- 1Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian, China
- 2School of Clinical Medicine, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian, China
- 4Department of Anorectal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian, China
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of the preoperative fibrinogen and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) combination score (F-PNI) in predicting long-term survival following radical gastrectomy in patients diagnosed with resectable gastric cancer.
Methods: A retrospective cohort analysis was performed using clinicopathological and follow-up data from 491 patients who underwent radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer at a single tertiary institution between January 2012 and December 2017. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 25.0 to identify independent prognostic factors associated with five-year overall survival.
Results: The optimal preoperative cut-off values were identified as 3.335 mg/L for fibrinogen and 52.7 for the PNI. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for the F-PNI score was 0.633, demonstrating higher discriminative ability compared to PNI alone (AUC = 0.592) and fibrinogen alone (AUC = 0.587). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed five-year survival rates as follows: low vs. high fibrinogen levels, 72.9% vs. 56.4%; high vs. low PNI, 82.6% vs. 58.0%; and F-PNI score 0, 1, and 2, 87.8%, 66.9%, and 50.0%, respectively. Both univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models identified a high F-PNI score, advanced age, pathological TNM stage IIIA–IIIC, and vascular invasion as independent prognostic factors for five-year survival. The F-PNI score demonstrated superior prognostic performance compared to either fibrinogen or PNI alone.
Conclusion: The F-PNI combination score is an independent prognostic marker for long-term survival in patients undergoing radical resection for resectable gastric cancer. Its enhanced predictive accuracy relative to fibrinogen or PNI individually suggests potential utility in preoperative prognostic stratification.
1 Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is a prevalent malignancy, ranking fifth in global cancer incidence and third in cancer-related mortality worldwide (1). In its early stages, GC is frequently asymptomatic or presents with nonspecific symptoms, leading to a high proportion of cases being diagnosed at an advanced stage. Although radical surgery combined with postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy has improved survival outcomes, a substantial number of patients experience postoperative recurrence, metastasis, or tumor-related mortality, resulting in suboptimal long-term prognosis (2).
Current prognostic evaluation for GC primarily relies on the tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging system, which assesses key pathological characteristics, including depth of tumor invasion (T), lymph node involvement (N), and the presence of distant metastasis (M). However, the TNM system alone does not fully account for the biological heterogeneity of GC, as various additional factors influence long-term outcomes. Previous studies have demonstrated that systemic inflammation, hypercoagulability, and malnutrition are significantly associated with unfavorable prognosis following radical gastrectomy (3).
In recent years, several prognostic scoring systems incorporating hematological biomarkers have been developed to improve the accuracy of survival prediction in GC. These systems evaluate parameters such as systemic inflammatory response, coagulation status, and nutritional condition, all of which have been shown to correlate with clinical outcomes. Given that these biomarkers are routinely assessed through accessible, cost-effective blood tests, they hold considerable clinical value in prognostic stratification for patients with GC.
Fibrinogen (Fib), is widely recognized as a marker of systemic inflammation and hypercoagulability. Multiple studies have confirmed a strong association between elevated Fib levels and poor oncologic outcomes (4). The Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI), calculated using serum albumin concentration and peripheral lymphocyte count, is a well-established indicator of nutritional and immune status.
Despite their individual prognostic relevance, the utility of single biomarkers may be constrained by limited sensitivity and specificity. While Fib predominantly reflects systemic inflammation and coagulation, PNI more accurately reflects nutritional status. Recent evidence supports the integration of multiple biomarkers to enhance predictive performance. Consequently, this study evaluates the combined prognostic value of preoperative Fib and PNI—the F-PNI score, in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy for resectable GC, with the aim of improving long-term survival prediction.
Given the substantial heterogeneity in physiological and pathological characteristics among patients with malignant disease, personalized therapeutic strategies are critical to optimizing clinical outcomes. Identifying high-risk subgroups and clinically relevant prognostic markers is essential for guiding individualized treatment planning in GC.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Research participants
A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients diagnosed with resectable GC who underwent radical gastrectomy at the Affiliated Hospital of Putian University between January 2012 and December 2017. Comprehensive clinical and pathological data were collected for analysis.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) histopathologically confirmed diagnosis of GC without evidence of distant metastasis detected preoperatively or intraoperatively; (2) no history of neoadjuvant chemotherapy or neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; (3) postoperative pathological confirmation of R0 resection; (4) availability of complete preoperative hematological examination results, including Fib levels, serum albumin values, and peripheral blood lymphocyte count; and (5) completeness of postoperative pathological data and follow-up information.
The exclusion criteria included the following: (1) presence of distant metastasis or primary malignant tumors in other internal organs; (2) acute inflammatory diseases, liver cirrhosis, chronic renal failure, autoimmune diseases, or hematopoietic system disorders; (3) incomplete clinical data or loss to follow-up. (4) patients with acute inflammatory diseases, liver cirrhosis, chronic renal failure, autoimmune diseases, hematologic disorders, or other primary malignancies in different organs.
A total of 491 patients met the inclusion criteria and were enrolled in the study. The surgical procedure and extent of lymphadenectomy were performed in accordance with the Japanese Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines. Pathological staging was conducted based on the eighth edition of the TNM classification system, jointly established by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC).
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Putian College. All procedures were conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments. As this was a retrospective study with anonymized data and no identifiable patient information, the requirement for informed consent was waived.
2.2 Data and general information
General patient information, including age and sex, was obtained from medical records. Tumor-related pathological data included maximum tumor diameter, anatomical location, histological differentiation, presence of vascular and perineural invasion, depth of invasion (T stage), regional lymph node metastasis (N stage), and overall TNM classification. Clinical parameters comprised preoperative Fib levels, serum albumin concentration, peripheral blood lymphocyte count, and whether postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy was administered.
Fasting peripheral blood samples were collected within one week prior to surgery for laboratory analysis. The PNI was calculated using the following formula:
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was employed to determine the optimal cut-off values for Fib and PNI, allowing for the stratification of patients into prognostic subgroups. The F-PNI was defined according to the following criteria: Patients with low Fib and high PNI were classified as F-PNI = 0. Those with either high Fib and high PNI or low fibrinogen and low PNI were assigned an F-PNI score of 1. Patients exhibiting high Fib and low PNI were designated as F-PNI = 2.
2.3 Follow-up data
Patients were followed up regularly through outpatient clinic visits, hospital admissions, or telephone consultations. During the first two years postoperatively, follow-up assessments were conducted every three months. From the third to the fifth postoperative year, evaluations occurred at six-month intervals. After five years, annual follow-up visits were scheduled.
Each follow-up included routine hematological and biochemical testing, measurement of gastric tumor markers, imaging studies such as abdominal ultrasonography or computed tomography (CT), and annual upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Survival time was defined as the interval from the date of surgery to either the date of death or the most recent follow-up contact. As of December 2022, the median follow-up duration was 48 months. The five-year survival time and overall survival rate were calculated accordingly.
