- 1Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Objectives: To determine the association between hysterectomy performed for benign indications and the risk of developing BC.
Methods: A literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library from database inception up to December 11, 2024. Eligible studies were observational design. Relative ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled using a random-effects model, I2 was used to assess the heterogeneity between studies.
Results: This meta-analysis included 12 studies, consisting of 4 case-control studies and 8 cohort studies. The pooled analysis of case-control studies indicated that hysterectomy reduced the risk of BC (RR = 0.839, 95% CI: 0.707-0.995, P = 0.043, I2 = 81.661%). However, the pooled analysis of cohort studies did not observe a significant association between hysterectomy and the occurrence of BC (RR = 0.981, 95% CI: 0.927-1.037, P = 0.495, I2 = 60.319%).
Conclusions: The present study reveals a protective effect of hysterectomy on the occurrence of BC in case-control studies. However, more studies, especially cohort studies, are needed to elucidate the potential beneficial effects of hysterectomy on the development of BC.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024596235, identifier CRD42024612164.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer among women worldwide and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. In 2022, there were approximately 2.3 million new cases of BC globally, with over 660,000 deaths (1). According to the latest statistics from the United States, the incidence of BC is expected to continue rising in the future, with a noticeable trend of affecting younger individuals (2). Although the emergence of new therapies represented by targeted therapy and immunotherapy in recent years has greatly improved patients’ prognosis (3), these treatments not only require precise molecular typing and entail the inevitable issue of drug resistance but also carry a higher risk of toxicity and adverse reactions (4). Therefore, it is particularly important to accurately identify high-risk groups and factors for BC and scientifically carry out prevention and screening measures. Several studies have demonstrated that the occurrence and progression of BC are closely associated with genetic, hormonal, lifestyle, and environmental factors (5–7, 12), primarily involving body weight, diet, physical activity, alcohol consumption, reproductive characteristics, and BRCA gene mutations (8–11).
Hysterectomy is one of the most common gynecologic surgeries around the world (13). According to statistical reports from 2006, approximately 153,000 hysterectomies were performed in Germany that year (14), while the annual number of such procedures in the United States was about 600,000 (15). As of 2023, the prevalence of hysterectomy in the United States remains at 21.1% (16). Most hysterectomy procedures are used to treat symptomatic benign gynecologic conditions (such as uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and dysfunctional uterine bleeding) (17, 18). Hysterectomy for these benign indications can cause significant changes in hormone levels, which may affect the risk of hormone-related cancer (19). Some studies focus on hysterectomy combined with ovariectomy (20–22), which confirmed that hysterectomy combined with bilateral fallopian ovariectomy can reduce the risk of BC (23). However, the impact of simple hysterectomy on the occurrence rate of BC remains controversial. Some studies have found no association between the procedure and BC risk (24–30), while others have indicated that surgery performed before the age of 45 may reduce risk (20, 21, 31, 32). Furthermore, a retrospective study reported an increased occurrence rate of BC after surgery among women under 60 years of age, whereas a decreased rate was observed in those aged 60 and above (22).
Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted of the available evidence, aiming to investigate the association between hysterectomy and BC risk and explore the potential impact of hysterectomy on BC.
2 Methods
The study was conducted in accordance with the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) and reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (33, 34). The study protocol was prospectively registered in PROSPERO (No.CRD42024612164) (35).
2.1 Search strategy
A comprehensive search was performed across PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library from database inception through November 11, 2024, using medical subject headings (MeSH) and free text words. The main search terms were used as follows: such as: (“Breast Neoplasms”[Mesh] OR “Breast Cancer” OR “Mammary Neoplasms”) AND (“Hysterectomy”[Mesh]) AND (“Risk Assessment” OR “Epidemiology”). Reference list was screened for eligible studies. Detailed search strategies are provided in Supplementary Table S1-S3.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
