- 1Department of General Medicine, The People’s Hospital of Leshan, Leshan, China
- 2Department of Urology, The People’s Hospital of Leshan, Leshan, China
Background: The relationship between sarcopenia and clinical outcomes in patients with bladder cancer (BC) has been inconsistently reported in the literature. Some studies have identified sarcopenia as a potential prognostic indicator associated with reduced survival following radical cystectomy (RC).
Objectives: This study was conducted to systematically evaluate the prognostic significance of sarcopenia in patients with bladder cancer undergoing RC.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of multiple databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CHINAHL, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) Databases, and Wanfang Database, up to August 23, 2023, to identify both retrospective and prospective cohort studies. To assess the methodological quality of the included studies, the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was utilized to evaluate the risk of bias. Furthermore, heterogeneity and potential publication bias were examined, and both subgroup and sensitivity analyses were performed to ensure the robustness of the findings.
Results: A total of 18 studies comprising 3,110 patients were included in the quantitative synthesis. The results of meta-analysis showed that the pooled prevalence of sarcopenia was estimated to be 49% (95% CI: 41% to 57%, I2 = 95.3%, P < 0.001), which was based on a random-effects model. We observed that BC patients with sarcopenia had a worse OS (HR:1.64, 95% CI: 1.30 to 1.97, I2 = 76.5%, P < 0.001} and CSS (HR:1.86, 95% CI: 1.45 to 2.27, I2 = 0.0%, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Sarcopenia is commonly observed among patients with bladder cancer and appears to be an important prognostic indicator associated with decreased OS and CSS in those undergoing radical cystectomy. Further prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42023456724.
Introduction
Bladder cancer (BC) is the ninth most commonly diagnosed malignancy worldwide, with an estimated annual incidence of approximately 430,000 new cases (1). BC is more prevalent in men and is the fourth most commonly diagnosed cancer among men in industrialized countries, including the United States and Germany (2, 3). Radical cystectomy (RC) is the gold standard treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) and for cases of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) unresponsive to intravesical therapy (4). Although RC is performed with curative intent, the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate remains relatively low, ranging from approximately 50% to 60% (3, 5). Established factors influencing survival outcomes following radical cystectomy (RC) encompass patient age, histopathological features, and the presence of comorbid conditions (6, 7). While these factors serve as important indicators of overall health status, they lack sufficient precision to guide preoperative clinical decision-making. Consequently, there is a need for a reliable preoperative prognostic marker that can effectively stratify patients to optimize surgical management.
Sarcopenia, the most commonly evaluated body composition parameter, is defined as a reduction in muscle mass, a key factor contributing to frailty (6). Recent studies found that sarcopenia was a predictor for survival in several malignancies including lung cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer (8–14). Sarcopenia has been shown to be a significant predictor of shorter overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) (8, 9). Various methods have been used to assess sarcopenia, including the skeletal muscle index (SMI), psoas muscle index (PMI), and total psoas index (TPI), among others (15). SMI is a widely used metric for assessing sarcopenia, calculated by normalizing the total muscle cross-sectional area measured at the third lumbar vertebral level on computed tomography (CT) scans by the patient’s height squared (16).
Many studies regarding the predictive value of sarcopenia in patients with bladder cancer have been conducted (17–19). However, the results of these studies are inconsistent and even controversial. For example, Almarzouq et al. (17) found that sarcopenia did not serve as an independent prognostic factor in patients diagnosed with bladder cancer patients. Conversely, Erdik et al. (19) found that sarcopenia was independently associated with poor outcomes in patients treated with RC. Thus, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to summarize the current evidence regarding the prognostic role of sarcopenia in bladder cancer patients undergoing RC.
Material
Protocol and registration
This review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (20) and is registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023456724). The review followed the registered protocol without any deviations.
Literature search
A comprehensive search of English literature using the database of PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, CHINAHL, China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI) Databases, Wanfang Database. Screen the reference of the included articles to identify any other eligible studies. The following Mesh terms and keywords were include: ‘bladder’, ‘urothelial carcinoma’, ‘muscle-invasive bladder cancer’, ‘non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer’ ‘ sarcopenia’, ‘skeletal muscle index’, ‘muscle strength’, ‘Psoas muscle index’, the detailed search strategy is shown in Supplementary Table S1.
We use the Boolean operators “OR” and “AND” between the groups. The publication year of these articles was limited to January 1, 2008 to September 2023, and only full-text original research articles are considered. All search results are downloaded and imported directly into Zotero, version 6.0.
