- 1Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 2Animal Center, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
- 3Department of General Surgery, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have profoundly transformed the treatment landscape for microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) colorectal cancer (CRC). However, immune-related adverse events (irAEs) remain a common and unpredictable complication among patients undergoing ICI therapy. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), a rare and life-threatening irAE, is triggered by hyperactivated immune cells and excessive secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. We report a case of an MSI-H female patient with a history of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who developed HLH after treatment with the anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody tislelizumab. After treated with tislelizumab 31 days, the patient presented with fever, pancytopenia, hemophagocytosis in bone marrow, elevated ferritin and triglyceride levels, and decreased fibrinogen. A diagnosis of HLH was confirmed with an H-score of 264. Despite steroid therapy, the patient’s HLH progressed rapidly. Etoposide was deemed intolerable, and tocilizumab and immunoglobulin were declined due to financial constraints. Regrettably, the patient succumbed to HLH within 16 days of diagnosis. This is the first reported case of ICI-induced HLH in an MSI-H colon cancer patient with a history of SLE, prompting an analysis of the potential mechanisms underlying the induction of HLH in this case. Clinicians should be vigilant for the development of HLH during ICI treatment and initiate combination therapy as early as possible upon onset of HLH.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer worldwide with an estimated incidence of over 1.9 million new cases annually, and it is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality with 904,000 deaths (1). Approximately 20% of patients present at an advanced stage without the opportunity for surgery (2). Fluorouracil-based and platinum-based combinations are frequently utilized as chemotherapeutic agents for these advanced patients (3). Targeted agents such as bevacizumab or cetuximab, depending on the RAS gene mutational status and tumor location, are combined to augment the anti-tumor effect of chemotherapy agents (4). Nevertheless, the prognosis for these patients remains bleak (5). Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) have made significant breakthroughs in cancer treatment. Following their initial approval for melanoma treatment, ICIs have been widely applied in adjuvant treatment for various types of cancer (6). The KEYNOTE-177 trial showed that an anti-PD-1 antibody of pembrolizumab significantly improved the progression-free survival (PFS) compared to chemotherapy (16.5 months versus 8.2 months) as a first-line treatment in advanced CRC patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) (7). Based on the result of KEYNOTE-177, pembrolizumab was approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as the first-line treatment for MSI-H advanced CRC patients.
ICIs are believed to primarily exert anti-tumor effects by activating immune responses, particularly T lymphocytes (8). However, as a result of antigens shared between the tumor tissue and the target organ, the activated immune response may lead to T cell cross-reactivity, thereby resulting in the development of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) (9). The incidence of irAEs for ICI treatment of MSI-H colorectal cancer is approximately 31%, with 9% classified as grade 3–4 irAEs. These frequently include hypothyroidism, colitis, hyperthyroidism, pneumonitis and adrenal insufficiency (7). Nevertheless, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) caused by ICIs in MSI-H colorectal cancer patients has not been reported yet.
HLH is a rare syndrome charactered by high fever, cytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, elevated levels of liver enzymes, and high serum levels of ferritin and triglyceride (10). The disease commonly results from the hyper-activation of immune cells, leading to excessive pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, progressive tissue injury, multi-organ failure, and ultimately mortality (11). HLH is classified as primary or acquired based on its etiology, with the latter typically triggered by malignancies, severe acute infections, autoimmune diseases and exposure to drugs including ICIs (12). A study indicates that 5.7% of all HLH cases are associated with the application of ICIs (13). However, cancer patients with ICIs-related HLH had a history of autoimmune disease were rarely reported. Here, we presented a case of HLH following treatment with an anti-PD-1 antibody of tislelizumab in a patient with MSI-H colon cancer and co-existing systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Case report
