- 1Department of Pharmacy, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center Xiamen Hospital, Xiamen, China
Background: HLX02 is the first China-manufactured trastuzumab biosimilar. Few data are currently available about HLX02 in clinical practice. This study was designed to evaluate the real-world safety and efficacy of HLX02 in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC), as well as assessed the effectiveness of switching from trastuzumab originator (Herceptin®) to HLX02 during treatment.
Methods: Between April 2021 and October 2022, all patients with HER-2-positive MBC who received at least one cycle of HLX02 at Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center were included in a retrospective analysis. Patients were divided into two groups: the naïve group (patients treated with HLX02 from the beginning) and the switched group (patients who switched from Herceptin® to HLX02). Efficacy evaluation and adverse events were compared between the two groups.
Results: A total of 124 eligible patients were finally included, with 80 patients (64.5%) in the naïve group, 44 patients (35.5%) in the switched group. The follow-up ranged from 0.7 to 40.2 months, the effectiveness rates were 57.5% in the naïve group and 54.5% in the switched group, respectively (P=0.751). The estimated median progression-free survival (PFS) were 13.70 (95% CI: 8.634–18.766) months and 14.70 (95% CI: 6.684–22.716) months in the naive and switched groups, respectively (P=0.192). Multivariate cox regression analysis suggested that brain metastasis and the current number of treatment lines were independent predictors of MBC PFS. Compared with first-line treatment, second-line treatment and third- or later-line treatment increased the disease risk by 2.095 times (95% CI: 1.043-4.210, P=0.038) and 3.035 times (95% CI:1.751-5.262, P<0.001), respectively. The incidence and distribution of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurrence between the two groups were relatively similar, with no significant statistical difference.
Conclusions: HLX02 demonstrated favorable efficacy and safety in real-world practice comparable to those observed in previous HLX02 studies. Switching between trastuzumab originator and biosimilar for MBC treatment had no impact on efficacy and did not increase safety risks.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer remains one of the most common malignancies worldwide. In 2022, 2.3 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer, and 670,000 women died from the disease (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer).
Human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER2), a growth factor receptor gene, women with breast cancers that overexpress HER2 have an aggressive form of the disease, with significantly shortened disease-free survival and overall survival (1). Trastuzumab (Herceptin®, Genentech/Roche, Inc.), a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against the extracellular domain of HER2, specifically acts on HER2 on cancer cell surfaces and has significantly improved patient prognosis, was approved for treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer and for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (2). However, its high cost makes it unaffordable for patients in developing countries such as China (3, 4).
The main advantages of biosimilars were cost savings and lower prices, it is essential to provide oncologists with comprehensive data on the safety and effect, and real-world evidence of biosimilars (5). Biosimilars are developed by different manufacturers, replicating the complex structures and maintaining similar therapeutic efficacy and safety profiles as the original innovator drugs is important (6). At present, many countries are committed to the development of trastuzumab biosimilars, comparing the biosimilars with trastuzumab originator (Herceptin®) (7–12). HLX02 (Zercepac®, Henlius, Inc.), launched in China in 2020, was the first China-manufactured trastuzumab biosimilar (13–16). It is more cost-effective than Herceptin® in China based on willingness-to-pay thresholds (17). A multicenter real-world has shown HLX02 and Herceptin® to have equivalent efficacy and adverse events in HER-2-positive breast cancer (18). However, real-world data on the safety and efficacy of HLX02 still remain limited, especially regarding switching from Herceptin® to HLX02.
This study aimed to evaluate HLX02’s efficacy and safety based in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC), and assess the effectiveness of switching from Herceptin® to HLX02 during treatment. It seeks to provide evidence for the clinical substitution of biosimilars in China.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and patients
This study was a retrospective, single-center, non-intervention real-world study. Patients who started therapy naïve to HLX02 and who switched from Herceptin® were collected at Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center between April 2021 to October 2022. The major inclusion criteria were (a) patients with a pathological diagnosis of HER-2-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC), HER2 positivity was defined as immunohistochemistry (ICH) 3+ or 2+/fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) amplification;(b) patients older than 18 years; (c) Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score 0–2. The main exclusion criteria were (a) patients with incomplete medical records, with missing values exceeding 30%; (b) patients with prior or concurrent malignancies (other than thyroid cancer or cancer in situ of other organs).
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center (No.2021-121-2424).
2.2 Data collection
Data variables collected from the patient’s medical records included the following categories: (a) demographic and clinical characteristics, such as sex, age, menopausal status, estrogen receptor status, Ki67 level, metastasis, comorbidities and ECOG performance score; (b) drugs and outcomes, such as trastuzumab utilization patterns, efficacy evaluation; (c) abnormal clinical or laboratory findings, such as nausea, diarrhea, leukopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia etc. Data and follow-up records were updated as of September 30, 2024.
2.3 Treatment and dosage information
In salvage treatment of MBC, the initial loading dose of HLX02 or Herceptin® was 8mg/kg, and the maintenance dose is 6mg/kg once a time, and it is administered once every 3 weeks. The salvage treatment regimen of HLX02 combined with other anti-tumor drugs was determined by the clinical doctor. The study did not intervene.
2.4 Assessments and definition of outcomes
Efficacy endpoints were assessed based on imaging reports following Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST 1.1 version). The outcomes were effectiveness rate and the progression-free survival (PFS). In HLX02-naïve patients, if the best overall response of complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) was achieved, HLX02 was considered “effective”. In patients who switched from Herceptin® to HLX02, if the best overall response remains the same as before the switch or improved somewhat, HLX02 was considered “effective” (19). PFS was defined as the time from initiation of HLX02 or Herceptin® treatment until disease progression, including any recurrence or death from any cause.
