- 1The Department of Nuclear Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 2The Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 3The Department of Computed Tomography (CT), The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 4The Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 5The Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the clinical usefulness of fluorine 18F−FAPI-04 PET/CT in diagnosing ground-glass nodules that are less than 3 cm in diameter in comparison with fluorine 18F-FDG PET/CT.
Methods: Prospective analysis of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans for 74 patients with 96 GGNs less than 3 cm from 09/2021 to 10/2024 were analyzed. 18F-FAPI-04 imaging was performed in patients with 18F-FDG PET/CT within a week. The images, parameters, and histopathological invasiveness from participants were analyzed. Tumor uptake was quantified by the maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax), standard uptake value mean (SUVmean), target-to-background ratio (TBR), and the ratio of SUVmax of the lesion to SUVmax of contralateral normal lung parenchyma (SUVindex).
Results: A total of 74 patients with 96 GGNs were evaluated. Different pathological subtypes of GGNs exhibited distinct uptake values on 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT. The invasive pathological subtypes showed higher uptakes than noninvasive subtypes, of which 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT showed significantly higher uptake than 18F-FDG PET/CT in all subtypes of GGNs (all P<0.05). Notably, the optimal cut-off values for specificity of SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVindex, and TBR of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT were notably higher than those of 18F-FDG PET/CT.
Conclusion: 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT is useful for detecting GGNs, outperforming 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting their invasiveness. It could provide valuable guidance for early-stage adenocarcinoma diagnosis, potentially impacting patient management.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR2100051406. Registered 23 September 2021 ‘Retrospectively registered’, https://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.html?proj=133033
Introduction
Among global malignant tumors, lung cancer has the highest mortality and morbidity rates (1). Early detection of pulmonary cancer is critical to management, and this often requires the use of multiple imaging modalities (2). To diagnose lung cancer accurately, a wide range of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET/CT is now being used, and lung cancer screening programs are constantly being developed (3–5). However, lung adenocarcinoma with ground-glass nodules (GGNs), which is considered a very heterogeneous tumor with different histopathology and disease processes (6, 7), has little information available regarding the use of 18F-FDG PET/CT for early cancer detection. Despite advances in 18F-FDG PET/CT lung cancer screening, surgical resection of GGNs with a diameter less than 3 cm is still needed in a considerable number of cases in order to differentiate early stages of lung adenocarcinoma from benign lesions (8–10). In order to manage GGNs effectively, it is crucial to detect them accurately, and new radiotracers may be required.
Fibroblast activation protein inhibitors (FAPI) are radiotracers that have shown high promise in prior studies involving various tumor types (11). It has been confirmed that lung cancer could be diagnosed using FAPI imaging with a high maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) and high contrast (12). Recent studies have also shown that FAPI PET/CT may be more accurate than FDG PET/CT when it comes to staging lung cancer, particularly when it comes to detecting metastatic disease in the brain, lymph nodes, bones, and pleurae (13). Nevertheless, previous records have neglected the use of FAPI PET/CT in detecting and predicting the growth pattern of lung adenocarcinoma with GGNs. A case report has highlighted that 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT showed a higher uptake of tracer than 18F-FDG when applied to malignant GGN, which was confirmed as invasive adenocarcinoma by postoperative pathological examination (14). Current research on molecular imaging probes targeting FAP commonly uses 68Ga-FAPI-04 for PET imaging. Despite the unprecedented success of 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT in detecting primary tumors, it has its drawbacks. The broad application of Ga-labeled FAPI in clinical practice is limited due to the short half-life 68Ga, high costs, and insufficient availability of radionuclides from the 68Ge/68Ga generator (15). Conversely, 18F is the most widely used radionuclide in PET imaging, as it can be mass-produced via a cyclotron and transported over long distances (16, 17). In this prospective study, we aimed to evaluate whether FAPI is superior to FDG PET/CT in lung adenocarcinoma with GGNs less than 3 cm in diameter.
Methods
Study participants
This study conducted prospective 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT scans and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans for 74 patients with 96 GGNs less than 3 cm in diameter, which were considered for surgical treatment or surgical biopsy in the First-affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University between September 2021 and October 2024. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant prior to 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT. Following the Drug Administration Law of the People’s Republic of China, indication and labeling of the FAPI-tracers were conducted under the physician’s direct responsibility, all patients underwent FAPI PET/CT. The clinical translational study of 18F-FAPI-04 was approved by the Ethics Committee (approval No. 2021XJSS01) and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2100051406). The 18F-FAPI PET/CT scan was performed at the Nuclear Medicine Imaging Diagnosis and Treatment Center at the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University within seven days of the 18F-FDG PET/CT scan after informed consent was taken.
The inclusion criteria included (a) participants with newly diagnosed GGNs who had not received any treatment before; (b) participants who had pathology results; (c) participants who had FDG PET/CT and wrote informed consent for undergoing FAPI PET/CT examinations within a week. Exclusion criteria included the presence of other primary malignancies at the time of examination, severe hepatic or renal insufficiency, or refusal to undergo FAPI scanning.
Histological diagnosis was based on the new classification of lung adenocarcinoma proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer and classified into atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH), adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), microinvasive adenocarcinoma (MIA), and invasive adenocarcinoma (IAC) (18). This study merged AAH, AIS and MIA into noninvasive lesions, IAC merged into invasive lesions. Therefore, cases were divided into two groups: noninvasive lesions and invasive lesions.
Synthesis of 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI-04
In line with standard methods, 18F-FDG was manufactured by the PET/CT Department of Nuclear Medicine at Harbin Medical University’s First Affiliated Hospital (19). Following standard methodology, 18F-FDG was routinely synthesized at the Department of Nuclear Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University. An earlier description of the synthesis and labeling of 18F-FAPI-04 can be found here (20). Injected activities were dependent on labeling yields. According to a previous dosimetry estimate, a sufficient count rate – an effective dose of 1.6 mSv/100 MBq - an upper limit of 370 MBq regarding radiation exposure, and a lower limit of 100 MBq per exam must be achieved (21). The minimum, maximum, and median dosages for FDG and FAPI were 166.87 MBq, 336.7 MBq, and 248.64 MBq, respectively. Both 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI-04 exhibited radiochemical purity exceeding 95%. 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG tracers met all standard criteria before being administered to humans.
PET/CT imaging
Paired 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT scans were obtained at intervals within 7 days of each other. Before 18F-FDG PET/CT scanning, participants were instructed to fast for at least 6 hours, and an average blood glucose level in peripheral blood was ensured. Before 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT imaging, fasting, and blood glucose measurements were not required. Patients received an intravenous injection of 18F-FAPI-04 and then rested for about 1 h before imaging. Both 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT images were acquired using a digital PET/CT scanner (uMI 780, United Imaging Healthcare). In addition to the CT scan, PET images (1 minute per bed position, 6–7 PET bed positions) were acquired after a CT scan (tube voltage: 120 kV, tube current: 100mAs). For suspected pulmonary nodules, additional local high-resolution CT was performed (tube voltage: 120kV, tube current: 180mAs). Respiratory gating calibration for the matching of pulmonary nodules. In accordance with the agency’s standard clinical protocols, the scan ranged from head to thigh. After automatic random and scattering correction, the images were reconstructed using a line-of-response reconstruction algorithm.
Image analysis
Ground-glass nodules (GGNs) were defined and classified according to the European guidelines for the surgical management of pure ground glass opacities and part-solid nodules (22). A pure GGN (also referred to as a non-solid nodule) was defined as a homogeneous area of increased attenuation without any solid component visible on thin-section CT, whereas a part-solid GGN (also called a mixed GGN) was defined as a lesion containing both ground-glass and solid components within the same nodule. Two experienced nuclear medicine specialists analyzed PET/CT data on a consensus decision (P.F. and Z.L.). The readers were blind to the results of 18F-FDG PET/CT when reporting 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT, including location of GGN (subpleural/perifissural and parenchymal), type of nodules (pGGN and mGGN), edge (smooth and lobulated/spiculated), internal features (bronchus sign), and adjacent structures (pleural indentation). The PET quantitative indicators included maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), mean value of standardized uptake (SUVmean), the ratio of tracer concentration in the lesion to that in the surrounding tissue (TBR), and the ratio of SUVmax of lesion to SUVmax of contralateral normal lung paranchyma (SUVindex). The boundary of the lesion was delineated on the axial PET scan, and this outline was automatically extended to a three-dimensional region of interest (ROI) using a 60% threshold, facilitating the calculation of the SUVmax. For TBR and SUVindex background ROIs were also circular, size-matched to the lesion ROIs, and with the 60% SUVmax threshold. Pleural (≥1cm away), hilar (≥2cm away) and mediastinum-adjacent areas were avoided in that delineation. The corresponding lesion is diagnosed as positive when the SUVmax value is greater than 2.0 (23). The diameter of GGN was the longest on the standard cross-sectional lung window image. For mGGN, the diameter of the solid component was the longest diameter of the solid component on standard cross-sectional lung window images. The same experienced nuclear medicine physician evaluated these CT values of lung nodules. The attenuation values of the GGN component (CTGGN) and normal lung parenchyma adjacent to GGN (CTLP) were measured with the same size circle ROI. The difference between CTGGN and CTLP was calculated as CTGGN-LP.
