- 1Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Cancer Center, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Infectious Disease, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China
Objectives: To investigate the relationship between the HALP score and recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and ablation.
Methods: We collected clinical data from 728 HCC patients who underwent TACE and ablation from January 2018 to December 2023. Patients with high HALP scores (H-HALP, n=422) were stratified into a training cohort (n=296) and an internal validation cohort (n=126), while an external validation cohort (n=147) was independently enrolled. Lasso-Cox regression was employed to identify independent risk factors for recurrence-free survival (RFS), and a nomogram was constructed. The predictive accuracy of nomogram was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: Although the median RFS in the H-HALP group longer than the L-HALP group (1.84 vs. 1.60 years, P=0.024), recurrence rates remained substantial in H-HALP patients (1-/3-/5-year RFS: 70.8%/36.2%/21.5%). The nomogram, integrating cirrhosis, tumor numbers, and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), demonstrated moderate predictive accuracy for 1-/3-/5-year RFS in the training cohort (AUC: 0.665/0.694/0.671) and internal validation cohort (AUC: 0.622/0.606/0.561). External validation yielded AUCs of 0.569 (1-year), 0.615 (3-year), and 0.662 (4-year). Calibration curves indicated strong agreement between predicted and observed outcomes, while DCA confirmed clinical utility. Risk stratification based on nomogram scores revealed significantly prolonged RFS in low-risk versus high-risk groups across all cohorts.
Conclusion: The HALP score alone showed limited prognostic value in this cohort; however, the Lasso-Cox regression-based nomogram effectively stratified recurrence risk in H-HALP patients treated with TACE and ablation.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth leading cause of cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally, characterized by high rate of recurrence and metastasis (1, 2). For early-stage HCC, surgical resection, liver transplantation and local ablation are considered potentially curative therapy (3). However, only approximately 20% of HCC patients derive a survival benefit from resection and transplantation (4). Locoregional therapies, particularly transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and ablation, play a leading part in the management of 50-60% of HCC cases (5).
TACE, a minimally invasive procedure, induces tumor ischemia by selectively delivering chemotherapeutic agents and embolic materials to tumor-feeding arteries, effectively downstaging lesions and reducing tumor burden (6). Nonetheless, incomplete embolization and residual microvascular invasion often lead to recurrence (7). Conversely, ablation techniques (e.g., radiofrequency or microwave ablation) achieve localized tumor destruction but face limitations in treating large (>3 cm) or perivascular tumors due to heat-sink effects (5). The synergistic combination of TACE and ablation addresses these shortcomings. TACE reduces tumor vascularity, enhancing thermal ablation efficacy, while ablation eradicates residual lesions post-TACE (8). Previous studies have confirmed that this combined approach significantly prolongs recurrence-free survival (RFS) compared to monotherapy (4, 9, 10). Despite these advancements, recurrence and distant metastasis remain seriously affecting the overall survival of HCC patients. Therefore, early identification and prompt treatment of individuals at high risk of recurrence is essential to improve outcomes for patients with HCC.
Nutrition and systemic inflammatory responses are associated with tumor efficacy and survival. The HALP score, defined as hemoglobin (Hb) × albumin (ALB) × lymphocytes (LYM)/platelets (PLT), comprehensively evaluate the inflammatory response and nutritional status (11, 12). It has been demonstrated as an effective prognostic predictor in various solid cancers, such as gastric carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and renal cell cancer (13–15). In HCC, a low HALP score is associated with poor prognosis in patients undergoing liver resection and is predictive of postoperative recurrence (16–18). However, its predictive value in patients undergoing TACE-ablation remains unexplored.
This study aims to evaluate the association between HALP scores and recurrence in HCC patients receiving combined ablation and TACE. Additionally, we seek to develop a nomogram to improve the individualized prediction of recurrence risk in this populations, which may identify the high-risk patients in advance to implement effective preventive measures.
Methods and materials
Patients selection
This study retrospectively enrolled 728 HCC patients who received TACE combined ablation at Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, between January 2018 and December 2023. HCC diagnosed by histological or radiological criteria as defined by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) guidelines (19). Patients were stratified into two groups based on the HALP score cutoff value (-56.8), as established in prior research (15): 422 patients with high HALP scores (> -56.8, H-HALP group) and 306 patients with low HALP scores (≤ -56.8, L-HALP group). The H-HALP cohort was further randomly divided into a training cohort (n=296) and an internal validation cohort (n=126) at a 7:3 ratio, with a randomization seed set at 400. Furthermore, an independent external validation cohort comprising 147 H-HALP patients treated at Beijing Ditan Hospital during the same period was included to test the model’s robustness. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) aged ≥ 18 years; (2) BCLC stage 0, A or B; (3) Child-Pugh class A or B liver function; (4) patients with tolerable general status: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0–2 and stable organ function adequate for interventional therapy; (5) underwent TACE followed by ablation, with radiological confirmation of complete ablation, defined as the absence of contrast enhancement in the treated lesion on follow-up imaging one month after the procedure. Exclusion criteria included: (1) received systemic drugs before TACE combined with ablation, including sorafenib, lenvatinib, PD-1 inhibitors, etc. (2) presence of other primary malignant tumors. (3) lost to follow-up. (4) contraindication to TACE or ablation.
This study was conducted by the Declaration of Helsinki, and experienced clinicians determined patient eligibility for combined therapy based on guidelines. In addition, this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, and informed consent from the patients was waived due to its retrospective nature. All patient data were de-identified to protect privacy.
Variable collection
Demographic and clinicopathological data were retrospectively collected for analyzed. Baseline characteristics included age, gender, tumor size, tumor number, hypertension, diabetes, cirrhosis, antiviral treatment, BCLC stage and Child-Pugh classification. Laboratory values were obtained from the closest test performed within 7 days before treatment. If multiple measurements were available, the most recent value prior to treatment initiation was used for analysis. Laboratory parameters included Hb, red blood cell (RBC) count, white blood cell (WBC) count, ALB, LYM count, PLT count, alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), globulin (Glob) and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). The HALP score was calculated as Hb (g/L) × ALB (g/L) × LYM (109/L)/PLT (109/L).
Therapeutic procedure
All patients underwent conventional TACE (cTACE) performed by two interventional radiologists with over five years of experience. The procedure was carried out under local anesthesia using the Seldinger technique via femoral artery access. Tumor-feeding arteries were identified through digital subtraction angiography (DSA). A chemotherapeutic emulsion consisting of 20 mg of epirubicin mixed with 6–10 mL of lipiodol was selectively injected into the tumor-feeding vessels. This was followed by embolization using gelatin sponge particles until stasis of blood flow was achieved. If any adverse reactions occurred during the procedure, symptomatic treatment was administered accordingly.
Ablation was conducted within two weeks post-TACE, utilizing radiofrequency ablation (RFA; Cool-tip RF Ablation System, Covidien, USA) and microwave ablation (MWA; ECO Microwave Ablation System, China). Among all patients, 312 (42.9%) received RFA and 416 (57.1%) received MWA. The ablation range completely covered the tumor to the edge of 0.5-1.0 cm to prevent marginal residue and recurrence. For MWA, a typical power setting of 40 to 60 watts was used, with an average ablation time of approximately 5 minutes per site. For more aggressive or multi-focal lesions requiring repeated ablation, total energy application ranged accordingly. In RFA procedures using emission-frequency modes, higher power outputs (120–160 watts) were employed, with each ablation site treated for 6–8 minutes. The selection of power and duration was individualized based on tumor location, size, and surrounding structures. The ablation protocol comprised the following steps: (1) determining the appropriate ablation position using contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); for MRI, a 1.5T system with T1-weighted dynamic contrast-enhanced sequences and T2-weighted imaging was used to assess tumor extent and vascular involvement. (2) inserting the ablation needle at the marked site and monitoring the procedure via imaging; (3) expanding the ablation area as necessary, considering multiple sites and potential overlapping or repeated ablation; (4) heating the needle track in the final phase to prevent tumor implantation and postoperative bleeding; and (5) conducting post-ablation imaging to evaluate treatment efficacy and complications, with follow-up contrast-enhanced CT or MRI performed one-month post-procedure.
Follow-up
All patients were followed up every three months during the first year and every six months thereafter in the outpatient clinic, in accordance with the Chinese Guidelines for Primary Liver Cancer (2024 edition) (20) and the AASLD guidelines (19). Follow-up assessments included liver function tests, routine blood tests, serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels, and imaging examinations (contrast-enhanced CT or MRI).
