- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the leading cause of cancer-related death among women, presenting a significant threat to their lives and health. Early-stage OC often lacks distinctive clinical symptoms, leading to most patients being diagnosed at advanced stages. Current treatment strategies primarily involve a combination of surgical resection and chemotherapy, but the therapeutic outcomes are limited, and prognosis remains poor. Therefore, there is a critical need to understand the pathogenesis of OC, identify biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis, and discover new therapeutic targets. Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1), recognized as a pro-oncogenic transcription factor (TF), is notably overexpressed in various malignancies, including OC. Research indicates that increased levels of FOXM1 correlate significantly with OC’s aggressive behaviors such as proliferation, invasion, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and resistance to chemotherapy. These observations suggest that FOXM1 could potentially function as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target, facilitating the early detection and treatment of OC.
1 Introduction
Ovarian cancer (OC) ranks as the third most prevalent gynecological cancer globally and is the deadliest among gynecological tumors, with a five-year survival rate hovering around 48% (1). This poses a significant threat to women’s health and well-being. The absence of distinct clinical symptoms and reliable biological markers makes early detection difficult, resulting in most patients being diagnosed at advanced stages (2, 3). Advanced OC frequently leads to intra-abdominal metastasis, which damages abdominal organs and tissues, contributing to the poor prognosis (4). Currently, the treatment of OC primarily involves a combination of surgical resection and chemotherapy (5). However, the therapeutic effect is limited, often accompanied by chemoresistance, and associated with a high risk of recurrence (6). Thus, there is an urgent need to understand the molecular mechanisms of OC, identify related target genes, and discover novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets. These efforts could significantly improve early diagnosis and treatment outcomes for OC (3).
Initially discovered in mice as Trident, FOXM1 belongs to the FOX family of transcription factors, essential in embryonic development (7–9). It has also been known as HFH-11 (10), FKHL-16 (11), WIN (12), and MPP-2 (13) across different species. FOXM1 orchestrates vital cellular functions including growth, proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, and apoptosis (14). Recent attention has focused on FOXM1 due to its significant overexpression in various human cancers and its crucial role in tumor advancement (15). As a result, FOXM1 has become a promising candidate for the early diagnosis and treatment of OC (8).
In this review, the oncogenic effects of FOXM1 in OC are deeply explored, which enhances understanding of its underlying mechanisms, discusses the relevant challenges of targeting FOXM1, and pays special attention to the latest FOXM1 inhibitors, such as EBT inhibitors and Thiostrepton, and analyzes their potential applications in the clinical context of OC, providing a new perspective for future translational medicine research.
2 FOXM1 overview
2.1 Structure and isoforms of FOXM1
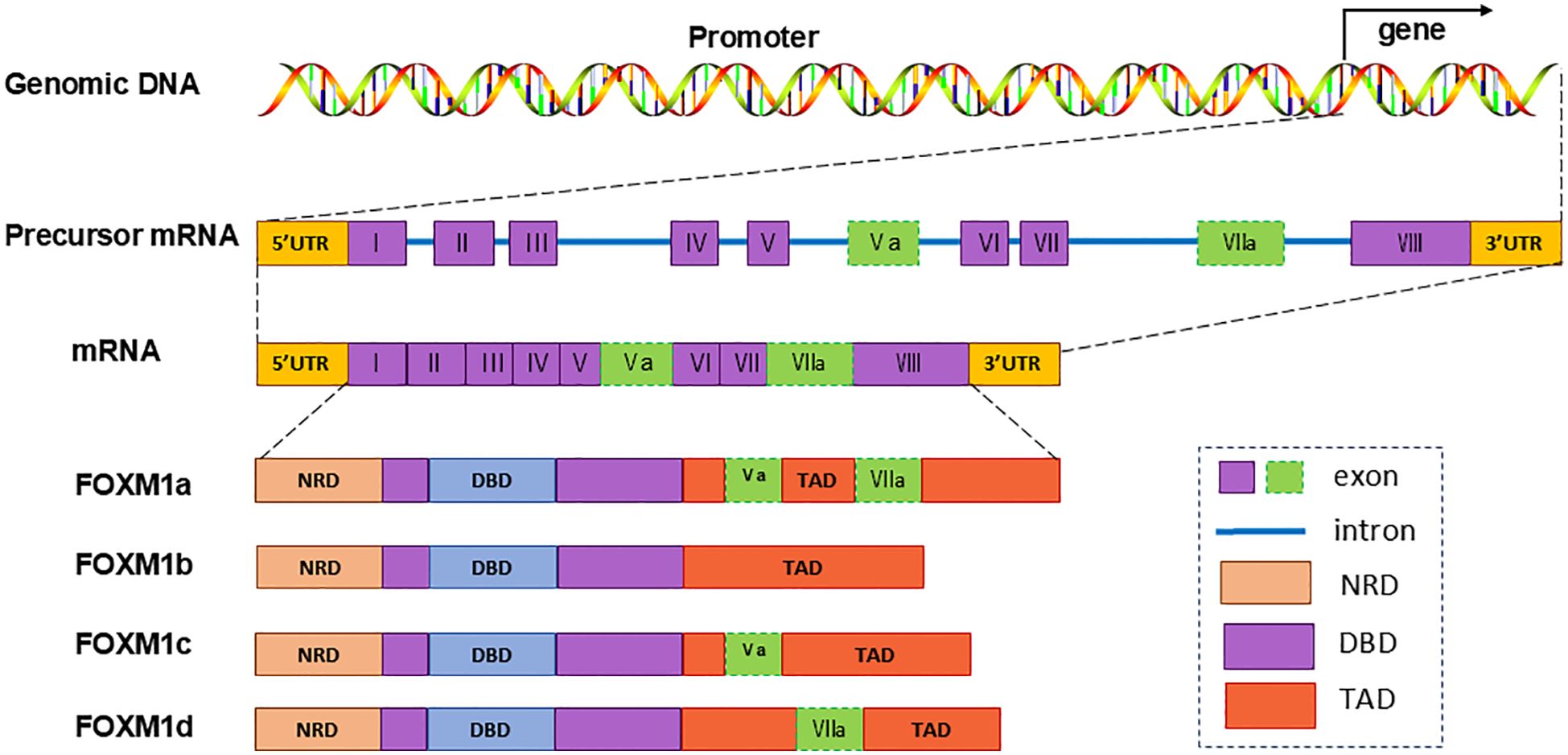
TFs within the FOX protein family share a conserved DNA-binding winged helix domain (9, 16) The human FOXM1 gene, comprising 10 exons, is situated on chromosome 12p13.33. Alternative splicing of exons Va and VII leads to the formation of four FOXM1 isoforms: FOXM1a, FOXM1b, FOXM1c, and FOXM1d (8, 16). FOXM1a, incorporating both exons Va and VIIa, loses transcriptional activity due to the insertion of exon VIIa into its activation domain. Conversely, FOXM1b, FOXM1c, and FOXM1d maintain transcriptional activity, each exhibiting distinct functional characteristic (8, 17, 18) (Figure 1).
2.2 Function and regulation of FOXM1
FOXM1 is a critical TF that regulates cell proliferation and exhibits a cell cycle-specific expression pattern (19). It controls the transcription of several cell cycle-related genes, ensuring accurate DNA replication and mitosis (20). Additionally, FOXM1 regulates various essential biological processes, playing an active role in cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, stem cell regeneration, DNA damage repair, apoptosis, and inflammation (14, 21).
The expression of FOXM1 is regulated at multiple levels. Transcriptional regulation of FOXM1 involves several factors, including the CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) (22), cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) (23), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) (24), Twist 1 (25), and E2F (26), which can directly bind to the FOXM1 promoter and enhance its expression. Post-transcriptionally, several miRNAs can regulate FOXM1 by binding to its 3’ UTR, a mechanism observed in many cancers (27–30). Furthermore, FOXM1 undergoes various post-translational modifications (PTMs), including ubiquitination, phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation (16, 31–33). These PTMs can either activate or inhibit its transcriptional activity, protein stability, and cellular localization (34).
2.3 FOXM1 and malignant tumors
As a proto-oncogene, FOXM1 is highly expressed in various human cancers, promoting malignant cell proliferation in tumors such as gastric, breast, lung, pancreatic, colorectal, cervical, and prostate cancers (8, 35–37). The upregulation of FOXM1 enhances the proliferation, migration, and invasive potential of cancer cells (8). Recent research has revealed that the expression of FOXM1 is notably increased in OC tissues as compared to adjacent non-cancerous tissues. This overexpression significantly contributes to the oncogenesis and metastatic spread of OC (38–40). Llauradó et al. found that FOXM1 expression was upregulated in most OC specimens. This was determined by examining FOXM1 expression in 34 OC and 11 normal ovarian specimens. The analysis revealed that FOXM1 expression was closely associated with the stage of OC and the malignant invasive tumor phenotype. The higher the cancer stage, the higher the expression level of FOXM1, and the poorer the prognosis (39). Ning et al. noted a marked elevation in FOXM1 levels within OC samples, particularly pronounced among patients who exhibited lymph node metastasis versus those who did not (40). These observations underscore the pivotal role of FOXM1 TFs in the progression of OC and highlight its potential as an innovative therapeutic target.