Eligibility criteria
We enrolled studies according to the following inclusion criteria: (1) study population: patients with any type of bladder cancer; (2)) indicator: sarcopenia (each study definition was applied, because no unique definition exists); (3) evaluated the prognostic value of preoperative sarcopenia; (4) outcomes: overall survival (OS), cancer-specific survival(CSS), the prevalence of sarcopenia, or other available data of survival; (5) study type: prospective or retrospective studies. The exclusion criteria are: (1) the sample size was less than 50; (2) no available data for analysis; (3) studies with incomplete data, such as prevalence of sarcopenia, incomplete baseline characteristics, or other critical survival data.
Study selection
The study selection process was conducted by two independent reviewers (Zhang and Liu), who initially screened titles and abstracts to identify potentially eligible articles. Subsequently, a separate pair of reviewers (Li and Cao) independently assessed the full texts to determine study inclusion or exclusion. Reasons for exclusion were documented, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion. If consensus could not be achieved, a third reviewer was consulted to make the final decision.
Data extraction
Two authors (Zhang and Yang) independently extracted relevant data from all eligible studies, including author names, study design, sample size, disease types, treatment modalities, patient age, sarcopenia definitions, and follow-up durations. The extracted datasets were cross-checked, and any discrepancies were resolved through consultation of the original articles. The study selection process is illustrated in the PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 1).
Quality appraisal
Two reviewers independently assessed the risk of bias and overall study quality using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS) (21). The NOS scores range from 0 to 9, with studies categorized as low (0–3), moderate (4–6), or high quality (7–9). Any disagreements were resolved through discussion until consensus was achieved.
Definition of outcomes
To ensure consistency in the analysis, we have adopted standardized operational definitions for OS and CSS based on widely accepted criteria in the oncology field. OS is defined as the time from the date of diagnosis or treatment initiation to the date of death from any cause, or the last known follow-up date if the patient is still alive. CSS is defined as the time from the date of diagnosis or treatment initiation to the date of death specifically due to cancer, with patients who die from other causes being censored.
Given the variability in definitions across studies, we have taken the following approaches:1. For studies that did not explicitly define OS or CSS or used a non-standard definition, we referred to the most commonly accepted definitions in the literature, as described above. When possible, we consulted with the authors of these studies for clarification to ensure the consistency of the outcomes. 2. For studies where the definition of OS or CSS significantly differed from the standardized definition, we excluded them from the pooled analysis to prevent excessive heterogeneity.
Data synthesis
For analysis, the results extracted from the included studies were input into Stata 15.0 software package. The endpoints of OS and CSS were characterized by HR and 95%CI, and the pooled prevalence were estimated by proportion. The degree of heterogeneity was tested by Cochrane’s Q test (p value) and the I2 statistic (22). We set the I2 values as 25%, 50%, and 75%, indicating low, medium, and high heterogeneity, respectively. When no significant heterogeneity was detected (I2 ≤ 50), the fixed-effects model was used for pooled prevalence and risk estimates, otherwise the random-effects model was used (23). We also employed funnel plot asymmetry to detect the potential publication bias. An Egger’s regression was applied to test the funnel plot symmetry (24).
Finally, the sensitivity analyses was performed to examine the influence of each study on the pooled estimates of the primary outcome. The data of included studies were divided into subgroups according to regions, measurement and median follow-up time. Due to the limited number of studies in certain subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses were performed only for meta-analyses comprising more than two studies. All statistical tests were two-sided, with a significance threshold set at P < 0.05.
Results
Study selection
In total, 950 related citations (PubMed: 259, EMBASE: 246, Web of science:160, Cochrane Library:160, CINAHL: 55, CNKI:15, Wanfang:12) were identified and qualified through electronic database search, of which 235 were duplicates. After screening titles and abstracts and removing duplicate references, 715 articles were selected on the basis of inclusion criteria. Of these studies, 45 were excluded because of irrelevant outcome and population, not evaluate the sarcopenia, not treated with RC. A total of 18 studies (17–19, 23, 25–38) were utilized in this study. The selection process for the study is shown in the PRISMA flow chart (Figure 1).
