- Department of Neurology, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-associated neurological immune-related adverse events (NAEs) are rare but serious side effects, of which autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) is a potentially fatal central nervous system disorder requiring more attention.
Methods: We performed a retrospective disproportionality analysis of NAE reports in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) and the Japanese Adverse Event Reporting Database (JADER) from 2004 to 2024, utilizing reporting odds ratio (ROR), proportional reporting ratio (PRR), the Bayesian confidence propagation neural network BCPNN, and the multi-item gamma Poisson shrinker (MGPS) for signal detection.
Results: In total, 3,999 reports of ICI-associated NAEs were identified from the FAERS database, of which 1,998 reports were AIE. 1,558,251 reports of AEs were collected from the JADER database, which contained 890 AIE reports. ICIs, including pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, ipilimumab, and durvalumab, were identified among the top 30 agents in both databases, demonstrating significant signals across all 4 algorithms. Except for noninfectious myelitis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and multiple sclerosis, positive signals were detected in all other preferred terms (PTs). These NAEs accounted for 23.7% of total mortality, with myasthenia gravis (MG) exhibiting the highest mortality rate at 30.63%. Specific PTs, such as aseptic meningitis, AIE, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, MG, myelitis, and immune-related myopathy, were associated with the severity of outcomes, showing significant statistical differences between severe and non-severe cases (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Our study found a notable correlation between ICIs and AIE and other specific NAEs, highlighting the demographic characteristics, time to onset, and disease severity of ICI-induced NAEs, thereby facilitating the timely recognition and treatment of these ICI therapy-related complications.
1 Introduction
Immune checkpoints constitute a critical group of regulatory molecules expressed on immune cells, pivotal in modulating immune response activation. Notable examples include cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand, programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), as well as lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3). Commonly used immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) encompass the CTLA-4 inhibitor, including ipilimumab, PD-1 inhibitors such as pembrolizumab, nivolumab, and cemiplimab, as well as PD-L1 inhibitors, including atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab. More than 10 ICI drugs have been approved for marketing by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Moreover, these agents have been widely utilized in clinical settings to treat multiple malignancies, such as melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, bladder cancer, and colorectal cancer. In clinical practice, CTLA-4 inhibitors are frequently combined with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. ICI therapy significantly advances tumor immunotherapy, augmenting the body’s defenses against cancer (1, 2).
Although ICIs have high efficacy compared with traditional chemotherapies and can effectively improve the survival rate of cancer patients, their adverse effects should not be neglected. These pharmacological agents are associated with various immune-related adverse events (irAEs). These events arise from inappropriate stimulation of the immune system, inadvertently targeting normal tissues, predominantly affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, thyroid, and musculoskeletal system (3). Neurological irAEs (NAEs) are relatively uncommon, with incidence rates of 3.8% associated with CTLA-4 inhibitors, 6% with PD-1 inhibitors, and 12% with combination therapies. ICI-induced NAEs include central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) irAEs. Documented NAEs encompass autoimmune encephalitis (AIE), aseptic meningitis (4), Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), myasthenia gravis (MG), and CNS demyelinating diseases such as neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) (5, 6), myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease (MOGAD) (7), and CNS vasculitis (8).
AIE is a CNS disorder characterized by antibodies targeting neuronal antigens. These antibodies predominantly target neuronal surface antigens, intracellular antigens, or synaptic proteins, resulting in alterations and damage to neural function. The pathogenesis of AIE is complex, involving various factors such as viral infections, vaccinations, and neoplasms (9). Tumor-associated AIE, particularly in the context of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes, has been extensively studied due to the resemblance between tumor cell antigens and neuronal antigens. As such, this triggers immune system attacks on the nervous system. Recent research indicates that the ICI therapy can also trigger AIE, although this occurrence is uncommon (10). In such cases, patients may require the discontinuation of ICI therapy and the initiation of immunosuppressive treatment to manage symptoms. Thus, the early identification and diagnosis of ICI-related AIE, along with balancing tumor and AIE treatment, present significant challenges.
There is still a lack of comprehensive studies on NAEs associated with ICIs. Recently, comprehensive real-world drug adverse event databases, such as the United States FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) and the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) of the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency, comprising spontaneous adverse event reports, are essential resources and analytical instruments in pharmacovigilance. Thorough examination of these databases enables researchers to gain a comprehensive insight into adverse drug event profiles, thereby furnishing crucial safety insights for clinical application. These discoveries improve drug safety protocols and provide empirical support for risk mitigation strategies and policy formulation in pharmacotherapy. Thus, we conducted a disproportionality analysis focusing on AIE and other NAEs associated with ICIs, utilizing real-world data from FAERS and JADER from 2004 to 2024.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data resources
Data were obtained from the FAERS website (https://fis.fda.gov/extensions/FPD-QDE-FAERS/FPD-QDE-FAERS.html), spanning 20 years from the first quarter of 2004 (2024Q1) to the fourth quarter of 2024 (2024Q4), and JADER website (https://www.pmda.go.jp/safety/info-services/drugs/adr-info/suspected-adr/0003.html) from the first quarter of 2004 (2024Q1) to the third quarter of 2024 (2024Q3). The data tables in the FAERS database include DEMO (demographic and administrative information), DRUG (drug information), INDI (indications for drug administration), REAC (coded AEs), and OUTC (outcomes of patients). In the JADER database, we utilized the following 3 data tables for analysis: DEMO, DRUG, and REAC.
2.2 Data extraction
Duplicate reports were eliminated by utilizing a unique safety report identifier, “primaryID”, assigned to each case. AEs in the REAC table were classified using the “Preferred Term” (PT) from the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA). In this research, we examine the following PTs in MedDRA 26.0: AIE (including autoimmune encephalopathy, encephalitis autoimmune, immune-mediated encephalitis, noninfective encephalitis), other NAEs include PNS immune-mediated diseases (including Guillain-Barre syndrome, Miller Fisher syndrome, acute motor axonal neuropathy, acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy), neuromuscular junction dysfunction (including immune-mediated myasthenia gravis, myasthenia gravis, myasthenia gravis crisis, myasthenic syndrome, ocular myasthenia), immune-related myopathy (including autoimmune myositis, dermatomyositis, immune-mediated myositis, myositis, necrotizing myositis, polymyositis), myelitis (including immune-mediated myelitis, myelitis, myelitis transverse, noninfectious myelitis), CNS demyelinating diseases (including neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, primary progressive multiple sclerosis, progressive multiple sclerosis, progressive relapsing multiple sclerosis, relapsing multiple sclerosis, relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease), aseptic meningitis (including meningitis aseptic, meningitis noninfective), and CNS vasculitis (central nervous system vasculitis).
In this study, we selected the following ICIs for research: ipilimumab (IPI), pembrolizumab (PEM), nivolumab (NIV), cemiplimab (CEM), atezolizumab (ATE), durvalumab (DUR), and avelumab (AVE). Due to inconsistent registration of drug names in the FAERS database, we employed both generic and brand names of ICIs as search keywords. The DRUG table categorizes drug role codes into 4 groups based on their involvement in AEs: primary suspect (PS), secondary suspect (SS), concomitant (C), and interaction (I). Notably, this research targeted the PS category as the study population. Figure 1 shows the flowchart for screening ICI-associated NAEs.
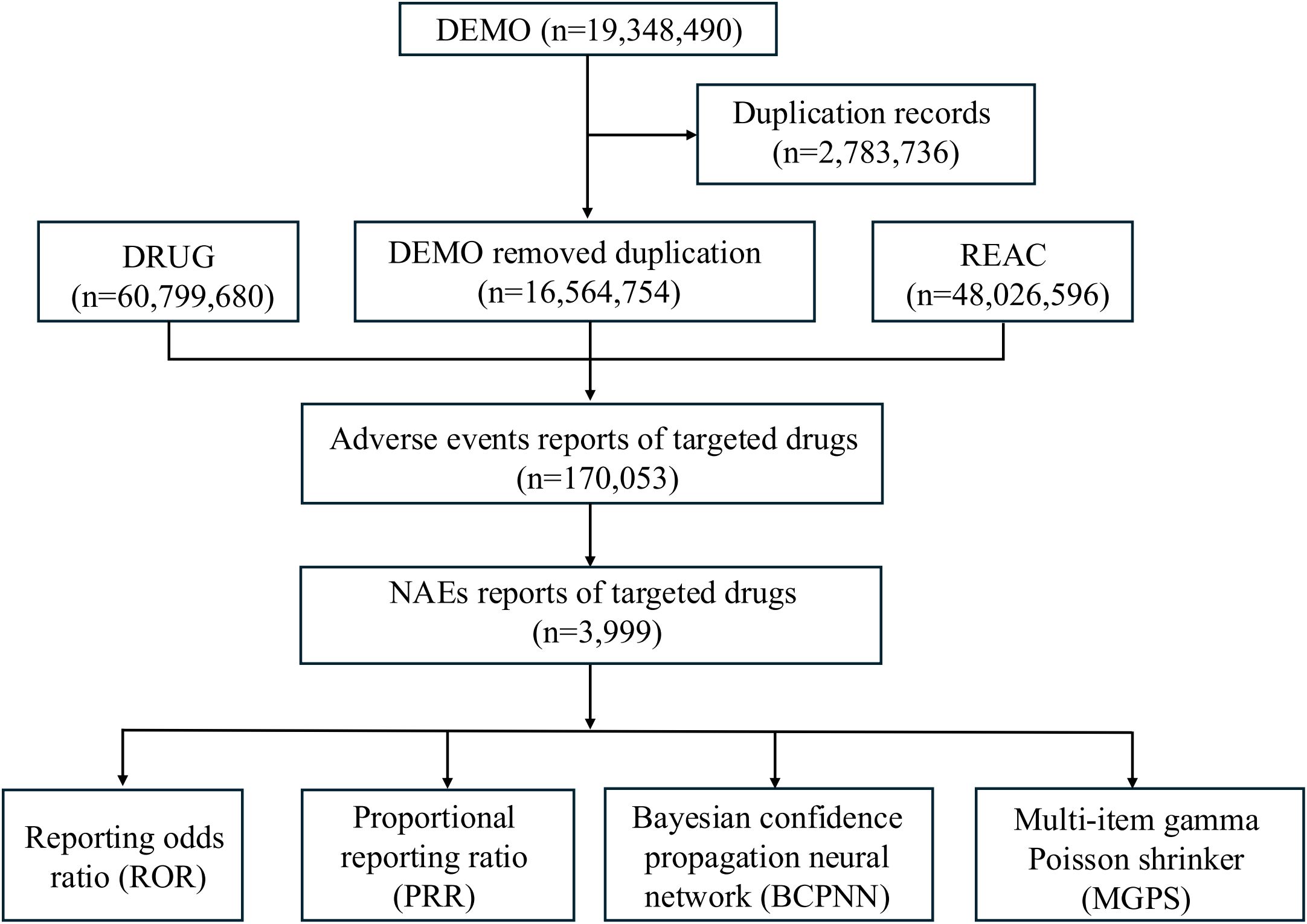
Figure 1. Flowchart of data extraction and disproportionality analysis of ICI-related NAEs in the FAERS database from 2004 Q1 to 2024 Q4.
