- 1Department of Chemotherapy, The District Hospital, Sucha Beskidzka, Poland
- 2Department of Chemotherapy, The Specialistic Hospital, Nowy Targ, Poland
- 3Department of Clinical Oncology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, Krakow, Poland
- 4Department of Clinical Oncology, University Hospital in Wroclaw, Wrocław, Poland
- 5Department of Oncology, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Krakow, Poland
- 6Oncology Clinical Department, The University Hospital, Krakow, Poland
- 7Department of Clinical Oncology, Ludwik Rydygier Hospital, Krakow, Poland
- 8Department of Surgery and Oncology, University of Zielona Góra, Zielona Góra, Poland
- 9Department of Clinical Oncology, Holy Cross Cancer Center, Kielce, Poland
- 10Clinical and Experimental Oncology Clinic, Institute of Oncology, Karol Marcinkowski Medical University, Poznań, Poland
- 11Clinical Oncology Department with Chemotherapy Subunit, Provincial Hospital Sain Luke, Tarnów, Poland
- 12Faculty of Health Protection, Tarnów University, Tarnów, Poland
- 13Department of Gynecological Oncology, Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, Krakow, Poland
- 14Department of Anatomy, Jagiellonian University, Medical College, Krakow, Poland
Background: Nivolumab and ipilimumab (nivo+ipi) are recommended for treating metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mRCC), though their safety and efficacy in older adults remain uncertain. This study examines the outcomes of this regimen in Polish patients aged ≥65 years.
Methods: In this multicenter observational study, 138 patients with mRCC who received nivo+ipi between May 2022 and October 2024 were analyzed. Key outcomes included objective response rates (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and progression-free survival (PFS) with comparisons between patients aged <65 and ≥65 years. Safety was assessed based on the incidence and severity of immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Survival outcomes were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier methods and Cox proportional hazards models, adjusting for potential confounders. A significance level of p < 0.05 was applied.
Results: After a median follow-up of 13 months, the median PFS for the entire cohort was 15.7 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 10.2–20.8); in patients <65 years, it was 11.3 months, while in those ≥65 years, it was 23 months. Patients ≥65 years had a 40% lower risk of progression than younger patients (hazard ratio 0.6, 95% CI: 0.3–0.9, p=0.03). Patients aged ≥65 years exhibited a higher ORR (46.2% vs. 26%) and DCR (73.8% vs. 63%, p=0.02 for both). The overall incidence of irAEs was comparable between age groups; however, older patients experienced a higher frequency of very severe irAEs (1 vs. 6, p=0.06).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that nivo+ipi are effective across age groups, with older patients achieving comparable or even superior outcomes with acceptable irAEs rates.
1 Introduction
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) play a well-established role in the treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in both adjuvant and palliative settings. Specifically, a combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab [an anti-programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1) and anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) antibodies] is recommended by international guidelines for intermediate- and poor-risk patients (1–3) according to the International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) criteria (4) (web calculator available at https://www.imdconline.com).
Although the median age at RCC diagnosis is 65 years (5), older patients are commonly underrepresented in clinical trials. Recent global estimates underscore a rising incidence in urinary malignancies, including kidney cancer, with aging identified as a major contributing factor to the projected burden by 2046 (6). There are theoretical concerns that the incidence of adverse events may be higher in older patients due to co-morbidities, use of other medications, functional impairments (decreased muscle mass, increased fat distribution), or reduced functional reserve (7). Additionally, immunosenescence, defined as the waning function of the immune system with advancing age, can theoretically impair the efficacy of ICIs (7). In the Checkmate 214 trial (8), which compared first-line treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab and standard-of-care sunitinib (a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor) in metastatic RCC (mRCC) across all risk groups, the median age of enrolled individuals who received combined immunotherapy was 62 (range: 26-85). However, patients ≥65 years old demonstrated poorer outcomes. Specifically, in terms of objective response rate (ORR) and overall survival (OS), this subgroup did not derive greater benefit from nivolumab and ipilimumab compared to sunitinib, as reported in the Supplementary Appendix of the trial. Conversely, the Checkmate 025 trial (9), which evaluated nivolumab versus everolimus (mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor) in mRCC patients previously treated with one or two antiangiogenic therapies, showed a more pronounced progression-free survival (PFS) benefit of nivolumab in patients aged 65–75 years but not ≥75 years. Furthermore, real-world studies from Japan and Italy did not reveal worse outcomes or higher incidences of toxicities in older adults (10–12). However, due to variable pharmacokinetics, ICIs may have different clinical outcomes depending on geographic regions. Additionally, combined immunotherapy is associated with a risk of serious immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in 46% of patients (8) compared to 19% in nivolumab monotherapy (9), regardless of patients’ age.
This raises concerns regarding the utility and safety of this regimen in older adults. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of the nivolumab and ipilimumab regimen in older individuals and compare the obtained results between patients ≥65 and those <65 years old.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patients
This observational study included 138 patients with clear cell mRCC (with or without sarcomatoid component) who received first-line combined immunotherapy within a national drug program of the Polish Ministry of Health (eligibility criteria for reimbursement are provided in the Supplementary Materials) (13). Eligible patients were treated with at least one cycle of nivolumab with ipilimumab with treatment initiation between May 1, 2022, and October 19, 2024, across nine oncology centers in Poland.
2.2 Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Bioethics Committee of Jagiellonian University Medical College (approval number 118.0043.1.115.2024, dated April 19, 2024), and all patients provided institutional, informed consent before initiating nivolumab and ipilimumab treatment. We followed the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Guidance for Reporting Oncology Real-World Evidence (GROW) criteria to describe the obtained results (14), and detailed examples of their implementation are provided in Supplementary Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials.
2.3 Data collection
The physicians collected data manually based on patients’ medical records, and the data cut-off was set on February 15, 2025. The research team reviewed the extracted data to ensure its completeness and accuracy. Missing data were managed using a complete-case analysis approach, where only patients with available data for relevant variables were included in the final analysis. Data regarding the patients’ baseline characteristics were recorded retrospectively with a prospective evaluation of the treatment course, response to therapy, and adverse events.
