for the delivery of antitumor RLT and other drug therapies (13). Together, these credentials support PSMA as a therapeutic target in mCRPC (13–16).
Diagnostic RLI, such as with the positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11, can visualize and semi-quantify PSMA expression in tumors, which can then be targeted by treatment with a cytotoxic RLT (8, 9). [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 is currently the only PSMA-targeted RLT agent approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency in patients with PSMA PET-positive mCRPC who have been treated with androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) therapy and for whom it is considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy, or patients who have received prior taxane-based chemotherapy (17, 18). [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 has been shown to improve survival outcomes in patients with mCRPC compared with historical agents; in the pivotal phase 3 VISION trial [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 plus best standard of care (BSoC), which included historically used approved hormonal treatments, bisphosphonates, radiation therapy, denosumab, or glucocorticoid, improved OS by 4 months compared with BSoC alone (median 15.3 vs 11.3 months; HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.52–0.74; p < 0.001) (19).
Several other PSMA-targeted RLT strategies are currently under investigation. These include beta-emitters such as [177Lu]Lu- PNT2002 (a [177Lu]Lu-based PSMA-targeted peptide RLT) (20), I-131-1095 ([131I]I-based small-molecule PSMA-targeted RLT) (11) and J591 ([177Lu]Lu-J591) (a [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-targeted monoclonal antibody) (21). Other RLTs in development include copper-based RLTs, such as [67Cu]Cu-SAR-bisPSMA (a [67Cu]Cu-based PSMA-targeted RLT with a double PSMA-binding moiety) (22) and alpha-emitters, including [225Ac]Ac-J591 (a[225Ac]Ac-based PSMA-targeted antibody) (23), [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-R2 (a[225Ac]Ac-linked PSMA-targeted RLT) (24), [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-617 (a[225Ac]Ac-linked PSMA-targeted RLT) (25) and [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-imaging & therapy (I&T; [225Ac]Ac-linked PSMA-targeted RLT used for both imaging and treatment) (26). Discussion on the management of PC with RLT is out of the scope of this manuscript; however, the recently published review article by Almeida et al. provides a comprehensive overview (27).
Although RLI-directed RLT is a promising approach, the expression of PSMA in PC varies both within and between individuals (28, 29). Between 15% and 20% of patients have detectable PSMA-negative metastases on PET scans (19, 30, 31). Even within PSMA-positive mCRPC, the detection and quantification of PSMA heterogeneity may differ based on imaging or immunohistopathology modalities and analysis methods (28). It is likely that the optimal use of a PSMA-targeted RLT as a component of a multi-agent treatment strategy will be needed to account for this therapy-relevant heterogeneity.
Given the expanding complexity of the mCRPC treatment landscape, practical guidance on utilizing prognostic and predictive biomarkers to optimize treatment outcomes is urgently required. Prognostic biomarkers can be used to identify the likelihood of a clinical event, such as disease recurrence or disease progression in a particular patient population, and can be identified from trends in observational data (32). Importantly, they can indicate a likely disease outcome independent of the treatment received (33). Conversely, predictive biomarkers are those that are specifically associated with a response to a particular therapy (32, 33). If the treatment effect (experimental vs control) is different for biomarker-positive patients compared with biomarker-negative patients, a biomarker can be considered as predictive (33). To establish whether a biomarker is prognostic or predictive (or both), a formal statistical test between the biomarker and treatment group needs to be performed (33). These concepts are summarized in Figure 1. The REMARK guidelines exist to assist in complete and transparent reporting of prognostic studies, such as reporting statistical significance (34).
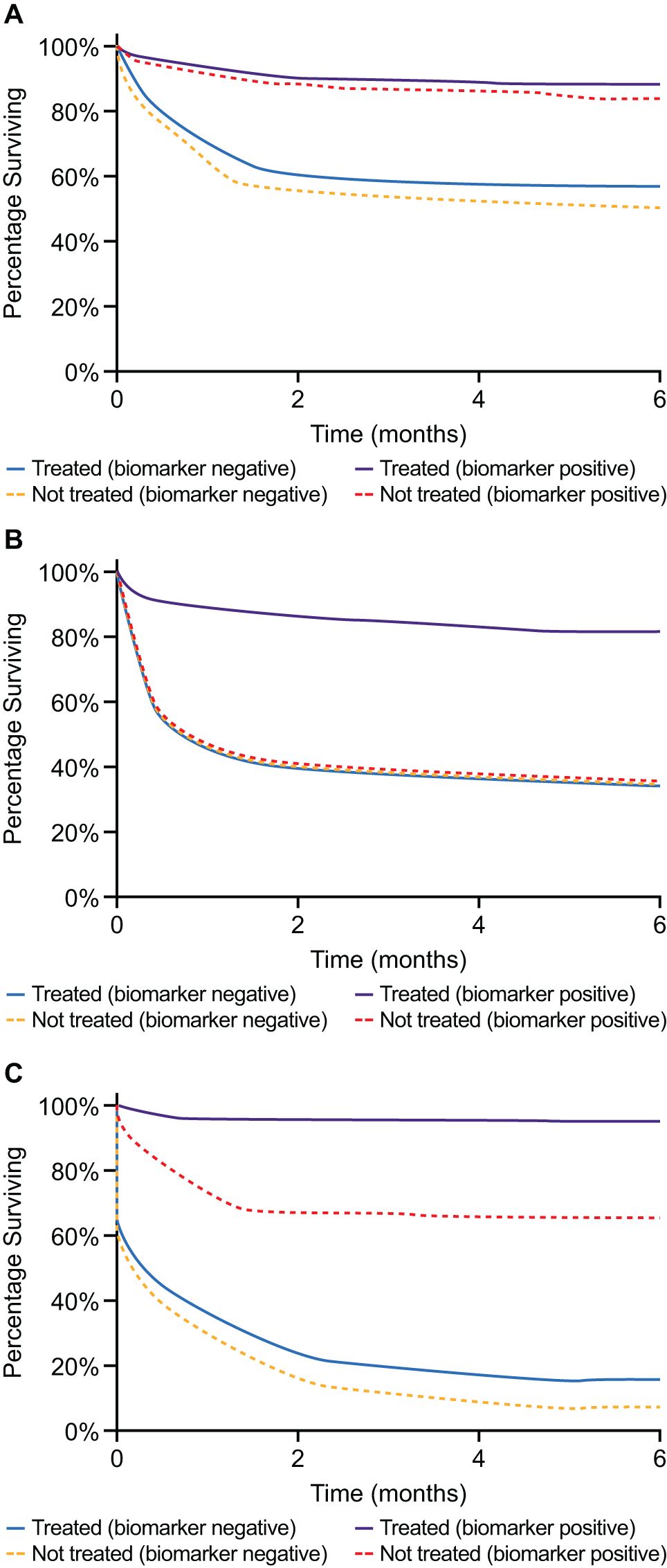
Figure 1. (A) Example of a purely prognostic biomarker. Patients with this biomarker have improved survival compared with biomarker-negative patients, independent of treatment. As the treatment effect is the same for both biomarker-negative and biomarker-positive patients, we can surmise that the biomarker is not predictive. (B) Example of a purely predictive marker. Biomarker-positive patients display a treatment effect, whereas no treatment effect is observed for biomarker-negative patients. Therefore, treatment effect differs in quality between the groups, suggesting this biomarker is predictive. Note that the untreated biomarker-positive patients have the same survival as the untreated biomarker-negative patients. (C) An example of a prognostic and predictive biomarker. The treatment effect is different for biomarker-negative and biomarker-positive patients, suggesting it is predictive. However, biomarker-positive patients have improved survival compared with biomarker-negative patients, independent of treatment group, suggesting it is prognostic.
Several potential prognostic and predictive biomarkers for responses to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment in mCRPC have been reported (35–37); however, most of these biomarkers still require standardized and validated measurement methods. This review aims to evaluate the current evidence for, and current clinical applicability of, potential prognostic and predictive biomarkers for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment of patients with mCRPC, including imaging, clinical, and molecular biomarkers at varying stages of evaluation, including total tumor and whole-body tumor PSMA expression. The summarized observations of this review are found in Table 1.
