- 1Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology Surgery, The Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 2Chinese Hospital Reform and Development Institute, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 3Department of Orthopedics; The Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 4Department of Urology. The Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
- 5Nursing Department, The Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
Objective: Assessing the impact of perioperative enteral nutrition (EN) on postoperative acute muscle atrophy following radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer(GC) (with changes in skeletal muscle mass as the primary outcome indicator).
Methods: Patients who underwent GC surgery at the Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology Surgery in a top-tier hospital in Nanjing were selected for the study. The control group, consisting of patients treated between January and June 2023, received routine perioperative nutritional management. The experimental group, consisting of patients treated between July and December 2023, followed a preoperative combined with early postoperative EN program. skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, 6-meter walk test speed, and body weight were compared between the two groups 7 d postoperatively.
Results: The intervention significantly reduced the loss of skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, and body weight from baseline (p<0.01). However, no significant differences in 6-meter walk test speed were observed between the two groups. After adjusting for confounding factors such as age, gender, nutritional risk screening 2002(NRS 2002) score, education level, diabetes comorbidity, tumor staging, surgical approach, intraoperative blood loss, and operation time, multivariate linear regression analysis showed that the EN program independently influenced the loss rates of skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, and body weight (p<0.01).
Conclusion: The perioperative EN program for GC developed in this study enables medical staff to efficiently gather relevant information, providing a more comprehensive and holistic approach to EN for GC patients. The program effectively reduces postoperative acute muscle wasting, grip strength loss, and weight loss. This study provides a reference for clinical perioperative EN management in GC patients.
Introduction
Gastric cancer persists as a critical global public health challenge, characterized by substantial unmet needs in prevention and therapeutic management. According to the 2024 global cancer statistics released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), gastric cancer accounted for 968,000 new cases worldwide in 2022, ranking as the fifth most prevalent malignancy, with 659,900 associated deaths (1). Surgery, serving as the foundational pillar of gastric cancer management, has demonstrated unequivocal efficacy in enhancing long-term patient survival rates. However, the postoperative stress response (2) can cause metabolic and physiological disorders, potentially leading to inflammation, hormonal imbalances, and genomic reactions. These effects contribute to excessive metabolic catabolism and postoperative acute muscle wasting, adversely influencing both short-term postoperative outcomes and long-term prognosis.Currently, there is no standardized definition for postoperative acute muscle wasting. Huang et al. (3) defined the condition as a >10% reduction in total abdominal muscle area (TAMA) measured at postoperative day (POD) 7. In contrast, Naoaki et al. (4) identified a median reduction rate of 4.4% in the total psoas major muscle mass index (TPI) measured at POD 3 as the critical threshold thereby stratifying patients into mild and severe acute muscle wasting. Huang et al. (3). demonstrated that patients exhibiting this early muscle loss experienced significantly elevated fatigue levels and reduced quality of life at both 1-month and 3-month postoperative assessments. Furthermore, these individuals showed higher complication rates, prolonged hospitalization, and increased medical costs particularly when accompanied by a ≥10% reduction in grip strength. Critically, patients with severe postoperative muscle wasting experience pronounced severe side effects from