- Department of Medical Oncology, The First People’s Hospital of Xiaoshan District, Hangzhou, China
Gastric cancer (GC) remains a major global health challenge, particularly in its advanced stages where prognosis is poor, and treatment responses are heterogeneous. Precision oncology aims to tailor therapies, but current biomarkers have limitations. Artificial Intelligence (AI), encompassing machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), offers powerful tools to analyze complex, multi-dimensional data from advanced GC patients, including clinical records, genomics, imaging (radiomics), and digital pathology (pathomics). This review synthesizes the current state of AI applications in unresectable, advanced GC. AI models demonstrate significant potential in refining diagnosis and staging, predicting treatment efficacy for chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, and assessing prognosis. Multi-modal AI approaches, integrating data from diverse sources, consistently show improved predictive performance over single-modality models, better reflecting the complexity of the disease. Key challenges remain, including data quality and standardization, model generalizability and interpretability, and the need for rigorous prospective validation. Future directions emphasize multi-center collaborations, development of robust and explainable AI (XAI), and seamless integration into clinical workflows. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial to translate AI’s potential into tangible clinical benefits, enabling truly personalized and effective management for patients with advanced gastric cancer.
1 Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) represents a significant global health burden, ranking as the fifth most common malignancy and a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide (1). Despite advances in treatment, the prognosis for patients diagnosed with advanced or metastatic GC remains poor, with 5-year overall survival rates often falling below 30%, and in metastatic settings, below 10% (2). A substantial proportion of patients present with unresectable disease at diagnosis due to non-specific early symptoms. Standard therapeutic approaches, including systemic chemotherapy, targeted therapy for specific molecular subtypes (e.g., human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive tumors), and immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICIs), form the backbone of management (3). However, patient responses to these treatments are highly heterogeneous, and many individuals derive limited benefit or develop resistance, highlighting a critical unmet need for more effective and personalized therapeutic strategies (4).
Precision oncology seeks to address this challenge by tailoring treatment strategies based on the unique characteristics of an individual patient’s tumor and host factors (5). This paradigm relies heavily on the identification and utilization of predictive biomarkers. In advanced GC, established biomarkers such as HER2 amplification, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression (often measured by Combined Positive Score, CPS), microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) status, and more recently, claudin 18.2 (CLDN18.2) expression, guide the use of specific targeted therapies and immunotherapies (6). However, these biomarkers have inherent limitations. Their assessment often requires invasive tissue sampling, which may not be feasible or representative, especially in the metastatic setting. Interpretation of immunohistochemistry (IHC) can be variable, and genomic sequencing assays like next-generation sequencing (NGS) can be costly with significant turnaround times. Crucially, existing biomarkers often fail to capture the full spectrum of tumor heterogeneity and the complex interplay within the tumor microenvironment (TIME), leading to imperfect prediction of treatment response (7, 8).
Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly its subfields of Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), offers a powerful set of tools to overcome these limitations. ML algorithms, such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forests (RF), and logistic regression, learn patterns from data to make predictions without explicit programming (9). DL models, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), utilize hierarchical layers of processing units to automatically extract complex features and relationships from high-dimensional data. These capabilities make AI uniquely suited to analyze the vast and complex datasets generated in modern oncology, including clinical records, genomic and transcriptomic data (NGS), medical images (computed tomography, positron emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, endoscopy), and digitized histopathology slides (Whole Slide Images, WSI) (10, 11). The confluence of pressing clinical needs in advanced GC, the exponential growth in digital biomedical data, and the maturation of AI algorithms has fueled a rapid increase in research exploring AI’s potential in this field (12). While much early AI research in GC focused on improving endoscopic detection of early-stage disease, a significant opportunity lies in leveraging AI for the complex decision-making required in advanced stages. The profound tumor heterogeneity, diverse treatment options, and high stakes associated with advanced GC management present challenges where AI’s capacity for integrating multi-faceted data can offer substantial clinical value (13).
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the current applications of AI in the precision oncology landscape specifically for advanced, unresectable gastric cancer. It synthesizes evidence on the use of AI for refining diagnosis relevant to treatment selection, predicting treatment efficacy and toxicity, enabling personalized therapy through multi-modal data integration, and exploring novel strategies for managing refractory disease. The aim is to critically evaluate the current state-of-the-art, highlighting both the practical utility of emerging AI tools for clinicians and researchers and the key challenges and future directions necessary to translate these technologies into improved patient outcomes.
2 AI-driven precision diagnostics and staging refinement in advanced gastric cancer
Although the primary focus of this review is unresectable advanced GC, the accurate characterization and staging of the disease remain fundamental for determining prognosis and guiding the selection and intensity of systemic therapies. AI offers capabilities to extract deeper insights from standard diagnostic modalities, potentially refining risk stratification beyond traditional Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) staging.