Safety endpoints were assessed and grated based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v5.0 grading. The evaluation of adverse events included general adverse events and adverse event of special interest. The predefined adverse event of special interest was cardiotoxicity (such as palpitation, ventricular arrhythmia and reduced left ventricular function) and infusion-related reaction.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Normally distributed continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and were calculated by an independent samples t test. Non-normally distributed variables were summarized as median values, range, and were compared by Mann–Whitney U test. Differences between categorical variables were assessed using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for PFS analysis, and the log-rank test was used to determine statistically significant variables. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed with the Cox proportional hazards regression model. Hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were determined. A two-sided P-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, and comparisons between groups were conducted with the log-rank test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical plotting was performed using GraphPad Prism software (version 10.1.2, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 25.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3 Result
3.1 Patient characteristics
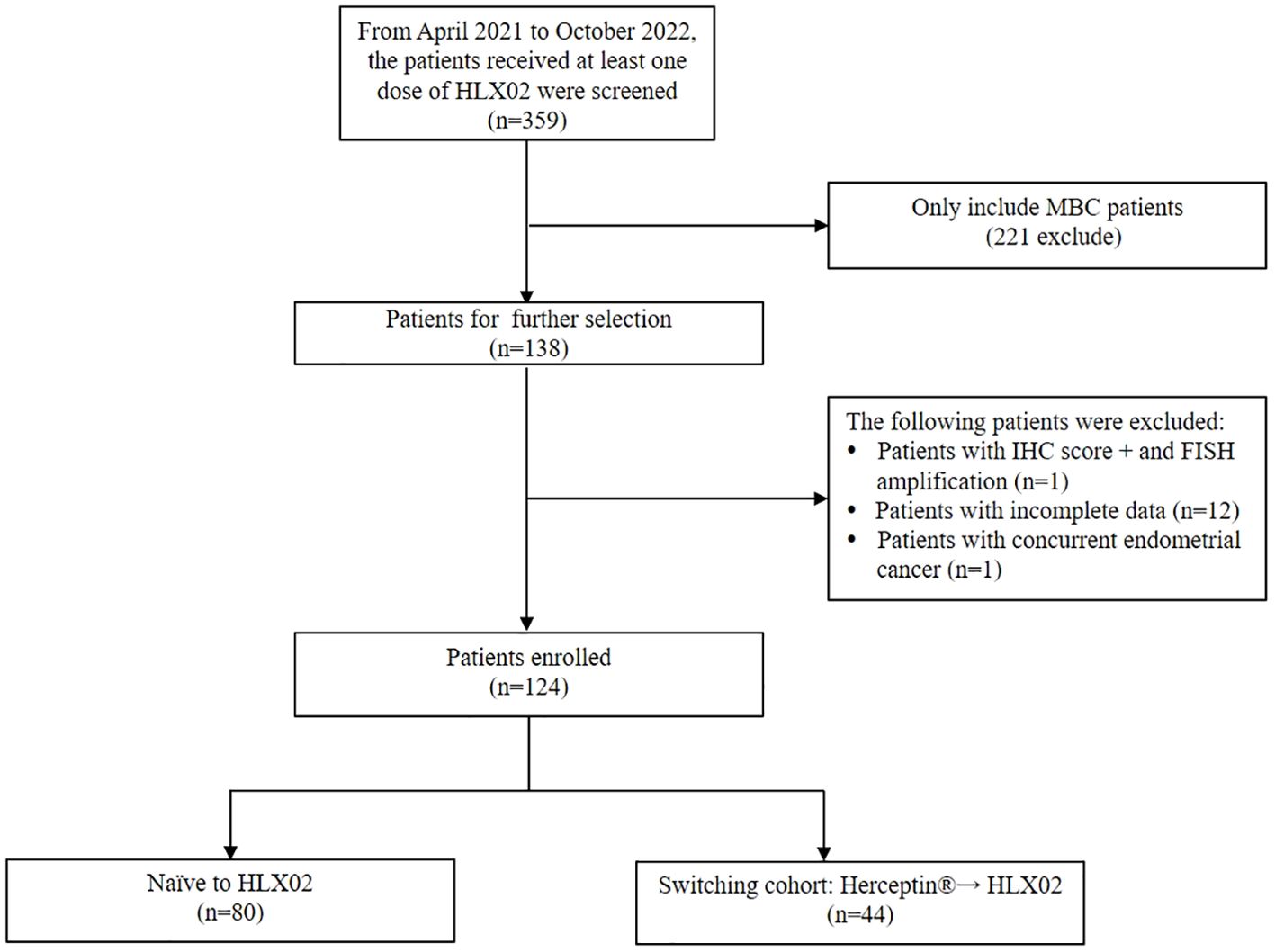
From April 2021 to October 2022, 359 patients received at least one dose of HLX02 were screened (Figure 1). Among them, 124 MBC patients were included in our study. Patients were classified into two groups according to their prior trastuzumab treatment status: 80 patients (64.5%) were naïve to HLX02, 44 patients (35.5%) switched from the originator Herceptin® to HLX02, respectively. In the switched group, the median exposure time of Herceptin® and HLX02 was 5.4 months (range, 0.8-51.3) and 5.1 months (range, 0.8-35), respectively. The median cycles of Herceptin® and HLX02 were 7 and 7, respectively.
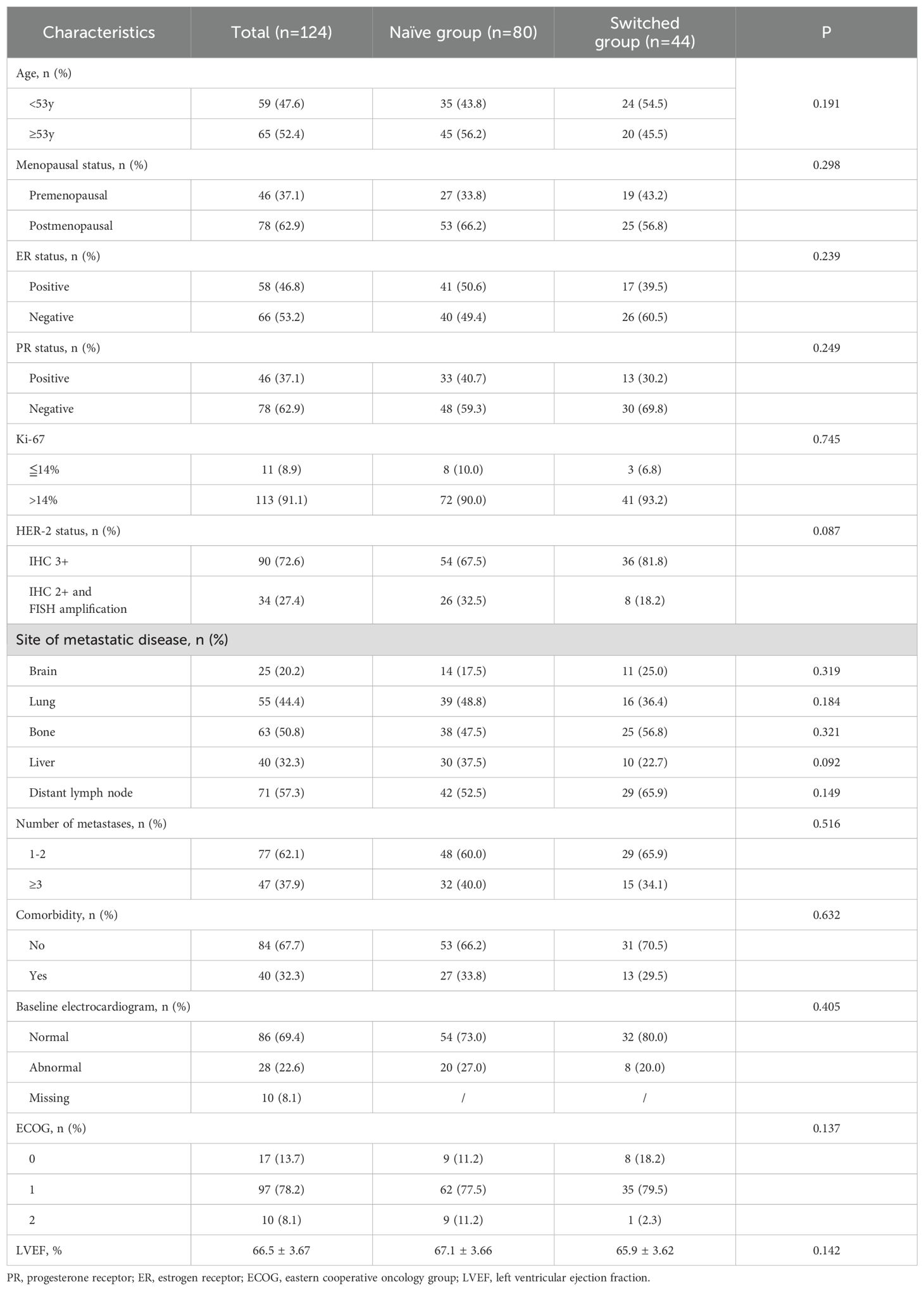
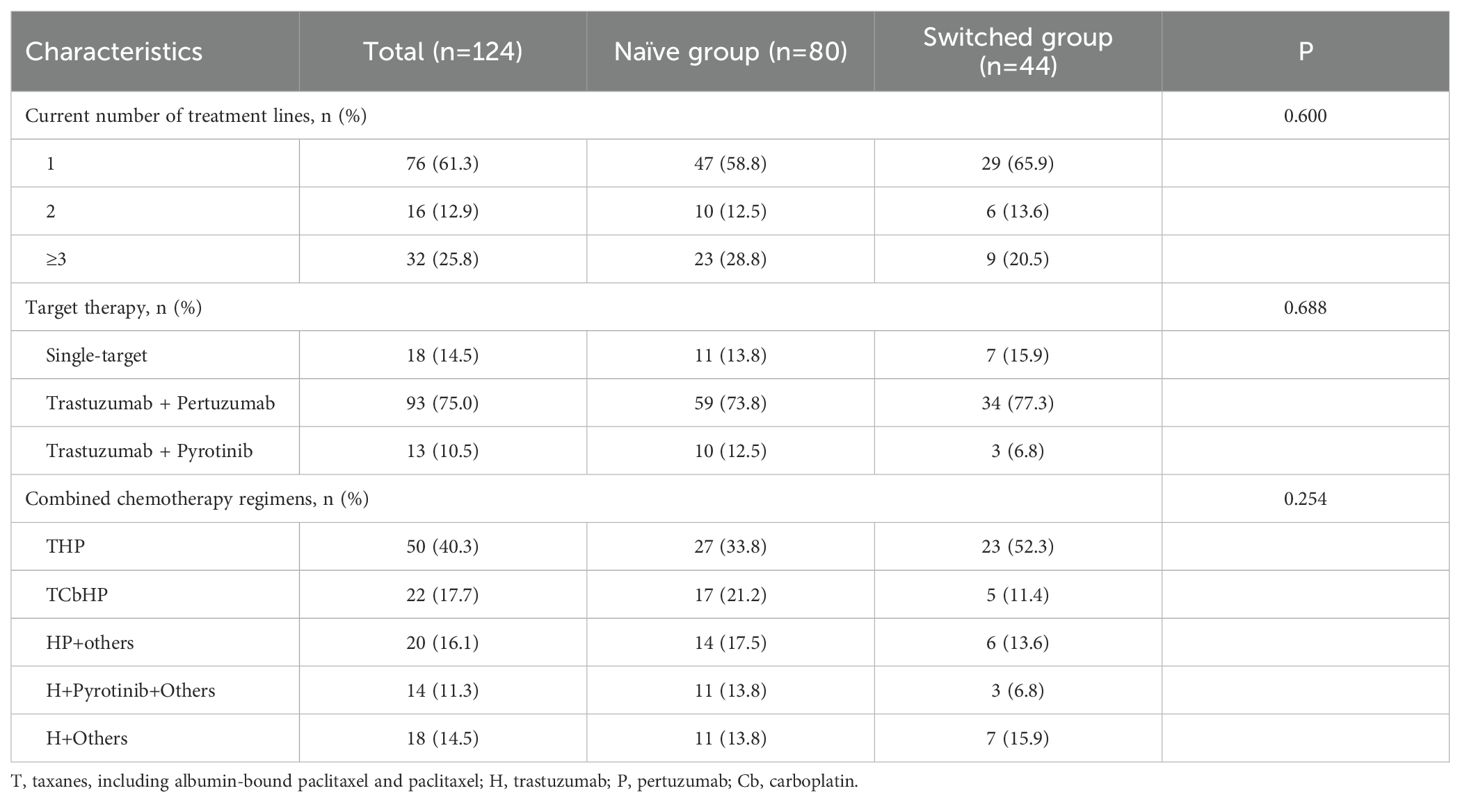
The demographics and clinical characteristics of the population are presented in Tables 1 and 2. All patients were female, the median age was 53 (range, 27-79) years. 78 (62.9%) patients were postmenopausal, 58 (46.8%) patients were ER positive, 46 (37.1%) patients were PR positive. Among them, 77 patients (62.1%) had 1 or 2 sites metastases, 47 patients (37.9%) had 3 or more sites metastases. 76 patients (61.3%), 16 patients (12.9%), 32 patients (25.8%) had who had previously received first-line, second-line, and third- or later-line treatments, respectively. The trastuzumab, pertuzumab and taxanes (THP) was the most commonly used dual-target therapy regimen. There were no significant statistical differences in demographics and clinical characteristic between the naïve group and switched group.