Statistical analysis
All statistical data was analyzed using SPSS software version 23.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) and GraphPad Prism (version 8.4.2; GraphPad Software, San Diego, Calif). Normally distributed values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Non-normally distributed values are expressed as median ± interquartile range (IQR). The analysis comparing the uptake of all lesions between FAPI and FDG PET/CT was conducted using the Mann-Whitney U test. Univariate analysis utilized the Cox proportional hazards regression model, while multivariate analysis employed stepwise variable selection within the Cox model. Comparing the abilities of semiquantitative PET/CT parameters for differential diagnosis of different findings was performed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and the area under the ROC curve (AUC). The sensitivity, specificity and optimal cut-off values were also calculated for each parameter. Optimal cut-offs were determined based on the Youden index. In order to test the correlation between continuous and non-continuous variables, the Spearman test was used. The results were considered statistically significant if the P-value was less than 0.05.
Results
Patient characteristics
From September 2021 to October 2024, 74 participants (28 men, 46 women; median age, 62 years [interquartile range: 55.5 - 69.0 years]) and 96 lesions were enrolled in the study eventually. Figure 1 shows the study flowchart. Table 1 summarizes these participants’ basic and clinical characteristics. Among these participants, 44 were diagnosed with pre-invasive GGNs (10 AAH, 14 AIS, and 25 MIA lesions), and 30 patients had invasive GGNs (47 IAC lesions). One case was a fibrotic lesion. All individuals were newly diagnosed with GGNs and had no previous treatment.
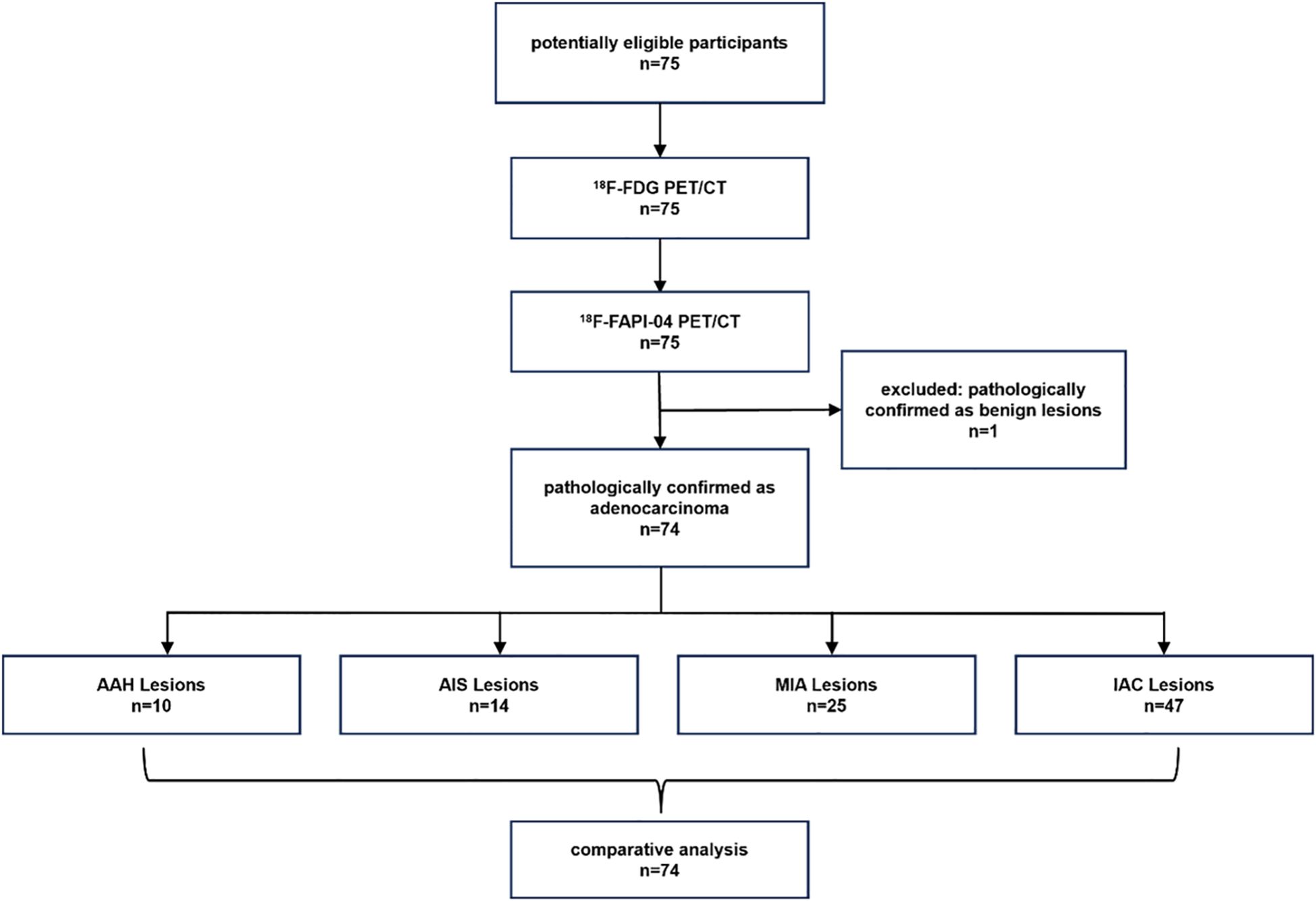
Figure 1. The flow diagram shows details of participants' selection and exclusions. FAPI, fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; 18F, fluorine 18; AAH, atypical adenomatous hyperplasia; AIS, adenocarcinoma in situ; MIA, microinvasive adenocarcinoma; IAC, invasive adenocarcinoma.
Detection rate of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT versus 18F-FDG PET/CT
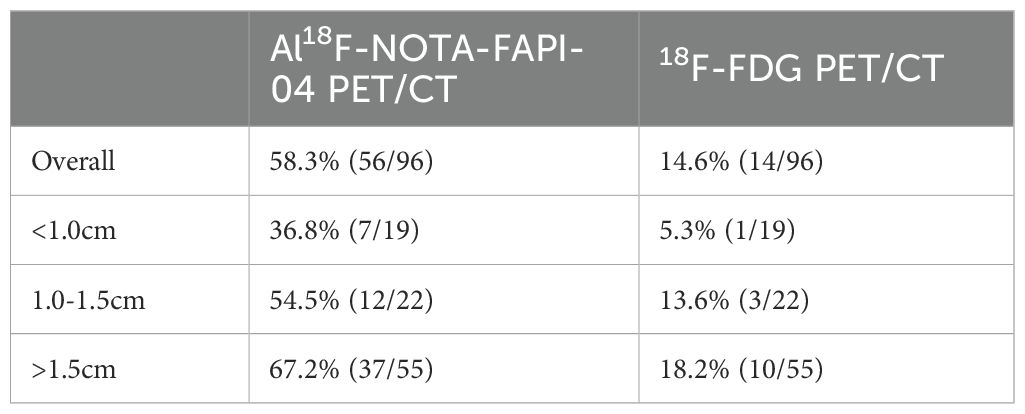
The 75 cases, including 96 GGN lesions and one benign lesion, were diagnosed with biopsy and histopathologic examination. To further validate the superiority of 18F-FAPI-04 in GGN detection, we compared the quantitative uptake parameters of the two radiopharmaceuticals. In the depiction of GGNs based on SUVmax, the detection rate was 58.3% (56 of 96) for 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 14.6% (14.6 of 96) for 18F-FDG PET/CT in malignant lesions, and both tracers were negative in the benign lesion (Table 2). When based on SUVindex, 18F-FAPI-04 demonstrated more positive lesions than that of 18F-FDG PET/CT (87 vs. 68). In total, 18F-FAPI-04 demonstrated a higher detection rate for GGNs than 18F-FDG PET/CT. Table 3 shows the detailed parameters in the lesions between 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT. Upon analysis of the different 18F-FAPI-04 uptake parameters in all lesions, we found that the SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVindex, and TBR of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the lesions were higher than those of 18F-FDG (all P < 0.05).
