- Department of General Surgery, Shenzhen Baoan Shiyan People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Background: Liver resection and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) are two common treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, their efficacy and safety remain unclear. We aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the effectiveness and safety of these two treatments.
Methods: We searched multiple databases to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared liver resection with RFA for the treatment of HCC. The primary outcome was 5-year overall survival rate. The secondary endpoint was the incidence of complications. We used RevMan 5.4 software to calculate the pooled effects and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Ten RCTs and 35 cohort studies were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled OR for 5-year overall survival rate favored liver resection (OR = 1.76, 95% CI = 1.19-2.61, P<0.00001). RFA was indicated with less postoperative complications (OR = 3.35, 95% CI = 2.52-4.45, P<0.00001).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggests that liver resection is more effective than RFA in treating HCC with regard to higher 5-year overall survival rate, while the safety of liver resection was concerning. We recommend liver resection as a first-line treatment for HCC, but RFA may be a preferable choice for patients who are not suitable for surgical procedures. More high-quality RCTs are needed to confirm these findings.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42025458621.
1 Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is among the most common cancers worldwide, and is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates (1). The primary treatment options for HCC include surgical liver resection (LR) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) (2). LR involves removing the tumor and surrounding liver tissue; however, compared to RFA, LR may be associated with higher perioperative risks, including morbidity and mortality (3). RFA is a minimally invasive technique that destroys cancer cells using high-frequency alternating currents. It is often used as an alternative to surgical LR, especially in patients with small tumors or contraindications to surgery (4).
LR and RFA are considered to be effective treatments for early stage HCC (5). Recent studies have compared effectiveness and outcomes of LR versus RFA in the treatment of HCC, although with varying results. Some studies have reported that LR results in better survival rates, whereas others have described comparable outcomes between the 2 approaches (6).
Despite various studies comparing the effectiveness of LR and RFA, the findings have not consistently favored one treatment over the other. Consequently, systematic reviews and meta-analyses are needed to provide more robust evidence-based recommendations for the optimal management of HCC (7).
However, there are some limitations to previous meta-analyses, including differences in patient selection criteria, surgical techniques, and outcome measures, which may have affected the results (8). As such, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the available evidence regarding the effectiveness of LR versus RFA in the treatment of HCC and to address existing limitations in the literature.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Literature search
This systematic review and meta-analysis used PubMed database search strategies in accordance with recommendations from the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, and complied with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (i.e., “PRISMA”), and Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews (i.e., “AMSTAR) guidelines (9–11). Randomized control trials (RCTs) and cohort studies published before Sep 1, 2024, were included. The search terms were liver resection AND radiofrequency ablation AND hepatocellular carcinoma. The reference lists of all retrieved studies were reviewed for additional, potentially eligible studies. Two authors independently reviewed the titles, abstracts, and full texts according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, while a third author adjudicated any disagreements.
2.2 Study selection and data extraction
Eligible studies compared survival outcomes between LR and RFA. Studies were excluded if overall survival (OS) was not reported. Studies involving overlapping populations have been conducted. Statistically unreliable estimates were avoided by excluding studies with < 10 patients per group. Two researchers independently extracted relevant information using a predefined data extraction sheet. Consensus was reached in discussions to resolve discrepancies and missing data. The mean and standard deviation were estimated using the median and interquartile range (IQR) or median and range (12, 13).
2.3 Outcomes
The primary outcome was OS (1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates). The secondary outcomes were operative duration, postoperative mortality, estimated blood loss (EBL), length of hospital stay, postoperative complications, and recurrence rates.
2.4 Risk of bias
All RCTs were critically appraised according to the revised Risk of Bias tool (ROB2.0), and non-randomized studies were evaluated using the ROBINS-I tool (14, 15). The risk of bias was independently assessed by 2 authors and adjudicated by a third when required.
2.5 Data analysis
This meta-analysis was performed in accordance with the Cochrane Guidelines for Systematic Reviews (9). A Mantel–Haenszel model was used to calculate odds ratio (OR) and corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) for categorical data. Continuous data were analyzed using the inverse variance model and expressed as mean difference (MD) with 95% CI. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 test. A fixed-effects model was used to pool effects. Review Manager version 5.4 and R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) were used to perform statistical analyses. A P value < 0.05 was defined as the threshold for statistical significance of the estimates. This study was registered with The International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (i.e., “PROSPERO”) (CRD CRD42025458621).
3 Results
The literature search retrieved 1790 studies. After duplicates were removed and titles and abstracts were screened, 1432 studies remained, of which 61 full-text articles were read. In total, 45 studies (14,849 patients; 7567 RFA and 7282 LR procedures) were included in the analysis (Figure 1).
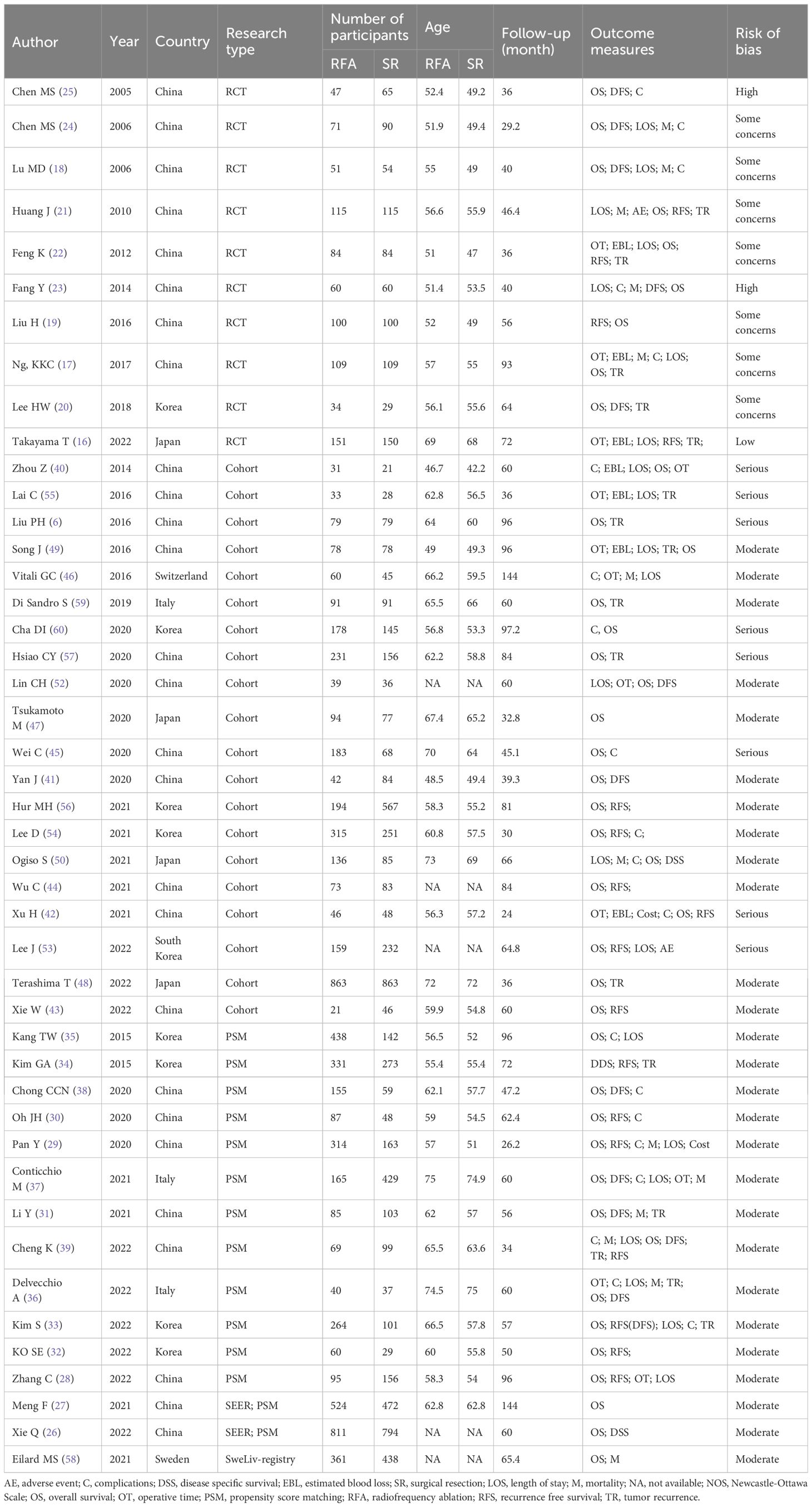
A summary of the 45 included studies, of which OS was reported in 39, is presented in Table 1. The systematic review included 10 RCTs (16–25) and 35 cohort studies (26–60), with 14 cohort studies using propensity score matching (PSM). Two RCTs demonstrated a high risk of bias, 7 studies indicated some concerns regarding the risk of bias, and 1 study had a low risk of bias. Eight non-randomized studies had a serious risk of bias, and 27 studies had a moderate risk of bias (Supplementary Figure S1).
