- Department of Breast Surgery, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, China
Background: Inflammation and nutritional status play critical roles in tumor initiation and progression. Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) has gained widespread attention as a novel biomarker for cancer prognosis evaluation.
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 163 advanced breast cancer patients with distant metastasis (Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, 2016-2023). Patients were stratified into high-ALI (n=64) and low-ALI (n=99) groups via K-means clustering. Kaplan-Meier survival curves with log-rank testing were used to assess survival differences, while Cox proportional hazards models were employed to evaluate the independent prognostic value of ALI. The predictive performance of ALI was assessed using time-dependent ROC curves.
Results: High ALI correlated with superior overall survival (log-rank p=0.0024) [HR=2.493 (95%CI 1.350-4.606) p = 0.004]. Multivariate analysis confirmed ALI as an independent prognostic factor (HR=0.39, 95% CI 0.16-0.95, p=0.037). ALI demonstrated stable predictive accuracy with 3-year AUC=0.645 and 5-year AUC=0.650 (C-index=0.65). Subgroup analyses confirmed prognostic consistency across clinical characteristics (p-interaction>0.05).
Conclusion: ALI is an independent prognostic factor for advanced breast cancer patients with good predictive ability. It provides an important supplementary prognostic marker for clinical practice and can help optimize personalized treatment strategies.
1 Background
According to the 2022 global statistics report from GLOBOCAN (1), breast cancer ranks second in incidence and fourth in mortality among 185 countries and 36 types of cancer. In China, the incidence and mortality of breast cancer continue to rise, making it a significant public health issue (2). With the increase in medical insurance coverage and advancements in cancer screening technologies, early diagnosis of breast cancer has significantly improved, and survival rates have risen accordingly (3–5). However, some patients are diagnosed with advanced breast cancer at the initial diagnosis, with metastatic cases constituting about 38% of newly diagnosed cases (6). Treatment for advanced breast cancer requires a multidisciplinary team approach, including endocrine therapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy (7). While precision oncology frameworks have advanced subtype-specific management, therapeutic optimization for metastatic breast cancer remains clinically challenging (8, 9). Prognostic prediction is crucial for guiding treatment strategies, but the prognosis of advanced breast cancer is difficult to predict. Therefore, new biomarkers are urgently needed to help predict the patient’s survival and enable early intervention and personalized treatment.
The growth and metastasis of tumors are closely related to systemic inflammation and nutritional status. Numerous studies have shown that nutritional and inflammatory markers can serve as effective prognostic predictors for malignant tumors (10–15). The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), a well-established inflammatory biomarker, has been widely employed in assessing treatment response, (16) monitoring complications, (17) and predicting survival in breast cancer patients. (18) NLR is calculated as the absolute neutrophil count divided by the absolute lymphocyte count in peripheral blood. Notably, elevated NLR levels are significantly associated with poorer prognosis and reduced survival rates. (19) However, NLR alone has limitations in comprehensively reflecting the complex relationship between inflammation and nutrition in cancer patients. The relationship between inflammation and cancer is inseparable because inflammation creates a favorable environment for the spread of cancer cells and triggers signaling pathways that promote carcinogenesis (20). Inflammation and the tumor microenvironment play significant roles in the progression and metastasis of breast cancer (21). Many cancer patients suffer from cachexia, and malnutrition weakens the body’s ability to fight tumors. Serum albumin (ALB), as an indicator of nutritional status, has been proven to be closely associated with poor prognosis in multiple cancer types (22–24).
The Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI), originally developed for lung cancer, synergistically quantifies nutritional-inflammation equilibrium through the formula: ALI = (BMI × albumin)/NLR (25). Compared to NLR, ALI offers a more comprehensive assessment of cancer patients’ condition. By integrating NLR with BMI and albumin levels, ALI simultaneously evaluates both the inflammatory response and nutritional status, two critical determinants of cancer progression and prognosis. Although the Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) has been extensively validated for prognostic assessment in malignancies such as lung, hepatic, gastric, and colorectal cancers, robust evidence confirms that low ALI correlates with adverse oncologic outcomes (26–29). However, a critical evidence gap persists regarding its clinical utility in breast cancer, particularly among Asian populations. This discrepancy may result from aerodigestive tract malignancies altering normal anatomical structures and physiological functions, which compromises the gastrointestinal barrier, leading to malabsorption syndromes, cachexia, and systemic inflammatory responses, thereby significantly enhancing the sensitivity of ALI. Notably, advanced breast cancer induces systemic inflammatory responses and metabolic reprogramming (30–32), suggesting that the ALI may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker in this patient population.
The primary goal of this study is to explore the application of the ALI in the survival prognosis of advanced breast cancer patients, with a focus on its predictive value in Asian populations. We will analyze the significance of ALI in predicting overall survival (OS) and hope that these findings will provide new biomarkers for the prognostic evaluation of breast cancer patients, offering more effective treatment guidance for clinical practice and ultimately improving patients’ quality of life and survival duration.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Patient selection
This study, conducted through a single-center retrospective cohort analysis, aims to explore the prognostic efficacy of the ALI on overall survival (OS) in patients with advanced breast cancer. The study included 163 breast cancer patients with distant metastases confirmed during their initial hospitalization at Guangxi Medical University Affiliated Tumor Hospital (September 2016-September 2023). The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Pathologically confirmed primary breast cancer; (2) Distant metastasis of breast cancer confirmed through imaging studies, including positron emission tomography (PET-CT), whole-body skeletal imaging, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or pathological biopsy; (3) Completion of clinical blood biomarker tests prior to surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or other treatments; (4) Complete clinical, pathological, and follow-up data. The exclusion criteria were: (1) Presence of other malignant tumors; (2) Severe underlying diseases, major organ dysfunction, autoimmune diseases, or psychiatric disorders. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital (KY2023868).
2.2 Data collection
The survival status of the patients was followed up via telephone, and baseline data, including age, height, weight, hypertension, diabetes, marital status, education level, medical insurance, residence, and menstrual status, were collected through electronic medical records. Clinical data such as pathological type, histological grade, molecular subtype, KI-67, TNM stage, sites of distant metastasis, and treatment methods (e.g., surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, etc., defined as all treatments received up to the subsequent follow-up time) were also collected. Peripheral blood data, including neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, and albumin levels, were used to calculate ALI. All baseline clinical parameters (excluding treatment regimens) were derived from the initial hematological and physical examination results obtained during patients’ first hospitalization for breast cancer - the same admission during which distant metastases were pathologically or radiologically confirmed. In this study, the follow-up period was defined as the interval between the date of first hospital admission for breast cancer (starting point) and the date of death or last follow-up (endpoint). It should be noted that due to variations in enrollment time and disease progression, not all patients had follow-up durations reaching 3 or 5 years.
2.3 Laboratory measurements and quality control procedures
All blood tests in this study were performed in strict accordance with the standardized protocols of Chinese public tertiary hospitals. After an 8-hour overnight fast, venous blood samples were collected from the antecubital vein in the morning and aliquoted into EDTA tubes (2 mL for complete blood count) and serum separator tubes (4 mL for liver function tests). Complete blood count analysis was performed within 2 hours after collection using a Mindray CAL8000plus automated hematology analyzer (Shenzhen, China). Liver function tests, including albumin measurement, were completed within 4 hours using a Siemens ADVIA Chemistry XPT automated biochemical analyzer (Germany). The laboratory strictly adhered to the quality control standards established by the National Center for Clinical Laboratories (NCCL), and all technicians were certified for clinical laboratory operations.