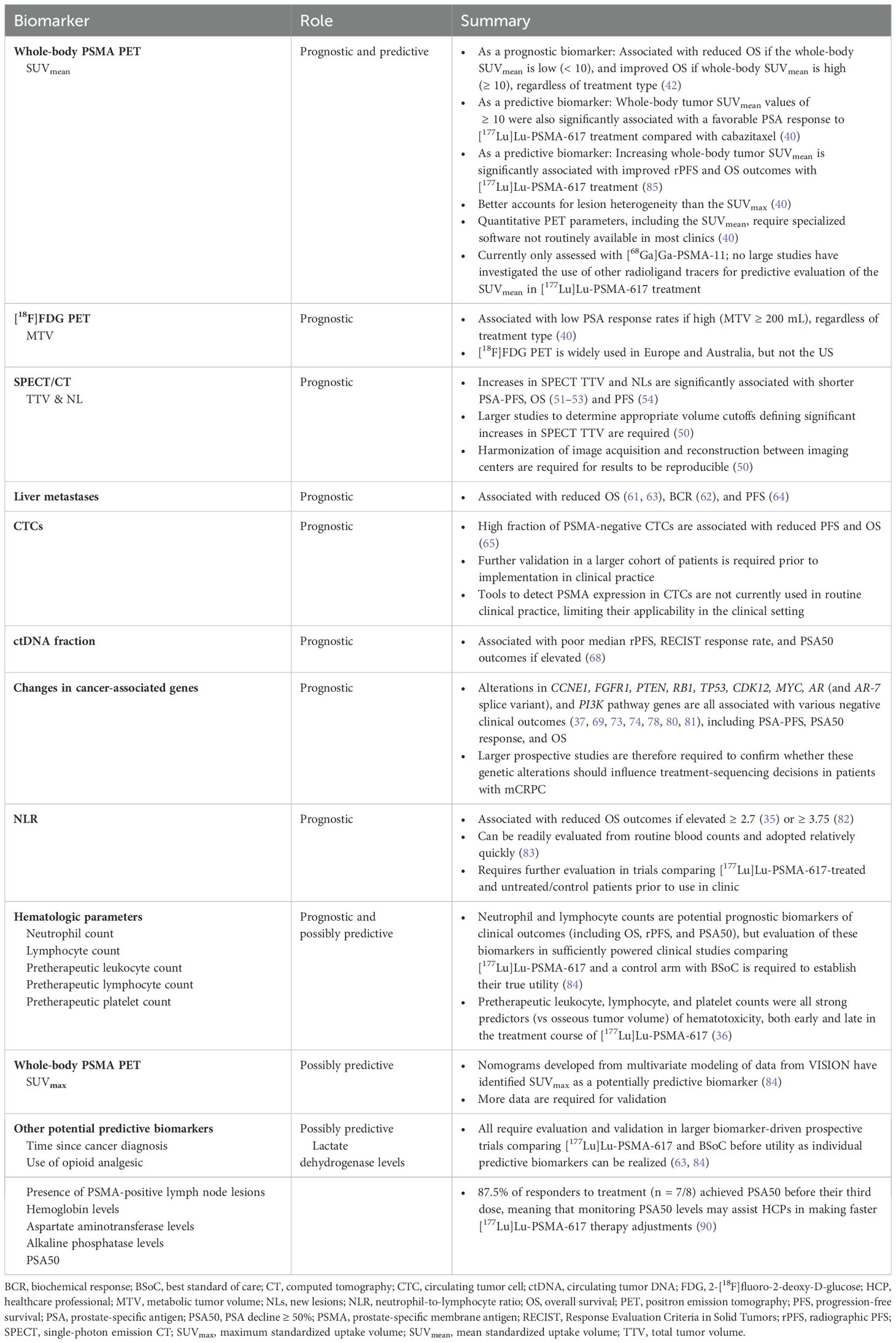
Table 1. Summary of current prognostic and predictive biomarkers for patients with mCRPC, in the context of treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617.
2 Prognostic biomarkers in mCRPC
A number of potential imaging and clinical prognostic biomarkers for patients with PSMA-positive mCRPC have been explored.
2.1 Total tumor PSMA expression
When evaluating the expression of PSMA throughout the body using PET imaging, a radioactive ligand (such as [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11) that targets PSMA is used (38). The radioactive tracer emits positrons that produce annihilation photons, which are in turn detected by the PET scanner, allowing a three-dimensional image of the tracer’s loci inside the body to be rendered (39). As an indicator of PSMA expression, the mean standardized uptake value (SUVmean) is a measurement parameter used in PET scans that quantifies the average concentration of radiotracer ligand uptake within the entire segmented tumor volume, whereas the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) is the SUV of the single voxel with the highest concentration of radiotracer ligand in the entire segmented tumor volume (40).
Current evidence suggests that PSMA levels may serve as a prognostic biomarker for patients with mCRPC, and one team of investigators recently released research showing that prognostic PSMA PET nomograms based on the PROMISE study criteria had prognostic utility across early and late stages of PC (41). The open-label, randomized, phase 2 TheraP study (NCT03392428) was the first ever randomized trial comparing [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 to the BSoC treatment for patients with mCRPC, with 200 eligible participants with PSMA-positive mCRPC randomly assigned (1:1) to treatment with either [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (n = 99) or cabazitaxel (n = 101) (30, 40). In an updated OS analysis, no significant differences in mean OS were observed between the [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and cabazitaxel arms (19.1 vs 19.6 months, respectively), irrespective of baseline SUVmean (40). Furthermore, patients with a high whole-body SUVmean (≥ 10) had improved OS outcomes, regardless of treatment type, compared with patients with an SUVmean < 10 (42), though patients with an SUVmean < 10 treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 were still likely to benefit from longer radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) compared with those treated with cabazitaxel (40). These data are important, as they come from a study for which we have the longest RLT versus BSoC follow-up data. The exploratory secondary analysis of the phase 3 VISION study (NCT03511664), in which eligible participants were randomized 2:1 to receive [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy plus BSoC (n = 548) or BSoC alone (n = 278), also provides evidence of the prognostic utility of SUVmean in patients with mCRPC (43). Here, median OS was longest in patients from the BSoC alone arm who were in the highest whole-body tumor SUVmean quartile, suggesting that higher mean PSMA expression could be a favorable prognostic factor for survival in patients with mCRPC (43). However, it is worth noting that while median OS was longest in the highest SUVmean quartile of the BSoC arm, the median OS in the lower three SUVmean quartiles were very similar (43). Furthermore, high SUVmean was not associated with improved median rPFS in the BSoC only arm; rPFS in this arm remained approximately the same regardless of SUVmean quartile (43), casting doubt on the value of SUVmean as a prognostic biomarker in the BSoC arm.
These results suggest that the SUVmean on treatment with [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 may be a prognostic factor for OS, independent of the treatment received (42). Investigators have commented that SUVmean gives an evaluation of tumor status that better accounts for therapeutically relevant intra- and interlesional PSMA heterogeneity, compared with SUVmax (40). However, it is important to note that SUVmean is not routinely reported in PSMA PET scan reports currently, and the implications this may have on its adoption in clinical practice are covered in the discussion section below.
2.2 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose PET metabolic tumor volume
Imaging with 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose ([18F]FDG) PET is a well-established and widely studied imaging tool assessing glucose metabolism in a variety of malignancies (44, 45). Investigators in a single-center, prospective, phase 2 trial observed that patients with mCRPC who have high intensity radioligand uptake at disease sites on [18F]FDG PET imaging may have poorer OS (46). The prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume (MTV), which refers to the metabolically active volume of the tumor segmented by [18F]FDG PET (47), was therefore examined in a post hoc biomarker analysis of the phase 2 TheraP study (40). The investigators who conducted this post hoc analysis observed that a high volume of [18F]FDG PET MTV (i.e. an MTV ≥ 200 mL) was associated with a lower prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate (vs MTV < 200 mL) for both treatment groups (RLT and cabazitaxel) combined (n = 200). Of note, patients were not included in the TheraP study if they presented with site(s) of discordant disease (i.e. sites of disease that are [18F]FDG-positive with minimal PSMA expression, defined as [18F]FDG intensity > [68Ga]Ga-PSMA activity or [68Ga]Ga-PSMA SUVmax < 10), so these findings must be viewed through the lens of patients without sites of discordant disease (40). Similar results were also observed by the investigators conducting the phase 2 LuPSMA trial, who found that [18F]FDG-positive MTV, when measured by [18F]FDG PET, had prognostic significance for the survival of patients with mCRPC (46). However, additional data from a larger patient group are required to fully evaluate the applicability of this method for prognostic evaluation in mCRPC in a routine clinical setting. It should also be noted that while [18F]FDG PET imaging is widely used in Europe and Australia for mCRPC, in the US, PSMA PET-only imaging criteria are predominantly used for identifying patients suitable for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, based upon the eligibility criteria of the VISION study (48). This discrepancy should be taken into account by physicians in countries where FDG PET is not routinely used.
2.3 [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/computed tomography (CT) allows lesions visualized by functional imaging to be correlated with anatomic structures, resulting in increased sensitivity and specificity of scintigraphic findings (49). The uptake of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 by tumor cells can be determined using SPECT and quantified as SPECT total tumor volume (TTV) (50). Increased SPECT TTV and new lesions (NLs) in early treatment cycles (1, 2) have been associated with reduced OS and PSA progression-free survival (PSA-PFS) in retrospective studies (51–53), showing promise as early prognostic biomarkers during PSMA-targeted RLT. In another retrospective analysis of 127 patients evaluated for change in SPECT/CT TTV at the week 6 (dose 2) timepoint, an increase in SPECT/CT TTV was found to potentially predict reduced PFS (54). Increased TTVs and NLs at the start of cycles 2 and 3, as determined by SPECT/CT, have also been shown to be independently associated with increased risk of death in a recently published retrospective study (52).