According to the OUTC table, death (DE) outcomes were categorized as serious. In contrast, other outcomes, including life-threatening (LT), hospitalization (HO), disability (DS), congenital anomaly (CA), required intervention (RI), and other outcomes (OT), were classified as non-serious.
2.3 Statistical analysis
In this study, we employ 4 algorithms for the detection of adverse event signals: the reporting odds ratio (ROR) (11), the proportional reporting ratio (PRR) (12), the Bayesian confidence propagation neural network (BCPNN) (13), and the multi-item gamma Poisson shrinker (MGPS) (14). The formulas and signal detection criteria for these 4 algorithms are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Notably, these are based on a four-cell table of disproportional methods. A signal of NAEs is considered present when at least one of these algorithms meets the established criteria, indicating a statistical association between drug treatment and AEs. All statistical analyses were conducted using R software (version 4.2.2). Correlations were evaluated through the non-parametric Spearman correlation test. Furthermore, we performed a Chi-square test to compare each PT’s serious and non-serious outcome groups. Statistical significance was considered when the p-value was < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 The top 30 drugs with the highest number of reported AIE cases in the FAERS and JADER databases, respectively
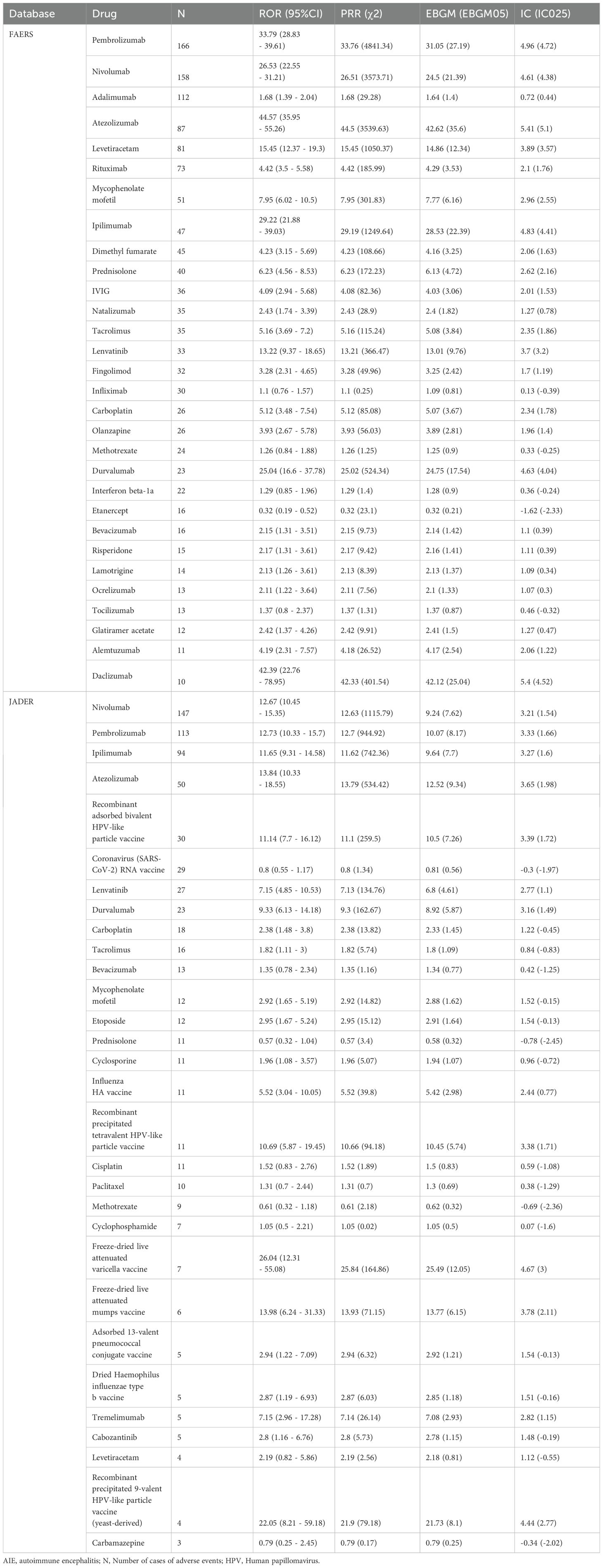
We utilize the FAERS and JADER databases to identify the top 30 drugs associated with AIE. A disproportionality analysis was performed to explore the potential association between drugs and AIE. Notably, the number of reported cases may exceed the count of target AEs, as a single case can encompass multiple such events.
The FAERS database contains 16,564,754 reports of AEs after removing duplication from 2004Q1 to 2024Q4, of which 1,998 reports were AIE. The JADER database contains 1,558,251 reports of AEs from 2004Q1 to 2024Q3, of which 890 reports were AIEs. Signal values determined by all 4 algorithms are listed in the Table 1.
In both databases, ICIs strongly correlated with AIE. In the TOP 30 drugs of FAERS database, the following ICI drugs showed significant signals: pembrolizumab (N= 166, ROR= 33.79, 95%CI [28.83~39.61], PRR= 33.76, χ2 = 4841.34, EBGM= 31.05, EBGM05 = 27.19, IC= 4.96, IC025 = 4.72), nivolumab (N= 158, ROR= 26.53, 95%CI [22.55~31.21], PRR= 26.51, χ2 = 3573.71, EBGM= 24.5, EBGM05 = 21.39, IC= 4.61, IC025 = 4.38), atezolizumab (N= 87, ROR= 44.57, 95%CI [35.95~55.26], PRR= 44.5, χ2 = 3539.63, EBGM= 42.62, EBGM05 = 35.6, IC= 5.41, IC025 = 5.1), ipilimumab (N= 47, ROR= 29.22, 95% CI [21.88~39.03], PRR= 29.19, χ2 = 1249.64, EBGM= 28.53, EBGM05 = 22.39, IC= 4.83, IC025 = 4.41), and durvalumab (N= 23, ROR= 25.04, 95%CI [16.6~37.78], PRR= 25.02, χ2 = 524.34, EBGM= 24.75, EBGM05 = 17.54, IC= 4.63, IC025 = 4.04).
In the TOP 30 drugs of JADER database, the following ICI drugs showed significant signals: nivolumab (N= 147, ROR= 12.67, 95%CI [10.45~15.35], PRR= 12.63, χ2 = 1115.79, EBGM= 9.24, EBGM05 = 7.62, IC= 3.21, IC025 = 1.54), pembrolizumab (N= 113, ROR= 12.73, 95%CI [10.33~15.7], PRR= 12.7, χ2 = 944.92, EBGM= 10.07, EBGM05 = 8.17, IC= 3.33, IC025 = 1.66), ipilimumab (N= 94, ROR= 11.65, 95%CI [9.31~14.58], PRR= 11.62, χ2 = 742.36, EBGM= 9.64, EBGM05 = 7.7, IC= 3.27, IC025 = 1.6), atezolizumab (N= 50, ROR= 13.84, 95%CI [10.33~18.55], PRR= 13.79, χ2 = 534.42, EBGM= 12.52, EBGM05 = 9.34, IC= 3.65, IC025 = 1.98), durvalumab (N= 23, ROR= 9.33, 95%CI [6.13~14.18], PRR= 9.3, χ2 = 162.67, EBGM= 8.92, EBGM05 = 5.87, IC= 3.16, IC025 = 1.49), and Tremelimumab (N= 5, ROR= 7.15, 95%CI [2.96~17.28], PRR= 7.14, χ2 = 26.14, EBGM= 7.08, EBGM05 = 2.93, IC= 2.82, IC025 = 1.15).