The final follow-up date was December 31, 2023. The median follow-up time was 25.1 months. Radiographic recurrence was defined as the appearance of new intrahepatic or extrahepatic enhancing lesions consistent with viable tumor, based on the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) (21). Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was calculated from the date of initial treatment to the date of radiologic diagnosis of recurrence.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis were performed using R software (version 4.1.3, http://www.rproject.org), with a two-sided P < 0.05 considered statistically significant. Demographic and clinical characteristics were compared among the training, internal validation and external validation cohorts. Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation and compared using the Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test, depending on data distribution. Categorical variables were described as frequencies (percentages) and compared by Chi-square test. RFS was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and differences between groups were assessed by the log-rank test. Independent predictive factors of RFS were evaluated using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models, incorporating variables with P < 0.05 from the univariate analysis into the multivariate analysis. Furthermore, LASSO-Cox regression was performed in the training cohort to identify independent prognostic factors for RFS, which were used to construct a nomogram. The predictive performance of the nomogram was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC). Additionally, the nomogram’s predictive accuracy was also compared with the latest version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging system and the factors (cirrhosis, tumor number and GGT) used to construct the nomogram. Calibration curves and decision curve analysis (DCA) were employed to assess the model’s calibration accuracy and clinical utility, respectively. External validation was conducted using an independent cohort from Beijing Ditan Hospital. The established prediction model was applied to the external data to calculate individual risk scores, and model performance was evaluated as described above. Patients in each cohort (training, internal validation, and external validation) were independently stratified into high- and low-risk groups based on the median risk score within the respective cohort. Kaplan-Meier analysis and the log-rank test were conducted separately in each cohort to compare RFS between risk groups.
Result
Survival analysis of the HALP score
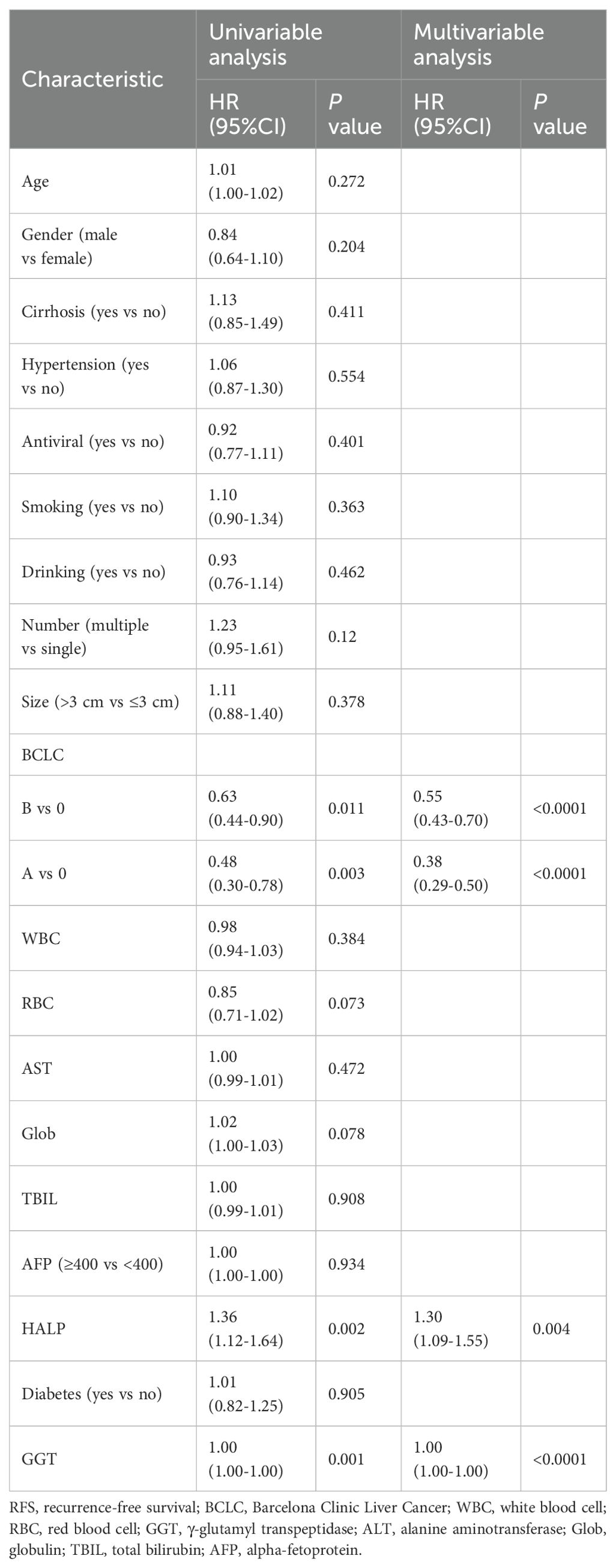
This study enrolled a total of 728 patients with HCC who received TACE combined with ablation at Beijing Youan Hospital. Among these, 422 patients stratified into the H-HALP group and 306 patients into the L-HALP group. Although a statistically significant difference was observed (P = 0.024), the median recurrence-free survival (mRFS) was similar for both groups: 1.84 years (95% CI: 1.44-2.04) for the H-HALP group and 1.60 years (95% CI: 1.39-1.89) for the L-HALP group (Figure 1). The 1-, 3-, and 5-year RFS rates for the H-HALP group were 70.8%, 36.2%, and 21.5%, respectively, which was only marginally higher than those of the L-HALP group (1-year: 66.3%; 3-year: 28.2%; 5-year: 16.7%). These findings suggest that despite the slightly improved outcomes in the H-HALP group, the prognosis and recurrence patterns still require further exploration. Furthermore, as shown in Table 1, both univariable and multivariable Cox regression analyses identified HALP as an independent predictor of RFS (HR: 1.30; 95% CI: 1.09-1.55; P = 0.04). Based on these findings, subsequent analyses focused on the subset of patients within the H-HALP group.
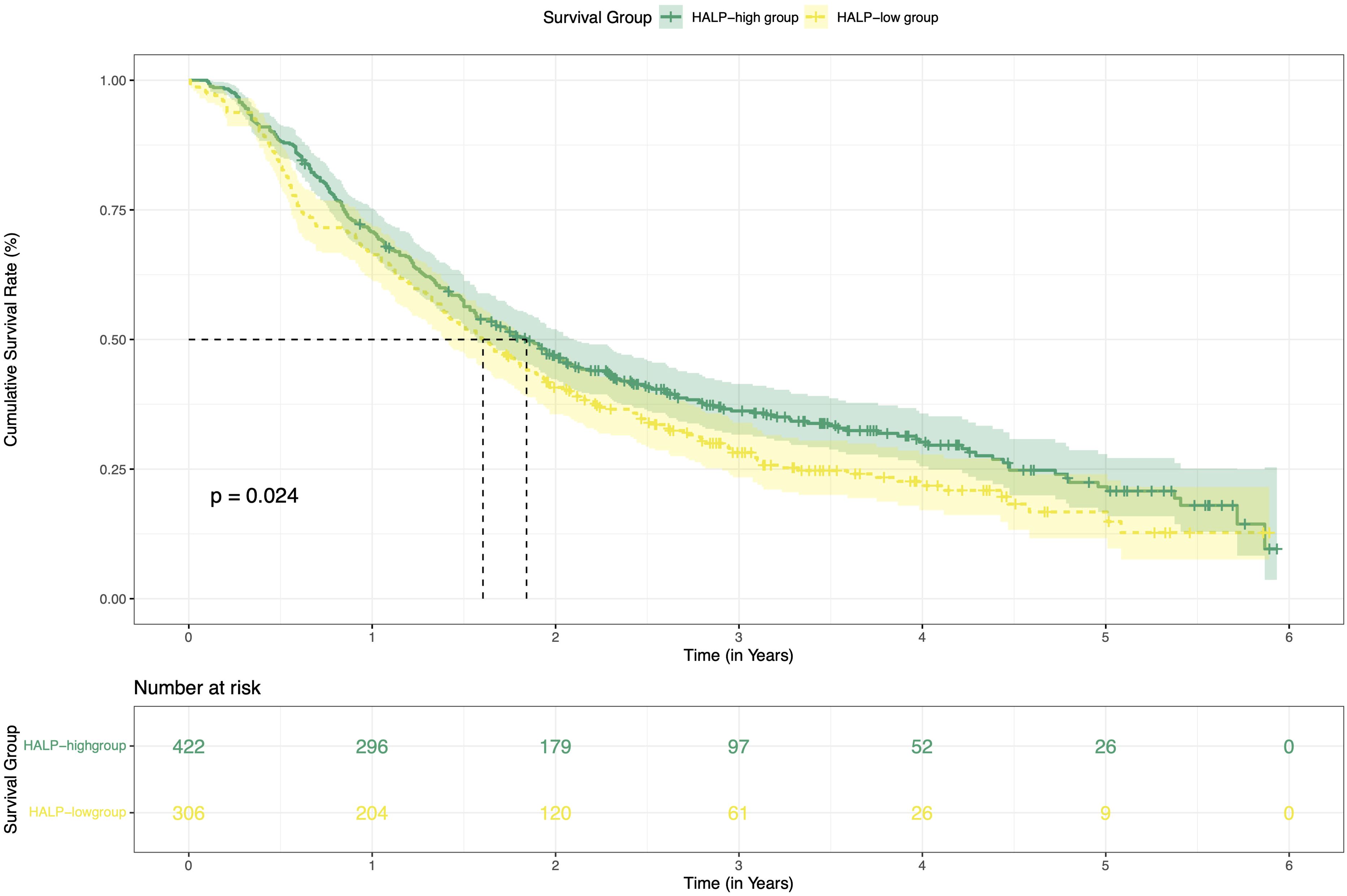
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves of RFS for the H-HALP and L-HALP patients. RFS, recurrence-free survival.
