- 1Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, China
- 2Teaching and Research Section of Oncology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, China
- 3Department of Oncology, Affiliated of Cancer Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, China
The anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene encodes a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase. Most mutations in ALK gene result from translocations with other genes, forming fusion oncogenes. To date, 21 different genes have been identified as ALK fusion partners, each activating distinct signaling pathways that influence cancer cell proliferation, invasiveness, and tumorigenicity. ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs) have demonstrated significant efficacy in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and are widely utilized as first-line therapy. Lorlatinib, a third-generation ALK inhibitor, is effective in both treatment-naïve and previously treated patients with advanced NSCLC, exhibiting strong systemic and intracranial antitumor activity. This report presented a case of lung adenocarcinoma with 51 genetic variants, including a rare fusion variant: exon 15 of KIF5B fused to exon 20 of ALK, KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20). Following lorlatinib treatment, partial remission was achieved, and disease stability was maintained for an extended period, suggesting a favorable response to therapy. This case highlighted the potential sensitivity of the KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion to lorlatinib and the need for further investigation into lorlatinib’s efficacy across different KIF5B-ALK fusion variants. Additionally, other fusion types and treatment options for KIF5B-ALK fusions with varying breakpoints were discussed.
1 Introduction
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 80-85% of all lung cancer cases, and lung cancer-related mortality represents 18.7% of all cancer deaths worldwide in 2022 (1). The overall 5-year survival rate for lung cancer is 19.7%. Among stage I NSCLC patients, the 5-year survival rate ranges from 77% to 92% after surgery, whereas for stage III–IV NSCLC patients, it drops to 17–36% (2). In the Chinese population, ALK fusion mutations occur in approximately 5.5% of NSCLC cases (3). Among them, the echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4-ALK) fusion is the most common, comprising approximately 85% of ALK fusion mutations. ALK fusions are the second most prevalent driver mutations in NSCLC after EGFR-sensitive mutations, and EML4-ALK served as a key therapeutic target. ALK-TKIs have demonstrated significant efficacy in treating NSCLC patients with ALK rearrangements. ALK gene fusions are primarily found in adenocarcinoma subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), mainly co-occurring with mutations in other genes, such as TP53 and BIM. ALK alterations are more frequently identified in younger, non-smoking patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma, and are associated with a higher propensity for brain metastases (4, 5). In addition to EML4, other ALK fusion partners include TRK, KIF5B, KLC1, TFG, TPR, HIP1, STRN, DCTN1, SQSTM1, NPM1, BCL11A, and BIRC6 (6). KIF5B is one such fusion partner, with multiple possible fusion breakpoints. In this case, exon 15 of KIF5B is fused to exon 20 of ALK. The KIF5B-ALK fusion was first described in 2009 by Takeuchi et al. (7), who reported a fusion between Intron 24 of KIF5B and intron 19 of ALK. Wong et al. (8) later identified the KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion mutation, corresponding to the variant observed in this case. NSCLC patients with ALK fusion have exhibited significant responses to ALK-TKIs. In phase I trials, crizotinib, the first-generation ALK-TKI, achieved an objective response rate (ORR) of 57% in ALK-positive advanced NSCLC, leading to its approval as the first ALK inhibitor for clinical use (9). Since 2014, second-generation ALK-TKIs have emerged, exhibiting improved efficacy. Compared with crizotinib, the second-generation ALK-TKIs alectinib and brigatinib have demonstrated longer median progression-free survival (PFS) of 34.8 and 30.8 months, respectively. Among ALK-TKIs, the third-generation inhibitor lorlatinib has shown the longest median PFS (10–12). A Canadian cohort study showed that the median OS of patients receiving multi-line treatment including the third-generation TKI was significantly longer than that of patients receiving only monotherapy (55 months vs. 26 months, HR=4.64, p < 0.0001) (13). According to the 2024 NCCN guidelines, alectinib, brigatinib, or lorlatinib are recommended as first-line monotherapies for patients with ALK-positive metastatic NSCLC. The case presented in this article highlights the importance of developing individualized treatment plans for patients with rare gene mutations.
