- 1Department of Hematology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, China
- 2Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory on Hematology, Fujian Institute of Hematology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, Fujian, China
Introduction: Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) is a rare type of acute leukemia with an incidence of less than 5% and Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) represents a distinct subtype.
Case description: An 18-year-old female complained of recurrent fever with fatigue and chills for one month, and a week of growing lymphadenectasis. Bone marrow examination revealed two distinct populations of blast cells and the presence of BCR::ABL1 fusion gene, leading to a diagnosis of Ph+ MPAL. The patient received induction chemotherapy of DVAP regimen combined with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), and underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after achieving complete remission. To date, the patient has maintained sustained hematological and molecular complete remission.
Conclusion: A literature review of 59 cases revealed that Ph+ MPAL is more common in adult, male patients and primarily manifests as B/myeloid subtype. Higher leukocyte counts and chromosome -7 abnormalities have been identified as poor prognostic markers. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia-type therapy is considered more effective for patients with MPAL, and in the TKI era Ph+ has become a subtype with a better prognosis.
Introduction
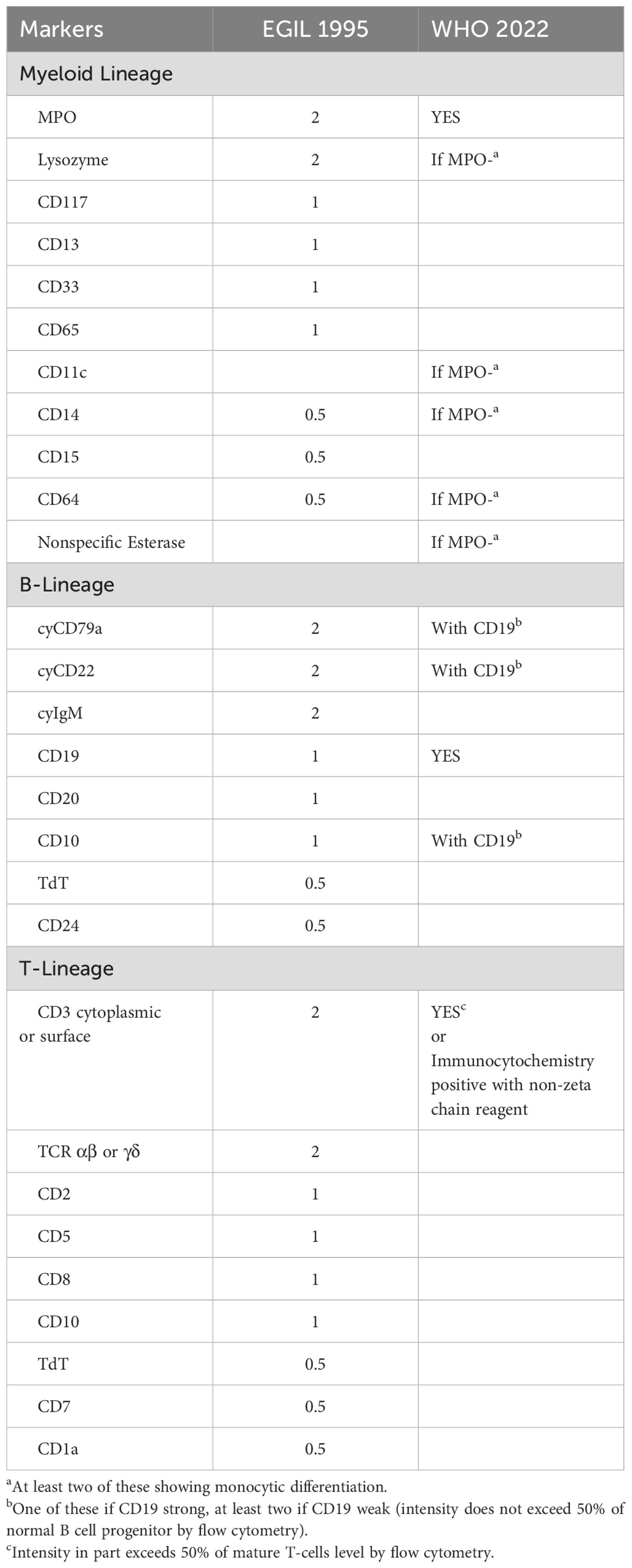
Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) represents a rare type of acute leukemia with an incidence of less than 5% (1) and has a slight predominance in adult and male patients (2). Characterized by multiple lineage markers on a single blast population (biphenotypic leukemia) or single-lineage markers on distinct blast populations (bilineal leukemia) (3), MPAL was recognized initially in the 2001 World Health Organization (WHO) classification. Cases of bilineal and biphenotypic leukemia were grouped together and categorized into acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage (ALAL) according to the 2008 WHO classification (4). The diagnosis of MPAL is identified by a number of immunophenotypic markers based on the European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL) or the WHO criteria (Table 1) (5, 6). Two large sample size retrospective studies on MPAL revealed that B/myeloid subtype accounted for 55-59%, followed by T/myeloid (33-35%), B/T (4-12%), and trilineage subtypes (0.9-2%) (7, 8).