LR significantly prolonged patient survival compared with RFA. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were used to compare survival outcomes between RFA and LR. The 1-year OS for RFA and LR was similar (LR versus [vs.] RFA, OR 1.10 [95% CI 0.96 – 1.27]; P = 0.18, I2 = 8%) (Figure 2), while LR was associated with better 3-year OS (LR vs. RFA, OR 1.34 [95% CI 1.22 – 1.47]; P<0.00001, I2 = 51%) (Figure 3), and 5-year OS (LR vs. RFA, OR 1.66 [95% CI 1.49 – 1.84]; P<0.00001, I2 = 42%) (Figure 4) compared with RFA. The recurrence rate for LR was consistently much lower than that of RFA (OR 0.61 [95% CI 0.54 – 0.70]; P<0.00001, I2 = 54%) (Figure 5).
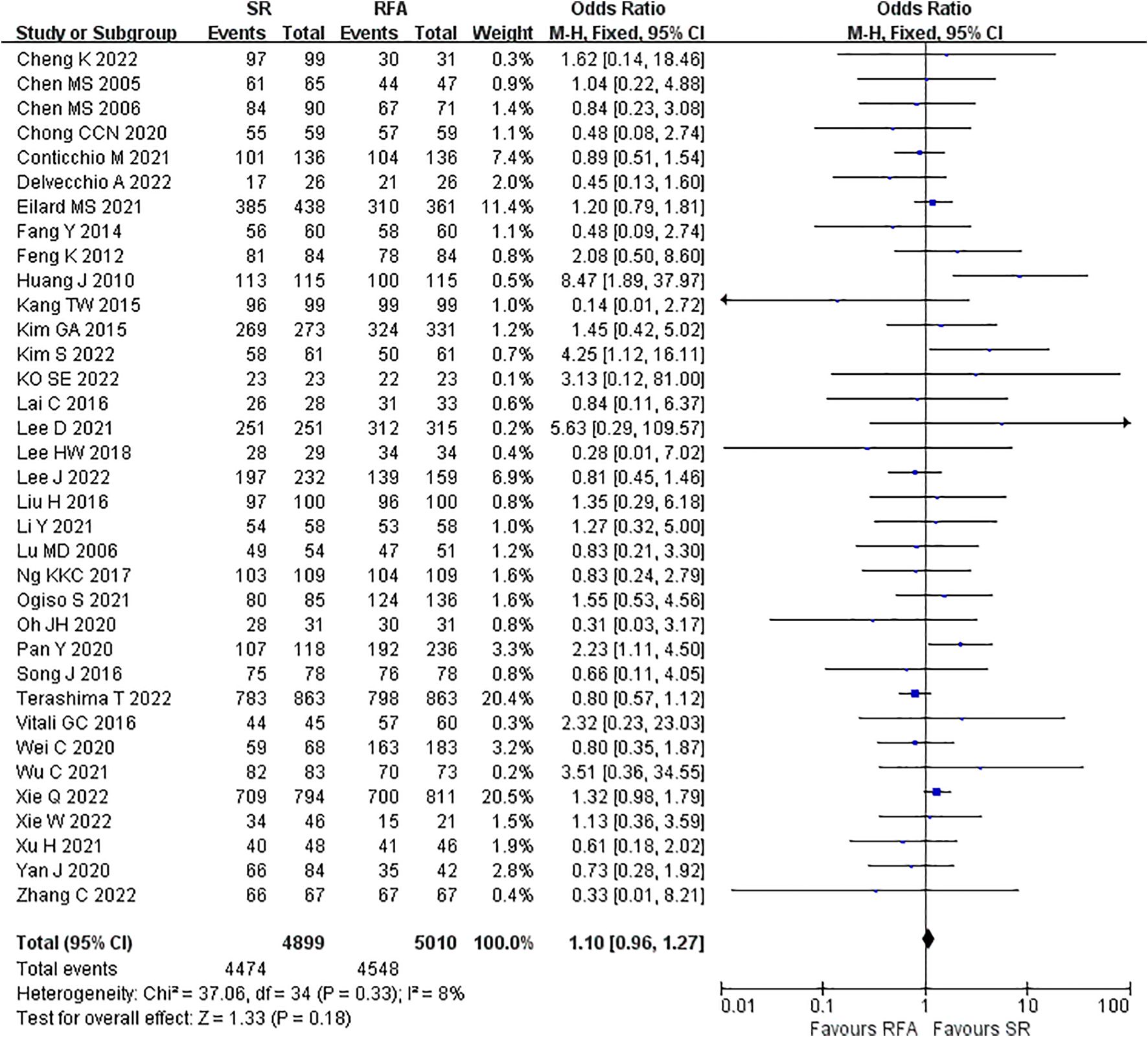
Figure 2. Meta-analysis of 1-year overall survival rate comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
