- 1Department of Pathology, Danyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
Ferroptosis is a novel class of programmed cell death that is mainly dependent on intracellular iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation. Ferroptosis is closely related to a variety of human diseases, especially different kinds of cancer. Several small molecule inducers have been developed to induce ferroptosis in tumor cells, some of which have been used in clinical studies. However, these chemical small molecules have toxic effects that limit its wide application. Natural products, however, have a natural advantage in cancer therapy due to their low toxicity and side effects. Some natural products have been found to inhibit tumor growth by inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells. In this review, we reviewed the molecular mechanism of ferroptosis and how natural products targeting ferroptosis signaling pathways affect tumor growth. We also analyzed the application of various natural products such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and alkaloids in inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells. This review will assist in the future discovery and study of more natural product inducers that can induce ferroptosis in tumor cells, and ultimately provide insights into identifying natural products that can be applied to clinical applications.
Introduction
The goal of tumor therapy is to remove tumor cells. Therefore, inducing tumor cell death is an attractive therapeutic target in cancer therapy. Currently, many drugs inhibit tumor growth by inducing programmed cell death (PCD) in tumor cells. These PCD include apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, autophagy-dependent cell death (ADCD) and the newly discovered ferroptosis (1). Many of these early anticancer drugs inhibit tumor growth by inducing tumor cell apoptosis. However, due to the heterogeneity of tumor cells and tumor resistance to apoptosis, many drugs that induce apoptosis may develop resistance and thus do not achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new drugs that inhibit tumor growth by inducing other types of programmed cell death. Many small molecules have been reported, such as the small molecule drugs emodin (2–4), shikonin (5, 6), and tanshinol A (7), which target necroptosis, and the small molecules berberine, fluoxetine, and ABTL081, which target ADCD.
The concept of ferroptosis was first proposed by Dixon et al. in 2012 (8). It’s a type of iron-dependent programmed cell death caused by an imbalance of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Increasing evidence suggests that ferroptosis is closely related to the tumorigenesis and therapeutic efficacy of various tumors. Key proteins on the ferroptosis-related signaling pathway are expected to be new targets for cancer therapy. Induction of ferroptosis can reverse anticancer drug resistance, while inhibition of ferroptosis can block specific death processes. Various inducers and inhibitors have been developed for key proteins of the ferroptosis signaling pathway, inducers such as Erastin, MEII, PE, AE, SAS, Sorafenib and inhibitors such as Fer-1, CPX and DFO (9).
On the other hand, many chemotherapy drugs have strong side effects in cancer treatment. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop drugs with fewer side effects to achieve better treatment outcomes. Natural products refer to compounds extracted from natural sources such as plants, microorganisms, and animals. Natural products usually have complex structures and specific biosynthetic pathways, while chemical small molecules are relatively small organic compounds prepared by chemical synthesis methods, with relatively simple structures and not necessarily naturally produced by living organisms. They have a range of unique advantages in cancer treatment, including abundant sources, low toxicity and side effects, multiple targets and the ability to overcome drug resistance. Many natural products have been used in the clinic, such as paclitaxel, camptothecin and doxorubicin, which have demonstrated their potential and efficacy in the treatment of a wide range of cancers in clinical applications (10). However, the number of these discovered natural products is limited, and many of them inhibit tumor growth by inducing apoptosis. Ferroptosis is a new type of cell death pathway that offers unparalleled advantages compared to traditional apoptosis and necrosis, such as selectively killing tumor cells, involving multiple pathways and reversing drug resistance. Therefore, inhibition of tumor growth by ferroptosis inducers, especially natural product inducers, will provide new therapeutic options for cancer patients, improve therapeutic efficacy, reduce side effects and improve patients’ quality of life.
Overview and molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis
In 2003, Sonam Dolma et al. first discovered that a new compound, erastin, could selectively kill tumor cells expressing ST and mutant RAS, but erastin-induced cell death did not show apoptotic features and could not be inhibited by caspase inhibitors. Therefore, it is suggested that erastin-induced cell death was presumed to be a completely new form of death (11). Subsequently, Yang and Yagoda et al. found that this form of death could be inhibited by iron chelators. In 2012, Dixon et al. officially named this type of death as ferroptosis (8). Ferroptosis is characterized by the accumulation of iron and a significant increase in lipid peroxidation. This type of cell death is different from traditional forms of death such as apoptosis and necrosis. It has unique biological and molecular characteristics. During ferroptosis, cell rupture does not occur. Morphological features include an increase in the density of mitochondrial membranes, a decrease in volume, a reduction in mitochondrial cristae, a decrease in cristae density and rupture of the mitochondrial outer membrane, but the nuclear morphology is normal but lacks chromatin condensation (12).
The main trigger of ferroptosis in cells is the excessive accumulation of lipid peroxides. This is reflected in the disrupts the balance between the execution of ferroptosis and the defense system of the cell, thereby inducing cell ferroptosis. The factors that drive ferroptosis are Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid – Phospholipids (PUFA-PLs) synthesis and oxidation, abnormal iron metabolism, and mitochondrial metabolism abnormalities. The defense mechanism against ferroptosis is mainly the cellular antioxidant system that neutralizes lipid peroxides. These antioxidant systems include the GPX4 system, free radical scavenging antioxidant systems (such as the FSP1-COQH2 system, DHODH-CoQH2 system, and GCH1-BH4 system), and membrane repair systems (Figure 1). When the promotion of ferroptosis execution exceeds the cellular defense system, the accumulation of lipid peroxides can induce cell ferroptosis (12, 13) Many ferroptosis inducers have now been designed based on the characteristics of the ferroptosis signaling pathway. Most of them are small molecule compounds and some compounds such as SRF and SAS have been used in the clinic (9).
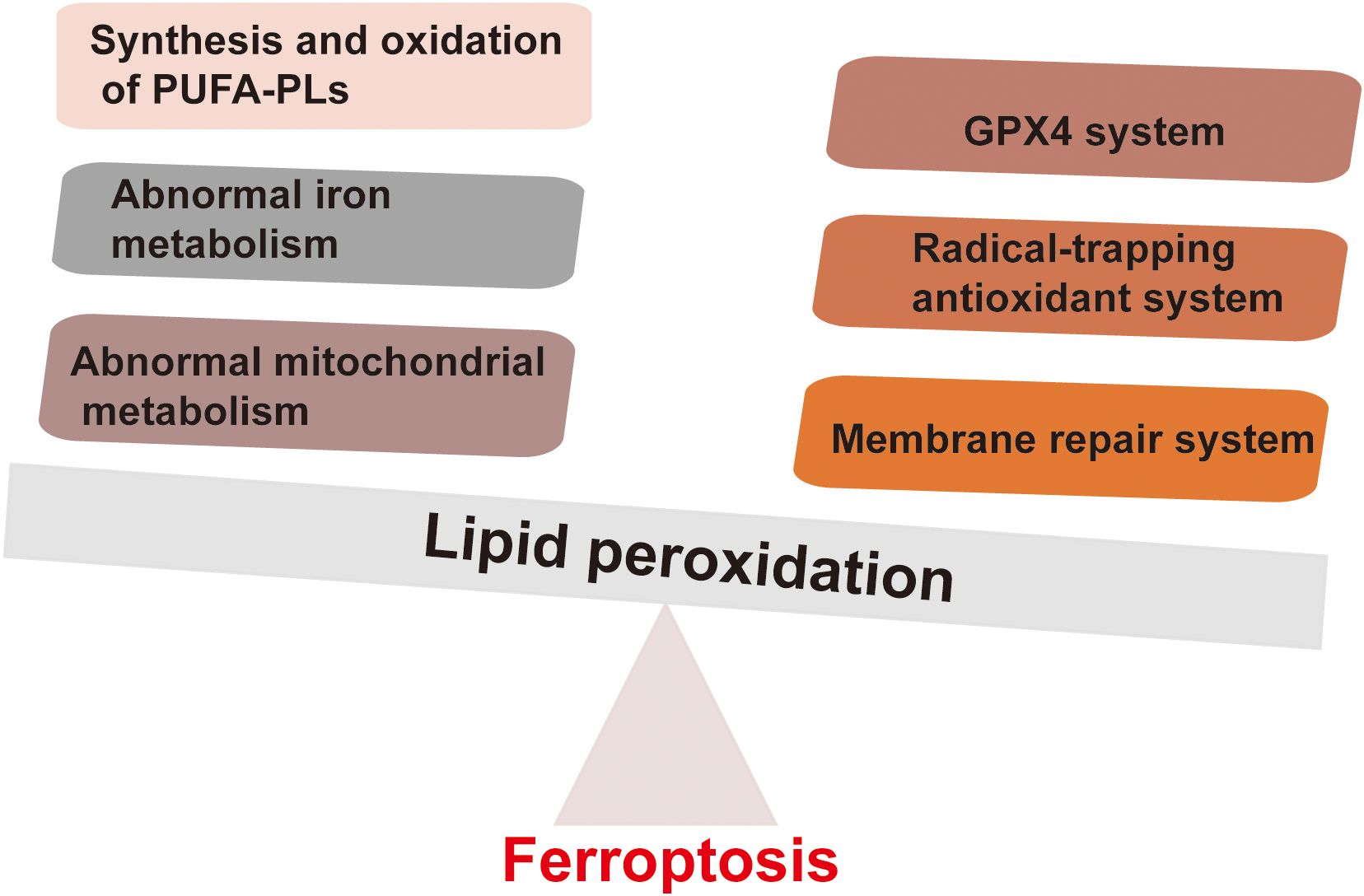
Figure 1. Factors driving ferroptosis and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. The main factors driving ferroptosis mainly include the synthesis and oxidation of PUFA-PLs, abnormal iron metabolism, and abnormal mitochondrial metabolism. The defense mechanisms against ferroptosis mainly involve the cell antioxidant system that neutralizes lipid peroxides. These antioxidant systems include the GPX4 system, free radical scavenging antioxidant systems (such as FSP1-COQH2 system, DHODH-CoQH2 system, and GCH1-BH4 system).
