- 1Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
Oral squamous cell carcinoma is among the most prevalent tumours of the oral and maxillofacial region. The initial symptoms are typically minor and may remain misdiagnosed until the disease advances, resulting in a significantly reduced five-year survival rate for patients. Early detection is critical, as it can improve five-year survival rates from below 50% to 70–90%. Due to their reduced sensitivity and intrusive nature, conventional screening methods such as serological testing and histopathological biopsies have limitations in their application. In contrast, emerging technologies including single-cell sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, nanopore sequencing, biosensor technology, and artificial intelligence, among other advanced detection methods, are redefining biomarker discovery. Scalability obstacles still exist, including clinical validation gaps, high implementation costs, and analytical complexity. In order to close the gap between invention and equitable implementation, future efforts should focus on multicenter validation of potential biomarkers and cost-effective integration of these technologies. This will ultimately improve patient prognosis and quality of life. This work aims to comprehensively investigate and evaluate the prospective applications and future developmental potential of these technologies while offering an extensive examination of oral squamous cell cancer biomarker research
Introduction
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the most prevalent malignancy of the oral cavity, accounting for over 90% of all oral cancers (1), with an estimated 389,000 new cases and 188,000 deaths annually globally each year (2). Significantly, incidence rates are increasing threefold in low- and middle-income nations (LMICs) relative to high-income regions (3), highlighting differences in healthcare access and delayed diagnosis. Early symptoms (e.g., painless ulcers or erythroplakia) are frequently overlooked, leading to diagnosis at advanced stages (T3/T4) in 60-70% of LMIC patients versus 30-40% in high-resource settings (4). This disparity stems from systemic barriers, including the high cost of molecular tests ($200–500 per analysis) (5), even exceeding monthly incomes in many LMICs, and their specialized oncology centers are concentrated in urban areas (6). Late diagnosis also reduces treatment efficacy; the 5-year survival rate plummets from 84% for localized tumors to 39% for metastatic disease (7). And even after treatment, extensive surgeries frequently cause permanent functional impairments, including speech deficits (45% of patients) and feeding tube dependence (32%) (6). These data underscore the urgent need for accessible early detection tools that can overcome geographic and economic divides.
Traditional diagnostic techniques for OSCC, such as direct inspection, histopathological analysis, chemical staining, and exfoliative cytology, remain the clinical standard. However, their invasive nature (e.g., requiring tissue biopsies), low sensitivity (60–75%) (4), high costs (5), and reliance on specialized pathology expertise hinder widespread adoption, particularly in low-resource settings where diagnostic delays are common (6). Recent advances in molecular biology and artificial intelligence (AI), particularly the appearance of deep learning-based image analysis (AUC=0.87 for OSCC detection) (8), have transformed OSCC biomarker discovery and early detection (Figure 1). Emerging technologies including single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq, profiling 20,000 cells per run) (9), spatial transcriptomics (10-μm resolution) (10), biosensors (95% sensitivity for salivary miRNAs) (11), and AI (different algorithms can analyze large amounts of data), have identified novel biomarkers like OSCC proliferation (e.g., TOP2A mRNA) (12) and immune evasion (e.g., Galectin-9+ TAMs) (13), as summarized in Table 11. These innovations provide minimally invasive alternatives for early OSCC detection, yet their clinical translation requires overcoming cost barriers and validation in diverse populations (55). This study critically evaluates recent advancements in OSCC biomarker detection, emphasizing technological innovation and barriers to equitable implementation. We assess the translational potential of these tools while advocating for cost-reduction strategies and multicenter validation to bridge healthcare disparities.
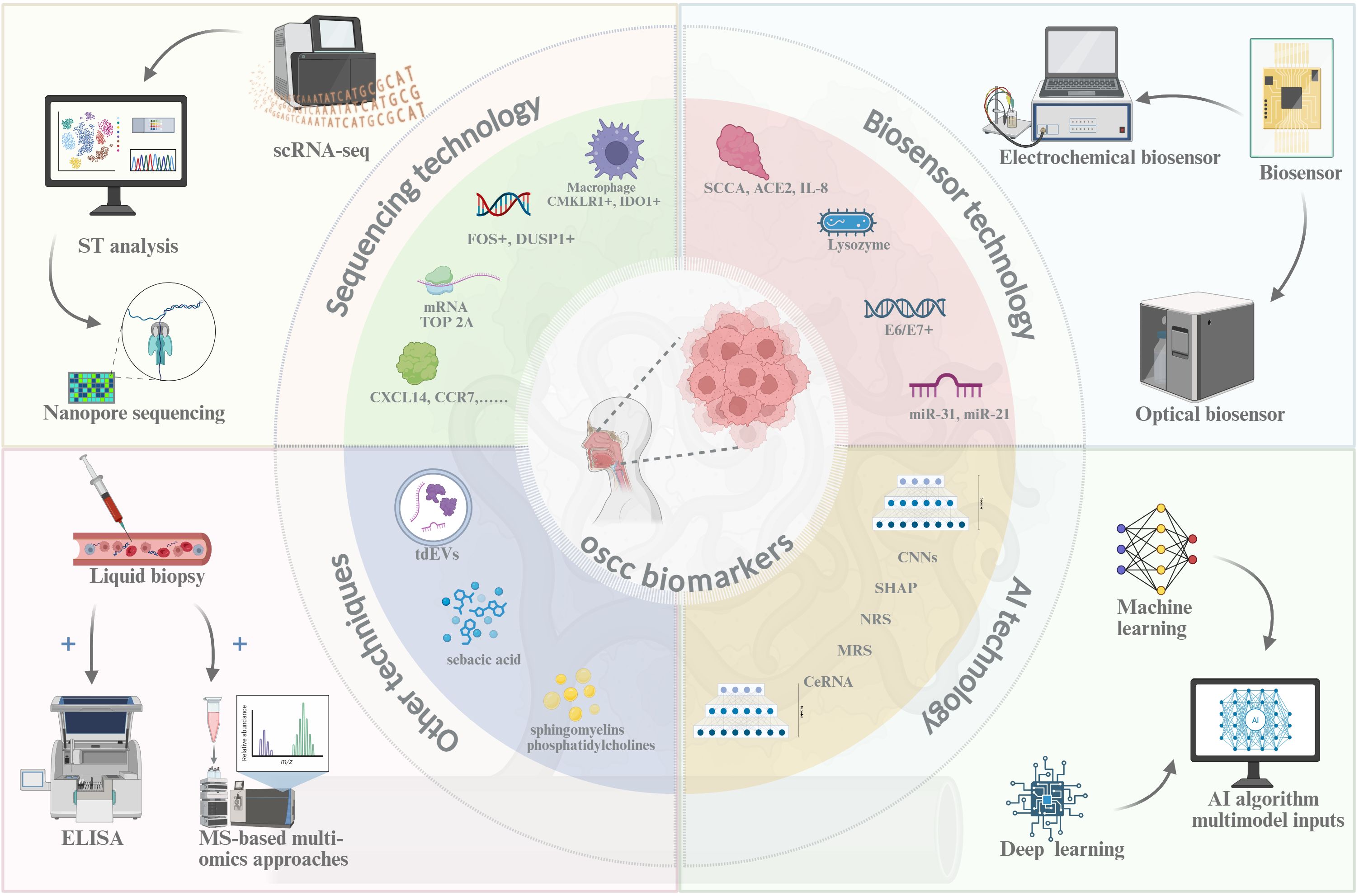
Figure 1. New detection technique of OSCC. Created in https://BioRender.com.
Progress in research on new detection methods
