- 1Department of Pharmacy, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 2Hubei Province Clinical Research Center for Precision Medicine for Critical Illness, Wuhan, China
- 3University of Wuhan, Wuhan, China
Objective: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus sorafenib has led to an increase in randomized controlled trials The efficacy and safety of sorafenib combined with TACE for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain controversial. We conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on this issue.
Methods: A literature search was conducted by using online database: PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and Wan-fang, with no language restrictions. A Meta-analysis was performed to calculate the pooled odds ratio (OR) and its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) for the efficacy and safety of sorafenib combined with TACE in the treatment of HCC. Review Manager 5.4 software was used for data analysis.
Results: A total of 19 randomized controlled trials involving 2,029 patients met the inclusion criteria for this meta-analysis, including sorafenib combined with TACE group (n=1023) and TACE group (n=1006). The results of meta-analysis showed that sorafenib combined with TACE had a better prognosis in partial response rate (PR) [OR = 1.58,95%CI (1.30,1.92), P < 0.00001] with low heterogeneity among studies (P = 0.67; I2 = 0%) and the objective response rate (ORR) [OR = 1.93, 95%CI (1.59,2.34), P < 0.00001] with low heterogeneity among studies (P = 0.42; I2 = 3%). The 12-month overall survival (OS) was also significantly increased by combination therapy [OR = 3.18, 95%CI (2.41,4.19), P < 0.00001]. In terms of safety, the incidences were significantly high in TACE plus sorafenib group compared to TACE group for hand-foot skin reaction OR = 4.48, 95%CI (3.28,6.13), P < 0.00001 and for abdominal pain or diarrhea OR = 3.10, 95%CI (2.24,4.29), P = 0.04. However, no significant difference was found in nausea or vomit [OR = 1.14,95%CI (0.81,1.59), P = 0.68] or fever [OR = 0.87, 95%CI (0.61,1.23), P = 0.87].
Conclusion: The current comprehensive evidence suggests that sorafenib combined with TACE is more effective than TACE alone, especially for patients with intermediate-advanced and primary HCC.
1 Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common types of primary malignant tumor of the liver, posing a significant threat to human health (1). The treatment of HCC presents challenges due to the disease’s complexity, which is typically diagnosed at an advanced stage and often develops in the context of cirrhosis (2). The treatment methods for liver cancer include surgical resection, liver transplantation, local ablation, transarterial embolization, and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Surgical resection and liver transplantation are considered as radical treatment methods for liver cancer. However, due to patients often with severe liver function impairment, the surgical resection rate remains relatively low. Local ablation techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation, are appropriate for patients with small hepatocellular carcinomas but show limited effectiveness for larger tumors. Consequently, for patients with intermediate to advanced liver cancer, TACE is often employed as a local interventional therapy.
TACE is a classic interventional treatment method for intermediate and advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma. It precisely delivered chemotherapeutic drugs and embolic agents directly to the tumor through the hepatic artery, cutting off the tumor’s blood supply and increasing the local concentration of medication (3). This method has been shown to prolong survival rates in patients with intermediate-stage HCC. However, it also has its limitations. Due to incomplete embolization and the establishment of collateral blood vessels in the tumor, TACE often fails to achieve pathological necrosis. Additionally, postoperative ischemia and hypoxia in tumor tissues can increase the level of hypoxia-inducible factors in residual tumors and elevate the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF), aggravating the disease and recurrence (4, 5).
In recent years, targeted therapy has made significant progress in the treatment of advanced liver cancer. Sorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor, suppresses tumor angiogenesis by targeting the VEGF signaling pathway, inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. As the standard first-line treatment drug, it can significantly extend the overall survival of patients with advanced liver cancer (6, 7). However, the efficacy of sorafenib monotherapy remains limited, potentially leading drug resistance in some patients. Exploring combination therapy regimens has become a research hotspot. Studies have shown that sorafenib plus TACE may enhance the control of local tumor after TACE and mitigate hypoxia-driven metastasis (8). Thus, the combination of sorafenib with TACE has gained attention as a potential therapeutic strategy (9, 10).
With the incidence of HCC rising, optimizing treatment strategies for patients with intermediate to advanced liver cancer has become increasingly urgent. Studies have indicated that the combination of sorafenib and TACE may offer potential benefits in the treatment of HCC. However, there is a lack of systematic summary and evaluation, and inconsistencies in their results (11). To address this issue and provide valuable insights for clinical practice, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis focusing on the efficacy and safety of TACE plus sorafenib for the treatment of HCC (12, 13).
2 Methods
2.1 Literature search
During this systematic review, we adhered to the PRISMA guidelines (14). A comprehensive system retrieved online databases: PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and the Wan-Fang Database in China without language restrictions on May 30, 2025. MeSH terms and free words related to “Hepatocellular Carcinoma”, “sorafenib” and “Therapeutic Chemoembolization” were used in this research. Details of search strategy were displayed in Supplementary File S1. Additionally, we manually screened the references of all identified articles for additional studies that might be relevant to this meta-analysis.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria
1. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
2. Study patients were pathologically or clinically diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma, regardless of the kind of treatment that they have experienced before.
3. Two intervention arms (TACE plus sorafenib vs TACE alone) were compared in the study.
4. One of the following must be reported in study: partial response rate (PR), objective response rate (ORR), 12-month OS rates and adverse reactions.
5. There is no language restriction.
Exclusion criteria
1. Duplicate studies.
2. Non-RCTs.
3. Inconsistent experimental groupings.
4. The basic data was incomplete and the original data was unavailable.
5. Reviews, meta-analyses, non-clinical reports, case reports, conference summaries, opinions, editorials and letters.
2.3 Data extraction
Data was extracted independently by two investigators (Lixiu Yu and Yi Xiong) according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. General information of the eligible studies including first author’s name, published year, study design, case of participants in the eligible studies, age, gender, Child-Pugh class. Efficacy outcome measures included PR, ORR, 12-month OS rates. Safety outcomes included typical adverse events (AEs) reported by patients. Disagreements between the investigators were resolved through discussion.
2.4 Quality assessment
The quality of the RCTs included in this meta-analysis was evaluated by Cochrane Collaboration’s risk of bias tool (15) from seven critical aspects: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, other bias. Each aspect was judged as low, unclear, or high risk of bias. The quality assessment was conducted independently by two researchers (Yi Xiong and Lixiu Yu). Disagreements were resolved by discussion.