3 Role of FOXM1 in the development of OC
FOXM1 upregulation impacts several fundamental tumor biological functions such as cell proliferation, apoptosis regulation, tissue invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, stem cell properties of tumors, and alterations in metabolic processes (Figure 2). FOXM1 exerts its biological effects through various molecular mechanisms, promoting the progression of OC.
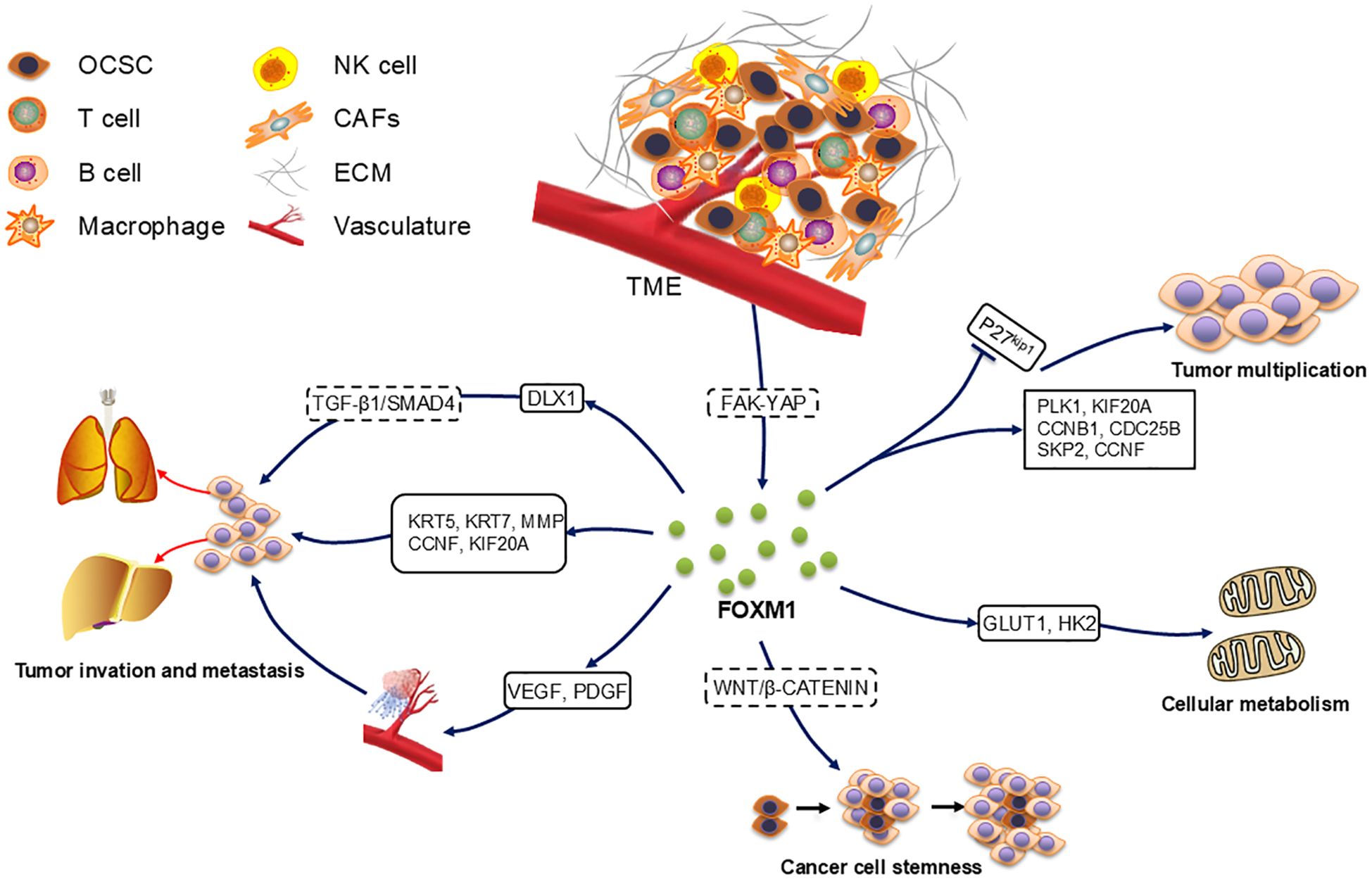
Figure 2. Role of FOXM1 in ovarian cancer development. FOXM1 accelerates the cell cycle and thus promotes cell proliferation by up-regulating the expression of downstream target genes PLK1, KIF20A, CCNB1, CDC25B, SKP2, and CCNF and by accelerating the degradation of p27KiP1. OCSC in contact with TME activated the FAK-YAP pathway to increase the expression of FOXM1, which increased cancer stemness through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. FOXM1 also accelerated cellular metabolic processes through the up-regulation of GLUT1 and HK2.FOXM1 up-regulated VEGF and PDGF to regulate angiogenesis, as well as through the downstream target genes KRT5, KRT7, MMP, CCNF, KIF20A and DLX1 promoted cancer cell metastasis.
3.1 FOXM1 promotes OC cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis
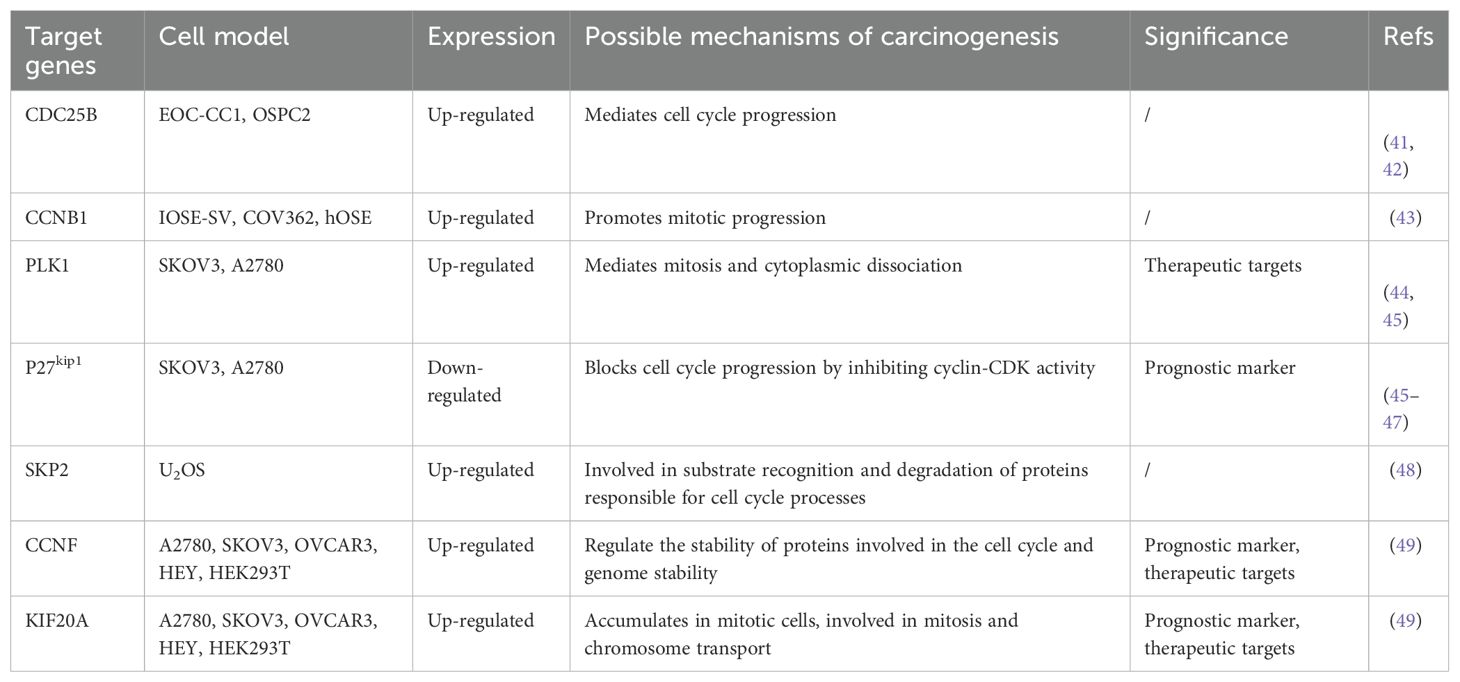
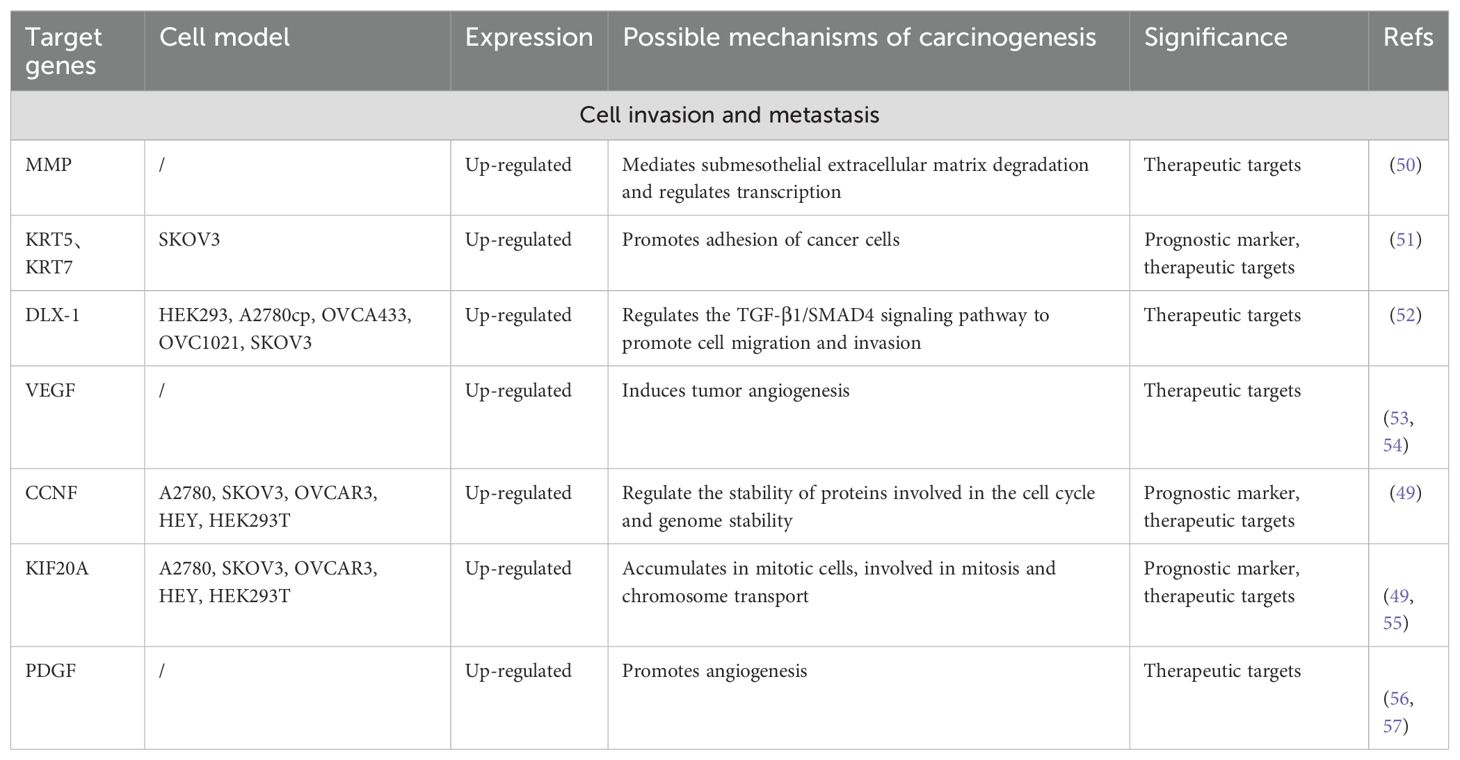
In multiple experimental models, FOXM1 promotes tumor cell proliferation by sustaining proliferative signaling and evading growth-inhibitory factors, which enhances cell viability and expedites cell cycle progression. Knockdown of FOXM1 inhibits the expression of cell cycle genes and suppresses cell proliferation, colony formation, and tumor growth. Further studies have confirmed FOXM1’s role in enhancing the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of OC cells through the modulation of gene expression downstream (Table 1a, Table 1b).
PLK1 and KIF20A are involved in cytoplasmic segregation during mitosis and contribute to cancer cell proliferation. As downstream genes of FOXM1, they are upregulated by FOXM1 (45, 49). In one study, Renata A. Tassi et al. reported that silencing FOXM1 in two epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) cell lines—clear cell (EOC-CC1) and serous (OSPC2)—led to decreased expression of cell cycle-related genes, such as CCNB1 and CDC25B (41). Additionally, SKP2, a key subunit of the ubiquitin ligase complex SCF, can be directly bound by FOXM1 to increase its transcription. This promotes the degradation of p27kip1 by SCF, accelerating cell cycle progression (48). CCNF stabilizes proteins involved in cell cycle progression and genome stability, and its expression is increased by FOXM1 overexpression (49). Certain miRNAs also regulate FOXM1 expression and influence OC cell proliferation (58–60). For example, In 92 OC patients, miR-506 overexpression reduces FOXM1 through the CDK4/CDK6-FOXM1 pathway (58), while miR-370 inhibits FOXM1, counteracting its effects on proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (60). Additionally, FOXM1 also regulates metabolic pathways to affect OC cell proliferation, upregulating key glycolytic enzymes including GLUT1 and HK2 to promote metabolic reprogramming (61). Notably, although FOXM1 is thought to be a regulator of cell cycle genes, little is known about the specific effects of its isoforms on downstream targets. Furthermore, the role of FOXM1 in metabolic re-editing may be masked by co-existing mutations, such as KRAS mutations, and subtype-specific analyses are needed to reconcile the different findings (62).
The metastatic process in tumors involves intricate stages including local tumor cell invasion, angiogenesis, formation of metastatic nodules, and eventual colonization at distant sites (63). Both tumor growth and metastasis depend on angiogenesis, which supplies necessary oxygen and nutrients (64). In OC cases, high FOXM1 expression positively correlates with increased microvessel density. As a TF, FOXM1 regulates angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF promoter activity, elevating VEGF mRNA and protein levels, and thus promoting angiogenesis, tumor proliferation, and invasion (65). Additionally, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) plays a significant role in the angiogenesis of OC tissues (66).
