- Three Gorges University Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine & Yichang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yichang, China
Digestive system cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), gastric cancer (GC), pancreatic cancer (PC), and colorectal cancer (CRC), pose a significant global health burden with high morbidity and mortality rates. Their tumorigenesis and progression are driven by complex interactions between genetic alterations and environmental factors. In recent years, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as critical regulators in cancer initiation, metastasis, and drug resistance through epigenetic modulation, transcriptional regulation, and post-transcriptional modifications. Among them, HULC, a well-characterized oncogenic lncRNA, was initially identified in HCC due to its remarkable upregulation. Subsequent studies have revealed that HULC is aberrantly overexpressed in multiple gastrointestinal malignancies, including GC, PC, and CRC, and its expression levels strongly correlate with advanced clinical stage, metastatic potential, and poor patient prognosis. Mechanistically, HULC exerts its oncogenic effects by interacting with genes, RNA, and proteins to promoting the Warburg effect, and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), thereby facilitating tumor progression. This review comprehensively summarizes recent advances in understanding the biological roles, molecular mechanisms, and clinical implications of HULC in digestive system cancers. Furthermore, we discuss its potential as a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target, providing insights into precision medicine strategies for gastrointestinal malignancies.
1 Introduction
Digestive system tumors, mainly including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), pancreatic cancer (PC), gastric cancer (GC), and colorectal cancer (CRC), represent a major cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. According to recent statistics, more than 5 million new cases are diagnosed annually, resulting in approximately 4 million deaths globally. This imposes a substantial economic burden on patients, families, and healthcare systems (1, 2). Despite the availability of diverse treatment modalities, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy and targeted therapies, therapeutic efficacy remains limited, particularly for patients with advanced or metastatic disease (3, 4). Consequently, the identification of novel molecular targets is urgently needed to improve diagnostic precision and develop more effective treatment strategies for digestive system cancers.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), a class of non-protein-coding transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides, are transcribed by RNA polymerase II and have emerged as key regulators in cancer biology (5). Increasing evidence indicates that lncRNAs play critical roles in tumor initiation, proliferation, invasion, and prognosis through various mechanisms, including epigenetic modification, chromatin remodeling, and post-transcriptional regulation (6–9). Among these mechanisms, the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network is particularly noteworthy. In this context, lncRNAs act as molecular sponges by binding to microRNAs(miRNAs), thereby modulating the expression of downstream target genes. This ceRNA-mediated regulatory axis is now recognized as a significant contributor to tumor progression (5, 10, 11).
HULC is located on chromosome 6p24.3 (12). Following transcription and post-transcriptional processing, a mature lncRNA is produced (12). Increasing evidence suggests that HULC is aberrantly expressed in various gastrointestinal cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer (13–15). Additionnally, HULC has also been shown to promote the progression of other systemic cancers, including breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, and osteosarcoma (16–19).For instance, HULC promotes the metastasis and cisplatin resistance of triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting the trans-IGF1R-PI3K-AKT axis35981570. Additionally, HULC enhances the proliferation of lung squamous cancer cells by regulating the PTPRO/NF-κB signaling pathway (17). However, in comparison to non-gastrointestinal cancers, HULC shows a stronger correlation with digestive system cancers (20, 21). Furthermore, HULC has been studied most extensively within the context of digestive system cancers.Therefore, we have decided to focus on digestive system tumors to thoroughly investigate the biological functions and clinical significance of HULC in this area.
The expression of HULC expression is regulated through multiple molecular mechanisms. For instance, HULC can interact with IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1), leading to reduced HULC stability and promoting transcript degradation (22). Additionally, miR-203 has been shown to participate in the post-transcriptional regulation of HULC (23). In this review, we summarize the expression patterns, biological functions, and molecular mechanisms of HULC in digestive system cancers, and discuss its potential as a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. The current body of evidence highlights the pivotal role of HULC in the initiation, progression, and metastasis of digestive system tumors, underscoring its promise as a target for future precision medicine strategies.
2 Characterization of HULC
HULC is located on chromosome 6, spanning positions 8,435,568 to 9,294,133 on the human genome reference sequence GRCh38.p14. According to Ensembl websites, there are a total of 217 transcripts(splice variants) for HULC. Among them, the transcript lncRNA HULC-202(Ensembl transcript ID: ENST00000503668.3; NCBI transcript ID: NR_004855.3) is the most well-characterized transcript, with a length of 434 base pairs. Additionally, lncRNA HULC-202 has been studied across various types of cancers, including liver, gastric, and colorectal cancer (24–26). Accumulating evidence shows that HULC is aberrantly expressed in various gastrointestinal malignancies, including liver, gastric, and colorectal cancers (13–15). Although the physiological functions and molecular mechanisms of HULC are not yet fully understood, current findings can be summarized into the following major functional roles:
1. HULC and gene activation and inhibition: HULC regulates the histone modification pattern in the promoter region of the YAP gene by increasing the enrichment of H3K4me3 and reducing the enrichment of H3K27me3. Under hyperglycemic conditions, HULC promotes the transcriptional activation of the YAP gene, which is linked to the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells and enhanced drug resistance (27). Furthermore, HULC may also influence the expression of neighboring genes. In radiation-induced liver cancer, HULC was found to downregulate the expression of the nearby gene CDKN1 through complementary base pairing, thereby affecting tumor progression. Additionally, Li Dan et al. reported that downregulation of HULC expression in hepatoma cell lines such as Hep3B and HepG2 led to reduced expression of the adjacent gene SLC35B3 (28).