2 Case presentation
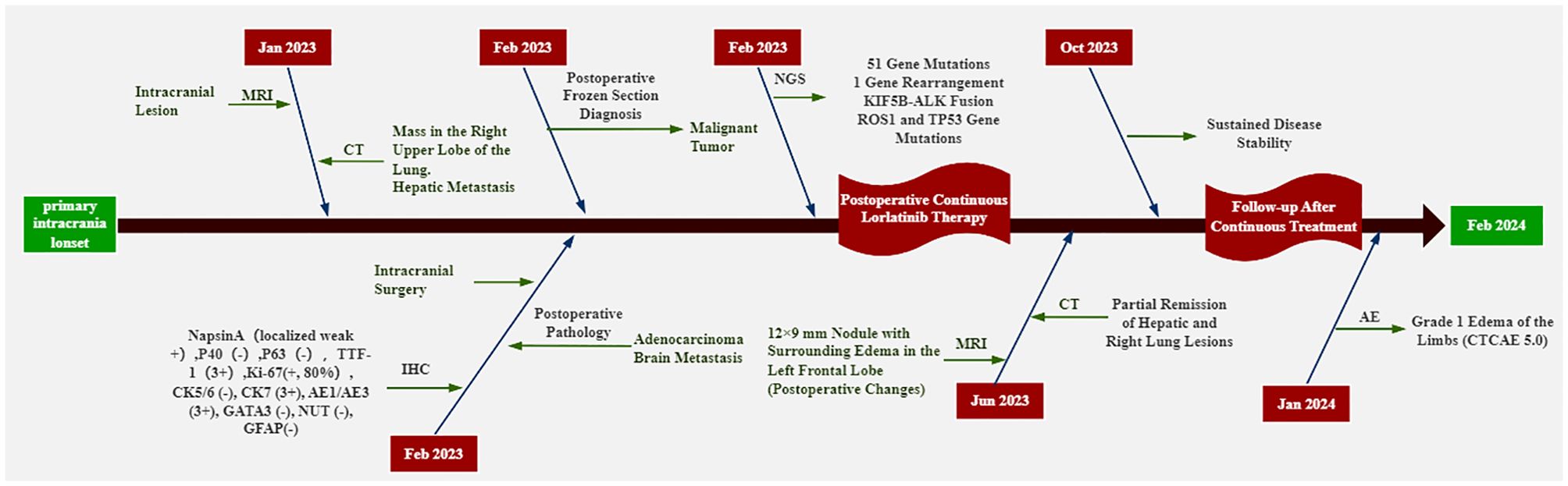
A 53-year-old Chinese female, with no history of smoking or family history of related tumors, was admitted to the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences with symptoms of hemiplegia, headache, and mental distress. On January 28, 2023, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed multiple abnormal signal foci in the brain parenchyma, the largest measuring approximately 24 × 21 mm², with a rightward midline shift and compression of the left lateral ventricle. Concurrently, chest-abdomen computed tomography (CT) identified a 38 × 33 mm² subpleural mass in the anterior segment of the upper lobe of the right lung. Multiple nodules of varying sizes were found in both lungs and bilateral pleura, the largest measuring approximately 10 × 8 mm². Additionally, two hepatic lesions were detected, measuring approximately 20 × 15 mm² and 44 × 55 mm², respectively. Based on the 9th Edition of the TNM staging system for lung cancer established by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC), the patient was staged as cT3N2bM1c2 IVB. To relieve symptoms and improve quality of life, the neurosurgery department recommended surgical intervention. After completing the necessary preoperative evaluations and excluding contraindications, the patient underwent “resection of the left central frontal lobe occupying lesion with bone flap reduction and fixation” on February 1, 2023. Frozen-section analysis of the left frontal lobe mass indicated a poorly differentiated malignant tumor with large cell atypia and evident mitotic activity. Postoperative pathology confirmed poorly differentiated carcinoma infiltrating brain tissue, exhibiting solid, sheet-like growth patterns. Immunohistochemistry and imaging findings were consistent with brain metastasis from primary lung adenocarcinoma.