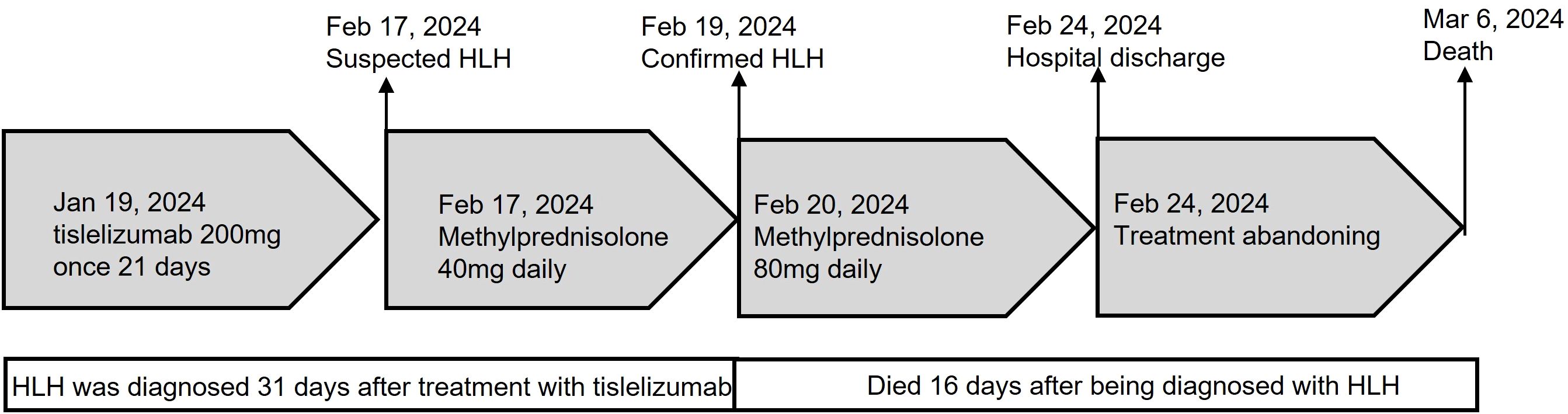
A 68-year-old Chinese female was admitted to the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University on January 15, 2024, presenting with a complaint of appetite loss persisting for over a month. Notably, her medical history included a three-year diagnosis of SLE. Upon admission, the patient was administered a daily dosage of 3 mg of methylprednisolone and 0.1 g of hydroxychloroquine, maintaining her SLE in a stable state. Twenty days prior to admission, a colonoscopy revealed an ulcerative mass in the ascending colon, causing lumen narrowing (Figure 1A). Pathological and immunohistochemical analyses confirmed the tumor as a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (Figure 1B) with MSI-H, characterized by PMS2 (-), MLH1 (-), MSH2 (+), and MSH6 (+) (Figures 1C–F). An enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan demonstrated ascending colon wall thickening accompanied by enlarged peripheral lymph nodes (Figure 2A), alongside suspected malignant lesions and multiple metastatic nodules in the pelvic and abdominal cavities, leading to a diagnosis of Stage IV colon carcinoma. Laboratory tests indicated a negative anti-dsDNA antibody, while the patient tested positive for ANA (1:320) with TOPO I and anti-Sm antibody. Additional laboratory findings revealed complement C3 was 0.69g/L (normal range: 0.7-1.4g/L), complement C4 0.12g/L (normal range: 0.1-0.4g/L), white blood cells (WBC) 9.01×1012/l (normal range: 3.8-5.1×1012/l), hemoglobin 81.7g/L (normal range: 115-150g/L), platelets 238×109/l (normal range: 125-350×109/l), D-dimer 0.193 mg/l (normal range: <0.243mg/L), triglyceride 1.98 mmol/L (normal range: 0.3-1.7mmol/L), and C-reactive protein (CRP) 82.3mg/L (normal range: 0-6.0mg/L). Routine urine analysis was within normal limits. Based on the patient’s clinical manifestations and laboratory results, the SLEDAI-2000 score was calculated as 0, confirming her SLE was in a stable phase. Given the patient’s stable SLE, she received tislelizumab - the only PD-1 monoclonal antibody with government-sponsored medical insurance coverage for MSI-H solid tumor indications in China, (200 mg intravenously once every 3 weeks) on January 19, 2024, and was successfully discharged post-treatment. The patient returned to the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University for the next treatment cycle on February 17, 2024. Since her last discharge, she experienced intermittent appetite loss and fatigue. Physical examination found no throat congestion or swelling, and cardiopulmonary and abdominal assessments revealed no significant abnormalities. The blood counts showed WBC was 3.23×1012/l, hemoglobin of 75 g/l and platelets 12×109/l. Her D-dimer was 4.782 mg/l, triglyceride 2.78mmol/L, fibrinogen 0.81 g/L (normal range: 2.38-4.98g/L), ferritin ≥2000ng/L (normal range: 13.0-150), C3 0.46g/L, and CRP 71mg/L. A follow-up CT scan (Figure 2B) showed persistent thickening of the ascending colon wall, but with a reduction in the number of abdominal and pelvic nodules, suggesting a partial response to colon cancer treatment. However, due to the patient’s predisposition to HLH induced by ICI, administration of tislelizumab was discontinued. Although a bone marrow aspiration was proposed, the patient declined. Consequently, the patient was treated with daily 40 mg of methylprednisolone, along with platelet and red blood cell transfusions, and symptomatic and supportive care. Three days later, the patient developed a non-infectious fever, peaking at 38.5°C. Following repeated and emphatic recommendations, the patient underwent a bone marrow aspiration, revealing mixed anemia and an irritable bone marrow image with prominent hemophagocytosis (Figure 1G). Based on these findings, the patient met the diagnostic criteria for HLH-2004, with an H-score of 264. Given her poor physical condition, chemotherapy with etoposide and cyclophosphamide was deemed unsuitable, and she refused cytokine antagonists and immunoglobulin due to financial constraints. The patient was then treated with 80 mg of methylprednisolone daily for an additional four days, but her condition failed to improve. Ultimately, the patient opted to discontinue treatment and passed away ten days after discharge. The treatment process of the patient is depicted in Figure 3.