2.5 Data synthesis and analysis
Meta-analyses were conducted by using Review Manager 5.4. The pooled odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were employed to evaluate efficacy and safety. The I2 statistic was used to measure heterogeneity of the studies. If significant heterogeneity was detected with I² > 50%, the estimated outcomes of eligible studies were calculated using a random-effects model. Otherwise, a fixed-effects model was applied. And statistical test with p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Study search and selection
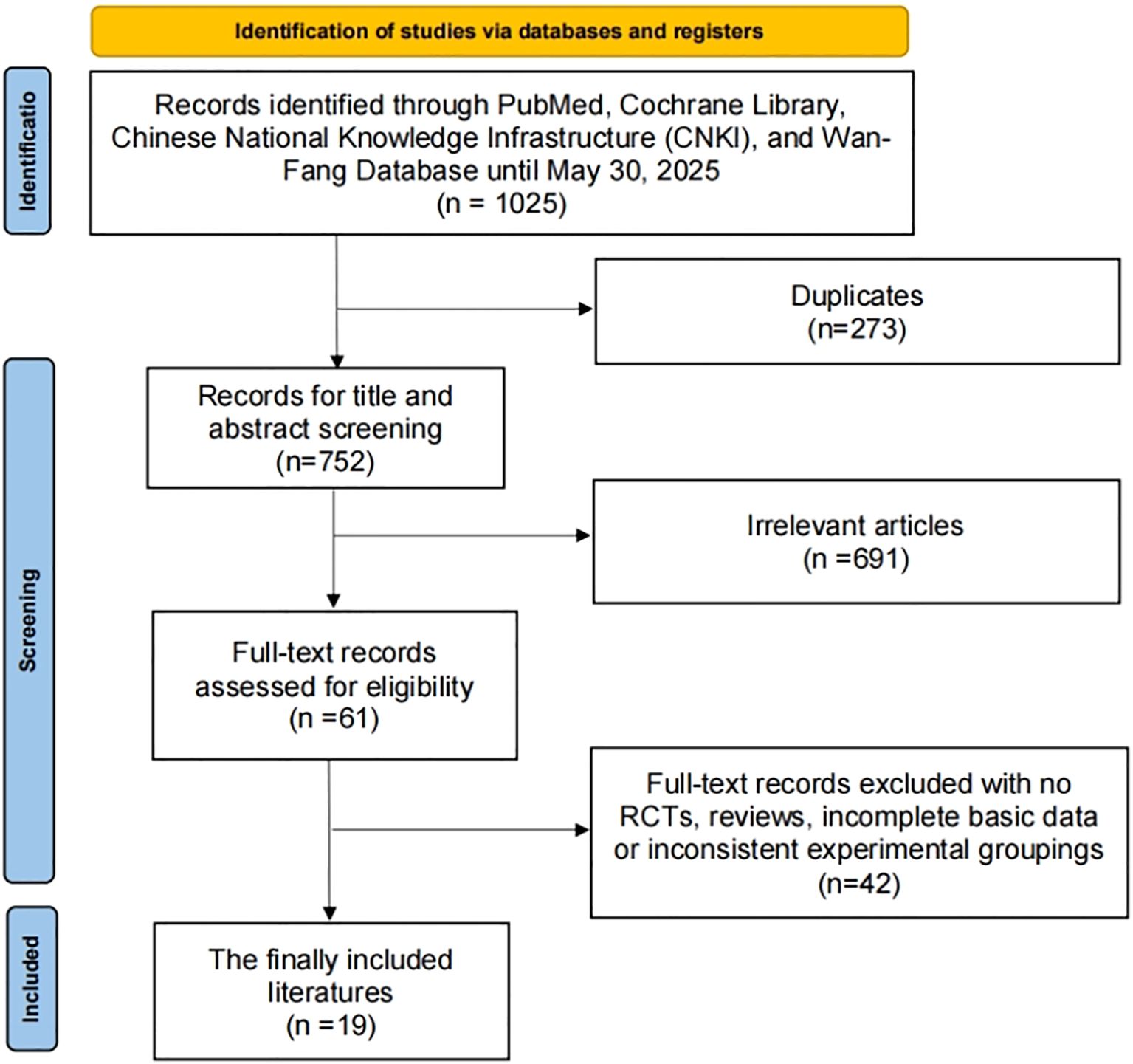
As depicted in Figure 1, the study selection process involved a comprehensive search of online databases and manual searches, yielding a total of 1025 articles. After eliminating 273 duplicate articles, further 691 articles were excluded based on their titles and abstracts. Upon full-text review and applying the inclusion criteria, 42 articles were excluded. Ultimately, 19 RCTs, comprising a total of 2,029 patients diagnosed with liver cancer, were included in this study (10, 16–33).