3.2 Efficacy results
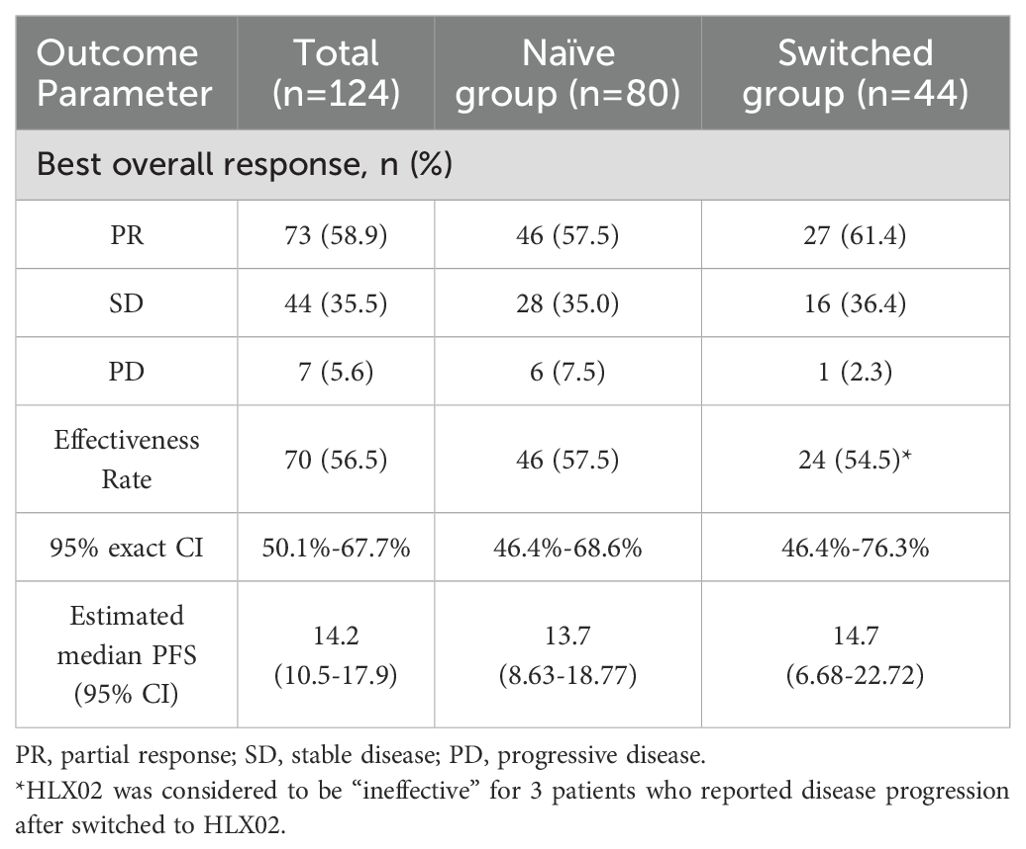
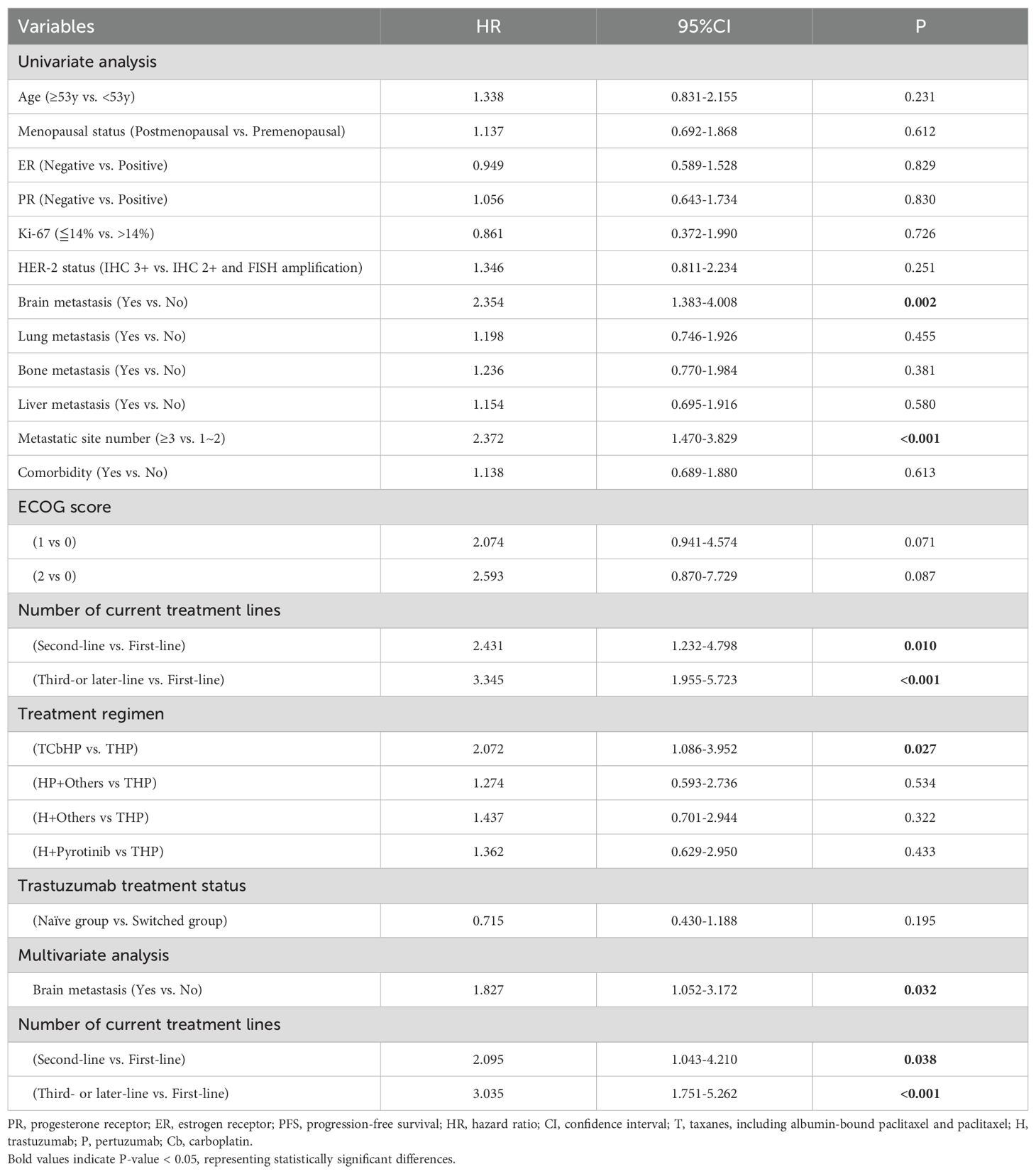
The follow-up ranged from 0.7 to 40.2 months, based on the RECISTv1.1 criteria for clinical efficacy evaluation, no patients achieved CR, 73 patients (58.9%) achieved the best response of PR, 44 patients (35.5%) achieved SD. Among them, 7 patients (5.6%) had PD and one patient eventually died due to disease progression. HLX02 was rated as “effective” in 46 (57.5%) of naïve patients and in 24 (54.5%) of switched patients (P=0.751) (Table 3). The median PFS is shown in Figure 2, which was 14.2 months (95% CI: 10.5 - 17.9). The results of univariate analysis indicated that the number of metastases, brain metastasis, the number of current treatment lines (second-line vs. first-line, third- or later-line vs. first-line), and treatment regimens (TCbHP vs. THP) were the influencing factors for the survival period of MBC. However, trastuzumab switching during treatment had no impact on the survival period, as shown in Table 4. Multivariate Cox analysis suggested that brain metastasis and the number of current treatment lines were the independent predictors of MBC PFS. Compared with first-line treatment, second-line treatment and third- or later-line above treatment increased the disease risk by 2.095 times (95% CI: 1.043-4.210, P = 0.038) and 3.035 times (95% CI: 1.751-5.262, P < 0.001), respectively.