2.4 Study objectives
The primary objective was to assess the efficacy of the nivolumab and ipilimumab regimen and compare outcomes between patients aged ≥65 and <65 years old. Primary endpoints were the ORR and the disease control rate (DCR). The secondary endpoints included PFS, time to treatment failure (TTF) and OS. The secondary objective was to evaluate the safety profile in this patient cohort and compare outcomes between age subgroups.
2.5 Interventions
The treatment protocol followed European Union product guidelines (15, 16). Patients underwent an initial four-cycle induction phase with ipilimumab (1 mg/kg) and nivolumab (3 mg/kg) administered intravenously every three weeks. Following induction, patients continued with maintenance nivolumab at 480 mg every four weeks until progressive disease (PD), unacceptable toxicity or withdrawal of consent.
2.6 Outcome measures
The definitions of comorbidities documented as baseline characteristics are available in the Supplementary Materials.
ORR was defined as complete (CR) or partial response (PR) and the DCR as CR, PR or stable disease (SD) according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (RECIST) 1.1 guidelines (17). OS was defined as the duration from the start of therapy to death; PFS was measured from the beginning of therapy to documented PD on a computed tomography (CT) scan or death; TTF was defined as the interval between treatment initiation and permanent discontinuation due to PD, treatment-related toxicity, patient death or withdrawal of consent. CT scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis were conducted every 12 weeks or earlier if clinically indicated and underwent local assessment as per national drug program requirements (13).
Safety was assessed by recording irAEs from health records, categorized and graded according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v.5.0 (18). IrAEs were classified into endocrine, hepatic, pulmonary, general (e.g., fatigue, infusion reactions, fever, decreased appetite), cutaneous, gastrointestinal (diarrhea/colitis), rheumatologic and hematologic groups.
Laboratory assessments were performed at local laboratories before treatment initiation to categorize patients into IMDC risk groups. Additionally, we calculated the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) by dividing the corresponding cell counts.
2.7 Bias and confounding
This study is subject to potential biases due to the retrospective nature of some data collection. To reduce selection bias, we included all eligible patients treated within the national drug program during the study period, with uniform, strict criteria across Poland, ensuring a representative sample. To minimize information bias, data were manually verified and cross-checked with treating physicians. Differences between centers were addressed by adhering to ESMO guidelines in the irAEs management (19) and using standardized RECIST v1.1 (17) criteria for tumor response assessment.
2.8 Follow-up
Patients were monitored during each treatment cycle or more frequently if clinically indicated. Follow-up for survival and adverse events continued until the data cut-off on February 15, 2025.
2.9 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using PS Imago Pro 9 (SPSS). Categorical variables were compared using Fisher’s exact test, chi-square test or proportion test to assess differences between the two age groups (<65 and ≥65 years). Continuous variables showed a non-normal distribution according to the Shapiro-Wilk test and were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test. PFS, TTF and OS were estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods, while Cox proportional hazards models and log-rank tests identified survival differences between the two age groups. Variables with p-value <0.05 in baseline comparisons were acknowledged as potential confounders and were included in multivariate Cox regression models. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Patients’ characteristics
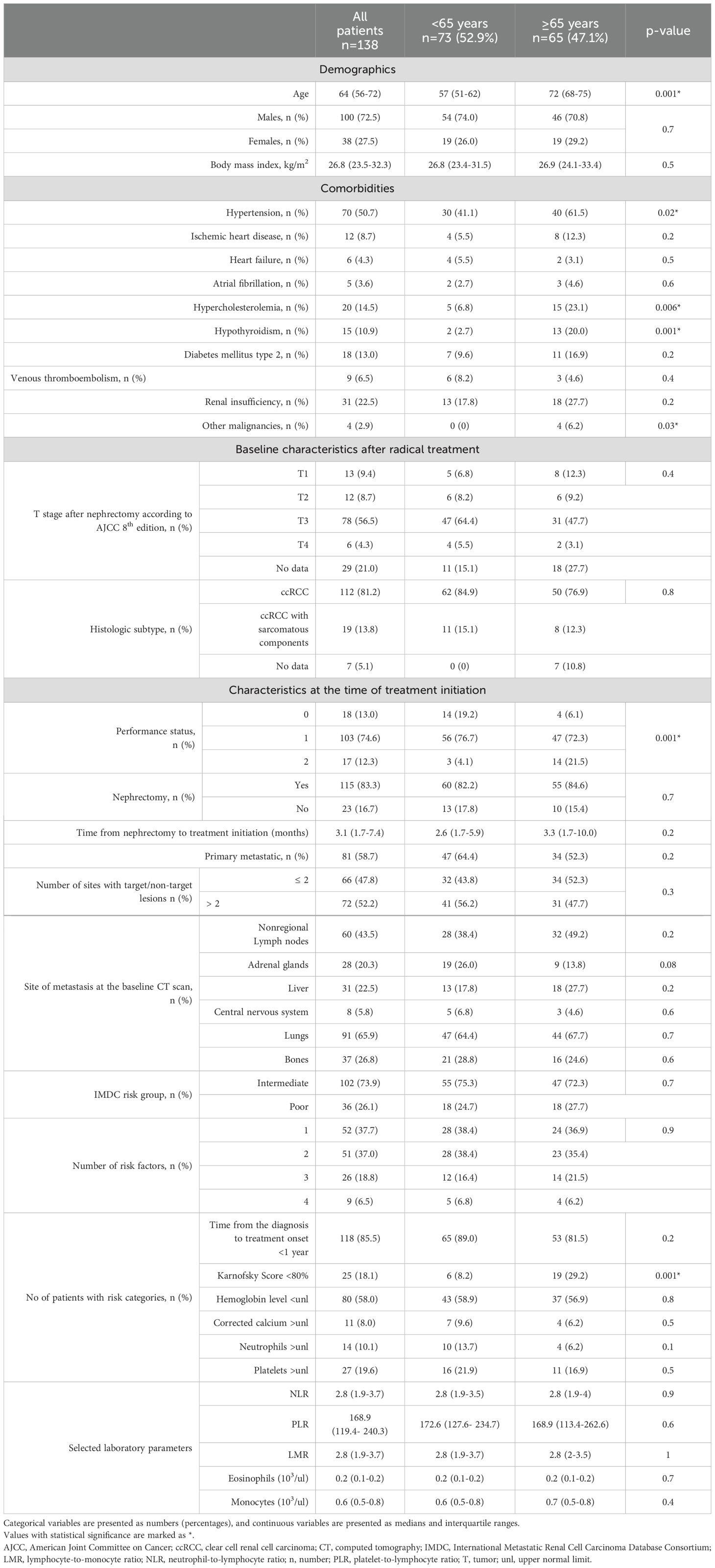
Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of patients, highlighting differences between those aged <65 years and ≥65 years. Older patients showed higher rates of comorbidities, including hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, hypothyroidism and a history of other malignancies. Additionally, these patients had poorer overall clinical status, as indicated by a lower Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status and a Karnofsky Score <80%. The above factors were considered potential confounders. Apart from these differences, the two groups were well-balanced in other characteristics. The most common metastatic sites were the lungs, non-regional lymph nodes, bones and liver. A majority of patients underwent nephrectomy (83%) and were classified as intermediate risk according to IMDC criteria (74%). Laboratory parameters were also comparable between the two cohorts.