3.2 Study characteristics
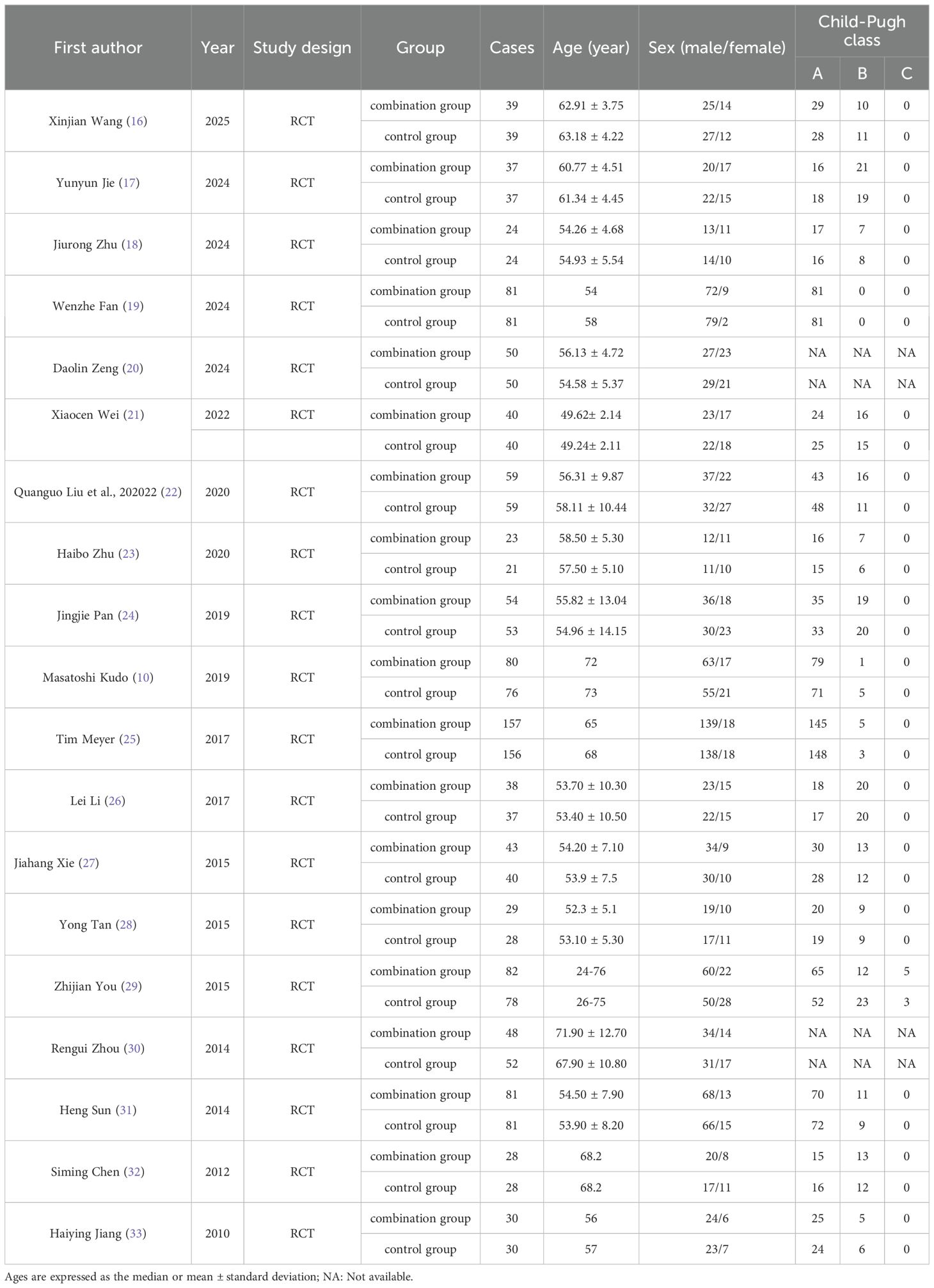
A total of 19 RCTs were included in this meta-analysis, of these 17 studies (10, 16–19, 21–29, 31–33) reported Child-Pugh classification system. Majority of patients were classified as Child-Pugh class A. The baseline characteristics of patients were summarized in Table 1. Of the 2029 enrolled patients with HCC, 1,023 received sorafenib plus TACE, and1,006 were treated with TACE alone. The patients’ ages were between 45 and 75 years old. Sorafenib was administered orally at a dosage of 400 mg twice daily. The details of intervention characteristics and outcome measures of all the included trials were summarized in Supplementary File S2. All the trials (10, 16–33) used PR and ORR as outcome metrics, and eleven trials (10, 16, 19, 21, 22, 27, 29–33) reported 12-month OS rates.
3.3 Quality assessment
The details of study quality assessment were summarized in Figure 2 and Supplementary File S3. The Cochrane Collaboration’s risk of bias tool was used to evaluate the quality of included studies. Overall, the included studies revealed a superior standard of methodological quality. Most studies presented a low risk of bias.
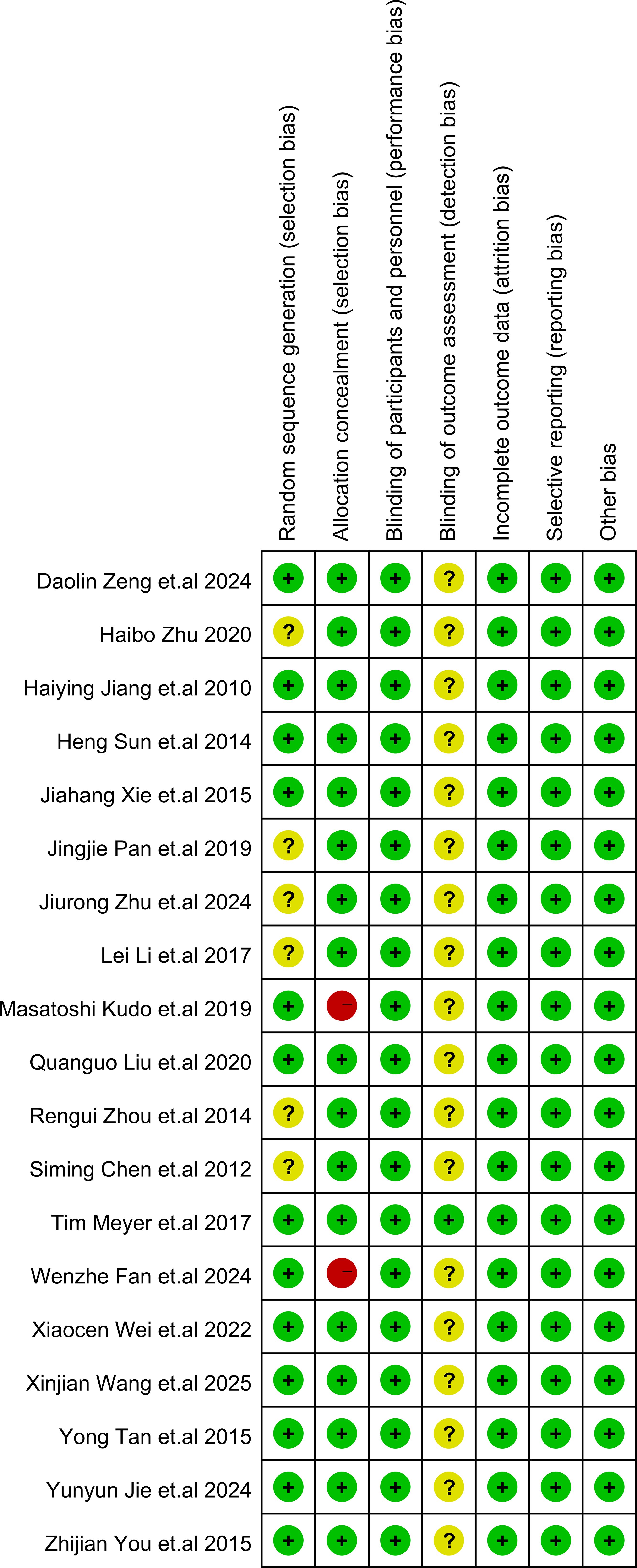
Figure 2. Risk of bias summary. In the illustration, green represents low risk, yellow represents unclear risk, and red represents high risk.