Downstream target genes of FOXM1 have been identified that affect cancer cell invasion and migration. For example, Zhang et al. found that FOXM1 expression was positively correlated with KRT5 and KRT7 expression, and knockdown of these genes reduced the migration of cancer cells (51). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), proteases that degrade extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, promote OC cell metastasis via ECM remodeling, EMT, and transcriptional regulation (50). High expression of DLX1 is strongly associated with advanced OC development, and FOXM1 can bind to the DLX1 promoter region, activating DLX1 expression. This enhances cancer cell migration and invasion through TGF-β1/SMAD4 signaling (52). The regulation of downstream target gene expression by FOXM1 promotes cancer cell proliferation and metastatic implantation via multiple pathways, further highlighting its critical role in OC development. Further studies may reveal other FOXM1 signaling pathways associated with OC formation, growth and metastasis.
3.2 FOXM1 promotes cancer stemness
Ovarian cancer stem cells (OCSCs) are noted for their robust self-renewal and adaptability. They significantly contribute to the persistence, low remission rates, high recurrence, and adverse outcomes associated with OC (66, 67). Prior research indicates that OCSCs endure standard chemotherapy and exhibit pronounced metastatic capacities. More importantly, metastatic OC often shows heightened resistance to chemotherapeutic agents, diminishing the efficacy of standard treatment protocols (68). In this context, FOXM1 emerges as a vital component for OC stem cells, playing a critical role in tumorigenesis.
Some studies have found that OCSCs, upon contact with the peritoneal tumor microenvironment (TME), activate the cell cycle pathway, increasing the self-renewal rate of cancer cells. This interaction also activated the FAK-YAP pathway, and induced FOXM1 expression. Interference with FOXM1 inhibited OCSC survival (69). Additionally, FOXM1 regulates the stemness of OC cells and promotes tumor progression by interacting with the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway (70). Chemotherapy resistance may indicate that cancer cells possess stem cell-like properties. A previous study reported an increase in the average expression of cancer cell markers (CD44, ALDH1A1, and CD133) in recurrent OC samples compared to primary OC samples from the same patients. Notably, CD133 was almost always elevated in recurrent samples, with the proportion of positive cells more than doubling in 58% of the samples (71).
Ning et al. showed that OCSC markers ALDH, CD133, and CD144 were highly expressed in OC cells. DFOG downregulated the expression of OCSC markers and FOXM1, inhibiting cancer cell self-renewal. However, overexpression of FOXM1 reversed this effect, enhancing the self-renewal capacity of OCSCs and promoting cancer cell stemness, leading to more severe disease (67). In addition to OC, cancer cell stemness has been associated with FOXM1 in other cancers, including breast, colon, prostate, lung, and endometrial cancers (72–76). These findings further suggest a strong correlation between FOXM1 and OCSCs, indicating that FOXM1 may serve as an important marker for evaluating the treatment and prognosis of OC patients.
4 Clinical transformation
4.1 The potential of FOXM1 as a biomarker for OC
Early tumor diagnosis depends largely on biomarker testing, which is crucial for personalized medicine (77). Despite the discovery of thousands of biomarkers in recent years, only a few are directly applicable in clinical practice (78). OC is a complex disease with varying cancer cell morphologies and biological behaviors (79). The detection of specific biomarkers can facilitate early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention (3). However, current tumor markers have limitations, particularly in the early stages of OC (3). Thus, there is an urgent need to identify more reliable biomarkers for this disease.
Studies have shown that FOXM1 is abnormally expressed in various cancer cells and can be used as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and treatment (80–83). A comprehensive meta-analysis by Andrew J. Gentles et al., involving around 18,000 tumor samples across 39 different cancers, highlighted FOXM1 as a critical prognostic marker indicative of poor outcomes across a broad cancer spectrum (84). Various studies have aligned FOXM1 overexpression with heightened tumor grade, stage, and increased disease severity (39, 41, 43, 85). In a specific investigation of 90 EOC patients, encompassing 50 cases of high-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC), 14 of clear cell-like EOC, and 26 of endometrioid EOC, elevated FOXM1 levels were significantly prevalent in plasmacytoid EOC and correlated with advanced FIGO stages (P = 0.004) (41).
