- 1Breast Disease Diagnosis and Treatment Center, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining, China
- 2Department of Urology, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining, China
- 3Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining, China
Background: Breast cancer is the most common malignancy among women globally. Organoid technology has emerged as a pivotal tool in breast cancer research due to its advantages in modeling tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment. Despite rapid advancements in this field, a systematic bibliometric analysis to delineate research trends and challenges is lacking. This study aimed to analyze the research landscape, hotspots, and future directions in the field of breast cancer organoids from 2005 to 2024.
Methods: Publications related to breast cancer organoids published between January 2005 and March 2024 were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. Bibliometric tools (CiteSpace and VOSviewer) were employed to analyze collaboration networks (countries/institutions), author contributions, keyword co-occurrence clusters, and burst keywords.
Results: Over the past two decades, the annual publication output on breast cancer organoids has shown continuous growth. The 1618 included English publications garnered a total of 7,323 citations, with a mean citation count of 35.20 per article. The United States (n=666) and China (n=257) contributed over 50% of the publications. Harvard University was the most productive institution. Mina J. Bissell authored the highest number of publications (n=17). High-frequency keywords centered on personalized therapy, immunotherapy, and 3D bioprinting. Burst keyword analysis identified “gene expression” and “signaling pathways” as emerging trends (2019–2024). Key research hotspots include the application of patient-derived organoids (PDOs) for drug screening, co-culture modeling of the tumor microenvironment (TME) with immune components, and the integration of 3D bioprinting technologies.
Conclusion: This study represents the first comprehensive bibliometric analysis to elucidate the evolution and research hotspots in breast cancer organoid research in recent years. The findings provide a thorough summary of the major achievements, persistent challenges, and future frontiers within this rapidly advancing field.
1 Introduction
As a revolutionary breakthrough in the biomedical field in the past two decades, organoid technology has broken through the traditional construction paradigm of in vitro models (1). Based on the lineage plasticity of adult stem cells or pluripotent stem cells, this technology achieves directional differentiation in 3D self-tissue culture system, and finally forms in vitro organ bionic system with organ-specific spatial topology and cell heterogeneity (2). Its histological complexity has reached the level of high similarity to the microscopic structure of physiological organs, showing the bionic advantage over the traditional two-dimensional culture system. The two-dimensional single-layer culture model widely used in the past has problems such as structure flatness defects and genetic stability attenuation, especially in the process of primary modeling, it faces bottlenecks such as low patient-derived sample conversion efficiency and rapid cell function degradation (3). In view of these limitations, the researchers developed a three-dimensional tissue engineering culture platform through in vitro microenvironment reconstruction technology, allowing cells to reconstruct the intercellular interaction network in a three-dimensional scaffold, so as to accurately reproduce the spatial regulatory mechanisms during organ development. This 3D biomanufacturing strategy not only maintains the long-term stability of tissue homeostasis, but also significantly improves the fidelity of pathophysiological simulations, providing a revolutionary tool for precision medicine research (4). Toshiro Sato et al. (5) successfully cultured mouse intestinal organoids in vitro, which opened the prelude to organoid technology. After more than ten years of development, organoids have gradually become a new in vitro model for biomedical research and a powerful tool for maintaining the properties of original cells in the near-native state. Over the past decade, 3D cultures of human embryonic stem cells (ES) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) have successfully engineered multiple organ types for culture, These include breast cancer (6), prostate cancer (7), ovarian cancer (8), lung cancer (9), stomach cancer (10), colorectal cancer (11, 12), liver cancer (13), pancreatic cancer (14), and brain cancer (15). For many years, efforts have been made to explore new ways to co-culture immune cells and organoids in various cancers, including breast cancer. Since breast cancer organoids retain their origin characteristics, tumor xenotransplantation and tumor organ models have become key preclinical models for cancer research (16). Breast cancer organoids can be used in immunotherapy. Cai-Ping Sun et al. (17) through the tumor organoid model, can promote preclinical trials of immunotherapy by retaining endogenous matrix components including various immune cells and simulating immunotherapy responses. Breast cancer organoid technology brings great hope for personalized medicine by creating individual tumor organs and implementing high-throughput drug screening. Meanwhile, breast cancer organoid technology provides a solid foundation for personalized medicine by creating individual tumor organs and implementing high-throughput drug screening. Providing the most effective cancer treatments for individual patients (18). In recent years, the application of breast cancer organoid technology in various fields has been growing, and the number of related publications has also increased year by year. Although breast cancer organoids show great potential in preclinical studies, there are still many challenges in this field, such as high cost, long time consuming, and low success rates. Hence, conducting a bibliometric analysis of breast cancer organoid research is essential to comprehensively summarize the existing achievements and delineate the future challenges within this field. In academic research, research performance is usually assessed by bibliometric indicators (number of publications and citations). Bibliometric methods are widely used because of their compact information, ease of processing and objectivity (19). At present, bibliometric analysis is mainly used to analyze the development trend, academic communication and core influence of literature in specific scientific fields. Not only that, bibliometric analysis can also be used to explore leading journals, core author teams, and current research frontiers and trends in the field. Therefore, it is possible to use bibliometric analysis to evaluate the research activities and trends of specific topics and the most prominent research trends in future studies, not only in the literature itself, but also involving authors,keywords, institutions, countries, etc (20). Despite remarkable progress in breast cancer organoids over the past two decades, bibliometric analyses in this field remain very limited. Therefore, this study employed three bibliometric tools (VOSviewer, R-bibliometrix, and CiteSpace) to analyze the overall landscape of breast cancer organoid-related research. It aims to synthesize the achievements attained over the last 20 years, identify key future challenges, and provide researchers with insights into the field while guiding future research hotspots and trends.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source and search strategy
As one of the most authoritative and comprehensive database platforms in the world, Web of Science has become the most commonly used database for bibliometric analysis with its rich content and high-quality academic journals. Therefore, this paper uses the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) as the data base. Literature search was performed simultaneously by Tao Wu and Baixin Li using the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) as the citation database. In order to ensure the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the retrieved data, SCIExpanded was selected as the citation index. The search keyword is set to “TS=((“Breast Cancer*” OR “Breast Neoplas*” OR “Breast Tumor*” OR “Mammary Cancer” OR “Mammary Tumor”) AND (Organoid* OR “3D model*” OR “3D culture*” OR “three-dimensional culture*” OR “patient-derived model” OR “primary culture”))AND document type = (ARTICLE OR REVIEW) AND language = (English) “, the time span selected is January 1, 2005 to December 31, 2024. In addition, all valid bibliographic data, including year of publication, title, author name, nationality, affiliation, abstract, keywords, journal name, etc., are stored in the WoSCC database in plain text format.
2.2 Bibliometric analysis and visualization
Bibliometrics is an independent discipline that provides quantitative methods for the review and study of existing literature in a specific field (21). During the analysis, detailed information such as authors, keywords, journals, countries, institutions, references, etc. can be obtained. Visualization helps to reveal the internal connections between this information, such as different authors working on the same topic, the research priorities of different institutions, new theories proposed by existing institutions, and so on. For data analysis and visualization, we use two tools, VOSviewer and CiteSpace, for country and regional co-occurrence, journal dual graph, high-frequency keyword trends, co-citations, literature citations surge, inter-country networks, institutional researchers, and co-occurrence analysis (22, 23).
3 Results
3.1 Trend of global publications and citations
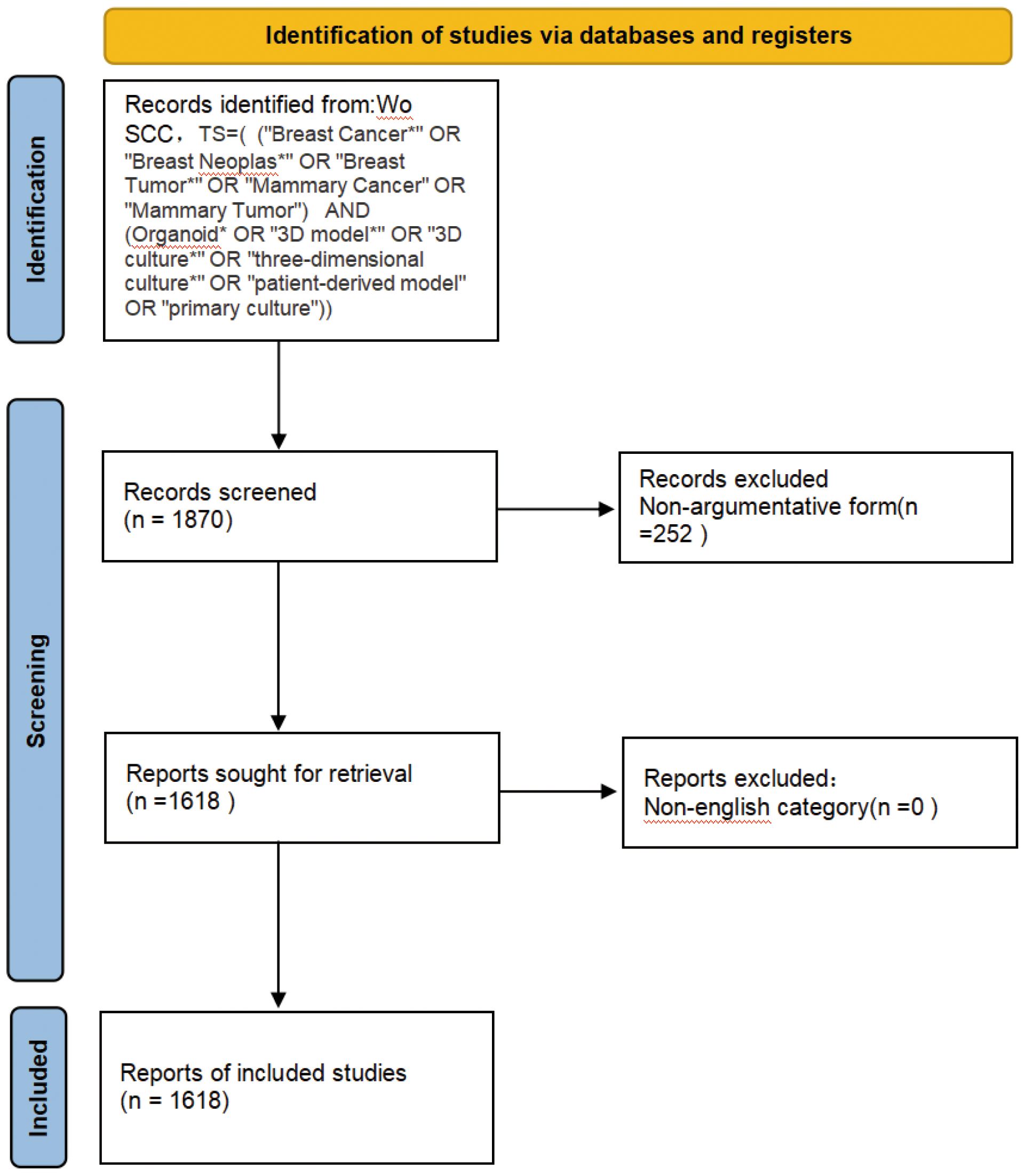
From 2005 to 2024, the Wo SCC collected a total of 1618 articles (Figure 1), all of which were published in English. The 1618 papers used in this study, authored by 1,000 authors from 206 institutions in 69 countries and published in 677 journals, represent an increasing number of studieson breast cancer organoids over the last 20 years (Figure 2A). These papers received an average of 35.20 citations per paper, for a total of 7,323 citations.
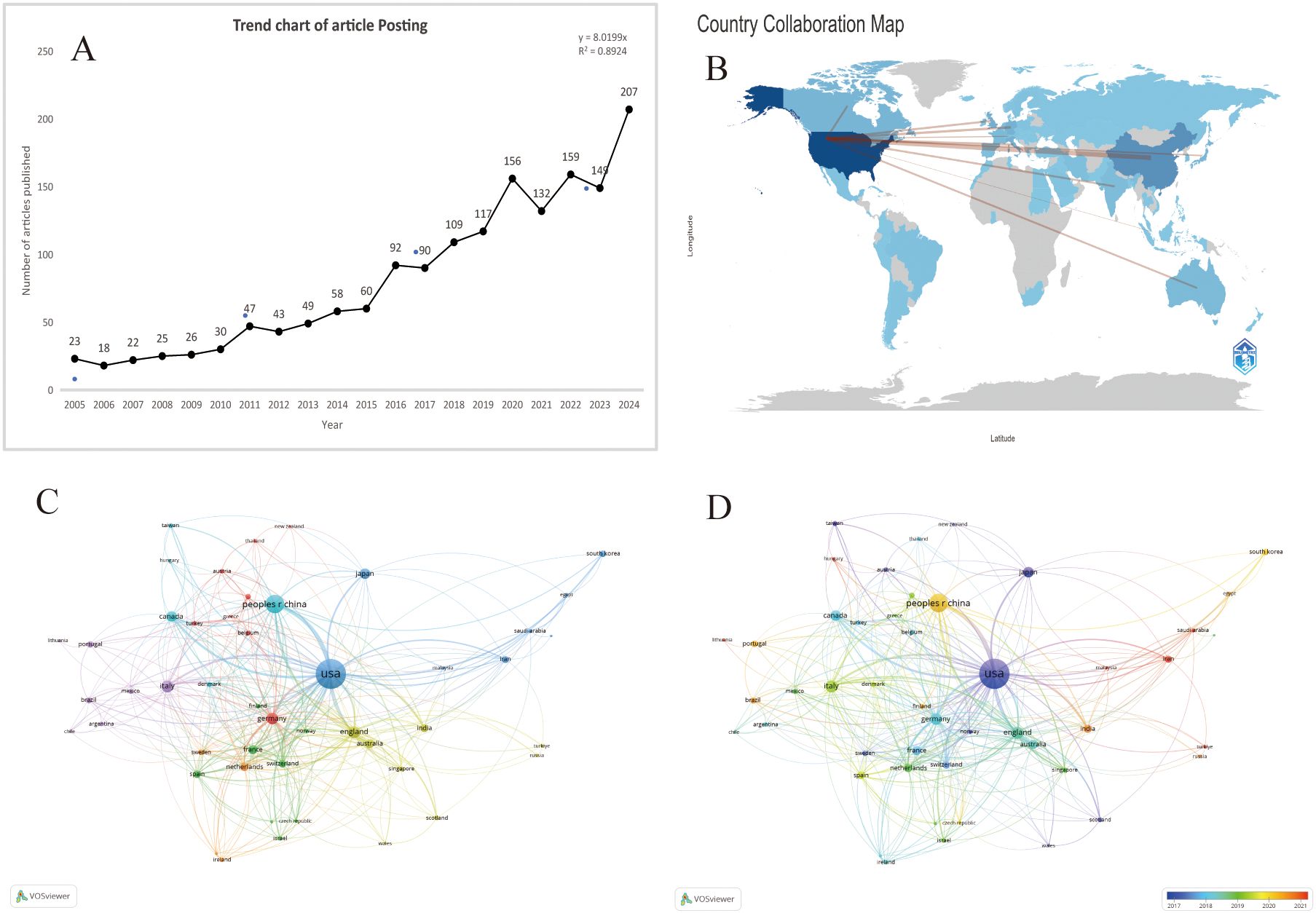
Figure 2. (A) Number of publications related to breast cancer organoids by year,2005-2024 . (B) Distribution of publications by countriesand regions in the word. (C) The citation network of countriesregions mapped through VOSviewer. (D) Visualization of citation coerage by country with VOSviewer.
