- 1Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Background: Gliomas make up almost half of primary central nervous system tumors. Despite advancements in surgery and neuro-oncology, developing an effective treatment remains challenging. The protein Growth Arrest and DNA-Damage-Inducible, Gamma (GADD45G) is crucial for key cellular functions like DNA repair, genomic stability, and apoptosis. While GADD45G dysregulation has been found in various cancers, its role in glioma is still unclear.
Methods: We analyzed unified pan-cancer datasets (TCGA, TARGET, GTEx) from UCSC Xena and integrated glioma data from CGGA and GEO (GSE108476). Prognostic value was assessed via multivariate Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis using Gliovis. Single-cell RNA-seq data (GSE103224, GSE138794, GSE173278) were processed with Seurat (R 4.2.2), with Harmony for batch correction and UMAP for visualization. Malignant subclusters were annotated using marker genes. Functional enrichment and cell-type proportion estimation were conducted. Single-cell analysis revealed GADD45G expression patterns and identified its top correlated genes in malignant glioblastoma cells. Overexpression of GADD45G was performed to investigate its impact on cell function. Western blot analysis was used to examine the role of GADD45G in glioma cell invasion and migration.
Results: Through comprehensive analysis across multiple datasets, it was found that GADD45G expression is higher in glioma patients compared to normal individuals, and its expression is generally higher in lower-grade gliomas than in glioblastoma. Cox regression analysis indicated that GADD45G has a protective effect. Survival curves further demonstrated that elevated GADD45G levels are associated with improved overall survival in patients. In this study, we identified four highly heterogeneous GBM cell subpopulations using single-cell data. The MES-like cells was significantly associated with poor prognosis. Spearman correlation analysis revealed the correlation between GADD45G and VIM. Further experiments revealed that GADD45G modulates glioma cell invasion and migration, potentially through its effects on EMT-like phenotypic features.
Conclusion: GADD45G expression is significantly associated with glioma outcomes and may serve as a promising biomarker for prognosis evaluation. Its involvement in regulating EMT-like phenotypic traits further highlights its therapeutic potential.
Background
Gliomas constitute approximately 50% of primary central nervous system tumors. Despite advancements in surgical techniques and neuro-oncology, the prognosis for gliomas remains dismal. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most malignant variant of glioma, exhibits a 1-year survival rate of approximately 30% and a 5-year survival rate of less than 5% (1). Although surgical resection, combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, constitute common treatment modalities, the survival rates for certain glioma patients remain low. Therefore, it is imperative to investigate the oncogenic molecular mechanisms underlying gliomas and to develop effective targeted gene therapies to enhance patient outcomes.
The growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene (GADD45) family, consisting of GADD45A, GADD45B, and GADD45G, is involved in various fundamental processes such as DNA repair (2), genomic stability (3), epigenetic regulation (4), cell cycle arrest (5), apoptosis (6), tumorigenesis (7), and embryogenesis (6). Studies have indicated that GADD45 proteins regulate tumor progression under oncogenic stress (3, 8, 9). In esophageal cancer cell lines, GADD45G is silenced by promoter methylation, whereas GADD45A and GADD45B are not affected (10). The methylation status and protein expression of GADD45G are significantly associated with the survival of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients, while the expression of GADD45A and GADD45B is not (10). GADD45G expression can be induced by cellular stress and cytokine subsets (11–13). Research indicates that the expression of GADD45G is frequently reduced in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (14), gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer (15), non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, cervical cancer, esophageal cancer, and lung cancer (16). GADD45G may play a crucial role in tumorigenesis. Although dysregulated expression of GADD45G has been observed in several human tumors, its role in gliomas remains unclear. Therefore, investigating the role of GADD45G in glioma and its underlying mechanisms could uncover novel therapeutic targets, potentially enhancing the survival rate and clinical prognosis of glioma patients.
In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of gliomas using bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing data, and further explored the potential role of GADD45G in glioma progression through in vitro experiments.
Materials and methods
Gene expression and survival analysis
The pan-cancer datasets TCGA, TARGET, and GTEx, which have been unified and standardized, were downloaded from the UCSC database (https://xenabrowser.net/). Expression data and survival information were subsequently obtained after appropriate filtering. In addition, data from the CGGA database (http://www.cgga.org.cn/) for glioma, as well as the glioma-related dataset (GSE108476) from the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), were integrated. We conducted a multivariate Cox regression analysis of GADD45G using TCGA GBM data to assess its potential as an independent prognostic indicator for glioblastoma. Based on this model, individual risk scores were calculated, and patients were subsequently stratified into high-risk and low-risk groups. Survival analyses of the CGGA, GSE108476, and TCGA datasets were performed using gliovis (https://gliovis.bioinfo.cnio.es/), employing Kaplan-Meier survival curves to evaluate the relationship between gene expression and overall survival (OS). The log-rank test was applied to assess the statistical significance of differences between survival curves.
ScRNA-seq data processing and integration
The scRNA-seq data from the GEO database, including GSE103224, GSE138794, and GSE173278, were analyzed using the Seurat package in R 4.2.2. Cells with fewer than 200 total feature RNAs, considered low-quality, were excluded. After normalizing gene expression for each cell, batch correction was conducted using the Harmony package, and the batch effects were assessed based on clustering of different cell types (17). Dimensionality reduction was performed using principal component analysis (PCA), followed by uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP). Following the application of the FindNeighbors and FindClusters functions, 29 clusters were initially identified. Manual annotation was performed based on typical markers, and small clusters were subsequently merged. A total of 98,216 cells were included, with six major cell clusters identified as Malignant cell, Endothelial, Tumor-Associated Macrophages, Pericyte, Oligodendrocyte, and T cell for subsequent analysis. After extracting the manually annotated Malignant cell cluster, five major subclusters were identified: MES-like, AC-like, NPC-like, OPC-like, and unknown (18, 19). Marker gene sets for MES-like, AC-like, NPC-like, and OPC-like cells were obtained (20), and cell feature scoring was conducted using the AddModuleScore function. Although batch correction was applied using the Harmony algorithm and clustering of cell types showed satisfactory alignment, some residual variability may still exist. In addition, as the analysis was based on publicly available datasets, the sample representation may be somewhat modest, which could influence the generalizability of single-cell findings.
Inference of CNV and downstream analysis in typical malignant cells
To differentiate malignant cells from normal cells, 400 cells from each cell type were isolated, and copy number variations (CNV) were inferred using the infercnv package. Genes with low expression (median expression < 0.1) were excluded. Genes were annotated based on their chromosomal locations, and CNV scores were computed using a moving average of 100 genes. Hierarchical clustering was conducted to distinguish non-malignant cells from malignant cells characterized by distinct chromosomal deletions or amplifications. A total of 1,000 cells from each typical malignant subpopulation were isolated to construct a single-cell reference matrix. We performed phylogenetic analysis of the four single-cell subtypes using the BuildClusterTree function to construct a phylogenetic tree. Cell-type proportions in GBM patients from the CGGA dataset were estimated using the default settings of CIBERSORTX (https://cibersortx.stanford.edu/). Subsequently, survival outcomes for different cell types were assessed using the survminer package. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) were conducted to assess the functional heterogeneity of the four typical subpopulations. CNV data were obtained from the TCGA-GBM project via TCGAbiolinks, and GISTIC2 (https://broadinstitute.github.io/gistic2/) was employed for analysis. The GeoTcgaData and tinyarray packages were utilized to group the CNV data and conduct differential analysis. The processed CNV data were integrated with gene expression data, and CNV scores and expression values for target genes were extracted to construct a unified data frame for analysis. Finally, survival outcomes at varying CNV levels were assessed using the survminer package.
Correlation analysis
Single-cell transcriptomic data were used to extract the expression levels of the target gene GADD45G, which were then subjected to Spearman correlation analysis. The ten genes most strongly correlated with GADD45G were identified. The expression patterns of these selected genes were visualized on a UMAP plot using the FeatureDimPlot function from the SCP package.