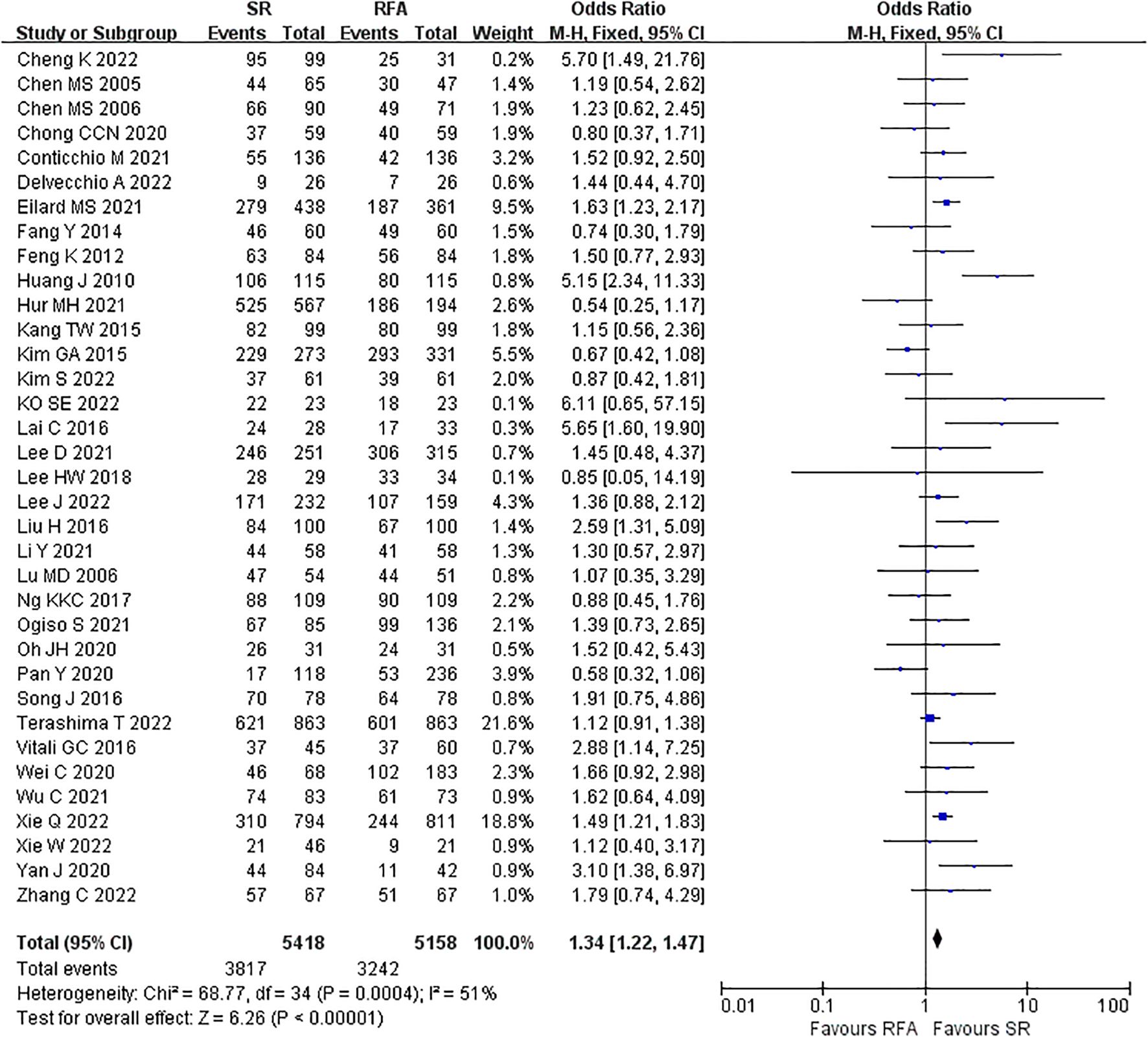
Figure 3. Meta-analysis of 3-year overall survival rate comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
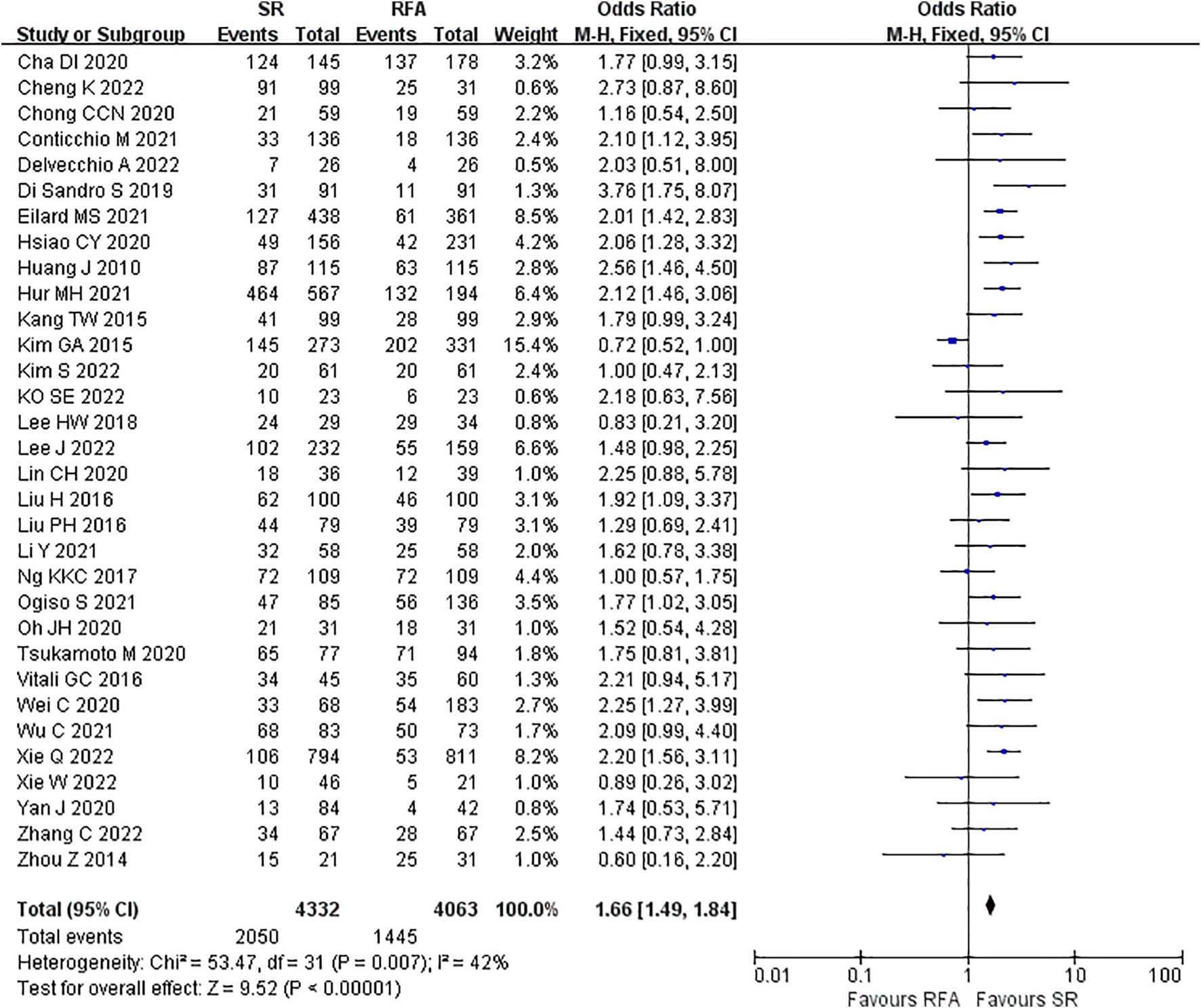
Figure 4. Meta-analysis of 5-year overall survival rate comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
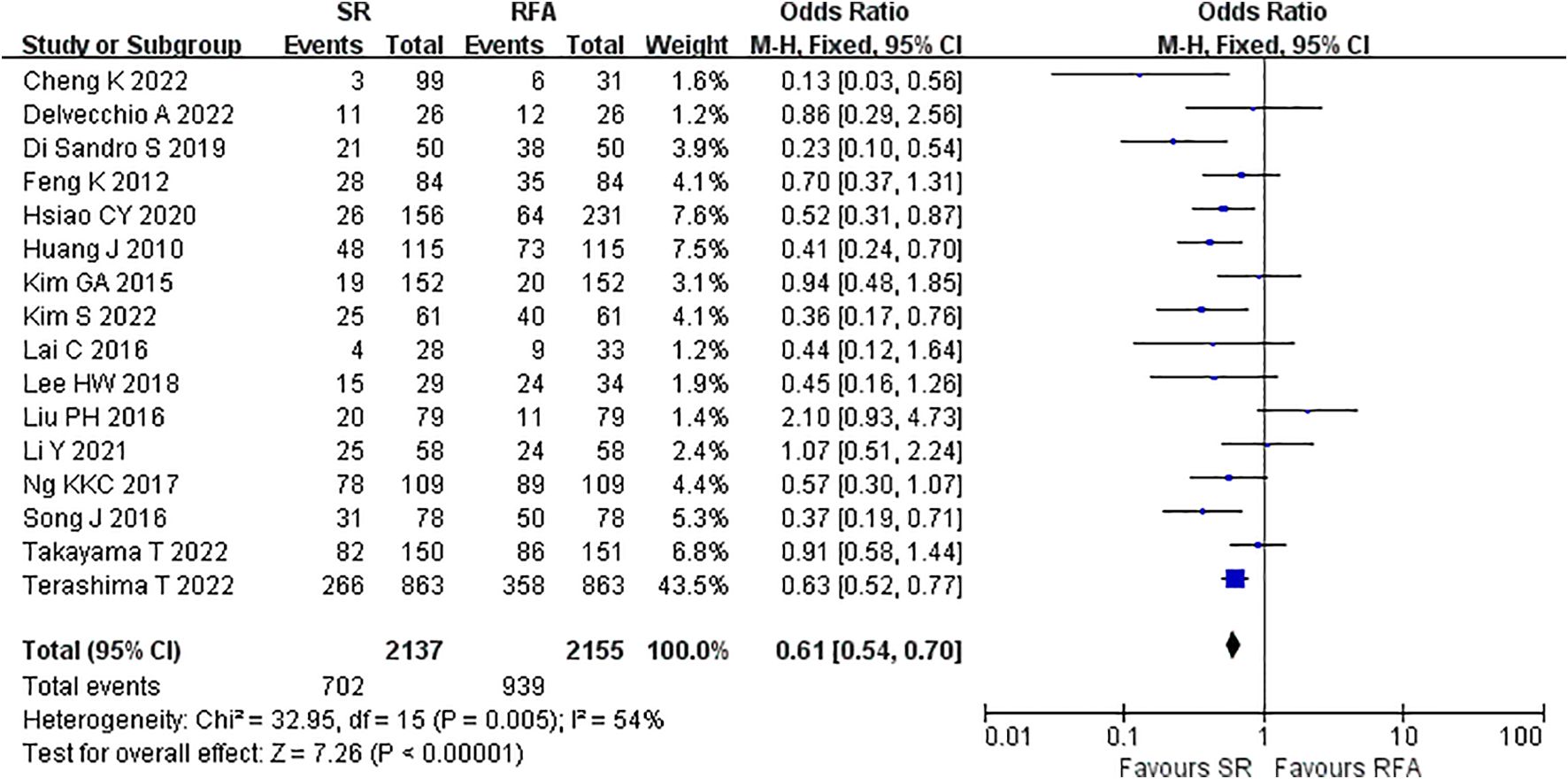
Figure 5. Meta-analysis of recurrence rate comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
RFA demonstrated a significant advantage over LR in terms of intraoperative outcomes. Operative duration was significantly shorter in the RFA vs. LR groups (LR vs. RFA, MD 117.80 [95% CI 113.30 – 122.30]; P<0.00001, I2 = 97%) (Figure 6). EBL was significantly lower in the RFA group than that in the LR group (LR vs. RFA, MD 99.67 [95% CI 93.56 – 105.77]; P<0.00001, I2 = 95%) (Figure 7).
