- 1Wuxi School of Medicine, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China
Introduction: Lysyl oxidase (LOX) is crucial for modifying collagen and elastin, thereby preserving tissue integrity. Aberrant LOX activity has been associated with a multitude of health disorders, including cutaneous, pulmonary, fibrotic, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. In cancer, LOX can either promote or inhibit tumor development, and its expression level is closely correlated with patient prognosis.
Methods: This research utilized data retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection on May 30, 2025. The search strategies were crafted to target LOX – related terms while excluding irrelevant ones, and the data were limited to English – language articles. Over the past 30 years, 9261 LOX – related publications were identified. The number of articles exhibited an upward trend, especially in the past decade. The United States, China, and Japan were the leading countries in terms of publication output, with institutions like Harvard University and Boston University being highly productive.
Results: This research utilized data retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection on May 30, 2025. The search strategies were crafted to target LOX – related terms while excluding irrelevant ones, and the data were limited to English – language articles. Over the past 30 years, 9261 LOX – related publications were identified. The number of articles exhibited an upward trend, especially in the past decade. The United States, China, and Japan were the leading countries in terms of publication output, with institutions like Harvard University and Boston University being highly productive.
Discussion: This study presents an overview of LOX - related research. Comprehending the mechanisms of LOX can offer valuable perspectives on tumor biology. Future research on LOX – extracellular matrix interactions and associated gene pathways may lead to the development of novel diagnostic and treatment modalities targeting LOX.
Introduction
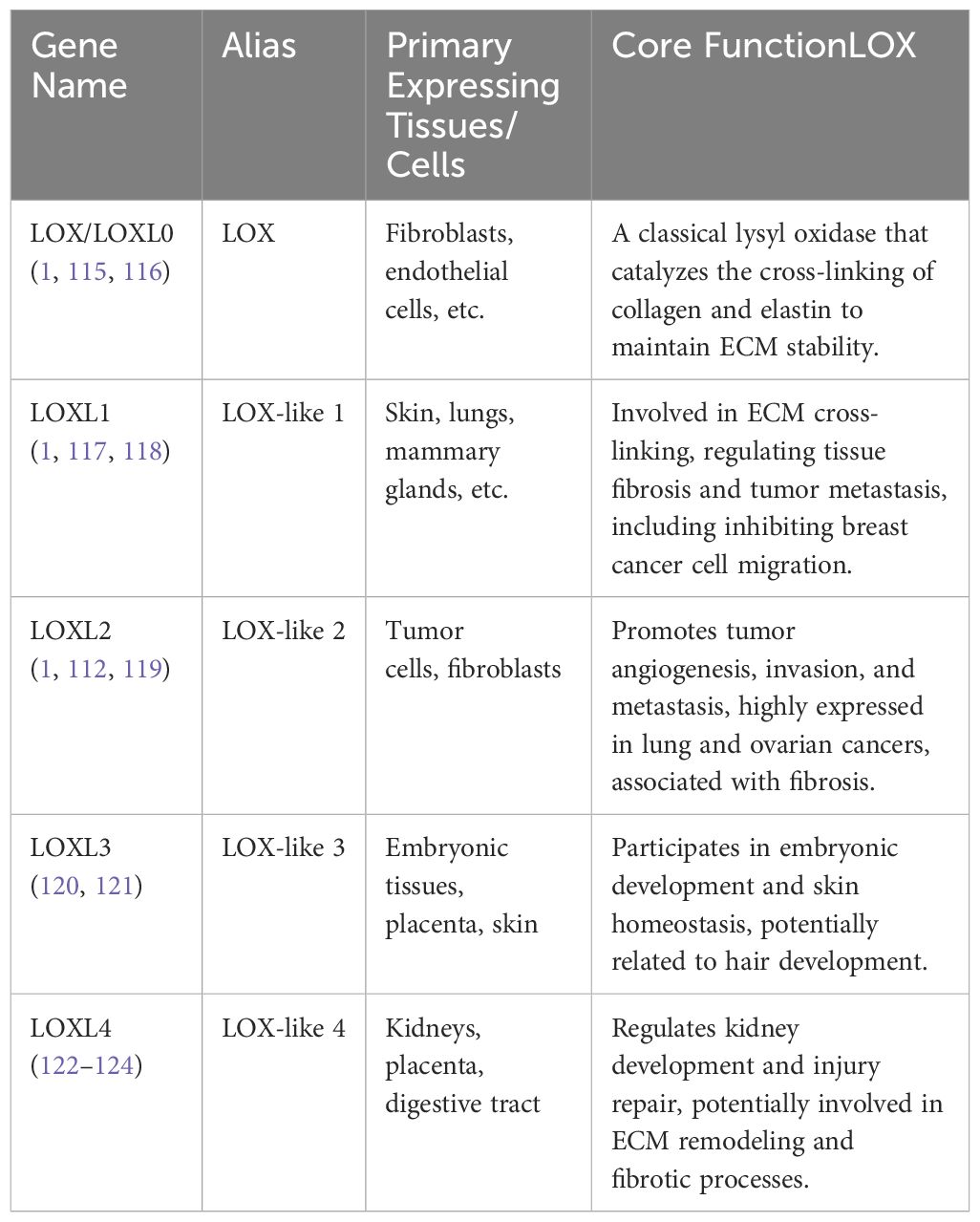
The Lysyl oxidase (LOX) family of enzymes plays indispensable roles in the cross-linking and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and participates in the post-translational modification of collagen and elastin (1). In mammals, the LOX family typically consists of four or five members: LOX, LOXL1, LOXL2, LOXL3, and LOXL4, depending on the nomenclature differences in the literature regarding LOX and LOXL0. Structurally, they are made up of three separate domains: an amino-terminal signal peptide that facilitates its secretion, a central catalytic domain that performs the oxidative deamination of lysine residues in collagens, and a carboxy-terminal regulatory domain (2–6). They share common features such as dependence on copper ions (Cu2+) and vitamin C as cofactors to catalyze the oxidation of lysine/hydroxylysine to aldehyde for ECM cross-linking. This unique structure enables LOX family to act as a critical regulator of tissue integrity, facilitating the formation of cross - linked collagen fibers that are essential for skin elasticity, vessel stability, and the strength of connective tissues (7–10)However, they differ in substrate preference, cellular signaling regulation, and expression during developmental stages. LOX primarily acts on collagen and elastin, while LOXLs can target a broader range of matrix proteins. LOXLs, especially LOXL2, can regulate signaling pathways in an enzyme-independent manner, whereas LOX function is more dependent on enzymatic activity. LOX is continuously expressed in adult tissues, while LOXLs are more active during embryonic development or tissue repair. Based on the characteristics of each LOX family member, we have compiled and described the LOX family members according to their molecular weight, primary tissue/cell expression, and core functions in Table 1.
LOX family of enzymes activity is crucial for preserving the structural integrity and mechanical properties of tissues like the skin, lungs, blood vessels, and other connective tissues (3–6, 8, 11). LOX facilitates the oxidation of lysine residues in proteins, leading to the formation of covalent cross-links essential for tissue elasticity and resilience (12). However, abnormal LOX activity has been associated with a broad spectrum of pathological conditions. For example, deficiencies in LOX or its isoforms are associated with severe cutaneous disorders like cutis laxa, characterized by skin fragility and reduced dermal elasticity due to impaired elastic fiber formation (13, 14). Similarly, LOX dysfunction is linked to pulmonary diseases, including alveolar wall destruction and impaired lung function, highlighting its importance in maintaining respiratory tissue architecture (15, 16). Moreover, altered LOX activity is involved in fibrotic diseases such as liver cirrhosis and pulmonary fibrosis, where excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling leads to tissue stiffening and organ dysfunction (17, 18). In addition to its role in connective tissues, LOX has attracted attention for its involvement in cardiovascular pathologies (19–21). Elastic fiber abnormalities caused by LOX deficiency can lead to vascular complications, such as aneurysms, emphasizing the enzyme’s critical function in maintaining vascular integrity (22–25).
Beyond these well - established roles, studies have also explored the potential of LOX in cancer biology (26). Emerging evidence suggests that LOX activity may contribute to tumor progression and metastasis by facilitating ECM remodeling, promoting cancer cell invasion, and enhancing angiogenesis (27, 28). Elevated LOX expression has been observed in various cancers, where it promotes ECM stiffening and the formation of a pro - tumorigenic niche (29, 30). Additionally, LOX activity triggers downstream signaling pathways like TGF-β and MAPK, which are strongly linked to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the preservation of cancer stem cells (31–33). LOX has also been shown to interact with key signaling pathways like focal adhesion kinase (FAK) - YAP/TAZ, which are crucial for tumor cell survival and proliferation (32, 34). Further clinical investigation into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues revealed that HIF-1α is implicated in LOXL2 protein expression, correlates with poor prognostic factors, and drives processes such as EMT, migration, invasion, and vasculogenic mimicry in HCC cells by regulating LOXL2 (35). Additionally, lysyl oxidase (LOX) released from hypoxic breast tumor cells accumulates in premetastatic niches, cross-links type IV collagen within the basement membrane, and critically contributes to the recruitment of CD11b+ myeloid cells (36).In most cases, LOX is a pivotal factor in the restructuring of the tumor-related extracellular matrix, metastasis, and the premetastatic niche. These findings indicate that the LOX family could be a viable target for preventing and treating metastatic conditions. Nevertheless, LOX can also display antitumor effects in certain cancers, with its metabolic by-products potentially counteracting oncogenesis. For example, the expression levels of LOX are closely related to gastric cancer patient prognosis, with low expression usually associated with poorer clinical outcomes (37). LOX expression is downregulated in epidermal tumor cells of carcinomas but upregulated in the stroma adjacent to invasive tumor cells, and also they proved that LOX enzymatic activity is crucial for preserving the integrity of the dermis as well as maintaining the epidermal homeostasis but not for cancer progression (38). LOX mRNA is translated into an inactive LOX proprotein (pro-LOX) within the cytoplasm. Subsequently, pro-LOX is secreted from the cell, where the N-terminus of the protein is cleaved by BMP-1, resulting in the LOX propeptide (LOX-PP) and the mature, active LOX protein (39). Another study showed that 18-kDa propeptide domain of LOX (LOX-PP) from LOX strongly suppresses the invasive characteristics of lung and pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Bcl2 and NF-kappaB (40). Furtherly, LOX-PP expression was found to diminish the proliferative, migratory, anchorage-independent growth, and tumorigenic abilities of Ewing sarcoma in immunocompromised mice, while the C-terminal of LOX enzymatically active domain of LOX exerted opposing effects, indicating that LOX’s tumor-suppressive role is specifically attributable to its propeptide domain (41). This implies that treatments targeting LOX should be selective, targeting only those cancers where LOX promotes progression, potentially necessitating molecular diagnostic tools, and that LOX or its by-products could potentially serve as anticancer agents (10, 42, 43). Through an extensive literature review, this study aims to systematically analyze the current research status of LOX family and propose innovative and feasible future research directions by integrating it with hot topics in fibrotic diseases and cancer research. This will enhance comprehension of the mechanisms behind LOX’s involvement in tumor growth and advancement, offering fresh perspectives and possible targets for clinical treatment.
Materials and methods
Data acquisition and processing
The data employed for this bibliometric study were acquired from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database, Scopus, PubMed, and Embase, incorporating the Science Citation Index Extended (SCIE), Social Science Citation Index (SSCI), and Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI). The information was obtained from the, Scopus, PubMed, and Embase from 1995 to 2025 on May 30, 2025. The search strategies were as follows:
1#. TS=“lysyl oxidase” OR “LOX” OR “LOXL1” OR “LOXL2” OR “LOXL3” OR “LOXL4” OR “lysyl oxidase like 1” OR “lysyl oxidase like 2” OR “lysyl oxidase like 3” OR “lysyl oxidase like 4”OR “Protein - lysine 6 - oxidase” OR “Copper - dependent amine oxidase”NOT TS=(“lipoxygenase” OR “lactate oxidase” OR “liquid oxygen”)
2#. TS=“lysyl oxidase” OR “LOX” OR “LOXL1” OR “LOXL2” OR “LOXL3” OR “LOXL4” OR “lysyl oxidase like 1” OR “lysyl oxidase like 2” OR “lysyl oxidase like 3” OR “lysyl oxidase like 4”OR “Protein - lysine 6 - oxidase” OR “Copper - dependent amine oxidase” AND TS=(“fibrosis” OR “fibrotic” OR “fibrogenesis”) NOT TS=(“lipoxygenase” OR “lactate oxidase” OR “liquid oxygen”)
3#. TS=“lysyl oxidase” OR “LOX” OR “LOXL1” OR “LOXL2” OR “LOXL3” OR “LOXL4” OR “lysyl oxidase like 1” OR “lysyl oxidase like 2” OR “lysyl oxidase like 3” OR “lysyl oxidase like 4”OR “Protein - lysine 6 - oxidase” OR “Copper - dependent amine oxidase”AND TS=(“cancer” OR “tumor” OR “neoplasm” OR “malignancy” OR “carcinoma”) NOT TS=(“lipoxygenase” OR “lactate oxidase” OR “liquid oxygen”)
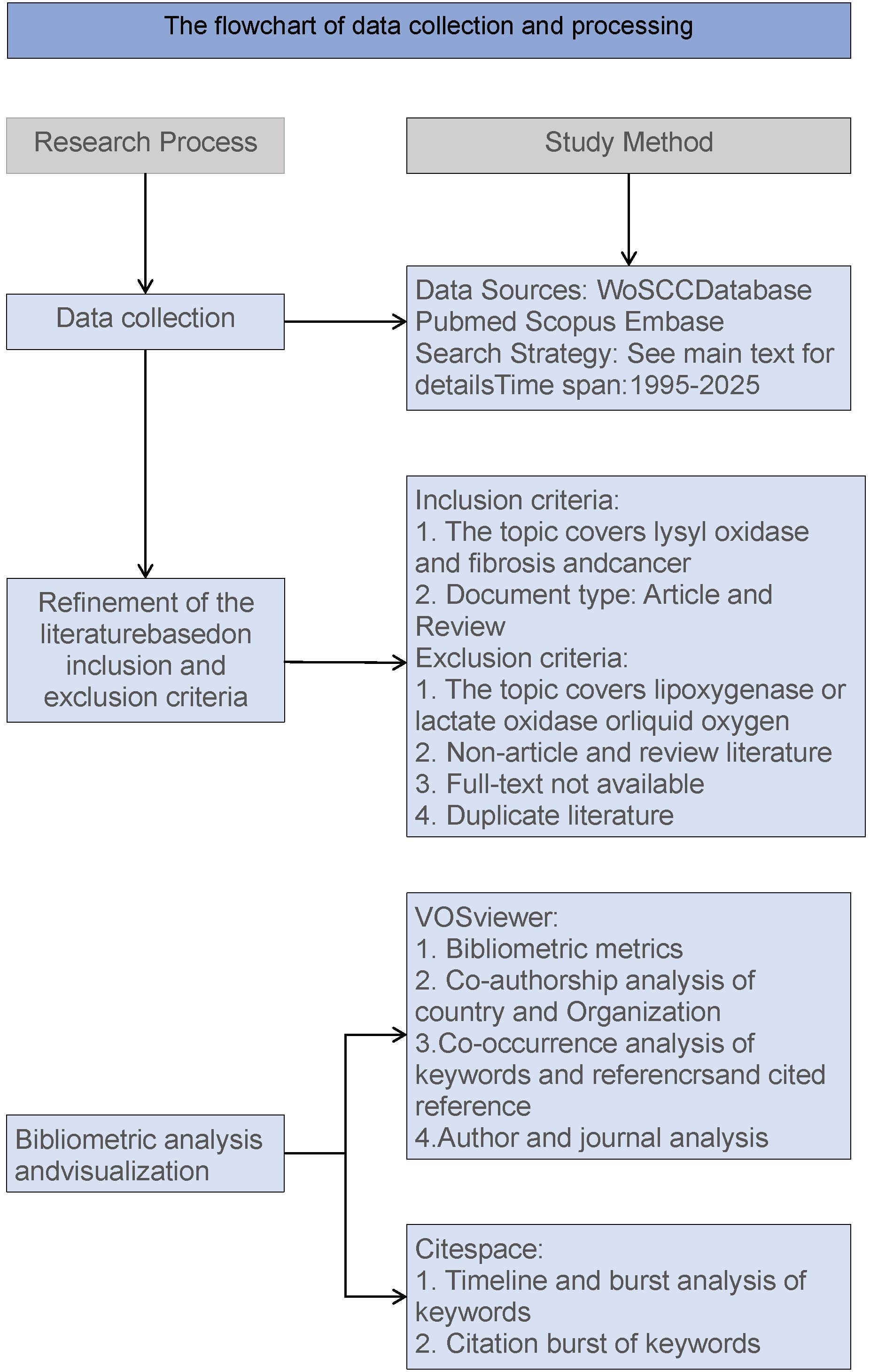
The data were limited to English - language articles. After the above - mentioned selection process, a total of 8255 for 1# search strategy, 831 for 2# search strategy and 2041 for 3# search strategy papers according to the above strategies were obtained for bibliometric analysis (Figure 1).
