- Department of Thoracic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Fortunately, the advent of precision medicine, which includes targeted therapy and immunotherapy, has significantly improved the survival rates of patients with locally advanced lung cancer. This article reports on a case of stage IVB (cT2bN1M1c1) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastases harboring compound mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 21 Leu858Arg and mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MEK1) exon 3 lle112Thr and with a high program death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression that successfully underwent radical lung cancer surgery following combined therapy. We report on a case of a 60-year-old man diagnosed preoperatively with stage IVB adenocarcinoma of the left upper lung (cT2bN1M1c1) who was diagnosed with multiple brain metastases. After multidisciplinary discussion, it was decided to administer targeted therapy with furmonertinib, chemotherapy with pemetrexed and lobaplatin, and immunotherapy with tislelizumab. Following 2 months of treatment, tumor assessment showed partial response (PR). After 11 months, assessment showed a PR of all lung lesions and complete response of the brain lesions, making the patient eligible for surgery. Finally, the patient underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy + mediastinal lymphadenectomy. Postoperative pathology confirmed complete response, and the patient continued adjuvant therapy with furmonertinib. For patients with metastatic advanced NSCLC, systemic treatment involving chemotherapy plus immunotherapy and targeted therapy is expected to become one of the options. Moreover, it is likely to achieve successful conversion surgery and further efficacy after combined therapy.
Introduction
In approximately 40%–60% of Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), mutations in the EGFR gene are present, enabling them to benefit from treatments involving epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKIs). Furmonertinib mesylate (AST2818) represents an innovative third-generation EGFR TKI with irreversible action. This medication has gained approval from the China National Medical Products Administration for use in individuals with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who have sensitive EGFR mutations along with the T790M resistance mutation (1). Due to its distinct trifluoroethoxypyridine configuration, furmonertinib exhibits an enhanced safety profile. Furthermore, both furmonertinib and its primary metabolite, AST5902, have demonstrated significant antitumor efficacy and excellent selectivity (2). Tislelizumab, an engineered immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), has been meticulously developed to reduce attachment to FC gamma receptors (FcγR) on macrophages. The RATIONALE-307 trial assessed the safety and effectiveness of combining chemotherapy with tislelizumab as an initial treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC, revealing that this combination resulted in a median progression-free survival (PFS) exceeding 7.6 months. In addition, the frequency of adverse events (AEs) observed was comparable between the experimental group and the control group. This study supports the use of tislelizumab in conjunction with chemotherapy as the primary treatment for advanced squamous NSCLC as granted by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) (3). Here, we report on a case of lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastases harboring compound mutations in EGFR exon 21 Leu858Arg and mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MEK1) exon 3 lle112Thr and with a high program death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression who responded well to combination therapy (targeted therapy with furmonertinib, chemotherapy with pemetrexed and lobaplatin, and immunotherapy with tislelizumab), successfully achieving a pathological complete response. We present this case in accordance with the CARE (Case Reporting) checklist.
Case presentation
A 60-year-old male patient, with a history of smoking, was admitted to our hospital in October 2023 with symptoms of cough and headache[Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score = 6/10] that persisted for 1 month. The contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan showed a 4.2-cm × 3.2-cm mass in the left upper lobe with hilar lymph node enlargement. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed multiple brain metastases. A left lung biopsy was obtained and established the pathologic diagnosis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma[immunohistochemistry: CK7(+), NapsinA(+)(G), TTF-1(+)(K), CK5/6(−), P40(−), Ki-67(+ approximately 20%), and CD56(−)]. His tumor DNA extracted from the tissue was subjected to DNA sequencing analysis, with genetic testing revealing that the patient had an EGFR exon 21 mutation (c.2573 T>G, p.Leu858Arg 10.5%), MEK1 exon 3 mutation (c.335T>C, p.lle112Thr 40.3%), and a high PD-L1 expression[tumor proportion score (TPS) = 95%]. Based on these data, the patient was diagnosed with stage IVB (cT2bN1M1c1) lung adenocarcinoma.
