- 1Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, National Medical Center, Binhai Campus of the First Affiliated Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 2Fujian Abdominal Surgery Research Institute, the First Affiliated Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 3Hepatobiliary Surgery, Department of General Surgery, Huashan Hospital & Cancer Metastasis Insititute, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 4Department of General Surgery, The Fifth People’s Hospital of Wuxi, Wuxi, China
Background and purpose: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is an aggressive malignancy with limited therapeutic options. Claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2), a tight junction protein aberrantly expressed in gastrointestinal cancers, has not been systematically evaluated in ICC. This study investigates CLDN18.2’s expression, clinical relevance, and interplay with the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) in ICC.
Method: CLDN18.2 expression was analyzed in 83 ICC and 47 matched non-tumor tissues on tissue microarray sections using immunohistochemistry (IHC). Bioinformatics validation utilized ArrayExpress (E-MTAB-6389) and GEO (GSE119336, GSE107943, GSE89749, GSE32225) datasets. Clinicopathological correlations, survival analysis, and CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) quantification were performed.
Results: CLDN18.2 was exclusively expressed in 24.1% (20/83) of ICC tissues, absent in non-tumor tissues. Positive CLDN18.2 expression correlated with elevated serum CA19-9 (P = 0.026), smaller tumor size (P = 0.03), unifocality (P = 0.03), and higher recurrence (P = 0.018). Multivariable analysis identified CLDN18.2 as an independent prognostic factor for reduced overall survival (OS: HR = 2.555, 95% CI = 1.250–5.223, P = 0.01) and disease-free survival (DFS: HR = 2.229, 95% CI = 1.125–4.415, P = 0.022). Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) analysis revealed an inverse correlation between CLDN18 expression and CD8+ T cells (P = 0.012), while IHC showed a trend toward negative correlation between CLDN18.2 expression and CD8+ TILs density (P = 0.12). Combined stratification showed optimal OS in CLDN18.2-/CD8high patients versus worst outcomes in CLDN18.2+/CD8low subgroup (P = 0.006).
Conclusions: CLDN18.2 is a tumor-specific prognostic biomarker in ICC, marking aggressive subsets with early recurrence. Combined CLDN18.2/CD8+ TILs stratification enhances prognostic precision and suggests synergistic potential for CLDN18.2 targeted therapies with immunomodulation. These findings warrant clinical validation to guide personalized treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is a highly heterogeneous malignancy originating from the epithelial cells of the intrahepatic bile ducts at grade II or above, and constitutes approximately 10% of primary liver cancers. Its incidence has risen globally, particularly in Asia (1, 2). Although surgical resection remains the sole potentially curative option, most patients present with advanced-stage disease, and only 20–30% are candidates for resection (3). Postoperative recurrence rates remain alarmingly high, with a dismal 5-year survival rate of 30% (4). Patients with recurrent or advanced ICC exhibit poor chemosensitivity. Recent advances in targeted therapies, including inhibitors against isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), have shown limited utility due to low mutation frequencies in ICC populations, particularly among Chinese cohorts (3, 5, 6). Therefore, these challenges underscore the urgent need to identify novel therapeutic targets and develop precision treatment strategies to improve ICC outcomes.
Claudins (CLDNs), a family of 27 transmembrane tight junction proteins, regulate paracellular permeability, maintain epithelial polarity, and modulate signal transduction (7, 8). Claudin18 (CLDN18), encoded by a gene located on chromosome 3q22.3, exists as two splice variants: CLDN18.1 (predominantly expressed in lung alveolar epithelial cells) and CLDN18.2 (primarily restricted to gastric mucosa) (9). CLDN18.2 is a highly selective marker protein with restricted expression in healthy tissues, being expressed only in differentiated gastric mucosal epithelial cells (10). Abnormal expression of CLDN18.2 can lead to structural damage and functional impairment of tissue epithelial and endothelial cells, which is observed in the tumorigenesis process of many malignant tumors (11–13). Emerging CLDN18.2 targeted therapies, such as the monoclonal antibody zolbetuximab, have demonstrated survival benefits in phase III trials (SPOTLIGHT and GLOW) for advanced gastric adenocarcinoma when combined with chemotherapy (14, 15). In addition, preclinical and early-phase trials are further exploring antibody-drug conjugates and CAR-T therapies for CLDN18.2-positive solid tumors, potentially extending therapeutic applicability to ICC (16). However, despite a report suggesting upregulated CLDN18 (encompassing both isoforms) in ICC, the specific biological significance of CLDN18.2, including its associations with clinicopathological features, prognosis, and the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME), remains uncharacterized in ICC (17).
This study aims to: investigate the expression of CLDN18.2 in ICC; analyze the correlation between CLDN18.2 expression and clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of ICC; and explore its relationship with the TIME in ICC, particularly CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). These investigations aim to seek potential new therapeutic targets and treatment strategies for ICC.
In this study, we used immunohistochemistry (IHC) to evaluate the expression level of CLDN18.2 in 83 ICC specimens and 47 adjacent non-tumor tissues. Multivariate analyses identified independent prognostic factors, while TILs quantification elucidated associations between CLDN18.2 and immune contexture.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population and tissue collection
This retrospective study included 83 ICC specimens and 47 adjacent non-tumor tissues obtained from patients undergoing curative-intent resection at Huashan Hospital, Fudan University between February 2017 and April 2021. All cases were histologically confirmed as ICC and independently validated by two board-certified pathologists. The study protocol adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Huashan Hospital. The clinicopathological features included age, sex, tumor size, tumor number, histological grade, bile duct and perineural invasion, vascular invasion (microvascular/macrovascular), TNM stage (the 8th edition of American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage), tumor markers (CA19–9 and CEA), and HBV status. The definition of recurrence relied on comprehensive assessment of imaging, tumor biomarkers and surgical pathology. Follow-up time was calculated from the date of initial surgery to the date of the observed event (death or recurrence), with a follow-up date up to February 2024.