3.2 Countries/regions and institutions analysis
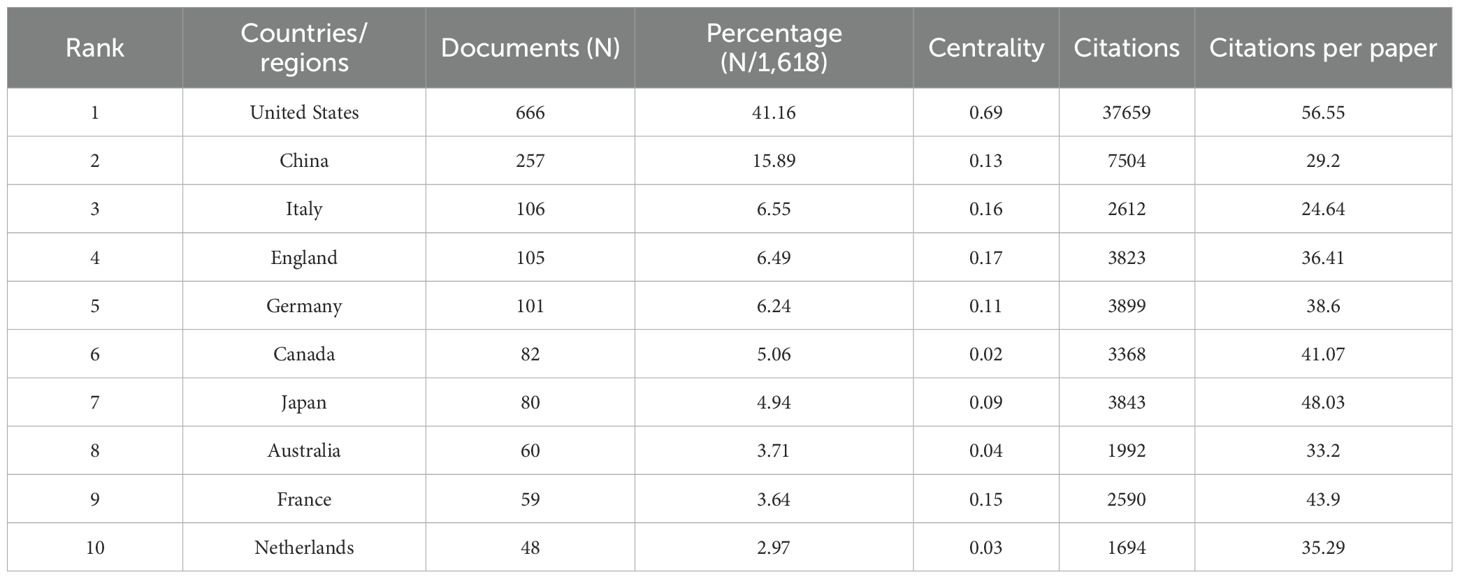
According to the World map (Figure 2B), publications on this topic come from researchers in 69 countries. The specific number of publications and citations by countries are shown in Table 1, among which the United States (666), China (257), India (106), the United Kingdom (105) and Germany (101) contributed the most. In addition, the United Kingdom, Germany and the United States have higher citation rates than China and India. According to Figure 2C, D, the citation relationships among 48 countries/regions with at least 5 publications are revealed. Despite publishing more documents, China is second only to the United States in terms of cooperation with other countries.
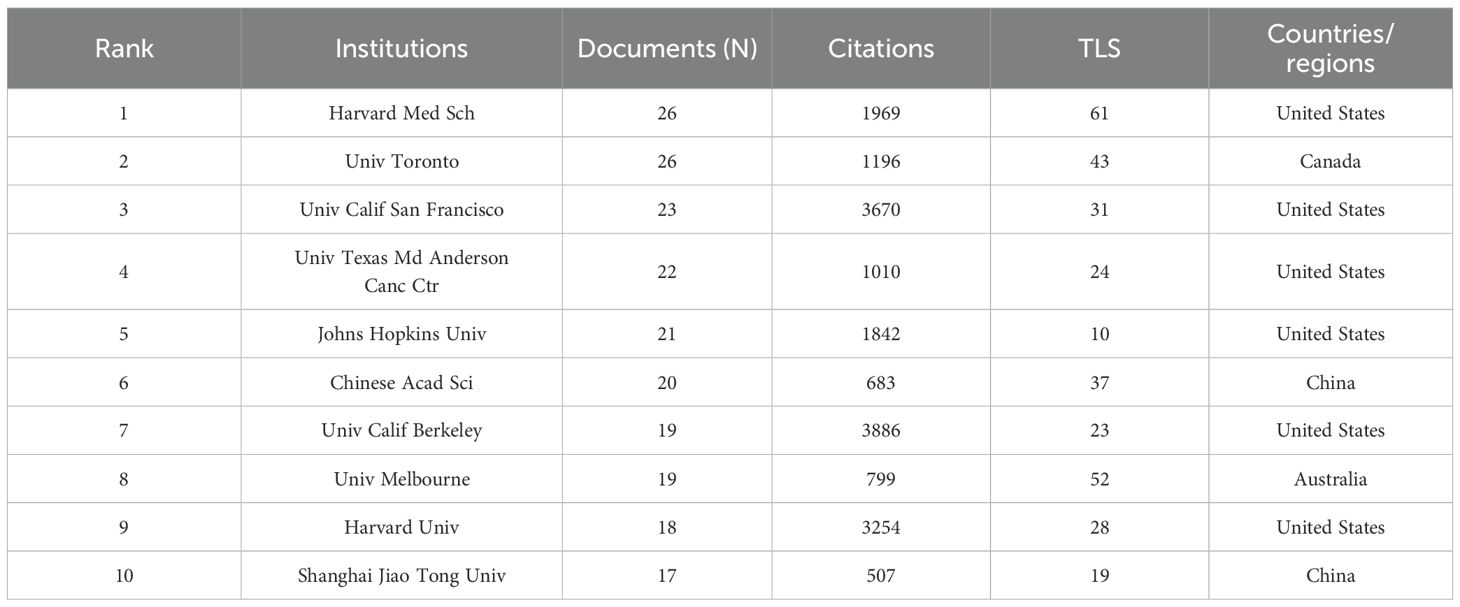
According to CiteSpace, a total of 1,618 papers were provided by 206 different institutions. Table 2 lists the top 10 institutions with the highest number of published papers. It can be found that the majority of these 10 institutions are from the United States, which is also in line with the country’s literature volume ranking. In Figure 3A, a VOSviewer chart of institutional collaboration, American institutions, centered on Harvard University, work more closely together than their Chinese counterparts. In terms of citation analysis of institutions, the top three most cited institutions are University of California, Berkeley (3,886), University of California, San Francisco (3,670), and Harvard University (3,254) (Figure 3B). In addition, the chart above shows that work in this area of research started earlier at the University of California, Berkeley.
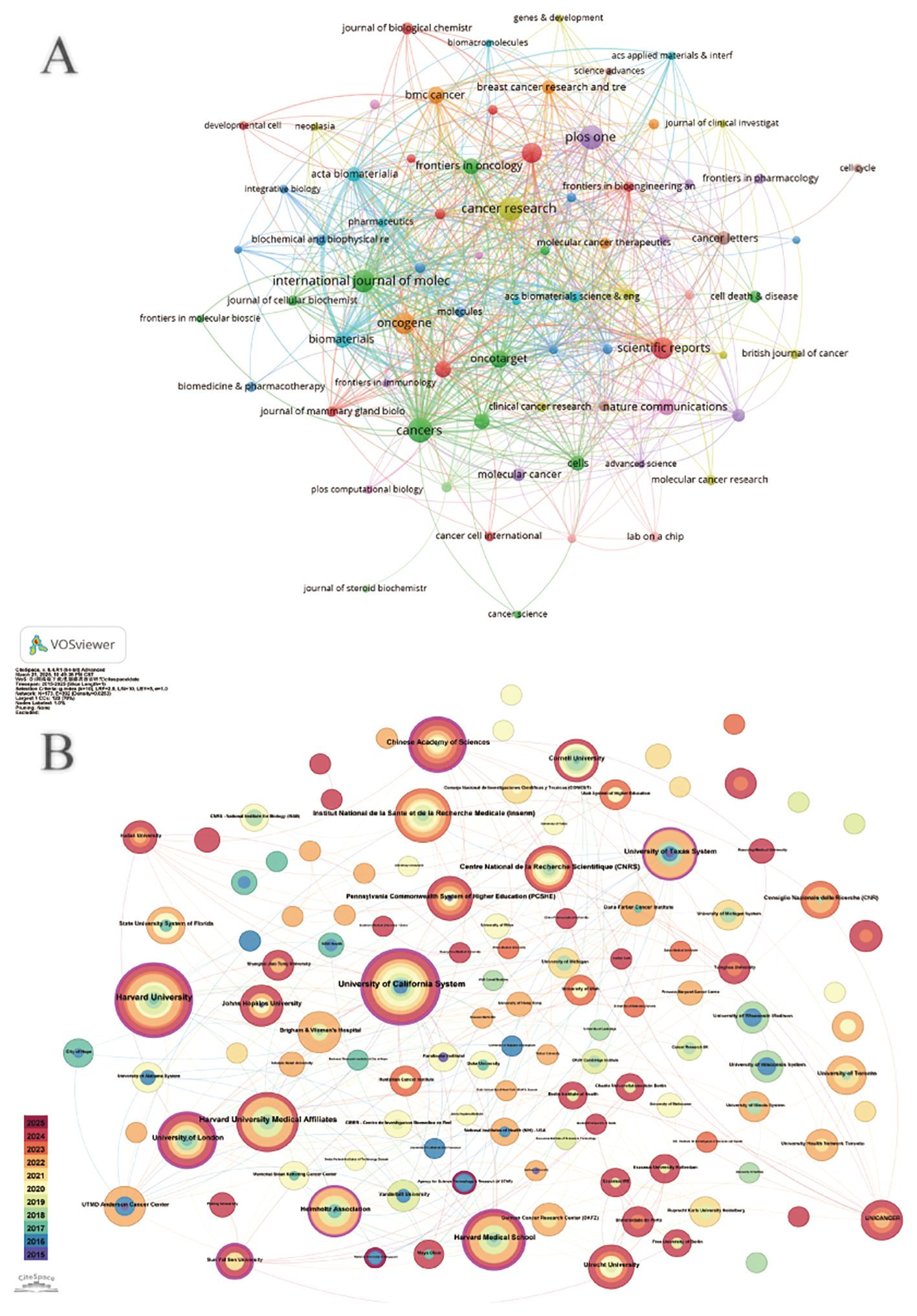
Figure 3. (A) Institutional cooperation diagram based on VOSviewer. (B) Institutional citation network generated by CiteSpace.