3.2 Demographic characteristics of AIE among ICI-treated patients in the FAERS and JADER
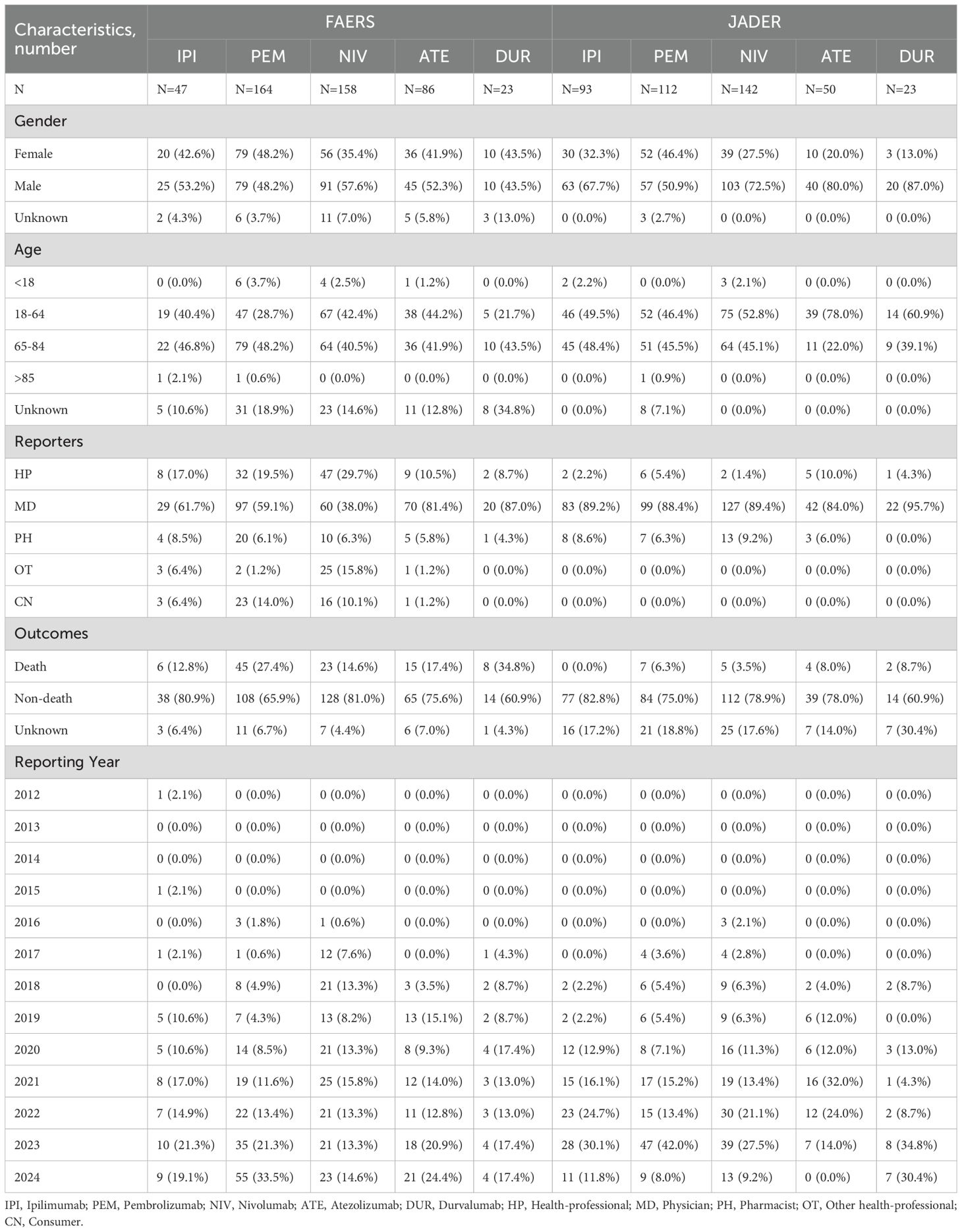
Table 2 summarizes the clinical characteristics and reporting patterns of autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) associated with 5 ICI drugs in 2 pharmacovigilance databases, FAERS and JADER. The analysis includes the number of reported cases, gender distribution, age distribution, reporter types, outcomes (death vs. non-death), and reporting year distribution for each of the ICI drugs: ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab, and durvalumab. Cempilimab and avelumab were excluded due to insufficient data.
ICI-related AIE was found to be more prevalent in males in both FAERS (52.3%) and JADER (67.4%). From the FAERS database, most cases are concentrated within the 65 to 84 age range, accounting for 44.1%. Conversely, from the JADER database, the predominant age group for cases is between 18 and 64 years, comprising 53.8%. Physicians constitute most reporters in both databases, with the JADER database exclusively composed of medical professionals as reporters. Within the FAERS database, 20.3% of AIE associated with ICIs resulted in fatalities, whereas this figure is significantly lower in the JADER database, at 4.3%. Notably, durvalumab is linked to the highest proportion of AIE-related deaths, accounting for 34.8% in the FAERS database and 8.7% in the JADER database.
3.3 NAEs among ICI-treated patients in FAERS from 2004Q1 to 2024Q4
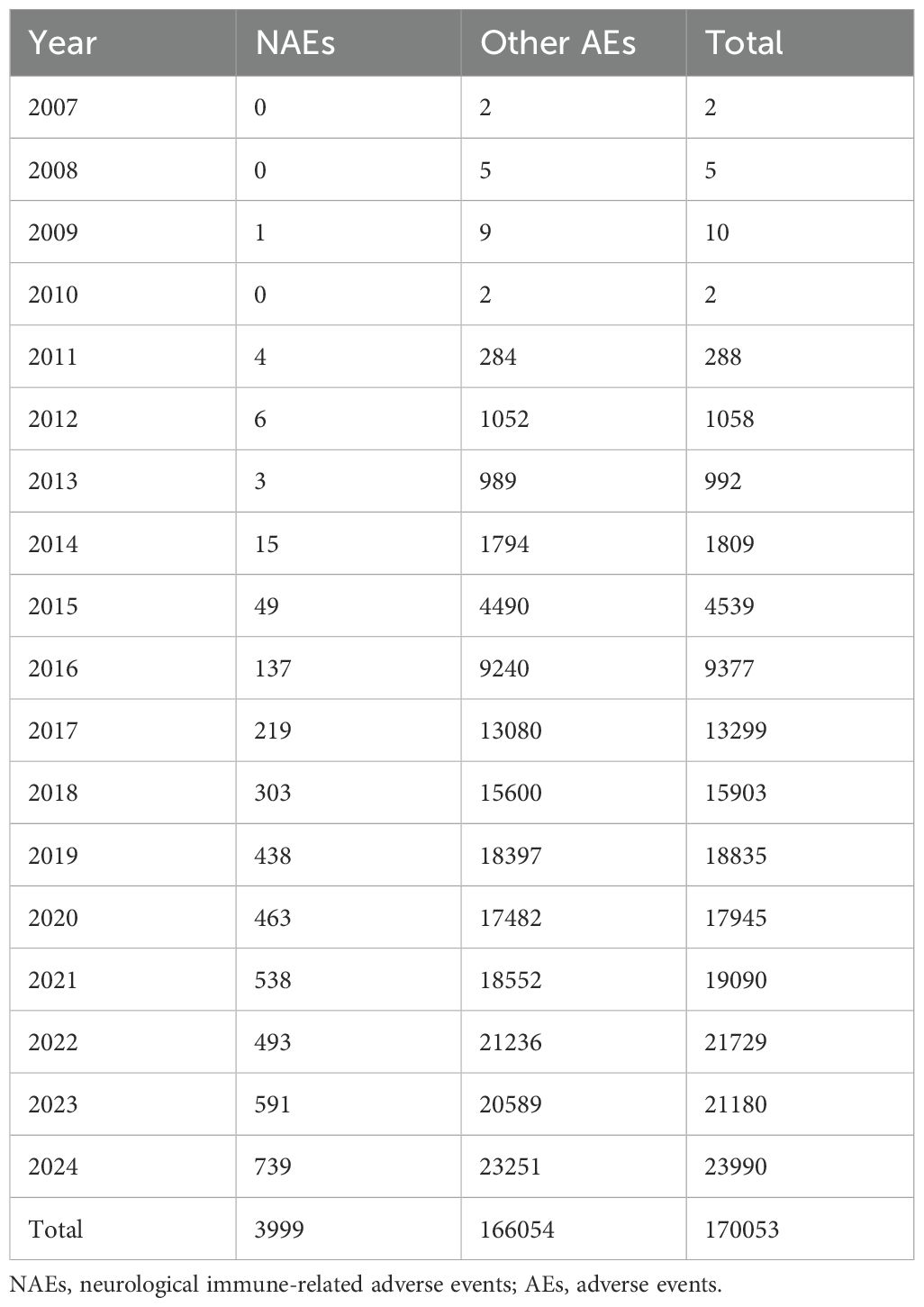
Using the FAERS database, we examined the incidence of NAEs in patients treated with ICIs between 2004Q1 and 2024Q4. A total of 19,348,490 AE reports were included in the FAERS database. 16,564,754 reports remained after exclusion of duplicate reports, and 3,999 cases of ICI-associated NAEs were identified. Neurologic AEs accounted for only 2.35% of the adverse reactions reported in all ICIs. Recently, the number of reported cases of ICI-associated NAEs has increased annually and has attracted widespread attention. Table 3 lists the reported annual cases of NAEs for all target drugs. The correlation analysis indicated a significant positive statistical relationship between the number of annually reported ICI-related NAE cases and the year (r = 0.9853, p < 0.0001). This finding suggests that the incidence of NAEs has progressively increased in tandem with the expanding utilization of ICIs.
As shown in Figure 2, the numbers of cases of NAEs associated with each ICI were nivolumab (N=1490), pembrolizumab (N=1325), atezolizumab (N=496), ipilimumab (N=362), durvalumab (N=200), avelumab (N=66), and cemiplimab (N=60). Although having the lowest number of cases with NAEs, cemiplimab [3.06% (60/1959)] and avelumab [3.05% (66/2165)] had the highest proportion of NAEs among all AEs.