The pathogenesis of MPAL remains unclear, and the dysregulation of multiple lineage differentiation due to genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity might play an important role (9). A retrospective study of 39 patients with ALAL revealed that gene mutations were present in approximately 90% of patients, and genes involved in genomic stability and transcriptional regulation were frequently detected in the MPAL cohort (10). Gene mutations identified in MPAL are typically detected in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) (11, 12). Genomic analysis revealed that ZNF384 rearrangements were common in B/myeloid-MPAL, whereas biallelic WT1 alterations were associated with T/myeloid subtype (13). Mutations in the putative chromatin modifier, PHF6, JAK-STAT and Ras signaling pathways are frequently observed in patients with B/T MPAL (14). Moreover, clonal chromosomal abnormalities (CAs) occur in 59%-91% of patients with MPAL (15). As two separate entities of MPAL, BCR::ABL1 fusion gene induced by t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2), also known as Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+), was observed in 15%-30% of patients, especially in adults (8); whereas KMT2A rearrangement due to t(v;11q23.3) occurred more frequently in the pediatric cohort (16, 17).
Here, we report a case of a young patient with Ph+ MPAL who achieved complete remission (CR) after the first induction therapy involving the combination of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) with the ALL-type regimen, and underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) with favorable clinical outcomes. Furthermore, we reviewed the relevant literature to further discuss the clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with Ph+ MPAL.
Case report
An 18-year-old female patient was admitted to Fujian Medical University Union Hospital in Aug. 2023, who complained of recurrent fever with fatigue and chills for one month, and a week of growing lymphadenectasis. Physical examination showed an anemic appearance, multiple superficial lymphadenectasis and hepatosplenomegaly. The complete blood count (CBC) indicated evident leukocytosis (white blood cell [WBC] counts 127.68×109/L), moderate anemia (hemoglobin 69.0 g/L), and normal platelet counts (223×109/L). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was markedly elevated at 888 IU/L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was weakly positive for mycoplasma and influenza B virus IgM antibodies, and a chest CT suggested infection in the middle and lower lobes of the right lung. Peripheral blood smear revealed 22% blasts together with 8.7% eosinophils (Figure 1A). Subsequent BM aspirates confirmed the occurrence of acute leukemia with 25.5% blast cells (Figure 1B), concomitant eosinophilia and secondary myelofibrosis (2+) (Figure 1C). Flow cytometry of the marrow aspirate revealed two populations of blast cells expressing T-lineage (cytoplasmic CD3, CD5, and CD7) or myeloid markers (MPO, CD117, CD33, CD13, and CD15), respectively (Figure 1D). Molecular studies involving gene mutations (Supplementary Table S1) and fusion genes (Supplementary Table S2) for leukemia identified a somatic mutation in STAG2 (c.459_462 + 10delinsA) with a variant allele frequency (VAF) of 12.4% and BCR::ABL1 fusion gene (e14a2). Karyotype analysis supported the presence of Ph chromosome (Figure 1E). Based on current evidence, the patient was diagnosed with T/myeloid MPAL with p210-BCR::ABL1 fusion gene and STAG2 mutations, then received DVAP regimen (daunorubicin [30 mg/m2/d ivgtt d1,8,15], vincristine [1.4 mg/m2/d ivgtt d1,8,15,22], cytarabine [100 mg/m2 q12h ivgtt d1-7], and prednisone [1 mg/kg/d d1-14, 0.5 mg/kg/d d15-28]) with imatinib (400 mg qd) for induction chemotherapy. The second bone marrow examination in Sep. 2023 revealed morphological CR with only 0.5% blasts, whereas the level of BCR::ABL1/ABL1 mRNA increased from 64.07% to 88.19% international scale (IS) (Figure 1F), indicating a poor response to imatinib. After the subsequent replacement with dasatinib, the level significantly decreased to 14.84% in Nov. 2023. Considering the young age, sustained CR status, and the presence of adverse genetic abnormalities (BCR::ABL1 and STAG2) for myeloid leukemia (18), the patient received six cycles of intrathecal chemotherapies consisting of methotrexate and cytarabine to prevent central nervous system leukemia (CNSL) and underwent 5/10 HLA-matched haploidentical allo-HSCT from her father in May 2024. The patient achieved deep molecular response (DMR) (BCR::ABL1/ABL1 mRNA ≤ 0.01% IS (19)) and hematologic CR after transplantation, and has maintained sustained remission to date with regular follow-up.