3.3 Authors and co-cited authors
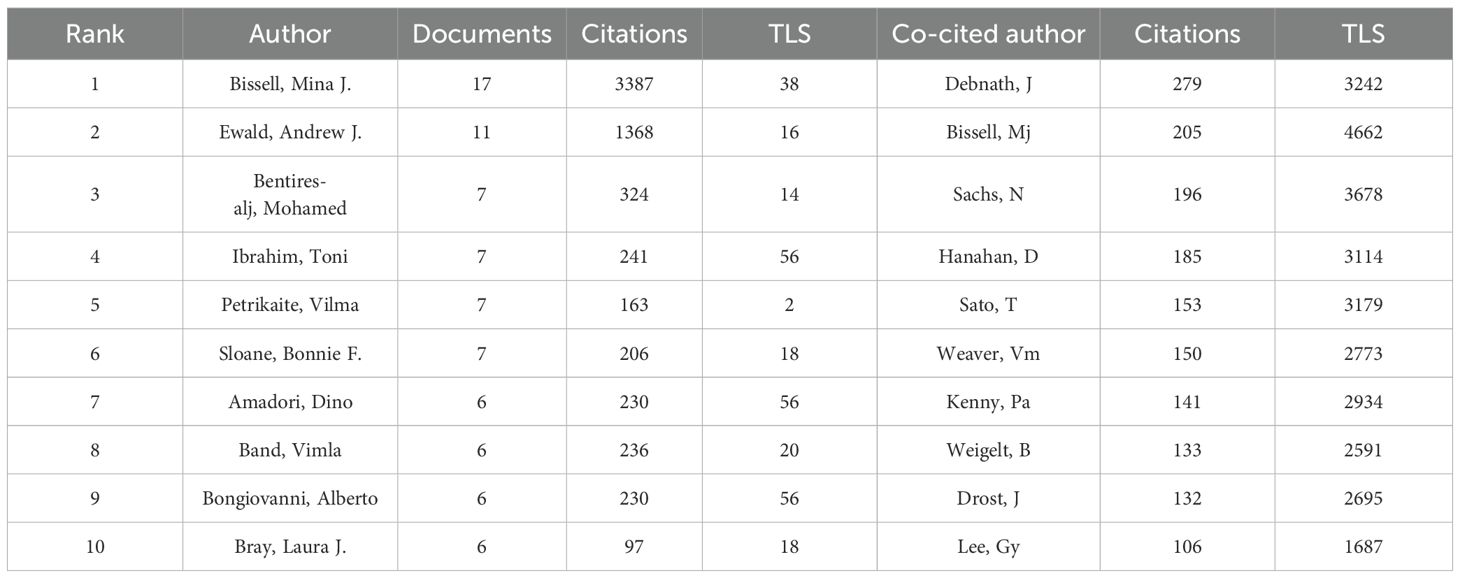
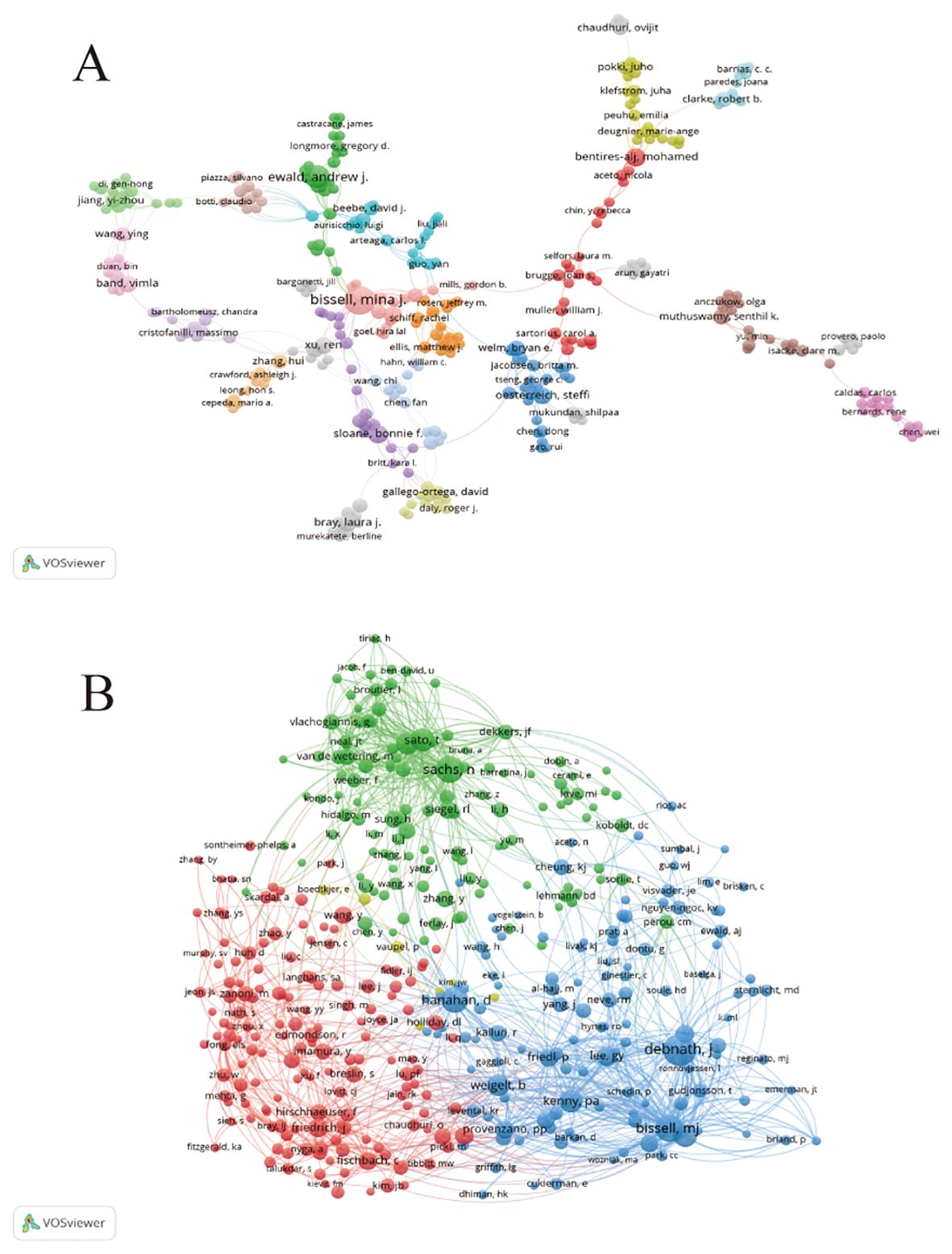
An analysis of the authors of publications on breast cancer organoid research gives us insight into the field’s representative scholars and core strengths. Table 3 lists the top ten authors in the field of organoid research. In terms of number of publications, from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Bissell, Mina J. With the largest number of published papers (17), followed by Ewald, Andrew J (11). Bissell challenged several established paradigms and was a pioneer in breast cancer research. Her work has provided much of the impetus for the current recognition of the important role that extracellular matrix (ECM) signaling and microenvironment play in the regulation of gene expression in normal and malignant cells, and she is also in the top 10 in terms of co-citations, indicating that he has made significant contributions and has a high reputation in the field. In addition to Bissell, Mina J. and Ewald, Andrew J. In addition, the number of papers published by other researchers is basically between 6 and 7, with little difference. Debnath, J., from the University of California, San Francisco, Parnassus Heights, has the most frequently cited paper. Overall, collaboration among authors has been more fragmented, and has been dominated by Bissell, Mina J. As the center. However, there is little collaboration among the top ten authors (Figure 4A). In the co-cited author network, the different colored parts reflect the same characteristics of the co-cited author research (Figure 4B). Except for the yellow group, which contained fewer researchers, the other three groups were evenly distributed in the number of research directions and were closely related to each other.
3.4 Journal analysis
To better understand the status of publications related to breast cancer organoids, we analyzed the publications of major journals in the field. As shown in Table 4, Cancer (impact factor 6.575, Q1) had the largest number of publications (n=46), followed by Cancer Research (impact factor 12.5, Q1), with 43 publications. In addition, 8 journals had impact factors (IF) of more than 1.5, mainly distributed in Q1 and Q2. This indicates that they all have a high academic reputation in the field. Research on breast cancer organoids shows a positive research trend and is more favored by journals with high impact factors. The most frequently cited journal is the American journal Cancer Research (impact factor 12.5, Q1), with a total of 3,671 citations, followed by the American journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (impact factor 9.4, Q1) and the American journal Cell (impact factor 45.5, Q1). These journals have an important position in the field of organoids.
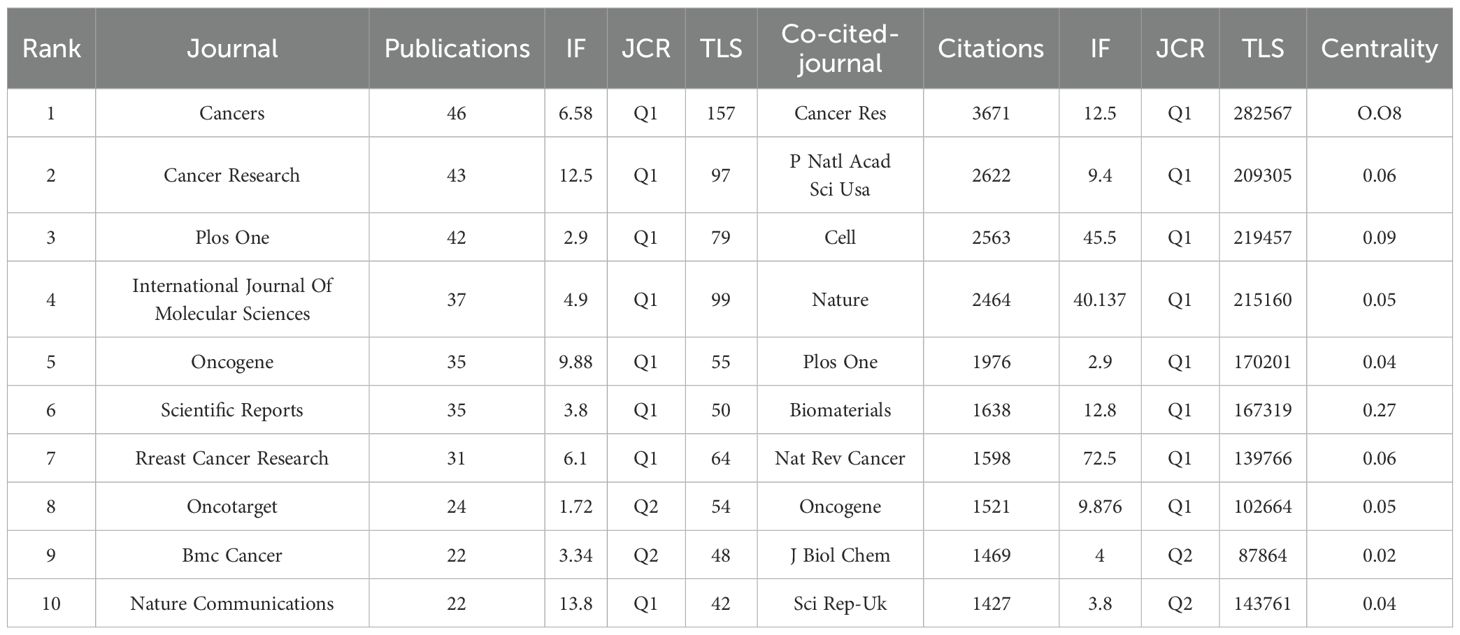
Table 4. The top 10 journals in terms of publication yolume, correlation strength and citation times.
Figure 5A shows the most cited journals, where there is some similarity between journals of the same color. Journals in red include the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Breast Cancer Research and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, which focus on organoid research in breast cancer. Blue journals such as Acta Biomaterials and Biomaterials focus on 3D culture such as Molecular Oncology, Cancer Research and the British Journal of Cancer focus on organoids in immunology. We can observe a strong association between these journals, suggesting that the various directions in organoid research complement and permeate each other. Each circle in (Figure 5B) represents a journal, and the size of the circle depends on the strength of the association and the number of citations. Journals with multiple co-citations indicate a strong association between them. For example, Nature, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Cancer Research have more common citations and influence. These journals are all related to breast cancer organoid culture raw materials, which indicates that this is the foundation of research in the field of breast cancer organoids.
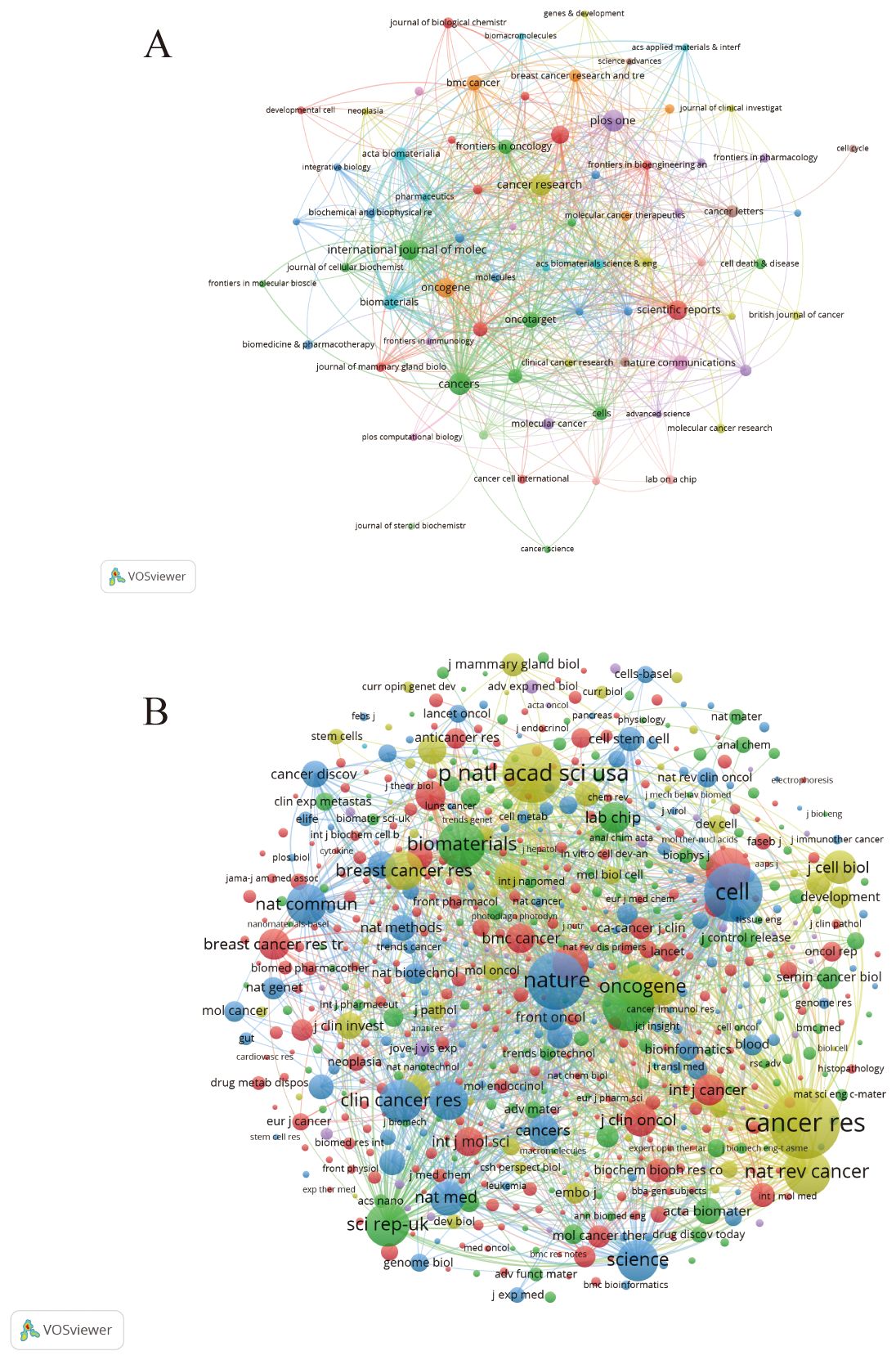
Figure 5. (A) Journals related to breast cancer organoids; (B) Co-cited journals related to breast cancer organoids.