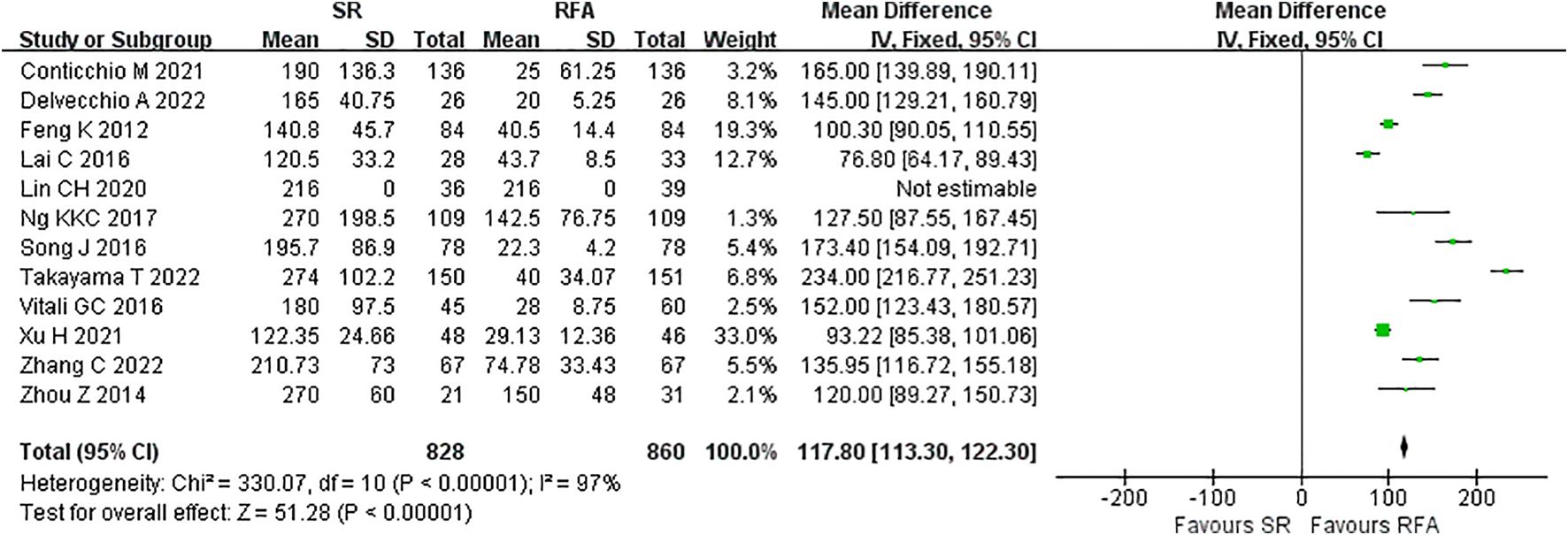
Figure 6. Meta-analysis of operative time comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
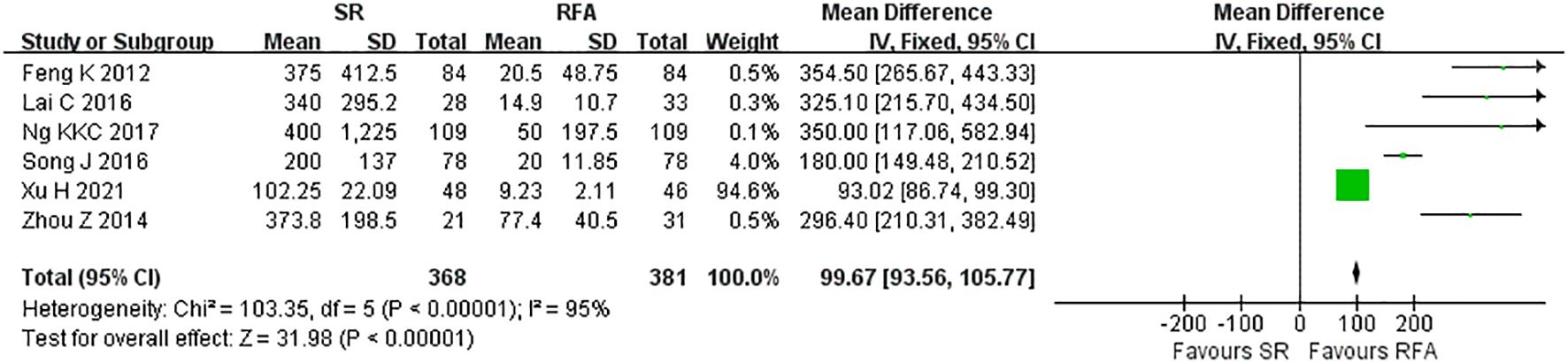
Figure 7. Meta-analysis of estimated blood loss comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
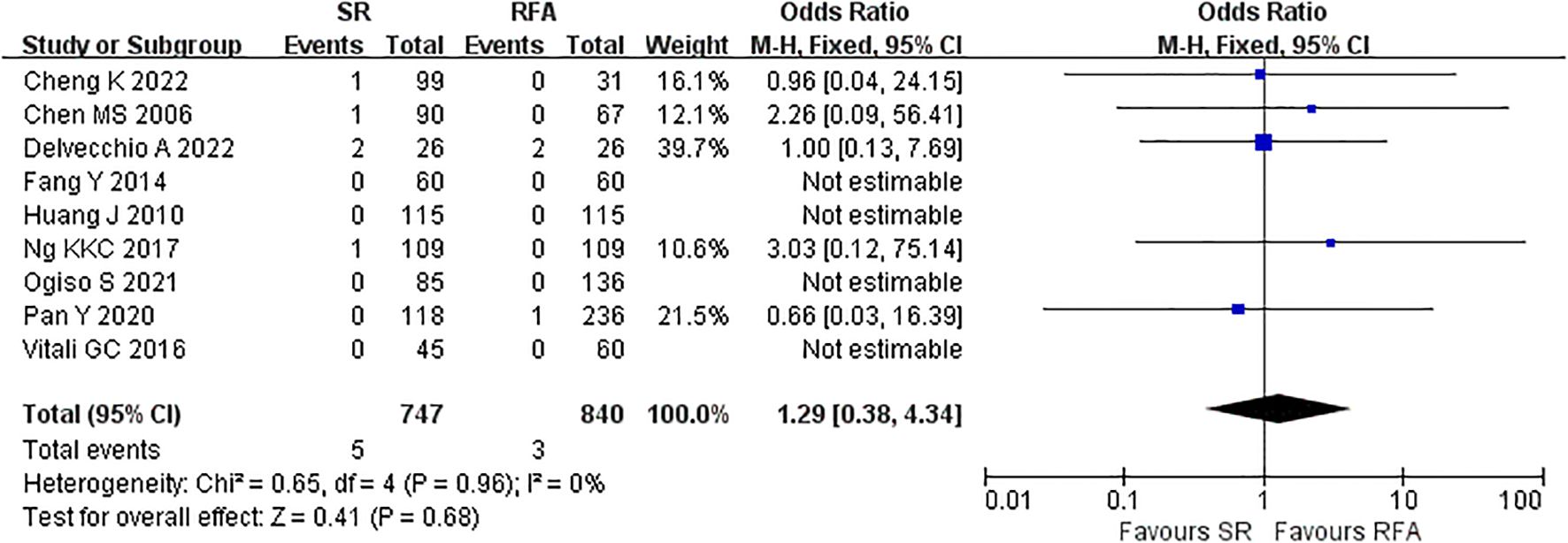
The short-term outcomes of RFA were better than those of LR. The RFA group experienced fewer postoperative complications than the LR group (LR vs. RFA, OR 3.35 [95% CI 2.52 – 4.45]; P<0.00001, I2 = 42%) (Figure 8). The postoperative length of hospital stay was consistently shorter in the RFA group (LR vs. RFA, MD 5.36 [95% CI 4.95 – 5.77]; P<0.00001, I2 = 93%) (Figure 9). However, mortality rates were similar between the LR and RFA groups (LR vs. RFA, OR 1.29 [95% CI 0.38 – 4.34]; P = 0.68, I2 = 0%) (Figure 10).