2. The interaction between HULC and RNA(Acting as a ceRNA): HULC functions as a ceRNA by sharing miRNA binding sites with target transcripts. Through this mechanism, HULC competitively binds miRNAs, thereby mitigating their inhibitory effects on downstream target gene expression. This is currently the most extensively studied mechanism. For example, in liver cancer, HULC directly binds to miR-372, leading to miR-372 decreased expression and activity. In turn, miR-372 normally reduces the phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), thus diminishing CREB’s binding to the HULC promoter and lowering HULC transcription. Consequently, a positive feedback loop is established, further enhancing HULC expression (29). Moreover, HULC promotes autophagy through the miR-675/PKM2 axis, leading to upregulation of Cyclin D1 and accelerated proliferation of liver cancer stem cells (30). Similarly, via the miR-9/PPARA signaling pathway, HULC activates ACSL1 and induces abnormal lipid metabolism in liver cancer cells, contributing to disease progression (31). In gastric cancer, HULC promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion and resistance to apoptosis through the miR-9-5p/MYH9 axis (25).
3. The interaction between HULC and proteins: Lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) are two key enzymes involved in glycolytic reprogramming, a hallmark of cancer that promotes rapid cell growth and survival. Studies have demonstrated that HULC can directly bind to and increase the phosphorylation of both LDHA and PKM2, thereby enhancing glycolysis in HCC cell lines and facilitating tumor progression (32). Furthermore, lncRNA MEG3 promotes the binding of the p53 protein to HULC, influencing the interaction between the telomere length maintenance complex and telomeric DNA, which leads to reduced telomere stability (33).
4. Overall, HULC interacts with genes, RNA, and proteins to promote tumor cell metabolism reprogramming(Warburg effect), and an anti-apoptotic phenotype. Ultimately, it contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasion and metastasis, and immune escape in cancers.
3 HULC in digestive tumors
Recent studies have highlighted the pivotal role of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of digestive system cancers. Aberrant expression of lncRNAs has been implicated in key oncogenic processes such as cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and resistance to apoptosis. As research has progressed, HULC has been found to be abnormally expressed in a range of digestive system malignancies, where it contributes to the regulation of tumor cell behavior (Figure 1).
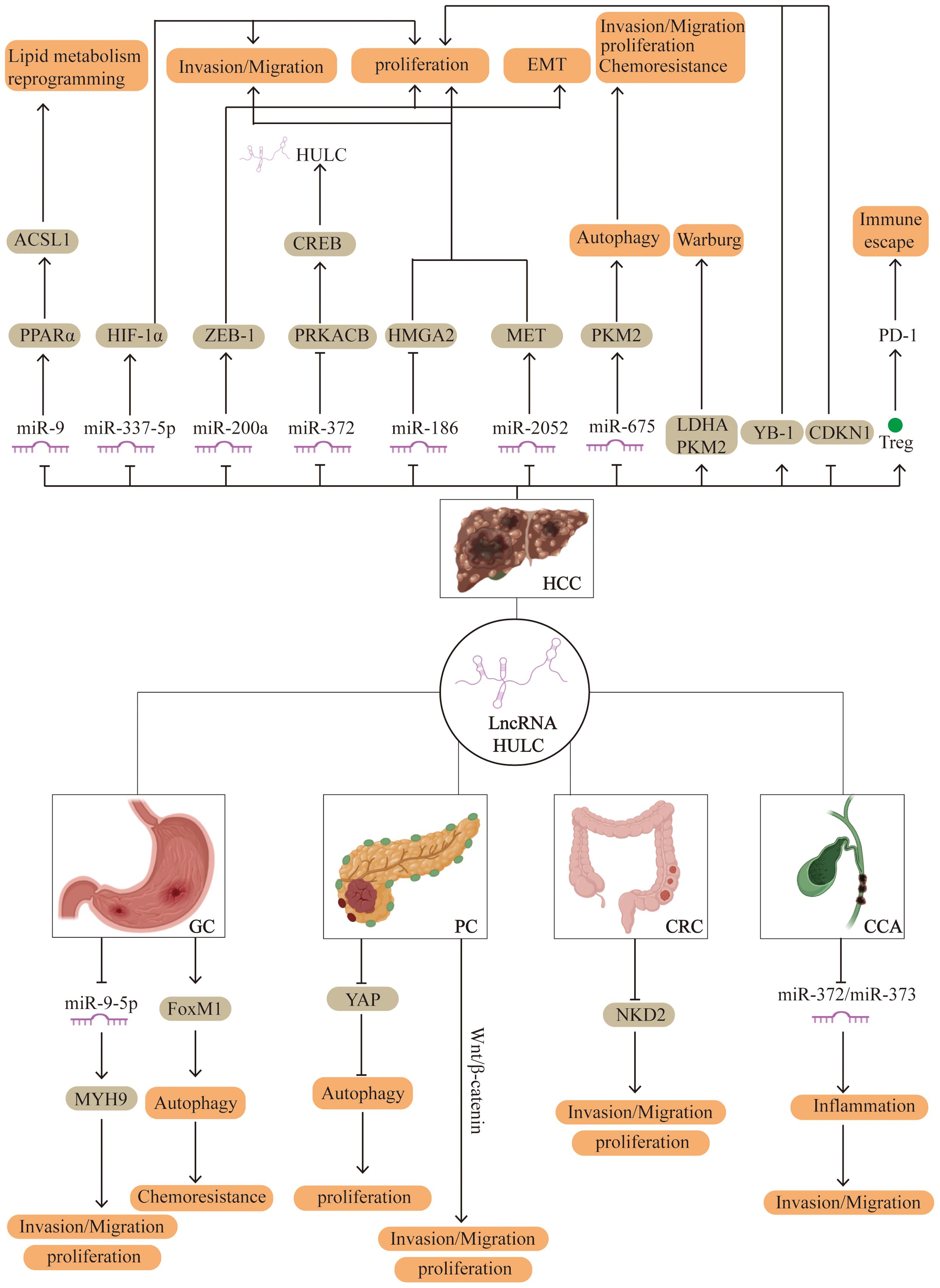
Figure 1. Potential regulatory mechanisms of HULC in human digestive system cancer. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PC, pancreatic cancer; GC, gastric cancer; CRC, colorectal cancer; CCA, Cholangiocarcinoma.
