- Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Background and objectives: Thyroid carcinoma, one of the most prevalent endocrine malignancies, has witnessed a gradual increase in incidence in recent years. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that inflammation plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis, progression, and prognosis of thyroid carcinoma, with a significant association between certain malignancies and chronic inflammatory processes. This study conducts a bibliometric analysis of literature on inflammation and thyroid carcinoma over 24 years, aiming to identify trends and research dynamics. The findings are expected to deepen understanding of thyroid carcinoma mechanisms and guide new therapeutic strategies.
Methods: We used the advanced search function of the Web of Science Core Collection to systematically screen and curate articles on inflammation and thyroid carcinoma published between 2000 and 2024. Using Microsoft Excel 2019, we analyzed and visualized publication volume and growth trends. For co-occurrence and clustering analysis of countries, institutions, authors, journals, references, and keywords, we employed VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and the ‘bibliometrix’ package in R. Keyword visualization identified 10 major clusters, including sodium iodide symporter, total thyroidectomy, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, papillary thyroid microcarcinoma, therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals, zoological gardens, endoscopic thyroidectomy, mixed cryoglobulinemia, fine needle aspiration, and clinical evaluation. The most frequent keywords were cancer, thyroid cancer, and inflammation.
Results: We included a total of 1,441 articles published between 2000 and 2024, contributed by 8,326 authors from 2,054 institutions across 70 countries. These articles were published in 625 journals, encompassing 59,808 references and 6,340 keywords. The publication output demonstrated a consistent upward trend over the study period. Among the contributing nations, China emerged as the most prolific country in terms of publication volume. The leading institution was the University of Pisa in Italy. The most productive author was Antonelli, Alessandro, and the leading journal was Thyroid.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis shows that research on inflammation and thyroid carcinoma is a rapidly evolving field, marked by diverse themes and in-depth studies. Advances in technology and extensive research are expected to clarify how inflammation drives thyroid carcinoma initiation and progression. This deeper understanding will lead to new approaches in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of thyroid carcinoma.
1 Introduction
Thyroid carcinoma is the most common endocrine-related malignancy, accounting for 3% of global cancer incidence (1). According to Global Cancer Statistics 2022, there were 821,173 new cases and 47,485 deaths from thyroid cancer in 2022. Thyroid cancer has become a significant global health issue, with its incidence steadily increasing over the past few decades, profoundly impacting patients’ physical health and quality of life (2, 3). Thyroid cancer originates from thyroid follicular cells and parafollicular cells. Among these, three main malignant types exist: well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma (WDTC), poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC), and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC). WDTC is further divided into papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC). These two types exhibit distinct histological features and retain key diagnostic markers, which are crucial for diagnosis and treatment strategies (4). PDTC primarily includes insular thyroid carcinoma (ITC) and large-cell PDTC. The rise in thyroid carcinoma incidence is most pronounced in Asia, particularly in South Korea (5). Although some understanding of thyroid tumor etiology exists, its exact causes remain incompletely understood. Radiation exposure and iodine deficiency or excess are widely recognized as key risk factors. Additionally, dietary habits and living environments are considered significant contributors. These factors collectively play an important role in the development of thyroid tumors (6).
Inflammation is a complex biological defense mechanism aimed at protecting the body from harmful substances and is widely recognized as one of the seven hallmarks of cancer. Over the past few decades, the role of inflammation in thyroid carcinoma has been actively studied. The causal link between inflammation and cancer was first established by Rudolf Virchow in 1863, who observed leukocyte infiltration in tumor tissues, providing direct evidence of their profound biological connection. This discovery deepened our understanding of cancer mechanisms and laid the theoretical foundation for subsequent cancer research and therapy (7). Evidence suggests a positive correlation between chronic inflammation and increased thyroid carcinoma risk. Inflammatory immune cells and mediators (e.g., interleukins, cytokines) influence thyroid carcinoma development. These cells and mediators enrich the tumor stroma, participating in tissue repair, remodeling, and angiogenesis (8). The cancer stroma contains both anti-tumor inflammatory cells and activated immune cells that promote tumor immune responses. The balance between anti-tumor and pro-tumor immune responses ultimately determines cancer suppression or progression (9, 10). The tumor microenvironment (TME) also plays a pivotal role in the initiation and progression of thyroid carcinoma. The active presence of lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and a range of chemokines within the TME not only directly contributes to tumor development and metastasis (11)but is also closely associated with metastatic dysregulation, tumor-related proliferation, and apoptotic processes (12). Studies show that the TME acts as a reservoir for pro-tumor and pro-angiogenic cytokines produced by tumor and immune cells, further stimulating tumor cell proliferation and immune cell recruitment, thereby advancing cancer progression (13). Additionally, multiple inflammatory factors (e.g., NF-κB, IL-6, IL-1β) interact through complex signaling networks to promote tumorigenesis and progression. These factors are not only associated with thyroid carcinoma staging and prognosis but also represent potential therapeutic targets (14). In thyroid carcinoma research, inflammation-related studies have gained significant attention. We systematically analyzed relevant articles from the past 24 years to identify core themes, trends, and future directions, providing guidance for further studies. This analysis clarifies inflammation’s role in thyroid carcinoma initiation, progression, and its impact on the TME, while exploring inflammatory factors as prognostic markers and therapeutic targets. Our findings aim to offer new strategies for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Bibliometrics is a quantitative analysis tool that applies mathematics and statistics to literature research, capable of processing and analyzing large, diverse datasets. Its strengths lie in objectively and intuitively showcasing the historical activities and achievements of academic research, offering a macro perspective on the evolution of scientific knowledge. Key metrics include publication volume, citation counts, author and institutional distributions, keyword analysis, and journal impact factors, helping to minimize bias in paper evaluation (15). It focuses not only on publication volume but also delves into the quality, distribution, and impact of literature across multiple dimensions. Alan Pritchard first introduced the concept of bibliometrics in 1969, defining it as the application of mathematical and statistical methods to analyze publication counts, revealing the processes of written communication and the nature and trends of disciplinary development. Pritchard’s work marked the birth of bibliometrics as an independent discipline, aiming to understand the research landscape, trends, and frontiers of specific fields by analyzing patterns and characteristics of academic papers (16). Currently, bibliometric analysis and visualization are widely applied across various fields to analyze research status, hotspots, and trends (17).
2 Materials and methods
Web of Science (WoS, Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA), encompassing over 12,000 international academic journals, is one of the most authoritative and influential data platforms globally. It features a critical citation indexing function and is extensively utilized for bibliometric analysis in the fields of medicine and health sciences (18–20). On November 12, 2024, we conducted a comprehensive literature search for this study using the advanced search strategy of the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC), covering research published between 1999 and 2024. The key search themes were as follows: TS=(“Thyroid Neoplasm*” OR “Cancer of Thyroid” OR “Cancer of the Thyroid” OR “Neoplasms, Thyroid” OR “Thyroid Adenoma*” OR “Thyroid Cancer*” OR “Thyroid Carcinoma*” OR “carcinoma of thyroid”) AND TS=(“inflammation*” OR “inflammatory” OR “inflammatory process” OR “inflammatory response*” OR “phlegmasia” OR “infection” OR “inflammatory reaction*” OR “Innate Inflammatory Response*” OR “Inflammation Mediator*” OR “Mediator* of Inflammation” OR “inflammatory factor” OR “inflammation medium*” OR “inflammatory media” OR “inflammatory factor*” OR “inflammatory cytokine*”). The search was restricted to English-language publications, and the document types were limited to “article” and “review article.” The publication years were set from 2000 to 2024. After final selection, a total of 1,441 articles were included for data analysis. The specific exclusion criteria are illustrated in Figure 1.
3 Results
3.1 Publication characteristics
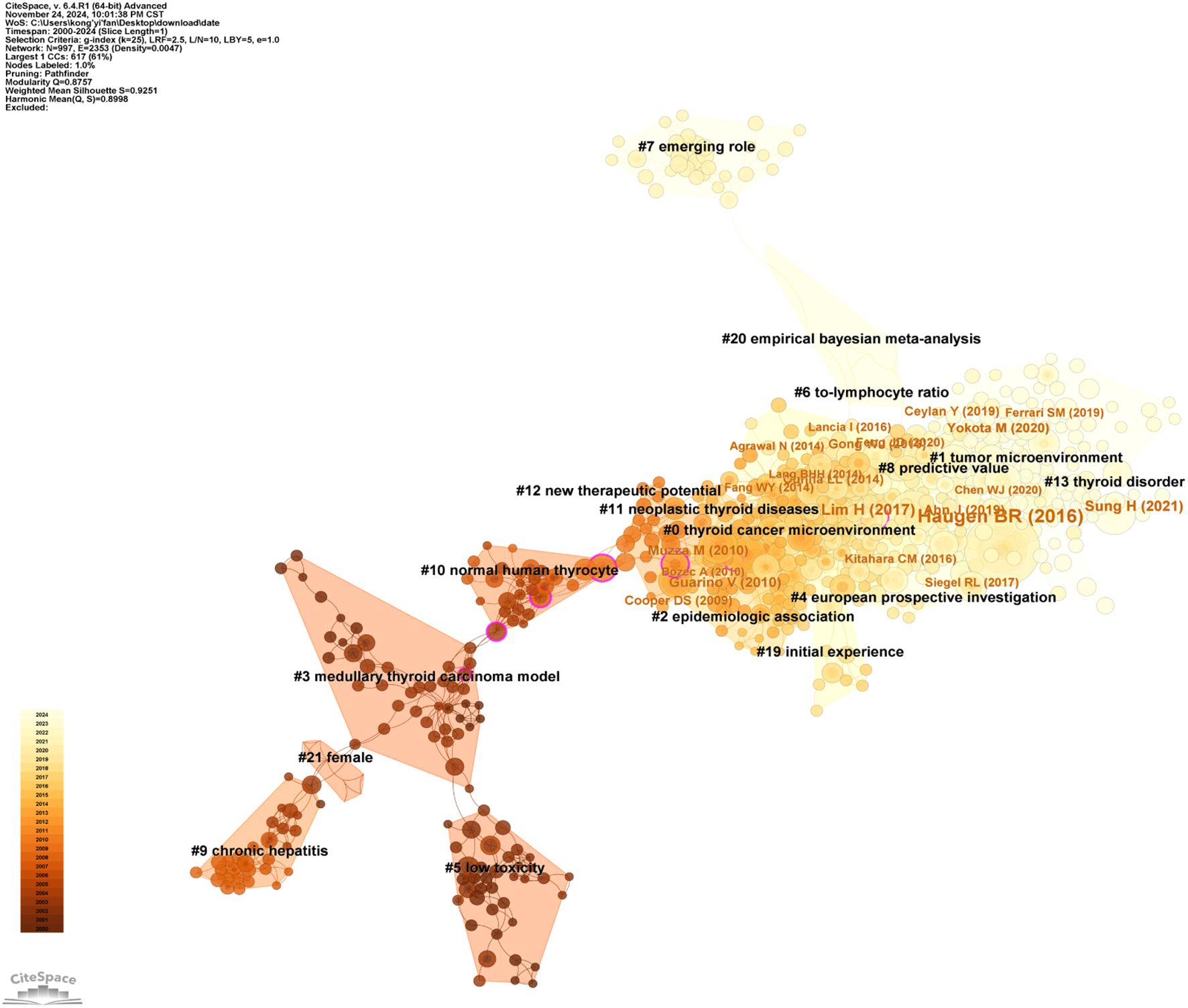
A comprehensive search was conducted using the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC), retrieving a total of 1,441 publications, including 1,169 articles and 272 review articles. As illustrated in Figure 2, the chart meticulously depicts the trends in annual publication volume and cumulative publication volume over the past 25 years. Between 2000 and 2008, the average annual publication volume was relatively low, approximately 20 articles, indicating that research on the relationship between inflammation and thyroid carcinoma was still in its foundational stages during this period. However, starting in 2009, the annual publication volume began to exhibit a steady upward trajectory, reaching its peak in 2023 (145 articles). This growth trend underscores the increasing significance of inflammation in thyroid carcinoma research, reflecting a rising academic interest and engagement in this field, with a growing number of researchers dedicating efforts to its exploration. Additionally, we constructed an exponential function model, y = 2.5759x² - 11.43x + 72.966 (R² = 0.9964, where X represents the year and Y represents the cumulative annual publication volume), to describe the trend in cumulative publication volume. The high goodness-of-fit (R² value close to 1) of this model demonstrates its accuracy in capturing and predicting the temporal changes in cumulative publication volume, providing a robust mathematical tool for understanding the research dynamics in this field. Through this model, we can anticipate future publication trends in the study of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma, offering valuable insights for the academic community.
Figure 2. Distribution of the number of publications related to the research on inflammation and thyroid cancer in disease areas.
3.2 Countries and institutions analysis
From 2000 to 2024, a total of 70 countries globally conducted research related to inflammation and thyroid carcinoma. According to the data provided in Table 1, the top three countries by publication volume are China (413 articles, 28.7%), the United States (319 articles, 22.1%), and Italy (201 articles, 13.9%). Other countries with more than 50 articles include South Korea (95 articles, 6.6%), Germany (76 articles, 5.3%), Japan (71 articles, 4.9%), France (59 articles, 4.1%), and the United Kingdom (53 articles, 3.7%). In addition to the number of publications, the citation count of a country’s published articles is also a critical factor in assessing its influence in this research field. Although the United States has fewer publications than China, its citation count (62,809 citations) far exceeds that of China (7,138 citations), making it the most cited country, followed by France (50,536 citations) and Italy (9,224 citations). While France’s publication volume (59 articles) and citation count (50,536 citations) are lower than those of the United States (319 articles, 62,809 citations), its average citation rate (856.54 average citations) is the highest, indicating the qualitative impact of its research contributions. In contrast, China’s high output contrasts sharply with its relatively lower citation count, revealing a need to enhance the quality of research in this potential field. We also analyzed collaborations between different countries and visualized them in Figures 3A–C. When the minimum publication threshold was set to 8 articles, 28 countries were included. Nodes represent countries, with the size of each node corresponding to the number of publications by that country in the collaboration network. Lines between nodes indicate collaborative relationships, with the thickness and color intensity of the lines representing the total link strength. Darker and thicker lines denote closer collaborations. The figure shows that China has the largest node, highlighting its significant role in this research field. Although its collaboration strength with other countries is not the highest, it maintains extensive international partnerships. The United States also emerges as a key node, with the highest total collaboration strength (183), particularly with Italy, China, and Germany, among others, with the most intensive collaboration observed with Italy.