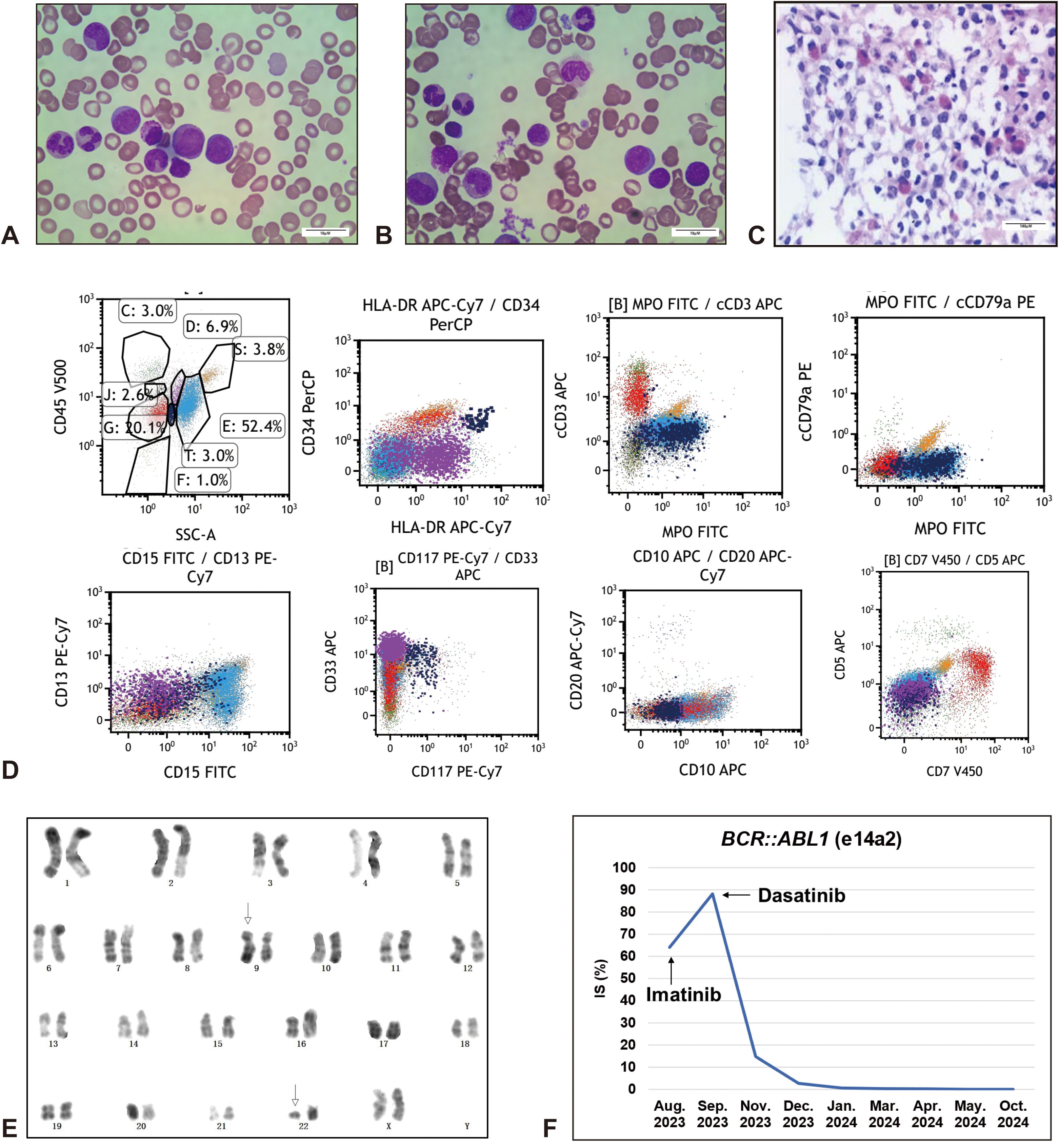
Figure 1. Paitent with Ph+ T/M-MPAL. Increased blast cells and eosinophils were evident in the peripheral blood smear (A) and bone marrow smear (B) (Wirght Giemsa, x1000, scale bar = 10 μm). (C) Bone marrow biospy suggested extremely active myeloproliferation (95%), with diffuse infiltration of myeloid blast cells and scattered primitive lymphocytes, marked eosinophilia, and myelofibrosis grade 2 (HE, x100, scale bar = 100 μm). Immunohistochemistry: MPO (+++), CD117 (-), CD34 (+), pax5 (-), CD3 (+), TDT(+), Lysozyme (+++), CD15 (+++), E-Cad (-), GPA (±), LEF1 (±). (D) Flow cytometry analysis showed two populations of blast cells by CD45/SSC gating, which were positive for T-lymphoid (cytoplasmic CD3, CD5, and CD7) (red, Group G, 20.1%) or myeloid differentiation (MPO, CD117, CD33, CD13, and CD15) (navy blue, Group T, 3.0%) markers, respectively. Group C, Lymphocytes; Group E, Granulocytes; Group D, Monocytes; Group J, Basophils; Group S, Eosinophils; F, Fragments and other cells. Data were acquired on a BD FACSCanto series flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using Kaluza Analysis software (Beckman Coulter). (E) Karyotype analysis by G-banding technique suggested a translocation between chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, t(9;22)(q34;q11), also known as Ph chromosome. (F) Dynamic analysis of BCR::ABL1 fusion gene quantification. IS, International Scale.