Characteristics of the included primary studies
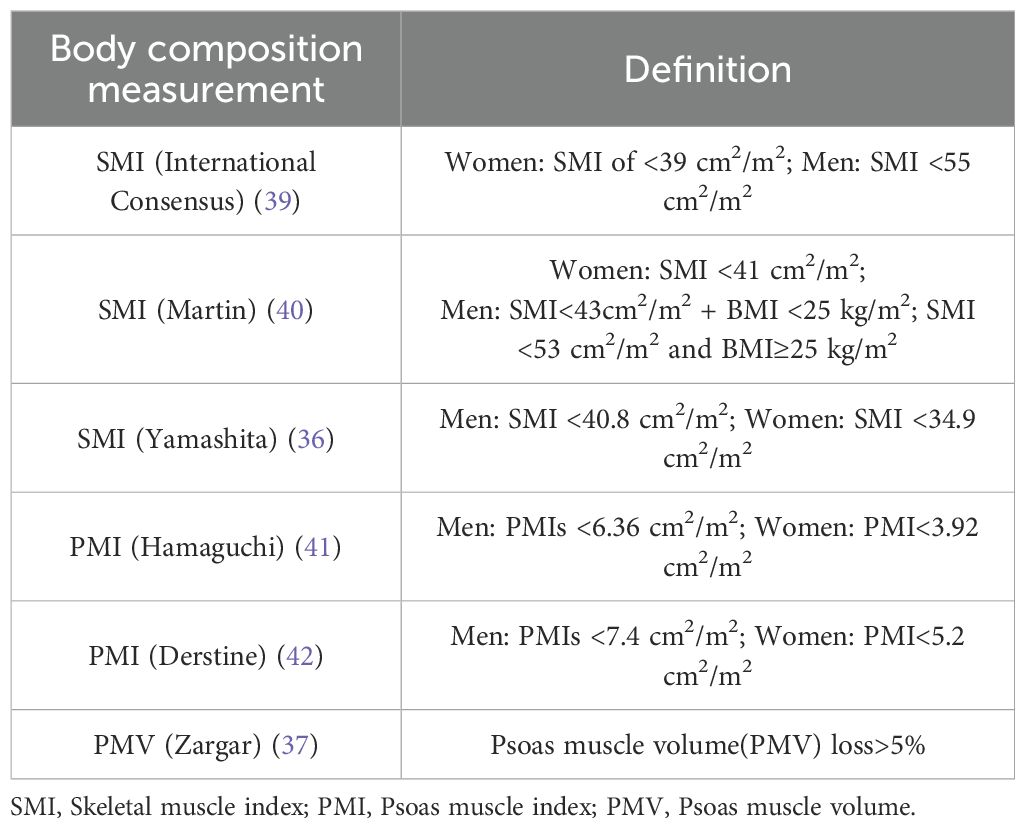
A total of 18 studies were included, all of which were retrospective and included 3,110 patients who were treated with RC. Eligible patients were relatively old, with a median age ranging from 44 to 92 years, and most were from the United States and Japan. In terms of the definition of sarcopenia, most of these studies identified sarcopenia by measuring SMI (17–19, 23, 25–28, 30–32, 34–36, 38) and PMI (29, 33, 37) at the level of the L3 using computed tomography (CT) images, only one study diagnosed based on PMV. The definition of sarcopenia is detailed in Table 1. The characteristics of the 18 studies are summarized in Table 2.
Quality assessment
The quality assessment and risk of bias were conducted in accordance with the NOS. The NOS score of each included study is listed in Table 1; All studies evaluated were of high quality (NOS score ≥ 6).The detailed quality assessment results are displayed in Supplementary Table S2.
Prevalence of sarcopenia
In the 18 studies available for the meta-analysis, the pooled prevalence of sarcopenia was estimated to be 49% (95% CI: 41% to 57%, I2 = 95.3%, P < 0.001), which was based on a random-effects model. Among them, the prevalence of sarcopenia defined by SMI (International Consensus) was estimated to be 56% (95% CI: 48% to 64%, I2 = 91.6%, P < 0.001), the sarcopenia defined as SMI(Martin) was estimated to be 49% (95% CI: 32% to 66%, I2 = 94%, P < 0.001)(Figure 2). In addition, a stratified analysis was conducted according to regions, and the results are shown in Figure 3.