Sequencing technology
The scRNA-seq has transformed OSCC research by enabling high-resolution profiling of tumor heterogeneity (9) by analyzing gene expression at the individual cell level, with modern platforms (e.g., DNBSEQ-T20×2) achieving throughputs of 50,000 cells per run (14), while maintaining a low per-cell cost (~$0.01/cell) (56). It has identified candidate biomarkers including tumor-specific gene clusters, though further validation is needed to confirm their clinical utility (57). Combining scRNA-seq with single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering analysis (SCENIC) analysis identified CMKLR1+ macrophages (HR=2.1 for poor prognosis) (15), which may directly influence epithelial cell proliferation and impede OSCC progression. Typically, scRNA-seq directly quantifies mRNA expression in OSCC cells, revealing upregulated oncogenic transcripts such as TOP2A (3.2-fold increase in T3/T4 tumors) (12) and NNMT (correlating with smoking status, p<0.01) (22). However, TOP2A’s diagnostic specificity is limited by its expression in 18–22% of oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMDs) (12), necessitating complementary biomarkers (e.g., CXCL12, AUC=0.81) (29) to improve early detection accuracy. To enhance reliability, scRNA-seq findings can be cross-validated through orthogonal methods including immunohistochemistry, qPCR, and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), establishing a multi-platform verification framework. Beyond transcriptional profiling, scRNA-seq has facilitated the discovery of protein-coding biomarkers including the Immune modulators [CXCL12 (29) and CXCL14 (27)], Metabolic regulators (NNMT) (22), and [DUSP1 (17) and ZNF71 (26)], which were evaluated for gene expression of proteinaceous substances. The variations in the expression levels of these genes suggest their potential role as biomarkers for OSCC, but these markers still require prospective validation in multicenter trials before clinical implementation.
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) preserves tissue architecture while mapping gene expression, allowing researchers to study cellular interactions within tumor niches, bridges single-cell resolution with tissue context, preserving architectural details at 10-μm resolution while capturing >20,000 RNA molecules per spot (10), with next-generation platforms like Stereo-seq achieving 500 nm resolution (58). In OSCC, ST has uncovered tumor-zone-specific signaling gradients, such as 3.5-fold elevated WNT5A expression at invasion fronts (p<0.001) (59). Through the use of CellPhoneDB and NicheNet for intercellular communication analysis, ST technology has revealed the upregulation of HIF1A (4.2-fold in hypoxic niches, FDR<0.01), PDGFRA (2.8-fold in αSMA+ iCAFs), and RGS5 (1.9-fold in perivascular zones) (30) in the high metabolic region, indicating that iCAF transformation dictates the metabolic signature of the immunosuppressive microenvironment. Integrated analysis using scRNA-seq, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and other techniques, the Galectin-9 (92% of CD163+ TAMs, HR=2.1 for poor prognosis), MHC-I (68% tumor cells vs normal, correlates with CD8+ T cell exclusion), SLC16A1 (PET-CT SUVmax correlation r=0.79), and the chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL12 (13) were found to be upregulated in OSCC tissues or cells, and detect the upregulated expression of these genes may facilitate the early diagnosis. These discoveries enable the early detection that combined biomarker panels achieve 89% sensitivity (8), and to better achieve treatment stratification such as CXCL12 high tumors show a 3.2-fold better response to immunotherapy (60).
Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT), a third-generation sequencing platform renowned for its real-time analysis capabilities, has demonstrated clinical utility in both pathogen detection (COVID-19 identification within 6 hours) (61), and cancer genomics (25). It can offer long-read-length sequencing and real-time detection via the electronic sequencing of raw DNA and RNA in OSCC detection. As the only commercially available direct RNA sequencing platform, ONT’s long-read capability resolves full-length lncRNA structures, revealing the Prognostic lncRNAs including DANCR isoforms (lymph node metastasis OR=3.2, 95%CI 1.8-5.7) and GAS5 variants (cisplatin resistance AUC=0.81) (37) and the microbial biomarkers including Prevotella spp. (detected in 68% OSCC cases vs 22% controls) (36), a prevalent aetiological factor in oral diseases intricately associated with the invasive and migratory characteristics of OSCC.