Assessment of the invasion of GGNs with 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT
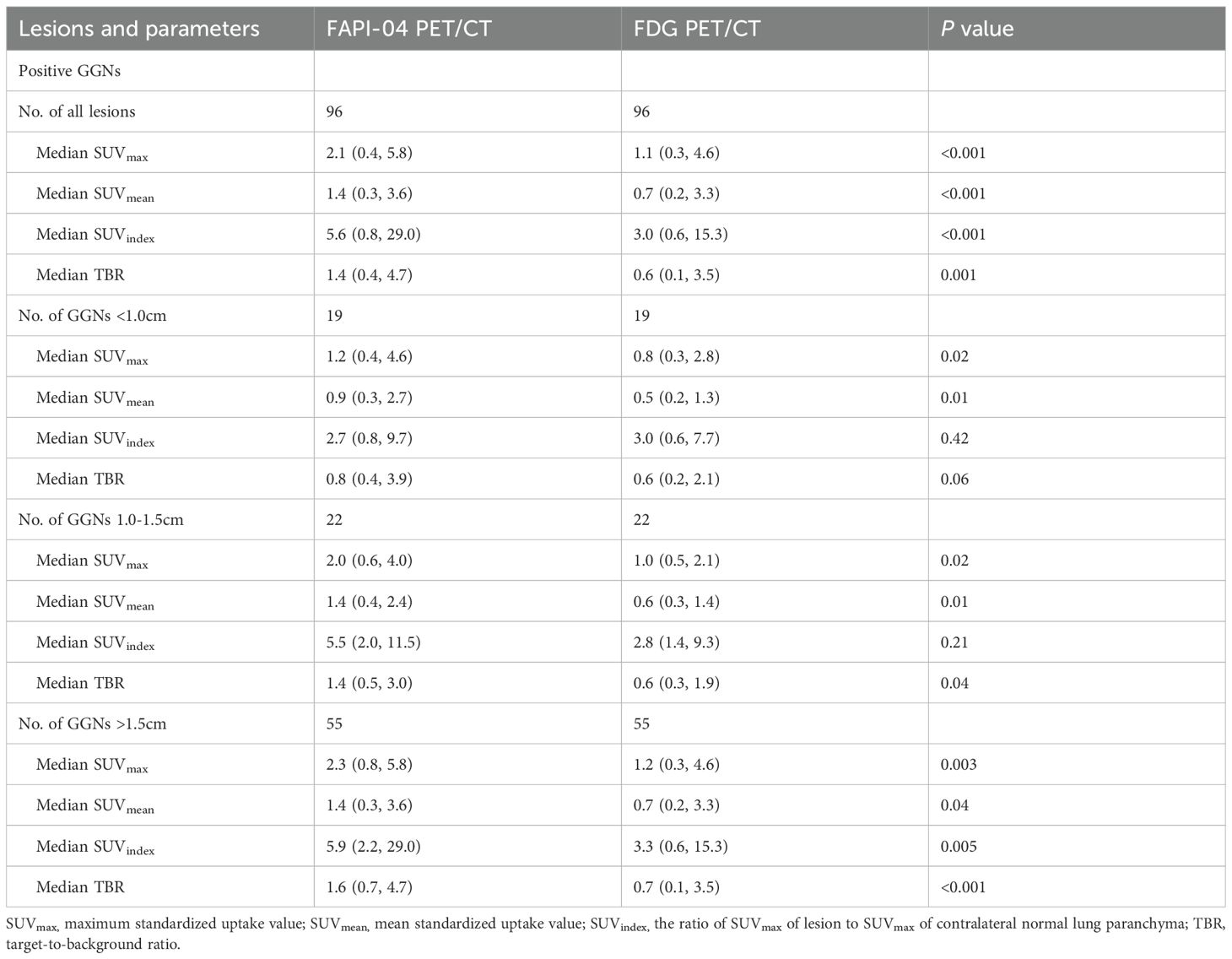
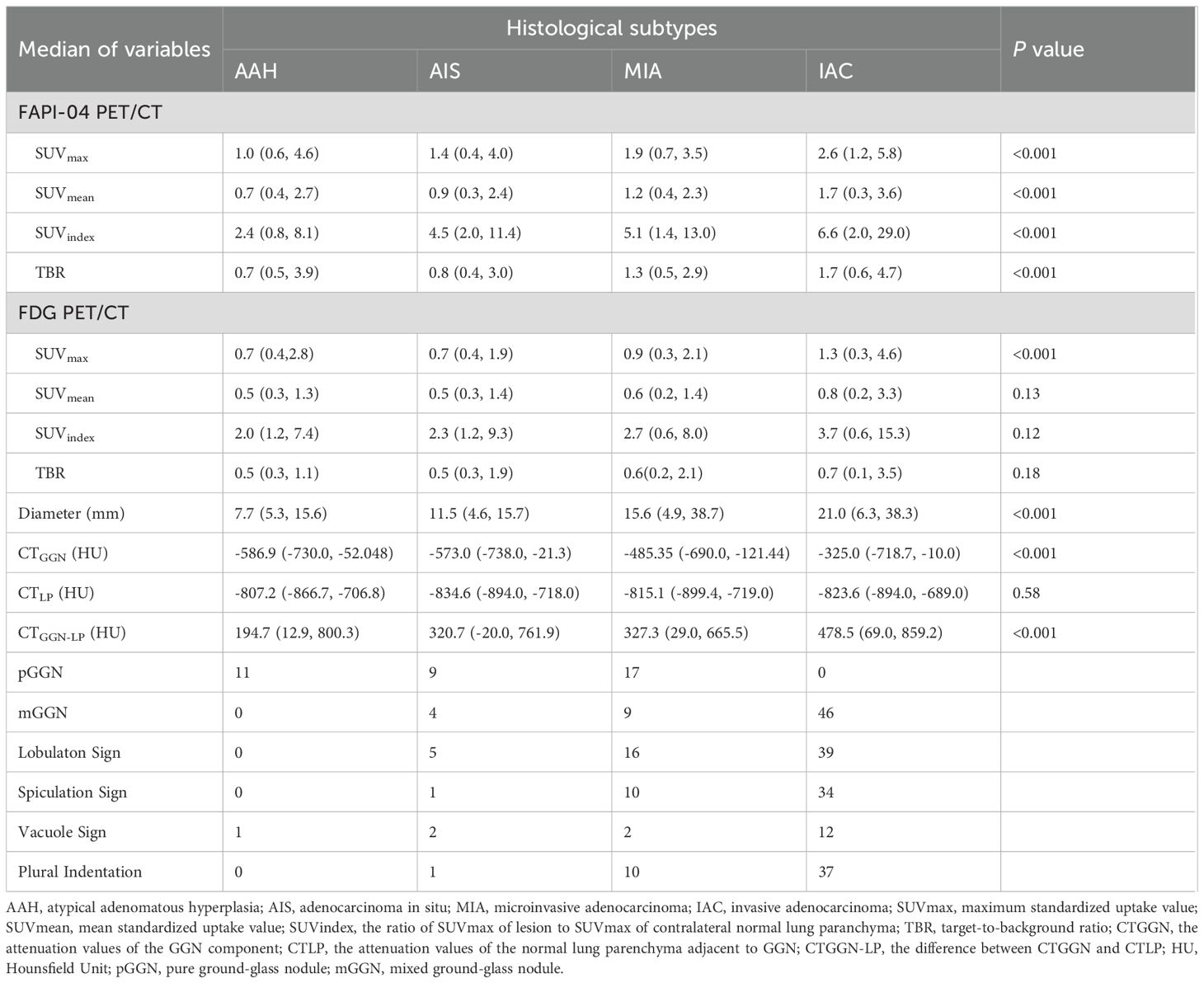
Based on histopathologic examination and biopsy results, 96 lesions (10 AAH lesions, 14 AIS lesions, 25 MIA lesions, and 47 IAC lesions) were enrolled. Figure 2A illustrates a representative 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT scan of four different pathological subtypes of GGNs and an 18F-FDG PET/CT scan of equivalent lesions (Figure 2B). Detailed uptake parameters for each tracer are presented in Table 4. 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT demonstrated a higher uptake value of SUVmax, SUVmean, TBR, and SUVindex of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT compared to 18F-FDG PET/CT in diagnosing GGNs (all P < 0.05). Figures 3A–D shows representative examples of four different histopathologic types.