Carter J. Barger et al. also reported significantly higher FOXM1 expression in patients with advanced and high-grade OC, suggesting that FOXM1 may serve as an independent marker of poor prognosis (43). While most studies have indicated a correlation between FOXM1 expression and the staging and grading of OC, some studies have reported no significant association. For example, Ning et al. found that FOXM1 expression is related to lymph node metastasis, but not significantly associated with FIGO staging (P = 0.127) or grading (P = 0.298) (40). These conflicting results may stem from various factors, such as differences in antibody specificity, sample size variations, or inconsistencies in study methodology. Additionally, biological heterogeneity among OC subtypes could also account for the inconsistencies. These observations underscore the urgent need for large-scale studies to address methodological discrepancies in current research and to probe the underlying causes of the contradictory findings on FOXM1’s role in cancer prognosis.
The expression of FOXM1 is significantly linked with survival outcomes in OC patients. Ning and colleagues reported that higher FOXM1 levels are associated with poorer prognoses and reduced survival rates (40). Additionally, Zhang and his team observed that patients with elevated FOXM1 expression experienced a higher rate of recurrence during progression-free survival (PFS) and exhibited trends towards shorter overall survival (OS). Additionally, their study showed that FOXM1 protein improved the accuracy of OC recurrence prediction (86). In a meta-analysis of 23 studies, FOXM1 overexpression was associated with 3-year OS (OR = 3.30, 95% CI = 2.56 to 4.25, P < 0.00001), 5-year OS (OR = 3.35, 95% CI = 2.64 to 4.26, P < 0.00001), and 10-year OS (OR = 5.24, 95% CI = 2.61 to 10.52, P < 0.00001). It was also linked to worse OS in most solid tumors (85). Thus, FOXM1 holds significant potential as a biomarker for diagnosing and determining the prognosis of OC. Targeting FOXM1 could offer a promising therapeutic approach.
4.2 Chemotherapy resistance and targeted therapy in OC
Chemotherapy remains a primary therapeutic approach for various tumors, significantly reducing cancer mortality (87). Nonetheless, resistance to chemotherapy constitutes a major challenge in OC treatment, being a primary cause of cancer fatalities among women (88). Chemoresistant OC cells exhibit stronger cancer stemness, invasive abilities, and metastatic potential (70). In recent years, the role of FOXM1 in chemoresistance has gained significant attention (7, 38) (Figure 3). Zhou et al. found that FOXM1 targets EXO1, a downstream gene related to DNA repair, and promotes DNA repair, leading to cisplatin resistance in cancer cells. Downregulation of FOXM1 increases the sensitivity of OC cells to cisplatin (38).
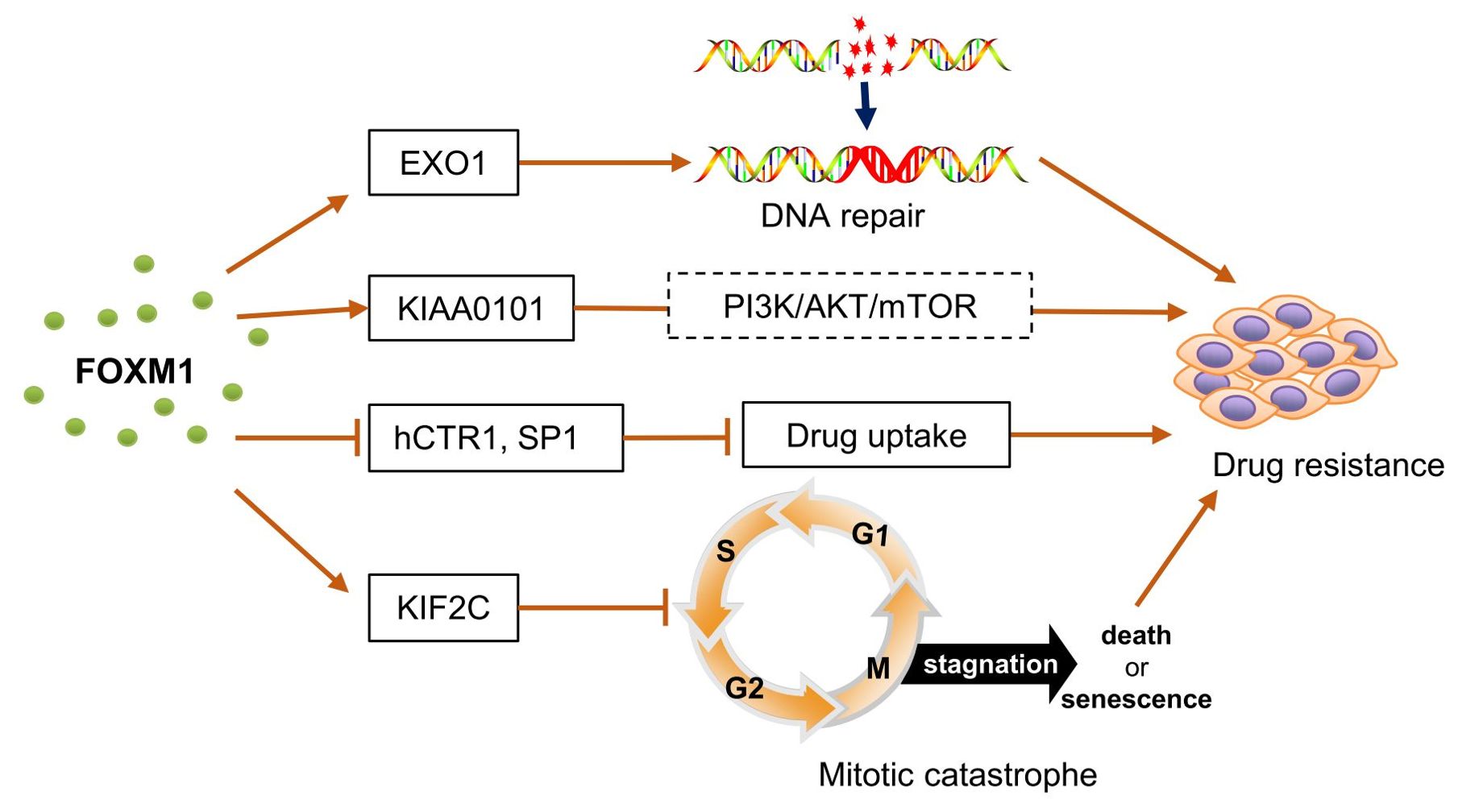
Figure 3. FOXM1 involved in chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. FOXM1 targeted and up-regulated EXO1 expression, which promoted DNA damage repair and led to cisplatin resistance in cancer cells.FOXM1 activated the expression of KIAA0101, which acted through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, enhancing the viability of cancer cells and promoting the development of chemotherapy resistance. FOXM1 inhibits the expression of hCTR1 and SP1, which prevents the entry of cisplatin into ovarian cancer cells and reduces the sensitivity of ovarian cancer to cisplatin. FOXM1 inhibited mitotic catastrophe by up-regulating the expression of KIF2C, enabling cancer cells to survive and proliferate under chemotherapeutic stress. hCTR1, a transmembrane transporter protein that allows cisplatin to cross the membrane barrier into cells. SP1, transcription factor that induces the expression of hCTR1. Mitotic catastrophe, a tumor suppressor mechanism that detects mitotic errors and subsequently drives cells to an irreversible anti-proliferative end, death or senescence.
In other cancers, FOXM1 has also been shown to increase drug resistance by regulating downstream DNA repair targets such as RAD51 (89), NBS1 (90), BRIP1 (91), and BRCA2 (92). Additionally, FOXM1 activates the expression of KIAA0101, which blocks cisplatin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in OC cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, reducing cisplatin sensitivity (93). KIF2C, identified as a target gene of FOXM1, shows a similar expression pattern to FOXM1. FOXM1 blocks mitotic catastrophe in OC cells, thereby increasing paclitaxel resistance, a process potentially mediated by KIF2C (94).
Chiu et al. found that the WNT/β-CATENIN pathway induces FOXM1 expression, which inhibits the expression of human copper transporter protein 1 (hCTR1) and SP1, preventing cisplatin uptake in OC cells and leading to cisplatin resistance (70). These findings suggest a strong association between FOXM1 and drug resistance in OC, but there are still significant gaps in understanding the exact mechanisms by which FOXM1 regulates resistance. Particularly, FOXM1b and FOXM1c show high activity in a wide range of cancer types and especially play important roles in the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells (95, 96). However, studies on FOXM1 subtypes in OC remain limited. Given the distinct roles of different FOXM1 isoforms in cell biology, developing specific inhibitors against these isoforms may offer greater targeted therapeutic potential and efficacy, potentially providing new insights for individualized OC treatment.