Baseline characteristics
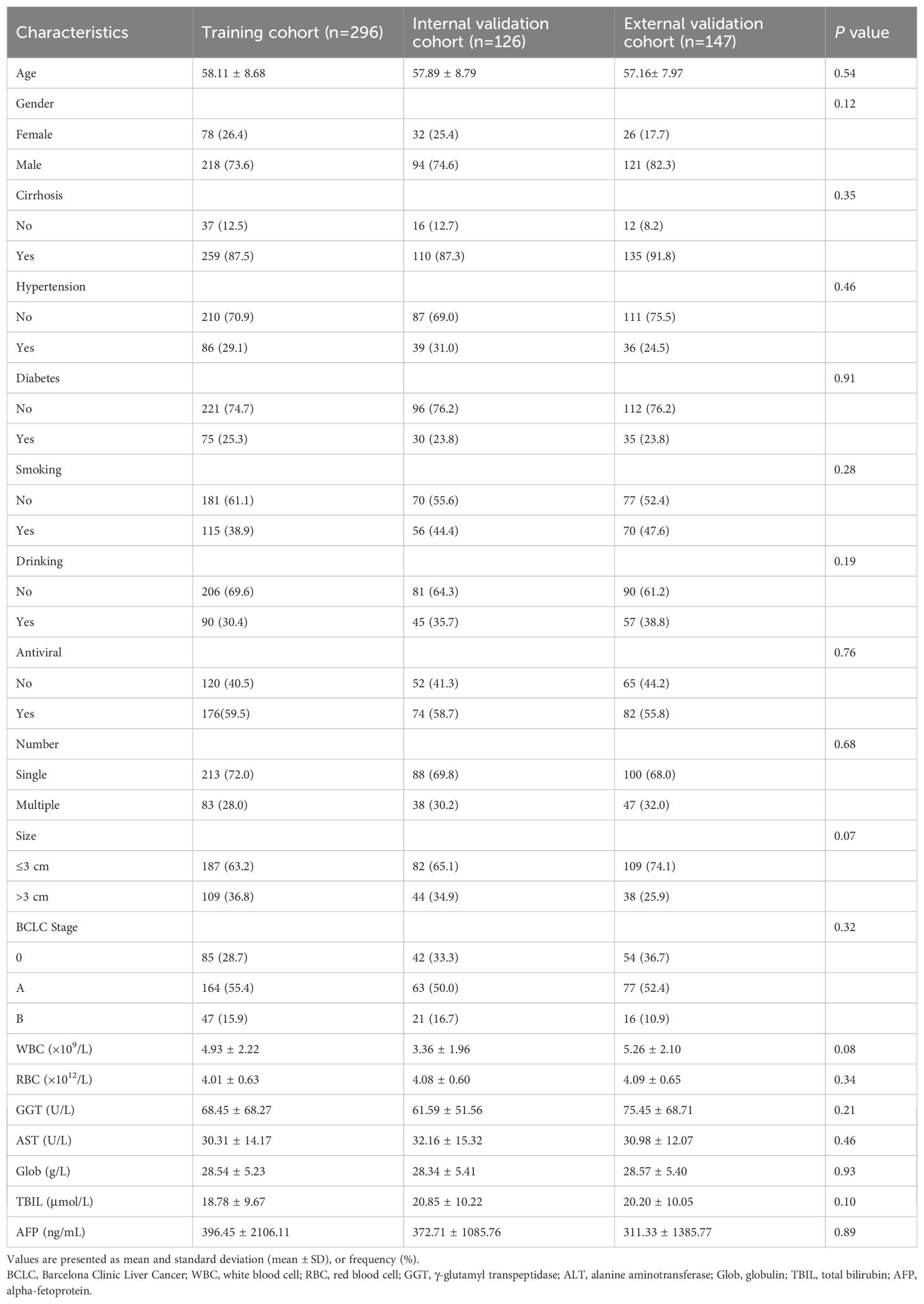
Patients in the H-HALP were randomly divided into the training cohort (n=296) and the internal validation cohort (n=126) in a 7:3 ratio. The external validation cohort consisted of 147 individuals. Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 2. In both cohorts, the majority of patients were male (73.6% vs. 74.6% vs. 82.3%) and aged over 55 years old (58.1 ± 8.68 vs. 57.9 ± 8.79 vs. 57.16 ± 7.97). In the training cohort, 259 (87.5%) patients were diagnosed with cirrhosis, 86 (29.1%) with hypertension, and 75 (25.3%) with diabetes mellitus, respectively. In the internal validation cohort, 110 (87.3%) had cirrhosis, 39 (31.0%) had hypertension, 30 (23.8%) had diabetes mellitus. In the external validation cohort, cirrhosis was diagnosed in 135 patients (91.8%), with hypertension and diabetes affecting 36 (24.5%) and 35 (23.8%), respectively. Furthermore, more than half of the patients had received antiviral treatment (59.5% vs. 58.7% vs. 55.8%). In terms of tumor characteristics, most patients had solitary tumor (72.0% vs. 69.8% vs. 68.0%) and tumor size were less than 3cm (63.2% vs. 65.0% vs. 74.1%). Statistical analysis indicated no significant differences between the training and validation cohorts (P > 0.05).
Identification of predictive factors
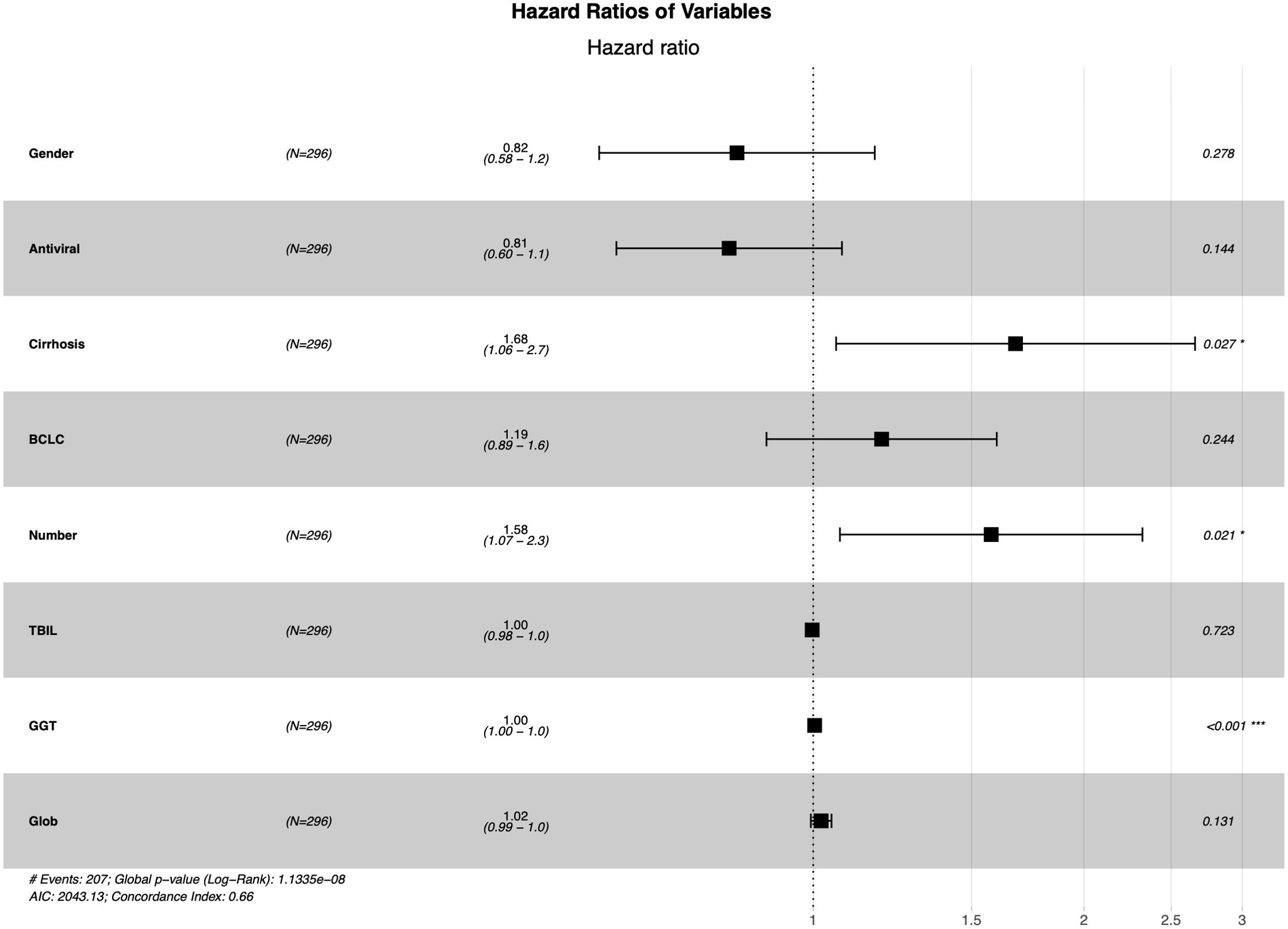
The LASSO regression analysis was used to screen parameters, and the variation characteristics of the coefficient of these variables were shown in Figure 2A. The 10-fold cross-validation method was applied to the iterative analysis, and a model with excellent performance but minimum number of variables was obtained when λ was 0.065 (Log λ = -1.19) (Figure 2B). Eight candidate predictors were identified, including gender, antiviral, cirrhosis, BCLC stage, tumor number, TBIL, GGT and Glob (Figure 3). These predictors were then assessed through multivariate Cox regression, revealing cirrhosis (P = 0.027), multiple tumor (P = 0.021) and GGT (P < 0.001) were independent predictors of RFS.