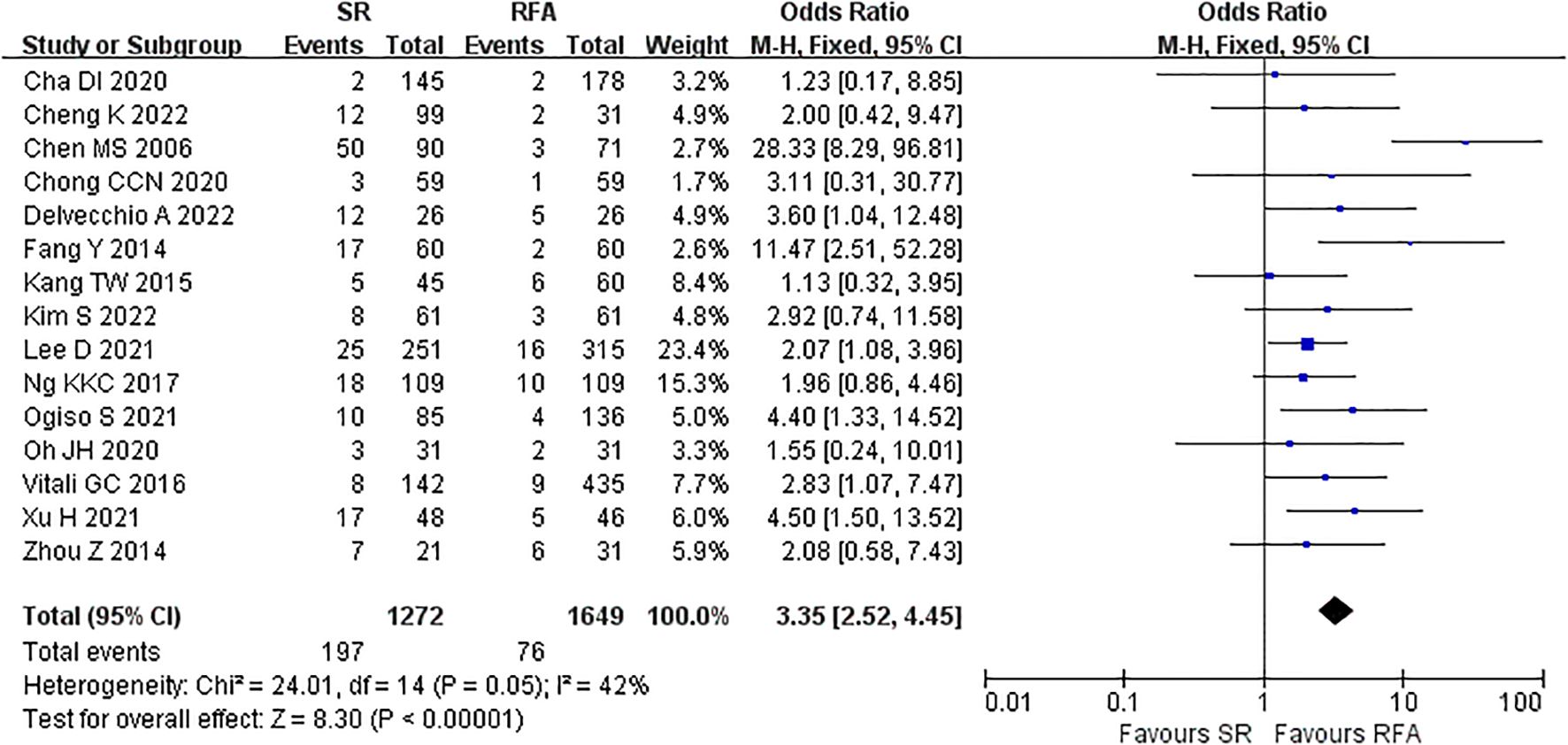
Figure 8. Meta-analysis of postoperative complications comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
![Forest plot showing a meta-analysis of seven studies comparing SR and RFA. Each study displays mean differences with confidence intervals, represented by green squares and horizontal lines. The overall effect size is shown as a black diamond, favoring SR with a mean difference of 5.36 [4.95, 5.77]. Heterogeneity is high (I² = 93%). Total participants: 570 (SR) and 527 (RFA).](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1607338/fonc-15-1607338-HTML-r2/image_m/fonc-15-1607338-g009.jpg)
Figure 9. Meta-analysis of postoperative length of hospital stay comparing surgical resection with radio frequency ablation.
When the study by Kim (34) was excluded, the OR and 95% CI changed significantly from 1.66 (1.49 – 1.84) to 1.83 (1.64 – 2.04), indicating that the study by Kim (34) was the main source of bias (Figure 11). To assess the robustness of primary outcomes, we performed comprehensive sensitivity analyses. Exclusion of studies with high risk of bias and non-propensity-score-matched cohorts consistently demonstrated superior outcomes for liver resection over radiofrequency ablation (OR 1.68, 95% CI 1.20 – 1.94; P<0.01, I²=57.7%, Supplementary Figure S2). Similarly, stratification by study design revealed concordant results: analysis restricted to randomized trials maintained significant advantage for resection (OR 1.60, 95% CI 1.08 – 2.37; P<0.0001, I²=40.2%), while observational studies alone yielded comparable effect sizes (OR 1.70, 95% CI 1.44 – 2.00; P<0.0001, I²=44.4%, Supplementary Figure S3). These methodologically distinct approaches collectively demonstrate the stability of our core findings across analytical frameworks. Trim-and-fill analysis indicated potential publication bias for the outcome of 5 year overall survival (OS), with imputation of 2 hypothetical studies reducing the HR magnitude from (LR vs. RFA, OR 1.66 [95% CI 1.49 – 1.84]; P<0.00001, I2 = 42%) to (LR vs. RFA, OR 1.63 [95% CI 1.41 – 1.90]; P<0.0001, I2 = 44%). While this suggests our pooled effect may overestimate LR’s benefit, the adjusted HR remained statistically significant and clinically relevant. Nevertheless, the possibility of unpublished null findings warrants caution in interpreting the magnitude of survival advantage (Figure 12). Moreover, publication bias resulted in asymmetry of the funnel plot.