Eligible studies were required to fulfill these criteria: 1) Studies involving human participants without a history of BC prior to hysterectomy; 2) Studies where hysterectomy serve as the primary exposure and the incidence of BC as the outcome; 3) Studies providing one of the following metrics: Risk Ratio (RR), Hazard Ratio (HR), or Odds Ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to assess BC risk in patients after hysterectomy. 4) Observational design (cohort studies or case-control studies). For overlapping populations, we prioritized studies with larger sample sizes, longer follow-up durations, or more recent publication dates.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria comprised: 1) Non-original research (reviews, commentaries, conference abstracts); 2) Insufficient outcome data for effect size calculation; 3) Duplicate literatures.
2.4 Study selection
Independent reviewers (LWJ, LTT) conducted the study selection. After removing duplicates, the remaining records were screened by title/abstract and then full text of eligible articles. Any discrepancies were resolved through consulting with a third investigator (YJQ).
2.5 Data extraction
Data extraction was conducted independently by two reviewers (LWJ, LTT) using structured data collection forms. First author, publication year, country, study design, sample size, study period, exposure assessment method, follow-up duration, participant demographics, outcome measures, and metric were extracted. Discrepancies were resolved through consulting with YJQ.
2.6 Quality assessment
Methodological quality was independently evaluated by the two reviewers(LWJ, LTT) using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (36). The NOS assesses three domains: selection process, group comparability, exposure (case–control study); or outcome (cohort study). Scores of 0-3, 4-6, and 7–9 were considered as low, moderate, and high quality, respectively.
2.7 Data synthesis and analysis
We conducted a meta-analysis based on different study types, such as case-control studies and cohort studies, rather than calculating an overall pooled effect estimate. This approach was taken to address the heterogeneity arising from differences in study design. RR was used as the common measure of association across studies, and HR and OR were considered approximate to RR given the low incidence rate of BC (37). Therefore, we converted the outcome metric (HR, and OR) into RR. Heterogeneity was evaluated by I2 value. I2 < 50% was considered as low heterogeneity, the fixed effect model was adopted. Otherwise, the random effect model was adopted. Sensitivity analyses evaluated result stability through sequential study exclusion. Publication bias was assessed by funnel plot symmetry and Egger’s test. Subgroup analyses were conducted according to age strata, follow-up duration, BC subtypes, and geographical regions. Statistical analysis was conducted using R 4.3.0 software. P value < 0.05 (bilateral) is considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search
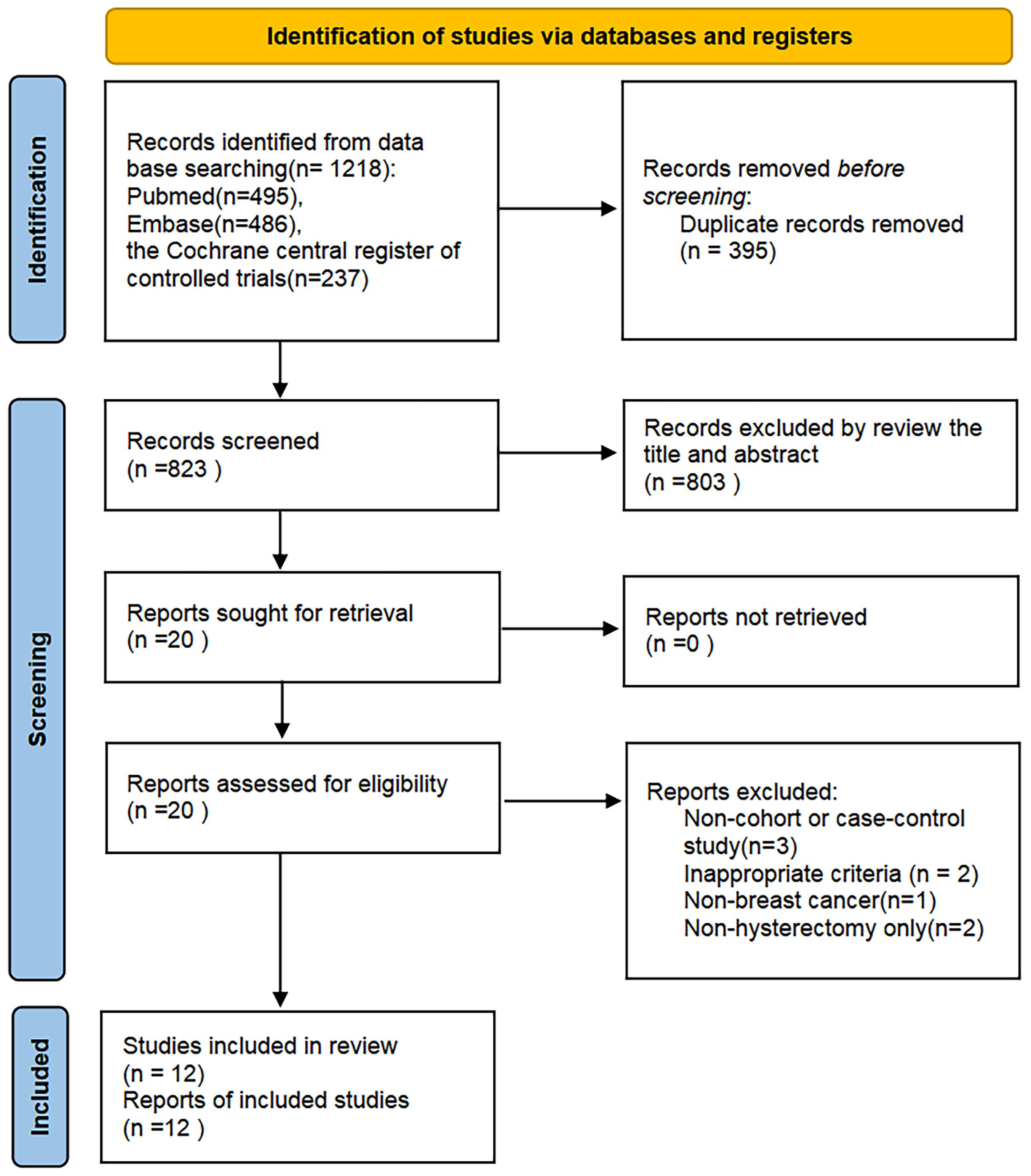
The literature search initially identified 1,218 relevant records. After eliminating 395 duplicates, 823 records remained for the title and abstract screening. 20 articles needed to be read in full-text to determine their eligibility for inclusion. Then, eight studies were excluded for the following reasons: non-observational designs (n=3), inappropriate criteria (n=2), non-BC(n=1), non-hysterectomy only(n=3), with one additional study identified through supplementary citation tracking. Twelve rigorously conducted studies fulfilling all inclusion parameters were ultimately selected for meta-analytic integration. The complete study selection workflow is detailed in Figure 1.
3.2 Study characteristics
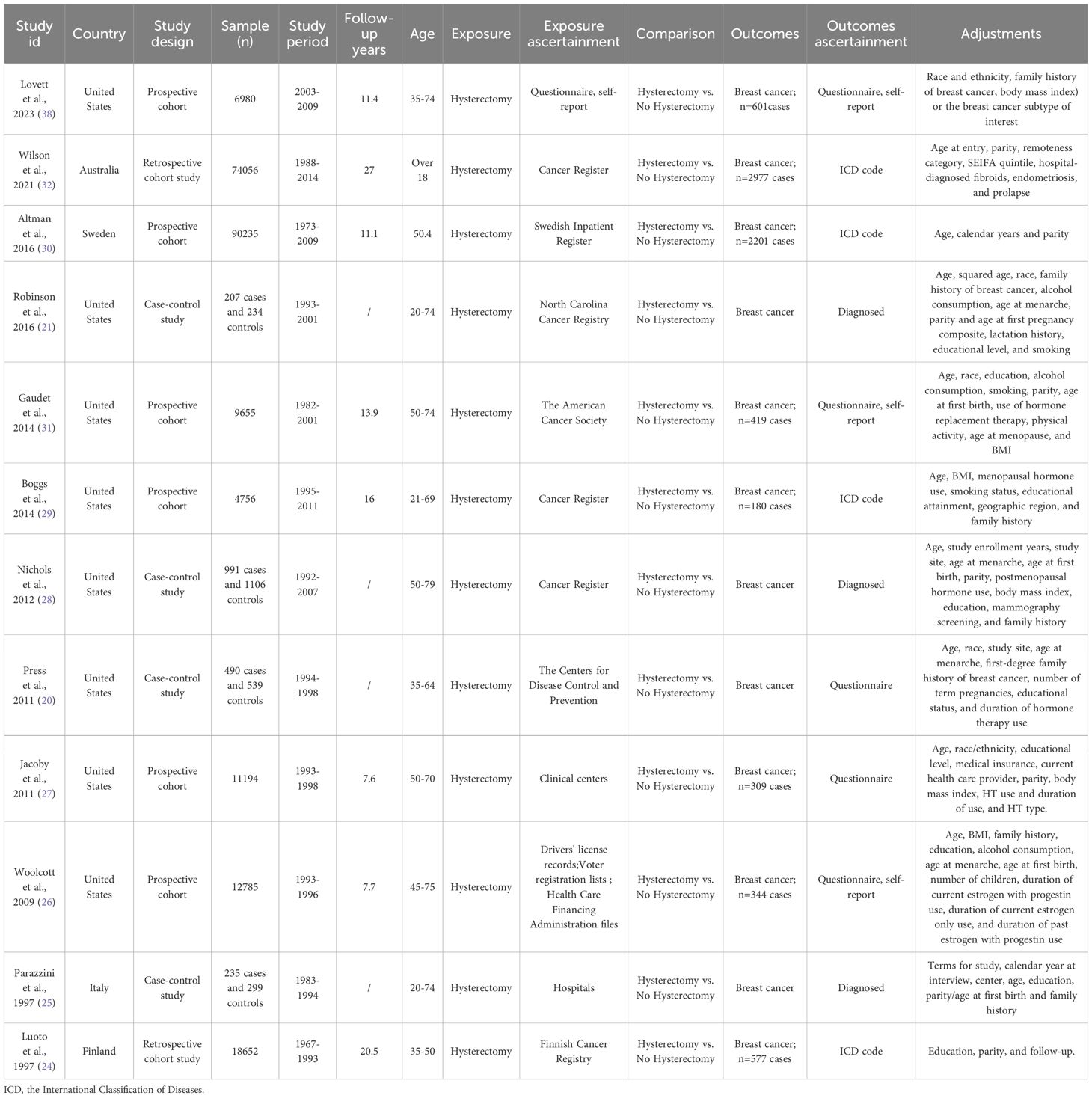
A total of 228313 participants were included in 12 studies between the years of 1997–2023.And the postoperative follow-up periods ranged from 0 to 27 years. Two studies were retrospective cohort studies (24, 32), 6 studies were prospective cohort studies (26, 27, 29–31, 38), and 4 studies were case-control studies (20, 21, 25, 28). Geographically, the majority originated from the United States (n=8), supplemented by single contributions from Australia, Sweden, Italy, and Finland. Detailed characteristics of included studies were summarized in Table 1 and Supplementary Table S3.
3.3 Quality assessment
Using the NOS evaluation criteria, 3 studies were classified as nine-star (20, 25, 32), 1 study received eight stars (31), and 4 studies achieved seven-star ratings (21, 28–30), demonstrating high methodological quality. Four studies were categorized as moderate quality (six-star rating) (24, 26, 27, 38). The mean NOS score across all 12 publications was 7.25, suggesting an acceptable overall methodological standard. A comprehensive summary of the quality assessment process and outcomes is provided in Supplementary Tables S2, S5.