SPECT/CT performed 24 hours after treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 has been shown to lead to changes in treatment management in 49% of patients (n = 60/122), highlighting its therapeutic value (52, 55). Importantly, tailoring RLTs based on early biomarker response (such as PSA response and changes in TTV and NLs) has also been shown to maintain comparable outcomes to continuous treatment, while allowing for the benefit of a treatment vacation (53). Dosimetric parameters on SPECT/CT have also been investigated in a retrospective study, which found baseline lesion-absorbed dose of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 was significantly correlated with PSA response, though SPECT/CT lesion-based responses had a limited relationship with absorbed dose (56). New generation multi-detector cadmium-zinc-telluride (CZT)-based SPECT/CT that can acquire scans much faster than current modalities has been shown to have comparable detection/targeting rates compared to the commonly used SPECT/CT systems (Discovery 670 Pro) (57). Furthermore, SPECT/CT at 4 hours post–[177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment shows promise as an alternative to 24-hour post-treatment SPECT/CT for assessing treatment response (58).
These results emphasize the practicality of using SPECT/CT for treatment response assessment, highlighting the potential utility of SPECT/CT as a prognostic tool for establishing likely disease outcomes in patients with mCRPC. However, these findings need to be validated in larger cohorts of patients and further research is needed to ensure the practical applicability of SPECT/CT, including appropriate volume cutoffs to define significant increases in SPECT TTV and harmonization of image acquisition and reconstruction between imaging centers and systems (50).
2.4 Liver metastases
The liver has a critical role in the metabolism, detoxification, and synthesis of a number of proteins and factors vital for fluid balance and blood clotting, and it is hypothesized that liver metastases contribute to cancer mortality through these vital physiological functions (59). In a meta-analysis of 83 studies evaluating 604,853 patients treated for a wide variety of cancer types, liver metastases were shown to negatively impact OS (HR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.62–1.93) (59). Liver metastases have also been associated with poor OS outcomes in mCRPC, regardless of treatment type (60). Of therapeutic relevance, liver metastases can also have heterogeneous levels of PSMA in mCRPC (31).
The prognostic utility of the presence of liver metastases, visualized by RLI, has been investigated in a number of observational and retrospective studies in patients with mCRPC treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (61–64). In the WARMTH multicenter retrospective analysis, the presence of PSMA-positive bone and liver metastases, as well as poor Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, were shown to be significantly associated with worse OS in univariate and multivariate analyses (61). A multicenter retrospective study of 145 patients with mCRPC also indicated a positive relationship between the presence of PSMA-positive visceral metastases and reduced biochemical response, as defined by a PSA decline of ≥ 50% (PSA50) from baseline to at least 2 weeks after the start of treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (p < 0.01) (62). In a single-center retrospective analysis of 52 patients with mCRPC treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, the presence (vs absence) of PSMA-positive liver metastases was also associated with poorer OS (HR, 6.981; 95% CI, 2.583–18.863; p < 0.001) (63). Furthermore, in a prospective observational study (n = 52), presence of PSMA-positive liver metastases was also associated with reduced PFS in patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (64).
These studies highlight that the presence of PSMA-positive liver metastases may have a role as a prognostic biomarker that could be applied in clinical practice, as they indicate individuals with likely poor clinical outcomes who may benefit from [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment. However, further evaluation is needed to prospectively determine their application in the clinical setting among patients with mCRPC.
2.5 Circulating tumor cells
While targeted imaging provides an opportunity for whole-body phenotyping of PSMA expression at the macroscopic level, liquid biopsy testing, specifically of circulating tumor cells (CTCs), could offer an alternative method of PC disease identification and characterization (65). The role of PSMA-positive (vs PSMA-negative) CTCs as a potential prognostic biomarker in the context of RLT was suggested by the results of a prospective proof-of-concept study in patients (n = 20) with advanced mCRPC (65). Here, the investigators found that a high fraction of PSMA-negative CTCs (high fraction: mean 54%, vs low fraction: mean 19%) was prognostic for both shorter PFS (odds ratio [OR], 1.236; 95% CI, 1.035–2.587; p = 0.0043) and shorter OS (OR, 1.056; 95% CI, 1.008–1.141; p = 0.0182) in patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (65). However, as commented by the investigators, this was a small, single-center, proof-of-principle study with only moderate statistical power, and further validation in a larger cohort of patients is required prior to implementation in clinical practice (65). Furthermore, tools to detect PSMA expression in CTCs are not currently used in routine clinical practice, limiting their applicability in the clinical setting.
2.6 Circulating tumor DNA fraction
In patients with cancer, tumor DNA is often shed into the blood and mixed with cell-free DNA from leukocytes that have undergone apoptosis (66). The prognostic utility of circulating tumor (ct)DNA and ctDNA fraction in plasma has been seen across several cancer types including mCRPC (67). ctDNA fraction can be associated with tumor burden and can help assess the likely disease trajectory of patients across different cancer types and clinical scenarios (66). In a real-world outcomes study conducted in the US, the prognostic value of ctDNA fraction was assessed in patients undergoing liquid biopsy testing for four cancer types including mCRPC (67). In this study, the investigators observed that a ctDNA fraction ≥ 10% was highly correlated with OS in a univariable analysis of patients with mCRPC (HR, 3.3; 95% CI, 2.04–5.34; p < 0.001), regardless of their treatment type (67). Furthermore, this finding was consistently seen in patients with all of the other cancer types evaluated, leading the investigators to conclude that plasma ctDNA tumor fraction is an independent prognostic biomarker, with the potential to guide clinical conversations around expected disease trajectory and, therefore, treatment selection (67). However, the investigators did also note that its predictive utility is still to be proven. Thus, the use of ctDNA tumor fraction or changes in ctDNA fraction that occur on therapy as a guide to optimize treatment outcomes in patients with mCRPC requires validation in prospective clinical trials before it can be incorporated into clinical practice (67).
In the context of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment, associations between baseline ctDNA levels and outcomes have been assessed as an exploratory analysis of the phase 3, open-label, randomized PSMAfore study (NCT04689828) (68). Of the 360 samples collected from 468 patients, investigators evaluated ctDNA levels, and observed increased ctDNA levels were associated with worse median rPFS, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors response rate, and PSA50 outcomes, regardless of therapy (68). It was noteworthy that patients with this negative prognostic biomarker still had longer median rPFS outcomes with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment compared with ARPIs (68). In a single-center observational cohort study (n = 46), higher levels of ctDNA were significantly correlated with shorter PFS in patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (69). The investigators found that a quartile index stratification of ctDNA levels identified three prognostic groups (low/undetectable, intermediate, and high ctDNA) with different Kaplan–Meier PFS estimates (median 7.3 vs 4.3 vs 2.4 months; p = 0.0023), though they also noted the small size of their study as a limitation (69). Similar findings were observed in a recently presented exploratory analysis of patients enrolled in the phase 2 TheraP trial (70). Here, the investigators analyzed baseline blood samples from 178 participants who received ≥ 1 cycle of protocol-assigned treatment, finding that the odds of a PSA50 response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with ctDNA < 2% were significantly higher than in those patients treated with cabazitaxel (p = 0.0067) (70). Furthermore, higher ctDNA fractions were associated with shorter PFS in patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (p < 0.001), though not cabazitaxel (p = 0.35) (70). The investigators concluded that ctDNA fraction is a candidate prognostic and predictive biomarker for differential response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment versus taxane chemotherapy in molecular imaging-identified patients with mCRPC who have progressed after docetaxel (70).
2.7 Changes in cancer-associated genes
In addition to quantifying tumor fraction, ctDNA analysis can detect specific genomic aberrations, including those involving DNA-repair genes (such as BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, PALB2, FANCA, RAD51D, CHEK2, and CDK12) (71). In a 2023 study, pretreatment mutations, deletions, fusions, and amplifications of 83 cancer-associated genes were evaluated in the ctDNA of 44 patients with PSMA-positive mCRPC prior to therapy with PSMA-targeted RLT ([177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T and [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617) (37). Non-responders (defined as PSA response < 50%) were significantly more likely to have amplifications of the cancer-related genes CCNE1 and FGFR1 prior to treatment (37). However, the investigators did note that additional studies to confirm these findings are required (37). Interestingly, alterations in DNA-repair genes were associated with an improved PSA50 response rate following treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, suggesting that the higher PSA50 response rates observed in the DNA-repair cohort might be due to an increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation (72).
Alterations in the tumor suppressor genes PTEN, RB1, and TP53 were found to be significantly associated with poorer outcomes (including PSA-PFS and OS) in a study of ctDNA in 32 patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 plus intermittent treatment with the small molecule transduction inhibitor idronoxil (73). As these data came from a small, single-center study, the investigators commented that further studies are required to fully establish the potential of these genetic variants as prognostic biomarkers for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 RLT (73). Similarly, in the PSMAfore study, median rPFS was also observed to be significantly shorter for patients with detected versus undetected alterations in key PC genes, such as the androgen receptor gene (AR) and TP53, suggesting a potential for prognostic significance (68).