Effects of sarcopenia on overall survival
Data from 15 studies, including 2,784 participants, were available to meta-analyze overall survival. Of the included studies, OS was defined in 12 from treatment initiation to death, or the last follow-up (15, 17–19, 26, 27, 29–33, 37); and from the time of diagnosis to death or the last follow-up, in the other 3 studies (25, 35, 38), OS was not clearly defined in the remaining two studies. We observed that patients with sarcopenia had a worse OS compared with those without sarcopenia, the pooled HR was 1.64 (95% CI: 1.30 to 1.97, I2 = 76.5%, P < 0.001; Figure 4). Because of high heterogeneity was revealed, so we used the random-effect model.

Figure 4. Forest plot of the hazard ratios of sarcopenia for overall survival and cancer-specific survival.
Effects of sarcopenia on cancer-specific survival
Data from 9 studies, including 1514 participants, were available to meta-analyze cancer-specific survival. Of the included studies, CSS in 7 studies was defined as the interval from RC to death attributable to bladder cancer progression or metastasis. CSS was not clearly defined in the remaining two studies. The results of meta-analysis showed that sarcopenia was associated with poor CSS, the pooled HR is 1.86 (95% CI: 1.45 to 2.27, I2 = 0.0%, P < 0.001; Figure 4).
Subgroup analyses
We conducted subgroup analyses based on geographical region, measurement methods, and follow-up time separately for the outcomes of OS and CSS, as shown in Table 3. The studies were divided into two groups: Asian and non-Asian regions, with 7 and 8 studies included, respectively. The meta-analysis results revealed that sarcopenia was a predictive factor associated with a decrease in both OS (HR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.45 to 2.27, P < 0.001; HR: 1.45, 95% CI: 1.06 to 1.84, P < 0.002) and CSS (HR: 2.34, 95% CI: 1.50 to 3.17, P < 0.001; HR: 1.75, 95% CI: 1.30 to 2.21, P < 0.001), irrespective of whether the cases originated from Asian or non-Asian populations.
In the subgroup analysis based on measurement methods, due to limited study numbers, we only conducted meta-analyses for SMI (International Consensus) and SMI(Martin). The results showed that sarcopenia measured using SMI (International Consensus) was correlated with a decrease in OS (HR: 1.53, 95% CI: 1.35 to 1.70, P < 0.001), while SMI(Martin) did not reach statistical significance (HR: 1.75, 95% CI: 0.66 to 2.83, P < 0.080). Both measurement methods, SMI (International Consensus) and SMI(Martin), had an impact on the decrease in CSS (HR: 1.76, 95% CI: 1.32 to 2.21, P < 0.001; HR: 2.34, 95% CI: 1.28 to 3.40, P < 0.001).
Regarding median follow-up time, we used a cut-off of 30 months for subgroup analysis. The results showed that sarcopenia was associated with a decrease in OS regardless of whether the median follow-up time exceeded 30 months (HR: 1.53, 95% CI: 1.36 to 1.71, P < 0.001; HR: 1.89, 95% CI: 1.12 to 2.67, P < 0.013). For CSS, subgroup analysis with a median follow-up time exceeding 30 months revealed an association with sarcopenia (HR: 1.88, 95% CI: 1.44 to 2.29), but no statistically significant association was observed in the subgroup with a median follow-up time of less than 30 months (HR: 2.08, 95% CI: 0.81 to 3.36, P < 0.187). Forest plots for all outcomes are provided in Supplementary Figures 5-10.
Sensitivity analyses and publication bias
To evaluate the robustness and reliability of the primary analysis, sensitivity analyses were conducted by sequentially excluding individual studies. The results indicated that the overall survival outcomes remained consistent regardless of the removal of any single study, including those of relatively lower methodological quality. The results are shown in Supplementary Figure 1.
Publication bias was assessed using Begg’s test, and funnel plots were examined for symmetry. The P-values for Begg’s test were 0.223 for OS and 0.978 for CSS, suggesting no significant evidence of publication bias in the meta-analysis. The funnel plots are provided in the Supplementary Materials.
Discussion
This meta-analysis of 18 studies including 3,110 patients aimed to determine the predictive value of sarcopenia for prognosis in patients treated with RC. Our results showed that the pooled prevalence of sarcopenia defined as SMI (International Consensus) was 56% (95% CI: 48% to 64%, I2 = 91.6%), and the pooled prevalence of sarcopenia defined as SMI(Martin) was 49% (95% CI: 32% to 66%, I2 = 94%). The high heterogeneity observed in both prevalence estimates could be attributed to several factors, including variations in patient populations (e.g., age, comorbidities, cancer stage) and regional differences in diagnostic practices. In addition, we observed a higher prevalence of sarcopenia in samples from Asia than from non-Asia(44% VS.54%), but this result may be confounded by the different measurement due to the limited number of studies. Other factors such as comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular diseases), treatment variations (e.g., neoadjuvant chemotherapy, radiation therapy), and the patient’s functional status could potentially confound the observed relationship between sarcopenia and survival outcomes. These factors may alter the survival prognosis in bladder cancer patients undergoing RC, and future studies should consider controlling for these potential confounders to better clarify the independent effect of sarcopenia on OS and CSS.