3.4 Meta-analysis
3.4.1 Risk of BC
A total of 12 studies, 4 case-control studies and 8 cohort studies, reported on the risk of BC. The results of the random effects model meta-analysis showed that hysterectomy was associated with 16% reduction in risk of cancer (RR = 0.839, 95% CI: 0.707-0.995, P = 0.043, I2 = 81.661%) (case-control studies, Figure 2A). However, the results of the random effects model meta-analysis showed that hysterectomy was not associated with BC (RR = 0.981, 95% CI: 0.927-1.037, P = 0.495, I2 = 60.319%) (cohort studies, Figure 2B).
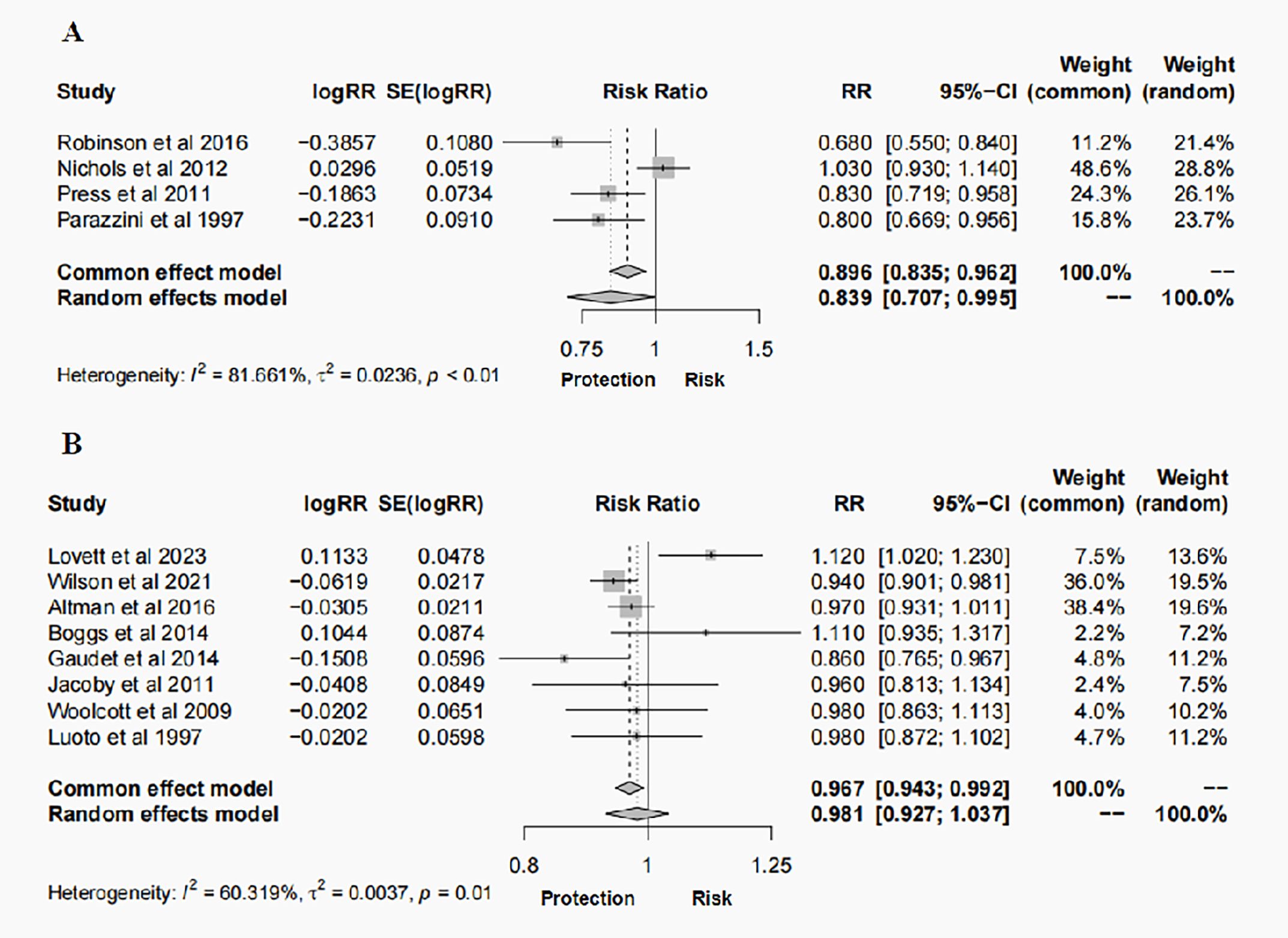
Figure 2. Forest plots of outcomes for the risk of BC following hysterectomy: (A) case–control studies; (B) cohort studies.
3.5 Subgroup analysis
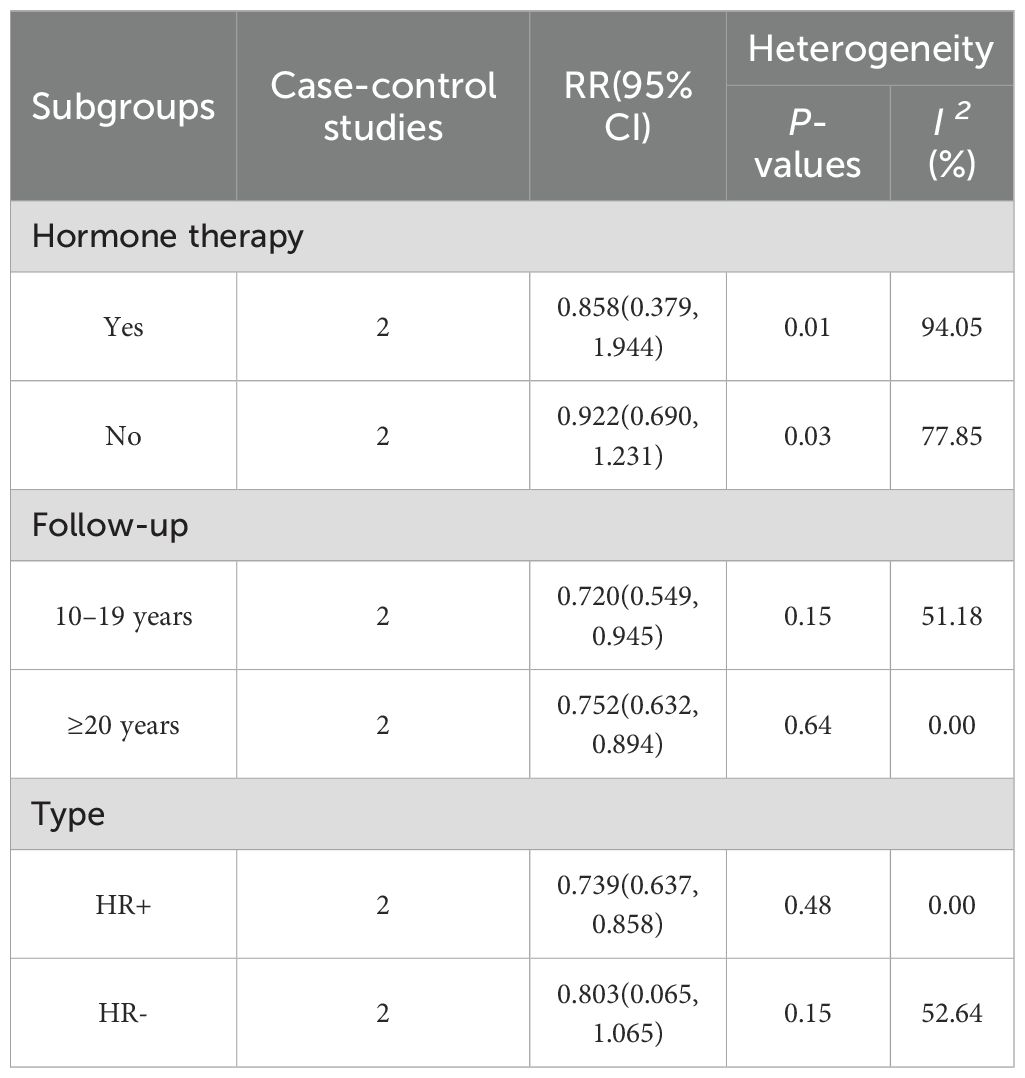
The case-control study results showed that people with more than 10 years of follow-up after hysterectomy (RR = 0.720, 95% CI: 0.549-0.945, I2 = 51.18%). When analyzed by subtype, hysterectomy was specifically associated with a reduced incidence of HR+ BC (RR = 0.739, 95% CI: 0.637-0.858, I² = 0.00%),which was consistent with the overall summary analysis. However, no association was observed between hysterectomy and the incidence of HR- BC. The results of subgroup analysis are presented in Table 2.