2.4 ALI calculation and stratification
The Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) integrates three indicators: serum albumin, body mass index (BMI), and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR). It is calculated as: , where:
2.5 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R 4.3.3 and SPSS 25. Continuous variables with a normal distribution were presented as means and standard deviations, non-normally distributed continuous variables as medians and interquartile ranges, and categorical variables as percentages. Based on the distribution characteristics of ALI in the study population, K-means clustering was used to divide the patients into a high-ALI group (n=64) and a low-ALI group (n=99). Two-sample independent t-tests were used for continuous variables with normal distribution, and chi-square tests were used for categorical variables to compare baseline characteristics and incidence rates between the high-ALI and low-ALI groups. Time-to-event endpoints were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier curves with log-rank testing. To further explore the relationship between ALI and survival, Cox proportional hazards models were constructed with sequential adjustment: Model 1: Unadjusted; Model 2: Adjusted for sociodemographic covariates (age, education, insurance, hypertension, diabetes, marital status, residence, and menstrual status);Model 3: Fully adjusted for clinical-pathological variables (age, education, insurance, hypertension, diabetes, marital status, residence, menstrual status, pathological type, histological grade, and molecular subtype). Results are presented as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Additionally, restricted cubic spline functions were used to visualize the dose-response relationship between ALI and OS in breast cancer. To evaluate the predictive ability of ALI at different time points (3 and 5 years), time-dependent ROC curve analysis was conducted, and the C-index was calculated. These time points were selected to align with clinical long-term prognostic assessment needs. The method accounted for censored data by utilizing all follow-up information until death or last contact, ensuring robust evaluation of ALI’s discriminative performance at predefined intervals. Finally, subgroup analysis was performed to validate the predictive ability of ALI in different populations, assessing its prognostic effect under varying patient characteristics.
3 Result
3.1 Median follow-up time
Among the 163 patients, 61 (37.4%) died. Since the Kaplan-Meier survival curve did not drop below 50% (minimum survival rate = 62.6%), the median survival time was not reached. The median follow-up was 43 months (95% CI 34.4–51.6) using reverse Kaplan-Meier estimation.
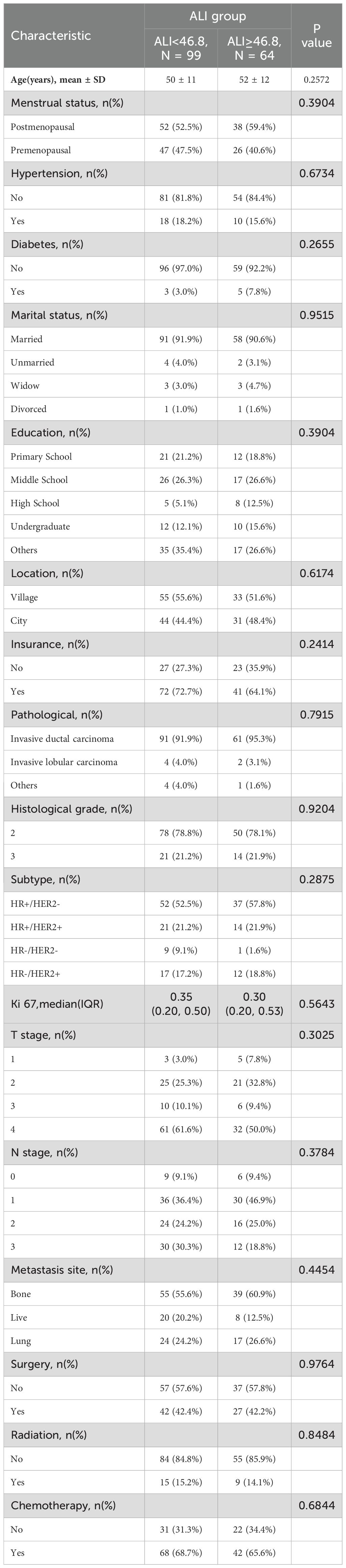
3.2 Baseline characteristics
K-means clustering divided ALI into high-ALI (n=64) and low-ALI (n=99) groups. Baseline characteristics were balanced between the two groups in terms of age, tumor location, tumor pathological type, molecular subtype, TNM stage, or treatment modalities(radiotherapy, chemotherapy, surgery, etc.) (all p>0.05)(Table 1). Specifically, regarding age distribution, the average age of patients in the high-ALI group was 52 years, while that in the low-ALI group was 50 years, with no statistically significant difference between the two groups. Concerning pathological types, whether it was invasive ductal carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma, or other types, the composition ratios of the two groups showed no significant differences. Among molecular subtypes, the distribution ratios of HR+/HER2-, HR+/HER2+, HR-/HER2-, and HR-/HER2+ subtypes were also comparable between the two groups. For TNM staging, the proportions of patients were basically the same in both groups. In terms of treatment modalities, the proportions of patients receiving radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgery were not significantly different between the two groups. This indicates that the high- ALI and low-ALI groups did not differ significantly in these confounding factors, thereby reducing their interference with survival analysis.