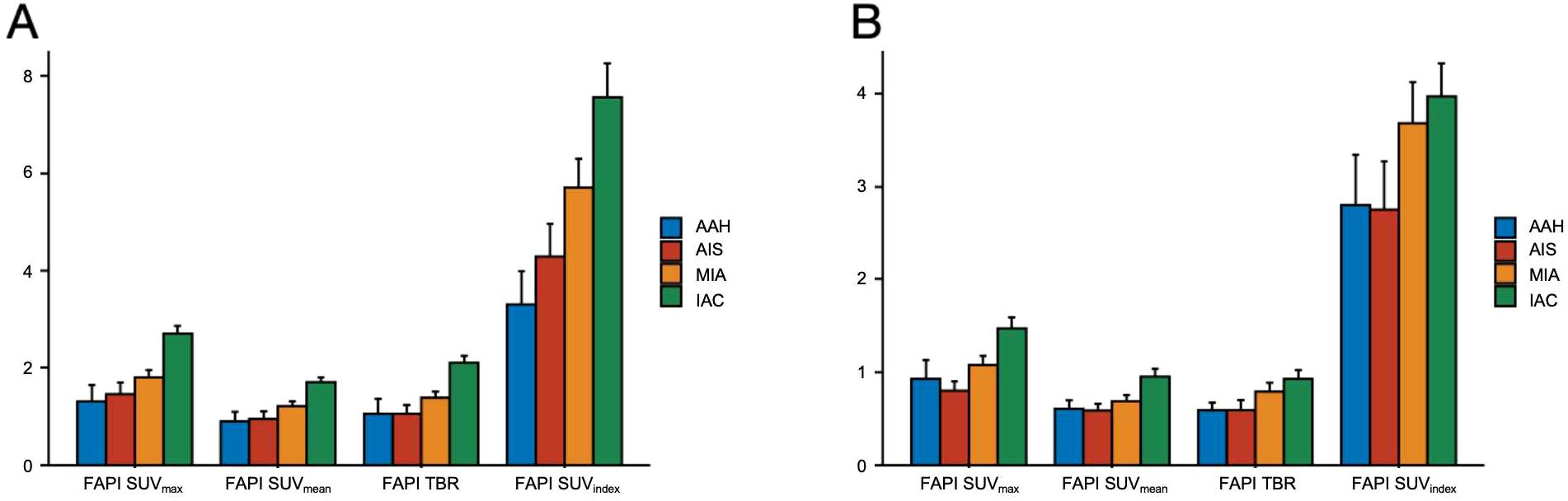
Figure 2. Comparison of 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT for different pathological subtypes of GGNs. (A) Bar chart shows a comparison of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT for different pathological subtypes of GGNs. (B) The bar graph compares different pathological subtypes of GGNs evaluated by 18F-FDG PET/CT. FAPI, fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; SUVmax, maximum standardized uptake value; SUVmean, mean standardized uptake value; SUVindex, the ratio of SUVmax of lesion to SUVmax of contralateral normal lung paranchyma; TBR, target-to-background ratio; AAH, atypical adenomatous hyperplasia; AIS, adenocarcinoma in situ; MIA, microinvasive adenocarcinoma; IAC, invasive adenocarcinoma.
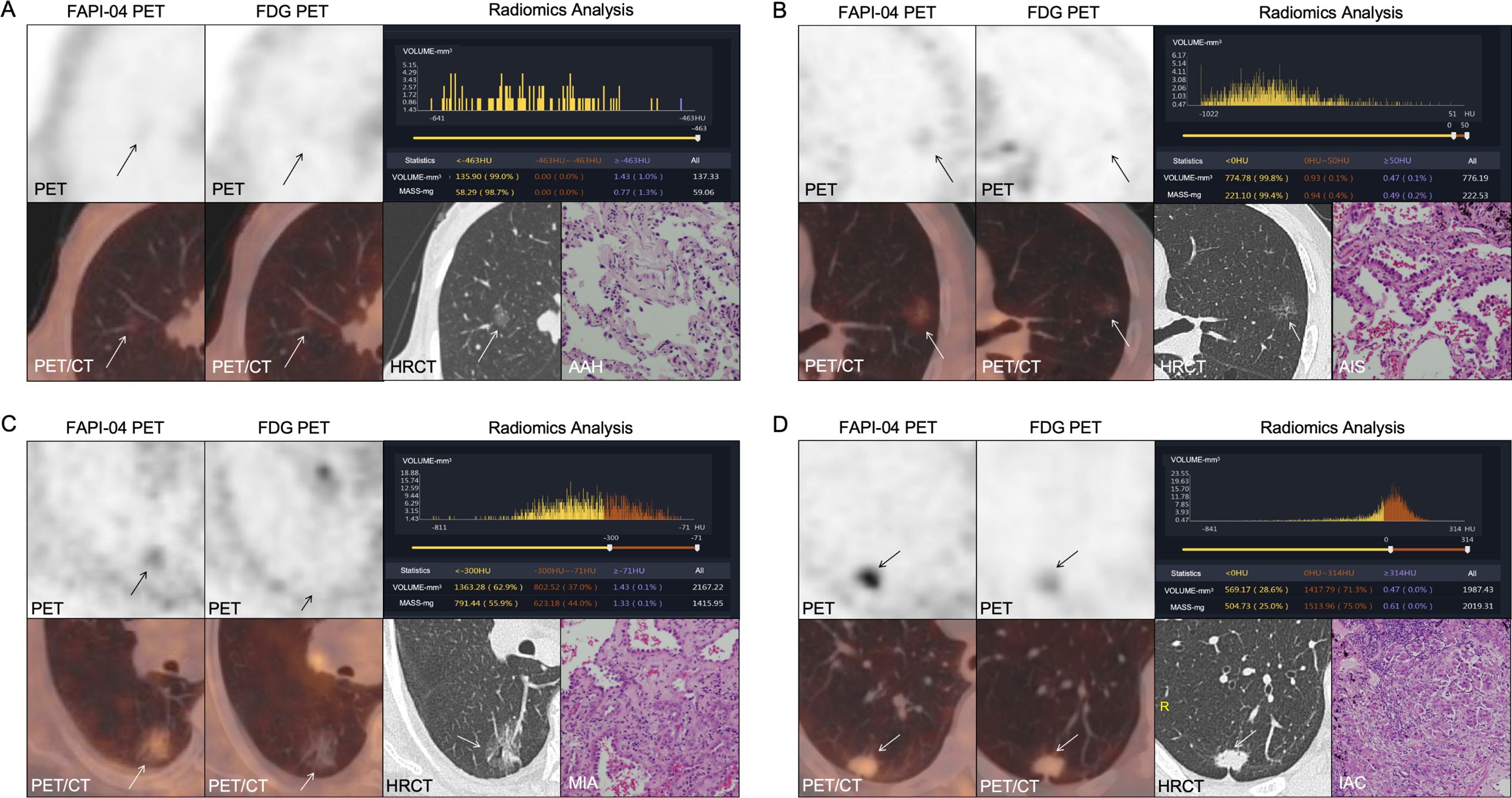
Figure 3. (A–D) 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT images, histogram distribution of CT attenuation values and pathological images of 4 different types GGNs (arrows): (A) AAH. (B) AIS. (C) MIA. (D) IAC. FAPI, fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; AAH, atypical adenomatous hyperplasia; AIS, adenocarcinoma in situ; MIA, microinvasive adenocarcinoma; IAC, invasive adenocarcinoma.