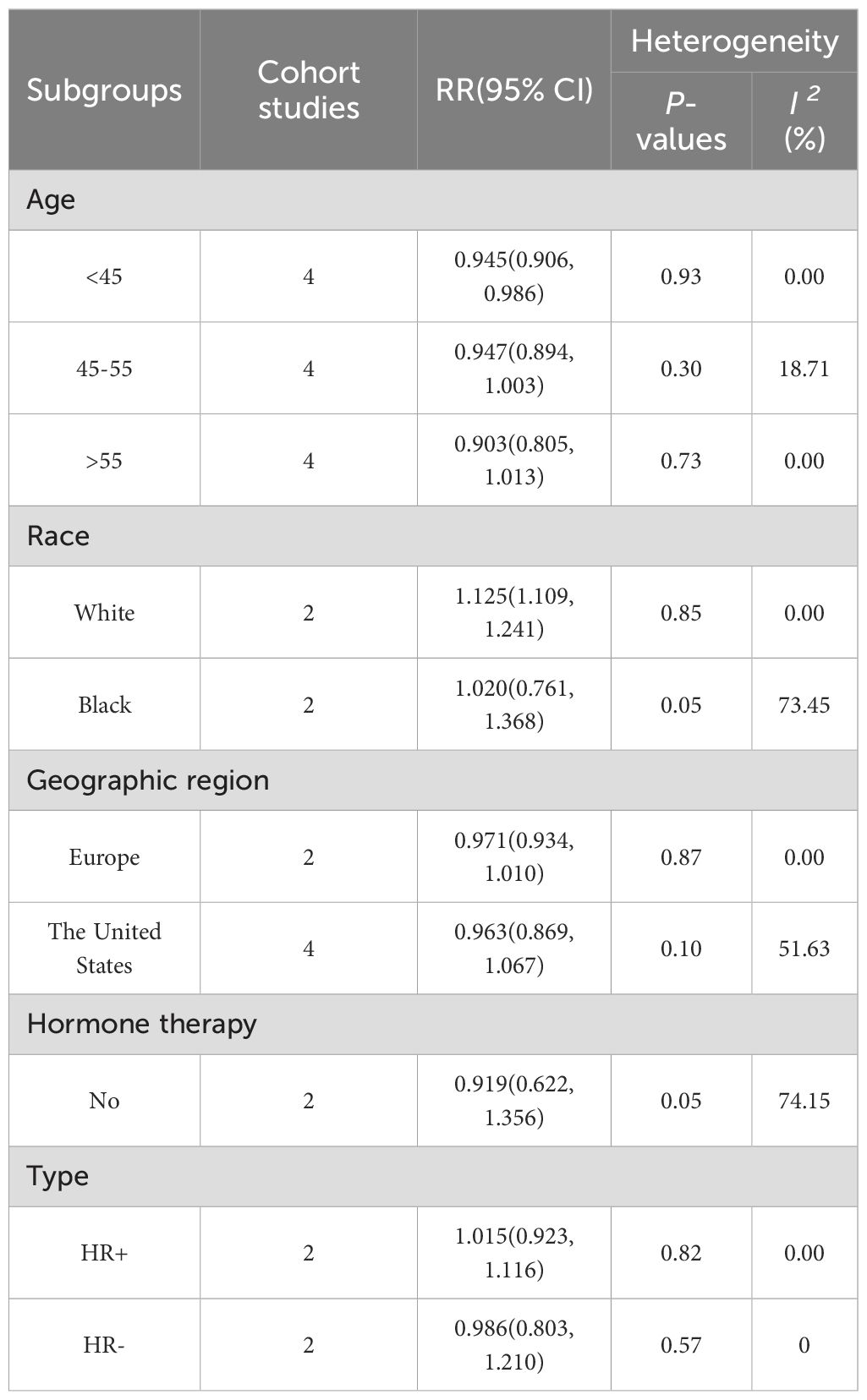
The cohort study results showed a lower risk of BC in those undergoing hysterectomy before the age of 45 (RR = 0.945, 95% CI: 0.906-0.986, I2 = 0.00%), while subgroup analyses of ethnicity showed a higher risk of BC after hysterectomy in whites (RR = 1.125, 95% CI: 1.109-1.241, I2 = 0.00%). No association was observed between the risk of BC among people who underwent surgery after age 45, black people, different geographical areas, and no postoperative hormone therapy. The results of subgroup analysis are presented in Table 3 and Supplementary Figures 1-6.
3.6 Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
Sensitivity analyses were performed to identify sources of heterogeneity by eliminating one study in each turn. In case-control study, when the Nichols, et al., 2012 (28) was excluded, heterogeneity was significantly reduced (RR = 0.785, 95% CI: 0.708- 0.869, P < 0.001, I2 = 16.198%). When Lovett, et al., 2023 was excluded from the cohort study, it was observed that not only was the heterogeneity significantly reduced, but the finding that hysterectomy was not related to BC risk changed to a profound 4.4% reduction in the risk of BC after hysterectomy (RR = 0.956, 95% CI: 0.931- 0.982, P = 0.001, I2 = 19.716%) (Figure 3). Notably, the narrow 95% CI (0.931-0.982) indicates a high degree of precision in this risk estimate. When other studies were removed, the initial results did not change significantly. Funnel plots and Egger’s test were performed to assess the risk of publication bias. While visual inspection of the funnel plots, particularly for cohort studies, suggested some asymmetry. However, the results of the Egger’s regression test showed no statistically significant evidence of publication bias (Case-control studies: P = 0.218; Cohort studies: P = 0.475) (Figure 4). And this may be due to the limited number of included studies, minor bias cannot be entirely ruled out in this meta-analysis.