The patient started receiving first-line chemotherapy with pemetrexed (800 mg) plus lobaplatin (60 mg) and immunotherapy with tislelizumab after his diagnosis (two cycles of chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy). After a course of treatment, the symptoms of cough and headache resolved (VAS score = 0/10). After 2 months, CT showed a partial response of the lung. He received maintenance targeted therapy with furmonertinib for 11 months. As common treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), the patient had diarrhea that lasted 1 month and itching for 10 days during this period. No grade ≥3 AEs occurred (Table 1). Notably, the patient received no corticosteroids or anticonvulsants during therapy, as he remained neurologically asymptomatic after month 1. The patient’s serial Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores remained stable at 30/30 throughout treatment. No seizures or focal deficits occurred. In December 2024, the patient underwent a thorough examination at the hospital. Adequate assessment resulted in a complete response of the brain metastases (Figure 1). Determining the optimal treatment for the patient is necessary to improve the prognosis; therefore, we conducted a multidisciplinary discussion including oncologists, respiratory physicians, neurosurgeons, radiologists, and radiation oncologists. Finally, the patient underwent thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy and lymph node dissection for lung cancer, and pathological examination confirmed ypT0N0M0: 0/13 lymph nodes involved (stations 5–7 and 10–12 dissected) (Figure 2). Minimal pleural adhesion (grade 1, Goldberg classification) and minor bleeding were observed during the procedure. No air leaks occurred after the procedure, and no signs of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) were present.
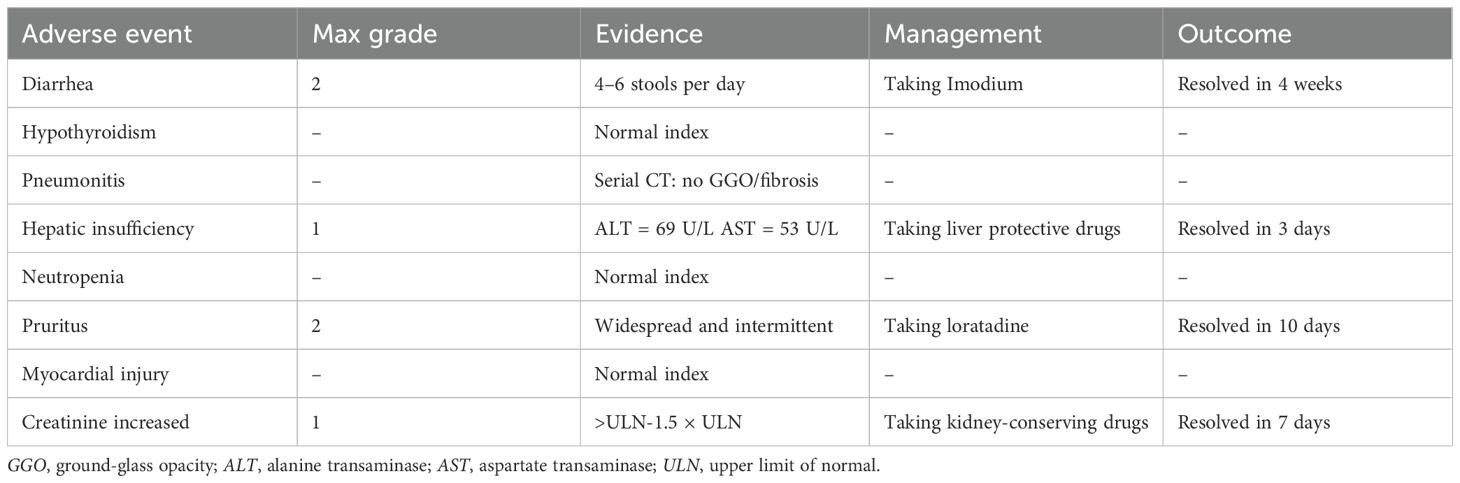
Table 1. Adverse events according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0 criteria.