3.1 HULC in hepatocellular carcinoma
3.1.1 Aberrant up‐regulation of HULC
In 2007, Panzitt et al. first identified the abnormal expression of HULC in HCC using genome-wide microarray analysis (12). This study included 46 HCC tissues, 4 liver focal nodular hyperplasia samples, 7 liver cirrhosis samples, and 2 normal liver samples. The results demonstrated a gradual upregulation of HULC expression across liver cirrhosis, focal nodular hyperplasia, and ultimately HCC. These findings have been consistently validated in subsequent studies (22, 34, 35). Furthermore, radioactive in situ hybridization confirmed the elevated expression of HULC in liver cancer tissues (12). In addition, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) has shown significantly increased HULC levels in HCC cell lines (29, 36). A clinical study conducted in Egypt further supported these findings, revealing that HULC expression in the blood of HCC patients was significantly higher than in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (35). These collective data suggest that HULC may serve as a novel biomarker for the early diagnosis of HCC. A meta-analysis involving 6,426 HCC patients indicated that HULC exhibits superior sensitivity and specificity for HCC diagnosis compared with traditional biomarkers or other non-coding RNAs (37). Moreover, elevated serum HULC levels are associated with poor prognosis and have clinical utility in predicting metastasis and outcomes after radical resection of HCC (38, 39).
Notably, Yao et al. recently developed a probe-based rolling circle amplification-induced fluorescence biosensor for detecting lncRNA HULC. This biosensor demonstrated high selectivity and sensitivity in both HCC cell lines and whole blood samples from HCC patients (40). These advancements highlight a promising new approach for the clinical application of HULC in the diagnosis, prognosis, and potentially treatment monitoring of HCC.
3.1.2 Mechanism of HULC in hepatocellular carcinoma
Studies have demonstrated that HULC plays a critical role in promoting the progression of liver cancer by interacting with genes, RNA, and proteins. This section summarizes the key regulatory mechanisms in HCC driven by HULC.
3.1.2.1 HULC/miRNA-9/PPARA
Aberrant lipid metabolism has been recognized as a key contributor to malignant tumor progression. Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 (ACSL1), a critical enzyme involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and fatty acid oxidation, plays a pivotal role in these metabolic alterations. Clinical studies in patients with HCC have shown that HULC expression is positively correlated with ACSL1 expression, as well as with serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Supporting these findings, in vitro experiments demonstrated that HULC activates ACSL1 expression in HepG2 hepatoma cells via the miRNA-9/PPARA signaling pathway, thereby inducing lipid metabolic reprogramming that facilitates HCC progression. Moreover, elevated intracellular cholesterol levels may further amplify HULC expression through activation of retinoid receptors in hepatoma cells, establishing a positive feedback loop that exacerbates tumor development (22).
3.1.2.2 HULC/miR-377-5p/HIF-1α
In the HCC cell lines, including HB611, H22 and HepG2, qRT-PCR showed significant increases in both HULC expression, while miR-377-5p expression was decreased. Inhibition of HULC expression in HepG2 cells suppressed both cell proliferation and invasion. Conversely, miR-377-5p inhibition promoted hepatoma cell proliferation and invasion. Further experiments suggested that HULC may promote HCC progression by directly targeting the miR-377-5p/HIF-1α pathway (36).
3.1.2.3 HULC in HBV-associated HCC
chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major cause of cirrhosis and HCC. Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) is the key pathogenic factor in HBV infection. Luciferase reporter gene and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays have demonstrated that HBx activates the HULC promoter via cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), thereby promoting HULC expression (41). Further studies revealed that HBx enhances hepatoma cell proliferation by upregulating the HULC/p18 pathway (41). In HBV-related HCC, metformin has been shown to inhibit tumor cell proliferation by negatively regulating the HULC/p18/miR-200a/ZEB1 signaling pathway. This regulation improves survival rates and reduces recurrence in HCC patients (42). Moreover, upregulation of HULC promotes the HBx/STAT3/miR-539/APOBEC3B pathway, which further supports HBV replication and accelerates hepatoma cell growth (43).
3.1.2.4 HULC/miR-372
Luciferase assays indicated that miR-372 reduced the promoter activity of HULC in Hep3B hepatoma cells. Overexpression of miR-372 inhibited the translation of its target gene PRKACB, leading to a decrease in CREB phosphorylation. This reduction impaired the binding of CREB to the proximal HULC promoter, thereby lowering HULC expression. Conversely, HULC inhibits miR-372 activity, leading to upregulation of HULC expression in liver cancer (29).
3.1.2.5 HULC/miR-186
High-mobility group protein A2 (HMGA2), a transcription factor, is involved in various cancers, including liver, colorectal, and gastric cancers. In HCC tissues, qRT-PCR analysis revealed a positive correlation between HULC and HMGA2 expression. In vitro studies demonstrated that HULC upregulates HMGA2 expression in HCC cells. Further investigation showed that HULC promotes the expression of HMGA2 by inhibiting miR-186, thereby facilitating liver cancer progression (44).
3.1.2.6 HULC/miR-2052
Bioinformatics analyses suggest that HULC acts as a sponge for miR-2052. In 42 pairs of HCC and matched non-cancer tissues, the expression of miR-2052 was negatively correlated with HULC levels. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed that HULC promotes HCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and progression through the miR-2052/MET axis (45).