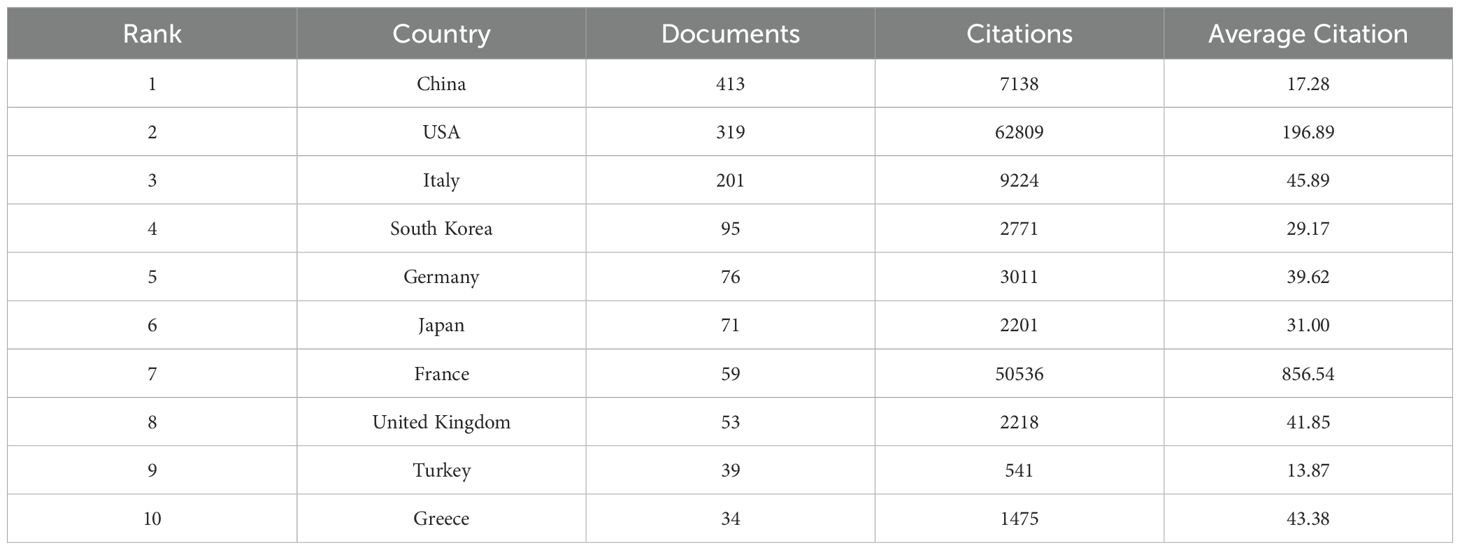
Table 1. Top 10 countries and with the most documents on research of inflammation in thyroid cancer.
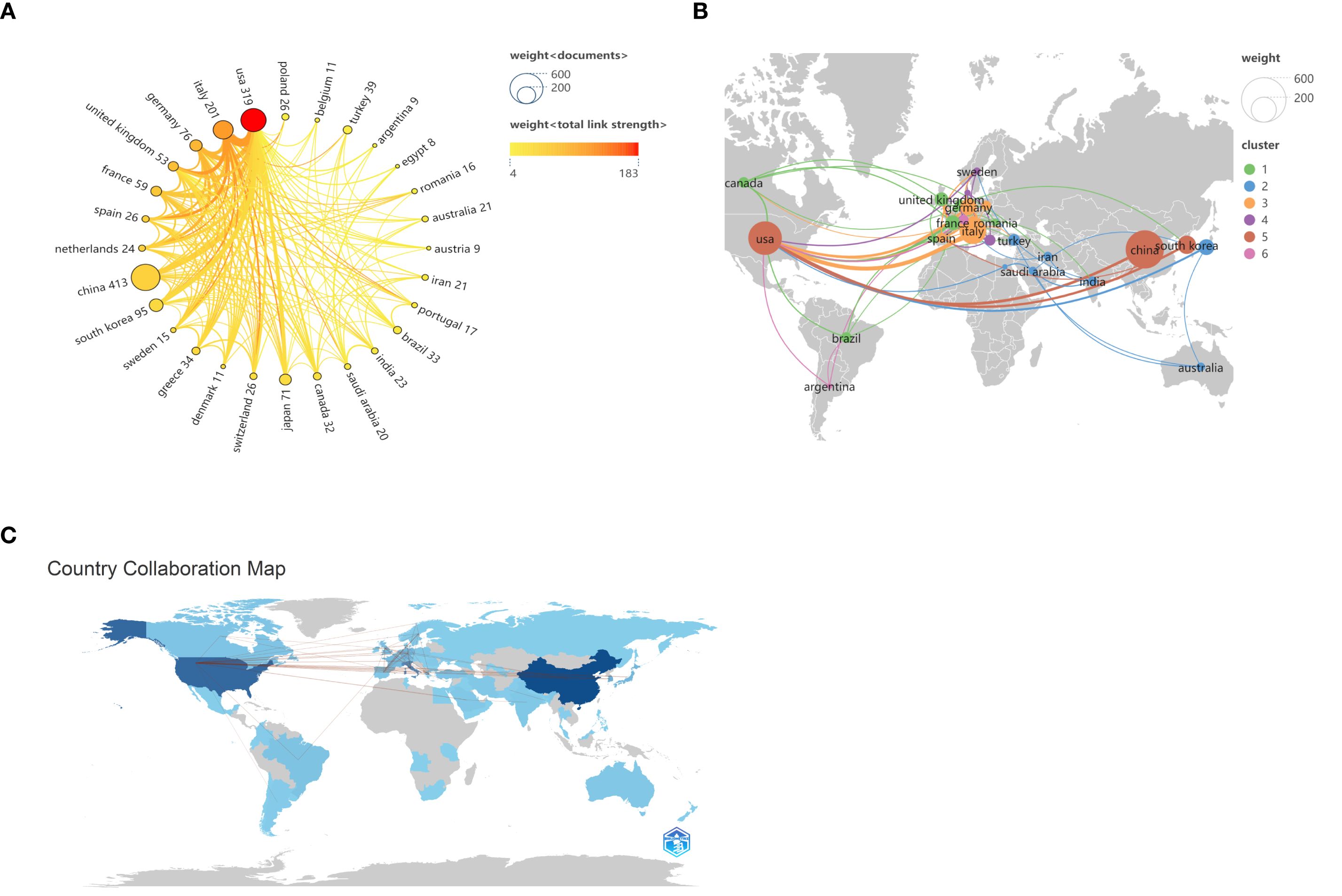
Figure 3. Map of national or regional cooperation. (A) Circular chart of national or regional cooperation, the connection between nodes represents cooperation, and the thickness of the line represents the strength of cooperation. (B) Map of countries or regions according to the proportion of published papers. (C)The contribution of various countries across the world. The darker shades correspond to higher contribution to the field.
A total of 2,054 institutions globally have conducted research on inflammation and thyroid carcinoma. Table 2 summarizes the top 10 institutions with the highest contributions. The top three institutions with the most publications in this field are the University of Pisa in Italy (N=44), China Medical University in China (N=31), and the University of Naples Federico II in Italy (N=29). Notably, the University of Pisa not only leads in publication volume but also has the highest citation count (3,206 citations), significantly surpassing other institutions. This underscores its leadership in this field. Additionally, among the top 10 institutions, four are from China: China Medical University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Sun Yat-sen University, and Zhejiang University. This highlights China’s strong research capabilities, influence, and high level of research activity in this field. When the minimum publication threshold was set to 5 articles, a total of 131 institutions were included in our analysis, forming six distinct clusters, as shown in Figure 4. Within these clusters, central nodes such as the University of Pisa, China Medical University, and the University of Naples Federico II play pivotal roles as key hubs, revealing robust collaborative partnerships and academic exchange networks. These central institutions facilitate knowledge exchange and deepen research through frequent collaborations. However, the analysis also reveals that most institutions remain relatively isolated, with limited close collaborations. This fragmented collaboration pattern may hinder the rapid dissemination of knowledge and the efficiency of research. Therefore, strengthening inter-institutional collaborations and building more cohesive academic networks is crucial for advancing research in inflammation and thyroid carcinoma. By fostering cross-institutional partnerships, research progress can be accelerated, and the impact of studies can be enhanced, ultimately leading to greater breakthroughs in scientific development and clinical applications in this field.
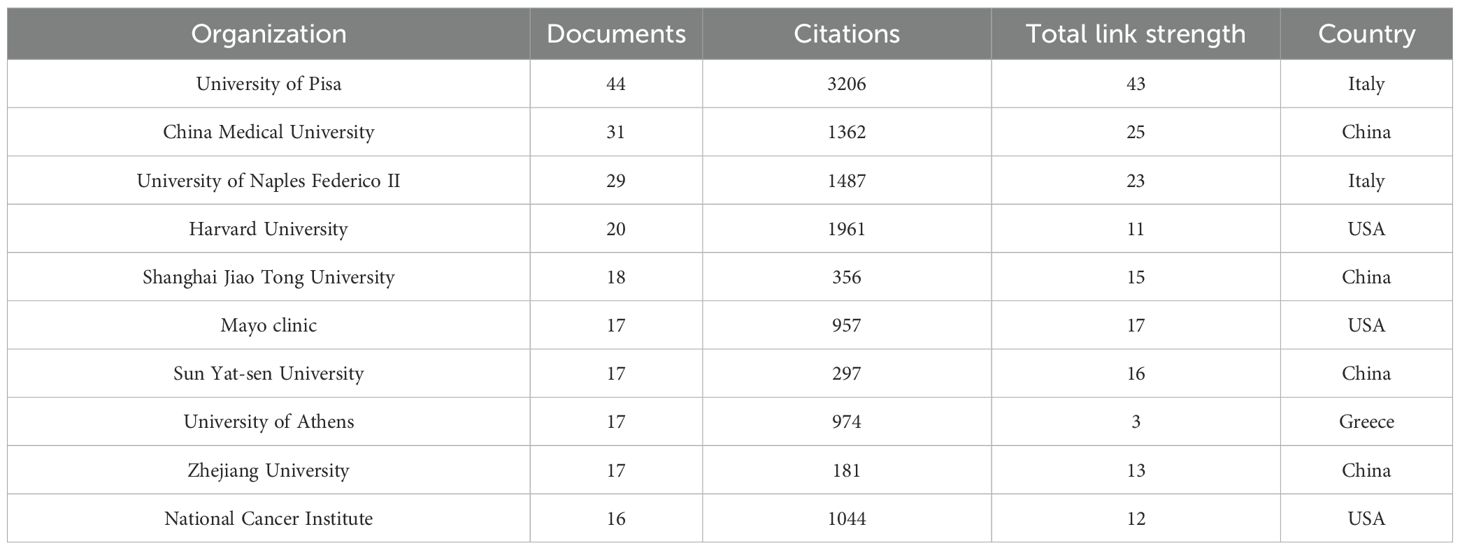
Table 2. Top 10 institutions with inflammation and thyroid cancer research publications in diseases.
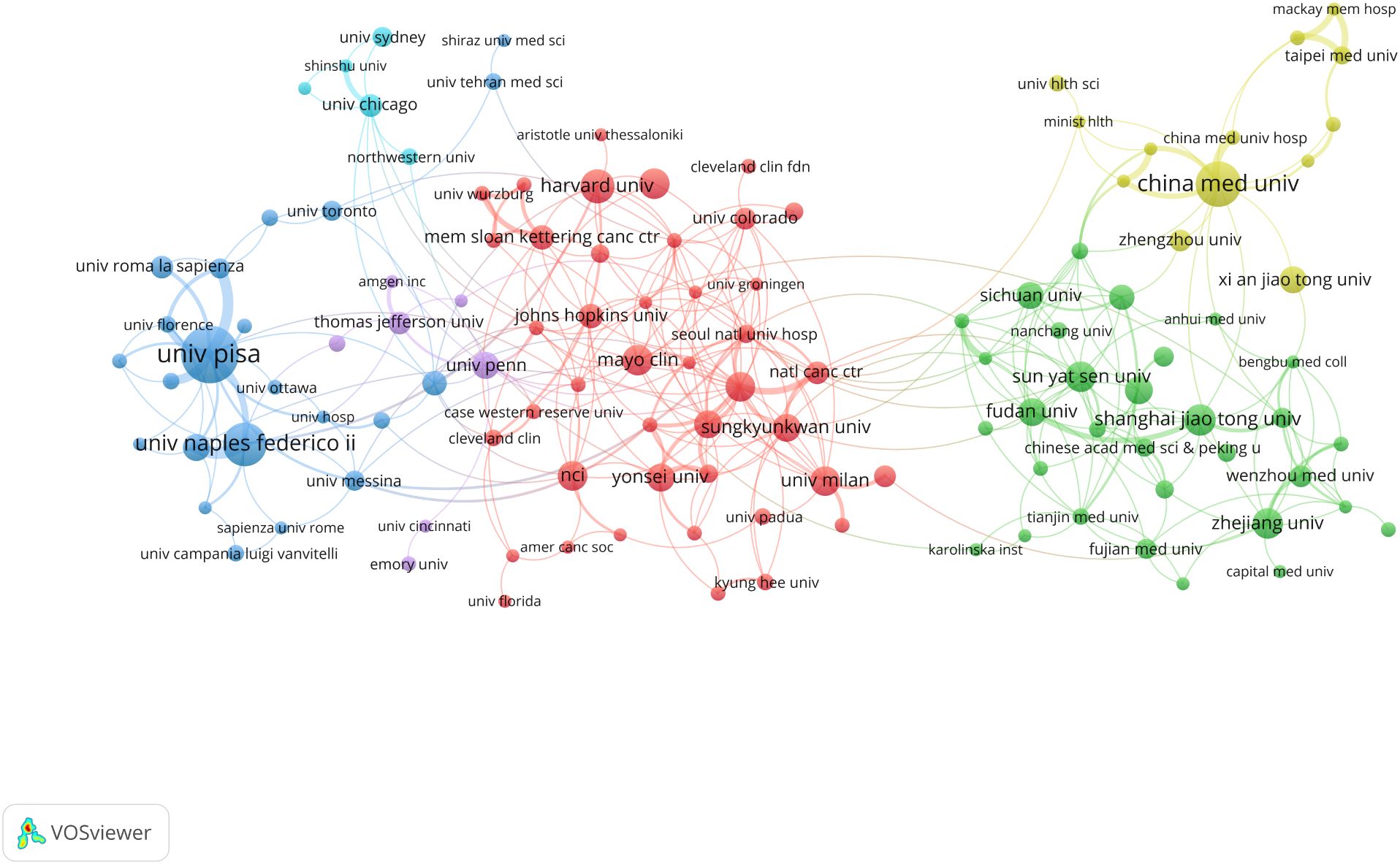
Figure 4. Institutional cooperation map, the size of the nodes indicates the number of publications, and the thickness and length of the links between the nodes indicate the strength and relevance of the connections between the nodes.