In a recently published retrospective study characterizing molecular prognosticators of benefit to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 among patients with mCRPC (n = 115), the investigators observed that baseline alterations in CDK12, MYC, and FGFR were associated with a reduced PSA50 response after [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment (74). Similarly, another group study assessing genomic alterations in 120 patients with mCRPC found that amplification of genes regulating cell-cycle pathways were associated with poorer OS (75). Conversely, another study in 71 patients with mCRPC found there were no significant associations between [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 outcomes and genomic alterations (in genes including ATM, ATR, BRCA1/2, BRIP1, CHEK2, EPCAM, FANCA, GEN1, HOXB13, MLH1, MSH2/6, NBN, PALB2, PMS2, RAD51C, RAD51D, and TP53), or prespecified pretreatment PET parameters (76). However, in the Phase 2 TheraP trial, ATM loss in baseline ctDNA was associated with more favorable outcomes in select patients treated with [¹⁷⁷Lu]Lu–PSMA-617 (70). Properly powered prospective studies specifically designed to determine links between somatic gene alterations and treatment-sequencing efficacy are required to apply the findings clinically. Given that these studies were conducted in patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, further validation is needed on whether these genomic alterations are predictive or prognostic.
Amplifications, mutations, and splice variants involving the AR gene are commonly seen in mCRPC (77). In a genomic analysis of 101 CRPC metastases, a region approximately 624 kb upstream of the AR gene was a commonly observed site of structural DNA variation (78). AR amplification occurred in 70% of analyzed cases and was associated with significantly elevated AR mRNA expression (p = 9 × 10−8) (78). This is consistent with previous research showing that genomic aberrations in AR are rare in localized PC but reasonably common in CRPC (6) and are an acquired mechanism of resistance to ADT and ARPIs (79). Other study groups have since conducted studies on how AR gene alterations and changes in gene expression could act as potential prognostic biomarkers in mCRPC (69, 80, 81). In one single-center, open-label, phase 2 trial (NCT03454750) evaluating the activity of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and pretreatment plasma AR DNA copy number in patients with mCRPC, patients who gained copies of the AR gene in their plasma were more likely to develop early progressive disease compared with patients with no gain of AR gene copies (p = 0.0002) (80). Patients with these AR gene amplifications had a shorter median OS compared with those who did not have these amplifications (7.4 vs 19.1 months respectively; p = 0.020) (80). The researchers concluded that AR status could therefore indicate cases of mCRPC with early resistance to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (80). In a single-center observational cohort study of 57 patients with late-stage mCRPC treated with a different PSMA-targeted RLT, [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T (69), structural rearrangements in the AR gene and gene alterations in the PI3K pathway were observed to be independently associated with poor prognosis, and patients with these changes did not gain lasting benefit from [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T (69). However, the investigators stated that prospective evaluation in larger biomarker-driven trials is warranted (69). In the PSMAfore study, median rPFS was significantly reduced in patients with detected versus undetected AR gene alterations (68). Moreover, a prospective analysis of patients (n = 19) undergoing [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy for mCRPC suggested that for both full-length AR and the truncated AR splice variant, AR-V7, mRNA copy numbers might serve as prognostic biomarkers for high tumor burden in patients with mCRPC prior to initiating [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment, although further study is required (81). Overall, these studies indicate that alterations in AR, ATM, CCNE1, FGFR1, PTEN, RB1, TP53, CDK12, MYC, and FGFR genes may serve as prognostic biomarkers for mCRPC, including in those treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, though as noted in many of these studies, further research to validate these findings is required.
2.8 Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is thought to be a marker of inflammation, host immune response, and the tumor microenvironment in patients with a wide variety of cancers (82, 83). The value of the NLR in prognosticating [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment outcomes in mCRPC has thus been explored in two retrospective studies (35, 82). In the first, a retrospective analysis of data from 180 patients with mCRPC treated in sequential prospective RLT trials (utilizing [177Lu]Lu‐J591, [90Y]Y‐J591, [177Lu]Lu‐PSMA‐617, or [225Ac]Ac‐J591), a median NLR of ≥ 3.75 (vs < 3.75) was found to be significantly associated with a worse OS (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.02–1.09; p = 0.002), regardless of treatment type (82). In the second retrospective study in 61 patients with mCRPC treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, high NLR (≥ 2.7) demonstrated the strongest (of five hematologic and inflammatory parameters) association with shorter OS (HR, 3.32; 95% CI, 1.66–6.65; p = 0.001) (35). However, as noted by the investigators, the prognostic utility of NLR requires further evaluation in trials comparing [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617-treated and control patients. Should additional research support its use as a prognostic (or predictive) biomarker, NLR may be a highly useful biomarker for the clinical setting, as it can be readily evaluated from routine blood counts and so may be widely adopted relatively quickly (83).
2.9 Hematologic parameters
Nomograms developed from multivariate modeling of data from the phase 3 VISION study identified neutrophil count as a potential prognostic biomarker for OS and lymphocyte count as a potential prognostic biomarker of OS, rPFS, and PSA50 in patients treated with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (84). Further evaluation of these biomarkers in a sufficiently powered clinical study comparing [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and a control arm with BSoC is required to firmly establish their prognostic (and possibly predictive) utility.
3 Predictive biomarkers for response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy in PSMA-positive mCRPC
The use of imaging and clinically based biomarkers is being evaluated for its predictive value in determining response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy in patients with PSMA-positive mCRPC. Understanding the role these biomarkers have in predicting patient response to treatment is a vital tool for optimizing treatment selection in an increasingly complex landscape. Below, we discuss the latest evidence for the utility of various biomarkers for predicting response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment in patients with mCRPC. It should also be noted that some biomarkers, such as whole-body PSMA levels, may have both prognostic and predictive utility.
3.1 Whole-body tumor PSMA expression
PSMA levels, as determined by the SUVmean of PSMA PET, were evaluated in post hoc analyses of two pivotal clinical trials of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 in mCRPC (40, 85). In the phase 2 TheraP study (n = 200) the investigators utilized prespecified cutoff points for SUVmean, observing that whole-body tumor SUVmean values of ≥ 10 were significantly associated with a favorable PSA response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment compared with cabazitaxel (OR, 12.19; 95% CI, 3.42–58.76 vs 2.22; 95% CI, 1.11–4.51; padj = 0.039 for treatment-by-SUVmean interaction) (40). Notably, however, 57 patients harboring tumors with SUVmean values < 10 also showed radiographic responses to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment (40). In an exploratory post hoc subgroup analysis (n = 548) of the VISION study, increasing whole-body tumor SUVmean was significantly associated with improved rPFS and OS outcomes with [177Lu]LuPSMA–617 treatment (43, 85). In the [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 plus BSoC treatment arm, every one-unit increase in whole-body tumor SUVmean was associated with a 12% decrease in the risk of an rPFS event and a 10% decrease in the risk of death (43). It is important to note that in this study, no cutoff or threshold SUVmean was identified, as survival was linearly correlated with whole-body SUVmean (85, 86). Nomograms developed from multivariate modeling of data from 831 patients in the phase 3 VISION study, who received [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 plus BSoC or BSoC alone, also identified SUVmax as a potentially predictive biomarker (84). However, evaluation of SUVmax in a sufficiently powered randomized clinical study comparing [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and BSoC is required to firmly establish its predictive potential.
Importantly, the quantitative PET parameters used in these exploratory [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 studies require specialized software, and the resources required to routinely assess whole-body tumor SUVmean are not available in most clinics (40); hence, the clinical applicability of SUVmean as a prognostic or predictive biomarker may be limited at this time. However, it should be noted that a four-category score that incorporates both heterogeneity and intensity of tumors, derived from tools on a standard PET workstation, was found to be comparable with quantitative SUVmean in terms of predictive utility for response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment (87). In addition, these studies utilized PSMA PET imaging with [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11, which is currently the only radiopharmaceutical approved by the FDA for assessing PSMA-positive PC lesions (88), although current NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) and American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines state that all FDA-approved radioligand tracers (namely [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11, [18F]DCFPyL, and [18F]rhPSMA-7.3) can be used for identifying suitable patients (71, 89). To our knowledge, there are no large studies that have investigated the use of other radioligand tracers for predictive evaluation of SUVmean in [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy.
In addition, the caveats noted above regarding the routine availability of specialized resources required to evaluate SUVmean (40) could also apply to SUVmax, thus limiting the widespread clinical adoption of SUV evaluations at this time.
3.2 Hematologic parameters
The value of hematologic parameters for prediction of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment hematotoxicity was also explored in a retrospective study of 67 patients (36). In this study, the investigators compared pretherapeutic hematologic parameters for prediction of hematotoxicity after [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment. The study found that pretherapeutic leukocyte, lymphocyte, and platelet counts were all strong predictors (vs osseous tumor volume) of hematotoxicity both early and late in the treatment course (36). This study suggests that hematological parameters may have potential as predictive biomarkers, though their utility needs to be formally validated in a prospective randomized controlled trial.
3.3 Other potential predictive biomarkers
Development of the nomograms outlined at the beginning of this section identified a number of other primarily clinical biomarkers with predictive potential in [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy (84), including time since cancer diagnosis; use of opioid analgesic; presence of PSMA-positive lymph node lesions; and levels of hemoglobin, aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, and alkaline phosphatase (63, 84). Again, these would require evaluation and validation in larger biomarker-driven prospective trials comparing [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 and BSoC before they could be utilized as individual predictive biomarkers. Furthermore, a recent real-world retrospective cohort study has shown that monitoring PSA50 levels in patients with mCRPC during treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 may assist clinicians in making faster therapy adjustments, as 87.5% of responders to treatment (n = 7/8) achieved PSA50 before their third dose (90).