2.4 Statistical methods
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 25.0. Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation, and intergroup comparisons were conducted using the independent samples t-test. Categorical variables were analyzed using the chi-squared test.
ROC curve analysis was used to determine the optimal cut-off values for preoperative fibrinogen and PNI. The prognostic performance of each variable was assessed accordingly. Survival outcomes were evaluated using the Kaplan–Meier method, with survival curves compared using the log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were performed to identify independent prognostic factors associated with five-year overall survival following radical gastrectomy for resectable GC. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Result
3.1 General clinical and pathological data
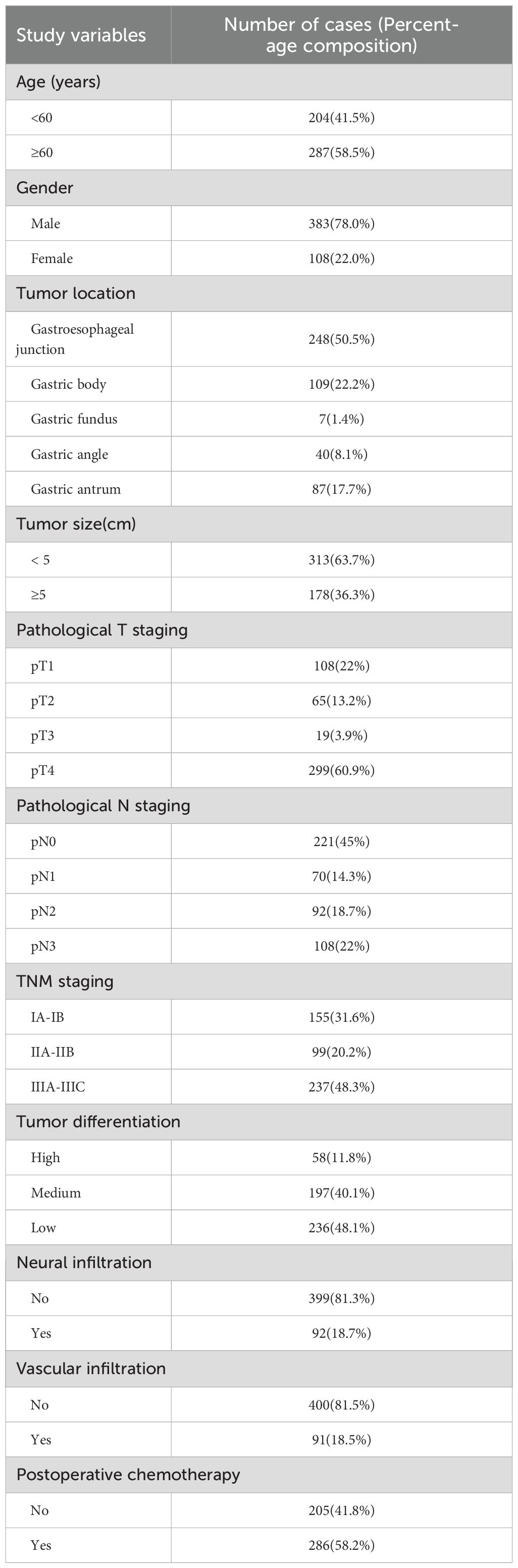
Among the 491 patients included in the study, a total of 168 deaths were recorded during the follow-up period. The five-year overall survival rate was 65.8%, with a median follow-up duration of 50 months. GC was more frequently diagnosed in male patients, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 3.8:1. The majority of cases occurred in older adults, and tumors were most commonly located in the cardia. A considerable proportion of patients received postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.
Pathological evaluation revealed that tumors with a maximum diameter of less than 5 cm were relatively common. The pathological T4 stage was the most frequently observed, and regional lymph node metastasis was identified in approximately 50% of cases. Pathological TNM stages II and III were predominant, comprising 336 patients (68.5%). Most tumors were classified as poorly or moderately differentiated, accounting for approximately 88.2% of the cohort. Perineural invasion was present in 18.7% of patients, while vascular invasion was observed in 18.0% (see Table 1).
These findings suggest that the majority of patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage of GC.
3.2 Determination of optimal cut-off values for preoperative Fib, PNI, and their correlation with clinical characteristics
ROC curve analysis was performed using preoperative Fib and PNI values to evaluate their predictive performance for five-year overall survival in the cohort of 491 patients. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) for Fib was 0.572 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.516 – 0.628, p = 0.012), while the AUC for PNI was 0.604 (95% CI: 0.552 – 0.606, p < 0.001) (see Figure 1). The optimal cut-off values, determined based on the maximum Youden’s index, were 3.335 mg/L for Fib (sensitivity: 0.553; specificity: 0.380) and 52.7 for PNI (sensitivity: 0.823; specificity: 0.369). Based on these thresholds, patients were stratified into low Fib (≤ 3.335 mg/L) and high Fib (> 3.335 mg/L) groups, as well as low PNI (≤ 52.7) and high PNI (> 52.7) groups.
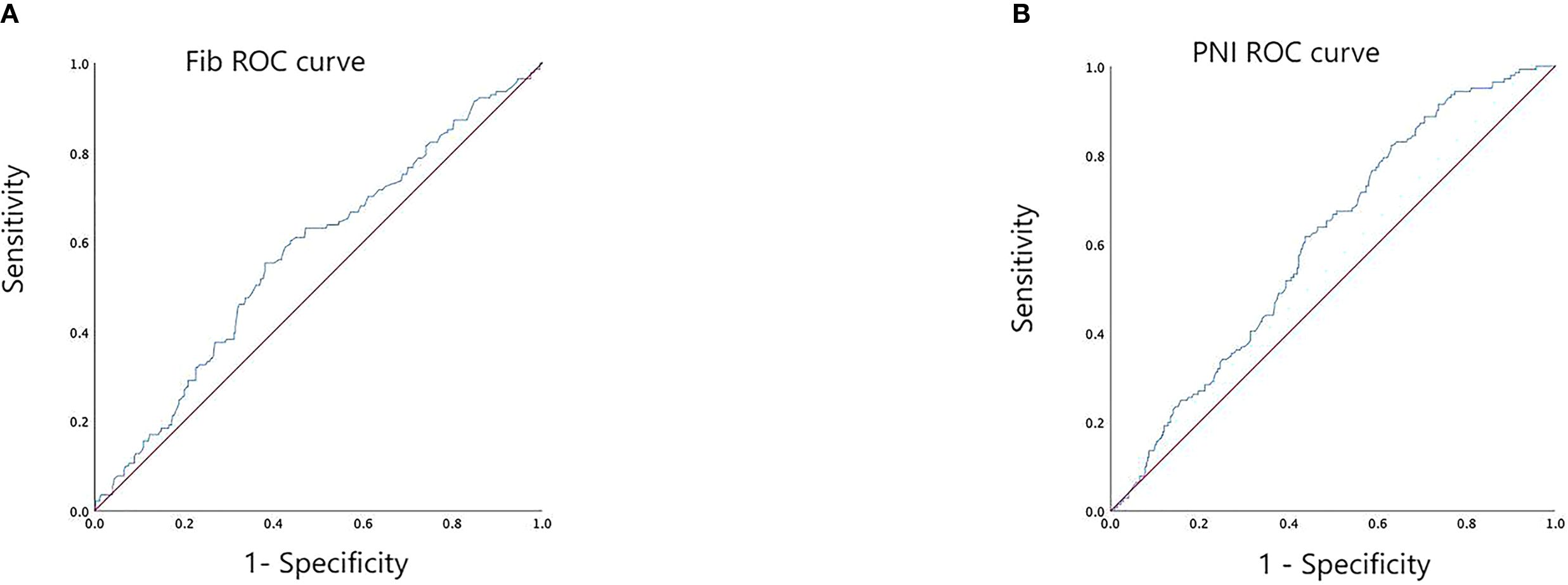
Figure 1. ROC curve analysis for determining the optimal cut-off values of preoperative Fib (A) and PNI (B).