2.1 Radiomics for advanced GC characterization
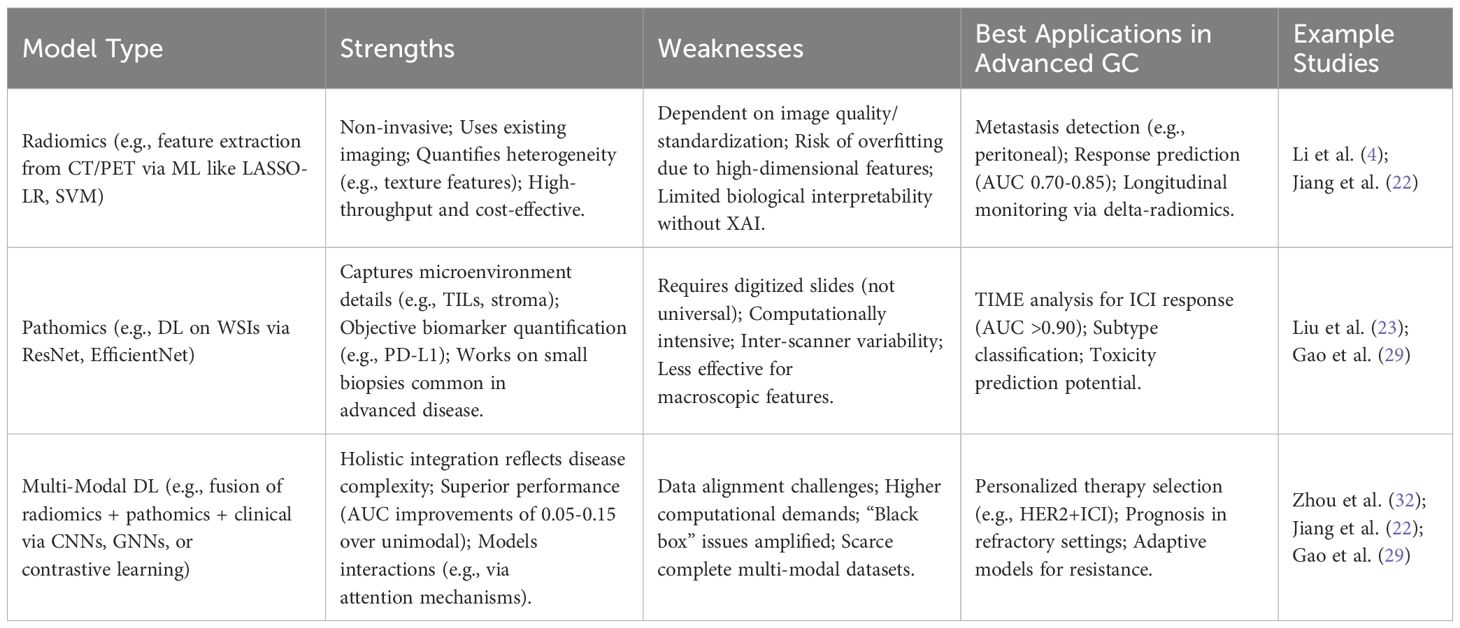
Radiomics involves the high-throughput extraction and analysis of quantitative features from medical images (CT, PET, MRI), converting them into mineable data that can reveal underlying pathophysiology often invisible to the human eye (14). In advanced GC, radiomics models have shown promise in several areas. AI algorithms, particularly CNNs and Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (FR-CNN), have been developed to identify preoperative peritoneal metastasis from CT images (15). Predicting lymph node metastasis (LNM) is another critical application, as conventional CT imaging has known limitations, especially after neoadjuvant therapy which can alter lymph node morphology and size (16). Several studies have demonstrated that CT-based radiomics models, often employing ML algorithms like K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), SVM, or DL approaches, can predict LNM status or quantify the number of metastatic nodes with significantly higher accuracy (Area Under the Curve [AUC] values often exceeding 0.75-0.80) compared to radiologists’ assessment alone (15). This improved LNM prediction, even in unresectable patients, provides valuable prognostic information that could influence decisions regarding the aggressiveness of palliative treatment or eligibility for clinical trials targeting specific metastatic patterns (13). Beyond metastasis detection, radiomics can quantify intra-tumoral heterogeneity, a known factor influencing treatment response and prognosis, by analyzing texture features within the tumor volume (17). Furthermore, AI applied to CT scans can perform automated body morphometry analysis, assessing features like sarcopenia (muscle wasting), which may correlate with patient frailty, treatment tolerance, and overall survival (18). The ability of radiomics to extract such detailed information non-invasively from standard-of-care imaging is a key advantage (19). Patients with advanced GC typically undergo repeated CT or PET scans for initial staging and treatment monitoring. Radiomics leverages this existing data to provide deeper biological insights without requiring additional invasive procedures, enabling longitudinal assessment of tumor characteristics and heterogeneity, which is crucial for adapting treatment in the dynamic advanced disease setting (20).
2.2 Radiomics for occult peritoneal metastasis detection
Peritoneal metastasis represents the most common pattern of distant metastasis in advanced GC, occurring in up to 66% of patients and serving as a major determinant of prognosis and treatment strategy selection (15, 20). The detection of occult peritoneal metastasis remains a critical clinical challenge, as patients with undetected peritoneal disease may undergo inappropriate surgical interventions or miss opportunities for optimal systemic therapy.
Conventional CT imaging demonstrates significant limitations in detecting early-stage peritoneal metastasis, with sensitivity as low as 28.3%-50.9%, particularly for tumor implants smaller than 1 cm (20, 21). These diagnostic limitations have led to the development of AI-driven approaches specifically targeting occult peritoneal metastasis detection. Dong et al. developed a pioneering radiomic nomogram incorporating both primary tumor and peritoneal region features, achieving excellent performance with AUCs of 0.958 in training and 0.928-0.941 in external validation cohorts across multiple centers (20). This approach demonstrated that both the tumor characteristics (“seed”) and peritoneal microenvironment features (“soil”) contribute to metastatic potential, reflecting the biological basis of the “seed and soil” hypothesis.
Building upon radiomics approaches, deep learning models have shown even greater promise. The Peritoneal Metastasis Network (PMetNet) developed by Jiang et al. achieved remarkable performance with AUCs of 0.946-0.920 in external validation, demonstrating sensitivities of 75.4%-87.5% and specificities of 92.9%-98.2% (22). Importantly, this model substantially outperformed conventional clinicopathological factors and could identify occult peritoneal metastasis missed by radiologist interpretation. The integration of gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) provided interpretability by highlighting intra-tumoral regions associated with metastatic potential, suggesting that tumor heterogeneity may be a key factor in determining peritoneal spread.
Beyond imaging-based approaches, novel AI-assisted molecular techniques are emerging. Chen et al. developed stimulated Raman molecular cytology (SRMC), combining three-color stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with deep learning for analyzing exfoliated cells in peritoneal lavage fluid (23). This approach achieved 81.5% sensitivity and 84.9% specificity within 20 minutes, representing a significant advancement over conventional cytology’s <60% sensitivity. The method’s ability to analyze both cellular morphology and molecular composition (lipid, protein, and DNA content) demonstrates the potential for AI-driven integration of multiple biological features.