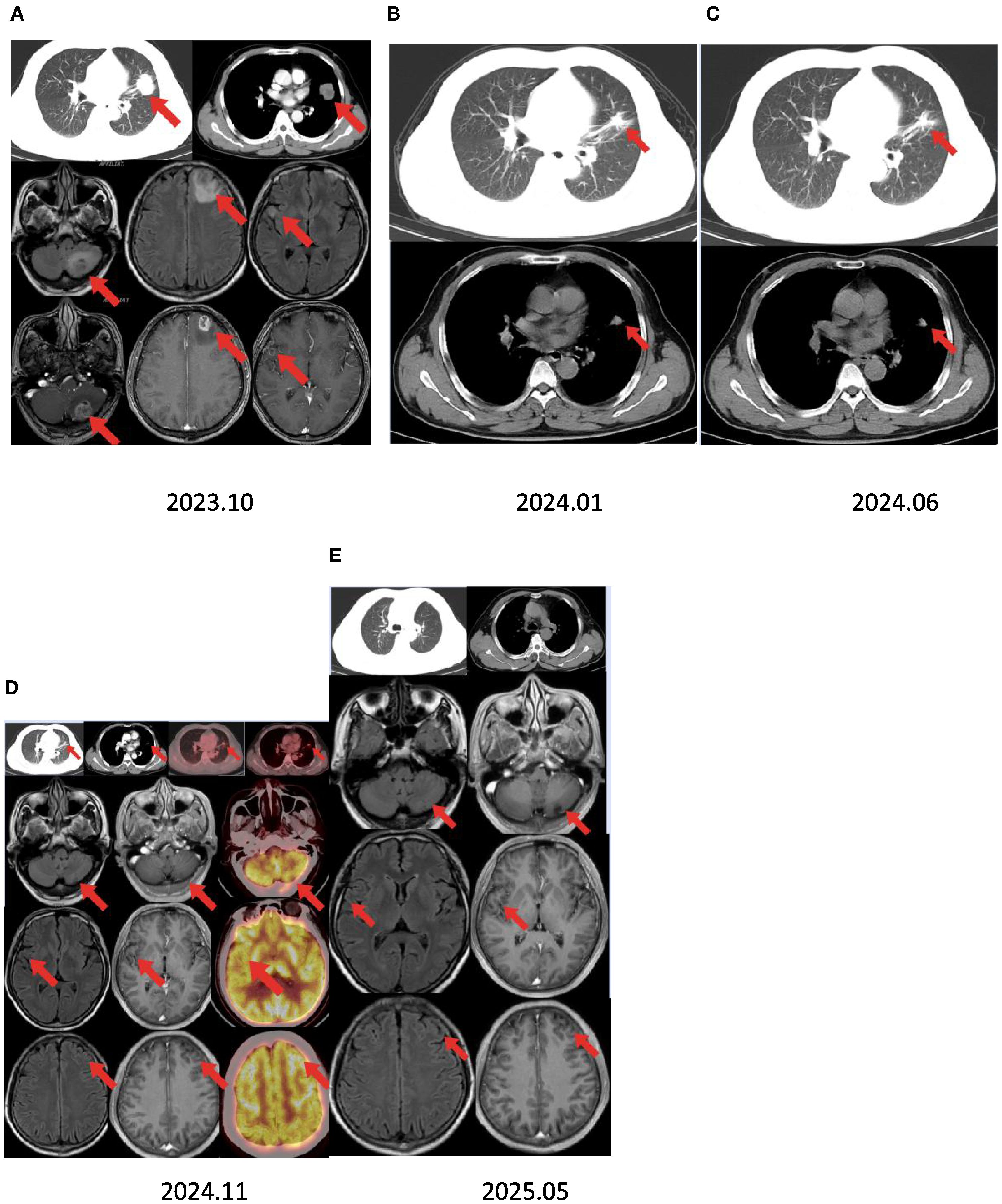
Figure 1. Timeline summary with dynamic imaging of the different therapeutic lines between October 2023 and May 2025. (A) Baseline chest CT showing a lung mass in the left upper lobe and brain MRI revealing multiple brain metastases. (B, C) Best response under chemotherapy and immunotherapy with a partial response after 2 and 7 months. Assessment showed a partial response of all lung lesions and complete response of the brain lesions after 11 months of furmonertinib. (D) Positron emission tomography/CT scan revealing a nodular soft tissue density shadow in the lingual segment of the left upper lobe and increased radioactive concentrations of foci, with a maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) of 3.8. There was no increased radioactive concentration of foci in the brain. (E) Brain MRI showing no recurrent lesions after 18 months.