Literature review
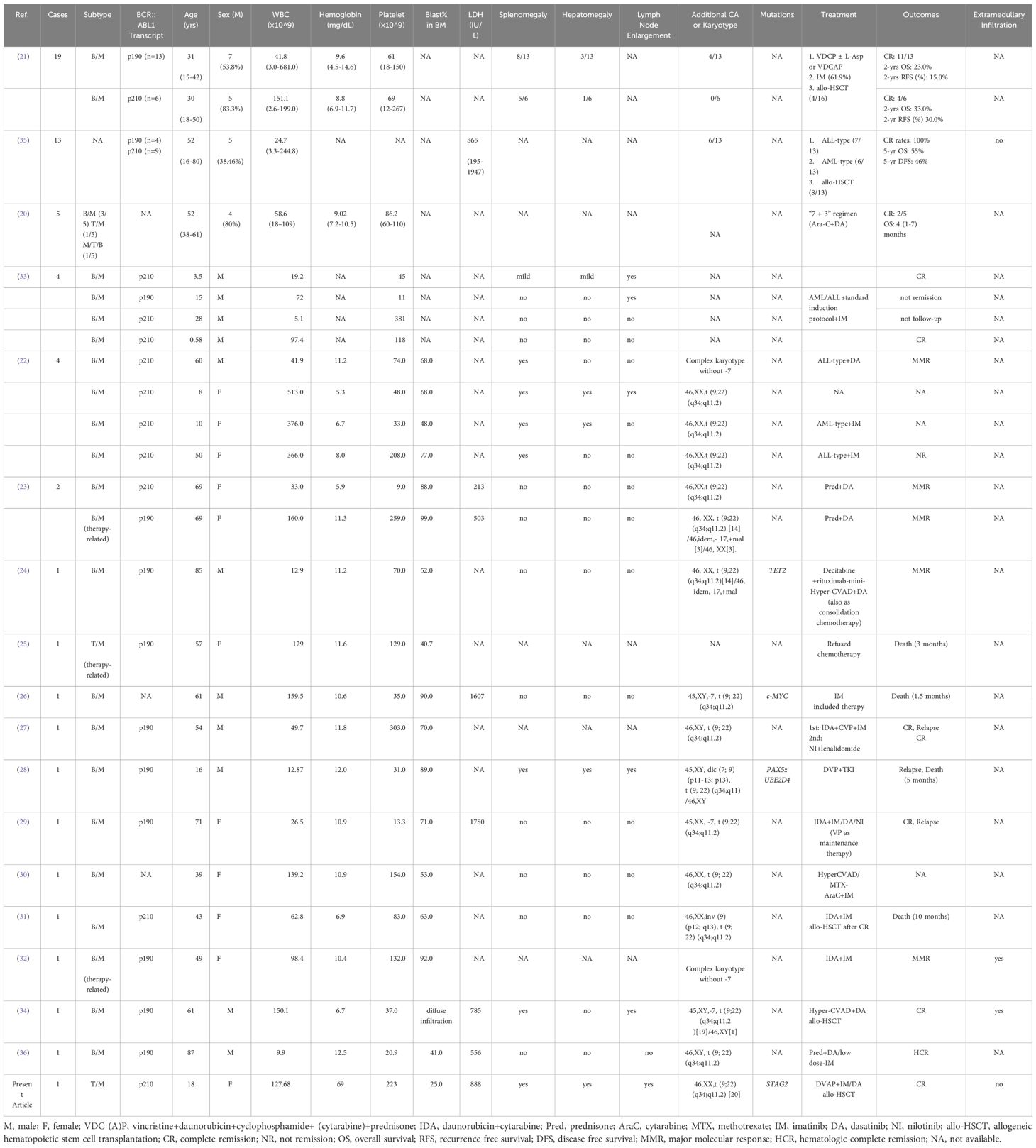
Ph chromosome in adult patients is more common in MPAL than in AML, while the frequency is similar to that in ALL (15, 20). The presence of p210-BCR::ABL1 in MPAL should raise suspicion for chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML) in blast crisis, with evidence of prominent splenomegaly and elevated granulocytes in prior history (11, 21, 22). In the present case, the diagnosis of blast phase CML cannot be excluded considering the classic characteristics of significant leukocytosis with eosinophilia, hepatosplenomegaly and secondary myelofibrosis. To clarify the clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with Ph+ MPAL, we conducted a systemic literature research up to Apr. 2025 on PubMed and Embase databases with keywords and MeSH terms for mixed-phenotype acute leukemia, MPAL, Philadelphia chromosome, and Ph. As summarized in Table 2 including 59 cases (20–36), patients with Ph+ MPAL are considered to have high WBC counts and primarily presented with B/myeloid phenotype (91.30%) (8, 15). There was no significant difference in sex, while a larger proportion of male patients were observed (54.24%) (7, 8, 20, 21). A slight tendency toward the p190 transcript (51.92%) was shown in patients with Ph+ MPAL. Analysis of 21 adult patients revealed no significant difference in clinical characteristics between patients with the p190 transcript and those with the p210 transcript (21). Whether different transcripts are involved in the phenotypic transition of MPAL needs further investigation given their different modes of signaling activation (37). Splenomegaly, hepatomegaly and lymph node enlargement were present in approximately 55.26%, 23.68% and 31.58% of patients, respectively. Additional CAs were shown in nearly 38.78% of cases. Deletion of chromosome 7 (-7), reported in 3/16 cases, appears to be a common CA and is considered an inferior prognostic biomarker, which is mostly a single anomaly in adults but is often accompanied with complex karyotype in children (15). Compared with those with AML or ALL, patients with biphenotypic acute leukemia more commonly present with complex karyotype and extramedullary infiltration (38), while extramedullary infiltration is relatively rare in patients with Ph+ MPAL with only two cases (32, 34). Concomitant IKZF1 frameshift mutations have been reported in patients with B/M Ph+ MPAL (8), which are more frequent in ALL patients with complex karyotype and associated with a poor prognosis (39).