Biosensor technology
Modern biosensors synergistically combine biorecognition elements (e.g., antibodies, aptamers) with advanced transducers, and convert molecular interactions into quantifiable optical/electrical signals within 10–15 minutes, enabling real-time monitoring of disease progression (11). Contemporary biosensor platforms are primarily categorized into two primary types based on the signal utilized: electrochemical sensors and optical sensors. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) enables real-time, label-free monitoring of biomolecular interactions with 0.1° phase resolution (62). By utilizing the characteristics of EIS, Lv et al. (39) developed a Pd@ACE2 nanosensor achieving 0.8 pM ACE2 detection in OSCC cells, single-cell analysis revealed ACE2 overexpression (3.2-fold) correlates with EMT markers (vimentin, E-cadherin), suggesting its role in OSCC metastasis. In addition, the EIS-based electrochemical sensor successfully identified the upregulation of IL-8 (2.4 ng/mL cutoff, 89% sensitivity for early OSCC) (42) and the downregulation of MGMT (83% specificity vs healthy controls) (41) in saliva, authentically achieved non-invasive sampling and cost-effective detection (48). Nanocomposite-based sensors enable breakthrough applications, gold nanoparticle/graphene nanosheet (Au/GN) complexes have been efficiently utilized as sensing electrochemical sandwich immunosensors, having proficiency in the detection of the squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) (40). Furthermore, a multi-analyte electrochemical gene sensor utilizing silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) infused with various redox indicators can identify the E6/E7 genes of HPV-16 and HPV-18 (38), thereby offering novel opportunities for the concurrent detection of multiple biomarkers, and expand the repertoire of biomarkers for OSCC.
Optical sensors detect biomarkers that leverage light absorption, fluorescence, aggregation-induced luminescence (AIE), and light scattering, with several types of sensors available, such as colorimetric, fluorescent, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors. Recent material innovations have pushed detection limits to the single-molecule level. Cutting-edge applications include AuNP-based colorimetric arrays detecting miR-141 at 0.01 pM (Δλ=52 nm redshift) with 93% clinical accuracy for OSCC staging (63), SiQD-FRET systems quantifying GSH in 2 μL serum (0.1–100 mM range, R^2 = 0.99) for redox status monitoring (64), and the cost-effective and portable supersurface plasmon biosensor (MetaSPR), integrated with artificial nanoenzymes for use with the nanoenzyme-linked immunosorbent surface plasmon resonance biosensor (Nano-ELISPR) (65), achieving 0.01 pg/mL IL-6 detection in saliva within 8 minutes, priced at $0.50/test. Nano-ELISPR can undergo a reversible etching reaction through Ag ions on gold and silver MetaSPR chips, facilitating ultrasensitive and specific detection.
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) leverages plasmonic nanostructures (e.g., Au/Ag nanoparticles) to achieve single-molecule detection sensitivity through localized surface plasmon resonance effects. It provides unique advantages including non-contact and non-destructive measurements, high resistance to interference, rapid data transmission, and telemetry control (66) for clinical translation, enabling simultaneous analysis of multiple targets in complex biological matrices. Integrated SERS platforms, which are combined with molecular dynamic (MD) simulation and analytical techniques, can achieve the IL-8 quantification [(2.4–100 ng/mL dynamic range)] (43) and lysozyme [(0.1-10 μg/mL)] detection (44) in saliva, as well as with lateral flow chromatography methods and catalytic hairpin assembly signal amplification strategies for the detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), such as TP53 (mutations at 0.01% allele frequency) and PIK3CA E545K in serum (45). Additionally, through hybridization chain reaction (HCR) amplification, SERS aims to identify diverse noncoding microRNAs, including miR-31 and miR-21 in saliva (46). Above all, SERS has emerged as a transformative OSCC diagnostic tool due to its sub-nm spectral resolution, single-cell sensitivity, and multiplex capacity while analysis, with 89% overall accuracy in a 500-patient cohort study (8).
Artificial intelligence technology
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems emulate human cognitive processes to analyze complex biological data, demonstrating preliminary success in OSCC biomarker discovery but requiring rigorous clinical validation (53). Deep learning architectures, particularly convolutional neural networks (cNNs), have improved OSCC detection by analyzing histopathological images with 86.7% accuracy in margin assessment (53), though their performance varies across imaging modalities (67). Multi-omics integration through AI has revealed tobacco-associated epigenetic markers (GPR15, GNG12, and GDNF), these epigenetic alterations show a stronger correlation with tobacco exposure (p<0.001) than with tumor staging (p=0.12) based on multivariate analysis. In heavy smokers (≥10 pack-years), the mean methylation β-values increase by 0.38-0.45 compared to non-smokers. This finding supports targeted screening for high-risk populations. Moreover, Explainable AI (XAI) approaches have enhanced biomarker discovery in OSCC. Using Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) analysis combined with particle swarm optimization, researchers identified three prognostic biomarkers: ECT2, LAMC2, and DSG2 (47), and the downregulation of these genes signature correlates with poor clinical outcomes, and patients showing concurrent downregulation of all three markers exhibit a 3.2-fold higher metastasis risk (95% CI: 1.8-5.6) according to recent TCGA data analysis.