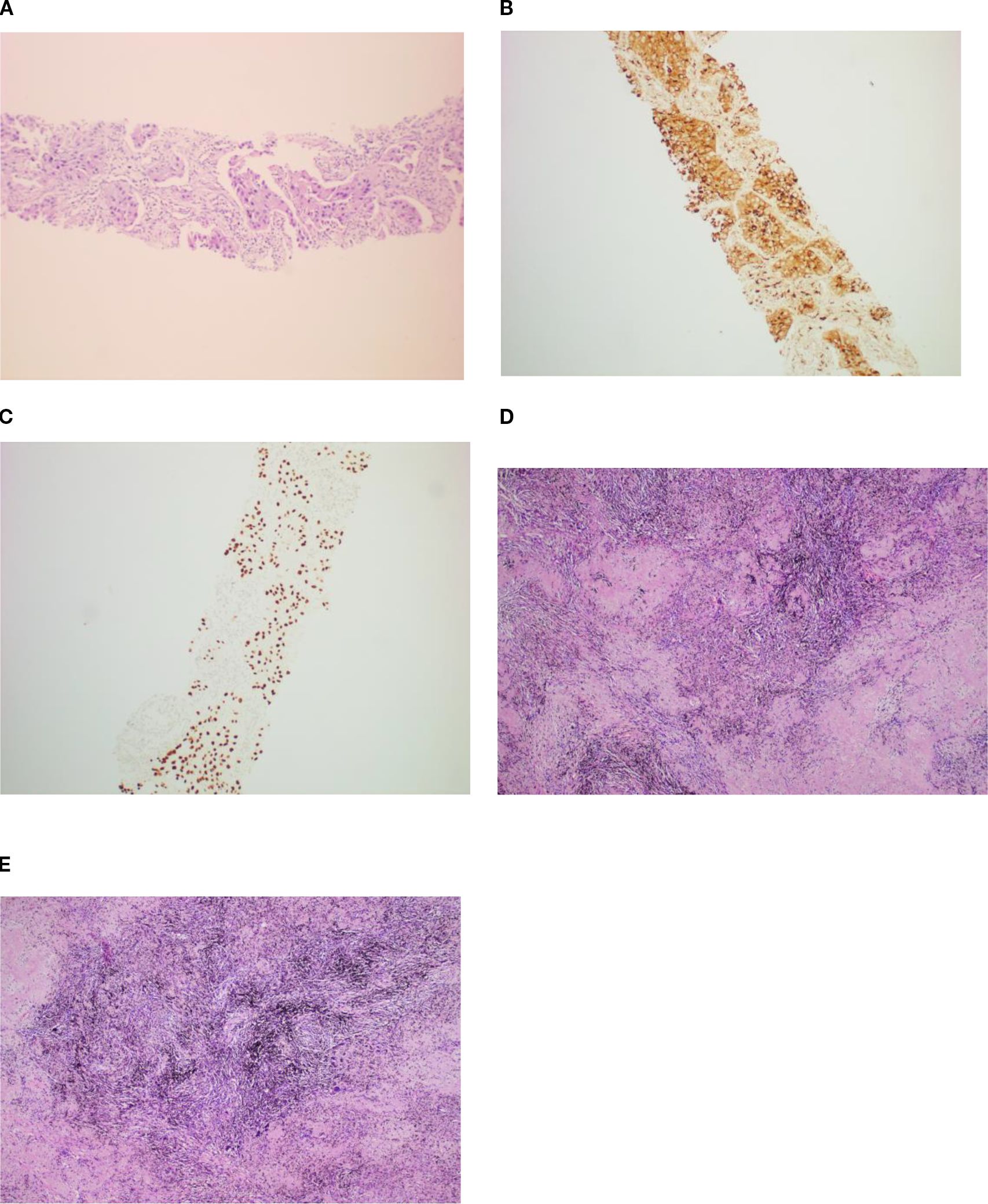
Figure 2. The patient was diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma via percutaneous CT-guided puncture biopsy (A) and immunohistochemistry[CK7(+), NapsinA(+) (B),TTF-1(+) (C), CK5/6(−), P40(−), Ki-67(+ approximately 20%), and CD56(−)]. During postoperative pathology, the residual lung adenocarcinoma was invisible under microscopy, with the area showing coagulative focal necroses, fibrous tissue hyperplasia, and lymphocytic infiltration (D, E). H&E staining, ×10.