3.3 Authors and their collaborations
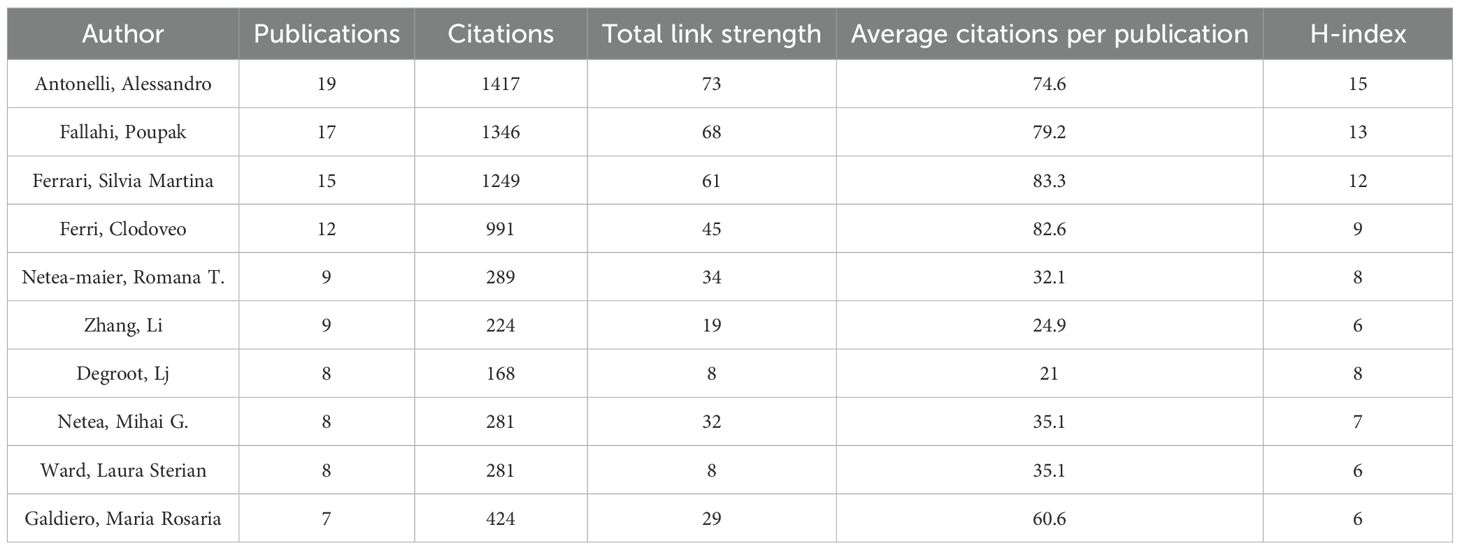
Over the past 24 years, this study has included a total of 8,326 authors. Table 3 presents the top 10 most prolific authors and their academic contributions in this field. The Italian research team demonstrates remarkable scholarly influence, with Professor Antonelli, Alessandro leading as the most published author (19 articles), accumulating 1,417 citations and achieving an H-index of 15 - all top metrics that underscore his pioneering status. His seminal work Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases has provided fundamental theoretical insights for autoimmune disease research (21). Following closely are Italian scholars Professor Fallahi, Poupak (17 publications) and Professor Ferrari, Silvia Martina (15 publications), whose representative works respectively investigate multisystem involvement in autoimmune thyroiditis (The association of other autoimmune diseases in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis) and immune regulation mechanisms within the thyroid cancer microenvironment (Immune and Inflammatory Cells in Thyroid Cancer Microenvironment) (22, 23), offering critical perspectives for the field. The scholars ranked fourth to tenth also made outstanding contributions, with their representative works as follows: Professor Ferri, Clodoveo from Italy focused on the relationship between HCV infection and thyroid diseases. His study Thyroid Involvement in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients with/without Mixed Cryoglobulinemia provided crucial evidence for the mechanisms of virus-related endocrine disorders (24); Professor Netea-maier, Romana T. from the Netherlands elucidated the regulatory role of autophagy in inflammation in her seminal work, Modulation of Inflammation by Autophagy: Consequences for Human Disease, thereby broadening the horizons of metabolism-immune crosstalk research (25).; The study Inflammatory tumor microenvironment of thyroid cancer promotes cellular dedifferentiation and silencing of iodide-handling genes expression by Professor Li Zhang’s team in China revealed how inflammatory microenvironments drive thyroid cancer cell dedifferentiation and functional loss, offering potential therapeutic targets for precision treatment (26).; Professor DeGroot, Lj (Japan) pioneered telomerase-targeted gene therapy strategies for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (Tumor-specific gene therapy for undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma utilizing the telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter) (27); Professor Netea, Mihai G. (USA) revealed differential inflammasome activation mechanisms for IL-1β processing in various immune cells (Differential requirement for the activation of the inflammasome for processing and release of IL-1β in monocytes and macrophages) (28); Professor Ward, Laura Sterian (Brazil) systematically demonstrated the central role of inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis (The role of the inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis) (9); and Professor Galdiero, Maria Rosaria (Italy) provided in-depth analysis of tumor-promoting mechanisms by tumor-associated macrophages and neutrophils (Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in tumor progression) (29). These representative works collectively construct the theoretical framework for thyroid disease and inflammation research, providing crucial references for subsequent studies. Figure 5A illustrates the distribution of authors’ nationalities and the extent of international collaboration. SCP (Single Country Publications) represents the number of co-authored papers by authors from the same country, while MCP (Multiple Country Publications) denotes the number of co-authored papers with authors from other countries. The SCP of the top 10 countries by publication volume is higher than their MCP, particularly in China, the United States, and Italy, where the contrast is most pronounced. This suggests that their research collaborations are predominantly domestic, with limited international cooperation. Figure 5B presents a visualization of the author collaboration network, revealing a relatively dispersed distribution of authors with only limited connections identifiable in the network, indicating a moderate overall collaboration intensity. Among these authors, Antonelli, Alessandro stands out as a central figure due to his substantial publication volume and high citation count. His average of 74.6 citations per article not only reflects the impact of his research but also underscores his academic contributions to the field.
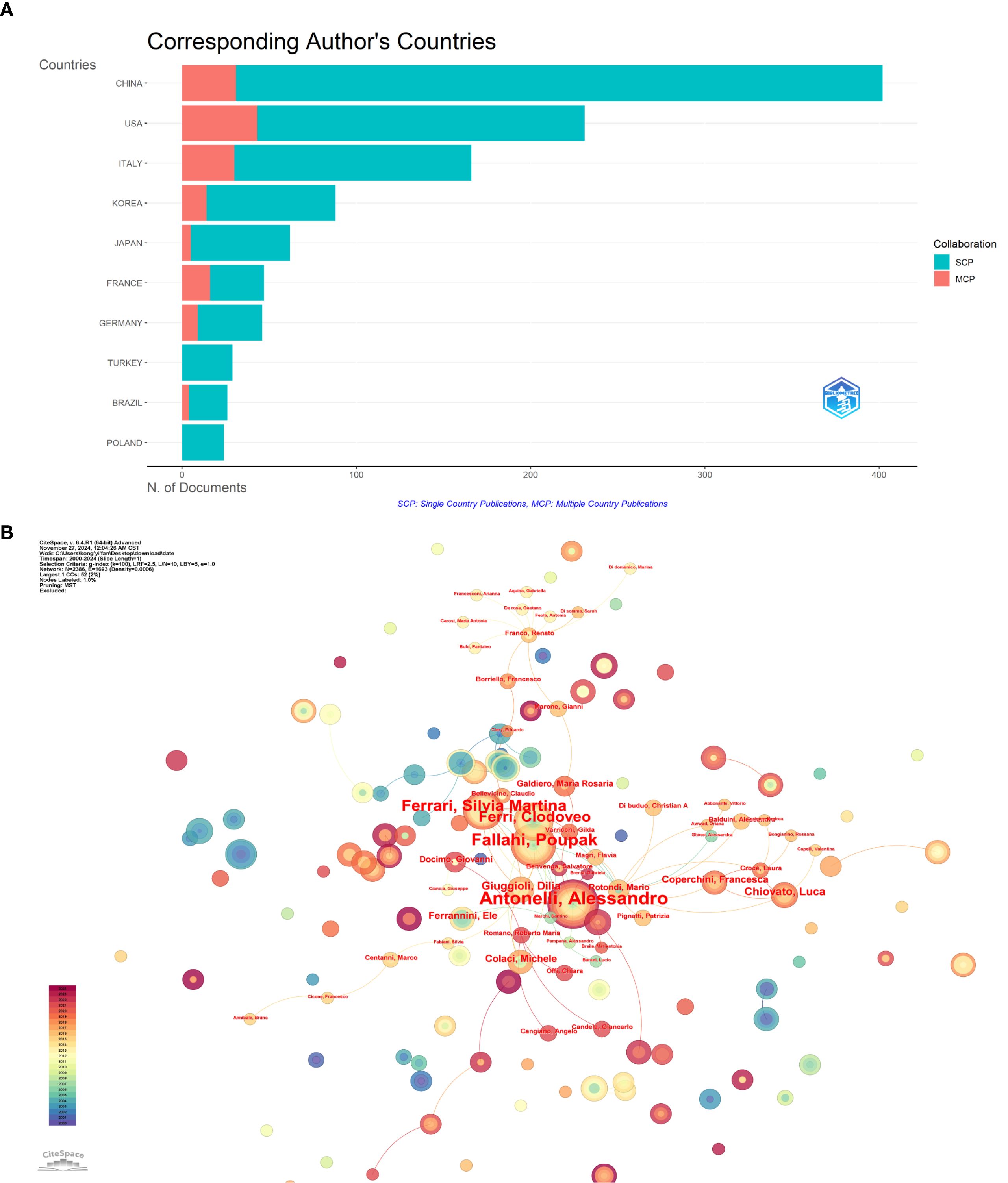
Figure 5. Author-level analysis: (A) Corresponding author’s countries, SCP represents the number of co-authored papers by authors of the same nationality, while MCP represents the number of co-authored papers with authors from other countries. (B) Co-occurrence of authors network map, nodes represent different authors, node size represents the number of author posts, the thickness of the connecting line between nodes represents the strength of cooperation.
Antonelli, Alessandro’s research primarily focuses on several key areas (1): Investigating the link between autoimmune diseases and thyroid carcinoma: Thyroid autoimmunity and thyroid cancer, particularly papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), can coexist, although the exact mechanisms remain unclear. The increased incidence of thyroid cancer coincides with the rise in autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD), suggesting an association between these pathologies. Additionally, elevated TSH levels and thyroid autoimmunity are considered independent risk factors for thyroid cancer. Future research is necessary to elucidate the connection between thyroid autoimmunity and cancer, which will aid in designing personalized therapies for TC patients with AITD (2). Immune cells and inflammatory cells in the thyroid cancer microenvironment: The ability of tumor cells to evade immune system destruction is a hallmark of cancer. Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME) promote tumor growth by secreting cytokines and chemokines, while cancer cells suppress immune responses through various mechanisms, evading immune surveillance. Understanding the molecular and immunological characteristics of the TME is crucial for developing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for thyroid carcinoma, particularly immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, which can activate the immune system to target cancer cells. These studies provide valuable insights into the complex pathology of thyroid cancer and offer a scientific foundation for developing novel therapeutic strategies. Through these high-quality research efforts, Antonelli, Alessandro has played a pivotal role in advancing the field of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma research.
3.4 Journals and co-cited journals analysis
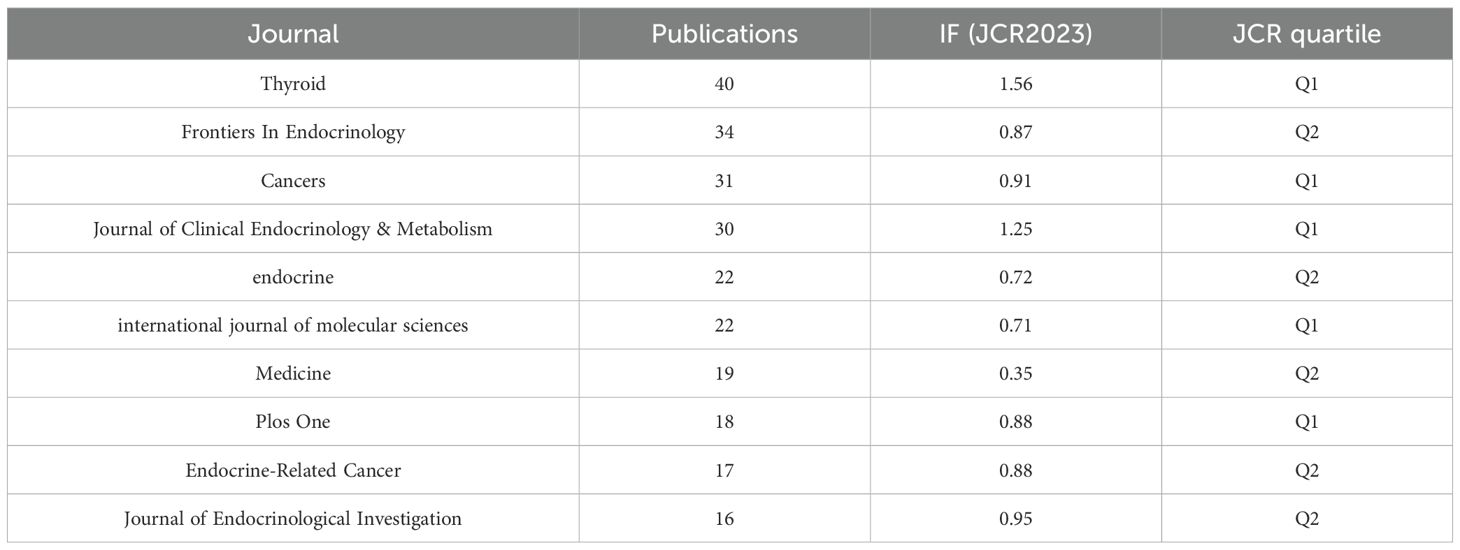
Journals serve as vital mediums for disseminating and exchanging academic knowledge. All papers related to this study were published in 625 journals. Table 4 lists the top 10 journals with the highest publication volume in this field. Thyroid ranks first with 40 articles, an impact factor of 1.56, and a Journal Citation Reports (JCR) division of Q1 (journals within the top 25% of impact factors). This peer-reviewed journal publishes original articles and reviews reflecting the ever-expanding activities in the thyroid field, ranging from the molecular biology of the cell to the clinical management of thyroid disorders. As the official journal of the American Thyroid Association, it is recognized as the most authoritative journal in the field of thyroid diseases. Ranking second is Frontiers in Endocrinology with 34 publications and an impact factor of 0.87. This journal primarily advances our understanding of the endocrine system and publishes research on novel therapies for prevalent health issues such as obesity, diabetes, reproductive system disorders, and aging endocrinology. Figure 6A, created using the VOSviewer tool, visualizes the interconnections and publication volumes of journals that have published at least five related articles. This visualization provides an intuitive platform for observing and analyzing collaborative and competitive relationships among journals. Figure 6B further deepens this analysis by presenting a dual-map overlay, illustrating the interaction between citing journals and cited journals. The left side of the map represents citing journals, typically reflecting the latest research trends and knowledge frontiers in a field, while the right side represents cited journals, which form the foundational knowledge base of the field. The map clearly shows that citing literature is concentrated in two domains: (1) Medicine/Medical/Clinical and (2) Molecular/Biology/Immunology. Correspondingly, cited journals are also primarily focused on two domains: (1) Health/Nursing/Medicine and (2) Molecular/Biology/Genetics. This distribution reveals the knowledge structure and research focus within the field of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma. Additionally, the main journal pathways in the map exhibit a cross-pattern, forming four primary citation paths, represented by two distinct colors. The yellow path indicates that journals in the Molecular/Biology/Immunology domain cite literature from the Molecular/Biology/Genetics and Health/Nursing/Medicine domains. The green path shows that journals in the Medicine/Medical/Clinical domain also cite literature from the Molecular/Biology/Genetics and Health/Nursing/Medicine domains. These pathways not only demonstrate citation relationships among journals but also reflect the mutual influence and knowledge flow between different research domains. Through this in-depth visualization analysis, we can better understand the academic network within the field of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma research, as well as the roles and contributions of individual journals.