3.5 Highly cited reference analysis
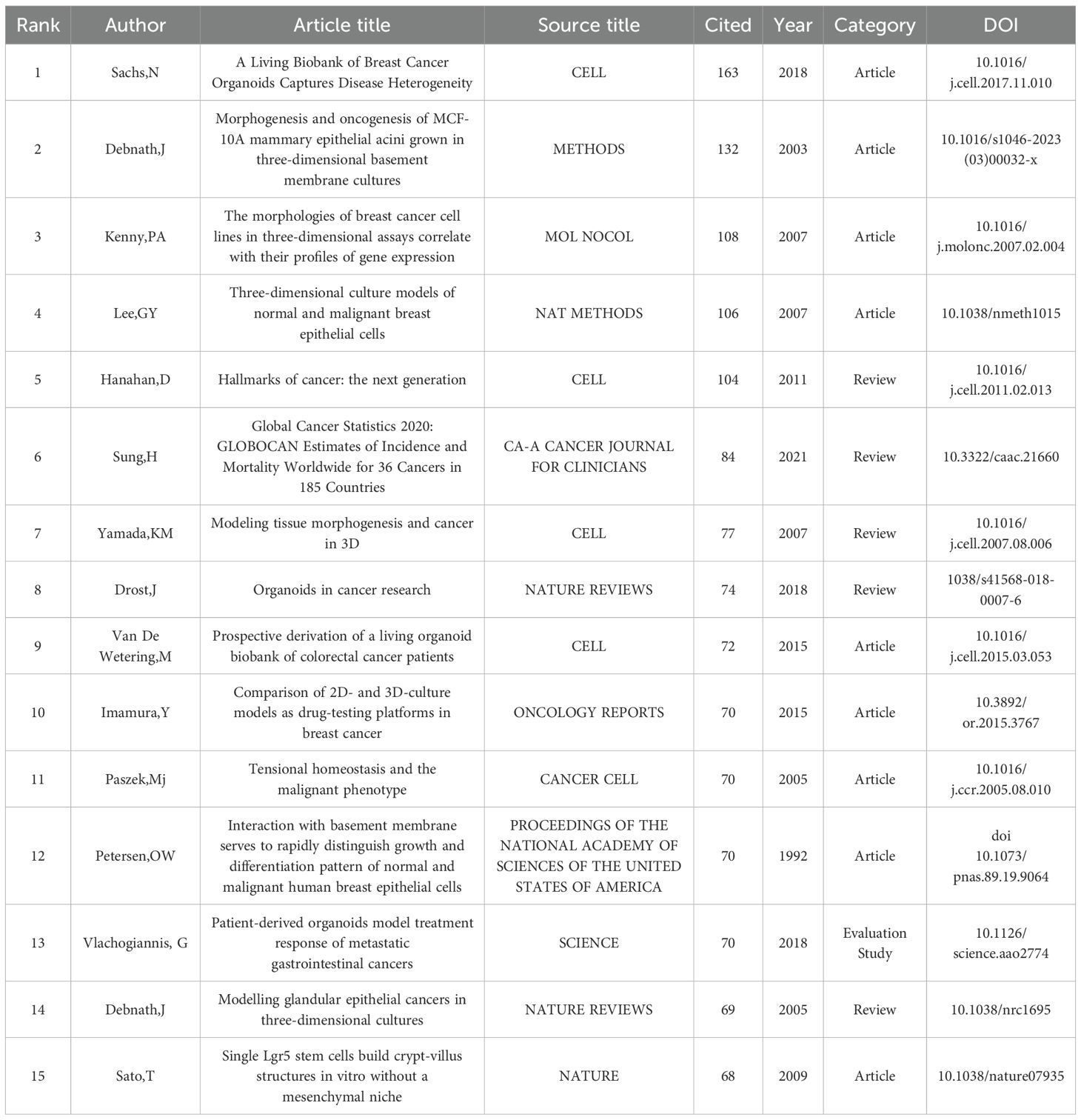
By analyzing the top 15 citations (Table 5) and the top 25 citations with the highest explosive power in organoid research (Figure 6A), we can detect the dynamic change of research direction in this field and provide an indication of future trends. We used CiteSpace software to divide the cited literature into different clusters to better outline the evolution of the topic in the field and the current research status of each research direction (Figure 6B). There are a total of eight different clusters. If the number of articles in a cluster is larger, its number is smaller. In this case, the largest cluster is the #0 cluster marked in red, representing the current status of breast cancer organoids, which is closely related to #4, representing the current research status of breast cancer organoids. From the year of publication of the articles represented by each cluster, we can get a rough idea of how organoid research has evolved.
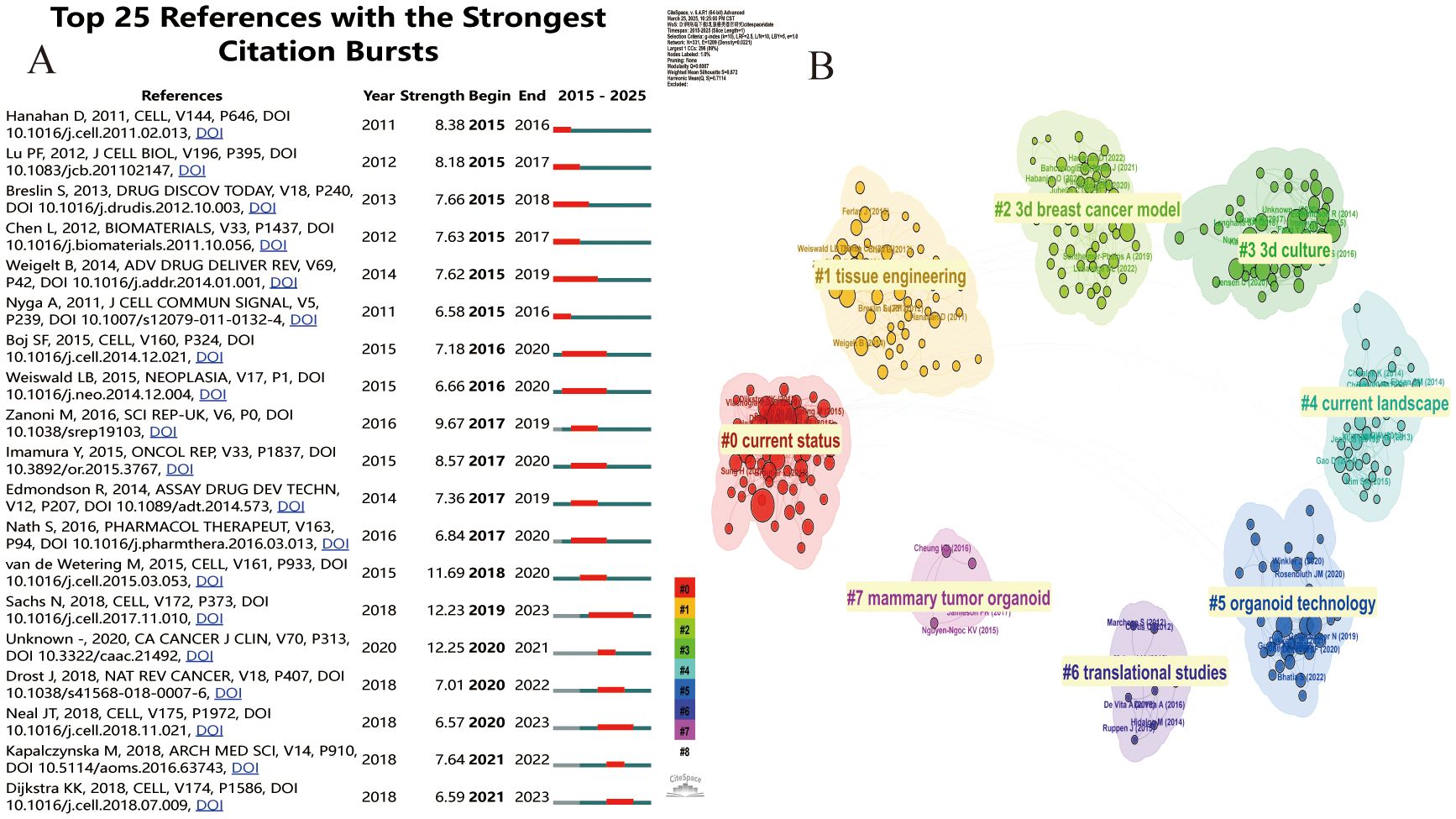
Figure 6. (A) Cite Space visualization map of the top 25 most frequently cited breast cancer organoids; (B) Cluster view of breast cancer organoids co-cited literature.
The most influential publications of the past two decades can be divided into early and recent sections. Early studies in this field focused on colony-forming units in #2current status and #19current landscape. During this period, Pengfei Lu et al (24) published that the local microenvironment of cancer cells plays an important role in cancer development. The extracellular matrix provides a theoretical basis for the construction of breast cancer organoids. May help develop new therapeutic interventions by targeting tumor niches. Agata Nyga et al (25) confirmed that 3D in vitro models have been used in cancer research, and 3D models can be customized to be bionic and can accurately summarize the natural in vivo scenarios in which they are found. These 3D in vitro models offer an important alternative, and ways to create more bionic 3D cancer models include, but are not limited to: (i) Provide appropriate matrix components in 3D configurations found in vivo, (ii) co-culture cancer cells, endothelial cells, and other associated cells in a spatially correlated manner, (iii) monitor and control hypoxia - mimicking levels found in natural tumors, and (iv) monitor the release of angiogenic factors by cancer cells in response to hypoxia. Building on previous research, in 2014 Britta Weigelt et al (26) used 3D culture models to reveal new pathways in breast cancer and identify accurate biomarkers. Recent high-impact articles relate to disease modeling using breast cancer organoid techniques. Two articles from 2020 cite 3D cultured breast cancer organoids that build better models of tumor response to drugs around cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) in the tumor microenvironment (TME), And it helps cancer researchers willing to use these models to study cancer biology and drug testing (27). And with the advent of human organoids, human organoids offer a unique opportunity to study human diseases and supplement animal models. Through the genetic engineering of human stem cells, human organoids have been used to study infectious diseases, genetic diseases and cancer, and can also be generated directly from patient biopsy samples (28).
3.6 Keyword analysis
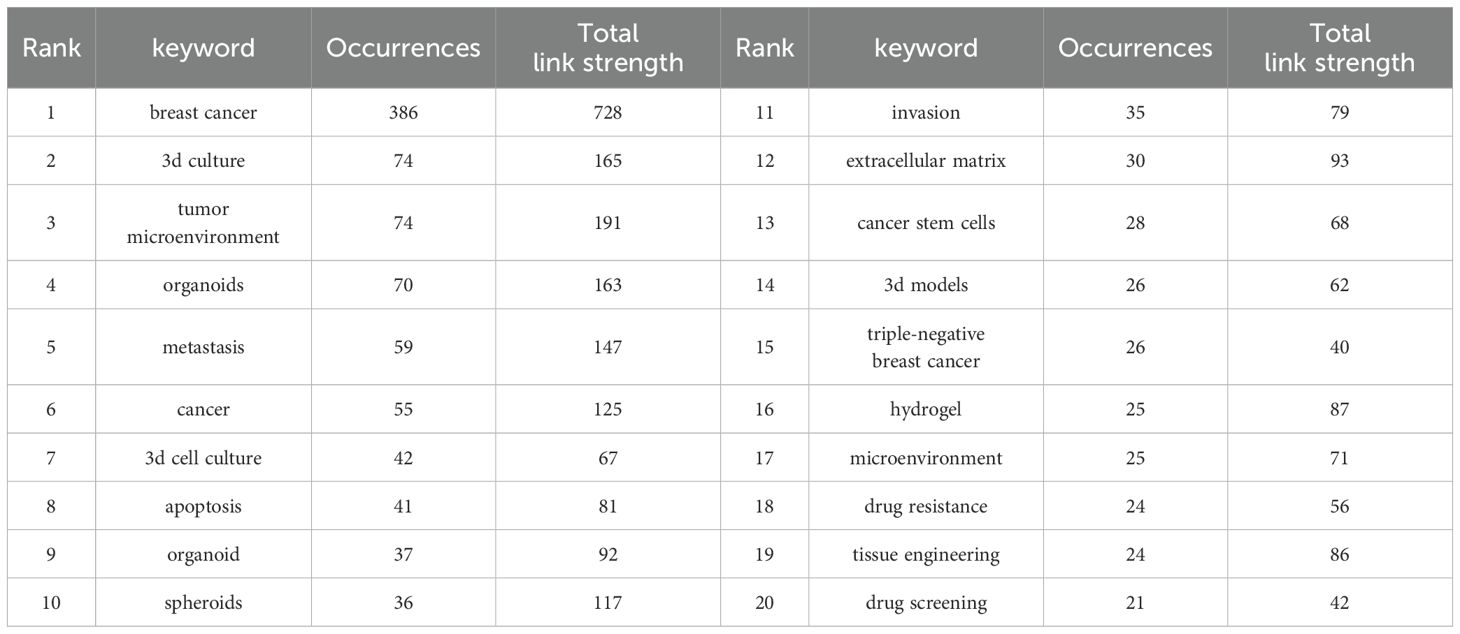
In bibliometrics, keyword analysis is one of the key indicators for frontier exploration in the research field. Table 6 lists the top 20 keywords that appear most frequently. These keywords are all related to each other in some way. Organoid construction techniques rely mainly on two types of core cell resources: adult stem cells (ASSCs) and pluripotent stem cell populations (including embryonic stem cell lines and induced pluripotent stem cell lines). The technology system needs to be coupled with key regulatory molecules, including matrix proteins that maintain the cell microenvironment, FGF family proteins that regulate developmental pathways, Wnt signaling ligands, and bone morphogenetic protein inhibitor Noggin. By integrating a three-dimensional bionic culture system, biomaterials engineering technology, and a microfluidic chip platform, researchers have successfully built a breast cancer organoid model. Such biosimulation systems show important value in basic medical research (analysis of pathological mechanisms), translational medicine applications (development and efficacy evaluation of novel drugs), and clinical practice (formulation of individualized treatment plans and precise tumor diagnosis and treatment).