Bibliometric visualized analysis
VOSviewer (version 1.6.20; https://www.vosviewer.com/) was employed to conduct analyses of countries, organizations, journals, authors, co - cited authors, reference co - occurrences, and keyword co-occurrences (44). CiteSpace (version 6.3.R1; https://citespace.podia.com/) was used to analyze citation burst frequencies, keyword bursts (45). Additionally, Graphpad Prism 8 (https://www.graphpad.com/) was applied to analyze thosepublications on LOX from 1995 to 30 May, 2025.
Results
General literature trends on LOX from 1995 - 2025
By applying the search strategy TS=((“lysyl oxidase” OR “LOX” OR “LOXL1” OR “LOXL2” OR “LOXL3” OR “LOXL4” OR “lysyl oxidase like 1” OR “lysyl oxidase like 2” OR “lysyl oxidase like 3” OR “lysyl oxidase like 4”OR “Protein - lysine 6 - oxidase” OR “Copper - dependent amine oxidase”)NOT(lipoxygenase OR “lactate oxidase” OR “liquid oxygen”)) in WoSCC, Scopus, PubMed, and Embase database, a total of 9,261 LOX - related publications were identified over the past 30 years. Among these, 8,255 (89.13%) were articles, and 1,006(10.87%) were reviews (Figure 2A). The total number of articles in the past decade was 4,440, accounting for 56.46% of the total articles in the past 30 years (Figure 2B). The number of article - type publications from 1995 to 2025 showed an upward trend (Figure 2C). Before 2000, the annual publication count was less than 100. After 2013, there was a sharp rise in the number of relevant publications, indicating growing attention and prosperity in this field over the past 10 years.
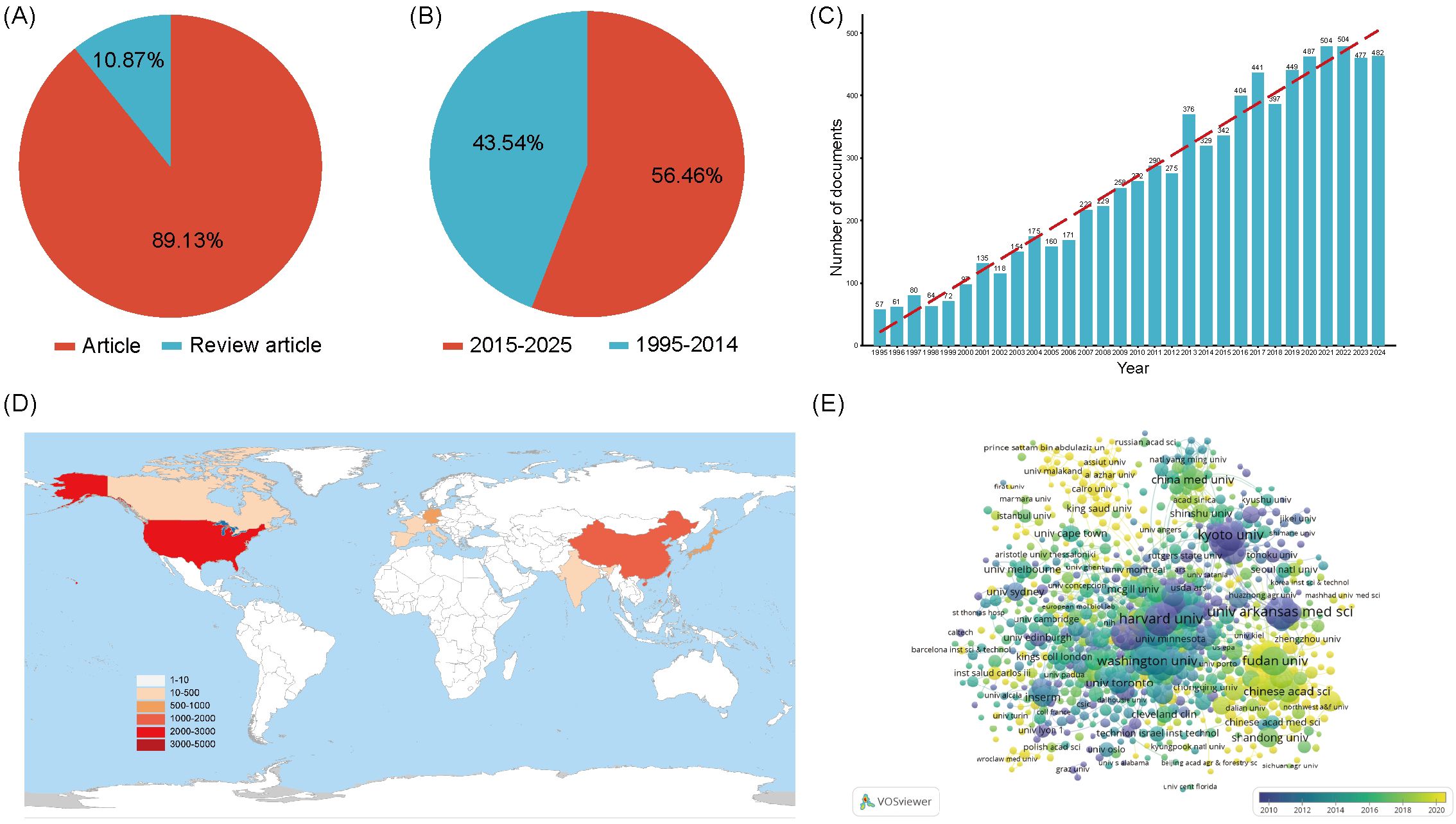
Figure 2. (A) The proportion of articles in the field of LOX. (B) The proportion of articles in the field of LOX over the past decade. (C) The number of publications in the field of LOX by year. (D) The top 10 most productive countries/regions in the field of LOX. (E) Distribution of publications from different organizations in the field of LOX. The thickness of the connecting lines between the nodes reflects the strength of the interaction. The color of the node represents the average year of publication for the country which the node represents.
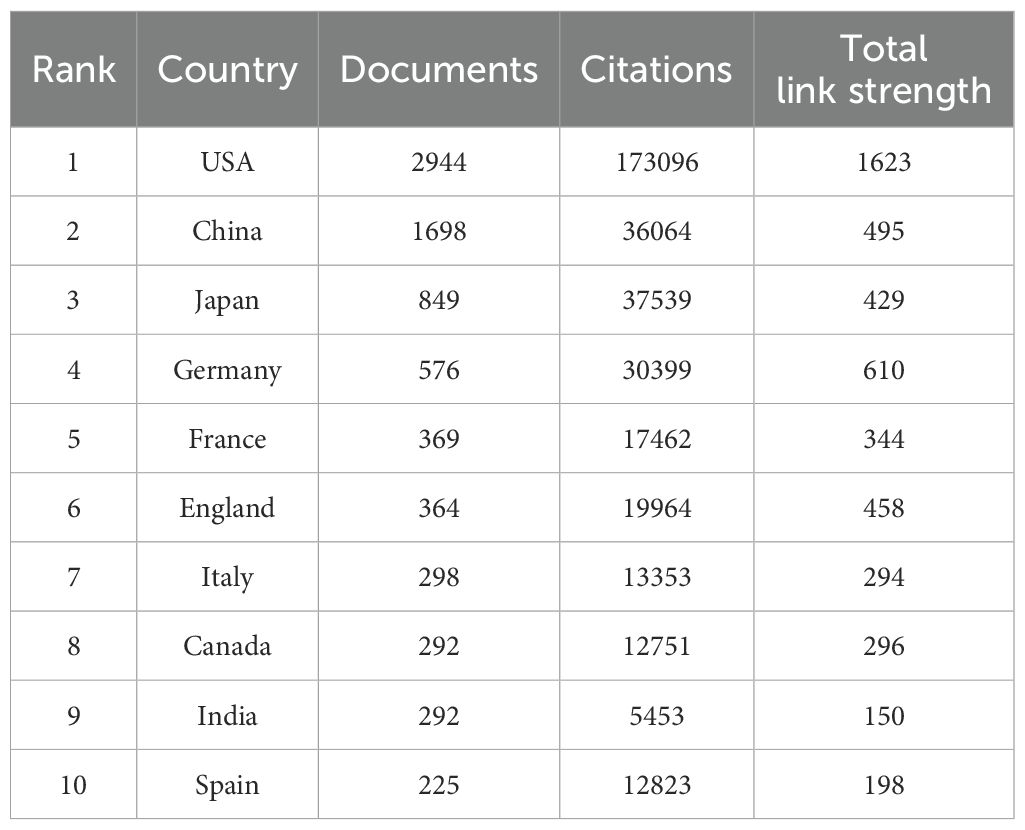
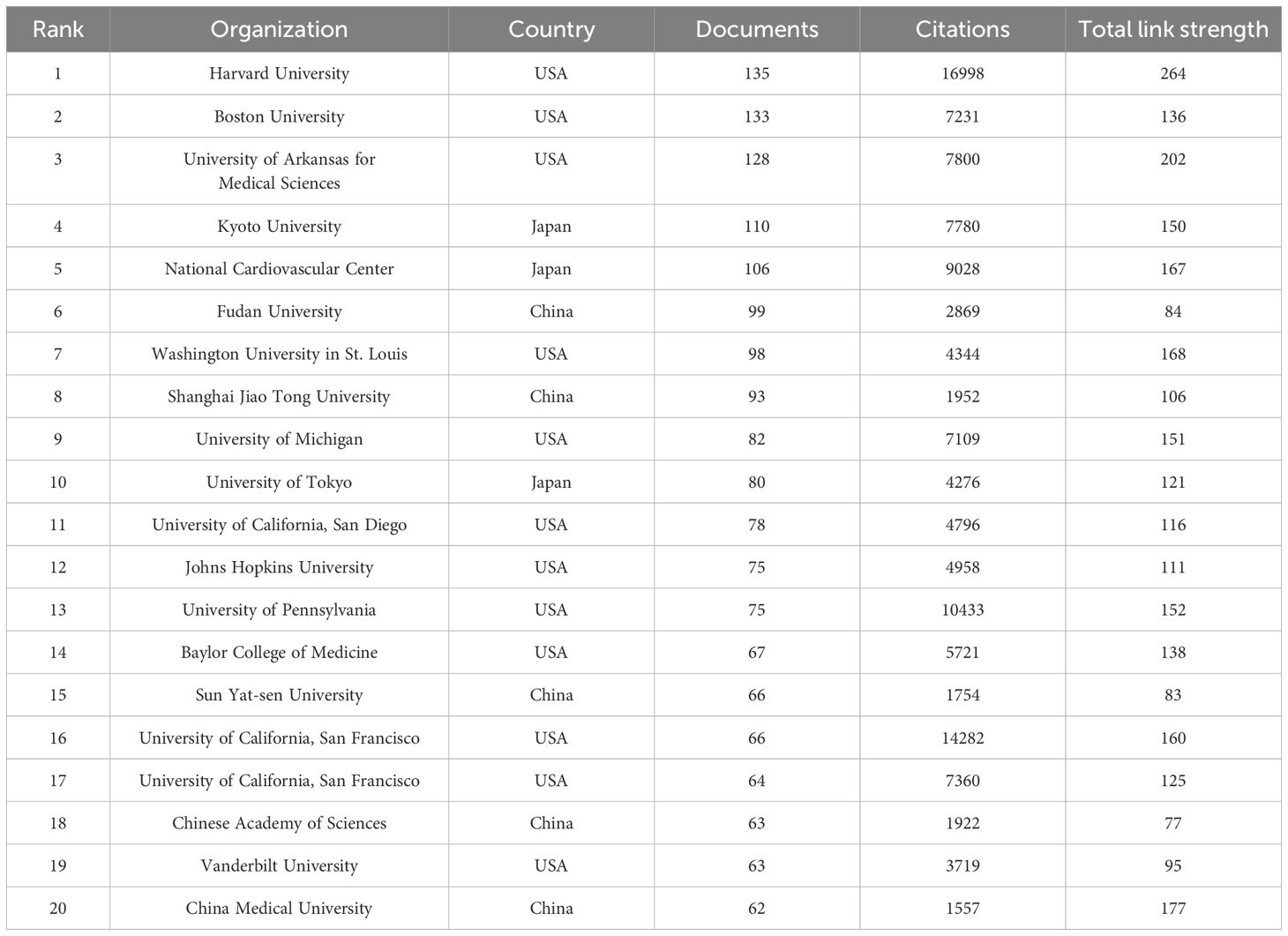
8,255 documents in total were published by 102 countries/regions. Figure 2D lists the top 10 productive countries/regions for LOX publications. The United States had the most publications and citations (n = 2,944, 35.7%), followed by China (n = 1,689, 20.5%) and Japan (n = 849, 10.3%). These three countries accounted for nearly 66.5% of the total publications (Table 2). The 8,255 analyzed documents were affiliated with 6,489 organizations. Table 3 shows the top 20 most productive institutions, with Harvard University and Boston University leading. Harvard University, the University of California, San Francisco, and the University of Pennsylvania had the highest citation counts (Table 3). Figure 2E depicts the overall connection strength and collaboration network among institutions.