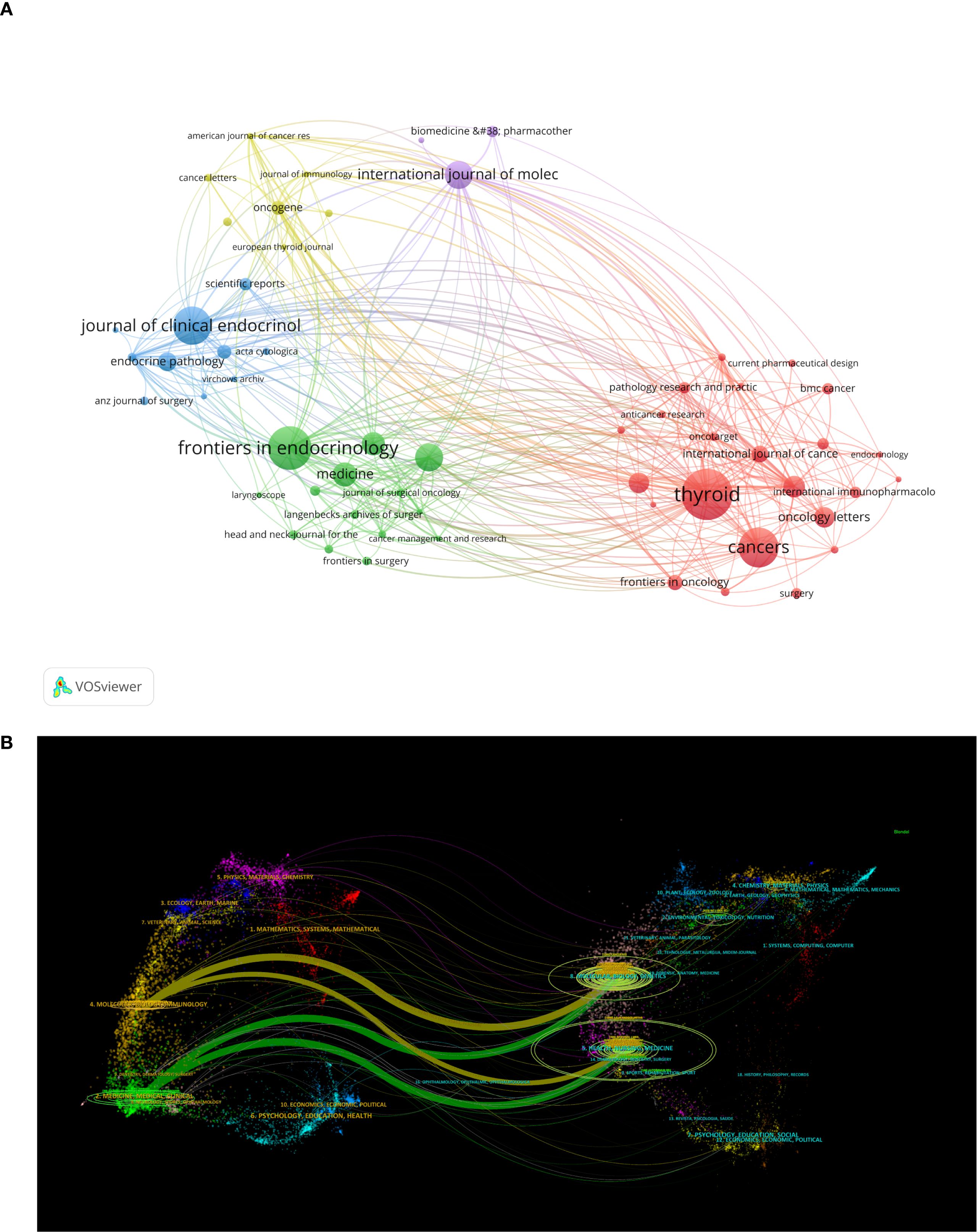
Figure 6. (A) Showcases visualizations of journals;(B) The dual-map overlay of journals, the left label in the figure represents citing journals, the right label represents cited journals, and the colored paths represent the citation relationships between them.
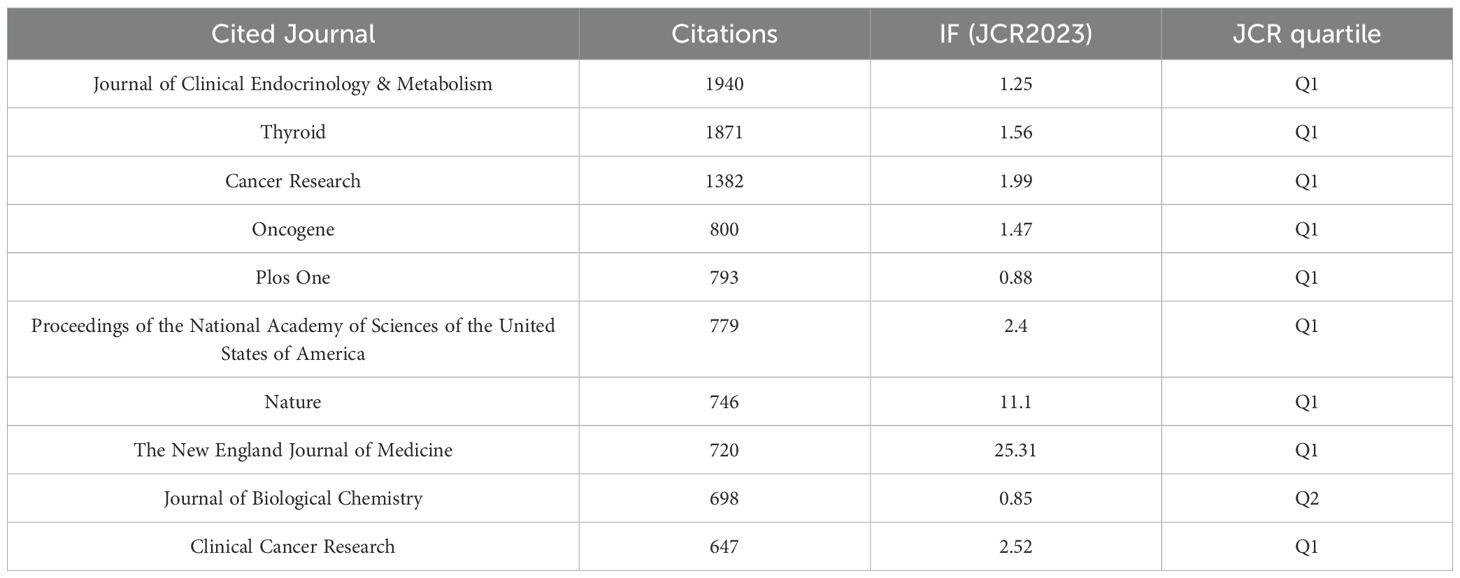
Table 5 lists the top 10 journals by co-citation frequency. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism ranks first with the highest number of citations (N=1,940), an impact factor of 1.25, and a Journal Citation Reports (JCR) division of Q1. Additionally, among the top 10 journals by co-citation frequency, the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) has the highest impact factor (IF=25.31). The top three journals by co-citation frequency have publication counts of 1,940, 1,871, and 1,382, significantly surpassing other journals.
3.5 Co-cited references and reference with citation bursts
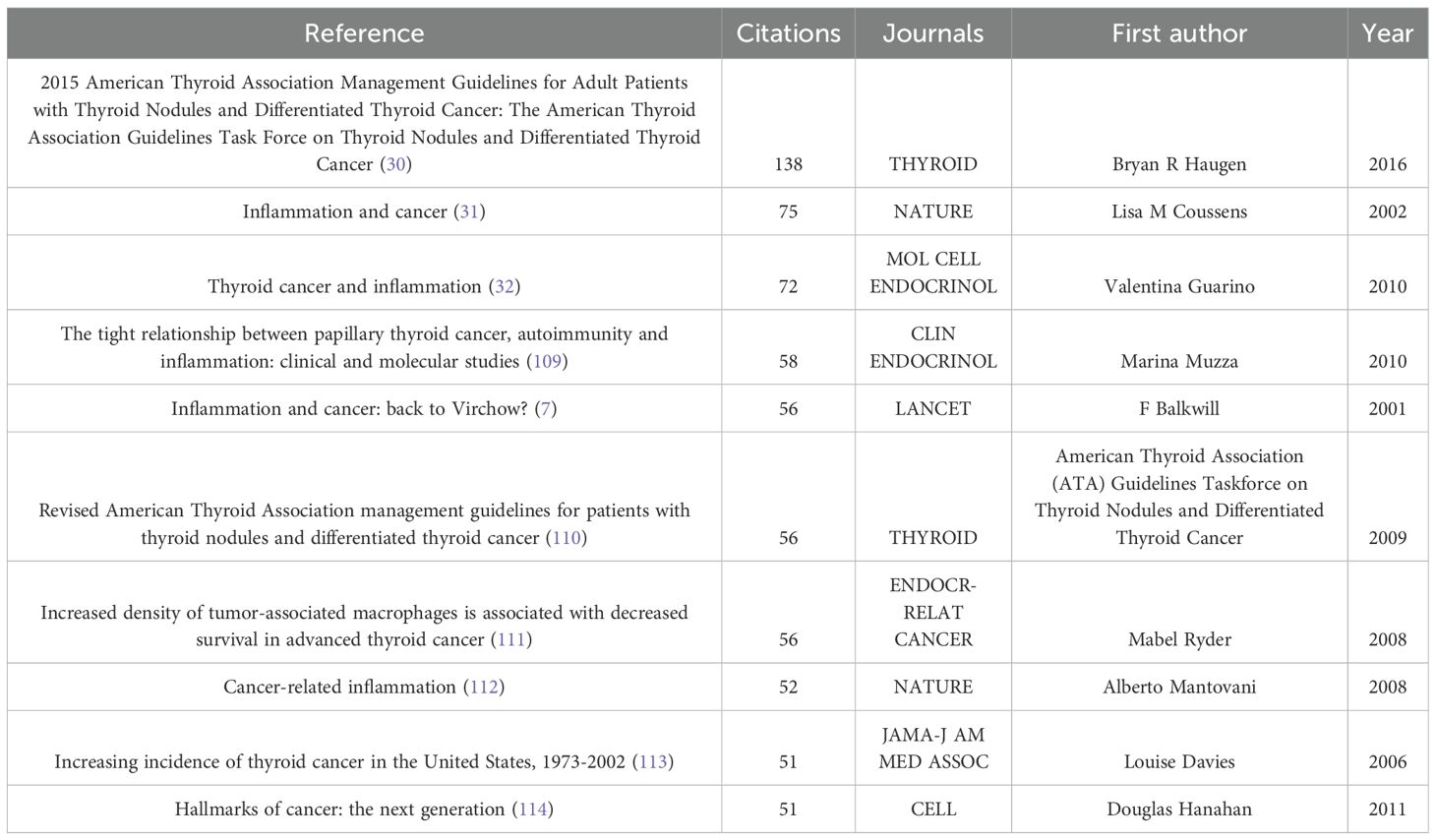
The study in this field included 1,441 articles, encompassing a total of 59,808 cited references. Table 6 lists the top 10 most cited references, with publications by Bryan R. Haugen (30), Lisa M. Coussens (31), and Valentina Guarino (32) as first authors ranking in the top three, with citation counts of 138, 75, and 72, respectively. Figure 7 provides an intuitive visualization of the co-citation network analysis of references, revealing the structural characteristics and clustering effects of the network. The analysis results indicate that the Modularity Q of the network reached 0.8757, a value close to 1, demonstrating a highly significant modular structure within the network. Additionally, the average Silhouette S was as high as 0.9251, reflecting the superior clustering effectiveness of the network, meaning that the references were effectively grouped into highly similar clusters. These metrics collectively confirm the efficiency and accuracy of the co-citation network analysis, providing a powerful tool for understanding the relationships among references and the knowledge structure of the research field. Furthermore, the network can be divided into 17 clusters, with the largest being Cluster #0: thyroid cancer microenvironment (33–37). The earliest cluster to initiate research in this field was Cluster #5: low toxicity (38–42), while Cluster #7: merging role (43–45), Cluster #8: predictive value (46–50), and Cluster #13: thyroid disorder (2, 51–53) represent recent research hotspots, indicating a growing interest and exploration of this field by researchers.
Figure 8 provides an in-depth analysis of the top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts, enabling the precise identification of publications that experienced a sharp increase in citations during specific time periods, thereby revealing research hotspots within those intervals. The phenomenon of citation bursts in this field began in 2006 and continues to the present, with many references still being widely cited. This indicates that research on the association between thyroid carcinoma and inflammation remains a focal point in recent years and is likely to persist in the coming years. Among these references, the study with the highest citation burst strength is the work by Bryan R. Haugen as the first author, titled 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (30). Its citation burst strength reached 27.73, with a significant surge in citations from 2016 to 2021. The duration of these citation bursts spans 5 to 6 years, with burst strengths ranging from 5.22 to 27.73. This not only highlights the vibrancy of research in this field but also underscores the continuous evolution and development of research dynamics. These data provide profound insights into the key scientific contributions and knowledge advancements within the field of thyroid carcinoma and inflammation research.
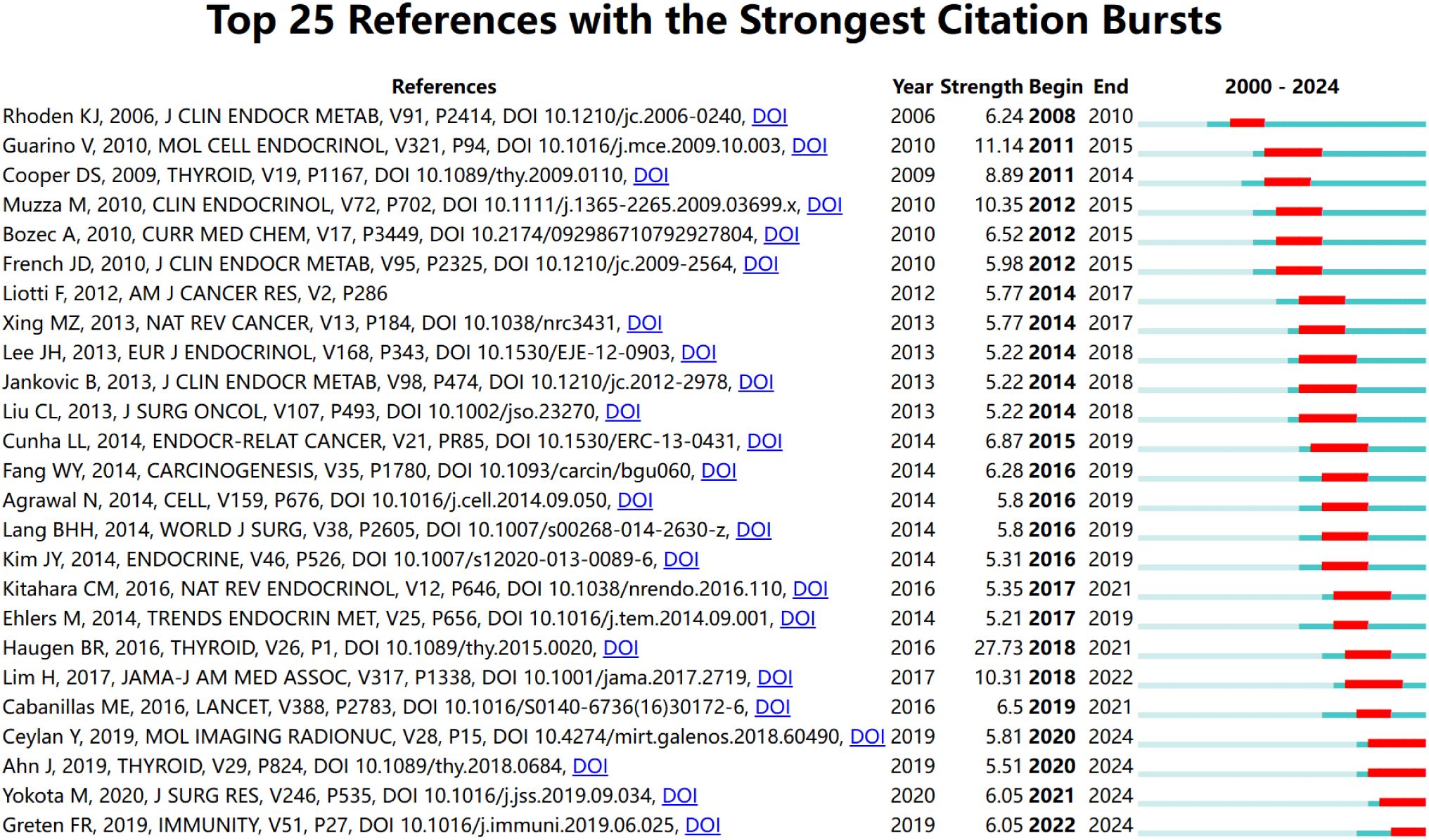
Figure 8. The most often cited top 20 sources. Citations that were particularly high that year are shown in red.