The co-occurrence network diagram and superposition diagram of the author’s keywords can reveal the characteristics of the cluster distribution and time variation of the keywords. According to Figure 7A, VOSviewer shows eight major clusters of author keywords. Cyan cluster focuses on “tumor microenvironment”, “three-dimensional model” and “microfluidics”. The pink cluster mainly includes the aspects of personalized treatment and precision tumor diagnosis and treatment. In the purple cluster, apoptosis becomes the focus of research. The blue cluster is mainly related to “invasion” and “migration” related to organoids. The red cluster is mainly around “stem cells” and “biomolecular materials”. In Figure 7B, author keywords are displayed in different colors based on the average yearin which they appear. In recent years, terms such as “personalized treatment”, “immunotherapy”, “precision therapy”, “3d biopprinting”, and “stem cell” have frequently appeared, indicating the future research direction and hot spots in the field of breast cancer organoid research.
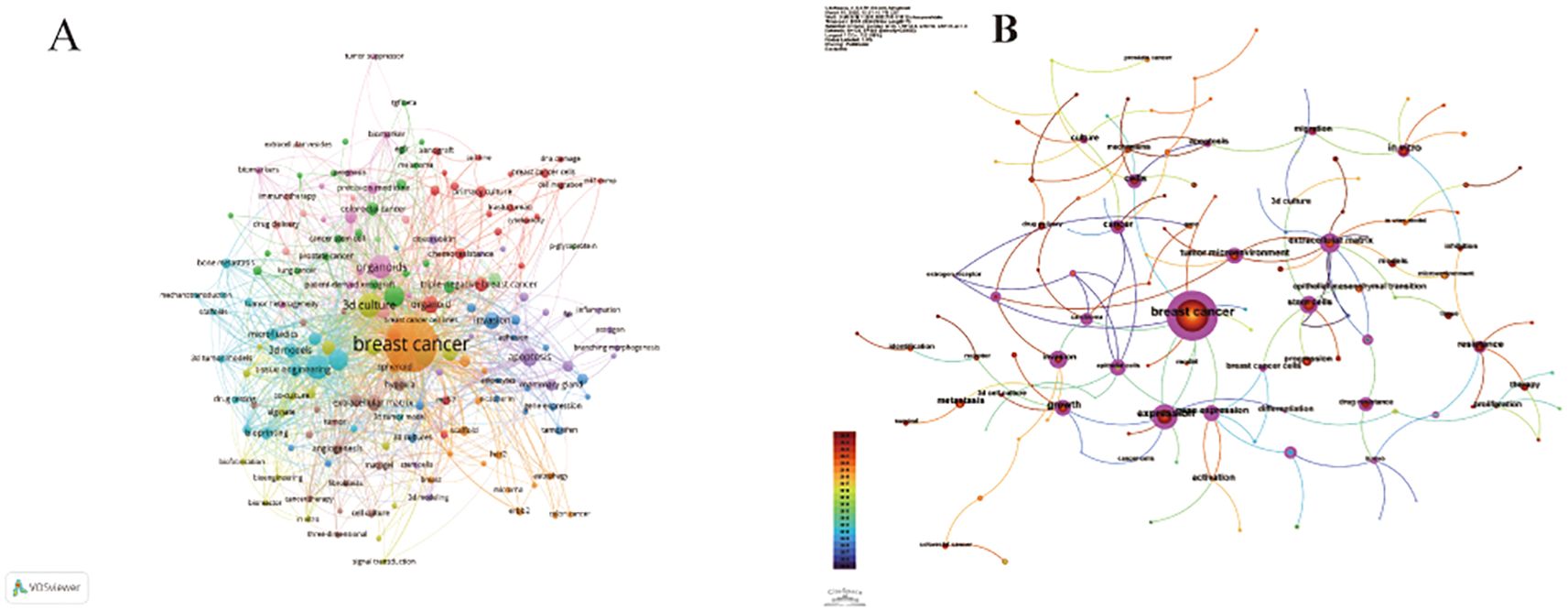
Figure 7. (A) Keyword co-occurrence analysis network cluster graph based on VOSviewer. The minimum keyword frequency threshold is 5. (B) Keyword contribution graph based on CiteSpace. Each keyword is represented as a node whose size is proportional to the frequency. The lines between the nodes represent the co-occurrence relationship. The distance between nodes indicates the degree of correlation, and the closer the distance, the higher the degree of correlation.
In Figure 8A, we also identify research hotspots by keywords with strong reference bursts. The burst of references to keywords like “gene expression,” “in vitro modeling,” “3d printing,” and “signaling pathway” continues, suggesting that these terms may translate into new research hotspots. In addition, we use CiteSpace to group keywords into different clusters to get a better overview of how the topic is evolving in the field and how much research is currently being done in each direction (Figure 8B). There are 10 different clusters in total. The greater the number of articles that belong to this cluster, the smaller its sequence number. In this case, the largest cluster is the red cluster #0 labeled as the extracellular matrix, which provides the basis for in vitro model studies of breast cancer organoids. #1 Cancer and #6 Breast cancer shed light on some of the fundamental research in breast cancer. The early areas of research were mainly reflected in the colony units formed in cells #7 and #8. The breakthrough study by Sato, T (5) published in Nature in 2009, revealed for the first time the unique self-organizing ability of intestinal stem cells labeled by the LGR5 gene. The study, titled “Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche, “activated the proliferative potential of LGR5-positive stem cells in vitro. It was successfully realized that single stem cells independently differentiated into intestinal organoids with crypto-villi polar structure without the support of mesenchymal microenvironment. This milestone achievement not only validates the intrinsic self-organization mechanism of epithelial stem cells, but also creates a paradigm of in vitro organoid model construction independent of stromal microenvironment, which lays an important theoretical foundation for subsequent organ regeneration research. As a core technology concept, “3D bioprinting “presents high frequency co-occurrence characteristics with sphere culture system and three-dimensional cell culture technology. By precisely constructing cell assemblies with spatial bionic microenvironments, this technique has become a key methodology for analyzing the mechanism of organ development and realizing the in vitro reconstruction of complex tissue structures, and its technical relevance has been particularly prominent in recent organoid research papers. The network cluster diagram (Figure 8C) shows the evolution process of each cluster by marking the first occurrence time of each keyword. At present, the most frequently used cluster is #6 breast cancer, while #0 extracellular matrix and #6 breast cancer are among the earliest research directions. Keyword time zone (Figure 8D) shows the changes in the research direction and hot spots of breast cancer organoids through the keywords that appear in each year, and reveals the focus of research in the field of breast cancer organoids.
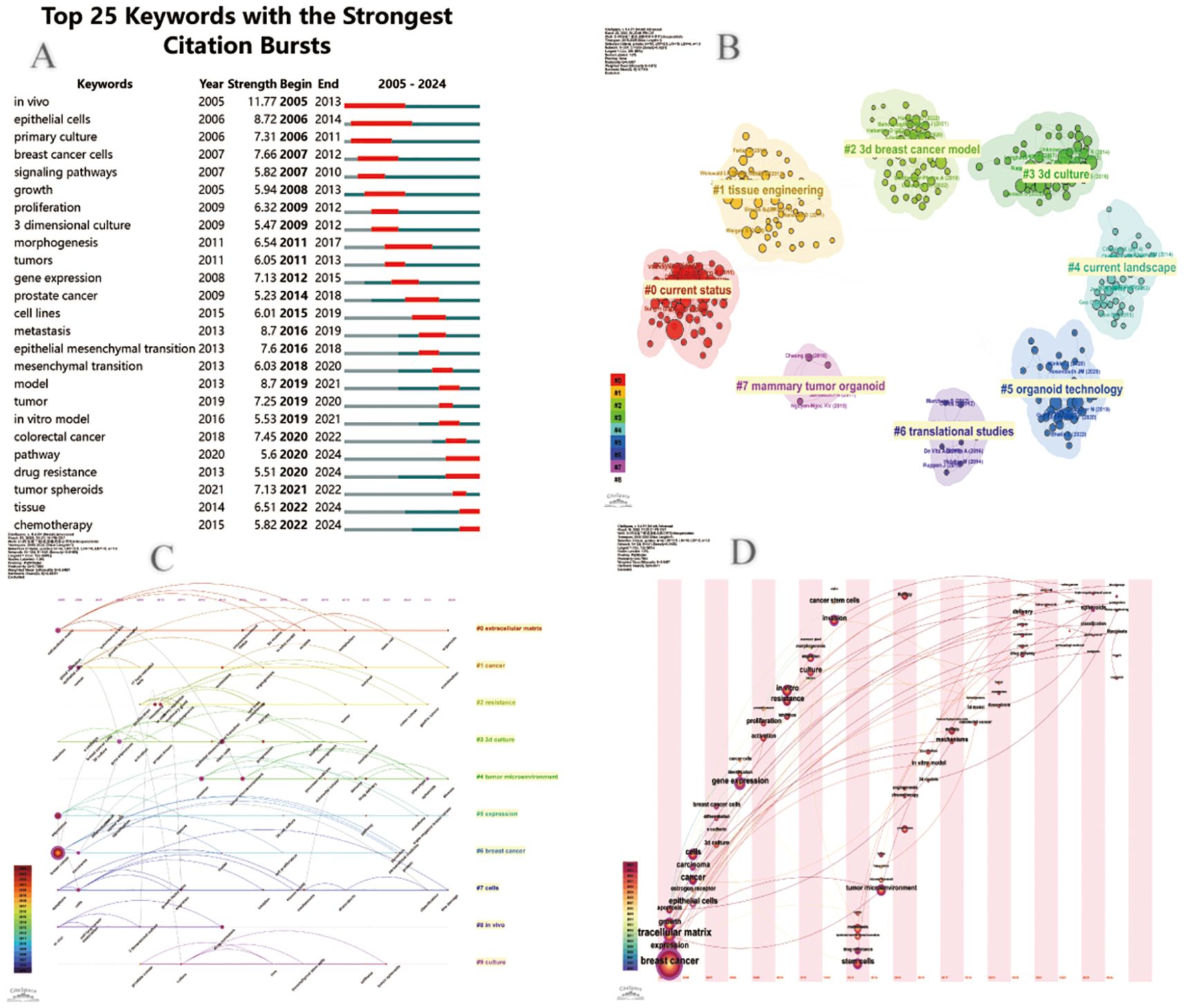
Figure 8. (A) Cite Space visualization map of the top 25 most frequently cited breast cancer organoids; (B) Cluster view of breast cancer organoids co-cited literature; (C) Timcline view of key words of breast cancer organoids; (D) Time zone view of breast cancer organoid keywords.
4 Discussion
Keyword analysis helps us identify the current hot research directions in the field of breast cancer organoids (Figure 9). These keywords can be divided into four categories: raw materials for organoid culture, organoid culture technology, organoid application, and the type of organoids produced. According to the keyword overlay map, the latter two are the most popular areas of recent research: the application of organoids (drug screening, personalized medicine, precision medicine) and the type of organoids being cultured (patient-derived organoids, 3d printed organoids). These topics are likely to be crucial for future research.
4.1 Major achievements in breast cancer organoid research (based on bibliometric evidence)
4.1.1 Successful establishment and application of patient-derived organoids
The application of breast cancer organoids has emerged as a significant research domain. This technology facilitates the testing of diverse anti-cancer therapeutics and guides personalized cancer treatment strategies. By modeling tumorigenesis in vitro, these systems enable researchers to observe the entire process of cancer initiation, infection (where applicable), and mutation. Furthermore, organoid technology provides physiologically relevant in vitro models capable of elucidating the relationships between infectious agents (e. g. , viruses like HPV or EBV potentially linked to some cancers) and cancer development. Contemporary breast cancer research has historically relied heavily on in vivo models and traditional two-dimensional (2D) cell culture techniques. However, these approaches frequently suffer from high failure rates in clinical translation, largely attributable to interspecies differences and the loss of native tissue architecture. To address these limitations, 3D culture systems utilizing organoids—structures that closely recapitulate organ-like morphology and function—have emerged as a highly promising alternative, as pioneered by researchers like Yen-Dun Tony Tzeng et al. (29)Significantly, Ping Chen et al. (30) demonstrated that patient-derived organoids (PDOs) serve as an effective platform for the in vitro assessment of patient-specific drug sensitivity, thereby providing critical data to guide personalized treatment decisions for patients with advanced breast cancer. Moreover, Chen Ping et al. (30) highlighted the utility of breast cancer organoids in modeling the complex breast cancer tumor microenvironment (BC-TME). Their research revealed that the BC-TME possesses distinct cellular composition and spatial heterogeneity, factors of profound clinical significance that critically influence therapeutic response.