receiving adjuvant chemotherapy than patients without significant muscle depletion (5). Postoperative acute muscle wasting is widely recognized as a significant concern (6), and muscle mass as a nutritional assessment index has drawn considerable interest (7). Patients undergoing gastrectomy for GC must maintain adequate nutrition before surgery to prevent severe weight loss and muscle mass depletion after surgery. Studies have shown that early EN after surgery can reduce the loss of upper and lower limb lean body mass in elderly patients with GC after 8 d (8). However, another study has indicated that preoperative EN exerts no significant effect on muscle mass in patients with esophageal cancer (9). Currently, studies on EN support for GC patients are mostly limited to preoperative or postoperative phases and report less on comprehensive perioperative management. The effectiveness of a comprehensive perioperative EN intervention, combining preoperative and postoperative phases, in reducing postoperative acute muscle wasting in GC remains inconclusive (10). Although the ESPEN guidelines recommend perioperative nutritional support, there are still significant differences in the specific implementation strategies of EN (11–13). The importance of perioperative nutritional management in the postoperative recovery of GC patients has been widely recognized. However, there remains a significant research gap in the intervention strategies for postoperative acute muscle wasting, a common complication (14, 15). This prospective exploratory study, by establishing a historical control cohort, aims to systematically evaluate the impact of standardized perioperative EN support on postoperative acute muscle wasting in GC patients. The findings of this study will provide new evidence-based insights to optimize the perioperative nutritional management pathway for GC patients.
Materials and methods
Study design and patients
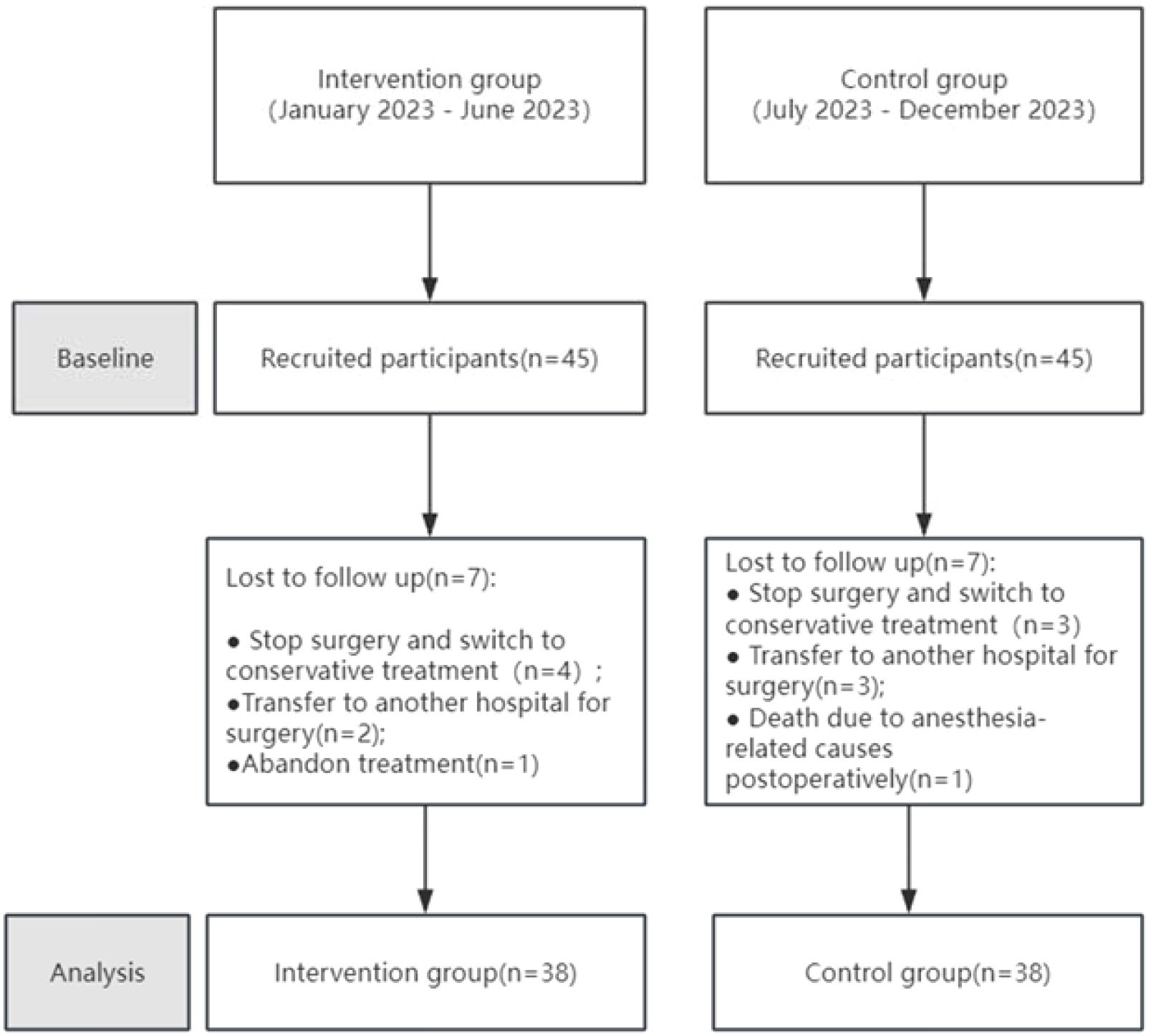
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (Project number: 2021-03-053-K01), and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry on August 2, 2023 (Registration number: ChiCTR2500097933). All patients signed informed consent forms and agreed to the use of research data for academic publication. Convenience sampling was used to select GC surgery patients hospitalized at our institution from January to December 2023 as the research subjects. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Patients aged 18–80 y; (2) A clear diagnosis of GC before surgery, based on endoscopy, imaging, and pathological examination, with tumor staging determined according to the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Staging System; (3) Patients who underwent elective radical or palliative gastrectomy in our department; (4) Patients who could cooperate in completing nutritional assessment and supplying basic information. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Patients participating in or who have participated in other clinical studies within the past year; (2) Patients with severe infections, respiratory insufficiency, or other conditions that impair active cooperation; (3) Patients with cognitive impairments, language barriers, or other conditions affecting communication; (4) Patients with hepatic and renal insufficiency; (5) Family members of the research staff involved in the project; (6) Bedridden patients who cannot have their weight measured; (7) Pregnant or lactating women; (8) Individuals unwilling to provide informed consent. Patients who underwent GC surgery and were admitted between January and June 2023 were assigned as the control group, whereas those admitted between July and December 2023 were designated as the experimental group. Initially, 45 patients were included in both the experimental and control groups. Among the 90 enrolled patients, 76 participants were included in the final analysis after excluding those who withdrew or had missing data (Table 1). Reasons for withdrawal included death; cessation of surgery and switching to conservative treatment; transfer to another hospital for surgery; and discontinuation of treatment (Figure 1).
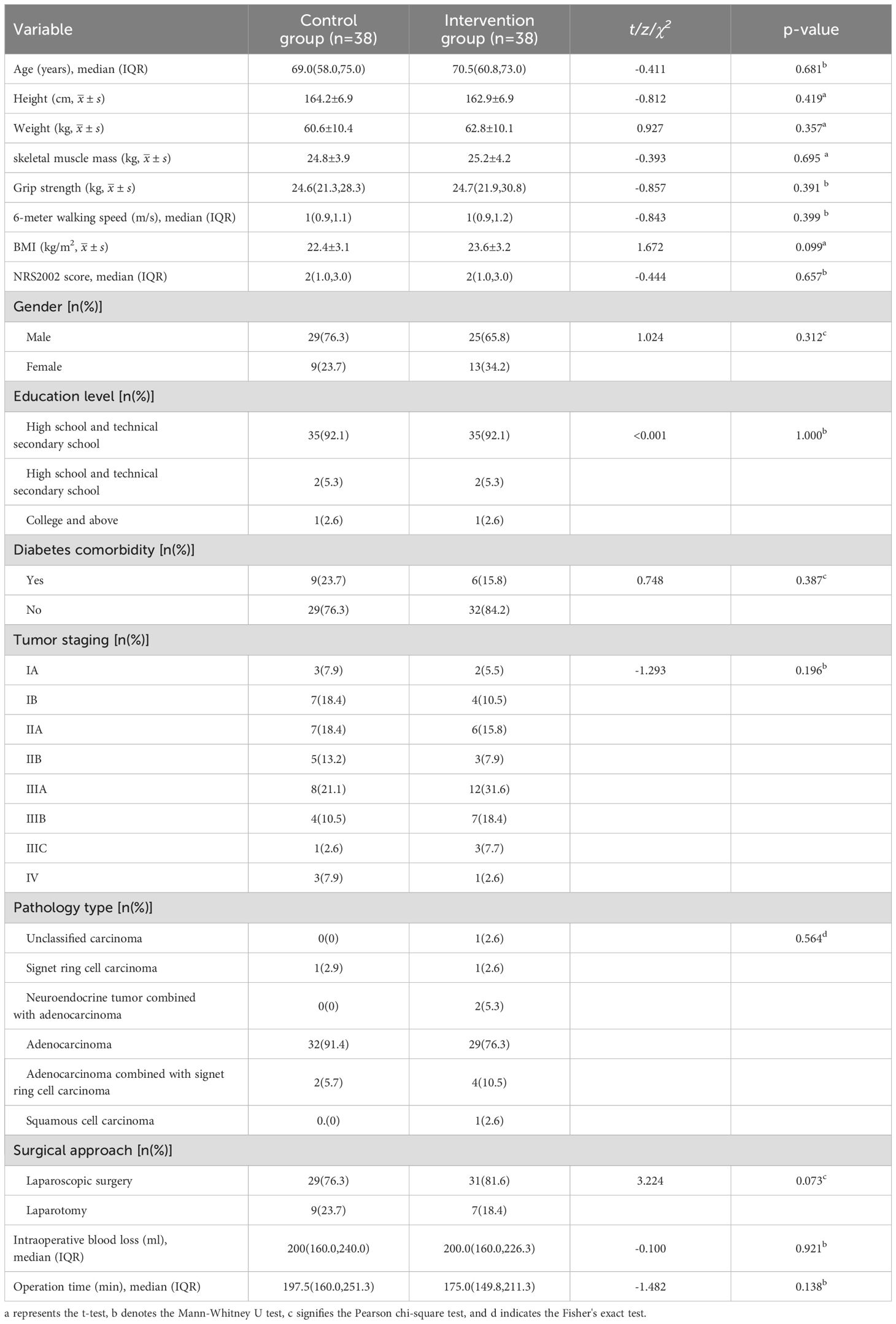
Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of gastric cancer surgery patients in pre- and post-implementation cohorts.