2.2 Immunohistochemical staining and evaluation
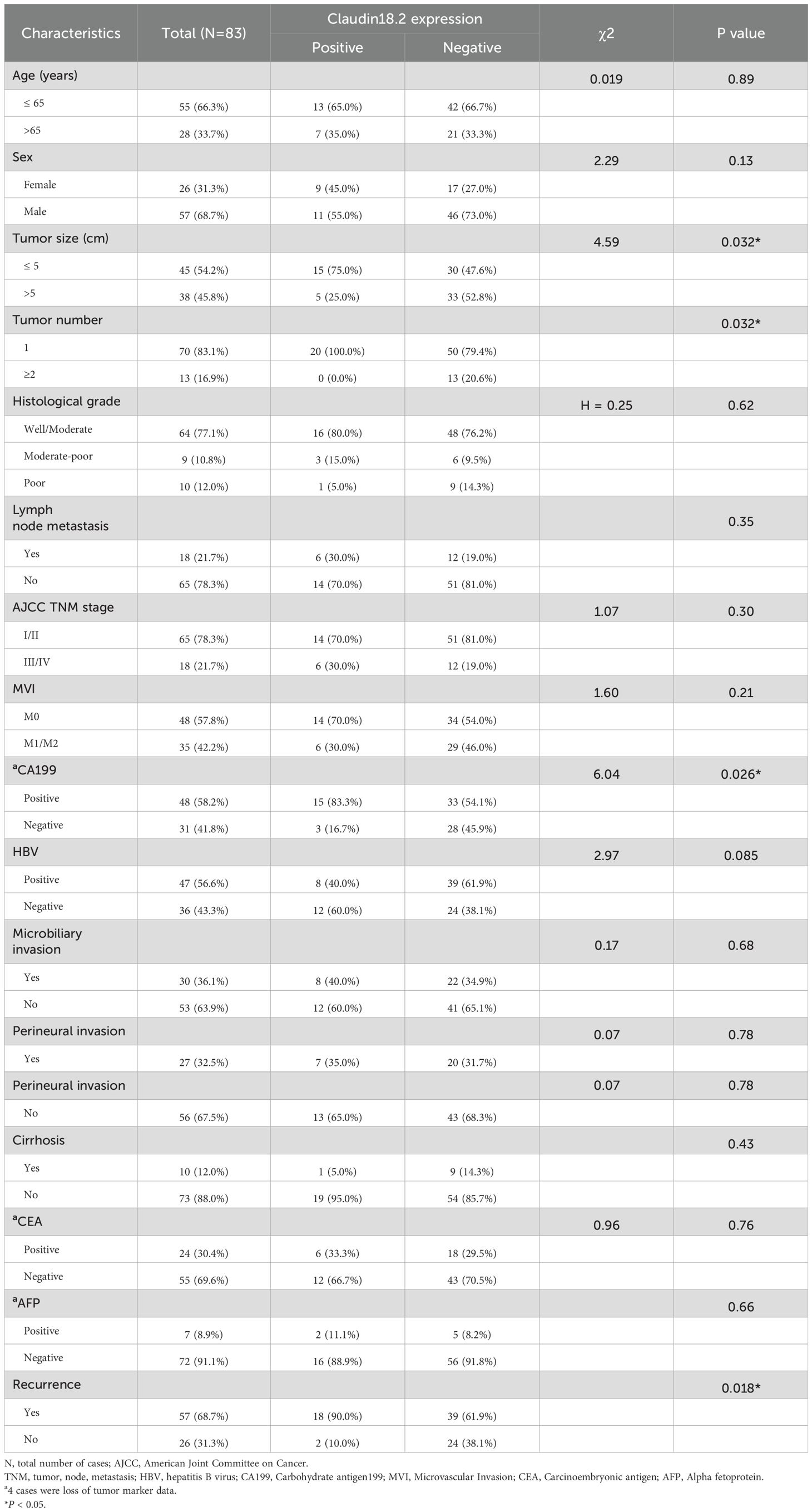
The tumor tissue samples and adjacent non-tumor tissue samples were fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin (FFPE). Then the FFPE slices were prepared for tissue microarrays (TMA). IHC staining was performed to analyze the expression of CLDN18.2 and the tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells using a KFBIO KF-PRO-120 automatic immunostaining device according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Primary antibodies used were anti-CLDN18.2 (Abcam, ab222512, dilution 1:100) and anti-CD8 (Abcam, ab245118, dilution 1:500). Membranous staining of CLDN18.2 in tumor cells was assessed using the H-score system. The H-score was calculated using the formula: H-score = ∑ (i × p), where i represents the staining intensity (0 = no staining, 1 = weak, 2 = intermediate, 3 = strong; Figure 1F) and p represents the proportion of positively stained tumor cells (0 = 0%, 1 = 1-25%, 2 = 26-50%, 3 = 51-75%, 4 = 76-100%). The H-scores ranged from 0 to 12, with H-scores ≥1 indicating positive CLDN18.2 expression; H-scores = 0 indicating negative CLDN18.2 expression (18). CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were quantified and categorized into high and low groups based on the median count per high-power field.
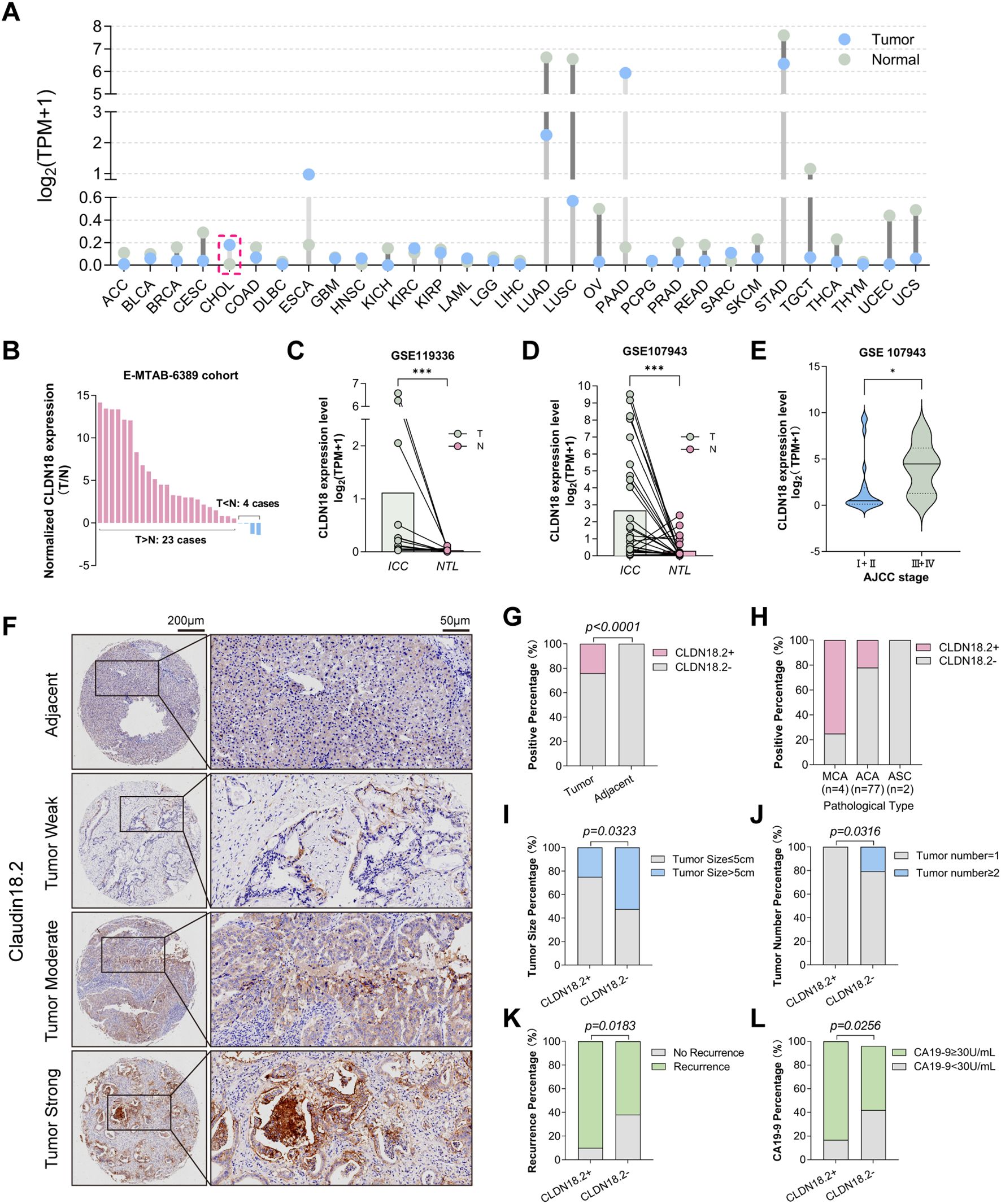
Figure 1. CLDN18.2 expression patterns and clinicopathological correlations in ICC. (A) CLDN18 expression in common malignant tumors in the TCGA database. (B) In the E-MTAB-6389 cohort, CLDN18 expression was elevated in ICC tumors in 23 paired samples, and decreased in only 4 paired samples. (C, D) Expression of CLDN18 in ICC tumors was higher than that in normal tissues, based on the GSE119336 and GSE107943 datasets (P < 0.001, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). (E) CLDN18 expression level in different ICC AJCC stages, based on the GSE107943 dataset (P < 0.05). (F) The immunohistochemical staining intensity of CLDN18.2 in ICC tissue and adjacent non-tumor tissues (no staining; weak staining; moderate staining; strong staining). (G) Differential expression of CLDN18.2 in tumor and adjacent non-tumor tissues of ICC (P < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test). (H) Differential expression of CLDN18.2 levels by pathological type. (I-L) The proportions of higher serum CA19-9, smaller tumor size, unifocal tumor and recurrence were significantly increased in the CLDN18.2- positive ICC patients (all P < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test or Chi-square test).
2.3 Bioinformatics analysis
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and ArrayExpress data were used to analyze the expression of the CLDN18 gene in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and adjacent non-tumor tissue, assess the impact of CLDN18 on survival in ICC patients and explore the relationships between CLDN18 expression and tumor-infiltrating cells. The analysis of CLDN18 expression and immune cell infiltration was performed using single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) and TIMER method in the IOBR R package (19).
2.4 Statistical analysis