4 Forecasting models
In the absence of clinically validated prognostic and predictive biomarkers, nomograms are among the most commonly used tools to estimate prognosis in oncology and medicine. They function by generating an individual numerical probability of a clinical event by integrating diverse prognostic and determinant variables (91). In a recent multicenter, retrospective study, data from 2414 patients were assessed to compare the prognostic value of PSMA PET staging, categorized by PROMISE criteria, with established clinical nomograms (92). Imaging, clinical, and follow-up data were collected, and PSMA PET data were then compared with established clinical risk scores for prediction of OS in patients at all stages of PC (92). The investigators found that their nomograms accurately stratified high-risk and low-risk groups for OS in early and late stages of PC, yielding equal or better prediction accuracy compared with established clinical risk tools (92).
Externally validated nomograms prognostic for mCRPC and predictive of response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment in patients with mCRPC have been developed for clinicians in institutions where PSMA-targeted RLT has been introduced as a novel therapeutic option (84, 93). Gafita et al. have developed three externally validated nomograms that assess OS, PSA-PFS, and PSA50 in males with mCRPC receiving [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, concluding that these prognostic models may assist in clinical trial design and individual clinical decision-making (93). Nomograms developed from multivariate modeling of data from 831 patients in the phase 3 VISION trial identified a number of parameters with potentially predictive value, such as PSMA expression (e.g. SUVmean) and lymphocyte count (84). However, it should be noted that these nomograms utilized [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 for patient identification (84, 93) and have not been validated with other radiotracers. Furthermore, while the predictive value of these nomograms was alluded to by the investigators for one of these models (93), formal statistical validation is difficult, because a comparator arm of patients that had not received [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 was not included in the study design. Therefore, before their use in clinical practice can be widely adopted, clinicians must adequately understand the assumptions and limitations of available nomograms, specifically regarding their ability to provide real-time prognostic information and to predict disease recurrence (91). Moreover, many clinical centers may not have the necessary resources to measure some of the parameters included in the available nomograms.
5 Discussion
This review examines and summarizes data for a number of potential prognostic and predictive biomarkers for [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment in patients with PSMA-positive mCRPC. While there are some promising candidates for prognostic and predictive biomarkers in this setting, further research is broadly needed to fully elucidate their utility in aiding treatment decision-making. The development of accurate tools for establishing the likelihood of disease progression and/or treatment response will provide invaluable assistance to clinicians in making optimal treatment-sequencing decisions, for example, where patients have shown an apparent “complete response” to treatment or where PSMA expression has become downregulated after treatment. Disease progression, or the development of adverse events, are also important considerations for continuing or initiating therapy. Moreover, further research is still needed to determine the right course of action when biomarkers are discordant, such as when serum PSA and whole-body PSMA PET SUVmean measurements are trending in opposite directions after therapy.
The boundary between defining a biomarker as predictive versus prognostic is often confusing, highlighting the importance of appropriately designed clinical trials and validation processes to identify the role of biomarkers as prognostic and/or predictive. Uncertainty around the prognostic or predictive value of a biomarker can arise from inadequate reporting of the criteria used to determine the prognostic/predictive value of factors (94, 95). Furthermore, it is important to recognize that selective and incomplete reporting of prognostic factors (such as the use of preferred definitions and omitting data) can lead to inflated conclusions (96). The REMARK guidelines should be utilized in the design of prognostic studies to ensure sufficient study quality and transparent reporting (34). There are several common limitations in study designs which further complicate interpretation of biomarker study data. Firstly, although studies that assess and compare treatment outcomes in biomarker-positive versus biomarker-negative patients are informative, they often neglect to include a comparator arm containing patients receiving a different treatment regimen (e.g. BSoC). This is important for ascertaining predictive utility, as a comparator arm is required for a formal statistical test for interaction between the treatment and biomarker (33).
Furthermore, inconsistent terminology in the literature, such as interchangeability between the use of “prognostic” and “predictive”, can cause confusion (33), especially when some biomarkers may be both prognostic and predictive (such as SUVmean). For instance, several articles cited in this review discuss the prognostic utility of a biomarker in predicting treatment response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, and so are therefore describing a predictive biomarker. Furthermore, to determine whether a biomarker is purely prognostic, a significant association between biomarker and outcomes needs to be established (regardless of treatment type), and it must be shown that treatment effects do not depend on the biomarker (33). Future clinical trials that attempt to elucidate the prognostic and/or predictive utility of specific biomarkers must take the above points into consideration if they wish to be optimally informative.
Much work is still required in order to validate accurate prognostic biomarkers for patients with mCRPC. With regard to SUVmean as a prognostic biomarker, although trial data provide evidence of poorer survival outcomes in patients with a lower SUVmean, regardless of their treatment (42), the resources such as the specialized software required to assess whole-body SUVmean are not routinely available in current clinical practice (40). This highlights an unmet need to validate existing software in large clinical trials, widen its availability, and provide training that will encourage its use among healthcare professionals (HCPs). Having said this, visual overall assessments of whole-body PSMA PET scans to determine the level of uptake can still be undertaken and may assist HCPs in gauging the spread of disease. Notably, [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 is currently the only radiopharmaceutical approved by the FDA for imaging PSMA-positive lesions in patients with mCRPC (88), although current guidelines allow for use of other PSMA radiotracers thus far, based on their observed near-equivalence to [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 (71, 89). In terms of utilizing [18F]FDG PET for evaluation of MTV and its influence on disease trajectory, it was observed that high [18F]FDG PET MTV was associated with lower treatment response (measured by PSA levels), regardless of treatment type (40). [18F]FDG-derived MTV is a promising candidate for a prognostic biomarker in patients with mCRPC, especially in countries (typically in Europe and Australia) that more routinely perform [18F]FDG PET in mCRPC.
Among other points to consider regarding PSMA PET imaging is that PSMA is regulated in part by the AR signaling pathway (13, 97, 98). PC cells can upregulate PSMA after acute AR blockade (99), while downregulation of PSMA is associated with tumor response to AR-directed treatment (100), and tumors can further upregulate PSMA at the time of AR-reactivation and treatment resistance (101). Loss of AR expression or AR signaling dependence in a subset of CRPC tumors, including those that develop neuroendocrine features, may account for variations in PSMA expression or loss of PSMA-positivity that can be seen in some cases of CRPC (31, 98). More research is thus needed to fully understand how AR signaling interactions affect PSMA protein levels and how serial PET imaging can dynamically capture this process. Furthermore, other mechanisms beyond AR signaling can also regulate PSMA expression, though these are still yet to be fully understood (98). Regardless, PSMA has been demonstrated to be a functionally relevant progression marker of PC in most patients, highlighting that imaging PSMA with PSMA PET to determine the optimal timing of treatment may be of paramount importance.
SPECT/CT measurement of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 uptake has also shown some promise as a biomarker prognostic for disease outcomes (50–53, 55), though the current data are limited and so larger studies and standardization are required for its validation. Though liver metastases are an established prognostic biomarker for poor clinical outcomes in advanced mCRPC (60), there is still a need for further prospective studies to generate data that can determine the extent that patients with liver metastases would benefit from [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment. However, if a patient presents with advanced mCRPC and liver metastases, their prognosis is poor, and so there may be an inclination to treat these patients with whatever treatment options remain. ctDNA fraction and CTCs also suggest promise as prognostic biomarkers (37), but again, studies with larger patient populations are required to elucidate whether these can be applied in the clinical setting at this stage, and whether dynamic changes in these parameters can be useful for treatment decision-making. Likewise, preliminary findings on specific cancer-related gene mutations and amplifications in ctDNA also point to alterations with potential prognostic utility (37, 66, 67), although again, further studies are required to establish their clinical utility when detected before or during [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 therapy. Taken together, the above points suggest that while there are several very promising biomarkers with potential prognostic utility, such as CTCs and ctDNA fraction, they all require further validation prior to use in clinic. However, some prognostic biomarkers such as [18F]FDG MTV and PSMA PET can potentially be adopted in clinic now, though their uptake may be limited by the factors discussed above. Of note, in addition to clinical decision-making, emerging biomarkers may also help understand the biologic mechanisms underlying primary and acquired resistance to PSMA-targeted RLT that could guide future combination treatment strategies.
While many of the data have been focused on the prognostic utility of these aforementioned biomarkers, there is also an unmet need to understand their predictive utility, as this informs on how particular biomarkers may influence/predict treatment outcomes with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, thus aiding optimal treatment selection for patients with mCRPC. While there is some evidence that pretreatment SUVmean is a prognostic biomarker for poorer outcomes in mCRPC, the data from analyses of randomized controlled studies all provide compelling evidence that it may also have utility as a predictor of response to treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, given that higher whole-body tumor SUVmean levels were consistently shown to predict favorable response to treatment in the TheraP and VISION trials (40, 43, 85). However, more data are needed, preferably from prospective randomized trials between treated and untreated comparator arms, regarding the utility of this biomarker as a predictor of response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617. Likewise, stronger evidence for the potential of NLR and other hematologic biomarkers as predictive biomarkers, and for predicting hematotoxicity, is also required. Should future studies confirm their utility, NLR and hematologic biomarkers could see rapid uptake in clinical practice due to their relatively simple acquisition and interpretation. Nonetheless, clinically validated data are lacking with respect to biomarkers that can be utilized to predict response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 treatment. Although multivariate modeling of VISION data identified a number of parameters with potentially predictive value, these require evaluation in larger, biomarker-driven, randomized prospective trials. A summary of all the biomarkers discussed in this review is available in Table 1.