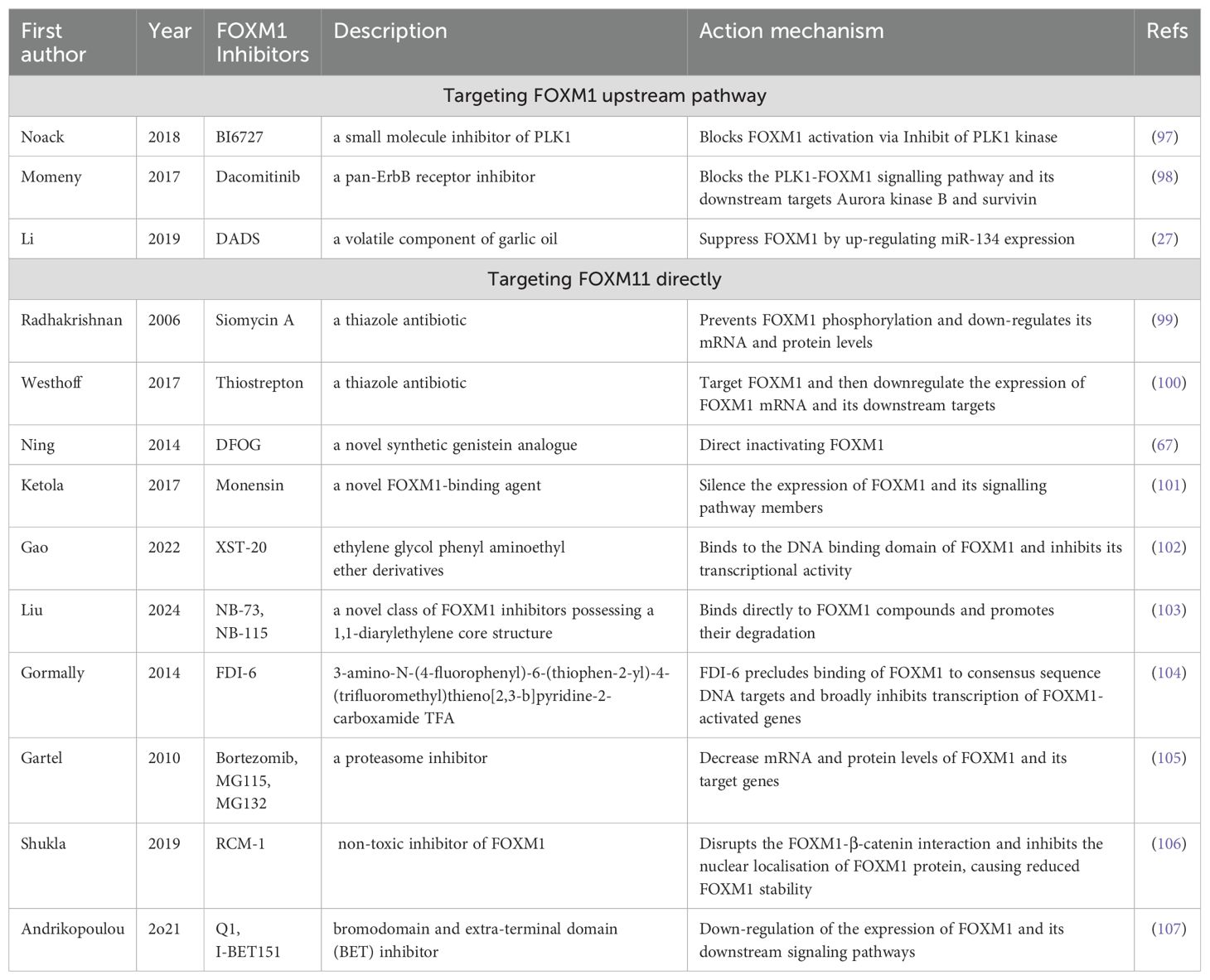
FOXM1 is highly expressed in OC cells, leading to chemotherapy resistance. This provides a strong rationale for targeting FOXM1 inhibition as a treatment strategy for OC. Two primary methods exist for inhibiting FOXM1: 1) inhibiting or activating upstream pathways of FOXM1, thereby indirectly affecting its activity, and 2) directly targeting and inhibiting FOXM1 (Table 2). Currently, few FOXM1 inhibitors are used in the clinic, and OC frequently develops drug resistance, making research into both indirect and direct FOXM1 inhibitors highly valuable.
FOXM1 expression is regulated by upstream signaling pathways, including MAPK/ERK, PLK1, and PI3K. Noack et al. demonstrated that the PLK1 inhibitor BI6727 reduced the viability of CCNE1-expanded OC cells, increased their sensitivity to paclitaxel, and induced apoptosis in cancer cells when combined with paclitaxel. Importantly, they suggested that PLK1 inhibitors may indirectly affect FOXM1 activity (97). This is because PLK1 is an upstream kinase that is essential for FOXM1 phosphorylation and activation based on the putative consensus phosphorylation sites (16, 97). This suggests a potential mechanistic link between PLK1 inhibitors and FOXM1 expression and activity, although further experiments are needed to fully elaborate this relationship. Dacomitinib can enhance OC cell sensitivity to cisplatin by inhibiting the ErbB receptor, reducing the expression of phosphorylated PLK1, and inhibiting FOXM1 activity (98). In osteosarcoma, diallyl disulfide (DADS) inhibits FOXM1 expression by activating miR-134, an upstream regulator of FOXM1, thereby reducing cancer cell proliferation and invasion (27).
Many compounds have been reported to directly inhibit FOXM1 expression. These include siomycin A (99), thiostrepton (100), DFOG (67), monensin (101), XST-20 (102), NB compounds (103), FDI-6 (104), Bortezomib (105), and RCM-1 (106), which exert their effects by regulating various biological processes involved in cancer cell development, including proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis. Siomycin A and thiostrepton, thiazole antibiotics, were first reported as FOXM1 inhibitors, with thiostrepton being the most commonly used (99, 100). It targets FOXM1 to reduce mRNA expression and its downstream targets, leading to OC cell death. When combined with paclitaxel and cisplatin, thiostrepton may offer a novel approach for treating chemotherapy-resistant OC (100).
Siomycin A disrupts FOXM1’s transcriptional activity by impeding its phosphorylation, curtails anchorage-independent cellular growth in soft agar assays, and selectively induces apoptosis in transformed cells while sparing normal cells, making it a potential candidate for anticancer therapy (99). Genistein (4’, 5, 7-trihydroxyisoflavone; GEN) has been proven to suppress the proliferative capabilities of breast cancer stem cells (108). Additionally, Ning and colleagues have shown that DFOG effectively curtails the enhanced self-renewal abilities of cancer stem cells induced by abnormally elevated FOXM1 expression in OC cells (67).
In a prostate cancer study, monensin was found to bind to the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of FOXM1, reducing its interaction with downstream target genes such as PLK1 and CDC25B, thereby exerting an anti-cancer effect (101). NB compounds (NB-73, NB-115) promote FOXM1 protein degradation and inhibit the expression of target genes. These compounds show synergistic effects with carboplatin in high-grade serous OC (HGSOC) cells, potentially enhancing therapeutic efficacy (103). Unlike NB compounds, RCM-1 reduces tumor growth by disrupting the interaction between FOXM1 and β-catenin (106). In addition, studies targeting BET (Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal domain) inhibitors in OC treatment continue to intensify (107). In particular, BET inhibitors such as JQ1 or I-BET151 have been shown to be able to effectively inhibit the proliferation and migration of OC cells by down-regulating the expression of FOXM1 and its downstream pathways, leading to therapeutic effects (109, 110).
These compounds that inhibit FOXM1 expression have demonstrated anti-tumor effects, with some also enhancing cancer cell sensitivity to drugs. This suggests that targeted inhibition of FOXM1 could offer a novel strategy for OC treatment. However, further studies are needed to explore the activation of other pathways and determine whether the observed anti-tumor effects are attributable to FOXM1 inhibition. Additionally, the precise mechanisms by which these compounds inhibit FOXM1 expression in OC require further investigation.
4.3 Clinical translational potential and challenges of FOXM1 inhibitors
Currently, most inhibitors remain in preclinical research, mainly assessing safety and efficacy (107, 111). Only a few BET inhibitors, such as JQ1, have entered early clinical trials in OC (107). Thiostrepton has shown efficacy in preclinical trials in OC and other tumors but lacks widespread clinical approval (111–113). Despite promising antitumor activity in vitro and animal models, FOXM1 inhibitors’ clinical application is hindered by poor pharmacokinetic properties and potential toxicity, with bioavailability, half-life, and tissue distribution issues affecting efficacy (114, 115). Therefore, optimizing the chemical structure of inhibitors to enhance their bioavailability and reduce their toxicity is the focus of current research.
To boost FOXM1 inhibitors’ clinical efficacy, researchers are exploring combination therapies (107). For example, combining the FOXM1 inhibitor thiostrepton with PARP inhibitors yields a synergistic effect (111). Combining FOXM1 inhibitors with immune checkpoint inhibitors also shows great therapeutic potential. PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, which alleviate immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment, enhance T-cell antitumor activity. Thiostrepton, in turn, directly inhibits tumor cell proliferation and metastasis, and their combination may produce a synergistic therapeutic effect (116). In melanoma models, combating CTLA-4 inhibitors with I-BET151 also shows a trend toward enhanced anti-tumor activity (117). Combining FOXM1 inhibitors, particularly with immune checkpoint inhibitors, is expected to open new tumor therapy avenues.