These advances in AI-powered peritoneal metastasis detection address a critical unmet clinical need in advanced GC management. The ability to accurately identify occult peritoneal disease preoperatively could significantly impact treatment decision-making, helping to avoid unnecessary surgical procedures while ensuring appropriate patients receive optimal systemic therapy or are considered for specialized peritoneal-directed treatments.
2.3 Pathomics for advanced GC characterization
Pathomics, or computational pathology, applies AI techniques to analyze digitized WSI obtained from tissue biopsies or surgical specimens (24). Even from small biopsy samples typically available in the advanced/metastatic setting, AI can extract a wealth of information. DL models, such as those based on ResNet or Inception architectures, have demonstrated high accuracy (often >90-95%) in classifying gastric tissue as normal, dysplastic, or cancerous, potentially aiding pathologists and reducing inter-observer variability (15). AI can also automate tasks like histological grading or classifying GC subtypes according to systems like the Lauren classification (25). A particularly promising application is the analysis of the TIME from H&E stained slides. AI algorithms can automatically detect and quantify TILs or assess stromal characteristics, features known to be associated with prognosis and response to immunotherapy (26). Furthermore, AI can assist in the interpretation of IHC staining for key biomarkers like HER2 and PD-L1. By objectively quantifying staining intensity and distribution, AI may improve the consistency and accuracy of biomarker assessment, which is critical for guiding targeted therapy and immunotherapy decisions (6). Similar to radiomics, pathomics offers a way to extract quantitative, objective data from routinely collected diagnostic materials (biopsy slides), providing insights into tumor biology and heterogeneity (27). This is valuable in advanced GC where metastatic tissue biopsies might be the only available samples, and understanding their characteristics is key to treatment planning.
3 AI for predicting treatment efficacy in advanced gastric cancer
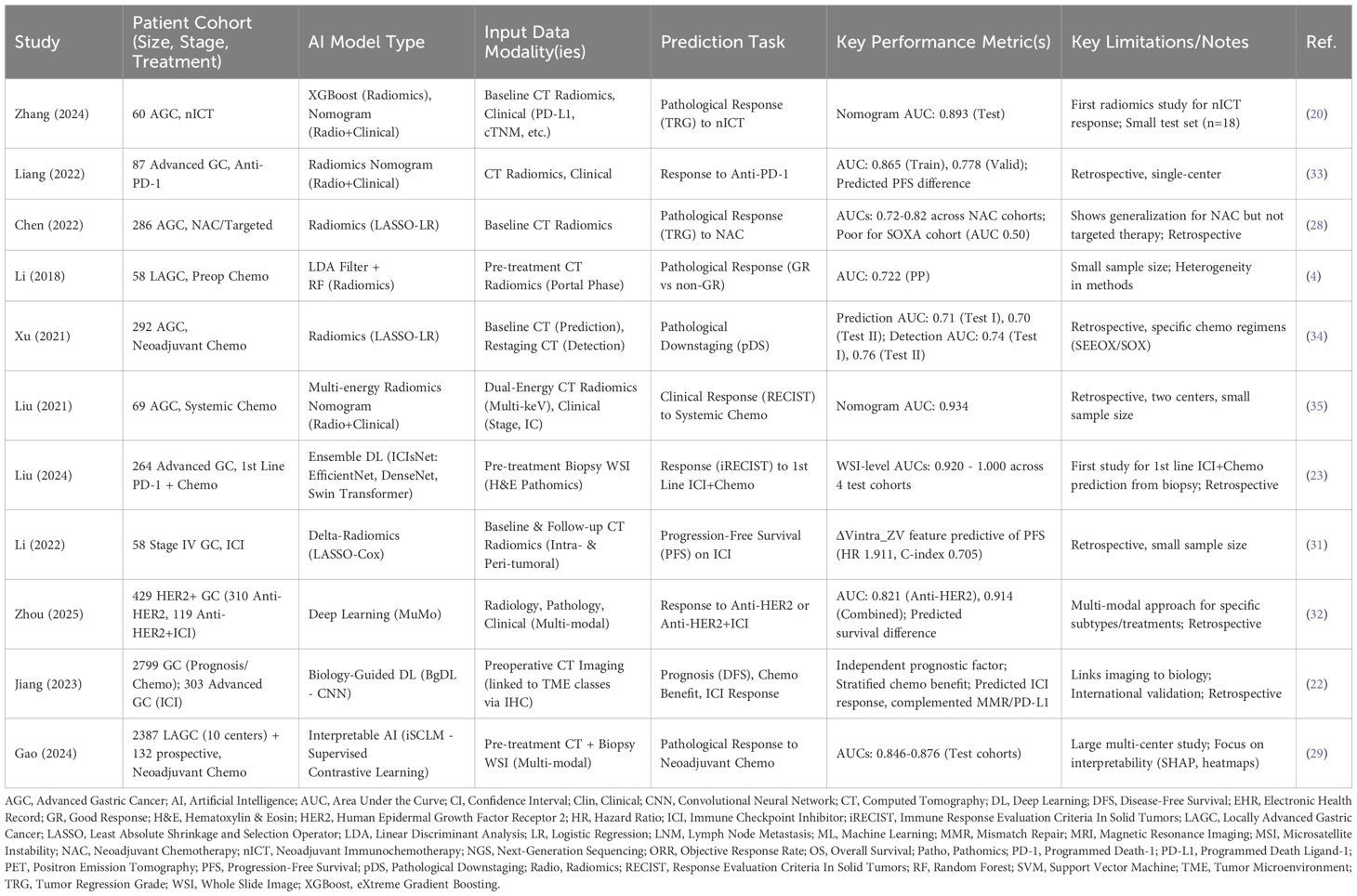
A major goal of precision oncology in advanced GC is to predict which patients are most likely to benefit from a specific therapy, thereby maximizing efficacy while minimizing unnecessary toxicity and cost. AI is being extensively investigated for its potential to predict responses to various systemic treatments (Table 1).