6 Conclusion
Although we provide insights into the potential role of certain biomarkers for providing prognostic and predictive utility, the field is still evolving and the biomarkers discussed need further research with appropriately designed trials before their value can be fully elucidated. It is also unlikely that any one biomarker will provide the adequate data needed for delivering optimal care to patients, so further work on producing nomograms or combinatorial biomarker scores will be required to help identify patients most suitable for treatment with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617. Improved understanding of the complex therapeutic environment that emerged with the approval of multiple life-prolonging agents will also be crucial to better integrate [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 in an effective treatment strategy. Ongoing discussions regarding how data from PSMA PET and other emergent biomarkers can become more widely used in clinical practice are therefore required. In the meantime, baseline whole-body PSMA PET visual assessments are possibly the most robust and readily available tool we currently have for prognosticating and predicting treatment response to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, until obtaining whole-body SUVmean data is more common in routine clinical practice.
Author contributions
HB: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LE: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PHK: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CJL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This manuscript was funded by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr Felix Feng of the University of San Francisco for his review and critical insightsincluded in this paper. Medical writing support was provided by Greg Rowe, MSc and editorial support was provided by Laura McArdle, BA, of Spark (a division of Prime, New York, USA) and was funded by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. This manuscript was developed in accordance with Good Publication Practice guidelines (www.https://www.ismpp.org/gpp-2022). The authors had full control of the content and made the final decision on all aspects of this article. (71) referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Prostate Cancer V.1.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2025. All rights reserved. Accessed June 2025. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org.
Conflict of interest
HB has served as consultant/advisory board member for Janssen, Astellas, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Harpoon Therapeutics, Blue Earth Diagnostics, Amgen, Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Novartis, and has received research funding to institution from Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Circle Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, and Novartis. JC has received compensation for a consulting, advisory, or blinded image reading role from Advanced Accelerator Applications, Amgen, Astellas, Bayer, Blue Earth Diagnostics Inc, Coretag, Curium Pharma, DS Pharma, General Electric Healthcare, Isoray, IBA RadioPharma Solutions, Janssen, Monrol, Lightpoint Medical, Lantheus, Novartis, Nucleus RadioPharma, Pfizer, POINT Biopharma, Progenics, Radiomedix, Radiopharm Theranostics, Sanofi, Siemens-Varian, SOFIE, and Telix Pharmaceuticals; and grant funding from the Prostate Cancer Foundation. LE received funding from a PCF challenge award, Movember, and St Vincent’s Curran and Clinic Foundations, and payment as an advisory board member for Clarity Pharma, Astellas, and Novartis. PHK is a consultant and/or speaker for Attralus, Blue Earth Diagnostics, Chimerix, dGenThera, Eli Lilly, Fusion Pharma, General Electric Healthcare, Invicro, Life Molecular Imaging, Navidea Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Radionetics, Telix Pharmaceuticals, and United Imaging. He is on the scientific advisory board for dGenThera. He is a recipient of research grants from Blue Earth Diagnostics and General Electric Healthcare. CJL has received honoraria from Bayer, Amgen, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Exelixis; and institutional research funding from Janssen, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Aragon Pharmaceuticals.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. National Cancer Institute. Cancer stat facts: prostate cancer (2022). Available online at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html (Accessed December, 2024).
2. National Cancer Institute. Cancer stat facts: common cancer sites (2024). Available online at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/common.html (Accessed December, 2024).
3. Poon DMC, Cheung WSK, Chiu PKF, Chung DHS, Kung JBT, Lam DCM, et al. Treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: review of current evidence and synthesis of expert opinions on radioligand therapy. Front Oncol. (2025) 15:1530580. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1530580
4. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
5. Huang X, Chau CH, and Figg WD. Challenges to improved therapeutics for metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer: from recent successes and failures. J Hematol Oncol. (2012) 5:35. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-35
6. Le TK, Duong QH, Baylot V, Fargette C, Baboudjian M, Colleaux L, et al. Castration-resistant prostate cancer: from uncovered resistance mechanisms to current treatments. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205047
7. Freedland SJ, Davis M, Epstein AJ, Arondekar B, and Ivanova JI. Real-world treatment patterns and overall survival among men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) in the US Medicare population. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. (2024) 27:327–33. doi: 10.1038/s41391-023-00725-8
8. Current K, Meyer C, Magyar CE, Mona CE, Almajano J, Slavik R, et al. Investigating PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy efficacy as a function of cellular PSMA levels and intratumoral PSMA heterogeneity. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:2946–55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-19-1485
9. Yordanova A, Eppard E, Kürpig S, Bundschuh RA, Schönberger S, Gonzalez-Carmona M, et al. Theranostics in nuclear medicine practice. OncoTargets Ther. (2017) 10:4821–8. doi: 10.2147/ott.S140671
10. Hope TA, Aggarwal R, Chee B, Tao D, Greene KL, Cooperberg MR, et al. Impact of (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET on management in patients with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. (2017) 58:1956–61. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.192476
11. Sartor AO, Laidley D, Pouliot F, Probst S, Sabbagh R, Esposito G, et al. A multicenter, randomized, controlled phase II study: Efficacy and safety of PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy I-131-1095 (1095) plus enzalutamide (enza) in 18F-DCFPyL PSMA scan avid, metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients post-abiraterone (abi) progression (ARROW). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:TPS187. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.6_suppl.TPS187
12. Pomykala KL, Czernin J, Grogan TR, Armstrong WR, Williams J, and Calais J. Total-body (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT for bone metastasis detection in prostate cancer patients: potential impact on bone scan guidelines. J Nucl Med. (2020) 61:405–11. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.230318
13. Bakht MK and Beltran H. Biological determinants of PSMA expression, regulation and heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. (2024) 22:26–45. doi: 10.1038/s41585-024-00900-z
14. Al Saffar H, Chen DC, Delgado C, Ingvar J, Hofman MS, Lawrentschuk N, et al. The current landscape of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) imaging biomarkers for aggressive prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050939
15. Ghosh A and Heston WD. Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem. (2004) 91:528–39. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10661
16. Donin NM and Reiter RE. Why targeting PSMA is a game changer in the management of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. (2018) 59:177–82. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.191874
17. European Medicines Agency. Pluvicto lutetium (177Lu) vipivotide tetraxetan (2022). Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/pluvicto (Accessed December, 2024).
18. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. PLUVICTO® (lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan) injection, for intravenous use (2025). Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/215833s021s024lbl.pdf (Accessed July, 2025).
19. Sartor O, de Bono J, Chi KN, Fizazi K, Herrmann K, Rahbar K, et al. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:1091–103. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107322
20. Chi KN, Metser U, Czernin J, Calais J, Prasad V, Eiber M, et al. Study evaluating metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) treatment using 177Lu-PNT2002 PSMA therapy after second-line hormonal treatment (SPLASH). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.TPS5087
21. Tagawa ST, Vallabhajosula S, Christos PJ, Jhanwar YS, Batra JS, Lam L, et al. Phase 1/2 study of fractionated dose lutetium-177-labeled anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen monoclonal antibody J591 ((177) Lu-J591) for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer. (2019) 125:2561–9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32072
22. Johnson G, Lengyelova E, Nordquist LT, Prasad V, Anderson M, Gervasio O, et al. SECuRE: A dose escalation/expansion study to assess the anti-tumor efficacy of 67Cu-SAR-bisPSMA in patients with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:TPS246–TPS. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.4_suppl.TPS246
23. Jang A, Kendi AT, and Sartor O. Status of PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy in prostate cancer: current data and future trials. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:17588359231157632. doi: 10.1177/17588359231157632
24. A phase I/II, open-label, multi-center study of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-R2 in men with PSMA-positive prostate cancer with or without prior 177Lu-psma radioligand therapy (2024). Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05983198 (Accessed December, 2024).
25. Sathekge M, Bruchertseifer F, Vorster M, Lawal IO, Knoesen O, Mahapane J, et al. mCRPC patients receiving (225)Ac-PSMA-617 therapy in the post-androgen deprivation therapy setting: response to treatment and survival analysis. J Nucl Med. (2022) 63:1496–502. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.263618
26. Zacherl MJ, Gildehaus FJ, Mittlmeier L, Böning G, Gosewisch A, Wenter V, et al. First clinical results for PSMA-targeted α-therapy using (225)Ac-PSMA-I&T in advanced-mCRPC patients. J Nucl Med. (2021) 62:669–74. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.251017
27. Almeida LS, Etchebehere E, García Megías I, Calapaquí Terán AK, Hadaschik B, Colletti PM, et al. PSMA radioligand therapy in prostate cancer: where are we and where are we heading? Clin Nucl Med. (2024) 49:45–55. doi: 10.1097/rlu.0000000000004919
28. Wang H, Remke M, Horn T, Schwamborn K, Chen Y, Steiger K, et al. Heterogeneity of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and PSMA-ligand uptake detection combining autoradiography and postoperative pathology in primary prostate cancer. EJNMMI Res. (2023) 13:99. doi: 10.1186/s13550-023-01044-8
29. Pouliot F, Saad F, Rousseau E, Richard PO, Zamanian A, Probst S, et al. Intrapatient intermetastatic heterogeneity determined by triple-tracer PET imaging in mCRPC patients and correlation to survival: the 3TMPO cohort study. J Nucl Med. (2024) 65:1710–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268020
30. Hofman M, Emmett L, Sandhu S, Iravani A, Joshua A, Goh J, et al. 177Lu-PSMA-617 versus cabazitaxel in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (TheraP): a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. (2021) 397:797–804. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00237-3
31. Bakht MK, Yamada Y, Ku SY, Venkadakrishnan VB, Korsen JA, Kalidindi TM, et al. Landscape of prostate-specific membrane antigen heterogeneity and regulation in AR-positive and AR-negative metastatic prostate cancer. Nat Cancer. (2023) 4:699–715. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00539-6
32. FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, endpointS, and other Tools) Resource [Internet]: Understanding Prognostic versus Predictive Biomarkers. Silver Spring (MD); Bethesda (MD: Food and Drug Administration (US); National Institutes of Health (US (2016). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK402284/.