3.2 Treatment efficacy
Patients were followed for a median of 13 months (interquartile ranges [IQR]: 7.4–22.4). The median treatment duration was 5.9 months (IQR: 2.1–11.8) and patients received a median of 6 treatment cycles (IQR: 4–12). No significant differences were observed between the two age cohorts in these parameters (p=0.3, p=0.3, and p=0.9, for a follow-up period, treatment duration and number of cycles, respectively).
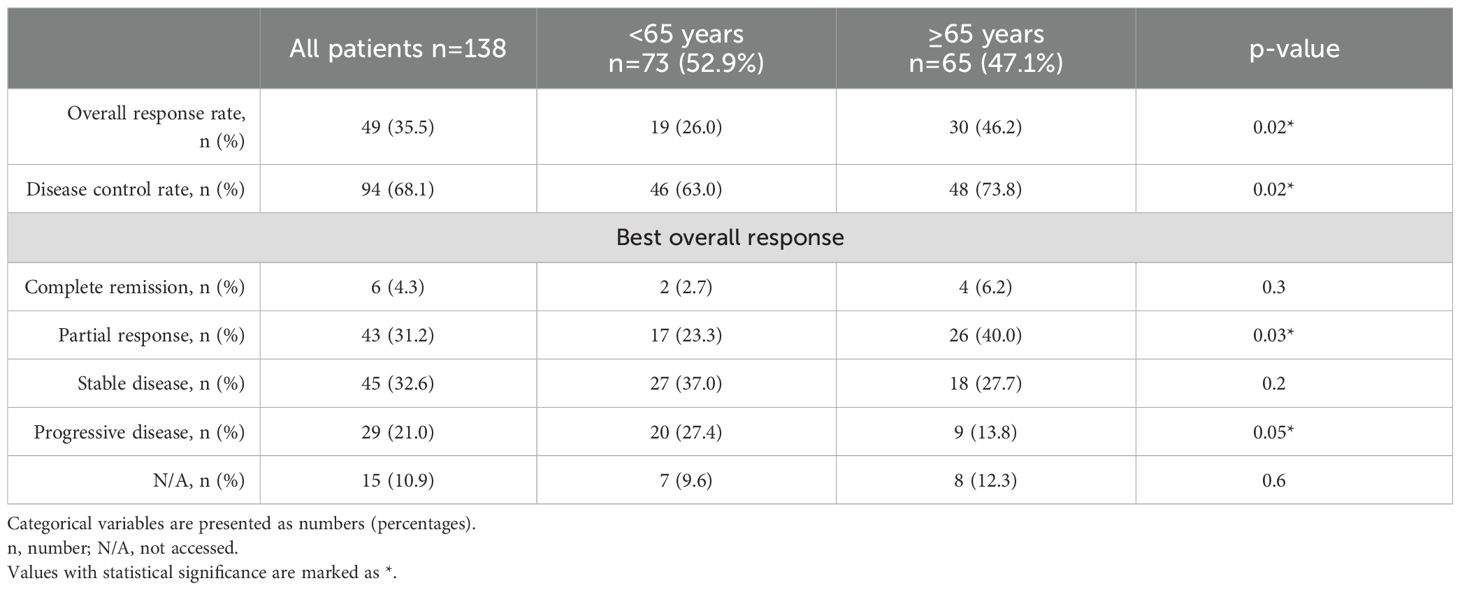
Two-thirds of the enrolled patients (n=94, 68.1%) achieved disease control after the nivolumab + ipilimumab treatment regimen. As shown in Table 2, patients aged ≥65 years exhibited a higher ORR (46.2% vs. 26%) and DCR (73.8% vs. 63%, p=0.02 for both) and they were more likely to demonstrate a PR on CT scans (40% vs. 23.3%, p=0.03). PD as the best overall response was significantly more frequent in younger patients (27.4% vs. 13.8%, p=0.05). At the data cutoff, 55 events of PD were recorded, with 36 events in patients <65 years and 19 events in patients ≥65 years (49.3% vs. 29.2%, p=0.02).
The median PFS for the entire cohort was 15.7 months (95% confidence interval [CI]: 10.2–20.8); for patients <65 years, it was 11.3 months (95% CI: 6.7–15.8) and for patients ≥65 years, it was 23 months (95% CI: 15.8–30.2), (Figure 1A). Patients ≥65 years had a 40% lower risk of disease progression than younger patients (hazard ratio [HR] 0.6, 95% CI: 0.3–0.9, p=0.03) and this value remained significant also in the multivariate regression model with p=0.02 (details in Supplementary Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials) after adjustment for potential confounders identified in baseline differences between two cohorts (hypertension, hypothyroidism, hypercholesterolemia, other malignancies and performance status). The median TTF was 11.9 months (95% CI: 6.7-17.2) for the entire cohort; for patients <65 years, it was 8.9 months (95% CI: 5.1-12.8) and for patients ≥65 years, it was 17.5 months (95% CI: 11-24.1) without differences between two subgroups (log-rank p=0.2).