Immunohistochemical results included: Napsin A (localized weak +), P40 (-), TTF-1 (3+), Ki-67 (80%+), CK5/6 (-), CK7 (3+), AE1/AE3 (3+), GATA3 (-), NUT (-), and GFAP (-). The PD-L1 value of the patient was not detected throughout the treatment. Capture-based next-generation sequencing (NGS) identified 51 gene mutations and one gene rearrangement, including a KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion, as well as TP53 (c.255del) and ROS1 (c.5912G). The ROS1 c.5912G>C mutation detected in this patient is currently classified as a variant of unknown significance (type 4 mutation). At present, the clinical relevance of this mutation is considered limited. Therefore, the ROS1 mutation detected in this case is not deemed to have clear clinical significance. The genetic testing was conducted by Genetron Health (Figure 1D). Based on the above examination results, the patient was discharged from the hospital after undergoing head surgery in February 2023 and received oral loratinib (100 mg daily) targeted therapy until June 2023. On June 5, 2023, the patient visited Guizhou Cancer Hospital for a follow-up examination. The CT scan revealed a 22 × 16 mm2 nodule in the upper tip segment of the right lung (Figure 1A), multiple nodules in the left lung, and a 5 mm nodule in segment S8 of the liver (Figure 1B). MRI of the head displayed a 12 × 9 mm2 nodule in the left frontal lobe with surrounding edema, aligning with postoperative changes (Figure 1C). Continued treatment up to October 16, 2023 demonstrated stable disease (SD) in the brain, liver, and upper lobe of the right lung compared to June. In June 2023, four months post-surgery and lorlatinib treatment, partial remission (PR) of intrahepatic, intracranial, and right lung lesions was achieved. Disease stability was maintained at eight months of follow-up with lorlatinib therapy (RECIST 1.1), with grade 1 limb edema (CTCAE 5.0) as the only reported adverse event (AE). Patient clinical management workflow is shown in Figure 2.
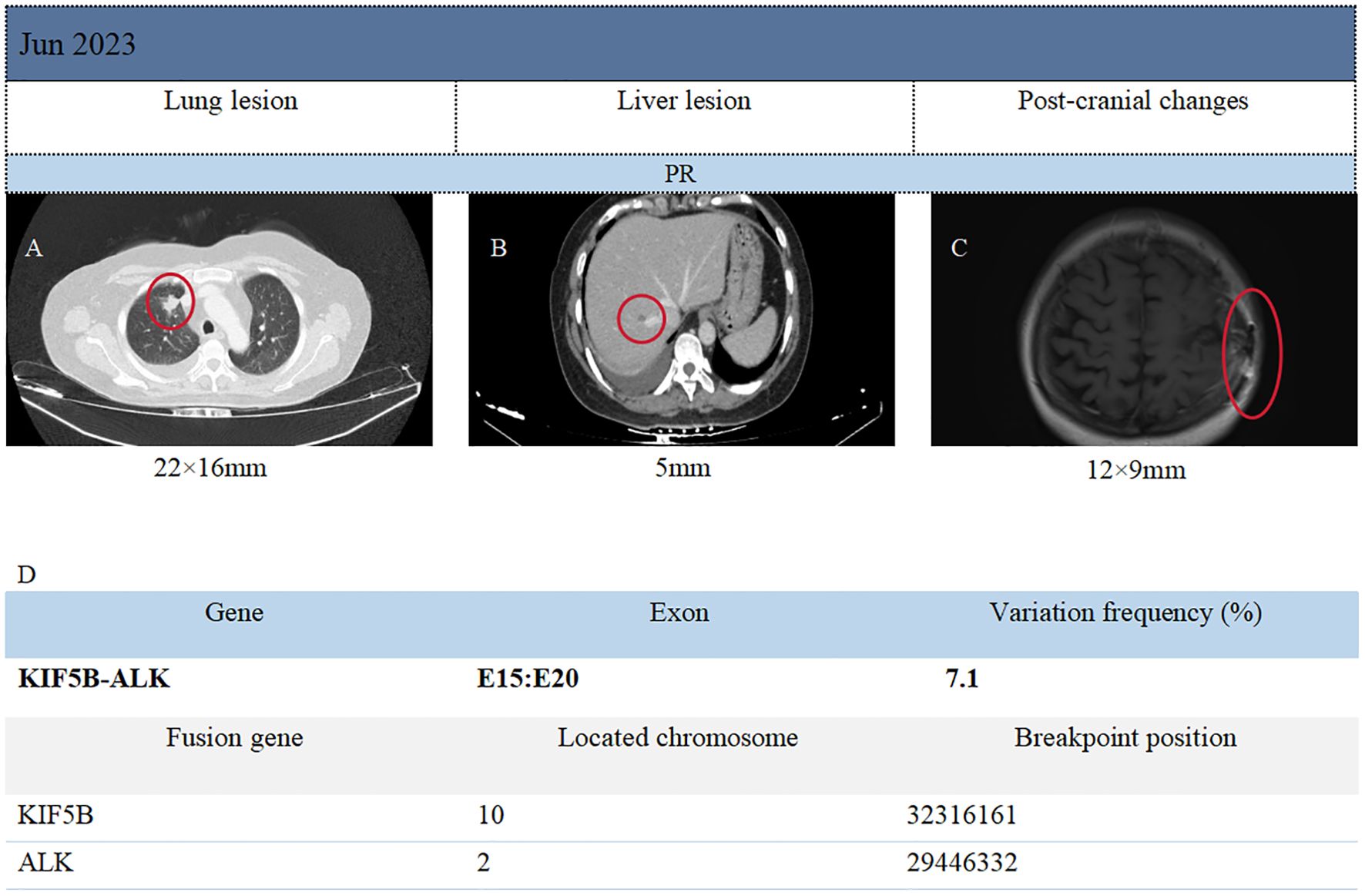
Figure 1. Imaging surveillance of primary and metastatic lesions, as well as presentation of genetic test results.
3 Discussion
3.1 KIF5B gene fusion and its biological functions