Immune cell infiltration analysis
Based on the bulk RNA-seq expression profiles of tumor tissue samples in the TCGA-GBM dataset, the relative abundance of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment was estimated using the single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) method. The signature gene sets for various immune cell types were constructed from their representative marker genes. Through enrichment analysis, enrichment scores of each immune cell type were obtained for every sample. Subsequently, Spearman correlation analysis was performed to assess the relationship between GADD45G expression levels and the degree of immune cell infiltration.
Drug analysis
Drugs capable of regulating the transcriptional expression levels of GADD45G were identified from the CTD database (https://ctdbase.org/). Drug sensitivity analysis for GADD45G was conducted using an online database (https://guolab.wchscu.cn/GSCA/#/).
Cell culture and transfection
The SKMG1 cell line was maintained by the State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, while the A172 cell line was provided by Dr. Shing-shun Tony To, from the Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. All cell lines were authenticated by short tandem repeat (STR) profiling within the last six months. The cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Carlsbad, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gemini Bio-Products, West Sacramento, CA, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin-streptomycin (HyClone, Logan, UT, USA), and 2 mM glutamine (HyClone). Cells were maintained at 37 °C in 5% CO2. The plasmid pCDNA3.1-CMV-GADD45G-3xFLAG-hGHpolya-EF1a-EGFP, constructed by Obio Technology (Shanghai, China), was used to overexpress the GADD45G gene (GenBank ID: NM_006705.4, 480 bp). Cells were seeded at 5 × 10^5 per well in 6-well plates and transfected at 60% confluency. The transfection mixture (2.5 µg plasmid and 5 µL Lipofectamine 3000) was incubated with cells for 48 hours. For the control group, cells were transfected with the empty vector H23990 pCDNA3.1-CMV-MCS-3xFLAG-hGHpolya-EF1a-EGFP (Obio Technology, Shanghai, China) under identical conditions to the experimental group.
Reverse transcription quantitative PCR
Total RNA was extracted using the RNA extraction kit (ESScience) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The RNA concentration was measured, and complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized via reverse transcription. This was followed by amplification and quantitative analysis of the cDNA using real-time PCR (qPCR) technology. The primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). The primer sequences were as follows: GADD45G: 5′-CAGATCCATTTTACGCTGATCCA-3′ (forward) and 5′-TCCTCGCAAAACAGGCTGAG-3′ (reverse). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as the internal control.
Western blot analysis
Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk and incubated overnight at 4°C with the primary antibody (GADD45G, 1:1000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Afterward, the membranes were incubated for 2 hours with a secondary antibody (1:5000). Protein levels were detected using a chemiluminescence and fluorescence imaging system.
Scratch assay
Cells were cultured in dishes until they reached 80%-90% confluency. A straight-line scratch was created in the monolayer using a cell scraper. Photographs of the scratch area were taken at 0, 24, and 48 hours to document the healing process.
Transwell migration assay
A cell suspension in serum-free medium was added to the upper chamber of the Transwell insert at a density of 5×104 cells per well. The lower chamber was filled with medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) as a chemoattractant. The Transwell chambers were incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 24 hours. After incubation, non-migrated cells on the upper surface were gently removed with a cotton swab. Migrated cells on the lower surface were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, stained, and then observed and counted under a microscope.
Transwell invasion assay
Cell suspensions (5×104 cells per well) were added to the upper chamber of Matrigel-coated Transwell inserts in serum-free medium. The lower chamber was filled with medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) to serve as a chemoattractant. The Transwell inserts were incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 24 hours. After incubation, the upper surface of the inserts was gently wiped with a cotton swab. Cells that had invaded the lower surface were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, stained, and subsequently observed and counted under a microscope.
CCK-8 assay
A172 and SKMG1 cells were seeded at 2,000 cells/well in 96-well plates and cultured for 24 – 96 hours. Then, 10 µL of CCK - 8 reagent (Dojindo) was added per well and mixed. The plates were incubated for 1 hour. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm, followed by statistical analysis.
Cell apoptosis assay
The apoptosis assay was performed using the Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit (Beyotime) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Cells were first collected and washed twice with PBS. The cells were then resuspended in 1X Annexin V binding buffer, and 5 µL of Annexin V-FITC and 5 µL of PI were added to each sample. The samples were gently mixed and incubated in the dark at room temperature for 15 minutes. After incubation, the apoptosis rate was measured using a flow cytometer.
Statistics and analysis
Statistical analyses and graphical representations were performed using R (v4.3.1), Python (v3.10.9), and GraphPad Prism (v8.3). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted using the log-rank test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficient was utilized to assess linear relationships. Comparisons between two groups were performed using Student’s t test, while comparisons among three or more groups were performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P-values are shown within the plots to indicate statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns: not significant).
Result
Differential expression of GADD45G in glioma
We analyzed the expression of GADD45G across various tumors and corresponding normal tissues using pan-cancer datasets from TCGA, TARGET, and GTEx (Figure 1A). To facilitate interpretation, we listed the full names corresponding to each cancer code shown in Figure 1A in Supplementary Table 1. Supplementary Figure S1 further illustrates the hazard ratios of GADD45G across different cancer types. The results showed that GADD45G expression was significantly downregulated in most tumors compared to normal tissues (Figure 1A). Notably, gliomas exhibited an opposite trend: GADD45G expression was higher in glioma tissues than in normal brain tissues (Figure 1A). Furthermore, we observed that GADD45G expression in low-grade gliomas (LGG) was higher than that in glioblastoma (GBM). Similar results were validated in three independent datasets, including GEO (Figures 1B, C), CGGA (Figures 1D, E), and TCGA (Figures 1F–H). In particular, comparisons across different histological types and WHO grades consistently showed that GADD45G expression was lower in GBM compared to lower-grade gliomas.
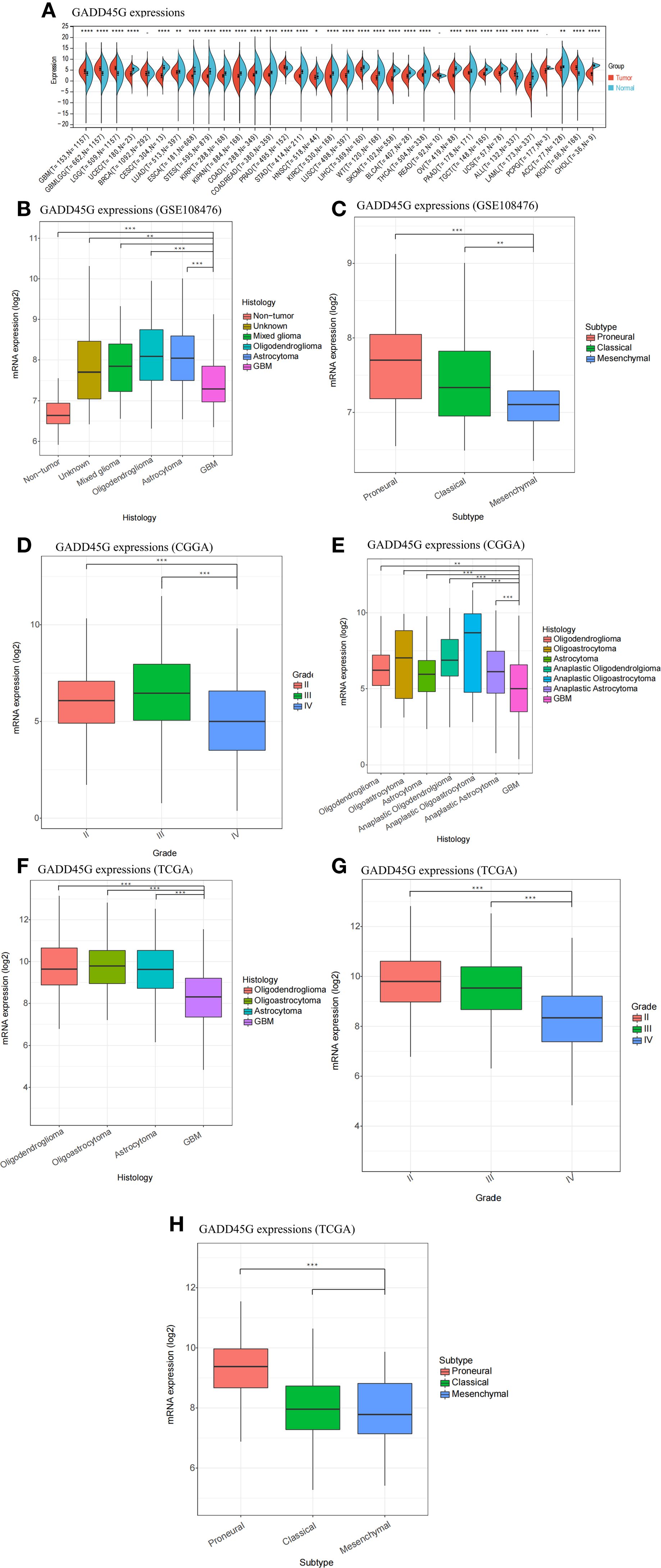
Figure 1. Differential expression of GADD45G in gliomas. (A) Expression of GADD45G across multiple cancer types (pan-cancer). (B–H) Transcriptional expression levels of GADD45G in glioma samples based on multiple datasets, including GSE108476 (B, C), CGGA (D), and TCGA (F–H). The full names corresponding to each cancer code are provided in the Supplementary Table 1 for reference. P-values are shown within the plots to indicate statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns, not significant).