5 Conclusions and perspectives
In conclusion, FOXM1 plays a crucial role in the development of OC. It possesses the distinct characteristics of a biomarker, making it valuable for predicting survival. Although its clinical utility has been demonstrated across various cancers, its role in immune escape mechanisms remains largely unexplored, including its interactions with immune checkpoint molecules and its impact on the activity and function of immune cells. The unique contributions of different FOXM1 subtypes to immune escape are also poorly understood. Tumor spatial heterogeneity has been widely recognized, and FOXM1 may play an important role in this process; however, its expression patterns across different tumor regions and its impact on the spatial organization of the tumor microenvironment remain unclear.
Currently, the application of FOXM1 inhibitors in OC treatment is limited. Before FOXM1 inhibitors can be used in clinical practice, further in-depth studies on their anti-tumor effects and thorough evaluations of their toxicity are needed. The development of novel and effective FOXM1-targeted therapies remains challenging. A deep understanding of FOXM1’s regulatory role, especially in immune evasion and tumor microenvironment heterogeneity, will offer fresh insights into OC research and may unveil new therapeutic avenues.
Author contributions
X-QT: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. A-YG: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation. L-FZ: Software, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Formal analysis. JX: Resources, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Science and Technology Programme of the Jiangxi Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission (No. 202210036), the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Senior Project (No. 20242BAB25485), and the Science and Technology Programme of the Jiangxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine General Project (2024B0268).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the helpful reviewer comments on this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
OC, Ovarian cancer; OCSCS, Ovarian cancer stem cells; TF, Transcription factor; PTM, Post-translational modifications; VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor; ECM, Extracellular matrix; EMT, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; PDGF, Platelet-derived growth factor; TME, Tumor microenvironment;
DFOG, 7-Difluoromethoxyl-5,4′-di-n-octylgenistein; CCNB1, Cyclin B1; PLK1, Polo-like kinase 1; SKP2, Sphase kinase-associated protein 2; CCNF, Cyclin F; KIF20A, Kinesin-like protein KIF20A; MMP, Matrix metalloproteinase; KRT, Keratin; DLX-1, Homeobox DLX-1; SCF, Ubiquitin ligase complex; OS, Overall survival; PFS, Progression-free survival.
References
2. Zhang R, Siu MKY, Ngan HYS, and Chan KKL. Molecular biomarkers for the early detection of ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12041. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912041
3. Matsas A, Stefanoudakis D, Troupis T, Kontzoglou K, Eleftheriades M, Christopoulos P, et al. Tumor markers and their diagnostic significance in ovarian cancer. Life (Basel). (2023) 13:1689. doi: 10.3390/life13081689
4. Yousefi M, Dehghani S, Nosrati R, Ghanei M, Salmaninejad A, Rajaie S, et al. Current insights into the metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer - hopes and hurdles. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2020) 43:515–38. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00513-9
5. Chandra A, Pius C, Nabeel M, Nair M, Vishwanatha JK, Ahmad S, et al. Ovarian cancer: current status and strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes. Cancer Med. (2019) 8:7018–31. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2560
6. Markman M. Pharmaceutical management of ovarian cancer: current status. Drugs. (2008) 68:771–89. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200868060-00004
7. Liu C, Barger CJ, and Karpf AR. Foxm1: A multifunctional oncoprotein and emerging therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:3065. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123065
8. Khan MA, Khan P, Ahmad A, Fatima M, and Nasser MW. Foxm1: A small fox that makes more tracks for cancer progression and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. (2023) 92:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.03.007
9. Korver W, Roose J, and Clevers H. The winged-helix transcription factor trident is expressed in cycling cells. Nucleic Acids Res. (1997) 25:1715–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.9.1715
10. Ye H, Kelly TF, Samadani U, Lim L, Rubio S, Overdier DG, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head homolog 11 is expressed in proliferating epithelial and mesenchymal cells of embryonic and adult tissues. Mol Cell Biol. (1997) 17:1626–41. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.3.1626
11. Korver W, Roose J, Heinen K, Weghuis DO, de Bruijn D, van Kessel AG, et al. The human trident/hfh-11/fkhl16 gene: structure, localization, and promoter characterization. Genomics. (1997) 46:435–42. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.5065
12. Yao KM, Sha M, Lu Z, and Wong GG. Molecular analysis of a novel winged helix protein, win. Expression pattern, DNA binding property, and alternative splicing within the DNA binding domain. J Biol Chem. (1997) 272:19827–36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.32.19827
13. Lüscher-Firzlaff JM, Westendorf JM, Zwicker J, Burkhardt H, Henriksson M, Müller R, et al. Interaction of the fork head domain transcription factor mpp2 with the human papilloma virus 16 E7 protein: enhancement of transformation and transactivation. Oncogene. (1999) 18:5620–30. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202967
14. Zhang Z, Li M, Sun T, Zhang Z, and Liu C. Foxm1: functional roles of foxm1 in non-malignant diseases. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:857. doi: 10.3390/biom13050857
15. Borhani S and Gartel AL. Foxm1: A potential therapeutic target in human solid cancers. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2020) 24:205–17. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1727888
16. Laoukili J, Stahl M, and Medema RH. Foxm1: at the crossroads of ageing and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2007) 1775:92–102. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.08.006
17. Liao GB, Li XZ, Zeng S, Liu C, Yang SM, Yang L, et al. Regulation of the master regulator foxm1 in cancer. Cell Commun Signal. (2018) 16:57. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0266-6
18. Barger CJ, Branick C, Chee L, and Karpf AR. Pan-cancer analyses reveal genomic features of foxm1 overexpression in cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2019) 11:251. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020251
19. Wierstra I. Foxm1 (Forkhead box M1) in tumorigenesis: overexpression in human cancer, implication in tumorigenesis, oncogenic functions, tumor-suppressive properties, and target of anticancer therapy. Adv Cancer Res. (2013) 119:191–419. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-407190-2.00016-2
20. Laoukili J, Kooistra MR, Brás A, Kauw J, Kerkhoven RM, Morrison A, et al. Foxm1 is required for execution of the mitotic programme and chromosome stability. Nat Cell Biol. (2005) 7:126–36. doi: 10.1038/ncb1217
21. Huang X, Zhang X, Machireddy N, Evans CE, Trewartha SD, Hu G, et al. Endothelial foxm1 reactivates aging-impaired endothelial regeneration for vascular repair and resolution of inflammatory lung injury. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15:eabm5755. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abm5755
22. Sur S, Steele R, Ko BCB, Zhang J, and Ray RB. Long noncoding rna eldr promotes cell cycle progression in normal oral keratinocytes through induction of a ctcf-foxm1-aurka signaling axis. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:101895. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101895
23. Xia L, Huang W, Tian D, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Hu H, et al. Upregulated foxm1 expression induced by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2012) 57:600–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.04.020
24. Mencalha AL, Binato R, Ferreira GM, Du Rocher B, and Abdelhay E. Forkhead box M1 (Foxm1) gene is a new stat3 transcriptional factor target and is essential for proliferation, survival and DNA repair of K562 cell line. PloS One. (2012) 7:e48160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048160
25. Qian J, Luo Y, Gu X, Zhan W, and Wang X. Twist1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation through up-Regulation of Foxm1. PloS One. (2013) 8:e77625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077625
26. Millour J, de Olano N, Horimoto Y, Monteiro LJ, Langer JK, Aligue R, et al. Atm and P53 regulate foxm1 expression via E2f in breast cancer epirubicin treatment and resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. (2011) 10:1046–58. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-11-0024
27. Li Y, Wang Z, Li J, and Sang X. Diallyl disulfide suppresses foxm1-mediated proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma by upregulating mir-134. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:7286–96. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28003
28. Huang X, Qin J, and Lu S. Up-regulation of mir-877 induced by paclitaxel inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation though targeting foxm1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2015) 8:1515–24.