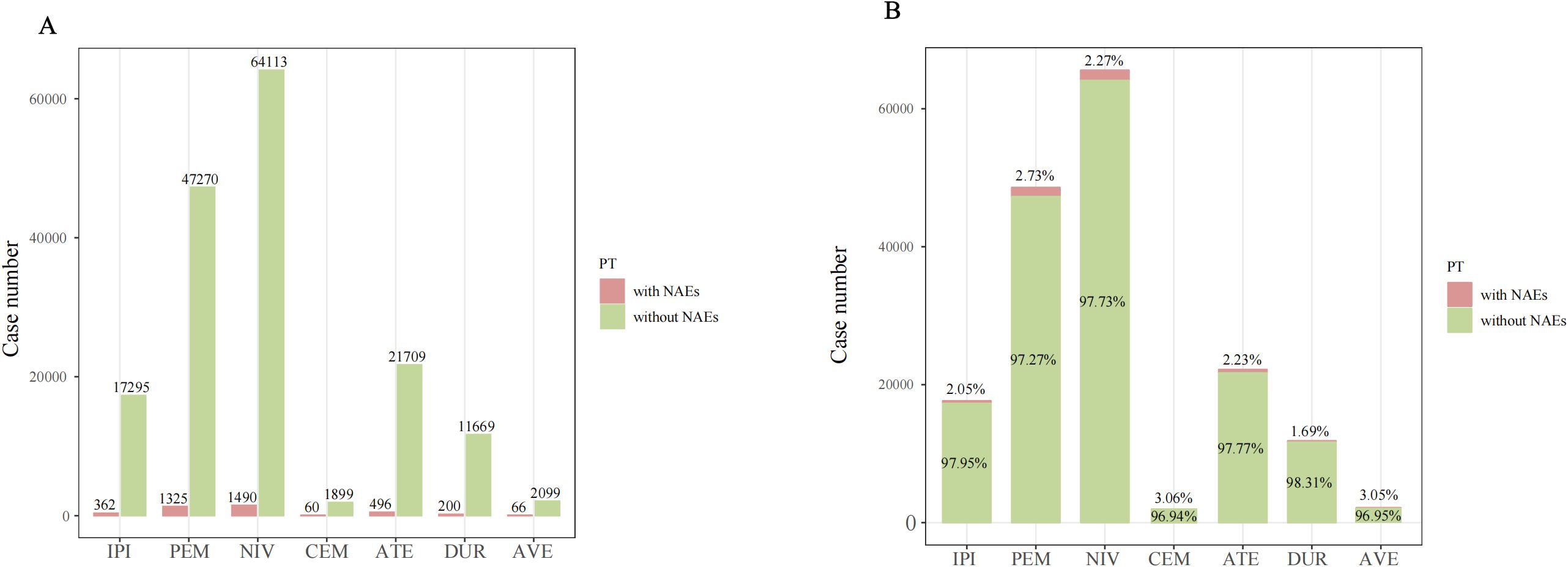
Figure 2. The case number (A) and percentage (B) of adverse event reports with NAEs and without NAEs of targeted ICIs in the FAERS database from 2004 Q1 to 2024 Q4. PT, preferred term; NAE, neurological immune-related adverse events.
3.4 Demographic characteristics of ICI-related NAEs
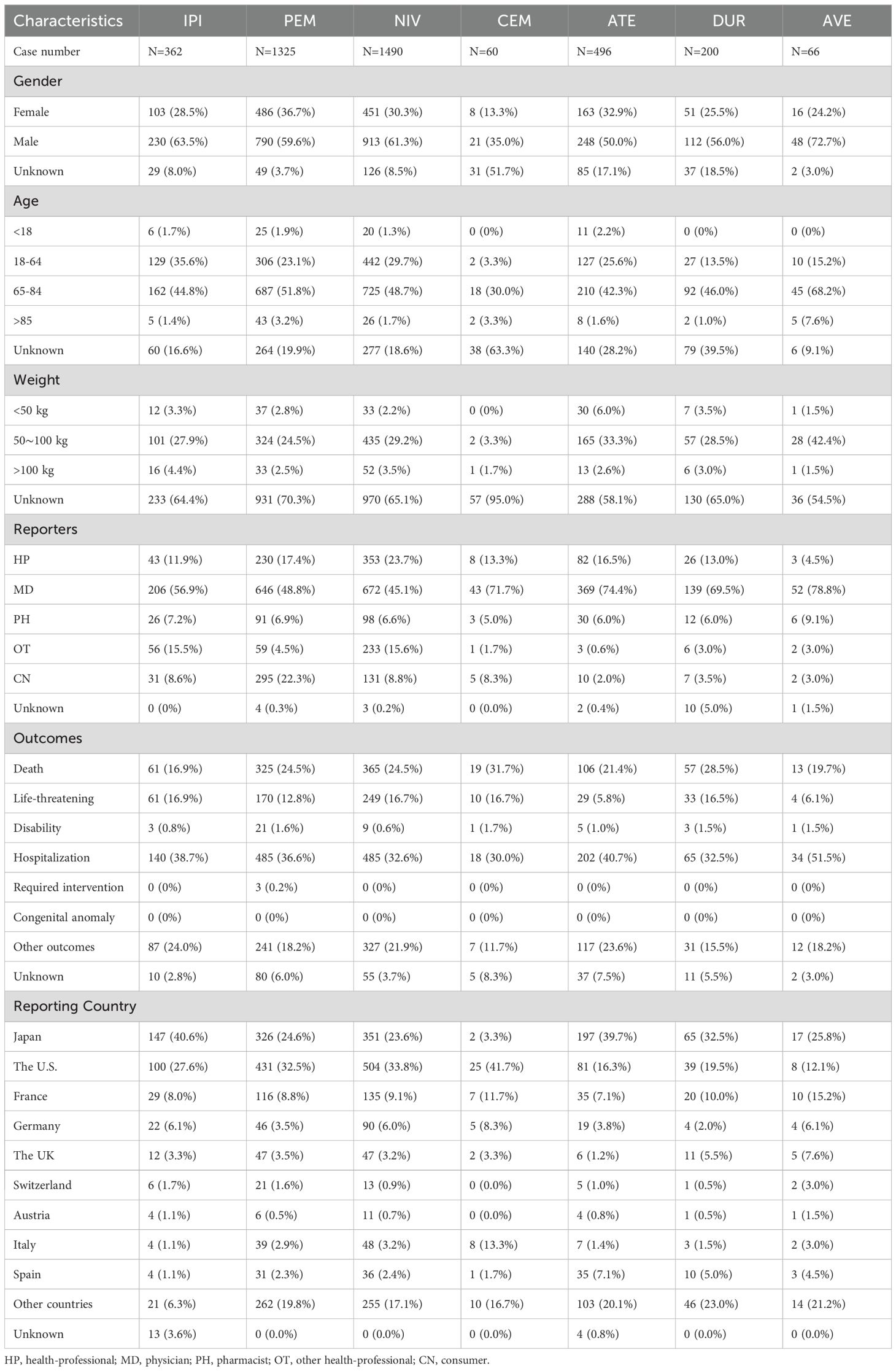
Table 4 demonstrates the demographic characteristics of NAEs correlated with ICI treatment. Among all ICI-related NAEs reported, males (59.1%) were at higher risk than females (32.0%). Gender information was not available for 9.0% of cases (359/3,999). The proportion of males treated with IPI, PEM, NIV, CEM, ATE, DUR, and AVE was 63.5% (230/362), 59.6% (790/1,325), 61.3% (913/1,490), 35.0% (21/60), 50.0% (248/496), 56.0% (112/200), and 72.7% (48/66). At the same time, the proportion of females was 28.5% (103/362), 36.7% (486/1325), 30.3% (451/1490), 13.3% (8/60), 32.9% (163/496), 25.5% (51/200), and 24.2% (16/66), respectively. The age of the reported cases was predominantly 65–85 years [48.5% (1,939/3,999)], followed by 18–64 years [26.1% (1,043/3,999)], >85 years [2.3% (91/3,999)], and <18 years [1.6% (62/3,999)]. The age of the remaining cases was unknown [21.6% (864/3,999)]. An analysis of the indications for ICI treatment reveals that the primary tumors with the highest prevalence, in descending order, are lung cancer [25.9% (1034/3,999)], malignant melanoma [23.6% (944/3,999)], renal cancer [11.8% (472/3,999)], hepatic cancer [4.2% (166/3,999)], and breast cancer [2.7% (106/3,999)]. The highest percentage of reported staff types was physician [53.2% (2,127/3,999)], followed by health professional [18.6% (745/3,999)]. Among all the NAEs related to ICIs, the outcome “hospitalization” is the most frequent [35.7%, (1,429/3,999)], and the death rate is 23.7% (946/3,999). Furthermore, cemiplimab was associated with the highest mortality rate among ICIs, at 31.7% (19/60). The top 2 highest rankings among all reporting countries were the United States [29.7% (1,188/3,999)] and Japan [27.6% (1,105/3,999)].
3.5 Disproportionality analysis for ICI-related NAEs
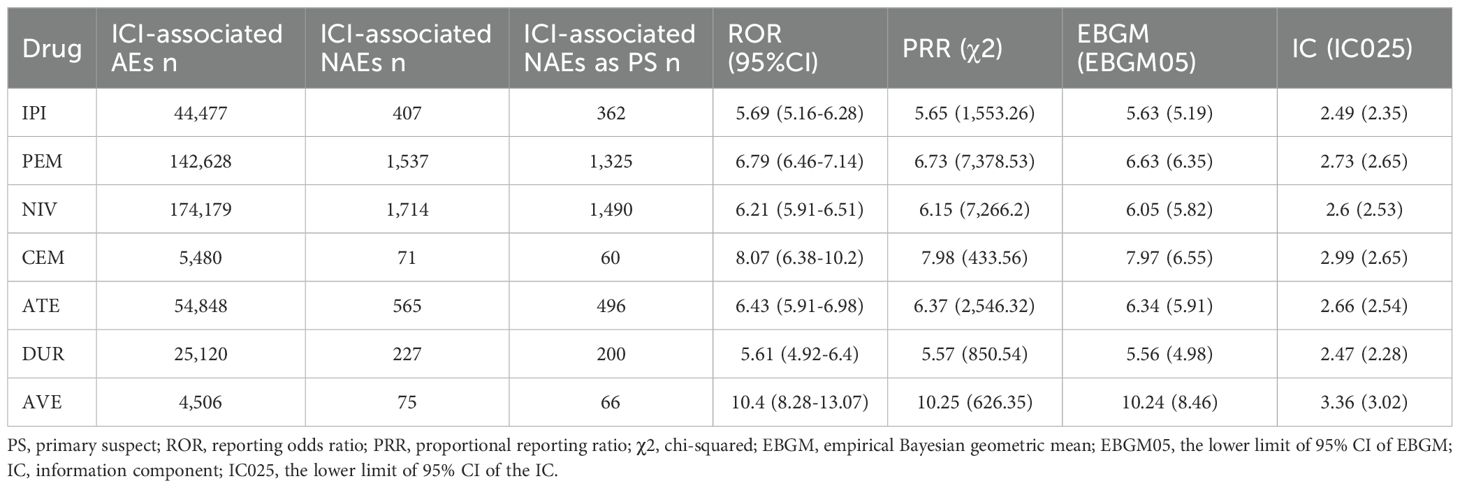
The signal values and correlations between ICIs and NAEs are presented in Table 5. All drugs showed significant signals: IPI (N = 362, ROR = 5.69, 95% CI [5.16~6.28], PRR= 5.65, χ2 = 1,553.26), PEM (N = 1,325, ROR = 6.79, 95% CI [6.46~7.14], PRR= 6.73, χ2 = 7,378.53), NIV (N = 1,490, ROR = 6.21, 95% CI [5.91~6.51], PRR= 6.15, χ2 = 7,266.2), CEM (N = 60, ROR = 8.07, 95% CI [6.38~10.2], PRR= 7.98, χ2 = 433.56), ATE (N = 496, ROR = 6.43, 95% CI [5.91~6.98], PRR= 6.37, χ2 = 2,546.32), DUR (N = 200, ROR = 5.61, 95% CI [4.92~6.4], PRR= 5.57, χ2 = 850.54), AVE (N = 66, ROR = 10.4, 95% CI [8.28~13.07], PRR= 10.25, χ2 = 626.35). Notably, avelumab showed the strongest association with the nervous system compared to other ICIs. In contrast, durvalumab showed few concerns about safety of the nervous system.