3.1 Predicting response to systemic chemotherapy
Systemic chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of treatment for many patients with advanced GC, either in the palliative setting or potentially as neoadjuvant treatment for initially unresectable patients who might become candidates for conversion surgery. Predicting response is crucial for optimizing treatment selection. Numerous studies have explored the use of CT-based radiomics to predict pathological response (often assessed by Tumor Regression Grade, TRG) or clinical response (e.g., according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, RECIST) to neoadjuvant or palliative chemotherapy (28). These studies employ various ML algorithms, including logistic regression (LR), SVM, RF, eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and DL models like DenseNet or V-Net, trained on features extracted from pre-treatment CT scans or changes observed between baseline and follow-up scans (delta-radiomics) (28). Reported performance metrics, such as AUC values, often range from 0.70 to over 0.85, suggesting a definite predictive signal. Some evidence suggests these radiomic signatures might generalize across different chemotherapy regimens, although inconsistencies in methodology and patient cohorts remain a challenge. Pathomics is also emerging as a predictive tool; for instance, interpretable AI frameworks like iSCLM (incremental Supervised Contrastive Learning Model), using supervised contrastive learning on pre-treatment biopsy WSIs combined with CT data, have achieved AUCs around 0.85 for predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy response (29). Additionally, older studies explored ML models like SVM using clinical and demographic data, or gene expression profiles, to predict benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy, indicating the potential of non-imaging data as well (15). While the numerous radiomics studies reflect a strong clinical need for pre-treatment stratification, the variability in methods and often moderate predictive accuracy suggest that radiomics alone may not be sufficient for robust clinical decision-making. Its value likely lies in capturing tumor phenotypic information that complements other data modalities within integrated models.
3.2 Predicting response to immunotherapy (ICI)
ICIs, particularly anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, have become integral to the treatment of advanced GC, both as monotherapy in later lines and increasingly in combination with chemotherapy in the first-line setting (23). However, only a subset of patients responds, making predictive biomarkers essential. AI offers promising avenues to improve upon or complement existing biomarkers like PD-L1 CPS, TMB, and MSI/dMMR status, which have recognized limitations related to predictive accuracy and assessment challenges (30). Radiomics models based on CT or PET imaging features have been developed to predict response or survival outcomes in patients receiving anti-PD-1 therapy, with reported AUCs reaching up to 0.86. Delta-radiomics, assessing changes in imaging features during treatment, may also provide prognostic information (31). Pathomics approaches using DL on diagnostic H&E biopsy WSIs have shown remarkable success in predicting response to first-line PD-1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy combinations, achieving AUCs exceeding 0.90 in some validation cohorts (23). These models likely capture subtle morphological features of the tumor cells and the surrounding microenvironment (e.g., TIL density, stromal characteristics) that correlate with immune response. On the genomic front, AI algorithms like SVM have been used to analyze immuno-oncology related gene expression signatures from tumor samples to generate predictive scores (e.g., ‘ Immuno-Oncology Score’) for durable clinical benefit (21). Furthermore, innovative approaches like biology-guided deep learning (BgDL) explicitly link imaging features (from CT) to predicted TME subtypes (based on IHC markers like IS_GC_ and POSTN) to predict ICI response (22). Notably, such models may identify potential non-responders even within biomarker-positive groups like dMMR patients, suggesting a role in refining patient selection beyond current guidelines (22). The ability of AI to leverage non-invasive imaging or readily available biopsy slides offers a significant practical advantage over repeated invasive sampling, potentially providing a more comprehensive and dynamic assessment of immunotherapy response likelihood (23).
3.3 Predicting response to targeted therapies
Anti-HER2 therapy (e.g., trastuzumab) is standard for HER2-positive advanced GC, but response rates are not universal, and resistance can develop. While HER2 status determined by IHC/FISH is the primary selection criterion, AI may offer ways to refine prediction within this group. Research is exploring whether radiomic or pathomic features can capture tumor heterogeneity or other biological factors associated with response or resistance to anti-HER2 agents (32). Multi-modal AI models, such as the MuMo (Multi-Modal) model, integrate radiology, pathology, and clinical data to specifically predict response to anti-HER2 monotherapy (achieving an AUC of ~0.82) and, importantly, to the increasingly used combination of anti-HER2 therapy plus ICIs (AUC ~0.91) (32). The development of AI models specifically targeting combination therapies reflects the evolving treatment landscape and AI’s capacity to handle the increased complexity of predicting outcomes for multi-agent regimens, moving beyond single-agent prediction to potentially guide more complex treatment selections.