3.6 The co-occurrence and clustering of keywords
The 1,441 articles in this study encompassed a total of 6,340 keywords. Using VOSviewer, after merging synonyms and setting a minimum occurrence threshold of 10 times per keyword, 239 keywords were included in the visualization analysis (Figures 9A, B), integrating keyword contributions. In the visualization map, each color represents a cluster, and each node represents a keyword. The size of the node indicates the frequency of the keyword’s occurrence, with larger nodes representing more prominent research hotspots in the field. Lines between nodes denote co-occurrence relationships between two keywords. The top 10 keywords by frequency include cancer (520 occurrences), thyroid cancer (431 occurrences), inflammation (272 occurrences), expression (232 occurrences), papillary thyroid cancer (202 occurrences), association (116 occurrences), risk (112 occurrences), cells (97 occurrences), management (96 occurrences), and Hashimotos-thyroiditis (94 occurrences). These keywords represent the primary research themes in thyroid carcinoma and inflammation from 2000 to 2024. The keywords were divided into six clusters, with the top five clusters being: the first cluster (red), focusing on the expression of inflammation-related factors in thyroid carcinoma to explore the role of inflammation in its development; the second cluster (green), investigating the link between inflammation and the management and diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma; the third cluster (blue), related to the tumor microenvironment of thyroid carcinoma; the fourth cluster (yellow), studying the association between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and thyroid carcinoma; and the fifth cluster (purple), exploring the link between obesity and thyroid carcinoma risk. Using CiteSpace for clustering analysis, 10 clusters were generated, and a timeline view reflecting the progression of keywords over time was created (Figure 9C). Each color represents a different cluster, and each cluster signifies a key theme in the field: Cluster #0 sodium iodide symporter, Cluster #1 total thyroidectomy, Cluster #2 peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, Cluster #3 papillary thyroid microcarcinoma, Cluster #4 therapeutic radiopharmaceutical, Cluster #5 zoological garden, Cluster #6 endoscopic thyroidectomy, Cluster #7 mixed cryoglobulinemia, Cluster #8 fine needle aspiration, and Cluster #9 clinical evaluation. The Modularity Q of this module was 0.756, and the mean Silhouette S was 0.9463. These 10 clusters span topics from sodium iodide symporter to clinical evaluation. From a chronological perspective, early research on thyroid carcinoma and inflammation focused on keywords such as thyroid autoimmunity, complications, gene expression, high prevalence, and chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. Recent trends, however, revolve around metabolites, lymphocyte, inflammatory biomarker, stress, Th-17, systemic immune-inflammation index, resolution of inflammation, video-assisted thyroidectomy, management guidelines, and PD-L1. Among these, Th-17 and systemic immune-inflammation index are two of the most frequently studied keywords in recent years. This highlights potential future research directions and hotspots in the field, while also contributing to the advancement and innovative development of scientific research in this area.
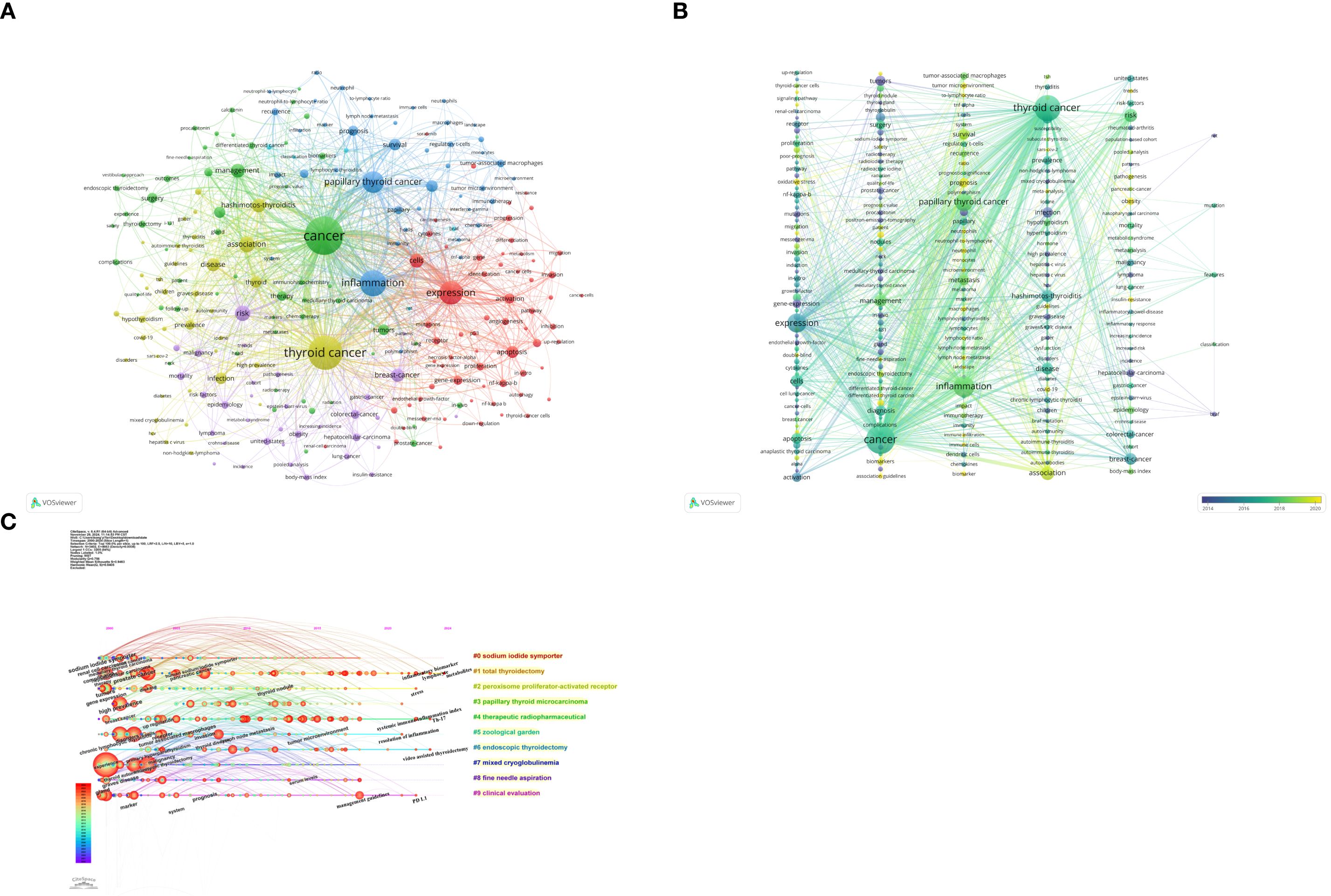
Figure 9. Cluster analysis and topic evolution of hot topics: (A) Network map of keywords occurring more than 10 times. (B) Overlay map of keywords based on average publication year. (C) Timeline view of keyword clustering, in the timeline view, the keywords on the same horizontal line belong to the right cluster. The colors of lines and keywords in the view correspond to the colors of the time bar in the lower left corner.
4 Discussion
With the advent of the big data era, researchers must thoroughly grasp the latest advancements in their fields. Bibliometric analysis, distinct from systematic reviews and meta-analyses, utilizes visualization tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace to conduct comprehensive analyses of existing literature, intuitively revealing research trends and predicting potential future hotspots. This approach provides researchers with a powerful tool to discern dynamic changes and emerging directions in academic domains (54). This study employs bibliometric analysis to summarize the role of inflammation in the development and progression of thyroid carcinoma, offering an intuitive perspective on the field’s trends and future research priorities.
4.1 General information related to publications
Relying on the Web of Science database, a comprehensive literature search was conducted to gather research on inflammation and thyroid carcinoma from 2000 to 2024. After a rigorous screening process, 1,441 articles were selected, originating from 70 countries, authored by 8,326 researchers from 2,054 institutions, and published in 625 academic journals. These articles encompass 59,808 references and 6,340 keywords, providing a comprehensive research perspective and rich data resources.
From the research results, the number of publications in this field has shown a steady annual increase, indicating that inflammation and thyroid carcinoma have become focal points of attention. Although China is the only developing country among the top 10 most productive nations, analysis of the national network distribution reveals that China ranks first in publication volume, accounting for 28.7% of global publications. This underscores China’s central role in inflammation and thyroid carcinoma research. This prominence may be attributed to the rising incidence and mortality of thyroid carcinoma in China, driven by lifestyle changes and an aging population, which has heightened the demand and urgency for related research.
Among the top 10 institutions by publication volume, the University of Pisa in Italy leads with outstanding research achievements and academic contributions, reflecting its leadership in the field and its pivotal role in global research collaboration. Notably, four of these top institutions are located in China, highlighting China’s significant advantage in publication volume and research influence, as well as its rapid rise and growing competitiveness on the global academic stage. This is attributed to China’s strengths: 1) A vast pool of researchers and medical professionals, providing abundant human resources for medical research. 2) Continuous increases in funding from the Chinese government and various institutions, offering robust financial support for scientific endeavors. 3) Significant investments in research facilities and experimental equipment, providing advanced infrastructure for medical research. 4) Encouragement of interdisciplinary collaboration, fostering innovation at the intersection of medicine and fields such as bioinformatics and materials science.5) Remarkable progress in translating medical research into clinical applications and industrial advancements, driving the evolution of medical technologies and the healthcare industry.
In our in-depth analysis of the author community, we observed that Antonelli, Alessandro stands out with a notable publication volume (N=19), establishing himself as one of the most active researchers in the field. This achievement not only reflects his extensive academic experience but also underscores the widespread recognition and citation of his research within the academic community. Such influence and recognition serve as strong evidence of his academic contributions and professional expertise. Further examination of the collaboration network among authors reveals an intriguing pattern: collaborations are predominantly regional, with most partnerships confined within national borders, and domestic collaborations being particularly robust. In contrast, international collaborations are relatively scarce. This pattern may be influenced by cultural, linguistic, resource allocation, and research policy factors. However, this limitation also highlights significant potential for expanding cross-border collaborations. To advance research on thyroid carcinoma and inflammation, we recommend that countries and authors with established close collaborations continue to strengthen their academic exchanges. Simultaneously, efforts should be made to build academic connections with countries and authors with fewer collaborations, fostering high-quality multicenter studies and promoting the globalization of thyroid carcinoma and inflammation research.
4.2 Research foundations
Impact factor (IF), Journal Citation Reports (JCR) category quartiles, and total citation counts are three key metrics for assessing a journal’s academic influence. In the field of endocrinology, particularly in publications related to thyroid carcinoma and inflammation, the following journals have demonstrated exceptional performance, ranking among the top ten: Thyroid leads with 40 publications, an impact factor of 1.56, and a JCR Q1 ranking, showcasing its leading position in the field. Frontiers in Endocrinology follows closely, having published 34 articles, with an impact factor of 0.87 and a JCR Q2 ranking, indicating its high academic value in endocrinology. Cancers has published 31 articles, with an impact factor of 0.91 and a JCR Q1 ranking, highlighting its influence in oncology. Particularly noteworthy is the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, which, although not the highest in publication volume, boasts a total citation count of 1,940, an impact factor of 1.25, and a JCR Q1 ranking. This not only reflects the journal’s authority in endocrinology and metabolism but also underscores its significant global influence. Looking ahead, these journals will undoubtedly remain premier platforms for publishing high-quality research in thyroid carcinoma and inflammation. As research continues to advance, it is anticipated that more academic articles on inflammation and thyroid-related topics will be prioritized in these journals, further driving academic progress and international exchange in the field.
Co-cited references refer to publications that are cited together across multiple studies, forming the foundational core of knowledge within a specific research domain. This co-citation relationship elucidates the interconnectedness and academic influence among research works. In the field of thyroid carcinoma and thyroid nodule research, the article by Bryan R. Haugen et al., published in 2016 in Thyroid—2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (30)—has emerged as the most cited reference in the field over the past 24 years. This distinction not only highlights the authoritative standing of this publication in thyroid disease management guidelines but also underscores its profound impact on clinical practice and academic research. The extensive citation of this work attests to its pivotal role in the therapeutic guidelines for thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid carcinoma, as well as its critical contribution to advancing knowledge and fostering international collaboration within this field.