The PT signals of all ICI-associated NAEs are listed in the Supplementary Table S2. Noninfectious myelitis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and multiple sclerosis had no positive signal in all 4 algorithms. Supplementary Table S3 displays the signal strength of PTs associated with each ICI agent. The signal ranges of ROR values for each drug were: IPI (0.19~203.14, median 11.94), PEM (0.17~284.55, median 9.66), NIV (0.13~177.49, median 9.02), CEM (2.34~137.59, median 23.895), ATE (0.09~104.26, median 11.195), DUR (0.05~102.83, median 14.515), and AVE (3.05~140.03, median 35.625).
Using high-level terms (HLT), AEs at the PT level were clustered into subsequent classifications according to neurological diseases. As shown in Figure 3, at the HLT level, the signal ranges of ROR values for the 7 drugs were: IPI (0.11~14.48, median 2.2), PEM (0.09~22.21, median 2.22), NIV (0.07~19.37, median 2.68), CEM (1.33~31.55, median 2.36), ATE (0.05~17.21, median 4.18), DUR (0.04~18.6, median 2.39), and AVE (1.4~38.43, median 2.44).
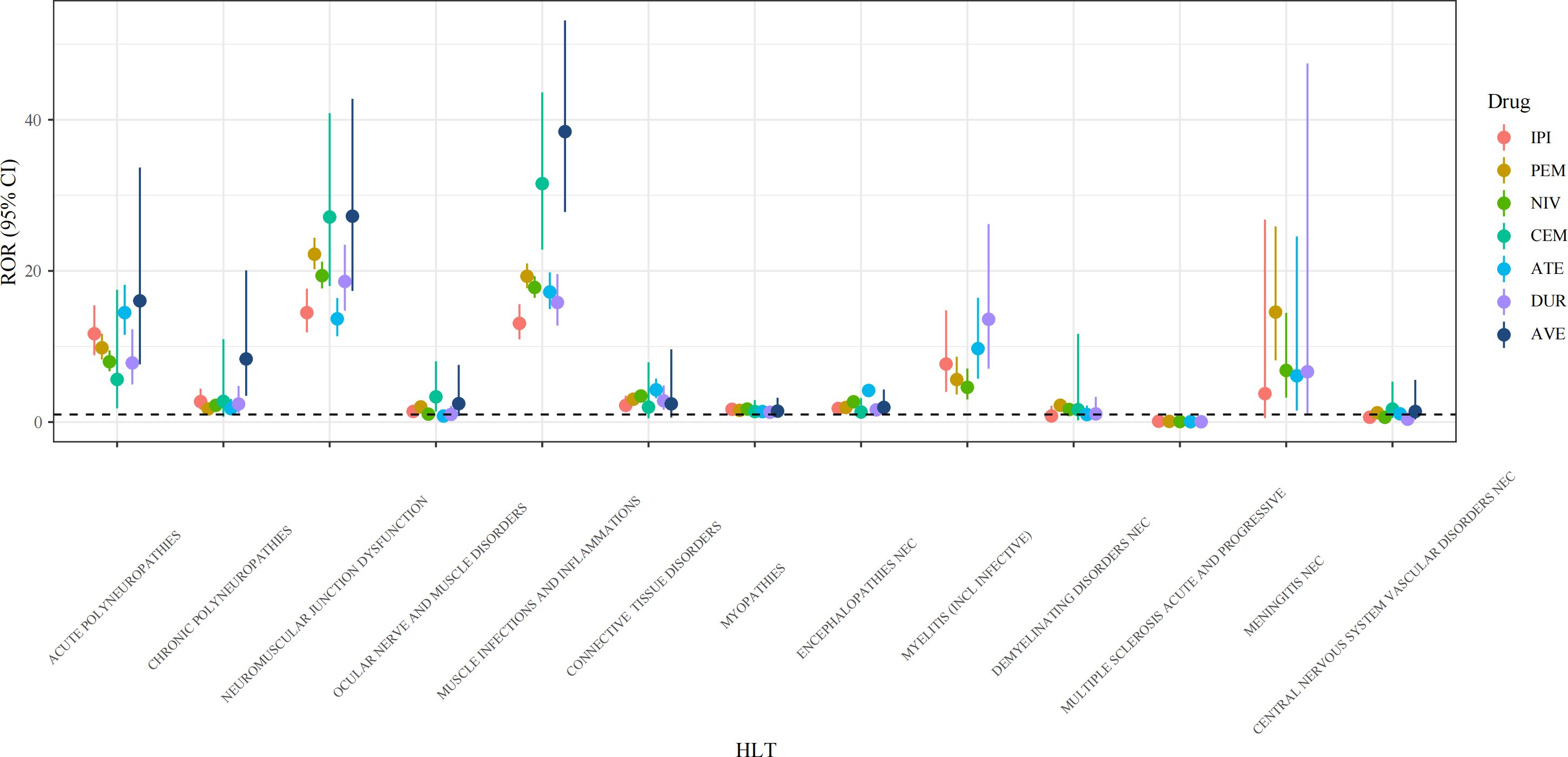
Figure 3. Forest plots of ROR values under HLT levels of different ICI agents. HLT, high level term; ROR, reporting odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; IPI, ipilimumab; PEM, pembrolizumab; NIV, nivolumab; CEM, cemiplimab; ATE, atezolizumab; DUR, durvalumab; AVE, avelumab.
To better understand the clinical features of NAEs, we combined the names of PTs representing the same disease identity. We also explored the top 10 most frequently reported NAEs following ICI treatment. As shown in Figure 4, the NAEs were: immune-mediated myopathy (N=1845), MG (N=1319), AIE (N=489), GBS (N=389), aseptic meningitis (N=251), myelitis (N=140), CIDP (N=51), NMOSD (N=26), CNS vasculitis (N=22), and MOGAD (N=6).
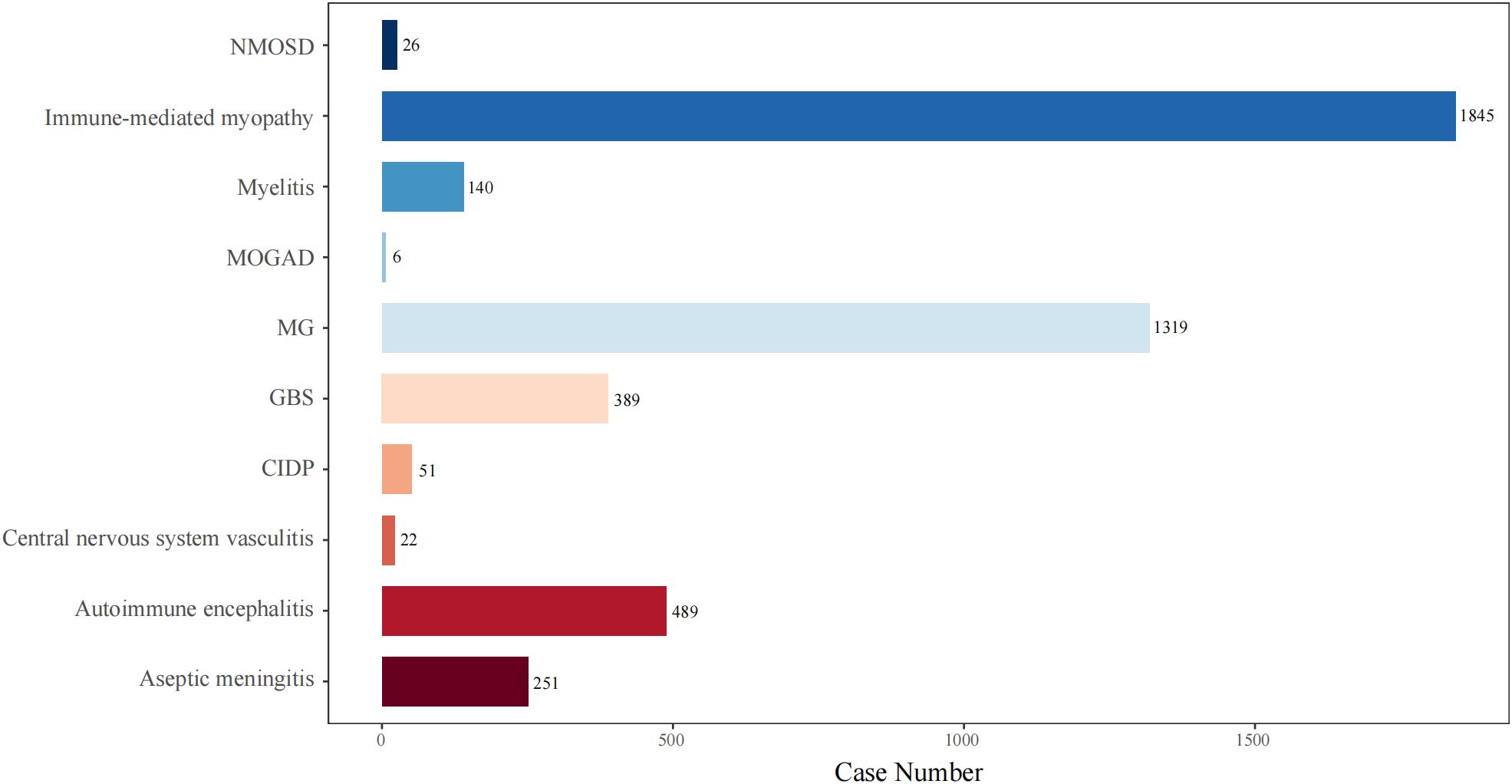
Figure 4. The number of reported cases of the top 10 types of NAEs associated with ICI therapies in the FAERS database. NMOSD, neuromyelitis spectrum disorder; MOGAD, myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease; MG, myasthenia gravis; GBS, Guillain-Barré syndrome; CIDP, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.