Discussion
The central nervous system (CNS) is a common site for metastasis originating from lung cancer, making it the most prevalent type of brain metastasis (4). In NSCLC, approximately 10%–30% of patients are found to have brain metastases at the time of their initial diagnosis, a figure that tends to increase as treatment progresses (5). The presence of brain metastasis is frequently associated with a poor prognosis, often leading to a fatal outcome for patients with lung cancer (6). Symptoms of brain tumors can be categorized into general and localized manifestations, and individuals frequently exhibit both types of symptoms. Common generalized symptoms may include headaches, cognitive dysfunction, renal girdle changes, and gait disorders. Unilateral and localized manifestations include hemiparesis, speech impairment, and visual field defects. Brain metastases can be treated with local therapy, such as surgery, radiotherapy, or systemic therapy with anticancer drugs. The selection of the therapeutic approach is influenced by the histological classification, the patient’s overall health, and the quantity and dimension of the brain metastases (7).
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)–Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO)–American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) guidelines (8) indicate that, for individuals with brain metastases, surgical intervention can be a viable choice when various factors are taken into account. However, patients presenting with multiple brain lesions and poorly managed systemic diseases might see limited advantages from surgery unless the systemic condition is effectively addressed. For single brain metastasis, the European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO)–European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines (9) emphasize the preference for neurosurgical resection over any other intervention in patients with controlled systemic disease. For patients with symptomatic brain metastases, consideration should be given to the use of localized treatments (such as radiosurgery or a combination of approaches). It is advisable not to postpone local interventions, even in patients with asymptomatic brain metastases. Nonetheless, it is justifiable to postpone local treatment for individuals with asymptomatic brain metastases who are undergoing therapy with EGFR TKIs, e.g., ALK TKIs, including pemetrexed combined with platinum and pembrolizumab for those who test positive for PD-L1. It is crucial that the choice to postpone local treatment is made following a comprehensive evaluation by a team of specialists, weighing the advantages and disadvantages that the patients might face (7).
Chemotherapy and targeted therapies have limited effectiveness against brain tumors due to the blood–brain barrier (BBB) (10). However, recent advancements in the availability of drugs that target brain metastases have made it sensible to consider systemic therapy prior to local interventions for cases of asymptomatic brain metastases.
The FLAURA study demonstrated that osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR TKI, is beneficial for patients presenting with brain metastases, indicating an effective rate of intracranial disease control (11). Moreover, it has been demonstrated that furmonertinib, as an initial therapy, outperforms gefitinib in terms of CNS PFS, CNS objective response rate, and the extent of CNS response in individuals with EGFR-mutated NSCLC and CNS metastases (1).
Immune checkpoint inhibitors play a crucial role in the treatment of lung cancer that lacks driver mutations, while the presence of PD-L1 on tumor cells serves as an indicator of the effectiveness of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatments. Clinical trials within the KEYNOTE framework (12) (specifically KEYNOTE-021, KEYNOTE-189, and KEYNOTE-407) indicated that the combination of pembrolizumab and chemotherapy resulted in improved survival rates compared with chemotherapy alone, irrespective of whether a patient had brain metastases at the start of treatment. The effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors as an initial therapy for advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC in individuals with brain metastases was further supported by the findings from CheckMate 817 (13) and CheckMate 227 (14). In the context of locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC, the combination of Tislelizumab with platinum-based chemotherapy and pemetrexed demonstrated a favorable PFS profile and was generally well accepted by patients, exhibiting manageable levels of toxicity.
Currently, the CTONG0803 study and the BRAIN study have confirmed that icotinib is superior to radiotherapy in the control of intracranial lesions in NSCLC patients with EGFR-positive multiple brain metastases (15, 16). Determining the optimal treatment for the patient is necessary to improve the prognosis; therefore, we conducted a multidisciplinary discussion including oncologists, respiratory physicians, neurosurgeons, radiologists, and radiation oncologists. Considering the multiple metastases in the brain, the neurosurgeons did not recommend surgery, while a radiation oncologist advised the patient to undergo brain radiotherapy. After understanding the final treatment regimen, the patient refused brain radiotherapy. He received chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. After a course of treatment, the symptoms of cough and headache resolved, and adequate assessment resulted in a complete response of the brain metastases after 13 months. The safety of the triple-combination therapy remains a concern. While the FURLONG trial reported 28.4% grade ≥3 TRAEs with furmonertinib monotherapy (17), our regimen added only grade 1–2 toxicities. Finally, the patient underwent thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy and lymph node dissection for lung cancer, and pathological examination confirmed ypT0N0M0. No tumor recurrence was found in the brain and the lung during follow-up.