Keyword analysis of hotpots on LOX in human diseases
Research themes and hotspots were identified through keyword analysis. The VOSviewer was applied to visualize the keyword network diagram for 8,255 articles. Specifically, 272 key keywords with a frequency of at least 40 were selected for visualization. Figure 3A shows an overlay map of the top 10 frequently occurring keywords, where the color corresponds to average publication year. Subsequently, disease - related keywords were extracted for further investigation. Clustering of these disease - related keywords resulted in 3 clusters, encompassing a total of 11 items. Among them, “cancer” and “fibrosis” appeared more than 440 times, likely representing prominent research topics. This study also presents the timeline viewer for “cancer” and “fibrosis” (Figure 3B).
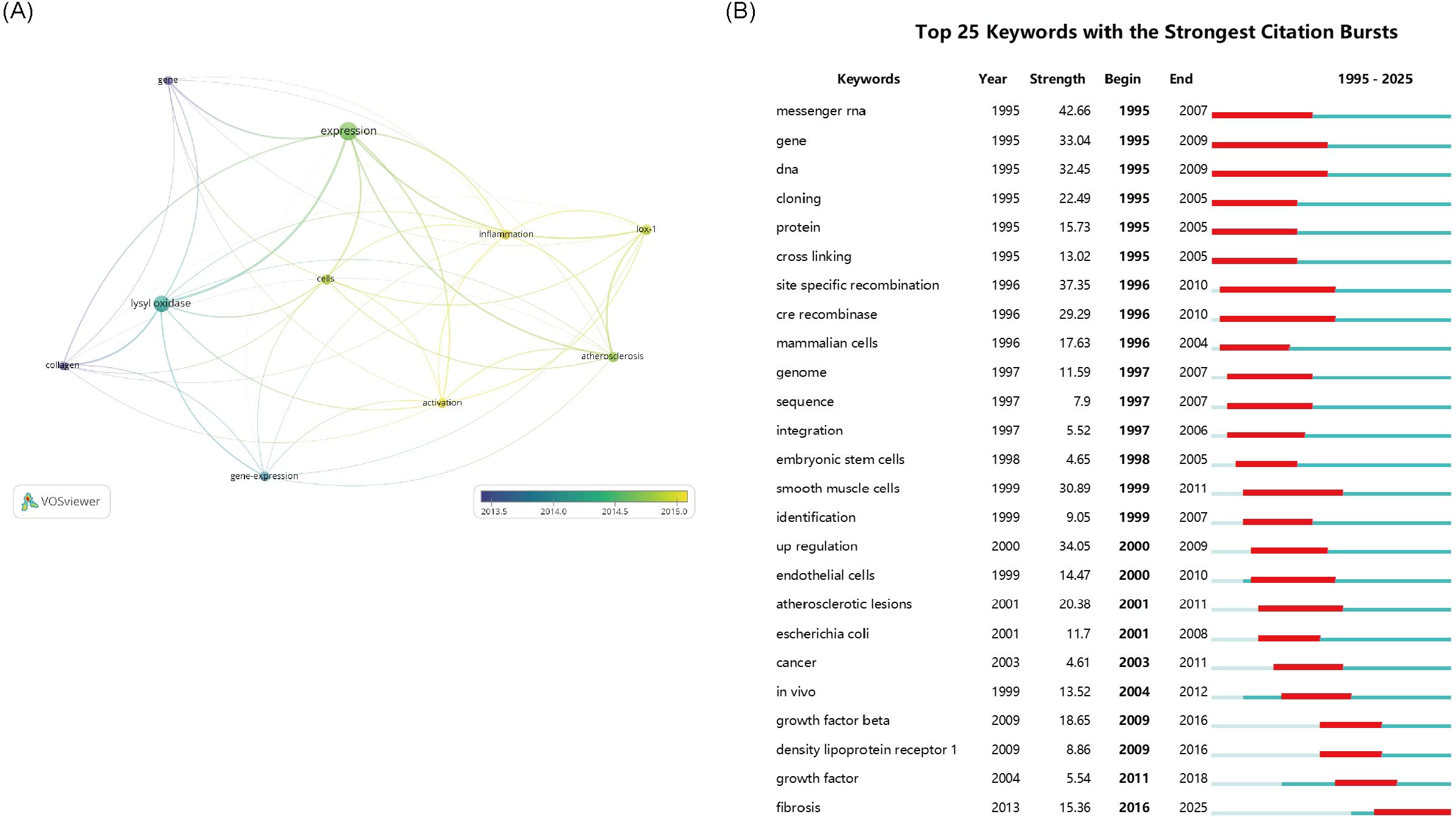
Figure 3. (A) The network visualization map of disease-related keywords. (B) The 25 keywords with the Strongest Citation Bursts. The thickness of the connecting lines between the nodes reflects the strength of the interaction. The color of the node represents the average year of publication for the country which the node represents.
Analysis of literatures on LOX in fibrosis research
To conduct an in - depth analysis of LOX - related literature within the realm of fibrosis research, we implemented a comprehensive search strategy. The search terms were configured as follows: TS=“lysyl oxidase” OR “LOX” OR “LOXL1” OR “LOXL2” OR “LOXL3” OR “LOXL4” OR “lysyl oxidase like 1” OR “lysyl oxidase like 2” OR “lysyl oxidase like 3” OR “lysyl oxidase like 4”OR “Protein - lysine 6 - oxidase” OR “Copper - dependent amine oxidase” AND TS=(“fibrosis” OR “fibrotic” OR “fibrogenesis”) NOT TS=(“lipoxygenase” OR “lactate oxidase” OR “liquid oxygen”)with the time span ranging from 1995 to 2025. Over these 30 years, a total of 993 LOX - related publications were identified. Among them, 831 (constituting approximately 83.7%) were original research articles, while 162 (roughly 16.3%) were review articles, as presented in Figure 4A. Notably, the past nine years have witnessed a remarkable upsurge in studies focusing on LOX in the context of fibrosis, as vividly illustrated in Figure 4B.
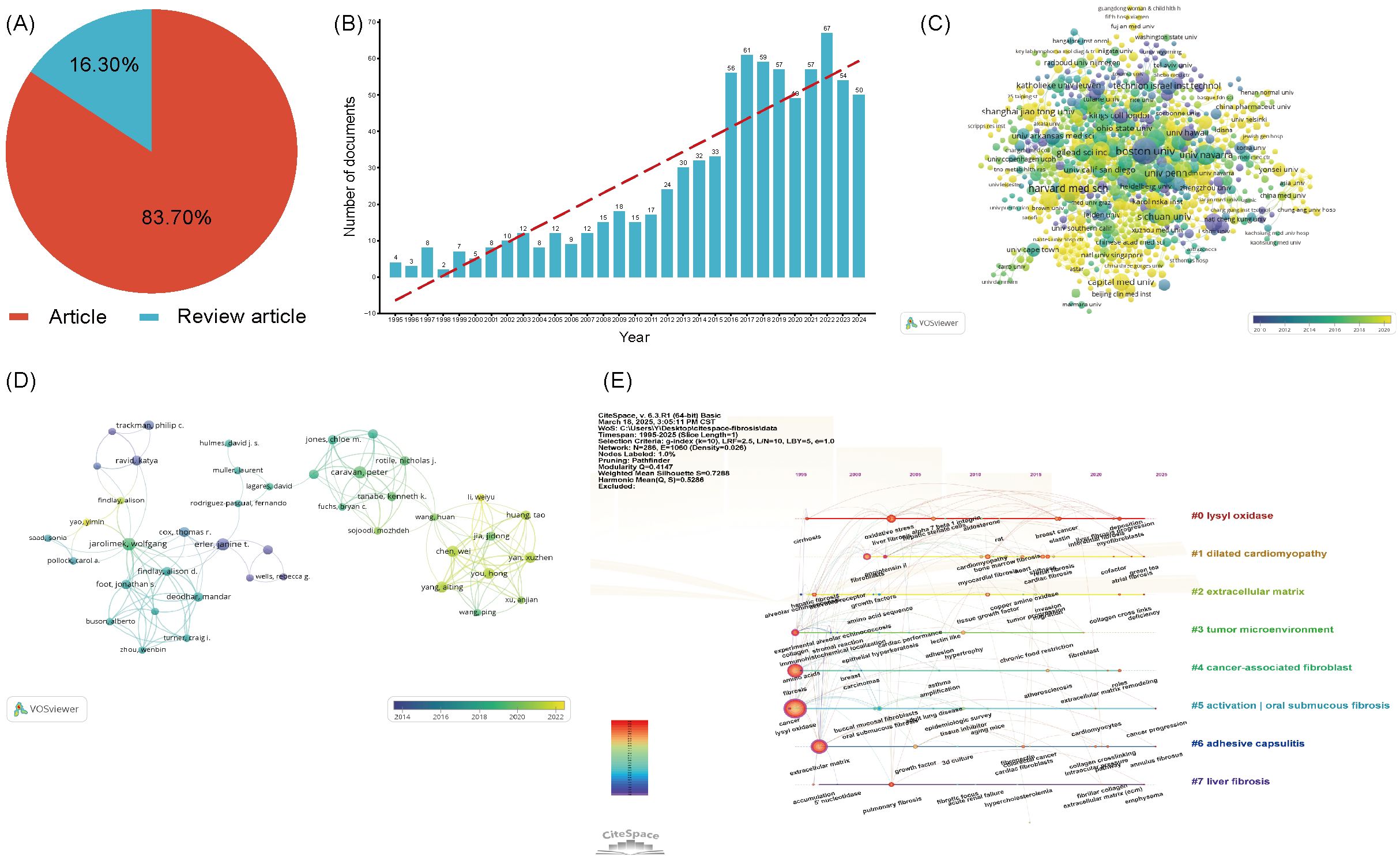
Figure 4. (A) The proportion of articles in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research. (B) The number of publications in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research by year. (C) Distribution of publications from different organizations in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research. (D) The co-occurrence author map of co-authors in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research. (E) Timeline view of keywords analysis in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research. The thickness of the connecting lines between the nodes reflects the strength of the interaction. The color of the node represents the average year of publication for the country which the node represents.
These 831 documents were sourced from 56 different countries and regions. The United States took the lead with 335 literatures, making up 40.3% of the total quantity, closely followed by China with 150 publications (18.1%). Together, these two countries contributed nearly 58.4% of all the relevant works, as detailed in Table 4. The 831 analyzed documents were affiliated with 1288 distinct organizations. Among the top 20 productive institutions, as presented in Table 5, Boston University (with 23 publications) and Harvard Medical School (19 publications) were particularly active. The University of Pennsylvania and the University of California, San Francisco boasted the highest citation counts, and their collaborative network is depicted in Figure 4C.
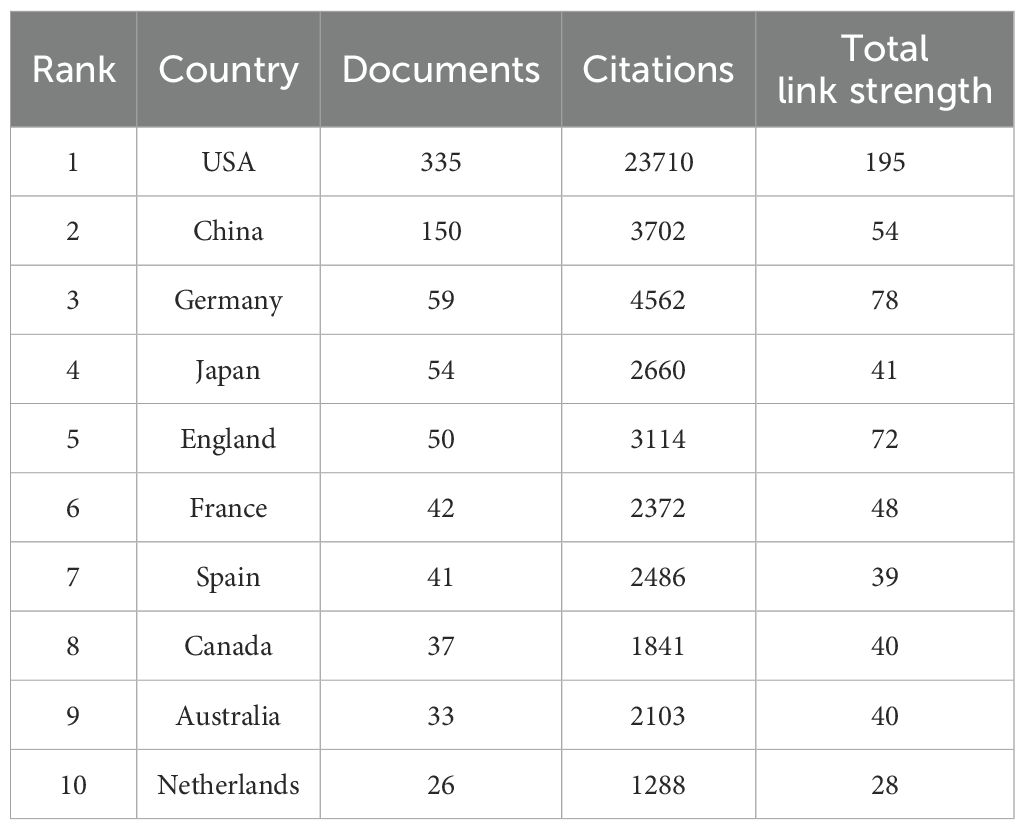
Table 4. The top 10 most productive countries/regions in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research.