GADD45G as a prognostic marker for favorable outcome in glioma
To assess the prognostic significance of GADD45G in glioma, we conducted a multivariate Cox regression analysis on TCGA-GBM data, categorizing patients into high-risk and low-risk groups based on their computed risk scores (Figure 2A). The analysis revealed that the low-risk group had a higher proportion of surviving patients, while the high-risk group exhibited an increased proportion of deceased patients (Figures 2B, C). Cox regression analysis revealed that patients with high GADD45G expression exhibited an 11.2% reduction in mortality risk compared to those with low expression, suggesting a potential protective role for GADD45G (Figure 2D). When patients were stratified by ascending risk scores, GADD45G expression levels exhibited a progressive decline (Figure 2E). To further validate our findings, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted. The results demonstrated that, across all datasets, higher GADD45G expression was significantly correlated with improved overall survival (OS) in both glioma and glioblastoma, suggesting that GADD45G may serve as a favorable prognostic biomarker for glioma patients (Figures 2F–K). The study of the correlation between GADD45G expression and the infiltration levels of various immune cells suggests that it may influence the progression of glioma by affecting myeloid-derived suppressor cells, activated CD4 T cells, and CD56bright natural killer cells (Supplementary Figure S2).
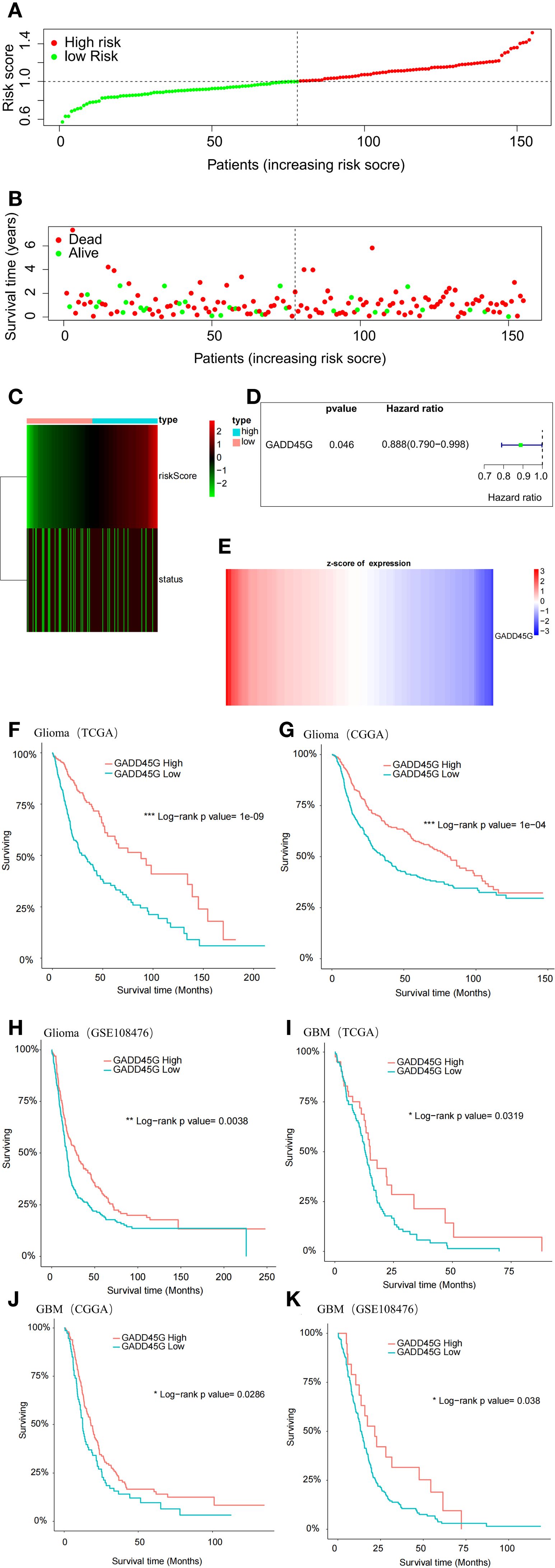
Figure 2. Prognostic significance of GADD45G in gliomas. (A) Multivariate Cox analysis based on TCGA-GBM data. (B, C) Survival status analysis based on risk stratification. (D) Hazard ratio analysis of GADD45G. (E) Expression analysis of GADD45G across risk groups. (F–K) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of overall survival (OS) for patients with different levels of GADD45G transcriptional expression based on TCGA, CGGA, and GSE108476 datasets.
Analysis of tumor microenvironment through single-cell data
Conventional bulk transcriptome analysis cannot fully capture the characteristics of different tumor cell subtypes. Therefore, we further investigate the relationship between GADD45G and glioblastoma (GBM) by utilizing single-cell data. We integrated GBM scRNA-seq data collected from three independent datasets and analyzed a total of 98,216 cells. Six important cell clusters were color-coded and labeled as shown in the figure (Figure 3A). The bubble plot displays the marker genes for each major cell type (Figure 3B). Copy number variation (CNV) analysis indicates that, compared to normal cells, tumor cells exhibit chromosome 7 amplification and chromosome 10 deletion, which is consistent with previous studies (21) (Figure 3C). The UMAP plot reveals five distinct cellular subpopulations within malignant GBM cells (Figure 3D). To evaluate the heterogeneity among GBM subpopulations, we calculated the geometric mean of gene feature expression. This approach provides a quantitative measure of variability within distinct cellular subtypes, allowing for a more comprehensive characterization of intratumoral diversity (Figure 3E). According to Neftel’s classification, GBM cells primarily comprise four distinct cell types: neural progenitor-like (NPC-like), oligodendrocyte progenitor-like (OPC-like), astrocyte-like (AC-like), and mesenchymal-like (MES-like) cells (18). The box plot illustrates the transcriptional expression of marker genes across four malignant GBM cell subpopulations (Figure 3F). From a developmental perspective, AC-like and MES-like cells exhibit greater similarity to each other, while OPC-like and NPC-like cells are more closely related (Figure 3G).