Ferroptosis is a form of iron-dependent programmed cell death, and its molecular mechanisms involve multiple signaling pathways. The System Xc−-GSH-GPX4 pathway is the core regulatory pathway of ferroptosis. During the process of ferroptosis, the process initially begins with the initiation phase, where the intracellular iron content increases due to enhanced iron uptake mediated by the transferrin receptor (TfR) or increased ferritinophagy. Meanwhile, the function of system Xc− is impaired, leading to a decrease in intracellular glutathione synthesis and a reduction in the activity of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Subsequently, in the progression phase, the reduced levels of glutathione and decreased GPX4 activity prevent the timely reduction of lipid peroxides, exacerbating lipid peroxidation reactions and generating a large amount of lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS directly damage the cell membrane and further promote iron release and mitochondrial dysfunction, creating a vicious cycle. Finally, in the effector phase, mitochondria suffer damage and dysfunction, characterized by a decrease in size, increased membrane density, and a reduction or even disappearance of cristae. Cellular energy metabolism is disrupted, and lipid peroxidation products accumulate in large amounts within the cell. Ultimately, the integrity of the cell membrane is compromised, leading to cell death (14). (Figure 2). In addition, NCOA4-mediated ferritin degradation, also known as ferritinophagy, increases the intracellular iron ion levels, promotes lipid peroxidation, and triggers ferroptosis (15). Recent studies have also found that USP13 can promote the transition of ferroptosis to autophagy in tumor cells by activating the NFE2L2/NRF2-SQSTM1/p62-KEAP1 axis in a KRAS signaling pathway-dependent manner (16).
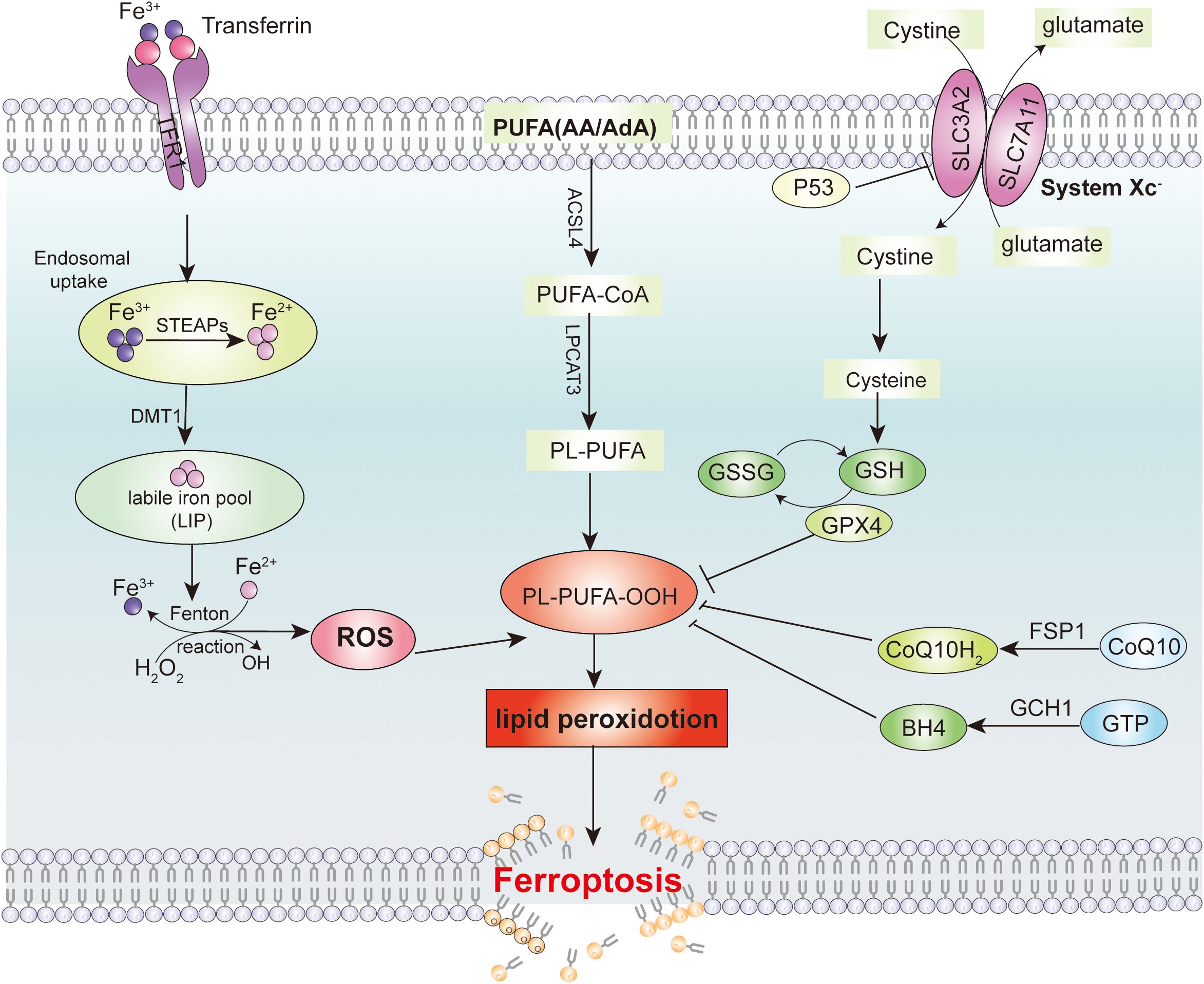
Figure 2. Signaling pathway for inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells. Intracellular iron metabolism and lipid peroxides are the main reasons that induce ferroptosis in tumor cells. The major cellular defense system to avoid ferroptosis are the System Xc-/GSH/GPX4 axis, the CoQ/FSP1 axis and the GCH1-BH4 defense system.
Ferroptosis has emerged as a promising target for cancer therapy (17). However, many small molecule compounds have shown drawbacks such as poor water solubility and targeting ability. Therefore, it is necessary to discover more molecules to induce tumor cell death by other routes. Among them, inducing tumor cell ferroptosis through natural products is a feasible approach.
Natural products targeting the iron death signaling pathway affect tumor growth
Based on the characteristics of the ferroptosis signaling pathway, natural products that can induce ferroptosis mainly include the following types: 1. Class I that inhibits the system Xc-. 2. Class II that inhibits or degrades GPX4. 3. Class III that depletes coenzyme Q10 (18). 4. Class IV that induces lipid peroxidation through iron or PUFA overload (19). These natural products target different targets of the ferroptosis signaling pathways, and ultimately induce ferroptosis in tumor cells to inhibit tumor growth.
Natural products inhibit system Xc- induce ferroptosis
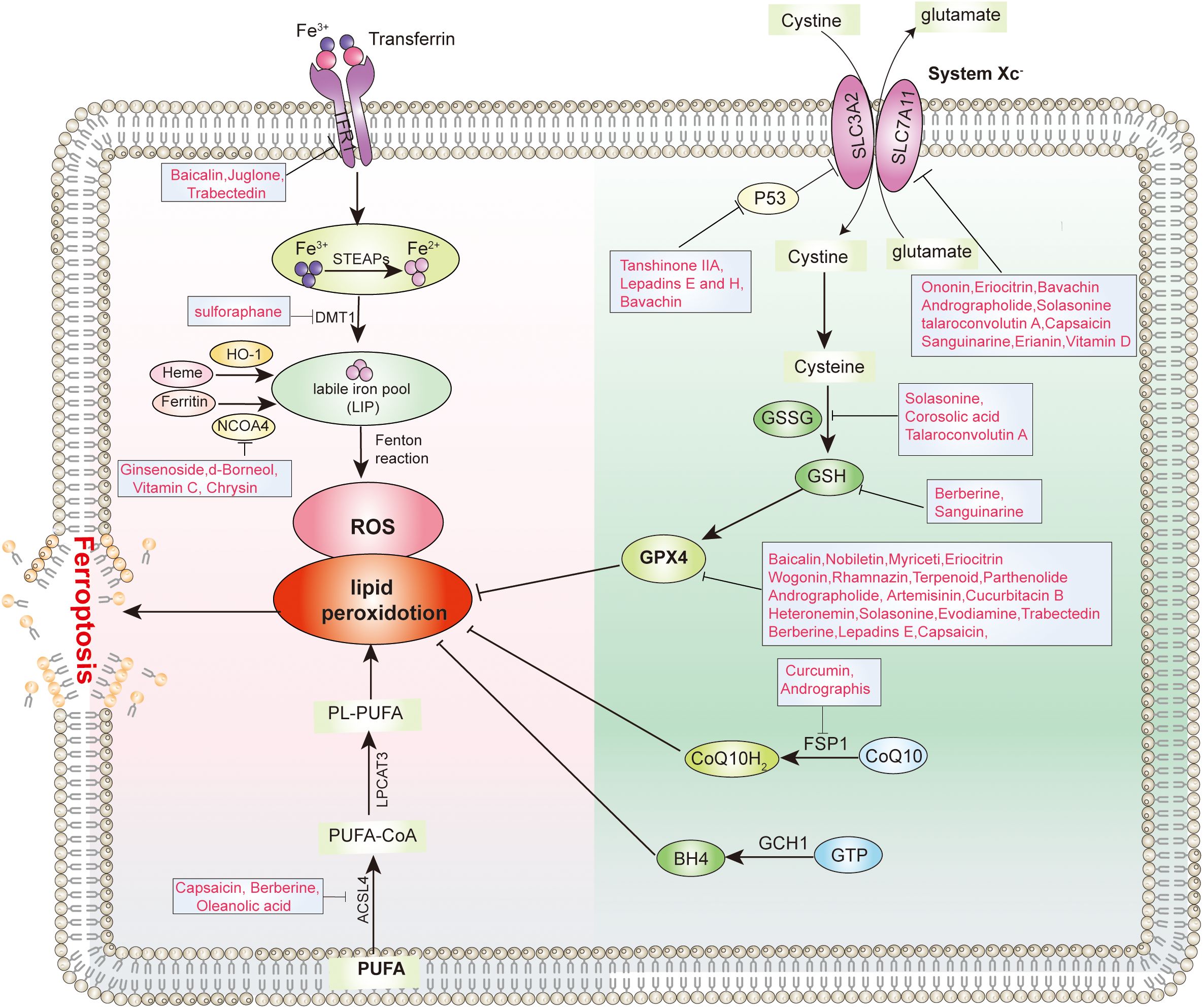
System Xc- is an important component of the antioxidant system in cells, mainly distributed in the phospholipid bilayer. System Xc- is composed of two subunits, a heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain subunit, SLC3A2, and a light chain subunit, SLC7A11, respectively (20). Cells use system Xc- to uptake cystine into the cell, and the cystine entering the cell is reduced to cysteine, which is an important raw material for synthesizing glutathione (GSH). GSH is an important antioxidant and free radical scavenger, which has a coordinated role with GPX4 to maintain intracellular oxidative balance. By inhibiting System Xc- to limit cysteine intake is the main rate-limiting step in inhibiting glutathione synthesis. Depletion of GSH leads to intracellular redox imbalance, which then leads to intracellular ROS accumulation and ultimately induces ferroptosis. Various natural products targeting System Xc- have been reported to induce ferroptosis, such as kayadiol (21), Bavachin (22), and tanshinone IIA (23) (Figure 3).