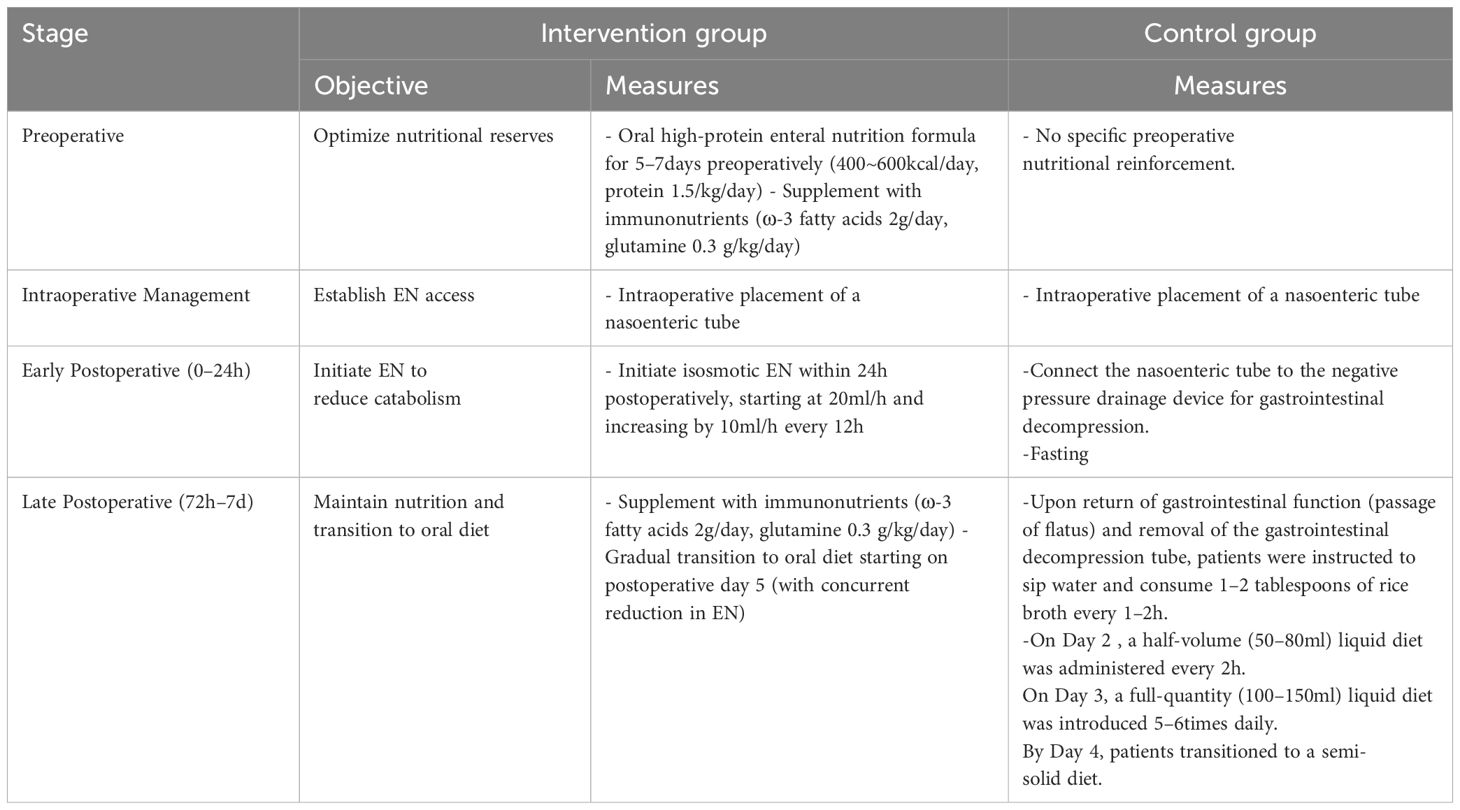
The control group received routine perioperative nutritional management, while the intervention group underwent a standardized protocol integrating preoperative nutritional optimization with early postoperative EN initiation (detailed in Table 2).Additionally, both groups received parenteral nutrition(PN) support at 850kcal/d during postoperative days 1 to 5. This program was implemented by a multidisciplinary team. For quality control, the head nurse of the department organized the training and interpretation of the implementation details of the program before the intervention. Only medical staff who passed the training assessment could administer the clinical intervention. During the intervention process, research team members and the head nurse of the general surgery department jointly supervised the execution to ensure its effectiveness. They summarized implementation problems weekly and conducted continuous quality enhancements based on the identified causes.
Data collection
Primary observational indicators
The rate of skeletal muscle mass loss on POD7 was calculated as follows:
Rate of skeletal muscle mass loss on POD7 = (Admission-POD 7)/Admission*100%.
The skeletal muscle mass measurement method involved the use of a body composition analyzer (Inbody 720, Inbody Co., South Korea), which operates on the principle of bioelectrical impedance. The device calculates muscle content in the body by determining impedance at different frequencies. Measurements were performed by ensuring that the patient was fasting or had not eaten for at least 2 h; instructing the patient to empty their bowels and bladder; and weighing the patient. Measurements were taken within 24 h of admission and on POD 7.
Secondary observational indicators
The rate of grip strength loss on POD 7 was determined as follows:
Rate of grip strength loss on POD 7 = (Admission-POD 7)/Admission*100%.
Grip strength, a primary indicator of hand force (particularly, upper limb strength) and human function, was assessed using an electronic grip dynamometer (EH101, CAMRY, Guangdong). This grip strength test adheres to the internationally recognized gold standard, as recommended by the American Society of Hand Therapists.