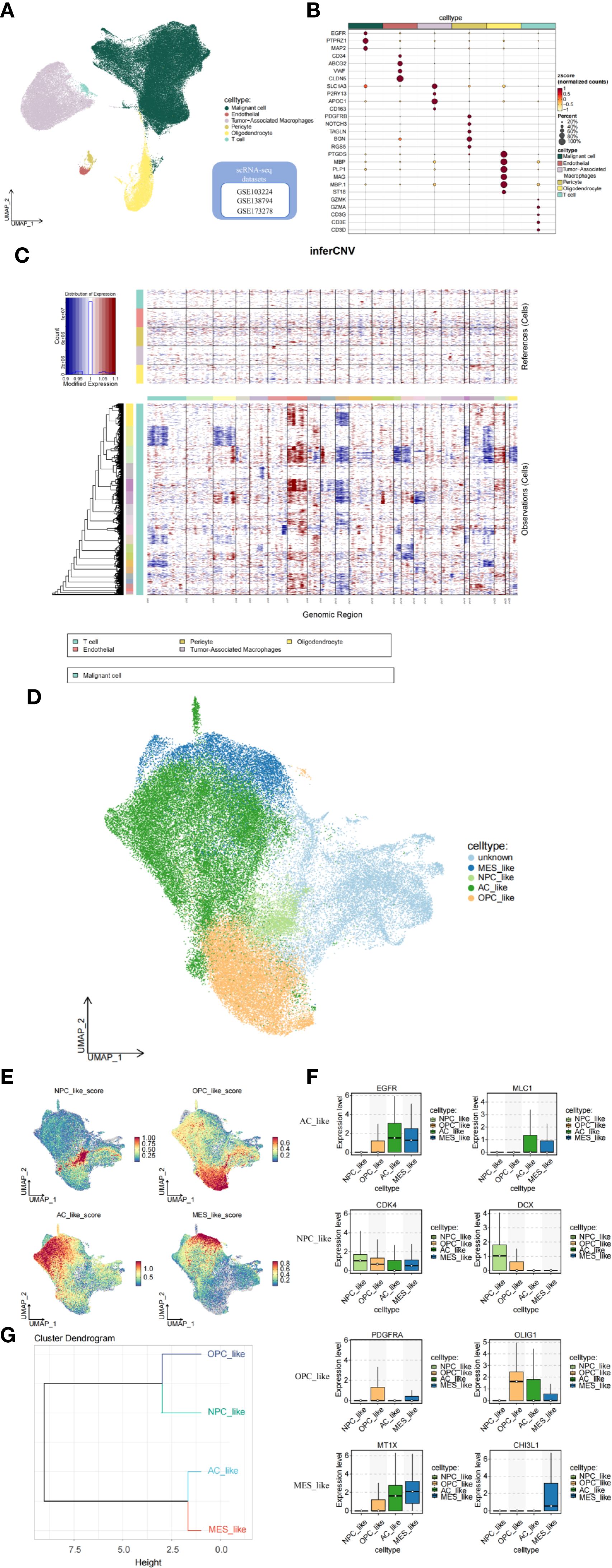
Figure 3. Analysis of the tumor microenvironment based on single-cell data. (A, B) Cell clusters and their marker genes. (C) CNV analysis indicating tumor cell characteristics. (D, E) Subgrouping and annotation of malignant GBM cells. (F) Marker genes of GBM malignant cell subpopulations. (G) Dendrogram of cell subcluster relationships.
Characterization of malignant GBM subpopulations
The proportions of cell subtypes vary significantly across different samples, reflecting the heterogeneity of GBM (Figure 4A). The CGGA dataset further supports our findings, reinforcing the robustness of our results (Figures 4B, C). Overall, the molecular subtypes identified at the single-cell level indicate that GBM patients exhibit a high degree of intratumoral subtype heterogeneity. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicates that higher expression of MES-like cells is associated with poorer survival outcomes (Figures 4D–G). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) were used to determine the functional heterogeneity of the four typical subgroups. The results indicated that MES-like cells were significantly enriched in biological processes associated with hypoxia and wound healing. An improved capacity to adapt to hypoxic conditions promotes tumor progression and invasion. The enrichment of wound healing-related functions suggests that MES-like cells may possess enhanced proliferative and migratory potential. Additionally, the enrichment of glucocorticoid response-related functions may contribute to immune evasion mechanisms (Figure 4H). Furthermore, MES-like cells were highly enriched in the HALLMARK_EPITHELIAL_MESENCHYMAL_TRANSITION (EMT) pathway, which is critically linked to cellular invasion, migration, and malignant progression. These findings indicate that GBM patients exhibiting mesenchymal characteristics tend to have worse survival outcomes (Figure 4I).
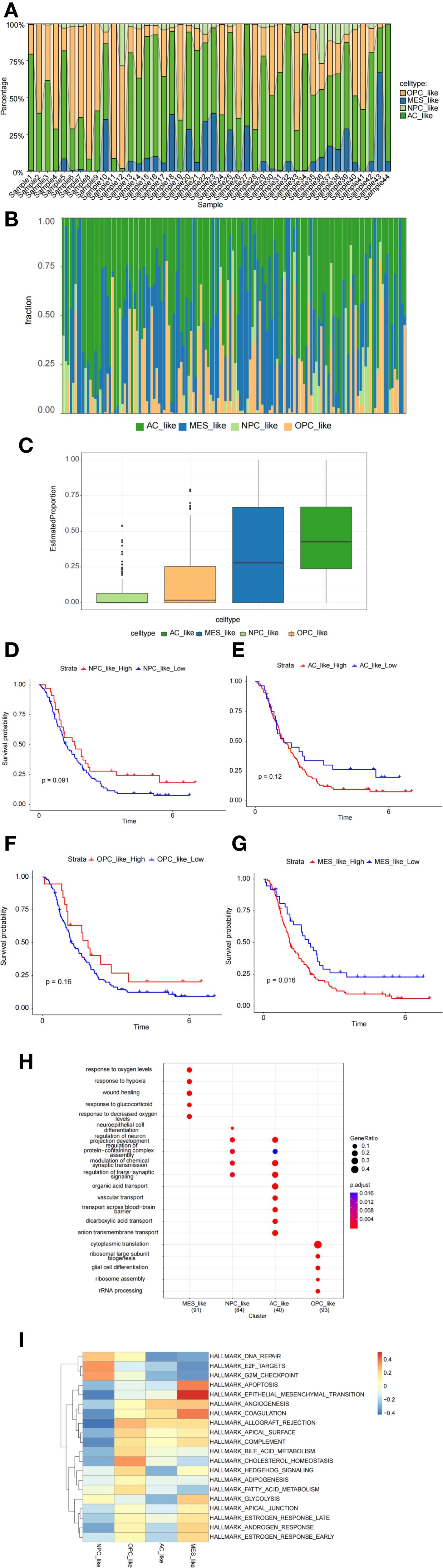
Figure 4. Characterization of malignant cell subpopulations. (A) Proportion analysis of malignant cell subpopulations based on single-cell data. (B, C) Proportion analysis of malignant cell subpopulations based on CGGA data. (D–G) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis exploring the prognostic significance of MES-like cells. (H, I) Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and gene set variation analysis (GSVA) revealing functional heterogeneity among cell subpopulations.
Expression levels of GADD45G and its correlated genes in malignant GBM cells
To examine the expression pattern of GADD45G across distinct cellular subpopulations in GBM, we employed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data to map its distribution among NPC-like, OPC-like, AC-like, and MES-like cell populations (Figures 5A, B). The analysis revealed that GADD45G exhibited the lowest expression levels in MES-like cells. Notably, this finding aligns with our results from other databases, which consistently indicate a downregulation of GADD45G in malignant cells. In order to identify and develop small molecule drugs capable of inducing GADD45G expression in cancer cells, we examined the correlation between GADD45G expression and various cancer-related drugs using the CTD database (Supplementary Figure S3). To elucidate the functional role of GADD45G in GBM, we conducted Spearman correlation analysis to identify genes strongly associated with GADD45G, thereby uncovering potential regulatory networks. The figure illustrates the top 10 genes most strongly correlated with GADD45G (Figures 5C, D). Among these genes, MT3 and VIM demonstrated the strongest inverse correlation with GADD45G (r = -0.27), indicating that their expression may be downregulated by GADD45G. Through the analysis of single-cell transcriptomic data, we discovered that VIM was markedly upregulated in MES-like cells relative to other cell populations (Figures 5E–H).