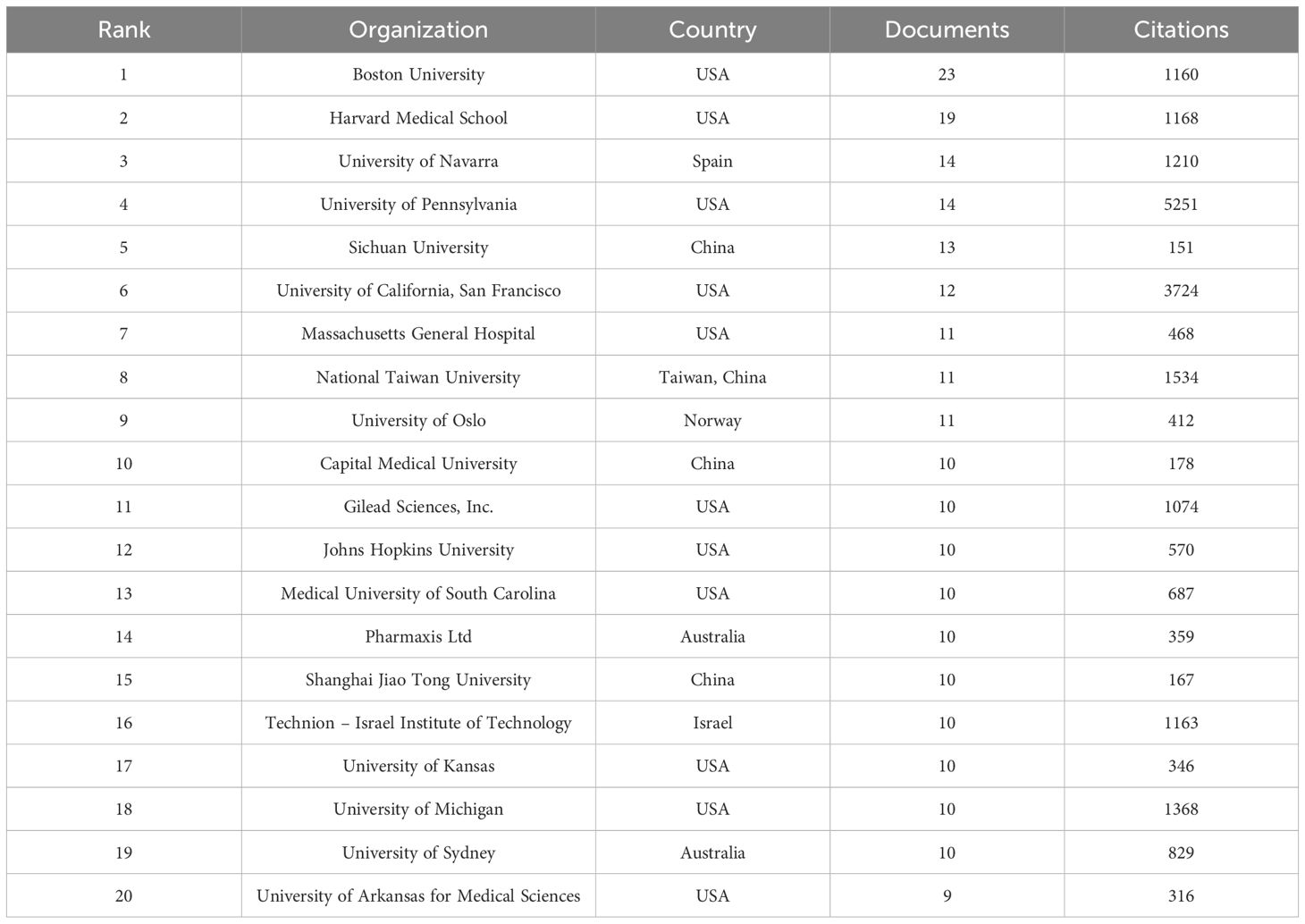
Table 5. The top 20 most productive organizations in the field of LOX associated with fibrosis research.
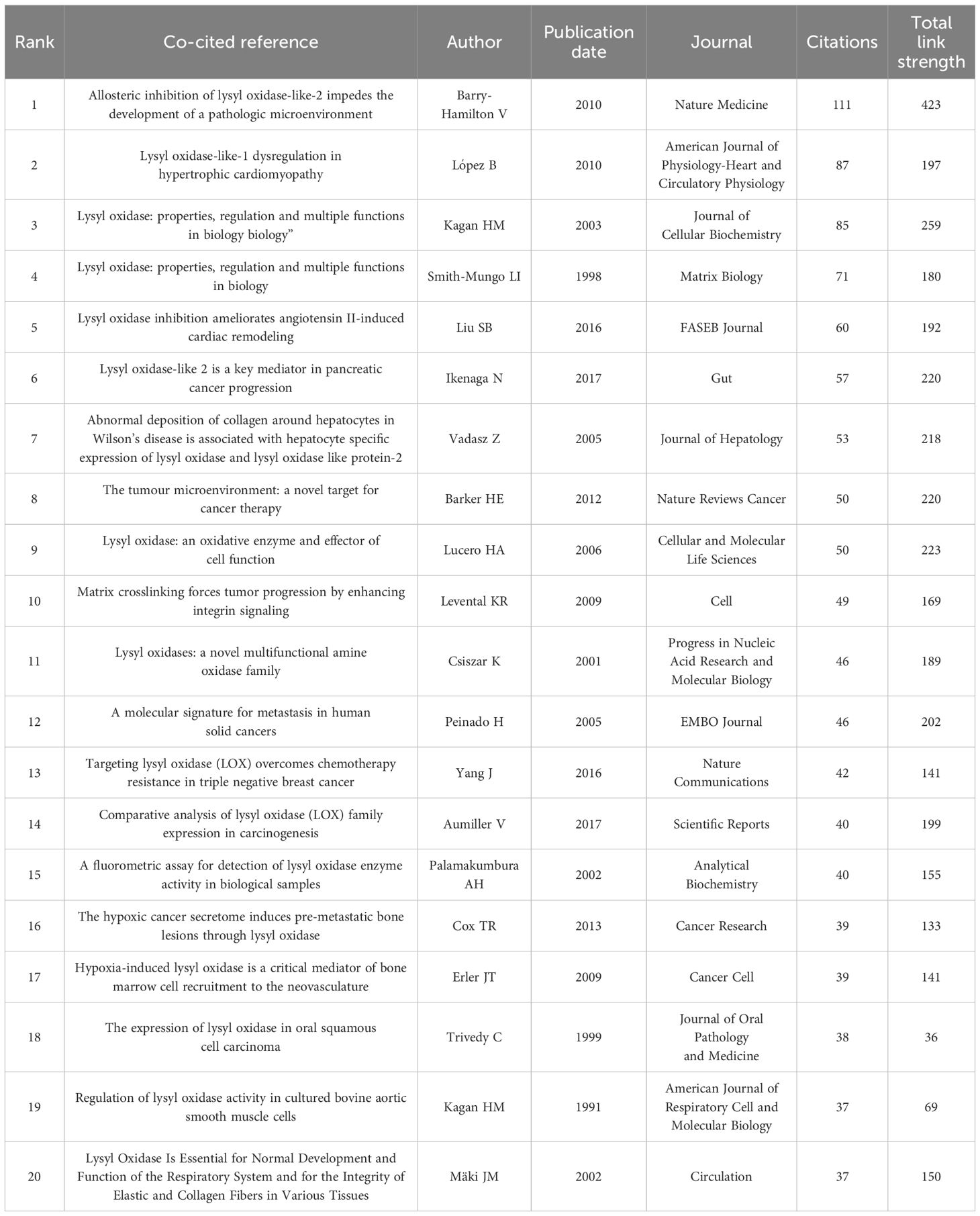
In the past decade, 5,438 authors made contributions to LOX and fibrosis - related articles. The most productive author had 10 publications. Core contributors were defined as those with at least two publications. Employing VOSviewer, a network visualization was constructed. Authors with three or more publications were selected for further in - depth analysis, including visualization, clustering, and mapping of co - author distribution. In the fibrosis - related LOX study, 37 authors publishing five or more papers. Javier Diez ranked first with 10 publications, trailed by Wolfgang Jarolimek (8) and caravan, peter (7), as shown in Figure 4D. Table 6 presents the top 20 co-cited references, with the most - cited one being from Nature Medicine in 2010 by Barry - Hamilton V. This reference explored LOX’s role in the tumor microenvironment, especially in metastasis and angiogenesis. Figure 4E showcases a keyword network for LOX research. “Lysyl oxidase” is interconnected with terms such as “dilated cardiomyopathy”, “tumor microenvironment”, and those related to fibrosis, vividly demonstrating LOX’s diverse functions across various medical conditions. Keywords like “cancer” and “extracellular matrix” stand out due to their high frequency, and the color - coded lines further reveal the complexity of the research landscape.
Analysis of literatures on LOX in cancer research
Our search strategy for LOX in cancer research was formulated as: TS=“lysyl oxidase” OR “LOX” OR “LOXL1” OR “LOXL2” OR “LOXL3” OR “LOXL4” OR “lysyl oxidase like 1” OR “lysyl oxidase like 2” OR “lysyl oxidase like 3” OR “lysyl oxidase like 4”OR “Protein - lysine 6 - oxidase” OR “Copper - dependent amine oxidase”AND TS=(“cancer” OR “tumor” OR “neoplasm” OR “malignancy” OR “carcinoma”) NOT TS=(“lipoxygenase” OR “lactate oxidase” OR “liquid oxygen”)from 1995 to 2025. In the past 30 years, 2490 LOX - related publications in the cancer domain were unearthed. Among these, 2,041 (8%) were articles, and 449 (18%) were review articles, as shown in Figure 5A. The number of such publications has been steadily increasing. In the recent nine years, the annual output was approximately ten - fold that of 1996, as depicted in Figure 5B. These 2,041 documents originated from 78 countries and regions. The United States had the greatest number of publications (n = 704), followed by China (n = 519) and Japan (n = 175), together accounting for 68.5% of the total, as shown in Table 7. The 2027 analyzed documents were associated with 2,486 organizations. Among the top 20 productive academic institutions in Table 8, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (44), and Fudan University (42) were at the forefront. The University of California, San Francisco had the highest citation count, as manifested in the collaboration network presented in Figure 5C.
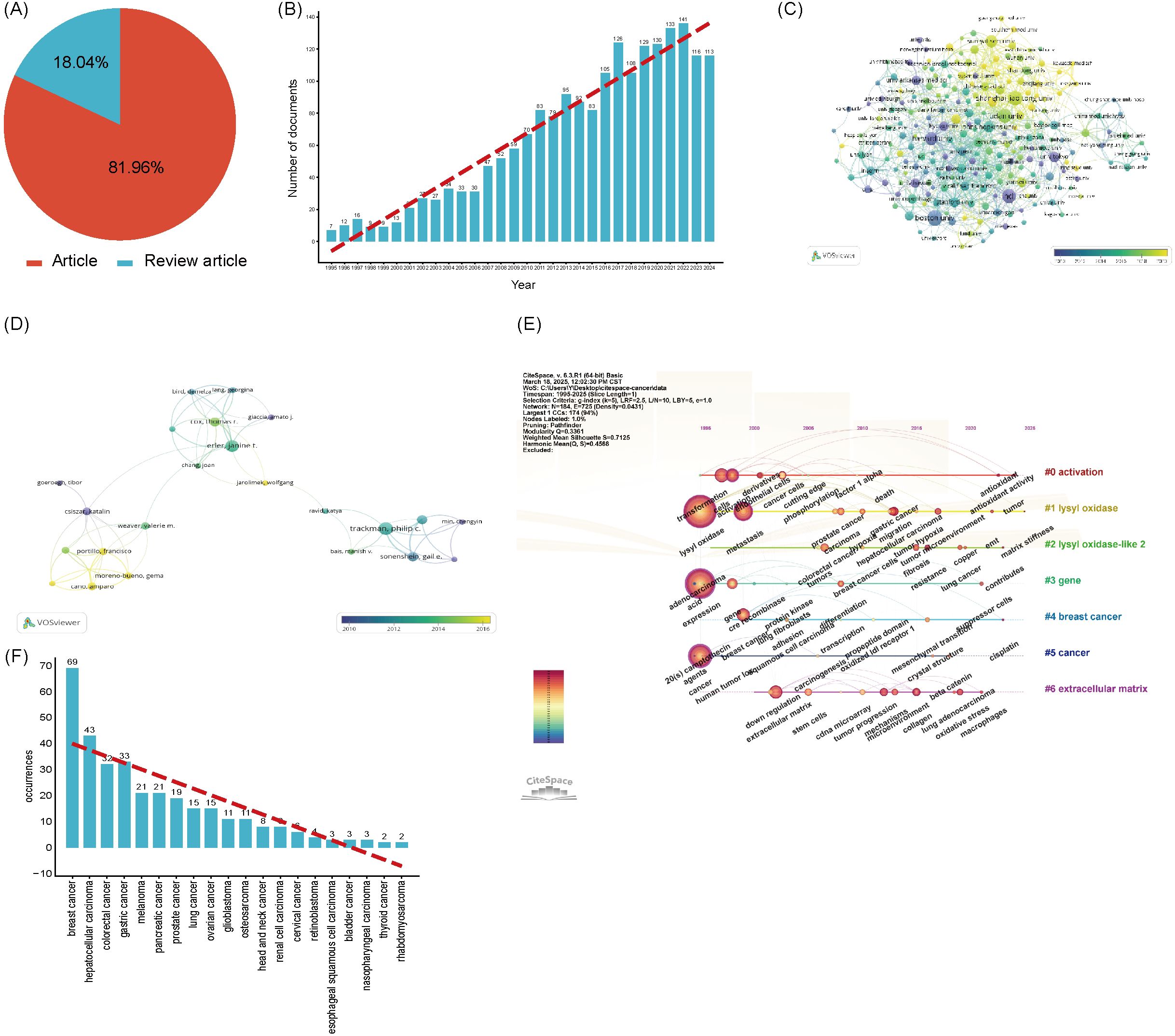
Figure 5. (A) The proportion of articles in the field of LOX associated with cancer research. (B) The number of publications in the field of LOX associated with cancer research by year. (C) Distribution of publications from different organizations in the field of LOX associated with cancer research. (D) Timeline view of keywords analysis in the field of LOX associated with cancer research. (E) The co-occurrence author map of co-authors in the field of LOX associated with cancer research. (F) The recurrence rate of cancer types. The thickness of the connecting lines between the nodes reflects the strength of the interaction. The color of the node represents the average year of publication for the country which the node represents.