In this study, the patients sat with legs shoulder-width apart, hips and knees bent at 90°, upper arms close to the chest in a neutral position, elbows bent at 90°, forearms parallel to the ground, and wrists extended at 0°–30°, maintaining 0°–15° of ulnar deviation. Each hand was measured three times, with intervals of more than 15 s between measurements, and the average value was determined. Measurements were conducted within 24 h of admission and on POD 7.
(2)The rate of 6-meter walking speed loss on POD 7 was determined using the 6-meter walk test. Patients were required to walk a straight line of 6 m at their usual pace. The average time of two trials was recorded to calculate the walking speed over a distance of 6 m. Measurements were taken within 24 h of admission and on POD 7.
(3)The rate of weight loss on POD 7 was determined. Data were collected within 24 h of admission and on POD 7.
Statistical analysis
All data were first checked for omissions and logical errors and then entered by two researchers using dual-core data entry. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0, with significance set at p<0.05. Quantitative data following normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and group comparisons were conducted using t-tests. For data not following a normal distribution, the median and interquartile range M (P25, P75) were used, and group comparisons were conducted using rank-sum tests. Categorical data were represented by frequency and proportion. When E≥5 and n>40, the Pearson chi-square test was used; when 1<E<5 and n>40, the continuity correction chi-square test was employed. When E<1 or n<40, Fisher’s exact test was used. Ordinal data were represented by frequency, and the nonparametric rank-sum test (Mann–Whitney U test) was used. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to control for confounding factors. Quantitative data not conforming to a normal distribution were analyzed by linear regression after logarithmic transformation. The corrected confounding factors included gender, age, education level, Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (NRS2002) score, tumor stage, presence of comorbid diabetes, surgical method, operation time, and intraoperative blood loss.
Result
General details
Details of demographics, anthropometrics, and clinical characteristics are listed in Table 1. No significant differences in demographics, anthropometrics, and clinical characteristics were observed between the intervention and control groups. For the intervention group, the median age was 69 y (58.0, 75.0), and the proportion of female patients was 23.7%; for the control group, the median age was 70.5 y (60.8, 73.0), and the female sex distribution was 34.2%.
Nutritional intervention outcomes
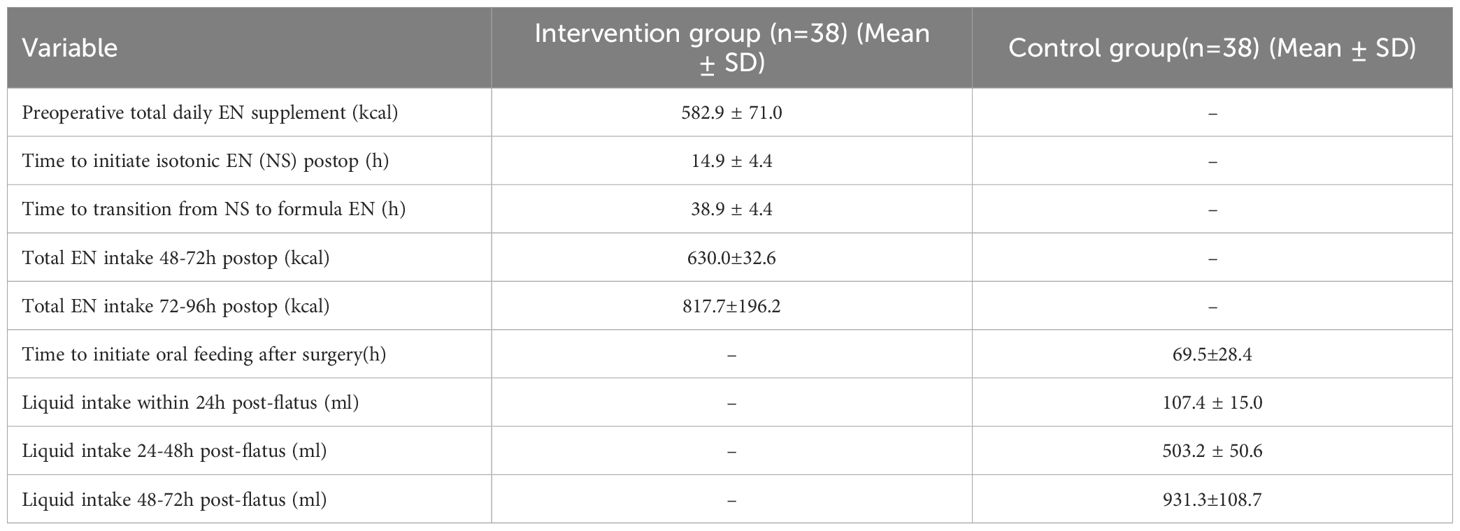
Quantitative details of nutritional delivery are presented in Table 3. For the intervention group, preoperative EN supplementation averaged 582.9 ± 71.0kcal/day. Postoperatively, isosmotic EN (0.9% sodium chloride, 250ml) was initiated at 14.9 ± 4.4hours, and transitioned to formula feed within 38.9 ± 4.4hours. The control group relied exclusively on oral liquid intake following return of bowel function, with no EN support administered. Oral feeding was initiated at 69.5± 28.4hours postoperatively, achieving 107.4 ± 15.0ml within 24h post-flatus.