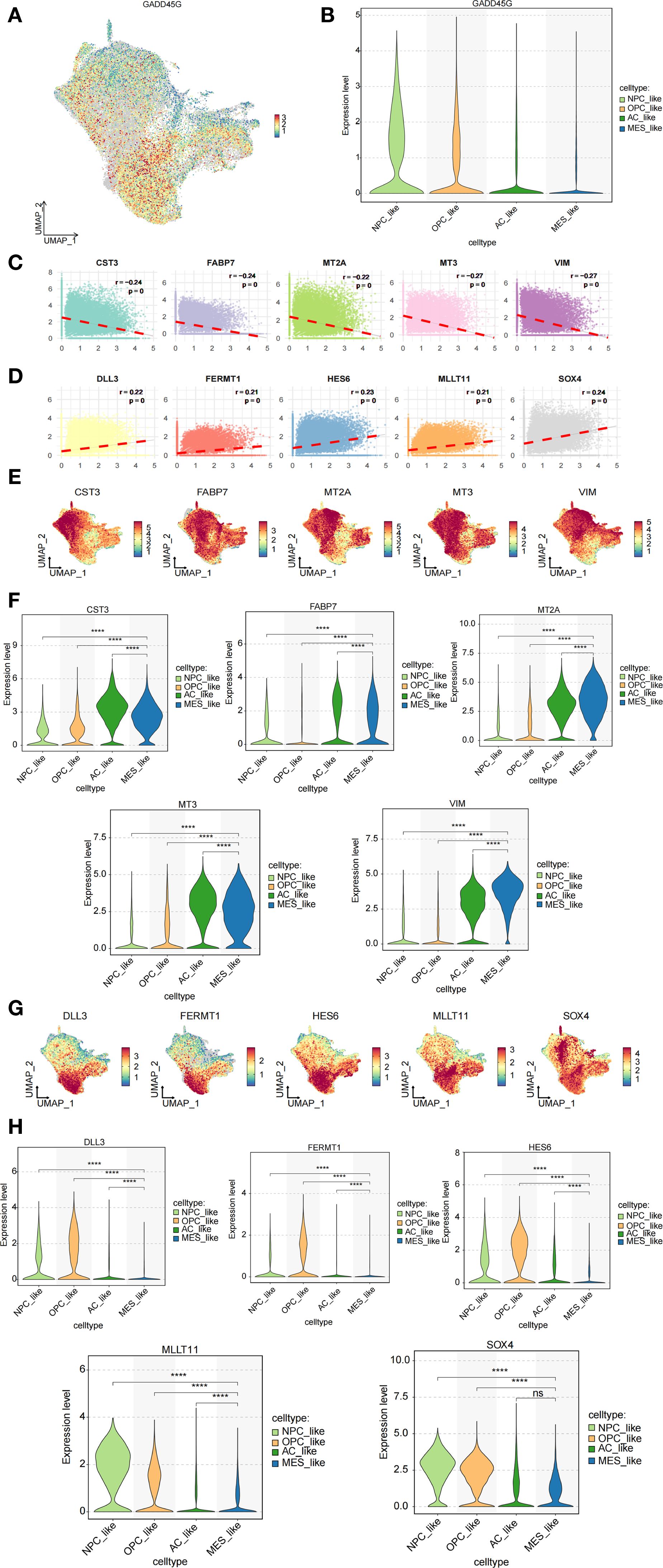
Figure 5. Analysis of GADD45G and its related genes in cell subpopulations. (A, B) Expression analysis of GADD45G across different cell subpopulations. (C, D) Spearman correlation analysis identifying highly correlated genes. (E–H) Expression analysis of the correlated genes across cell subpopulations.
The role of GADD45G in cell invasion and migration in glioma through regulation of EMT-like phenotypes
In the present study, we demonstrated that MES-like cells are significantly enriched in the EMT-related gene sets, and Spearman correlation analysis revealed a strong negative correlation between GADD45G and VIM. Although gliomas are not epithelial in origin and do not undergo classical epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), they can exhibit an EMT-like transcriptional program characterized by loss of polarity, enhanced motility, and expression of mesenchymal markers (22–24). Based on this concept, we hypothesized that GADD45G might regulate glioma progression by modulating EMT-like features. To test this, we performed plasmid transfection experiments in glioma cell lines A172 and SKMG1. Western blotting and RT-qPCR confirmed successful overexpression of GADD45G (Figures 6A, B). Following GADD45G overexpression, both cell lines showed significantly reduced invasion and migration abilities in Transwell and wound healing assays (Figures 6C–G). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a key role in tumor metastasis, acting as a critical driver for the invasion and migration of tumor cells (25, 26). To further investigate whether GADD45G affects EMT-like marker expression, we analyzed E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin levels by Western blotting (Figure 6H). Overexpression of GADD45G increased E-cadherin expression while suppressing mesenchymal markers N-cadherin and vimentin. These results suggest that GADD45G attenuates glioma cell invasiveness in part by regulating EMT-like phenotypic traits. In conclusion, although gliomas do not undergo canonical EMT, our data support that GADD45G plays a role in modulating EMT-like processes that contribute to tumor cell migration and invasion. To further investigate the biological effects of GADD45G overexpression in glioma cells, we performed CCK - 8 proliferation assays and Annexin V-FITC/PI double-staining flow cytometry to assess its impact on cell proliferation and apoptosis. As shown in Figures 6I, J, overexpression of GADD45G significantly inhibited the proliferation of A172 and SKMG1 glioma cells compared to the control group. Meanwhile, flow cytometry results demonstrated that GADD45G overexpression markedly increased the apoptotic rate in both cell lines (Figures 6K, L), suggesting that GADD45G not only suppresses glioma cell growth but also induces apoptosis. These findings indicate that GADD45G exerts tumor-suppressive functions in glioma by simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and promoting apoptosis.
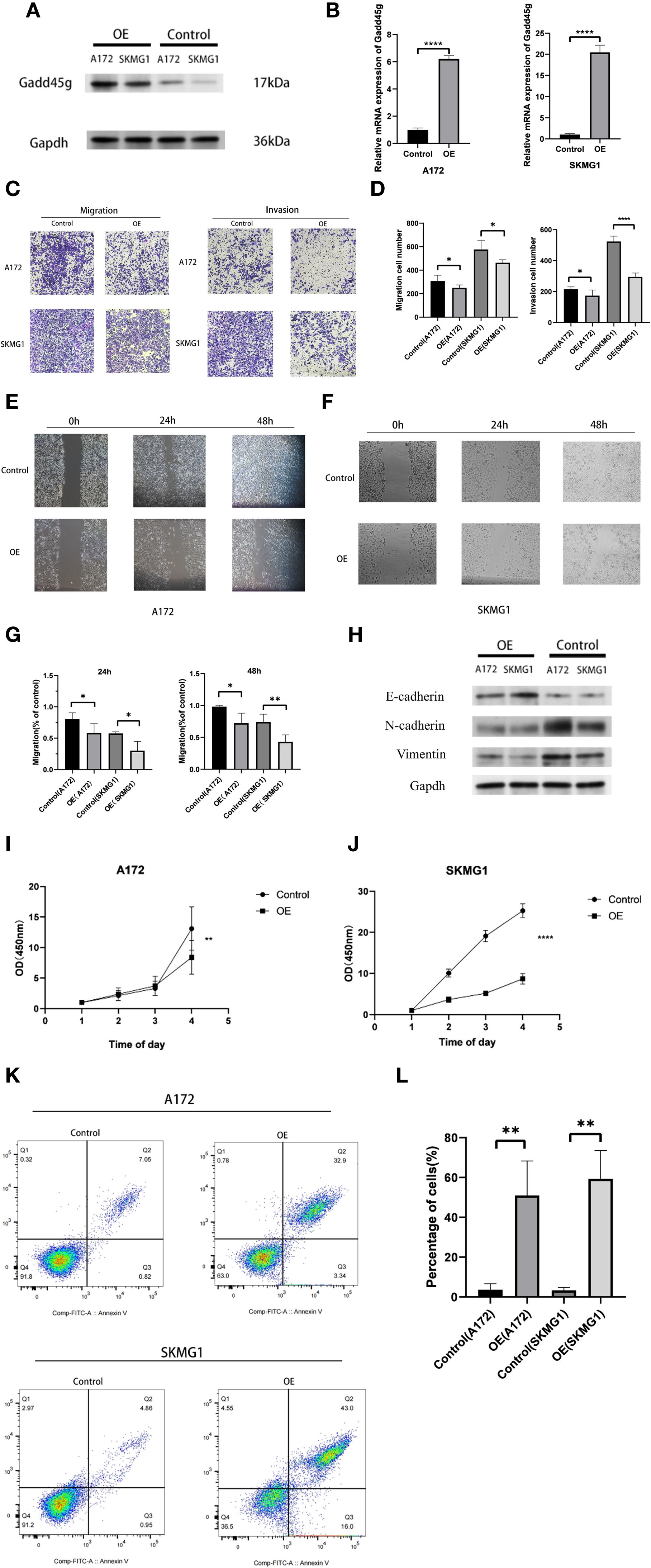
Figure 6. Functional effects of GADD45G on glioma cells. (A) Western blot analysis of GADD45G expression in A172 and SKMG1 cells after plasmid transfection. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of GADD45G expression in A172 and SKMG1 cells after plasmid transfection. (C, D) Transwell migration and invasion assays and their quantification in A172 and SKMG1 cells. (E–G) Wound healing assays showing the migration ability of A172 and SKMG1 cells at 0, 24, and 48 hours and their quantification. (H) Western blot analysis of EMT-like phenotypic markers. (I, J). CCK - 8 assay evaluating changes in cell proliferation of A172 and SKMG1 cells. (K, L). Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in A172 and SKMG1 cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Discussion
Gliomas, particularly Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), are characterized by high invasiveness, rapid growth, and the ability to spread to other brain regions, which complicates complete surgical resection. An urgent need exists for the development of novel early diagnostic and prognostic targets to overcome the challenges associated with glioma treatment. A significant body of research has focused on identifying potential biomarkers that could open new therapeutic avenues for gliomas (27–30). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to elucidate the role of GADD45G in gliomas.