In general, patients with MPAL are considered to have an inferior prognosis, especially in the older cohort (7, 40). A meta-analysis revealed that ALL-type therapy was statistically associated with a better CR rate and overall survival (OS) than AML-type regimen in the MPAL cohort (41). A multicenter retrospective study indicated that hyper-CVAD therapy (hyper-fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone) showed a significant effectivity and tolerance in patients with ALAL (42). Meanwhile, a study classified MPAL into AML-type and AML-type based on genome-wide methylation signatures, and claimed a better response when giving the lineage-matched therapy (43). B/T-MPAL has been found to share similar genetic characteristics with T-ALL rather than B-ALL, and was defined as a high-risk subgroup of ALL which could also benefit from ALL-based therapy (14). In contrast to subsequent consolidation chemotherapy, early allo-HSCT after initial CR may lead to a better prognosis (44). Prior to the TKI era, patients with Ph+ MPAL were considered to present dismal outcomes without allo-HSCT, especially female patients and those with WBC counts above 100×109/L (7, 21). Nevertheless, TKI-combined therapy substantially improved the prognosis of patients with Ph+ MPAL, which is comparable to those with Ph+ ALL (21, 35, 45). In a small Japanese Ph+ acute leukemia cohort, there were no significant difference in the CR rate, 5-year OS or disease-free survival (DFS) rates between patients with Ph+ MPAL and those with Ph+ B-cell precursor (BCP)-ALL, when matched for influencing factors including age, sex, WBC counts, LDH levels, and the prevalence of additional CAs (35). A cancer registry analysis of 241 patients with MPAL revealed that the Ph+ cohort had a better prognosis than all other subtypes, whereas cases with MLL rearrangement were closely associated with poor OS (45). Among the specific cases listed in Table 2, six patients showed no response to TKIs or relapsed after remission. Primary resistance to imatinib was also observed in our present case. It currently unclear whether this is related to myelofibrosis, and further research is needed to explore the superiority of dasatinib over imatinib in such population. In elderly patients with Ph+ MPAL, low-dose TKIs in combination with prednisolone has been identified as a safe and effective therapeutic strategy (23, 36). Moreover, combination therapy with the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax is worth trying, as its great advantages in the treatment of elderly patients with AML (46). Given Ph as an adverse prognostic marker in AML, allo-HSCT at an early stage is recommended for eligible patients with myeloid-involved mixed-phenotype leukemia (18, 34). For patients who are not suitable for allo-HSCT, chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T)-cell therapy may be considered as an alternative option in future research (47).