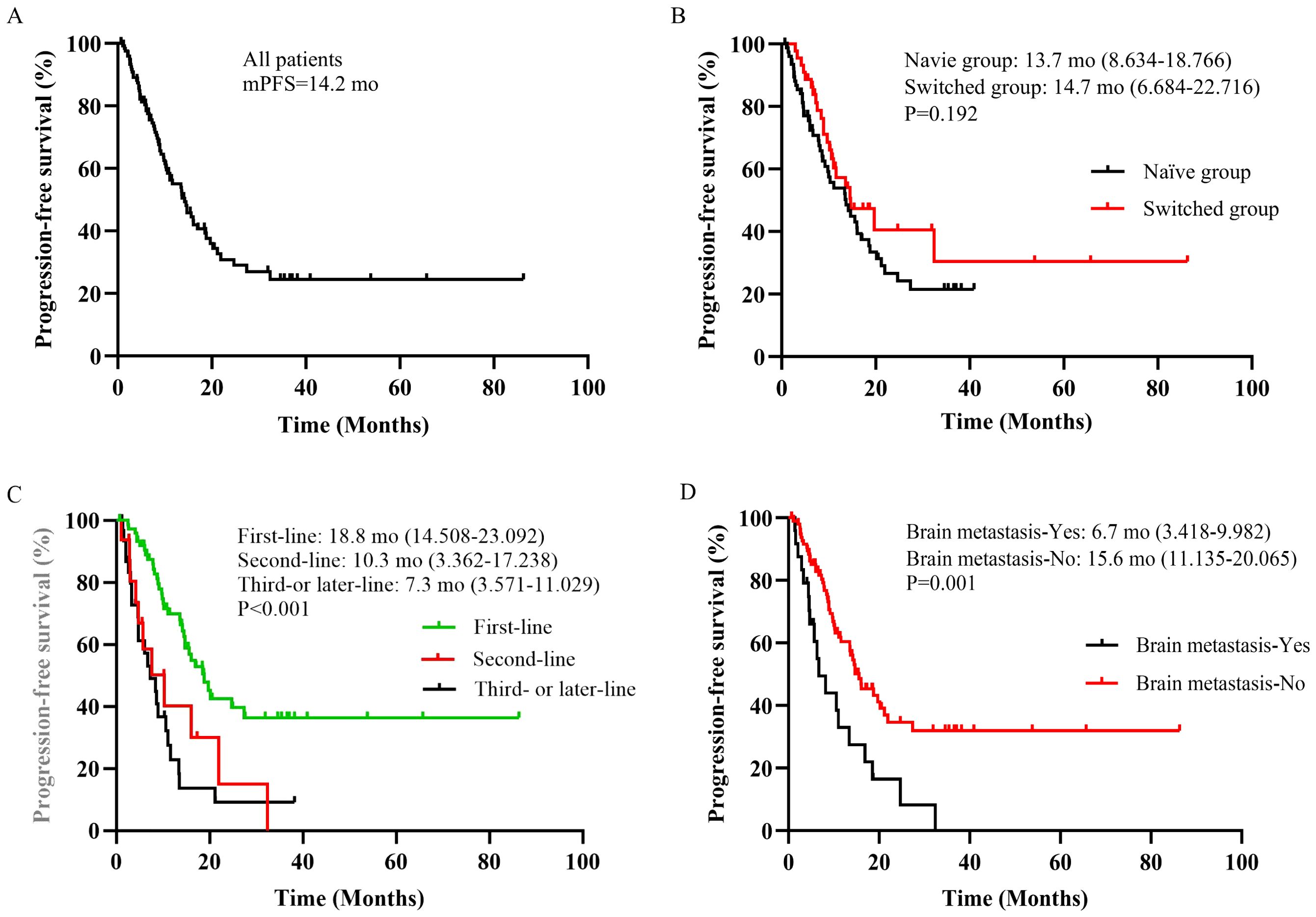
Figure 2. (A) Overall cohort. (B) Patients stratified by trastuzumab treatment status. (C) Patients stratified by current number of treatment lines. (D) Patients stratified by brain metastasis. mo, months.