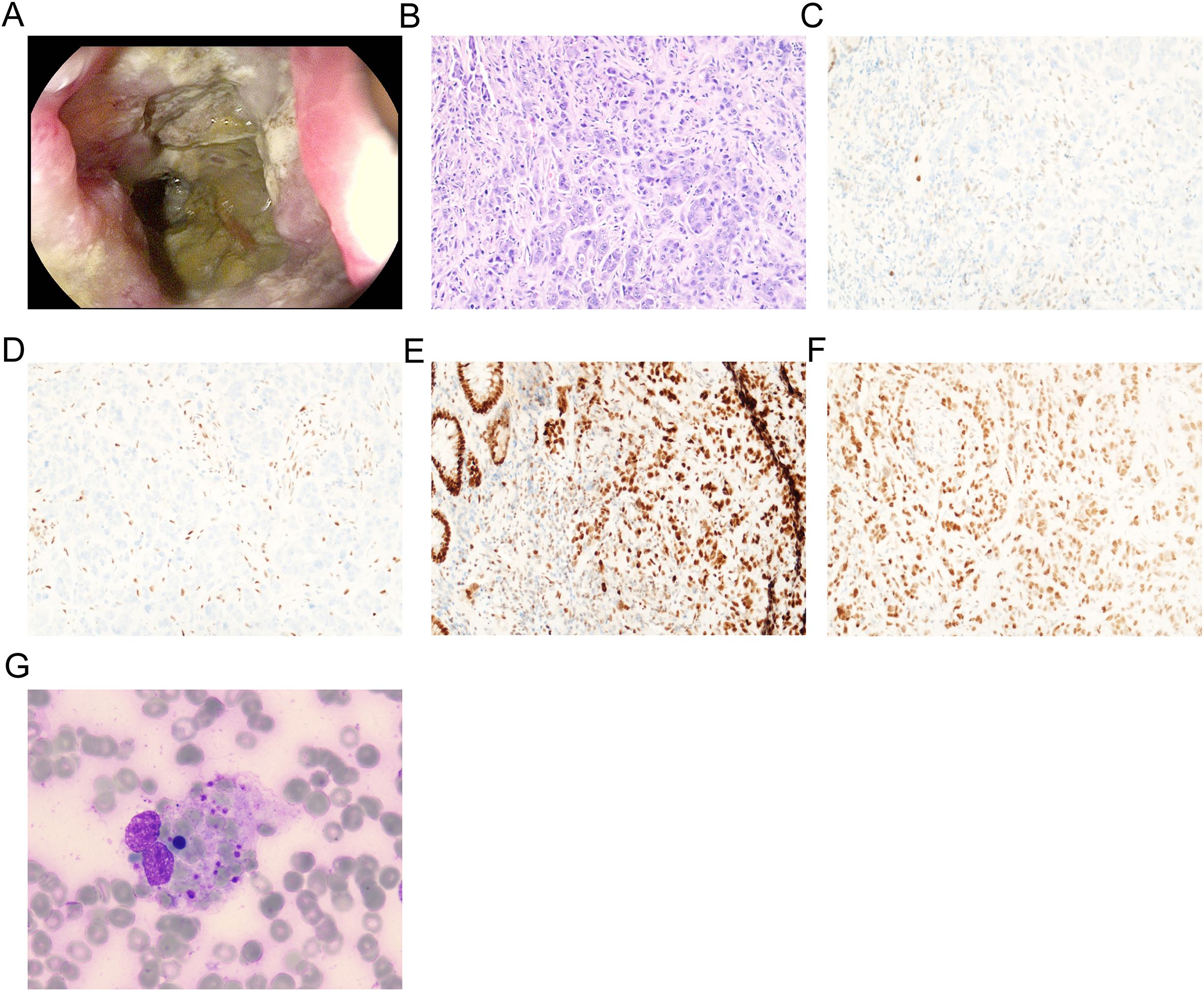
Figure 1. Gastroscopy and biopsy of the patient. (A) The colonoscopy examination revealed an ulcerative mass in the ascending colon; (B) The histopathological examination of biopsies sampled revealed poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (stained using the H&E method, magnification, x200); (C) PMS2(-) by immunohistochemistry (magnification, x200); (D) MLH1(-) by immunohistochemistry (magnification, x200); (E) MSH2(+) by immunohistochemistry (magnification, x200); (F) MSH6(+) by immunohistochemistry (magnification, x200); (G) Bone marrow biopsy of the patient (magnification, x400).
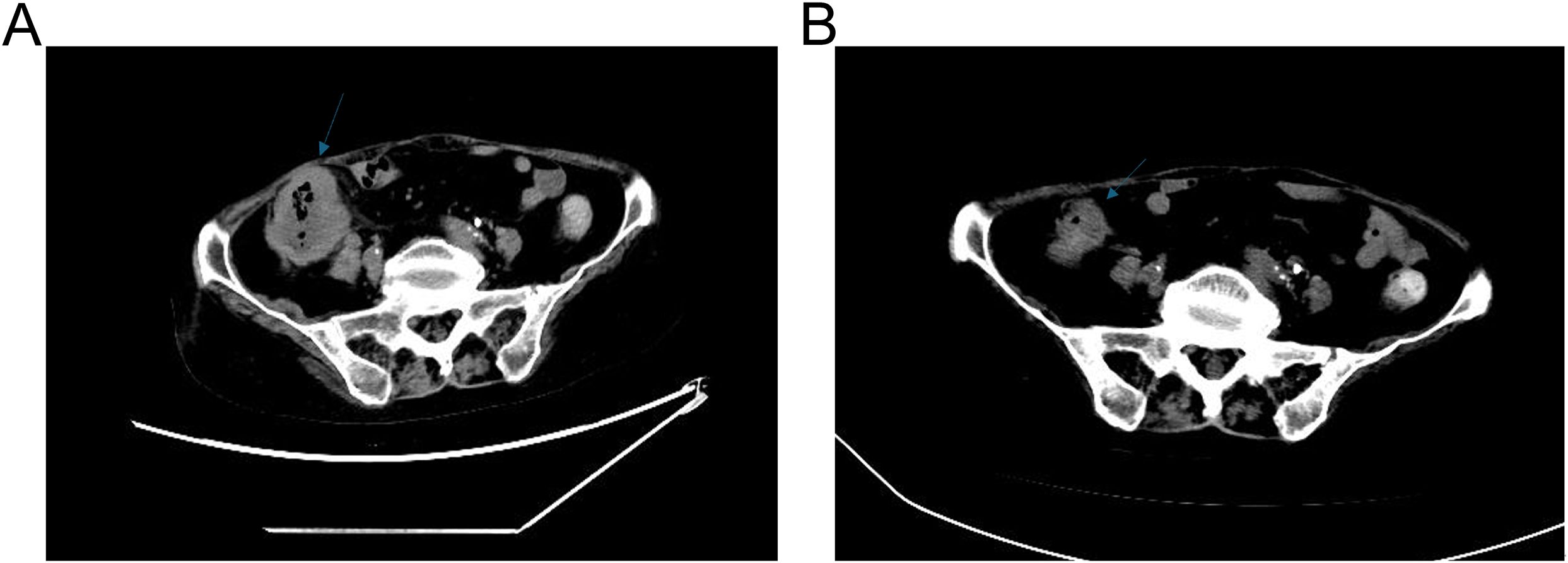
Figure 2. CT of the patient. (A) Abdominal CT scan prior to the treatment of tislelizumab. (B) Abdominal CT scan after the treatment of tislelizumab.