29. Liu X, Xie T, Mao X, Xue L, Chu X, and Chen L. Microrna-149 increases the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil by targeting forkhead box transcription factor foxm1. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2016) 39:617–29. doi: 10.1159/000445653
30. Hong H, Zhu H, Zhao S, Wang K, Zhang N, Tian Y, et al. The novel circclk3/mir-320a/foxm1 axis promotes cervical cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:950. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2183-z
31. Wang X, Arceci A, Bird K, Mills CA, Choudhury R, Kernan JL, et al. Vprbp/dcaf1 regulates the degradation and nonproteolytic activation of the cell cycle transcription factor foxm1. Mol Cell Biol. (2017) 37:e00609-16. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00609-16
32. Lv C, Zhao G, Sun X, Wang P, Xie N, Luo J, et al. Acetylation of foxm1 is essential for its transactivation and tumor growth stimulation. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:60366–82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11332
33. Cohn O, Feldman M, Weil L, Kublanovsky M, and Levy D. Chromatin associated setd3 negatively regulates vegf expression. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:37115. doi: 10.1038/srep37115
34. Littler DR, Alvarez-Fernández M, Stein A, Hibbert RG, Heidebrecht T, Aloy P, et al. Structure of the foxm1 DNA-recognition domain bound to a promoter sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. (2010) 38:4527–38. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq194
35. Qi W, Li X, Zhang Y, Yao R, Qiu W, Tang D, et al. Overexpression of her-2 upregulates foxm1 in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Med. (2014) 33:1531–8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1732
36. Zhang X, Wang M, Zhang Y, Yang J, and Duan W. Knockdown of cenpu inhibits cervical cancer cell migration and stemness through the foxm1/wnt/β-catenin pathway. Tissue Cell. (2023) 81:102009. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.102009
37. Yang Q, Wu F, Zhang Y, and Wang R. Foxm1 regulates glycolysis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through pdk1. J Cell Mol Med. (2022) 26:3783–96. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17413
38. Zhou J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Yin X, He Y, Chen L, et al. Foxm1 modulates cisplatin sensitivity by regulating exo1 in ovarian cancer. PloS One. (2014) 9:e96989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096989
39. Llauradó M, Majem B, Castellví J, Cabrera S, Gil-Moreno A, Reventós J, et al. Analysis of gene expression regulated by the etv5 transcription factor in ov90 ovarian cancer cells identifies foxm1 overexpression in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. (2012) 10:914–24. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-11-0449
40. Wen N, Wang Y, Wen L, Zhao SH, Ai ZH, Wang Y, et al. Overexpression of foxm1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Transl Med. (2014) 12:134. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-134
41. Tassi RA, Todeschini P, Siegel ER, Calza S, Cappella P, Ardighieri L, et al. Foxm1 expression is significantly associated with chemotherapy resistance and adverse prognosis in non-serous epithelial ovarian cancer patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 36:63. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0536-y
42. Bansal P and Lazo JS. Induction of cdc25b regulates cell cycle resumption after genotoxic stress. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:3356–63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-3685
43. Barger CJ, Zhang W, Hillman J, Stablewski AB, Higgins MJ, Vanderhyden BC, et al. Genetic determinants of foxm1 overexpression in epithelial ovarian cancer and functional contribution to cell cycle progression. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:27613–27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4546
44. Chiappa M, Petrella S, Damia G, Broggini M, Guffanti F, and Ricci F. Present and future perspective on plk1 inhibition in cancer treatment. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:903016. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903016
45. Jiang L, Cao XC, Cao JG, Liu F, Quan MF, Sheng XF, et al. Casticin induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis by repressing foxm1 through the activation of foxo3a. Oncol Lett. (2013) 5:1605–10. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1258
46. Yu M, Tang Z, Meng F, Tai M, Zhang J, Wang R, et al. Elevated expression of foxm1 promotes the tumor cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. (2016) 37:1289–97. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3436-9
47. Zhao Y, Li Q, Wu X, and Chen P. Upregulation of P27kip1 by demethylation sensitizes cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer skov3 cells. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:1659–66. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5399
48. Petrovic V, Costa RH, Lau LF, Raychaudhuri P, and Tyner AL. Foxm1 regulates growth factor-induced expression of kinase-interacting stathmin (Kis) to promote cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:453–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705792200
49. Li Y, Guo H, Wang Z, Bu H, Wang S, Wang H, et al. Cyclin F and kif20a, foxm1 target genes, increase proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 395:112212. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112212
50. Carey P, Low E, Harper E, and Stack MS. Metalloproteinases in ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3403. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073403
51. Zhang Z, Tu K, Liu F, Liang M, Yu K, Wang Y, et al. Foxm1 promotes the migration of ovarian cancer cell through krt5 and krt7. Gene. (2020) 757:144947. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144947
52. Chan DW, Hui WW, Wang JJ, Yung MM, Hui LM, Qin Y, et al. Dlx1 acts as a crucial target of foxm1 to promote ovarian cancer aggressiveness by enhancing tgf-β/smad4 signaling. Oncogene. (2017) 36:1404–16. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.307
53. Ai B, Bie Z, Zhang S, and Li A. Paclitaxel targets vegf-mediated angiogenesis in ovarian cancer treatment. Am J Cancer Res. (2016) 6:1624–35.
54. Shaw P, Dwivedi SKD, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee P, and Rao G. Vegf signaling: role in angiogenesis and beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2024) 1879:189079. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189079
55. Liu J, Wang QC, Cui XS, Wang ZB, Kim NH, and Sun SC. Mklp2 inhibitor paprotrain affects polar body extrusion during mouse oocyte maturation. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2013) 11:117. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-11-117
56. Gavalas NG, Liontos M, Trachana SP, Bagratuni T, Arapinis C, Liacos C, et al. Angiogenesis-related pathways in the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2013) 14:15885–909. doi: 10.3390/ijms140815885
57. Zou X, Tang XY, Qu ZY, Sun ZW, Ji CF, Li YJ, et al. Targeting the pdgf/pdgfr signaling pathway for cancer therapy: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 202:539–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.113
58. Liu G, Sun Y, Ji P, Li X, Cogdell D, Yang D, et al. Mir-506 suppresses proliferation and induces senescence by directly targeting the cdk4/6-foxm1 axis in ovarian cancer. J Pathol. (2014) 233:308–18. doi: 10.1002/path.4348
59. Huang H, Yan L, Zhong J, Hong L, Zhang N, and Luo X. Circ_0025033 deficiency suppresses paclitaxel resistance and Malignant development of paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cells by modulating the mir-532-3p/foxm1 network. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2022) 44:275–86. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2038194
60. Chen Q, Zhang J, He Y, and Wang Y. Hsa_Circ_0061140 knockdown reverses foxm1-mediated cell growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer through mir-370 sponge activity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 13:55–63. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.08.010
61. Wang Y, Yun Y, Wu B, Wen L, Wen M, Yang H, et al. Foxm1 promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activation of glut1 and hk2 transcription. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:47985–97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10103
62. Wu H, Zhang J, Wang Q, Li Z, Li L, and Xie Y. Metformin combined with cb-839 specifically inhibits kras-mutant ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:6072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90963-8
63. Fu LQ, Du WL, Cai MH, Yao JY, Zhao YY, and Mou XZ. The roles of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cell Immunol. (2020) 353:104119. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104119
64. Farhan M, Silva M, Xingan X, Huang Y, and Zheng W. Role of foxo transcription factors in cancer metabolism and angiogenesis. Cells. (2020) 9:1586. doi: 10.3390/cells9071586
65. Zhang Y, Zhang N, Dai B, Liu M, Sawaya R, Xie K, et al. Foxm1b transcriptionally regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and promotes the angiogenesis and growth of glioma cells. Cancer Res. (2008) 68:8733–42. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-08-1968
66. Testa U, Petrucci E, Pasquini L, Castelli G, and Pelosi E. Ovarian cancers: genetic abnormalities, tumor heterogeneity and progression, clonal evolution and cancer stem cells. Medicines (Basel). (2018) 5:16. doi: 10.3390/medicines5010016
67. Ning YX, Li QX, Ren KQ, Quan MF, and Cao JG. 7-difluoromethoxyl-5,4’-di-N-octyl genistein inhibits ovarian cancer stem cell characteristics through the downregulation of foxm1. Oncol Lett. (2014) 8:295–300. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2080
68. Motohara T and Katabuchi H. Ovarian cancer stemness: biological and clinical implications for metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. Cancers (Basel). (2019) 11:907. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070907
69. Battistini C, Kenny HA, Zambuto M, Nieddu V, Melocchi V, Decio A, et al. Tumor microenvironment-induced foxm1 regulates ovarian cancer stemness. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:370. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06767-7
70. Chiu WT, Huang YF, Tsai HY, Chen CC, Chang CH, Huang SC, et al. Foxm1 confers to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:2349–65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2957
71. Steg AD, Bevis KS, Katre AA, Ziebarth A, Dobbin ZC, Alvarez RD, et al. Stem cell pathways contribute to clinical chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:869–81. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-11-2188
72. Fu Z, Cao X, Yang Y, Song Z, Zhang J, and Wang Z. Upregulation of foxm1 by mnsod overexpression contributes to cancer stem-like cell characteristics in the lung cancer H460 cell line. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2018) 17:1533033818789635. doi: 10.1177/1533033818789635
73. Yuan B, Liu Y, Yu X, Yin L, Peng Y, Gao Y, et al. Foxm1 contributes to taxane resistance by regulating uhrf1-controlled cancer cell stemness. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:562. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0631-9
74. Song IS, Jeong YJ, Jeong SH, Heo HJ, Kim HK, Bae KB, et al. Foxm1-induced prx3 regulates stemness and survival of colon cancer cells via maintenance of mitochondrial function. Gastroenterology. (2015) 149:1006–16.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.06.007