Conclusion
For brain metastases from lung cancer, both surgery and radiotherapy are the basic treatment options. However, it is necessary to assess the patient’s general condition and to determine who qualifies for treatment as it may not be optimal in certain cases. With drug development and the updated data on drug therapy, chemotherapy, molecular targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are currently available as effective treatment methods. Multidisciplinary treatment has become increasingly important for application of the latest information in clinical practice.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
XR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Data curation. JX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MF: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patient who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Shi Y, Chen G, Wang X, et al. Furmonertinib (AST2818) versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (FURLONG): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 study[J. Lancet Respir Med. (2022) 10:1019–28. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00168-0
2. Wu YL, Xue YR, Guo ZT, et al. Furmonertinib (Alflutinib, AST2818) is a potential positive control drug comparable to rifampin for evaluation of CYP3A4 induction in sandwich-cultured primary human hepatocytes[J. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2022) 43:747–56. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00692-7
3. Wang J, Lu S, Yu X, et al. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for advanced squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J. JAMA Oncol. (2021) 7:709–17. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0366
4. Brain tumor registry of Japan (2005-2008). Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). (2017) 57:9–102. doi: 10.2176/nmc.sup.2017-0001
5. Waqar SN, Samson PP, Robinson CG, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastasis at presentation[J. Clin Lung Cancer. (2018) 19:e373–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2018.01.007
6. Peters S, Bexelius C, Munk V, et al. The impact of brain metastasis on quality of life, resource utilization and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. (2016) 45:139–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.009
7. Okuno T, Isobe T, and Tsubata Y. Current pharmacologic treatment of brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2024) 41:549–65. doi: 10.1007/s10585-024-10276-4
8. Vogelbaum MA, Brown PD, Messersmith H, et al. Treatment for brain metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO guideline. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:492–516. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02314
9. Le Rhun E, Guckenberger M, Smits M, et al. EANO-ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with brain metastasis from solid tumours. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:1332–47. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.07.016
10. Banks WA. From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: new opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2016) 15:275–92. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.21
11. Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC, et al. CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2018), O2018783118. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.3118
12. Powell SF, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Langer C, et al. Outcomes with pembrolizumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy for patients with NSCLC and sta ble brain metastases: pooled analysis of KEYNOTE-021, -189, and -407. J Thorac Oncol. (2021) 16:1883–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.06.020
13. Ready NE, Audigier-Valette C, Goldman JW, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, including patients with ECOG performance status 2 and other special populations: CheckMate. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:817. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006127
14. Reck M, Ciuleanu TE, Lee JS, et al. Systemic and intracranial outcomes with first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic NSCLC and baseline brain metastases from checkMate 227 part 1. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:1055–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.04.021
15. Soffietti R, Ahluwalia M, Lin N, et al. Management of brain metastases according to molecular subtypes. Nat Rev Neurol. (2020) 16:557–74. doi: 10.1038/s41582-020-0391-x
16. Nardone V, Romeo C, D’ippolito E, et al. The role of brain radiotherapy for EGFR- and ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases: a review. Radiol Med. (2023) 128:316–29. doi: 10.1007/s11547-023-01602-z
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, brain metastasis, furmonertinib, conversion therapy, pathological complete response
Citation: Ran X, Luo T, Xiong J and Fu M (2025) Pathological complete response to conversion therapy for lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis: a case report. Front. Oncol. 15:1625918. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1625918
Received: 09 May 2025; Accepted: 08 September 2025;
Published: 14 October 2025.
Edited by:
Weimin Gao, Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI), United StatesReviewed by:
Yu-Shun Yang, Nanjing University, ChinaMaira Cristina Velho, Clinical Hospital of Porto Alegre, Brazil
Zsuzsanna Orosz, University of Debrecen, Hungary
Copyright © 2025 Ran, Luo, Xiong and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maoyong Fu, ZnVtYW95b25nbWRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xingqiang Ran
Xingqiang Ran Tao Luo
Tao Luo Jie Xiong
Jie Xiong Maoyong Fu
Maoyong Fu