The statistical data were analyzed with IBM SPSS 26.0 for Windows, RStudio (R version 4.5.0) and GraphPad Prism software (Version 9.1). A comparison between groups was made using the Wilcoxon rank-sum, chi-square or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and one-sample t-test or one-way ANOVA for continuous variables. Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed using Cox proportional hazards regression. A P-value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Overall survival (OS) was assessed from the day of first surgery to the date of death. Disease-free survival (DFS) was defined from the day of tumor resection to disease recurrence.
3 Results
3.1 Clinicopathological features of ICC patients
The baseline clinicopathological characteristics of 83 ICC patients are summarized in Table 1. The cohort comprised 57 males (68.7%) and 26 females (31.3%), with a median age of 60.1 years (range: 32–82 years). Tumors ≤ 5 cm in diameter were observed in 45 cases (54.2%), and 69 patients (83.1%) presented with unifocal tumors. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection was detected in 47 patients (56.6%), while elevated serum CA19–9 levels were found in 46 of 79 patients (58.2%; data missing for 4 patients). Pathological assessment revealed lymph node metastasis in 18 patients (21.7%). Most ICC cases (65/83; 78.3%) were classified as early-stage ICC (stage I/II according to the 8th edition AJCC TNM staging system), and tumor recurrence occurred in 57 patients (68.7%).
3.2 CLDN18.2 is specifically expressed in ICC
Due to the difficulty of distinguishing between CLDN18 isoforms in bioinformatics transcriptomic databases, we used CLDN18 to represent CLDN18.2 expression in ICC. The results of the bioinformatics analysis demonstrated significantly elevated CLDN18 mRNA levels in ICC versus adjacent non-tumor tissues (P < 0.05; Figures 1A-D), with positive correlation between CLDN18 expression and advanced AJCC stage (P < 0.05; Figure 1E). Representative images of CLDN18.2 immunohistochemical staining in ICC are shown in Figure 1F (detailed explanations are provided in the Materials and Methods section). Immunohistochemical analysis of TMAs revealed CLDN18.2 positivity (H-score ≥ 1) exclusively in ICC specimens (20/83, 24.1%), absent in adjacent non-tumor tissues (0/47; P < 0.0001; Figures 1G, H). Subtype-specific analysis showed positive expression in 75% of mucinous carcinomas (3/4), 22% of adenocarcinomas (17/77), and no expression in adenosquamous carcinomas (0/2; Figure 1H).
3.3 Relationship between clinicopathological features and the expression of CLDN18.2 in ICC
CLDN18.2 expression showed significant correlation with smaller tumor size (P = 0.032), unifocal tumors (P = 0.032), elevated serum CA19-9 (P = 0.026), and higher recurrence rates (P = 0.018; Table 1, Figures 1I-L). No associations were observed with AJCC stage, lymph node metastasis, histological grade, microvascular invasion, microbiliary invasion or perineural invasion (Table 1).
3.4 Prognostic significance of CLDN18.2 in ICC
In our cohort, with a median follow-up of 34.5 months (range: 1–84 months), Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated significantly shorter OS (median OS: 18 vs. 84 months; P = 0.002) and disease-free survival (DFS) (median DFS: 9 vs. 12 months; P = 0.02) in CLDN18.2-positive versus CLDN18.2-negative groups (Figures 2A, B). Similarly, transcriptomic analysis (GSE89749) indicated ICC patients with high CLDN18 expression had a trend toward poorer overall survival (OS) (P=0.058; Figure 2C).