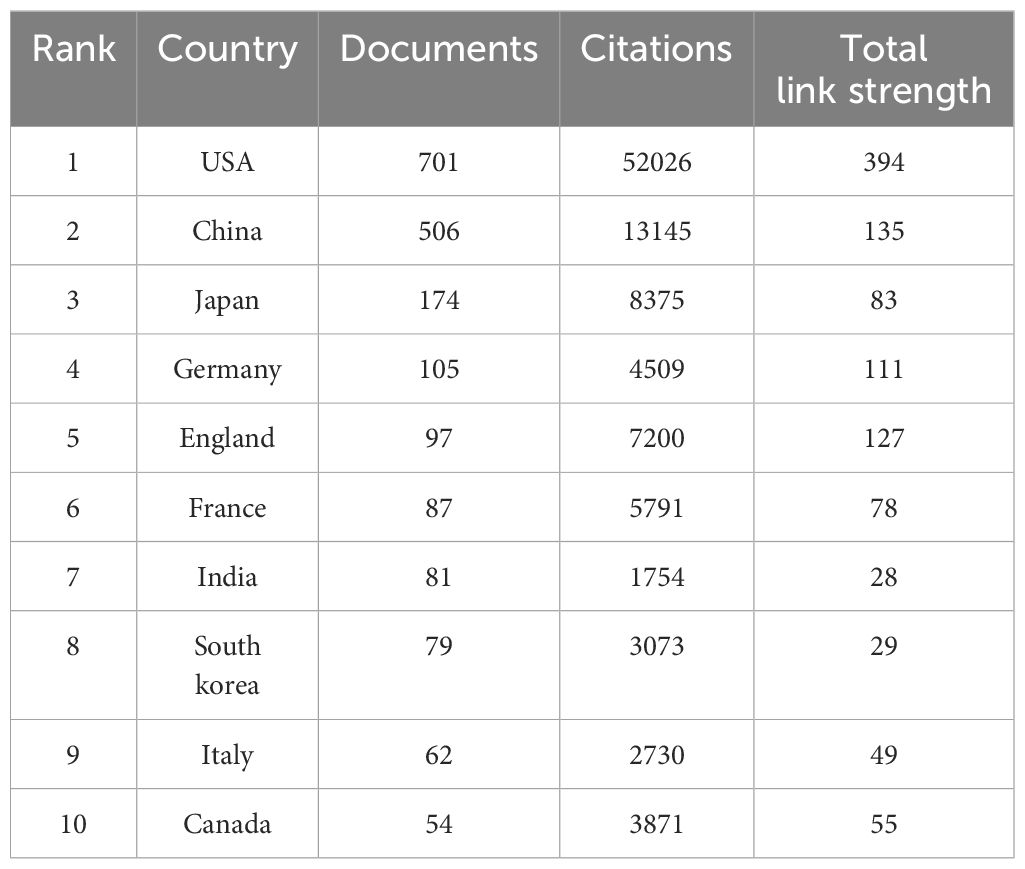
Table 7. The top 10 most productive countries/regions in the field of LOX associated with cancer research.
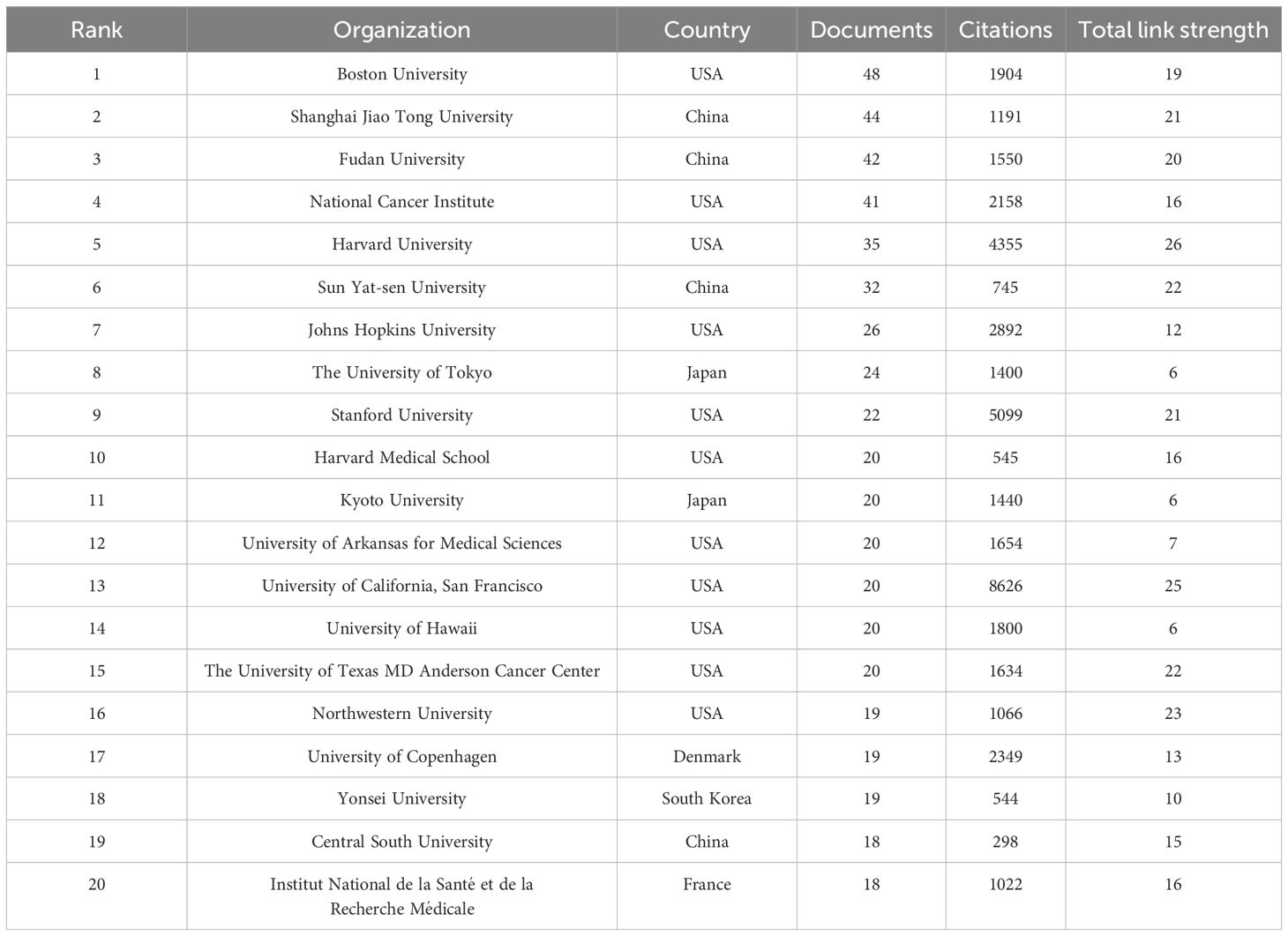
Table 8. The top 20 most productive organizations in the field of LOX associated with cancer research.
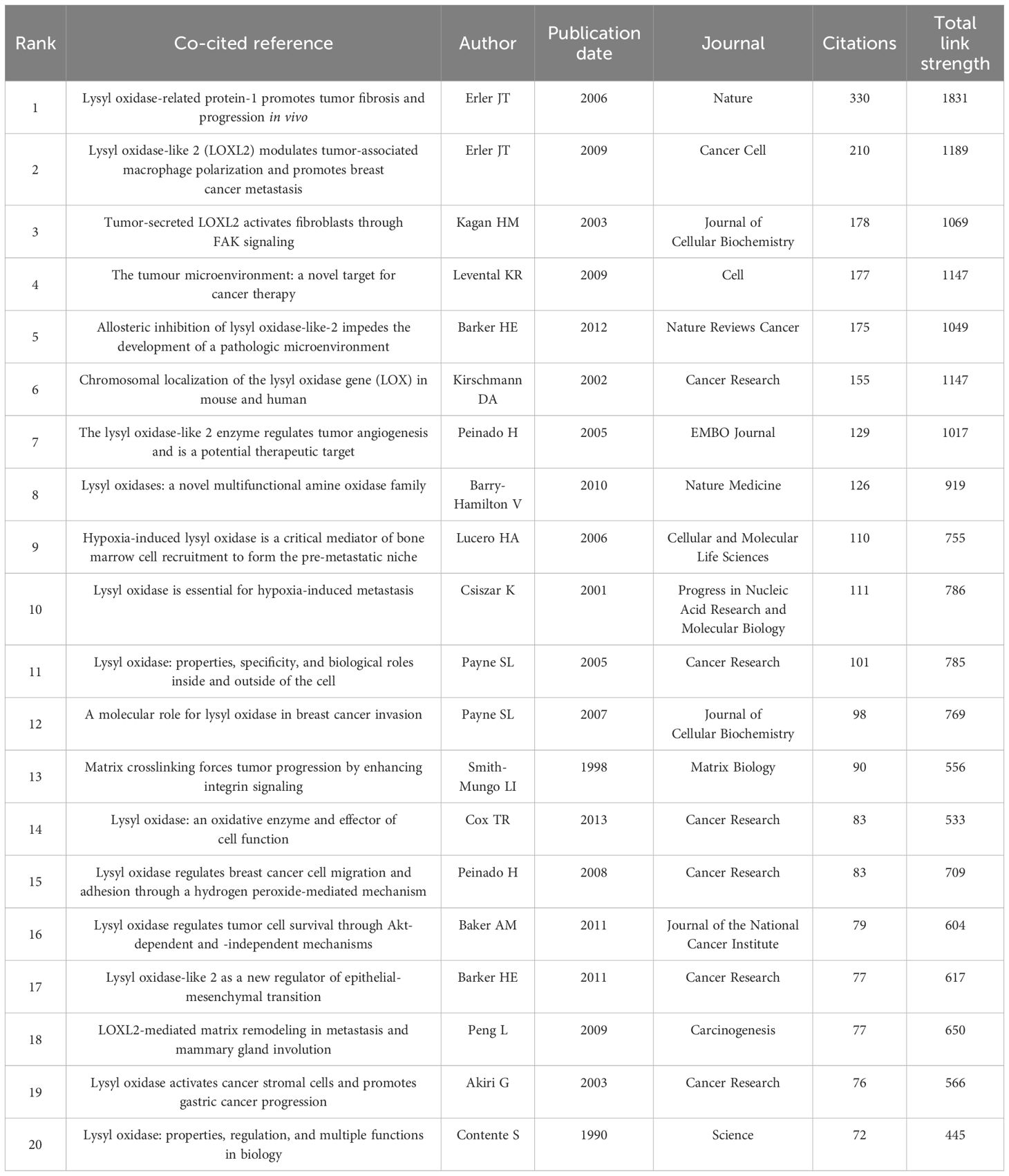
Over the past decade, 13,219 authors published on LOX and cancer. Using VOSviewer, a network visualization was generated. Authors with four or more publications were selected for further analysis. In the cancer - related LOX study, 137 authors were involved. Philip C. Trackman had the most publications (25), followed by Janine T. Erler (22) and Thomas R. Cox (15). Their co - authorship map is presented in Figure 5D. Table 9 enumerates the top 20 co - cited references. The reference with the highest citation count was from a 2006 publication in Nature, authored by Janine T. Erler. This study delved into LOX’s role in tumor metastasis, especially its ECM - regulating mechanism for tumor invasion. Figure 5E’s keyword visualization displays nodes such as “activation”, “lysyl oxidase”, “lysyl oxidase - 2”, “gene”, “breast cancer”, “cancer”, and “extracellular matrix” connected by lines, highlighting the intricate relationships within LOX research. It clearly indicates that LOX research is closely intertwined with cancer, particularly breast cancer, the extracellular matrix, biological activation, and genetics.
Figure 5F is a bar chart illustrating the recurrence occurrences of various cancer types. The x - axis lists different cancer types, ranging from breast cancer to rhabdomyosarcoma. The y - axis represents the number of recurrences. Blue bars are used to depict the recurrence counts for each cancer. Breast cancer has the highest number of recurrences, reaching 69, while rhabdomyosarcoma has the lowest, with only 2 occurrences. A red dashed line is overlaid on the chart, which shows a downward trend, indicating that the recurrence numbers generally decrease from one cancer type to another. This chart effectively presents the differences and trends in recurrence frequencies among these cancers. This research on LOX encompasses the top ten most common tumors globally, with studies on lung cancer (15 documents), breast cancer (69 documents), colorectal cancer (32 documents), prostate cancer (19 documents), stomach cancer (33 documents), liver cancer (43 documents), cervical cancer (6 documents), thyroid cancer (2 documents), and bladder cancer (3 documents), but excludes research on esophageal cancer.
Discussion
In one of their other studies, it was revealed that LOX, secreted by hypoxic breast tumor cells, accumulates at pre - metastatic sites. It crosslinks collagen IV in the basement membrane, playing a pivotal role in the recruitment of CD11b+ myeloid cells (36). These CD11b+ cells bind to the crosslinked collagen IV and produce matrix metalloproteinase - 2, which cleaves collagen, thereby facilitating the invasion and recruitment of bone marrow - derived cells (BMDCs) and metastasizing tumor cells (46, 47).Regarding human colorectal carcinoma cell lines, the induction of LOX augmented HIF - 1 expression, whereas LOX silencing led to a reduction. Mechanistic investigations disclosed that LOX activated the PI3K (phosphoinositide 3 - kinase) - Akt signaling pathway, which, in turn, upregulated the synthesis of HIF - 1α protein in a manner contingent on LOX - mediated hydrogen peroxide production (48–50).
LOX proteins, especially LOXL2, are enzymes involved in the cross - linking of collagen fibers, thus playing a critical role in the stabilization of the extracellular matrix (ECM) (51–53). In cancer, dysregulation of these enzymes has been implicated in tumor progression and metastasis (42). The ECM serves as both a structural scaffold and a signaling hub, and its abnormal remodeling by LOX proteins contributes to the mechanical properties of tumors, facilitating invasion and metastasis. Emerging evidence suggests that LOX activity is regulated by various signaling pathways, including TGF - β and Wnt/β - catenin, which are frequently dysregulated in cancer (30, 54–56). Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying LOX function could offer novel insights into tumor biology and therapeutic strategies (35, 57, 58).
The expression of LOX proteins has been shown to correlate with poor clinical outcomes in several cancers, such as breast, prostate, and ovarian cancers (59–61). This is largely attributable to their role in enhancing tumor stiffness, which promotes cancer cell survival, proliferation, and migration. Additionally, LOX enzymes may contribute to the maintenance of cancer stem cell properties by altering the ECM niche, thereby supporting tumor recurrence and resistance to therapy (28, 62, 63). Furthermore, LOX proteins are known to interact with other components of the tumor microenvironment, including immune cells, further complicating their role in cancer progression. These findings underscore the necessity for a comprehensive understanding of LOX - mediated ECM remodeling in cancer pathogenesis (64–67).