4 AI-powered multi-modal data integration for personalized treatment selection
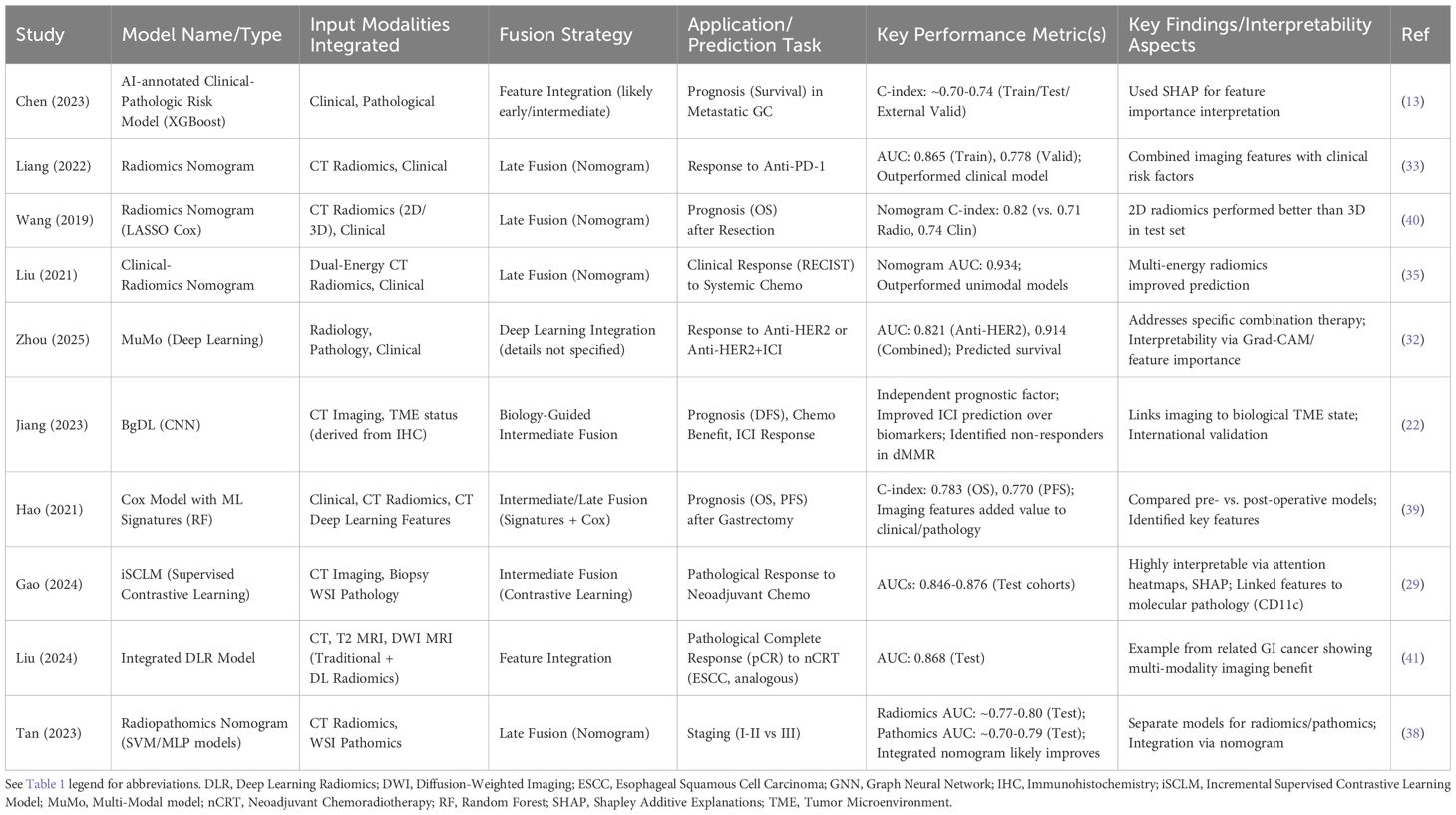
The inherent complexity and heterogeneity of advanced GC necessitate a holistic understanding that often transcends the information available from any single data source (36). Clinicians naturally integrate diverse information—patient history, physical examination, laboratory results, imaging reports, pathology findings—to make treatment decisions. AI, particularly through multi-modal learning, aims to replicate and enhance this integrative process by computationally combining data from various modalities, such as clinical records, genomics/transcriptomics, radiomics (from CT, PET, MRI), and pathomics (from WSI) (36). This approach promises a more comprehensive patient profile, potentially leading to more accurate predictions and truly personalized treatment selection (37).
Several strategies exist for integrating multi-modal data within AI frameworks. Early fusion involves concatenating raw or processed features from different modalities before feeding them into a single model. Intermediate fusion learns separate representations for each modality first, then integrates these representations at one or more hidden layers within the model; this allows for more flexibility and can utilize techniques like attention mechanisms, gating mechanisms, graph neural networks (GNNs), or Kronecker products to model cross-modal interactions effectively (29). Late fusion involves training separate models for each modality and then combining their outputs or predictions (e.g., through averaging, voting, or meta-learning) to reach a final decision (37). The choice of fusion strategy often depends on the specific task, data types, and desired level of interaction modeling.
Numerous studies are now demonstrating the value of multi-modal AI in advanced GC. Integrating radiomic features derived from CT or PET scans with clinical variables (like TNM stage, performance status, lab values) has consistently shown improved performance in predicting survival or treatment response compared to using either modality alone, often reflected in higher C-indices or AUCs (13). Similarly, combining pathomic features from WSIs with clinical data has enhanced prognostic accuracy (37). More advanced integrations are also emerging. The iSCLM framework successfully combined pre-treatment CT scans and H&E biopsy images to predict neoadjuvant chemotherapy response with high accuracy across multiple centers (29). Radiopathomics models integrating features from both imaging and pathology slides are being developed for improved staging (38). Biology-guided approaches explicitly link imaging features to molecular or TME characteristics (derived from IHC or genomics) to predict outcomes, as seen in the BgDL model (22). Perhaps the most comprehensive examples involve integrating three or more modalities; the MuMo model effectively combined radiology, pathology, and clinical data to predict response to HER2-targeted therapy with or without immunotherapy (32), and other studies have integrated CT-derived radiomic and DL features with clinical variables for survival prediction (39). These studies consistently report that multi-modal models outperform their unimodal counterparts, underscoring the benefit of data integration (37). The increasing focus on such integrative models signals a maturation of the field, moving beyond single-modality proofs-of-concept towards approaches that better mirror the complexity of clinical reality and offer potentially more robust and relevant predictions (Table 2).
Despite the promise, significant challenges remain in multi-modal AI. Acquiring complete datasets with all desired modalities for the same patient cohort can be difficult. Aligning data from different sources (e.g., mapping genomic alterations to specific regions on an image) is non-trivial. The computational cost and complexity of training these models are higher and ensuring the interpretability of how different data types contribute to the final prediction is crucial for clinical trust and adoption (36). Addressing the “black box” nature of complex models is vital. The development of interpretable multi-modal models, such as those using attention mechanisms (e.g., Grad-CAM for visualizing image focus) or Shapley values to quantify feature contributions, or those explicitly guided by biological principles (like BgDL or iSCLM linking predictions to TME or molecular features), represents a critical step towards clinical acceptance. By providing insights into the model’s reasoning process and linking predictions to recognizable biological or visual features, these approaches enhance transparency and facilitate validation.
Radiomics excels in non-invasive applications but struggles with generalizability, as seen in variable AUCs across regimens (28). Pathomics provides granular biological insights but is biopsy-dependent, limiting its use in serial monitoring. Multi-modal DL addresses these by synergizing modalities, consistently outperforming unimodal approaches (e.g., C-index gains in (39)), though it demands advanced XAI for clinical trust. Overall, multi-modal models represent the frontier but require prospective validation to mitigate data gaps (Table 3).