The KIF5B gene, first identified in 1996, belongs to the kinesin family of proteins. These proteins facilitate the movement of organelles, proteins, and other cellular components along microtubules. KIF5B exhibits a structural tendency to fuse with kinase genes, such as RET and ALK, leading to the formation of chimeric proteins with constitutive activation that persistently drive downstream signaling pathways, including MAPK and PI3K/AKT (14). The chromosomal region harboring KIF5B may contain fragile sites prone to breakage during DNA replication or repair, increasing the likelihood of rearrangements with other genes. For instance, KIF5B-RET fusions result from breakage and rearrangement of the short arm of chromosome 10 (14). This fusion brings together the RET kinase domain and the coiled-coil domain of KIF5B, producing a constitutively active tyrosine kinase. Similarly, ROS1 and MET can fuse with the 5’ end of KIF5B via their kinase domains, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways. The gene structure, chromosomal location, compatibility of functional domains, transcriptional regulation, and cell type specificity of KIF5B collectively contribute to its frequent rearrangement with other genes, forming a fusion gene with carcinogenic potential (14–16).
KIF5B is particularly important in cell division, ensuring the even distribution of organelles to daughter cells during mitosis, thereby supporting normal cell proliferation and function (15, 17).
3.2 KIF5B-ALK fusion gene
In NSCLC, KIF5B can fuse with ALK, forming the KIF5B-ALK fusion gene. Compared with the more common EML4-ALK fusion, KIF5B-ALK is a rare genetic alteration. Prior research demonstrated that overexpression of KIF5B-ALK in mammalian cells could enhance proliferation, migration, and invasion (8). This fusion protein activates key oncogenic signaling pathways, including:
PI3K/Akt pathway: It promotes cell survival and anti-apoptotic mechanisms, increasing resistance to therapy.
RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway: It drives cell proliferation, migration, and cell cycle regulation.
JAK/STAT pathway: It contributes to cell proliferation and immune evasion.
Additionally, KIF5B-ALK fusion promotes the transition from the G1 to the S phase by activating cyclin-related proteins, such as cyclin D1, further facilitating tumor progression (8, 18).