Natural products inhibit or degrade GPX4-induced ferroptosis
Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is the only enzyme in cells that can reduce lipid peroxides to lipids, and GPX4 plays a crucial role in ferroptosis (24). GPX4 is a selenoprotein that primarily functions to inhibit the formation of lipid peroxides. GPX4 can use GSH as a substrate to specifically catalyze the reduction of lipid peroxides to normal phospholipid molecules. In ferroptosis, when the activity of GPX4 is inhibited, it leads to the accumulation of intracellular peroxides, which in turn causes ferroptosis. RSL3 is one of the most typical inducers of ferroptosis. RSL3 inhibits the activity of GPX4 by covalently binding to the active site of selenocysteine in GPX4, thereby inducing ferroptosis (25). It has been reported that GPX4 is highly expressed in various types of tumors, which may be related to the tumorigenesis (26). Several natural products have been reported to induce ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4, such as Capsaicin (27), heteronemin (28) and Eriocitrin (29) (Figure 3).
Natural products target iron metabolism to induce ferroptosis
Iron is an important trace element for maintaining the life of living organisms and a cofactor for many biochemical reactions within cells. In ferroptosis, excess intracellular Fe2+ can promote the accumulation of lipid ROS through the Fenton reaction, ultimately leading to the induction of ferroptosis. When Fe2+ from food is absorbed into the blood, it is oxidized to Fe3+. Subsequently, Fe3+ binds to transferrin (TF) and is transported to tissues. The transferrin receptor (TFR) on the cell membrane can bind to TF carrying Fe3+ and enter the cell through endocytosis. Subsequently, the intracellular Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ by STEAP3 and stored in the labile iron pool (LIP) and in the ferritin consisting of ferritin light chain (FTL) and ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), and small molecule complex GSH. Excess intracellular Fe2+ is eliminated from the body mainly through SLC40A1. Due to the instability and high reactivity of Fe2+, it participates in the Fenton reaction. The Fenton refers to the reaction where Fe2+ reacts with hydrogen peroxide to generate Fe3+ and oxygen free radicals. Excessive intracellular iron can generate oxygen free radicals and reactive oxygen through an iron-dependent Fenton reaction, leading to oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in cells, ultimately inducing cell ferroptosis. Various natural products have been reported to target iron metabolism to induce ferroptosis, such as Baicalin (30), Juglone (31), Trabectedin (32), Vitamin C (33) (Figure 3).
Natural products target lipid metabolism to induce ferroptosis
The formation of lipid peroxides in membrane phospholipids in cells usually leads to ferroptosis. Unsaturated PUFAs, especially arachidonic acid (AA) and adrenoyl acid (AdA), are prone to react with ROS, leading to lipid peroxidation and inducing cell ferroptosis. phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) containing AA or AdA are key phospholipids that induce ferroptosis. The oxidation of unsaturated PUFAs such as AA is regulated by ACSL4. ACSL4 catalyzes the binding of free AA or AdA with coenzyme A (CoA) to form AA-CoA or AdA-CoA. It is then esterified to membrane AA-PEs by lysophosphatidyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3) and finally undergoes lipid peroxidation catalyzed by the lipoxygenase protein family (LOXs). Therefore, ferroptosis can be inhibited by inhibiting ACSL4 and LPCAT3 or LOXs. Various natural products targeting lipid metabolism have been reported to induce ferroptosis, such as Capsaicin (34), Berberine (35), Oleanolic acid (36) (Figure 3).
Natural products target other pathways to induce iron death
Currently, there are reports showing that there are other pathways and proteins that can affect cell death by ferroptosis. These include coenzyme Q10, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), selenium, p53, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NRF2), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2) and Vitamin E.
Application of natural products in inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells
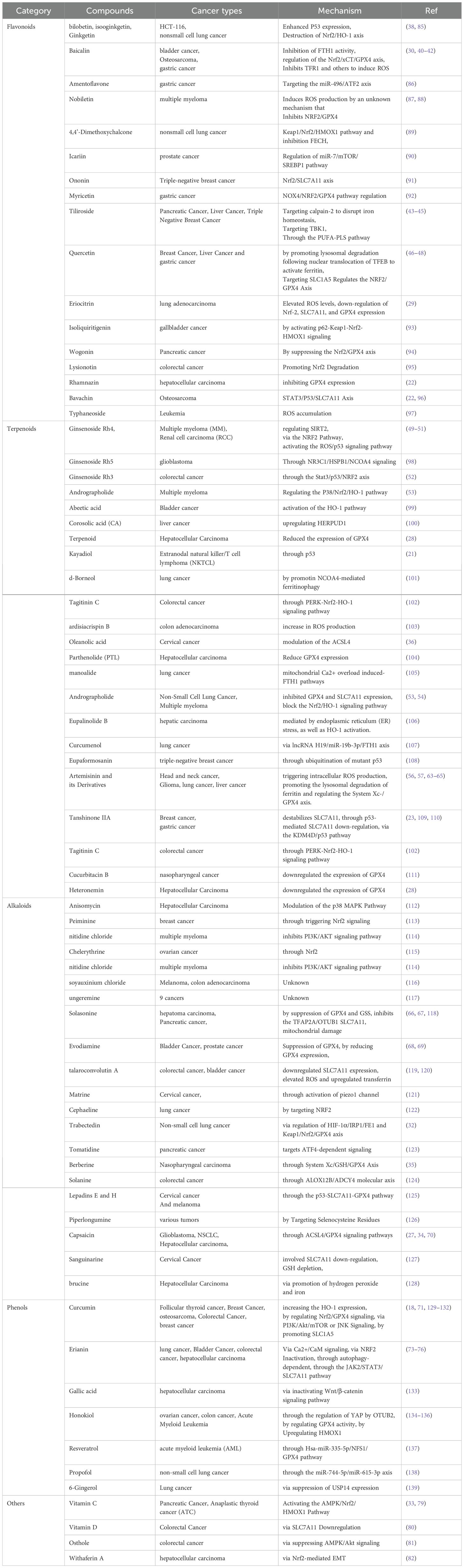
The active ingredients of natural products originating from the plant kingdom mainly include flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides, volatile oils, quinones, terpenoids, lignans, coumarins, saponins, cardiac glycosides, phenolic acids, amino acids and enzymes. Currently, reports show that most of these types of natural products can induce ferroptosis in tumor cells through various signaling pathways (Table 1).
Flavonoids induce ferroptosis in tumor cells
Flavonoids are a class of compounds with a flavone skeleton, widely distributed in certain plants and herbs. Most natural flavonoids exist in the form of glycosides. Among the flavonoids reported to induce ferroptosis in tumor cells are Ginkgetin, Baicalin, Amentoflavone, Nobiletin, and 4,4-Dimethoxychalcone (Table 1) (37).