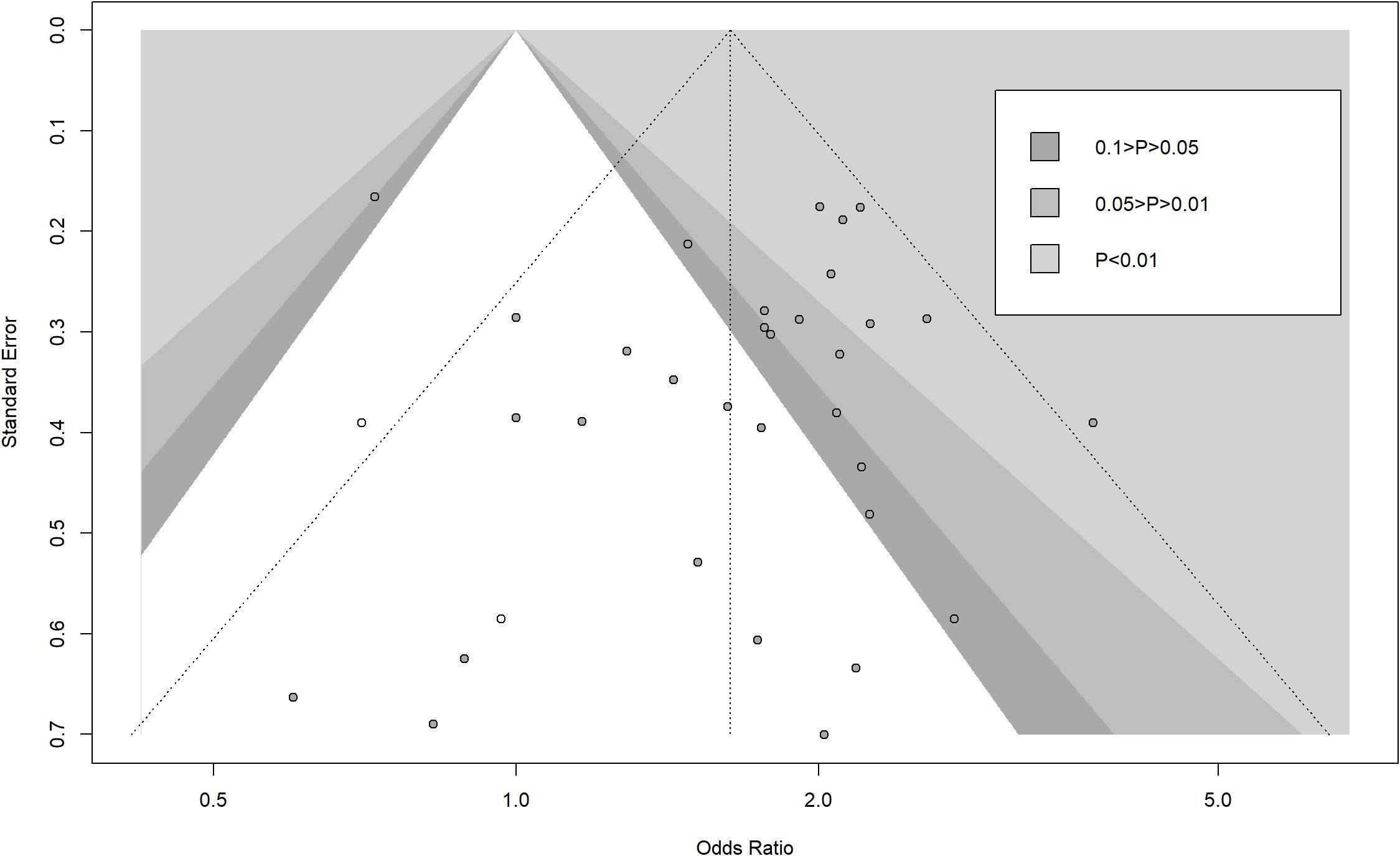
Figure 12. Contour-enhanced funnel plot with trim-and-fill method (white dot) for publication bias of 5-year overall survival.
4 Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis compared the efficacy and safety of LR and RFA for the treatment of HCC (Table 2). Our analysis included 45 studies comprising 14,849 patients, of whom 7567 underwent RFA and 7282 underwent LR. Results of analysis revealed that LR significantly prolonged OS of patients with HCC compared with RFA. The recurrence rate after LR was significantly lower than RFA. The intraoperative outcomes favored RFA, with a significantly shorter operative duration, reduced EBL, fewer postoperative complications, and shorter postoperative length of hospital stay.
Our meta-analysis revealed that LR was associated with a better OS rate than RFA (61). This finding is consistent with those of several previous investigations. One possible explanation is that surgical LR offers complete tumor removal with sufficient margins to reduce the risk for recurrence (62, 63). However, RFA relies on thermal energy to destroy tumors, which may not be completely effective in eliminating HCC (64). Our results are important for clinical decision-making because they provide support for recommending LR for patients with HCC who are physically able to tolerate invasive surgical procedures.
However, RFA had a superior effect on intra- and postoperative outcomes compared with LR. Our study and several RCTs suggest that RFA minimizes operative duration and reduces intraoperative EBL (65). This finding may have important implications, especially in reducing operative risk in patients with poor liver function, performing repeated treatments, or managing more challenging lesions, such as large tumors or those located near vital structures (66). In addition, our findings demonstrated that RFA resulted in shorter hospital stays and fewer postoperative complications. These are important benefits for improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs (67).
One of the strengths of our study is its large sample size, which provides robust data for the comparison between LR and RFA in the treatment of HCC. We also included high-quality studies that minimized the impact of bias and increased the reliability of the results (16). Furthermore, although the positive results from the sensitivity and publication bias analyses suggested that there may have been some degree of bias, the fact that the conclusion of the meta-analysis remained favorable for long-term survival after bias adjustment indicates that the conclusion of this meta-analysis is robust.
However, this study also had several limitations. First, the heterogeneity of the included studies may have affected the consistency of findings. Second, although we performed a subgroup analysis to reduce heterogeneity, results may have been affected due to the various surgical techniques and devices used. Although our findings demonstrate LR’s survival advantage in broad HCC populations, further research is needed to clarify its benefit in specific clinical scenarios—particularly among elderly patients, those with marginal liver reserve (Child-Pugh B), or complex tumor locations where RFA’s minimally invasive profile may offset oncologic trade-offs. Future individual patient data meta-analyses or propensity-matched cohort studies targeting these subgroups are warranted.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, based on pooled evidence from randomized and high-quality observational studies, liver resection demonstrates superior survival outcomes compared to RFA, particularly for patients with preserved liver function and resectable tumors. However, given the inherent selection bias in non-randomized comparisons and heterogeneity in patient populations, treatment decisions should be individualized, considering comorbidities, tumor location, and local expertise. LR represents a preferred curative-intent option where clinically feasible, rather than a universal ‘first-line’ approach.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZH: Methodology, Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Investigation, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. GS: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Software. GY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XF: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Validation. MT: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation, Validation. YZ: Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shenzhen Municipality (JCYJ20230807150601003 to ZH).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1607338/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Risk of bias evaluation.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Sensitivity analysis of primary outcomes after exclusion of high-risk-of-bias studies and non-propensity-score-matched cohorts.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Stratified analysis by study design showing maintained advantage of liver resection in both randomized trials and observational studies.