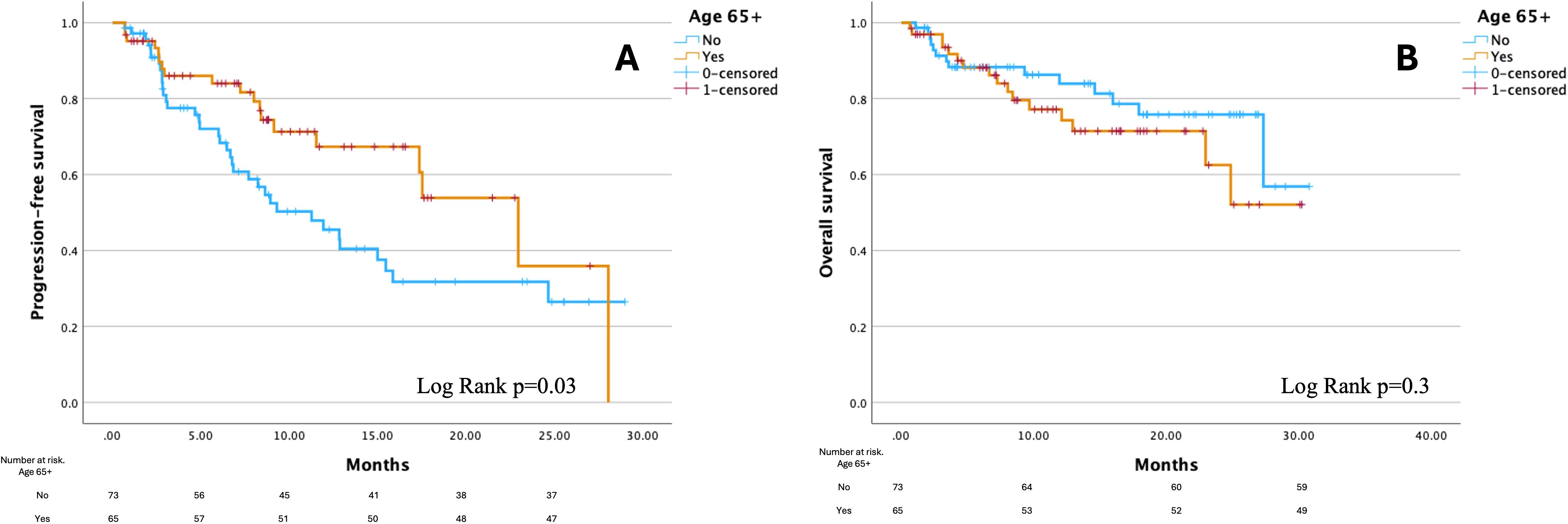
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (A) and overall survival (B) by age group. Figure created using PS Imago Pro 9 (SPSS).
Median OS was not reached (NR) for the entire cohort or either age group. No significant difference in survival was observed between the two age cohorts (log-rank p=0.3, Figure 1B) and this remained consistent after adjustment for confounders in the multivariate regression model (details in Supplementary Table S3 of the Supplementary Materials). The 6-month survival rate for the entire cohort was 89%, while the 12-month survival rate was 84%. Among patients <65 years, the 6-month survival rate was 89% and the 12-month survival rate was 86%. In patients ≥65 years, the corresponding survival rates were 89.2% at 6 months and 81.5% at 12 months. At the data cutoff, there were 30 recorded deaths: 14 in patients <65 years and 16 in patients ≥65 years (19.2% vs. 24.6%, p=0.5).
3.3 Safety
In total, 77 patients experienced irAEs (42 patients <65 years and 35 patients ≥65 years, p=0.8), accounting for 123 events (63 events in patients <65 years and 60 in patients ≥65 years, p=0.9). A single episode occurred in 47 patients, two in 17, three in 10 and four in 3.
The majority of irAEs were mild (grade, G1), recorded in 57 cases (30 in patients <65 years and 27 in those, p=0.8). Moderate irAEs (G2) were documented in 36 cases (20 vs. 16, p=0.6). Severe events (G3) were seen in 23 cases (11 vs. 12, p=1.00), while very severe irAEs (G4) were noted in 7 cases (1 vs. 6, p=0.06).
Figure 2 illustrates the distribution of irAEs across adverse events categories, grouped by age (<65 years and ≥65 years) and severity (G1-G2 and G3-G4). Analysis of event rates across irAEs categories showed a statistically significant difference between age groups in the endocrine category (p=0.04). No statistically significant differences were found in other categories (details in Supplementary Table S4 in the Supplementary Materials).