Change of observational indicators
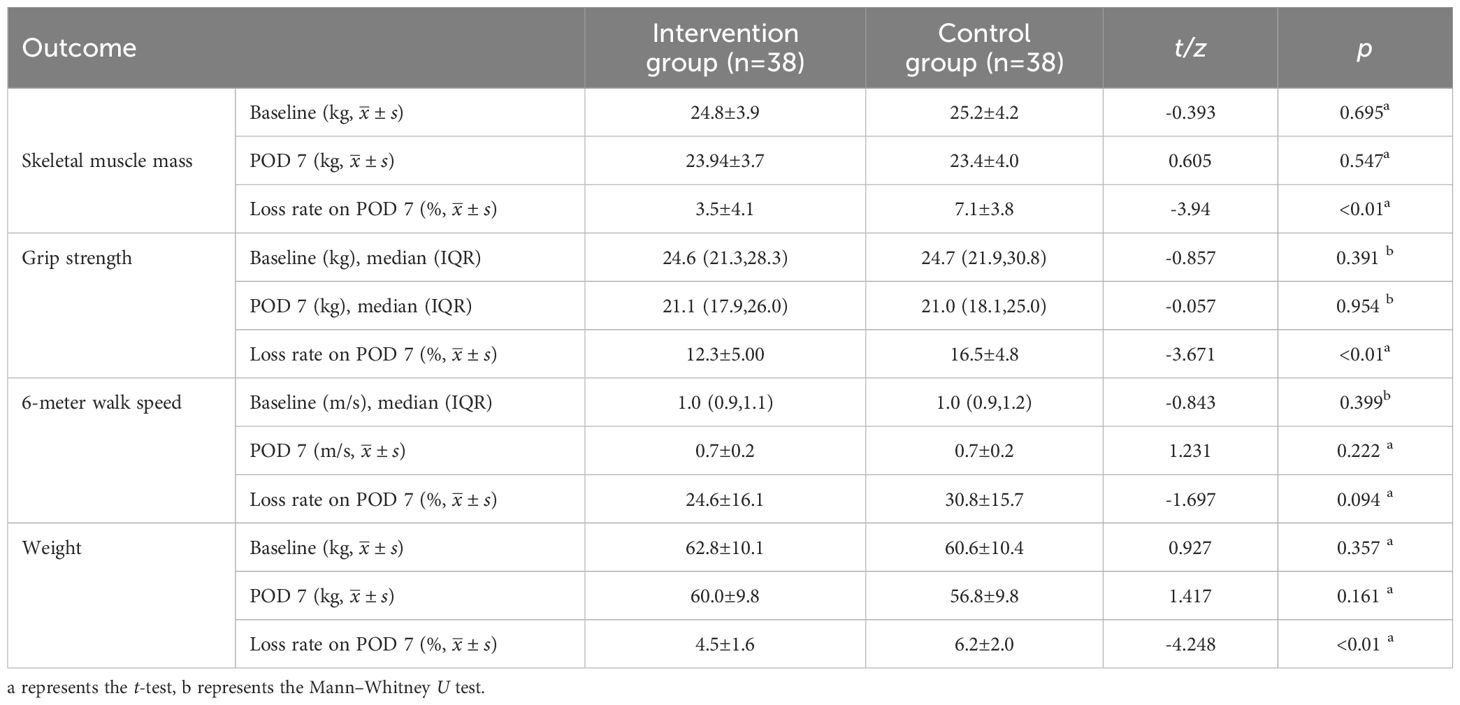
After the intervention, no significant differences were found in all indicators between the groups at baseline and on POD 7 (Table 4). All measured indicators exhibited a downward trend on POD 7. However, the rates of skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, and weight loss on POD 7 were lower in the intervention group than in the control group, with significant differences (p<0.01) (Table 4) (Figure 2). The effect of the evidence-based perioperative EN program intervention on the changes in observational indicators was evaluated based on the results derived from the multiple linear regression model, adjusted for age, gender, NRS2002, education level, diabetes comorbidity, tumor staging, surgical approach, intraoperative blood loss, and operation time, were used to evaluate (Table 5).
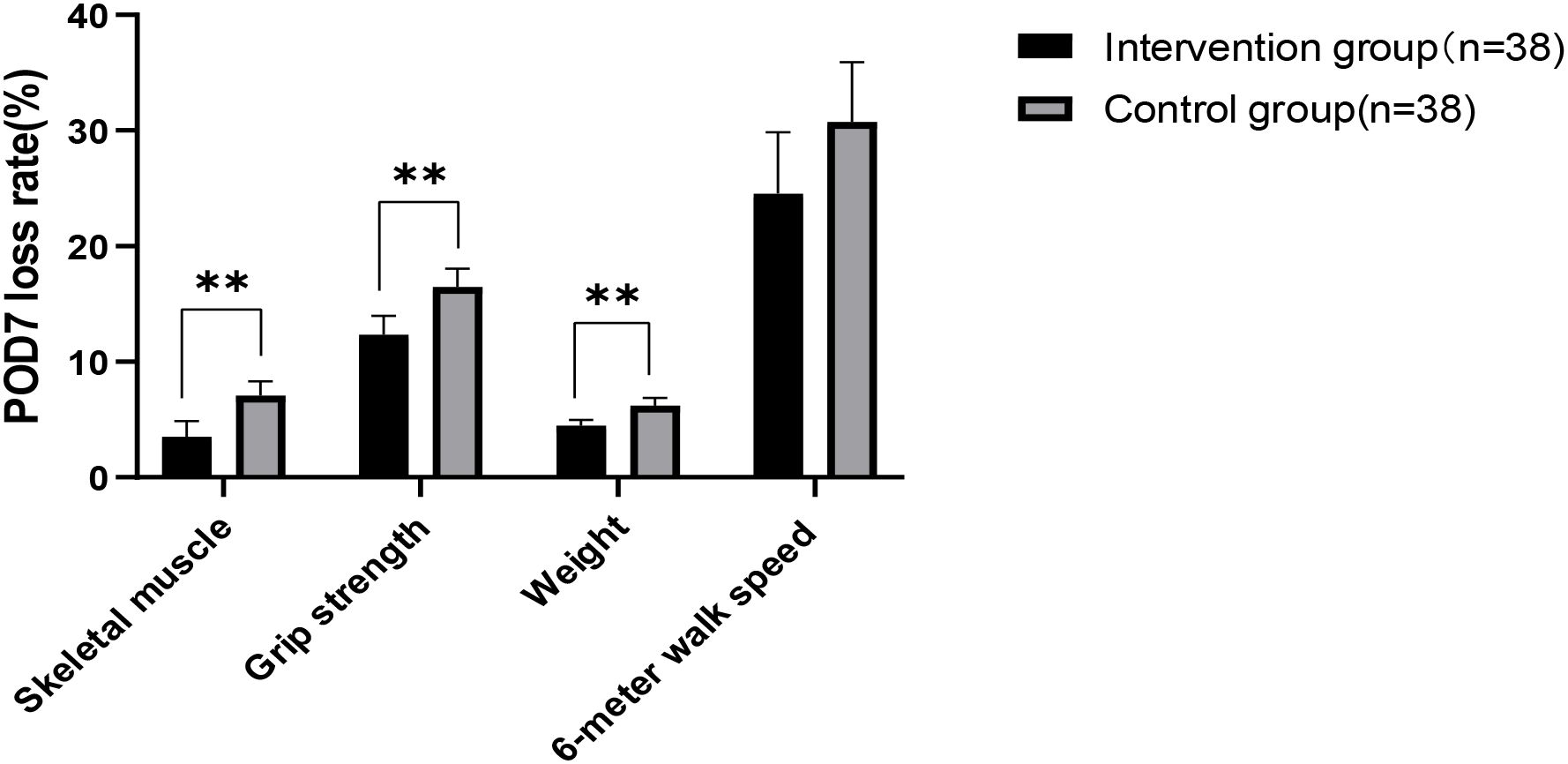
Figure 2. Analysis of changes in observational indicators. Significant differences between the intervention group and control group derived using the t-test (**: p < 0.01).