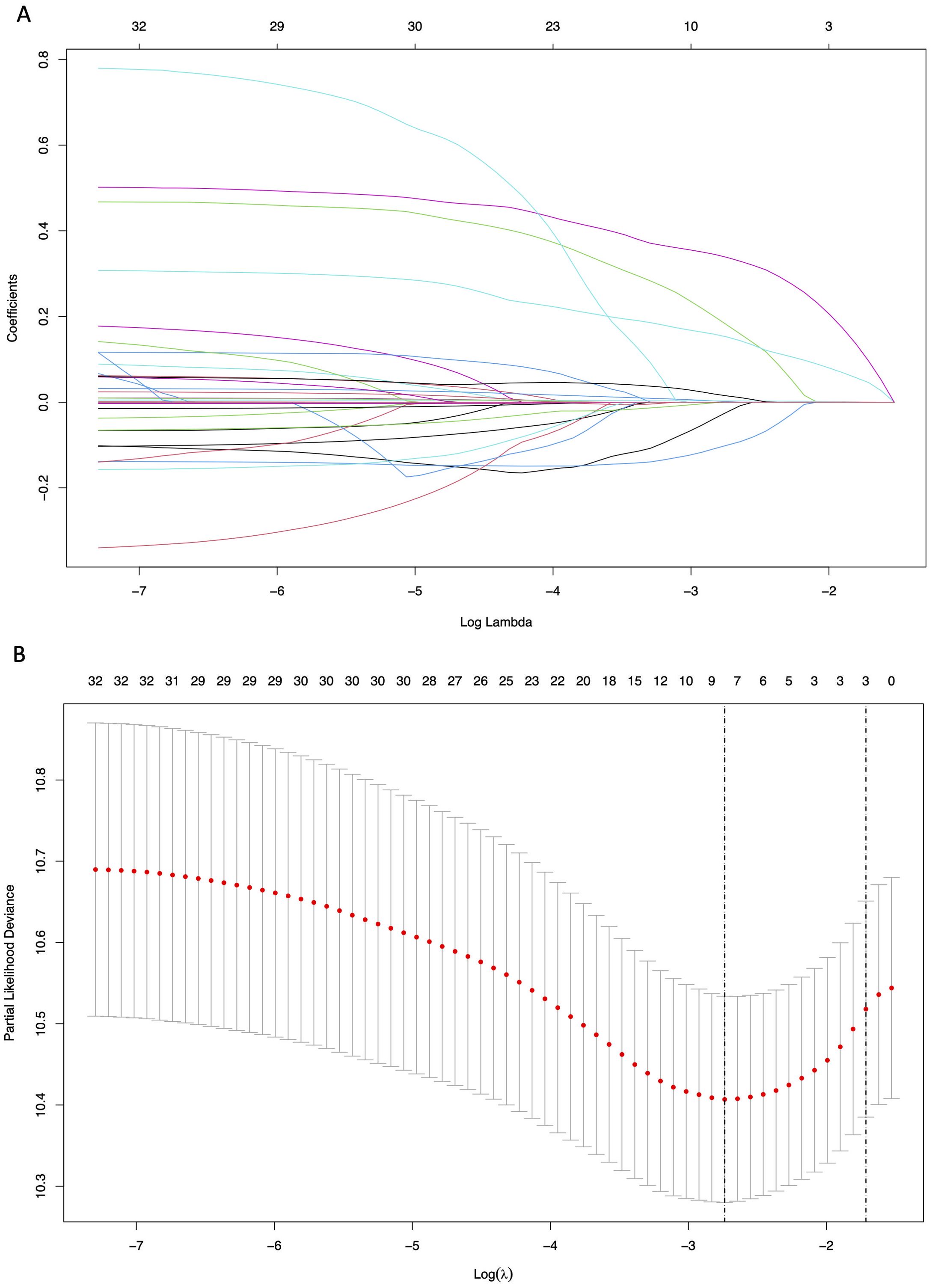
Figure 2. Results of the Lasso regression analysis in the training cohort. (A) The variation characteristics of the coefficient of variables; (B) The selection process of the optimum value of the parameter λ by cross-validation method.
Discrimination performance
The constructed nomogram incorporated above three screened features identified through multivariate Cox regression (Figure 4). To facilitate clinical translation, we developed an interactive web-based version of the nomogram, which is publicly accessible at https://joenomogogogo.shinyapps.io/DynNomapp/. To comprehensively evaluate its discriminatory performance, we compared the nomogram with the AJCC staging system and the individual predictors (cirrhosis, tumor number, and GGT) using time-dependent ROC analysis at 1-, 3-, and 5-year time points. Notably, five-year RFS data were unavailable in the external validation cohort due to insufficient follow-up time in 18.4% of patients. Therefore, 4-year AUC was reported as an alternative endpoint. The nomogram consistently demonstrated superior or comparable AUC values across all cohorts.
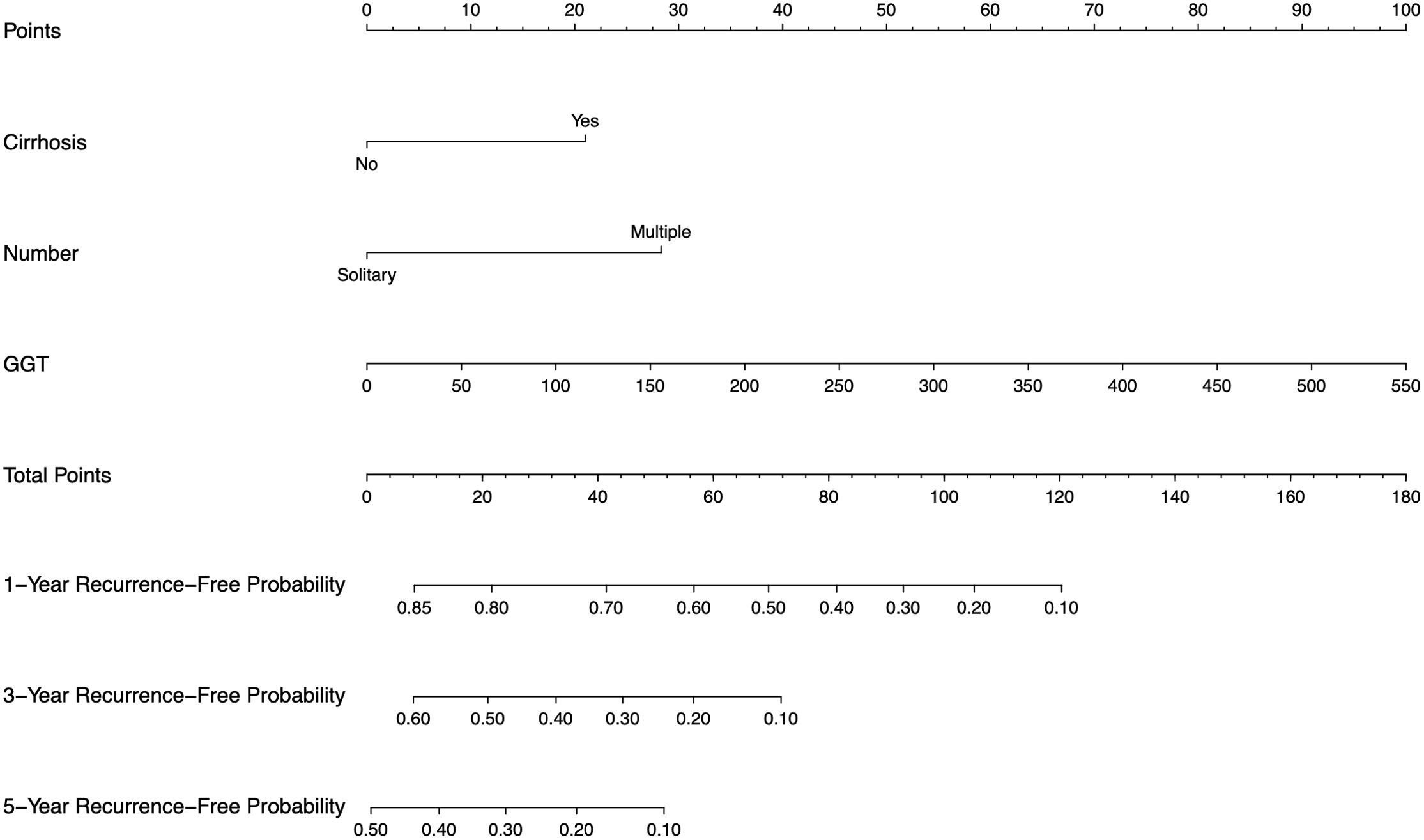
Figure 4. Nomogram, including cirrhosis, tumor number, and GGT for 1-, 3-, and 5-year RFS in HCC patients with high levels of HALP. The nomogram is valued to obtain the probability of 1-, 3-, and 5- years recurrence by adding up the points identified on the points scale for each variable. GGT, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.