3.1.2.7 HULC and autophagy
Autophagy plays a critical role in the initiation and progression of HCC, and HULC has emerged as a key modulator of this process. In liver cancer stem cells, HULC was shown to induce autophagy via the miR-675/PKM2 pathway, leading to upregulation of Cyclin D1 and promoting the proliferation of liver cancer stem cells (30). Additionally, HULC activates autophagy by enhancing the expression of LC3-I and LC3-II (canonical markers of autophagy) through the deacetylase Sirt1 (24). Further studies by Liu et al. demonstrated that HULC also promotes phosphorylation of p65 and IκBκB, thereby increasing LC3-II levels in an NF-κB-dependent manner (46). Mechanistically, HULC inhibits PTEN via autophagy-mediated degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which in turn activates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to promote hepatocarcinogenesis (24). Moreover, autophagy contributes to chemoresistance in HCC. Anti-tumor agents such as oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and pirarubicin have been observed to increase both HULC expression and autophagic activity in human HCC tissues. In vivo data indicate that HULC overexpression reduces HCC cell sensitivity to oxaliplatin, whereas silencing HULC enhances drug sensitivity. Further in vitro experiments revealed that the USP22/Sirt1/autophagy axis underlies this effect, suggesting that targeting this pathway could provide a novel therapeutic approach to overcoming chemoresistance in HCC (47, 48).
3.1.2.8 HULC and Warburg effect
Warburg effect is a hallmark of cancer metabolism wherein cancer cells preferentially undergo glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation, even under normoxic conditions. This metabolic shift supports rapid tumor growth and survival. HULC has been found to bind directly to and increase the phosphorylation of key glycolytic enzymes LDHA and PKM2, thereby promoting glycolysis and enhancing tumor progression (32).
3.1.2.9 HULC and EMT
EMT is essential for tumor invasion and metastasis. Clinical data reveal that HULC expression is positively correlated with EMT phenotypes in HCC. In vitro studies further demonstrated that HULC upregulates EMT markers such as N-cadherin and vimentin. Mechanistically, HULC induces EMT via the miR-200a-3p/ZEB1 signaling pathway, thereby facilitating tumor progression and metastasis (49).
3.1.2.10 HULC/YB-1
HULC interacts with Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1), a multifunctional protein involved in mRNA splicing, translation regulation and DNA repair. Mass spectrometry, localization, and co-immunoprecipitation studies revealed that HULC binds YB-1 and promotes its phosphorylation via extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling. This phosphorylation leads to the release of YB-1 from silenced oncogenic mRNAs, including cyclin D1, cyclin E1, and matrix metalloproteinase 3, thereby enhancing their translation and accelerating tumor growth (50).
3.1.2.11 HULC/CDKN1
In radiation-induced liver carcinogenesis, HULC also plays a significant role. Downregulation of HULC impairs hepatocyte proliferation following radiation exposure. CDKN1, a gene located adjacent to HULC, has been implicated in radiation-induced cell cycle regulation. In vitro studies indicate that HULC suppresses CDKN1 expression via complementary base pairing, thereby promoting cell cycle progression and contributing to radiation-related liver cancer (51).
3.1.2.12 HULC/Treg/PD-1
Immune escape represents a major challenge in malignant tumor therapy. In a liver cancer xenograft model, overexpression of HULC increased regulatory T cell (Treg) proliferation and upregulated PD-1 expression in the tumor microenvironment. Additional studies revealed that the HULC–Treg–PD-1 axis suppresses IL-10 and TGF-β1 expression, facilitating immunosuppression and promoting immune escape. Targeting this axis may represent a promising strategy to overcome immune resistance in HCC (52).
Collectively, these findings underscore the multifaceted role of HULC in hepatocellular carcinoma. HULC expression is significantly elevated in HCC, especially in cases with focal nodular hyperplasia and liver cirrhosis, highlighting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker. It promotes HCC initiation, progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance by modulating key mechanisms such as interactions with multiple miRNAs/transcription factors, autophagy, the Warburg effect, EMT, and immune escape. Inhibition of HULC and its downstream pathways may offer new therapeutic opportunities for HCC treatment and prognosis improvement.
3.2 HULC in gastric cancer
Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated that HULC is significantly overexpressed in both plasma and tissue samples from patients with GC compared to healthy controls. Survival analyses have shown that elevated HULC expression is significantly associated with poorer overall survival (53, 54). In addition, circulating HULC levels correlate with tumor size, lymph node involvement, distant metastasis, and Helicobacter pylori infection in GC patients (13, 55). Notably, the combination of HULC expression and H. pylori status improves the predictive accuracy for GC risk (56). These findings suggest that HULC is a promising biomarker for GC diagnosis and prognosis.
In vivo, silencing HULC significantly inhibited tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model of gastric cancer (25). In vitro, overexpression of HULC promotes the proliferation and invasion of human gastric cancer cells, while inhibiting cell apoptosis. Conversely, knockdown of HULC reverses these effects (57). Mechanistically, dual-luciferase reporter assays and RNA pull-down experiments revealed that HULC directly targets miR-9-5p to exert its biological functions. Further studies have demonstrated that HULC enhances proliferation, EMT, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells through the miR-9-5p/MYH9 axis (25, 57). Additionally, HULC promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis by epigenetically suppressing the expression of p53. Specifically, RIP- and ChIP-qPCR assays have shown that HULC recruits EZH2 to the p53 promoter region, mediating its transcriptional repression in gastric cancer cells (58). Moreover, HULC plays a critical role in regulating chemoresistance. Inhibition of HULC enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells (47), and the HULC/FoxM1 signaling pathway has been shown to promote cisplatin resistance by inducing autophagy (52).
Taken together, these findings highlight HULC as an important regulator of tumor growth, metastasis, and drug resistance in gastric cancer. HULC represents a promising biomarker for early detection and prognosis and may serve as a novel therapeutic target in the prevention and treatment of GC.