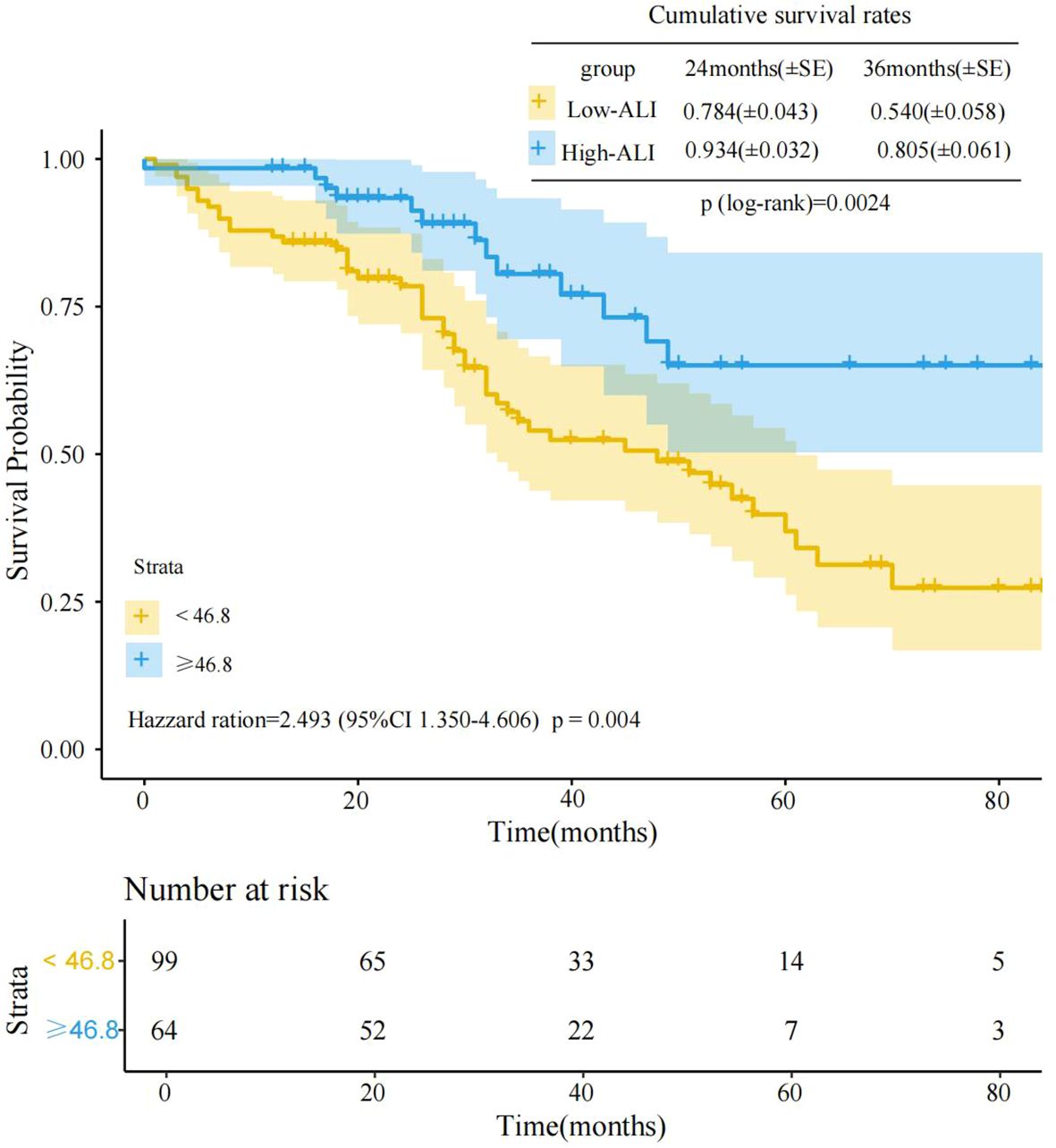
Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of the two groups’ prognostic differences revealed significant survival differences between the high-ALI and low-ALI groups(log-rank p=0.0024)(Figure 1). As clearly shown in Figure 1, at the initial stage of follow-up, the survival rate curves of the two groups were relatively close. However, as time progressed, the survival rate curve of the high-ALI group was significantly higher than that of the low-ALI group. At 36 months of follow-up, the cumulative survival rate was 0.805 (80.5%) in the high-ALI group versus only 0.540 (54.0%) in the low-ALI group. Cox proportional hazards regression further quantified this association, revealing that the low-ALI group had a 2.493-fold higher risk of poor outcomes compared to the high-ALI group (HR = 2.493, 95% CI: 1.350–4.606, p = 0.004). These results robustly support ALI as an independent prognostic indicator for advanced breast cancer, with low ALI signaling significantly worse survival.
3.3 Dose–response relationship
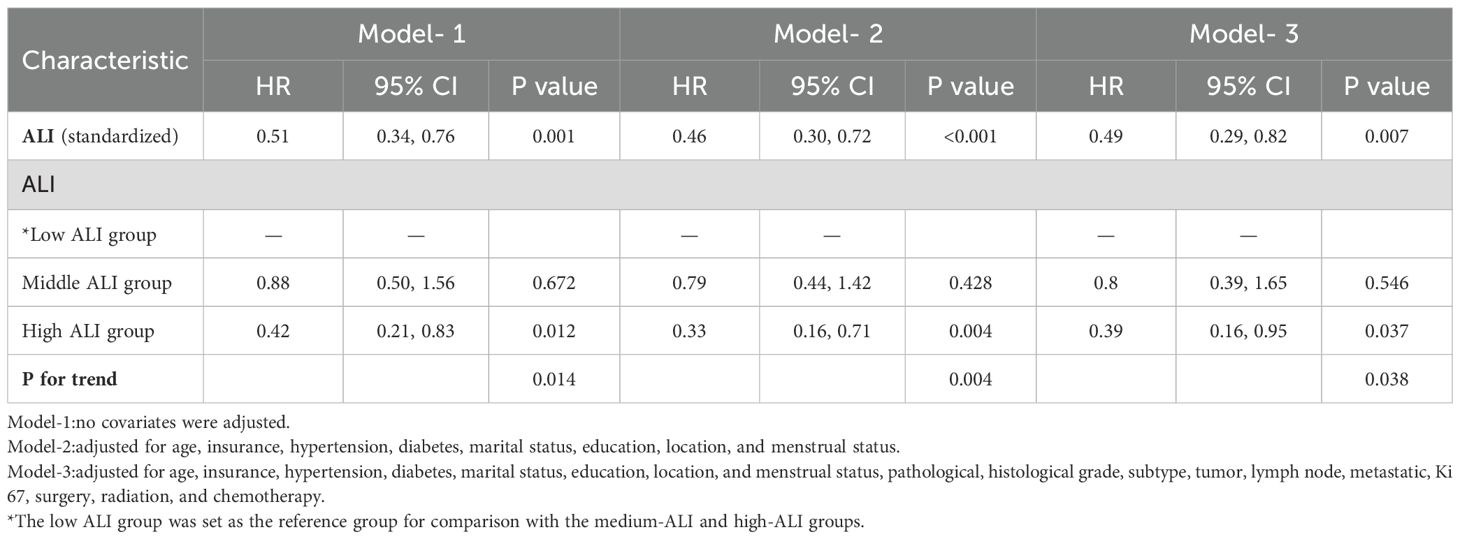
In Cox regression models (Table 2), the results demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between ALI and mortality risk in advanced breast cancer patients. Three progressively adjusted models consistently revealed this protective association: When ALI was treated as a continuous variable, the unadjusted model (Model 1), the adjusted model (Model 2), and the fully adjusted model (Model 3) all suggested that the risk of death in advanced breast cancer decreased with increasing ALI; each unit increase in ALI corresponded to a 49% to 54% reduction in mortality risk. When using tertiles as a categorical variable, at least one quartile of each index was significantly related to the prognosis of advanced breast cancer, with trend tests showing statistical significance (p for trend<0.05). The three models confirmed ALI as an independent protective factor for survival in advanced breast cancer patients. In Model 2, after adjusting for clinical characteristics (e.g., age, marital status, diabetes), patients in the high-ALI group had significantly better survival compared to those in the low-ALI group (HR=0.33, 95% CI: 0.16-0.71, P=0.004). Even with further adjustments for potential prognostic factors (e.g., pathological type, molecular subtype, treatment methods) in Model 3, the prognostic significance of ALI remained (HR=0.39, 95% CI: 0.16-0.95, p=0.037). These results indicate that high ALI is an independent protective factor for survival in advanced breast cancer patients. To further explore the possible nonlinear relationship between ALI and survival, we conducted a restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis (Figure 2). The results showed that no significant nonlinear association was observed between ALI and survival (p-nonlinear = 0.724). This suggests that the relationship between ALI and survival may be approximately linear, with survival time increasing linearly as ALI values rise, indicating that ALI can effectively reflect the prognosis of patients with advanced breast cancer.