Machine learning (ML) models have demonstrated 75-89% cross-validation accuracy in analyzing OSCC gene expression profiles from TCGA datasets (68), are increasingly applied to analyze gene expression profiles in OSCC. These models quantify tumor heterogeneity through cellular diversity indices (e.g., Shannon entropy) and spatial patterning metrics, achieving 0.81 AUC for distinguishing early-stage lesions, though with variable performance across histological subtypes (54). AI-enhanced histopathology has revealed recurrent loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at chromosome 9p (38% frequency), implicating tumor suppressor genes such as CDKN2A (8). This finding suggests a potential role in early carcinogenesis, though functional validation is ongoing. Furthermore, Gradient boosting machine (GBM) models have identified CDKN2A inactivation in 72% of TCGA-analyzed OSCC cases, correlating with dysregulated G1/S checkpoint control (51). This positions CDKN2A as a high-priority biomarker candidate, pending multicenter validation. Multiparametric ML-MRI integration has demonstrated prognostic utility, with Ki-67 expression serving as an independent predictor of poor survival (HR=2.3, 95% CI 1.7–3.1) (52). However, its clinical adoption is limited by interobserver variability in immunohistochemical scoring. Advanced neural networks (e.g., SurvNet) integrated with explainable AI (XAI) frameworks have optimized the selection of multimodal biomarkers. Specifically, a recent multicenter study validated the prognostic value of combining p16 status (AUC=0.87), FDG-PET-derived MTV50 (HR=2.1), DCE-MRI blood volume (cut-off >12 mL/100g), and ADC values (<1.2×10–3 mm²/s) (55). These indicators are crucial for OSCC staging, evaluating treatment response, and assessing prognosis.
AI-driven multimodal systems demonstrate emerging potential for OSCC management, though their clinical implementation faces scalability challenges due to computational complexity and validation gaps (56). Through integrative analysis of histopathology, transcriptomics, and clinical data, these systems achieve 71-89% concordance with gold-standard diagnoses in controlled trials, yet real-world performance varies significantly across healthcare settings (69). AI-enhanced Raman imaging achieves 86.7% accuracy for intraoperative margin assessment in single-center studies, though multicenter validation is needed to confirm generalizability (67). Age-stratified AI models improve TNM staging prognostic value (AUC 0.65-0.72), with the most significant benefits observed in elderly cohorts where clinical judgment variability is highest (70). Nodal risk prediction models (NRS) combining radiomic features (e.g., DCE-MRI blood volume >12 mL/100g) and histomorphometric data achieve 82% accuracy for metastasis detection, surpassing conventional imaging by 15-20% (55). Network analysis-derived macrophage signatures (e.g., IGF2BP2, CTLA4) show 3.2-fold increased metastasis risk in high-risk subgroups but require prospective validation given potential overfitting in TCGA data (54). Validation in TCGA cohorts showed high-risk MRS patients had a 3.2-fold increased metastasis risk (p<0.001). Moreover, multiple ML algorithms have identified critical ceRNA networks involving HOXC13 and KLHL40, with TGFBR3 showing context-dependent roles. In elderly patients (≥65 years), HOXC13 downregulation correlates with advanced TNM stages (OR=3.22, p=0.002), while KLHL40 mutations are associated with smoking-related epigenetic changes (71). These integrated models (NRS, MRS, ceRNA) exemplify the convergence of multi-omics and clinical informatics in OSCC management and underscore the potential of AI to translate complex biomarker patterns into actionable clinical strategies.
Other techniques
Beyond conventional histopathological methods, emerging multi-omics approaches have enhanced OSCC biomarker detection by integrating liquid biopsy, metabolomics, and lipidomic profiling. Liquid biopsy facilitates non-invasive OSCC monitoring by analyzing circulating tumor cells (CTCs), cell-free DNA (cfDNA), exosomes, and tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (tdEVs), with tdEVs exhibiting the highest sensitivity (AUC = 0.89) for early-stage detection (72). Dysregulated miRNAs, particularly miR-21 (upregulated in 78% of OSCC cases) and miR-31 (associated with lymph node metastasis) (73), serve as diagnostic biomarkers, whereas miR-200 family members (e.g., miR-200a/b/c) predict poor prognosis by promoting EMT (74). Mass spectrometry (MS)-based multi-omics approaches, particularly proteomics and lipidomics, have identified OSCC-specific metabolic alterations, such as aberrant glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation. Salivary metabolomics via GC–MS has revealed elevated sebacic acid levels (2.1-fold increase, p < 0.01) in OSCC patients compared to healthy controls, suggesting its potential as a non-invasive biomarker (75). In contrast, Lipidomic profiling further distinguishes OSCC by elevated sphingomyelins (SM d18:1/16:0, AUC = 0.91) and phosphatidylcholines (PC 34:1, AUC = 0.88), which correlate with tumor aggressiveness (76). Furthermore, an MS study integrated with lipidomics demonstrated that cholesterol and various phospholipids were markedly elevated in OSCC tissues (77), with machine learning models utilizing sphingolipid profiles achieving high diagnostic accuracy (AUC >0.95) (74).