Comparative analysis between the low and high Fib groups showed that patients in the high Fib group were more likely to present with larger tumors, more advanced pathological T, N, and TNM stages, lower histological differentiation, and an increased likelihood of receiving postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. These differences were statistically significant (p < 0.05). No significant differences were observed between the groups with respect to age, sex, tumor location, or the presence of perineural or vascular invasion (p > 0.05).
Similarly, comparison between the low and high PNI groups revealed that patients in the low PNI group were more likely to be older, male, and have tumors exceeding 5 cm in diameter. These patients more frequently presented with tumors of intermediate to advanced pathological T, N, and TNM stages, poorer differentiation, and a higher incidence of perineural and vascular invasion. A greater proportion of patients in the low PNI group also received postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. These differences were statistically significant (p < 0.05). No significant association was found between PNI group and tumor location (p > 0.05) (see Table 2).
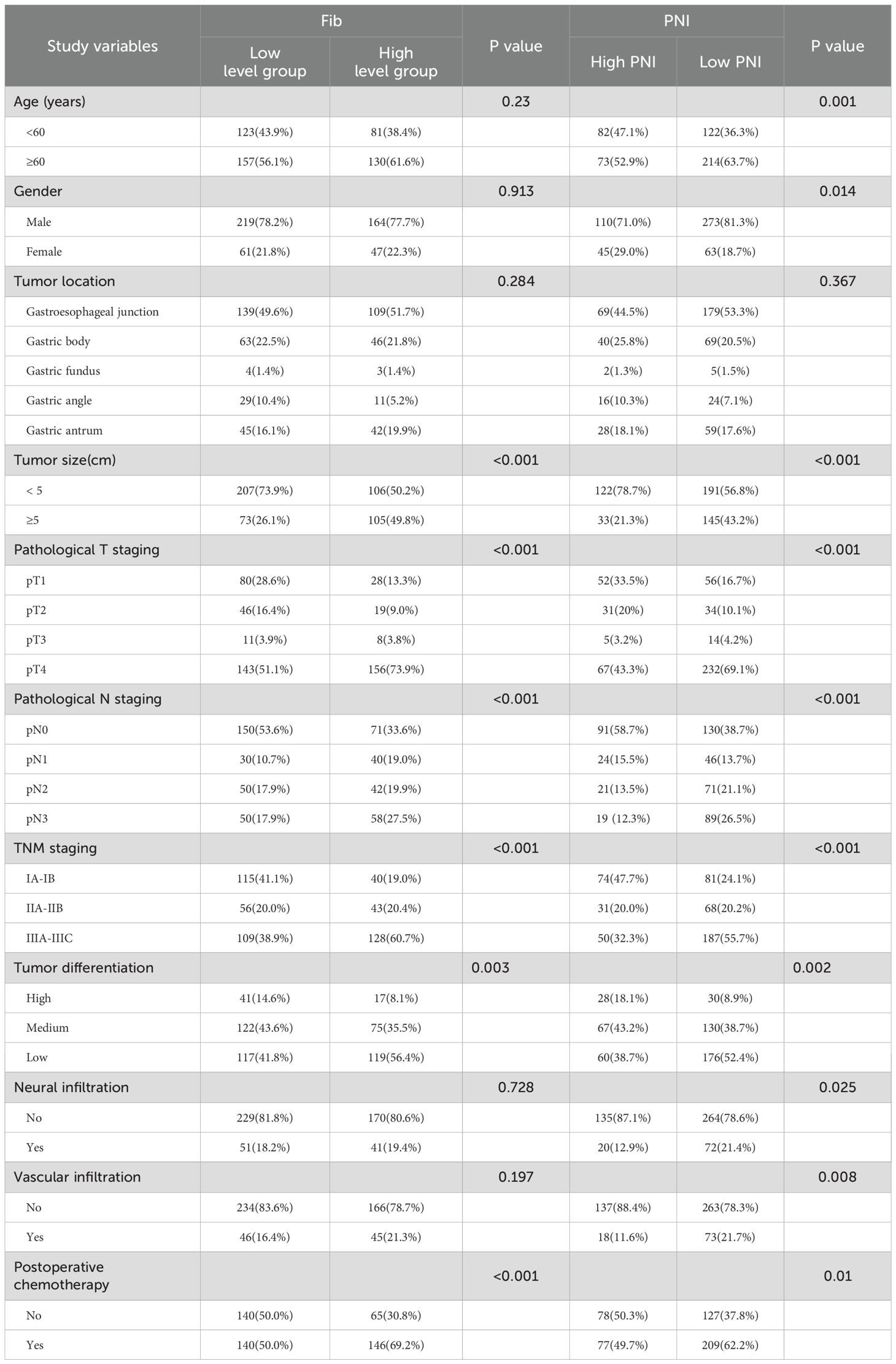
Table 2. Relationship between preoperative Fib and PNI and clinicopathological features of gastric cancer patients.
3.3 The value of Fib, PNI, and F-PNI in prognostic assessment
The F-PNI score was calculated based on preoperative Fib and PNI levels. A score of 0 was assigned to patients with low Fib and high PNI levels. A score of 1 was assigned when both Fib and PNI levels were either high or low. A score of 2 was assigned to patients with high Fib and low PNI levels. Based on this classification, the study cohort was divided into three groups: 98 patients (F-PNI = 0), 239 patients (F-PNI = 1), and 154 patients (F-PNI = 2).