The outcomes of the mapping in Figure 4E suggest promising future research directions. These include delving into the interactions between LOX and the extracellular matrix during cancer metastasis and invasion, as well as exploring related gene regulatory pathways (68–72). Such research could potentially unlock novel approaches for diagnosing and treating diseases by targeting LOX (73–75). Inhibiting Lox enzymes has emerged as a promising therapeutic approach to combat cancer metastasis (76–81). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that targeting LOXL2 can reduce tumor stiffness, impair cancer cell invasion, and sensitize tumors to chemotherapy. Currently, several inhibitors of LOX enzymes are undergoing preclinical development and early - stage clinical trials (82, 83). These inhibitors aim to disrupt the cross - linking of collagen fibers, thereby reducing tumor stiffness and limiting cancer cell dissemination (84–90). Additionally, understanding the regulatory mechanisms of LOX expression could lead to novel therapeutic approaches, such as targeting upstream signaling pathways or combining LOX inhibition with immunotherapy to enhance anti - tumor immune responses (91–93). However, further research is needed to optimize these strategies and address potential off - target effects (94–96).
Lysyl oxidase (LOX) fulfills a critical function in vascular fibrosis and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling by catalyzing the oxidation of lysine residues in collagen and elastin, thereby facilitating ECM cross-linking and contributing to vascular wall stiffening (22). It orchestrates the phenotypic transition of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) from a contractile to a synthetic phenotype via the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/Smad signaling cascade, which accelerates fibrotic processes and diminishes vascular compliance (97). LOX exacerbates vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction by activating the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway, culminating in the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (98). Additionally, LOX contributes to oxidative stress-induced damage to vascular endothelial cells, compromising endothelial barrier integrity and initiating atherosclerotic plaque formation (99). It enhances matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) activity, leading to collagen degradation in the fibrous cap, which impacts plaque stability and the risk of acute cardiovascular events (100). LOX may also polarize macrophages toward a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, augmenting lipid phagocytosis and foam cell formation, while suppressing polarization to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, thereby exacerbating intra-plaque inflammation and lipid accumulation (101). LOX interacts with lipid metabolism by promoting LDL oxidation to form oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) and can inhibit ATP-binding cassette transporters, obstructing cholesterol reverse transport from foam cells to high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (102). Therapeutic interventions targeting LOX, such as β-aminopropionitrile (BAPN) and LOXL2-specific inhibitors like GSK2878163, have demonstrated efficacy in mitigating ECM cross-linking and decelerating atherosclerosis progression in animal models (20). Early studies in chickens and pigs exhibited variable effects of dietary interventions on LOX activity, whereas in rabbits with advanced atherosclerosis and ApoE-deficient mice on a high-fat diet, LOX activity was elevated, and BAPN treatment ameliorated atherosclerosis (103). LOX expression is also implicated in human plaque stability. Its involvement in collagen cross-linking and its regulation by factors such as hypoxia and cytokines highlight its pivotal role in plaque stability, necessitating further investigation into its contribution to plaque instability (7, 20, 104)
Fibrosis and cancer intersect through the lysyl oxidase (LOX) enzyme, both sharing a disrupted extracellular matrix (ECM) microenvironment. LOX acts as a pivotal mediator in this context. Current fibrosis research has emphasized a detailed analysis of LOX isoform expression, uncovering its overexpression in lung, liver, heart, skin fibrosis, and hypertension. Barry-Hamilton discovered that LOXL2 drives the pathologic microenvironment of cancer and fibrotic diseases in lung and liver, with elevated levels in diseased stroma. AB0023, an inhibitory antibody targeting LOXL2, effectively reduced disease markers in both cancer and fibrosis models (95). Inflammation-driven conditions such as hepatitis not only foster fibrosis but also contribute to carcinogenic mutations, with LOX sustaining a pro-inflammatory and ECM rigidifying niche, thereby perpetuating an “inflammation-fibrosis-cancer” continuum (105, 106). Conversely, in fibrosis linked to cancer, LOX and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-activated myofibroblasts secrete growth factors like HGF and FGF, which promote tumor cell viability and angiogenesis LOX’s enzymatic role extends to myelofibrosis, influencing megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet formation, and is critical for PDGF signaling and cell proliferation (107, 108). In a GATA-1-deficient myelofibrosis model, LOX overexpression drives ECM buildup and marrow fibrosis, which BAPN can mitigate. Elevated LOX activity in the marrow significantly contributes to myelofibrosis, with human myeloproliferative neoplasms showing heightened expression of several LOX isoforms (109). In mesothelioma, the build-up of asbestos in the pleural cavity causes prolonged inflammation, which prompts the malignant transformation of mesothelial cells and leads to fibrosis (110, 111). Therapeutically, LOX inhibition could concurrently benefit fibrosis and cancer treatment, such as LOXL2 inhibitors reducing ECM stiffness in fibrotic tumors to improve drug efficacy. Antifibrotic approaches include non-selective LOX inhibitors like BAPN and selective LOXL2 inhibitors, as well as MSC therapy, which can decrease LOX expression in liver injury models (3). The relationship between LOX family and extracellular matrix remodeling among various diseases is graphically represented in Figure 6.
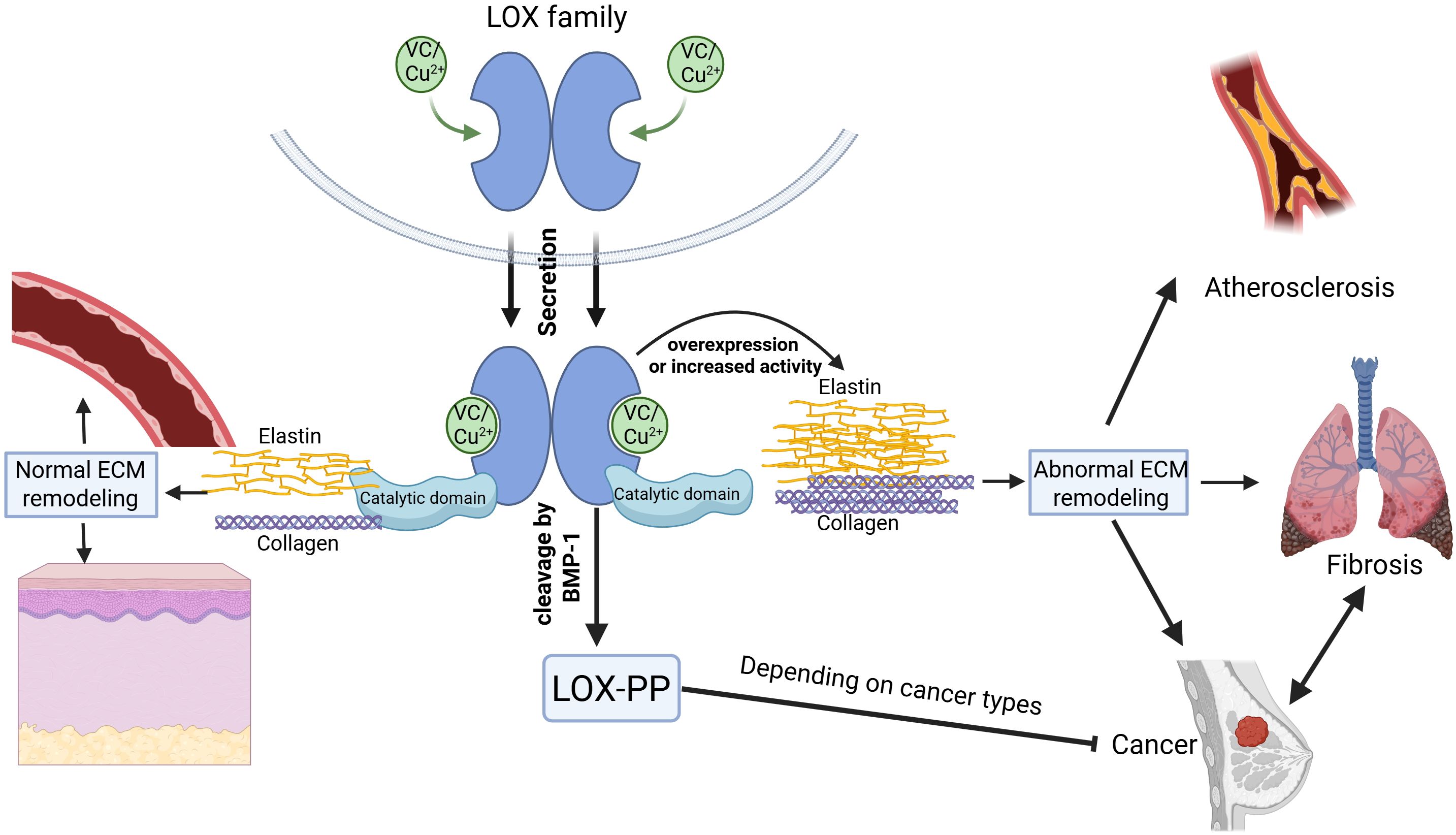
Figure 6. The role of the LOX family in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. The LOX family proteins, dependent on vitamin C and copper ions for their activity, contain both a catalytic domain and a propeptide domain. They play a crucial role in normal ECM remodeling involving elastin and collagen under physiological conditions. Overexpression or increased activity of LOX proteins, however, results in abnormal ECM remodeling linked to pathologies such as atherosclerosis, organ fibrosis, and various cancers. The LOX family acts as a key regulator in the transition between fibrosis and cancer. When LOX is secreted outside the cell, the N - terminus of the protein is cleaved by BMP – 1, forming the LOX propeptide (LOX - PP) and the catalytic domain of LOX protein. The catalytic domain of LOX proteins can promote cancer progression, whereas the LOX-PP has been shown to suppress cancer growth in certain types of cancer. WANG, Z. (2025) https://BioRender.com/2pa62d9.
Conclusion
This bibliometric analysis of LOX research from 1995 to 2025 identified 9,261 related publications. Keyword analysis showed “cancer” and “fibrosis” as key hotspots. LOX’s diverse functions and its links to cancer and fibrosis. This study provides an overview of LOX research trends, hotspots, and collaborations, guiding future research on LOX in diseases and therapies.
Future perspectives
Through our analysis of original research on LOX, we found that breast cancer accounts for the largest number of LOX-related studies. Therefore, we conducted a further in-depth analysis of LOX research in breast cancer. The results showed that: in breast cancer, the expression of LOXL1 is significantly upregulated, while that of LOX, LOXL2, and LOXL3 remains unchanged. Conversely, LOXL4 shows significant downregulation. Among these, only elevated LOXL2 expression demonstrates a strong correlation with a shortened disease - free survival duration in breast cancer patients, highlighting its potential as a critical biomarker for prognosis (59). The promotion of breast cancer progression by LOX family molecules is primarily mediated through several key mechanisms. Firstly, collagen cross - linking occurs, which contributes to the alteration of the extracellular matrix microenvironment (112). Secondly, the induction of epithelial - mesenchymal transition (EMT) is achieved by downregulating the expression of the E - cadherin epithelial marker and simultaneously upregulating the transcription of TWIST, thus facilitating the acquisition of a mesenchymal phenotype by cancer cells (113). Thirdly, the activation of the FAK/Src signalling pathway plays a pivotal role, triggering a cascade of intracellular events that enhance cell motility and invasiveness (28). Finally, the establishment of a premetastatic niche involving bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs) is accomplished via collagen restructuring, providing a supportive microenvironment for the dissemination and colonization of cancer cells (114). As we look to the future of breast cancer research and treatment, the exploration of LOX family proteins holds immense promise. Despite the significant strides made in breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis with medical advancements and biomarker discoveries, distant metastasis remains a formidable challenge to patient survival.
The emerging role of LOX family proteins in promoting breast cancer, from regulating initiation and spread to mediating intracellular EMT remodelling, positions them as pivotal players in the disease process. Their potential as biomarkers for early detection, disease staging, and evaluating chemotherapy effectiveness, along with their candidacy as targets for metastasis prevention, has already been recognized. The development of various inhibitors, though showing promise, also underscores the need for a more refined therapeutic approach considering their differential selectivity for LOX family enzymes.
Moving forward, novel drug therapies targeting LOX family proteins are likely to be at the forefront of personalized and precise treatment strategies for breast cancer patients. An especially exciting frontier lies in investigating the role of LOX family proteins in the tumour immune microenvironment. Unravelling the regulatory mechanisms of these proteins on the breast cancer immune microenvironment and exploring the synergistic effects with immunotherapy could open new vistas in treatment.
To fully harness the potential of LOX family proteins in breast cancer management, several key research areas demand attention. There is an urgent need to bridge the knowledge gap regarding the oncogenic effects of LOXL1 and LOXL3 in breast cancer through in - depth fundamental and clinical studies. Additionally, while downstream targets of LOX family proteins have been the focus of existing research, understanding their upstream gene regulation and degradation pathways is essential. The use of gene - edited cells and mouse models can facilitate such investigations.
Identifying effective biomarkers, clarifying substrate - binding mechanisms, and understanding the molecular intricacies of LOX family proteins in breast cancer are crucial steps. Determining the optimal time for intervention to maximize treatment efficacy is another promising avenue. Given the pre - clinical success of LOX - targeting drugs in breast cancer and their efficacy in other cancer types’ clinical trials, further research into miR - mediated mechanisms of LOX family member activity could illuminate the tumour microenvironment’s molecular landscape and lead to innovative clinical therapies.