5 AI applications in refractory advanced gastric cancer
Patients with advanced GC whose disease progresses despite standard first- and second-line therapies face a particularly challenging situation with limited treatment options and a dismal prognosis (5). Identifying effective strategies for this refractory setting is a critical unmet need. AI offers potential avenues to address this challenge, although applications are currently more exploratory than established.
One potential role for AI is in understanding the mechanisms of treatment resistance. By analyzing longitudinal multi-modal data (e.g., serial imaging, sequential biopsies with genomic/transcriptomic profiling) from patients who develop resistance, AI algorithms might identify patterns or biomarkers predictive of failure. For example, identifying an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype, potentially detectable through imaging or molecular analysis, has been linked to resistance to both chemotherapy and immunotherapy in some cancers, and AI could help detect such signatures (42).
AI-driven drug repurposing represents another promising strategy (43). This involves using computational methods to identify existing drugs, approved for non-cancer indications, that may have anti-cancer activity in GC. AI algorithms can analyze vast databases encompassing drug structures, protein targets, gene expression profiles, pathway interactions, and scientific literature to predict potential drug-disease associations much faster than traditional screening methods. While numerous drugs have been investigated for repurposing in GC (e.g., metformin, statins, certain antibiotics, antidepressants), the use of AI specifically to identify these candidates for refractory GC is not yet widely documented in validated studies. However, the potential to rapidly screen existing compounds with known safety profiles makes this an attractive approach for finding new options quickly.71 This approach holds particular promise for refractory GC because it offers a potentially faster and less expensive route to finding effective therapies compared to the lengthy and costly process of de novo drug development.
Furthermore, AI could facilitate cross-cancer learning to generate treatment recommendations (44). Models trained on large datasets encompassing multiple cancer types might identify shared molecular vulnerabilities or predictive signatures for response to specific drugs, even if those drugs are not typically used in GC (45). This aligns with the concept behind basket trials like the NCI-MATCH study, which enrolls patients based on molecular alterations rather than tumor histology (46). However, the clinical utility of simply identifying an “actionable alteration” via NGS alone has been limited in advanced GC, with low rates of enrollment onto genotype-matched trials and uncertain clinical benefit. This highlights a potential key role for AI: moving beyond simple mutation matching to integrate genomic data with clinical context, imaging phenotypes, and pathway information, potentially learned from broader cross-cancer datasets, to more accurately predict the likelihood of benefit from a targeted therapy in a refractory patient (47, 48). AI might be a necessary component to effectively translate genomic findings into successful therapeutic strategies in the complex refractory setting.
Currently, these AI applications for refractory GC remain largely conceptual or in early research stages. Realizing their potential will require significant advancements in data infrastructure (integrated knowledge graphs, cross-institutional data sharing), robust predictive modeling capable of handling diverse data types, and validation in prospective clinical settings.
6 Bridging the gap: challenges, future directions, and clinical translation
Despite the significant progress and immense potential of AI in managing advanced GC, several substantial challenges must be addressed to bridge the gap between research findings and routine clinical practice.
6.1 Recap of key challenges
A recurring theme throughout the literature is the set of obstacles hindering the widespread adoption of AI tools. Data-related issues are paramount, including limitations in data quality, quantity, and heterogeneity across institutions. Lack of standardized data acquisition protocols (especially for imaging and digital pathology) and annotation methods makes it difficult to compare results and train generalizable models. Accessing large, well-curated, multi-modal datasets representing diverse patient populations remains a major hurdle, often leading to studies based on single-center, retrospective cohorts with limited external validity. Data privacy and security concerns also complicate data sharing efforts. Model-related challenges include the risk of overfitting to training data and poor generalizability to new, unseen data. The inherent “black box” nature of many complex DL models poses a significant barrier to clinical trust and adoption, as clinicians require transparency and understanding of how predictions are generated. Validation represents another critical bottleneck. The vast majority of studies rely on retrospective validation, with a striking lack of prospective trials evaluating AI tools in real-world clinical workflows. Standardized evaluation metrics and benchmarks are needed for objective comparison of different models. Finally, implementation challenges include integrating AI tools seamlessly into existing clinical decision support systems, navigating complex regulatory approval pathways (e.g., FDA clearance), and addressing ethical considerations surrounding algorithmic bias and accountability. The evidence suggests that the primary impediment to clinical translation may not be the sophistication of AI algorithms themselves, but rather these persistent issues surrounding data infrastructure and robust validation.
6.2 Future research directions
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach. Data strategies should focus on fostering multi-center collaborations and establishing data sharing consortia to build larger, more diverse datasets. Implementing standardized protocols for data acquisition (e.g., imaging parameters, WSI scanning) and annotation is crucial. Techniques like federated learning, which allow models to be trained across multiple institutions without centralizing sensitive patient data, offer a promising solution to privacy concerns. Model development must prioritize robustness, generalizability, and interpretability. Continued research into Explainable AI (XAI) techniques is essential to build trust and facilitate clinical adoption. Advancing multi-modal fusion techniques to better capture synergistic information from different data sources remains a key area. Developing dynamic models that can incorporate longitudinal data (e.g., changes in imaging or biomarkers over time) could enable adaptive treatment strategies. Validation efforts must shift towards rigorous prospective clinical trials designed to assess the real-world impact of AI tools on clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. Head-to-head comparisons against current clinical standards and biomarkers are necessary. Specific needs for advanced GC include developing AI tools tailored for predicting response to novel combination therapies, identifying mechanisms of acquired resistance, guiding optimal therapy sequencing, improving toxicity prediction, and potentially incorporating patient-reported outcomes into predictive models.
6.3 Path to clinical translation
The journey from AI research to clinical practice requires careful navigation. Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of AI medical devices. Successful implementation necessitates designing AI tools that are user-friendly and integrate smoothly into existing clinical workflows, providing actionable information to clinicians at the point of care. Education and training programs will be vital to equip clinicians with the knowledge and skills to effectively use and interpret AI-driven insights. Crucially, achieving meaningful clinical integration will demand a paradigm shift towards sustained interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, AI scientists, bioinformaticians, implementation scientists, ethicists, and regulatory bodies. This collaborative ecosystem is essential for ensuring that AI tools address genuine clinical needs, are rigorously validated, ethically deployed, and ultimately contribute to improved patient care.