75. De Luca A, Fiorillo M, Peiris-Pagès M, Ozsvari B, Smith DL, Sanchez-Alvarez R, et al. Mitochondrial biogenesis is required for the anchorage-independent survival and propagation of stem-like cancer cells. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:14777–95. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4401
76. Song IS, Jeong YJ, Seo YJ, Byun JM, Kim YN, Jeong DH, et al. Peroxiredoxin 3 maintains the survival of endometrial cancer stem cells by regulating oxidative stress. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:92788–800. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21580
77. Kaushal A, Kaur N, Sharma S, Sharma AK, Kala D, Prakash H, et al. Current update on biomarkers for detection of cancer: comprehensive analysis. Vaccines (Basel). (2022) 10:2138. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122138
78. Srivastava A and Creek DJ. Discovery and validation of clinical biomarkers of cancer: A review combining metabolomics and proteomics. Proteomics. (2019) 19:e1700448. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201700448
79. Skubitz AP, Pambuccian SE, Argenta PA, and Skubitz KM. Differential gene expression identifies subgroups of ovarian carcinoma. Transl Res. (2006) 148:223–48. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2006.06.001
80. Zhang YL, Ma Y, Zeng YQ, Liu Y, He EP, Liu YT, et al. A narrative review of research progress on foxm1 in breast cancer carcinogenesis and therapeutics. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:1704. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5271
81. Lindskog C, Edlund K, Mattsson JS, and Micke P. Immunohistochemistry-based prognostic biomarkers in nsclc: novel findings on the road to clinical use? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. (2015) 15:471–90. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1002772
82. Fan W, Ma H, and Jin B. Expression of foxm1 and plk1 predicts prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. (2022) 23:146. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13266
83. Bian Y, Xu S, Gao Z, Ding J, Li C, Cui Z, et al. M(6)a modification of lncrna abhd11-as1 promotes colorectal cancer progression and inhibits ferroptosis through trim21/igf2bp2/foxm1 positive feedback loop. Cancer Lett. (2024) 596:217004. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217004
84. Gentles AJ, Newman AM, Liu CL, Bratman SV, Feng W, Kim D, et al. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat Med. (2015) 21:938–45. doi: 10.1038/nm.3909
85. Li L, Wu D, Yu Q, Li L, and Wu P. Prognostic value of foxm1 in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:32298–308. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15764
86. Zhang Q, Zhang R, Liu M, Wu H, and Yang B. An integrated model of cdca5 and foxm1 expression combined with a residual disease that predicts prognosis in ovarian cancer patients. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). (2023) 69:143–9. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2023.69.10.20
87. Hou Y, Zhu Q, Li Z, Peng Y, Yu X, Yuan B, et al. The foxm1-abcc5 axis contributes to paclitaxel resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e2659. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.53
88. Hunn J and Rodriguez GC. Ovarian cancer: etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2012) 55:3–23. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31824b4611
89. Zhang N, Wu X, Yang L, Xiao F, Zhang H, Zhou A, et al. Foxm1 inhibition sensitizes resistant glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by downregulating the expression of DNA-repair gene rad51. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:5961–71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-12-0039
90. Khongkow P, Karunarathna U, Khongkow M, Gong C, Gomes AR, Yagüe E, et al. Foxm1 targets nbs1 to regulate DNA damage-induced senescence and epirubicin resistance. Oncogene. (2014) 33:4144–55. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.457
91. Monteiro LJ, Khongkow P, Kongsema M, Morris JR, Man C, Weekes D, et al. The forkhead box M1 protein regulates brip1 expression and DNA damage repair in epirubicin treatment. Oncogene. (2013) 32:4634–45. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.491
92. Kwok JM, Peck B, Monteiro LJ, Schwenen HD, Millour J, Coombes RC, et al. Foxm1 confers acquired cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. (2010) 8:24–34. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-09-0432
93. Jin C, Liu Z, Li Y, Bu H, Wang Y, Xu Y, et al. Pcna-associated factor P15(Paf), targeted by foxm1, predicts poor prognosis in high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients. Int J Cancer. (2018) 143:2973–84. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31800
94. Zhao F, Siu MK, Jiang L, Tam KF, Ngan HY, Le XF, et al. Overexpression of forkhead box protein M1 (Foxm1) in ovarian cancer correlates with poor patient survival and contributes to paclitaxel resistance. PloS One. (2014) 9:e113478. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113478
95. Klinhom-On N, Seubwai W, Sawanyawisuth K, Lert-Itthiporn W, Waraasawapati S, Detarya M, et al. Foxm1c is the predominant foxm1 isoform expressed in cholangiocarcinoma that associated with metastatic potential and poor prognosis of patients. Heliyon. (2021) 7:e06846. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06846
96. Lam AK, Ngan AW, Leung MH, Kwok DC, Liu VW, Chan DW, et al. Foxm1b, which is present at elevated levels in cancer cells, has a greater transforming potential than foxm1c. Front Oncol. (2013) 3:11. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00011
97. Noack S, Raab M, Matthess Y, Sanhaji M, Krämer A, Győrffy B, et al. Synthetic lethality in ccne1-amplified high grade serous ovarian cancer through combined inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 and microtubule dynamics. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:25842–59. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25386
98. Momeny M, Zarrinrad G, Moghaddaskho F, Poursheikhani A, Sankanian G, Zaghal A, et al. Dacomitinib, a pan-inhibitor of erbb receptors, suppresses growth and invasive capacity of chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:4204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04147-0
99. Radhakrishnan SK, Bhat UG, Hughes DE, Wang IC, Costa RH, and Gartel AL. Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor forkhead box M1. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:9731–5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-1576
100. Westhoff GL, Chen Y, and Teng NNH. Targeting foxm1 improves cytotoxicity of paclitaxel and cisplatinum in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2017) 27:1602–9. doi: 10.1097/igc.0000000000001063
101. Ketola K, Munuganti RSN, Davies A, Nip KM, Bishop JL, and Zoubeidi A. Targeting prostate cancer subtype 1 by forkhead box M1 pathway inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:6923–33. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-0901
102. Gao Y, Geng J, Xie Z, Zhou Z, Yang H, Yi H, et al. Synthesis and antineoplastic activity of ethylene glycol phenyl aminoethyl ether derivatives as foxm1 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. (2022) 244:114877. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114877
103. Liu C, Vorderbruggen M, Muñoz-Trujillo C, Kim SH, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS, et al. Nb compounds are potent and efficacious foxm1 inhibitors in high-grade serous ovarian cancer cells. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:94. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01421-4
104. Gormally MV, Dexheimer TS, Marsico G, Sanders DA, Lowe C, Matak-Vinković D, et al. Suppression of the foxm1 transcriptional programme via novel small molecule inhibition. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:5165. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6165
105. Gartel AL. A new target for proteasome inhibitors: foxm1. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2010) 19:235–42. doi: 10.1517/13543780903563364
106. Shukla S, Milewski D, Pradhan A, Rama N, Rice K, Le T, et al. The foxm1 inhibitor rcm-1 decreases carcinogenesis and nuclear β-catenin. Mol Cancer Ther. (2019) 18:1217–29. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-18-0709
107. Andrikopoulou A, Liontos M, Koutsoukos K, Dimopoulos MA, and Zagouri F. Clinical perspectives of bet inhibition in ovarian cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2021) 44:237–49. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00578-6
108. Kwon H, Kim Y, and Kim JH. A combination of myokines and genistein suppresses cancer stemness in mcf-7 human breast cancer cells. Nutr Res Pract. (2024) 18:436–45. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.3.436
109. Zhang Z, Ma P, Jing Y, Yan Y, Cai MC, Zhang M, et al. Bet bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in ovarian cancer by downregulating foxm1. Theranostics. (2016) 6:219–30. doi: 10.7150/thno.13178
110. Momeny M, Eyvani H, Barghi F, Ghaffari SH, Javadikooshesh S, Hassanvand Jamadi R, et al. Inhibition of bromodomain and extraterminal domain reduces growth and invasive characteristics of chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. (2018) 29:1011–20. doi: 10.1097/cad.0000000000000681
111. Brückner L, Reinshagen A, Hoang NA, Höhn AK, Lordick F, Bechmann I, et al. Foxm1 inhibition in ovarian cancer tissue cultures affects individual treatment susceptibility ex vivo. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:956. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050956
112. Liu SX, Zhou Y, Zhao L, Zhou LS, Sun J, Liu GJ, et al. Thiostrepton confers protection against reactive oxygen species-related apoptosis by restraining foxm1-triggerred development of gastric cancer. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 193:385–404. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.09.018
113. Li Y, Jiang Y, Tong R, Ding B, Ge J, Du K, et al. Thiostrepton suppresses intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression via foxm1-mediated tumor-associated macrophages reprogramming. Transl Oncol. (2025) 54:102327. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102327
114. Asikaer A, Sun C, and Shen Y. Thiostrepton: multifaceted biological activities and its applications in treatment of inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology. (2025) 33:183–94. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01587-9
115. Kedjar N, Iannuzzi E, Kreuzer M, Alonso-Moreno C, and Moya-Lopez C. Fine-tuning the physicochemical properties of poly(Lactic acid) nanoparticles for the controlled release of the bet inhibitor jq1: influence of pva concentration. Polymers (Basel). (2025) 17:123. doi: 10.3390/polym17010123
116. Madhi H, Lee JS, Choi YE, Li Y, Kim MH, Choi Y, et al. Foxm1 inhibition enhances the therapeutic outcome of lung cancer immunotherapy by modulating pd-L1 expression and cell proliferation. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2022) 9:e2202702. doi: 10.1002/advs.202202702
Keywords: ovarian cancer, FOXM1, cancer biomarkers, early detection, cancer diagnosis
Citation: Tan X-Q, Guo A-Y, Zheng L-F and Xiong J (2025) Research progress on FOXM1 in ovarian cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Front. Oncol. 15:1598868. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1598868
Received: 24 March 2025; Accepted: 03 June 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Maria Gazouli, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceReviewed by:
Ugo Cavallaro, European Institute of Oncology (IEO), ItalyNaresh Sah, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Tan, Guo, Zheng and Xiong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Xiong, NDQzNTI1Mjc2QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiao-Qing Tan
Xiao-Qing Tan Ai-Ying Guo†
Ai-Ying Guo†