In accordance with the results of the meta-analysis, the forest plots clearly demonstrated that sarcopenia could significantly predict worse OS and CSS. The association between sarcopenia and decreased survival has been previously described in various malignancies. For instance, Peng et al. (43) reported an independent correlation between sarcopenia and an increased risk of all-cause mortality in a cohort of 296 patients who had undergone surgical resection for pancreatic cancer. Notably, patients without sarcopenia had a median overall survival of 18 months, compared to 13.7 months in those with sarcopenia (P < 0.01). Furthermore, multivariable analysis revealed that sarcopenia was associated with a 67% increased risk of all-cause mortality at 3 years ([HR]: 1.67; 95% CI: 1.28–2.07; P < 0.001).Similarly, Harimoto et al. (44) reported a significantly lower OS rate in sarcopenic patients undergoing partial hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma compared to non-sarcopenic patients (71% vs. 83.7%; P = 0.001). Furthermore, in the series by Martin et al. (40) series involving 1471 patients afflicted with gastrointestinal or respiratory tract malignancies, patients with sarcopenia had a median OS of 13.0 months, contrasting with the 20.1 months observed in those with normal SMI. Comparable adverse impacts of sarcopenia on OS have also been documented in patients with pancreatic, lung, and colorectal cancers. To our knowledge, few studies have specifically addressed the impact of sarcopenia on CSS. Nonetheless, inferior oncological outcomes have been observed among patients with hepatobiliary cancer24 and melanoma,16 where sarcopenia was noted as a contributing factor.
Moreover, we methodically stratified the dataset based on geographic region, the measurement of sarcopenia, and the median duration of follow-up. The subgroup analyses consistently underscored the significant statistical association between sarcopenia and OS following RC. Given the disparities inherent to the Asian and Western populations, we conducted an evaluation of the relationship between sarcopenia and OS in two regions. The results demonstrate that sarcopenia was independently associated with increased risks of postoperative CSS in both the Asian and non-Asian subsets, which was consistent with previous research endeavors. For example, Miyake et al. (30) examined postoperative cystectomy for bladder carcinoma in Japan. Their work substantiates the assertion that sarcopenia status at baseline and a ≤-10% loss in the psoas muscle were identified as independent prognostic factors for overall survival. A study conducted in Korea by Ha et al. (27) similarly reported that the overall mortality rate was significantly higher in patients with sarcopenia than in those without sarcopenia 1 year after RC. Taking into consideration that the duration of follow-up can potentially introduce bias into the study outcomes, we categorized all studies into two groups using a threshold of 30 months for analysis. The results consistently indicate that sarcopenia remains a significant risk factor for OS, regardless of whether the median follow-up time exceeds 30 months. It is noteworthy that when we used Martin’s criteria (40) as the diagnostic standard for sarcopenia, no statistically significant association between sarcopenia and OS was observed. In contrast to the international consensus, Martin’s definition of sarcopenia incorporates not only the SMI but also factors such as gender and BMI when considering a patient’s condition. However, the generalizability of his conclusions remains contentious, primarily due to the retrospective nature of the study. Furthermore, the study cohort consists of Canadian gastrointestinal and lung cancer patients, potentially leading to thresholds that differ from those applicable to bladder cancer patients or individuals with other medical conditions. This discrepancy may impede its feasibility for simplified utilization in routine clinical practice. The findings from Fraisse et al.’s study similarly reported that sarcopenia was not significantly associated with OS and complications.