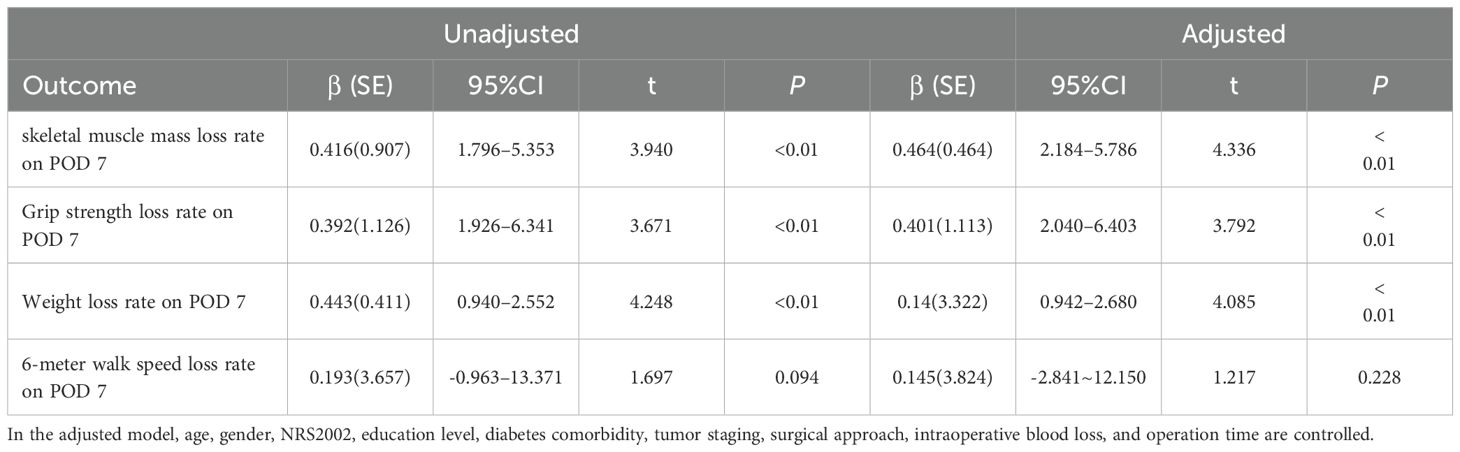
Table 5. Effect of the program for gastric cancer intervention on observational indicators, as determined using the multiple linear regression model.
Discussion
Preoperative combined with early postoperative EN program improves postoperative acute muscle wasting and nutritional status in GC patients
Skeletal muscle mass and grip strength are closely related as primary indicators for assessing postoperative acute muscle wasting. Grip strength is an important measure for evaluating upper limb muscle strength, and the skeletal muscle mass directly affects its magnitude (16). Otsuji H et al. defined surgery-related muscle loss as a percent change in the total psoas muscle area of less than 5.0% (17). Huang DD et al. reported that 31.82% of GC patients experience a muscle mass loss exceeding 10% by POD 7 (3). This finding underscores the importance of monitoring and intervening to address muscle conditions after GC surgery. Muscle loss not only affects physical recovery but may also increase the risk of complications, prolong hospital stays, and higher costs (18).A systematic review demonstrates that severe postoperative skeletal muscle loss occurred in 25.7% of GC patients and was significantly correlated with poorer Overall survival (14). Skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, and body weight are important indicators for assessing the nutritional status of GC patients in the perioperative period. A systematic review study found no significant differences (p>0.05) in skeletal muscle mass between the group receiving oral nutritional supplements and the control group (19). However, the effect of EN on the rate of skeletal muscle mass loss within 7 d postoperatively was not examined. This study showed that in GC patients who received preoperative combined with early postoperative EN intervention, the mean loss rates of skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, and weight on POD 7 were 3.5%, 12.3%, and 4.5% in the intervention group and 7.1%, 16.5%, 6.2% in the control group. There was a significant difference between the two groups (p<0.01).
This finding indicates that the program effectively reduce acute postoperative skeletal muscle mass and weight loss, maintaining muscle function. Several potential mechanisms may explain this result:
First, the fragmented nutritional management provided to the control group lacked multidisciplinary coordination and a systematic approach. In contrast, the experimental group’s scientifically rigorous program featured dynamic, phase-specific adaptations across the perioperative continuum, enhancing its clinical utility and ensuring adequate nutritional support for GC patients. Preoperative EN optimized patients’ physiological reserves before surgery, establishing a foundation for accelerated postoperative recovery. Postoperative EN effectively maintained nutritional status following resection. Critically, during postoperative days 2–3 (48–72 hours), combined nutritional support delivered 630 ± 32.6kcal/day via EN and 850kcal/day via PN, achieving a total energy supply of 1,480kcal/day. This closely approximated the early-phase requirement baseline for gastrectomy patients (15–25kcal/kg/day) consistent with expert consensus endorsing hypocaloric provision in the immediate postoperative period (20).
Second, GC patients often experience weight loss and malnutrition due to the tumor or the treatment process before surgery. Postoperative impairment of digestive function and limited food intake lead to insufficient nutritional intake. Initiating EN within 24 hours after surgery can maintain intestinal mucosal integrity. EN is administered directly into the digestive tract to provide nutrients, helping maintain the structure and function of the intestinal mucosa, promoting the proliferation and repair of intestinal cells, thereby preserving the integrity of the intestinal barrier (21). A healthy intestinal barrier can effectively prevent bacterial and endotoxin translocation reducing systemic inflammatory responses (22) and protecting skeletal muscle mass from inflammatory damage.
Third, standardized EN management ensures that patients meet their nutritional requirements, ensuring that patients receive adequate nutrition. The EN formula contains essential amino acids, particularly branched-chain amino acids, which are crucial for skeletal muscle mass protein synthesis. Moreover, the energy provided by EN helps meet the increased metabolic demands postoperatively, reducing reliance on skeletal muscle mass for energy and decreasing muscle protein breakdown.The experimental group received a protein target of 1.5 g/kg/day during the intermediate postoperative phase. This aligns with evidence-based recommendations for GC patients, whose protein requirements typically range between 1.2–1.5 g/kg/day to 2.0 g/kg/day depending on clinical status and recovery goals (23). Adequate protein intake can activate the mTOR pathway, promoting muscle protein synthesis (24).