3.4 Meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Efficacy of sorafenib combined with TACE
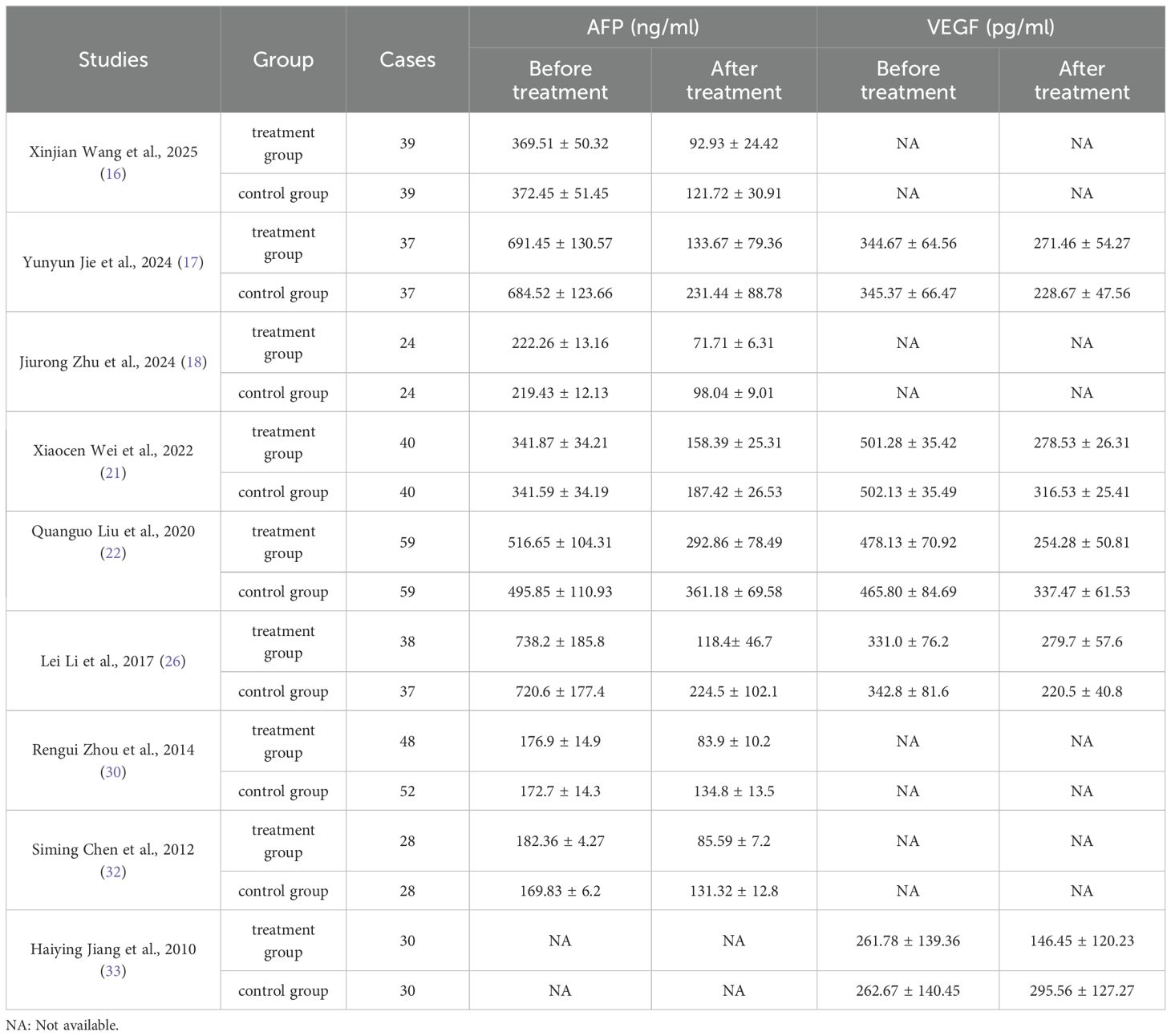
The meta-analysis of all the included studies indicated that compared with TACE alone, Sorafenib combined with TACE had a favorable partial response rate (PR) with integrated OR = 1.58 (95% CI: 1.30–1.92), P = 0.67, I² = 0%. In addition, the result of objective response rate (ORR) with pooled OR = 1.93, 95%CI (1.59,2.34)] and 12-months OS rate with pooled OR = 3.18, 95%CI (2.41,4.19) demonstrated that TACE plus sorafenib had better clinical outcomes than TACE alone. The details of the efficacy and funnel plot were summarized in Figures 3 and 4 respectively. One the other hand, the available data in Table 2 suggested that both APF and VEGF levels decreased after treatment especially for TACE plus sorafenib, which further proved that the combination of TACE and sorafenib was an effective strategy.