4.3 Identifying emerging themes and research hotspots
Keyword co-occurrence analysis using VOSviewer is an effective methodology for uncovering the primary research directions and hotspots within a specific academic field. In this study, we extracted 6,340 keywords from the literature, of which 239 were identified as high-frequency keywords due to their occurrence in more than 10 publications. These high-frequency keywords not only represent the commonly used terminology in the research domain but also reflect its focal points. Through clustering analysis, these 239 high-frequency keywords were further categorized into six distinct clusters, each representing a specific theme or research direction within the field. This clustering approach not only aids in identifying and understanding key concepts within the research domain but also reveals potential connections and interactions among different research directions. By employing this method, researchers can more clearly grasp the dynamics of the field, uncover new research opportunities, and provide guidance for future research directions. The primary themes of the top five clusters are as follows:
The first cluster primarily investigates the expression of inflammation-related factors in thyroid carcinoma to explore the role of inflammation in its developmental mechanisms, thereby summarizing therapeutic strategies and prognostic predictions. Key inflammation-related factors include the IL-1 family, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, chemokines, NF-κB, UHRF1, and EGR1. These factors play significant roles in the pathogenesis and metastasis of thyroid carcinoma. IL-1α and IL-1β, encoded by the IL1A and IL1B genes, promote inflammatory responses and tumor progression in thyroid carcinoma. Studies have shown that IL1A gene polymorphisms (e.g., rs3783521, rs3783546) are significantly associated with thyroid carcinoma risk, particularly in male patients (55). Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 promote tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by activating the STAT3 and NF-κB pathways. Elevated IL-8 levels are correlated with lymph node metastasis and may serve as a prognostic marker (56). Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is highly expressed in the thyroid carcinoma microenvironment and enhances cancer cell invasiveness by regulating pathways such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Clinical data indicate that serum TNF-α levels are significantly elevated in thyroid carcinoma patients and are associated with tumor staging (57). TNF-α also exhibits cytostatic effects and acts as a growth inhibitor for thyroid carcinoma cells (58). Additionally, the chemokine network plays a crucial role in thyroid carcinoma progression. Thyroid carcinoma cells secrete chemokines such as CCL2 and CXCL8 to recruit immunosuppressive cells (e.g., TAMs), creating an immune escape microenvironment (59). In thyroid carcinoma cell lines, different markers are expressed depending on the degree of tumor differentiation. NF-κB, a major player in inflammation, regulates the expression and function of various chemokines and cytokines in inflammatory cells. By stimulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in tumor-infiltrating immune cells, NF-κB promotes thyroid carcinoma initiation and metastasis. Therefore, drugs targeting NF-κB activity may improve chemotherapy and radiotherapy outcomes for thyroid carcinoma (60). Furthermore, the expression of inflammation-related factors in thyroid carcinoma can also facilitate metastasis. For example, inflammatory cytokines downregulate EGR1 expression, leading to a significant reduction in LNCRTCTS, a tumor-suppressive lncRNA controlled by EGR1. LNCRTCTS significantly inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of PTC cells both in vivo and in vitro. Understanding the mechanisms of thyroid carcinoma metastasis is crucial for developing novel clinical therapies to improve outcomes in advanced PTC (61). Moreover, UHRF1, an oncogene that promotes cancer cell development, induces c-Jun/AP-1 activation and transcription of inflammation/metastasis-related cytokines, facilitating cancer cell migration and invasion. Targeting this pathway may offer new therapeutic strategies for thyroid carcinoma patients (62). Inflammation-associated mediators orchestrate tumor progression through dual mechanisms: (1) by activating pivotal signaling pathways that enhance neoplastic proliferation, suppress apoptosis, and bolster cellular survival—effectively promoting the expansion of tumor-sensitive cells; and (2) by facilitating angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and immune evasion, thereby accelerating malignancy and enhancing drug resistance. The chronic inflammatory microenvironment substantially elevates recurrence risk, primarily by sustaining cancer stemness and immune-escaping capacities in residual tumor cells. In contrast, acute or therapy-induced inflammation may transiently suppress relapse through immune activation—though this protective effect remains subordinate to the overarching pro-tumorigenic trajectory (56). In summary, these inflammatory factors play pivotal roles in the development and metastasis of thyroid carcinoma, providing new perspectives and potential therapeutic targets for its treatment and prognosis.
The second cluster explores the link between inflammation and the diagnosis and management of thyroid carcinoma. In terms of diagnosis, inflammation primarily manifests through serum inflammatory biomarkers (e.g., NMPLR, LMR, NLR, PLR, SII) and their role in diagnosing and predicting different types of thyroid carcinoma. Given the differing treatment approaches for aDTC and ATC, rapid and reliable diagnosis of these conditions is crucial. While pathological examination via fine-needle aspiration or core needle biopsy is considered the gold standard for ATC diagnosis, it often requires significant time to obtain results. Recent studies have proposed the NMPLR, a composite index based on four immune cell types, as a biomarker for differentiating ATC from aDTC and predicting prognosis (63). Ahn et al. reported that a low LMR is associated with poor prognosis in ATC (64). Yokota et al. demonstrated that a preoperative low LMR strongly predicts high-risk recurrence in thyroid carcinoma patients (65). However, other studies suggest that a high NLR is a risk factor for thyroid carcinoma recurrence (36). Generally, elevated NLR, PLR, and SII are associated with poorer cancer outcomes. While NLR, PLR, and SII may serve as useful biomarkers indicating increased clinicopathological aggressiveness in MTC, their utility in independently predicting lymph node or distant metastasis appears limited (66). In 2023, Roberta Modica et al. evaluated the potential role of NLR, PLR, and SII as biomarkers in MTC. Although high NLR, PLR, and SII are linked to adverse outcomes in several cancer types, their role in MTC patients remains undetermined. Future research should focus on measuring these inflammatory markers during the disease course to determine their utility in early recurrence detection (67).In terms of treatment, inflammation in thyroid carcinoma is primarily studied in the context of postoperative infections. Surgery, as a therapeutic intervention, inevitably causes trauma to the patient, triggering an inflammatory response at the wound site and leading to transient increases in inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, Gal-3, and IL-6 (68). In thyroid carcinoma treatment, traditional open surgery and endoscopic surgery have been the primary options (69, 70). However, with the growing emphasis on postoperative quality of life in contemporary clinical practice, aesthetic outcomes in head and neck surgery have become a critical factor in enhancing patient satisfaction. Consequently, research has increasingly focused on endoscopic thyroidectomy, a minimally invasive approach valued for its aesthetic benefits (71). Beyond its cosmetic advantages, endoscopic thyroidectomy significantly reduces inflammatory responses at the incision site. Differences in postoperative inflammatory factor levels have been observed between traditional open surgery and endoscopic surgery. Due to its minimally invasive nature, endoscopic surgery effectively lowers the risk of postoperative bleeding, thereby reducing patient pain. In a 2021 study by Li He et al., measurements of TNF-α, Gal-3, and IL-6 levels before and after surgery in thyroid carcinoma patients revealed increased levels of these inflammatory factors on the first postoperative day in both traditional open surgery and endoscopic surgery groups. This indicates an acute inflammatory response post-surgery, but the increase was significantly lower in the endoscopic surgery group, demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing postoperative inflammation. Thus, endoscopic surgery not only minimizes postoperative pain but also mitigates inflammatory responses, significantly improving the quality of life for thyroid carcinoma patients (72).
The third cluster focuses on the tumor microenvironment (TME) of thyroid carcinoma. Tumors, as unique speciation events, employ an evolutionary strategy termed pathological niche construction by modulating microenvironmental conditions and resources to foster their own proliferation (73).The tumor microenvironment in thyroid carcinoma resembles a sophisticated ecosystem, comprising both malignant and non-malignant cellular components, stromal elements, vascular networks, and immune cell populations that collectively establish an intricate web of resource acquisition and metabolic exchange (74).Through dynamic reciprocal interactions, malignant cells undergo continuous co-evolutionary adaptation with neighboring tumor cells and stromal components, thereby augmenting their oncogenic fitness (75).The microenvironmental constituents collectively exert pivotal influence on thyroid cancer pathogenesis, mediating disease progression through multidimensional pathways encompassing immune escape strategies, extracellular matrix reorganization, and metabolic intervention. By studying immune cells within the TME of thyroid carcinoma, cancer-related inflammatory factors may serve as valuable targets for novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies (76). During tumor development, interactions between the tumor and its surrounding immune microenvironment promote immune tolerance, leading to immune escape and ultimately preventing the complete eradication of the tumor. Studies have shown that M2 macrophages, Tregs, monocytes, neutrophils, dendritic cells (DCs), mast cells (MCs), and M0 macrophages within the TME contribute to tumor promotion in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). In contrast, M1 macrophages, CD8+ T cells, B cells, NK cells, and T follicular helper (TFH) cells (with weaker evidence for eosinophils, γδ T cells, and Th17 cells) exert anti-tumor effects. During PTC progression, overall immune activity increases, with significant elevations in the abundance and proportions of pro-tumor immune cells (M2 macrophages, Tregs, monocytes, neutrophils, DCs, MCs, and M0 macrophages) (33).Additionally, most anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) tumor cells are PD-L1 positive, and their TME is enriched with PD-1/PD-L1-positive infiltrating lymphocytes. Current research on immunotherapy for ATC patients indicates that ATC tumors express immune markers such as PD-L1, which has become a recent hotspot in inflammation and thyroid carcinoma research. The American Thyroid Association guidelines recommend checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., PD-L1, PD-1) as first-line or advanced therapy for stage IVC ATC patients with high PD-L1 expression in the absence of other targetable alterations (77). Cancer immunotherapy may represent an alternative treatment for tumors unresponsive to conventional therapies, such as recurrent or persistent differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC), poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC), or ATC. Monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-1/PD-L1, such as pembrolizumab, are currently available (76). Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), fundamental cellular architects of the tumor microenvironment, actively remodel the extracellular matrix (ECM) through elevated secretion of structural proteins such as fibronectin and type I collagen, while preferentially expressing the pathologically significant oncofetal fibronectin isoform (78).Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) orchestrate tumorigenesis through paracrine secretion of cytokines and growth factors that coordinately regulate cancer cell proliferation, survival, and stemness, while driving intratumoral angiogenesis and modulating immune cell recruitment and differentiation (74).Furthermore, CAFs mediate stromal ECM remodeling by upregulating the expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This CAF-driven matrix reorganization potently facilitates cancer cell migration and invasion (79). Metabolically, this intervention manifests through lactate accumulation and microenvironmental acidification - a phenomenon termed “nutrient competition.” Tumor cells predominantly generate lactate via the Warburg effect (aerobic glycolysis), consequently inducing acidification of the tumor microenvironment (TME) (80). As tumor proliferation advances, its expansive growth frequently outpaces vascular supply capacity, thereby generating a pathological microenvironment characterized by regional hypoxia, nutrient deprivation, and accumulated acidic metabolites. This dysregulated micro-ecosystem stands in stark contrast to the metabolically orchestrated milieu observed in healthy tissues (81, 82). The necrotic cellular debris interacts synergistically with tumor-derived proinflammatory factors, collectively forging a hostile ‘toxic swamp’-like microenvironment. This distinctive ‘tumor swamp’ ecology not only furnishes malignant cells with unique survival advantages but, more critically, imposes formidable selective pressures that ultimately drive the evolution of adaptive tumor clones with enhanced migratory and metastatic competence (75, 83).
The fourth cluster investigates the association between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) and thyroid carcinoma. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common inflammatory thyroid disorder and the leading cause of hypothyroidism. The relationship between HT and papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) was first described by Dailey et al. in 1955 (84). Since its initial proposal, the association between these conditions has been extensively studied and remains highly debated (85). Some scholars argue that HT may promote the development of PTC, while others suggest that HT could act as a protective factor against PTC (86). In a 2024 meta-analysis by Yali Le et al., the study aimed to examine the risk relationship between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) and thyroid carcinoma (TC), with a focus on gender differences. By conducting a comprehensive search across online databases, including PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Web of Science, the study analyzed the correlation between HT and TC. The results indicated a significant association between HT and TC (OR: 2.22, 95% CI: 1.85–2.67), suggesting that HT may increase the risk of TC. Additionally, the study performed a supplementary analysis of gender-specific data to determine the odds ratios (ORs) for females and males, as well as the prevalence of TC in HT patients by gender. However, the supplementary analysis revealed no statistically significant difference in TC prevalence between female (0.31, 95% CI: 0.17–0.45) and male (0.37, 95% CI: 0.21–0.53) HT patients. The final discussion highlighted that HT patients have a higher incidence of TC compared to non-HT patients. HT is considered a precancerous lesion for TC, and autoimmune thyroiditis may be a risk factor for TC, with the inflammatory processes of HT playing a significant role in TC development (50). The malignant transformation of the thyroid may be driven by cellular mediators from immune cells in a chronic inflammatory state or by elevated TSH levels stimulating follicular epithelial cell proliferation (87). Evidence suggests that HT patients have a higher risk of thyroid carcinoma compared to the general population aged 9–15. According to relevant literature, the pathogenesis of HT-associated thyroid carcinoma may involve apoptosis of thyroid epithelial cells, diffuse lymphocyte infiltration, fibrous replacement, and follicular destruction in HT. Therefore, evaluating the association between autoimmune thyroiditis and PTC is meaningful (88). Furthermore, since oxidative stress (OS) and inflammatory environments are implicated in the development of various cancers, studies have further explored the systemic and microenvironmental involvement of oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in HT and PTC patients. The results showed increased systemic OS in thyroid disease patients, with PTC-only patients exhibiting higher systemic OS levels than those with both PTC and HT, potentially leading to worse prognoses in PTC-only patients compared to those with PTC and HT (89).
The fifth cluster explores the link between obesity and thyroid carcinoma risk. Over recent decades, the global prevalence of overweight and obesity has surged, with the incidence of differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) increasing alongside rising obesity rates, supporting a potential correlation between the two conditions (90). Obesity is defined as a chronic, low-grade inflammatory and non-communicable disease, often accompanied by a state of mild chronic inflammation characterized by elevated systemic inflammatory markers and nonspecific activation of the immune system (91). Adipose tissue is not merely a site for energy storage; it should also be regarded as an endocrine organ composed of various cell types, including adipocytes, preadipocytes, and immune cells. Adipocytes readily secrete pro-inflammatory adipokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which recruit immune cells and amplify inflammatory processes, thereby promoting cancer development, progression, and metastasis (92). It is now widely accepted that obesity-associated immune dysregulation, compensatory hyperinsulinemia, hyperlipidemia, and enhanced oxidative stress are risk factors for cancer development and/or progression (93). Some data suggest that increased inflammasome activity in adipose tissue is a key mediator of obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance (94). Inflammasomes can be activated by fatty acids and high glucose levels, linking metabolic danger signals to the activation of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma development. Thus, inflammasome activation may represent a critical step in obesity-related thyroid carcinoma pathogenesis (95).Additionally, obesity influences the secretion of adipokines (hormones secreted by adipocytes), with data supporting the notion that adipokines such as leptin and adiponectin may be directly related to adiposity. Increased leptin and decreased adiponectin levels are well-documented examples (96). Scientific research has robustly demonstrated an inverse correlation between adiponectin (APN) levels and the risk of endocrine tumors (97). Given that obesity often leads to hypoadiponectinemia, the increased risk of thyroid carcinoma in obese individuals may be at least partially attributed to the loss of this hormone-induced immunosuppressive effect (91). Furthermore, high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity accelerates thyroid carcinoma growth and progression, particularly by shortening survival and promoting anaplastic transformation. The core mechanism underlying these changes lies in HFD-induced elevation of leptin levels, which activates the JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Preclinical studies using the STAT3-specific inhibitor S3I-201 have further confirmed the pivotal role of leptin downstream effectors in obesity-related thyroid carcinoma development (98).In summary, obesity promotes the initiation and progression of thyroid carcinoma through multiple mechanisms, including chronic inflammation, adipokine imbalance, HFD-induced metabolic dysregulation, and inflammasome activation. These mechanisms provide potential targets for the prevention and treatment of thyroid carcinoma in the future.
Using CiteSpace for keyword co-occurrence analysis, this study highlights the field’s trending topics, revealing emerging frontiers and shifts in research hotspots over time. Future research will increasingly focus on the ‘systemic immune-inflammation index’ and ‘Th17 cells,’ reflecting their growing significance in the study of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma.
The systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is a novel inflammatory marker derived from the absolute counts of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and platelets, which can be calculated from routine complete blood count (CBC) data. In thyroid carcinoma research, this inflammatory marker is manifested in four key aspects: 1)Association with Tumor Multifocality: SII is significantly higher in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) compared to healthy individuals, and elevated SII values are strongly correlated with tumor multifocality (i.e., the presence of multiple independent tumor foci) (p=0.01). This suggests that SII may reflect the aggressive biological behavior of tumors, although it shows no significant association with tumor diameter, histological type, or neural/lymphatic/capsular invasion (99). 2)Predictive Marker for Lymph Node Metastasis: In thyroid carcinoma patients, the diagnosis of central lymph node metastasis (CLNM) is complicated by false negatives in imaging studies, leading to many clinically node-negative (cN0) patients having undetected central lymph node metastases. This can interfere with clinical decision-making. Fortunately, a retrospective study of cN0 papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients undergoing radical surgery determined CLNM through postoperative histopathological examination. A comprehensive analysis of various inflammatory biomarkers concluded that SII effectively predicts CLNM in cN0 PTC and papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) patients. This finding is significant for distinguishing between non-CLNM and CLNM PTC patients, as it may help clinicians avoid unnecessary prophylactic central lymph node dissection in patients without actual lymph node metastasis (100). Additionally, preoperative SII is an independent risk factor for lateral lymph node metastasis (LLNM). Multivariate analysis shows that elevated SII is associated with an increased risk of LLNM (101). 3)Potential Link to Thyroid Carcinoma Prognosis: SII is believed to be associated with thyroid carcinoma prognosis. Studies indicate that higher SII values may correlate with aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis, although its precise prognostic value requires validation through long-term follow-up studies. For example, high SII may indirectly influence metastasis risk or treatment response by promoting inflammatory reactions in the tumor microenvironment (102).4)Differentiation Between Benign and Malignant Thyroid Diseases: With the rising incidence of thyroid carcinoma, the healthcare system faces increased pressure and a higher risk of overtreatment. In this context, accurately distinguishing between thyroid carcinoma and benign nodules preoperatively is crucial. This step is essential to avoid unnecessary surgical interventions, reduce patient burden, minimize complication risks, and implement more precise treatment strategies (103). In a 2023 study by Selahattin Vural et al., preoperative SII levels were significantly higher in PTC patients compared to those with benign thyroid diseases, suggesting that this simple marker can differentiate between benign and malignant thyroid conditions. Moreover, high SII is associated with increased invasiveness in PTC (104).
The role of SII in thyroid carcinoma has become a research hotspot in recent years, and future studies will delve deeper into its mechanisms and applications.
Helper T cells 17 (Th17) are a recently identified subset of T cells capable of secreting interleukin-17 (IL-17), playing a significant role in autoimmune diseases and host defense mechanisms. Chronic inflammation and carcinogenesis are often associated with the relative roles of two specific lymphocyte subsets: regulatory T cells (Tregs) and Th17 cells (105). The pro-inflammatory IL-23/Th17 axis has emerged as a critical mediator in inflammation-related cancers. The role of the Th17 spectrum, including immune cells, cytokines, chemokines, and their receptors, may either be protective or act as a trigger for thyroid tumors, depending on the histological classification of the tumor (32). Research by Denise Faria Galano Carvalho et al. demonstrated an association between Th17 cell infiltration and poor prognosis, suggesting that Th17 cells may suppress anti-tumor responses (106). Given that IL-17, expressed by Th17 cells, is involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory responses and is known to induce the production of high concentrations of IL-1β, TNF-α, TGF-β, CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), and matrix metalloproteinase mediators—all of which are prevalent in the tumor microenvironment—this cytokine represents a potential therapeutic target in thyroid carcinoma (107). In 2023, Sohini Banerjee et al. found that IL-17A expression is significantly correlated with smaller thyroid tumor diameter and disease progression, highlighting its importance as a biomarker for early diagnosis and future prognosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) (108).
5 Limitations of the study
This study has several methodological limitations that require explicit acknowledgment. First, regarding data sources, we deliberately restricted our literature search to the Web of Science (WoS) database, excluding other repositories such as PubMed and Scopus. This decision was based on two primary considerations (1): WoS offers unique advantages in interdisciplinary coverage, enabling more comprehensive cross-disciplinary analysis compared to PubMed’s specialized focus on biomedical and life sciences; and (2) WoS provides unparalleled citation tracking capabilities (both forward and backward citations), allowing for robust assessment of academic impact through complete citation network analysis - a distinctive feature that sets it apart from other databases. The WoS platform integrates sophisticated bibliometric tools that facilitate high-precision data mining, including citation frequency analysis and journal impact factor evaluation. These advanced features enable precise identification of research hotspots and emerging frontiers, offering analytical depth unavailable in general-purpose databases. Nevertheless, we recognize that this selective approach may introduce certain biases, particularly the potential omission of significant biomedical literature not indexed in WoS. An additional limitation stems from our inclusion of English-language publications only, which may overlook important contributions published in other languages, especially from high-output non-English-speaking countries. However, we note that English remains the predominant language of scientific communication, with most prolific researchers publishing in English regardless of their native language. Furthermore, our 24-year timeframe, while ensuring focus on contemporary trends, means that recently published works may not yet have accumulated substantial citation counts. It is important to emphasize that these limitations represent inherent challenges in bibliometric research methodology. We have carefully considered their potential impact throughout our study design and results interpretation to ensure balanced and meaningful conclusions.
6 Conclusion
In summary, this study employs bibliometric methods to conduct an in-depth evaluation and visual presentation of the literature corpus in the field of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma. Using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) as the data source, we meticulously examined English articles and reviews published between January 1, 2000, and November 12, 2024. Leveraging bibliometric tools such as CiteSpace and VOSviewer, our analysis revealed the current research landscape, outlined core themes, and predicted emerging trends in inflammation-related thyroid carcinoma research. Key research focuses include the tumor microenvironment, the expression of inflammation-related factors, the role of inflammation in thyroid carcinoma management, and the link between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and thyroid carcinoma. This comprehensive bibliometric analysis not only highlights the achievements of existing research but also lays a solid foundation for future academic exploration and progress in understanding the relationship between inflammation and thyroid carcinoma. Through this systematic approach, we provide researchers and practitioners in the field with a valuable roadmap and research directions for future studies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YF: Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Software, Visualization. CH: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology. ZX: Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. JM: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Nature Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTB2024NSCQ-MSX0260).
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to all researchers and institutions whose work contributed to this study. Special thanks to the Web of Science database for providing access to the necessary literature. We also acknowledge the support of our colleagues and institutions for their valuable insights and resources. This research would not have been possible without their contributions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Alonso-Gordoa T, Jimenez-Fonseca P, Martinez-Trufero J, Navarro M, Porras I, Rubió-Casadevall J, et al. Seom-getne-ttcc clinical guideline thyroid cancer (2023). Clin Trans Oncol. (2024) 26:2902–16. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03736-6
2. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
3. Hu S, Wu X, and Jiang H. Trends and projections of the global burden of thyroid cancer from 1990 to 2030. J Global Health. (2024) 14:4084. doi: 10.7189/jogh.14.04084
4. Kondo T, Ezzat S, and Asa SL. Pathogenetic mechanisms in thyroid follicular-cell neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. (2006) 6:292–306. doi: 10.1038/nrc1836
5. Bolf EL, Sprague BL, and Carr FE. A linkage between thyroid and breast cancer: A common etiology? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2019) 28:643–9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-18-0877
6. Agate L, Lorusso L, and Elisei R. New and old knowledge on differentiated thyroid cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J Endocrinol Invest. (2012) 35:3–9. doi: 10.1155/2012/872478
7. Balkwill F and Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to virchow? Lancet (London England). (2001) 357:539–45. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)04046-0
8. Hanahan D and Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. (2000) 100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9
9. Cunha LL, Marcello MA, and Ward LS. The role of the inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis. Endocrine-related Cancer. (2014) 21:R85–r103. doi: 10.1530/erc-13-0431
10. Poschke I, Mougiakakos D, and Kiessling R. Camouflage and sabotage: tumor escape from the immune system. Cancer Immunol Immunother: CII. (2011) 60:1161–71. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1012-8
11. Fernandes Q, Inchakalody VP, Bedhiafi T, Mestiri S, Taib N, Uddin S, et al. Chronic inflammation and cancer; the two sides of a coin. Life Sci. (2024) 338:122390. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122390
12. Bozec A, Lassalle S, Hofman V, Ilie M, Santini J, and Hofman P. The thyroid gland: A crossroad in inflammation-induced carcinoma? An ongoing debate with new therapeutic potential. Curr Med Chem. (2010) 17:3449–61. doi: 10.2174/092986710792927804
13. Park S, Kim M, Zhu J, Lee WK, Altan-Bonnet G, Meltzer P, et al. Inflammation suppression prevents tumor cell proliferation in a mouse model of thyroid cancer. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:1857–70.
14. Pasquali D, Giacomelli L, Pedicillo MC, Conzo G, Gentile G, De Stefano IS, et al. Tumor inflammatory microenvironment of the thyroid cancer: relationship between regulatory T-cell imbalance, and P-nfκb (P65) expression-a preliminary study. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(21):6817. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216817
15. Nakagawa S, Samarasinghe G, Haddaway NR, Westgate MJ, O’Dea RE, Noble DWA, et al. Research weaving: visualizing the future of research synthesis. Trends Ecol Evol. (2019) 34:224–38. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2018.11.007
16. Khalil GM and Gotway Crawford CA. A bibliometric analysis of U.S.-based research on the behavioral risk factor surveillance system. Am J Prev Med. (2015) 48:50–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2014.08.021
17. Shen J, Shen H, Ke L, Chen J, Dang X, Liu B, et al. Knowledge mapping of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A bibliometric study. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:815575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.815575
18. Luo YX, Zhu YH, and Yao XQ. Knowledge mapping of exercise and physical activity research in older adults: hotspots, bursts, and trends of the last decade. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e23181. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23181
19. Wu H, Cheng K, Guo Q, Yang W, Tong L, Wang Y, et al. Mapping knowledge structure and themes trends of osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: A bibliometric analysis. Front Med. (2021) 8:787228. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.787228
20. Cheng K, Guo Q, Yang W, Wang Y, Sun Z, and Wu H. Mapping knowledge landscapes and emerging trends of the links between bone metabolism and diabetes mellitus: A bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2021. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:918483. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.918483
21. Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Giuggioli D, Ferrannini E, Ferri C, and Fallahi P. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (Cxcl)10 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2014) 13:272–80. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.10.010
22. Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Ruffilli I, Elia G, Biricotti M, Vita R, et al. The association of other autoimmune diseases in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis: review of the literature and report of a large series of patients. Autoimmun Rev. (2016) 15:1125–8. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.09.009
23. Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, Galdiero MR, Ruffilli I, Elia G, Ragusa F, et al. Immune and inflammatory cells in thyroid cancer microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(18):4413. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184413
24. Ferri C, Colaci M, Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Antonelli A, and Giuggioli D. Thyroid involvement in hepatitis C virus-infected patients with/without mixed cryoglobulinemia. Front Endocrinol. (2017) 8:159. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00159
25. Netea-Maier RT, Plantinga TS, van de Veerdonk FL, Smit JW, and Netea MG. Modulation of inflammation by autophagy: consequences for human disease. Autophagy. (2016) 12:245–60. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1071759
26. Zhang L, Xu S, Cheng X, Wu J, Wang Y, Gao W, et al. Inflammatory tumor microenvironment of thyroid cancer promotes cellular dedifferentiation and silencing of iodide-handling genes expression. Pathol Res Pract. (2023) 246:154495. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154495
27. Takeda T, Inaba H, Yamazaki M, Kyo S, Miyamoto T, Suzuki S, et al. Tumor-specific gene therapy for undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma utilizing the telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 88:3531–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-021856
28. Netea MG, Nold-Petry CA, Nold MF, Joosten LA, Opitz B, van der Meer JH, et al. Differential requirement for the activation of the inflammasome for processing and release of il-1beta in monocytes and macrophages. Blood. (2009) 113:2324–35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-146720
29. Galdiero MR, Garlanda C, Jaillon S, Marone G, and Mantovani A. Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in tumor progression. J Cell Physiol. (2013) 228:1404–12. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24260
30. Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the american thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2016) 26:1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020
31. Coussens LM and Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. (2002) 420:860–7. doi: 10.1038/nature01322
32. Guarino V, Castellone MD, Avilla E, and Melillo RM. Thyroid cancer and inflammation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2010) 321:94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.10.003
33. Xie Z, Li X, He Y, Wu S, Wang S, Sun J, et al. Immune cell confrontation in the papillary thyroid carcinoma microenvironment. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:570604. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.570604
34. Riguetto CM, Barreto IS, Maia FFR, Assumpção L, and Zantut-Wittmann DE. Usefulness of pre-thyroidectomy neutrophil-lymphocyte, platelet-lymphocyte, and monocyte-lymphocyte ratios for discriminating lymph node and distant metastases in differentiated thyroid cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo Brazil). (2021) 76:e3022. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e3022
35. Pani F, Caria P, Yasuda Y, Makoto M, Mariotti S, Leenhardt L, et al. The immune landscape of papillary thyroid cancer in the context of autoimmune thyroiditis. Cancers. (2022) 14(17):4287. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174287
36. Yamazaki H, Sugino K, Matsuzu K, Masaki C, Akaishi J, Hames K, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers and dynamics of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine. (2020) 70:115–22. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02313-5
37. Jacquemin V, Antoine M, Dom G, Detours V, Maenhaut C, and Dumont JE. Dynamic cancer cell heterogeneity: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cancers. (2022) 14(2):280. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020280
38. Zhang R, Straus FH, and DeGroot LJ. Adenoviral-mediated gene therapy for thyroid carcinoma using thymidine kinase controlled by thyroglobulin promoter demonstrates high specificity and low toxicity. Thyroid. (2001) 11:115–23. doi: 10.1089/105072501300042749