Fourth, The immunonutrients delivered via EN in this protocol specifically ω-3 fatty acids (2 g/day) and glutamine (0.3 g/kg/day) effectively protect skeletal muscle mass against catabolic stress. As highlighted by Triantafillidis, glutamine plays a vital role in maintaining nitrogen balance and enhancing protein synthesis (25). Furthermore, glutamine modulates immune function by reducing tissue glutathione levels while elevating plasma glutathione concentrations, promoting T lymphocyte proliferation, augmenting natural killer (NK) cell activity, and suppressing TNF-α secretion (25). Critically, TNF-α serves as a core inflammatory mediator that directly induces muscle atrophy through activation of downstream signaling pathways, including NF-κB, p38MAPK, and JAK/STAT (26).Otherwise ω-3 fatty acids reduce the synthesis of eicosanoids and the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) (25). In inflammatory environments, pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 directly promote muscle atrophy through pathways including NF-κB and p38MAPK (26). The French Society of Digestive Surgery (Société Française de Chirurgie Digestive, SFCD) recommends preoperative immunonutrition support even for well-nourished GC patients. Such interventions in nutritionally adequate abdominal surgery patients improve outcomes by reducing postoperative infections, shortening hospitalization, and decreasing medical costs (27). Kabata et al. further reinforced this in a prospective randomized controlled trial, demonstrating that preoperative nutritional support in non-malnourished oncology patients maintains nutritional status and reduces the incidence and severity of postoperative complications (28). Collectively, these findings suggest that even patients with adequate baseline nutrition may experience underlying disease-induced metabolic alterations; when compounded by surgical stress, these changes can precipitate malnutrition and poorer outcomes. Thus, preoperative nutritional intervention may optimize metabolic resilience, though validation through multicenter, large-sample randomized controlled trials (RCTs) remains imperative. Concurrently, a systematic review reveals substantial heterogeneity in current immunoenutrition research: while only 45.5% of the included studies initiating interventions postoperatively reported definitive clinical benefits, 80% of the included studies indicated that the perioperative application of immunoenutrition provided some benefit for patients with GC undergoing gastrectomy (29), underscoring the need to standardize immunoenutrition formulations and intervention durations while developing tailored protocols for distinct nutritional risk populations.
Fifth, postoperative patients often rest in bed, potentially leading to rapid muscle loss due to lack of exercise. Meanwhile, malnutrition can accelerate muscle breakdown, affecting body weight and handgrip strength. Timely and effective individualization setting of energy target requirements, particularly for protein, can maintain nitrogen balance, slow down muscle loss, and facilitate postoperative muscle function recovery and rehabilitation in patients. In summary, implementing a perioperative EN program is crucial for improving postoperative acute muscle wasting and nutritional status in GC patients. Adequate EN support can enhance patient recovery and survival, reduce complications. Therefore, perioperative EN management programs should be actively promoted and applied in clinical practice to promote patient recovery and health.
The program failed to improve the walking activity ability of GC patients after surgery
The 6-meter walking speed is an important indicator for assessing physical body function, which is closely related to skeletal muscle mass strength and mass. In diagnosing sarcopenia, the 6-meter walking speed is often used as one of the assessment criteria (30). The results of the current study indicate that the mean loss rate of the 6-meter-walk speed on POD 7 was 24.6% in the intervention group and 30.8% in the control group. No significant difference was found between the two groups (p>0.05). Postoperative 6-meter walking speed is influenced by various factors:
First, the physical condition of patients, including muscle strength and cardiopulmonary function, plays a crucial role in their postoperative walking ability. Second, the effect of the surgery cannot be overlooked. The type and extent of the procedure, along with patient recovery, can influence mobility. Third, pain management is a critical factor that can limit postoperative activity (31). If pain is not well-controlled, it can restrict movement, consequently affecting walking speed. The EN program may need to be integrated with effective pain management strategies to optimize outcomes. Psychological factors, such as anxiety and depression, can also hinder patient recovery and ability to stay active. Last, complications such as infections or thromboembolic events can also affect patient recovery and mobility. If not managed promptly and effectively, these issues can overshadow the benefits of EN. In conclusion, while EN is a vital component of perioperative care, walking speed is determined by multiple factors. A comprehensive approach that includes personalized EN program, pain management, psychological support, social engagement, and proactive complication management is necessary to improve walking speed in GC patients after surgery. Future studies should explore these factors in greater detail to develop more effective perioperative intervention programs.
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the small sample size and single-center design limit its representativeness. In future studies, the program should be implemented in a multicenter setting. Second, the enrollment times of the control and experimental groups in this study are inconsistent, which may introduce a selection bias and affect the validity of the research results. The research results should be interpreted with caution. Future randomized controlled studies can be conducted to further clarify the effectiveness of the program. Third, the program does not distinguish the effects of different surgical methods or surgical approaches on the use of EN in GC patients. The need for EN may depend on the surgical method (total or partial gastrectomy, and the surgical approach (open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or robotic surgery. Future research should clarify the effectiveness of different EN management methods for various surgical methods and approaches. The final limitation of this study is the relatively short observation period. This brief time frame may prevent the observation of long-term effects or outcomes, potentially affecting the accuracy and generalizability of the findings. Future studies with extended observation periods are necessary to elucidate the long-term implications and effectiveness of the interventions or phenomena under investigation.