As shown in Figure 5, we calculated the mortality rates (number of reported deaths/number of reported AEs) for various NAEs following ICI treatment. Importantly, MG exhibited the highest mortality rate at 30.63%, followed by immune-mediated myopathy at 28.08%, and AIE at 20.25%. Therefore, these findings underscore the importance of early recognition and proactive immunotherapeutic intervention by clinicians.
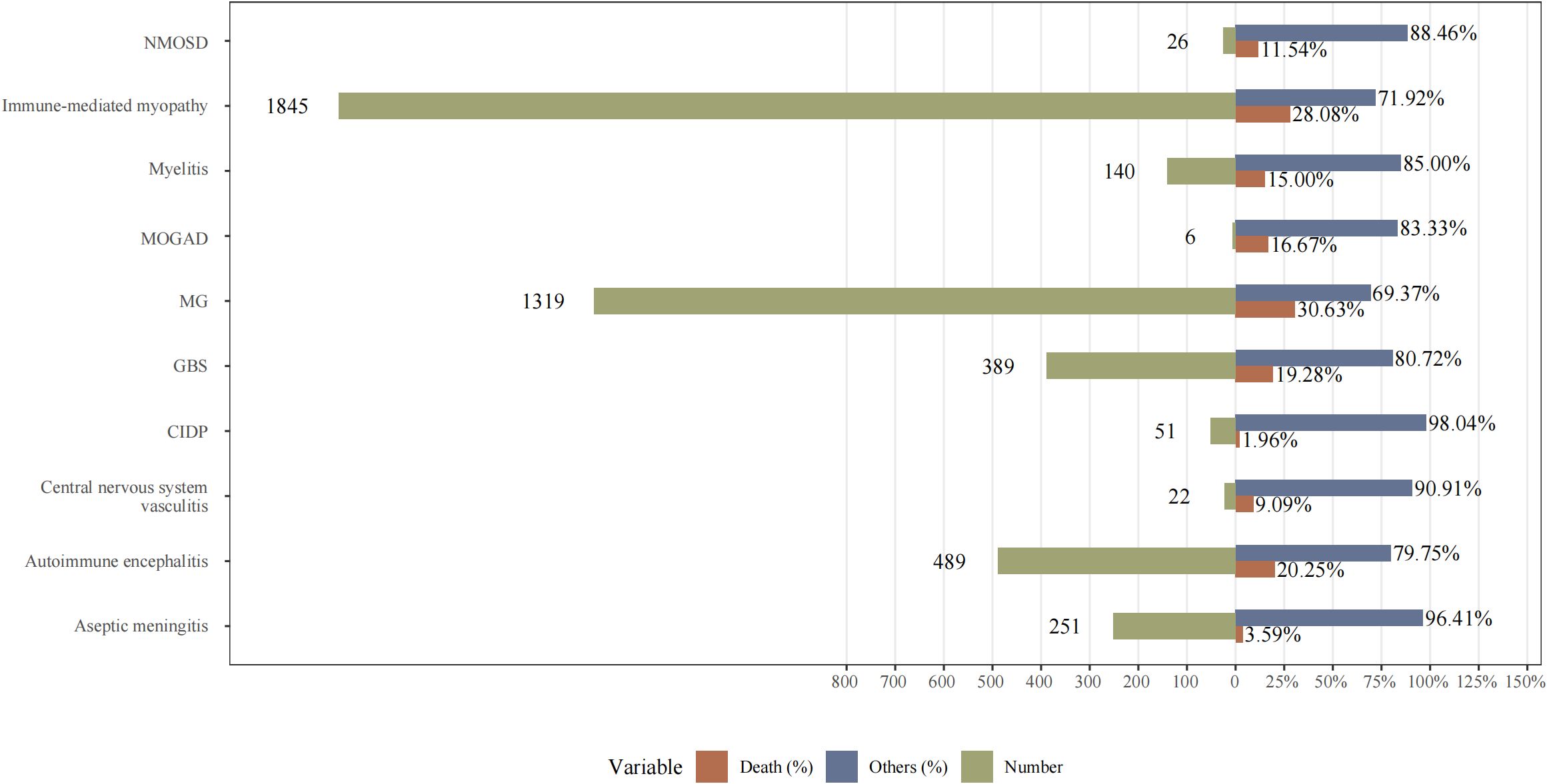
Figure 5. The mortality rates (number of reported deaths/number of reported adverse events) for various NAEs following ICI treatment. NMOSD, neuromyelitis spectrum disorder; MOGAD, myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease; MG, myasthenia gravis; GBS, Guillain-Barré syndrome; CIDP, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.
3.6 Time to onset of neurological adverse event
Figure 6a presents a histogram showing the incidence of NAEs during ICI treatment. Figure 6b depicts the duration of NAE episodes induced by each ICI drug. The median onset time of NAEs associated with all target drugs was 30 days (interquartile range [IQR]: 17–69 days). Additionally, the median time to onset of NAEs was earliest in the CEM and ATE groups, at 21 days (IQR: 10 to 39 days in the CEM group and IQR: 12 to 82.5 days in the ATE group). Notably, the ATE group had the widest range of time to onset. The median time to onset of NAEs in the AVE group was the longest at 32 days (IQR: 26 to 49.25 days). The median times to onset of NAEs for IPI, PEM, NIV and DUR were 27.5 days (IQR: 16–50 days), 28.5 days (IQR: 17.75–77 days), 31 days (IQR: 19–70 days) and 28.5 days (IQR: 19–58 days), respectively. Thus, the investigation into the onset time of NAEs induced by ICIs provides novel insights into the clinical application of these drugs and the early identification of neurological toxicity.
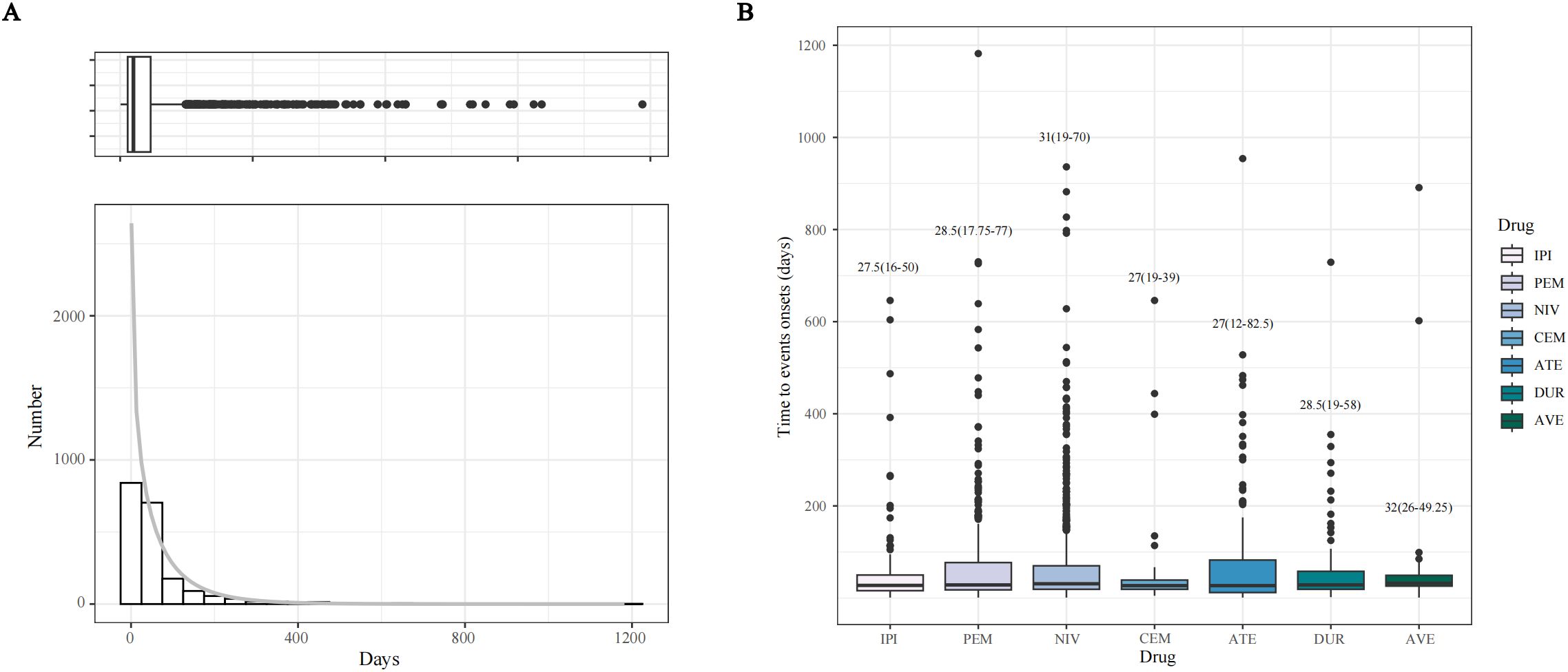
Figure 6. Time to onset (TTO) analysis (counted in days) of ICI-related NAEs. (A) Histogram displaying the adverse event numbers corresponding to TTO of ICI-related NAEs. (B) Boxplot of the TTO of NAEs for each ICI agents.