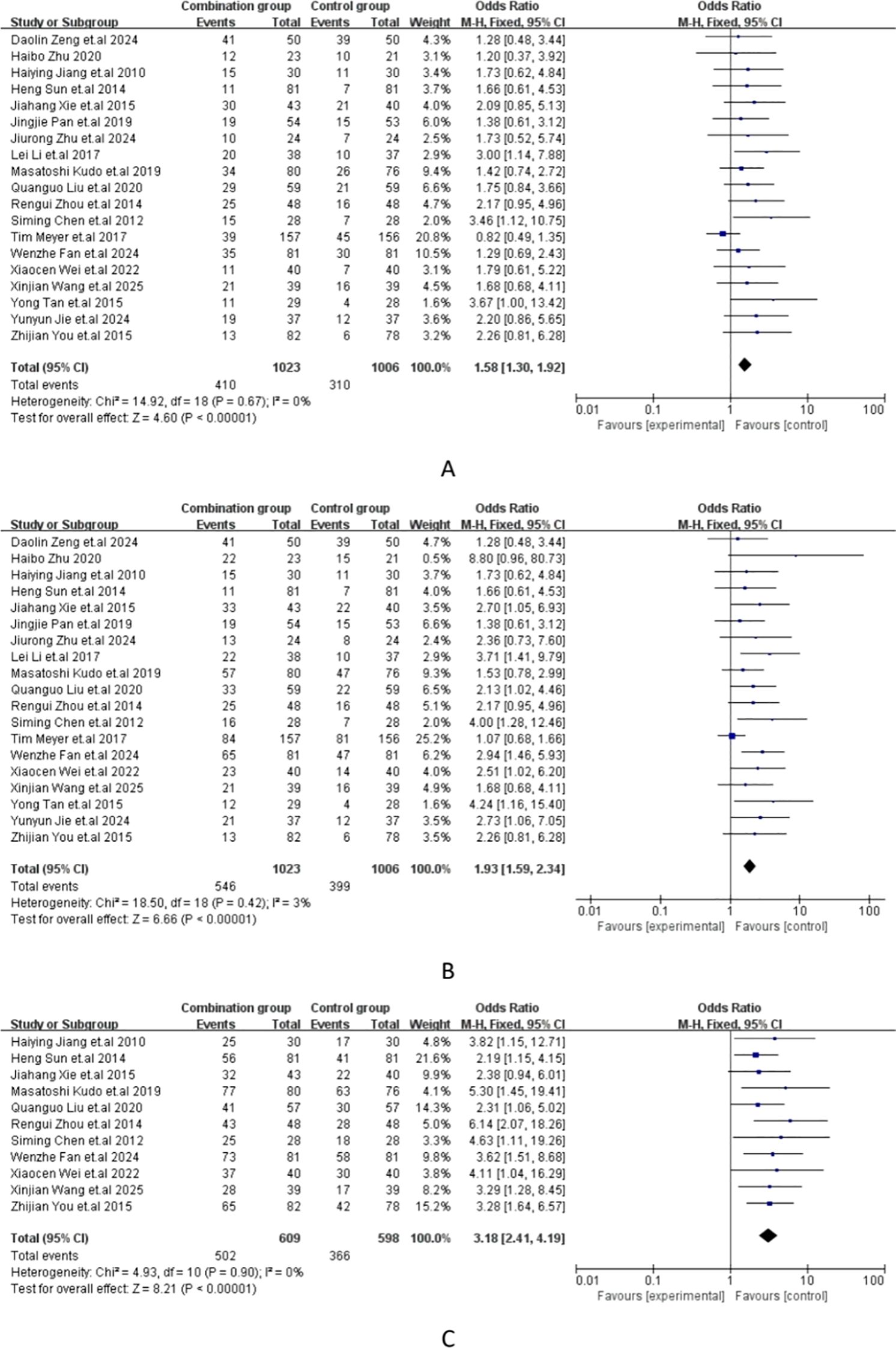
Figure 3. (A) Forest plot of partial response rate (PR); (B) Forest plot of objective response rate(ORR); (C) Forest plot of the 12-month OS rates.
Figure 4. Funnel plot of ORR. (A) Funnel plot of PR; (B) Funnel plot of ORR; (C) Funnel plot of the 12-month OS rates.
3.4.2 Subgroup analysis
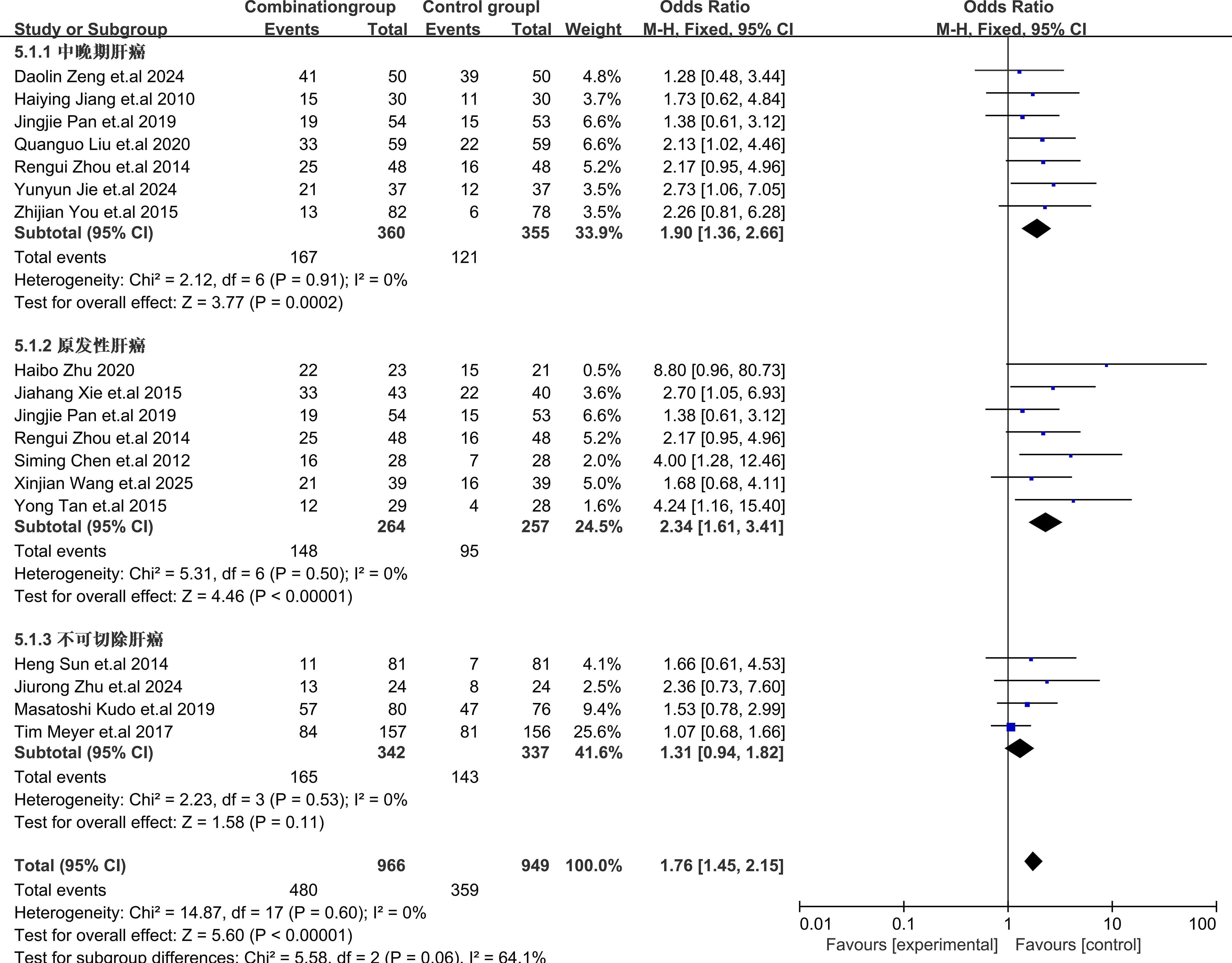
Subgroup analysis of different types of HCC showed that TACE plus sorafenib for patients with primary HCC provided the best benefits with OR = 2.34, 95% CI (1.61,3.41), I2 = 0%, P = 0.50, for intermediate-advanced HCC OR = 1.90, 95% CI (1.36,2.66), I2 = 0%, P = 0.91], and for unresectable HCC OR = 1.31, 95% CI (0.94,1.81), I2 = 0%, P = 0.53. These results indicated that sorafenib combined with TACE showed a statistically significant difference in efficacy compared with TACE alone for the treatment of intermediate-advanced and primary HCC. However, for the treatment of unresectable HCC, there was no statistically significant difference in efficacy. The subgroup analysis details were presented in Figure 5.