Challenges and prospects
Current OSCC biomarker detection methods face multifaceted challenges, including high costs (particularly for advanced sequencing technologies), inconsistencies in data interpretation due to heterogeneous sample processing protocols, difficulties in integrating emerging technologies with existing clinical workflows, and a lack of standardized validation frameworks, all of which hinder their widespread clinical adoption and result reproducibility. Despite advancements in sequencing technology enhancing the velocity of biomarker research, their reliance on complex bioinformatics pipelines for data analysis and substantial computational resource requirements disproportionately limit accessibility in resource-limited settings (56). Although Nanopore sequencing has demonstrated utility in pathogen surveillance due to its portability and real-time analysis capabilities, its application in early tumor detection requires substantial improvements in accuracy and cost-effectiveness (78). Emerging biosensor platforms, such as ELISA-based salivary biomarker detection systems, demonstrate high sensitivity for OSCC screening (e.g., detecting EGF: EGFR ratio changes with AUC >0.8) (79). However, their performance is influenced by pre-analytical variables including sample collection protocols, storage conditions, and ambient temperature fluctuations, mandating stringent standardization of operating procedures to ensure reliability (11). AI-driven approaches enhance diagnostic precision, although their clinical translation depends on overcoming challenges such as the scarcity of large-scale annotated datasets in oral oncology and the “black-box” nature of deep learning models, which complicates clinical validation and trust-building among practitioners (69). The transition from biomarker discovery to clinically actionable tools faces dual barriers. One is technical limitations in validating candidate biomarkers across diverse populations (e.g., single-center studies with limited sample sizes), and the other is regulatory and practical hurdles in implementing detection platforms within existing healthcare infrastructures. Above all, progress in this field demands innovative solutions for multimodal data harmonization (e.g., combining omics data with imaging and clinical records) and advanced computational frameworks.
Emerging innovations in OSCC biomarker detection are poised to revolutionize clinical practice, particularly through the integration of temporal-spatial multiomics and AI-enabled data synthesis. For instance, the Well-TEMP-seq platform enables dynamic tracking of gene expression changes at single-cell resolution during early carcinogenesis, providing critical insights into biomarker evolution (80). Recent breakthroughs in single-cell spatial transcriptomics, exemplified by STALocator (81) (integrating scRNA-seq with spatial transcriptomics for subcellular localization), have enabled high-resolution mapping of immune-stromal interactions within OSCC tumor niches. Nanotechnology-enabled biosensors are achieving unprecedented sensitivity thresholds with emerging applications in intraoperative margin assessment (67). AI-driven frameworks are overcoming data heterogeneity challenges through innovations like differentiable modeling architectures, offering novel insights for oral cancer biomarker identification. Additional technologies, such as ultrasensitive liquid biopsy assays, will further augment ctDNA and ctRNA detection, presenting a new avenue for non-invasive tumor identification. Interdisciplinary collaboration enhances technology integration, whereas governments and regulatory bodies must establish regulations to guarantee the safety and efficacy of developing technologies while facilitating their clinical implementation. In conclusion, technical innovation, interdisciplinary collaboration, and governmental endorsement will propel oral cancer biomarker detection into a new epoch of precision medicine, thereby improving patient survival and quality of life
Author contributions
LAL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. LIL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Scientific Research Development Plan Project, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (grant no. 2024PTZK004), and Scientific Research Development Plan Project, North Sichuan Medical College (grant no. CBY22-ZDA03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
- ^ That listed biomarkers require multicenter validation before clinical adoption.
References
1. Ding L, Fu Y, Zhu N, Zhao M, Ding Z, Zhang X, et al. OXTRHigh stroma fibroblasts control the invasion pattern of oral squamous cell carcinoma via ERK5 signaling. Nat Commun. (2022) 13(1):5124. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32787-y
2. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
3. Crosby D, Bhatia S, Brindle KM, Coussens LM, Dive C, Emberton M, et al. Early detection of cancer. Sci (New York NY). (2022) 375:eaay9040. doi: 10.1126/science.aay9040
4. Warnakulasuriya S and Kerr AR. Oral Cancer Screening: Past, Present, and Future. J Dent Res. (2021) 100:1313–20. doi: 10.1177/00220345211014795
5. Xie L and Shang Z. Burden of oral cancer in asia from 1990 to 2019: Estimates from the global burden of disease 2019 study. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0265950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265950
6. Chamoli A, Gosavi AS, Shirwadkar UP, Wangdale KV, Behera SK, Kurrey NK, et al. Overview of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Risk factors, mechanisms, and diagnostics. Oral Oncol. (2021) 121:105451. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105451
7. Hashim D, Genden E, Posner M, Hashibe M, and Boffetta P. Head and neck cancer prevention: From primary prevention to impact of clinicians on reducing burden. Ann Oncology: Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2019) 30:744–56. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz084
8. Cai X-J, Peng C-R, Cui Y-Y, Li L, Huang M-W, Zhang H-Y, et al. Identification of genomic alteration and prognosis using pathomics-based artificial intelligence in oral leukoplakia and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A multicenter experimental study. Int J Surg. (2024) 111(1):426–38. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002077
9. Jovic D, Liang X, Zeng H, Lin L, Xu F, and Luo Y. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and applications: A brief overview. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e694. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.694
10. Moses L and Pachter L. Museum of spatial transcriptomics. Nat Methods. (2022) 19:534–46. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01409-2
11. Aksoy ZB, Il DB, Celik D, Sengun DN, Unal MA, Kaya SI, et al. Bridging the gap: Advanced biosensor technologies for early-stage oral cancer diagnosis based on biomarker detection. Trac Trends Anal Chem. (2024) 180:117923. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2024.117923