3.3 Safety
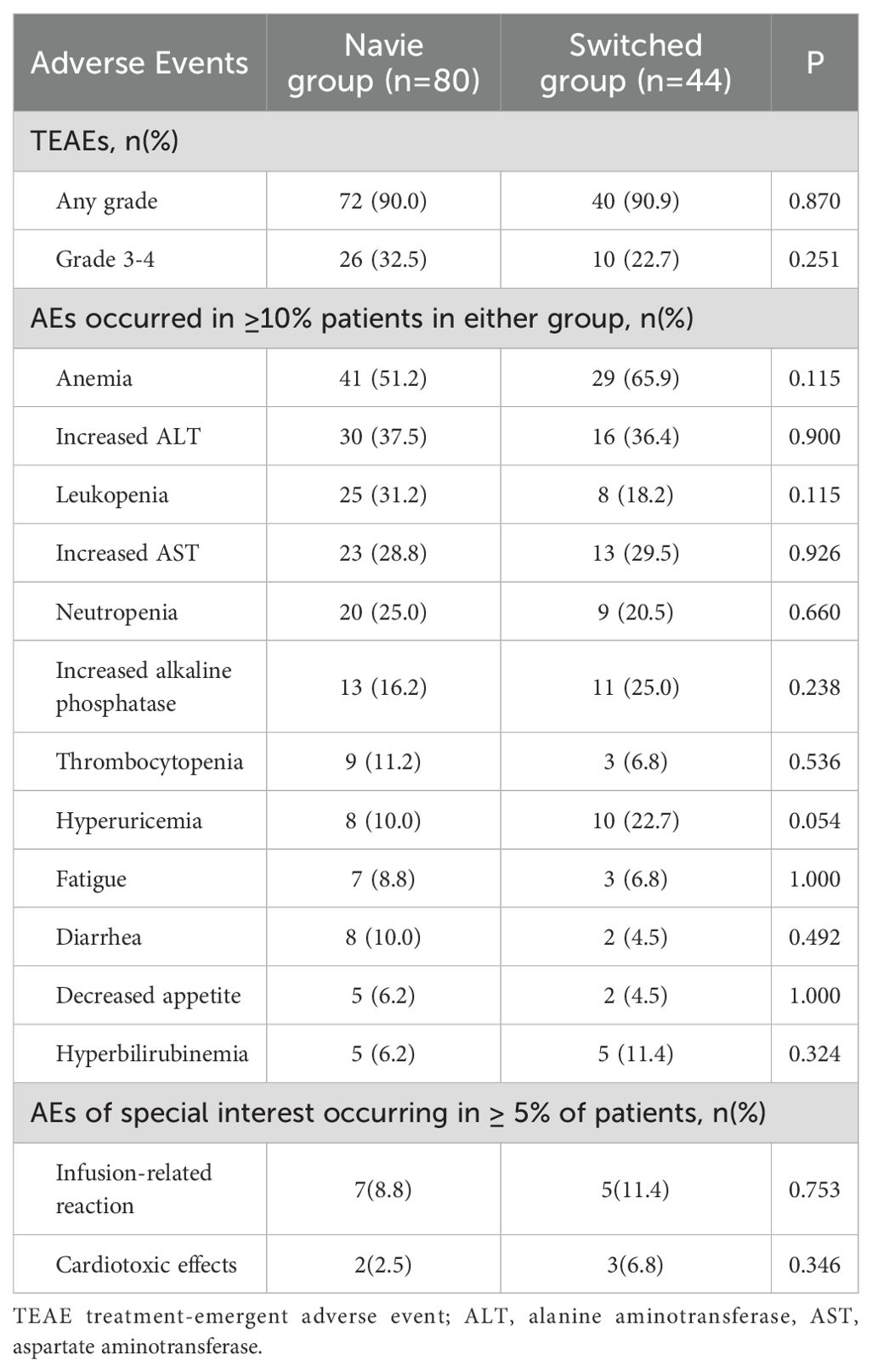
During the study period, a total of 375 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were occurred, involving 112 patients (90.3%). The severity of most TEAEs was grade 1-2, and 36 patients (29.0%) occurred 120 episodes of grade 3–4 TEAEs. As shown in Table 5, the incidence of any-grade TEAEs between the naïve group and the switched group were similar, and there were no significant differences (72 patients [90.0%] vs. 40 patients [90.9%], P=0.870). The incidence of grade 3–4 TEAEs was higher in the naïve group than that in the switched group, but the difference was not statistically significant (26 patients [32.5%] vs. 10 patients [22.7%], P=0.251). The most common (≥10%) TEAEs were hematological toxicity and liver function abnormalities, exhibiting anemia (51.2% vs 65.9%, P=0.115), increased ALT (37.5% vs 36.4%, P=0.900), leukopenia (31.2% vs 18.2%, P=0.115), increased AST (28.8% vs 29.5%, P=0.926), neutropenia (25.0% vs 20.5%, P=0.660), but there was no significant difference between the two groups. One death case was occurred due to disease progression, but it was recorded as not related to HLX02. No new safety signals detected during the real-world practice.
It is worth noting that infusion-related reaction and cardiotoxicity were reported, a total of 12 patients developed infusion-related reactions, with 7 patients (8.8%) in the naïve group, and 5 patients (11.4%) in the switched group (P=0.753). A total of 5 patients reported cardiotoxicity, with 2 patients (2.5%) in the naïve group and 3 patients (6.8%) in the switched group, and there was no significant difference between the two groups (P=0.346).
4 Discussion
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of HLX02 in patients with MBC based on real-world clinical data, and provided evidence for the effectiveness of trastuzumab switching during treatment.
As the first China-manufactured trastuzumab biosimilar, HLX02 is approved in Europe (EU) and China, Zhou et al. confirmed that HLX02 is bioequivalent to the originator Herceptin®, with similar safety and immunogenicity profiles (16). Xu et al. shows that the objective response rate (ORR) at week 24 (71.3%), PFS (11.7 months), and OS (not reached) observed in the HLX02 treatment group (18). In addition, after a median follow-up duration of 35.0 months, 39.5% patients had died in the HLX02 group, median overall survival (OS) was 37.3 months, with a 3-year OS rate of 57.5%. Median PFS at this long-term follow-up assessment was 11.7 (95% CI 11.5, 12.1) months for the HLX02 group (15).
However, there are few studies on the real-world clinical application of HLX02 in the treatment of HER-2 positive MBC, especially in combination with other antitumor agents, such as pertuzumab. Deng et al. demonstrated that 32 patients (86.5%) achieved CR, 2 patients (5.4%) achieved PR in the HLX02 group (20). However, as the majority (6/96, 93.8%) of the included patients were in the early stage, this study has certain limitations for MBC. Our study focused on patients with MBC, and the results showed that 73 patients (58.9%) achieved PR, but no patients achieved CR. After a median follow-up of 0.7-40.2 month, the median PFS for HLX02 first-line treatment was 18.8 months, and the median PFS for second-line treatment was 10.3 months, the median PFS of third- or later-line treatment was 7.3 months. In previous phase III studies, the median PFS of trastuzumab or trastuzumab biosimilar combined with taxanes in first-line treatment of MBC was 10.6-12.8 months (8, 12, 18, 21, 22). At present, there are few efficacy data about second-line or later treatment of HLX02 in MBC. In the Phase II clinical trial of HLX02, 45 patients with HER-2 positive MBC were enrolled to receive HLX02, pertuzumab and physician selection chemotherapy, 12 patients (26.7%) were treated with second-line therapy, 33 patients (73.3%) were treated with third- or later-line treatment (23). Median follow-up was 1.2-43.9 months, the median PFS for second-line treatment was 6.26 months (range: 0-18.9), and the median PFS for third- or later-line treatment was 7.6 months (range: 4.8-10.3) (23). The results of our study were slightly different from the Phase II/III trial. The possible reasons are as follows: (1) the efficacy results might be affected by the characteristics of the enrolled patients, previous treatment experiences, and methodological factors (such as dosing regimens and efficacy assessment); (2) in the treatment regimen of the phase III trial, pertuzumab was not added. However, in real-world practice, more than 75% of patients received “trastuzumab plus pertuzumab” dual-targeted therapy, which to some extent increased the PFS.