In the training set, the nomogram achieved AUCs of 0.665 (95% CI: 0.599-0.731), 0.694 (95% CI: 0.619-0.768), and 0.671 (95% CI: 0.564-0.779) at 1-, 3-, and 5-year time points, respectively, outperforming the AJCC staging system (AUCs: 0.587 [95% CI: 0.527-0.647], 0.580 [95% CI: 0.520-0.640], and 0.578 [95% CI: 0.484-0.673]; P = 0.00361, 2.4e-05, and 0.0244) as well as individual predictors (Figures 5A-C). In the internal validation cohort, the nomogram yielded AUCs of 0.622 (95% CI: 0.506-0.738), 0.606 (95% CI: 0.485-0.727), and 0.561 (95% CI: 0.372-0.751) at the same time points, comparable to those of the AJCC system (0.612 [95% CI: 0.515-0.709], 0.556 [95% CI: 0.462-0.650], and 0.577 [95% CI: 0.424-0.730]; P = 0.789, 0.179, and 0.826) (Figures 5D-F). Similar trends were observed in the external validation cohort, where the nomogram achieved AUCs of 0.569 (95% CI: 0.465-0.673), 0.615 (95% CI: 0.499-0.730), and 0.662 (95% CI: 0.505-0.819) (at 1-, 3-, and 4-year time points), compared with 0.554 (95% CI: 0.470-0.637; P = 0.656), 0.611 (95% CI: 0.528-0.693; P = 0.931), and 0.636 (95% CI: 0.538-0.734; P = 0.667) for the AJCC system (Figures 5G-I).
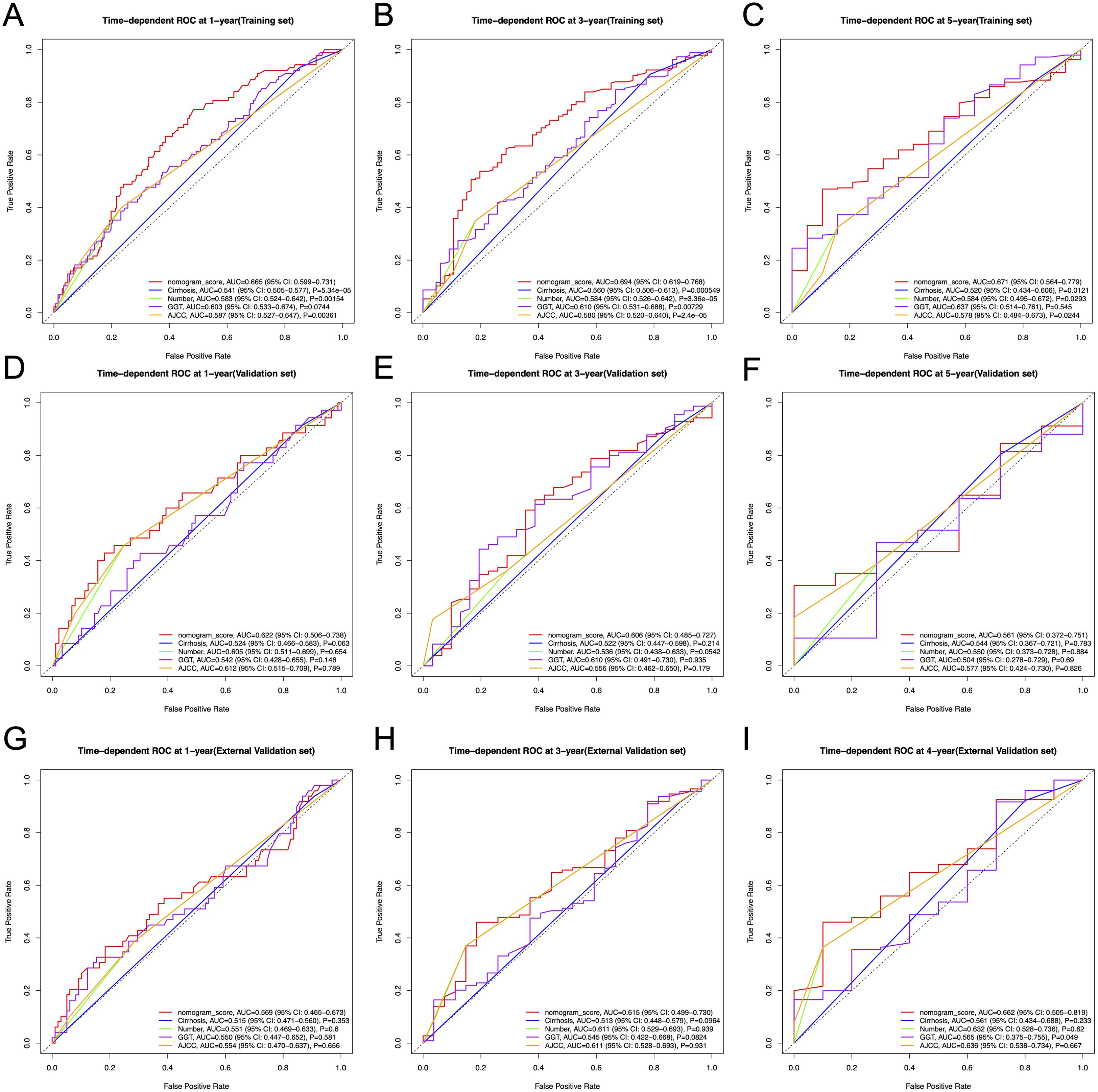
Figure 5. Time-dependent ROC curves for 1-, 3-, and 5-year RFS prediction in the training, internal validation, and external validation cohorts, comparing the nomogram with the AJCC staging system and individual predictors (cirrhosis, tumor number, and GGT). (A-C) Time-dependent ROC curves for 1-, 3- and 5-year RFS in the training cohort. (D-F) Time-dependent ROC curves for 1-, 3- and 5-year RFS in the internal validation cohort. (G-I) Time-dependent ROC curves for 1-, 3- and 4-year RFS in the external validation cohort. ROC, receiver operating characteristic curve; AUC, area under the ROC curve; RFS, recurrence-free survival; AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer.
Although the differences in the validation cohorts did not reach statistical significance, likely due to relatively small sample sizes and limited follow-up time, the nomogram demonstrated a consistent trend of improved discrimination across all cohorts.
Calibration, concordance, and clinical utility
To further evaluate predictive accuracy, we calculated the concordance index (C-index) for each model. In the training set, the nomogram achieved a C-index of 0.646 (95% CI: 0.608-0.684), comparable to AJCC (0.678; 95% CI: 0.615-0.741), while cirrhosis, tumor number, and GGT yielded C-indices of 0.650 (95% CI: 0.542-0.759), 0.692 (95% CI: 0.624-0.759), and 0.579 (95% CI: 0.537-0.621), respectively. In the internal validation cohort, the nomogram’s C-index was 0.614 (95% CI: 0.546-0.683), close to that of AJCC (0.662; 95% CI: 0.565-0.759), and tumor number (0.661; 95% CI: 0.551-0.771), and clearly higher than cirrhosis (0.402; 95% CI: 0.243-0.561) and GGT (0.560; 95% CI: 0.49-0.631). In the external validation cohort, the nomogram attained a C-index of 0.577 (95% CI: 0.519-0.636), similar to AJCC (0.612; 95% CI: 0.517-0.706) and tumor number (0.622; 95% CI: 0.523-0.720), and superior to cirrhosis (0.524; 95% CI: 0.359-0.689) and GGT (0.546; 95% CI: 0.485-0.607). These results suggest that the nomogram offers stable and balanced discriminatory performance across datasets, supporting its potential clinical utility in predicting RFS in patients with HCC undergoing TACE combined with ablation.