33. Ballman KV. Biomarker: predictive or prognostic? J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:3968–71. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.63.3651
34. McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, and Clark GM. Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK). J Natl Cancer Inst. (2005) 97:1180–4. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dji237
35. Şahin E, Kefeli U, Zorlu Ş, Seyyar M, Ozkorkmaz Akdag M, Can Sanci P, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, systemic immune-inflammation index, and pan-immune-inflammation value in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients who underwent 177Lu-PSMA-617. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e35843. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000035843
36. Widjaja L, Werner RA, Ross TL, Bengel FM, and Derlin T. Comparison of pretherapeutic osseous tumor volume and standard hematology for prediction of hematotoxicity after PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2021) 48:4077–88. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05412-1
37. Sartor O, Ledet E, Huang M, Schwartz J, Lieberman A, Lewis B, et al. Prediction of resistance to (177)Lu-PSMA therapy by assessment of baseline circulating tumor DNA biomarkers. J Nucl Med. (2023) 64:1721–5. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.266167
38. Tsechelidis I and Vrachimis A. PSMA PET in imaging prostate cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:831429. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.831429
39. Kapoor M and Kasi A. PET scanning. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL (2024).
40. Buteau JP, Martin AJ, Emmett L, Iravani A, Sandhu S, Joshua AM, et al. PSMA and FDG-PET as predictive and prognostic biomarkers in patients given [(177)Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 versus cabazitaxel for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (TheraP): a biomarker analysis from a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:1389–97. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(22)00605-2
41. Fendler WP, Karpinski J, Hüsing J, Claassen K, Möller L, Kajüter H, et al. Prognostic PSMA-PET PROMISE nomograms for patients with prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:5016. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.5016
42. Hofman MS, Emmett L, Sandhu S, Iravani A, Buteau JP, Joshua AM, et al. Overall survival with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 versus cabazitaxel in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (TheraP): secondary outcomes of a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2024) 25:99–107. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00529-6
43. Kuo PH, Morris MJ, Hesterman J, Kendi AT, Rahbar K, Wei XX, et al. Quantitative (68)Ga-PSMA-11 PET and clinical outcomes in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following (177)Lu-PSMA-617 (VISION trial). Radiology. (2024) 312:e233460. doi: 10.1148/radiol.233460
44. Berger A. How does it work? Positron emission tomography. BMJ. (2003) 326:1449. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7404.1449
45. Wibmer AG, Morris MJ, Gonen M, Zheng J, Hricak H, Larson S, et al. Quantification of metastatic prostate cancer whole-body tumor burden with (18)F-FDG PET parameters and associations with overall survival after first-line abiraterone or enzalutamide: a single-center retrospective cohort study. J Nucl Med. (2021) 62:1050–6. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.256602
46. Ferdinandus J, Violet J, Sandhu S, Hicks RJ, Ravi Kumar AS, Iravani A, et al. Prognostic biomarkers in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving [177Lu]-PSMA-617. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2020) 47:2322. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04723-z
47. Im HJ, Bradshaw T, Solaiyappan M, and Cho SY. Current methods to define metabolic tumor volume in positron emission tomography: which one is better? Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2018) 52:5–15. doi: 10.1007/s13139-017-0493-6
48. Kuo PH, Benson T, Messmann R, and Groaning M. Why we did what we did: PSMA PET/CT selection criteria for the VISION Trial. J Nucl Med. (2022) 63:816–8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.263638
49. Buck AK, Nekolla S, Ziegler S, Beer A, Krause BJ, Herrmann K, et al. SPECT/CT. J Nucl Med. (2008) 49:1305–19. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.050195
50. Pathmanandavel S, Crumbaker M, Ho B, Yam AO, Wilson P, Niman R, et al. Evaluation of (177)Lu-PSMA-617 SPECT/CT quantitation as a response biomarker within a prospective (177)Lu-PSMA-617 and NOX66 combination trial (LuPIN). J Nucl Med. (2023) 64:221–6. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264398
51. Neubauer MC, Nicolas GP, Bauman A, Fani M, Nitzsche E, Afshar-Oromieh A, et al. Early response monitoring during [(177)Lu]Lu-PSMA I&T therapy with quantitated SPECT/CT predicts overall survival of mCRPC patients: subgroup analysis of a Swiss-wide prospective registry study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2024) 51:1185–93. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06536-2
52. Demirci RA, Gulati R, Hawley JE, Yezefski T, Haffner MC, Cheng HH, et al. SPECT/CT in early response assessment of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving (177)Lu-PSMA-617. J Nucl Med. (2024) 65:1945–51. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.267665
53. Emmett L, John N, Pathmanandavel S, Counter W, Ayers M, Sharma S, et al. Patient outcomes following a response biomarker-guided approach to treatment using 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in men with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (Re-SPECT). Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2023) 15:17588359231156392. doi: 10.1177/17588359231156392
54. John N, Pathmanandavel S, Crumbaker M, Counter W, Ho B, Yam AO, et al. (177)Lu-PSMA SPECT quantitation at 6 weeks (dose 2) predicts short progression free survival for patients undergoing lu PSMA I&T therapy. J Nucl Med. (2022) 64:410–5. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264677
55. Yadav S, Lowery B, Tuchayi AM, Jiang F, Saelee R, Aggarwal RR, et al. Impact of posttreatment SPECT/CT on patient management during (177)Lu-PSMA-617 radiopharmaceutical therapy. J Nucl Med. (2024) 65:1395–401. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.267955
56. Yadav S, Jiang F, Kurkowska S, Saelee R, Morley A, Feng F, et al. Assessing response to PSMA radiopharmaceutical therapies with single SPECT imaging at 24 hours after injection. J Nucl Med. (2024) 65:1064–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.267208
57. Song H, Ferri V, Duan H, Aparici CM, Davidzon G, Franc BL, et al. SPECT at the speed of PET: a feasibility study of CZT-based whole-body SPECT/CT in the post (177)Lu-DOTATATE and (177)Lu-PSMA617 setting. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2023) 50:2250–7. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06176-6
58. Swiha M, Pathmanandavel S, Papa N, Sabahi Z, Li S, Zheng A, et al. Comparison of posttherapy 4- and 24-hour [(177)Lu]Lu-PSMA SPECT/CT and pretherapy PSMA PET/CT in assessment of disease in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. (2024) 65:1939–44. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.267606
59. Waninger JJ, Ma VT, Chopra Z, Pearson AN, and Green MD. Evaluation of the prognostic role of liver metastases on patient outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer J. (2023) 29:279–84. doi: 10.1097/ppo.0000000000000683
60. Halabi S, Kelly WK, Ma H, Zhou H, Solomon NC, Fizazi K, et al. Meta-analysis evaluating the impact of site of metastasis on overall survival in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:1652–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.7270
61. Ahmadzadehfar H, Rahbar K, Baum RP, Seifert R, Kessel K, Bögemann M, et al. Prior therapies as prognostic factors of overall survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with [(177)Lu]Lu-PSMA-617. A WARMTH multicenter study (the 617 trial). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2021) 48:113–22. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04797-9
62. Rahbar K, Ahmadzadehfar H, Kratochwil C, Haberkorn U, Schäfers M, Essler M, et al. German multicenter study investigating 177Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy in advanced prostate cancer patients. J Nucl Med. (2017) 58:85–90. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.116.183194
63. Wrenger R, Jüptner M, Marx M, Zhao Y, Zuhayra M, Caliebe A, et al. Pre- and intratherapeutic predictors of overall survival in patients with advanced metastasized castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving Lu-177-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy. BMC Urol. (2022) 22:96. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01050-3
64. Telli T, Tuncel M, Karabulut E, Aksoy S, Erman M, Akdogan B, et al. Prognostic factors of overall and prostate-specific antigen-progression-free survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with (177) Lu-PSMA-617. A single-center prospective observational study. Prostate. (2023) 83:792–800. doi: 10.1002/pros.24518
65. Derlin T, Riethdorf S, Schumacher U, Lafos M, Peine S, Coith C, et al. PSMA-heterogeneity in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: circulating tumor cells, metastatic tumor burden, and response to targeted radioligand therapy. Prostate. (2023) 83:1076–88. doi: 10.1002/pros.24549
66. Fonseca NM, Maurice-Dror C, Herberts C, Tu W, Fan W, Murtha AJ, et al. Prediction of plasma ctDNA fraction and prognostic implications of liquid biopsy in advanced prostate cancer. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:1828. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45475-w
67. Reichert ZR, Morgan TM, Li G, Castellanos E, Snow T, Dall’Olio FG, et al. Prognostic value of plasma circulating tumor DNA fraction across four common cancer types: a real-world outcomes study. Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:111–20. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.09.163
68. Bono JSD, Morris MJ, Sartor O, Wei XX, Fizazi K, Herrmann K, et al. Baseline ctDNA analyses and associations with outcomes in taxane-naive patients with mCRPC treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 versus change of ARPI in PSMAfore. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:5008. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.5008
69. Vanwelkenhuyzen J, Van Bos E, Van Bruwaene S, Lesage K, Maes A, Üstmert S, et al. AR and PI3K genomic profiling of cell-free DNA can identify poor responders to Lutetium-177-PSMA among patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol Open Sci. (2023) 53:63–6. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2023.05.008
70. Kwan EM, Ng SWS, Tolmeijer SH, Emmett L, Sandhu S, Buteau JP, et al. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 or cabazitaxel in metastatic prostate cancer: circulating tumor DNA analysis of the randomized phase 2 TheraP trial. Nature medicine. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03704-9
71. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Prostate Cancer V.1.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. (2025). All rights reserved. Available online at: https://www.nccn.org/ (Accessed June 2025).