3.4.3 Safety evaluation
The major adverse events (AEs) from all included studies were presented in Supplementary File S4. Compared with TACE alone, the incidence of hand-foot skin reaction [OR = 4.48, 95%CI (3.28,6.13), P < 0.00001] (Figure 6A) and abdominal pain or diarrhea [OR = 3.10, 95%CI (2.24,4.29), P = 0.04] (Figure 6B) were both higher than those with TACE plus sorafenib. However, the incidence of nausea or vomiting [OR = 1.14, 95%CI (0.81,1.59), P = 0.68] (Figure 6C) or fever [OR = 0.87, 95%CI (0.61,1.23), P = 0.87] (Figure 6D) between the two groups was no significant difference. The comprehensive details of the safety were outlined in Figure 6.
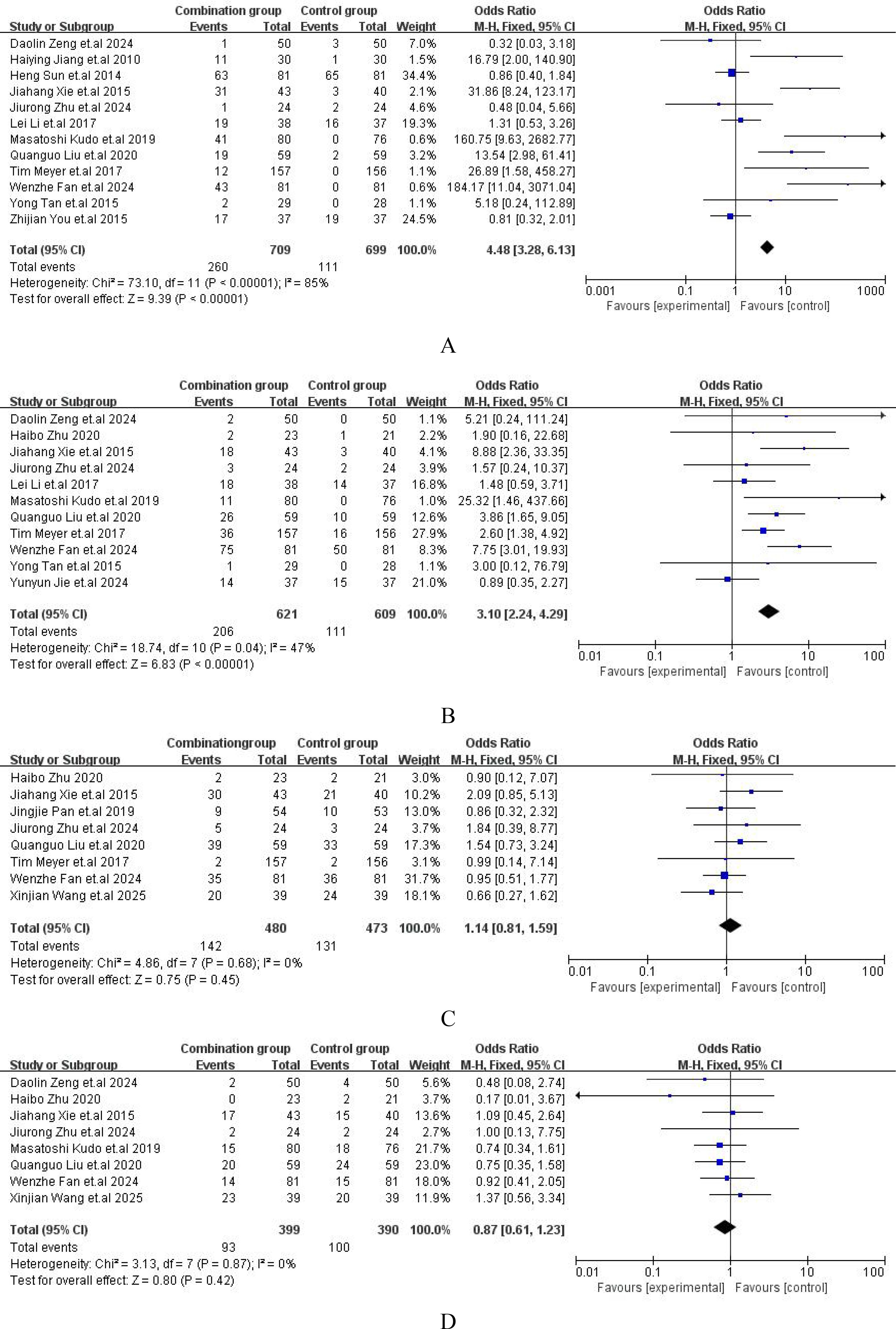
Figure 6. Forest plot of safety analysis. (A) Hand and foot skin reaction; (B) Diarrhea or abdominal pain; (C) Nausea or vomit; (D) Fever.
4 Discussion
In the present study, we systematically evaluated the efficacy and safety of sorafenib in combination with TACE versus TACE alone on the treatment of HCC, providing a definitive systematic review with updated data. A total of 19 randomized controlled trials (10, 16–33), encompassing 2029 patients, were identified and included in this meta-analysis. The results indicated that compared with TACE alone, the combination of sorafenib and TACE significantly improved patient prognosis. Our findings further confirmed the combination of TACE and sorafenib significantly improved the clinical outcomes for the treatment of HCC.