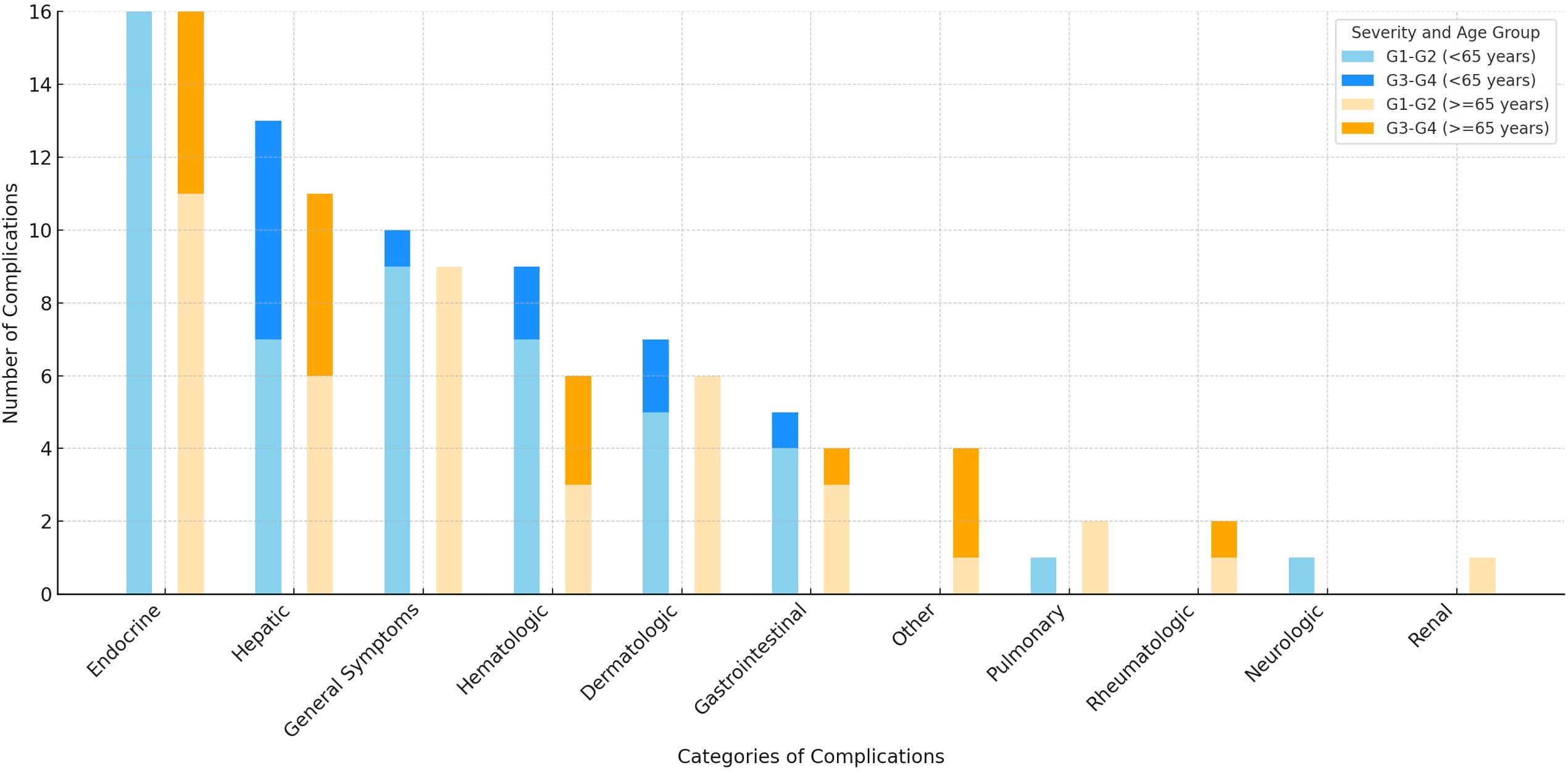
Figure 2. Number of immune-related adverse events by severity and age group graded according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v.5.0. Figure created using Microsoft Excel, version 16.99 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). Abbreviations: G- grade.
In the Cox regression model, the occurrence of irAEs did not significantly impact PFS in the entire cohort (p=0.5), in patients <65 years (p=0.4) or in those ≥65 years (p=0.9). A similar trend was observed for OS (p=0.8 for the entire cohort, p=0.9 for patients <65 years and p=0.8 for those ≥65 years).
Systemic steroids were administered to 29 patients (21%), including 17 patients <65 years (23.3%) and 12 patients ≥65 years (18.5%), with p=0.5. The median steroid dose was 1 mg/kg of prednisone/equivalent (IQR: 0.75–2 mg/kg). Two patients (1.4%) required treatment with mycophenolate mofetil. No other immunosuppressive treatment was administered in this cohort.
3.4 Treatment discontinuation and subsequent therapy in the entire cohort
Sixty-eight patients (49.3%) continued treatment at the data cut-off, while 70 patients (50.7%) had treatment withdrawal, primarily due to PD/death (n=55, 78.6%) or toxicity (n=15, 21.4%). Of those who discontinued, 29 patients (41.4%) began a subsequent line of therapy with cabozantinib (n=27) or axitinib (n=2) and six patients (8.6%) are under active surveillance and expected to start the next treatment line in case of PD. A total of 35 patients (50%) were ineligible for further treatment, with 30 of them having already passed away.
4 Discussion
In this analysis, we observed significant differences in treatment outcomes and safety profiles between younger and older patients with mRCC undergoing nivolumab and ipilimumab treatment. Older patients, despite having higher rates of comorbidities and poorer baseline performance status, achieved comparable or even favorable treatment outcomes relative to their younger counterparts. Specifically, patients aged ≥65 demonstrated a higher ORR and DCR, alongside a longer PFS, with age being identified as an independent prognostic factor for disease progression. Safety outcomes revealed that the frequency of irAEs was similar across age groups, with most of them being mild and moderate (G1-G2). Older patients experienced more severe adverse events and higher incidences of cardiac events such as myocarditis and pericarditis.
Traditionally, the term “elderly” refers to individuals aged 65 and older (20, 21) but with the aging population, many studies have redefined “older patients” as those over 70–75 years (10, 11). In the pivotal Checkmate 214 trial (8), patients were categorized into three age groups (<65 years, ≥65 and <75 years and ≥75 years), where those over 65 showed no significant ORR and OS benefit from nivolumab and ipilimumab. Additionally, in our recent report (22), we found that age ≥65 was linked to a significantly reduced risk of disease progression (HR=0.5, 95% CI: 0.3-0.8, p=0.01). Accordingly, we chose this landmark for our analysis and aimed to further explore this observation in the current study.
Our findings appear to contrast with the results of the pivotal CheckMate 214 trial (8). Several factors may help explain this difference. First, real-world populations may differ from clinical trial cohorts in terms of baseline characteristics and comorbidities. In our study, treatment decisions were made in routine practice and may have favored patients with preserved organ function and better performance status. Second, improvements in the recognition and management of irAEs since the time of the CheckMate 214 (8) trial may have contributed to better outcomes in real-world settings.
In a network meta-analysis (23), most first-line treatments had less favorable outcomes in older patients, yet the combination of nivolumab + ipilimumab followed by second-line cabozantinib showed the greatest efficacy in this population. Additionally, in the large Italian multicenter study, patients who were older than 70 years had comparable OS to younger patients (12), like in our study. However, OS is influenced by multiple factors, including additional lines of therapy and deaths from non-cancer-related comorbidities. Consequently, PFS may serve as a more accurate measure of the direct impact of nivolumab and ipilimumab in this population.