Our analysis identified a significant association between sarcopenia and reduced CSS, regardless of whether sarcopenia was defined according to the international consensus criteria or Martin’s definition. Likewise, we performed a subgroup analysis of the predictive value of Sarcopenia for CSS in patients with bladder cancer. No disparities were observed between populations in Asian and non-Asian regions, as sarcopenia exhibited significant predictive value for CSS in both groups. Nevertheless, within the subgroups categorized by follow-up duration, we did not identify statistically significant findings for the groups with a median follow-up time of less than 30 months. This may be attributed to the limited inclusion of studies in this group, and further confirmation of these results necessitates additional cohort studies in the future. Yamashita et al. (36) investigated the prognostic relevance of preoperative muscle depletion—including both sarcopenia and myosteatosis—in patients undergoing RC for bladder cancer. Their findings indicated that sarcopenia was an independent and significant predictor of reduced CSS. Similarly, Psutka et al. (32) performed a retrospective cohort study involving 205 patients who underwent RC. Baseline characteristics, including sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index, American Society of Anesthesiologists score, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, receipt of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, TNM stage, and tumor grade, were comparable between sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic patients (P > 0.05 for all). However, sarcopenic patients demonstrated significantly worse 5-year CSS compared to their non-sarcopenic counterparts (49% vs. 72%; P = 0.003). Furthermore, sarcopenia was independently associated with an increased risk of cancer-specific mortality (HR: 2.14; P = 0.007).
In summary, our systematic review reinforces the clinical significance of sarcopenia in patients undergoing RC for bladder cancer, as it serves as a noteworthy predictive factor for both overall survival OS and CSS. The identification of sarcopenia as a predictor for OS and CSS carries important clinical implications. Early screening for sarcopenia in bladder cancer patients could help clinicians make more informed treatment decisions, such as incorporating preoperative nutritional optimization, physical therapy, or sarcopenia-related interventions. This could improve postoperative recovery and long-term survival outcomes for these patients. Nevertheless, an undeniable issue persists in the field—there remains a lack of consensus regarding the definition of sarcopenia. Despite all included studies diagnosing sarcopenia through CT scans, variations in measurement criteria across multiple studies continue to pose a substantial hindrance to inter-study comparisons. Further diagnostic research is imperative for determining the optimal criteria for CT scan-based diagnosis of sarcopenia in bladder cancer patients. Furthermore, in future research within this field, it is essential to not only report patients’ survival outcomes but also specify the start and end times of follow-up periods for both OS and CSS. Additionally, focus should be directed toward aspects such as postoperative care management, surgical complications, cancer-related fatigue, and quality of life, among other pertinent factors. This approach will reduce heterogeneity between studies and better assess the prognostic value of sarcopenia in bladder cancer.
Limitations
While this meta-analysis consolidates current evidence and highlights sarcopenia as an important prognostic indicator in BC, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, substantial clinical heterogeneity among the included studies limited the feasibility of performing meta-analyses for several outcome measures. Second, the diverse definitions of sarcopenia employed across the studies, despite primarily relying on CT scans, exhibited variations in scanning levels and thresholds. Such differences between studies may have biased our results. Likewise, inconsistencies in the definitions of OS and CSS may introduce bias in the pooled results. Third, all included studies were retrospective in nature, which may have introduced a higher risk of bias and contributed to the observed inter-study heterogeneity. Furthermore, it is important to note that all of the included studies were published in English or Chinese, which may have led to language bias. Consequently, the findings should be interpreted with caution, and their applicability to clinical practice remains limited. Prospective, well-designed studies are warranted to further validate the prognostic significance of sarcopenia.