Conclusion
In this study, we report a patient with Ph+ MPAL who received DVAP regimen combined with TKIs, followed by allo-HSCT, ultimately achieving hematologic and molecular CR. Through a literature review, similar to the overall MPAL population, the Ph+ subtype is more commonly observed in adult, male patients, and primarily presents as B/myeloid subtype. As an inferior prognostic marker, high WBC count has also been identified as one of the main characteristics of patients with Ph+ MPAL, while extramedullary infiltration is relatively rare. Chromosome -7 abnormalities have been occasionally reported in patients with Ph+ MPAL and are associated with a poor prognosis. ALL-type therapy is considered to more effective for patients with MPAL. In the TKI era, Ph+ MPAL has gradually become a subtype with a better prognosis. Meanwhile, novel therapeutic strategies are eagerly expected with the emergence of targeted therapeutic agents and immunotherapy.
Author contributions
LY: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. MH: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Writing – original draft. YW: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was sponsored by Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (Grant no. 2018Y0962) and Health Science and Technology Program of Fujian Province (Grant no. 2023CZ003).
Acknowledgments
Special acknowledgment for the sequencing technique for molecular studies including quantitative analysis of BCR::ABL1 fusion gene and genetic mutation analysis provided by Kindstar Globalgene Technology, Inc. (Beijing, China).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1623528/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
MPAL, mixed phenotype acute leukemia; Ph+, Philadelphia chromosome-positive; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; WHO, World Health Organization; ALAL, acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage; EGIL, European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CAs, chromosomal abnormalities; CR, complete remission; allo-HSCT, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; CBC, complete blood count; WBC, white blood cell; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; VAF, variant allele frequency; CNSL, central nervous system leukemia; DMR, deep molecular response; IS, international scale; CML, chronic myelocytic leukemia; -7, deletion of chromosome 7; OS, overall survival; DFS, disease-free survival; BCP, B-cell precursor; CAR-T, chimeric antigen receptor-T.
References
1. Matutes E, Morilla R, Farahat N, Carbonell F, Swansbury J, Dyer M, et al. Definition of acute biphenotypic leukemia. Haematologica. (1997) 82:64–6.
2. Rasekh EO, Osman R, Ibraheem D, Madney Y, Radwan E, Gameel A, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia-like treatment regimen provides better response in mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a comparative study between adults and pediatric MPAL patients. Ann Hematol. (2021) 100:699–707. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04354-2
3. Weinberg OK and Arber DA. How I diagnose acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage. Am J Clin Pathol. (2022) 158:27–34. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqac070
4. Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. (2009) 114:937–51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-209262
5. Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, Ludwig WD, Matutes E, Orfao A, et al. Proposals for the immunological classification of acute leukemias. European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL). Leukemia. (1995) 9:1783–6.
6. Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y, Alaggio R, Apperley JF, et al. The 5th edition of the world health organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Leukemia. (2022) 36:1703–19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1
7. Matutes E, Pickl WF, Van't Veer M, Morilla R, Swansbury J, Strobl H, et al. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: clinical and laboratory features and outcome in 100 patients defined according to the WHO 2008 classification. Blood. (2011) 117:3163–71. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-314682
8. Yan L, Ping N, Zhu M, Sun A, Xue Y, Ruan C, et al. Clinical, immunophenotypic, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic features in 117 adult patients with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia defined by WHO-2008 classification. Haematologica. (2012) 97:1708–12. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.064485
9. Khan M, Siddiqi R, and Naqvi K. An update on classification, genetics, and clinical approach to mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL). Ann Hematol. (2018) 97:945–53. doi: 10.1007/s00277-018-3297-6
10. Huang J, Zhou J, Xiao M, Mao X, Zhu L, Liu S, et al. The association of complex genetic background with the prognosis of acute leukemia with ambiguous lineage. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:24290. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03709-7
11. Andrews C, Tierens A, and Minden M. The genomic and biological complexity of mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. (2021) 58:153–66. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2020.1829537