3.3 HULC in pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer ranks as the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States and the sixth in China (14, 27). Bioinformatics analyses have identified HULC as one of the most significantly dysregulated lncRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells (27). A clinical study involving tumor and matched normal tissues from 304 PC patients revealed that HULC is highly expressed in both the tissues and serum of PC patients. Notably, elevated HULC levels were significantly associated with larger tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and vascular invasion.
In vivo, using PC xenografts in nude mice demonstrated that HULC knockdown significantly suppressed tumor growth compared to controls (59). Complementary in vitro studies further showed that silencing HULC reduced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, viability, invasion, and migration. HULC knockdown also led to decreased expression of EMT markers(N-cadherin, vimentin, and Snail), while increasing the expression of E-cadherin (59). Mechanistically, HULC appears to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression via multiple pathways. It inhibits YAP activation, thereby promoting autophagy and enhancing tumor cell proliferation (27). Additionally, HULC may facilitate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and invasion through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (14). HULC also plays a role in intercellular communication through extracellular vesicles, where it promotes invasion and migration by inducing EMT in recipient cells. This effect can be counteracted by miR-622, which targets HULC to suppress EMT-related signaling, providing new insights into pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets (60).
3.4 HULC in colorectal carcinoma
Colorectal cancer is one of the main causes of cancer deaths worldwide. By bioinformatics analysis, lncRNA HULC is regarded as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer (2, 61). Additionally, previous research has demonstrated that serum HULC levels are significantly elevated in patients with CRC compared to healthy individuals. This elevation suggests that HULC may serve as a promising biomarker for the diagnosis of CRC (15). HULC expression was significantly upregulated in human primary colorectal cancer and colorectal cancer cell lines. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the upregulation of HULC was significantly associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Knockdown of HULC significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells and promoted cell apoptosis in vitro. In BALB/c nude mice tumorigenic experiments show that knockdown of HULC can inhibit the proliferation of CRC cells. Mechanically speaking, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RNA pull-down experiments indicated that in colorectal cancer cells, HULC promoted CRC by directly binding to EZH2 to inhibit the expression of NKD2 (62).
3.5 Others
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a highly fatal malignancy with a poor overall survival rate. Bioinformatics analysis of 36 CCA tumor tissues and 9 normal control tissues from WMU cohort revealed that HULC was significantly upregulated and strongly associated with shorter overall survival in CCA patients (63). Functional assays, including cell migration, and invasion experiments, demonstrated that HULC overexpression enhances the migratory and invasive capacities of CCA cells. Further mechanistic studies showed that HULC acts by targeting miR-372/miR-373, leading to upregulation of inflammation-related genes such as IL-6 and CXCR4. This, in turn, induces aberrant inflammatory responses and promotes cancer cell migration and invasion (64).
HULC is also implicated in the pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), one of the most prevalent malignancies in the oral and maxillofacial region worldwide (65). In a murine xenograft model, depletion of HULC reduced tumor growth and suppressed EMT. In vitro, HULC knockdown inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion of OSCC cells, while increasing apoptosis (66). These findings suggest that HULC plays a key role in OSCC tumorigenesis and progression.
In nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), clinical studies have shown that HULC is highly expressed in tumor tissues and is associated with poor patient prognosis. HULC overexpression promotes the growth of NPC cells, whereas its downregulation activates the tumor suppressor p53, increases p21 expression, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (67). These data support a role for HULC as a carcinogenic lncRNA and highlight its potential as a therapeutic target in NPC.
Although HULC has been strongly implicated in the development and progression of several digestive system cancers, its role in esophageal cancer remains unclear. From 2014 to 2018, comparative analyses of tumor tissues from 95 patients with esophageal cancer and 121 healthy control samples showed no significant association between HULC expression and cancer prognosis across any clinical subgroup (68, 69). This suggests that the contribution of HULC to esophageal cancer may be limited or context-dependent, warranting further investigation.
4 Conclusion
HULC has emerged as a critical molecule in the progression of various digestive system malignancies, including hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Multiple studies have shown that HULC is significantly upregulated in various digestive system cancers. Its abnormal upregulation is thought to result from a complex interplay between environmental factors (such as HBV infection) and intrinsic cellular dysregulation involving transcription factors and miRNAs.Importantly, the overexpression of HULC is associated with poor prognosis, highlighting its potential as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. Mechanistically, HULC induces malignant phenotypes such as Warburg effect and EMT in tumor cells through interactions with genes, RNA, and proteins. These mechanisms do not exist in isolation but have extensive interactions. Therefore, as a promising therapeutic target, HULC has the following advantages: 1) High tissue specificity: HULC is significantly upregulated in digestive system tumors and is expressed at a lower level in most normal tissues, minimizing potential off-target effects. 2) Multimechanism carcinogenicity: It mediates the Warburg effect, EMT, and resistance to cell apoptosis through multiple mechanisms, making it a core node in combined therapy. 3) Non-coding features: As an LncRNA, HULC is less prone to mutation than protein-coding genes, reducing the risk of developing treatment resistance through genetic variations. 4) Detectability in liquid biopsy: HULC is elevated and stable in the blood of digestive system cancers, facilitating non-invasive monitoring and early intervention. Currently, the related mechanism studies of HULC in liver cancer are the most in-depth. In pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer and other digestive system cancers, the research on HULC is relatively less. This suggests two possible interpretations: either HULC may warrant further investigation in other digestive system cancers, or it may possess higher specificity and clinical utility in liver cancer. Notably, clinical evidence indicates that HULC is associated with nearly all digestive system cancers, with the exception of esophageal cancer. Therefore, further research on HULC is crucial for comprehensively elucidating its biological function and clinical application.