Conclusion
Sarcopenia is highly prevalent in patients with bladder cancer and emerges as a significant prognostic factor for impaired OS and CSS in BC patients undergoing RC. Further diagnostic research is imperative for determining the optimal criteria for CT scan-based diagnosis of sarcopenia in bladder cancer patients. More prospective studies are required to confirm our findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FL: Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – review & editing. JC: Writing – review & editing. XY: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1642833/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Lenis AT, Lec PM, Chamie K, and Mshs M. Bladder cancer: A review. JAMA. (2020) 324:1980. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17598
2. Malkowicz SB, Van Poppel H, Mickisch G, Pansadoro V, Thüroff J, Soloway MS, et al. Muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. (2007) 69:3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.10.040
3. Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. (2022) 72:409–36. doi: 10.3322/caac.21731
4. Vale CL. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Eur Urol. (2005) 48:202–6. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.04.006
5. Herr HW, Dotan Z, Donat SM, and Bajorin DF. Defining optimal therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Urol. (2007) 177:437–43. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.09.027
6. Sabel MS, Lee J, Cai S, Englesbe MJ, Holcombe S, and Wang S. Sarcopenia as a prognostic factor among patients with stage III melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2011) 18:3579–85. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-1976-9
7. Prado CM, Lieffers JR, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, Sawyer MB, Martin L, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. (2008) 9:629–35. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70153-0
8. Yang M, Shen Y, Tan L, and Li W. Prognostic value of sarcopenia in lung cancer. Chest. (2019) 156:101–11. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.04.115
9. Xie K, He D, Zhao T, Liu T, and Tang M. Gastric cancer with sarcopenia: an area worth focusing on. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2023) 24(10):1305–27. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01122-y
10. Ubachs J, Ziemons J, Minis-Rutten IJG, Kruitwagen RFPM, Kleijnen J, Lambrechts S, et al. Sarcopenia and ovarian cancer survival: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2019) 10:1165–74. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12468
11. Choi MH and Yoon SB. Sarcopenia in pancreatic cancer: Effect on patient outcomes. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2022) 14:2302–12. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2302
12. Vergara-Fernandez O, Trejo-Avila M, and Salgado-Nesme N. Sarcopenia in patients with colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review. World J Clin Cases. (2020) 8:1188–202. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1188
13. Kovač MB, Pavlin T, Čavka L, Ribnikar D, Spazzapan S, Templeton AJ, et al. The trajectory of sarcopenia following diagnosis of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Geriatr Oncol. (2023) 14:101594. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2023.101594
14. Geng D, Wu X, Wang Y, He J, and Hu X. Sarcopenia defined by the psoas muscle mass or quality is associated with poor survival in patients with aortic aneurysm undergoing surgery: A meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. (2023) 88:101964. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.101964
15. Yamaguchi K, Matsumoto S, Abe T, Nakajima K, Senoo S, Shimizu M, et al. Predictive value of total psoas muscle index for postoperative physical functional decline in older patients undergoing emergency abdominal surgery. BMC Surg. (2023) 23:171. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02085-5
16. McGovern J, Dolan RD, Horgan PG, Laird BJ, and McMillan DC. Computed tomography-defined low skeletal muscle index and density in cancer patients: observations from a systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2021) 12:1408–17. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12831
17. Almarzouq A, Kool R, Al Bulushi Y, Marcq G, Souhami L, Cury FL, et al. Impact of sarcopenia on outcomes of patients treated with trimodal therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. (2022) 40:194.e15–194.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.11.002
18. Engelmann SU, Pickl C, Haas M, Kaelble S, Hartmann V, Firsching M, et al. Body composition of patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: sarcopenia, low psoas muscle index, and myosteatosis are independent risk factors for mortality. Cancers. (2023) 15:1778. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061778
19. Erdik A, Haci Ibrahim C, Yavuz TA, Deniz G, and Osman K. Sarcopenia is an independent predictor of survival undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: A single-center, retrospective study. Cent Eur J Urol. 76(2):81–9. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2023.14
20. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 10(1):89. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
21. Zeng X, Zhang Y, Kwong JSW, Zhang C, Li S, Sun F, et al. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: a systematic review: Methodological quality assessment tools. J Evid-Based Med. (2015) 8:2–10. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12141
22. Higgins JPT. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
23. Lyon TD, Frank I, Takahashi N, Boorjian SA, Moynagh MR, Shah PH, et al. Sarcopenia and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2019) 17:216–222.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.03.007
24. Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, and Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