12. Cheng X, Wei Y, Deng L, Dong H, Wei H, Xie C, et al. Expression and biological significance of topoisomerase II α (TOP2A) in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Discov Onc. (2024) 15:423. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01295-4
13. Li C, Guo H, Zhai P, Yan M, Liu C, Wang X, et al. Spatial and single-cell transcriptomics reveal a cancer-associated fibroblast subset in HNSCC that restricts infiltration and antitumor activity of CD8+ T cells. Cancer Res. (2024) 84:258–75. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1448
14. Lou J, Luo G, Zhao L, and Zhang H. CONSORT article: Single-cell sequencing analysis revealed CMKLR1+ macrophage as a subpopulation of macrophage with tumor-suppressive characteristics in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med (baltimore). (2024) 103:e39399. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039399
15. Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhao S, Xu Y, Huang Y, Liu S, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing highlights the immunosuppression of IDO1+ macrophages in the Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia. Theranostics. (2024) 14:4787–805. doi: 10.7150/thno.99112
16. Zhang Q, Ding L, Li J, Liu K, Xia C, Chen S, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of OSCC primary tumors and lymph nodes reveals distinct origin and phenotype of fibroblasts. Cancer Lett. (2024) 600:217180. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217180
17. Kurkalang S, Roy S, Acharya A, Mazumder P, Mazumder S, Patra S, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of gingivo-buccal oral cancer reveals two dominant cellular programs. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:4732–46. doi: 10.1111/cas.15979
18. Yao L, Liu L, Xu W, Xi H, Lin S, Piao G, et al. mRNA-seq-based analysis predicts: AEG-1 is a therapeutic target and immunotherapy biomarker for pan-cancer, including OSCC. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1484226. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1484226
19. Wang Z, Cheng L, Huang J, and Shen Y. Integrative machine learning and neural networks for identifying PANoptosis-related lncRNA molecular subtypes and constructing a predictive model for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (2024) 281:5481–95. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08765-z
20. Wu L, Yang J, She P, Kong F, Mao Z, and Wang S. Single-cell RNA sequencing and traditional RNA sequencing reveals the role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinoma cohort. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1195520. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1195520
21. Yang W, Zhang S, Li T, Zhou Z, and Pan J. Single-cell analysis reveals that cancer-associated fibroblasts stimulate oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion via the TGF-β/Smad pathway. ABBS. (2023) 55:262–73. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022132
22. Wang X, Zhao H, Luo X, Chen Y, Shi C, Wang Y, et al. NNMT switches the proangiogenic phenotype of cancer-associated fibroblasts via epigenetically regulating ETS2/VEGFA axis. Oncogene. (2024) 43:2647–60. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03112-2
23. He Y, Dong Y, Zhang X, Ding Z, Song Y, Huang X, et al. Lipid droplet-related PLIN2 in CD68+ tumor-associated macrophage of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Implications for cancer prognosis and immunotherapy. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:824235. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.824235
24. Yan C, Du W, Kirkwood KL, Wang Y, Zhou W, Li Z, et al. CCR7 affects the tumor microenvironment by regulating the activation of naïve CD8+ T cells to promote the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Transl Oncol. (2024) 44:101924. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.101924
25. Chen J, Yang J, Li H, Yang Z, Zhang X, Li X, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveal the intratumoral landscape of infiltrated T-cell subpopulations in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Oncol. (2021) 15:866–86. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12910
26. Jiang F-C, Li G-S, Luo J-Y, Huang Z-G, Dang Y-W, Chen G, et al. Downregulation of zinc finger protein 71 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues and its underlying molecular mechanism. Pathology Res Pract. (2022) 238:154109. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154109
27. Parikh A, Shin J, Faquin W, Lin DT, Tirosh I, Sunwoo JB, et al. Malignant cell-specific CXCL14 promotes tumor lymphocyte infiltration in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e001048. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001048
28. Miao Y, Wang P, Huang J, Qi X, Liang Y, Zhao W, et al. Metabolomics, Transcriptome and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis of the Metabolic Heterogeneity between Oral Cancer Stem Cells and Differentiated Cancer Cells. Cancers. (2024) 16:237. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020237
29. Yorozu A, Sekiguchi S, Takasawa A, Okazaki F, Niinuma T, Kitajima H, et al. CXCL12 is expressed by skeletal muscle cells in tongue oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:5953–63. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5392
30. Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou W, Zhang X, Peng C, et al. Spatial transcriptomics reveals that metabolic characteristics define the tumor immunosuppression microenvironment via iCAF transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Sci. (2024) 16:9. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00267-8
31. Xu X, Zhao Y, Ying Y, Zhu H, Luo J, Mou T, et al. m7G-related genes-NCBP2 and EIF4E3 determine immune contexture in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating CCL4/CCL5 expression. Mol Carcinog. (2023) 62:1091–106. doi: 10.1002/mc.23548
32. Gessain G, Anzali A-A, Lerousseau M, Mulder K, Bied M, Auperin A, et al. TREM2-expressing multinucleated giant macrophages are a biomarker of good prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Discov. (2024) 14:2352–66. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0018
33. Shaikh S, Dhar H, Moorthy M, Bhat V, Basu S, Banerjee D, et al. The spatial distribution of intermediate fibroblasts and myeloid-derived cells dictate lymph node metastasis dynamics in oral cancer. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:759. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05511-1
34. Tojo S, Nakashiro K-I, Kuribayashi N, and Uchida D. Serum CXCL13 as a novel biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2024) 13:e70263. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70263