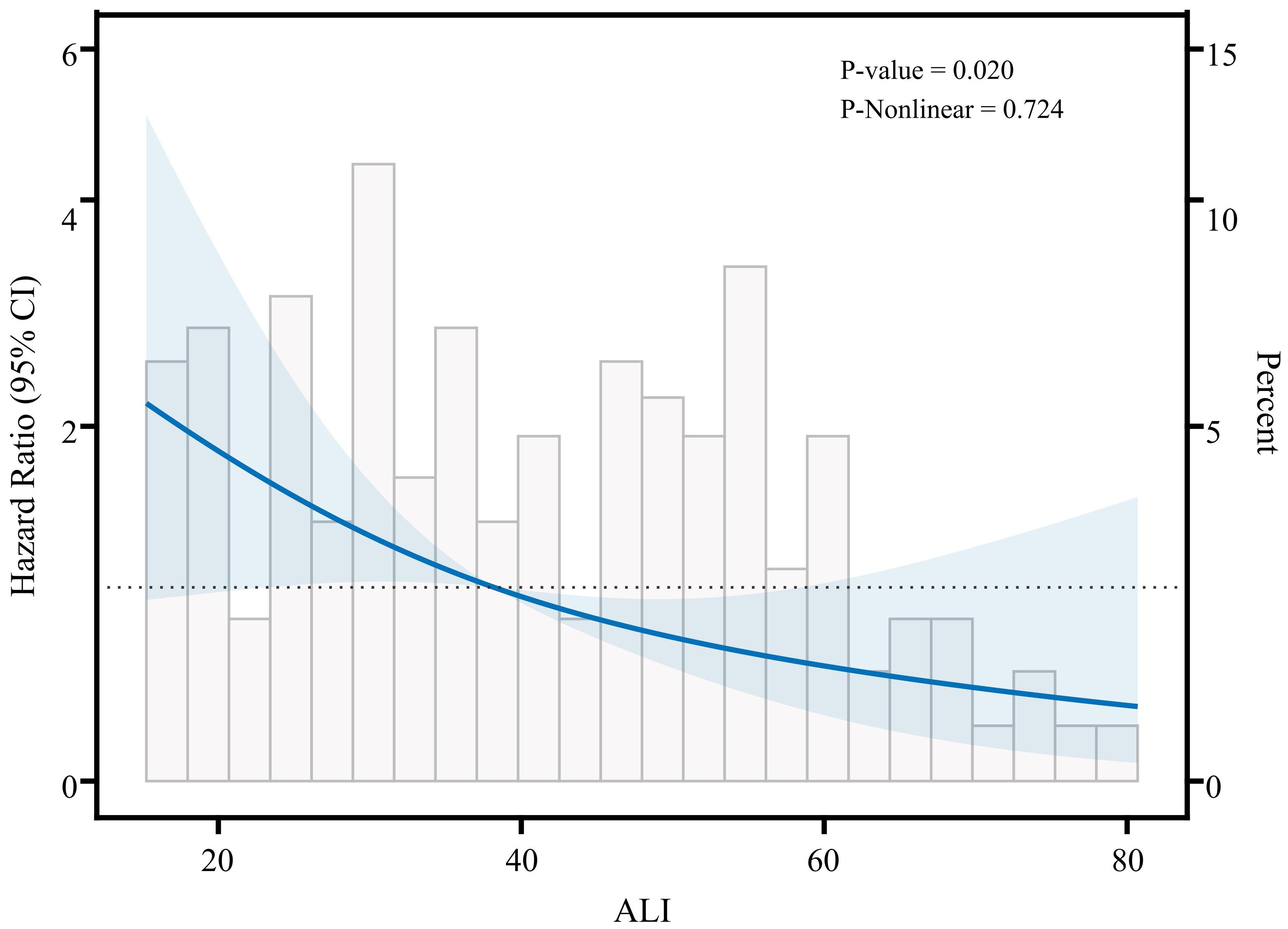
Figure 2. Restricted cubic spline analysis showing the relationship between ALI and survival risk in patients with advanced breast cancer.
3.4 Predictive ability of ALI
Time-dependent ROC curve analysis Figure 3A was used to evaluate the predictive ability of ALI for survival in advanced breast cancer patients at different time points (3 years and 5 years). The ROC curves demonstrated consistent discriminative performance across both time points, with an AUC value of 0.645 at 3 years and 0.650 at 5 years. Time-dependent C-index analysis (Figure 3B) further confirmed that ALI maintained moderate predictive ability throughout the follow-up period (C-index=0.65).These results suggest that ALI is clinically valuable for predicting both short- and long-term survival in advanced breast cancer patients and can serve as an important auxiliary indicator for prognostic evaluation.
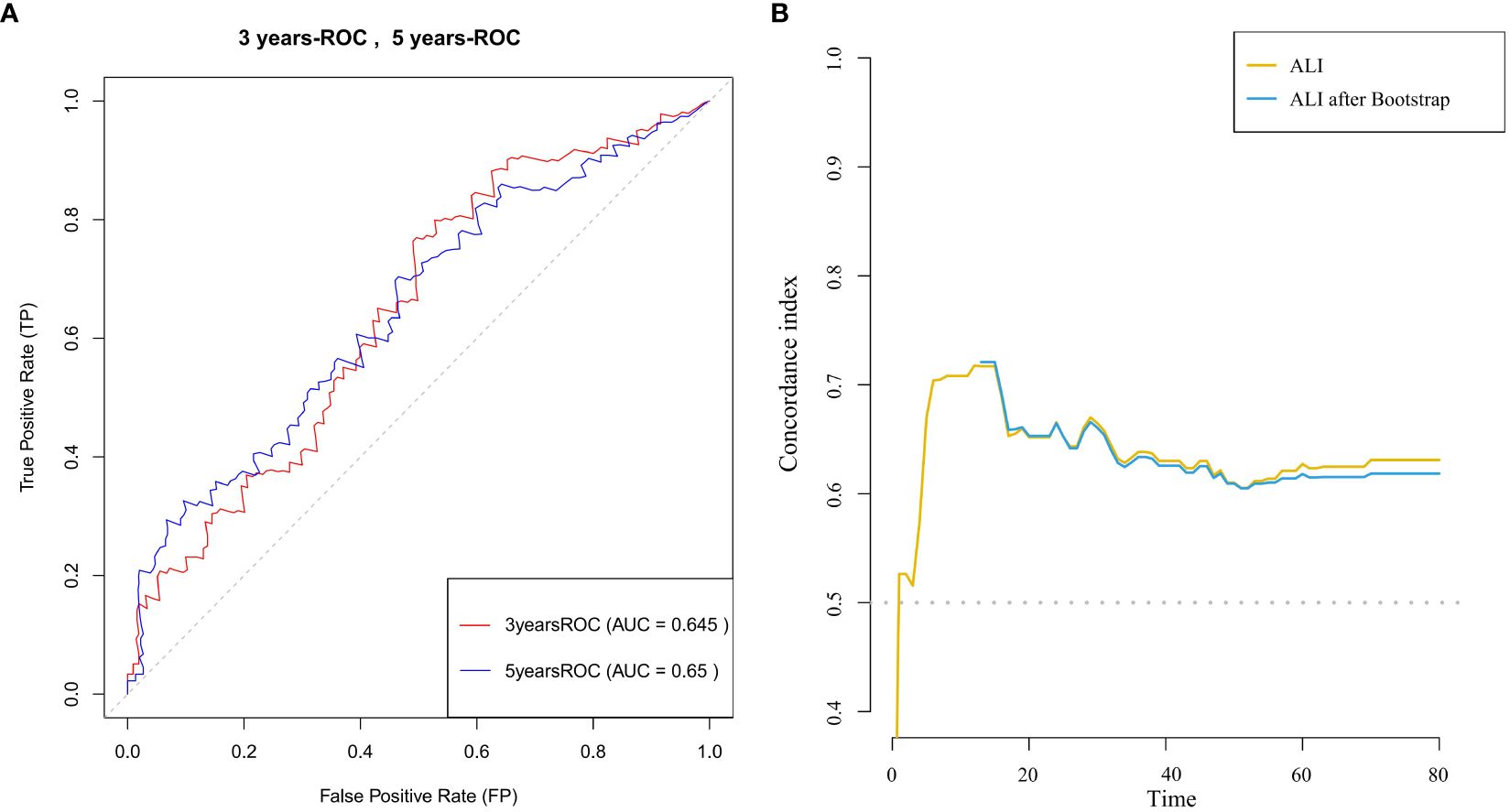
Figure 3. (A) ROC curves for 3-year and 5-year survival prediction in patients with advanced breast cancer, with the area under the curve (AUC) for each time point shown. (B) C-index curve illustrating the relationship between ALI and survival time in patients with advanced breast cancer.