Notably, during the development of various cancer types, GADD45G is underexpressed and is regarded as a functional tumor suppressor. Comprehensive analysis of multiple databases has revealed that GADD45G is highly expressed in glioma patients, suggesting its potential role as an oncogene. However, Cox regression analysis indicates that GADD45G possess a protective function. Survival curves further demonstrate that elevated levels of GADD45G are correlated with improved overall survival in patients. To explore this further, we modulated GADD45G expression using plasmid overexpression, thereby confirming its tumor-suppressive role in glioma. Notably, GADD45G expression is markedly reduced in glioblastoma relative to lower-grade gliomas. GADD45G expression can be induced by cellular stress and certain subsets of cytokines (11–13). Deficiencies in the GADD45 pathway have been implicated in the initiation and progression of malignant tumors (31, 32). We hypothesize that in low-grade gliomas, GADD45G upregulation may inhibit tumor progression, whereas, in malignant tumors, the suppression of GADD45G expression by tumor cells could contribute to tumor deterioration. To test this hypothesis, we conducted in vitro experiments where we overexpressed GADD45G in glioma cells. As anticipated, GADD45G overexpression led to a significant inhibition of glioma cell migration and proliferation.
Prior to the advent of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), traditional transcriptomic approaches were the primary methods used for identifying prognostic biomarkers and anti-cancer targets. However, bulk RNA sequencing, which cannot capture the expression profiles of individual cells, is limited in its ability to detect the tumor microenvironment at the cellular level. Therefore, we utilized scRNA-seq data from GBM samples to investigate the heterogeneity within GBM tumor subgroups. In this study, we systematically identified four highly heterogeneous GBM cell subgroups through a series of stringent protocols. In contrast, MES-like cells were predominantly characterized by epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), hypoxic conditions, and wound healing pathways. Survival analysis revealed a significant association between the mesenchymal (MES) subtype and poor patient prognosis, suggesting that the MES subtype may represent the most aggressive form of glioblastoma. As demonstrated in the study by Yang et al., the MES subtype corresponds to the terminal stage of GBM cellular evolution (33). To further elucidate the role of GADD45G, we examined its expression across distinct GBM cellular subpopulations. Consistent with trends observed in bulk transcriptomic data, GADD45G expression was notably suppressed in malignant cell populations, further supporting our prior hypothesis. To explore the functional role of GADD45G in GBM, we conducted Spearman correlation analysis and examined the transcriptional expression levels of related genes across four distinct cell subpopulations. Notably, we observed that VIM expression was significantly elevated in the MES cell population compared to other subpopulations. In the context of oncology, Vimentin is widely recognized as a mesenchymal marker and is strongly upregulated during epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process critical to tumor invasion and metastasis. We observed a significant inverse correlation between GADD45G and VIM expression.
Although gliomas are not epithelial in origin, the concept of an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like (EMT-like) process has been increasingly discussed in the context of glioma biology, particularly to describe transcriptional programs associated with enhanced cell plasticity and invasion. EMT-like programs refer not to a full transdifferentiation between epithelial and mesenchymal cell states, but rather to a transcriptional and phenotypic shift that promotes tumor cell plasticity, invasiveness, and resistance to treatment. This concept is supported by transcriptomic analyses showing that glioma cells, including primary GBM and established cell lines, express a mesenchymal signature comparable to TGF-β-induced EMT in epithelial tumors (34). EMT-like markers and pathways, including Snail, ZEB1/2, Twist, and Wnt/TGF-β signaling, have been widely detected in glioblastoma and are implicated in tumor progression (35–43). Therefore, the observed relationship between GADD45G and EMT markers in our study is not indicative of classical EMT, but rather reflects a regulatory interaction within this EMT-like phenotypic modulation that is biologically relevant in glioma. Based on this conceptual framework, we next sought to investigate whether GADD45G influences EMT-like features in glioma cells through experimental validation. We subsequently conducted cell-based experiments to determine whether GADD45G modulates EMT and thereby influences the invasive and metastatic behavior of glioma cells. Overexpression of GADD45G reduced cell invasion and migration, and the protein levels of EMT markers were also downregulated. Overall, these results strongly support the role of GADD45G in inhibiting tumor metastasis. In fact, GADD45G has been studied in various cancers. Wei Guo et al. reported that reduced expression of GADD45G is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (10). Xinbao Zhang et al. demonstrated that GADD45G initiates the differentiation of embryonic stem cells and inhibits carcinogenesis in breast cancer cells (44). Other studies have also suggested that GADD45G, a novel vitamin D-regulated gene, exerts anti-proliferative effects in prostate cancer cells (45). In conclusion, GADD45G may serve as a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
p53 is a classical tumor suppressor that plays a pivotal role in cellular stress responses, DNA repair, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation. It can inhibit tumor growth by inducing apoptosis or causing cell cycle arrest (46). PTEN, a phosphatase, primarily exerts its tumor-suppressive effect through negative regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. By dephosphorylating PIP3, PTEN reduces Akt activation, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis (47). Similarly, members of the GADD45 family act as stress response genes that can be activated by various intracellular and extracellular stimuli, such as DNA damage and oxidative stress, to initiate downstream signaling pathways involved in tumor suppression (12, 48, 49). Our findings suggest that GADD45G may exert its anti-tumor effects through a dual mechanism of EMT inhibition and apoptosis induction, functionally resembling classical tumor suppressors like p53 and PTEN. Given its dual role in regulating both tumor cell invasiveness and survival, GADD45G holds promise as a potential therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker in various malignancies. Further investigation into its molecular mechanisms is warranted.