Discussion
Patients with cancer and concurrent autoimmune diseases (ADs) including SLE, have historically been excluded from ICIs clinical trials. This exclusion primarily stems from concerns that ADs may be exacerbated, leading to an increased risk of severe irAEs. Nevertheless, in clinical practice, an increasing number of such patients are being encountered, and evidence suggests that ICIs treatment can be both safe and effective for them. A retrospective study evaluated the therapeutic outcomes of 85 individuals diagnosed with both cancer and ADs who received anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies therapy. Their outcomes were compared with those of patients without ADs. Although a higher proportion of AD patients experienced irAEs of any grade (65.9% compared to 39.9%), no significant difference was observed in the incidence of grade 3–4 events between the two groups. Furthermore, no notable differences were identified in prognosis (14). Three additional studies have similarly demonstrated the safety of ICIs in patients with cancer and coexisting ADs. In these studies, only 20% - 40% of patients experienced worsening of their autoimmune conditions, and all adverse effects were manageable. Discontinuation of ICI therapy was rare, and tumor responses were reported (15–19). A systematic review evaluated the use of ICIs in 123 cancer patients with a history of ADs (20). Overall, 92 patients (75%) experienced irAEs. Among them, 50 patients (41%) had exacerbations of pre-existing ADs, 31 patients (25%) developed new irAEs, and 11 patients (9%) experienced both types of events.
Based on these findings, the following conclusions can be drawn: 1) Patients with ADs including SLE, experience a higher overall incidence of irAEs than those without ADs; however, there is no significant difference in the occurrence of high-grade (grade 3–4) events. 2) The most common types of irAEs involve exacerbations of underlying ADs. This may result from PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition-induced activation of T cells and other immune cells, which leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (21, 22), potentially triggering off-target inflammation and irAEs (23). 3) Flare-ups of ADs generally do not necessitate discontinuation of ICIs therapy and can be effectively managed. 4) The effectiveness of ICIs appears similar in patients with and without ADs (24). Despite this evidence, patients with cancer and ADs currently lack standardized treatment guidelines and reliable methods for assessing individual benefit-risk ratios. This gap represents a significant unmet need in oncology. Therefore, prospective studies are urgently needed to establish optimal strategies for administering ICIs in this patient population.
The H-score, which integrates various clinical indicators such as recognized immunosuppression, elevated temperature, and organomegaly; laboratory findings encompassing triglycerides, ferritin, serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase levels, fibrinogen levels, and cytopenia; as well as a specific cytological criterion (the presence of hemophagocytosis in bone marrow aspirate), is extensively employed for diagnosing HLH (25). A score exceeding 250, accompanied by a clinical presentation devoid of detectable infection, strongly indicates HLH. The patient exhibited a clinical profile characterized by fever, pancytopenia, hemophagocytosis in the bone marrow, elevated ferritin and triglyceride levels, and decreased fibrinogen, collectively pointing towards a diagnosis of HLH. The onset of HLH can be precipitated by multiple external factors, including malignancies, severe acute infections, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to ICIs (26). Hematological malignancies are the most common malignancies associated with HLH, whereas solid tumors are infrequently reported (27). Notably, no cases have established a direct link between colon cancer and the initiation of HLH.
During ICIs treatment, the inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway disrupts the normal inhibitory control that negatively regulates T-cell function. This leads to hyperactivation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and excessive secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in healthy tissues (9, 28). HLH, a rare and severe irAE, can be triggered by hyperactivated immune cells and oversecretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (12). Pathological features of HLH reveal abundant infiltration of immune cells, including CTLs and macrophages, along with oversecretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interferon (IFN)-γ, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-18 (29, 30). The molecular mechanisms underlying HLH are not fully understood. However, some studies suggest that excessive CTLs secrete significant amounts of IFN-γ, which potently stimulates macrophages. These macrophages then release large quantities of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18, and TNF-α, potentially leading to tissue injury (31). Subsequent tissue damage produces high levels of IL-1β and IL-33, which continue to activate macrophages (30, 32). Additionally, IL-18, in combination with IL-12, is believed to facilitate further activation of CTLs and their production of IFN-γ (33, 34). On the other hand, IFN-γ enhances the expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I on immune cells, thereby amplifying the feed-forward loops (12). This cytokine storm may exacerbate hematopoietic failure, contribute to various clinical manifestations of HLH, and worsen the disease (31). An HLH animal model suggests that IFN-γ contributes to anemia via inhibiting erythropoiesis and promoting hemophagocytosis (35). Another animal model indicates that release of IFN-γ leads to splenomegaly in HLH (12, 36). Furthermore, ferritin secreted by macrophages elevates plasminogen activator levels and triggers hyperfibrinolysis (37). Other pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, are thought to be associated with fever and multi-organ dysfunction in HLH (38). Considering the critical role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of HLH, we strongly recommended that the patient undergo cytokine testing at the time of HLA diagnosis. However, the patient’s family declined the examination for economic reasons, as it was not covered by government-sponsored medical insurance.