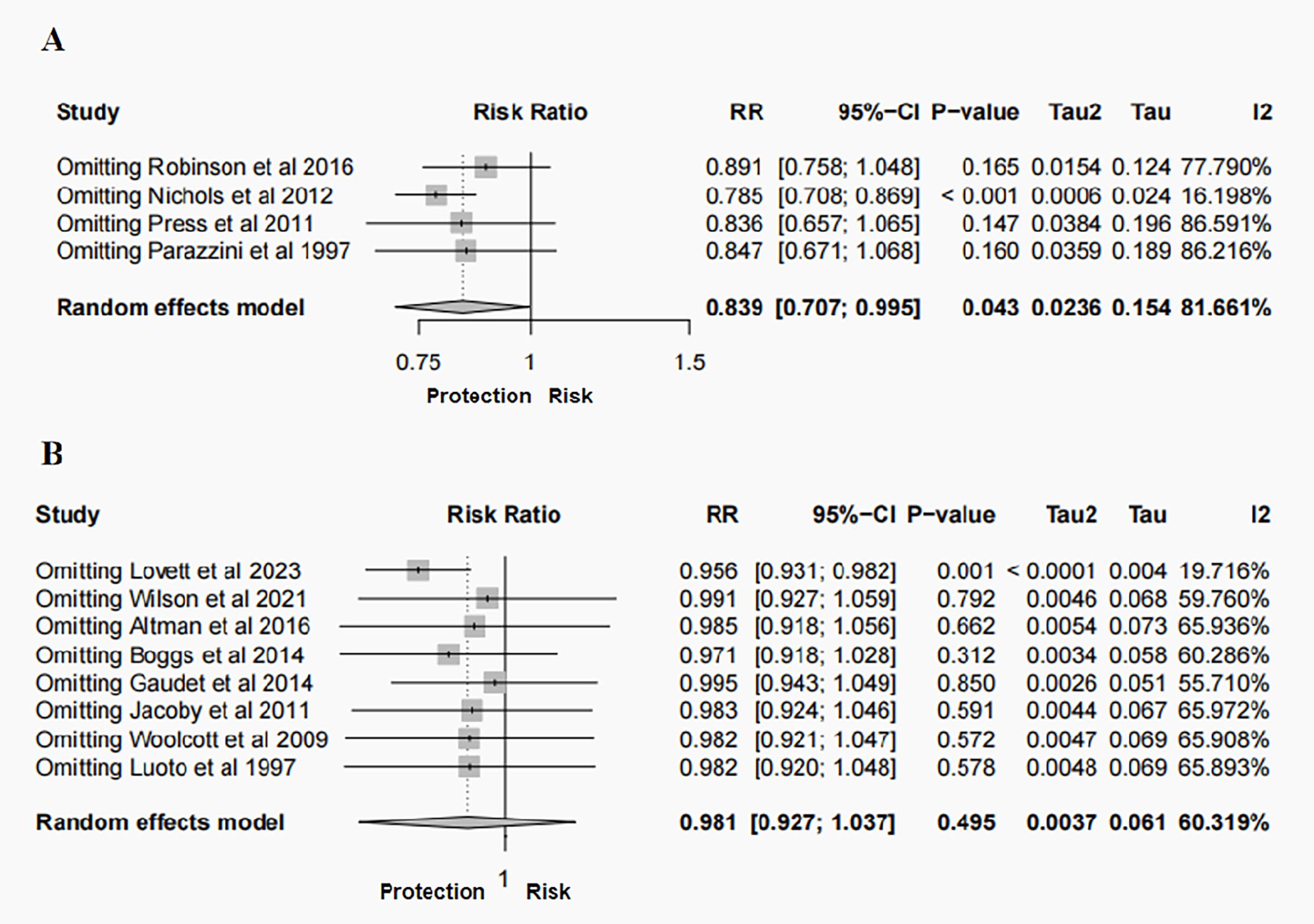
Figure 3. Sensitivity analysis of the meta-analysis for the risk of BC following hysterectomy: (A) case–control studies; (B) cohort studies.
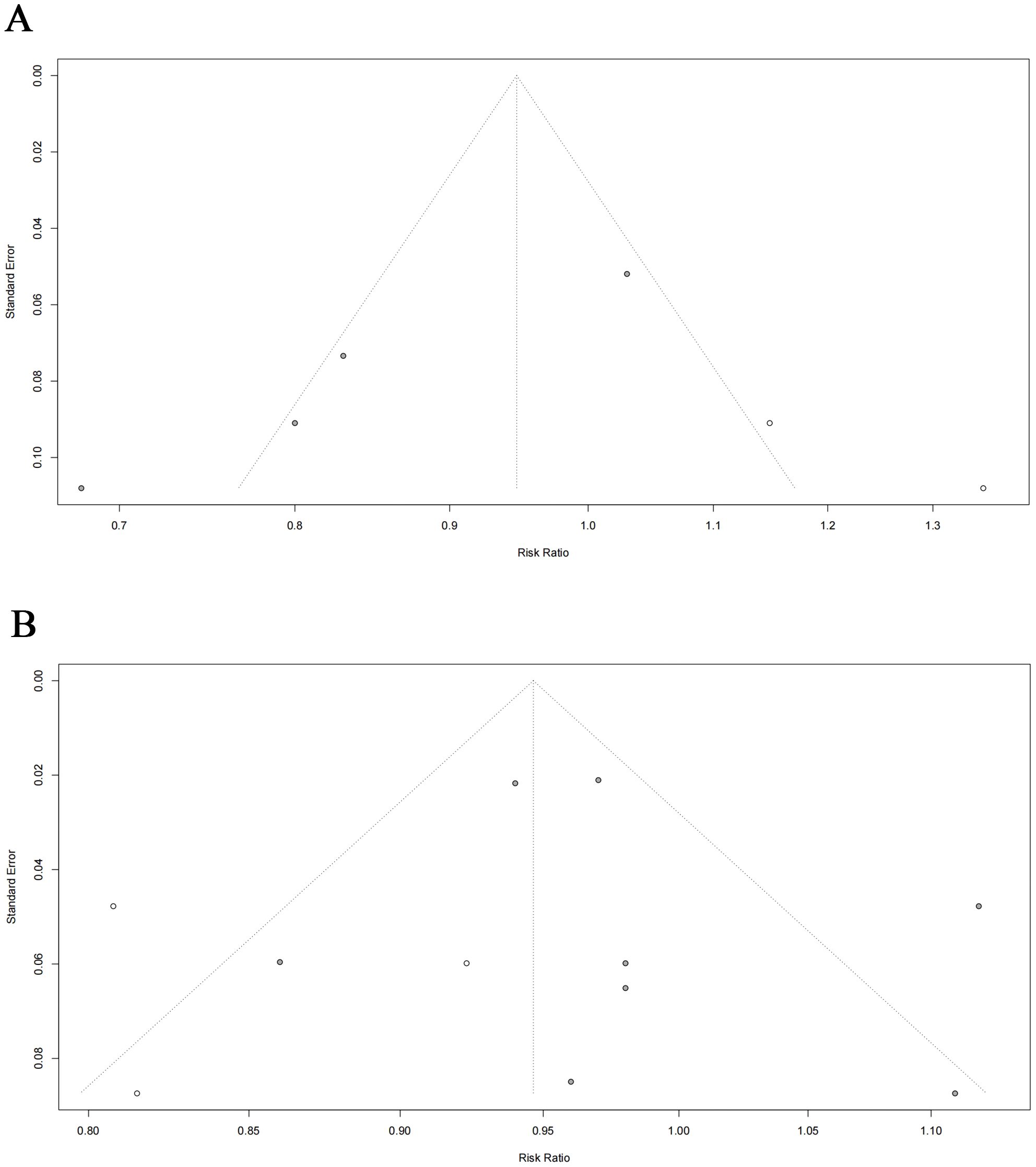
Figure 4. Egger’s funnel plots of the meta-analysis for the risk of BC following hysterectomy: (A) case–control studies ; (B) cohort studies.
4 Discussion
In this systematic review and meta-analysis, the meta-analysis results of case-control studies indicate that compared to those who did not undergo surgery, patients subjected to hysterectomy have a 0.16-fold reduced risk of developing BC. However, the meta-analysis of cohort studies shows no correlation between hysterectomy and BC occurrence. Both analyses exhibit significant heterogeneity, particularly in the cohort studies. Sensitivity analysis reveals that after excluding the Lovett et al., 2023 study (38), not only does the heterogeneity decrease significantly, but the finding of no association between hysterectomy and BC occurrence is reversed, indicating a notable reduction in BC risk among those who underwent hysterectomy. The profound impact of this study stems from the combination of its unique population characteristics and methodological rigor, which collectively untangle a key confounding factor potentially obscured in other studies. First, the study is based on the “Sister Study” cohort, in which all participants had a sister with BC, indicating that this population inherently possesses a higher baseline risk related to genetic factors. More importantly, through detailed stratified analyses, the authors demonstrated that hysterectomy alone was only weakly associated with BC risk (HR = 1.08, 95% CI: 0.94-1.23). In contrast, the exposure combination that significantly increased risk was “hysterectomy plus estrogen-progestin therapy” (HR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.01-1.55). By comparison, most of the other cohort studies included in the present meta-analysis (with the exception of the study by Jacoby et al., 2011) failed to adequately control for this critical confounder—postoperative combined hormone therapy. Consequently, the additional risk attributable to combined therapy in those studies may have been erroneously attributed to hysterectomy itself, leading to an overestimation of risk in the “hysterectomy-only” group. This sensitivity analysis does not merely involve excluding one large study; rather, it removes a major source of confounding, thereby clarifying the origin of heterogeneity. Furthermore, the sensitivity analysis of the cohort studies not only untangled a significant protective association but also provided a precise estimate of the effect, as evidenced by the narrow confidence interval. Our subgroup analysis yields interesting findings, albeit with a small sample size and less reliability compared to the primary analysis. Subgroup analysis based on case-control studies shows a significant negative correlation between hysterectomy and BC risk in populations with more than 10 years of follow-up and in BC patients with a post-disease pathological diagnosis of HR +. Meanwhile, subgroup analysis based on cohort studies suggests that those who underwent hysterectomy before the age of 45 have a lower risk of BC, while white individuals show a 1.13-fold increased risk of BC after hysterectomy.