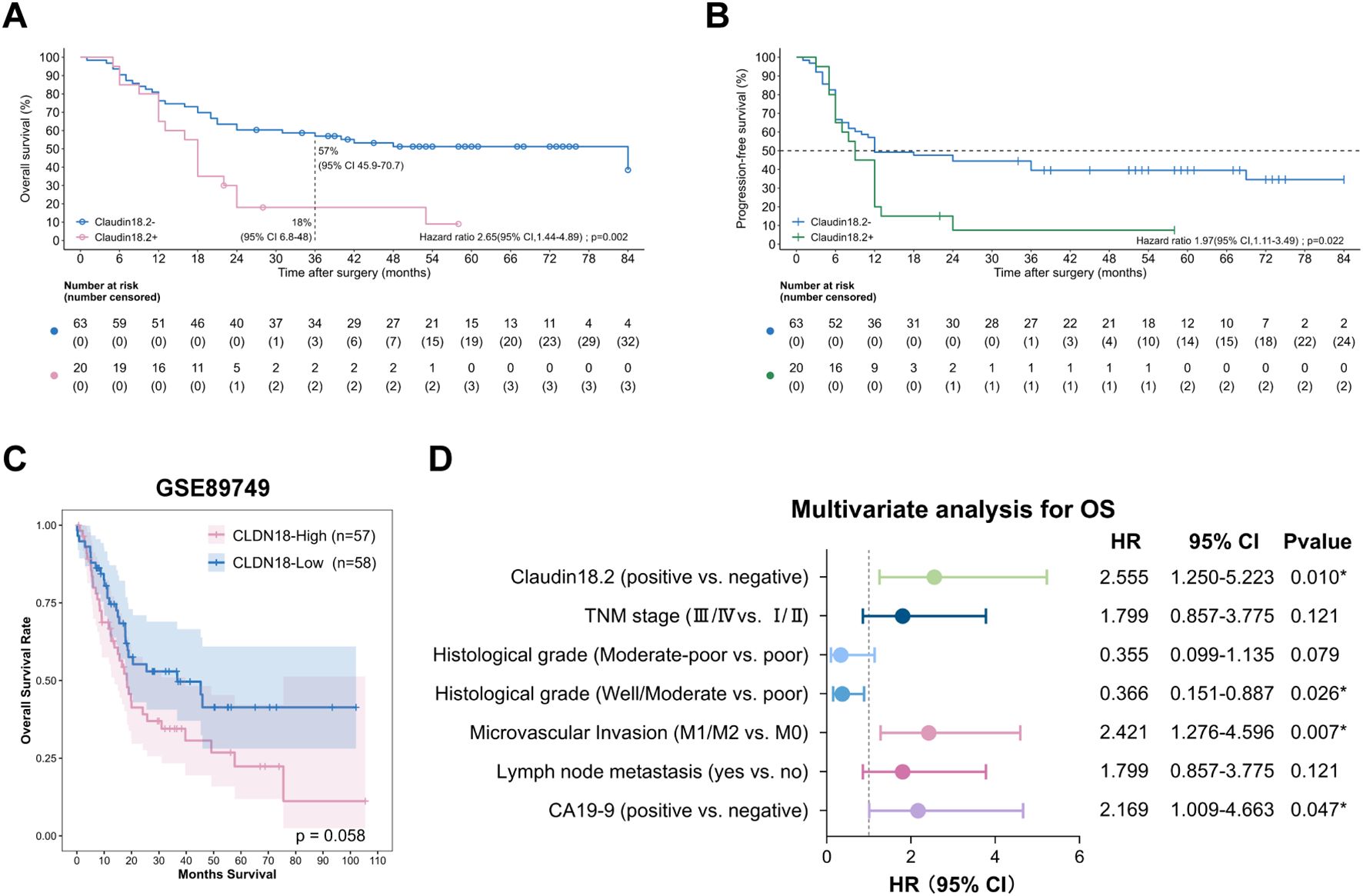
Figure 2. Prognostic significance of CLDN18.2 expression in ICC patients. (A) Kaplan–Meier OS curves of ICC patients with different CLDN18.2 expression levels in tumor tissues (log-rank test; P = 0.002). (B) Kaplan–Meier DFS curves of ICC patients with different CLDN18.2 expression levels in tumor tissues (log-rank test; P = 0.02). (C) The OS with different CLDN18 expression levels in ICC patients, analyzed with the GSE89749 dataset. (D) Forest plot of the results of the multivariate COX regression model for exploring potential risk factors for OS in ICC patients.