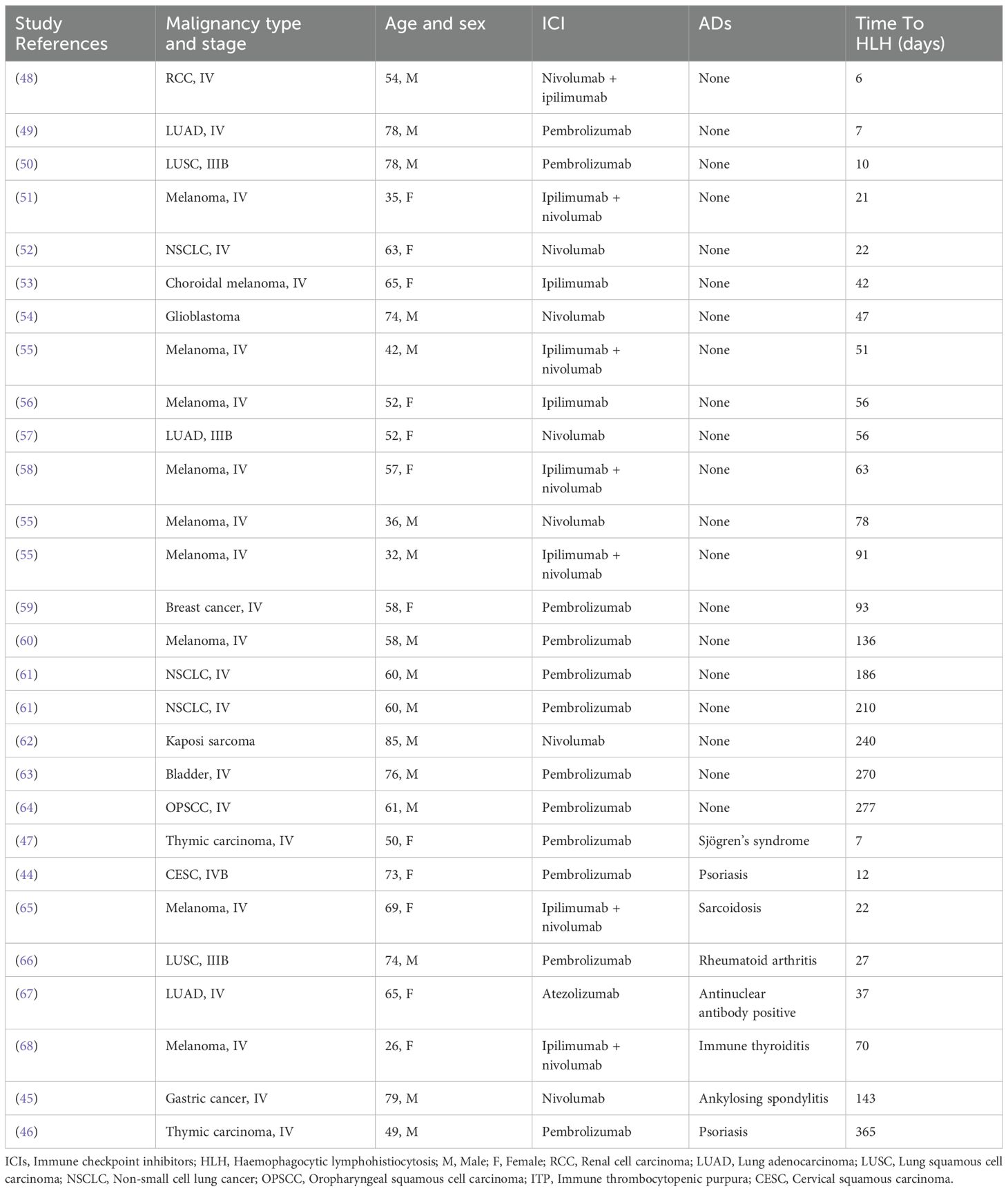
To evaluate the impact of ADs on the onset time of ICIs-related HLH, we identified 28 cases of ICIs- related HLH from 25 articles with sufficient clinical data. The cohort characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Our analysis reveals that 8 patients had concomitant ADs. The median time from ICI infusion to HLH onset was 59.5 days in patients without ADs, compared to 32 days in those with ADs, suggesting ADs may accelerate the occurrence of ICI-related HLH. This temporal disparity could be attributed to pre-existing cytokine storm and excessive immune cell infiltration in ADs (21, 22). Specifically, in SLE, impaired antigen clearance triggers aberrant activation of lymphocytes and macrophages, along with excessive pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Such a hyperinflammatory milieu primes the immune system, increasing susceptibility to rapid HLH progression upon ICI exposure (39, 40). Additionally, MSI-H status, a feature of this case, confers high tumor mutational burden due to defective mismatch repair. This generates abundant neoantigens that persistently activate CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells, sustaining immune hyperactivation and providing a pathological basis for HLH (41). The synergy between SLE-driven autoimmunity and MSI-H immunogenicity establishes a “dual-engine” immune stimulation mechanism. This likely ignited a cascading inflammatory response, culminating in fulminant HLH within 31 days in our patient. Despite these insights, our conclusions require cautious interpretation due to clinical heterogeneity: variations in ADs subtypes, malignancy types, and ICI regimens across the cohort may confound onset-time comparisons. Moreover, our patient’s non-adherence to regular hematological monitoring outside the hospital, along with initial refusal of bone marrow aspiration may obscure the true HLH onset timeline.