The Gadd45 family has been widely studied in the context of various cancers, such as pancreatic, hepatocellular, lung, cervical, and gastrointestinal cancers, as well as different types of lymphomas. These studies highlight the dysfunctional roles and regulatory mechanisms of the Gadd45 family in tumorigenesis. Consequently, the Gadd45 family has been identified as a promising target for cancer therapies (50). Emerging functional evidence suggests that GADD45 proteins act as tumor suppressors in response to various stimuli, linking multiple cellular signaling modules. Inducing the expression of GADD45 is a necessary step in mediating the anticancer activity of various chemotherapy drugs, while the loss of GADD45 may eliminate its function in cancer cells. NAC1-mediated downregulation of GADD45G has been shown to contribute to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells (51). In a breast cancer cell line resistant to farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTI), (-)-Xanthatin was found to induce GADD45G, which subsequently activated p38 and JNK pathways, leading to decreased cell proliferation and caspase-independent apoptosis. Research has shown that structurally varied NSAIDs can trigger apoptosis in ovarian, prostate, renal, breast, and stomach cancer cell lines by activating melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7/Interleukin-24 (mda-7/IL-24) (52–55). The induction and activation of mda-7/IL-24 by NSAIDs result in the upregulation of GADD45A and GADD45G, which are crucial for the execution of cancer cell death through JNK activation (52).
Our study uncovers the regulatory mechanism of tumor development mediated by GADD45G in glioma, offering a promising avenue for future research. Future research focused on understanding how GADD45 pathways are regulated by the tumor microenvironment and cancer stem cells will offer new opportunities to target and manipulate GADD45 function. Moreover, we explored the correlation between GADD45G and various cancer drugs through the CTD database. Many of these drugs were found to upregulate the expression of GADD45G, which is clearly a research avenue worth further exploration.
Although this study integrates multiple bioinformatics analyses and in vitro experimental validations, we acknowledge that these findings represent only the preliminary phase of a broader investigation. A major limitation is the lack of validation using animal models or clinical tissue samples, which is essential for supporting the translational potential of GADD45G as a biomarker or therapeutic target in glioma. While our cellular models revealed correlations between GADD45G expression and tumor progression as well as an EMT-like phenotype, further validation in animal models and patient-derived tissues is necessary. We plan to establish a tissue microarray (TMA) resource based on clinical glioma samples and conduct qPCR or protein-level analyses to assess associations between GADD45G expression and tumor grade, subtype, and prognosis, providing stronger evidence for its clinical utility. In parallel, in vivo models such as orthotopic xenografts will be used to investigate the role of GADD45G in tumor growth, metastasis, and therapeutic response. Additionally, our single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis, based on three public datasets with limited sample sizes, may be affected by residual technical or biological variability despite batch effect correction, and may not fully capture GBM’s intratumoral heterogeneity. We have addressed this limitation in the manuscript and plan to expand our scRNA-seq analyses to include more publicly available datasets with spatial information and treatment-specific contexts, as well as generate our own high-resolution scRNA-seq data from freshly collected clinical glioma samples, thereby enabling more controlled analyses of GADD45G expression across distinct cellular and microenvironmental contexts. Lastly, the use of public transcriptomic and clinical datasets may introduce confounding factors such as inconsistencies in sample processing, differences in sequencing platforms, and incomplete clinical annotations, which should be carefully addressed in future prospective studies. In summary, although our in vitro experiments provide preliminary insights into the regulatory role of GADD45G in glioma cell migration, invasion, and EMT-like transitions, further systematic mechanistic studies and validations using clinical specimens and animal models are required to fully establish its prognostic and therapeutic potential.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used. Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
CS: Visualization, Formal Analysis, Validation, Data curation, Writing – original draft. HC: Visualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Data curation. CM: Visualization, Validation, Writing – original draft. JY: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation. KT: Project administration, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study design, data collection, data analysis, manuscript preparation and publication decisions of this work were supported by NSFC Incubation Project of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (KY0120220043) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82203081) to HC; Guangzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (201904010348) to KT.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1608710/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Stupp R, Mason WP, and van den Beuf MJ. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Ann Oncol. (2005) 16:949–. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330
2. Smith ML, Chen IT, Zhan Q, Bae I, Chen CY, Gilmer TM, et al. Interaction of the p53-regulated protein Gadd45 with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Science. (1994) 266:1376–80. doi: 10.1126/science.7973727
3. Hollander MC, Sheikh MS, Bulavin DV, Lundgren K, Augeri-Henmueller L, Shehee R, et al. Genomic instability in Gadd45a-deficient mice. Nat Genet. (1999) 23:176–84. doi: 10.1038/13802
4. Wang XW, Zhan Q, Coursen JD, Khan MA, Kontny HU, Yu L, et al. GADD45 induction of a G2/M cell cycle checkpoint. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1999) 96:3706–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3706
5. Harkin DP, Bean JM, Miklos D, Song YH, Truong VB, Englert C, et al. Induction of GADD45 and JNK/SAPK-dependent apoptosis following inducible expression of BRCA1. Cell. (1999) 97:575–86. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80769-2
6. Tamura RE, de Vasconcellos JF, Sarkar D, Libermann TA, Fisher PB, and Zerbini LF. GADD45 proteins: central players in tumorigenesis. Curr Mol Med. (2012) 12:634–51. doi: 10.2174/156652412800619978
7. Hoffman B and Liebermann DA. Gadd45 modulation of intrinsic and extrinsic stress responses in myeloid cells. J Cell Physiol. (2009) 218:26–31. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21582
8. Qiu W, David D, Zhou B, Chu PG, Zhang B, Wu M, et al. Down-regulation of growth arrest DNA damage-inducible gene 45beta expression is associated with human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol. (2003) 162:1961–74. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64329-5
9. Wang W, Huper G, Guo Y, Murphy SK, Olson JA Jr., and Marks JR. Analysis of methylation-sensitive transcriptome identifies GADD45a as a frequently methylated gene in breast cancer. Oncogene. (2005) 24:2705–14. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208464
10. Guo W, Zhu T, Dong Z, Cui L, Zhang M, and Kuang G. Decreased expression and aberrant methylation of Gadd45G is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2013) 30:977–92. doi: 10.1007/s10585-013-9597-2
11. Zhang W, Bae I, Krishnaraju K, Azam N, Fan W, Smith K, et al. CR6: A third member in the MyD118 and Gadd45 gene family which functions in negative growth control. Oncogene. (1999) 18:4899–907. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202885
12. Takekawa M and Saito H. A family of stress-inducible GADD45-like proteins mediate activation of the stress-responsive MTK1/MEKK4 MAPKKK. Cell. (1998) 95:521–30. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81619-0
13. Chakravarty D, Cai Q, Ferraris JD, Michea L, Burg MB, and Kultz D. Three GADD45 isoforms contribute to hypertonic stress phenotype of murine renal inner medullary cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2002) 283:F1020–9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00118.2002
14. Chung HK, Yi YW, Jung NC, Kim D, Suh JM, Kim H, et al. Gadd45gamma expression is reduced in anaplastic thyroid cancer and its reexpression results in apoptosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 88:3913–20. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-022031
15. Zhang W, Li T, Shao Y, Zhang C, Wu Q, Yang H, et al. Semi-quantitative detection of GADD45-gamma methylation levels in gastric, colorectal and pancreatic cancers using methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2010) 136:1267–73. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0777-z
16. Ying J, Srivastava G, Hsieh WS, Gao Z, Murray P, Liao SK, et al. The stress-responsive gene GADD45G is a functional tumor suppressor, with its response to environmental stresses frequently disrupted epigenetically in multiple tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2005) 11:6442–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0267
17. Stuart T, Butler A, Hoffman P, Hafemeister C, Papalexi E, Mauck WM 3rd, et al. Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell. (2019) 177:1888–902.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.031
18. Neftel C, Laffy J, Filbin MG, Hara T, Shore ME, Rahme GJ, et al. An integrative model of cellular states, plasticity, and genetics for glioblastoma. Cell. (2019) 178:835–49.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.024
19. Darmanis S, Sloan SA, Croote D, Mignardi M, Chernikova S, Samghababi P, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis of infiltrating neoplastic cells at the migrating front of human glioblastoma. Cell Rep. (2017) 21:1399–410. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.030