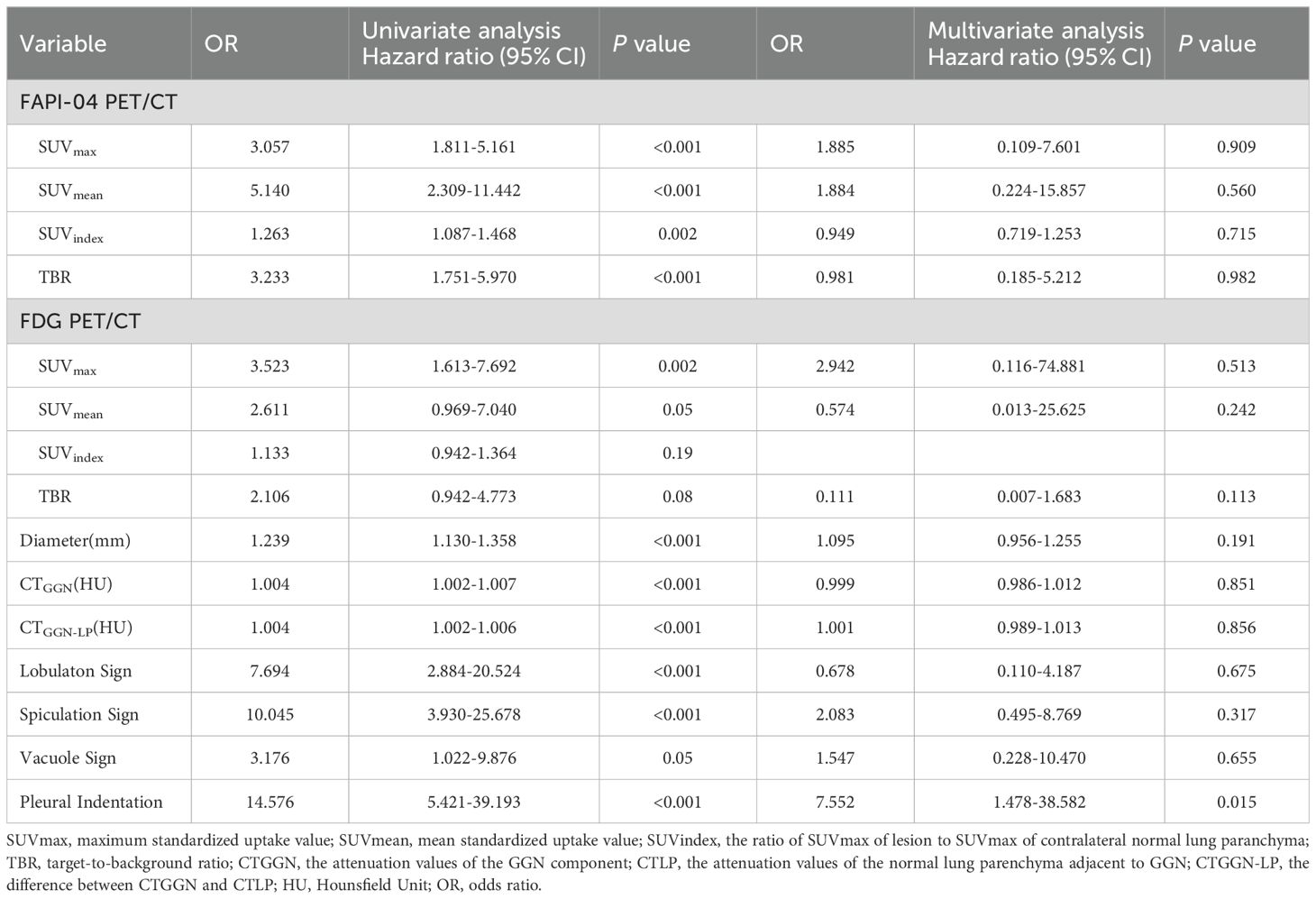
The parameters of 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT showed different diagnostic performances between the pre-invasive and invasive GGNs. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to analyze the association between the invasion of GGNs and clinical factors, including 18F-FAPI-04, 18F-FDG PET/CT, and CT-associated parameters. Table 5 demonstrates plural sign (OR = 7.552, P = 0.015) was the independent significant factor. Figures 4A–I shows the comparison of pre-invasive and invasive subtypes of GGNs with all parameters. The invasive pathological subtypes showed higher uptakes than the pre-invasive subtypes. Compared with 18F-FDG PET/CT, 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT also showed significantly higher uptake in all subtypes of GGNs (all P < 0.05).
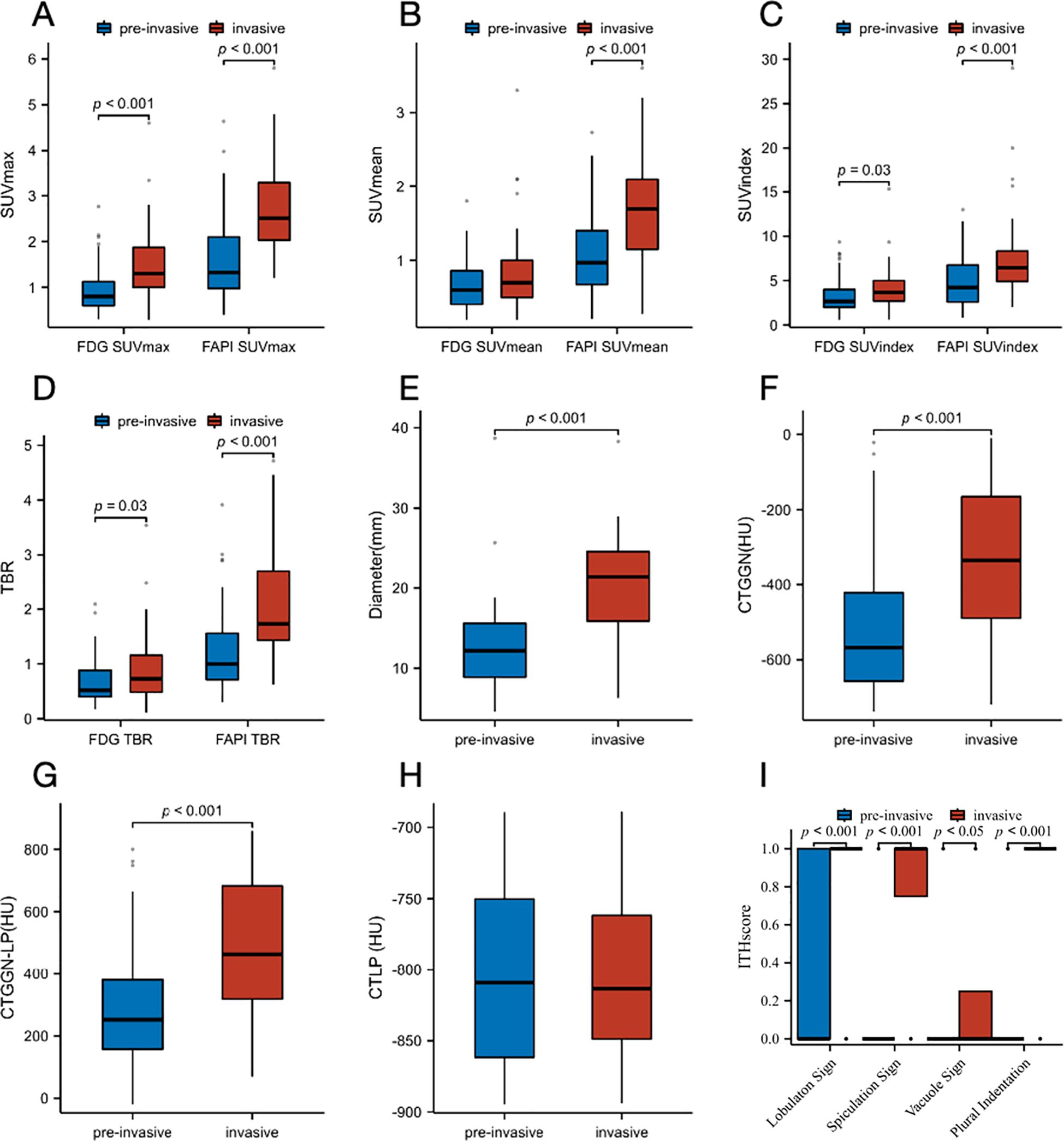
Figure 4. Box plots for the comparison of distribution of pre-invasive and invasive subtypes of GGNs. (A) SUVmax on 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT. (B) SUVmean on Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT. (C) SUVindex on Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT. (D) TBR on Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT. (E) Diameter (mm). (F) CTGGN (HU). (G) CTLP (HU). (H) CTGGN-LP (HU). (I) Imaging manifestations (lobulaton sign, spiculation sign, vacuole sign and plural indentation). FAPI, fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; SUVmax, maximum standardized uptake value; SUVmean, mean standardized uptake value; SUVindex, the ratio of SUVmax of lesion to SUVmax of contralateral normal lung paranchyma; TBR, target-to-background ratio; CTGGN, the attenuation values of the GGN component; CTLP, the attenuation values of normal lung parenchyma adjacent to GGN; CTGGN-LP, the difference between CTGGN and CTLP; HU, Hounsfield Unit; ITH, intratumor heterogeneity.
Impacts of 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT on the identification of the invasion of GGNs
All four 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT parameters showed reasonable diagnostic accuracy according to the ROC curves. Based on SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVindex, and TBR, optimal cut-off values were determined for all lesions. For 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT, it is shown that the SUVmax AUC value for pre-invasive and invasive GGNs was 0.801, 0.770 of the SUVmean, 0.711 of the SUVindex, and 0.784 of the TBR. According to ROC curve comparisons, SUVmax has a cut-off value of 2.5, SUVmean of 1.4, SUVindex of 4.7, and TBR of 1.4 (Figure 5A).