In terms of efficacy, the combined therapy demonstrated a significant advantage over TACE alone in PR, ORR and the 12-month OS rates. Notably, the combination regimen yielded a substantial clinical benefit with an OR = 1.93 for ORR, which was consistent with the report by Chen et al. (34) (OR = 2.19). Sorafenib is a multi-kinase inhibitor that inhibits the activity of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and the platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) and reduce the formation of new blood vessels in HCC tumors. It can also reduce the number and activity of immune-suppressive cells (such as regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells), and strengthen anti-tumor immunity (35). TACE works by embolizing the feeding arteries to the tumor, and reducing its blood supply, leading to tumor shrinkage and has an improved prognosis for HCC patients. Studies proved that TACE plus sorafenib had significantly enhanced the efficacy for HCC patients (36–39).
Subgroup analysis revealed that the efficacy of combination therapy was superior to TACE alone in patients with intermediate-advanced HCC and primary HCC. However, the benefit for unresectable HCC patients was not significant with OR = 1.31(0.94,1.82). There were some discrepancies between these findings and the TACTICS trial (10) which conducted by several domestic centers and reported significant clinical benefits of sorafenib plus TACE in unresectable HCC. The variation for this may be related to sample size and differences in sorafenib regimens. Increasing sample size tends to reduce the error. TACTICS trial only included 156 patients with unresectable HCC, while our work included 679 patients with this subtype. Additionally, the regimens for sorafenib may have some impacts on the outcomes. Among TACTICS trial sorafenib was initiated 14–21 days before TACE at a dose of 400 mg once daily, while this systematical study included both sorafenib initiated before TACE and after TACE regimens. Subgroup analysis indicated that for sorafenib initiated before TACE OR = 1.68(1.25, 2.27), while for sorafenib initiated after TACE OR = 2.32(1.74, 3.11). It still needs further confirmation by more high-quality RCTs with large samples and reliable design.
The present work indicated that there was no significant difference between TACE plus sorafenib group and TACE alone group in aspects of nausea, vomiting and fever. However, the safety results also suggested that compared with TACE alone, the combination of TACE and sorafenib significantly increased the risk of hand-foot skin reaction (HFSR) [OR = 4.48,95%CI (3.28,6.13)], abdominal pain and diarrhea [OR = 3.10,95%CI (2.24,4.29)]. The increased risk of these may relate to the pharmacological properties of sorafenib. It inhibited multiple intracellular signaling pathways in liver carcinoma cells. It can inhibit angiogenesis in tumor tissues and block cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting kinase activities, such as those of c-Raf, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, which can affect the function of the skin and blood vessels leading to HFSR (42). Sorafenib can also lead to a decrease in intestinal mucosal blood supply and repair ability, thereby causing abdominal pain and diarrhea (40). Prioritizing the management of treatment-related toxicities is essential to maintain patient quality of life and ensure treatment adherence (25). It is crucial to find potential ways to reduce adverse reactions, such as providing skin care guidance, adjusting drug doses, and administering antidiarrheal and rehydration therapies.
This study boasts several notable strengths: firstly, our work systematically analyzed 19 RCTs, which had been significantly enhanced in terms of credibility. Secondly, by applying rigorous literature screening criteria and utilizing the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for quality assessment, the reliability of our research findings is significantly enhanced. Thirdly, in this study, we conducted subgroup analyses to explore differential treatment responses among various patient and comprehensively evaluated the efficacy and safety of TACE plus sorafenib, which indicated that further research needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms behind these observations.
There were some limitations to this study that warranted attention. Firstly, although a quality assessment was conducted, the majority of the trials included exhibited uncertain risks of bias. These uncertainties could potentially impact the accuracy of our study results (41). Secondly, there were some variations in the studies whose data have been complied together not only with different patient characteristics but geographic regions, and most of the articles did not stratify the severity of adverse events. We were also unable to adjust for confounders such as age, sex and medical duration of HCC. In addition, HCC is a highly heterogeneous disease in treatment responses among patients. Other factors related to tumor biology (such as genetic mutation profiles and tumor microenvironment), host factors (such as liver function status and overall health condition), and environmental and lifestyle factors also influence disease progression and prognosis. Due to limited data, information on other relevant factors were not extracted, which may cause some bias in our results. In light of these limitations, future research should conduct more large-scale, multicenter RCTs to minimize individual variability and sampling bias.