Although the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) classifies HLH as a fatal irAE, it fails to provide specific treatment recommendations (42). Typical management guidelines for HLH propose potential benefits from therapeutic interventions such as steroids, immunosuppressive agents like cyclophosphamide and etoposide, intravenous immunoglobulin, and the anti-IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (12, 43). In this particular case, despite attempting steroid therapy, the patient’s condition rapidly deteriorated. Given the patient’s frail physical state, chemotherapy was deemed unfeasible, and etoposide was consequently not recommended. Notably, a study has reported a low mortality rate of 1 in 10 HLH cases treated with tocilizumab (44). However, due to financial constraints, the patient declined both tocilizumab and immunoglobulin treatments. Ultimately, the patient succumbed to HLH within 16 days of diagnosis.
While previous reports have associated irAE-related HLH with pre-existing autoimmune disorders, including ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, and Sjögren’s syndrome (44–47), this represents the first instance of irAE-related HLH occurring in conjunction with SLE. The patient’s unsuccessful treatment outcome was attributed to the rapid progression of the disease, exacerbated by an excessive number of precursors, and further complicated by the patient’s non-compliance, including the refusal of timely evaluations and the use of a cytokine inhibitor proven effective against cytokine storms. In conclusion, the coexistence of MSI-H tumors and pre-existing SLE may exacerbate the prognose of irAE-related HLH, suggesting a potential interplay between these factors. Clinicians should maintain heightened vigilance regarding the potential emergence of HLH in patients with MSI-H cancers and SLE undergoing ICIs therapy. It is crucial to promptly initiate a combination of other pharmacological agents and steroid therapy upon the onset of HLH.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
PJ: Project administration, Writing – original draft. SW: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. JW: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. YZ: Project administration, Writing – original draft. JH: Writing – original draft. ZS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Medical Science Research Projectof Hebei (20260491).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the patient and her family for granting consent to publicize their case.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Dienstmann R, Salazar R, and Tabernero J. Personalizing colon cancer adjuvant therapy: selecting optimal treatments for individual patients. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:1787–96. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.0213
3. Wu J, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Tian Y, and Guo Z. Dicer increases the indication for trastuzumab treatment in gastric cancer patients via overexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:6993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86485-8
4. Hou W, Yi C, and Zhu H. Predictive biomarkers of colon cancer immunotherapy: Present and future. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1032314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1032314
5. Wu C. Systemic therapy for colon cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. (2018) 27:235–42. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2017.11.001
6. Siddiqui AZ and Almhanna K. Beyond chemotherapy, PD-1, and HER-2: novel targets for gastric and esophageal cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174322
7. Andre T, Shiu KK, Kim TW, Jensen BV, Jensen LH, Punt C, et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2207–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2017699
8. Okazaki T, Chikuma S, Iwai Y, Fagarasan S, and Honjo T. A rheostat for immune responses: the unique properties of PD-1 and their advantages for clinical application. Nat Immunol. (2013) 14:1212–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.2762
9. Postow MA, Sidlow R, and Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:158–68. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1703481
10. Lambotte O, Khellaf M, Harmouche H, Bader-Meunier B, Manceron V, Goujard C, et al. Characteristics and long-term outcome of 15 episodes of systemic lupus erythematosus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Med (Baltimore). (2006) 85:169–82. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000224708.62510.d1
11. Henter JI, Elinder G, and Ost A. Diagnostic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The FHL Study Group of the Histiocyte Society. Semin Oncol. (1991) 18:29–33.
12. Griffin G, Shenoi S, and Hughes GC. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: An update on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 34:101515. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2020.101515
13. Diaz L, Jauzelon B, Dillies AC, Le Souder C, Faillie JL, Maria ATJ, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with immunological checkpoint inhibitors: A pharmacovigilance study. J Clin Med. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051985
14. Cortellini A, Buti S, Santini D, Perrone F, Giusti R, Tiseo M, et al. Clinical outcomes of patients with advanced cancer and pre-existing autoimmune diseases treated with anti-programmed death-1 immunotherapy: A real-world transverse study. Oncologist. (2019) 24:e327–37. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0618
15. Johnson DB, Sullivan RJ, Ott PA, Carlino MS, Khushalani NI, Ye F, et al. Ipilimumab therapy in patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune disorders. JAMA Oncol. (2016) 2:234–40. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.4368
16. Menzies AM, Johnson DB, Ramanujam S, Atkinson VG, Wong ANM, Park JJ, et al. Anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune disorders or major toxicity with ipilimumab. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:368–76. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw443
17. Leonardi GC, Gainor JF, Altan M, Kravets S, Dahlberg SE, Gedmintas L, et al. Safety of programmed death-1 pathway inhibitors among patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and preexisting autoimmune disorders. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:1905–12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.0305
18. Freitas JAS, Bendicho MT, and Junior AFS. Use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of patients with cancer and preexisting autoimmune disease: An integrative review. J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2023), 10781552231171881. doi: 10.1177/10781552231171881