Furthermore, calibration curves illustrated well agreement between the predicted outcomes and the actual observations (Figures 6A-C). And the DCA confirmed the clinical utility of the nomogram, with net benefits consistently exceeding default strategies across risk thresholds (Figures 6D-L).
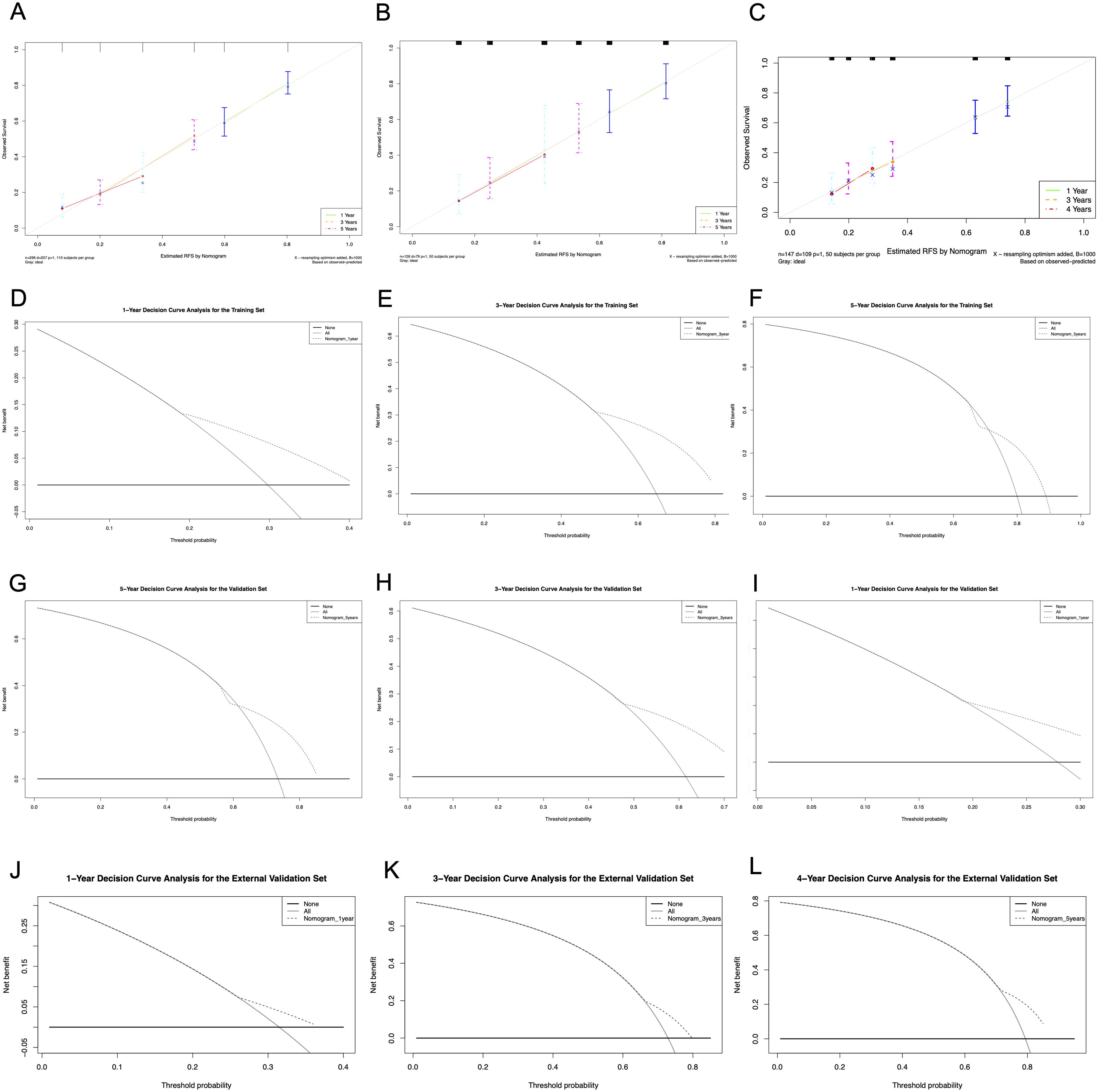
Figure 6. Calibration curves and DCA curves of the nomogram in the training and validation cohort. (A) Calibration curves of the training cohort; (B) Calibration curves of the internal validation cohort. (C) Calibration curves of the external validation cohort. (D-F) DCA for 1-, 3- and 5-year RFS in the training cohort. (G–I) DCA for 1-, 3- and 5-year RFS in the internal validation cohort. (J-L) DCA for 1-, 3- and 4-year RFS in the external validation cohort. DCA, decision curve analysis; RFS, recurrence-free survival.
Risk stratification and survival outcomes
The above analyses demonstrated the good predictive effect of the nomogram. We calculated the prediction score based on the three variables in the nomogram. A median cutoff value was used to separate the patients in the training cohort into a low-risk group (n = 149) and a high-risk group (n = 147). In the training cohort, a significantly prolonged RFS have been observed in the low-risk group (3.76 years, 95% CI: 2.29-4.44) compared with the high-risk group (1.33 years, 95% CI: 1.03-1.50, P < 0.0001) (Figure 7A). Additionally, the cumulative RFS rates for low-risk patients at 1-, 3-, and 5-year were 0.81, 0.52 and 0.29, respectively, while for high-risk patients, the rates were 0.59, 0.19 and 0.11. In the internal validation cohort, there were 63 patients in each of the low-risk and high-risk groups. The low-risk group achieved a median RFS of 4.48 years (95% CI: 2.48-not reached), with 1-, 3-, and 5-year RFS rates of 0.81, 0.53 and 0.40, respectively. In contrast, the high-risk cohort displayed markedly reduced survival, registering a median RFS of 1.53 years (95% CI: 1.11-2.18, P = 5e-04). Corresponding 1-, 3-, and 5-year RFS rates were 0.63, 0.25 and 0.14, respectively (Figure 7B). External validation further corroborated this risk stratification pattern. Patients in the low-risk group had significantly longer RFS compared to patients in the high-risk group (1.84 years [95% CI: 1.51-2.79] vs. 1.38 years [95% CI: 1.13-1.97], P = 0.025) (Figure 7C). The 1-, 3-, and 5-year RFS rates were 0.74, 0.34 and 0.22 in the low-risk patients, while 0.63, 0.20 and 0.08 in the high-risk patients, respectively. All these results proved that our model can effectively distinguish the recurrence risk.
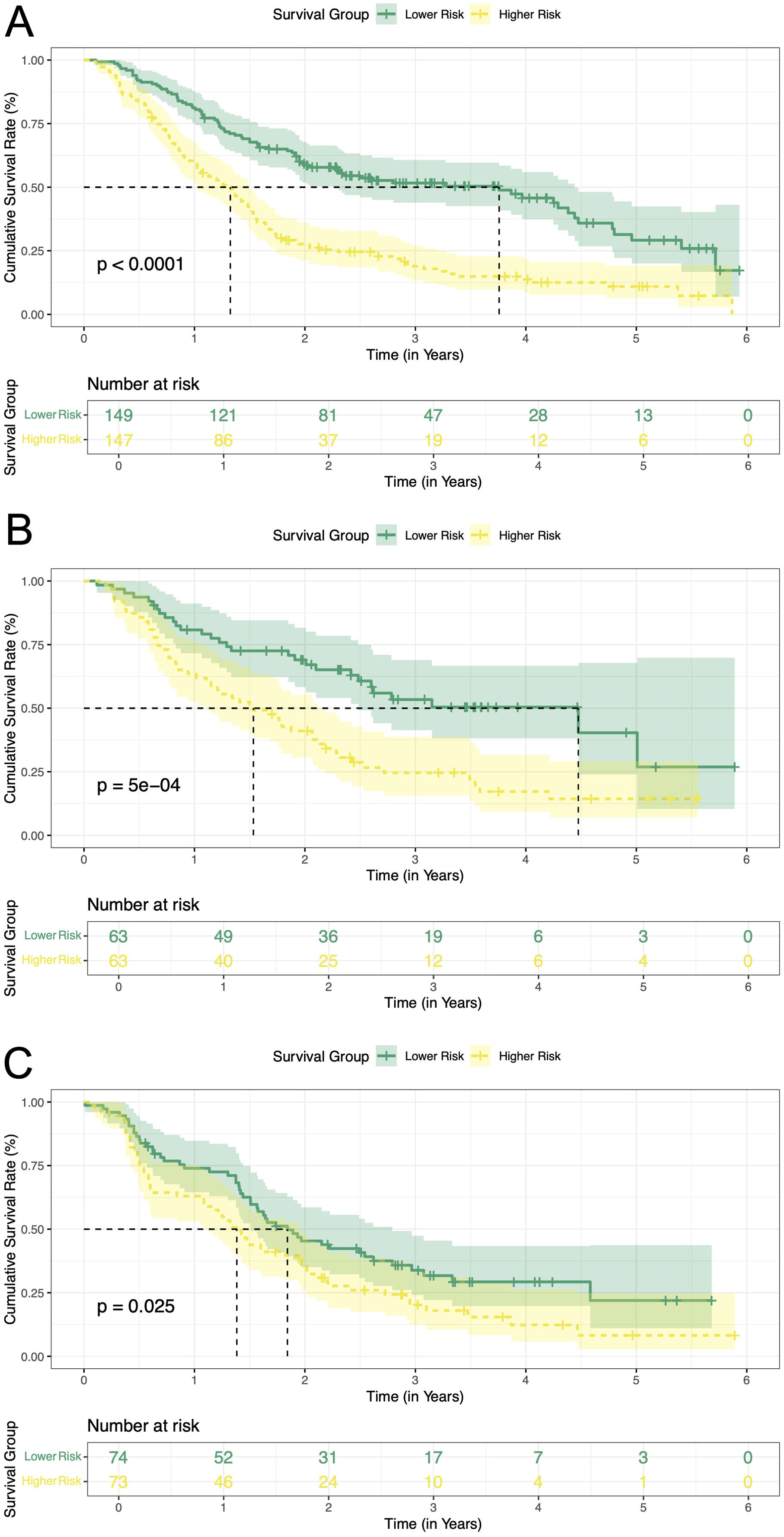
Figure 7. Kaplan-Meier curves of RFS for two risk groups classified by the nomogram in training and validation cohort. (A) training cohort; (B) internal validation cohort. (C) external validation cohort. RFS, recurrence-free survival.