3.5 Stratified analysis
Finally, to assess the differential prognostic effect of ALI under different patient characteristics, we performed a subgroup analysis focusing on its survival prediction ability in different clinical subgroups. Patients were categorized based on age (<50 years vs ≥50 years), menopausal status (premenopausal vs postmenopausal), molecular subtype (HR+/HER2-, HR+/HER2+, HR-/HER2-, HR-/HER2+), and treatment modality (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy) (Figure 4). Subgroup analysis showed that after adjusting for all known confounders, ALI consistently predicted survival across all subgroups (p for interaction > 0.05), indicating that ALI retains its prognostic value in various clinical contexts. This suggests that ALI has independent prognostic significance across different patient populations, unaffected by individual characteristics and treatment methods. Therefore, ALI can be considered a robust biomarker for survival prediction in advanced breast cancer patients.
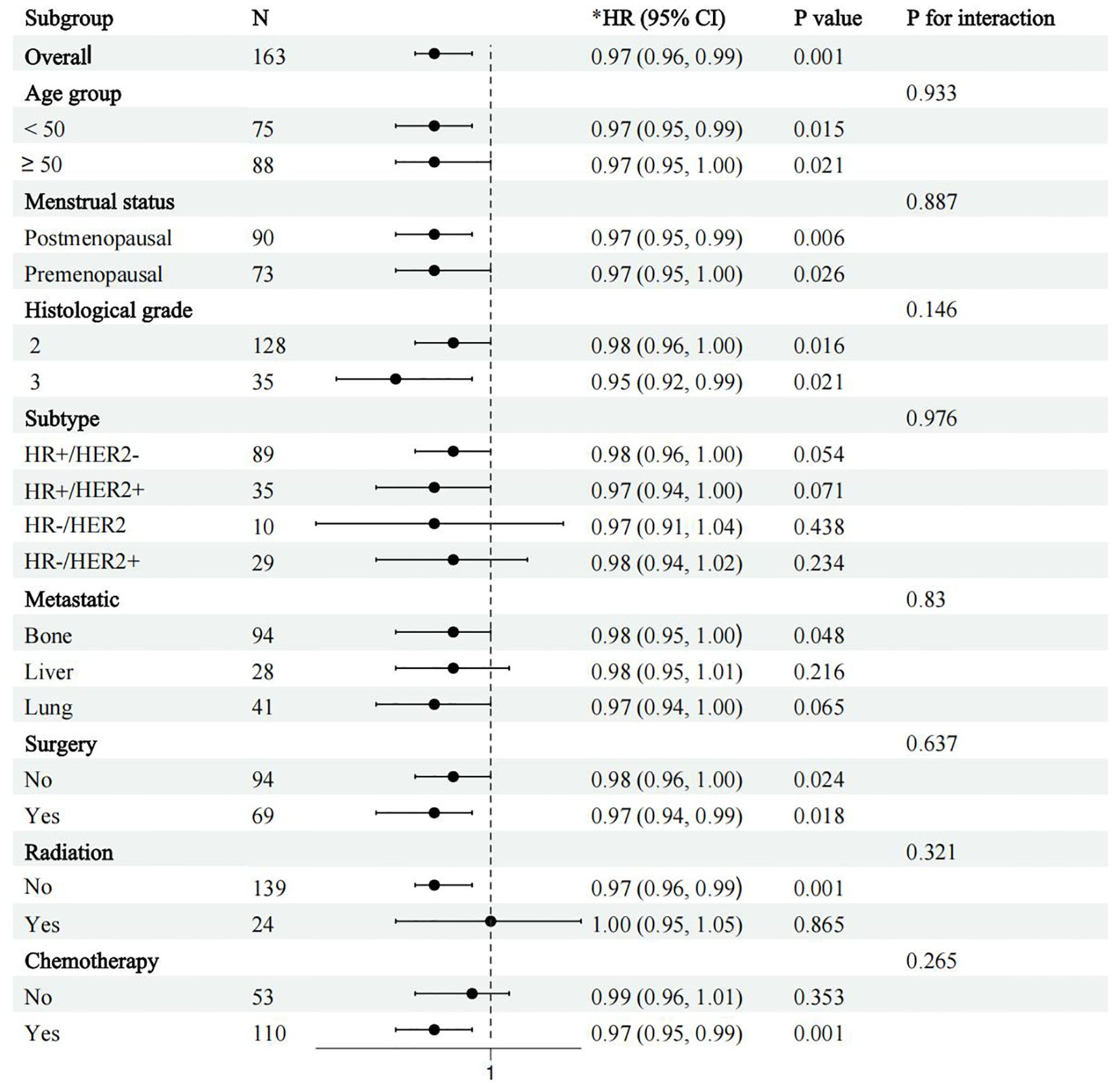
Figure 4. Forest plot of subgroup analysis showing survival outcomes by age, molecular subtype, and treatment modality (surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, etc.) in patients with advanced breast cancer. *adjusted for age, insurance, hypertension, diabetes, marital status, education, location, and menstrual status, pathological, histological grade, subtype, tumor, lymph node, metastatic, Ki 67, surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
4 Discussion
To our knowledge, this represents the first investigation applying ALI to prognostication in advanced breast cancer, extending its validation beyond gastrointestinal and lung malignancies. The results show that patients in the high-ALI group have significantly better survival compared to those in the low-ALI group. More importantly, this relationship remains independently significant in the multivariate Cox regression model (HR = 0.39). Furthermore, through 1-year and 3-year time-dependent ROC curve analysis, ALI demonstrates stable predictive ability. Although the AUC values are slightly lower, it is noteworthy that ALI, as an integrated index of inflammation and nutritional status, may compensate for the shortcomings of individual indicators, thus highlighting its potential in prognostic evaluation. Overall, ALI provides a new biomarker for survival prognosis in advanced breast cancer patients and could offer more precise personalized guidance for clinical treatment strategies.