19. Kennedy LC, Bhatia S, Thompson JA, and Grivas P. Preexisting autoimmune disease: implications for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in solid tumors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2019) 17:750–7. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.7310
20. Abdel-Wahab N, Shah M, Lopez-Olivo MA, and Suarez-Almazor ME. Use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of patients with cancer and preexisting autoimmune disease: A systematic review. Ann Intern Med. (2018) 168:121–30. doi: 10.7326/M17-2073
21. Dulos J, Carven GJ, van Boxtel SJ, Evers S, Driessen-Engels LJ, Hobo W, et al. PD-1 blockade augments Th1 and Th17 and suppresses Th2 responses in peripheral blood from patients with prostate and advanced melanoma cancer. J Immunother. (2012) 35:169–78. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e318247a4e7
22. von Euw E, Chodon T, Attar N, Jalil J, Koya RC, Comin-Anduix B, et al. CTLA4 blockade increases Th17 cells in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Transl Med. (2009) 7:35. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-35
23. Calabrese L and Velcheti V. Checkpoint immunotherapy: good for cancer therapy, bad for rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:1–3. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209782
24. Haanen J, Ernstoff MS, Wang Y, Menzies AM, Puzanov I, Grivas P, et al. Autoimmune diseases and immune-checkpoint inhibitors for cancer therapy: review of the literature and personalized risk-based prevention strategy. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:724–44. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.285
25. Fardet L, Galicier L, Lambotte O, Marzac C, Aumont C, Chahwan D, et al. Development and validation of the HScore, a score for the diagnosis of reactive hemophagocytic syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:2613–20. doi: 10.1002/art.38690
26. Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zeron P, Lopez-Guillermo A, Khamashta MA, and Bosch X. Adult haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet. (2014) 383:1503–16. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61048-X
27. Tamamyan GN, Kantarjian HM, Ning J, Jain P, Sasaki K, McClain KL, et al. Malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults: Relation to hemophagocytosis, characteristics, and outcomes. Cancer. (2016) 122:2857–66. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v122.18
28. Ofuji K, Hiramatsu K, Nosaka T, Naito T, Takahashi K, Matsuda H, et al. Pembrolizumab-induced autoimmune side effects of colon and pancreas in a patient with lung cancer. Clin J Gastroenterol. (2021) 14:1692–9. doi: 10.1007/s12328-021-01499-z
29. Al-Samkari H and Berliner N. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Annu Rev Pathol. (2018) 13:27–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-043625
30. Crayne CB, Albeituni S, Nichols KE, and Cron RQ. The immunology of macrophage activation syndrome. Front Immunol. (2019) 10: 119. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00119
31. Billiau AD, Roskams T, Van Damme-Lombaerts R, Matthys P, and Wouters C. Macrophage activation syndrome: characteristic findings on liver biopsy illustrating the key role of activated, IFN-gamma-producing lymphocytes and IL-6- and TNF-alpha-producing macrophages. Blood. (2005) 105:1648–51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-08-2997
32. Rood JE, Rao S, Paessler M, Kreiger PA, Chu N, Stelekati E, et al. ST2 contributes to T-cell hyperactivation and fatal hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in mice. Blood. (2016) 127:426–35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-659813
33. Nakamura K, Okamura H, Wada M, Nagata K, and Tamura T. Endotoxin-induced serum factor that stimulates gamma interferon production. Infect Immun. (1989) 57:590–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.590-595.1989
34. Kaplanski G. Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. (2018) 281:138–53. doi: 10.1111/imr.2018.281.issue-1
35. Canna SW, Wrobel J, Chu N, Kreiger PA, Paessler M, and Behrens EM. Interferon-gamma mediates anemia but is dispensable for fulminant toll-like receptor 9-induced macrophage activation syndrome and hemophagocytosis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. (2013) 65:1764–75. doi: 10.1002/art.37958
36. Jordan MB, Hildeman D, Kappler J, and Marrack P. An animal model of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH): CD8+ T cells and interferon gamma are essential for the disorder. Blood. (2004) 104:735–43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-10-3413
37. Janka GE and Lehmberg K. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: pathogenesis and treatment. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. (2013) 2013:605–11. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2013.1.605
38. Zhang HQ, Yang SW, Fu YC, Chen MC, Yang CH, Yang MH, et al. Cytokine storm and targeted therapy in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Immunol Res. (2022) 70:566–77. doi: 10.1007/s12026-022-09285-w
39. Zeng Z, Tu W, Ji B, Liu J, Huang K, Nie D, et al. IFN-alpha induced systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report and literature review. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1223062. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1223062
40. Aziz A, Castaneda EE, Ahmad N, Veerapalli H, Rockferry AG, Lankala CR, et al. Exploring macrophage activation syndrome secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus in adults: A systematic review of the literature. Cureus. (2021) 13:e18822. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18822
41. Viale G, Trapani D, and Curigliano G. Mismatch repair deficiency as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapy efficacy. BioMed Res Int. (2017) 2017:4719194. doi: 10.1155/2017/4719194
42. Brahmer JR, Abu-Sbeih H, Ascierto PA, Brufsky J, Cappelli LC, Cortazar FB, et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immune checkpoint inhibitor-related adverse events. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002435
43. Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2007) 48:124–31. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039
44. Zhai C, Jin X, You L, Yan N, Dong J, Qiao S, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following pembrolizumab and bevacizumab combination therapy for cervical cancer: a case report and systematic review. BMC Geriatr. (2024) 24:32. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04625-3
45. Long C, Al-Abdulmalek A, Lai J, Haegert DG, Isnard S, Cournoyer D, et al. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following the anti-PD-1 nivolumab in a patient with gastric cancer and ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. (2024) 11:004370. doi: 10.12890/2024_004370
46. Laderian B, Koehn K, Holman C, Lyckholm L, and Furqan M. Association of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and programmed death 1 checkpoint inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. (2019) 14:e77–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.11.035