Biflavonoids like bilobetin, isooginkgetin, and ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba can inhibit MDM2 to boost wild-type P53 expression. This significantly raises ROS levels in colon cancer HCT-116 cells, triggering ferroptosis. Ginkgetin also enhances 5-fluorouracil’s anti-tumor effect in these cells (38). Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that ginkgetin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of cisplatin (DDP) in EGFR wild-type non-small cell lung cancer by inducing ferroptosis via disruption of the Nrf2/HO-1 axis. These findings indicate that ginkgetin not only induces ferroptosis in tumor cells but also potentiates the therapeutic effects of certain chemotherapeutic agents. Nevertheless, further research is required to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Baicalin, a flavonoid compound extracted from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, exhibits significant anti-tumor activity. It induces ferroptosis in tumor cells through multiple mechanisms (39). In bladder cancer and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), baicalin induces ferroptosis by suppressing the activity of FTH1 (30, 40). In osteosarcoma (OS), it triggers ferroptosis through the regulation of the Nrf2/xCT/GPX4 axis (41). Furthermore, in gastric cancer, baicalin inhibits TFR1 to facilitate ROS-mediated ferroptosis, thereby enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of 5-fluorouracil (42).
Tiliroside, a compound present in various plants, has been demonstrated to inhibit the growth of multiple tumors through ferroptosis, such as triple-negative breast cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer (43–45). In pancreatic cancer, it disrupts iron homeostasis and triggers ferroptosis through direct targeting of calpain-2 (43). In liver cancer, it induces ferroptosis by targeting TBK1 and sensitizes tumors to the chemotherapy drug sorafenib (44). In triple-negative breast cancer, tiliroside induces ferroptosis in TNBC cells through the PUFA-PLS pathway, which is associated with the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (45). Thus, tiliroside can induce ferroptosis in tumor cells through multiple mechanisms. Quercetin is a natural flavonoid abundant in various plants. In human liver cancer cells, it mediates ferritin degradation through TFEB-dependent lysosomal activation, thereby promoting ferroptosis via iron release and subsequent lipid oxidation (46). A similar mechanism is also found in breast cancer, where quercetin induces ferroptosis by promoting lysosomal degradation of ferritin through TFEB nuclear translocation (47). In gastric cancer, quercetin induces ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells by targeting SLC1A5 and regulating the p-Camk2/p-DRP1 and NRF2/GPX4 axis (48).
Terpenoids induce ferroptosis in tumor cells
Terpenoids are widely distributed in nature and constitute the main components of fragrances, resins, and pigments in certain plants. As polymers formed by the head-to-tail linkage of isoprene units in various configurations, they exhibit structural diversity. A variety of terpenoids, including Heteronemin, Kayadiol, Corosolic acid, Parthenolide, Curcumenol and Manoalide, have been reported to inhibit tumor growth by inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells (Table 1).
Ginsenosides, key bioactive components in ginseng, are triterpene glycosides. Over 40 compounds have been isolated from ginseng roots. Those reported to induce tumor cell ferroptosis include primarily Rh4, Rh3, and Rg5, with Rh4 being the most extensively studied. Notably, Rh4 triggers ferroptosis in malignancies like multiple myeloma (MM) and colorectal cancer (CRC).
In renal cell carcinoma (RCC), Rh4 induces ferroptosis primarily via the NRF2 pathway (49). In multiple myeloma, Rh4 induces ferroptosis mainly through SIRT2 (50). In gastric cancer, it induced ferroptosis through the activation of ROS/p53 signaling pathway and activation of autophagy (51). In glioma, ginsenoside Rg5 inhibits the progression of glioblastoma by activating ferroptosis via the NR3C1/HSPB1/NCOA4 axis (50). Meanwhile, ginsenoside Rh3 (GRh3), a semi-natural product derived from chemical processing, induces both pyroptosis and ferroptosis in CRC cells via the Stat3/p53/NRF2 axis (52).
Andrographolide, the primary bioactive component of Andrographis paniculata, is a diterpenoid lactone with potent anticancer activity. In multiple myeloma, it induces ferroptosis in MM cells by activating p38 and subsequently blocking the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (53). In NSCLC cells, andrographolide downregulates the ferroptosis-related proteins GPX4 and SLC7A11, exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction, and ultimately triggers ferroptosis (54).
Terpene lactones (NTLs), including γ-lactones and δ-lactones, are a large part of terpenes. Such compounds have a wide range of biological activities. Sesquiterpene lactones, a large group of secondary metabolites predominantly derived from Asteraceae plants, include artemisinin, a sesquiterpene lactone with an endoperoxide bridge extracted from Artemisia annua. Its derivatives comprise artemether (ARM), arteether (ARTE), dihydroartemisinin (DHA), and artesunate (ATS), and various derivatives have been reported to induce ferroptosis in tumor cells (55).
Artemisinin can induce ferroptosis of tumor cells through multiple mechanisms, such as triggering intracellular ROS production, promoting lysosomal degradation of ferritin, and regulating the System Xc-/GPX4 axis to induce ferroptosis (56, 57). Among artemisinin derivatives, DHA has been most extensively studied, with its mechanisms well characterized. DHA is produced by reducing artemisinin with sodium borohydride; compared to the parent compound, it exhibits greater water solubility, a higher metabolic rate, faster absorption, lower cytotoxicity, and reduced drug resistance. Early studies demonstrated that in head and neck cancer, DHA specifically inhibits cancer cell growth by inducing both ferroptosis and apoptosis (58, 59). Subsequently, it was found that DHA induces ferroptosis in glioma cells through the PERK-ATF4-HSPA5-GPX4 pathway (60), with GPX4 identified as a key target of DHA-mediated ferroptosis in glioblastoma (61). In liver cancer, DHA induces hepatocyte ferroptosis by inhibiting ATF4, SLC7A11 or xCT, and also induces ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PEBP1/15-LO formation (62). Additionally, other reports suggest DHA triggers ferroptosis in primary liver cancer cells by upregulating CHAC1 expression, which is induced through interactions with unfolded proteins (63). The molecular mechanisms behind this difference still need further in-depth study. In lung cancer, DHA inhibits proliferation and colony formation, increases cell death, and induces ferroptosis in lung cancer cells by inactivating the PRIM2/SLC7A11 axis (64). Subsequently, it was found that DHA not only induces ferroptosis through lipid peroxide (LPO) accumulation but also promotes immunogenic cell death of lung cancer cells, thereby enhancing anti-tumor effects (65).
Alkaloids induce ferroptosis in tumor cells
Solasonine, a steroidal alkaloid derived from the natural herb Solanum melongena, exhibits potent anticancer activity. In gastric cancer, it induces ferroptosis by inhibiting GPX4 and GSS, thereby elevating lipid ROS levels; this effect can be significantly reversed by ferroptosis inhibitors (66). In pancreatic cancer, by contrast, solasonine activates ferroptosis and suppresses cancer cell progression through inhibition of the TFAP2A/OTUB1/SLC7A11 axis. In lung adenocarcinoma, it triggers tumor cell ferroptosis by disrupting redox balance and causing mitochondrial oxidative stress damage (67) (Table 1).
Evodiamine, an alkaloid from Hemerocallis fulva fruits, has antitumor effects. In bladder cancer, it induces ferroptosis mainly by inhibiting GPX4 expression (68). In prostate cancer, Evodiamine acts as a metabolic epigenetic regulator. It increases Sema3A expression to impair angiogenesis and induces ferroptosis by decreasing GPX4 expression. After ferroptosis, HIF1A protein lactylation is inhibited. This blocks lactate-induced angiogenesis, enhances Sema3A transcription and inhibits PD-L1 transcription, boosting antitumor effects (69).
Capsaicinoids, the active components of chili peppers and secondary metabolites, show antitumor activity in various tumors. In glioblastoma, capsaicin induces redox imbalance and ferroptosis in U87-MG and U251 cells primarily via the ACSL4/GPX4 signaling pathway (27). Similar findings were observed in NSCLC, where capsaicin induces ferroptosis mainly by inactivating SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling (34), suggesting its potential as an anticancer agent for NSCLC. Additionally, the synthetic capsaicin analog Arvanil induces high mitochondrial calcium flux, opening the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore (mPTP) and triggering ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (70).
Phenol induce ferroptosis in tumor cells
Phenolic compounds, formed by hydroxyl groups directly attached to aromatic hydrocarbons, are produced by plants and microorganisms. Curcumin, a yellow pigment extracted from turmeric rhizomes, is an unsaturated polyphenolic compound. It inhibits tumor growth by inducing ferroptosis in various tumor cells, primarily by upregulating HO-1 expression. For example, in Follicular Thyroid Cancer (FTC), HO-1 overexpression activates ferroptosis signaling. Curcumin suppresses FTC growth by inducing ferroptosis through increased HO-1 expression (71) (Table 1).
Erianin, extracted from Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl, shows anti-cancer activity across various cancers, inhibiting tumor growth via ferroptosis in lung, liver, bladder, and colon cancers (72). In lung cancer, it induces ferroptosis and inhibits cell migration through Ca2+/CaM signaling (73). In bladder cancer, Erianin triggers ferroptosis by inactivating NRF2 (74). In colon cancer, it suppresses growth and metastasis via autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in KRAS (75). In liver cancer, Erianin induces ferroptosis by activating JAK2/STAT3 and inhibiting SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression, reducing HCC cell proliferation and invasion (76). Additionally, in kidney cancer, Erianin promotes ferroptosis in cancer stem cells by enhancing ALOX12/p53 mRNA N6-methyladenosine modification (77). It also inhibits lung cancer stemness and improves chemosensitivity by inducing ferroptosis, highlighting its potential in cancer therapy (78).
Other natural products induce ferroptosis in tumor cells
Other natural products can also induce ferroptosis in tumor cells, including vitamins, coumarins, and steroids (Table 1). Vitamin C induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth by activating AMPK/Nrf2/HMOX1 (33, 79). while vitamin D promotes ferroptosis in colorectal cancer stem cells by downregulating SLC7A11 (80). Osthole, a natural coumarin from fungi and umbelliferous plants, induces ferroptosis in colon cancer cells by inhibiting the AMPK/Akt/mTOR pathway (81). Withaferin A, a sterol lactone from the medicinal plant Withania somnifera, induces EMT and ferroptosis in liver cancer cells through Nrf2 mediation (82).
Flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids and phenols all induce ferroptosis in tumor cells by interfering with the antioxidant system, promoting lipid peroxidation and regulating iron metabolism. However, they differ in their specific mechanisms. Flavonoids induce ferroptosis by releasing iron ions via ferritinophagy and inhibiting antioxidant enzymes. Terpenoids activate ACSL4 to boost lipid peroxidation substrate synthesis and affect mitochondrial function. Alkaloids suppress xCT to block cystine uptake or inhibit the mitochondrial respiratory chain to produce ROS. Phenols directly promote oxidation through the Fenton reaction and inhibit repair of peroxidized phospholipids at high concentrations.
Conclusion
Ferroptosis is a recently discovered novel mode of programmed death, mainly caused by intracellular iron accumulation and an increase in lipid peroxidation. There are significant differences between ferroptosis and other types of programmed death in terms of cell morphology and molecular mechanisms. Current reports show that ferroptosis is closely related to a variety of human diseases, such as neurological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases and cancer. Inhibiting tumor growth by inducing ferroptosis in various tumor cells has become a popular target in cancer therapy. Some small molecule compounds that can induce tumor cell ferroptosis such as SRF and SAS have been used in clinical studies. However, small molecule compounds have always had side effects in cancer treatment, causing toxic effects on normal cells. Natural products have unique advantages in cancer therapy, such as low toxicity and side effects as well as overcoming drug resistance. Therefore, discovering and studying the use of natural product therapy to induce ferroptosis of tumor cells has important theoretical and practical significance. We systematically analyzed the molecular mechanisms of natural products inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells and the applications of various types of natural products reported in inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells. These analyses provide a theoretical basis and guidance for the discovery and study of more natural product inducers in the future. Although many natural products have been found to induce ferroptosis in tumor cells, however, further research is needed to discover and study the molecular mechanisms and clinical efficacy of these natural products.
Natural products hold certain therapeutic potential in inducing ferroptosis in tumors, but they also face many limitations and challenges. First, tumor cells show significant differences in sensitivity to ferroptosis. Different tumor types vary in their sensitivity to ferroptosis due to differences in metabolic characteristics, gene expression profiles, and genetic mutation patterns. For example, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, and breast cancer are relatively sensitive to ferroptosis, while some tumor cells may develop tolerance to ferroptosis inducers because they contain high levels of antioxidant enzymes or iron regulatory proteins. In addition, the complexity of the tumor microenvironment can also affect the occurrence of ferroptosis, and genetic mutations that may occur during the process of cell carcinogenesis, such as mutations in the p53 gene, can also change the sensitivity of cells to ferroptosis (83).
Second, the potential side effects of natural products in inducing ferroptosis cannot be ignored. Natural products may have toxic effects on normal tissues, especially at high doses or with long-term use. Some natural products may be photosensitive, thermosensitive, or chemically unstable, which limits their clinical application prospects. Moreover, ferroptosis inducers may increase oxidative stress levels, which in some cases may promote the occurrence and development of tumors. For example, excessive lipid peroxidation can lead to DNA damage, thereby triggering mutations and tumor development. Certain natural products may interact with ferroptosis inducers to produce unknown side effects or enhance toxicity. In summary, although natural products have potential in inducing ferroptosis in tumors, their limitations and challenges should not be overlooked (84).
In future research, we need to focus more on the following issues. First, different types of tumor cells have varying sensitivities to natural products inducing ferroptosis in these tumor cells, and the underlying mechanisms have been unknown. Therefore, future research needs to focus on studying the molecular mechanisms that cause differences in sensitivity. Secondly, many natural products have disadvantages such as poor water solubility, limiting their wider application. Therefore, future studies need to focus on the structurally modifying these natural products that can induce ferroptosis in tumor cells to make them more soluble in water and more easily absorbed by the body. Alternatively, the development of more effective drug delivery vehicles that can deliver these natural products to the tumor site in the human body. Finally, the combination of natural products with chemotherapeutic or targeted drugs for the treatment of tumors can achieve better therapeutic effects, so future research needs to focus on this combination of drug therapy. The in-depth study of the above issues will eventually provide broader prospects for the application of natural products in cancer therapy.
In future research, the induction of ferroptosis by natural products should focus on addressing existing limitations. On the one hand, improving the solubility and bioavailability of natural products through means such as nanotechnology, microemulsion technology, and liposome encapsulation, and developing tumor-targeted nanocarriers or drug delivery systems to enhance their accumulation and efficacy in tumor tissues while reducing toxicity to normal tissues. On the other hand, delving into the molecular mechanisms underlying the sensitivity of tumor cells to ferroptosis, identifying predictive biomarkers, and providing a basis for precision therapy. Research should be committed to the development of combination therapies, integrating ferroptosis inducers with traditional chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy to enhance therapeutic effects and reduce the resistance associated with monotherapy. For example, combining ferroptosis inducers with radiotherapy can enhance DNA damage induced by radiotherapy, while combining them with immune checkpoint inhibitors can improve the immune microenvironment. In addition, it is necessary to explore the interactions between ferroptosis and other forms of cell death, as well as the regulatory role of the tumor microenvironment in these processes, to provide a more comprehensive strategy for cancer treatment.
Author contributions
XY: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Validation. XJ: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by key research and development program of Zhenjiang (SH2023039).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mao C, Wang M, Zhuang L, and Gan B. Metabolic cell death in cancer: Ferroptosis, cuproptosis, disulfidptosis, and beyond. Protein Cell. (2024) 15(9):642–60. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae003
2. Zhou X, Yeasmin Khusbu F, Xie Y, and Yang P. Emodin-induced necroptosis in prostate cancer cells via the mitochondrial fission HSP90/MLKL/PGAM pathway. Chem Biodivers. (2023) 20:e202201130. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202201130
3. Wang KJ, Meng XY, Chen JF, Wang KY, Zhou C, Yu R, et al. Emodin induced necroptosis and inhibited glycolysis in the renal cancer cells by enhancing ROS. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2021) 2021:8840590. doi: 10.1155/2021/8840590
4. Zhou J, Li G, Han G, Feng S, Liu Y, Chen J, et al. Emodin induced necroptosis in the glioma cell line U251 via the TNF-alpha/RIP1/RIP3 pathway. Invest New Drugs. (2020) 38:50–9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00764-w
5. Liu X, Liu L, Wang X, Jin Y, Wang S, Xie Q, et al. Necroptosis inhibits autophagy by regulating the formation of RIP3/p62/Keap1 complex in shikonin-induced ROS dependent cell death of human bladder cancer. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2023) 118:154943. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154943
6. Ding Y, He C, Lu S, Wang X, Wang C, Wang L, et al. MLKL contributes to shikonin-induced glioma cell necroptosis via promotion of chromatinolysis. Cancer Lett. (2019) 467:58–71. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.007
7. Liu X, Zhang Y, Gao H, Hou Y, Lu JJ, Feng Y, et al. Induction of an MLKL mediated non-canonical necroptosis through reactive oxygen species by tanshinol A in lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. (2020) 171:113684. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113684
8. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
9. Du Y and Guo Z. Recent progress in ferroptosis: inducers and inhibitors. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:501. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01297-7
10. Ghosh S, Das SK, Sinha K, Ghosh B, Sen K, Ghosh N, et al. The emerging role of natural products in cancer treatment. Arch Toxicol. (2024) 98(8):2353–91. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03786-3
11. Dolma S, Lessnick SL, Hahn WC, and Stockwell BR. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell. (2003) 3:285–96. doi: 10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00050-3
12. Lei G, Zhuang L, and Gan B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:381–96. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00459-0
13. Zhou Q, Meng Y, Li D, Yao L, Le J, Liu Y, et al. Ferroptosis in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:55. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01769-5
14. Li YT, Chen YY, Xu Y, and Wu DP. Advances of ferroptosis pathways in acute myeloid leukemia. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. (2023) 44:525–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2023.06.019
15. Zhu J, Yuan A, Le Y, Chen X, Guo J, Liu J, et al. Yi-Qi-Jian-Pi-Xiao-Yu formula inhibits cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through suppressing ferroptosis via STING-NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 135:156189. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156189
16. Chen L, Ning J, Linghu L, Tang J, Liu N, Long Y, et al. USP13 facilitates a ferroptosis-to-autophagy switch by activation of the NFE2L2/NRF2-SQSTM1/p62-KEAP1 axis dependent on the KRAS signaling pathway. Autophagy. (2025) 21:565–82. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2410619
17. Miura K, Satoh M, Kinouchi M, Yamamoto K, Hasegawa Y, Philchenkov A, et al. The preclinical development of regorafenib for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Drug Discov. (2014) 9:1087–101. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.924923