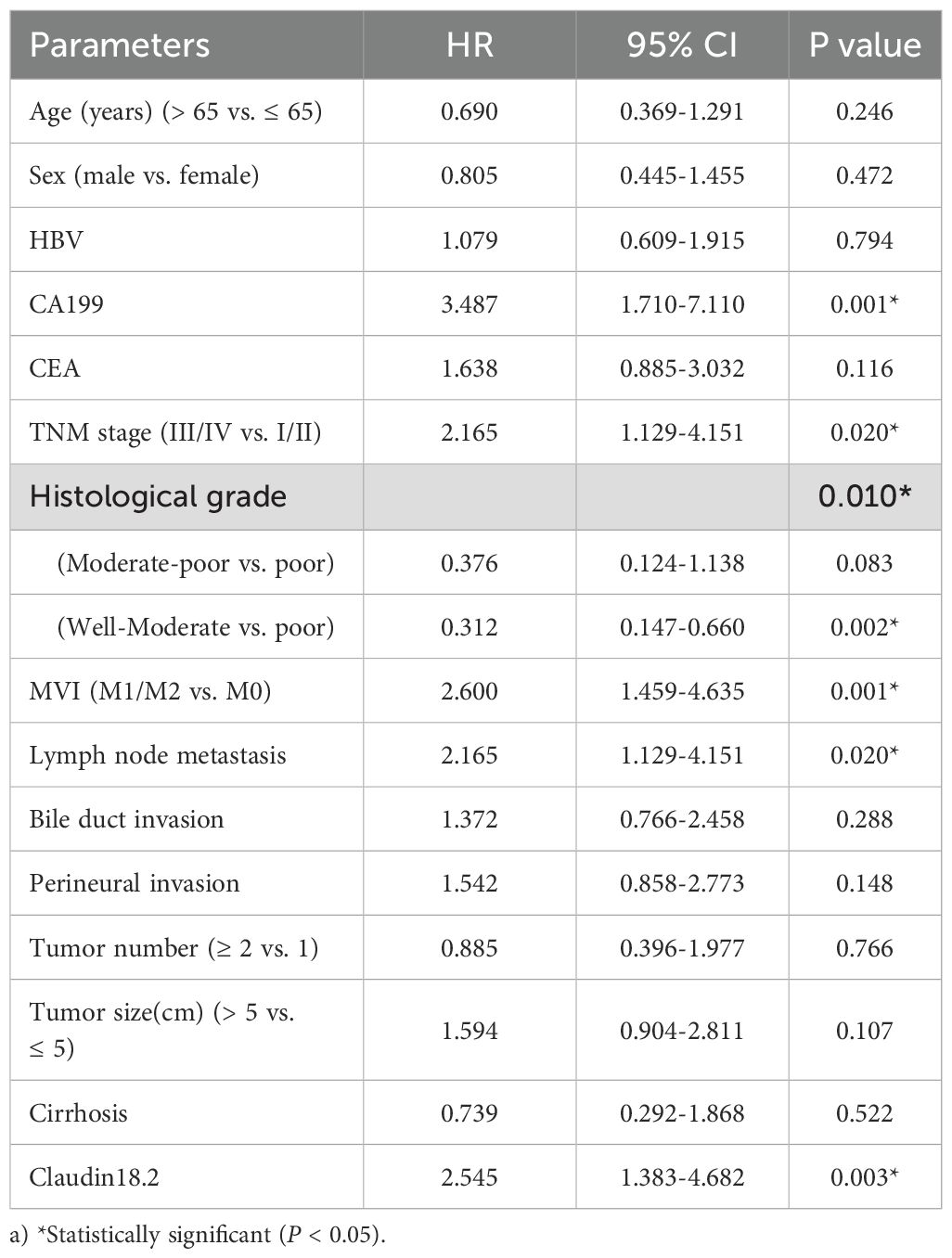
Cox regression analysis was employed to identify independent risk factors that may influence the prognosis of ICC. For OS, univariate Cox analysis identified positive CLDN18.2 expression (HR = 2.545, 95% CI = 1.383-4.682; P = 0.003), serum CA19–9 elevation, advanced TNM stage, poor histological grade, microvascular invasion (MVI) and lymph node metastasis as significant factors (Table 2, all P < 0.05). Subsequent multivariable Cox analysis confirmed that positive CLDN18.2 expression remained significantly associated with OS (HR = 2.555, 95% CI = 1.250-5.223; P = 0.01). Additionally, serum CA19–9 elevation, poor histological grade and MVI were significantly associated with OS (Figure 2D, all P < 0.05). These findings indicate that positive CLDN18.2 expression is an independent prognostic factor for ICC.
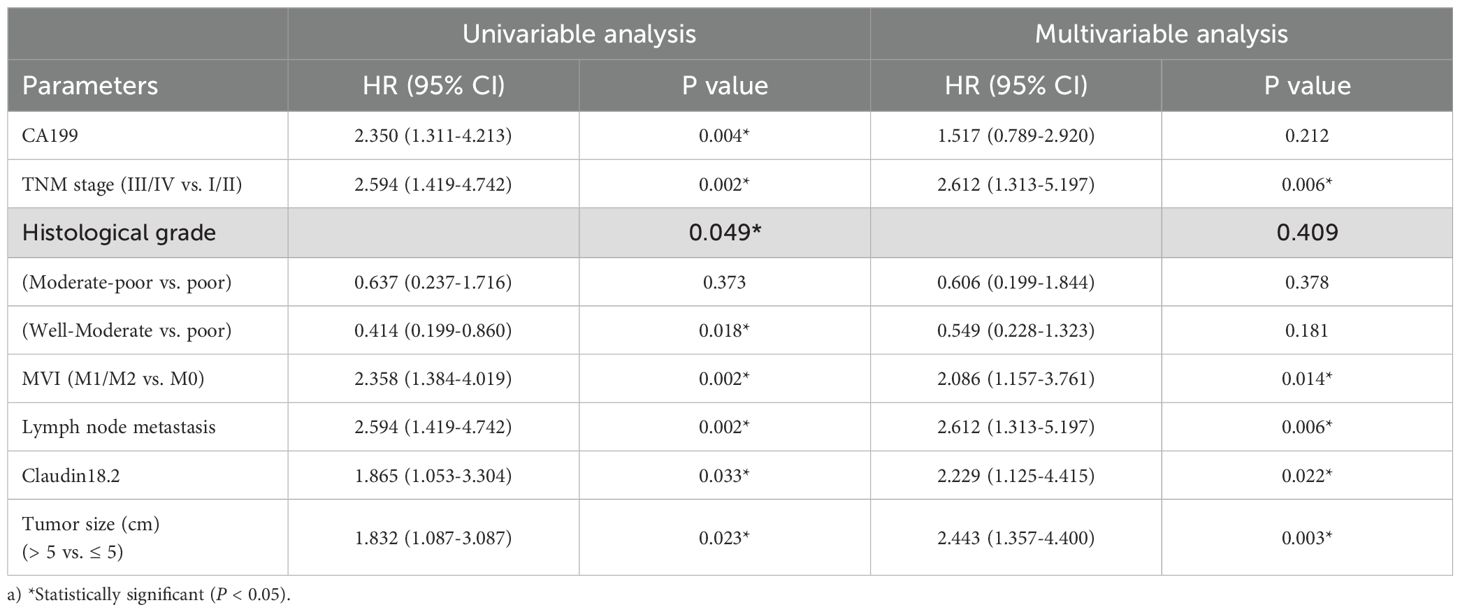
For DFS, univariate Cox analysis showed that positive CLDN18.2 expression (HR = 1.865, 95% CI = 1.053-3.304; P = 0.033), large tumor size, serum CA19–9 elevation, advanced TNM stage, poor histological grade, MVI and lymph node metastasis were all significantly associated with disease recurrence. The other clinicopathologic features were not significantly associated with recurrence. Further multivariable Cox regression identified positive CLDN18.2 expression (HR = 2.229, 95% CI = 1.125-4.415; P = 0.022), large tumor size, advanced TNM stage, poor histological grade, MVI and lymph node metastasis as independent prognostic factors for disease recurrence (Table 3, all P < 0.05).