Researchers have begun exploring the suitability of breast cancer organoids for high-throughput drug screening (HTS) platforms. Typically, these screening procedures aim to simulate clinically applied therapies and are particularly valuable for rare diseases where large-scale clinical trials are unfeasible. The technology enables assessment of the predictive capacity of organoids for drug response by comparing patient outcomes with the responses observed in their matched patient-derived organoids (PDOs).Significant efforts have been dedicated to validating the feasibility of utilizing breast cancer organoids in drug screening applications. For instance, Katrin P. Guillen et al. (31) leveraged matched patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) and PDX-derived organoids (PDxOs) for drug screening. Using a case of early metastatic recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), they demonstrated the feasibility of employing these models for real-time clinical decision-making in precision oncology. This work underscores the substantial potential of breast cancer organoids in predicting drug response.
Breast cancer organoids also enable standardized screening applications. For instance, Zhuolong Zhou et al. (32) employed a high-throughput screening (HTS) platform based on the functional interaction between murine or patient-derived mammary tumor organoids and tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells. This approach facilitated the identification of epigenetic inhibitors that promote antigen presentation and enhance T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Critically, the standardized measurement of tumor cell-killing activity afforded by this tumor-organoid-T cell co-culture screening system holds significant promise for identifying candidate immunotherapeutic agents across a range of cancers. Furthermore, breast cancer organoids serve as valuable tools for investigating anti-tumor immune responses. For example, Tengku Ibrahim Maulana et al. (33) integrated primary breast cancer organoids to evaluate the efficacy of patient-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. Their work demonstrates the potential of this platform for broad application in bench-to-bedside translation, thereby accelerating the preclinical development of CAR-T cell products. Similarly, Cai-Ping Sun et al. (17) highlighted the utility of tumor organoid models in facilitating preclinical immunotherapy trials. These models achieve this by either (1): preserving endogenous stromal components, including diverse immune cell populations, or (2) incorporating exogenous immune cells to simulate immunotherapy responses in vitro.
Breast cancer organoids serve as powerful platforms for novel drug discovery and identifying patient populations likely to benefit from specific (including existing) therapeutics. For instance, employing breast cancer organoids to validate genomically-driven targeted therapies could significantly aid in selecting personalized drugs for individual patients. Supporting this, Maryam Arshad et al. (34) demonstrated the potential efficacy of neratinib alone or in combination with trastuzumab in HER2-low breast cancer cell and organoid models, providing valuable insights and direction for future research. Additionally, breast cancer organoids are instrumental in exploring potential combination therapies. As exemplified by Sergey V. Nikulin et al. (35), these models were utilized to identify 3,3’-Diindolylmethane (DIM) as a potent microRNA-21 antagonist. This discovery offers novel mechanistic insights and suggests avenues for potentially beneficial chemotherapeutic combinations. Furthermore, breast cancer organoids enable pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) assessments. In their study, Kristen M. Van Eaton et al. (36) employed organoid models to evaluate hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)-mediated effects on autophagy inhibition, cell proliferation, and cell death, aiming to delineate the role of autophagy in standard anticancer therapies.
Breast cancer organoids also hold potential for applications within nanotechnology. As reviewed by Paz Boix-Montesinos et al. (37), strategies aimed at overcoming limitations in traditional cell culture—including co-culture systems, advanced 3D cell culture, patient-derived cells, bioprinting, and microfluidics (MF)—were explored. Their analysis further proposes the promising development of cancer nanomedicines utilizing breast cancer organoid platforms’ Pranav et al. (38) demonstrated that breast cancer organoids retain the functional physiology of solid tumors, including native gene expression profiles. Critically, the utilization of patient-derived organoids (PDOs) for in vitro testing provides crucial support for realizing personalized treatment strategies. Supporting this, Norman Sachs et al. (6) established a well-characterized, representative biobank of breast cancer organoids for cancer research and drug development, coupled with strategies to assess in vitro drug responses in a personalized manner. Similarly, Sonam Bhatia et al. (39) highlighted that PDO models recapitulate the intrinsic properties of patient tumors. Specifically, triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) PDOs serve as robust models for understanding breast cancer biology and progression, thereby paving the way for individualized medicine and tailored therapeutic regimens.
Significant progress has also been made using breast cancer organoids in precision medicine. Cai-Jin Lin et al. (18) revealed, through functional validation in patient-derived organoids, tumor fragments, and in vivo models, that precision therapeutic strategies informed by co-occurring alterations hold promise for improving patient outcomes. Furthermore, K Ding et al. (40) leveraged integrative bulk and single-cell analyses of primary tumors and matched PDOs to unveil intra-tumoral heterogeneity, evolutionary trajectories, and actionable therapeutic opportunities for precision medicine. Despite these advances, several limitations persist. Current organoid systems often fail to ideally recapitulate the intricate gene networks and interactions within mature organs, frequently exhibiting immature or “fetal-like” characteristics. This immaturity may constrain their ability to accurately model complex disease phenotypes, particularly those associated with late-onset disorders. Moreover, the long-term culture and maintenance of organoids remain technically complex, especially in the absence of a fully reconstituted native microenvironment, often leading to tissue degradation and loss of function. Additionally, the inherent heterogeneity within and between breast cancer organoid lines can confound data interpretation and potentially impact the reliability of drug screening outcomes.
4.1.2 Advances in modeling tumor microenvironment and immune interactions
Beyond genetic alterations within tumor cells themselves, the microenvironment—composed of diverse non-epithelial cell types, immune cells, and stromal cells—plays a crucial role in tumor growth and eventual metastasis. Conventional tumor models (e.g., 2D cell lines, patient-derived xenografts (PDX)) are severely limited in their ability to dissect the mechanisms of immunotherapy due to their failure to recapitulate the multicellular interactive ecosystem of the tumor microenvironment (TME). Recent breakthroughs in immune-enhanced patient-derived organoids (Immuno-PDOs) have enabled dynamic simulation of the TME by integrating tri-culture systems of tumor cells, stromal cells, and immune cells, providing a revolutionary platform for immunotherapy development. Achieving Functional Reconstruction of Core TME Components. Shijia Liuyang et al. (41) constructed a “TME-on-Chip” microfluidic system modeling tumor-stroma interactions. This system co-cultured patient-derived organoids (PDOs), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and endothelial cells within a biomimetic matrix (a collagen/Matrigel hybrid scaffold). Their study demonstrated that CAFs, through the secretion of IL-6 and HGF, activated the EGFR-MAPK signaling pathway in tumors, thereby inducing chemotherapy resistance. Critically, targeting CAFs (e.g., with FAK inhibitors) restored drug sensitivity. This model reproduced, for the first time in vitro, the CAF-mediated physical barrier function (via collagen fiber remodeling), elucidating the underlying mechanism of immune exclusion in pancreatic concordance Sun et al. (42) developed an “Immuno-organoid” platform by co-culturing patient-derived organoids (PDOs) with autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), supplemented with key cytokines (IL-2, IL-15, IFN-γ) to maintain immune cell viability. Spatiotemporal dynamic monitoring revealed that PD-1 inhibitors promoted the infiltration of CD8+ T cells into the organoid core and facilitated the formation of tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS)—a key histological correlate predictive of response to immunotherapy.
Johanna Englund et al. (43) summarized recent advances in tools and models for breast cancer organoids, covering key aspects such as hormone signaling, tissue architecture, tumor microenvironment (TME), and species-specific mammary gland development, thereby significantly advancing the field. Johanna F. Dekkers et al. (43) employed clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-Cas9 to knockout four breast cancer-associated tumor suppressor genes (TP53, PTEN, RB1, and NF1) in mammary progenitor cells derived from six donors. The genetically modified organoids acquired long-term proliferative capacity and, upon transplantation into mice, formed estrogen receptor (ER)-positive luminal tumors. These breast cancer organoid models exhibited responses to endocrine therapy and chemotherapy. Furthermore, using three triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) lines and four patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models, the study enabled systematic evaluation of tumor latency, growth, and metastasis, offering novel insights for immunotherapy research design and paving the way for patient-specific drug development to ultimately improve clinical outcomes (44). Kelvin K. Tsai et al. (45) leveraged breast cancer organoid models to demonstrate that elevated NCOR2 expression in patient tumors predicts chemotherapy refractoriness, tumor recurrence, and poor prognosis. Their work revealed that targeting the stress- and inflammation-repressing NCOR2-HDAC3 complex could overcome therapy resistance and enhance patient survival. Michael U.J. Oliphant et al. (46) established patient-derived ER+ breast cancer organoid models, providing a robust platform to investigate treatment responses and disease progression in ER+ breast cancer. In 2016, Boussommier-Calleja et al. (47) proposed that microfluidic systems could replicate the complex TME to study tumor-immune interactions. The researchers first analyzed the cellular composition of primary tumors and micro-tumor arrays using flow cytometry.
4.1.3 Integration of 3D bioprinting and advanced engineering technologies
The 3D model in breast cancer organoid technology is the core carrier that simulates the structure, function and pathological features of human organs through an in vitro three-dimensional culture system. Its construction breaks through the limitations of traditional 2D cell culture and provides a revolutionary tool for disease research, drug development and regenerative medicine. Although mouse models and two-dimensional (2D) cell culture systems have become research tools in cancer biology, three-dimensional (3D) culture has gained appeal as a new approach that retains the characteristics of in vivo biology within in vitro systems. Over time, 3D culture systems have evolved from spheres and tumor spheres to organoids, and by doing so, they have become more complex and better representative of primitive tissues. Eleonore Frohlich et al. (48) believe that compared with traditional 2D culture, 3D cancer models can better represent tumor physiology. The important components of 3D models related to physiology were summarized, and the spectra of 3D breast cancer models, such as spheres, organoids, breast cancer on chips and bioprinter tissues, were described. The generation of spheres is relatively standardized and easy to implement. Microfluidic systems allow for the control of the environment and include sensors, which can be combined with spherical or bioprinter models. The intensity of bioprinting depends on the spatial control of cells and the regulation of extracellular matrix. In addition to the main uses of breast cancer cell lines, these models differ in terms of stromal cell composition, matrix and fluid flow.
Recent years have witnessed rapid advancements in 3D in vitro models using breast cancer organoids. Anamitra Bhattacharya’s research (49) highlights the critical importance of developing 3D in vitro models that recapitulate the complex architecture and physiology of breast tumors. Compared to scaffold-dependent 3D models, scaffold-free in vitro disease models better simulate breast cancer pathophysiology by enabling cellular self-assembly/patterning into 3D structures. These models—particularly when incorporating patient-derived primary cells (fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and cancer cells)—demonstrate potential for accurately replicating observed tumor heterogeneity. They also serve as powerful tools for investigating disease molecular mechanisms, identifying novel therapeutic targets, and evaluating treatment modalities. Nakka Sharmila Roy et al. (50) characterized various mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)- and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived 3D breast cancer models that emulate tumor biology, aiming to elucidate potential therapeutic targets. They emphasized that cell- and patient-derived 3D organoid models can advance personalized medicine and accelerate drug discovery pipelines. Natalija Glibetic et al. (51) evaluated state-of-the-art tools for studying cancer metabolism in 3D culture systems, including: Optical Metabolic Imaging (OMI),Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MALDI-MSI),Recent advances in conventional techniques adapted for 3D cultures. Their work further explored progress in identifying and targeting metabolic vulnerabilities for breast cancer therapy. Cristiano Ceron Jayme et al. (52) leveraged 3D organoid cultures to mimic the tumor microenvironment (TME) observed during early human breast cancer progression. This approach enables photo diagnostic strategies for early-stage detection at initial progression phases. It paves the way for on-demand bioprinting of patient-specific organ surrogates, propelling oncology into an era of closed-loop “Design-Validate-Treat” therapeutic paradigms.
The model system for tumor research has gradually matured, with its core lying in more accurately simulating the complexity of human tumors. The successful establishment of patient-derived organoids (PDOs) provides a powerful personalized platform, preserving the key genomic and pathological features of the patient’s tumor, and greatly promoting the exploration of drug sensitivity testing, biomarker discovery, and individualized treatment strategies. Meanwhile, significant progress has been made in modeling the tumor microenvironment (TME) and immune interactions. Researchers are integrating multiple cell types (such as immune cells, fibroblasts, and vascular endothelial cells) and complex biochemical signals to reproduce the dynamic processes of immunosuppression, immune escape, and immunotherapy response in PDOs or more advanced co-culture models. To further enhance the structural mimic ability and controllability of the model, the deep integration of 3D bioprinting with advanced engineering technologies (such as microfluidic chips, intelligent biomaterials, and mechanical force regulation) plays a crucial role, achieving precise construction and manipulation of the TME spatial structure, matrix stiffness, nutrient/drug gradients, and dynamic fluid environment. These three fields - personalized PDOs models, complex TME/immune modeling, and engineered 3D bioprinting platforms - are interwoven and mutually reinforcing, jointly deepening the understanding of tumor biology, accelerating the development and evaluation of novel therapies, and paving the way for more precise and predictive tumor research.
4.2 Persistent challenges and future frontiers (identified through bibliometric trends)
4.2.1 Organoid vascularization
Vascularization of tumor organoid models has emerged as a cutting-edge research focus in recent years, with its core challenge lying in the dynamic regulation of neovascularization on drug delivery within the heterogeneous tumor microenvironment (53). Conventional organoid models fail to recapitulate the reduced drug penetration efficiency caused by the tumor vascular barrier due to the absence of a functional vasculature. This results in significant discrepancies between in vitro drug sensitivity assays and clinical responses, underscoring the necessity of developing vascularized tumor organoids (VTOs) for precision drug evaluation.