Most ALK fusion mutations involve breakpoints at exon 20 of ALK. Different fusion partners influence the sensitivity of ALK fusions to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs) (19). Various KIF5B-ALK fusion breakpoints have been reported, each exhibiting different responses to targeted therapies:
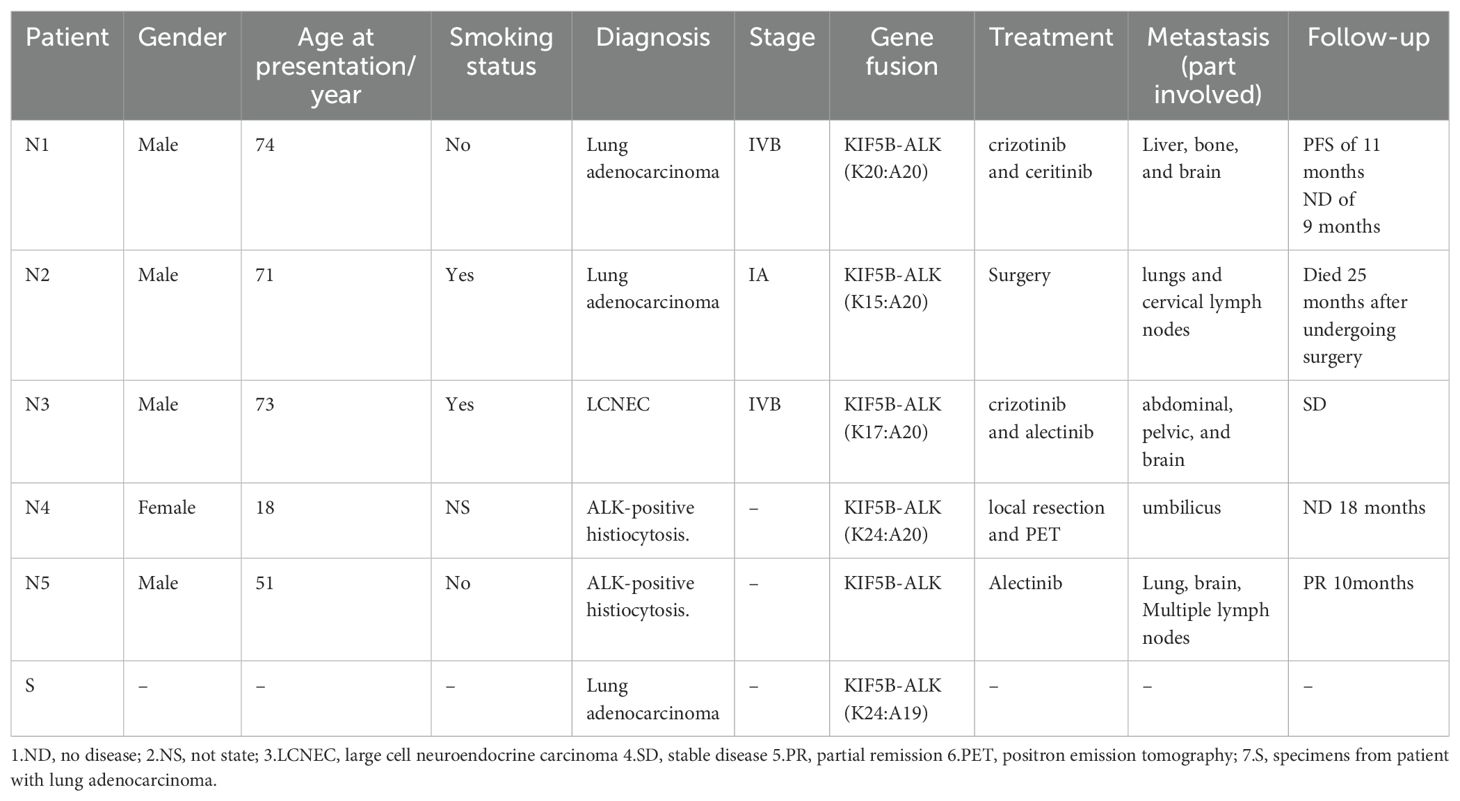
KIF5B-ALK (K24:A19): Takeuchi et al. (7) identified this fusion in a lung adenocarcinoma case (Table 1, case S).
KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20): Wong et al. (8) first reported this fusion in a 71-year-old female with a 5 pack-year smoking history who had quit smoking 30 years prior. The patient was diagnosed with primary lung adenocarcinoma with a maximum tumor diameter of 3 cm. Fourteen months after surgery, recurrence was found in the lung and neck lymph nodes. Without further treatment, the patient succumbed 25 months post-surgery (Table 1, case N2).