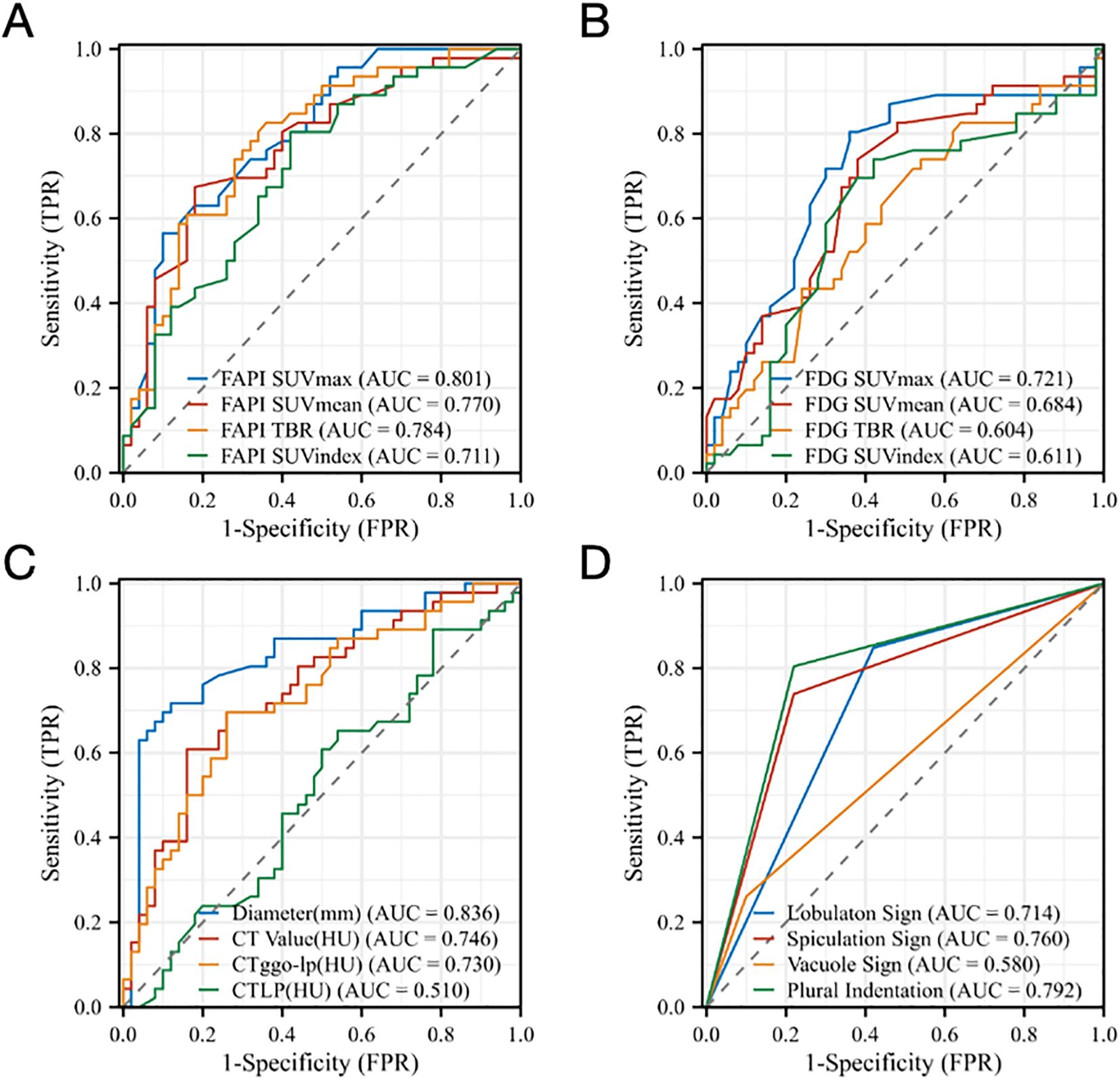
Figure 5. ROC analysis for different parameters (A) SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVindex, and TBR of Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT, (B) SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVindex, and TBR of 18F-FDG PET/CT, (C) Diameter (mm), CTGGN (HU), CTLP (HU), CTGGN-LP (HU) and (D) Imaging manifestations (lobulaton sign, spiculation sign, vacuole sign and plural indentation) derived from the two tracers for identifying the Invasion of GGNs. FAPI, fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; SUVmax, maximum standardized uptake value; SUVmean, mean standardized uptake value; SUVindex, the ratio of SUVmax of lesion to SUVmax of contralateral normal lung paranchyma; TBR, target-to-background ratio; CTGGN, the attenuation values of the GGN component; CTLP, the attenuation values of normal lung parenchyma adjacent to GGN; CTGGN-LP, the difference between CTGGN and CTLP; AUC, area under the curve; TPR, true positive rate; FPR, false positive rate.
For 18F-FDG PET/CT, the SUVmax cut-off value for noninvasive and invasive GGNs was 0.9, the SUVmean was 0.6, the SUVindex was 2.7, and the TBR was 0.5. According to ROC curve comparisons, SUVmax has an AUC value of 0.721, SUVmean of 0.684, SUVindex of 0.611, and TBR of 0.604, which suggested that the ROC curves showed 18F-FAPI-04 is better at identifying the invasion of GGNs than 18F-FDG PET/CT (Figure 5B).
Our data suggested that the diameters of lesions, CTGGN and CTGGN-LP, may also relate to the invasion of GGNs. It is shown that the diameter cut-off value for pre-invasive and invasive GGNs was 16.5mm and the AUC value of 0.836, the CTGGN cut-off value was -363.1HU and the AUC value of 0.746, and the CTGGN-LP cut-off value was 395.0HU and the AUC value of 0.730, which showed good diagnostic accuracy. The CTLP showed no diagnostic accuracy according to the ROC curve (Figure 5C). In addition, Figure 5D demonstrated that the imaging manifestations (including lobulation sign, spiculation sign, vacuole sign and plural indentation) show a certain correlation of invasion of GGNs. The AUC value of lobulation sign was 0.714, 0.760 of spiculation sign, 0.580 of vacuole sign and 0.792 of pleural indentation by ROC analysis, respectively.
Discussion
In this study, we evaluated patients with various pathologically confirmed GGNs using 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT for a prospective clinical trial. This pilot study demonstrated the superior diagnostic performance of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT in GGNs with different pathological stages compared with that of 18F-FDG PET/CT. The underlying advantages of radiolabeled FAPI application on lung cancer have been discussed in several articles, focusing on the efficiency of detecting primary and metastatic lesions (18–20), which showed that lung cancer is a FAPI–avid tumor, and FAPI PET/CT showed some superiorities to FDG PET/CT in the detection of suspected metastases to the lymph nodes, brain, bone, and pleura but showed similar performance in the delineation of primary tumors and detection of suspected metastases in the lungs, liver, and adrenal glands.
Although the sensitivity of detecting advanced lung cancers with FAPI has been well reported, there is little information on diagnosing FAPI in GGNs. In the current analysis, we observed that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT resulted in higher SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVindex, and TBR values and better detection rates based on TBR compared to 18F-FDG PET/CT (24–26). Meanwhile, we found that when based on SUVindex, 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT would have a reasonable detection rate. However, from a visual evaluation, it is hard to distinguish between normal tissue uptake and mild uptake of lesions in clinical practice. Our data demonstrated that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT showed some superiorities to 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting primary tumors in early adenocarcinoma.
A case report indicated that FAPI showed higher uptake in a GGN than FDG PET/CT (14). At this point, our conclusions were consistent with the previous case. In addition, our study has demonstrated that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT showed significantly different uptake values in different subtypes of GGNs and significantly higher uptake in all subtypes of GGNs compared with 18F-FDG PET/CT. Specific to each GGN type investigated, our study suggested that on 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/CT, the invasive pathological subtypes showed higher uptakes than noninvasive ones. The latest lung cancer treatment guidelines recommend observation for patients with multiple GGNs to further develop a treatment plan (27). FAPI may help evaluate nodules that require priority removal or focus follow-up. Figure 6 presents imaging of a specific patient with multiple GGNs, highlighting the detection of the largest nodules in the left superior lobe, which exhibited the highest SUVmax uptake in FAPI and was subsequently recommended for removal by the thoracic surgeon. Considering our patient-based findings, we infer that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT might guide treatments for early-stage adenocarcinoma patients with multiple GGNs. However, it is noteworthy that S. McDermott et al.’s study suggested benign GGOs, and the benign GGN subgroup demonstrated significantly higher FDG uptake at PET than malignant GGOs/GGNs (28). Awareness of this finding may prevent misinterpretation of highly 18FDG-avid pure GGOs/GGNs as definitively malignant, which could lead to unnecessary thoracic surgery and its associated risks.