In this study, 44 patients (35.5%) MBC patients experienced switching between trastuzumab originator and biosimilar. At present, the available research data are limited regarding whether the switching between the originator and biosimilar would have an impact on efficacy and safety. The LILAC study reported that among 342 HER-2 positive EBC patients who received neoadjuvant Herceptin® treatment, 171 patients switched to trastuzumab biosimilar ABP 980 during the postoperative adjuvant treatment (24). In terms of prognosis, there was no significant statistical difference in disease progression, recurrence or mortality between the switched group and the non-switched group (HR = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.181 - 1.292); in terms of safety, there was no significant statistical difference in the overall AE incidence (26.3% vs. 22.8%, P > 0.05) and the incidence of severe AEs (7.6% vs. 6.4%, P > 0.05) between the two groups after a follow-up of 12.0 months; in terms of immunogenicity, the positive rate of anti-drug antibodies in the switched group was 1.2%, which was higher than 0.6% in the non-switched group (24). Overall, after the one-way switch (originator→biosimilar), the efficacy, safety and immunogenicity indicators of HER-2 positive breast cancer patients did not undergo significant changes. We also conducted a preliminary exploration on the impact of trastuzumab switching on outcome indicators during the research. No significant differences were observed in effectiveness rates for patients in the naïve group or in the switched group. Furthermore, the univariate analysis showed that trastuzumab switching had no impact on PFS (P=0.195).
One strength of our study is that it included the heterogeneous characteristics of clinical practice, that is more representative of entire patient population than the carefully selected individuals in clinical trials. A network meta-analysis evaluated efficacy and serious adverse reactions among various trastuzumab biosimilars and trastuzumab originator. The cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) probability indicated that the ORR from best to worst was CT-P6, Herceptin, HLX02, PF-05280014, R-TPR-016, BCD-022, MYL-1401O, SB3. There was no statistical difference in both ORR and pathological complete response (pCR) of various trastuzumab biosimilars and Herceptin except SB3 (25). According to the result, HLX02 performs might be an optional trastuzumab biosimilar compared with others in China.
The SUCRA probability indicated that severe AEs from best to worst was MYL-1401O, Herceptin, PF-05280014, SB3, HLX02, BCD-22, CT-P6 (25). Our study showed that the safety profiles were comparable with the known safety profiles of trastuzumab in patients with breast cancer (18, 20). Anemia, increased ALT and AST, leukopenia, neutropenia, increased alkaline phosphatase and thrombocytopenia were the most common TEAEs identified in this study. These events were also consistent with previous studies of trastuzumab biosimilars (8, 12, 19, 20). There were no notable differences between the naïve group and the switched group regarding the type, incidence, or severity of TEAEs. Trastuzumab has been reported in most research as related to increased risks of cardiac toxicity (26, 27). Thus, cardiotoxicity in the two groups were carefully assessed. The frequency of related events was low and similar between the two groups (2 vs. 3 patients), and without significant differences in this study.
The irrational use can be found both in resource-abundant regions and in resource-limited regions in China. A study showed the patients who lived in areas with a relatively high gross domestic product were more likely to receive trastuzumab originator than those in areas with a lower gross domestic product (28). In developing countries such as China, where biopharmaceuticals often limit patient access due to high costs, biosimilars provide an additional treatment option for enabling patient access, the introduction of biosimilars into clinical practice is necessary to sustainably reduce the healthcare burden. Treatment with biosimilars is not only a direct cost-saving approach, but also drives the clinical practice of new therapies and drugs (29). This study offers reliable real-world evidence for assessing the quality and safety of HLX02 as a crucial foundation for future evaluations. Switching to different trastuzumab combinations regimens for cancer treatment had no effects on PFS and did not increase safety risks. These real-world findings could help to optimize HER-2 therapy in advanced breast cancer, especially in regions with limited access to these expensive targeted drugs.
This study has several limitations. Firstly, as it utilizes retrospective real-world data with limited sample of patients using HLX02. Limited sample may lead to low statistical power of the association analysis, so it is necessary to expand the sample size and conduct a large-scale clinical trial with multi-center cooperation. Future studies with larger sample sizes also could validate stratified analysis based on the co-administered drugs, such as adjunctive medications, target therapy or combined with different chemotherapy. Secondly, patients are recruited from single centers and only included Chinese populations. As such, the findings are probably representative in this region, may not be generalizable globally. Finally, the patients received trastuzumab in combination with other drugs during the treatment, it may interfere whether some adverse events were caused by trastuzumab.
5 Conclusion
This study provided the real-world use of trastuzumab originator and its biosimilars (HLX02), the safety and efficacy of biosimilars were confirmed. These findings offered valuable information for implementation of switching from trastuzumab originator to a biosimilar.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center (No.2021-121-2424). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Without intervention in the patients’ treatment, this study is a retrospective analysis.
Author contributions
XY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Software, Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Methodology, Conceptualization. LW: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Software. WL: Software, Visualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. MW: Supervision, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Validation. ZG: Conceptualization, Resources, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. HS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. QZ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation, Project administration, Conceptualization, Visualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QD: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. QZ was supported by the Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (SHDC2020CR3085B).