39. Westphal EM and Melchner Hv H. Gene therapy approaches for the selective killing of cancer cells. Curr Pharm Design. (2002) 8:1683–94. doi: 10.2174/1381612023393927
40. Zhang R and DeGroot LJ. An adenoviral vector expressing functional heterogeneous proteins herpes simplex viral thymidine kinase and human interleukin-2 has enhanced in vivo antitumor activity against medullary thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine-related Cancer. (2001) 8:315–25. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0080315
41. Takeda T, Yamazaki M, Minemura K, Imai Y, Inaba H, Suzuki S, et al. A tandemly repeated thyroglobulin core promoter has potential to enhance efficacy for tissue-specific gene therapy for thyroid carcinomas. Cancer Gene Ther. (2002) 9:864–74. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700511
42. Zhang R, Straus FH, and DeGroot LJ. Cell-specific viral gene therapy of a hurthle cell tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 87:1407–14. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.3.8276
43. Murugan AK and Alzahrani AS. Sars-cov-2: emerging role in the pathogenesis of various thyroid diseases. J Inflammation Res. (2021) 14:6191–221. doi: 10.2147/jir.S332705
44. Lisco G, De Tullio A, Jirillo E, Giagulli VA, De Pergola G, Guastamacchia E, et al. Thyroid and covid-19: A review on pathophysiological, clinical and organizational aspects. J Endocrinol Invest. (2021) 44:1801–14. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01554-z
45. Scappaticcio L, Pitoia F, Esposito K, Piccardo A, and Trimboli P. Impact of covid-19 on the thyroid gland: an update. Rev Endocrine Metab Disord. (2021) 22:803–15. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09615-z
46. Gu Y, Yu M, Deng J, and Lai Y. The association of pretreatment systemic immune inflammatory response index (Sii) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (Nlr) with lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Gen Med. (2024) 17:2887–97. doi: 10.2147/ijgm.S461708
47. Gambardella C, Mongardini FM, Paolicelli M, Bentivoglio D, Cozzolino G, Ruggiero R, et al. Role of inflammatory biomarkers (Nlr, lmr, plr) in the prognostication of Malignancy in indeterminate thyroid nodules. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(7):6466. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076466
48. Wang G, Ma Y, Liu Y, Fan Y, Miao X, Zhang Y, et al. Predictive value of systemic inflammatory markers for recurrence of papillary thyroid cancer. J Surg Oncol. (2023) 128:743–8. doi: 10.1002/jso.27363
49. Stanciu AE, Verzia A, Stanciu MM, Zamfirescu A, and Gheorghe DC. Analysis of the correlation between the radioactive iodine activity and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Cancers. (2022) 14(8):1899. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081899
50. Le Y, Geng C, Gao X, and Zhang P. The risk of thyroid cancer and sex differences in hashimoto’s thyroiditis, a meta-analysis. BMC Endocrine Disord. (2024) 24:151. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01670-w
51. Lathigara D, Kaushal D, and Wilson RB. Molecular mechanisms of western diet-induced obesity and obesity-related carcinogenesis-a narrative review. Metabolites. (2023) 13(5):675. doi: 10.3390/metabo13050675
52. Ludgate ME, Masetti G, and Soares P. The relationship between the gut microbiota and thyroid disorders. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2024) 20:511–25. doi: 10.1038/s41574-024-01003-w
53. Xie Z, Zhou J, Zhang X, and Li Z. Clinical potential of microbiota in thyroid cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:166971. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166971
54. Zhang Y, Duan Z, Shu P, and Deng J. Exploring acceptable risk in engineering and operations research and management science by bibliometric analysis. Risk Anal. (2023) 43:1539–56. doi: 10.1111/risa.14049
55. Li H, Duan N, Zhang Q, and Shao Y. Il1a & Il1b genetic polymorphisms are risk factors for thyroid cancer in a chinese han population. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 76:105869. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105869
56. Okda TM, Atwa GMK, Eldehn AF, Dahran N, Alsharif KF, and Elmahallawy EK. A novel role of galectin-3 and thyroglobulin in prognosis and differentiation of different stages of thyroid cancer and elucidation of the potential contribution of bcl-2, il-8 and tnf-α. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(2):352. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020352
57. Lv N, Liu F, Cheng L, Liu F, and Kuang J. The expression of transcription factors is different in papillary thyroid cancer cells during tnf - α Induced emt. J Cancer. (2021) 12:2777–86. doi: 10.7150/jca.53349
58. Lumachi F, Basso SM, and Orlando R. Cytokines, thyroid diseases and thyroid cancer. Cytokine. (2010) 50:229–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2010.03.005
59. Menicali E, Guzzetti M, Morelli S, Moretti S, and Puxeddu E. Immune landscape of thyroid cancers: new insights. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:637826. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.637826
60. Pacifico F and Leonardi A. Role of nf-kappab in thyroid cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2010) 321:29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.10.010
61. Ma C, Zhang N, Wang T, Guan H, Huang Y, Huang L, et al. Inflammatory cytokine-regulated lncptcts suppresses thyroid cancer progression via enhancing snail nuclear export. Cancer Lett. (2023) 575:216402. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216402
62. Kuang BH, Lin GH, Liu Q, and Wang BC. Uhrf1 induces metastasis in thyroid cancer. J Oncol. (2022) 2022:7716427. doi: 10.1155/2022/7716427
63. Zhang L, Luo H, Wang L, Liu Y, Rui S, Wu Z, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of preoperative systemic inflammatory markers in anaplastic thyroid cancer. J Surg Oncol. (2020) 122:897–905. doi: 10.1002/jso.26089
64. Ahn J, Song E, Oh HS, Song DE, Kim WG, Kim TY, et al. Low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratios are associated with poor overall survival in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma patients. Thyroid. (2019) 29:824–9. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0684
65. Yokota M, Katoh H, Nishimiya H, Kikuchi M, Kosaka Y, Sengoku N, et al. Lymphocyte-monocyte ratio significantly predicts recurrence in papillary thyroid cancer. J Surg Res. (2020) 246:535–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.09.034
66. Figueiredo AA, Esteves S, Moura MM, Marques P, Simões-Pereira J, and Leite V. Preoperative serum inflammation-based scores in medullary thyroid cancer. Endocrinol Diabetes y nutricion. (2023) 70:48–55. doi: 10.1016/j.endien.2022.06.015
67. Modica R, Minotta R, Liccardi A, Cannavale G, Benevento E, and Colao A. Evaluation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (Nlr), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (Plr) and systemic immune-inflammation index (Sii) as potential biomarkers in patients with sporadic medullary thyroid cancer (Mtc). J Personal Med. (2023) 13(6):953. doi: 10.3390/jpm13060953
68. Alves Bersot CD, Ferreira Gomes Pereira L, Goncho VGV, Pereira JEG, and Falcão L. Enhancing recovery and reducing inflammation: the impact of enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations on inflammatory markers in laparoscopic surgery-a scoping review. Front Surg. (2024) 11:1450434. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1450434
69. Choi MH, Kim KA, Hwang SS, and Byun JY. Ct-quantified muscle and fat change in patients after surgery or endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer and its impact on long-term outcomes. Medicine. (2018) 97:e13878. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000013878
70. Bellantone R, Raffaelli M, De Crea C, Sessa L, Traini E, Princi P, et al. Video-assisted thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma: oncologic outcome in patients with follow-up ≥ 10 years. World J Surg. (2018) 42:402–8. doi: 10.1007/s00268-017-4392-x
71. Li N, Shen H, Zhang J, Dong B, Wang Y, and Li T. A new transoral vestibulum single incision endoscopic-assisted thyroidectomy with gasless. Laryngoscope. (2024) 134:2976–84. doi: 10.1002/lary.31197
72. He L, Qing F, Li M, and Lan D. Effects of laparoscopic and traditional open surgery on the levels of il-6, tnf-α, and gal-3 in patients with thyroid cancer. Gland Surg. (2021) 10:1085–92. doi: 10.21037/gs-21-60
73. Luo WR. Rethinking cancer. Zhonghua zhong liu za. (2025) 47:463–7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20250401-00145
74. Bantug GR and Hess C. The immunometabolic ecosystem in cancer. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:2008–20. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01675-y
75. Luo W. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma ecology theory: cancer as multidimensional spatiotemporal “Unity of ecology and evolution” Pathological ecosystem. Theranostics. (2023) 13:1607–31. doi: 10.7150/thno.82690
76. Zheng X, Sun R, and Wei T. Immune microenvironment in papillary thyroid carcinoma: roles of immune cells and checkpoints in disease progression and therapeutic implications. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1438235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1438235
77. Febrero B, Ruiz-Manzanera JJ, Ros-Madrid I, Hernández AM, Orenes-Piñero E, and Rodríguez JM. Tumor microenvironment in thyroid cancer: immune cells, patterns, and novel treatments. Head Neck. (2024) 46:1486–99. doi: 10.1002/hed.27695
78. Miles FL and Sikes RA. Insidious changes in stromal matrix fuel cancer progression. Mol Cancer Res. (2014) 12:297–312. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-13-0535
79. Erdogan B and Webb DJ. Cancer-associated fibroblasts modulate growth factor signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling to regulate tumor metastasis. Biochem Soc Trans. (2017) 45:229–36. doi: 10.1042/bst20160387
80. Fischer K, Hoffmann P, Voelkl S, Meidenbauer N, Ammer J, Edinger M, et al. Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid on human T cells. Blood. (2007) 109:3812–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-035972
81. Pouysségur J, Dayan F, and Mazure NM. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature. (2006) 441:437–43. doi: 10.1038/nature04871
82. Maley CC, Aktipis A, Graham TA, Sottoriva A, Boddy AM, Janiszewska M, et al. Classifying the evolutionary and ecological features of neoplasms. Nat Rev Cancer. (2017) 17:605–19. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.69
83. Amend SR and Pienta KJ. Ecology meets cancer biology: the cancer swamp promotes the lethal cancer phenotype. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:9669–78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3430
84. Dailey ME, Lindsay S, and Skahen R. Relation of thyroid neoplasms to hashimoto disease of the thyroid gland. AMA Arch Surg. (1955) 70:291–7. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1955.01270080137023
85. Azizi G, Keller JM, Lewis M, Piper K, Puett D, Rivenbark KM, et al. Association of hashimoto’s thyroiditis with thyroid cancer. Endocrine-related Cancer. (2014) 21:845–52. doi: 10.1530/erc-14-0258
86. Zheng K and Mao J. Comparison and analysis of clinical features of papillary thyroid cancer complicated with hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Clin Med Insights Oncol. (2024) 18:11795549241287085. doi: 10.1177/11795549241287085
87. Resende de Paiva C, Grønhøj C, Feldt-Rasmussen U, and von Buchwald C. Association between hashimoto’s thyroiditis and thyroid cancer in 64,628 patients. Front Oncol. (2017) 7:53. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00053
88. Liu C, Pan Y, Li Q, and Zhang Y. Bioinformatics analysis identified shared differentially expressed genes as potential biomarkers for hashimoto’s thyroiditis-related papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Med Sci. (2021) 18:3478–87. doi: 10.7150/ijms.63402
89. Lopes NMD, Lens HHM, da Silva Brito WA, Bianchi JK, Marinello PC, Cecchini R, et al. Role of papillary thyroid carcinoma patients with hashimoto thyroiditis: evaluation of oxidative stress and inflammatory markers. Clin Trans Oncol. (2022) 24:2366–78. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02891-y
90. Pazaitou-Panayiotou K, Polyzos SA, and Mantzoros CS. Obesity and thyroid cancer: epidemiologic associations and underlying mechanisms. Obes Rev. (2013) 14:1006–22. doi: 10.1111/obr.12070
91. Masone S, Velotti N, Savastano S, Filice E, Serao R, Vitiello A, et al. Morbid obesity and thyroid cancer rate. A Rev Literature J Clin Med. (2021) 10(9):1894. doi: 10.3390/jcm10091894
92. Coppack SW. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipose tissue. Proc Nutr Soc. (2001) 60:349–56. doi: 10.1079/pns2001110
93. Olefsky JM and Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. (2010) 72:219–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135846
94. Guo B, Fu S, Zhang J, Liu B, and Li Z. Targeting inflammasome/il-1 pathways for cancer immunotherapy. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:36107. doi: 10.1038/srep36107
95. Le Moli R, Vella V, Tumino D, Piticchio T, Naselli A, Belfiore A, et al. Inflammasome activation as a link between obesity and thyroid disorders: implications for an integrated clinical management. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:959276. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.959276
96. Pappa T and Alevizaki M. Obesity and thyroid cancer: A clinical update. Thyroid. (2014) 24:190–9. doi: 10.1089/thy.2013.0232
97. Izadi V, Farabad E, and Azadbakht L. Serum adiponectin level and different kinds of cancer: A review of recent evidence. ISRN Oncol. (2012) 2012:982769. doi: 10.5402/2012/982769
98. Kim WG and Cheng SY. Mechanisms linking obesity and thyroid cancer development and progression in mouse models. Hormones Cancer. (2018) 9:108–16. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0320-7
99. Kars A, Sahin A, Kılıc K, Sakat MS, and Bilen A. Systemic immune inflammation index in differentiated thyroid cancers. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Italica. (2022) 42:150–4. doi: 10.14639/0392-100x-n1665
100. Zhang Z, Xia F, Wang W, Huang Y, and Li X. The systemic immune-inflammation index-based model is an effective biomarker on predicting central lymph node metastasis in clinically nodal-negative papillary thyroid carcinoma. Gland Surg. (2021) 10:1368–73. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-666
101. Zhao L, Zhou T, Zhang W, Wu F, Jiang K, Lin B, et al. Blood immune indexes can predict lateral lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:995630. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.995630
102. Ecin SM and Gezer D. Evaluation of the clinical and prognostic importance of infection parameters in thyroid cancers: A cross-sectional study. Medicine. (2023) 102:e36532. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000036532
103. Tang ZW, Li XX, and Luo J. Development and validation of the nomogram based on ultrasound, thyroid stimulating hormone, and inflammatory marker in papillary thyroid carcinoma: A case-control study. Trans Cancer Res. (2023) 12:490–501. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2478
104. Vural S, Muhtaroğlu A, and Güngör M. Systemic immune-inflammation index: A new marker in differentiation of different thyroid diseases. Medicine. (2023) 102:e34596. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000034596
105. Eisenstein EM and Williams CB. The T(Reg)/th17 cell balance: A new paradigm for autoimmunity. Pediatr Res. (2009) 65:26r–31r. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31819e76c7
106. Carvalho DFG, Zanetti BR, Miranda L, Hassumi-Fukasawa MK, Miranda-Camargo F, Crispim JCO, et al. High il-17 expression is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in thyroid cancer. Oncol Lett. (2017) 13:1925–31. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5638
107. Ouyang W, Kolls JK, and Zheng Y. The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity. (2008) 28:454–67. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.004
108. Banerjee S, Nahar U, Dahiya D, Gupta R, Mukherjee S, Sachdeva N, et al. Il-17 a correlates with disease progression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. (2023) 18:93. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01362-4
109. Muzza M, Degl’Innocenti D, Colombo C, Perrino M, Ravasi E, Rossi S, et al. The tight relationship between papillary thyroid cancer, autoimmunity and inflammation: clinical and molecular studies. Clin Endocrinol. (2010) 72:702–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03699.x
110. Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, et al. Revised american thyroid association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. (2009) 19:1167–214. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0110
111. Ryder M, Ghossein RA, Ricarte-Filho JC, Knauf JA, and Fagin JA. Increased density of tumor-associated macrophages is associated with decreased survival in advanced thyroid cancer. Endocrine-related Cancer. (2008) 15:1069–74. doi: 10.1677/erc-08-0036
112. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, and Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:436–44. doi: 10.1038/nature07205
113. Davies L and Welch HG. Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973-2002. JAMA. (2006) 295:2164–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.18.2164
Keywords: thyroid carcinoma, inflammation, bibliometric analysis, Web of Science, VOSviewer, CiteSpace
Citation: Feng Y, Huang C, Liu X, Xiao Z, Wang L, Lu Z and Ming J (2025) A bibliometric analysis of inflammation and thyroid carcinoma: research trends and future perspectives. Front. Oncol. 15:1593006. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1593006
Received: 13 March 2025; Accepted: 16 July 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Malgorzata Gabriela Wasniewska, University of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
Weiren Luo, The Second Affiliated hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology, ChinaBarbara Maria Jarzab, Maria Skłodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, Poland
Victor De Mello Palma, Federal University of Santa Maria, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Feng, Huang, Liu, Xiao, Wang, Lu and Ming. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jia Ming, bWluZ2ppYUBjcW11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors share first authorship
 Yanhui Feng
Yanhui Feng Caiqi Huang†
Caiqi Huang† Xiaoman Liu
Xiaoman Liu Lu Wang
Lu Wang Jia Ming
Jia Ming