Regarding the reduced risk of BC among patients who have undergone simple hysterectomy, we hypothesize that this may be influenced by both anatomical and endocrine pathways. Firstly, although simple hysterectomy preserves the ovaries, the disruption of utero-ovarian vascular anastomoses during surgery can lead to a 50%-70% reduction in ovarian blood flow, inducing ischemic ovarian failure (39, 40). The pathological features include a decrease in antral follicle count (AFC) and anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) levels within six months postoperatively, which can also be evidenced by various menopausal symptoms, bone loss, and increased risk of hypertension (41–43). Meanwhile, the uterus, as a crucial endocrine organ, its removal results in the sudden loss of uterine-derived regulatory factors (such as prostaglandin F2α and relaxin), which may alter the negative feedback mechanism of the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis, leading to elevated serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels postoperatively (44). Studies have shown that these changes collectively advance the average natural menopause age by 3.7 years compared to the non-surgical population (39). Epidemiological models indicate that for every one-year advance in menopause age, the relative risk of BC decreases by 2.3% (45, 46). Therefore, an early menopause of 3.7 years may imply a 7% to 11% risk reduction. This aligns with our subgroup analysis findings, where women under 45 years old who underwent surgery had a reduced risk of BC. Postoperative endocrine changes include increased estradiol fluctuation, decreased estrone/estradiol ratio, and downregulation of ERα expression and aromatase activity, which may confer protection (47). Notably, preoperative medical treatments may enhance this protective effect. For instance, patients with endometriosis receiving GnRH agonist therapy for ≥6 months can reduce their risk by 31% (48). Secondly, over 90% of hysterectomies are performed for benign indications, including uterine fibroids (leiomyomas), endometriosis, uterine prolapse, and menstrual disorders (49). However, some risk factors for these diseases contradict those for BC. For example, alcohol consumption and body mass index (BMI) can reduce the risk of endometriosis but increase the risk of postmenopausal BC (50–52). Childbirth and early first pregnancy can elevate the risk of prolapse but lower the risk of BC (53–55). This suggests that due to these conflicting risk factors, hysterectomy may reduce the risk of BC.
The finding of no correlation between hysterectomy and BC risk may stem from preoperative and postoperative interventions. These interventions may produce a biological neutralizing effect. Since women may have already received medical treatment for hysterectomy indications before surgery, and these treatments potentially influence BC risk. For instance, treatments for endometriosis include danazol, oral contraceptives, and growth hormone-releasing hormone agonists (56–58). The preoperative hormone therapy may balance the hormonal changes postoperatively, forming a biological neutralization mechanism, which could lead to the observed zero association between hysterectomy and BC risk. It’s worth noting that the pathophysiological characteristics of the surgical indication disease itself may produce reverse regulation: endometrial cells in patients with endometriosis show a 2.3-fold upregulation of BRCA1 expression, and this enhanced DNA repair capability may partially offset the carcinogenic effects of estrogen exposure; while abnormal pelvic floor collagen metabolism in patients with uterine prolapse may inhibit breast tumor microenvironment formation by altering stroma-epithelial interactions (59).
An interesting finding from our subgroup analysis is that the risk of BC among white women increases by 1.23 times after hysterectomy. Previous studies have indicated that the incidence of simple hysterectomy varies among different races (60–62). Compared to black women, white women have a lower prevalence of hysterectomy for benign diseases, a higher average age at surgery, and a higher proportion of hormone therapy use (63). We believe these differences may be due to racial disparities in the incidence and severity of uterine pathologies, early treatments to prevent hysterectomy, or medical practices (61, 64, 65). Therefore, regarding the increased risk of BC, we hypothesize that it is related to the interaction between genetic susceptibility and environmental exposure. Firstly, diseases leading to hysterectomy may share the same hormonal etiology with BC. Some risk factors for these diseases are also known as risk factors for BC, such as early menarche, low parity, BMI, and inadequate physical activity (66). Secondly, diseases like endometriosis may be associated with BC risk, although the correlation is not yet clear. However, some studies have shown that they may slightly increase the risk of BC (59, 67). Additionally, the retention of adnexa after hysterectomy may lead to the formation of pelvic fluid, and this chronic inflammatory state may promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by activating the NF-κB pathway, affecting cancer development (68). Finally, postoperative use of estrogen combined with progesterone therapy may also increase BC risk. Although our subgroup analysis did not observe a significant impact of postoperative hormone use on the study results, it may be related to the limited number of studies included (only two with high heterogeneity). Therefore, more high-quality studies are needed in the future to further validate these findings.
The primary source of heterogeneity in our cohort study was the 2023 study by Lovett et al (38). We analyzed possible reasons for this heterogeneity. One reason may be the inclusion of patients with a family history of BC, which may increase their risk of developing the disease. Another reason could be potential measurement errors in hysterectomy status, as self-reporting and recall may introduce inaccuracies. Future research should construct multi-dimensional predictive models that integrate surgical parameters, dynamic hormone monitoring, and genomic features. Simultaneously, multi-omics longitudinal studies covering the epigenome, metabolome, and immune microenvironment (such as dynamic monitoring from preoperative to 3 and 10 years postoperatively) should be conducted. In clinical practice, it is recommended to establish an individualized BC risk assessment system for patients under 45 years old undergoing hysterectomy. This system should incorporate genetic risk scores, and postoperative hormone replacement therapy plans into the decision-making process and develop targeted monitoring programs for high-risk populations. These measures will help unravel the precise dose-effect relationship between hysterectomy and BC risk and provide evidence-based medical support for the cancer prevention value of gynecological surgery.
Prior to the initiation of this study, existing research had investigated the impact of hysterectomy combined with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy on cancer risk and mortality through meta-analysis (23). However, the uniqueness of the present study lies in the fact that it is the first to specifically examine the association between hysterectomy performed solely for benign indications and the risk of BC. It separately analyzes the included case-control studies and cohort studies and conducts an in-depth subgroup analysis to explore the influence of factors such as age, ethnicity, follow-up time, and hormone therapy. Notably, it reveals a significant reduction in risk for young women (<45 years old) and patients with HR+ BC.