Limitations
Despite the significant contributions of existing research on LOX family, several limitations should be noted. First, potential omissions may arise due to inappropriate synonyms or abbreviations, as the keyword-based search strategy might have missed or mis-included relevant studies using alternative terminology introducing risks of incomplete retrieval due to semantic variability, particularly in fields with evolving nomenclature. Second, database-specific coverage limitations exist: although representative databases (e.g., PubMed, Web of Science) were systematically searched, other databases (e.g., CINAHL, BIOSIS Previews) and non-English/regional databases (e.g., CNKI) may have led to unintentional gaps, potentially missing valuable data on LOX in fibrosis or cancer. Third, temporal gaps in database updates constrain timeliness: even with a standardized search date, newly published studies—especially in rapidly advancing fields like precision oncology—may not yet be indexed, risking omission of breakthroughs in LOX-targeted therapies published shortly before the search date and affecting the review’s currency. Finally, the inability to capture post-submission retractions poses a challenge: studies retracted after manuscript submission could not be excluded, as retraction notices often lag behind original publications. While study integrity was verified at the time of review, unforeseen post-submission retractions introduce a minor risk of outdated or invalid data persisting, a common limitation in cross-sectional reviews that underscores the importance of ongoing critical evaluation in scientific discourse.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
TY: Writing – original draft. WZ: Writing – review & editing. NZ: Writing – review & editing. ZT: Writing – review & editing. HW: Writing – review & editing. HL: Writing – review & editing. YF: Writing – review & editing. YC: Writing – review & editing. ZW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chen W, Yang A, Jia J, Popov YV, Schuppan D, and You H. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) family members: rationale and their potential as therapeutic targets for liver fibrosis. Hepatology. (2020) 72:729–41. doi: 10.1002/hep.31236
2. Csiszar K. Lysyl oxidases: A novel multifunctional amine oxidase family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. (2001) 70:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)70012-8
3. Trackman PC. Lysyl oxidase isoforms and potential therapeutic opportunities for fibrosis and cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2016) 20:935–45. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1151003
4. Stoyell-Conti FF, Suresh Kumar M, Zigmond ZM, Rojas MG, Santos Falcon N, Martinez L, et al. Gene inactivation of lysyl oxidase in smooth muscle cells reduces atherosclerosis burden and plaque calcification in hyperlipidemic mice. Atherosclerosis. (2024) 397:118582. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2024.118582
5. Langton AK, Tsoureli-Nikita E, Griffiths CEM, Katsambas A, Antoniou C, Stratigos A, et al. Lysyl oxidase activity in human skin is increased by chronic ultraviolet radiation exposure and smoking. Br J Dermatol. (2017) 176:1376–8. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14959
6. Kumarasamy A, Schmitt I, Nave AH, Reiss I, van der Horst I, Dony E, et al. Lysyl oxidase activity is dysregulated during impaired alveolarization of mouse and human lungs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2009) 180:1239–52. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200902-0215OC
7. Rodríguez C, Martínez-González J, Raposo B, Alcudia JF, Guadall A, and Badimon L. Regulation of lysyl oxidase in vascular cells: lysyl oxidase as a new player in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc Res. (2008) 79:7–13. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn102
8. Kagan HM and Li W. Lysyl oxidase: properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the cell. J Cell Biochem. (2003) 88:660–72. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10413
9. Mäki JM, Räsänen J, Tikkanen H, Sormunen R, Mäkikallio K, Kivirikko KI, et al. Inactivation of the lysyl oxidase gene lox leads to aortic aneurysms, cardiovascular dysfunction, and perinatal death in mice. Circulation. (2002) 106:2503–9. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000038109.84500.1e
10. Mayorca-Guiliani A and Erler JT. The potential for targeting extracellular lox proteins in human Malignancy. Onco Targets Ther. (2013) 6:1729–35. doi: 10.2147/ott.S38110
11. Lucero HA and Kagan HM. Lysyl oxidase: an oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol Life sciences: CMLS. (2006) 63:2304–16. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6149-9
12. Yamauchi M and Sricholpech M. Lysine post-translational modifications of collagen. Essays Biochem. (2012) 52:113–33. doi: 10.1042/bse0520113
13. Reversade B, Escande-Beillard N, Dimopoulou A, Fischer B, Chng SC, Li Y, et al. Author correction: mutations in PYCR1 cause cutis laxa with progeroid features. Nat Genet. (2022) 54:213. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01013-2
14. Huang M, Liu Z, Baugh L, DeFuria J, Maione A, Smith A, et al. Lysyl oxidase enzymes mediate TGf-β1-induced fibrotic phenotypes in human skin-like tissues. Lab Invest. (2019) 99:514–27. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0159-8
15. Ramis J, Middlewick R, Pappalardo F, Cairns JT, Stewart ID, John AE, et al. Lysyl oxidase like 2 is increased in asthma and contributes to asthmatic airway remodelling. Eur Respir J. (2022) 60:2004361. doi: 10.1183/13993003.04361-2020
16. Jones MG, Andriotis OG, Roberts JJ, Lunn K, Tear VJ, Cao L, et al. Nanoscale dysregulation of collagen structure-function disrupts mechano-homeostasis and mediates pulmonary fibrosis. eLife. (2018) 7:e36354. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36354
17. Bellaye PS, Shimbori C, Upagupta C, Sato S, Shi W, Gauldie J, et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 1 protein deficiency protects mice from adenoviral transforming growth factor-β1-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2018) 58:461–70. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0252OC
18. Lin YC, Sung YK, Jiang X, Peters-Golden M, and Nicolls MR. Simultaneously targeting myofibroblast contractility and extracellular matrix cross-linking as a therapeutic concept in airway fibrosis. Am J Transplant. (2017) 17:1229–41. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14103
19. Poe A, Martinez Yus M, Wang H, and Santhanam L. Lysyl oxidase like-2 in fibrosis and cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2023) 325:C694–c707. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00176.2023
20. Martínez-González J, Varona S, Cañes L, Galán M, Briones AM, Cachofeiro V, et al. Emerging roles of lysyl oxidases in the cardiovascular system: new concepts and therapeutic challenges. Biomolecules. (2019) 9:610. doi: 10.3390/biom9100610
21. Jheng JR, Bai Y, Noda K, Huot JR, Cook T, Fisher A, et al. Skeletal muscle sirt3 deficiency contributes to pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension due to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation. (2024) 150:867–83. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.124.068624
22. Wang ZJ, Guan QW, Zhou HH, Mao XY, and Chen FH. Mechanistic insight into lysyl oxidase in vascular remodeling and angiogenesis. Genes Dis. (2023) 10:771–85. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.05.011
23. Remus EW, O’Donnell RE Jr., Rafferty K, Weiss D, Joseph G, Csiszar K, et al. The role of lysyl oxidase family members in the stabilization of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am J Physiol Heart Circulatory Physiol. (2012) 303:H1067–75. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00217.2012
24. Yu Y, Shi E, Gu T, Tang R, Gao S, Wang Y, et al. Overexpression of microrna-30a contributes to the development of aortic dissection by targeting lysyl oxidase. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2017) 154:1862–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.06.019
25. Onoda M, Yoshimura K, Aoki H, Ikeda Y, Morikage N, Furutani A, et al. Lysyl oxidase resolves inflammation by reducing monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Atherosclerosis. (2010) 208:366–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.07.036
26. Wang W, Wang X, Yao F, and Huang C. Lysyl oxidase family proteins: prospective therapeutic targets in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12270. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012270
27. Lee M, Cho HJ, Park KS, and Jung HY. ELK3 controls gastric cancer cell migration and invasion by regulating ECM remodeling-related genes. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3709. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073709
28. Saatci O, Kaymak A, Raza U, Ersan PG, Akbulut O, Banister CE, et al. Targeting lysyl oxidase (LOX) overcomes chemotherapy resistance in triple negative breast cancer. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:2416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16199-4
29. Boufraqech M, Patel D, Nilubol N, Powers A, King T, Shell J, et al. Lysyl oxidase is a key player in BRAF/MAPK pathway-driven thyroid cancer aggressiveness. Thyroid. (2019) 29:79–92. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0424
30. Levental KR, Yu H, Kass L, Lakins JN, Egeblad M, Erler JT, et al. Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing integrin signaling. Cell. (2009) 139:891–906. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.027
31. Li H, Zhu X, Cao X, Lu Y, Zhou J, and Zhang X. Single-cell analysis reveals lysyl oxidase (LOX)(+) fibroblast subset involved in cardiac fibrosis of diabetic mice. J advanced Res. (2023) 54:223–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.01.018
32. Liu X, Li J, Yang X, Li X, Kong J, Qi D, et al. Carcinoma-associated fibroblast-derived lysyl oxidase-rich extracellular vesicles mediate collagen crosslinking and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition via P-FAK/P-paxillin/YAP signaling. Int J Oral Sci. (2023) 15:32. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00236-1
33. Wu Y, Wu Y, Yang Y, Yu J, Wu J, Liao Z, et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 inhibitor rescues D-galactose-induced skeletal muscle fibrosis. Aging Cell. (2022) 21:e13659. doi: 10.1111/acel.13659
34. Goodwin AF, Chen CP, Vo NT, Bush JO, and Klein OD. YAP/TAZ regulate elevation and bone formation of the mouse secondary palate. J Dental Res. (2020) 99:1387–96. doi: 10.1177/0022034520935372
35. Wang M, Zhao X, Zhu D, Liu T, Liang X, Liu F, et al. HIF-1α Promoted Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through LOXL2 up-Regulation in Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 36:60. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0533-1
36. Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird D, Koong A, et al. Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell. (2009) 15:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.11.012
37. Kaneda A, Wakazono K, Tsukamoto T, Watanabe N, Yagi Y, Tatematsu M, et al. Lysyl oxidase is a tumor suppressor gene inactivated by methylation and loss of heterozygosity in human gastric cancers. Cancer Res. (2004) 64:6410–5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-04-1543
38. Bouez C, Reynaud C, Noblesse E, Thépot A, Gleyzal C, Kanitakis J, et al. The lysyl oxidase lox is absent in basal and squamous cell carcinomas and its knockdown induces an invading phenotype in a skin equivalent model. Clin Cancer Res. (2006) 12:1463–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-05-1456
39. Attaran S, Skoko JJ, Hopkins BL, Wright MK, Wood LE, Asan A, et al. Peroxiredoxin-1 Tyr194 phosphorylation regulates LOX-dependent extracellular matrix remodelling in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. (2021) 125:1146–57. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01510-x
40. Wu M, Min C, Wang X, Yu Z, Kirsch KH, Trackman PC, et al. Repression of BCL2 by the tumor suppressor activity of the lysyl oxidase propeptide inhibits transformed phenotype of lung and pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:6278–85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-07-0776
41. Agra N, Cidre F, García-García L, de la Parra J, and Alonso J. Lysyl oxidase is downregulated by the EWS/FLI1 oncoprotein and its propeptide domain displays tumor supressor activities in Ewing sarcoma cells. PloS One. (2013) 8:e66281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066281
42. Barker HE, Cox TR, and Erler JT. The rationale for targeting the LOX family in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:540–52. doi: 10.1038/nrc3319
43. Farhat A, Ferns GA, Ashrafi K, and Arjmand MH. Lysyl oxidase mechanisms to mediate gastrointestinal cancer progression. Gastrointest Tumors. (2021) 8:33–40. doi: 10.1159/000511244
44. van Eck NJ and Waltman L. Software survey: vosviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. (2010) 84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
45. Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, and Tseng H. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: A scientometric analysis in citespace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2012) 12:593–608. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
46. Wong CC, Gilkes DM, Zhang H, Chen J, Wei H, Chaturvedi P, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a master regulator of breast cancer metastatic niche formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2011) 108:16369–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113483108
47. Bernabei I, Hansen U, Ehirchiou D, Brinckmann J, Chobaz V, Busso N, et al. CD11b deficiency favors cartilage calcification via increased matrix vesicles, apoptosis, and lysyl oxidase activity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:9776. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119776
48. Mer AS, Ba-Alawi W, Smirnov P, Wang YX, Brew B, Ortmann J, et al. Integrative pharmacogenomics analysis of patient-derived xenografts. Cancer Res. (2019) 79:4539–50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0349
49. Yoshikawa Y, Takano O, Kato I, Takahashi Y, Shima F, and Kataoka T. Ras inhibitors display an anti-metastatic effect by downregulation of lysyl oxidase through inhibition of the Ras-PI3K-Akt-HIF-1α Pathway. Cancer Lett. (2017) 410:82–91. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.017
50. Pez F, Dayan F, Durivault J, Kaniewski B, Aimond G, Le Provost GS, et al. The HIF-1-inducible lysyl oxidase activates HIF-1 via the Akt pathway in a positive regulation loop and synergizes with HIF-1 in promoting tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:1647–57. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-10-1516
51. Zhang X, Zhou W, Niu Y, Zhu S, Zhang Y, Li X, et al. Lysyl oxidase promotes renal fibrosis via accelerating collagen cross-link driving by β-arrestin/ERK/STAT3 pathway. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22427. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200573R
52. Schuppan D, Ashfaq-Khan M, Yang AT, and Kim YO. Liver fibrosis: direct antifibrotic agents and targeted therapies. Matrix Biol. (2018) 68-69:435–51. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.04.006
53. Peng L, Sun W, Cheng D, Jia X, Lian W, Li Z, et al. NUDT21 regulates lysyl oxidase-like 2(LOXL2) to influence ECM protein cross-linking in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Ecotoxicology Environ Saf. (2025) 290:117572. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117572
54. Cox TR, Bird D, Baker AM, Barker HE, Ho MW, Lang G, et al. LOX-mediated collagen crosslinking is responsible for fibrosis-enhanced metastasis. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:1721–32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-2233
55. Pickup MW, Mouw JK, and Weaver VM. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. (2014) 15:1243–53. doi: 10.15252/embr.201439246
56. Zhang J, Ye F, Ye A, and He B. Lysyl oxidase inhibits BMP9-induced osteoblastic differentiation through reducing Wnt/β-catenin via HIF-1a repression in 3T3-L1 cells. J orthopaedic Surg Res. (2023) 18:911. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04251-0
57. Reynaud C, Ferreras L, Di Mauro P, Kan C, Croset M, Bonnelye E, et al. Lysyl oxidase is a strong determinant of tumor cell colonization in bone. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:268–78. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-15-2621
58. Cox TR and Erler JT. Lysyl oxidase in colorectal cancer. Am J Physiol Gastrointestinal liver Physiol. (2013) 305:G659–66. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00425.2012
59. Li J, Wang X, Liu R, Zi J, Li Y, Li Z, et al. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) family proteins: key players in breast cancer occurrence and progression. J Cancer. (2024) 15:5230–43. doi: 10.7150/jca.98688
60. De Donato M, Petrillo M, Martinelli E, Filippetti F, Zannoni GF, Scambia G, et al. Uncovering the role of nuclear lysyl oxidase (LOX) in advanced high grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecologic Oncol. (2017) 146:170–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.05.001