Discussion
The combination of TACE and ablation has been widely adopted in clinical practice, which offers clear visualization of HCC lesions, expands the ablation zone, reduces tumor volume, and thereby enhancing the complete ablation rate (22). However, it cannot be ignored that a high recurrence rate after therapy. The HALP score, developed by Chen et al. in 2015, provides a comprehensive assessment of both nutritional and immune status (15). Recent studies have identified it as an independent predictor of RFS in pancreatic cancer and early-stage breast cancer, with lower HALP scores associated with shorter RFS (11, 23). Although the prognostic value of the HALP score has been explored in HCC patients undergoing hepatic resection (16–18), its significance in those treated with TACE and ablation remains unclear. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the relationship between the HALP score and recurrence in HCC patients treated with TACE and ablation.
Our study indicated that the H-HALP group exhibited a marginally prolonged median RFS compared to the L-HALP group (1.84 vs. 1.60 years, P = 0.024). However, the 5-year RFS rates in the high HALP group remained as low as 21.5%, underscoring the limited standalone predictive efficacy of the HALP score for recurrence risk. This aligns with findings by Chen et al. (15) in gastric cancer, where HALP required integration with other indicators to improve predictive power. Notably, the H-HALP patients who defined as “low-risk” by HALP yet experience considerable recurrence rates, need to further risk-stratify in this subgroup. Through Lasso-Cox regression analysis, we developed a nomogram to predict 1-, 3-, and 5-year recurrence of H-HALP patients. This regression method effectively addresses the limitations in overfitting and multicollinearity compared with univariate regression. The nomogram incorporating cirrhosis, tumor multiplicity, and GGT significantly enhanced individualized risk stratification, with marked median RFS disparities between high- and low-risk subgroups across training and validation cohorts.
The HALP score functions as a composite biomarker, reflecting both nutritional depletion and inflammatory activation in HCC. Local inflammation is associated with tumor development and forms part of the tumor microenvironment, while systemic inflammation arises as a response to malignant tumors, mediated by immune proteins, cytokines, and immune cell (24–26). The inflammatory markers such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) have demonstrated prognostic value in predicting HCC recurrence (27). Low LYM and elevated PLT levels may indicate compromised immunity and an increased risk of infection (11). LYM are critical to the body’s antitumor immune response. CD4+ cells, for instance, enhance this response by promoting the production of antibodies from B lymphocytes and facilitating the differentiation of CD8+ cells, which are responsible for recognizing tumor antigens and directly eliminating cancer cells (28, 29). Additionally, PLT plays a critical role in cancer metastasis by releasing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and promoting tumor angiogenesis (30). Factors secreted by tumors, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), can alter the hematopoietic environment, leading to decreased Hb levels (31). Low Hb levels induce tumor hypoxia, activating HIF-1α to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (32, 33). Meanwhile, low ALB levels reflect hepatic inflammatory status and high nutritional risk, leading to decreased antioxidant capacity and MMP-9 overexpression, further disrupting the extracellular matrix and promoting angiogenesis, both of which contribute to poor oncologic outcomes (34).
The three variables (cirrhosis, tumor number, GGT) that we used to construct prognostic models played important roles in the recurrence and progression of HCC (35–37). Liver function impairment in patients with cirrhosis was a major risk factor for the occurrence of HCC (38). Sasaki et al. (39) found that the recurrence risk in HCC patients with cirrhosis was 6% to 15% higher than those without cirrhosis. Similarly, Jung et al. (40) established a correlation between HCC recurrence and cirrhosis. The scarring caused by cirrhosis compresses intrahepatic blood vessels, impairing oxygen delivery within the liver (41). Consequently, in cirrhotic nodules, the expression of angiogenic factors in hepatocytes is elevated, primarily through the production of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and other cytokines, which subsequently induce fibrosis and angiogenesis, ultimately leading to portal hypertension and tumor development (42). The presence of multiple tumors is indicative of greater tumor aggressiveness (35). Chan et al. (43) and Xu et al. (44) found 2~3 tumors correlate with a higher recurrence rate than solitary tumor in HCC patients. GGT is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of glutathione and the conversion of γ-glutamyl compounds (45). Elevated GGT levels have been consistently associated with various stages of HCC progression and may serve as a potential biomarker for HCC treatment response (46–49).
Our study also has some limitations. First, as a retrospective analysis, it may introduce selection bias. Second, molecular biomarkers (e.g., ctDNA, PD-L1) were not included due to limited data availability. The HALP score, as a routine blood test parameter, offers advantages of low cost and strong accessibility. Future prospective studies could integrate this nomogram with genomic features (e.g., TP53 mutations, TMB) to further enhance predictive accuracy. Furthermore, the optimal HALP cutoff remains uncertain. Our study consistent with the developers’ choice, using a cutoff value of 56.8 (15). However, some studies have found that the median HALP score varies by cancer type, highlighting the need for further exploration of the heterogeneity of the HALP score (12). Importantly, while we conducted external validation using an independent cohort, all patients were from similar clinical settings in China, which may limit generalizability. Future prospective, multicenter studies with diverse populations are needed to validate our model.