7 Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in the management of advanced gastric cancer. Significant progress has been demonstrated in leveraging AI, particularly ML and DL techniques, to analyze complex data derived from radiomics, pathomics, genomics, and clinical records. These approaches show considerable promise in refining diagnostic accuracy relevant to treatment planning, predicting patient prognosis with greater precision, and, crucially, forecasting response to various systemic therapies including chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted agents. The development of multi-modal AI models, capable of integrating information from diverse sources, represents a particularly important advancement, offering a more holistic understanding of tumor biology and patient characteristics, often leading to superior predictive performance compared to unimodal approaches. Furthermore, nascent applications of AI in identifying potential therapeutic avenues for refractory disease highlight its potential to address critical unmet needs.
The ultimate potential of AI lies in its ability to facilitate truly personalized medicine for patients with advanced gastric cancer. By uncovering subtle patterns hidden within complex data, AI can provide deeper insights into individual tumor biology, predict responses to specific treatments with greater accuracy, identify patients at high risk of toxicity, and optimize therapeutic strategies in ways previously unattainable.
However, the translation of this potential into routine clinical practice faces significant hurdles. Challenges related to data quality, accessibility, and standardization, coupled with the need for robust, prospective validation of AI models in diverse, real-world settings, remain major obstacles. Ensuring model interpretability and generalizability, navigating regulatory pathways, and achieving seamless integration into clinical workflows are also critical steps. Overcoming these challenges will require sustained, collaborative efforts involving researchers, clinicians, data scientists, industry partners, and regulatory agencies. Continued rigorous research focusing on high-quality data, robust validation, and the development of interpretable, clinically integrated AI tools is paramount. If these efforts are successful, AI holds the promise to fundamentally reshape the management of advanced gastric cancer, moving beyond empirical approaches towards a future of data-driven, personalized care that offers improved outcomes and hope for patients facing this challenging disease.
Author contributions
MF: Data curation, Visualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JX: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. YL: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Visualization. BJ: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Huang X, Qin M, Fang M, Wang Z, Hu C, Zhao T, et al. The application of artificial intelligence in upper gastrointestinal cancers. J Natl Cancer Cent. (2025) 5:113–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2024.12.006
2. Lin JL, Lin JX, Lin GT, Huang CM, Zheng CH, Xie JW, et al. Global incidence and mortality trends of gastric cancer and predicted mortality of gastric cancer by 2035. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:1763. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19104-6
3. Guan WL, He Y, and Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:57. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01451-3
4. Li Z, Zhang D, Dai Y, Dong J, Wu L, Li Y, et al. Computed tomography-based radiomics for prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy outcomes in locally advanced gastric cancer: A pilot study. Chin J Cancer Res. (2018) 30:406–14. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.04.03
5. Zeng Z and Zhu Q. Progress and prospects of biomarker-based targeted therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1382183. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1382183
6. Sun Y, Puspanathan P, Lim T, and Lin D. Advances and challenges in gastric cancer testing: the role of biomarkers. Cancer Biol Med. (2025) 22:212–30. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0386
7. Imodoye SO, Adedokun KA, and Bello IO. From complexity to clarity: unravelling tumor heterogeneity through the lens of tumor microenvironment for innovative cancer therapy. Histochem Cell Biol. (2024) 161:299–323. doi: 10.1007/s00418-023-02258-6
8. Jia Q, Wang A, Yuan Y, Zhu B, and Long H. Heterogeneity of the tumor immune microenvironment and its clinical relevance. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2022) 11:24. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00277-y
9. Choi S and Kim S. Artificial intelligence in the pathology of gastric cancer. J Gastric Cancer. (2023) 23:410–27. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2023.23.e25
10. Shams A. Leveraging state-of-the-art AI algorithms in personalized oncology: from transcriptomics to treatment. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14(1):24. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14192174
11. Chakrabarty N and Mahajan A. Imaging analytics using artificial intelligence in oncology: A comprehensive review. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2024) 36:498–513. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2023.09.013
12. Zhang G, Song J, Feng Z, Zhao W, Huang P, Liu L, et al. Artificial intelligence applicated in gastric cancer: A bibliometric and visual analysis via CiteSpace. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1075974. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1075974
13. Chen Y, Shou L, Xia Y, Deng Y, Li Q, Huang Z, et al. Artificial intelligence annotated clinical-pathologic risk model to predict outcomes of advanced gastric cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1099360. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1099360
14. Rogers W, Thulasi Seetha S, Refaee TAG, Lieverse RIY, Granzier RWY, Ibrahim A, et al. Radiomics: from qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br J Radiol. (2020) 93:20190948. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190948
15. Niu PH, Zhao LL, Wu HL, Zhao DB, and Chen YT. Artificial intelligence in gastric cancer: Application and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. (2020) 26:5408–19. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5408
16. Micciche F, Rizzo G, Casa C, Leone M, Quero G, Boldrini L, et al. Role of radiomics in predicting lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer: a systematic review. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1189740. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1189740
17. Petinrin OO, Saeed F, Toseef M, Liu Z, Basurra S, Muyide IO, et al. Machine learning in metastatic cancer research: Potentials, possibilities, and prospects. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2023) 21:2454–70. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.046
18. Kim KW, Huh J, Urooj B, Lee J, Lee J, Lee IS, et al. Artificial intelligence in gastric cancer imaging with emphasis on diagnostic imaging and body morphometry. J Gastric Cancer. (2023) 23:388–99. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2023.23.e30
19. Tabari A, Chan SM, Omar OMF, Iqbal SI, Gee MS, and Daye D. Role of machine learning in precision oncology: applications in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 15(1):63 doi: 10.3390/cancers15010063