5 Limitation
5.1 Heterogeneity among patients and tissues
Digestive system cancers exhibit tumor heterogeneity, both across different cancer types and among individual patients. This heterogeneity complicates the interpretation of findings and may affect the generalizability of results. Specifically, the expression levels and functional roles of HULC can differ significantly among patients. To elucidate the broader patterns and clinical relevance of HULC, larger, well-powered studies are necessary. In future research, machine learning algorithms may be employed to construct predictive models capable of identifying HULC expression signatures from diverse patient-derived samples.
5.2 Complexity of mechanisms
HULC exerts its effects through multiple molecular interactions, involving genes, RNA, and proteins. These interactions include diverse epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and regulation by non-coding RNAs. The diversity of these epigenetic processes present a substantial challenge for studying the potential mechanisms of HULC in tumorigenesis. To address this, future studies should incorporate high-throughput sequencing, single-cell analysis, multi-omics integration, and large-scale sample validation, along with investigations into newly discovered epigenetic modifications.
5.3 Methodological challenges in studying HULC
Accurate detection and quantification of HULC require highly sensitive and specific techniques, which depend on sophisticated laboratory infrastructure and skilled personnel to ensure data quality and reproducibility. Furthermore, high-throughput technologies generate vast amounts of data, the analysis of which demands advanced bioinformatics tools and expertise. Extracting biologically meaningful insights from these datasets remains a critical challenge. Future investigations should leverage cutting-edge sequencing platforms and innovative functional assays to elucidate the oncogenic role and clinical significance of HULC in digestive system cancers.
Author contributions
LH: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Software, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Project administration, Data curation, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Validation, Conceptualization, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Assarzadegan N and Montgomery E. What is new in the 2019 world health organization (Who) classification of tumors of the digestive system: review of selected updates on neuroendocrine neoplasms, appendiceal tumors, and molecular testing. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2021) 145:664–77. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0665-RA
2. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
3. Lee YT, Tan YJ, and Oon CE. Molecular targeted therapy: treating cancer with specificity. Eur J Pharmacol. (2018) 834:188–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.07.034
4. Hojman P, Gehl J, Christensen JF, and Pedersen BK. Molecular mechanisms linking exercise to cancer prevention and treatment. Cell Metab. (2018) 27:10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.015
5. Bhan A, Soleimani M, and Mandal SS. Long noncoding rna and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:3965–81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2634
6. Hu Y, Wang J, Qian J, Kong X, Tang J, Wang Y, et al. Long noncoding rna gaplinc regulates cd44-dependent cell invasiveness and associates with poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:6890–902. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0686
7. Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K, Imoto S, Sudo T, et al. Long noncoding rna hotair regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:6320–6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1021
8. Qiu M, Xu Y, Wang J, Zhang E, Sun M, Zheng Y, et al. A novel lncrna, luadt1, promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation via the epigenetic suppression of P27. Cell Death Dis. (2015) 6:e1858. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.203
9. Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson G, Frank J, Burghardt R, et al. Hotair is a negative prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. (2013) 32:1616–25. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.193
10. Lorenzi L, Avila Cobos F, Decock A, Everaert C, Helsmoortel H, Lefever S, et al. Long noncoding rna expression profiling in cancer: challenges and opportunities. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. (2019) 58:191–9. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22709
11. Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, and Pandolfi PP. A cerna hypothesis: the rosetta stone of a hidden rna language? Cell. (2011) 146:353–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
12. Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MMO, Guelly C, Moustafa T, Stradner M, Strohmaier HM, et al. Characterization of hulc, a novel gene with striking up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding rna. Gastroenterology. (2007) 132:330–42. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.026
13. Jin C, Shi W, Wang F, Shen X, Qi J, Cong H, et al. Long non-coding rna hulc as a novel serum biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis prediction of gastric cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:51763–72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10107
14. Ou Z-L, Luo Z, and Lu Y-B. Long non-coding rna hulc as a diagnostic and prognostic marker of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. (2019) 25:6728–42. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i46.6728
15. Shaker OG, Senousy MA, and Elbaz EM. Association of rs6983267 at 8q24, hulc rs7763881 polymorphisms and serum lncrnas ccat2 and hulc with colorectal cancer in Egyptian patients. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16246. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16500-4
16. Zhou L, Li H, Sun T, Wen X, Niu C, Li M, et al. Hulc targets the igf1r-pi3k-akt axis in trans to promote breast cancer metastasis and cisplatin resistance. Cancer Lett. (2022) 548:215861. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215861
17. Xu Y, Li J, Wang P, Zhang Z, and Wang X. Lncrna hulc promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating ptpro via nf-κb. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:19415–21. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29119
18. Li Y, Liu J-J, Zhou J-H, Chen R, and Cen C-Q. Lncrna hulc induces the progression of osteosarcoma by regulating the mir-372-3p/hmgb1 signalling axis. Mol Med. (2020) 26:26. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00155-5
19. Chen S, Wu D-D, Sang X-B, Wang L-L, Zong Z-H, Sun K-X, et al. The lncrna hulc functions as an oncogene by targeting atg7 and itgb1 in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e3118. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.486
20. Li D, Wang R, Wu N, and Yu Y. Lncrna hulc as a potential predictor of prognosis and clinicopathological features in patients with digestive system tumors: A meta-analysis. Aging (Albany NY). (2022) 14:1797–811. doi: 10.18632/aging.203903
21. Gao X, Yang J, Wang D, Zeng Q, Li F, Zhou S, et al. Association between hulc rs7763881 and cancer risk: an updated meta-analysis. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. (2022) 41:85–96. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2021.2008433
22. Hämmerle M, Gutschner T, Uckelmann H, Ozgur S, Fiskin E, Gross M, et al. Posttranscriptional destabilization of the liver-specific long noncoding rna hulc by the igf2 mrna-binding protein 1 (Igf2bp1). Hepatology. (2013) 58:1703–12. doi: 10.1002/hep.26537
23. Wang YF, Zhang S, Li XQ, and Wang Y. Expression of lncrna hulc in cervical cancer and its correlation with tumor progression and patient survival. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2016) 20:3987–91.