18. Li R, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Gao Q, Wang R, Fu Y, et al. Transcriptome investigation and in vitro verification of curcumin-induced HO-1 as a feature of ferroptosis in breast cancer cells. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2020) 2020:3469840. doi: 10.1155/2020/3469840
19. Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. (2022) 185:2401–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003
20. Liu J, Xia X, and Huang P. xCT: A critical molecule that links cancer metabolism to redox signaling. Mol Ther. (2020) 28:2358–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.08.021
21. He C, Wang C, Liu H, and Shan B. Kayadiol exerted anticancer effects through p53-mediated ferroptosis in NKTCL cells. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:724. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09825-5
22. Mei F, Liu Y, and Zheng S. Rhamnazin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness in vitro via glutathione peroxidase 4-dependent ferroptosis. Tohoku J Exp Med. (2022) 258:111–20. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2022.J061
23. Luo N, Zhang K, Li X, Hu Y, and Guo L. Tanshinone IIA destabilizes SLC7A11 by regulating PIAS4-mediated SUMOylation of SLC7A11 through KDM1A, and promotes ferroptosis in breast cancer. J Adv Res. (2024) 69:313–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.009
24. Liu Y, Wan Y, Jiang Y, Zhang L, and Cheng W. GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2023) 1878:188890. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188890
25. Cheff DM, Huang C, Scholzen KC, Gencheva R, Ronzetti MH, Cheng Q, et al. The ferroptosis inducing compounds RSL3 and ML162 are not direct inhibitors of GPX4 but of TXNRD1. Redox Biol. (2023) 62:102703. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102703
26. Gu Y, Li Y, Wang J, Zhang L, Zhang J, and Wang Y. Targeting ferroptosis: Paving new roads for drug design and discovery. Eur J Med Chem. (2023) 247:115015. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.115015
27. Hacioglu C and Kar F. Capsaicin induces redox imbalance and ferroptosis through ACSL4/GPx4 signaling pathways in U87-MG and U251 glioblastoma cells. Metab Brain Dis. (2023) 38:393–408. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-00983-w
28. Chang WT, Bow YD, Fu PJ, Li CY, Wu CY, Chang YH, et al. A marine terpenoid, heteronemin, induces both the apoptosis and ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involves the ROS and MAPK pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2021) 2021:7689045. doi: 10.1155/2021/7689045
29. Gao M, Lai K, Deng Y, Lu Z, Song C, Wang W, et al. Eriocitrin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) in lung adenocarcinoma cells via triggering ferroptosis. Aging. (2023) 15:10089–104. doi: 10.18632/aging.205049
30. Kong N, Chen X, Feng J, Duan T, Liu S, Sun X, et al. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in bladder cancer cells by downregulating FTH1. Acta Pharm Sinica B. (2021) 11:4045–54. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.03.036
31. Zhang YY, Ni ZJ, Elam E, Zhang F, Thakur K, Wang S, et al. Juglone, a novel activator of ferroptosis, induces cell death in endometrial carcinoma Ishikawa cells. Food Funct. (2021) 12:4947–59. doi: 10.1039/D1FO00790D
32. Cai S, Ding Z, Liu X, and Zeng J. Trabectedin induces ferroptosis via regulation of HIF-1α/IRP1/TFR1 and Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Chemico Biol Interact. (2023) 369:110262. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110262
33. Liu Y, Huang P, Li Z, Xu C, Wang H, Jia B, et al. Vitamin C sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to erastin-induced ferroptosis by activating the AMPK/Nrf2/HMOX1 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2022) 2022:5361241. doi: 10.1155/2022/5361241
34. Liu XY, Wei DG, and Li RS. Capsaicin induces ferroptosis of NSCLC by regulating SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling in vitro. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:11996. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16372-3
35. Wu Y, Jia Q, Tang Q, Deng H, He Y, and Tang F. Berberine-mediated ferroptosis through system Xc(-)/GSH/GPX4 axis inhibits metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer. (2024) 15:685–98. doi: 10.7150/jca.90574
36. Xiaofei J, Mingqing S, Miao S, Yizhen Y, Shuang Z, Qinhua X, et al. Oleanolic acid inhibits cervical cancer Hela cell proliferation through modulation of the ACSL4 ferroptosis signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 545:81–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.01.028
37. Wang HJ, Dong LF, Ding LL, Miao XY, Zhang YW, Zhao LP, et al. TFEB promotes Ginkgetin-induced ferroptosis via TRIM25 mediated GPX4 lysosomal degradation in EGFR wide-type lung adenocarcinoma. Theranostics. (2025) 15:2991–3012. doi: 10.7150/thno.106469
38. Zhang S, Sun Y, Yao F, Li H, Yang Y, Li X, et al. Ginkgo Biflavones Cause p53 Wild-Type Dependent Cell Death in a Transcription-Independent Manner of p53. J Nat Prod. (2023) 86:346–56. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00959
39. Jin Y, Wen J, Geng Z, Wang L, Fang W, Zhao H, et al. Baicalin inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation and migration via ALOX12-mediated ferroptosis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. (2025). doi: 10.2174/0118715206342238250428115441
40. Wen Z, Zhang Y, Gao B, and Chen X. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing the activity of FTH1. J Gene Med. (2024) 26:e3669. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3669
41. Wen RJ, Dong X, Zhuang HW, Pang FX, Ding SC, Li N, et al. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in osteosarcomas through a novel Nrf2/xCT/GPX4 regulatory axis. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2023) 116:154881. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154881
42. Yuan J, Khan SU, Yan J, Lu J, Yang C, and Tong Q. Baicalin enhances the efficacy of 5-Fluorouracil in gastric cancer by promoting ROS-mediated ferroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 164:114986. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114986
43. Xu M, Zhong W, Yang C, Liu M, Yuan X, Lu T, et al. Tiliroside disrupted iron homeostasis and induced ferroptosis via directly targeting calpain-2 in pancreatic cancer cells. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 127:155392. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155392
44. Yang C, Lu T, Liu M, Yuan X, Li D, Zhang J, et al. Tiliroside targets TBK1 to induce ferroptosis and sensitize hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2023) 111:154668. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154668
45. Hu C, Zhao JF, Wang YM, Wu XL, and Ye L. Tiliroside induces ferroptosis to repress the development of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Tissue Cell. (2023) 83:102116. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102116
46. Wang ZX, Ma J, Li XY, Wu Y, Shi H, Chen Y, et al. Quercetin induces p53-independent cancer cell death through lysosome activation by the transcription factor EB and Reactive Oxygen Species-dependent ferroptosis. Br J Pharmacol. (2021) 178:1133–48. doi: 10.1111/bph.15350
47. An S and Hu M. Quercetin promotes TFEB nuclear translocation and activates lysosomal degradation of ferritin to induce ferroptosis in breast cancer cells. Comput Intell Neurosci. (2022) 2022:5299218. doi: 10.1155/2022/5299218
48. Ding L, Dang S, Sun M, Zhou D, Sun Y, Li E, et al. Quercetin induces ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells by targeting SLC1A5 and regulating the p-Camk2/p-DRP1 and NRF2/GPX4 Axes. Free Radical Biol Med. (2024) 213:150–63. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.01.002
49. Zhao H, Ding R, and Han J. Ginsenoside Rh4 facilitates the sensitivity of renal cell carcinoma to ferroptosis via the NRF2 pathway. Archivos Espanoles Urol. (2024) 77:119–28. doi: 10.56434/j.arch.esp.urol.20247702.16
50. Ying Q, Lou J, and Zheng D. Ginsenoside Rh4 inhibits the Malignant progression of multiple myeloma and induces ferroptosis by regulating SIRT2. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2023) 50:757–65. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13805
51. Wu Y, Pi D, Chen Y, Zuo Q, Zhou S, and Ouyang M. Ginsenoside Rh4 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation by inducing ferroptosis via autophagy activation. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med: eCAM. (2022) 2022:6177553. doi: 10.1155/2022/6177553
52. Wu Y, Pi D, Zhou S, Yi Z, Dong Y, Wang W, et al. Ginsenoside Rh3 induces pyroptosis and ferroptosis through the Stat3/p53/NRF2 axis in colorectal cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. (2023) 55:587–600. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023068
53. Li W, Fu H, Fang L, Chai H, Ding B, and Qian S. Andrographolide induced ferroptosis in multiple myeloma cells by regulating the P38/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2023) 742:109622. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109622
54. Jiaqi L, Siqing H, Qin W, di Z, Bei Z, and Jialin Y. Andrographolide promoted ferroptosis to repress the development of non-small cell lung cancer through activation of the mitochondrial dysfunction. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2023) 109:154601. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154601
55. Ooko E, Saeed ME, Kadioglu O, Sarvi S, Colak M, Elmasaoudi K, et al. Artemisinin derivatives induce iron-dependent cell death (ferroptosis) in tumor cells. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2015) 22:1045–54. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.08.002
56. Zhu S, Yu Q, Huo C, Li Y, He L, Ran B, et al. Ferroptosis: A novel mechanism of artemisinin and its derivatives in cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem. (2021) 28:329–45. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200121124404
57. Hu Y, Guo N, Yang T, Yan J, Wang W, and Li X. The potential mechanisms by which artemisinin and its derivatives induce ferroptosis in the treatment of cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2022) 2022:1458143. doi: 10.1155/2022/1458143
58. Lin R, Zhang Z, Chen L, Zhou Y, Zou P, Feng C, et al. Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) induces ferroptosis and causes cell cycle arrest in head and neck carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. (2016) 381:165–75. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.033
59. Molleken J, Kragl A, Monecke A, Metelmann I, Kramer S, and Kallendrusch S. Artemisinin derivatives differently affect cell death of lung cancer subtypes by regulating GPX4 in patient-derived tissue cultures. Cell Death Discov. (2025) 11:256. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02537-2
60. Chen Y, Mi Y, Zhang X, Ma Q, Song Y, Zhang L, et al. Dihydroartemisinin-induced unfolded protein response feedback attenuates ferroptosis via PERK/ATF4/HSPA5 pathway in glioma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:402. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1413-7