References
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, and Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. (2015) 65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262
2. European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2018) 69:182–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019
3. Marasco G, Colecchia A, Colli A, Ravaioli F, Casazza G, Bacchi Reggiani ML, et al. Role of liver and spleen stiffness in predicting the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Hepatol. (2019) 70:440–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.022
4. Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. (2008) 47:82–9. doi: 10.1002/hep.21933
5. Forner A, Reig M, and Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. (2018) 391:1301–14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2
6. Liu PH, Hsu CY, Hsia CY, Lee YH, Su CW, Huang YH, et al. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Assessment of eleven staging systems. J Hepatol. (2016) 64:601–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.10.029
7. Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Cescon M, Colecchia A, Ercolani G, Bolondi L, et al. Cost-effectiveness of hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2013) 59:300–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.009
8. Cho YK, Rhim H, and Noh S. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection as primary treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma meeting the Milan criteria: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2011) 26:1354–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06812.x
9. Higgins JPT TJ CJ, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, and Welch VA. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.0 (updated july 2019). Cochrane. (2019). doi: 10.1002/9781119536604
10. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. (2021) 88:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
11. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Bmj. (2017) 358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008
12. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, and Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2005) 5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
13. Higgins JPT LT DJ. Chapter 6: Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of effect. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane. (2019). doi: 10.1002/9781119536604
14. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
15. Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. Bmj. (2016) 355:i4919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4919
16. Takayama T, Hasegawa K, Izumi N, Kudo M, Shimada M, Yamanaka N, et al. Surgery versus radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized controlled trial (SURF trial). Liver Cancer. (2022) 11:209–18. doi: 10.1159/000521665
17. Ng KKC, Chok KSH, Chan ACY, Cheung TT, Wong TCL, Fung JYY, et al. Randomized clinical trial of hepatic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. (2017) 104:1775–84. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10677
18. Lu MD, Kuang M, Liang LJ, Xie XY, Peng BG, Liu GJ, et al. Surgical resection versus percutaneous thermal ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized clinical trial. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2006) 86:801–5. doi: 10.3760/j:issn:0376-2491.2006.12.003
19. Liu H, Wang ZG, Fu SY, Li AJ, Pan ZY, Zhou WP, et al. Randomized clinical trial of chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus partial hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. Br J Surg. (2016) 103:348–56. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10061
20. Lee HW, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Kim YJ, Park JW, Park SJ, et al. A prospective randomized study comparing radiofrequency ablation and hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Treat Res. (2018) 94:74–82. doi: 10.4174/astr.2018.94.2.74
21. Huang J, Yan L, Cheng Z, Wu H, Du L, Wang J, et al. A randomized trial comparing radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for HCC conforming to the Milan criteria. Ann Surg. (2010) 252:903–12. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181efc656
22. Feng K, Yan J, Li X, Xia F, Ma K, Wang S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2012) 57:794–802. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.05.007
23. Fang Y, Chen W, Liang X, Li D, Lou H, Chen R, et al. Comparison of long-term effectiveness and complications of radiofrequency ablation with hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2014) 29:193–200. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12441
24. Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y, Guo RP, Liang HH, Zhang YQ, et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. (2006) 243:321–8. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000201480.65519.b8
25. Chen MS, Li JQ, Liang HH, Lin XJ, Guo RP, Zheng Y, et al. Comparison of effects of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection on small hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2005) 85:80–3. doi: 10.3760/j:issn:0376-2491.2005.02.003
26. Xie Q, Yang Y, Qu B, Xiao P, Tang F, and Shen H. Comparison of surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for stages I and II elderly hepatocellular carcinoma patients (≥ = 65 years): A SEER population-based propensity score matching’s study. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:903231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903231
27. Meng F, Zhang H, Peng H, and Lu S. Comparison of 10-year survival outcomes for early single hepatocellular carcinoma following different treatments. BioMed Res Int. (2021) 2021:6638117. doi: 10.1155/2021/6638117
28. Zhang C, Gao R, Guo S, Ning C, Li A, Wang X, et al. Anatomic resection versus radiofrequency ablation with an ablative margin ≥ = 1.0 cm for solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma measuring ≤ = 3 cm: Comparison of long-term outcomes using propensity score matching analysis. Eur J Radiol. (2022) 155:110498. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110498
29. Pan YX, Long Q, Yi MJ, Chen JB, Chen JC, Zhang YJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A real world single center study. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2020) 46:548–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.10.026
30. Oh JH, Sinn DH, Choi GS, Kim JM, Joh JW, Kang TW, et al. Comparison of outcome between liver resection, radiofrequency ablation, and transarterial therapy for multiple small hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. Ann Surg Treat Res. (2020) 99:238–46. doi: 10.4174/astr.2020.99.4.238
31. Li YC, Chen PH, Yeh JH, Hsiao P, Lo GH, Tan T, et al. Clinical outcomes of surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation in very-early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2021) 21:418. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01995-z
32. Ko SE, Lee MW, Ahn S, Rhim H, Kang TW, Song KD, et al. Laparoscopic hepatic resection versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinomas smaller than 3 cm: analysis of treatment outcomes using propensity score matching. Korean J Radiol. (2022) 23:615–24. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0786
33. Kim S, Yoon CJ, Cho JY, Han HS, Yoon YS, Lee HW, et al. Comparative long-term outcomes of laparoscopic hepatectomy and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma located in the anterolateral segments of the liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. (2022) 29:349–58. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.1064
34. Kim GA, Shim JH, Kim MJ, Kim SY, Won HJ, Shin YM, et al. Radiofrequency ablation as an alternative to hepatic resection for single small hepatocellular carcinomas. Br J Surg. (2016) 103:126–35. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9960
35. Kang TW, Kim JM, Rhim H, Lee MW, Kim YS, Lim HK, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation versus nonanatomic resection–propensity score analyses of long-term outcomes. Radiology. (2015) 275:908–19. doi: 10.1148/radiol.15141483
36. Delvecchio A, Inchingolo R, Laforgia R, Ratti F, Gelli M, Anelli MF, et al. Liver resection vs radiofrequency ablation in single hepatocellular carcinoma of posterosuperior segments in elderly patients. World J Gastrointest Surg. (2021) 13:1696–707. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i12.1696
37. Conticchio M, Inchingolo R, Delvecchio A, Laera L, Ratti F, Gelli M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs surgical resection in elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Milan criteria. World J Gastroenterol. (2021) 27:2205–18. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i18.2205
38. Chong CC, Lee KF, Chu CM, Chan AW, Yu SC, and Lai PB. Laparoscopic Hepatectomy (with or without Robotic Assistance) versus Radiofrequency Ablation as a Minimally Invasive Treatment for Very Early-Stage or Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig Surg. (2020) 37:65–71. doi: 10.1159/000497112
39. Cheng KC and Ho KM. Pure laparoscopic liver resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score and multivariate analysis. Transl Cancer Res. (2022) 11:43–51. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1045