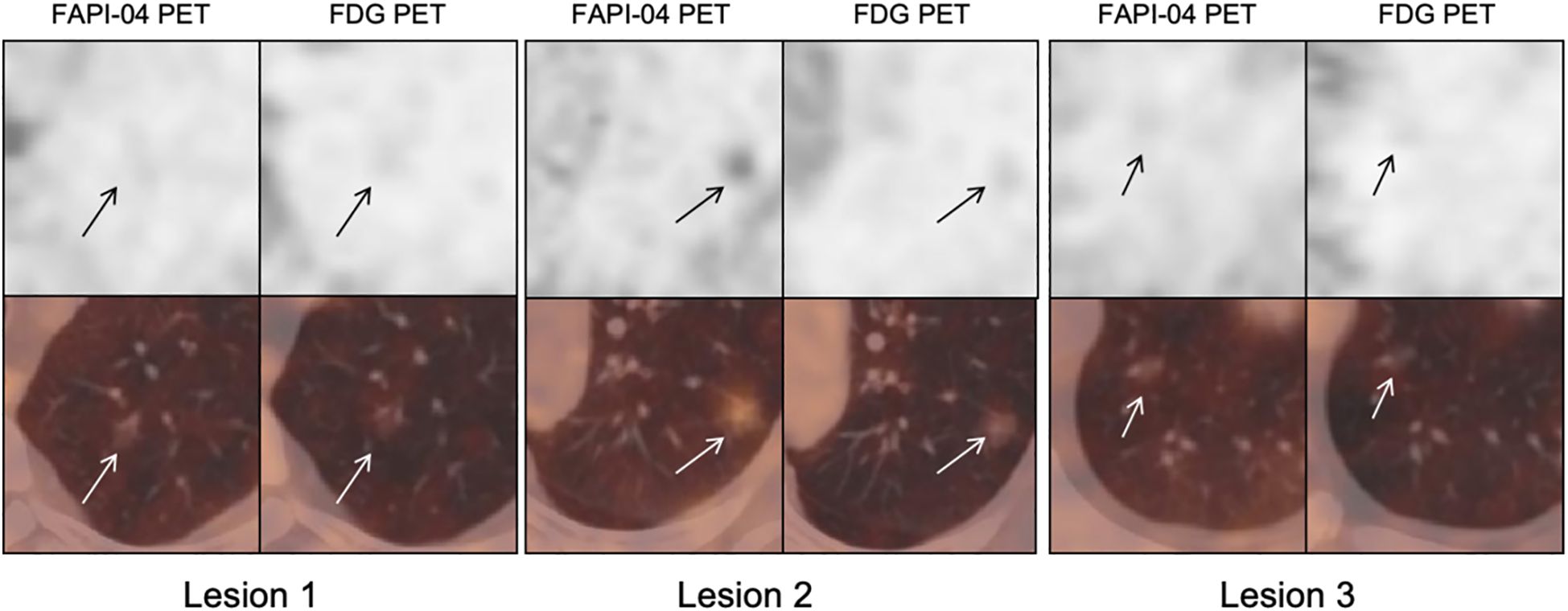
Figure 6. Male, 62 years old, CT showed multiple ground-glass nodules. 18F-FDG PET imaging showed all nodules negative uptake, while Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET showed an intense uptake nodule in superior lobe of left lung (arrows). FAPI, fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose.
The current study shows that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT is better at identifying the invasion of GGNs than 18F-FDG PET/CT. Whereas 18F-FDG PET/CT had an AUC value for SUVmax of 0.721 and SUVmean of 0.684 according to the ROC curve, 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT has a better value of 0.801 and 0.770. Our findings on all four parameters of the ROC curves agree with those reported by Shao et al. (29), who found that GGNs in the invasive adenocarcinoma (IAC) group showed higher SUVmax and SUVindex on FDG PET than those in the pre-invasive MIA group. Given that the growth and development of GGNs usually follow the natural progression from pre-invasive lesions (AAH, AIS, and MIA) to IAC (30), and that GGNs at different stages have different SUV uptake values (9, 31), our findings support that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT may have the potential to differentiate pathological subtypes and predict invasiveness of GGNs. The radiologic–pathologic correlation of ground-glass nodules is summarized in Table 6, illustrating how CT and PET characteristics reflect the histopathological spectrum from pre-invasive to invasive adenocarcinoma.
Additionally, Zheng et al. (9) reported diameter [odds ratio (OR), 1.159; P < 0.001], lobulation (OR = 2.953; P = 0.002), and vascular changes (OR = 3.431; P< 0.001) were retained as independent predictors of the IAC group. Niu et al. (8) also reported that the proportions of mixed GGN type, polygonal or irregular shape, lobulated or spiculated edge, and dilated, distorted, or cut-off bronchial sign were higher for IAC GGNs than for preinvasive GGNs, and the attenuation value of the ground-glass opacity component on CT (CTGGO), which showed a similar result in our study. Our study shows that the diameter cut-off value for noninvasive and invasive GGNs was 16.5mm, and the AUC value of 0.836. Our results imply that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT has the potential to identify IAC in early lung adenocarcinoma preoperatively, but it must be confirmed in further research.
The study had several limitations. First, the number of patients was small; more GGNs were required for further study. In addition, as this was a single-center study, the findings should be interpreted with caution and require validation through larger multicenter clinical trials to confirm the generalizability and robustness of the results. Second, intratumor heterogeneity and sampling bias were inherent in the histopathology and immunochemistry analysis. Another limitation is the potential influence of the partial volume effect (PVE), particularly in ground-glass nodules smaller than 1 cm in diameter. PVE may have led to underestimation of radiotracer uptake in some pre-invasive lesions. This effect is inherent to PET imaging and applies to both 18F-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG; however, it is likely more pronounced in FDG due to its lower lesion-to-background contrast. Importantly, since both tracers were equally subject to this limitation, the observed superiority of 18F-FAPI-04 over FDG in differentiating invasive from pre-invasive lesions remains valid.
Despite these limitations, our results provide new evidence of the value of 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT in detecting GGNs and overcoming the bias of PET/CT diagnosis in early-stage adenocarcinoma. From a practical perspective, 18F-FAPI-04 is currently available mainly for research use. Several academic and clinical centers in Europe, Asia, and the United States have established routine production of 18F-FAPI-04 under good manufacturing practice (GMP) conditions. The synthesis and quality-control procedures are similar to those of 18F-FDG, and the overall production cost is comparable. However, the global availability of FAPI tracers remains limited because of ongoing regulatory approvals and the absence of commercial distribution in many regions. With the expansion of multicenter clinical trials and increasing industrial collaboration, the accessibility and clinical application of 18F-FAPI-04 are expected to improve substantially in the near future.
Our study indicates that 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT is useful for detecting early-stage adenocarcinoma. Our results show that it also outperforms 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of GGNs and can potentially be an alternative to 18F-FDG for detecting the invasiveness of GGNs.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available. Data, analytic methods, and study materials will not be made available to other researchers. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to PF, ZnVwZW5nMDQ1MUAxNjMuY29t.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR2100051406 (Ethics Committee approval No. 2021XJSS01). Registered 23 September 2021 ‘Retrospectively registered’, https://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.html?proj=133033. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ZL: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal Analysis. JL: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Formal Analysis. WH: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Investigation, Resources. SG: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Investigation. CD: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Validation. LL: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Data curation. HZ: Writing – review & editing, Software. YS: Writing – review & editing, Validation. HW: Resources, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Writing – review & editing, Resources. LT: Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. PF: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Cultivation Project of the Joint Fund, Heilongjiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation(Grant Number PL2024H077), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 82371994).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AAH, atypical adenomatous hyperplasia; AIS, adenocarcinoma in situ; AUC, area under the curve; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; FAPI, FAP inhibitor; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; FPR, false positive rate; GGN, ground-glass nodule; GGNs, ground-glass nodules; GMP, good manufacturing practice; HU, Hounsfield Unit; IAC, invasive adenocarcinoma; IQR, interquartile range; MIA, microinvasive adenocarcinoma; mGGN, mixed ground-glass nodule; OR, odds ratio; PET, positron emission tomography; pGGN, pure ground-glass nodule; PVE, partial volume effect; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; SD, standard deviation; SUVmax, maximum standardized uptake value; SUVmean, mean standardized uptake value; SUVindex the ratio of SUVmax of lesion to SUVmax of contralateral normal lung paranchyma; TPR, true positive rate; TBR, target-to-background ratio.