3.5 Association between CLDN18.2 and CD8+ TILs in ICC
Using the ssGSEA algorithm, analysis of CLDN18 expression and tumor-infiltrating immune cells based on GEO dataset GSE32225 revealed inverse correlations between CLDN18 expression and CD8+ TILs (Figures 3A, B), which was consistent with outcomes using TIMER algorithm (Figure 3C). Furthermore, CLDN18high ICC tumors exhibited downregulated CD8+ TILs activation markers (TNFRSF4, GZMB) and upregulated immune checkpoints (PD-L1, CTLA-4) (Figures 3D, E, all P < 0.05). We therefore further assessed the expression levels of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ TILs in ICC samples using IHC. Given the limited sample size, we found that the CLDN18.2 expression showed a weak negative correlation with the density of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ TILs (Figure 3F, P = 0.12). The CD8+ TILs density alone had no significant effect on the prognosis of ICC patients (Figure 3G, P = 0.2). However, combining CLDN18.2 expression with CD8+ TILs resulted in notable differences in the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Combined stratification showed optimal OS in CLDN18.2-/CD8high patients versus worst outcomes in CLDN18.2+/CD8low subgroup (Figure 3H, P < 0.05).
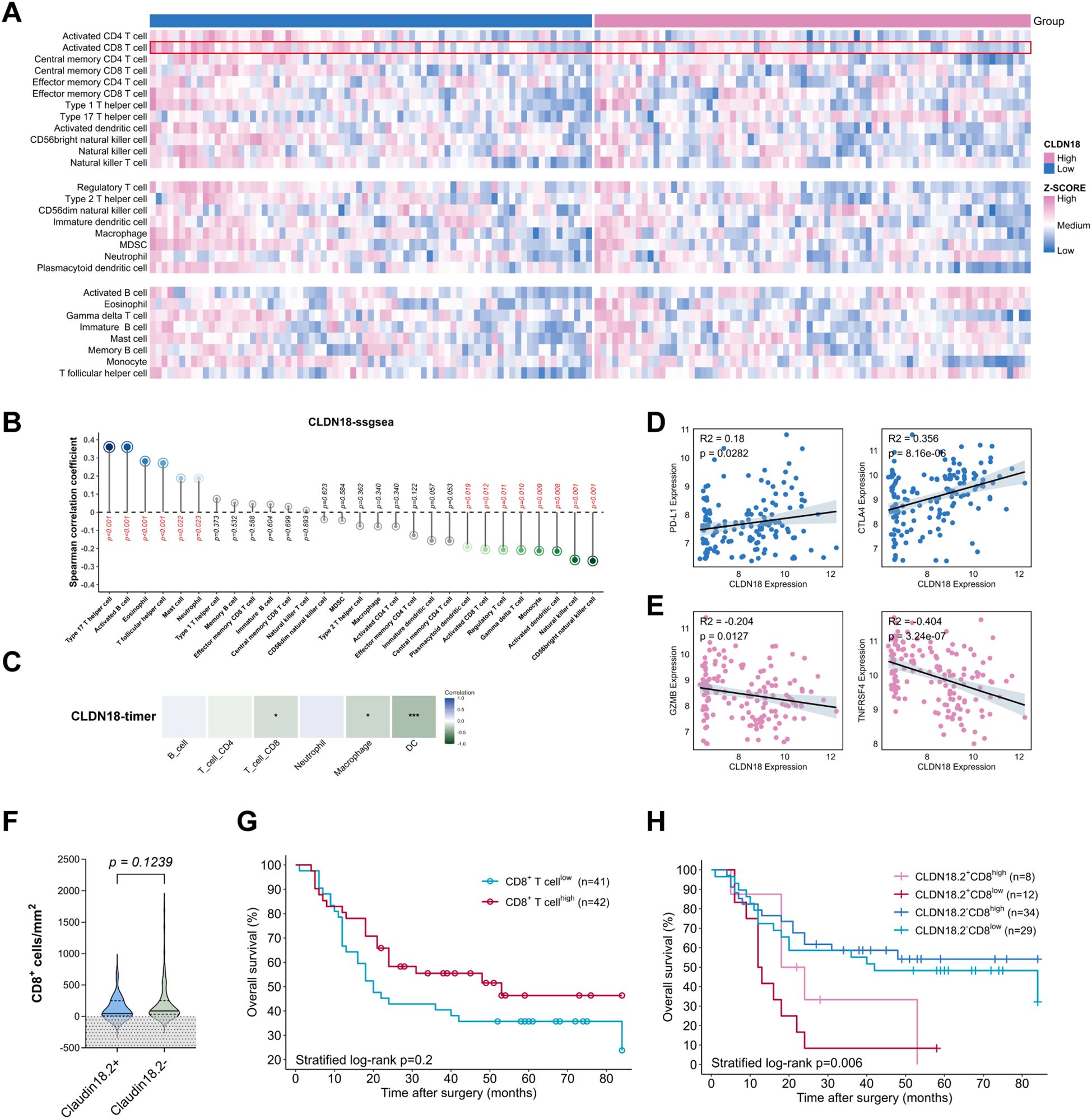
Figure 3. Association between CLDN18.2 expression and tumor immune microenvironment. (A-C) Relationship between CLDN18 expression levels and immune-infiltrating cells based on the GSE32225 dataset. (D, E) Relationship between CLDN18 expression levels and CD8+ T cell-related immune molecules (all P < 0.05). (F) The density of CD8+ TILs in CLDN18.2+ ICC compared with CLDN18.2- ICC (P > 0.05; Mann Whitney test). (G) Kaplan–Meier OS curves of ICC patients with high/low densities of CD8+ TILs in tumor tissues (P > 0.05; log-rank test). (H) Kaplan–Meier OS curves of ICC patients based on CLDN18.2 expression in combination with densities of CD8+ TILs (P < 0.05; log-rank test).
4 Discussion
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) represents a highly aggressive malignancy with a 5-year survival rate of 5–10%, significantly worse than hepatocellular carcinoma (20, 21). Despite advances in targeted therapies (e.g., IDH/FGFR inhibitors), <10% of Chinese ICC patients harbor actionable mutations, underscoring the need for novel therapeutic strategies. CLDN18.2, a tight junction protein physiologically restricted to gastric mucosa, has emerged as a promising pan-cancer target due to its tumor-selective overexpression in gastric, pancreatic, and esophageal malignancies (10, 13, 16, 22–24). Our study provides evidence of CLDN18.2 expression in ICC, with 24.1% positivity (20/83) exclusively in tumor tissues, aligning with prior transcriptomic reports but resolving isoform-specific ambiguity through CLDN18.2-specific IHC.