20. Zhang J, Wang Q, Guo TH, Gao W, Yu YM, Wang RF, et al. Computed tomography-based radiomic model for the prediction of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy response in patients with advanced gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2024) 16:4115–28. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4115
21. Li M, Kaili D, and Shi L. Biomarkers for response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2022) 14:19–37. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i1.19
22. Jiang Y, Zhang Z, Wang W, Huang W, Chen C, Xi S, et al. Biology-guided deep learning predicts prognosis and cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5135. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40890-x
23. Liu Y, Chen W, Ruan R, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Guan T, et al. Deep learning based digital pathology for predicting treatment response to first-line PD-1 blockade in advanced gastric cancer. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:438. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05262-z
24. Moscalu M, Moscalu R, Dascalu CG, Tarca V, Cojocaru E, Costin IM, et al. Histopathological images analysis and predictive modeling implemented in digital pathology-current affairs and perspectives. Diagnostics (Basel). (2023) 13(14):2379. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142379
25. Li R, Li J, Wang Y, Liu X, Xu W, Sun R, et al. The artificial intelligence revolution in gastric cancer management: clinical applications. Cancer Cell Int. (2025) 25:111. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03756-4
26. Ye Z, Zeng D, Zhou R, Shi M, and Liao W. Tumor microenvironment evaluation for gastrointestinal cancer in the era of immunotherapy and machine learning. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:819807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.819807
27. Chen S, Ding P, Guo H, Meng L, Zhao Q, and Li C. Applications of artificial intelligence in digital pathology for gastric cancer. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1437252. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1437252
28. Chen Y, Xu W, Li YL, Liu W, Sah BK, Wang L, et al. CT-based radiomics showing generalization to predict tumor regression grade for advanced gastric cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:758863. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.758863
29. Gao P, Xiao Q, Tan H, Song J, Fu Y, Xu J, et al. Interpretable multi-modal artificial intelligence model for predicting gastric cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cell Rep Med. (2024) 5:101848. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101848
30. Choi S, Park S, Kim H, Kang SY, Ahn S, and Kim KM. Gastric cancer: mechanisms, biomarkers, and therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(3):543. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030543
31. Li J, Chen Z, Chen Y, Zhao J, He M, Li X, et al. CT-based delta radiomics in predicting the prognosis of stage IV gastric cancer to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1059874. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1059874
32. Zhou S, Xie Y, Feng X, Li Y, Shen L, and Chen Y. Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal cancer research: Image learning advances and applications. Cancer Lett. (2025) 614:217555. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217555
33. Liang Z, Huang A, Wang L, Bi J, Kuang B, Xiao Y, et al. A radiomics model predicts the response of patients with advanced gastric cancer to PD-1 inhibitor treatment. Aging (Albany NY). (2022) 14:907–22. doi: 10.18632/aging.203850
34. Xu Q, Sun Z, Li X, Ye C, Zhou C, Zhang L, et al. Advanced gastric cancer: CT radiomics prediction and early detection of downstaging with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:8765–74. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07962-2
35. Liu YY, Zhang H, Wang L, Lin SS, Lu H, Liang HJ, et al. Predicting response to systemic chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer using pre-treatment dual-energy CT radiomics: A pilot study. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:740732. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.740732
36. Chang L, Liu J, Zhu J, Guo S, Wang Y, Zhou Z, et al. Advancing precision medicine: the transformative role of artificial intelligence in immunogenomics, radiomics, and pathomics for biomarker discovery and immunotherapy optimization. Cancer Biol Med. (2025) 22:33–47. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0376
37. Yang H, Yang M, Chen J, Yao G, Zou Q, and Jia L. Multimodal deep learning approaches for precision oncology: a comprehensive review. Brief Bioinform. (2024) 26(1):bbae699. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae699
38. Tan Y, Feng LJ, Huang YH, Xue JW, Long LL, and Feng ZB. A comprehensive radiopathological nomogram for the prediction of pathological staging in gastric cancer using CT-derived and WSI-based features. Transl Oncol. (2024) 40:101864. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101864
39. Hao D, Li Q, Feng QX, Qi L, Liu XS, Arefan D, et al. Identifying prognostic markers from clinical, radiomics, and deep learning imaging features for gastric cancer survival prediction. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:725889. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.725889
40. Wang Y and Jin ZY. Radiomics approaches in gastric cancer: a frontier in clinical decision making. Chin Med J (Engl). (2019) 132:1983–9. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000360
41. Liu Y, Wang Y, Hu X, Wang X, Xue L, Pang Q, et al. Multimodality deep learning radiomics predicts pathological response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Insights Imaging. (2024) 15:277. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01851-0
42. Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T, and Kawakami Y. Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell. (2009) 15:195–206. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.023
43. Araujo D, Ribeiro E, Amorim I, and Vale N. Repurposed drugs in gastric cancer. Molecules. (2022) 28(1):319. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010319
44. Cao R, Tang L, Fang M, Zhong L, Wang S, Gong L, et al. Artificial intelligence in gastric cancer: applications and challenges. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). (2022) 10:goac064. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goac064
45. Baptista D, Ferreira PG, and Rocha M. Deep learning for drug response prediction in cancer. Brief Bioinform. (2021) 22:360–79. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz171
46. Ku GY. Next generation sequencing in gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:56. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2020.01.09
47. Fountzilas E, Tsimberidou AM, Vo HH, and Kurzrock R. Clinical trial design in the era of precision medicine. Genome Med. (2022) 14:101. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01102-1
Keywords: artificial intelligence, advanced gastric cancer, precision oncology, treatment response prediction, multi-modal data
Citation: Fu M, Xu J, Lv Y and Jin B (2025) Artificial intelligence in advanced gastric cancer: a comprehensive review of applications in precision oncology. Front. Oncol. 15:1630628. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1630628
Received: 18 May 2025; Accepted: 31 July 2025;
Published: 19 August 2025.
Edited by:
Zhen Liu, Zhejiang University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Fu, Xu, Lv and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Baijun Jin, bTE4MTA2NTEzMDI2QDE2My5jb20=
 Min Fu
Min Fu Baijun Jin
Baijun Jin