A large number of studies have confirmed that inflammatory indices based on peripheral blood tests, such as the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII), Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), Lymphocyte-Monocyte Ratio (LMR), C-reactive protein (CRP), and albumin (ALB),have significant value in early cancer diagnosis and screening (33), treatment monitoring (34), tumor metastasis and invasiveness (35), and prognostic evaluation (36). It is noteworthy that a meta-analysis by Mei et al. (including 66 cohort studies) showed that NLR is significantly associated with prognosis in patients with various advanced cancers, including breast cancer. High NLR values were significantly associated with poor overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) (37). Moreover, a study conducted on an important cohort of 1763 breast cancer patients revealed that a low NLR was an independent predictor of 5-year local recurrence-free survival (LRRFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), and disease-free survival (DFS) (38). Further studies by Lafrenie et al. on triple-negative breast cancer indicated that NLR was a more accurate predictor of long-term survival than LMR. In comparison, LMR showed limited effectiveness in prognostic evaluation (39). This suggests that NLR, as a simple and readily accessible indicator, is more universal for prognostic assessment. Given the significant predictive value of NLR, this study integrates it into ALI to improve predictive performance using multi-dimensional indices.
Besides inflammatory markers, nutritional status has also been confirmed to be closely related to cancer prognosis. For example, a meta-analysis by Polański et al. demonstrated that nutritional indicators such as serum albumin, weight loss, and BMI are related to the survival and quality of life in lung cancer patients (40). A meta-analysis by Prasetiyo et al. on the impact of nutritional status on survival in breast cancer patients found that good nutritional status significantly improved survival rates (41). Although indices such as Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) mentioned in the analysis differ from ALI, they offer insights for assessing patients’ nutritional status and predicting survival prognosis. Regarding the relationship between nutritional status and tumor development, Hopkins et al. emphasized the link between obesity and cancer metabolism, discovering that a patient’s nutritional status affects metabolic pathways, alters the tumor microenvironment, and thus impacts clinical prognosis (42). Based on this evidence, ALB and BMI, which reflect energy reserves and protein metabolism status, support the integrated consideration of both factors in the prognostic evaluation of advanced breast cancer.
Currently, many studies have shown that combined indices of nutritional status and inflammatory markers perform better than single inflammatory or nutritional indicators in prognostic prediction. For example, in a prospective multicenter study, the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) standard based on inflammatory markers had stronger predictive value for short- and long-term prognosis in cancer patients compared to the original GLIM standard (13). Similarly, in the development of cancer prognosis models, Zhu et al. demonstrated that combining an inflammation-nutrition model could significantly predict post-surgical outcomes in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (43). Compared to the above studies, the innovation of ALI lies in its mathematical integration of BMI, ALB (nutrition), and NLR (inflammation), using a simplified formula to capture multi-dimensional information. This design enables ALI to combine clinical usability with predictive efficacy, especially in limited medical settings.
ALI was first applied to prognosis prediction in advanced lung cancer and has gradually been extended to other types of cancers, with low ALI levels often correlating with worse survival (44). In a study by Song M et al., which included 1,772 lung cancer patients, 16 nutritional or systemic inflammatory indices were assessed using time-ROC and C-index. Results showed that ALI had superior prognostic predictive ability compared to other inflammatory or nutritional indices for all lung cancer patients (29). As a multi-cancer prognostic biomarker, ALI has also been validated in gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, and post-surgical prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma (45–47). Moreover, ALI is not only applicable to solid tumors but can also predict chemotherapy response and infection risks in multiple myeloma patients, with low ALI associated with a higher risk of adverse reactions (48). Consistent with previous studies, this study found that high ALI is independently associated with improved survival in advanced breast cancer (HR = 0.39), and the C-index for ALI in predicting OS at 1, 3, and 5 years in lung cancer was greater than 0.6 (29), which is consistent with findings in gastric cancer (low ALI is a risk factor for OS in gastric cancer, HR = 1.55, 95% CI: 1.11-2.16, P = 0.010) (28). Mechanistically, ALI may affect prognosis through two pathways: firstly, high NLR reflects systemic inflammation, which promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-6, TNF-α) and drives tumor invasion via the STAT3 pathway (49, 50). Secondly, low BMI and ALB indicate a pre-cachexia state, leading to metabolic reprogramming (51, 52). These mechanisms support the findings of this study, suggesting that ALI, by integrating nutritional and inflammatory factors, serves as a potential prognostic tool for advanced breast cancer.
The detection of cytokines such as interleukin-8 (IL-8) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) holds significant importance in studying tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients. (53, 54) However, current detection methodologies—including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), flow cytometry (FCM), and enzyme-linked immunospot assay (ELISPOT)—face substantial challenges such as high costs and technical complexity, which significantly limit their clinical translation and widespread adoption. By integrating nutritional status indicators (BMI, serum albumin) with inflammatory surrogate markers (NLR), ALI achieves reliable assessment of systemic inflammatory response. All components of this system derive from standard blood tests, featuring operational simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and strong reproducibility, enabling rapid implementation across healthcare institutions at all levels. Compared with advanced detection technologies like genomic sequencing and functional imaging, the ALI evaluation system demonstrates distinct advantages in clinical scenarios such as county-level hospitals and community-based cancer follow-up. Its “low-cost, high-efficiency” characteristics not only offer a practical tool for tumor prognosis assessment but also bridge the technological gap in systemic inflammation monitoring within primary healthcare systems.
Based on the findings of this study, the C-index for ALI remains stable over time Figure 3B, indicating its reliability for long-term predictive efficacy. Therefore, we recommend incorporating ALI into existing prognostic systems (e.g., TNM staging). Specifically, setting a threshold (ALI <46.8) could help identify high-risk patients, enabling more frequent follow-up or adjustments to treatment plans (e.g., early nutritional support intervention). Moreover, considering the key role of nutritional status in advanced breast cancer prognosis, we further suggest incorporating ALI into regular nutritional assessment systems, initiating multidisciplinary interventions (e.g., personalized dietary guidance, anti-inflammatory treatment) for low-ALI patients, in hopes of improving survival outcomes by correcting nutritional-inflammation imbalances.
Although previous studies have explored the relationship between the ALI and the occurrence of breast cancer (55), this study further applies this index to the survival prognosis evaluation of advanced breast cancer patients. This innovative shift not only enriches the existing literature but also provides a new perspective for clinical treatment and individualized management of advanced breast cancer. However, this study is a single-center retrospective analysis with a small sample size and single-source data. Although statistical adjustments controlled for various confounding factors, the retrospective design still limits causal inference. Nevertheless, it lays the foundation for subsequent large-sample, multi-center prospective studies.
Specifically, future research can first validate our findings. Secondly, dynamic NLR (the dynamic changes in the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio) may reflect tumor progression and immune response more sensitively than traditional static NLR. Inspired by this, Moldoveanu et al. found that dynamic NLR had better prognostic prediction in triple-negative breast cancer patients, with higher dynamic NLR changes closely associated with worse OS and PFS (56). This discovery offers new ideas for clinical treatment and prognostic evaluation in breast cancer. Future studies may explore dynamic changes in ALI to capture clinical pathophysiological changes more effectively. Additionally, although time-dependent ROC curves in this study showed stable predictive ability at 3and 5 years, the AUC values were not very high, possibly due to the high heterogeneity of breast cancer or the more significant modulation of inflammatory status by targeted treatments. Therefore, future research will further explore ALI combined with other molecular markers, immune responses, tumor microenvironment, and other potential influencing factors to refine prognostic models. Additionally, the predictive differences of ALI in different regions, ethnicities, tumor types, subtypes of breast cancer (e.g., HER2+ vs triple-negative), and different treatment strategies should be studied to provide personalized clinical references.