In an exploratory analysis of patients with mRCC, melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab in clinical trials, the incidence of irAEs was similar in patients aged <65 and ≥65; however, G3–5 adverse events were more frequent in patients over 70 (58.4% vs. 71.7%) (24) what stays in line with our findings and in our previous report (25). In a cohort of 103 melanoma patients aged ≥80 who received either single-agent ICIs or nivolumab + ipilimumab, the adverse event rate was consistent with phase III data across all age groups (26). In other reports of melanoma patients, survival and toxicity in older patients treated with ICIs were similar to younger patients (27, 28). While growing evidence suggests that irAEs occurrence may correlate with improved outcomes (29–32), Johns et al. (33) did not find this relationship in patients aged ≥70 (similar to our findings), contrasting with Schulz et al. (34) who did observe it in patients with genitourinary cancers, though only 10 of these patients received combination immunotherapy. We may hypothesize that improved outcomes in older adult patients are related to higher rates of irAEs with predictive value, as we previously reported (30).
As the immune system ages, it undergoes metabolic and structural changes, collectively known as immunosenescence. Key alterations include thymic atrophy, shifts in T and B cell ratios, reduced hematopoietic stem cell function, mitochondrial dysfunction and increased inflammation. These changes weaken immune efficiency and reduce the body’s ability to respond to new antigens, including tumors, leading to fewer tumor-infiltrating immune cells and potentially reducing the effectiveness of some immunotherapies (35). However, chronic low-grade inflammation, a feature of immunosenescence, may paradoxically enhance immunotherapy response in older adults by promoting inflammatory factors, like interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6 and IL-8, through the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) (36–38). SASP components in the tumor microenvironment have been linked to tumor progression and drug resistance, yet may also limit aggressive tumor growth, as seen in older patients with bronchial cancer and elderly mouse cancer models, where slower tumor growth and fewer metastases were observed (39, 40). In terms of immune checkpoint dynamics, certain checkpoints like CTLA-4 appear stable with age, while slight changes in PD-1 and increases in PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression have been observed, suggesting that therapies targeting these checkpoints may remain effective in older patients (7, 41, 42). These observations might explain why our study found better treatment outcomes in older patients, as their unique immune landscape and altered inflammatory profile could improve responsiveness to ICIs. However, no differences were observed in inflammatory markers derived from the complete blood count, including the NLR, PLR, LMR, eosinophil counts or monocyte counts. Currently, in the novel Meet-URO Score, NLR has been added, providing higher prognostic accuracy (web calculator available at: https://proviso.shinyapps.io/Meet-URO15_score/) (43). Further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
5 Study limitations
The primary limitation of this study is the relatively small sample size, which may reduce statistical power and impact the robustness of our findings. Additionally, the retrospective data collection for certain variables may introduce recall or selection bias. While our findings contribute important information on PFS and OS, the follow-up period may not be long enough to capture delayed effects or longer-term outcomes associated with the nivolumab and ipilimumab regimen. We acknowledge that the retrospective nature of the study and variability in imaging schedules may have influenced the accuracy of PFS estimates and the relatively short follow-up period limits the maturity of OS data. The absence of a standardized comorbidity index (e.g., Charlson Comorbidity Index) limits the granularity of our assessment, as comorbidities were retrospectively extracted from medical records without formal geriatric evaluation. Assessments of safety, laboratory and imaging were conducted locally, which may introduce reporting bias and variability in assessments. Variations in the management of irAEs could influence outcomes, as local practices may differ in steroid administration or other interventions for irAEs. The study’s restriction to a Polish cohort and the necessity to strictly adhere to reimbursement criteria may also limit the generalizability of results to mRCC populations in other regions with differing genetic backgrounds, environmental exposures and healthcare practices. Furthermore, despite the use of multivariate analyses, unmeasured confounding factors could still influence the observed outcomes. Propensity score matching (PSM) in statistical analysis was not applied due to the relatively small sample size, which would have led to a significant reduction in the number of analyzed patients and decreased statistical power. Instead, multivariate Cox regression models were used to adjust for potential confounders while preserving the full dataset. Additionally, as this is a real-world study, applying PSM could introduce selection bias by excluding patients without a matched counterpart, limiting the generalizability of the findings.
6 Conclusions
This study demonstrates that nivolumab and ipilimumab are effective across age groups, with older patients (≥65 years) achieving comparable or even better ORR, DCR and PFS than younger patients despite higher comorbidity rates. However, older patients were more susceptible to severe irAEs, highlighting the need for close monitoring and personalized management in this group. These findings support immunotherapy as a viable option for older patients and that chronological age should not be a direct contraindication for such treatment. As a pilot multicenter study, our findings offer preliminary insight into age-specific treatment outcomes and warrant confirmation in larger, prospective cohorts.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Bioethics Committee of Jagiellonian University Medical College (approval number 118.0043.1.115.2024, dated April 19, 2024). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AD: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization. ŁS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AG-W: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. JC: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. NV: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JD: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AR: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. MS: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. AB: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. DT-M: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AG-U: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. MP: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Conceptualization. RP-M: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Conceptualization, Visualization, Data curation, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. APC funding was provided by the PTOK Scholarship Fund for Young Oncologists.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1617743/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Powles T, Albiges L, Bex A, Comperat E, Grünwald V, Kanesvaran R, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up 5 behalf of the ESMO Guidelines Committee. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:692–706. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.05.537
2. Singer EA, Rumble RB, and Van Veldhuizen PJ. Management of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: ASCO guideline Q&A. JCO Oncol Pract. (2023) 19:127–31. doi: 10.1200/OP.22.00660/ASSET/D113D15D-DB85-4D67-B46A-3DBD08196D7E/ASSETS/IMAGES/LARGE/OP.22.00660F3.JPG
3. Wysocki PJ, Chłosta P, Chrzan R, Czech AK, Gronostaj K, Konopka K, et al. Zalecenia postępowania diagnostyczno-terapeutycznego w raku nerkowokomórkowym-aktualizacja Polish Society of Clinical Oncology and Polish Urological Association guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell cancer-update, Vol. 6. (2022). WYTYCZNE POSTĘPOWANIA DIAGNOSTYCZNO-TERAPEUTYCZNEGO. 424–57.