KIF5B-ALK (K20:A20): Zeng et al. (20) described a lung adenocarcinoma patient with this fusion who responded to crizotinib, achieving 11 months of PFS before intracranial progression. Upon detection of an ALK L1196M mutation, ceritinib was administered, maintaining efficacy for an additional 9 months. Intracranial lesions showed partial remission (PR) without significant drug-related adverse effects (Table 1, case N1).
KIF5B-ALK (K17:A20): This fusion was first identified in a large-cell neuroendocrine tumor. The patient developed nausea after 8 months of continuous crizotinib use and later experienced gait disturbances 10 months after drug withdrawal. Disease stability was maintained for 4 months following alectinib treatment (21) (Table 1, case N3). Consequently, lung cancer patients with different KIF5B-ALK fusion mutations have demonstrated varying degrees of response to first-generation crizotinib and second-generation TKIs, such as ceritinib and alectinib.
3.3 The efficacy of lorlatinib
Loratinib was approved for second-line and subsequent treatment of ALK-positive metastatic NSCLC, and its indication has since expanded to include first-line treatment (22). It has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in patients with baseline brain metastases, achieving durable intracranial responses. However, current evidence on lorlatinib’s effectiveness in patients with non-EML4 ALK fusion variants remains limited and is primarily focused on ROS1-positive NSCLC. In one reported case, a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma harboring ROS1 rearrangement achieved disease remission following second-line lorlatinib treatment (23). Nonetheless, clinical experience has shown that prolonged lorlatinib use may induce complex ALK resistance mutations, such as G1202R or I1171N/S/T. Ongoing research concentrates on developing more selective lorlatinib analogues through structural modifications to overcome acquired resistance (24).
In this case, the patient’s immunohistochemical analysis confirmed a primary invasive lung adenocarcinoma with high proliferative activity (Ki-67, 80%), indicating aggressive biological behavior. Studies have demonstrated that patients with concurrent ALK mutations experience significantly shorter PFS and lower ORRs after immunotherapy compared with those with wild-type tumors (25). Cai et al. (26) reported that although EML4-ALK mutations are associated with high PD-L1 expression, they do not correlate with increased infiltration of effector T cells, which are critical for anti-tumor immune responses. Numerous clinical studies have confirmed that immunotherapy is largely ineffective in NSCLC patients with EML4-ALK mutations and may even increase the risk of developing resistance to subsequent targeted therapies. Modulating the tumor immune microenvironment may help enhance the sensitivity of these patients to later TKI treatments (27). The intracranial and systemic lesions achieved PR after four months of postoperative lorlatinib treatment and sustained SD after eight months of continuous lorlatinib therapy. The primary AE was grade 1 limb edema. Most lorlatinib-related side effects were grade 1 or 2, while the most common grade 3 AEs were hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia. The dose reduction rate due to AEs was 23%, the temporary withdrawal rate was 62%, and the permanent withdrawal rate was 11%. Notably, dose reductions during the first 16 weeks did not compromise lorlatinib’s efficacy (12, 28). In a phase 1/2 study (29), lorlatinib demonstrated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to free plasma concentration ratios ranging from 0.61 to 0.96, significantly higher than those observed with alectinib (0.002–0.005) and crizotinib (0.0006–0.026), indicating its efficient penetration across the blood-brain barrier. The remarkable intracranial response in this patient provides further clinical evidence, supporting the efficacy of lorlatinib in ALK-positive NSCLC patients with central nervous system involvement. A five-year analysis from the phase 3 CROWN study, presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) meeting, reported that the median PFS for lorlatinib had not yet been reached. This prolonged PFS highlights the drug’s strong systemic and intracranial efficacy, significantly improving outcomes for patients with ALK-positive advanced NSCLC. Among patients with TP53 mutations, lorlatinib achieved a median PFS of 51.6 months versus 5.7 months with crizotinib. In patients without TP53 mutations, the median PFS for lorlatinib-treated cases remains unreached (12). TP53 is a tumor suppressor gene, and its mutation or deletion can result in genomic instability and uncontrolled cell proliferation. The presence of TP53 mutations is generally associated with a poor prognosis and reduced efficacy of TKI therapy in ALK-positive NSCLC patients (23). In the present case, the patient harbored a TP53 frameshift mutation, which could introduce premature stop codons, leading to truncated and potentially non-functional protein products. The patient achieved SD after 8 months of lorlatinib treatment. Ongoing follow-up is required to further assess the patient’s tumor response and disease progression.