24. Xin X, Wu M, Meng Q, Wang C, Lu Y, Yang Y, et al. Long noncoding rna hulc accelerates liver cancer by inhibiting pten via autophagy cooperation to mir15a. Mol Cancer. (2018) 17:94. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0843-8
25. Liu T, Liu Y, Wei C, Yang Z, Chang W, and Zhang X. Lncrna hulc promotes the progression of gastric cancer by regulating mir-9-5p/myh9 axis. BioMed Pharmacother. (2020) 121:109607. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109607
26. Ghafouri-Fard S, Esmaeili M, Taheri M, and Samsami M. Highly upregulated in liver cancer (Hulc): an update on its role in carcinogenesis. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:9071–9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29765
27. Sharma A, Chowdhury S, Mukherjee S, and Chowdhury R. Lncrna hulc augments high glucose-associated pancreatic cancer progression and drug resistance by enhancing yap activity and autophagy. Biol Cell. (2024) 116:e2400034. doi: 10.1111/boc.202400034
28. Li D, Y-m S, and Zhan Q-m. Specifically up-regulated non-coding rna gene hulc in tumor cell lines and its effects on the expression of neighboring gene slc35b3. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2010) 90:3156–9.
29. Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, Ni P, Gu Z, Qiao Y, et al. Creb up-Regulates Long Non-Coding Rna, Hulc Expression through Interaction with Microrna-372 in Liver Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. (2010) 38:5366–83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq285
30. Wang C, Jiang X, Li X, Song S, Meng Q, Wang L, et al. Long noncoding rna hulc accelerates the growth of human liver cancer stem cells by upregulating cyclind1 through mir675-pkm2 pathway via autophagy. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:8. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1528-y
31. Cui M, Xiao Z, Wang Y, Zheng M, Song T, Cai X, et al. Long noncoding rna hulc modulates abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an mir-9-mediated rxra signaling pathway. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:846–57. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1192
32. Wang C, Li Y, Yan S, Wang H, Shao X, Xiao M, et al. Interactome analysis reveals that lncrna hulc promotes aerobic glycolysis through ldha and pkm2. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:3162. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16966-3
33. Jiang X, Wang L, Xie S, Chen Y, Song S, Lu Y, et al. Long noncoding rna meg3 blocks telomerase activity in human liver cancer stem cells epigenetically. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:518. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02036-4
34. Xie H, Ma H, and Zhou D. Plasma hulc as a promising novel biomarker for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. BioMed Res Int. (2013) 2013:136106. doi: 10.1155/2013/136106
35. Gaber DA, Shaker O, Younis AT, and El-Kassas M. Lncrna hulc and mir-122 expression pattern in hcc-related hcv Egyptian patients. Genes (Basel). (2022) 13(9):1669. doi: 10.3390/genes13091669
36. Yan C, Wei S, Han D, Wu L, Tan L, Wang H, et al. Lncrna hulc shrna disinhibits mir-377-5p to suppress the growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo. Ann Transl Med. (2020) 8:1294. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5556
37. Lumkul L, Jantaree P, Jaisamak K, Wongkummool W, Lapisatepun W, Orrapin S, et al. Combinatorial gene expression profiling of serum hulc, hotair, and uca1 lncrnas to differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma from liver diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(2):1258. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021258
38. Li J, Wang X, Tang J, Jiang R, Zhang W, Ji J, et al. Hulc and linc00152 act as novel biomarkers in predicting diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2015) 37:687–96. doi: 10.1159/000430387
39. Sonohara F, Inokawa Y, Hayashi M, Yamada S, Sugimoto H, Fujii T, et al. Prognostic value of long non-coding rna hulc and malat1 following the curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16142. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16260-1
40. Yao Y, Duan C, Chen Y, Hou Z, Cheng W, Li D, et al. Long non-coding rna detection based on multi-probe-induced rolling circle amplification for hepatocellular carcinoma early diagnosis. Anal Chem. (2023) 95:1549–55. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04594
41. Du Y, Kong G, You X, Zhang S, Zhang T, Gao Y, et al. Elevation of highly up-regulated in liver cancer (Hulc) by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via down-regulating P18. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:26302–11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.342113
42. Jiang Z and Liu H. Metformin inhibits tumorigenesis in hbv-induced hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing hulc overexpression caused by hbx. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:4482–95. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26555
43. Liu Y, Feng J, Sun M, Yang G, Yuan H, Wang Y, et al. Long non-coding rna hulc activates hbv by modulating hbx/stat3/mir-539/apobec3b signaling in hbv-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. (2019) 454:158–70. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.04.008
44. Wang Y, Chen F, Zhao M, Yang Z, Li J, Zhang S, et al. The long noncoding rna hulc promotes liver cancer by increasing the expression of the hmga2 oncogene via sequestration of the microrna-186. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:15395–407. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.783738
45. Zhang H, Liao Z, Liu F, Su C, Zhu H, Li Y, et al. Long noncoding rna hulc promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Aging (Albany NY). (2019) 11:9111–27. doi: 10.18632/aging.102378
46. Liu S, Huttad L, He G, He W, Liu C, Cai D, et al. Long noncoding rna hulc regulates the nf-κb pathway and represents a promising prognostic biomarker in liver cancer. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:5124–36. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5263
47. Xiong H, Ni Z, He J, Jiang S, Li X, He J, et al. Lncrna hulc triggers autophagy via stabilizing sirt1 and attenuates the chemosensitivity of hcc cells. Oncogene. (2017) 36:3528–40. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.521