4. Heng DYC, Xie W, Regan MM, Harshman LC, Bjarnason GA, Vaishampayan UN, et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. (2013) 14:141–8. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70559-4
5. SEER*Explorer Application . Available online at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html?site=630&data_type=1&graph_type=14&compareBy=sex&chk_sex_3=3&chk_sex_2=2&series=9&race=2&hdn_view=1 (Accessed January 12, 2025).
6. Feng DC, Li DX, Wu RC, Wang J, Xiao YH, Yoo KH, et al. Global burden and cross-country inequalities in urinary tumors from 1990 to 2021 and predicted incidence changes to 2046. Mil Med Res. (2025) 12(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40779-025-00599-y
7. Alkharabsheh O, Kannarkatt P, Kannarkatt J, Karapetyan L, Laird-Fick HS, and Al-Janadi A. An overview of the toxicities of checkpoint inhibitors in older patients with cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. (2018) 9:451–8. doi: 10.1016/J.JGO.2018.02.002
8. Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. New Engl J Med. (2018) 378:1277–90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMOA1712126/SUPPL_FILE/NEJMOA1712126_DISCLOSURES.PDF
9. Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. New Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1803–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMOA1510665/SUPPL_FILE/NEJMOA1510665_DISCLOSURES.PDF
10. Kobayashi M, Numakura K, Hatakeyama S, Ishida T, Koizumi A, Tadachi K, et al. Real clinical outcomes of nivolumab plus ipilimumab for renal cell carcinoma in patients over 75 years old. Int J Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:1530–7. doi: 10.1007/S10147-023-02394-Y/METRICS
11. Numakura K, Kobayashi M, Hatakeyama S, Naito S, Horikawa Y, Tanaka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab for renal cell carcinoma in patients over 75 years old from multiple Japanese institutes. Int J Clin Oncol. (2020) 25:1543–50. doi: 10.1007/S10147-020-01693-Y/TBLES/4
12. Basso U, Paolieri F, Rizzo M, De Giorgi U, Bracarda S, Antonuzzo L, et al. Compassionate use program of ipilimumab and nivolumab in intermediate or poor risk metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A large multicenter italian study. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14(9):2293. doi: 10.3390/CANCERS14092293
13. Ministerstwo Zdrowia - Portal Gov.pl. Obwieszczenie Ministra Zdrowia z dnia 18 grudnia 2024 r. w sprawie wykazu refundowanych leków, środków spożywczych specjalnego przeznaczenia żywieniowego oraz wyrobów medycznych na 1 stycznia 2025 r . Available online at: https://www.gov.pl/web/zdrowie/obwieszczenie-ministra-zdrowia-z-dnia-18-grudnia-2024-r-w-sprawie-wykazu-refundowanych-lekow-srodkow-spozywczych-specjalnego-przeznaczenia-zywieniowego-oraz-wyrobow-medycznych-na-1-stycznia-2025-r (Accessed December 26, 2024).
14. Castelo-Branco L, Pellat A, Martins-Branco D, Valachis A, Derksen JWG, Suijkerbuijk KPM, et al. ESMO Guidance for Reporting Oncology real-World evidence (GROW). Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:1097–112. doi: 10.1016/J.ANNONC.2023.10.001/ATTACHMENT/1DE7E9A7-7499-484F-A53B-2901B1714FBA/MMC1.DOCX
15. Nivolumab. SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS . Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/opdivo-epar-product-information_en.pdf (Accessed January 16, 2025).
16. Ipilimumab. SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS . Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/yervoy-epar-product-information_en.pdf (Accessed January 16, 2025).
17. Somarouthu B, Lee SI, Urban T, Sadow CA, Harris GJ, and Kambadakone A. Immune-related tumour response assessment criteria: a comprehensive review. Br J Radiol. (2018) 91:736. doi: 10.1259/BJR.20170457
18. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 . Available online at: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (Accessed January 21, 2025).
19. Haanen J, Obeid M, Spain L, Carbonnel F, Wang Y, Robert C, et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33(12):1217–38. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.001
20. Orimo H, Ito H, Suzuki T, Araki A, Hosoi T, and Sawabe M. Reviewing the definition of “elderly. ” Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2006) 6:149–58. doi: 10.1111/J.1447-0594.2006.00341.X
21. Singh S and Bajorek B. Defining ‘elderly’ in clinical practice guidelines for pharmacotherapy. Pharm Pract (Granada). (2014) 12:489. doi: 10.4321/S1886-36552014000400007
22. Pacholczak-Madej R, Drobniak A, Grela-Wojewoda A, Calik J, Viegas NV, Tusień-Małecka D, et al. Prognostic significance of peripheral blood biomarkers in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab and ipilimumab-a polish multicenter, observational study. Clin Exp Med. (2025) 25:45. doi: 10.1007/S10238-024-01544-4/FGURES/3
23. Hale P, Hahn AW, Rathi N, Pal SK, Haaland B, and Agarwal N. Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in older patients: A network meta-analysis. J Geriatr Oncol. (2019) 10:149–54. doi: 10.1016/J.JGO.2018.05.010
24. Singh H, Kim G, Maher VE, Beaver JA, Pai-Scherf LH, Balasubramaniam S, et al. FDA subset analysis of the safety of nivolumab in elderly patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:10010–0. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_SUPPL.10010
25. Drobniak A, Stokłosa Ł, and Pacholczak-Madej R. Combined immunotherapy for renal-cell carcinoma (RCC) in geriatric patients. Biuletyn Polskiego Towarzystwa Onkologicznego Nowotwory. (2024) 9:263–3. Available online at: https://journals.viamedica.pl/biuletyn_pto/article/view/101827/78728 (November 19, 2024).