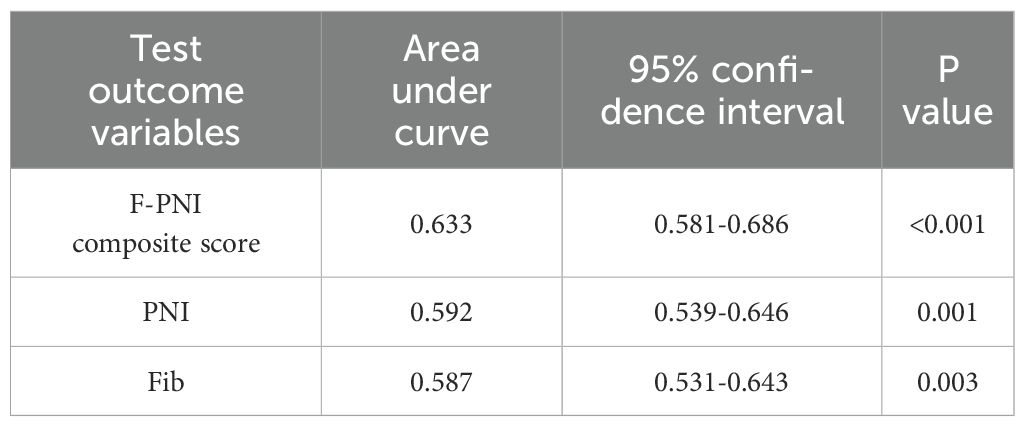
ROC curve analysis was used to compare the prognostic performance of Fib, PNI, and the combined F-PNI score. The AUC for the F-PNI score was 0.633, which was greater than that of PNI (AUC = 0.592) and Fib (AUC = 0.587), as shown in Table 3. These results suggest that the F-PNI score offers superior prognostic discrimination for long-term survival following radical gastrectomy compared to either biomarker alone. The comparative ROC curves are shown in Figure 2.
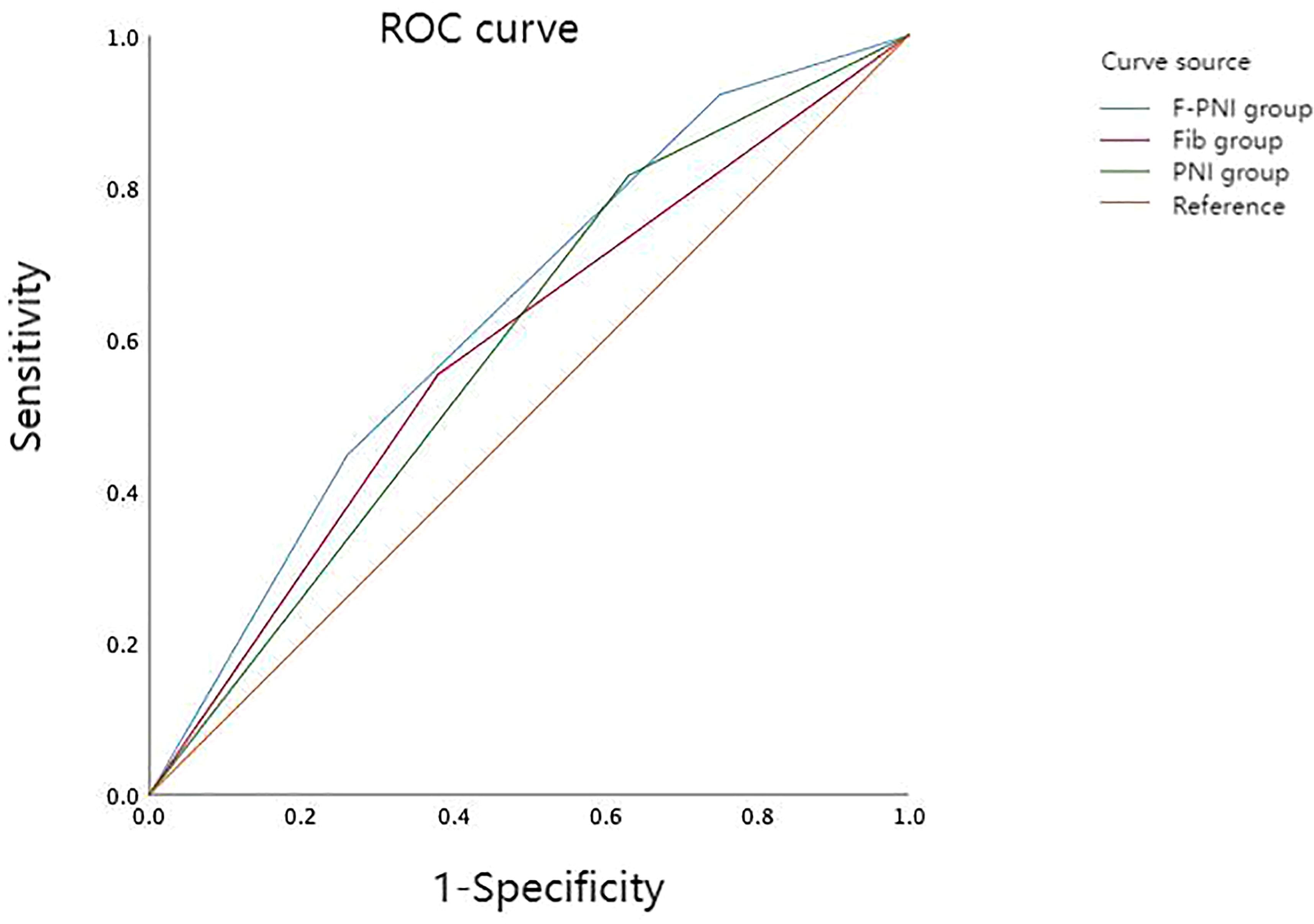
Figure 2. Comparison of predictive performance among prognostic indicators for overall survival in GC. AUC for F-PNI = 0.633; PNI = 0.592; Fib = 0.587.
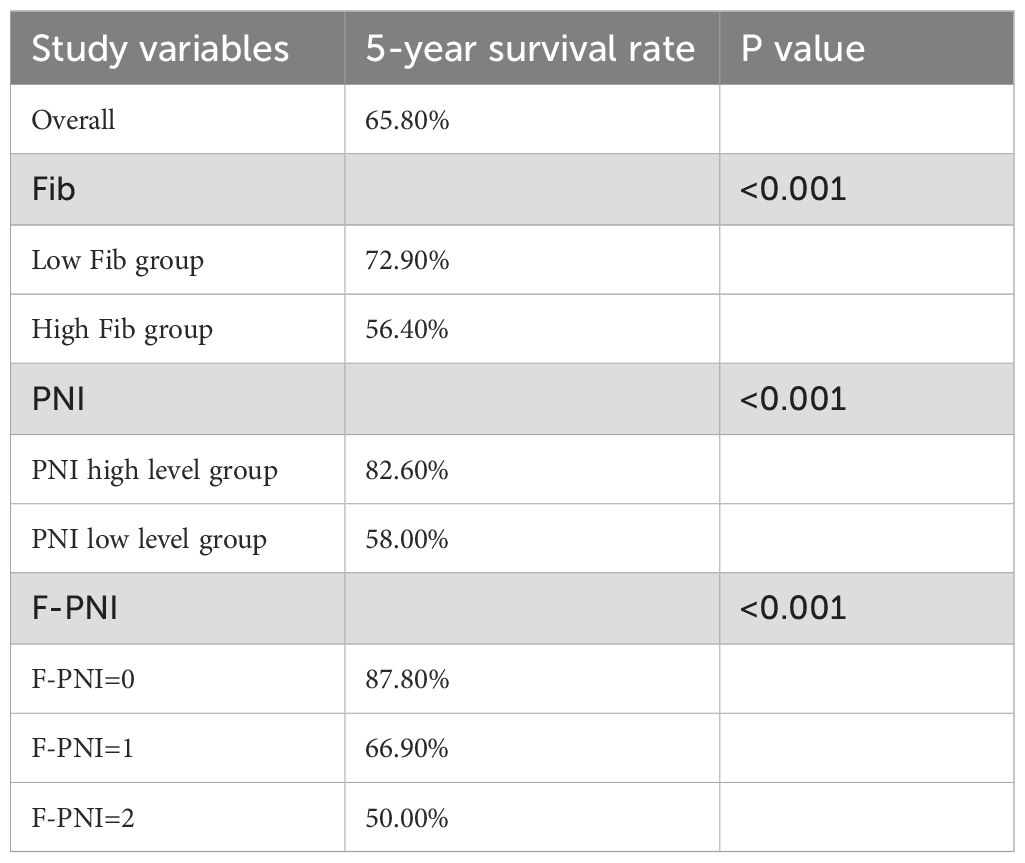
The association between Fib, PNI, and F-PNI scores and five-year overall survival was further examined using Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. The overall five-year survival rate among the 491 patients was 65.8%.