Notably, subgroup analysis in this study shows that the prognostic value of ALI is not affected by treatment modality (p-interaction > 0.05), suggesting that ALI may serve as a universal marker across treatment regimens. Prospective studies should clarify ALI-treatment synergies, especially for low-ALI patients who may benefit from combo therapies (e.g., nutrition + immunotherapy). Finally, we did not explore its potential molecular mechanisms or its role in assessing treatment responses in breast cancer patients receiving different therapies. These are areas that require further investigation.
5 Conclusion
This study confirms that ALI, as a comprehensive biomarker assessing nutritional status and inflammatory response, holds significant value in predicting the survival prognosis of advanced breast cancer patients. Moreover, the ALI system is an easy-to-use, low-cost solution for monitoring inflammation and predicting tumor outcomes, making it especially useful in areas with limited medical resources. ALI not only serves as an independent prognostic factor but also demonstrates good time-dependent predictive ability, providing a strong basis for personalized treatment in breast cancer patients. Prospective validation should evaluate dynamic ALI monitoring during treatment response and explore synergy with emerging biomarkers (e.g., ctDNA, PD-L1). Additionally, the integration of ALI with immune responses, the tumor microenvironment, and other factors should be expanded to enhance the accuracy and clinical applicability of prognostic models, promoting the realization of personalized treatment.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital (KY2023868). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by-product of routine care or industry. The requirement for written informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Author contributions
CL: Software, Investigation, Conceptualization, Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Visualization, Methodology. CY: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Project administration, Data curation, Software, Conceptualization, Investigation. QY: Resources, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Validation, Software. YT: Validation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Software, Data curation. WZ: Data curation, Visualization, Validation, Software, Writing – review & editing. QT: Project administration, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. QQ: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82160481, 82460522) The Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (General Program, Grant No. 2019GXNSFAA245067).
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to all the staff contributing to this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cancer Today.Global Cancer Observatory (2024). Available online at: https://gco.iarc.fr/en (Accessed September 15, 2024).
2. Lei S, Zheng R, Zhang S, Chen R, Wang S, Sun K, et al. Breast cancer incidence and mortality in women in China: temporal trends and projections to 2030. Cancer Biol Med. (2021) 18:900–9. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0523
3. Ko NY, Hong S, Winn RA, and Calip GS. Association of insurance status and racial disparities with the detection of early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2020) 6(3):385–92. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5672
4. Fields BKK and Joe BN. Screening breast MRI effectively detects early-stage breast cancer in high-risk patients without prior history of breast cancer. Radiology: Imaging Cancer. (2024) 6(2):e249005. doi: 10.1148/rycan.249005
6. Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. (2018) 391:1023–75. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)33326-3
7. Cardoso F, Harbeck N, Fallowfield L, Kyriakides S, and Senkus E. Locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2012) 23:vii11–9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds232
8. Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C, and Curigliano G. Breast cancer. Lancet. (2021) 397:1750–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32381-3
9. Hong R and Xu B. Breast cancer: an up-to-date review and future perspectives. Cancer Commun. (2022) 42:913–36. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12358
10. Wang D, Bai N, Hu X, OuYang XW, Yao L, Tao Y, et al. Preoperative inflammatory markers of NLR and PLR as indicators of poor prognosis in resectable HCC. PeerJ. (2019) 7:e7132. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7132
11. Li J, Cao D, Huang Y, Xiong Q, Tan D, Liu L, et al. The prognostic and clinicopathological significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in bladder cancer. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:865643. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.865643
12. Zeng D, Wen N-Y, Wang Y-Q, Cheng N-S, and Li B. Prognostic roles of the prognostic nutritional index in patients with resectable and advanced biliary tract cancers. World J Gastroenterology. (2025) 31(6):976–97. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i6.97697
13. Xie H, Yuan K, Ruan G, Wei L, Zhang H, Ge Y, et al. Improving the assessment of malnutrition in cancer: Using systemic inflammation markers as a supplement to the inflammation items of the GLIM criteria. Clin Nutr. (2023) 42:2036–44. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.08.020
14. Xie H, Wei L, Ruan G, Zhang H, Shi J, Lin S, et al. Performance of anthropometry-based and bio-electrical impedance-based muscle-mass indicators in the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria for predicting prognosis in patients with cancer. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:1791–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.05.039
15. Guo W, Lu X, Liu Q, Zhang T, Li P, Qiao W, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for breast cancer patients: An updated meta-analysis of 17079 individuals. Cancer Med. (2019) 8:4135–48. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2281
16. von Au A, Shencoru S, Uhlmann L, Mayer L, Michel L, Wallwiener M, et al. Predictive value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte-ratio in neoadjuvant-treated patients with breast cancer. Arch Gynecology Obstetrics. (2022) 307:1105–13. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06726-7
17. Baruch R, Zahler D, Zornitzki L, Arbel Y, Rozenbaum Z, Arnold JH, et al. High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an early sign of cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients treated with anthracycline. Clin Cardiol. (2023) 46:328–35. doi: 10.1002/clc.23966
18. Corbeau I, Jacot W, and Guiu S. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as prognostic and predictive factor in breast cancer patients: A systematic review. Cancers. (2020) 12(4):958. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040958
19. Ethier JL, Desautels D, Templeton A, Shah PS, and Amir E. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. (2017) 19(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0794-1
20. Philip M, Rowley DA, and Schreiber H. Inflammation as a tumor promoter in cancer induction. Semin Cancer Biol. (2004) 14:433–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2004.06.006
21. Ham M and Moon A. Inflammatory and microenvironmental factors involved in breast cancer progression. Arch Pharmacal Res. (2013) 36:1419–31. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0271-7
22. Wang X, Xu J, Zhang H, and Qu P. The effect of albumin and hemoglobin levels on the prognosis of early-stage cervical cancer: a prospective, single-center–based cohort study. BMC Women's Health. (2023) 23(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02713-5
23. Zhou X, Fu G, Zu X, Xu Z, Li H-T, D'Souza A, et al. Albumin levels predict prognosis in advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Urologic Oncology: Semin Original Investigations. (2022) 40:12.e13–22. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.08.001
24. Zhang C-L, Gao M-Q, Jiang X-C, Pan X, Zhang X-Y, Li Y, et al. Research progress and value of albumin-related inflammatory markers in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer: a review of clinical evidence. Ann Med. (2023) 55:1294–307. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2192047
25. Jafri SH, Shi R Fau - Mills G, and Mills G. Advance lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) at diagnosis is a prognostic marker in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a retrospective review. BMC Cancer. (2013). doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-158
26. Li Q, Ma F, and Wang JF. Advanced lung cancer inflammation index predicts survival outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving immunotherapy. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:997314. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.997314