Conclusions
This study develops a perioperative EN program for GC that helps enable medical staff to quickly and comprehensively obtain relevant information and provide a more comprehensive and holistic EN program for GC patients. This program helps reduce postoperative acute muscle wasting, grip strength loss, and weight loss, and also demonstrates clinical value for promoting its broader implementation
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: http://www.medresman.org.cn/pub/cn/proj/projectshshow.aspx?proj=6148.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
XZ: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XN: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. ZS: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. DY: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CL: Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Nanjing Health Science and Technology Development Special Fund Project (YKK21230), Medical Education Collaborative Innovation Fund of Jiangsu University (JDYY2023098), and the Project of Chinese Hospital Reform and Development Institute, Nanjing University (NDYG2023057).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Finnerty CC, Mabvuure NT, Ali A, Kozar RA, and Herndon DN. The surgically induced stress response. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2013) 37:S21–9. doi: 10.1177/0148607113496117
3. Huang DD, Ji YB, Zhou DL, Li B, Wang SL, Chen XL, et al. Effect of surgery-induced acute muscle wasting on postoperative outcomes and quality of life. J Surg Res. (2017) 218:58–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.05.045
4. Maeda N, Shirakawa Y, Tanabe S, Sakurama K, Noma K, and Fujiwara T. Skeletal muscle loss in the postoperative acute phase after esophageal cancer surgery as a new prognostic factor. World J Surg Oncol. (2020) 18:143. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01908-6
5. Prado CM, Antoun S, Sawyer MB, and Baracos VE. Two faces of drug therapy in cancer: drug-related lean tissue loss and its adverse consequences to survival and toxicity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2011) 14:250–4. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283455d45
6. Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Expert Committee on Oncology Nutrition Therapy. Expert consensus on nutritional therapy for patients with Malignant tumors. J Nurs Sci. (2012) 17:59–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2012.01.013
7. Lim HS, Lee B, Cho I, and Cho GS. Nutritional and clinical factors affecting weight and fat-free mass loss after gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1905. doi: 10.3390/nu12071905
8. Wang F, Wang QH, and Chen QP. Influence of early enteral nutrition on nutritional status, immunity and body composition in postoperative elderly. J Nurs Sci. (2011) 36:75–7. doi: 10.3870/hlxzz.2011.24.075
9. Guo Z, Sai JG, Xu Y, Cong ZZ, Hu LW, and Shen Y. The effect of preoperative prehabilitation on nutritional status and body composition of patients with esophageal cancer after operation. Parenter Enteral Nutr. (2018) 25:156–60. doi: 10.16151/j.1007-810x.2018.03.008
10. A’zim AZA, Zaid ZA, Yusof BNM, Jabar MF, and Shahar ASM. Effectiveness of intensive perioperative nutrition therapy among adults undergoing gastrointestinal and oncological surgery in a public hospital: study protocol for a pragmatic randomized control trial. Trials. (2022) 23:961. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06898-2
11. Muscaritoli M, Arends J, Bachmann P, Baracos V, Barthelemy N, Bertz H, et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical Nutrition in cancer. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:2898–913. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.02.005
12. Thompson KL, Elliott L, Fuchs-Tarlovsky V, Levin RM, Voss AC, and Piemonte T. Oncology evidence-based nutrition practice guideline for adults. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2017) 117:297–310. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2016.05.010
13. Zhang Y, Tan S, and Wu G. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:5071. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.07.012
14. Zhan C, Bu J, Li S, Huang X, and Quan Z. Postoperative skeletal muscle loss as a prognostic indicator of clinical outcomes in patients with gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. (2025) 29:101898. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2024.101898
15. Kang MK and Lee HJ. Impact of malnutrition and nutritional support after gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. (2024) 8:534–52. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12788
16. Lee SY. Handgrip strength: an irreplaceable indicator of muscle function. Ann Rehabil Med. (2021) 45:167–9. doi: 10.5535/arm.21106
17. Otsuji H, Yokoyama Y, Ebata T, Igami T, Sugawara G, Mizuno T, et al. Surgery-related muscle loss and its association with postoperative complications after major hepatectomy with extrahepatic bile duct resection. World J Surg. (2017) 41:498–507. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3732-6
18. Zhao H, Dong Q, Chen C, Pan L, Liu S, Cheng J, et al. Perioperative body composition changes and their clinical implications in patients with gastric cancer undergoing radical gastric cancer surgery: a prospective cohort study. J Gastrointest Surg. (2025) 29:101877. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2024.101877
19. Rinninella E, Cintoni M, Raoul P, Pozzo C, Strippoli A, Bria E, et al. Effects of nutritional interventions on nutritional status in patients with gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2020) 38:28–42. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.05.007
20. Li ZY, Yan C, and Li S. Consensus of Chinese expert panel on perioperative nutrition therapy of gastric cancer(2019 edition). Chin J Pract Surg. (2020) 40:145–50. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZGWK.0.2020-02-004
21. Niu RH, Wu AP, Wu YF, and Xu JP. Research progress in nutritional support therapy after gastric cancer surgery. Chin Nurs Res. (2016) 30:3. doi: CNKI:SUN:SXHZ.0.2016-26-005
22. Chinese Society of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Colorectal Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, et al. Chinese expert consensus on perioperative whole course nutrition management for gastrointestinal surgery (2021Edition). Chin J Pract Surg. (2021) 41:1111–25. doi: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2021.10.05
23. Triantafillidis JK, Papakontantinou J, Antonakis P, Konstadoulakis MM, and Papalois AE. Enteral nutrition in operated-on gastric cancer patients: an update. Nutrients. (2024) 16:1639. doi: 10.3390/nu16111639
24. He W, Posey EA, Steele CC, Savell JW, Bazer FW, and Wu G. Dietary glycine supplementation activates mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling pathway in tissues of pigs with intrauterine growth restriction. J Anim Sci. (2024) 102:skae141. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae141
25. Triantafillidis JK and Malgarinos K. Immunonutrition in operated-on gastric cancer patients: an update. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:2876. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122876
26. Ji Y, Li M, Chang M, Liu R, Qiu J, Wang K, et al. Inflammation: roles in skeletal muscle atrophy. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:1686. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091686
27. Mariette C, De Botton ML, and Piessen G. Surgery in esophageal and gastric cancer patients: what is the role for nutrition support in your daily practice? Ann Surg Oncol. (2012) 19:2128–34. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2225-6
28. Kabata P, Jastrzębski T, Kąkol M, Król K, Bobowicz M, Kosowska A, et al. Preoperative nutritional support in cancer patients with no clinical signs of malnutrition–prospective randomized controlled trial. Support Care Cancer. (2015) 23:365–70. doi: 10.1007/s00520-014-2363-4
29. Xin C, Wang Y, Luo Y, Gai Y, and Han B. Effect of perioperative immunonutrition on outcomes in gastric cancer surgery patients: A systematic review and evidence map. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2025) 67:90–104. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.02.029
30. Chen LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Chou MY, Iijima K, et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:300–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
Keywords: gastric cancer, perioperative period, enteral nutrition, postoperative acute muscle wasting, management
Citation: Zeng X, Ni X, Shen Z, Yang D, Gu Y, Li A, Liu H and Li C (2025) Impact of perioperative enteral nutrition on postoperative acute muscle wasting in gastric cancer: a prospective exploratory study with a historical control group. Front. Oncol. 15:1607756. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1607756
Received: 08 April 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Yang Wo, Qingdao University, ChinaReviewed by:
John Triantafillidis, Metropolitan General Hospital, GreeceFeifei Chong, Daping Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zeng, Ni, Shen, Yang, Gu, Li, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Liu, NDkzNzU0NDU5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Changdi Li, MTI3NDI0OTMxM0BxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xing Zeng
Xing Zeng Xuan Ni3†
Xuan Ni3†