Patients in the low Fib group demonstrated a significantly higher five-year survival rate (72.9%) compared to those in the high Fib group (56.4%) (p < 0.001) (see Figure 3A). Similarly, survival outcomes were significantly better in the high PNI group (82.6%) compared to the low PNI group (58.0%) (p < 0.001) (see Figure 3B). A strong association was also observed between the F-PNI score and long-term survival. The five-year survival rates were 87.8% for patients with F-PNI = 0, 66.9% for those with F-PNI = 1, and 50.0% for those with F-PNI = 2 (p < 0.001), indicating statistically significant differences among the three groups (see Figure 3C).
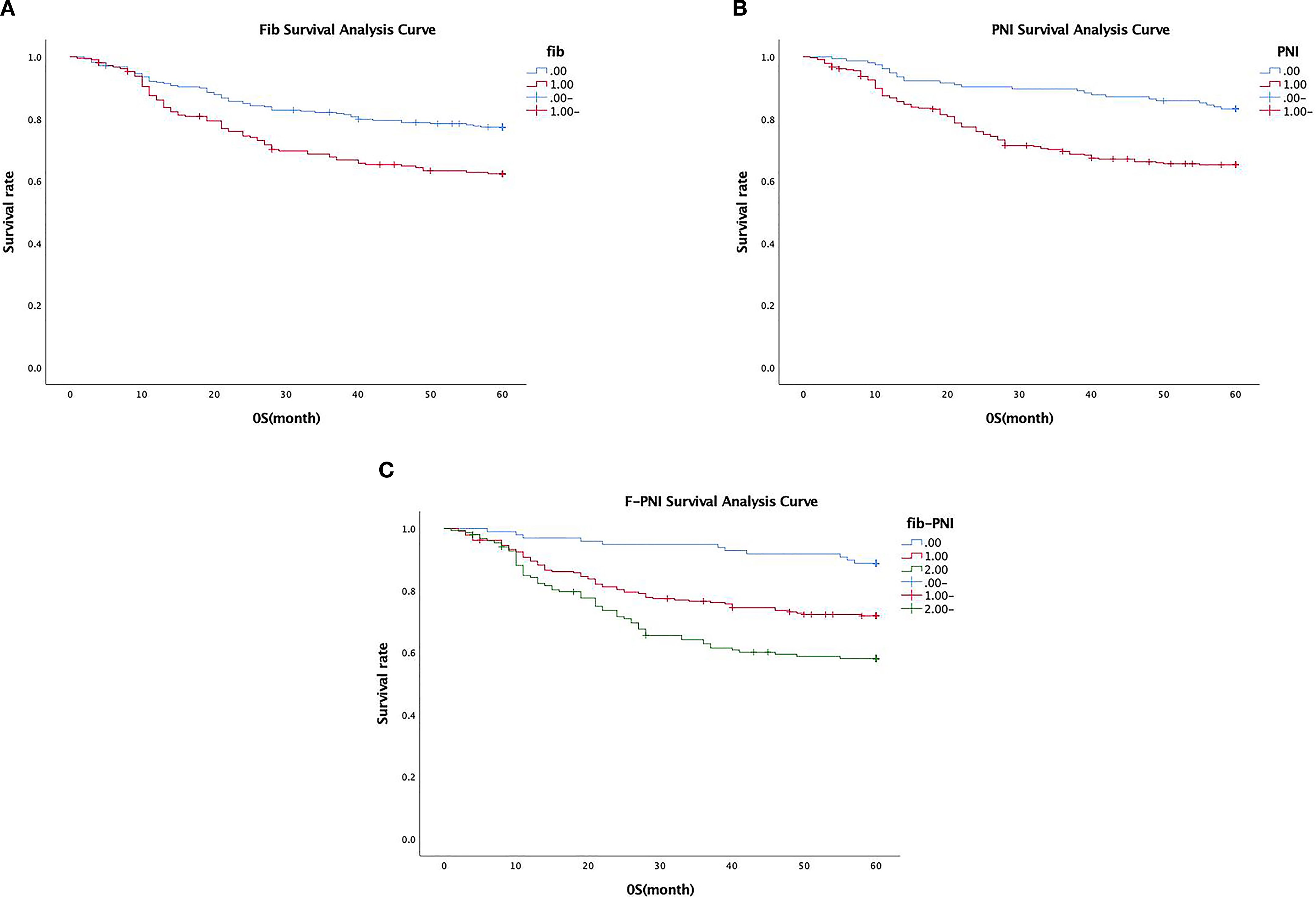
Figure 3. Association between preoperative Fib (A), PNI (B), and combined F-PNI (C) scores and five-year survival in GC. All differences were statistically significant (p < 0.01).
Detailed five-year survival data stratified by Fib, PNI, and F-PNI scores are presented in Table 4.
3.4 Correlation between the composite F-PNI score and clinicopathological characteristics
The composite F-PNI score demonstrated significant associations with several clinicopathological parameters. Higher F-PNI scores were observed in a greater proportion of older patients and were associated with larger tumor diameters and more advanced pathological staging, including T stage, N stage, and overall TNM classification. An increase in F-PNI score also corresponded with poorer tumor differentiation, a higher incidence of vascular invasion, and a greater likelihood of receiving postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. These differences among the F-PNI score groups were statistically significant (p < 0.05).
In contrast, no statistically significant associations were identified between the F-PNI score and patient sex, tumor location, or the presence of perineural invasion (p > 0.05) (see Table 5).