3.4 Limitations
This report provided an overview of several KIF5B-ALK fusion mutations with different breakpoints, including a case of advanced lung adenocarcinoma with KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion mutation that responded favorably to lorlatinib. However, several limitations are noteworthy. Firstly, data on the response of other KIF5B-ALK breakpoint variants to lorlatinib are lacking, and the mechanisms underlying differential sensitivity to ALK-TKIs remain elusive. Additionally, the presence of multiple genetic mutations in this patient was not considered when evaluating treatment efficacy. The impact of coexisting TP53 mutation on lorlatinib’s effectiveness warrants further investigation. Long-term follow-up is essential to assess overall survival and quality of life in patients with this fusion mutation.
4 Conclusion
This report described a rare case of advanced lung adenocarcinoma with an ALK fusion and a high number of genetic mutations. The patient, harboring 52 genetic variants, including the KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion, achieved prolonged disease control with lorlatinib following intracranial surgery. This case provided valuable clinical evidence, supporting the use of lorlatinib in patients with the KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion mutation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. WO: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Medjaden Inc. for the scientific editing and proofreading of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cannone G, Comacchio GM, Pasello G, Faccioli E, Schiavon M, and Dell’Amore A. Precision surgery in NSCLC. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:1571. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051571
2. Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Ji JS, and Zou X. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob Health. (2018) 6:e555–e67. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30127-X
3. Sun M, Guo Y, Shao G, Duan X, Yang Z, and Zhang P. Analysis of real-word mutations of lung cancer driver genes in five regions of China. Trans Cancer Res. (2019) 8:2581–92. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.10.28
4. Kong W, Yu Z, Wang W, Yang J, Wang J, and Zhao Z. Gene mutation and its association with clinicopathological features in young patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Emerg Med Int. (2022) 2022:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2022/6333282
5. Li Y, Lu S, Yao P, Huang W, Huang Y, and Zhou Y. Lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis detected dual fusion of LOC399815-ALK and ALK-EML4 in combined treatment of Alectinib and CyberKnife: A case report. Medicine. (2024) 103:e36992. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036992
6. Du X, Shao Y, Qin HF, Tai YH, and Gao HJ. ALK-rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac Cancer. (2018) 9:423–30. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12613
7. Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Togashi Y, Soda M, Hatano S, and Inamura K. KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:3143–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3248
8. Wong DW, Leung EL, Wong SK, Tin VP, Sihoe AD, and Cheng LC. A novel KIF5B-ALK variant in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. (2011) 117:2709–18. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25843
9. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, and Maki RG. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med. (2010) 363:1693–703. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1006448
10. Camidge DR, Kim HR, Ahn MJ, Yang JCH, Han JY, and Hochmair MJ. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK inhibitor-naive advanced ALK-positive NSCLC: final results of phase 3 ALTA-1L trial. J Thorac Oncol. (2022) 16:S1556–0864(22)00349-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.07.035
11. Mok T, Camidge DR, Gadgeel SM, Rosell R, Dziadziuszko R, and Kim DW. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1056–64. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.478
12. Solomon BJ, Liu G, Felip E, Mok TSK, Soo RA, and Mazieres J. Lorlatinib versus crizotinib in patients with advanced ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: 5-year outcomes from the phase III CROWN study. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:3400–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.00581
13. Chayab L, Leighl NB, Tadrous M, Warren CM, and Wong WWL. Trends in real-world clinical outcomes of patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receiving one or more ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): A cohort study in Ontario, Canada. Curr Oncol. (2024) 32. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32010013
14. Lee MR, Shin JY, Kim MY, Kim JO, Jung CK, and Kang J. FOXA2 and STAT5A regulate oncogenic activity of KIF5B-RET fusion. Am J Cancer Res. (2023) 13:638–53.