Previous research has shown that the CLDN18.2 protein is expressed exclusively in differentiated gastric mucosal epithelial cells in normal tissues, but is retained during malignant transformation (10). In addition to in situ expression in gastric cancer, CLDN18.2 has been found to be aberrantly expressed in many malignant tumors (13). This makes it an attractive target for cancer therapy (25). Aya Shinozaki et al. revealed that Claudin18 was expressed in ICC tissue, but not in normal biliary epithelial tissue (17). This is consistent with our bioinformatics analysis results. However, the immunohistochemical analysis of previous study employed a non-specific polyclonal antibody against CLDN18.2, which is a drawback due to the cross-reactivity of CLDN18.1. In the present study, we used an antibody specific for CLDN18.2. This is the first report on the expression of CLDN18.2 in patients with ICC. Our findings confirm exclusive CLDN18.2 expression in 24.1% of ICC cases with complete absence in normal adjacent tissue, highlighting its therapeutic target potential. These findings demonstrate that CLDN18.2 is specifically expressed in ICC, which is consistent with the results of previous studies. This implies that CLDN18.2 may act as a potential immunotherapeutic target for ICC patients. Currently, a number of pharmaceutical agents and therapeutic modalities targeting CLDN18.2 are undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of various solid tumors (26), with encouraging outcomes, particularly in gastric cancer (14, 15). Recent phase 1 trials demonstrate that Claudin18.2-specific CAR T cell therapy (satri-cel/CT041) is entering clinical exploration for gastrointestinal cancers, showing promising activity with a 50% objective response rate in biliary tract cancer patients and overall response rates of 42.2% across various digestive system malignancies (27, 28). Nevertheless, it is important to recognize that the presence of a target expression in a tumor does not necessarily indicate that the patient will derive benefit from the corresponding targeted drug. Therefore, further clinical trial studies should be designed to confirm the efficacy of CLDN18.2 targeted drugs in ICC patients.
Mechanistically, CLDN18.2-positive ICCs demonstrated aggressive clinical behavior, correlating with elevated serum CA19-9, early recurrence, and poor prognostic value (OS: HR = 2.555, 95% CI = 1.250-5.223, P = 0.01). These findings extend observations by Takasawa et al., who implicated CLDN18-driven EGFR/ERK activation in cholangiocarcinoma progression (29). Notably, 90% (18/20) of CLDN18.2-positive cases recurred post-resection, suggesting CLDN18.2 may mark a subset of ICCs with inherent metastatic propensity, even among early-stage tumors.
To our knowledge, the local immune response to tumors is primarily mediated by TILs (30). One of the most important cell types is CD8+ TILs, which exert anti-tumor immune effects by directly killing the tumor cells (31). The high density of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells in tumor tissue is consistently associated with a favorable prognosis in numerous malignant neoplasms (32–34). While transcriptomic data (GSE32225) indicated CLDN18high ICCs exhibit CD8+ T-cell exclusion and upregulated immune checkpoints (PD-L1/CTLA-4), our IHC cohort showed weak direct correlation, possibly due to the small sample size. This discrepancy may reflect spatial heterogeneity or post-transcriptional regulation. Crucially, combined CLDN18.2/CD8+ T-cell stratification identified distinct prognostic subgroups, CLDN18.2+/CD8low ICC patients had the worst prognosis (P = 0.006). This suggests synergistic therapeutic potential for CLDN18.2 targeted agents (e.g., zolbetuximab) combined with PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade, warranting preclinical validation.
Our study has several limitations. First, the data presented in this study was collected from a single medical center, and the number of samples is relatively limited. Therefore, the results may not be fully representative of the wider ICC patient population. Large-scale, multi-center studies are required for further validation in the future. Second, while both previous and our current study have identified obvious intra-tumor heterogeneity in CLDN18.2 expression (35), the use of tissue microarrays as a proxy resulted in an incomplete assessment of CLDN18.2 expression. Multiple tissue cores or whole tumor sections could be used in the future to better assess CLDN18.2 expression in ICC. Third, athough this study provides valuable insights through IHC, it did not utilize multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC), which limits the ability to analyze the spatial distribution and interactions of multiple immune markers simultaneously. Future studies could incorporate mIHC for more detailed immune profiling and a better understanding of marker interactions. Fourth, lack of standardized CLDN18.2 scoring criteria for ICC, requiring harmonization with gastric cancer thresholds (H-score ≥1) until disease-specific guidelines emerge. Further studies are required to ascertain this criterion.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study establishes CLDN18.2 as a tumor-specific biomarker in ICC, expressed in 24.1% of ICC patients with absent normal tissue expression. CLDN18.2 positivity independently predicts early recurrence and reduced overall survival, while combined CLDN18.2/CD8+ T-cell stratification enhances prognostic precision. These findings position CLDN18.2-directed therapies (e.g., antibody-drug conjugates, CAR-T) as viable strategies for ICC, particularly when integrated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Prospective trials validating CLDN18.2 as both a predictive biomarker and therapeutic target are urgently needed to translate these insights into clinical practice.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Huashan Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
CY: Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. YP: Formal Analysis, Software, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Visualization. FL: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Validation, Investigation. ZG: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. DX: Software, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. YZ: Methodology, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. BY: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision, Resources, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by China National Natural Science Foundation (82273312).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer TS declared a shared parent affiliation with the author(s) DX, YZ, YP to the handling editor at the time of review.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bertuccio P, Malvezzi M, Carioli G, Hashim D, Boffetta P, El-Serag HB, et al. Global trends in mortality from intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. (2019) 71:104–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.013
2. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
3. Moris D, Palta M, Kim C, Allen PJ, Morse MA, and Lidsky ME. Advances in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: An overview of the current and future therapeutic landscape for clinicians. CA Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:198–222. doi: 10.3322/caac.21759
4. Kelley RK, Bridgewater J, Gores GJ, and Zhu AX. Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. (2020) 72:353–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.009
5. Oh DY, Ruth He A, Qin S, Chen LT, Okusaka T, Vogel A, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Evid. (2022) 1:EVIDoa2200015. doi: 10.1056/EVIDoa2200015
6. Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, Finn RS, Furuse J, Ren Z, et al. Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2023) 401:1853–65. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00727-4