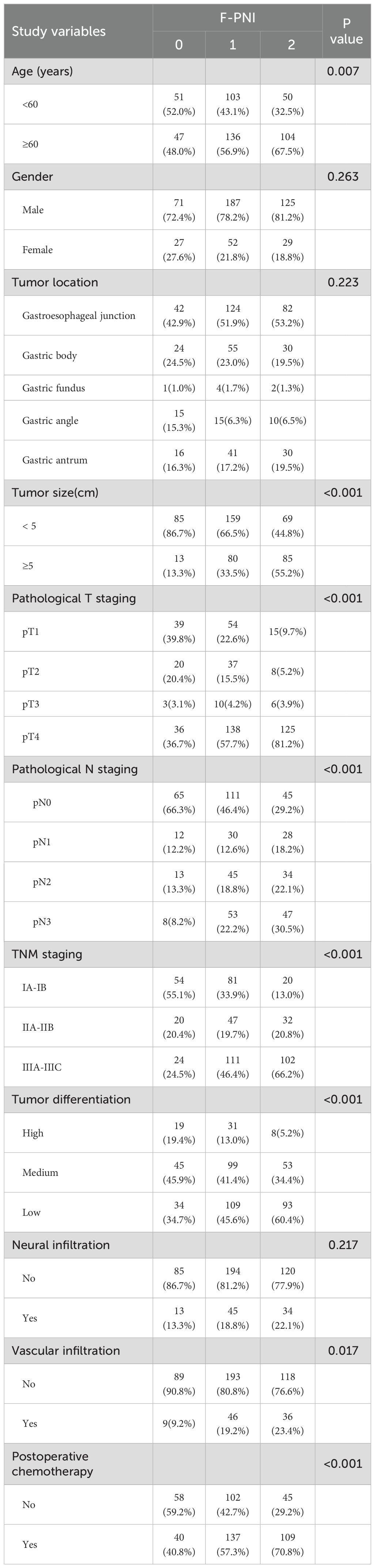
Table 5. The relationship between F-PNI analysis and clinicopathological features of gastric cancer patients.
3.5 Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis of factors influencing the 5-year survival rate
Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were conducted to evaluate factors associated with five-year overall survival, incorporating Fib, PNI, the combined F-PNI score, and other relevant clinicopathological variables. The multivariate analysis identified the F-PNI score as an independent prognostic factor. Using F-PNI = 0 as the reference category, patients with F-PNI = 1 had a significantly increased risk of mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 2.554, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.275 – 5.117, p = 0.008), and those with F-PNI = 2 had an even greater risk (HR 2.736, 95% CI: 1.357 – 5.518, p = 0.005).
Additional independent prognostic factors included advanced age (HR 1.664, 95% CI: 1.177 – 2.353, p = 0.004), pathological TNM stage IIIA–IIIC (HR 13.713, 95% CI: 6.312 – 29.790, p < 0.001), and the presence of vascular invasion (HR 1.499, 95% CI: 1.062 – 2.117, p = 0.021).
These findings support the superior prognostic value of the combined F-PNI score over Fib and PNI as individual biomarkers in predicting long-term survival following radical gastrectomy (see Table 6).
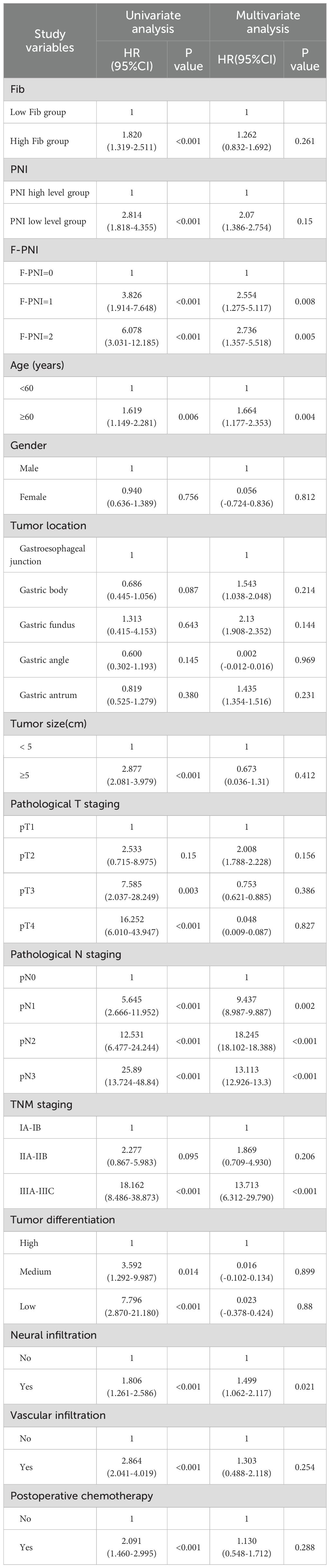
Table 6. Univariate analysis and Multivariate analysis on the 5-year survival rate of gastric cancer patients.
4 Discussion
Advancements in the comprehensive management of GC in recent years have contributed to improved survival rates and enhanced quality of life for patients (5). Despite these gains, GC continues to be associated with poor prognosis, largely due to late-stage diagnosis in a substantial proportion of cases. In the present study, most patients were diagnosed at advanced stages, consistent with the ongoing clinical challenge of early detection and the associated negative impact on long-term outcomes.
Various prognostic scoring systems based on hematological biomarkers have recently demonstrated potential in predicting survival outcomes in GC. These systems typically assess clinical features such as hypercoagulability, nutritional status, and systemic inflammation—factors that have been shown to influence tumor progression and overall prognosis (6). In this study, Fib and the PNI were selected as representative biomarkers reflecting these physiological domains.
Both Fib and PNI are derived from routine blood tests, making them simple, accessible, and cost-effective tools in clinical practice. Because these parameters can be obtained through standard preoperative testing, they hold considerable clinical value for the prognostic evaluation of patients with GC. The integration of such streamlined screening measures facilitates the early identification of high-risk patients and supports the development of personalized, risk-adapted treatment strategies. These individualized approaches may contribute to improved survival outcomes and more efficient allocation of clinical resources.
4.1 Impact of Fib on the five-year post-operative survival rate
Fib is a glycoprotein synthesized by the liver that plays a central role in the coagulation cascade and serves as a biomarker of hypercoagulability (7). Previous studies have established strong associations between elevated Fib levels and tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Fib contributes to tumor progression through its conversion into fibrin, which promotes angiogenesis and facilitates tumor invasion and metastasis (8).
Fib plays a key role in the coagulation cascade and has been identified as a relevant biomarker in oncologic prognostication. Numerous studies have demonstrated that elevated plasma Fib levels are associated with tumor progression, local invasion, distant metastasis, and poor clinical outcomes in patients with GC (9, 10). Increased Fib concentrations are often indicative of more advanced tumor stages and are linked to reduced survival durations.