15. Flex E, Albadri S, Radio FC, Cecchetti S, Lauri A, and Priolo M. Dominantly acting KIF5B variants with pleiotropic cellular consequences cause variable clinical phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. (2023) 32:473–88. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac213
16. Gupta A, Avadhanula S, and Bashyam MD. Evaluation of the gene fusion landscape in early onset sporadic rectal cancer reveals association with chromatin architecture and genome stability. Oncogene. (2024) 43:2449–62. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03088-z
17. Hirokawa N, Noda Y, Tanaka Y, and Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2009) 10:682–96. doi: 10.1038/nrm2774
18. Kemps PG, Picarsic J, Durham BH, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z, Hiemcke-Jiwa L, and van den Bos C. ALK-positive histiocytosis: a new clinicopathologic spectrum highlighting neurologic involvement and responses to ALK inhibition. Blood. (2022) 139:256–80. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021013338
19. Hallberg B and Palmer RH. The role of the ALK receptor in cancer biology. Ann Oncol. (2016) 27 Suppl 3:iii4–iii15. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw301
20. Zeng H, Liu Y, Wang W, Tang Y, Tian P, and Li W. A rare KIF5B-ALK fusion variant in a lung adenocarcinoma patient who responded to crizotinib and acquired the ALK L1196M mutation after resistance: a case report. Ann Palliat Med. (2021) 10:8352–7. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-2081
21. Shimizu N, Akashi Y, Fujii T, Shiono H, Yane K, and Kitahara T. Use of ALK immunohistochemistry for optimal therapeutic strategy of pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and identification of a novel KIF5B-ALK fusion oncokinase. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39:413–20. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13127
22. Liu G and Lam VK. Podcast on lorlatinib as a first-line treatment option for patients with ALK-positive metastatic NSCLC with brain metastasis. Adv Ther. (2023) 40:4117–26. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02606-x
23. Jóri B, Falk M, Hövel I, Weist P, Tiemann M, Heukamp LC, et al. Acquired G2032R resistance mutation in ROS1 to lorlatinib therapy detected with liquid biopsy. Curr Oncol. (2022) 29:6628–34. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090520
24. Shiba-Ishii A, Johnson TW, Dagogo-Jack I, Mino-Kenudson M, Johnson TR, and Wei P. Analysis of lorlatinib analogs reveals a roadmap for targeting diverse compound resistance mutations in ALK-positive lung cancer. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:710–22. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00399-6
25. Hu H. Complete response to anti-PD1 therapy and chemotherapy in a patient with ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2025) 18:37–41. doi: 10.62347/XWHW6190
26. Cai R, Zhu H, Liu Y, Sha H, Peng W, and Yin R. To be, or not to be: the dilemma of immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer harboring various driver mutations. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:10027–40. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04919-4
27. Hernández de Córdoba I, Mielgo-Rubio X, Cejas P, Palomar Ramos J, Garrido-Rubiales B, and Falagán Martínez S. Transformation to neuroendocrine phenotype in non-small-cell lung carcinoma: A literature review. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115096
28. El Darsa H, Abdel-Rahman O, and Sangha R. Pharmacological and clinical properties of lorlatinib in the treatment of ALK-rearranged advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. (2020) 21:1547–54. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1774552
Keywords: KIF5B-ALK gene fusion, non-small cell lung cancer, anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors, loratinib, case report
Citation: Luo Y and Ouyang W (2025) Case Report: A rare case of ALK-KIF5B gene fusion benefited from treatment with lorlatinib. Front. Oncol. 15:1594072. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1594072
Received: 15 March 2025; Accepted: 09 July 2025;
Published: 07 August 2025.
Edited by:
Lucia Anna Muscarella, Home for Relief of Suffering (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Domenico Trombetta, IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza Hospital, ItalyMarco Donatello Delcuratolo, IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza Hospital, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Luo and Ouyang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weiwei Ouyang, b3V5YW5nd3cxMDMxNzNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Yuxi Luo
Yuxi Luo Weiwei Ouyang
Weiwei Ouyang