40. Zhou Z, Lei J, Li B, Yan L, Wang W, Wei Y, et al. Liver resection and radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma cases (single nodule <2 cm): a single-center study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2014) 26:339–44. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000012
41. Yan J, Man Z, Lu Q, and Ma K. Long-term survival in patients receiving combination therapy with resection and radiofrequency ablation for multi-focal hepatocellular carcinoma classified as barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B: A retrospective controlled study. Cancer Manag Res. (2020) 12:2613–21. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S237635
42. Xu H, Zhou L, and Jin Q. The effects of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation and laparoscopic hepatectomy in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective analysis. Transl Cancer Res. (2021) 10:4794–801. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-367
43. Xie W, Tan J, Li B, Chen S, Liu B, Shen J, et al. Comparison of hepatic resection with percutaneous ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in the caudate lobe within milan criteria. J Gastrointest Surg. (2022) 26:323–32. doi: 10.1007/s11605-021-05111-0
44. Wu CC, Tseng CW, Tseng KC, Chen YC, Wu TW, Chang SY, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for the treatment of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma 2 cm or smaller: A cohort study in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. (2021) 120:1249–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2020.11.010
45. Wei CY, Chau GY, Chen PH, Liu CA, Huang YH, Huo TI, et al. A comparison of prognoses between surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and esophagogastric varices. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:17259. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74424-y
46. Vitali GC, Laurent A, Terraz S, Majno P, Buchs NC, Rubbia-Brandt L, et al. Minimally invasive surgery versus percutaneous radio frequency ablation for the treatment of single small (≤ =3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study. Surg Endosc. (2016) 30:2301–7. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4295-6
47. Tsukamoto M, Imai K, Yamashita YI, Kitano Y, Okabe H, Nakagawa S, et al. Endoscopic hepatic resection and endoscopic radiofrequency ablation as initial treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. Surg Today. (2020) 50:402–12. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01903-9
48. Terashima T, Higashibeppu Y, Yamashita T, Sakata Y, Azuma M, Munakata H, et al. Comparative analysis of medical costs after hepatectomy versus radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in real-world clinical practice. Hepatol Res. (2022) 52:471–8. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13756
49. Song J, Wang Y, Ma K, Zheng S, Bie P, Xia F, et al. Laparoscopic hepatectomy versus radiofrequency ablation for minimally invasive treatment of single, small hepatocellular carcinomas. Surg Endosc. (2016) 30:4249–57. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4737-1
50. Ogiso S, Seo S, Eso Y, Yoh T, Kawai T, Okumura S, et al. Laparoscopic liver resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). (2021) 23:533–7. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.08.009
51. Liu PH, Hsu CY, Lee YH, Hsia CY, Huang YH, Su CW, et al. When to perform surgical resection or radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma?: A nomogram-guided treatment strategy. Med (Baltimore). (2015) 94:e1808. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001808
52. Lin CH, Ho CM, Wu CH, Liang PC, Wu YM, Hu RH, et al. Minimally invasive surgery versus radiofrequency ablation for single subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ = 2 cm with compensated liver cirrhosis. Surg Endosc. (2020) 34:5566–73. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07357-x
53. Lee J, Jin YJ, Shin SK, Kwon JH, Kim SG, Suh YJ, et al. Surgery versus radiofrequency ablation in patients with Child- Pugh class-A/single small (≤ =3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. (2022) 28:207–18. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0294
54. Lee DH, Kim JW, Lee JM, Kim JM, Lee MW, Rhim H, et al. Laparoscopic liver resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for small single nodular hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of treatment outcomes. Liver Cancer. (2021) 10:25–37. doi: 10.1159/000510909
55. Lai C, Jin RA, Liang X, and Cai XJ. Comparison of laparoscopic hepatectomy, percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and open hepatectomy in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2016) 17:236–46. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500322
56. Hur MH, Lee JH, Kim JY, Hong JH, Park MK, Cho HJ, et al. Comparison of overall survival between surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:6009. doi: 10.3390/cancers13236009
57. Hsiao CY, Hu RH, Ho CM, Wu YM, Lee PH, and Ho MC. Surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer very early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results of a single-center study. Am J Surg. (2020) 220:958–64. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.03.017
58. Eilard MS, Naredi P, Helmersson M, Hemmingsson O, Isaksson B, Lindell G, et al. Survival and prognostic factors after transplantation, resection and ablation in a national cohort of early hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). (2021) 23:394–403. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.07.010
59. Di Sandro S, Benuzzi L, Lauterio A, Botta F, De Carlis R, Najjar M, et al. Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma approached by curative-intent treatment: A propensity score analysis comparing radiofrequency ablation and liver resection. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2019) 45:1691–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.04.023
60. Cha DI, Song KD, Kang TW, Lee MW, and Rhim H. Small masses (≤ =3 cm) diagnosed as hepatocellular carcinoma on pre-treatment imaging: comparison of therapeutic outcomes between hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation. Br J Radiol. (2020) 93:20190719. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190719
61. Jia Z, Zhang H, and Li N. Evaluation of clinical outcomes of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma conforming to the Milan criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis of recent randomized controlled trials. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 36:1769–77. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15440
62. Wang FS, Fan JG, Zhang Z, Gao B, and Wang HY. The global burden of liver disease: the major impact of China. Hepatology. (2014) 60:2099–108. doi: 10.1002/hep.27406
63. Zhong JH, Ke Y, Gong WF, Xiang BD, Ma L, Ye XP, et al. Hepatic resection associated with good survival for selected patients with intermediate and advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. (2014) 260:329–40. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000236
64. Llovet JM and Villanueva A. Liver cancer: Effect of HCV clearance with direct-acting antiviral agents on HCC. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2016) 13:561–2. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.140
65. Yu C, Wu S, Zhao J, Lu J, Zhao T, Wei Y, et al. Evaluation of efficacy, safety and treatment-related outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus partial hepatectomy for small primary liver cancer meeting the Milan criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2020) 44:718–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2019.12.012
66. Shin SW, Ahn KS, Kim SW, Kim TS, Kim YH, and Kang KJ. Liver resection versus local ablation therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma within the milan criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. (2021) 273:656–66. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004350
Keywords: meta-analysis, hepatectomy, radio frequency ablation, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cancer
Citation: He Z, Song G, Yang G, Fu X, Tian M and Zhu Y (2025) Liver resection versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1607338. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1607338
Received: 07 April 2025; Accepted: 19 August 2025;
Published: 09 September 2025.
Roberta Vella, University of Palermo, Italy
Copyright © 2025 He, Song, Yang, Fu, Tian and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanhui Zhu, enloMjAyNDEyMTJAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zheng He†
Zheng He† Yanhui Zhu
Yanhui Zhu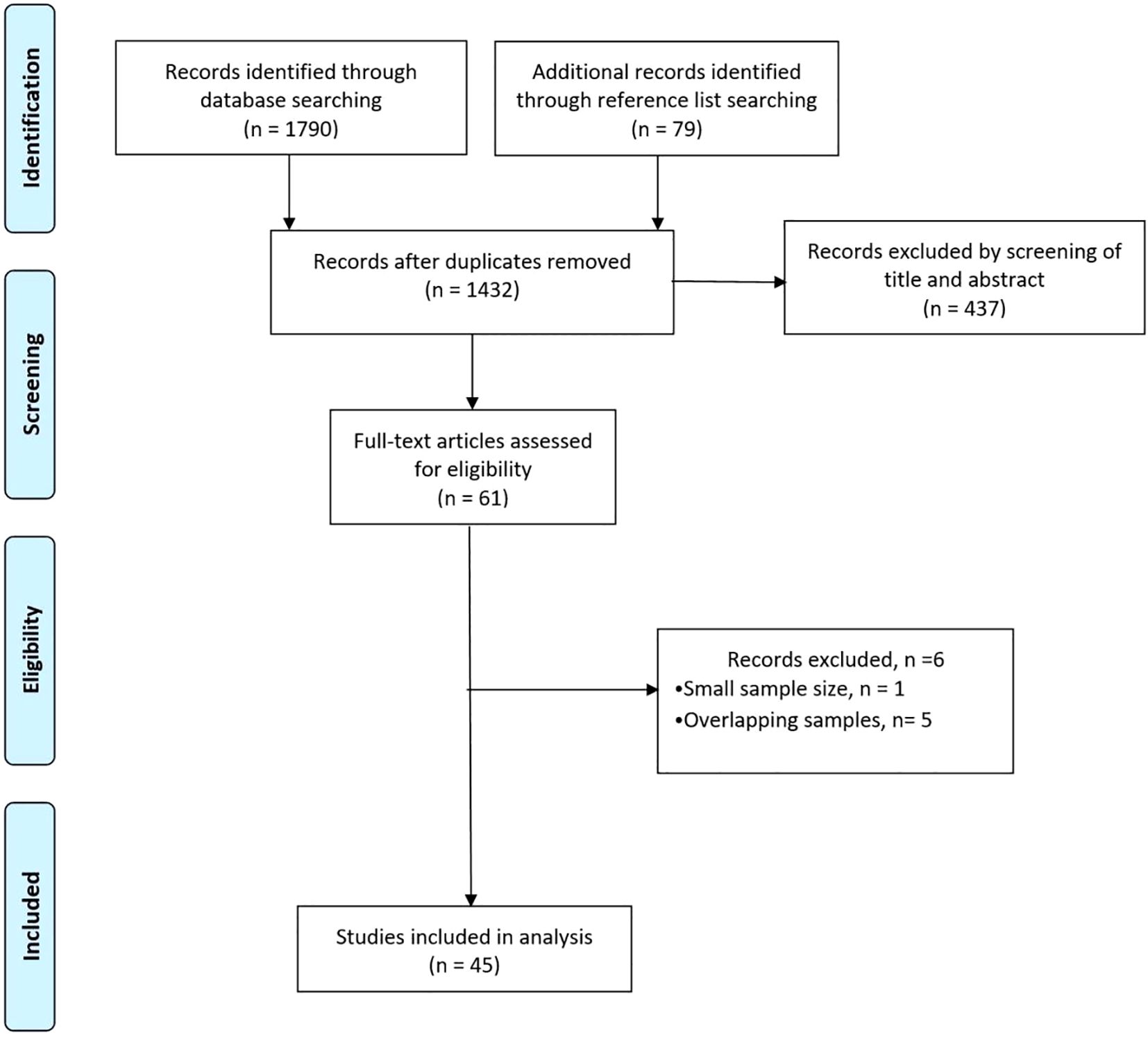
![Forest plot displaying odds ratios and confidence intervals for various studies. Each row represents a study labeled “Omitting [Study, Year]”. The plot shows odds ratios ranging from 1.607 to 1.826, with confidence intervals and additional statistics such as p-values, Tau2, Tau, and I2. The common effect model at the bottom shows an odds ratio of 1.656 with a confidence interval of 1.493 to 1.837 and includes overall measures like Tau2 and I2. Each study is visualized with a gray box and horizontal line indicating its confidence interval.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1607338/fonc-15-1607338-HTML-r2/image_m/fonc-15-1607338-g011.jpg)