48. Xiong H, Li B, He J, Zeng Y, Zhang Y, and He F. Lncrna hulc promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via stabilizing cox-2 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 490:693–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.06.103
49. Li S-P, Xu H-X, Yu Y, He J-D, Wang Z, Xu Y-J, et al. Lncrna hulc enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via the mir-200a-3p/zeb1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:42431–46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9883
50. Li D, Liu X, Zhou J, Hu J, Zhang D, Liu J, et al. Long noncoding rna hulc modulates the phosphorylation of yb-1 through serving as a scaffold of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and yb-1 to enhance hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. (2017) 65:1612–27. doi: 10.1002/hep.29010
51. Li Y, Ge C, Feng G, Xiao H, Dong J, Zhu C, et al. Low dose irradiation facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma genesis involving hulc. Mol Carcinog. (2018) 57:926–35. doi: 10.1002/mc.22813
52. Wang X, Mo X, Yang Z, and Zhao C. Qntrolling the lncrna hulc-tregs-pd-1 axis inhibits immune escape in the tumor microenvironment. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e28386. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28386
53. Zhang Y, Song X, Wang X, Hu J, and Jiang L. Silencing of lncrna hulc enhances chemotherapy induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer. J Med Biochem. (2016) 35:137–43. doi: 10.1515/jomb-2015-0016
54. Esfandi F, Salehnezhad T, Taheri M, Afsharpad M, Hafez AA, Oskooei VK, et al. Expression assessment of a panel of long non-coding rnas in gastric Malignancy. Exp Mol Pathol. (2020) 113:104383. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104383
55. Xian H-P, Zhuo Z-L, Sun Y-J, Liang B, and Zhao X-T. Circulating long non-coding rnas hulc and znfx1-as1 are potential biomarkers in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. (2018) 16:4689–98. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9199
56. Wang B-G, Ding H-X, Lv Z, Xu Q, and Yuan Y. Interaction of hulc polymorphisms with helicobacter pylori infection plays a strong role for the prediction of gastric cancer risk. Future Oncol. (2020) 16:1997–2006. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-0228
57. Zhao Y, Guo Q, Chen J, Hu J, Wang S, and Sun Y. Role of long non-coding rna hulc in cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor metastasis of gastric cancer: A clinical and in vitro investigation. Oncol Rep. (2014) 31:358–64. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2850
58. Yang D, Shi M, You Q, Zhang Y, Hu Z, Xu J, et al. Tumor- and metastasis-promoting roles of mir-488 inhibition via hulc enhancement and ezh2-mediated P53 repression in gastric cancer. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39:1341–58. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09760-y
59. Takahashi K, Ota Y, Kogure T, Suzuki Y, Iwamoto H, Yamakita K, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicle-encapsulated hulc is a potential biomarker for human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. (2020) 111(1):98–111. doi: 10.1111/cas.14232
60. Takahashi K, Koyama K, Ota Y, Iwamoto H, Yamakita K, Fujii S, et al. The interaction between long non-coding rna hulc and microrna-622 via transfer by extracellular vesicles regulates cell invasion and migration in human pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:1013. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01013
61. Pang Q, Huang S, Wang H, and Cao J. Hulc-igf2bp2 interaction drives proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Cancer. (2024) 15:6686–97. doi: 10.7150/jca.101989
62. Yang X-J, Huang C-Q, Peng C-W, Hou J-X, and Liu J-Y. Long noncoding rna hulc promotes colorectal carcinoma progression through epigenetically repressing nkd2 expression. Gene. (2016) 592:172–8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.08.002
63. Xie X, Wang Y, Zhang S, Li J, Yu Z, Ding X, et al. A novel five-lncrna signature panel improves high-risk survival prediction in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:2959–81. doi: 10.18632/aging.202446
64. Wang W-T, Ye H, Wei P-P, Han B-W, He B, Chen Z-H, et al. Lncrnas H19 and hulc, activated by oxidative stress, promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma through a cerna manner. J Hematol Oncol. (2016) 9:117. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0348-0
65. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, and Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. (2005) 55(2):74–108. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74
66. Su W, Tang J, Wang Y, Sun S, Shen Y, and Yang H. Long non-coding rna highly up-regulated in liver cancer promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition process in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:2645–55. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14160
67. Jiang X and Liu W. Long noncoding rna highly upregulated in liver cancer activates P53-P21 pathway and promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth. DNA Cell Biol. (2017) 36:596–602. doi: 10.1089/dna.2017.3686
68. Baili E, Gazouli M, Lazaris AC, Kanavidis P, Boura M, Michalinos A, et al. Genetic impact of hotair, linc00951, polr2e and hulc polymorphisms in histopathological and laboratory prognostic factors in esophageal cancer in the west: A case-control study. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16(3):537. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030537
69. Baili E, Gazouli M, Lazaris AC, Kanavidis P, Boura M, Michalinos A, et al. Associations of long non-coding rnas hotair, linc00951, polr2e and hulc polymorphisms with the risk of esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancer in a western population: A case-control study. Mol Biol Rep. (2024) 51:249. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09206-0
Keywords: lncRNA, HULC, digestive system cancers, cancer, ceRNA
Citation: Huang L (2025) Roles of long non-coding RNA HULC in human digestive system cancers. Front. Oncol. 15:1642425. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1642425
Received: 19 June 2025; Accepted: 29 July 2025;
Published: 20 August 2025.
Edited by:
Daniel P. Bezerra, Oswaldo Cruz Foudantion (FIOCRUZ), BrazilReviewed by:
Ziyan Rao, Peking University, ChinaHuang Dan, Anhui Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liqing Huang, aHVhbmdsaXFpbmcyMDI0MDdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Liqing Huang
Liqing Huang