72. Raychaudhuri R, Mo G, Haffner MC, Morrissey C, Ha G, Yu EY, et al. PSMA expression and response to 177Lu-PSMA-617 (LuPSMA) in men with vs. without DNA damage repair (DDR) mutations. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:5055. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.5055
73. Crumbaker M, Goldstein LD, Murray DH, Tao J, Pathmanandavel S, Boulter N, et al. Circulating tumour DNA biomarkers associated with outcomes in metastatic prostate cancer treated with Lutetium-177-PSMA-617. Eur Urol Open Sci. (2023) 57:30–6. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2023.08.007
74. Panian J, Henderson N, Barata PC, Bilen MA, Graham L, Heath E, et al. Association of tumor genetics with outcomes in patients (pts) with PSMA-positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.5050
75. Gauntner T, Gheeya JS, Khorasanchi A, Xu M, Hasanov E, Collier KA, et al. Association of genomic alterations with clinical outcomes following lutetium-177-PSMA vipivotide tetraxetan in men with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.5057
76. Yilmaz B, Chalker C, Yu Y, Kaempf A, Mittra E, MallaK N, et al. Genetic analysis of metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer patients treated with Lu-177 PSMA radioligand therapy. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:e17063. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.e17063
77. Rajwa P, Zapała P, and Merseburger AS. Targeting androgen receptor alterations in metastatic prostate cancer. Eur Urol Focus. (2024) 11:79–81. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2024.07.012
78. Quigley DA, Dang HX, Zhao SG, Lloyd P, Aggarwal R, Alumkal JJ, et al. Genomic hallmarks and structural variation in metastatic prostate cancer. Cell. (2018) 174:758–69.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.039
79. Jernberg E, Bergh A, and Wikström P. Clinical relevance of androgen receptor alterations in prostate cancer. Endocr Connect. (2017) 6:R146–R61. doi: 10.1530/ec-17-0118
80. De Giorgi U, Sansovini M, Severi S, Nicolini S, Monti M, Gurioli G, et al. Circulating androgen receptor gene amplification and resistance to (177)Lu-PSMA-617 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: results of a Phase 2 trial. Br J Cancer. (2021) 125:1226–32. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01508-5
81. Kessel K, Seifert R, Weckesser M, Roll W, Humberg V, Schlack K, et al. Molecular analysis of circulating tumor cells of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients receiving (177)Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy. Theranostics. (2020) 10:7645–55. doi: 10.7150/thno.44556
82. Stangl-Kremser J, Sun M, Ho B, Thomas J, Nauseef JT, Osborne JR, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving prostate-specific membrane antigen targeted radionuclide therapy. Prostate. (2023) 83:1351–7. doi: 10.1002/pros.24597
83. Cupp MA, Cariolou M, Tzoulaki I, Aune D, Evangelou E, and Berlanga-Taylor AJ. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cancer prognosis: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies. BMC Med. (2020) 18:360. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01817-1
84. Hermann K, Gafita A, de Bono J, Sartor AO, Chi KN, Krause BJ, et al. Building a predictive model for outcomes with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer using VISION data. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:208. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.4_suppl.208
85. Kuo P, Hesterman J, Rahbar K, Kendi AT, Wei XX, Fang B, et al. 68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET baseline imaging as a prognostic tool for clinical outcomes to [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with mCRPC: A VISION substudy. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:5002. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.5002
86. Kuo PH, Morris M, Kendi AT, Rahbar K, Wei XX, Fang B, et al. Association of baseline quantitative [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET imaging parameters with clinical outcomes in patients with mCRPC receiving [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617: a VISION sub-study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2023) 50:S155. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06333-x
87. Swiha M, Papa N, Sabahi Z, Ayati N, John N, Pathmanandavel S, et al. Development of a visually calculated SUV(mean) (HIT score) on screening PSMA PET/CT to predict treatment response to (177)Lu-PSMA therapy: comparison with quantitative SUV(mean) and patient outcomes. J Nucl Med. (2024) 65:904–8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.267014
88. FDA Press Release. FDA approves first PSMA-targeted PET imaging drug for men with prostate cancer (2020). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-psma-targeted-pet-imaging-drug-men-prostate-cancer (Accessed December, 2024).
89. Garje R, Hope TA, Rumble RB, and Parikh RA. Systemic therapy update on (177)Lutetium-PSMA-617 for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: ASCO guideline rapid recommendation Q and A. JCO Oncol Pract. (2023) 19:132–5. doi: 10.1200/op.22.00753
90. Maslov DV, New J, Patel N, Kosty MO, and Bhangoo MS. Pluvicto in the real world setting and timing to PSA50 as a predictive marker of treatment response. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:e17026. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.e17026
91. Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, and DeMatteo RP. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. (2015) 16:e173–80. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71116-7
92. Karpinski MJ, Hüsing J, Claassen K, Möller L, Kajüter H, Oesterling F, et al. Combining PSMA-PET and PROMISE to re-define disease stage and risk in patients with prostate cancer: a multicentre retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. (2024) 25:1188–201. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(24)00326-7
93. Gafita A, Calais J, Grogan TR, Hadaschik B, Wang H, Weber M, et al. Nomograms to predict outcomes after (177)Lu-PSMA therapy in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: an international, multicentre, retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1115–25. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00274-6
94. Sauerbrei W, Haeussler T, Balmford J, and Huebner M. Structured reporting to improve transparency of analyses in prognostic marker studies. BMC Med. (2022) 20:184. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02304-5
95. Azuaje F, Devaux Y, and Wagner D. Challenges and standards in reporting diagnostic and prognostic biomarker studies. Clin Transl Sci. (2009) 2:156–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2008.00075.x
96. Kyzas PA, Loizou KT, and Ioannidis JP. Selective reporting biases in cancer prognostic factor studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2005) 97:1043–55. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dji184
97. Sheehan B, Guo C, Neeb A, Paschalis A, Sandhu S, and de Bono JS. Prostate-specific membrane antigen biology in lethal prostate cancer and its therapeutic implications. Eur Urol Focus. (2022) 8:1157–68. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.06.006
98. Hyväkkä A, Virtanen V, Kemppainen J, Grönroos TJ, Minn H, and Sundvall M. More than meets the eye: Scientific rationale behind molecular imaging and therapeutic targeting of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) in metastatic prostate cancer and beyond. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:2244. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092244
99. Lückerath K, Wei L, Fendler WP, Evans-Axelsson S, Stuparu AD, Slavik R, et al. Preclinical evaluation of PSMA expression in response to androgen receptor blockade for theranostics in prostate cancer. EJNMMI Res. (2018) 8:96. doi: 10.1186/s13550-018-0451-z
100. Sommer U, Siciliano T, Ebersbach C, Beier AK, Stope MB, Jöhrens K, et al. Impact of androgen receptor activity on prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1046. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031046
Keywords: metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, prostate-specific membrane antigen, radioligand therapy, [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, biomarkers
Citation: Beltran H, Calais J, Emmett L, Kuo PH and Logothetis CJ (2025) Biomarkers to optimize PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1583168. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1583168
Received: 25 February 2025; Accepted: 11 June 2025;
Published: 20 August 2025.
Edited by:
Johnny Kao, Good Samaritan Hospital Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Roberto C. Delgado Bolton, Hospital San Pedro, SpainMaria Luisa Garo, Mathsly Research, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Beltran, Calais, Emmett, Kuo and Logothetis. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Phillip H. Kuo, cGhrdW9AY29oLm9yZw==
 Himisha Beltran1
Himisha Beltran1 Jeremie Calais
Jeremie Calais Phillip H. Kuo
Phillip H. Kuo