47. Wei Y, He W, Sun W, Wu C, Ren D, Wang X, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in two patients following treatment with pembrolizumab: two case reports and a literature review. Transl Cancer Res. (2022) 11:2960–6. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-154
48. Azari AE, Stratton R, and Singh A. First case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to cabozantinib with checkpoint inhibitors. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2021) 60:e167–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa750
49. Takahashi H, Koiwa T, Fujita A, Suzuki T, Tagashira A, and Iwasaki Y. A case of pembrolizumab-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis successfully treated with pulse glucocorticoid therapy. Respir Med Case Rep. (2020) 30:101097. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101097
50. Okawa S, Kayatani H, Fujiwara K, Ozeki T, Takada K, Iwamoto Y, et al. Pembrolizumab-induced autoimmune hemolytic anemia and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Intern Med. (2019) 58:699–702. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1001-18
51. Hantel A, Gabster B, Cheng JX, Golomb H, and Gajewski TF. Severe hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a melanoma patient treated with ipilimumab + nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer. (2018) 6:73. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0384-0
52. Takeshita M, Anai S, Mishima S, and Inoue K. Coincidence of immunotherapy-associated hemophagocytic syndrome and rapid tumor regression. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:186–9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw537
53. Olivares-Hernandez A, Figuero-Perez L, Amores Martin MA, Bellido Hernandez L, Mezquita L, Vidal Tocino MDR, et al. Response to treatment with an anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody (Tocilizumab) in a patient with hemophagocytic syndrome secondary to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Case Rep Oncol Med. (2021) 2021:6631859. doi: 10.1155/2021/6631859
54. Thummalapalli R, Heumann T, Stein J, Khan S, Priemer DS, Duffield AS, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to PD-1 and IDO inhibition in a patient with refractory glioblastoma. Case Rep Oncol. (2020) 13:508–14. doi: 10.1159/000507281
55. Ozdemir BC, Latifyan S, Perreau M, Fenwick C, Alberio L, Waeber G, et al. Cytokine-directed therapy with tocilizumab for immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1775–8. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.08.2101
56. Michot JM, Pruvost R, Mateus C, Champiat S, Voisin AL, Marabelle A, et al. Fever reaction and haemophagocytic syndrome induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ann Oncol. (2018) 29:518–20. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx701
57. Honjo O, Kubo T, Sugaya F, Nishizaka T, Kato K, Hirohashi Y, et al. Severe cytokine release syndrome resulting in purpura fulminans despite successful response to nivolumab therapy in a patient with pleomorphic carcinoma of the lung: a case report. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:97. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0582-4
58. Pacholczak-Madej R, Grela-Wojewoda A, Lompart J, Zuchowska-Vogelgesang B, and Ziobro M. Effective treatment of a melanoma patient with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis after nivolumab and ipilimumab combined immunotherapy. Prague Med Rep. (2022) 123:35–42. doi: 10.14712/23362936.2022.4
59. Al-Samkari H, Snyder GD, Nikiforow S, Tolaney SM, Freedman RA, and Losman JA. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis complicating pembrolizumab treatment for metastatic breast cancer in a patient with the PRF1A91V gene polymorphism. J Med Genet. (2019) 56:39–42. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105485
60. Sadaat M and Jang S. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with immunotherapy: brief review and case report. J Immunother Cancer. (2018) 6:49. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0365-3
61. Oyama S, Shirai T, Abe Y, Tsuchiya M, Inui T, Suhara K, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with non-small cell lung carcinoma. Respirol Case Rep. (2023) 11:e01117. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.v11.4
62. Choi S, Zhou M, Bahrani E, Martin BA, Ganjoo KN, and Zaba LC. Rare and fatal complication of immune checkpoint inhibition: a case report of haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with severe lichenoid dermatitis. Br J Haematol. (2021) 193:e44–7. doi: 10.1111/bjh.v193.6
63. Shah D, Shrestha R, Ramlal R, Hatton J, and Saeed H. Pembrolizumab associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:1403. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx113
64. Kalmuk J, Puchalla J, Feng G, Giri A, and Kaczmar J. Pembrolizumab-induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: an immunotherapeutic challenge. Cancers Head Neck. (2020) 5:3. doi: 10.1186/s41199-020-0050-3
65. Mizuta H, Nakano E, Takahashi A, Koyama T, Namikawa K, and Yamazaki N. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with advanced Malignant melanoma accompanied by ipilimumab and nivolumab: A case report and literature review. Dermatol Ther. (2020) 33:e13321. doi: 10.1111/dth.13321
66. Akagi Y, Awano N, Inomata M, Kuse N, Tone M, Yoshimura H, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis on pembrolizumab for lung adenocarcinoma. Intern Med. (2020) 59:1075–80. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3889-19
67. Endo Y, Inoue Y, Karayama M, Nagata Y, Hozumi H, Suzuki Y, et al. Marked, lasting disease regression and concomitantly induced autoimmune hemolytic anemia and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma and autoantibodies receiving atezolizumab plus chemotherapy: A case report. JTO Clin Res Rep. (2022) 3:100263. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100263
Keywords: MSI-H, PD-1, colon cancer, SLE, HLH
Citation: Jiao P, Wang S, Wu J, Zhao Y, Han J and Sha Z (2025) Tislelizumab-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with microsatellite instability-high colon cancer and coexisting systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 15:1585133. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1585133
Received: 28 February 2025; Accepted: 15 July 2025;
Published: 06 August 2025.
Edited by:
Shisan (Bob) Bao, The University of Sydney, AustraliaReviewed by:
Hang Li, Shenzhen Bao’an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, ChinaXiaonan Wang, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Jiao, Wang, Wu, Zhao, Han and Sha. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ziyue Sha, dmljdG9yYW5kNzcyQHZpcC5xcS5jb20=
 Pengqing Jiao
Pengqing Jiao Song Wang1
Song Wang1 Yufei Zhao
Yufei Zhao Ziyue Sha
Ziyue Sha