35. Lin G, Cai H, Hong Y, Yao M, Ye W, Li W, et al. Implications of m5C modifications in ribosomal proteins on oxidative stress, metabolic reprogramming, and immune responses in patients with mid-to-late-stage head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Insights from nanopore sequencing. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e34529. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34529
36. Mauceri R, Coppini M, Vacca D, Bertolazzi G, Cancila V, Tripodo C, et al. No clear clustering dysbiosis from salivary microbiota analysis by long sequencing reads in patients affected by oral squamous cell carcinoma: A single center study. Cancers. (2023) 15:4211. doi: 10.3390/cancers15174211
37. Weber R, Ghoshdastider U, Spies D, Duré C, Valdivia-Francia F, Forny M, et al. Monitoring the 5′UTR landscape reveals isoform switches to drive translational efficiencies in cancer. Oncogene. (2023) 42:638–50. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02578-2
38. Chaibun T, Thanasapburachot P, Chatchawal P, Yin LS, Jiaranuchart S, Jearanaikoon P, et al. A multianalyte electrochemical genosensor for the detection of high-risk HPV genotypes in oral and cervical cancers. Biosensors. (2022) 12(5):290. doi: 10.3390/bios12050290
39. Lv K, Cy C, Sy H, Pw W, Ch H, Ct L, et al. Development of flexible electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based biosensing platform for rapid screening of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. Biosensors bioelectronics. (2021) 183:113213. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113213
40. Jiang Y, Yang M, Yu M, Huang L, Ke Y, and Yang L. β-cyclodextrin-functionalized Ti3C2Tx MXene nanohybrids as innovative signal amplifiers for the electrochemical sandwich-like immunosensing of squamous cell carcinoma antigen. Analytical Methods: Advancing Methods Appl. (2023) 15:1336–44. doi: 10.1039/d2ay01716d
41. Carr O, Raymundo-Pereira PA, Shimizu FM, Sorroche BP, Melendez ME, de Oliveira Pedro R, et al. Genosensor made with a self-assembled monolayer matrix to detect MGMT gene methylation in head and neck cancer cell lines. Talanta. (2020) 210:120609. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120609
42. Bhardwaj H, Hashmi Z, Singh AK, Kumar G, Lakshmi GBVS, and Solanki PR. An electrochemical immunosensor based on a nano-ceria integrated microfluidic chip for interleukin-8 biomarker detection. Nanoscale Adv. (2024) 7(1):196–208. doi: 10.1039/d4na00636d
43. Rashidova G, Tilegen M, Pham TT, Bekmurzayeva A, and Tosi D. Functionalized optical fiber ball-shaped biosensor for label-free, low-limit detection of IL-8 protein. BioMed Opt Express. (2024) 15:185–98. doi: 10.1364/BOE.504780
44. Farnesi E, Rinaldi S, Liu C, Ballmaier J, Guntinas-Lichius O, Schmitt M, et al. Label-free SERS and MD analysis of biomarkers for rapid point-of-care sensors detecting head and neck cancer and infections. Sensors (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 23:8915. doi: 10.3390/s23218915
45. Li G, Ge S, Niu P, Zhang J, Mao Y, Wang Y, et al. Simultaneous detection of circulating tumor DNAs using a SERS-based lateral flow assay biosensor for point-of-care diagnostics of head and neck cancer. BioMed Opt Express. (2022) 13:4102–17. doi: 10.1364/BOE.463612
46. Wang Y, Zhang Y, Du Q, Cao D, Lu X, and Meng Z. Sensitive SERS detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma-related miRNAs in saliva via a gold nanohexagon array coupled with hybridization chain reaction amplification. Anal Methods. (2022) 14:4563–75. doi: 10.1039/d2ay01180h
47. Sekaran K, Varghese RP, Krishnan S, Zayed H, El Allali A, and Doss GPC. Dissecting crucial gene markers involved in HPV-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma from RNA-sequencing data through explainable artificial intelligence. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2024) 29:220. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2906220
48. Hu Y, Guo G, Li J, Chen J, and Tan P. Screening key lncRNAs with diagnostic and prognostic value for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on machine learning and mRNA-lncRNA co-expression network analysis. Cancer biomark. (2020) 27:195–206. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190694
49. Xing L, Zhang X, Zhang X, and Tong D. Expression scoring of a small-nucleolar-RNA signature identified by machine learning serves as a prognostic predictor for head and neck cancer. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:8071–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29462
50. McRae MP, Kerr AR, Janal MN, Thornhill MH, Redding SW, Vigneswaran N, et al. Nuclear F-actin cytology in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res. (2021) 100:479–86. doi: 10.1177/0022034520973162
51. Wang Y, Zhou C, Li T, and Luo J. Prognostic value of CDKN2A in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via pathomics and machine learning. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e18394. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18394
52. Chen W, Lin G, Chen Y, Cheng F, Li X, Ding J, et al. Prediction of the ki-67 expression level in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with machine learning-based multiparametric MRI radiomics: A multicenter study. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:418. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12026-x
53. Viet CT, Asam KR, Yu G, Dyer EC, Kochanny S, Thomas CM, et al. Artificial intelligence-based epigenomic, transcriptomic and histologic signatures of tobacco use in oral squamous cell carcinoma. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2024) 8:130. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00605-x
54. Wang Y, Mou Y-K, Liu W-C, Wang H-R, Song X-Y, Yang T, et al. Machine learning developed a macrophage signature for predicting prognosis, immune infiltration and immunotherapy features in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:19538. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70430-6
55. Wei L, Aryal MP, Lee C, Shah JL, Mierzwa ML, and Cao Y. Interpretable survival network for progression risk analysis of multimodality imaging biomarkers in poor-prognosis head and neck cancers. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:30004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80815-2
56. Vandereyken K, Sifrim A, Thienpont B, and Voet T. Methods and applications for single-cell and spatial multi-omics. Nat Rev Genet. (2023) 24:494–515. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00580-2
57. Zhang Y and Zhang Z. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:807–21. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6
58. Wu L, Yan J, Bai Y, Chen F, Zou X, Xu J, et al. An invasive zone in human liver cancer identified by stereo-seq promotes hepatocyte-tumor cell crosstalk, local immunosuppression and tumor progression. Cell Res. (2023) 33:585–603. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00831-1