Conclusion
HCC patients with a high HALP score who underwent TACE combined with ablation had a high recurrence risk. This study developed a nomogram to predict recurrence for these H-HALP patients. For patients identified as high-risk by the nomogram, intensified surveillance (e.g., quarterly imaging) and early initiation of systemic therapy (e.g., TKIs or PD-1 inhibitors) may be considered to mitigate recurrence risk. Integration of the model into clinical decision-making could facilitate risk-adapted therapeutic strategies.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
DF: Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XY: Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Beijing Bethune Charitable Foundation (QZHX-21-ZQN-014) and the Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research (SF202222175).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all members of the study group.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Vogel A, Meyer T, Sapisochin G, Salem R, and Saborowski A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. (2022) 400:1345–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4
2. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, and Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
3. Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, and Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:589–604. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y
4. Liu B, Zhang Y, Chen H, Li W, and Tsochatzis E. The combination of transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation (TACE) and thermal ablation versus TACE alone for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2022) 1:Cd013345. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013345.pub2
5. Llovet JM, De Baere T, Kulik L, Haber PK, Greten TF, Meyer T, et al. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:293–313. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00395-0
6. Wu H, Lv S, Zhang R, Gu L, Xu J, Li C, et al. Next-generation flexible embolic systems: Targeted transarterial chemoembolization strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Mater. (2025):e2503971. doi: 10.1002/adma.202503971
7. Sakr OS, Zaitoun MMA, Amer MS, Qubisi M, Elshafeey AH, Jordan O, et al. Explosomes: A new modality for DEB-TACE local delivery of sorafenib: In vivo proof of sustained release. J Control Release. (2023) 364:12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.10.013
8. Zhang YJ, Chen J, Zhou Z, Hu D, Wang J, Pan Y, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization with radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for small late-recurrence hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. (2025) 314:e241096. doi: 10.1148/radiol.241096
9. Wang Q, Zhao P, He N, Sun JP, Li K, Zang CR, et al. Combination of the gamma-glutamyltransferase-to-prealbumin ratio and other indicators may be a novel marker for predicting the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing locoregional ablative therapies. Infect Agent Cancer. (2019) 14:49. doi: 10.1186/s13027-019-0266-1
10. Tak WY, Lin SM, Wang Y, Zheng J, Vecchione A, Park SY, et al. Phase III HEAT study adding Lyso-Thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin to radiofrequency ablation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma lesions. Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 24:73–83. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2433
11. Zhao Z and Xu L. Prognostic significance of HALP score and combination of peripheral blood multiple indicators in patients with early breast cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1253895. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1253895
12. Antar R, Farag C, Xu V, Drouaud A, Gordon O, and Whalen MJ. Evaluating the baseline hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score in the United States adult population and comorbidities: an analysis of the NHANES. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1206958. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1206958
13. Jiang H, Li H, Li A, Tang E, Xu D, Chen Y, et al. Preoperative combined hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet levels predict survival in patients with locally advanced colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:72076–83. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12271
14. Ekinci F, Balcik OY, Oktay E, and Erdogan AP. HALP Score as a new prognostic index in metastatic renal cell cancer. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. (2022) 32:313–8. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2022.03.313
15. Chen XL, Xue L, Wang W, Chen HN, Zhang WH, Liu K, et al. Prognostic significance of the combination of preoperative hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet in patients with gastric carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:41370–82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5629
16. Zhou J and Yang D. Prognostic significance of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet (HALP) score in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2023) 10:821–31. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S411521
17. Toshida K, Itoh S, Kayashima H, Nagao Y, Yoshiya S, Tomino T, et al. The hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet score is a prognostic factor for Child-Pugh A patients undergoing curative hepatic resection for single and small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. (2023) 53:522–30. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13885
18. Liu X, Qiu Z, Ndhlovu E, Wan Y, Sun H, Wang S, et al. Establishing and externally validating a hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelet (HALP) score-based nomogram for predicting early recurrence in BCLC Stage 0/A hepatocellular carcinoma patients after radical liver resection: A multi-center study. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2024) 11:1127–41. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S465670
19. Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, Sirlin CB, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2018) 67:358–80. doi: 10.1002/hep.29086
20. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2024 edition)[J. J Clin Hepatol. (2024) 40:893–918.
21. Lencioni R and Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. (2010) 30:52–60. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132
22. Chen YT, Chen BW, Xu JM, You XC, Tang Y, Wu SJ, et al. Multicenter study on transarterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Primary versus recurrent HCC. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2024) 11:2441–52. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S497956
23. Xu SS, Li S, Xu HX, Li H, Wu CT, Wang WQ, et al. Haemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte and platelet predicts postoperative survival in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. (2020) 26:828–38. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i8.828
24. Sohrab SS, Raj R, Nagar A, Hawthorne S, Paiva-Santos AC, Kamal MA, et al. Chronic inflammation's transformation to cancer: A nanotherapeutic paradigm. Molecules. (2023) 28:4413. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114413
25. Diakos CI, Charles KA, Mcmillan DC, and Clarke SJ. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. (2014) 15:e493–503. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70263-3
26. Balkwill FR and Mantovani A. Cancer-related inflammation: common themes and therapeutic opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. (2012) 22:33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.12.005
27. Wenpei G, Yuan L, Liangbo L, Jingjun M, Bo W, Zhiqiang N, et al. Predictive value of preoperative inflammatory indexes for postoperative early recurrence of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1142168. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1142168
28. Kennedy R and Celis E. Multiple roles for CD4+ T cells in anti-tumor immune responses. Immunol Rev. (2008) 222:129–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00616.x
29. Janssen EM, Lemmens EE, Wolfe T, Christen U, von Herrath MG, and Schoenberger SP. CD4+ T cells are required for secondary expansion and memory in CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nature. (2003) 421:852–6. doi: 10.1038/nature01441
30. Gay LJ and Felding-Habermann B. Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. (2011) 11:123–34. doi: 10.1038/nrc3004
31. Banzet S, Sanchez H, Chapot R, Bigard X, Vaulont S, and Koulmann N. Interleukin-6 contributes to hepcidin mRNA increase in response to exercise. Cytokine. (2012) 58:158–61. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.01.006
32. Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM, Shrimanker N, Akai Y, Hohenstein B, et al. Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1 stimulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:3810–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI30487
33. Auvinen J, Tapio J, Karhunen V, Kettunen J, Serpi R, Dimova EY, et al. Systematic evaluation of the association between hemoglobin levels and metabolic profile implicates beneficial effects of hypoxia. Sci Adv. (2021) 7:eabi4822. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abi4822
34. Eckart A, Struja T, Kutz A, Baumgartner A, Baumgartner T, Zurfluh S, et al. Relationship of nutritional status, inflammation, and serum albumin levels during acute illness: A prospective study. Am J Med. (2020) 133:713–22.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.031
35. Wang Q, Qiao W, Zhang H, Liu B, Li J, Zang C, et al. Nomogram established on account of Lasso-Cox regression for predicting recurrence in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1019638. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019638
36. Qiao W, Li J, Wang P, Zhang Y, Jin R, and Li J. Prognostic nomogram based on the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio for patients with compensated cirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma after local ablation. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1406764. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1406764
37. Gavriilidis P and Pawlik TM. Inflammatory indicators such as systemic immune inflammation index (SIII), systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic factors of curative hepatic resections for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2024) 13:509–11. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-631
38. GBD 2017 Cirrhosis Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:245–66. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8
39. Sasaki K, Shindoh J, Margonis GA, Nishioka Y, Andreatos N, Sekine A, et al. Effect of background liver cirrhosis on outcomes of hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. JAMA Surg. (2017) 152:e165059. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.5059
40. Jung KS, Kim SU, Choi GH, Park JY, Park YN, Kim DY, et al. Prediction of recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma using liver stiffness measurement (FibroScan)? Ann Surg Oncol. (2012) 19:4278–86. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2422-3
41. Rappaport AM, Macphee PJ, Fisher MM, and Phillips MJ. The scarring of the liver acini (Cirrhosis). Virchows Archiv A. (2004) 402:107–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00695054
42. Onori P, Morini S, Franchitto A, Sferra R, Alvaro D, and Gaudio E. Hepatic microvascular features in experimental cirrhosis: a structural and morphometrical study in CCl 4 -treated rats. J Hepatol. (2000) 33:555–63. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(00)80007-0
43. Chan AWH, Zhong J, Berhane S, Toyoda H, Cucchetti A, Shi K, et al. Development of pre and post-operative models to predict early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. J Hepatol. (2018) 69:1284–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.08.027
44. Xu XF, Xing H, Han J, Li ZL, Lau WY, Zhou YH, et al. Risk Factors, Patterns, and outcomes of late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter study from China. JAMA Surg. (2019) 154:209–17. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.4334
45. Mitrić A and Castellano I. Targeting gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: A pleiotropic enzyme involved in glutathione metabolism and in the control of redox homeostasis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 208:672–83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.09.020
46. Xia J, Song P, Sun Z, Sawakami T, Jia M, and Wang Z. Advances of diagnostic and mechanistic studies of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug Discov Ther. (2016) 10:181–7. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2016.01052
47. Wang K, Chen XY, Zhang B, Yue Y, Wen XL, Yang Y, et al. Near-infrared imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma and its medicinal treatment with a γ-glutamyl transpeptidase-monitoring fluorescence probe. Biosens Bioelectron. (2023) 241:115721. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115721
48. Waidely E, Al-Yuobi AR, Bashammakh AS, El-Shahawi MS, and Leblanc RM. Serum protein biomarkers relevant to hepatocellular carcinoma and their detection. Analyst. (2016) 141:36–44. doi: 10.1039/C5AN01884F
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, HALP score, Lasso-Cox regression, recurrence, nomogram
Citation: Fang D, Yin X, Ding X, Chen J, Cui X and Hu C (2025) Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with high HALP score in TACE combined with ablation. Front. Oncol. 15:1609260. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1609260
Received: 10 April 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Rodrigo Xavier Das Neves, National Cancer Institute (NIH), United StatesReviewed by:
Shuanggang Chen, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (SYSUCC), ChinaQiang Tang, Zhejiang University, China
Copyright © 2025 Fang, Yin, Ding, Chen, Cui and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyan Ding, ZGluZ3hpYW95YW4xOTgxMTFAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Jinglong Chen, Y2psNjQxMkBjY211LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiongwei Cui, Y3VpeHc2QHNpbmEuY29t; Caixia Hu, aHVjYWl4aWExMjE3QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Da Fang1†
Da Fang1† Xue Yin
Xue Yin Xiaoyan Ding
Xiaoyan Ding Caixia Hu
Caixia Hu