61. Yi R, Wang H, Deng C, Wang X, Yao L, Niu W, et al. Dihydroartemisinin initiates ferroptosis in glioblastoma through GPX4 inhibition. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40(6):BSR20193314. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193314
62. Su Y, Zhao D, Jin C, Li Z, Sun S, Xia S, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces ferroptosis in HCC by promoting the formation of PEBP1/15-LO. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2021) 2021:3456725. doi: 10.1155/2021/3456725
63. Wang Z, Li M, Liu Y, Qiao Z, Bai T, Yang L, et al. Dihydroartemisinin triggers ferroptosis in primary liver cancer cells by promoting and unfolded protein response−induced upregulation of CHAC1 expression. Oncol Rep. (2021) 46(5):240. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8191
64. Yuan B, Liao F, Shi ZZ, Ren Y, Deng XL, Yang TT, et al. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the proliferation, colony formation and induces ferroptosis of lung cancer cells by inhibiting PRIM2/SLC7A11 axis. OncoTargets Ther. (2020) 13:10829–40. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S248492
65. Han N, Yang ZY, Xie ZX, Xu HZ, Yu TT, Li QR, et al. Dihydroartemisinin elicits immunogenic death through ferroptosis-triggered ER stress and DNA damage for lung cancer immunotherapy. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2023) 112:154682. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154682
66. Jin M, Shi C, Li T, Wu Y, Hu C, and Huang G. Solasonine promotes ferroptosis of hepatoma carcinoma cells via glutathione peroxidase 4-induced destruction of the glutathione redox system. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 129:110282. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110282
67. Zeng YY, Luo YB, Ju XD, Zhang B, Cui YJ, Pan YB, et al. Solasonine causes redox imbalance and mitochondrial oxidative stress of ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:874900. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.874900
68. Hu CY, Wu HT, Shan YS, Wang CT, Shieh GS, Wu CL, et al. Evodiamine exhibits anti-bladder cancer activity by suppression of glutathione peroxidase 4 and induction of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(7):6021. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076021
69. Yu Y, Huang X, Liang C, and Zhang P. Evodiamine impairs HIF1A histone lactylation to inhibit Sema3A-mediated angiogenesis and PD-L1 by inducing ferroptosis in prostate cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 957:176007. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176007
70. Deng X, Gui Y, Zhao L, Li N, and Li L. Arvanil induces ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by binding to MICU1. Cancer Gene Ther. (2024) 31:148–57. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00690-3
71. Chen H, Li Z, Xu J, Zhang N, Chen J, Wang G, et al. Curcumin induces ferroptosis in follicular thyroid cancer by upregulating HO-1 expression. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2023) 2023:6896790. doi: 10.1155/2023/6896790
72. Zheng Y, Zheng Y, Chen H, Tan X, Zhang G, Kong M, et al. Erianin triggers ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells by facilitating the ubiquitination and degradation of GPX4. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2025) 139:156465. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156465
73. Chen P, Wu Q, Feng J, Yan L, Sun Y, Liu S, et al. Erianin, a novel dibenzyl compound in Dendrobium extract, inhibits lung cancer cell growth and migration via calcium/calmodulin-dependent ferroptosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:51. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0149-3
74. Xiang Y, Chen X, Wang W, Zhai L, Sun X, Feng J, et al. Natural product erianin inhibits bladder cancer cell growth by inducing ferroptosis via NRF2 inactivation. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:775506. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.775506
75. Miao Q, Deng WQ, Lyu WY, Sun ZT, Fan SR, Qi M, et al. Erianin inhibits the growth and metastasis through autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in KRAS(G13D) colorectal cancer. Free Radical Biol Med. (2023) 204:301–12. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.05.008
76. Chen L, Sun R, and Fang K. Erianin inhibits tumor growth by promoting ferroptosis and inhibiting invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma through the JAK2/STAT3/SLC7A11 pathway. Pathol Int. (2024) 74:119–28. doi: 10.1111/pin.13403
77. Shen H, Geng Z, Nie X, and Liu T. Erianin Induces Ferroptosis of Renal Cancer Stem Cells via Promoting ALOX12/P53 mRNA N6-methyladenosine Modification. J Cancer. (2023) 14:367–78. doi: 10.7150/jca.81027
78. Lv J, Wang Z, and Liu H. Erianin suppressed lung cancer stemness and chemotherapeutic sensitivity via triggering ferroptosis. Environ Toxicol. (2024) 39:479–86. doi: 10.1002/tox.23832
79. Wang X, Xu S, Zhang L, Cheng X, Yu H, Bao J, et al. Vitamin C induces ferroptosis in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells by ferritinophagy activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 551:46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.02.126
80. Guo S, Zhao W, Zhang W, Li S, Teng G, and Liu L. Vitamin D promotes ferroptosis in colorectal cancer stem cells via SLC7A11 downregulation. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2023) 2023:4772134. doi: 10.1155/2023/4772134
81. Zhou X, Kang J, Zhang L, and Cheng Y. Osthole inhibits Malignant phenotypes and induces ferroptosis in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer cells via suppressing AMPK/Akt signaling. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2023) 92:119–34. doi: 10.1007/s00280-023-04549-0
82. Zhang Y, Tan Y, Liu S, Yin H, Duan J, Fan L, et al. Implications of Withaferin A for the metastatic potential and drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Nrf2-mediated EMT and ferroptosis. Toxicol Mech Methods. (2023) 33:47–55. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2022.2075297
83. Chen J, Yang X, Fang X, Wang F, and Min J. The role of ferroptosis in chronic diseases. Zhejiang Da Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2020) 49:44–57. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.02.24
84. Liang Y, Zhao Y, Qi Z, Li X, and Zhao Y. Ferroptosis: CD8(+)T cells’ blade to destroy tumor cells or poison for self-destruction. Cell Death Discov. (2025) 11:128. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02415-x
85. Lou JS, Zhao LP, Huang ZH, Chen XY, Xu JT, Tai WC, et al. Ginkgetin derived from Ginkgo biloba leaves enhances the therapeutic effect of cisplatin via ferroptosis-mediated disruption of the Nrf2/HO-1 axis in EGFR wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2021) 80:153370. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153370
86. Tang F, Xu Y, Gao E, Zhang W, Zhang F, Xiang Y, et al. Amentoflavone attenuates cell proliferation and induces ferroptosis in human gastric cancer by miR-496/ATF2 axis. Chem Biol Drug Design. (2023) 102:782–92. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14288
87. N Adham A, F Hegazy ME, Naqishbandi AM, and Efferth T. Induction of Apoptosis, Autophagy and Ferroptosis by Thymus vulgaris and Arctium lappa Extract in Leukemia and Multiple Myeloma Cell Lines. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2020) 25(21):5016. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215016
88. Song W, Zhang L, Cui X, Wang R, Ma J, Xu Y, et al. Nobiletin alleviates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity via activating autophagy and inhibiting NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:7889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55614-4
89. Yang C, Wang T, Zhao Y, Meng X, Ding W, Wang Q, et al. Flavonoid 4,4’-dimethoxychalcone induced ferroptosis in cancer cells by synergistically activating Keap1/Nrf2/HMOX1 pathway and inhibiting FECH. Free Radical Biol Med. (2022) 188:14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.06.010
90. Xu W, Ding J, Li B, Sun T, You X, He Q, et al. Effects of icariin and curcumol on autophagy, ferroptosis, and lipid metabolism based on miR-7/m-TOR/SREBP1 pathway on prostate cancer. BioFactors (Oxford England). (2023) 49:438–56. doi: 10.1002/biof.1927
91. Gong G, Wan Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z, and Zheng Y. Ononin triggers ferroptosis-mediated disruption in the triple negative breast cancer both in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 132:111959. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111959
92. Lu Y, Sun J, Yang M, Xing Y, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al. Myricetin induces ferroptosis and inhibits gastric cancer progression by targeting NOX4. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:6178–88. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05243
93. Wang Z, Li W, Wang X, Zhu Q, Liu L, Qiu S, et al. Isoliquiritigenin induces HMOX1 and GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in gallbladder cancer cells. Chin Med J. (2023) 136:2210–20. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002675
94. Liu X, Peng X, Cen S, Yang C, Ma Z, and Shi X. Wogonin induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting the Nrf2/GPX4 axis. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1129662. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1129662
95. Gao Z, Jiang J, Hou L, and Ji F. Lysionotin induces ferroptosis to suppress development of colorectal cancer via promoting Nrf2 degradation. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2022) 2022:1366957. doi: 10.1155/2022/1366957
96. Luo Y, Gao X, Zou L, Lei M, Feng J, and Hu Z. Bavachin induces ferroptosis through the STAT3/P53/SLC7A11 axis in osteosarcoma cells. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2021) 2021:1783485. doi: 10.1155/2021/1783485
97. Zhu HY, Huang ZX, Chen GQ, Sheng F, and Zheng YS. Typhaneoside prevents acute myeloid leukemia (AML) through suppressing proliferation and inducing ferroptosis associated with autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 516:1265–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.070
98. Zhang G, Hu J, Li A, Zhang H, Guo Z, Li X, et al. Ginsenoside Rg5 inhibits glioblastoma by activating ferroptosis via NR3C1/HSPB1/NCOA4. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 129:155631. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155631
99. Xu Y, Tong Y, Lei Z, Zhu J, and Wan L. Abietic acid induces ferroptosis via the activation of the HO-1 pathway in bladder cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 158:114154. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114154
100. Peng Y, Li N, Tang F, Qian C, Jia T, Liu J, et al. Corosolic acid sensitizes ferroptosis by upregulating HERPUD1 in liver cancer cells. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:376. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01169-0