25. Borrelli A, Pecoraro M, Del Giudice F, Cristofani L, Messina E, Dehghanpour A, et al. Standardization of body composition status in patients with advanced urothelial tumors: the role of a CT-based AI-powered software for the assessment of sarcopenia and patient outcome correlation. Cancers. (2023) 15:2968. doi: 10.3390/cancers15112968
26. Fraisse G, Renard Y, Lebacle C, Masson-Lecomte A, Desgrandchamps F, Hennequin C, et al. La sarcopénie est-elle un facteur de morbi-mortalité dans le traitement des tumeurs localisées de la vessie infiltrant le muscle? Prog En Urol. (2020) 30:41–50. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2019.11.002
27. Ha YS, Kim SW, Kwon TG, Chung SK, and Yoo ES. Decrease in skeletal muscle index one year after radical cystectomy as a prognostic indicator in patients with urothelial bladder cancer. Int Braz J Urol. (2019) 45:686–94. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2018.0530
28. Hirasawa Y, Nakashima J, Yunaiyama D, Sugihara T, Gondo T, Nakagami Y, et al. Sarcopenia as a novel preoperative prognostic predictor for survival in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:1048–54. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5606-4
29. Miyake M, Morizawa Y, Hori S, Marugami N, Iida K, Ohnishi K, et al. Integrative assessment of pretreatment inflammation-, nutrition-, and muscle-based prognostic markers in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. Oncology. (2017) 93:259–69. doi: 10.1159/000477405
30. Miyake M, Morizawa Y, Hori S, Marugami N, Iida K, Ohnishi K, et al. Clinical impact of postoperative loss in psoas major muscle and nutrition index after radical cystectomy for patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:237. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3231-7
31. Psutka SP, Boorjian SA, Moynagh MR, Schmit GD, Frank I, Carrasco A, et al. Mortality after Radical Cystectomy: Impact of Obesity Versus Adiposity after Adjusting for Skeletal Muscle Wasting. J Urol. (2015) 193:1507–13. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.11.088
32. Psutka SP, Carrasco A, Schmit GD, Moynagh MR, Boorjian SA, Frank I, et al. Sarcopenia in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy: Impact on cancer-specific and all-cause mortality: Sarcopenia and Survival After RC for UC. Cancer. (2014) 120:2910–8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28798
33. Stangl-Kremser J, Ahmadi H, Derstine B, Wang SC, Englesbe MJ, Daignault-Newton S, et al. Psoas muscle mass can predict postsurgical outcomes in patients who undergo radical cystectomy and urinary diversion reconstruction. Urology. (2021) 158:142–9. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2021.08.013
34. Taguchi S, Akamatsu N, Nakagawa T, Gonoi W, Kanatani A, Miyazaki H, et al. Sarcopenia evaluated using the skeletal muscle index is a significant prognostic factor for metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2016) 14:237–43. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2015.07.015
35. Wang K, Gu Y, Ni J, Zhang H, Xie J, Xu T, et al. Combination of total psoas index and albumin–globulin score for the prognosis prediction of bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy: A population-based study. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:724536. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.724536
36. Yamashita S, Iguchi T, Koike H, Wakamiya T, Kikkawa K, Kohjimoto Y, et al. Impact of preoperative sarcopenia and myosteatosis on prognosis after radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer. Int J Urol. (2021) 28:757–62. doi: 10.1111/iju.14569
37. Zargar H, Almassi N, Kovac E, Ercole C, Remer E, Rini B, et al. Change in psoas muscle volume as a predictor of outcomes in patients treated with chemotherapy and radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Bladder Cancer. (2017) 3:57–63. doi: 10.3233/BLC-160080
38. Mao W, Ma B, Wang K, Wu J, Xu B, Geng J, et al. Sarcopenia predicts prognosis of bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy: A study based on the Chinese population. Clin Transl Med. (2020) 10:e105. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.105
39. Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I, Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, et al. Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncol. (2011) 12:489–95. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70218-7
40. Martin L, Birdsell L, MacDonald N, Reiman T, Clandinin MT, McCargar LJ, et al. Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J Clin Oncol. (2013) 31:1539–47. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.2722
41. Hamaguchi Y, Kaido T, Okumura S, Kobayashi A, Hammad A, Tamai Y, et al. Proposal for new diagnostic criteria for low skeletal muscle mass based on computed tomography imaging in Asian adults. Nutrition. (2016) 32:1200–5. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.04.003
42. Derstine BA, Holcombe SA, Goulson RL, Ross BE, Wang NC, Sullivan JA, et al. Quantifying sarcopenia reference values using lumbar and thoracic muscle areas in a healthy population. J Nutr Health Aging. (2018) 22:180–5. doi: 10.1007/s12603-017-0983-3
43. Peng P, Hyder O, Firoozmand A, Kneuertz P, Schulick RD, Huang D, et al. Impact of sarcopenia on outcomes following resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. (2012) 16:1478–86. doi: 10.1007/s11605-012-1923-5
Keywords: sarcopenia, bladder cancer, radical cystectomy, prognosis, meta-analysis
Citation: Zhang L, Li F, Liu L, Cao J and Yang X (2025) Prevalence and prognostic value of sarcopenia in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1642833. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1642833
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 29 August 2025;
Published: 18 September 2025.
Edited by:
Nicola Pavan, University of Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Anil Erdik, Sakarya Karasu State Hospital, TürkiyeFabio Traunero, Istituto Superiore di Sanità/University of Udine, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Li, Liu, Cao and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Zhang, bGVpemhhbmdsc3NybXl5QDE2My5jb20=
 Lei Zhang
Lei Zhang Fanmin Li1
Fanmin Li1