5 Conclusion
The combination of TACE plus sorafenib offers therapeutic benefits in the treatment of HCC and may be a choice of treatment in patients with unresectable HCC.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LY: Writing – original draft, Software, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology. YX: Software, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology. JL: Validation, Software, Writing – review & editing. YD: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Software. XZ: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the scholars who contributed to this study for their valuable efforts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1640879/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Lesi O, Cabasag CJ, Vignat J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J Hepatol. (2022) 77:1598–606. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021
2. Alawyia B and Constantinou C. Hepatocellular carcinoma: a narrative review on current knowledge and future prospects. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2023) 24:711–24. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01098-9
3. Chang Y, Jeong SW, Young Jang J, and Jae Kim Y. Recent updates of transarterial chemoembolilzation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8165. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218165
4. Zhou B, Wang J, and Yan Z. Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates hepatoma VEGF overexpression after hepatic artery embolization in an orthotopic transplantation hepatocellular carcinoma rat model. Onco Targets Ther. (2014) 7:1945–54. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S69830
5. Tao Z, Chen B, Tan X, Zhao Y, Wang L, Zhu T, et al. Coexpression of VEGF and angiopoietin-1 promotes angiogenesis and cardiomyocyte proliferation reduces apoptosis in porcine myocardial infarction (MI) heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2011) 108:2064–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018925108
6. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2018) 69:182–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019
7. Kelley RK, Rimassa L, Cheng AL, Kaseb A, Qin S, Zhu AX, et al. Cabozantinib plus atezolizumab versus sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (COSMIC-312): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:995–1008. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00326-6
8. Kimura Y, Kaneko R, Yano Y, Kamada K, Ikehara T, Nagai H, et al. The prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib in combination with TACE. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2020) 21:1797–805. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.6.1797
9. Pawlik TM, Reyes DK, Cosgrove D, Kamel IR, Bhagat N, and Geschwind JF. Phase II trial of sorafenib combined with concurrent transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. (2011) 29:3960–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.1021
10. Kudo M, Ueshima K, Ikeda M, Torimura T, Tanabe N, Aikata H, et al. Randomised, multicentre prospective trial of transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) plus sorafenib as compared with TACE alone in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: TACTICS trial. Gut. (2020) 69:1492–501. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318934
11. Zhang L, Hu P, Chen X, and Bie P. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus sorafenib versus TACE for intermediate or advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. PloS One. (2014) 9:e100305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100305
12. Leal CRG, Magalhães C, Barbosa D, Aquino D, Carvalho B, Balbi E, et al. Survival and tolerance to sorafenib in Child-Pugh B patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study. Invest New Drugs. (2018) 36:911–18. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0621-x
13. Pan S, Zheng J, and Shi C. Analysis and prediction of the efficacy and influencing factors of camrelizumab combined with TACE and sorafenib in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:12479–87. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05050-0
14. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg (Lond Engl). (2021) 88:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
15. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
16. Wang X, Wang P, He Y, and Men C. Effects of Sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in treatment of patients with primary liver cancer. Med J Chin People’s Health. (2025) 37:44–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2025.01.014
17. Jie Y, Yu R, Zhang F, Fan X, and Liu H. Clinical effects of sorafenib combined with TACE in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and its impact on serum factor levels in patients. Chin J Clin Rational Drug Use. (2024) 17:12–5. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2024.25.004
18. Zhu J, Yue K, Ye Y, and Wu Y. Efficacy analysis of sorafenib tosylate with TACE in the treatment of unresectable localized liver cancer patients. Pract J Cancer. (2024) 39:648–651+677. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5930.2024.04.032
19. Fan W, Zhu B, Chen S, Wu Y, Zhao X, Qiao L, et al. Survival in patients with recurrent intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: sorafenib plus TACE vs TACE alone randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2024) 10:1047–54. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.1831
20. Zeng D, Yu C, Chen S, Zou L, Chen J, and Xu L. Assessment of disease control rate and safety of sorafenib in targeted therapy for advanced liver cancer. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22:93. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03364-y
21. Wei X. Effects of sorafenib combined with TACE on immune function and alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Innovation China. (2022) 19:56–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2022.21.014
22. Liu Q and Dai Y. Sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization prolongs survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J BUON. (2020) 25:945–51. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32521890/
23. Zhu H. Observation on the efficacy and safety of thalafinil combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in the treatment of primary liver cancer. Health Guide. (2020) 27:7–8. Available online at https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/ysbjzn-x202027006
24. Pan J, Liu T-y, Huang J, and Liu W. Clinical observation of transarterial chemoembolization combined with corafinil and compound berberine in treating patients with advanced liver cancer. J Oncol Chin Med. (2019) 1:38–44. doi: 10.19811/j.cnki.issn2096-6628.2019.04.009
25. Meyer T, Fox R, Ma YT, Ross PJ, James MW, Sturgess R, et al. Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolisation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (TACE 2): a randomised placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 2:565–75. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30156-5
26. Li L, Zhong M, and Song H. Effects of sorafenib combined with TACE on serum cytokine expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Modern Digest Intervent. (2017) 22:482–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2017.04.010
27. Xie J and Wang J. Analysis of efficacy and complications of sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Control Treat. (2015) 28:152–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0904.2015.03.010
28. Tan Y, Zhang T, Peng J, and Zhao Y. Curative effect of sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in treatment of large primary liver cancer. Med J Natl Defending Forces Southwest China. (2015) 25:386–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.004-0188.2015.04.014
29. You Z, Zheng R, Hu X, Lin S, and Ye Z. Curative efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Clin Oncol Rehabil. (2015) 22:1212–4. doi: 10.13455/j.cnki.cjcor.2015.10.19
30. Zhou R, Zhou X, Li X, Xia Y, Song P, and Guo X. Clinical effects of sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on the treatment of advanced primary hepatocellular. Prog Modern Biomed. (2014) 14:2494–6. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2014.13.025
31. Sun H and Han W. Analysis of curative effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for not operation resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2014) 23:486–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2014.05.002
32. Chen S, Wang Y, and Xie H. Clinical observation of sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chem oembolization for treating senile primary carcinoma of the liver. China Joumal Modem Med. (2012) 22:71–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2012.25.018
33. Jiang H and Xie X. Sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hainan Med J. (2010) 21:6–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2010.23.003
34. Chen A, Li S, Yao Z, Hu J, Cao J, Topatana W, et al. Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization to sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 36:302–10. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15180
35. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359:378–90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
36. Chao Y, Chung YH, Han G, Yoon JH, Yang J, Wang J, et al. The combination of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is well tolerated and effective in Asian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: final results of the START trial. Int J Cancer. (2015) 136:1458–67. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29126
37. Li Y, Zheng YB, Zhao W, Liu B, Hu BS, He X, et al. Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. (2013) 30:730. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0730-5
38. Liang HY, Lu LG, Hu BS, Li Y, and Shao PJ. Effects of sorafenib combined with chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for large, unresectable hepatocellular carcinomas. Chin Med J (Engl). (2013) 126:4270–6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.20120478
39. Yang HJ, Ye B, Liao JX, Lei L, and Chen K. Sorafenib plus transarterial chemoembolization vs sorafenib alone for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Hepatol. (2024) 16:91–102. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i1.91
40. Mir O, Coriat R, Boudou-Rouquette P, Durand JP, and Goldwasser F. Sorafenib-induced diarrhea and hypophosphatemia: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Ann Oncol. (2012) 23:280–1. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr525
41. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, sorafenib, transarterial chemoembolization, randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis
Citation: Yu L, Xiong Y, Liao J, Deng Y and Zhai X (2025) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Oncol. 15:1640879. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1640879
Received: 04 June 2025; Accepted: 27 October 2025;
Published: 10 November 2025.
Edited by:
Sharon R Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesReviewed by:
Shengjun Xu, Zhejiang University, ChinaKai Chen, The First Affliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Xiong, Liao, Deng and Zhai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuejia Zhai, emhhaXh1ZWppYUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Lixiu Yu
Lixiu Yu Yi Xiong
Yi Xiong Jing Liao1,2
Jing Liao1,2 Xuejia Zhai
Xuejia Zhai