101. Li J, Yuan J, Li Y, Wang J, Xie Q, Ma R, et al. d-Borneol enhances cisplatin sensitivity via autophagy dependent EMT signaling and NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2022) 106:154411. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154411
102. Wei R, Zhao Y, Wang J, Yang X, Li S, Wang Y, et al. Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:2703–17. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59404
103. Mbaveng AT, Ndontsa BL, Kuete V, Nguekeu YMM, Çelik İ, Mbouangouere R, et al. A naturally occuring triterpene saponin ardisiacrispin B displayed cytotoxic effects in multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells via ferroptotic and apoptotic cell death. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2018) 43:78–85. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.035
104. LoBianco FV, Krager KJ, Johnson E, Godwin CO, Allen AR, Crooks PA, et al. Parthenolide induces rapid thiol oxidation that leads to ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Front Toxicol. (2022) 4:936149. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.936149
105. Ni Y, Liu J, Zeng L, Yang Y, Liu L, Yao M, et al. Natural product manoalide promotes EGFR-TKI sensitivity of lung cancer cells by KRAS-ERK pathway and mitochondrial Ca(2+) overload-induced ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1109822. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1109822
106. Zhang Y, Zhang H, Mu J, Han M, Cao Z, Dong F, et al. Eupalinolide B inhibits hepatic carcinoma by inducing ferroptosis and ROS-ER-JNK pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. (2022) 54:974–86. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022082
107. Zhang R, Pan T, Xiang Y, Zhang M, Xie H, Liang Z, et al. Curcumenol triggered ferroptosis in lung cancer cells via lncRNA H19/miR-19b-3p/FTH1 axis. Bioactive Mater. (2022) 13:23–36. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.11.013
108. Wei Y, Zhu Z, Hu H, Guan J, Yang B, and Zhao H. Eupaformosanin induces apoptosis and ferroptosis through ubiquitination of mutant p53 in triple-negative breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 924:174970. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174970
109. Guan Z, Chen J, Li X, and Dong N. Tanshinone IIA induces ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells through p53-mediated SLC7A11 down-regulation. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40(8):BSR20201807. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201807
110. Xia M, Wu Y, Zhu H, and Duan W. Tanshinone I induces ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells via the KDM4D/p53 pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2023) 42:9603271231216963. doi: 10.1177/09603271231216963
111. Huang S, Cao B, Zhang J, Feng Y, Wang L, Chen X, et al. Induction of ferroptosis in human nasopharyngeal cancer cells by cucurbitacin B: molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:237. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03516-y
112. Chen W, Yang W, Zhang C, Liu T, Zhu J, Wang H, et al. Modulation of the p38 MAPK Pathway by Anisomycin Promotes Ferroptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Phosphorylation of H3S10. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2022) 2022:6986445. doi: 10.1155/2022/6986445
113. Yi N, Wang L, Jiang Z, Xu G, Li L, Zhang Y, et al. Peiminine triggers ferroptosis to inhibit breast cancer growth through triggering Nrf2 signaling. Tissue Cell. (2024) 87:102323. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2024.102323
114. Yin Z, Lv Y, Deng L, Li G, Ou R, Chen L, et al. Targeting ABCB6 with nitidine chloride inhibits PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to promote ferroptosis in multiple myeloma. Free Radical Biol Med. (2023) 203:86–101. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.04.003
115. Zhou J, Wang Y, Fu Y, Lin Z, Lin H, Lv G, et al. Chelerythrine induces apoptosis and ferroptosis through Nrf2 in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand France). (2024) 70:174–81. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.3.26
116. Mbaveng AT, Noulala CGT, Samba ARM, Tankeo SB, Abdelfatah S, Fotso GW, et al. The alkaloid, soyauxinium chloride, displays remarkable cytotoxic effects towards a panel of cancer cells, inducing apoptosis, ferroptosis and necroptosis. Chemico Biol Interact. (2021) 333:109334. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109334
117. Mbaveng AT, Bitchagno GTM, Kuete V, Tane P, and Efferth T. Cytotoxicity of ungeremine towards multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells and induction of apoptosis, ferroptosis, necroptosis and autophagy. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2019) 60:152832. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152832
118. Liang X, Hu C, Han M, Liu C, Sun X, Yu K, et al. Solasonine inhibits pancreatic cancer progression with involvement of ferroptosis induction. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:834729. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.834729
119. Xia Y, Liu S, Li C, Ai Z, Shen W, Ren W, et al. Discovery of a novel ferroptosis inducer-talaroconvolutin A-killing colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:988. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03194-2
120. Xia Y, Xiang L, Yao M, Ai Z, Yang W, Guo J, et al. Proteomics, transcriptomics, and phosphoproteomics reveal the mechanism of talaroconvolutin-A suppressing bladder cancer via blocking cell cycle and triggering ferroptosis. Mol Cell Proteom: MCP. (2023) 22:100672. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100672
121. Jin J, Fan Z, Long Y, Li Y, He Q, Yang Y, et al. Matrine induces ferroptosis in cervical cancer through activation of piezo1 channel. Phytomed: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. (2024) 122:155165. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155165
122. Chen P, Ye Q, Liang S, and Zeng L. Cephaeline promotes ferroptosis by targeting NRF2 to exert anti-lung cancer efficacy. Pharm Biol. (2024) 62:195–206. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2309891
123. Mukherjee D, Chakraborty S, Bercz L, D’Alesio L, Wedig J, Torok MA, et al. Tomatidine targets ATF4-dependent signaling and induces ferroptosis to limit pancreatic cancer progression. iScience. (2023) 26:107408. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107408
124. Ma X, Li Y, Liang D, Jiang F, Zhang L, Song W, et al. Solanine induces ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells through ALOX12B/ADCY4 molecular axis. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2024) 76:224–35. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgad122
125. Wang W, Ma F, Cheung YT, Zeng G, Zhou Y, Chen Z, et al. Marine alkaloid lepadins E and H induce ferroptosis for cancer chemotherapy. J Med Chem. (2023) 66:11201–15. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00659
126. Yang Y, Sun S, Xu W, Zhang Y, Yang R, Ma K, et al. Piperlongumine inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 by targeting selenocysteine residues and sensitizes cancer cells to erastin. Antioxid (Basel Switzerland). (2022) 11(4):710. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040710
127. Alakkal A, Thayyullathil F, Pallichankandy S, Subburayan K, Cheratta AR, and Galadari S. Sanguinarine induces H(2)O(2)-dependent apoptosis and ferroptosis in human cervical cancer. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(8):1795. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081795
128. Lu S, Wang XZ, He C, Wang L, Liang SP, Wang CC, et al. ATF3 contributes to brucine-triggered glioma cell ferroptosis via promotion of hydrogen peroxide and iron. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2021) 42:1690–702. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00700-w
129. Yuan C, Fan R, Zhu K, Wang Y, Xie W, and Liang Y. Curcumin induces ferroptosis and apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by regulating Nrf2/GPX4 signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood NJ). (2023) 248:2183–97. doi: 10.1177/15353702231220670
130. Xin W and Zhang Y. Curcumin activates the JNK signaling pathway to promote ferroptosis in colon cancer cells. Chem Biol Drug Design. (2024) 103:e14468. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14468
131. Chen M, Tan AH, and Li J. Curcumin represses colorectal cancer cell proliferation by triggering ferroptosis via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Nutr Cancer. (2023) 75:726–33. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2022.2139398
132. Cao X, Li Y, Wang Y, Yu T, Zhu C, Zhang X, et al. Curcumin suppresses tumorigenesis by ferroptosis in breast cancer. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0261370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261370
133. Xie J, Wang H, Xie W, Liu Y, and Chen Y. Gallic acid promotes ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 397:2437–45. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02770-5
134. Liu F, Zhang Y, Xia X, Han J, and Cao L. Honokiol induces ferroptosis in ovarian cancer cells through the regulation of YAP by OTUB2. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. (2024) 50:864–72. doi: 10.1111/jog.15922
135. Guo C, Liu P, Deng G, Han Y, Chen Y, Cai C, et al. Honokiol induces ferroptosis in colon cancer cells by regulating GPX4 activity. Am J Cancer Res. (2021) 11:3039–54.
136. Lai X, Sun Y, Zhang X, Wang D, Wang J, Wang H, et al. Honokiol induces ferroptosis by upregulating HMOX1 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:897791. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.897791
137. Liu J, Gao W, Sheng Y, Sun J, and Wen D. Resveratrol drives ferroptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells through Hsa-miR-335-5p/NFS1/GPX4 pathway in a ROS-dependent manner. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand France). (2023) 69:131–7. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2023.69.7.21
138. Han B, Liu Y, Zhang Q, and Liang L. Propofol decreases cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by inducing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis through the miR-744-5p/miR-615-3p axis. J Proteomics. (2023) 274:104777. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2022.104777
Keywords: cancer, molecular mechanisms, ferroptosis, natural products, applications
Citation: Ye X and Ju X (2025) Natural products targeting ferroptosis in cancer: molecular mechanisms and applications. Front. Oncol. 15:1588668. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1588668
Received: 06 March 2025; Accepted: 25 July 2025;
Published: 09 September 2025.
Edited by:
Omowumi Adewale, Osun State University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Gang Fu, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaTemidayo Adigun, Chrisland University, Nigeria
Copyright © 2025 Ye and Ju. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Ye, eWV4aW42MjE3QHNpbmEuY29t
 Xin Ye1*
Xin Ye1* Xiaoli Ju
Xiaoli Ju