Acknowledgments
We appreciated all patients who contributed to this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chia S, Norris B, Speers C, Cheang M, Gilks B, Gown AM, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 overexpression as a prognostic factor in a large tissue microarray series of node-negative breast cancers. J Clin Oncol. (2008) 26:5697–704. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.8659
2. Wyrwicz L, Rodriguez SC, Sanchez-Rovira P, Lewis S, Sandschafer D, and San T. Real-world clinical scenarios during introduction of trastuzumab biosimilar for HER2-positive breast cancer in the European Union. Future Oncol. (2024) 20:821–32. doi: 10.2217/fon-2023-0421
3. Lammers P, Criscitiello C, Curigliano G, and Jacobs I. Barriers to the use of trastuzumab for HER2+ Breast cancer and the potential impact of biosimilars: A physician survey in the United States and emerging markets. Pharm (Basel). (2014) 7:943–53. doi: 10.3390/ph7090943
4. Cherny N, Sullivan R, Torode J, Saar M, and Eniu A. ESMO European Consortium Study on the availability, out-of-pocket costs and accessibility of antineoplastic medicines in Europe. Ann Oncol. (2016) 27:1423–43. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw213
5. Bas TG and Duarte V. Biosimilars in the era of artificial intelligence-international regulations and the use in oncological treatments. Pharm (Basel). (2024) 17(7):925. doi: 10.3390/ph17070925
6. Cazap E, Jacobs I, McBride A, Popovian R, and Sikora K. Global acceptance of biosimilars: importance of regulatory consistency, education, and trust. ONCOLOGIST. (2018) 23:1188–98. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0671
7. Mamori T, Tanioka M, Takada K, Hamano H, Tsukioki T, Takahashi Y, et al. Real-World comparative analysis of trastuzumab originator and biosimilars: safety, efficacy, and cost effectiveness. BIODRUGS. (2025) 39:131–42. doi: 10.1007/s40259-024-00686-x
8. Rugo HS, Barve A, Waller CF, Hernandez-Bronchud M, Herson J, Yuan J, et al. Effect of a proposed trastuzumab biosimilar compared with trastuzumab on overall response rate in patients with ERBB2 (HER2)-Positive metastatic breast cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2017) 317:37–47. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.18305
9. Stebbing J, Baranau YV, Baryash V, Manikhas A, Moiseyenko V, Dzagnidze G, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of CT-P6 versus trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: final results from a randomized phase III trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2021) 188:631–40. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06240-5
10. Pivot X, Bondarenko I, Nowecki Z, Dvorkin M, Trishkina E, Ahn JH, et al. Phase III, randomized, double-Blind study comparing the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of SB3 (Trastuzumab biosimilar) and reference trastuzumab in patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-Positive early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:968–74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.0126
11. Stebbing J, Baranau Y, Baryash V, Manikhas A, Moiseyenko V, Dzagnidze G, et al. CT-P6 compared with reference trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer: a randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 equivalence trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:917–28. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30434-5
12. Pegram MD, Bondarenko I, Zorzetto M, Hingmire S, Iwase H, Krivorotko PV, et al. PF-05280014 (a trastuzumab biosimilar) plus paclitaxel compared with reference trastuzumab plus paclitaxel for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a randomised, double-blind study. Br J Cancer. (2019) 120:172–82. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0340-2
13. Xie L, Zhang E, Xu Y, Gao W, Wang L, Xie MH, et al. Demonstrating analytical similarity of trastuzumab biosimilar HLX02 to herceptin((R)) with a panel of sensitive and orthogonal methods including a novel fcgammaRIIIa affinity chromatography technology. BIODRUGS. (2020) 34:363–79. doi: 10.1007/s40259-020-00407-0
14. Zhu X, Ding Y, Yu Y, Wang M, Zhou W, Wang J, et al. A Phase 1 randomized study compare the pharmacokinetics, safety and immunogenicity of HLX02 to reference CN- and EU-sourced trastuzumab in healthy subjects. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2021) 87:349–59. doi: 10.1007/s00280-020-04196-9
15. Xu B, Zhang Q, Sun T, Li W, Teng Y, Hu X, et al. Updated efficacy and safety of HLX02 versus reference trastuzumab in metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer: A randomized phase III equivalence trial. BREAST. (2025) 80:104413. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2025.104413
16. Zhou W, Wang M, Yu Y, Wang J, Wu Y, Yang G, et al. Comparing the pharmacokinetics, safety, and immunogenicity of HLX02 to US- and EU-approved trastuzumab in healthy Chinese male subjects: A Phase I, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2023) 23:717–25. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2183117
17. Deng W, Hu J, Li M, Yang S, Xie Z, and Chen J. Trastuzumab biosimilar HLX02 versus reference trastuzumab in patients with recurrent or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer: a model-based economic evaluation for China. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. (2022) 22:1117–26. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2022.2107506
18. Xu B, Zhang Q, Sun T, Li W, Teng Y, Hu X, et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of HLX02 compared with reference trastuzumab in patients with recurrent or metastatic HER2-Positive breast cancer: A randomized phase III equivalence trial. BIODRUGS. (2021) 35:337–50. doi: 10.1007/s40259-021-00475-w
19. Park MH, Seo JH, Park JH, Seong MK, Park KU, Kim MK, et al. Efficacy and safety of biosimilar trastuzumab (CT-P6) in routine clinical practice in the Republic of Korea: a real-world post-marketing surveillance study. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2024) 24:305–12. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2024.2334386
20. Deng W, Hu J, Yang S, Xie Z, Li M, Li J, et al. A multicenter real-world study comparing the clinical equivalence of trastuzumab biosimilar HLX02 and reference trastuzumab in the treatment of HER-2-positive breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. (2023) 13:3113–22.
21. Marty M, Cognetti F, Maraninchi D, Snyder R, Mauriac L, Tubiana-Hulin M, et al. Randomized phase II trial of the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer administered as first-line treatment: the M77001 study group. J Clin Oncol. (2005) 23:4265–74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.173
22. Baselga J, Cortes J, Kim SB, Im SA, Hegg R, Im YH, et al. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab plus docetaxel for metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:109–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113216
23. Zhang R, Liu X, Song G, Zhang Y, and Li H. Trastuzumab biosimilar (HLX02), pertuzumab plus chemotherapy in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after progression of trastuzumab: A prospective, phase II study. Cancer Res Treat. (2024) 56:795–801. doi: 10.4143/crt.2023.1151
24. von Minckwitz G, Colleoni M, Kolberg HC, Morales S, Santi P, Tomasevic Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of ABP 980 compared with reference trastuzumab in women with HER2-positive early breast cancer (LILAC study): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:987–98. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30241-9
25. Liu T, Liu D, Jin Y, and Dong M. Trastuzumab biosimilars vs trastuzumab originator in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2022) 44:809–15. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2090956
26. Pei J, Feng L, Mu Q, Wang Q, Wu Z, Wang Z, et al. Exploring an novel diagnostic gene of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity based on bioinformatics and machine learning. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:30067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81335-9
27. Wang Y, Xu J, Xie Y, Zhou D, Guo M, Qin Y, et al. Interventions for prevention and treatment of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1479983. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1479983
28. Li J, Wang S, Wang Y, Wang X, Wang H, Feng J, et al. Disparities of trastuzumab use in resource-Limited or resource-Abundant regions and its survival benefit on HER2 positive breast cancer: A real-World study from China. ONCOLOGIST. (2017) 22:1333–8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0088
Keywords: HLX02, trastuzumab, biosimilar, metastatic breast cancer, real-world study
Citation: Ye X, Wang L, Liu W, Wang M, Guo Z, Shan H, Zhai Q and Du Q (2025) Efficacy and safety of biosimilar trastuzumab (HLX02) in patients with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer: a retrospective real-world analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1622854. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1622854
Received: 04 May 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Raquel Diaz, University of Genova, ItalyReviewed by:
Marco Cavaco, Gulbenkian Institute of Science (IGC), PortugalHarika Nagandla, Houston Methodist Research Institute, United States
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Wang, Liu, Wang, Guo, Shan, Zhai and Du. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing Zhai, emhhaXFpbmc2M0AxMjYuY29t; Qiong Du, ZHVqb2FuLTg4QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xuan Ye
Xuan Ye Linlin Wang
Linlin Wang Wensheng Liu
Wensheng Liu Mengmeng Wang
Mengmeng Wang Zihan Guo1,2
Zihan Guo1,2 Han Shan
Han Shan Qing Zhai
Qing Zhai Qiong Du
Qiong Du