61. Palamakumbura AH, Vora SR, Nugent MA, Kirsch KH, Sonenshein GE, and Trackman PC. Lysyl oxidase propeptide inhibits prostate cancer cell growth by mechanisms that target FGF-2-cell binding and signaling. Oncogene. (2009) 28:3390–400. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.203
62. Cheng F, Yang F, Wang Y, Zhou J, Qian H, and Yan Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-27b-3p alleviates liver fibrosis via downregulating YAP/LOXL2 pathway. J nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:195. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01942-y
63. Maller O, Drain AP, Barrett AS, Borgquist S, Ruffell B, Zakharevich I, et al. Tumour-associated macrophages drive stromal cell-dependent collagen crosslinking and stiffening to promote breast cancer aggression. Nat materials. (2021) 20:548–59. doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-00849-5
64. Wang TH, Hsia SM, and Shieh TM. Lysyl oxidase and the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 18:62. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010062
65. Zhang C, Xu M, Zeng Z, Wei X, He S, Huang J, et al. A polymeric extracellular matrix nanoremodeler for activatable cancer photo-immunotherapy. Angewandte Chemie (International ed English). (2023) 62:e202217339. doi: 10.1002/anie.202217339
66. Yu G, Corn PG, Mak CSL, Liang X, Zhang M, Troncoso P, et al. Prostate cancer-induced endothelial-cell-to-osteoblast transition drives immunosuppression in the bone-tumor microenvironment through Wnt pathway-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2024) 121:e2402903121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2402903121
67. Lu PY, Niu GJ, Hong PP, and Wang JX. Lysyl oxidase-like protein recognizes viral envelope proteins and bacterial polysaccharides against pathogen infection via induction of expression of antimicrobial peptides. Viruses. (2022) 14:2072. doi: 10.3390/v14092072
68. Xia Q, Du Z, Chen M, Zhou X, Bai W, Zheng X, et al. A protein complex of LCN2, LOXL2 and MMP9 facilitates tumour metastasis in oesophageal cancer. Mol Oncol. (2023) 17:2451–71. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13529
69. Urooj T, Wasim B, Mushtaq S, Shah SNN, and Shah M. Cancer cell-derived secretory factors in breast cancer-associated lung metastasis: their mechanism and future prospects. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2020) 20:168–86. doi: 10.2174/1568009620666191220151856
70. Tang X, Hou Y, Yang G, Wang X, Tang S, Du YE, et al. Stromal miR-200s Contribute to Breast Cancer Cell Invasion through Caf Activation and ECM Remodeling. Cell Death differentiation. (2016) 23:132–45. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.78
71. Dinca SC, Greiner D, Weidenfeld K, Bond L, Barkan D, and Jorcyk CL. Novel mechanism for OSM-promoted extracellular matrix remodeling in breast cancer: LOXL2 upregulation and subsequent ECM alignment. Breast Cancer research: BCR. (2021) 23:56. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01430-x
72. Adhikari S, Singh V, Nandi S, Ghosal M, Raj NS, Khanna J, et al. UBR7 in concert with EZH2 inhibits the TGF-β Signaling leading to extracellular matrix remodeling. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114394. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114394
73. Miana M, Galán M, Martínez-Martínez E, Varona S, Jurado-López R, Bausa-Miranda B, et al. The lysyl oxidase inhibitor β-aminopropionitrile reduces body weight gain and improves the metabolic profile in diet-induced obesity in rats. Dis Models Mech. (2015) 8:543–51. doi: 10.1242/dmm.020107
74. Liu SB, Ikenaga N, Peng ZW, Sverdlov DY, Greenstein A, Smith V, et al. Lysyl oxidase activity contributes to collagen stabilization during liver fibrosis progression and limits spontaneous fibrosis reversal in mice. FASEB J. (2016) 30:1599–609. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-268425
75. Kunadt D, Kramer M, Dill C, Altmann H, Wagenführ L, Mohr B, et al. Lysyl oxidase expression is associated with inferior outcome and extramedullary disease of acute myeloid leukemia. biomark Res. (2020) 8:20. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00200-9
76. Nguyen LT, Saad S, Shi Y, Wang R, Chou ASY, Gill A, et al. Lysyl oxidase inhibitors attenuate cyclosporin a-induced nephropathy in mouse. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:12437. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91772-5
77. Lewinska M, Zhuravleva E, Satriano L, Martinez MB, Bhatt DK, Oliveira D, et al. Fibroblast-derived lysyl oxidase increases oxidative phosphorylation and stemness in cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. (2024) 166:886–901.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.11.302
78. Johnston KA and Lopez KM. Lysyl oxidase in cancer inhibition and metastasis. Cancer Lett. (2018) 417:174–81. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.006
79. Jiang D, Zhao J, Zheng J, Zhao Y, Le M, Qin D, et al. LOX-mediated ECM mechanical stress induces Piezo1 activation in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage and identification of novel inhibitor of LOX. Redox Biol. (2024) 76:103346. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103346
80. Chitty JL, Yam M, Perryman L, Parker AL, Skhinas JN, Setargew YFI, et al. A first-in-class pan-lysyl oxidase inhibitor impairs stromal remodeling and enhances gemcitabine response and survival in pancreatic cancer. Nat Cancer. (2023) 4:1326–44. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00614-y
81. Chen KN, Peng QL, Cao DF, Wang ZJ, Zhang K, Zhou XY, et al. Inhibition of lysyl oxidase by pharmacological intervention and genetic manipulation alleviates epilepsy-associated cognitive disorder. Brain Res Bull. (2024) 210:110928. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.110928
82. Verstovsek S, Savona MR, Mesa RA, Dong H, Maltzman JD, Sharma S, et al. A phase 2 study of simtuzumab in patients with primary, post-polycythaemia vera or post-essential thrombocythaemia myelofibrosis. Br J haematology. (2017) 176:939–49. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14501
83. Raghu G, Brown KK, Collard HR, Cottin V, Gibson KF, Kaner RJ, et al. Efficacy of simtuzumab versus placebo in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2017) 5:22–32. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(16)30421-0
84. Zhu B, Li F, Yu J, Liang Z, Ke X, Wang Y, et al. PIEZO1 mediates matrix stiffness-induced tumor progression in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma by activating the Ca(2+)/Calpain/YAP pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2025) 1872:119871. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119871
85. Wei B, Zhou X, Liang C, Zheng X, Lei P, Fang J, et al. Human colorectal cancer progression correlates with lox-induced ECM stiffening. Int J Biol Sci. (2017) 13:1450–7. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.21230
86. Schütze F, Röhrig F, Vorlová S, Gätzner S, Kuhn A, Ergün S, et al. Inhibition of lysyl oxidases improves drug diffusion and increases efficacy of cytotoxic treatment in 3D tumor models. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:17576. doi: 10.1038/srep17576
87. Lv Y, Wang H, Li G, and Zhao B. Three-dimensional decellularized tumor extracellular matrices with different stiffness as bioengineered tumor scaffolds. Bioactive materials. (2021) 6:2767–82. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.02.004
88. Leiva O, Leon C, Kah Ng S, Mangin P, Gachet C, and Ravid K. The role of extracellular matrix stiffness in megakaryocyte and platelet development and function. Am J Hematol. (2018) 93:430–41. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25008
89. Kozma KJ, Done SJ, and Egan SE. The tumor cell-derived matrix of lobular breast cancer: A new vulnerability. EMBO Mol Med. (2021) 13:e13807. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202013807
90. González-Santamaría J, Villalba M, Busnadiego O, López-Olañeta MM, Sandoval P, Snabel J, et al. Matrix cross-linking lysyl oxidases are induced in response to myocardial infarction and promote cardiac dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res. (2016) 109:67–78. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv214
91. Tuleta I, Hanna A, Humeres C, Aguilan JT, Sidoli S, Zhu F, et al. Fibroblast-specific TGF-β Signaling mediates cardiac dysfunction, fibrosis, and hypertrophy in obese diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Res. (2024) 120:2047–63. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvae210
92. Lu Y, Li H, Chen M, Lin Y, and Zhang X. LOX-induced tubulointerstitial fibrosis via the TGF-β/LOX/snail axis in diabetic mice. J Trans Med. (2025) 23:35. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06056-z
93. Jeay S, Pianetti S, Kagan HM, and Sonenshein GE. Lysyl oxidase inhibits ras-mediated transformation by preventing activation of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. (2003) 23:2251–63. doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.7.2251-2263.2003
94. Huang X, Wang L, Guo H, Zhang W, and Shao Z. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals the regulative roles of cancer associated fibroblasts in tumor immune microenvironment of recurrent osteosarcoma. Theranostics. (2022) 12:5877–87. doi: 10.7150/thno.73714
95. Barry-Hamilton V, Spangler R, Marshall D, McCauley S, Rodriguez HM, Oyasu M, et al. Allosteric inhibition of lysyl oxidase-like-2 impedes the development of a pathologic microenvironment. Nat Med. (2010) 16:1009–17. doi: 10.1038/nm.2208
96. Tebbi CK and Gaeta J. Osteosarcoma. Pediatr Ann. (1988) 17:285–300. doi: 10.3928/0090-4481-19880401-08
97. Lin W, Song Y, Li T, Yan J, Zhang R, Han L, et al. Triptolide attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting fibrotic extracellular matrix remodeling mediated by MMPs/LOX/integrin. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 166:115394. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115394
98. Ding Z, Pothineni NVK, Goel A, Lüscher TF, and Mehta JL. Corrigendum to: PCSK9 and inflammation: role of shear stress, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and LOX-1. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118:2031. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab352
99. Kattoor AJ, Goel A, and Mehta JL. LOX-1: regulation, signaling and its role in atherosclerosis. Antioxidants (Basel). (2019) 8:218. doi: 10.3390/antiox8070218
100. Jiao Y, Qin Y, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Liu H, and Li C. Early identification of carotid vulnerable plaque in asymptomatic patients. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2020) 20:429. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01709-5
101. Zhang K, Jordan PM, Pace S, Hofstetter RK, Werner M, Chen X, et al. Modulation of inflammation-related lipid mediator pathways by celastrol during human macrophage polarization. J Inflammation Res. (2022) 15:3285–304. doi: 10.2147/jir.S356964
102. Chistiakov DA, Melnichenko AA, Myasoedova VA, Grechko AV, and Orekhov AN. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med (Berl). (2017) 95:1153–65. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1575-8
103. Ballester-Servera C, Alonso J, Cañes L, Vázquez-Sufuentes P, Puertas-Umbert L, Fernández-Celis A, et al. Lysyl oxidase-dependent extracellular matrix crosslinking modulates calcification in atherosclerosis and aortic valve disease. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 167:115469. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115469
104. Fukai T, Ushio-Fukai M, and Kaplan JH. Copper transporters and copper chaperones: roles in cardiovascular physiology and disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2018) 315:C186–c201. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00132.2018
105. Radmanić L, Korać P, Gorenec L, Šimičić P, Bodulić K, Vince A, et al. Distinct expression patterns of genes coding for biological response modifiers involved in inflammatory responses and development of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: upregulation of SMAD-6 and MMP-8 and downregulation of CAV-1, CTGF, CEBPB, PLG, TIMP-3, MMP-1, ITGA-1, ITGA-2 and LOX. Medicina (Kaunas). (2022) 58:1734. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121734
106. Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, Huang C, Huang Y, Zhang L, et al. Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions. Biochimie. (2013) 95:2326–35. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.09.003
107. Eliades A, Papadantonakis N, Bhupatiraju A, Burridge KA, Johnston-Cox HA, Migliaccio AR, et al. Control of megakaryocyte expansion and bone marrow fibrosis by lysyl oxidase. J Biol Chem. (2011) 286:27630–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.243113
108. Piasecki A, Leiva O, and Ravid K. Lysyl oxidase inhibition in primary myelofibrosis: A renewed strategy. Arch Stem Cell Ther. (2020) 1:23–7. doi: 10.46439/stemcell.1.005
109. Sangiorgio VFI, Nam A, Chen Z, Orazi A, and Tam W. Gata1 downregulation in prefibrotic and fibrotic stages of primary myelofibrosis and in the myelofibrotic progression of other myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leuk Res. (2021) 100:106495. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106495
110. Perryman L and Gray SG. Fibrosis in mesothelioma: potential role of lysyl oxidases. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:981. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040981
111. Carbone M, Adusumilli PS, Alexander HR Jr., Baas P, Bardelli F, Bononi A, et al. Mesothelioma: scientific clues for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. (2019) 69:402–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21572
112. Ferreira S, Saraiva N, Rijo P, and Fernandes AS. LOXL2 inhibitors and breast cancer progression. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 10:312. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020312
113. Hellinger JW, Schömel F, Buse JV, Lenz C, Bauerschmitz G, Emons G, et al. Identification of drivers of breast cancer invasion by secretome analysis: insight into CTGF signaling. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:17889. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74838-8
114. Zheng Q, Zhou T, and Yao D. The roles of immune cells and non-immune cells in pre-metastatic niche of breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2025) 211:104744. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2025.104744
115. Jasmer KJ, Shanbhag VC, Forti KM, Woods LT, Gudekar NS, Weisman GA, et al. Pulmonary lysyl oxidase expression and its role in seeding lewis lung carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2024) 42:7. doi: 10.1007/s10585-024-10325-y
116. Foehr R, Anderson K, Dombrowski O, Foehr A, and Foehr ED. Dysregulation of extracellular matrix and lysyl oxidase in ehlers-danlos syndrome type IV skin fibroblasts. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2024) 19:9. doi: 10.1186/s13023-023-03007-7
117. Zhao Z, Liu W, and Luo B. The oncogenic role of lysyl oxidase-like 1 (LOXL1): insights into cancer progression and therapeutic potential. Gene. (2025) 947:149312. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2025.149312
118. Sflomos G, Battista L, Aouad P, De Martino F, Scabia V, Stravodimou A, et al. Intraductal xenografts show lobular carcinoma cells rely on their own extracellular matrix and LOXL1. EMBO Mol Med. (2021) 13:e13180. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202013180
119. Li SY, Zhang N, Zhang H, Wang N, Du YY, Li HN, et al. Deciphering the TCF19/miR-199a-5p/SP1/LOXL2 pathway: implications for breast cancer metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. (2024) 597:216995. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216995
120. Vázquez-Naharro A, Bustos-Tauler J, Floristán A, Yuste L, Oltra SS, Vinyals A, et al. LOXL3 promotes melanoma progression and dissemination influencing cell plasticity and survival. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:1200. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051200
121. Liu M, Wang J, and Liu M. Lysyl oxidase inhibitors in colorectal cancer progression. Transl Oncol. (2025) 52:102233. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102233
122. Liu R, Li B, Zi J, Zhang R, Yu M, Zhou J, et al. The dual role of LOXL4 in the pathogenesis and development of human malignant tumors: A narrative review. Transl Cancer Res. (2024) 13:2026–42. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2003
123. Chen J, Zhou D, Liao H, and Li Y. miR-183-5p regulates ECM and EMT to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression by targeting LOXL4. J Thorac Dis. (2023) 15:1734–48. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-329
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, lysyl oxidase, diseases, fibrosis, cancer, extracellular matrix
Citation: Yang T, Li H, Zhou W, Zhang N, Tian Z, Wang H, Feng Y, Chen Y and Wang Z (2025) Bibliometric analysis combined with visualization on universal trends and hot topics of LOX family in human diseases: 1995 to 2025. Front. Oncol. 15:1601261. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1601261
Received: 27 March 2025; Accepted: 11 June 2025;
Published: 30 June 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Chen, Capital Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Li, Zhou, Zhang, Tian, Wang, Feng, Chen and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhen Wang, emhlbndhbmdAamlhbmduYW4uZWR1LmNu
 Tingting Yang
Tingting Yang Heng Li1
Heng Li1 Zhen Wang
Zhen Wang