However, this study also has some limitations. Firstly, the contradictory results between case-control and cohort studies may stem from methodological differences. The high heterogeneity observed within each study type suggests the potential presence of unmeasured confounding factors. Second, most studies did not document medication history or provide risk estimates stratified by surgical indications, which may have led to observed associations being attributable to underlying diseases or medication use rather than to the surgery itself. Additionally, the geographical and ethnic distribution of the included studies is uneven, with a predominance of research based in the United States, which may limit the generalizability of the results. Finally, some subgroups have small sample sizes, such as those involving two studies on hormone therapy, which results in insufficient statistical power and higher uncertainty in the findings. Future prospective studies should collect more detailed data on surgical indications, medication history, and other relevant factors, as well as include more diverse populations.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the study demonstrated a potential association between hysterectomy and BC risk, especially for premenopausal women. However, given the limitations of the available data, future studies are needed to further validate these factors, including the potential biases introduced using hormones after hysterectomy and whether preoperative disease is analyzed as an exposure factor in BC risk investigations.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JY: Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for theresearch and/or publication of this article. This study was supportedby the Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science andTechnology Major Project(No.2024ZD0520800, No.2024ZD0520801) and Research on the Construction of an Ecological Chain ofEvidence for the Integration of Advantageous Diseases in Chineseand Western Medicine(No.C2021A05502).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the reviewers for their valuable comments and to the following institutions for their financial support: the Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project and the Research on the Construction of an Ecological Chain of Evidence for the Integration of Advantageous Diseases in Chinese and Western Medicine.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1600459/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Allen I, Hassan H, Walburga Y, Huntley C, Loong L, Rahman T, et al. Second primary cancer risks after breast cancer in brca1 and brca2 pathogenic variant carriers. J Clin Oncol. (2025) 43:651–61. doi: 10.1200/jco.24.01146
3. Sarhangi N, Hajjari S, Heydari SF, Ganjizadeh M, Rouhollah F, and Hasanzad M. Breast cancer in the era of precision medicine. Mol Biol Rep. (2022) 49:10023–37. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07571-2
4. Li X, Zhang X, Yin S, and Nie J. Challenges and prospects in her2-positive breast cancer-targeted therapy. Crit Rev Oncology/hematol. (2025) 207:104624. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2025.104624
5. Hawazie A and Druce M. Breast cancer risk and management in the endocrine clinic: A comprehensive review. Clin Endocrinol. (2025). doi: 10.1111/cen.15209
6. Armenta-Guirado BI, González-Rocha A, Mérida-Ortega Á, López-Carrillo L, and Denova-Gutiérrez E. Lifestyle quality indices and female breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Nutr (Bethesda Md). (2023) 14:685–709. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.04.007
7. Tippila J, Wah NLS, Akbar KA, Bhummaphan N, Wongsasuluk P, and Kallawicha K. Ambient air pollution exposure and breast cancer risk worldwide: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2024) 21:1713. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21121713
8. Engin A. Obesity-associated breast cancer: analysis of risk factors and current clinical evaluation. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2024) 1460:767–819. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_26
9. Sohi I, Rehm J, Saab M, Virmani L, Franklin A, Sánchez G, et al. Alcoholic beverage consumption and female breast cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. (2024) 48:2222–41. doi: 10.1111/acer.15493
10. Vatankhah H, Khalili P, Vatanparast M, Ayoobi F, Esmaeili-Nadimi A, and Jamali Z. Prevalence of early and late menopause and its determinants in rafsanjan cohort study. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:1847. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28526-y
11. Garnæs KK, Elvebakk T, Salvesen Ø, Stafne SN, Mørkved S, Salvesen K, et al. Dietary intake in early pregnancy and glycemia in late pregnancy among women with obesity. Nutrients. (2021) 14:105. doi: 10.3390/nu14010105
12. Ye DM, Bai X, Xu S, Qu N, Zhao N, Zheng Y, et al. Association between breastfeeding, mammographic density, and breast cancer risk: A review. Int Breastfeed J. (2024) 19:65. doi: 10.1186/s13006-024-00672-7
13. Stang A, Merrill RM, and Kuss O. Hysterectomy in Germany: A drg-based nationwide analysis, 2005-2006. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int. (2011) 108:508–14. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2011.0508
14. Wu JM, Wechter ME, Geller EJ, Nguyen TV, and Visco AG. Hysterectomy rates in the United States, 2003. Obstet Gynecol. (2007) 110:1091–5. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000285997.38553.4b
15. Tuesley KM, Protani MM, Webb PM, Dixon-Suen SC, Wilson LF, Stewart LM, et al. Hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy and all-cause and cause-specific mortality. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2020) 223:723.e1–.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.04.037
16. Harvey SV, Pfeiffer RM, Landy R, Wentzensen N, and Clarke MA. Trends and predictors of hysterectomy prevalence among women in the United States. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2022) 227:611.e1–.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.06.028
17. Lycke KD, Kahlert J, Damgaard R, Mogensen O, and Hammer A. Trends in hysterectomy incidence rates during 2000–2015 in Denmark: shifting from abdominal to minimally invasive surgical procedures. Clin Epidemiol. (2021) 13:407–16. doi: 10.2147/clep.S300394
18. Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Jamieson DJ, Morrow B, Podgornik MN, Brett KM, et al. Inpatient hysterectomy surveillance in the United States, 2000-2004. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2008) 198:34.e1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.039
19. Flory N, Bissonnette F, and Binik YM. Psychosocial effects of hysterectomy: literature review. J Psychosom Res. (2005) 59:117–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2005.05.009
20. Press DJ, Sullivan-Halley J, Ursin G, Deapen D, McDonald JA, Strom BL, et al. Breast cancer risk and ovariectomy, hysterectomy, and tubal sterilization in the women’s contraceptive and reproductive experiences study. Am J Epidemiol. (2011) 173:38–47. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwq339
21. Robinson WR, Nichols HB, Tse CK, Olshan AF, and Troester MA. Associations of premenopausal hysterectomy and oophorectomy with breast cancer among black and white women: the carolina breast cancer study, 1993-2001. Am J Epidemiol. (2016) 184:388–99. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwv448
22. Chow S, Raine-Bennett T, Samant ND, Postlethwaite DA, and Holzapfel M. Breast Cancer Risk after Hysterectomy with and without Salpingo-Oophorectomy for Benign Indications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2020) 223:900.e1–.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.040
23. Hassan H, Allen I, Sofianopoulou E, Walburga Y, Turnbull C, Eccles DM, et al. Long-term outcomes of hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2024) 230:44–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.06.043
24. Luoto R, Auvinen A, Pukkala E, and Hakama M. Hysterectomy and subsequent risk of cancer. Int J Epidemiol. (1997) 26:476–83. doi: 10.1093/ije/26.3.476
25. Parazzini F, Braga C, La Vecchia C, Negri E, Acerboni S, and Franceschi S. Hysterectomy, oophorectomy in premenopause, and risk of breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. (1997) 90:453–6. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(97)00295-0
26. Woolcott CG, Maskarinec G, Pike MC, Henderson BE, Wilkens LR, and Kolonel LN. Breast cancer risk and hysterectomy status: the multiethnic cohort study. Cancer Causes Control: CCC. (2009) 20:539–47. doi: 10.1007/s10552-008-9262-2
27. Jacoby VL, Grady D, Wactawski-Wende J, Manson JE, Allison MA, Kuppermann M, et al. Oophorectomy vs ovarian conservation with hysterectomy: cardiovascular disease, hip fracture, and cancer in the women’s health initiative observational study. Arch Internal Med. (2011) 171:760–8. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2011.121
28. Nichols HB, Trentham-Dietz A, Newcomb PA, Titus LJ, Egan KM, Hampton JM, et al. Postoophorectomy estrogen use and breast cancer risk. Obstet Gynecol. (2012) 120:27–36. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31825a717b
29. Boggs DA, Palmer JR, and Rosenberg L. Bilateral oophorectomy and risk of cancer in african american women. Cancer Causes Control: CCC. (2014) 25:507–13. doi: 10.1007/s10552-014-0353-y