3.7 Comparison between serious and non-serious groups for ICI-related NAEs
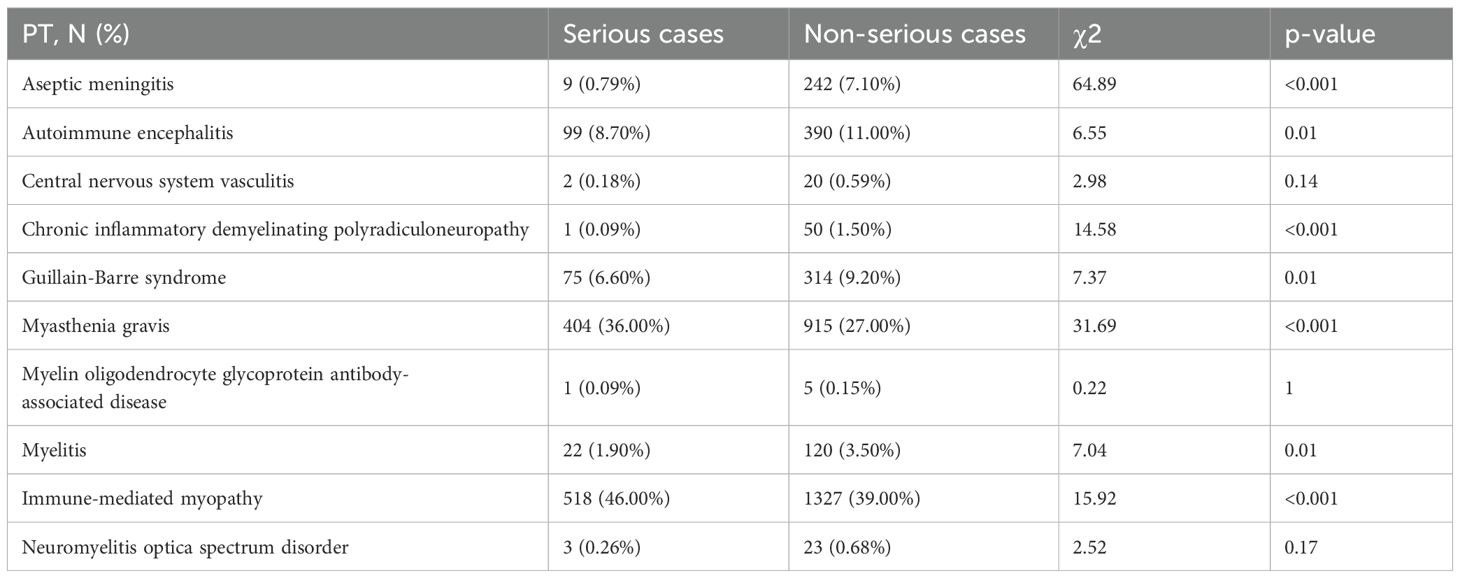
As presented in Table 6, the following NAE types correlated with the severity of case outcome with a p-value <0.05: aseptic meningitis (χ2 = 64.89, p<0.001), AIE (χ2 = 6.55, p=0.01), CIDP (χ2 = 14.58, p<0.001), GBS (χ2 = 7.37, p=0.01), MG (χ2 = 31.69, p<0.001), myelitis (χ2 = 7.04, p=0.01), immune-related myopathy (χ2 = 15.92, <0.001). In contrast, there was no significant correlation between other NAE types and the severity of the outcome: CNS vasculitis (χ2 = 2.98, p=0.14), and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease (χ2 = 0.22, p=1).
4 Discussion
ICI therapies have been revolutionizing the treatment of malignant neoplasms. Characterizing neurological immunotoxicity associated with emerging cancer immunotherapies constitutes a new and growing area of research. As such, the prevalence of NAEs is expected to increase with the expansion of ICI indications. Currently, there is no unified diagnostic standard for immunotherapy-related neurological toxicity, which remains a diagnosis of exclusion that requires differentiation from infectious diseases, metabolic disorders, and tumor metastasis.
In this study, data from the FAERS database suggest a higher likelihood of NAEs following ICI therapy in males compared to females, aligning with prior systematic reviews (15). The median onset time for ICI-induced NAEs was 30 days (IQR: 17~69 days). Prior findings from institutions like the Mayo Clinic and the Royal Marsden Hospital suggested a median onset time for NAEs of around 3 treatment cycles (16, 17). Furthermore, delayed immune-related events (DIRE) were noted, with a median interval of 6 months after immunotherapy (18). The longest time until the onset of AEs in this research was 1182 days, observed in a patient undergoing pembrolizumab treatment for malignant melanoma.
AIE is the most common CNS irAE. Manifestations of ICI-induced AIE may include headache, altered mental status, cognitive deficits, seizures, ataxia, dysphagia, and aphasia. Approximately 50% of patients exhibit positive neuronal antibodies, most commonly against intracellular antigens (especially Ma2 or Hu), the presence of which usually indicates a poor prognosis (19, 20). Patients with positive anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase or anti-neuronal surface antigen antibodies respond to treatment well and tend to have a favorable prognosis. Neuropathologic features include diffuse, cytotoxic CD8+ T cell infiltration, reactive astrogliosis, and activation of microglial cells (10).
Approximately two-thirds of ICI-induced NAEs involve the PNS. Consistent with prior studies, myopathy is the most prevalent ICI-mediated NAE. Unlike idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, immune-related myopathy predominantly involves extraocular and bulbar muscles. It can also coexist with MG and myocarditis (21). Immune-related myopathy typically manifests within the first 4 weeks of ICI therapy, often following the initial or second treatment cycle (22, 23). Patients with overlap syndrome exhibit more severe symptoms, such as ptosis, bulbar dysfunction, and dyspnea, compared to those with myositis alone. Notably, most patients display elevated creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels, exceeding more than twice the upper limit of the normal range. Some cases test positive for myositis-specific antibodies, myositis-associated antibodies, and anti-striated muscle antibodies (AsM-Ab) (24). Approximately 5% of patients with immune-related myopathy present with a dermatomyositis-like rash, and those with this rash often have high titers of autoantibodies against TIF1γ (25). In most instances, muscle biopsies commonly exhibit notable necrosis, macrophagy, and muscle regeneration, along with perivascular inflammatory infiltrates marked by a significant abundance of macrophagic cells (26). In prior research, transcriptomic analysis of muscle biopsies has revealed 3 distinct types of ICI-myositis. The IL-6 pathway was overexpressed across all groups. Type I interferon pathway activation was unique to ICI-DM (dermatomyositis). In contrast, the type 2 IFN pathway was overexpressed in ICI-DM and ICI-MYO1. Myocarditis was observed exclusively in ICI-MYO1 patients (23).
MG is an autoimmune disorder characterized by impaired neuromuscular transmission due to autoantibodies targeting postsynaptic membrane components at the neuromuscular junction. A retrospective clinical study on ICI-induced MG reported a serum anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibody positivity rate of approximately 66% and an AsM-Ab positivity rate of about 67%. A noteworthy observation is that a small subset of patients demonstrated anti-AChR antibodies before initiating ICI treatment, with antibody titers increasing by at least twofold following treatment. Elevated serum CPK levels were also observed in 84% of the patients, and those with elevated CPK levels were more likely to experience respiratory failure. Overall, the mortality rate among patients with ICI-related MG was approximately 37%, with 15% succumbing to complications related to MG (27).
The precise mechanism underlying NAEs remains poorly understood; however, several contributing factors have been identified (1): ICIs may deplete regulatory T cells (Tregs), leading to a loss of immune tolerance (28); (2) ICIs can elevate the titers of preexisting autoantibodies that target normal nervous system tissues, and may also enhance cross-reactivity between antigens shared by tumor cells and normal neurons (29); (3) pro-inflammatory factors such as C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL)-10, C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL)-3, CCL4, CCL5, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) have been found elevated in prior studies (30). (4) The activation of the complement system may further promote an inflammatory response (31). (5) Specific gut microbiota modulate immune and nervous system functions, thereby influencing the pathophysiological processes associated with neuroinflammation and neural injury (32, 33). Given that potential pathogenic mechanisms underlying NAEs may involve shared antigens between tumors and normal tissues, there may be a possible association between the occurrence of NAEs and the type of primary tumor. In this study, the tumor types most frequently associated with NAEs following ICI treatment include lung cancer, malignant melanoma, renal cancer, hepatic cancer, and breast cancer.
According to Common Terminology Criteria for AEs, for irAEs exceeding Grade 2, glucocorticoids are the first-line therapy for NAEs. Additionally, the high-dose pulse therapy is usually applied to control symptoms rapidly. For those who do not respond well to glucocorticoids, it may be necessary to consider using other agents such as intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), immunosuppressants, rituximab, TNF-α antibodies, and interleukin-6 receptor inhibitors. Patients experiencing Grade ≥3 irAEs need to discontinue ICIs permanently (34–36). Immune-related markers, including peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets and pro-inflammatory factors, in patients undergoing ICI therapy may aid in predicting the onset of NAEs. Nonetheless, effective preventive strategies remain insufficient, and the prophylactic administration of medications such as glucocorticoids is discouraged due to potential complications, including severe infections. Despite these challenges, achieving an early and accurate diagnosis following the emergence of NAEs and administering treatment tailored to the severity of the condition can enhance patient prognosis. Thus, engaging a multidisciplinary team in decision-making is essential for patients undergoing ICI treatment. Furthermore, discontinuation of tumor therapy may compromise treatment effectiveness, whereas severe neurological irAEs could potentially impact patient survival.
Previous research indicated that the occurrence of irAEs may be associated with the therapeutic efficacy of ICIs. Patients who experience irAEs exhibit a 23-fold higher probability of clinical response than those without irAEs, suggesting that irAEs might indicate an immune response against tumors. Correspondingly, patients with effective tumor regression are more likely to develop autoimmune toxicity. Therefore, oncologists should remain highly vigilant for the occurrence of NAEs in patients with tumor regression following ICI treatment. However, the underlying mechanism of this association remains unclear (37).
In this study, the proportion of total death cases among all ICI-induced NAEs included was 23.7%. Death rates for different NAEs ranged from 1.96% to 30.63%, with myositis and dermatomyositis exhibiting the highest mortality rate (30.63%) and CIDP the lowest (1.96%). Moreover, we found that some PTs are associated with the severity of outcomes. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between severe and non-severe cases across various NAEs, including aseptic meningitis, AIE, CIDP, GBS, MG, myelitis, and immune-related myopathy.