The key bottleneck currently faced in the field of organoid research lies in the limitations of material transport efficiency within the in vitro culture system - specifically manifested as the inefficient diffusion of nutrients and the retention of metabolic products. These physical barriers severely restrict the developmental maturity and functional expression of organoids. To address this scientific challenge, the bionic vascular network construction strategy can significantly enhance the efficiency of material exchange and prolong the survival period of organoids by simulating the physiological microcirculation system. The current mainstream vascularization technologies mainly include two research directions: In terms of in vitro construction strategies, three-dimensional biomanubicin technology has achieved in vitro reconstruction of engineered vascular networks by precisely positioning the spatial arrangement of endothelial cells and other functional cells. This technology preplaces vascular structures in target tissues through a layered printing process, especially demonstrating advantages in the construction of myocardial tissues (54) and Mark vessels (55). In the in vivo induction pathway, the microenvironment of the transplanted host can activate the natural angiogenesis mechanism and achieve the self-assembly process of the functional vascular network through the complex cellular interaction between the host and the graft. It is worth noting that microfluidic chip technology, as an emerging platform technology (56), has successfully simulated the three-dimensional microenvironment characteristics of capillary networks in vitro, providing an innovative solution for studying the mechanism of angiogenesis and optimizing the organoid culture system.
However, the biomimetic construction of physiological vascular networks faces multiple technical barriers (57):The aberrant branching, disordered spatial topology, and leaky endothelial phenotype characteristic of tumor vasculature require dynamic spatiotemporal control over extracellular matrix-endothelial interfaces at the micron scale. This critically constrains organoid growth dimensions and structural complexity. Effective coupling of capillary beds with tumor parenchyma demands not only structural fusion but also precise coordination of biochemical-biomechanical signaling networks, Gradients of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)Spatiotemporal pericyte recruitment Hemodynamic Force Deficiency: Static culture systems fail to replicate the regulatory effects of hemodynamic shear stress on vascular maturation. This absence of mechanical signaling directly compromises modeling fidelity for critical pathological processes such, Current models cannot adequately simulate tissue-specific drug penetration barriers, leading to inaccurate predictions of drug bioavailability. These collective bottlenecks fundamentally hinder the translational application of vascularized tumor models in key research areas like: Anti-angiogenic therapy development Nanomedicine delivery optimization.
4.2.2 Standardized integration of the complex immune microenvironment
Currently, the organoid field is garnering increasing attention. The advancement of tumor organoid models hinges on reconstructing dynamic interaction networks between malignant cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME). However, conventional approaches face dual barriers: Deficient Immunologic Niches: >90% of tumor organoids contain only epithelial cancer cells, lacking critical immune components such as CD8+ T cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). This limitation precludes modeling of immune checkpoint blockade responses. Lucie Thorel et al. (58) established the first autologous immune cell-tumor organoid co-culture system, whose clinical implementation holds significant implications for the future of precision oncology. Stromal Biomechanical Distortion: The elastic modulus of Matrigel (2–4 kPa) is substantially lower than that of metastatic foci (8–12 kPa), resulting in attenuated invasive phenotypes. Research by Bauer L. LeSavage demonstrates (59) that engineered matrices combined with patient-derived organoids provide compelling evidence for elucidating how extracellular matrices influence human disease pathophysiology.
Cancer immunotherapies targeting the immune TME show growing validation in clinical trials, yet exhibit dramatically divergent response rates across tumor histologists responses are often transient, idiosyncratic, and confounded by acquired resistance. experimental models capable of recapitulating patient-specific tumor-immune microenvironments—faithfully mirroring tumor biology and immunotherapy effects—would substantially improve: Patient stratification for immuno-oncology Therapeutic target identification and Definition of resistance mechanisms. Such models pave the way for organoid-based immuno-oncology research, drug development, and personalized precision medicine.
4.2.3 Manufacturing cost, throughput and standardization
Currently, as global research in the organoid field deepens, the associated costs are substantial and often underestimated. Key drivers include: 1. Dependence on expensive growth factors in culture media. 2. Increased experimental consumption due to batch-to-batch variability of natural matrices (e.g., Matrigel™). 3. The need for continuous acquisition of patient samples for personalized modeling. 4. The inherent difficulty in scaling production of patient-specific models. Regarding cost control: Traditional organoid culture heavily relies on costly biological reagents and matrices with significant batch variation. Adriana Mulero-Russe et al. (60) reported a promising approach using synthetic polyethylene glycol-laminin (PEG-laminin) hydrogels. This technology not only reduces matrix costs but also minimizes batch variability to <5% through tunable mechanical properties, thereby significantly enhancing the reproducibility of drug screening assays.
Significant throughput enhancement relies on the deep integration of automation and artificial intelligence. Current manual workflows typically process <100 samples per week, and the analysis of high-content imaging data from 3D organoids remains inefficient (61). Carlos A. Tristan et al. (62) established a robotic platform capable of automating all essential steps for hips culture and differentiation under chemically defined conditions. This approach enables the rapid and standardized production of billions of hiPSCs, allowing parallel generation from up to 90 distinct patient- and disease-specific cell lines. Moreover, Alexandra Sockell et al. (63) developed a microwell-based method enabling high-throughput quantitative analysis of image parameters from single-cell-derived organoids. Crucially, these organoids can be subsequently retrieved from their microwells for molecular profiling, facilitating the precise identification of drug-induced subpopulation heterogeneity.
The absence of standardized protocols stems primarily from the lack of unified quality control (QC) systems. Significant variations in passaging procedures and functional assessment methodologies across different laboratories hinder cross-study data comparability. To enable real-time monitoring of culture quality, Johannes Dornhof et al. (64) developed a microfluidic QC chip integrating glucose, lactate, and pH sensors. This system automatically triggers alerts when microenvironmental parameters deviate from set thresholds (e.g., pH > 7.8), thereby preventing functional drift in the organoids. Notably, pioneering progress in standardization has been achieved for high-throughput drug screening (HTS) using breast cancer organoids. Yichun Wang et al. (65) successfully implemented 3D cell culture technology for HTS, demonstrating its utility in drug discovery and development pipelines.
With the implementation of these engineering strategies—establishing standardized protocols, reducing reagent costs, and enhancing both culture success rates and throughput—organoid technology is poised for gradual maturation towards industrial translation. This convergence of advancements enables robust, cost-effective, high-throughput platforms capable of meeting the demands of industrial-scale applications.
4.2.4 Long-term cultivation and maturity
Over the past two decades, organoid technology has advanced rapidly, demonstrating significant potential for modeling human diseases, particularly cancers. However, key challenges remain. A primary limitation in organoid model development is that most organoids fail to fully recapitulate the mature gene networks of adult organs during long-term culture. Instead, they frequently exhibit embryonic or fetal gene expression signatures. For instance, Toshiro Sato and colleagues (5) demonstrated that excessive Wnt pathway activation leads to sustained expression of stem cell markers like LGR5 in intestinal organoids. Lineage tracing experiments further revealed that the Lgr5+ stem cell hierarchy remains largely static within these organoids. This immature state is manifested by high expression of fetal-type transcription factors and aberrant metabolic pathways. Consequently, such organoids are often inadequate for accurately modeling late-onset complex diseases. Similarly, Yuan Guan et al. (66), aiming to investigate the pathogenesis of congenital hepatic fibrosis, designed human liver organoids to study autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). These liver organoids persistently expressed fetal markers AFP and DLK1, while lacking the adult hepatocyte marker CYP3A4.Moreover, while the advent of three-dimensional human brain organoids by Mario Yanakiev et al. provides a unique opportunity to study Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in human-relevant model systems, conventional brain organoids lack an aging microenvironment and fail to spontaneously develop β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques.
Furthermore, maintaining long-term organoid functionality faces challenges due to microenvironmental deficiencies. These include inadequate vascularization and lack of biomechanical cues (67), as well as organoid destabilization resulting from cumulative cellular stress (68). Such deficiencies can lead to the disintegration of tissue architecture. For instance, Kouki K. Touhara et al. (69) demonstrated that oxidative damage and telomere shortening cause the loss of the characteristic crypt-villus structure in intestinal organoids, ultimately compromising the reliability of drug response predictions. To address these limitations, researchers are developing innovative strategies:Jingsi Yang et al (70). engineered 3D-bioprinted endothelialized channels within organoids to enhance oxygen/nutrient delivery and improve microenvironmental maintenance. Ricardo Cruz-Acuña et al (71). developed polyethylene glycol-laminin (PEG-laminin) hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties, aiming to enhance the reproducibility of drug screening assays.
Finally, breast cancer organoids often retain the high heterogeneity of the patient’s original tumor, including the coexistence of subclones with distinct molecular profiles (e.g., HER2+/ER+) (6). However, K. Ding, and colleagues (40) demonstrated through scRNA-seq and ATAC-seq profiling of 50 breast cancer organoid lines prior to drug screening that HER2+/ER- subclones can selectively expand during culture. This expansion can lead to false-negative responses to anti-estrogen therapies. Crucially, without validation using single-cell sequencing or spatial transcriptomics, drug screening results may misrepresent the true sensitivity to targeted therapies, potentially overlooking resistant subpopulations. To address this critical challenge of dynamic heterogeneity, Johannes Dornhof et al. (64) developed a microfluidic organ-on-a-chip platform enabling matrix-based heterogeneous 3D culture. This system allows dynamic tracking of differential drug responses by integrating live-cell imaging with single-cell secretome profiling.
4.3 Cooperation and data sharing
Future progress in organoid technology will be critically driven by intensified international collaboration. The dominant partnership between the United States and China—which collectively account for ~50% of publications in this field (Table 1)—is emerging as a key force propelling breast cancer organoid research. Institutional network analysis (Figure 3A) reveals Harvard University as a central hub, demonstrating strong existing collaborations with US institutions (e.g., UC Berkeley, UCSF) and forging nascent partnerships with Chinese centers (e.g., Shanghai Jiao Tong University). However, interactions between institutions from diverse regions remain limited. To overcome translational barriers, we urge the strategic expansion of multinational consortia—particularly among top-producing nations (US, China, Germany, UK, Italy)—to integrate complementary resources, accelerate technical standardization, and validate findings across diverse patient populations.
Concurrently, deep interdisciplinary integration is paramount. Breakthroughs demand synergistic expertise from: 1. Biologists elucidating tumor heterogeneity and signaling pathways; 2. Engineers developing advanced 3D bioprinting, vascularization, and microfluidic systems (addressing Challenges 1–2 outlined in Section 4.2); 3. Clinicians ensuring physiological relevance and clinical applicability of models. Furthermore, prioritizing open science initiatives is essential to transcend research silos. This requires: 1. Establishing living organoid biobanks with standardized annotation of clinical metadata, genomic profiles, and drug response data; 2. Creating FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) digital platforms for organoid protocols, omics datasets, and phenotypic screens to support meta-analysis and AI-driven discovery; 3. Mandating that funding agencies and journals enforce data/organoid sharing as a publication requirement, mirroring initiatives such as the Human Tumor Atlas Network. Breaking down geographical and disciplinary boundaries and investing in collaborative infrastructure and open data ecosystems will be transformative, propelling the field towards clinically actionable precision oncology.
4.4 Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the investigation relied solely on the Web of Science Core Collection database, excluding other major biomedical databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and EMBASE. Second, the research sample may lack full representativeness due to restrictions in language coverage, publication types, and time frame. Additionally, as databases are continuously updated, some recently published articles may not have been included in our analysis. Consequently, the findings may not fully capture the complete research landscape.
5 Conclusions
This bibliometric analysis delineates the dynamic evolution of breast cancer organoid research over the past two decades, highlighting the United States and China as the leading contributors. Key achievements encompass the successful implementation of patient-derived organoids (PDOs) for personalized drug testing and disease modeling, significant progress in recapitulating the tumor microenvironment and immune interactions, and the integration of innovative 3D bioprinting and engineering approaches. Despite these advances, critical challenges persist. These are most notably the integration of functional vasculature, standardization of complex immune co-cultures, and barriers related to cost, scalability, and long-term maturation. This study provides researchers with a comprehensive overview of the field, serving as a valuable resource for: 1. Identifying key stakeholders and potential collaborators; 2. Understanding achieved successes and current bottlenecks; 3. Focusing research efforts on pressing challenges, such as vascularization; 4. Guiding the development of more physiologically relevant and clinically predictive breast cancer organoid models. Addressing these challenges through enhanced collaboration and technological innovation is crucial for realizing the full potential of organoids in advancing breast cancer precision medicine and therapeutic development.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
TW: Writing – original draft, Methodology. BL: Writing – original draft. HL: Writing – original draft. FZ: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work has been supported by the “Kunlun Talent High end Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talent” project in Qinghai Province in 2023.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lancaster MA and Knoblich JA. Organogenesis in a dish: modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science. (2014) 345:1247125. doi: 10.1126/science.1247125
2. Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell. (2016) 165:1586–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.082
3. Neal JT and Kuo CJ. Organoids as models for neoplastic transformation. Annu Rev Pathol. (2016) 11:199–220. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044249
4. Waseem M and Wang B-D. Organoids: an emerging precision medicine model for prostate cancer research. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1093. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021093
5. Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. (2009) 459:262–5. doi: 10.1038/nature07935
6. Sachs N, de Ligt J, Kopper O, Gogola E, Bounova G, Weeber F, et al. A living biobank of breast cancer organoids captures disease heterogeneity. Cell. (2018) 172:373–386.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.010
7. Beshiri ML, Tice CM, Tran C, Nguyen HM, Sowalsky AG, Agarwal S, et al. A PDX/organoid biobank of advanced prostate cancers captures genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity for disease modeling and therapeutic screening. Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 24:4332–45. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0409
8. Kopper O, de Witte CJ, Lõhmussaar K, Valle-Inclan JE, Hami N, Kester L, et al. An organoid platform for ovarian cancer captures intra- and interpatient heterogeneity. Nat Med. (2019) 25:838–49. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0422-6
9. Kim M, Mun H, Sung CO, Cho EJ, Jeon H-J, Chun S-M, et al. Patient-derived lung cancer organoids as in vitro cancer models for therapeutic screening. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:3991. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11867-6
10. Yan HHN, Siu HC, Law S, Ho SL, Yue SSK, Tsui WY, et al. A comprehensive human gastric cancer organoid biobank captures tumor subtype heterogeneity and enables therapeutic screening. Cell Stem Cell. (2018) 23:882–897.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.09.016
11. Yao Y, Xu X, Yang L, Zhu J, Wan J, Shen L, et al. Patient-derived organoids predict chemoradiation responses of locally advanced rectal cancer. Cell Stem Cell. (2020) 26:17–26.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.10.010
12. Weeber F, van de Wetering M, Hoogstraat M, Dijkstra KK, Krijgsman O, Kuilman T, et al. Preserved genetic diversity in organoids cultured from biopsies of human colorectal cancer metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:13308–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516689112
13. Broutier L, Mastrogiovanni G, Verstegen MM, Francies HE, Gavarró LM, Bradshaw CR, et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat Med. (2017) 23:1424–35. doi: 10.1038/nm.4438
14. L H AH, I J MB, I L N, C N, R W, Lb M, et al. Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell- and patient-derived tumor organoids. Nat Med. (2015) 21:118–33. doi: 10.1038/nm.3973
15. Jacob F, Salinas RD, Zhang DY, Nguyen PTT, Schnoll JG, Wong SZH, et al. A patient-derived glioblastoma organoid model and biobank recapitulates inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity. Cell. (2020) 180:188–204.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.036
16. Bleijs M, van de Wetering M, Clevers H, and Drost J. Xenograft and organoid model systems in cancer research. EMBO J. (2019) 38:e101654. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101654
17. Sun C-P, Lan H-R, Fang X-L, Yang X-Y, and Jin K-T. Organoid models for precision cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:770465. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.770465
18. Lin C-J, Jin X, Ma D, Chen C, Ou-Yang Y, Pei Y-C, et al. Genetic interactions reveal distinct biological and therapeutic implications in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. (2024) 42:701–719.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.03.006
19. Diem A and Wolter SC. The use of bibliometrics to measure research performance in education sciences. Res High Educ. (2013) 54:86–114. doi: 10.1007/s11162-012-9264-5
20. Roldan-Valadez E, Salazar-Ruiz SY, Ibarra-Contreras R, and Rios C. Current concepts on bibliometrics: a brief review about impact factor, Eigenfactor score, CiteScore, SCImago Journal Rank, Source-Normalised Impact per Paper, H-index, and alternative metrics. Ir J Med Sci. (2019) 188:939–51. doi: 10.1007/s11845-018-1936-5
21. Lv L-L, Feng Y, Wen Y, Wu W-J, Ni H-F, Li Z-L, et al. Exosomal CCL2 from tubular epithelial cells is critical for albumin-induced tubulointerstitial inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 29:919–35. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017050523