References
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
2. Kadota K, Villena-Vargas J, Yoshizawa A, Motoi N, Sima CS, Riely GJ, et al. Prognostic significance of adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, and nonmucinous lepidic predominant invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung in patients with stage I disease. Am J Surg Pathol. (2014) 38:448–60. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000134
3. Hattori A, Suzuki K, Matsunaga T, Fukui M, Tsushima Y, Takamochi K, et al. Tumour standardized uptake value on positron emission tomography is a novel predictor of adenocarcinoma in situ for c-Stage IA lung cancer patients with a part-solid nodule on thin-section computed tomography scan. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. (2014) 18:329–34. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivt500
4. Jacobson FL, Tarascio JN, and Fox SW. Can PET/CT help manage ground glass nodules? J Surg Oncol. (2018) 117:457–8. doi: 10.1002/jso.24975
5. Kim TJ, Park CM, Goo JM, and Lee KW. Is there a role for FDG PET in the management of lung cancer manifesting predominantly as ground-glass opacity? Am J Roentgenology. (2012) 198:83–8. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.6862
6. Wahidi MM, Govert JA, Goudar RK, Gould MK, and McCrory DC. Evidence for the Treatment of Patients With Pulmonary Nodules: When Is It Lung Cancer?: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest. (2007) 132:94S–107S. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-1352
7. Bak SH, Lee HY, Kim JH, Um SW, Kwon OJ, Han J, et al. Quantitative CT scanning analysis of pure ground-glass opacity nodules predicts further CT scanning change. Chest. (2016) 149:180–91. doi: 10.1378/chest.15-0034
8. Niu R, Shao X, Shao X, Wang J, Jiang Z, and Wang Y. Lung adenocarcinoma manifesting as ground-glass opacity nodules 3 cm or smaller: evaluation with combined high-resolution CT and PET/CT modality. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2019) 213:W236–45. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.21382
9. Zheng H, Zhang H, Wang S, Xiao F, and Liao M. Invasive prediction of ground glass nodule based on clinical characteristics and radiomics feature. Front Genet. (2022) 12:783391. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.783391
10. Wang Z, Zhu W, Lu Z, Li W, and Shi J. Invasive adenocarcinoma manifesting as pure ground glass nodule with different size: radiological characteristics differ while prognosis remains the same. Transl Cancer Res TCR. (2021) 10:2755–66. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-78
11. Mori Y, Dendl K, Cardinale J, Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, and Haberkorn U. FAPI PET: fibroblast activation protein inhibitor use in oncologic and nononcologic disease. Radiology. (2023) 306:e220749. doi: 10.1148/radiol.220749
12. Borgonje PE, Andrews LM, Herder GJM, and de Klerk JMH. Performance and prospects of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI PET/CT scans in lung cancer. Cancers. (2022) 14:5566. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225566
13. Wei Y, Ma L, Li P, Lu J, Ren J, Yan S, et al. FAPI compared with FDG PET/CT for diagnosis of primary and metastatic lung cancer. Radiology. (2023) 308:e222785. doi: 10.1148/radiol.222785
14. Chen H, Pang Y, Meng T, Yu X, and Sun L. 18F-FDG and 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in the evaluation of ground-glass opacity nodule. Clin Nucl Med. (2021) 46:424–6. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003600
15. Giesel FL, Adeberg S, Syed M, Lindner T, Jiménez-Franco LD, Mavriopoulou E, et al. FAPI-74 PET/CT using either 18F-alF or cold-kit 68Ga labeling: biodistribution, radiation dosimetry, and tumor delineation in lung cancer patients. J Nucl Med. (2021) 62:201–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.245084
16. Yang L, Xu S, Cheng L, Gao C, Cao S, Chang Z, et al. 18F] AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT as a promising tool for imaging fibroblast activation protein in gastrointestinal system cancers: a prospective investigation of comparative analysis with 18F-FDG. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2023) 50:4051–63. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06351-9
17. Wang H, Zhu W, Ren S, Kong Y, Huang Q, Zhao J, et al. 68Ga-FAPI-04 versus 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:693640. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.693640
18. Succony L, Rassl DM, Barker AP, McCaughan FM, and Rintoul RC. Adenocarcinoma spectrum lesions of the lung: Detection, pathology and treatment strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. (2021) 99:102237. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102237
19. Lyu Z, Han W, Zhang Q, Zhao H, Liu S, Wang Y, et al. Clinical application of Al18F-NOTA-FAPI PET/CT in diagnosis and TNM staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, compared to 18F-FDG. Cancer imaging. (2023) 23:86. doi: 10.1186/s40644-023-00596-1
20. Wang S, Zhou X, Xu X, Ding J, Liu S, Hou X, et al. Clinical translational evaluation of Al18F-NOTA-FAPI for fibroblast activation protein-targeted tumour imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2021) 48:4259–71. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05470-5
21. Giesel FL, Kratochwil C, Lindner T, Marschalek MM, Loktev A, Lehnert W, et al. 68 ga-FAPI PET/CT: biodistribution and preliminary dosimetry estimate of 2 DOTA-containing FAP-targeting agents in patients with various cancers. J Nucl Med. (2019) 60:386–92. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.215913
22. Cardillo G, Petersen RH, Ricciardi S, Patel A, Lodhia JV, Gooseman MR, et al. European guidelines for the surgical management of pure ground-glass opacities and part-solid nodules: Task Force of the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. (2023) 64:ezad222. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezad222
23. Shao X, Niu R, Jiang Z, Shao X, and Wang Y. Role of PET/CT in management of early lung adenocarcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2020) 214:437–45. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.21585
24. Wei Y, Cheng K, Fu Z, Zheng J, Mu Z, Zhao C, et al. 18F] AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT uptake in metastatic lesions on PET/CT imaging might distinguish different pathological types of lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2022) 49:1671–81. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05638-z
25. Wu J, Liu H, Ou L, Jiang G, and Zhang C. FAPI uptake in a vertebral body fracture in a patient with lung cancer: A FAPI imaging pitfall. Clin Nucl Med. (2021) 46:520–2. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003560
26. Shang Q, Zhao L, Pang Y, Meng T, and Chen H. Differentiation of reactive lymph nodes and tumor metastatic lymph nodes with 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in a patient with squamous cell lung cancer. Clin Nucl Med. (2022) 47:458–61. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000003998
27. Chen H, Kim AW, Hsin M, Shrager JB, Prosper AE, Wahidi MM, et al. The 2023 American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) Expert Consensus Document: Management of subsolid lung nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2024) 168:631–647.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2024.02.026
28. McDermott S, Kilcoyne A, Wang Y, Scott JA, Halpern EF, and Ackman JB. Comparison of the 18F-FDG avidity at PET of benign and Malignant pure ground-glass opacities: a paradox? Clin Radiol. (2019) 74:187–95. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2018.12.009
29. Shao X, Shao X, Niu R, Jiang Z, Xu M, and Wang Y. Investigating the association between ground-glass nodules glucose metabolism and the invasive growth pattern of early lung adenocarcinoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2021) 11:3506–17. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-1189
30. Li Y, Li X, Li H, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Sun K, et al. Genomic characterisation of pulmonary subsolid nodules: mutational landscape and radiological features. Eur Respir J. (2020) 55:1901409. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01409-2019
Keywords: early stage adenocarcinoma, ground-glass nodules, FAPI PET/CT, FDG PET/CT, cancer-associated fibroblast
Citation: Lyu Z, Liu J, Han W, Guo S, Duan C, Liu L, Zhao H, Su Y, Wang H, Zhang Q, Tian L and Fu P (2025) 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the evaluation of ground-glass nodules less than 3 cm in diameter comparing to 18F-FDG PET/CT. Front. Oncol. 15:1605678. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1605678
Received: 03 April 2025; Accepted: 24 October 2025;
Published: 10 November 2025.
Edited by:
Yeon Wook Kim, Seoul National University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Carmelo Caldarella, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, ItalyGiuseppe Cardillo, San Camillo Forlanini Hospital, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Lyu, Liu, Han, Guo, Duan, Liu, Zhao, Su, Wang, Zhang, Tian and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peng Fu, ZnVwZW5nMDQ1MUAxNjMuY29t; Lin Tian, dGlhbmxpbjYyMjUxMDhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhehao Lyu
Zhehao Lyu Jianing Liu1†
Jianing Liu1† Hongyue Zhao
Hongyue Zhao Yexin Su
Yexin Su Peng Fu
Peng Fu