Similar to other spontaneous reporting systems, the FAERS and JADER databases have inherent limitations. Thus, it exclusively documents drug-related adverse reactions, rendering it inadequate for assessing the incidence of specific AEs within the general population. The databases comprise complex data sources characterized by substantial missing information, including variables such as gender, age, dosage, and method of administration. Additionally, challenges such as non-standardized reporting nomenclature, redundant reports, and non-professional reporters may introduce reporting bias. Within the FAERS and JADER, reports are not required to establish a causal link between drugs and adverse events prior to submission. The disproportionality analysis employed can only indicate a statistical association rather than establish causation between ICIs and NAEs. This study focused on data where ICIs were identified as the primary suspect (PS) agents, without accounting for the potential influence of patients’ concurrent medications and other variables such as infections. This limitation complicates the task of distinguishing signals attributable solely to ICIs from those arising from the combined effects of concurrent medications. Consequently, large-scale epidemiological studies are necessary for future validation.
5 Conclusion
This study has demonstrated a significant association between ICIs and certain NAEs, including AIE. While NAEs occur less frequently than irAEs affecting other organ systems, their clinical impact can be severe, leading to life-threatening complications and necessitating vigilant monitoring. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of these complications, facilitating earlier detection and more effective management strategies for patients undergoing ICI therapy. The insights gained may help clinicians optimize treatment protocols while minimizing neurological risks associated with immunotherapy. Significantly, consensus guidelines currently rely on empirical data. Therefore, future large-scale prospective clinical studies will be essential for investigating the pathogenesis of NAEs and developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
XD: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XS: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FG: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. JW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82271384).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the FAERS and JADER for providing the data in this study. Also, the authors thank AiMi Academic Services (www.aimieditor.com) for English language editing and review services.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1621045/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Naimi A, Mohammed RN, Raji A, Chupradit S, Yumashev AV, Suksatan W, et al. Tumor immunotherapies by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); the pros and cons. Cell Commun Signal CCS. (2022) 20:44. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00854-y
2. Arafat Hossain M. A comprehensive review of immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer treatment. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 143:113365. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113365
3. Ramos-Casals M, Brahmer JR, Callahan MK, Flores-Chávez A, Keegan N, Khamashta MA, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Dis Primer. (2020) 6:38. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-0160-6
4. Nannini S, Koshenkova L, Baloglu S, Chaussemy D, Noël G, and Schott R. Immune-related aseptic meningitis and strategies to manage immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A systematic review. J Neurooncol. (2022) 157:533–50. doi: 10.1007/s11060-022-03997-7
5. Narumi Y, Yoshida R, Minami Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeguchi S, Kano K, et al. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder secondary to treatment with anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab: The first report. BMC Cancer. (2018) 18:95. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-3997-2
6. Hirano S, Kojima A, Nakayama Y, Takeda T, Kishimoto T, Takahashi T, et al. A case report of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder induced by pembrolizumab treatment for lung adenocarcinoma: A clinical and immunohistochemical study. BMC Neurol. (2022) 22:483. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02987-6
7. Liu Q, Wang B, and Zhao W. MOG-IgG-associated demyelination induced by pembrolizumab treatment in a patient with Malignant melanoma. Neurology. (2022) 98:501–2. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200055
8. Erritzøe-Jervild M, Møller SN, Kruuse C, and Stenør C. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related CNS vasculitis - a systematic review and report of 6 cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc. (2025) 34:108265. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2025.108265
9. Dalmau J and Graus F. Antibody-mediated encephalitis. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:840–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1708712
10. Velasco R, Villagrán M, Jové M, Simó M, Vilariño N, Alemany M, et al. Encephalitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review. JAMA Neurol. (2021) 78:864–73. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0249
11. van Puijenbroek EP, Bate A, Leufkens HGM, Lindquist M, Orre R, and Egberts ACG. A comparison of measures of disproportionality for signal detection in spontaneous reporting systems for adverse drug reactions. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. (2002) 11:3–10. doi: 10.1002/pds.668
12. Evans SJ, Waller PC, and Davis S. Use of proportional reporting ratios (PRRs) for signal generation from spontaneous adverse drug reaction reports. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. (2001) 10:483–6. doi: 10.1002/pds.677
13. Bate A, Lindquist M, Edwards IR, Olsson S, Orre R, Lansner A, et al. A Bayesian neural network method for adverse drug reaction signal generation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (1998) 54:315–21. doi: 10.1007/s002280050466
14. Dumouchel W. Bayesian data mining in large frequency tables, with an application to the FDA spontaneous reporting system. Am Stat. (1999) 53:177–90. doi: 10.1080/00031305.1999.10474456
15. Triggianese P, Novelli L, Galdiero MR, Chimenti MS, Conigliaro P, Perricone R, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced autoimmunity: The impact of gender. Autoimmun Rev. (2020) 19:102590. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102590
16. Kao JC, Liao B, Markovic SN, Klein CJ, Naddaf E, Staff NP, et al. Neurological complications associated with anti-programmed death 1 (PD-1) antibodies. JAMA Neurol. (2017) 74:1216–22. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.1912
17. Spain L, Walls G, Julve M, O’Meara K, Schmid T, Kalaitzaki E, et al. Neurotoxicity from immune-checkpoint inhibition in the treatment of melanoma: A single centre experience and review of the literature. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2017) 28:377–85. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw558
18. Couey MA, Bell RB, Patel AA, Romba MC, Crittenden MR, Curti BD, et al. Delayed immune-related events (DIRE) after discontinuation of immunotherapy: Diagnostic hazard of autoimmunity at a distance. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:165. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0645-6
19. Vogrig A, Muñiz-Castrillo S, Joubert B, Picard G, Rogemond V, Marchal C, et al. Central nervous system complications associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2020) 91:772–8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-323055
20. Farina A, Villagrán-García M, Ciano-Petersen NL, Vogrig A, Muñiz-Castrillo S, Taillandier L, et al. Anti-hu antibodies in patients with neurologic side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation. (2023) 10:e200058. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200058
21. O’Hare M and Guidon AC. Peripheral nervous system immune-related adverse events due to checkpoint inhibition. Nat Rev Neurol. (2024) 20:509–25. doi: 10.1038/s41582-024-01001-6
22. Aldrich J, Pundole X, Tummala S, Palaskas N, Andersen CR, Shoukier M, et al. Inflammatory myositis in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Arthritis Rheumatol Hoboken NJ. (2021) 73:866–74. doi: 10.1002/art.41604
23. Pinal-Fernandez I, Quintana A, Milisenda JC, Casal-Dominguez M, Muñoz-Braceras S, Derfoul A, et al. Transcriptomic profiling reveals distinct subsets of immune checkpoint inhibitor induced myositis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:829–36. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223792
24. Liewluck T, Kao JC, and Mauermann ML. PD-1 inhibitor-associated myopathies: Emerging immune-mediated myopathies. J Immunother Hagerstown Md 1997. (2018) 41:208–11. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000196
25. Guerra NL, Matas-García A, Serra-García L, Morgado-Carrasco D, Padrosa J, Aldecoa I, et al. Dermatomyositis unleashed by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Three additional cases and a review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103375. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103375
26. Matas-García A, Milisenda JC, Selva-O’Callaghan A, Prieto-González S, Padrosa J, Cabrera C, et al. Emerging PD-1 and PD-1L inhibitors-associated myopathy with a characteristic histopathological pattern. Autoimmun Rev. (2020) 19:102455. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102455
27. Safa H, Johnson DH, Trinh VA, Rodgers TE, Lin H, Suarez-Almazor ME, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor related myasthenia gravis: Single center experience and systematic review of the literature. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:319. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0774-y
28. Alissafi T, Hatzioannou A, Legaki AI, Varveri A, and Verginis P. Balancing cancer immunotherapy and immune-related adverse events: The emerging role of regulatory T cells. J Autoimmun. (2019) 104:102310. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102310
29. Harrison RA, Tummala S, and de Groot J. Neurologic toxicities of cancer immunotherapies: a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2020) 20:27. doi: 10.1007/s11910-020-01038-2
30. Müller-Jensen L, Schulz AR, Mei HE, Mohr R, Ulrich C, Knape P, et al. Immune signatures of checkpoint inhibitor-induced autoimmunity-A focus on neurotoxicity. Neuro-Oncol. (2024) 26:279–94. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad198
31. Nelke C, Pawlitzki M, Kerkhoff R, Schroeter CB, Aktas O, Neuen-Jacob E, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibition-related myasthenia-myositis-myocarditis responsive to complement blockade. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation. (2024) 11:e200177. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200177
32. Dubin K, Callahan MK, Ren B, Khanin R, Viale A, Ling L, et al. Intestinal microbiome analyses identify melanoma patients at risk for checkpoint-blockade-induced colitis. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10391. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10391
33. Liu W, Ma F, Sun B, Liu Y, Tang H, Luo J, et al. Intestinal microbiome associated with immune-related adverse events for patients treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors, a real-world study. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:756872. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.756872
34. Boutros C, Tarhini A, Routier E, Lambotte O, Ladurie FL, Carbonnel F, et al. Safety profiles of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies alone and in combination. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2016) 13:473–86. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.58
35. Dougan M, Luoma AM, Dougan SK, and Wucherpfennig KW. Understanding and treating the inflammatory adverse events of cancer immunotherapy. Cell. (2021) 184:1575–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.011
36. Fa’ak F, Buni M, Falohun A, Lu H, Song J, Johnson DH, et al. Selective immune suppression using interleukin-6 receptor inhibitors for management of immune-related adverse events. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:e006814. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006814
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitor, autoimmune encephalitis, immune-related adverse events, pharmacovigilance, FAERS
Citation: Di X, Shi X, Gai F and Wang J (2025) Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated autoimmune encephalitis and other neurological immune-mediated adverse events: a pharmacovigilance study using the FAERS and JADER. Front. Oncol. 15:1621045. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1621045
Received: 30 April 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 17 July 2025.
Edited by:
Zhida Liu, Shanxi Academy of Advanced Research and Innovation, ChinaReviewed by:
Tongyi Huang, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaSongyan Han, Shanxi Cancer Hospital Urology Surgery, China
Copyright © 2025 Di, Shi, Gai and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiawei Wang, d2FuZ2p3Y3FAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiaomeng Di
Xiaomeng Di Xiaohong Shi†
Xiaohong Shi† Jiawei Wang
Jiawei Wang