26. Friedman CF, Horvat TZ, Minehart J, Panageas K, Callahan MK, Chapman PB, et al. Efficacy and safety of checkpoint blockade for treatment of advanced melanoma (mel) in patients (pts) age 80 and older (80+). J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:10009–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_SUPPL.10009
27. Cybulska-Stopa B, Ługowska I, Jagodzińska-Mucha P, Koseła-Paterczyk H, Kozak K, Klimczak A, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors therapy in older patients (≥ 70 years) with metastatic melanoma: A multicentre study. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. (2019) 36:566–71. doi: 10.5114/ada.2018.79940
28. Cybulska-Stopa B, Piejko K, Pacholczak R, Domagała-Haduch M, Drosik-Kwaśniewska A, Rolski J, et al. Real-world treatment practice in patients with advanced melanoma. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). (2020) 24:118–24. doi: 10.5114/wo.2020.97607
29. Cybulska-Stopa B, Pacholczak-Madej R, Kamińska-Winciorek G, Ziętek M, Czarnecka AM, Piejko K, et al. First-line treatment of advanced/metastatic melanoma with anti-PD-1 antibodies: multicenter experience in Poland. Immunotherapy. (2021) 13:297–307. doi: 10.2217/imt-2020-0217
30. Pacholczak-Madej R, Drobniak A, Stokłosa Ł, Bidas A, Dobrzańska J, Grela-Wojewoda A, et al. Adverse events after nivolumab and ipilimumab combined immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a multicentre experience in Poland. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:1–11. doi: 10.1186/S12885-024-13192-8
31. Pacholczak-Madej R, Grela-Wojewoda A, Puskulluoglu M, Lompart J, Las-Jankowska M, Krawczak K, et al. Relationship of adverse events after combined immunotherapy and treatment outcomes in patients with advanced melanoma: A multicenter experience in Poland. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:e21511–1. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_SUPPL.E21511
32. Pacholczak-Madej R, Grela-Wojewoda A, Puskulluoglu M, Lompart J, Las-Jankowska M, Krawczak K, et al. Early effects of nivolumab and ipilimumab combined immunotherapy in the treatment of metastatic melanoma in Poland: A multicenter experience. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(10):2528. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102528
33. Johns AC, Wei L, Grogan M, Hoyd R, Bridges JFP, Patel SH, et al. Checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy toxicity and overall survival among older adults with advanced cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. (2021) 12:813–9. doi: 10.1016/J.JGO.2021.02.002
34. Schulz GB, Rodler S, Szabados B, Graser A, Buchner A, Stief C, et al. Safety, efficacy and prognostic impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors in older patients with genitourinary cancers. J Geriatr Oncol. (2020) 11:1061–6. doi: 10.1016/J.JGO.2020.06.012
35. Lian J, Yue Y, Yu W, and Zhang Y. Immunosenescence: a key player in cancer development. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:1–18. doi: 10.1186/S13045-020-00986-Z
36. Pawelec G. Hallmarks of human “immunosenescence”: Adaptation or dysregulation? Immun Ageing. (2012) 9:1–4. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-9-15/METRICS
37. Accardi G and Caruso C. Immune-inflammatory responses in the elderly: An update. Immun Ageing. (2018) 15:1–4. doi: 10.1186/S12979-018-0117-8/METRICS
38. Feng Y, He C, Liu C, Shao B, Wang D, and Wu P. Exploring the complexity and promise of tumor immunotherapy in drug development. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6444. doi: 10.3390/IJMS25126444
39. Ershler WB, Stewart JA, Hacker MP, Moore AL, and Tindle BH. B16 murine melanoma and aging: slower growth and longer survival in old mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. (1984) 72:161–4. doi: 10.1093/JNCI/72.1.161
40. Socinski MA and Greene CJ. Bronchogenic cancer, metastases, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. (1983) 31:673–6. doi: 10.1111/J.1532-5415.1983.TB04153.X
41. Canaday DH, Parker KE, Aung H, Chen HE, Nunez-Medina D, and Burant CJ. Age-dependent changes in the expression of regulatory cell surface ligands in activated human T-cells. BMC Immunol. (2013) 14:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-45
42. Leng Q, Bentwich Z, and Borkow G. CTLA-4 upregulation during aging. Mech Ageing Dev. (2002) 123:1419–21. doi: 10.1016/S0047-6374(02)00077-5
43. Damassi A, Cremante M, Signori A, Rebuzzi SE, Fornarini G, Giudice GC, et al. Prognostic stratification by the meet-URO score in real-world older patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) receiving cabozantinib: A subanalysis of the prospective ZEBRA study (Meet-URO 9). Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2024) 22:126–133.e2. doi: 10.1016/J.CLGC.2023.10.001
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma, nivolumab and ipilimumab, immune checkpoint inhibitors, elderly, treatment outcome
Citation: Drobniak A, Stokłosa Ł, Grela-Wojewoda A, Calik J, Versuti Viegas N, Dobrzańska J, Roman A, Szwiec M, Bidas A, Tusień-Małecka D, Gawlik-Urban A, Puskulluoglu M and Pacholczak-Madej R (2025) Effectiveness and safety of nivolumab and ipilimumab in older adults with renal cell carcinoma: findings from a multicenter observational study in Poland. Front. Oncol. 15:1617743. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1617743
Received: 24 April 2025; Accepted: 31 July 2025;
Published: 19 August 2025.
Edited by:
Guang-Liang Chen, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Dechao Feng, University College London, United KingdomZhouwei Zhan, Fujian Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Drobniak, Stokłosa, Grela-Wojewoda, Calik, Versuti Viegas, Dobrzańska, Roman, Szwiec, Bidas, Tusień-Małecka, Gawlik-Urban, Puskulluoglu and Pacholczak-Madej. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mirosława Puskulluoglu, bWlyYS5wdXNrdWxsdW9nbHVAZ21haWwuY29t; Renata Pacholczak-Madej, cmVuYXRhLnBhY2hvbGN6YWtAdWouZWR1LnBs
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
 Artur Drobniak1
Artur Drobniak1 Angelika Gawlik-Urban
Angelika Gawlik-Urban Mirosława Puskulluoglu
Mirosława Puskulluoglu Renata Pacholczak-Madej
Renata Pacholczak-Madej