22. Synnestvedt MB, Chen C, and Holmes JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. (2005) 2005:724–8.
23. van Eck NJ and Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. (2010) 84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
24. Lu P, Weaver VM, and Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. (2012) 196:395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201102147
25. Nyga A, Cheema U, and Loizidou M. 3D tumour models: novel in vitro approaches to cancer studies. J Cell Commun Signal. (2011) 5:239–48. doi: 10.1007/s12079-011-0132-4
26. Weigelt B, Ghajar CM, and Bissell MJ. The need for complex 3D culture models to unravel novel pathways and identify accurate biomarkers in breast cancer. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2014) 69–70:42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.01.001
27. Bahcecioglu G, Basara G, Ellis BW, Ren X, and Zorlutuna P. Breast cancer models: Engineering the tumor microenvironment. Acta Biomater. (2020) 106:1–21. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.006
28. Kim J, Koo B-K, and Knoblich JA. Human organoids: model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 21:571–84. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0259-3
29. Tzeng Y-DT, Hsiao J-H, Tseng L-M, Hou M-F, and Li C-J. Breast cancer organoids derived from patients: A platform for tailored drug screening. Biochem Pharmacol. (2023) 217:115803. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115803
30. Chen P, Zhang X, Ding R, Yang L, Lyu X, Zeng J, et al. Patient-derived organoids can guide personalized-therapies for patients with advanced breast cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8:e2101176. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101176
31. Guillen KP, Fujita M, Butterfield AJ, Scherer SD, Bailey MH, Chu Z, et al. A human breast cancer-derived xenograft and organoid platform for drug discovery and precision oncology. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:232–50. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00337-6
32. Zhou Z, van der Jeught K, Fang Y, Yu T, Li Y, Ao Z, et al. An organoid-based screen for epigenetic inhibitors that stimulate antigen presentation and potentiate T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nat BioMed Eng. (2021) 5:1320–35. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00805-x
33. Maulana TI, Teufel C, Cipriano M, Roosz J, Lazarevski L, van den Hil FE, et al. Breast cancer-on-chip for patient-specific efficacy and safety testing of CAR-T cells. Cell Stem Cell. (2024) 31:989–1002.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.04.018
34. Arshad M, Azad A, Chan PYK, Vigneswara V, Feldinger K, Nafi SNM, et al. Neratinib could be effective as monotherapy or in combination with trastuzumab in HER2-low breast cancer cells and organoid models. Br J Cancer. (2024) 130:1990–2002. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02665-z
35. Nikulin SV, Alekseev BY, Sergeeva NS, Karalkin PA, Nezhurina EK, Kirsanova VA, et al. Breast cancer organoid model allowed to reveal potentially beneficial combinations of 3,3’-diindolylmethane and chemotherapy drugs. Biochimie. (2020) 179:217–27. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.10.007
36. Van Eaton KM and Gustafson DL. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic assessment of hydroxychloroquine in breast cancer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2021) 379:331–42. doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000730
37. Boix-Montesinos P, Soriano-Teruel PM, Armiñán A, Orzáez M, and Vicent MJ. The past, present, and future of breast cancer models for nanomedicine development. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2021) 173:306–30. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.03.018
38. Pranav P, Palaniyandi T, Baskar G, Ravi M, Rajendran BK, Sivaji A, et al. Gene expressions and their significance in organoid cultures obtained from breast cancer patient-derived biopsies. Acta Histochem. (2022) 124:151910. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2022.151910
39. Bhatia S, Kramer M, Russo S, Naik P, Arun G, Brophy K, et al. Patient-derived triple-negative breast cancer organoids provide robust model systems that recapitulate tumor intrinsic characteristics. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:1174–92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-2807
40. Ding K, Chen F, Priedigkeit N, Brown DD, Weiss K, Watters R, et al. Single cell heterogeneity and evolution of breast cancer bone metastasis and organoids reveals therapeutic targets for precision medicine. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:1085–8. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.06.005
41. Liuyang S, Wang G, Wang Y, He H, Lyu Y, Cheng L, et al. Highly efficient and rapid generation of human pluripotent stem cells by chemical reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. (2023) 30:450–459.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.02.008
42. Sun D, Guan X, Moran AE, Wu L-Y, Qian DZ, Schedin P, et al. Identifying phenotype-associated subpopulations by integrating bulk and single-cell sequencing data. Nat Biotechnol. (2022) 40:527–38. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01091-3
43. Dekkers JF, van Vliet EJ, Sachs N, Rosenbluth JM, Kopper O, Rebel HG, et al. Long-term culture, genetic manipulation and xenotransplantation of human normal and breast cancer organoids. Nat Protoc. (2021) 16:1936–65. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00474-1
44. Kurani H, Razavipour SF, Harikumar KB, Dunworth M, Ewald AJ, Nasir A, et al. DOT1L is a novel cancer stem cell target for triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28:1948–65. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1299
45. Tsai KK, Huang S-S, Northey JJ, Liao W-Y, Hsu C-C, Cheng L-H, et al. Screening of organoids derived from patients with breast cancer implicates the repressor NCOR2 in cytotoxic stress response and antitumor immunity. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:734–52. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00375-0
46. Oliphant MUJ, Akshinthala D, and Muthuswamy SK. Establishing conditions for the generation and maintenance of estrogen receptor-positive organoid models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. (2024) 26:56. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01798-6
47. Boussommier-Calleja A, Li R, Chen MB, Wong SC, and Kamm RD. Microfluidics: A new tool for modeling cancer-immune interactions. Trends Cancer. (2016) 2:6–19. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2015.12.003
48. Fröhlich E. The variety of 3D breast cancer models for the study of tumor physiology and drug screening. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:7116. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087116
49. Bhattacharya A, Alam K, Roy NS, Kaur K, Kaity S, Ravichandiran V, et al. Exploring the interaction between extracellular matrix components in a 3D organoid disease model to replicate the pathophysiology of breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:343. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02926-4
50. Roy NS, Kumari M, Alam K, Bhattacharya A, Kaity S, Kaur K, et al. Development of bioengineered 3D patient derived breast cancer organoid model focusing dynamic fibroblast-stem cell reciprocity. Prog BioMed Eng (Bristol). (2024) 7:1–15. doi: 10.1088/2516-1091/ad9dcb
51. Glibetic N, Bowman S, Skaggs T, and Weichhaus M. The use of patient-derived organoids in the study of molecular metabolic adaptation in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:10503. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910503
52. Jayme CC, Pires AF, Fernandes DS, Bi H, and Tedesco AC. DNA polymer films used as drug delivery systems to early-stage diagnose and treatment of breast cancer using 3D tumor spheroids as a model. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2022) 37:102575. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102575
53. Teixeira FC, Chaves S, Torres AL, Barrias CC, and Bidarra SJ. Engineering a vascularized 3D hybrid system to model tumor-stroma interactions in breast cancer. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2021) 9:647031. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.647031
54. Figtree GA, Bubb KJ, Tang O, Kizana E, and Gentile C. Vascularized cardiac spheroids as novel 3D in vitro models to study cardiac fibrosis. Cells Tissues Organs. (2017) 204:191–8. doi: 10.1159/000477436
55. Silvestri VL, Henriet E, Linville RM, Wong AD, Searson PC, and Ewald AJ. A tissue-engineered 3D microvessel model reveals the dynamics of mosaic vessel formation in breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:4288–301. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1564
56. Schuster B, Junkin M, Kashaf SS, Romero-Calvo I, Kirby K, Matthews J, et al. Automated microfluidic platform for dynamic and combinatorial drug screening of tumor organoids. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:5271. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19058-4
57. Pinto MP, Badtke MM, Dudevoir ML, Harrell JC, Jacobsen BM, and Horwitz KB. Vascular endothelial growth factor secreted by activated stroma enhances angiogenesis and hormone-independent growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:2655–64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4373
58. Thorel L, Perréard M, Florent R, Divoux J, Coffy S, Vincent A, et al. Patient-derived tumor organoids: a new avenue for preclinical research and precision medicine in oncology. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:1531–51. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01272-5
59. LeSavage BL, Zhang D, Huerta-López C, Gilchrist AE, Krajina BA, Karlsson K, et al. Engineered matrices reveal stiffness-mediated chemoresistance in patient-derived pancreatic cancer organoids. Nat Mater. (2024) 23:1138–49. doi: 10.1038/s41563-024-01908-x
60. Mulero-Russe A and García AJ. Engineered synthetic matrices for human intestinal organoid culture and therapeutic delivery. Adv Mater. (2024) 36:e2307678. doi: 10.1002/adma.202307678
61. Rossi G, Manfrin A, and Lutolf MP. Progress and potential in organoid research. Nat Rev Genet. (2018) 19:671–87. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0051-9
62. Tristan CA, Ormanoglu P, Slamecka J, Malley C, Chu P-H, Jovanovic VM, et al. Robotic high-throughput biomanufacturing and functional differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. (2021) 16:3076–92. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.11.004
63. Sockell A, Wong W, Longwell S, Vu T, Karlsson K, Mokhtari D, et al. A microwell platform for high-throughput longitudinal phenotyping and selective retrieval of organoids. Cell Syst. (2023) 14:764–776.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2023.08.002
64. Dornhof J, Kieninger J, Muralidharan H, Maurer J, Urban GA, and Weltin A. Microfluidic organ-on-chip system for multi-analyte monitoring of metabolites in 3D cell cultures. Lab Chip. (2022) 22:225–39. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00689d
65. Wang Y and Jeon H. 3D cell cultures toward quantitative high-throughput drug screening. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2022) 43:569–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.03.014
66. Guan Y, Enejder A, Wang M, Fang Z, Cui L, Chen S-Y, et al. A human multi-lineage hepatic organoid model for liver fibrosis. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:6138. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26410-9
67. Polak R, Zhang ET, and Kuo CJ. Cancer organoids 2.0: modelling the complexity of the tumour immune microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. (2024) 24:523–39. doi: 10.1038/s41568-024-00706-6
68. Aggarwal D, Russo S, Naik P, Bhatia S, and Spector DL. Establishment and culture of patient-derived breast organoids. J Vis Exp. (2023) (192):e64889. doi: 10.3791/64889
69. Touhara KK, Rossen ND, Deng F, Castro J, Harrington AM, Chu T, et al. Topological segregation of stress sensors along the gut crypt-villus axis. Nature. (2025) 640:732–42. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08581-9
70. Yang J, Lei W, Xiao Y, Tan S, Yang J, Lin Y, et al. Generation of human vascularized and chambered cardiac organoids for cardiac disease modelling and drug evaluation. Cell Prolif. (2024) 57:e13631. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13631
Keywords: breast cancer, organoids, bibliometrics, drug discovery, research hotspots, 3d bioprinting, tumor microenvironment
Citation: Wu T, Li B, Lei H, Zhao F and Liu Z (2025) Evolution and hotspots in breast cancer organoid research: insights from a bibliometric and visual knowledge mapping study (2005-2024). Front. Oncol. 15:1604362. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1604362
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Sharon R. Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesReviewed by:
Marco Cavaco, Gulbenkian Institute of Science (IGC), PortugalEleonore Fröhlich, Medical University of Graz, Austria
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Li, Lei, Zhao and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhen Liu, cWhkeGx6QHFxLmNvbQ==; FuXing Zhao, MTg3OTczNDk2MjFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Tao Wu1†
Tao Wu1† BaiXin Li
BaiXin Li Zhen Liu
Zhen Liu