59. Elhanani O, Ben-Uri R, and Keren L. Spatial profiling technologies illuminate the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:404–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.01.010
60. Hsieh Y-P, Wu Y-H, Cheng S-M, Lin F-K, Hwang D-Y, Jiang S-S, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis for oncogenic mechanisms underlying oral squamous cell carcinoma carcinogenesis with candida albicans infection. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:4833. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094833
61. Bull RA, Adikari TN, Ferguson JM, Hammond JM, Stevanovski I, Beukers AG, et al. Analytical validity of nanopore sequencing for rapid SARS-CoV-2 genome analysis. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:6272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20075-6
62. Brett CMA. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in the characterisation and application of modified electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Molecules. (2022) 27:1497. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051497
63. Jindal M, Nagpal M, Singh M, Aggarwal G, and Dhingra GA. Gold nanoparticles- boon in cancer theranostics. Curr Pharm Des. (2020) 26:5134–51. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200701151403
64. Ahmad M, Anjum NA, Asif A, and Ahmad A. Real-time monitoring of glutathione in living cells using genetically encoded FRET-based ratiometric nanosensor. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:992. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57654-y
65. Li R, Fan H, Zhou H, Chen Y, Yu Q, Hu W, et al. Nanozyme-catalyzed metasurface plasmon sensor-based portable ultrasensitive optical quantification platform for cancer biomarker screening. Advanced Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2023) 10:e2301658. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301658
66. Qi X, Cheng Y, Xu R, Li X, Zhang Z, Chen L, et al. Designing of a functional paper-tip substrate for sensitive surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection. Anal Chim Acta. (2023) 1280:341872. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.341872
67. Yan B, Wen Z, Xue L, Wang T, Liu Z, Long W, et al. GenAI synthesis of histopathological images from Raman imaging for intraoperative tongue squamous cell carcinoma assessment. Int J Oral Sci. (2025) 17:12. doi: 10.1038/s41368-025-00346-y
68. Tseng Y-J, Wang Y-C, Hsueh P-C, and Wu C-C. Development and validation of machine learning-based risk prediction models of oral squamous cell carcinoma using salivary autoantibody biomarkers. BMC Oral Health. (2022) 22:534. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02607-2
69. Seibert K, Domhoff D, Bruch D, Schulte-Althoff M, Fürstenau D, Biessmann F, et al. Application scenarios for artificial intelligence in nursing care: Rapid review. J Med Internet Res. (2021) 23:e26522. doi: 10.2196/26522
70. Ritter A, Yosefof E, Edri N, Kurman N, Bachar G, Shpitzer T, et al. Reappraising the TNM staging system for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: an age-related prognosis analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09385-x
71. Zhang W, Xu S, Shi L, Zhu Z, and Xie X. Construction and analysis of a competing endogenous RNA network to reveal potential prognostic biomarkers for oral floor squamous cell carcinoma. PloS One. (2020) 15:e0238420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238420
72. Pillai J, Chincholkar T, Dixit R, and Pandey M. A systematic review of proteomic biomarkers in oral squamous cell cancer. World J Surg Oncol. (2021) 19:315. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02423-y
73. Piao Y, Jung S-N, Lim MA, Oh C, Jin YL, Kim HJ, et al. A circulating microRNA panel as a novel dynamic monitor for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:2000. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28550-y
74. Suri S, Boora GS, Kaur R, Chauhan A, Ghoshal S, and Pal A. Recent advances in minimally invasive biomarkers of OSCC: from generalized to personalized approach. Front Oral Health. (2024) 5:1426507. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1426507
75. Tantray S, Sharma S, Prabhat K, Nasrullah N, and Gupta M. Salivary metabolite signatures of oral cancer and leukoplakia through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. (2022) 26:31–7. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.jomfp_335_21
76. Rebaudi F, De Rosa A, Greppi M, Pistilli R, Pucci R, Govoni FA, et al. A new method for oral cancer biomarkers detection with a non-invasive cyto-salivary sampling and rapid-highly sensitive ELISA immunoassay: a pilot study in humans. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1216107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1216107
77. Dickinson A, Saraswat M, Joenväärä S, Agarwal R, Jyllikoski D, Wilkman T, et al. Mass spectrometry-based lipidomics of oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue reveals aberrant cholesterol and glycerophospholipid metabolism - a pilot study. Transl Oncol. (2020) 13:100807. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100807
78. Chen J and Xu F. Application of nanopore sequencing in the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary infections. Mol Diagn Ther. (2023) 27:685–701. doi: 10.1007/s40291-023-00669-8
79. Kaul-Ghanekar R, Kharat RS, Raina P, Chaudhary A, and Walekar-Ghaisas S. Salivary EGF: EGFR ratio as potential early diagnostic biomarker for oral cancer detection in tobacco chewers: a preliminary cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health. (2025) 25:663. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05982-8
80. Lin S, Yin K, Zhang Y, Lin F, Chen X, Zeng X, et al. Well-TEMP-seq as a microwell-based strategy for massively parallel profiling of single-cell temporal RNA dynamics. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:1272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36902-5
Keywords: oral squamous cell carcinoma, single-cell sequencing technology, spatial transcriptomics, nanopore sequencing, artificial intelligence technology, biosensor technology
Citation: Liu L, Zhong X, Zhong Y and Li L (2025) Recent advances in biomarker detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 15:1597086. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1597086
Received: 20 March 2025; Accepted: 26 May 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Oreste Iocca, University of Turin, ItalyReviewed by:
Annie Wai Yeeng Chai, Cancer Research Malaysia, MalaysiaMark Gormley, University of Bristol, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Zhong, Zhong and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lihua Li, YW5nZWxfbGk3N0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lan Liu
Lan Liu Xiaowu Zhong
Xiaowu Zhong Yue Zhong
Yue Zhong Lihua Li
Lihua Li