Ding et al. reported that malignant tumors are frequently accompanied by hypercoagulable states and enhanced conversion of Fib to fibrin, a process that contributes to tumor proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastatic spread, thereby resulting in worse prognostic outcomes (10). In the present study, both univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that patients with elevated preoperative Fib levels had significantly lower five-year survival rates and shorter overall survival compared to those with lower Fib levels. These findings reinforce the role of Fib as an independent prognostic risk factor in resectable GC and are consistent with previous literature.
4.2 Impact of PNI on the five-year post-surgery survival rate
PNI, derived from serum albumin concentration and peripheral lymphocyte count, is a well-established indicator for assessing preoperative immune competence and nutritional status in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery (11). Prior research has consistently demonstrated that nutritional and immune status at the time of diagnosis significantly influences clinical outcomes and overall prognosis in patients with malignant tumors (12). Reduced PNI values are frequently indicative of malnutrition and immunosuppression, both of which have been associated with poor survival outcomes.
In recent years, PNI has gained increasing recognition as a simple, cost-effective, and clinically relevant prognostic biomarker across various malignancies (13). Malignant tumors often increase systemic metabolic demands, leading to enhanced protein catabolism and nutritional depletion. In the present study, PNI was identified as an independent prognostic factor affecting long-term survival in patients with resectable GC. Patients with lower PNI values exhibited shorter survival durations, decreased five-year survival rates, and poorer overall prognoses.
Multiple studies have validated the prognostic utility of PNI in colorectal, gastric, lung, urothelial, and hepatic cancers, as well as in several other malignancies (14). A prospective study reported that PNI not only predicts postoperative complications in colorectal cancer but may also confer a protective effect against their occurrence (15). Furthermore, PNI has been established as a significant predictor of short-term postoperative complications following radical resection of colorectal tumors. Sugawara et al. found that lower PNI levels were strongly associated with advanced patient age and more advanced pathological staging, findings that are consistent with the present study (16). Similarly, Luo et al. identified low PNI as an independent risk factor for overall survival and recurrence-free survival following gastrectomy (17). Migita et al. also reported that changes in PNI levels were independent predictors of disease-specific and overall survival in patients with GC following radical resection (18). Patients with decreased PNI were more prone to distant metastasis than those with increased or stable PNI.
4.3 Comparison of combined Fib and PNI scoring versus the predictive ability of individual Fib and PNI indicators
This study evaluated the prognostic value of preoperative Fib and PNI in predicting long-term survival in patients undergoing radical resection for resectable GC. Analysis of clinicopathological characteristics demonstrated that elevated Fib levels and low PNI values were significantly associated with advanced tumor stage, decreased five-year survival rates, and shorter overall survival durations. Both biomarkers were identified as potential prognostic risk factors in this patient population.
Given the limitations of Fib and PNI as standalone indicators, a combined scoring system (F-PNI) was investigated to improve predictive accuracy. ROC curve analysis was used to assess the prognostic performance of each marker. The AUC was 0.587 for Fib and 0.592 for PNI. When integrated into the composite F-PNI score, the AUC increased to 0.633, which was significantly higher than that of either biomarker alone (p < 0.05). This finding indicates that the F-PNI score provides superior discriminatory ability in predicting overall mortality following radical gastrectomy.
Although the individual AUC values fell within the moderate range (0.60 – 0.65), their combined use improved prognostic accuracy. This suggests that single biomarkers may not sufficiently capture the multifactorial nature of GC progression and prognosis. Despite the moderate AUC, Fib, PNI, and F-PNI were all included in both univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Among these, only the F-PNI score emerged as an independent prognostic factor influencing five-year overall survival.
The findings of this study confirm that the combined F-PNI score demonstrates superior prognostic performance compared to Fib and PNI when used independently. Higher F-PNI scores were associated with more advanced tumor stages, lower five-year survival rates, and poorer overall outcomes, underscoring its relevance as a prognostic biomarker in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy for resectable GC. As an easily obtainable and cost-effective parameter derived from routine preoperative testing, the F-PNI score holds significant clinical value for risk stratification and individualized treatment planning. However, the absence of external validation and the lack of sensitivity analyses represent limitations of this study. Further prospective, multicenter investigations are warranted to validate the generalizability and clinical applicability of the F-PNI scoring system.
4.4 Preoperative optimization strategies for high F-PNI scores
There is increasing international recognition of the importance of comprehensive management strategies for GC, which now encompass not only neoadjuvant therapy, surgical resection, and postoperative adjuvant chemoradiotherapy, but also interventions aimed at improving nutritional and inflammatory status (19–22). Nutritional support, in particular, has emerged as a key component of cancer care. Evidence suggests that effective nutritional interventions can significantly reduce the incidence of treatment-related complications and improve both immune and nutritional function in patients with GC (23).
For patients with a low PNI, targeted nutritional support plays a pivotal role in improving clinical outcomes. In those with preserved gastrointestinal function, the use of enteral nutrition formulas enriched with immunomodulatory components is recommended (24). Daily protein intake should be increased to 1.5–2.0 g/kg of body weight, with additional supplementation of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and glutamine. ω-3 fatty acids may indirectly reduce Fib levels by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (25), while glutamine contributes to the protection of the intestinal mucosal barrier and mitigates inflammatory responses associated with endotoxin translocation (26).
In patients with impaired oral intake or malabsorption, parenteral nutrition should be initiated. This includes supplementation with amino acids, fat emulsions, and vitamins via central venous access to address hypoalbuminemia and overall nutritional deficiencies. In cases of elevated Fib levels, nutritional support should be complemented by anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant therapies. Low-molecular-weight heparin is recommended due to its dual function in inhibiting coagulation factors and modulating inflammatory responses, thereby reducing Fib synthesis (27).
For patients with markedly elevated Fib concentrations (>5 g/L), short-term use of low-dose antifibrinolytic agents such as batroxobin may be considered (28). Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be administered to attenuate systemic inflammation and suppress Fib production by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 activity (29).
Importantly, these preoperative interventions should be closely integrated into the broader oncologic treatment plan. During the course of nutritional, anti-inflammatory, and anticoagulant support, regular monitoring of PNI and Fib levels is essential. A multidisciplinary, synergistic approach to regulating these parameters within an optimal range prior to surgery may reduce the incidence of postoperative complications and improve long-term outcomes in patients with GC.
5 Conclusion
The combined F-PNI score was identified as an independent prognostic factor for long-term survival in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy for resectable GC. Compared with Fib and PNI assessed individually, the F-PNI score demonstrated superior predictive performance. Given its accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and association with key pathological features and survival outcomes, the F-PNI score holds significant clinical utility as a preoperative risk stratification tool in the management of GC.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Putian University (No. 2025133). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. CZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YC: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. WL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, No. 2022J011442.