30. Altman D, Yin L, and Falconer H. Long-term cancer risk after hysterectomy on benign indications: population-based cohort study. Int J Cancer. (2016) 138:2631–8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30011
31. Gaudet MM, Gapstur SM, Sun J, Teras LR, Campbell PT, and Patel AV. Oophorectomy and hysterectomy and cancer incidence in the cancer prevention study-ii nutrition cohort. Obstet Gynecol. (2014) 123:1247–55. doi: 10.1097/aog.0000000000000270
32. Wilson LF, Tuesley KM, Webb PM, Dixon-Suen SC, Stewart LM, and Jordan SJ. Hysterectomy and risk of breast, colorectal, thyroid, and kidney cancer - an Australian data linkage study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2021) 30:904–11. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-20-1670
33. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The prisma 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
34. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (Moose) Group. Jama. (2000) 283:2008–12. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
35. Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. Prisma extension for scoping reviews (Prisma-scr): checklist and explanation. Ann Internal Med. (2018) 169:467–73. doi: 10.7326/m18-0850
36. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the newcastle-ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
37. Greenland S. Quantitative methods in the review of epidemiologic literature. Epidemiol Rev. (1987) 9:1–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036298
38. Lovett SM, Sandler DP, and O’Brien KM. Hysterectomy, bilateral oophorectomy, and breast cancer risk in a racially diverse prospective cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2023) 115:662–70. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djad038
39. Farquhar CM, Sadler L, Harvey SA, and Stewart AW. The association of hysterectomy and menopause: A prospective cohort study. BJOG: an Int J Obstet Gynaecol. (2005) 112:956–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00696.x
40. Xiangying H, Lili H, and Yifu S. The effect of hysterectomy on ovarian blood supply and endocrine function. Climacteric. (2006) 9:283–9. doi: 10.1080/13697130600865774
41. Chan CC, Ng EH, and Ho PC. Ovarian changes after abdominal hysterectomy for benign conditions. J Soc Gynecol Invest. (2005) 12:54–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsgi.2004.07.004
42. Watson NR, Studd JW, Garnett T, Savvas M, and Milligan P. Bone loss after hysterectomy with ovarian conservation. Obstet Gynecol. (1995) 86:72–7. doi: 10.1016/0029-7844(95)00100-6
43. Luoto R, Kaprio J, Reunanen A, and Rutanen EM. Cardiovascular morbidity in relation to ovarian function after hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. (1995) 85:515–22. doi: 10.1016/0029-7844(94)00456-n
44. Ahmed Ebbiary NA, Lenton EA, and Cooke ID. Hypothalamic-pituitary ageing: progressive increase in fsh and lh concentrations throughout the reproductive life in regularly menstruating women. Clin Endocrinol. (1994) 41:199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1994.tb02530.x
45. Rosner B and Colditz GA. Nurses’ Health study: log-incidence mathematical model of breast cancer incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. (1996) 88:359–64. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.6.359
46. Beral V, Bull D, Doll R, Key T, Peto R, Reeves G, et al. Breast cancer and hormone replacement therapy: collaborative reanalysis of data from 51 epidemiological studies of 52,705 women with breast cancer and 108,411 women without breast cancer. Collaborative group on hormonal factors in breast cancer. Lancet (London England). (1997) 350:1047–59. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)08233-0
47. Huang Y, Wu M, Wu C, Zhu Q, Wu T, Zhu X, et al. Effect of hysterectomy on ovarian function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ovarian Res. (2023) 16:35. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01117-1
48. Ma L, Yang B, and Wu J. Revisiting ovarian function suppression with gnrh agonists for premenopausal women with breast cancer: who should use and the impact on survival outcomes. Cancer Treat Rev. (2024) 129:102770. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102770
49. Moorman PG, Myers ER, Schildkraut JM, Iversen ES, Wang F, and Warren N. Effect of hysterectomy with ovarian preservation on ovarian function. Obstet Gynecol. (2011) 118:1271–9. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318236fd12
50. Missmer SA, Hankinson SE, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, Marshall LM, and Hunter DJ. Incidence of laparoscopically confirmed endometriosis by demographic, anthropometric, and lifestyle factors. Am J Epidemiol. (2004) 160:784–96. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh275
51. Ballweg ML. Selected food intake and risk of endometriosis. Hum Reprod (Oxford England). (2005) 20:312–3; author reply 3. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh561
52. Viganò P, Parazzini F, Somigliana E, and Vercellini P. Endometriosis: epidemiology and aetiological factors. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. (2004) 18:177–200. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2004.01.007
53. Nygaard I, Bradley C, and Brandt D. Pelvic organ prolapse in older women: prevalence and risk factors. Obstet Gynecol. (2004) 104:489–97. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000136100.10818.d8
54. Rortveit G, Brown JS, Thom DH, Van Den Eeden SK, Creasman JM, and Subak LL. Symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse: prevalence and risk factors in a population-based, racially diverse cohort. Obstet Gynecol. (2007) 109:1396–403. doi: 10.1097/01.Aog.0000263469.68106.90
55. Tegerstedt G, Miedel A, Maehle-Schmidt M, Nyrén O, and Hammarström M. Obstetric risk factors for symptomatic prolapse: A population-based approach. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2006) 194:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2005.06.086
56. Moore J, Kennedy S, and Prentice A. Modern combined oral contraceptives for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2000) 2):Cd001019. doi: 10.1002/14651858.Cd001019
57. Parker WH. Uterine myomas: management. Fertil Steril. (2007) 88:255–71. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.06.044
58. Selak V, Farquhar C, Prentice A, and Singla A. Danazol for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2007) 4):Cd000068. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000068.pub2
59. Anifantaki F, Boutas I, Kalampokas T, Kalampokas E, Sofoudis C, and Salakos N. Association of endometriosis and breast cancer: mini review of the literature. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2016) 293:5–10. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3809-8
60. Bower JK, Schreiner PJ, Sternfeld B, and Lewis CE. Black-white differences in hysterectomy prevalence: the cardia study. Am J Public Health. (2009) 99:300–7. doi: 10.2105/ajph.2008.133702
61. Jacoby VL, Fujimoto VY, Giudice LC, Kuppermann M, and Washington AE. Racial and ethnic disparities in benign gynecologic conditions and associated surgeries. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2010) 202:514–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.02.039
62. Powell LH, Meyer P, Weiss G, Matthews KA, Santoro N, Randolph JF Jr., et al. Ethnic differences in past hysterectomy for benign conditions. Women’s Health Issues. (2005) 15:179–86. doi: 10.1016/j.whi.2005.05.002
63. Brown AF, Pérez-Stable EJ, Whitaker EE, Posner SF, Alexander M, Gathe J, et al. Ethnic differences in hormone replacement prescribing patterns. J Gen Internal Med. (1999) 14:663–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.1999.10118.x
64. Adedayo P. Examining disparities in route of surgery and postoperative complications in black race and hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. (2019) 133:829. doi: 10.1097/aog.0000000000003209
65. Katon JG, Bossick AS, Doll KM, Fortney J, Gray KE, Hebert P, et al. Contributors to racial disparities in minimally invasive hysterectomy in the us department of veterans affairs. Med Care. (2019) 57:930–6. doi: 10.1097/mlr.0000000000001200
66. Michaels E, Worthington RO, and Rusiecki J. Breast cancer: risk assessment, screening, and primary prevention. Med Clinics North America. (2023) 107:271–84. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2022.10.007
67. Yuk JS, Yang SW, Yoon SH, Kim MH, Seo YS, Lee Y, et al. Association between breast diseases and symptomatic uterine fibroids by using South Korean national health insurance database. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:16772. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43443-w
Keywords: hysterectomy, breast cancer, risk, meta-analysis, systematic review
Citation: Liu W, Lu T, Yang J and Liu J (2025) Association between hysterectomy for benign indications and the risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta- analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1600459. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1600459
Received: 26 March 2025; Accepted: 03 November 2025;
Published: 20 November 2025.
Edited by:
Sharon R. Pine, University of Colorado, United StatesReviewed by:
Gayatri Vishwakarma, Indian Spinal Injuries Centre, IndiaHangcheng Xu, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Lu, Yang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Liu, ZHIubGl1amllQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Wenjing Liu
Wenjing Liu Tingting Lu
Tingting Lu Jingqi Yang3
Jingqi Yang3 Jie Liu
Jie Liu