7. Günzel D and Yu AS. Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol Rev. (2013) 93:525–69. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2012
8. Zihni C, Mills C, Matter K, and Balda MS. Tight junctions: from simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2016) 17:564–80. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.80
9. Türeci O, Koslowski M, Helftenbein G, Castle J, Rohde C, Dhaene K, et al. Claudin-18 gene structure, regulation, and expression is evolutionary conserved in mammals. Gene. (2011) 481:83–92. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.04.007
10. Cao W, Xing H, Li Y, Tian W, Song Y, Jiang Z, et al. Claudin18.2 is a novel molecular biomarker for tumor-targeted immunotherapy. biomark Res. (2022) 10:38. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00385-1
11. Kyuno D, Takasawa A, Takasawa K, Ono Y, Aoyama T, Magara K, et al. Claudin-18.2 as a therapeutic target in cancers: cumulative findings from basic research and clinical trials. Tissue Barriers. (2022) 10:1967080. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2021.1967080
12. Micke P, Mattsson JS, Edlund K, Lohr M, Jirström K, Berglund A, et al. Aberrantly activated claudin 6 and 18.2 as potential therapy targets in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. (2014) 135:2206–14. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28857
13. Sahin U, Koslowski M, Dhaene K, Usener D, Brandenburg G, Seitz G, et al. Claudin-18 splice variant 2 is a pan-cancer target suitable for therapeutic antibody development. Clin Cancer Res. (2008) 14:7624–34. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1547
14. Shah MA, Shitara K, Ajani JA, Bang YJ, Enzinger P, Ilson D, et al. Zolbetuximab plus CAPOX in CLDN18.2-positive gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: the randomized, phase 3 GLOW trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:2133–41. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02465-7
15. Shitara K, Lordick F, Bang YJ, Enzinger P, Ilson D, Shah MA, et al. Zolbetuximab plus mFOLFOX6 in patients with CLDN18.2-positive, HER2-negative, untreated, locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (SPOTLIGHT): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2023) 401:1655–68. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00620-7
16. Nakayama I, Qi C, Chen Y, Nakamura Y, Shen L, and Shitara K. Claudin 18.2 as a novel therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2024) 21:354–69. doi: 10.1038/s41571-024-00874-2
17. Shinozaki A, Shibahara J, Noda N, Tanaka M, Aoki T, Kokudo N, et al. Claudin-18 in biliary neoplasms. Its significance in the classification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Virchows Arch. (2011) 459:73–80. doi: 10.1007/s00428-011-1092-z
18. Wang C, Wang Y, Chen J, Wang Y, Pang C, Liang C, et al. CLDN18.2 expression and its impact on prognosis and the immune microenvironment in gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:283. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02924-y
19. Zeng D, Fang Y, Qiu W, Luo P, Wang S, Shen R, et al. Enhancing immuno-oncology investigations through multidimensional decoding of tumor microenvironment with IOBR 2.0. Cell Rep Methods. (2024) 4:100910. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100910
20. Squires MH, Cloyd JM, Dillhoff M, Schmidt C, and Pawlik TM. Challenges of surgical management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 12:671–81. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2018.1489229
21. Ilyas SI, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK, and Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:95–111. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.157
22. Tanaka M, Shibahara J, Fukushima N, Shinozaki A, Umeda M, Ishikawa S, et al. Claudin-18 is an early-stage marker of pancreatic carcinogenesis. J Histochem Cytochem. (2011) 59:942–52. doi: 10.1369/0022155411420569
23. Jun KH, Kim JH, Jung JH, Choi HJ, and Chin HM. Expression of claudin-7 and loss of claudin-18 correlate with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Int J Surg. (2014) 12:156–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.11.022
24. Moentenich V, Gebauer F, Comut E, Tuchscherer A, Bruns C, Schroeder W, et al. Claudin 18.2 expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma and its potential impact on future treatment strategies. Oncol Lett. (2020) 19:3665–70. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11520
25. Chong X, Madeti Y, Cai J, Li W, Cong L, Lu J, et al. Recent developments in immunotherapy for gastrointestinal tract cancers. J Hematol Oncol. (2024) 17:65. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01578-x
26. Zhou KI, Strickler JH, and Chen H. Targeting Claudin-18.2 for cancer therapy: updates from 2024 ASCO annual meeting. J Hematol Oncol. (2024) 17:73. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01595-w
27. Qi C, Liu C, Gong J, Liu D, Wang X, Zhang P, et al. Claudin18.2-specific CAR T cells in gastrointestinal cancers: phase 1 trial final results. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2224–34. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03037-z
28. Qi C, Gong J, Li J, Liu D, Qin Y, Ge S, et al. Claudin18.2-specific CAR T cells in gastrointestinal cancers: phase 1 trial interim results. Nat Med. (2022) 28:1189–98. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01800-8
29. Takasawa K, Takasawa A, Osanai M, Aoyama T, Ono Y, Kono T, et al. Claudin-18 coupled with EGFR/ERK signaling contributes to the Malignant potentials of bile duct cancer. Cancer Lett. (2017) 403:66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.05.033
30. Lin B, Du L, Li H, Zhu X, Cui L, and Li X. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: Warriors fight against tumors powerfully. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 132:110873. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110873
31. Farhood B, Najafi M, and Mortezaee K. CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: A review. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:8509–21. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27782
32. Mardanpour K, Rahbar M, Mardanpour S, Mardanpour N, and Rezaei M. CD8+ T-cell lymphocytes infiltration predict clinical outcomes in Wilms’ tumor. Tumour Biol. (2020) 42:1010428320975976. doi: 10.1177/1010428320975976
33. Chen J, He Q, Liu J, Xiao Y, Xiao C, Chen K, et al. CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes as a novel prognostic biomarker in lung sarcomatoid carcinoma, a rare subtype of lung cancer. Cancer Manag Res. (2018) 10:3505–11. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S169074
34. Giuşcă SE, Wierzbicki PM, Amălinei C, Căruntu ID, and Avădănei ER. Comparative analysis of CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes - evidences for different distribution in primary and secondary liver tumors. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. (2015) 53:272–81. doi: 10.5603/fhc.a2015.0027
Keywords: CLDN18.2, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, prognosis, clinicopathological features, CD8+ T-cell
Citation: Yu C, Pan Y, Li F, Guo Z, Xu D, Zhu Y and Yin B (2025) Claudin18.2 defines a prognostically distinct subgroup of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via CD8+ T-cell exclusion. Front. Oncol. 15:1636367. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1636367
Received: 28 May 2025; Accepted: 07 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Zhaohui Tang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Yu, Pan, Li, Guo, Xu, Zhu and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Zhu, eXpodTE0QGZ1ZGFuLmVkdS5jbg==; Baobing Yin, eWluYmFvYmluZ0AxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Chengui Yu
Chengui Yu Yuren Pan
Yuren Pan Fuli Li4†
Fuli Li4† Da Xu
Da Xu