20. Xiong A, Zhang J, Chen Y, Zhang Y, and Yang F. Integrated single-cell transcriptomic analyses reveal that GPNMB-high macrophages promote PN-MES transition and impede T cell activation in GBM. EBioMedicine. (2022) 83:104239. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104239
21. Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A, Campos B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell. (2013) 155:462–77. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.034
22. Christiansen JJ and Rajasekaran AK. Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:8319–26. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0410
23. Li S, Wang J, Lu Y, Zhao Y, Prinz RA, and Xu X. Inhibition of the sonic hedgehog pathway activates TGF-beta-activated kinase (TAK1) to induce autophagy and suppress apoptosis in thyroid tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:459. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03744-2
24. Tan TZ, Miow QH, Miki Y, Noda T, Mori S, Huang RY, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition spectrum quantification and its efficacy in deciphering survival and drug responses of cancer patients. EMBO Mol Med. (2014) 6:1279–93. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404208
25. Bakir B, Chiarella AM, Pitarresi JR, and Rustgi AK. EMT. MET, plasticity, and tumor metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. (2020) 30:764–76. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.07.003
26. Wu D, Zhao B, Qi X, Peng F, Fu H, Chi X, et al. Nogo-B receptor promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer cells through the Ras/ERK/Snail1 pathway. Cancer Lett. (2018) 418:135–46. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.030
27. Wang F, Zhao F, Zhang L, Xiong L, Mao Q, Liu Y, et al. CDC6 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in glioma. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:153. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01623-8
28. Zhu C, Zhao Y, and Zheng W. CDC14B is a favorable biomarker for recurrence and prognosis of GBM. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2023) 227:107665. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2023.107665
29. Xu L, Shao F, Luo T, Li Q, Tan D, and Tan Y. Pan-cancer analysis identifies CHD5 as a potential biomarker for glioma. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:8489. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158489
30. Liu Y, Yao R, Shi Y, Liu Y, Liu H, Liu J, et al. Identification of CD101 in glioma: A novel prognostic indicator expressed on M2 macrophages. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:845223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845223
31. Fornace AJ Jr., Nebert DW, Hollander MC, Luethy JD, Papathanasiou M, Fargnoli J, et al. Mammalian genes coordinately regulated by growth arrest signals and DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol. (1989) 9:4196–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4196-4203.1989
32. Fornace AJ Jr., Alamo I Jr., and Hollander MC. DNA damage-inducible transcripts in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1988) 85:8800–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8800
33. Yang Y, Liu Z, Wei Y, He S, Gu A, Li Z, et al. Single-cell multi-omics analysis reveals candidate therapeutic drugs and key transcription factor specifically for the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma. Cell Biosci. (2024) 14:151. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01332-3
34. Iser IC, Pereira MB, Lenz G, and Wink MR. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like process in glioblastoma: an updated systematic review and in silico investigation. Med Res Rev. (2017) 37:271–313. doi: 10.1002/med.21408
35. Myung JK, Choi SA, Kim SK, Wang KC, and Park SH. Snail plays an oncogenic role in glioblastoma by promoting epithelial mesenchymal transition. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2014) 7:1977–87.
36. Siebzehnrubl FA, Silver DJ, Tugertimur B, Deleyrolle LP, Siebzehnrubl D, Sarkisian MR, et al. The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol Med. (2013) 5:1196–212. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201302827
37. Expression of concern: ZEB2 mediates multiple pathways regulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in glioma. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0231386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231386
38. Mikheeva SA, Mikheev AM, Petit A, Beyer R, Oxford RG, Khorasani L, et al. TWIST1 promotes invasion through mesenchymal change in human glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. (2010) 9:194. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-194
39. Velpula KK, Dasari VR, Tsung AJ, Dinh DH, and Rao JS. Cord blood stem cells revert glioma stem cell EMT by down regulating transcriptional activation of Sox2 and Twist1. Oncotarget. (2011) 2:1028–42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.367
40. Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA, and Massague J. Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation. Cell. (2004) 117:211–23. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00298-3
41. Joseph JV, Conroy S, Tomar T, Eggens-Meijer E, Bhat K, Copray S, et al. TGF-beta is an inducer of ZEB1-dependent mesenchymal transdifferentiation in glioblastoma that is associated with tumor invasion. Cell Death Dis. (2014) 5:e1443. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.395
42. Liu C, Tu Y, Sun X, Jiang J, Jin X, Bo X, et al. Wnt/beta-Catenin pathway in human glioma: expression pattern and clinical/prognostic correlations. Clin Exp Med. (2011) 11:105–12. doi: 10.1007/s10238-010-0110-9
43. Kahlert UD, Maciaczyk D, Doostkam S, Orr BA, Simons B, Bogiel T, et al. Activation of canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling enhances in vitro motility of glioblastoma cells by activation of ZEB1 and other activators of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. (2012) 325:42–53. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.05.024
44. Zhang X, Li Y, Ji J, Wang X, Zhang M, Li X, et al. Gadd45g initiates embryonic stem cell differentiation and inhibits breast cell carcinogenesis. Cell Death Discov. (2021) 7:271. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00667-x
45. Flores O and Burnstein KL. GADD45gamma: a new vitamin D-regulated gene that is antiproliferative in prostate cancer cells. Endocrinology. (2010) 151:4654–64. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0434
46. Liu Y, Su Z, Tavana O, and Gu W. Understanding the complexity of p53 in a new era of tumor suppression. Cancer Cell. (2024) 42:946–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.04.009
47. Castellino RC and Durden DL. Mechanisms of disease: the PI3K-Akt-PTEN signaling node–an intercept point for the control of angiogenesis in brain tumors. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. (2007) 3:682–93. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0661
48. Vairapandi M, Balliet AG, Hoffman B, and Liebermann DA. GADD45b and GADD45g are cdc2/cyclinB1 kinase inhibitors with a role in S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoints induced by genotoxic stress. J Cell Physiol. (2002) 192:327–38. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10140
49. Azam N, Vairapandi M, Zhang W, Hoffman B, and Liebermann DA. Interaction of CR6 (GADD45gamma) with proliferating cell nuclear antigen impedes negative growth control. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:2766–74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005626200
50. Sultan FA and Sweatt JD. The role of the Gadd45 family in the nervous system: a focus on neurodevelopment, neuronal injury, and cognitive neuroepigenetics. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2013) 793:81–119. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-8289-5_6
51. Jinawath N, Vasoontara C, Yap KL, Thiaville MM, Nakayama K, Wang TL, et al. NAC - 1, a potential stem cell pluripotency factor, contributes to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer through inactivating Gadd45 pathway. Oncogene. (2009) 28:1941–8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.37
52. Zerbini LF, Czibere A, Wang Y, Correa RG, Otu H, Joseph M, et al. A novel pathway involving melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 mediates nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced apoptosis and growth arrest of cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:11922–31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2068
53. Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, and Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. (1995) 11:2477–86.
54. Jiang H, Su ZZ, Lin JJ, Goldstein NI, Young CS, and Fisher PB. The melanoma differentiation associated gene mda-7 suppresses cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1996) 93:9160–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.9160
Keywords: GADD45G, gliomas, prognostic biomarker, therapeutic target, EMT-like
Citation: Shen C, Cai H, Mao C, Yang J and Tang K (2025) GADD45G as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in glioma: integrative analysis of bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing. Front. Oncol. 15:1608710. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1608710
Received: 09 April 2025; Accepted: 27 August 2025;
Published: 11 September 2025.
Edited by:
Fabio Torregrossa, University of Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Jaldeep Langhnoja, University of Cincinnati, United StatesXin Xu, Evozyne, Inc., United States
Yohei Niikura, Nanjing University, China
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Cai, Mao, Yang and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai Tang, dGFuZ2thaUBnZHBoLm9ybi5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Cong Shen
Cong Shen Haiping Cai
Haiping Cai Chengliang Mao
Chengliang Mao Jiahao Yang2
Jiahao Yang2