27. Zhang B, Li Z-W, Tong Y, Yuan C, Liu X-Y, Wei Z-Q, et al. The predictive value of advanced lung cancer inflammation index for short-term outcomes and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients who underwent radical surgery. Int J Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:1616–24. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02410-1
28. Chen H, Zhang F, Luo D, Guo J, Lin Y, Chen S, et al. Advanced lung cancer inflammation index predicts the outcomes of patients with non-metastatic gastric cancer after radical surgical resection. J Gastrointestinal Oncol. (2023) 14:85–96. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-657
29. Song M, Zhang Q, Song C, Liu T, Zhang X, Ruan G, et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index is the optimal inflammatory biomarker of overall survival in patients with lung cancer. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:2504–14. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13032
30. Chauhan SK, Dunn C, Andresen NA-O, Røssevold AA-O, Skorstad G, Sike A, et al. Peripheral immune cells in metastatic breast cancer patients display a systemic immunosuppressed signature consistent with chronic inflammation. NPJ Breast Cancer. (2024) 10(1):30. doi: 10.1038/s41523-024-00638-2
31. Liu S, Zhang X, Wang W, Li X, Sun X, Zhao Y, et al. Metabolic reprogramming and therapeutic resistance in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02165-x
32. Biondini M, Lehuédé C, Tabariès S, Annis MG, Pacis A, Ma EH, et al. Metastatic breast cancer cells are metabolically reprogrammed to maintain redox homeostasis during metastasis. Redox Biol. (2024) 75:103276. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103276
33. Nøst TH, Alcala K, Urbarova I, Byrne KS, Guida F, Sandanger TM, et al. Systemic inflammation markers and cancer incidence in the UK Biobank. Eur J Epidemiol. (2021) 36:841–8. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00752-6
34. Choucair K, Nebhan C, Cortellini A, Hentzen S, Wang Y, Liu C, et al. Characterization of age-associated, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) as biomarkers of inflammation in geriatric patients with cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: impact on efficacy and survival. Cancers. (2023) 15(20):5052. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205052
35. Zhang X, Wang X, Li W, Sun T, Diao D, and Dang C. Predictive value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for distant metastasis in gastric cancer patients. Sci Rep. (2022) 12(1):10269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14379-4
36. Liu W, Ren S, Yang L, Xiao Y, Zeng C, Chen C, et al. The predictive role of hematologic markers in resectable nsclc patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Surgery. (2023). doi: 10.1097/js9.0000000000000650
37. Mei Z, Shi L, Wang B, Yang J, Xiao Z, Du P, et al. Prognostic role of pretreatment blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in advanced cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 66 cohort studies. Cancer Treat Rev. (2017) 58:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.05.005
38. Truffi M, Piccotti F, Albasini S, Tibollo V, Morasso CF, Sottotetti F, et al. Preoperative systemic inflammatory biomarkers are independent predictors of disease recurrence in ER+ HER2- early breast cancer. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:773078. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.773078
39. Lafrenie RM, Jia W, Wu J, Jia H, Yang Y, Zhang X, et al. The peripheral blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is superior to the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio for predicting the long-term survival of triple-negative breast cancer patients. PloS One. (2015) 10(11):e143061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143061
40. Polański J, Chabowski M, Świątoniowska-Lonc N, Dudek K, Jankowska-Polańska B, Zabierowski J, et al. Relationship between nutritional status and clinical outcome in patients treated for lung cancer. Nutrients. (2021) 13(10):3332. doi: 10.3390/nu13103332
41. Prasetiyo PD, Baskoro BA, and Hariyanto TI. The role of nutrition-based index in predicting survival of breast cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon. (2024) 10(1):e23541. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23541
42. Hopkins BD, Goncalves MD, and Cantley LC. Obesity and cancer mechanisms: cancer metabolism. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:4277–83. doi: 10.1200/jco.2016.67.9712
43. Zhu J, Wang D, Liu C, Huang R, Gao F, Feng X, et al. Development and validation of a new prognostic immune–inflammatory–nutritional score for predicting outcomes after curative resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A multicenter study. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1165510. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165510
44. Ma S, Li Z, and Wang L. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) predicted the postoperative survival rate of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and the construction of a nomogram model. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03432-3
45. Qiu X, Shen S, Lu D, Jiang N, Feng Y, Li J, et al. Predictive efficacy of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index in hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Inflammation Research Volume. (2024) 17:5197–52 10. doi: 10.2147/jir.S468215
46. Liu X-R, Wang L-L, Zhang B, Liu X-Y, Li Z-W, Kang B, et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index is a prognostic factor for gastrointestinal cancer patients undergoing surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. (2023) 21(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02972-4
47. Kusunoki K, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Yamamoto A, Omura Y, Ohi M, et al. Advanced lung cancer inflammation index predicts outcomes of patients with colorectal cancer after surgical resection. Dis Colon Rectum. (2020) 63:1242–50. doi: 10.1097/dcr.0000000000001658
48. Cheng J, Li Q, Xiao S, Nie L, Liao J, Jiang Q, et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index predicts chemotherapy response and infection risk in multiple myeloma patients receiving induction chemotherapy. Front Genet. (2022) 13:1047326. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1047326
49. Greten FR and Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity. (2019) 51:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025
50. Siersbæk R, Scabia V, Nagarajan S, Chernukhin I, Papachristou EK, Broome R, et al. IL6/STAT3 signaling hijacks estrogen receptor α Enhancers to drive breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell. (2020) 38:412–423.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.06.007
51. Dias AS, Almeida CR, Helguero LA, and Duarte IF. Metabolic crosstalk in the breast cancer microenvironment. Eur J Cancer. (2019) 121:154–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.09.002
52. Choi J, Cha YJ, and Koo JS. Adipocyte biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active facilitator. Prog Lipid Res. (2018) 69:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2017.11.002
53. Benoy IH, Salgado R, Dam P, Geboers K, Van Marck E, Scharpé S, et al. Increased serum interleukin-8 in patients with early and metastatic breast cancer correlates with early dissemination and survival. Clin Cancer Res. (2004) 10:7157–62. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0812
54. Shibabaw T, Teferi B, and Ayelign B. The role of Th-17 cells and IL-17 in the metastatic spread of breast cancer: As a means of prognosis and therapeutic target. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1094823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1094823
55. Gao X, Qi J, Du B, Weng X, Lai J, and Wu R. Combined influence of nutritional and inflammatory status and breast cancer: findings from the NHANES. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24(1):2245. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19727-9
Keywords: advanced breast cancer, survival prognosis, advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI), inflammation, nutritional status
Citation: Liang C, Yang C, Yang Q, Tang Y, Zhang W, Tan Q and Qin Q (2025) Survival prognosis evaluation in advanced breast cancer patients: a study on the application of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index. Front. Oncol. 15:1598069. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1598069
Received: 22 March 2025; Accepted: 20 May 2025;
Published: 04 June 2025.
Edited by:
Mariana Segovia-Mendoza, National Autonomous University of Mexico, MexicoReviewed by:
Yu Xiao, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, ChinaFrancesca Piccotti, Scientific Clinical Institute Maugeri (ICS Maugeri), Italy
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Yang, Yang, Tang, Zhang, Tan and Qin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenhai Zhang, MTY2NTAxMjI1OEBxcS5jb20=; Qixing Tan, cWl4aW5ndGFuQGhvdG1haWwuY29t; Qinghong Qin, cXFoMjAwMTUwOTgyQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Chunfeng Liang
Chunfeng Liang Chunyan Yang†
Chunyan Yang† Wenhai Zhang
Wenhai Zhang Qixing Tan
Qixing Tan Qinghong Qin
Qinghong Qin