12. Hennawi M, Pakasticali N, Tashkandi H, and Hussaini M. Genomic landscape of mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(19):11259. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911259
13. Alexander TB, Gu Z, Iacobucci I, Dickerson K, Choi JK, Xu B, et al. The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia. Nature. (2018) 562:373–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0436-0
14. Mi X, Griffin G, Lee W, Patel S, Ohgami R, Ok CY, et al. Genomic and clinical characterization of B/T mixed phenotype acute leukemia reveals recurrent features and T-ALL like mutations. Am J Hematol. (2018) 93:1358–67. doi: 10.1002/ajh.v93.11
15. Manola KN. Cytogenetic abnormalities in acute leukaemia of ambiguous lineage: an overview. Br J Haematol. (2013) 163:24–39. doi: 10.1111/bjh.2013.163.issue-1
16. Rubnitz JE, Onciu M, Pounds S, Shurtleff S, Cao X, Raimondi SC, et al. Acute mixed lineage leukemia in children: the experience of St Jude Children's Research Hospital. Blood. (2009) 113:5083–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-10-187351
17. Al-Seraihy AS, Owaidah TM, Ayas M, El-Solh H, Al-Mahr M, Al-Ahmari A, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of children with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica. (2009) 94:1682–90. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.009282
18. Dohner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, Craddock C, DiNardo CD, Dombret H, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. (2022) 140:1345–77. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016867
19. Shah NP, Bhatia R, Altman JK, Amaya M, Begna KH, Berman E, et al. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, Version 2.2024, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2024) 22:43–69. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2024.0007
20. Atfy M, Al Azizi NM, and Elnaggar AM. Incidence of Philadelphia-chromosome in acute myelogenous leukemia and biphenotypic acute leukemia patients: And its role in their outcome. Leuk Res. (2011) 35:1339–44. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.04.011
21. Wang Y, Gu M, Mi Y, Qiu L, Bian S, and Wang J. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of mixed phenotype acute leukemia with Philadelphia chromosome positive and/or bcr-abl positive in adult. Int J Hematol. (2011) 94:552–5. doi: 10.1007/s12185-011-0953-1
22. Choi W, Kim M, Lim J, Han K, Lee S, Lee JW, et al. Four cases of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mixed phenotype blast phase at initial presentation mimicking mixed phenotype acute leukemia with t(9;22). Ann Lab Med. (2014) 34:60–3. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.60
23. Takata H, Ikebe T, Sasaki H, Miyazaki Y, Ohtsuka E, Saburi Y, et al. Two elderly patients with philadelphia chromosome positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia who were successfully treated with dasatinib and prednisolone. Intern Med. (2016) 55:1177–81. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.5223
24. Jain P, Tang G, Huh YO, Yin CC, Zuo Z, Pemmaraju N, et al. Philadelphia-positive dimorphic blasts in mixed-phenotype acute leukemia with TET2 mutation. Am J Hematol. (2016) 91:647–8. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24295
25. Yang D, Cho SR, Jung S, Lee W, Hwang HY, Lee HS, et al. A case of therapy-related acute leukemia with mixed phenotype with BCR-ABL1 after treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Lab Med. (2017) 37:166–8. doi: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.2.166
26. Xu Z, Padmore R, Shier L, and Beaulieu Bergeron M. A rare case of acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage overexpressing C-MYC with monosomy 7 and Philadelphia chromosome. Ann Hematol. (2015) 94:1761–3. doi: 10.1007/s00277-015-2443-7
27. Lai B, Mu Q, Zhu H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Xu K, et al. Durable remission in a patient of mixed phenotype acute leukemia with Philadelphia chromosome-positive treated with nilotinib and lenalidomide: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e0294. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010294
28. Yu Y, Zeng Z, Xie J, Lu Q, Cai W, Zhang R, et al. Case report: the formation of a truncated PAX5 transcript in a case of ph-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia with dic(7;9)(p11-p13;p13). Front Oncol. (2021) 11:703612. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.703612
29. Kawajiri C, Tanaka H, Hashimoto S, Takeda Y, Sakai S, Takagi T, et al. Successful treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia by appropriate alternation of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors according to BCR-ABL1 mutation status. Int J Hematol. (2014) 99:513–8. doi: 10.1007/s12185-014-1531-0
30. Yong WL, Yusof N, Ithnin A, Shuib S, Tumian R, Yousuf R, et al. Mixed phenotype acute leukaemia with t(9,22), BCR-ABL1: A case report. Malays J Pathol. (2020) 42:469–76.
31. Kim HN, Hur M, Kim H, Ji M, Moon HW, Yun YM, et al. First case of biphenotypic/bilineal (B/myeloid, B/monocytic) mixed phenotype acute leukemia with t(9;22)(q34;q11.2);BCR-ABL1. Ann Clin Lab Sci. (2016) 46:435–8.