Acknowledgments
We are particularly grateful to all the people who have given us help on our article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AUC, Area under the curve; GC, Gastric cancer; Fib, Fibrinogen; PNI, Prognostic Nutritional Index; ROC, Receiver operating characteristic curve; AUC, area under the ROC curve.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Zhang Y, Zhu C, and Lu X. Advances in serum biomarkers for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2019) 48:326–33. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2019.06.14
3. Xie K, Feng W, Liu Z, Lei H, Liu H, and Tang M. Predictive value of preoperative L3-SMI, AGR, and PNI for overall survival in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2025) 50:204–14. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2025.240521
4. Gao W, Zhang F, Ma T, and Hao J. High preoperative fibrinogen and systemic inflammation response index (F-SIRI) predict unfavorable survival of resectable gastric cancer patients. J Gastric Cancer. (2020) 20:202–11. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2020.20.e18
5. Tan Z. Recent advances in the surgical treatment of advanced gastric cancer: A review. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:3537–41. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916475
6. Aoyama T, Hara K, Kazama K, and Maezawa Y. Clinical impact of nutrition and inflammation assessment tools in gastric cancer treatment. Anticancer Res. (2022) 42:5167–80. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16023
7. Yamamoto M, Kurokawa Y, Miyazaki Y, Makino T, Takahashi T, Yamasaki M, et al. Usefulness of preoperative plasma fibrinogen versus other prognostic markers for predicting gastric cancer recurrence. World J Surg. (2016) 40:1904–9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3474-5
8. Nasser NJ, Fox J, and Agbarya A. Potential mechanisms of cancer-related hypercoagulability. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:566. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030566
9. Takeuchi H, Ikeuchi S, Kitagawa Y, Shimada A, Oishi T, Isobe Y, et al. Pretreatment plasma fibrinogen level correlates with tumor progression and metastasis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2007) 22:2222–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04736.x
10. Ding P, Zheng C, Cao G, Gao Z, Lei Y, Deng P, et al. Combination of preoperative plasma fibrinogen and AJCC staging improves the accuracy of survival prediction for patients with stage I-II gastric cancer after curative gastrectomy. Cancer Med. (2019) 8:2919–29. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2086
11. Senkal M, Bonavina L, Reith B, Caruso R, Matern U, and Duran M. Perioperative peripheral parenteral nutrition to support major gastrointestinal surgery: Expert opinion on treating the right patients at the right time. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2021) 43:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.04.006
12. Maejima K, Taniai N, and Yoshida H. The prognostic nutritional index as a predictor of gastric cancer progression and recurrence. J Nippon Med Sch. (2022) 89:487–93. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-507
13. Raimondi A, Nichetti F, Peverelli G, Di Bartolomeo M, De Braud F, and Pietrantonio F. Genomic markers of resistance to targeted treatments in gastric cancer: potential new treatment strategies. Pharmacogenomics. (2018) 19:1047–68. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2018-0077
14. Yan L, Nakamura T, Casadei-Gardini A, Bruixola G, Huang YL, and Hu ZD. Long-term and short-term prognostic value of the prognostic nutritional index in cancer: a narrative review. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:1630. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4528
15. Bailón-Cuadrado M, Pérez-Saborido B, Sánchez-González J, Rodríguez-López M, Velasco-López R, C Sarmentero-Prieto J, et al. Prognostic Nutritional Index predicts morbidity after curative surgery for colorectal cancer. Cir Esp (Engl Ed). (2019) 97:71–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ciresp.2018.08.015
16. Sugawara K, Aikou S, Yajima S, Uemura Y, Okumura Y, Nishida M, et al. Pre- and post-operative low prognostic nutritional index influences survival in older patients with gastric carcinoma. J Geriatr Oncol. (2020) 11:989–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.02.007
17. Luo Z, Zhou L, Balde AI, Li Z, He L, ZhenWei C, et al. Prognostic impact of preoperative prognostic nutritional index in resected advanced gastric cancer: A multicenter propensity score analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2019) 45:425–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.09.004
18. Migita K, Matsumoto S, Wakatsuki K, Ito M, Kunishige T, Nakade H, et al. A decrease in the prognostic nutritional index is associated with a worse long-term outcome in gastric cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Surg Today. (2017) 47:1018–26. doi: 10.1007/s00595-017-1469-y
19. Sexton RE, Al Hallak MN, Diab M, and Azmi AS. Gastric cancer: a comprehensive review of current and future treatment strategies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2020) 39:1179–203. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09925-3
20. Yu H, Li L, Gu J, Wang J, Su H, Lu H, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of gastric cancer patients toward nutritional therapy. Front Med (Lausanne). (2025) 12:1433849. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1433849
21. Sobocki J, Bogdanowska-Charkiewicz D, Budnicka-Borkowicz A, Chełmicka M, Dudkowiak R, Guzek M, et al. Clinical nutrition in gastrointestinal diseases: an up-to-date clinical practice guideline. Pol Arch Intern Med. (2025) 135:16967. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16967
22. Rinninella E, Cintoni M, Raoul P, Pozzo C, Strippoli A, Bria E, et al. Effects of nutritional interventions on nutritional status in patients with gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2020) 38:28–42. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.05.007
23. Xu R, Chen XD, and Ding Z. Perioperative nutrition management for gastric cancer. Nutrition. (2022) 93:111492. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2021.111492
24. Fan Y, Li N, Zhang J, Fu Q, Qiu Y, and Chen Y. The Effect of immunonutrition in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. (2023) 23:351. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10820-7
25. Jing S, Chen H, Bao L, Lyu R, Xu B, Pu L, et al. Effects of perioperative ω-3 fish oil fat emulsion on postoperative gastric emptying function following Roux-en-Y reconstruction for gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. (2025) 29:102066. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2025.102066
26. Pan YP, Chang PH, Fan CW, Tseng WK, Huang JS, Chen CH, et al. Relationship between pre-treatment nutritional status, serum glutamine, arginine levels and clinicopathological features in Taiwan colorectal cancer patients. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2015) 24:598–604. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.2015.24.4.23
27. Liao J, Lu G, and Wang Z. Low-molecular-weight heparin combined with somatosensory evoked potential monitoring for prevention of postoperative lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in patients with spinal fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. (2025) 85:1–12. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-24-01437
28. Lan D, Song S, Liu Y, Jiao B, and Meng R. Use of Batroxobin in Central and Peripheral Ischemic Vascular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:716778. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.716778
Keywords: F-PNI, fibrinogen, gastric cancer, prognosis, prognostic nutritional index
Citation: Lin S, Zheng C, Chen Z, Chen Y and Lin W (2025) Prognostic value of the combined fibrinogen and prognostic nutritional index score in resectable gastric cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1596774. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1596774
Received: 20 March 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 09 September 2025.
Edited by:
Vasileios I. Lagopoulos, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceReviewed by:
Maximos Frountzas, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceAkile Zengin, Eskişehir Osmangazi University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Zheng, Chen, Chen and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Lin, bGlud2JqQG91dGxvb2suY29t; Yulin Chen, Y2hlbnl1bGluY3lsMDFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Shuxiang Lin1,2†
Shuxiang Lin1,2† Yulin Chen
Yulin Chen