32. Cho JH, Hur M, Moon HW, Yun YM, Ko YS, Kim WS, et al. Therapy-related acute leukemia with mixed phenotype and t(9;22)(q32;q11.2): a case report and review of the literature. Hum Pathol. (2012) 43:605–9. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.07.010
33. Bhatia P, Binota J, Varma N, Bansal D, Trehan A, Marwaha RK, et al. A study on the expression of BCR-ABL transcript in mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL) cases using the reverse transcriptase polymerase reaction assay (RT-PCR) and its correlation with hematological remission status post initial induction therapy. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. (2012) 4:e2012024. doi: 10.4084/mjhid.2012.024
34. Chan O, Jamil AR, Millius R, Kaur R, and Anwer F. Mixed phenotype acute leukemia with t(9;22): success with nonacute myeloid leukemia-type intensive induction therapy and stem cell transplantation. Clin Case Rep. (2017) 5:435–9. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2017.5.issue-4
35. Shimizu H, Yokohama A, Hatsumi N, Takada S, Handa H, Sakura T, et al. Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia in the imatinib era. Eur J Haematol. (2014) 93:297–301. doi: 10.1111/ejh.2014.93.issue-4
36. Okayama Y, Takakuwa T, Otomaru I, Horiuchi M, Miura A, Araki T, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose imatinib in an elderly patient with mixed phenotype acute leukemia with t(9;22)(q34;q11.2);BCR-ABL1. Clin Case Rep. (2021) 9:e04126. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4126
37. Cutler JA, Tahir R, Sreenivasamurthy SK, Mitchell C, Renuse S, Nirujogi RS, et al. Differential signaling through p190 and p210 BCR-ABL fusion proteins revealed by interactome and phosphoproteome analysis. Leukemia. (2017) 31:1513–24. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.61
38. Xu XQ, Wang JM, Lu SQ, Chen L, Yang JM, Zhang WP, et al. Clinical and biological characteristics of adult biphenotypic acute leukemia in comparison with that of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case series of a Chinese population. Haematologica. (2009) 94:919–27. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2008.003202
39. Kirtek T, Chen W, Laczko D, Bagg A, Koduru P, Foucar K, et al. Acute leukemias with complex karyotype show a similarly poor outcome independent of mixed, myeloid or lymphoblastic immunophenotype: A study from the Bone Marrow Pathology Group. Leuk Res. (2023) 130:107309. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2023.107309
40. Shi R and Munker R. Survival of patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemias: A large population-based study. Leuk Res. (2015) 39:606–16. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.03.012
41. Maruffi M, Sposto R, Oberley MJ, Kysh L, and Orgel E. Therapy for children and adults with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Leukemia. (2018) 32:1515–28. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0058-4
42. Duong VH, Begna KH, Kashanian S, Sweet K, Wang ES, Caddell R, et al. Favorable outcomes of acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage treated with hyperCVAD: a multi-center retrospective study. Ann Hematol. (2020) 99:2119–24. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04179-z
43. Takahashi K, Wang F, Morita K, Yan Y, Hu P, Zhao P, et al. Integrative genomic analysis of adult mixed phenotype acute leukemia delineates lineage associated molecular subtypes. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:2670. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04924-z
44. Wolach O and Stone RM. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: current challenges in diagnosis and therapy. Curr Opin Hematol. (2017) 24:139–45. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000322
45. Qasrawi A, Ramlal R, Munker R, and Hildebrandt GC. Prognostic impact of Philadelphia chromosome in mixed phenotype acute leukemia (MPAL): A cancer registry analysis on real-world outcome. Am J Hematol. (2020) 95:1015–21. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25873
46. Fowler-Shorten DJ, Hellmich C, Markham M, Bowles KM, and Rushworth SA. BCL-2 inhibition in haematological Malignancies: Clinical application and complications. Blood Rev. (2024) 65:101195. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2024.101195
Keywords: mixed-phenotype acute leukemia, BCR::ABL1 fusion gene, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, case report, literature review
Citation: Yang L, Huang M, Chen Y and Wu Y (2025) Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: a case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 15:1623528. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1623528
Received: 06 May 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Carlo Finelli, Sant’Orsola-Malpighi Polyclinic, ItalyReviewed by:
Zhaodong Xu, Vancouver General Hospital, CanadaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Huang, Chen and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Wu, d3V5b25nOTE5NUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Liqing Yang, orcid.org/0000-0003-2646-4359
Meijuan Huang, orcid.org/0000-0002-2536-9600
Yuanzhong Chen, orcid.org/0000-0002-9411-1427
Yong Wu, orcid.org/0000-0002-2873-0334
 Liqing Yang
Liqing Yang Meijuan Huang
Meijuan Huang Yuanzhong Chen1,2‡
Yuanzhong Chen1,2‡