- 1Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Nanbu People’s Hospital, Nanchong, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Meishan People’s Hospital, Meishan, Sichuan, China
- 4Department of Center For Hepatobiliary-Pancreatic-Splenic Diseases, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong, Sichuan, China
Objective: To systematically compare the clinical efficacy and adverse events between stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in treating hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria through a meta-analysis.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, and Web of Science from database inception to May 1, 2025, for studies comparing SBRT and RFA in HCC patients meeting the Milan criteria. Data were analyzed using RevMan 5.4 software for meta-analysis.
Results: Ten studies (9 retrospective and 1 randomized controlled trial) involving 1505 patients were included. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival (OS: HR = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.72–1.32, P = 0.87) and progression-free survival (PFS: HR = 0.84, 95% CI = 0.67–1.06, P = 0.14) demonstrated no significant differences between SBRT and RFA. Subgroup analyses based on tumor diameter, tumor origin type, and study design revealed no significant differences in pooled HRs for OS or PFS. The incidence of adverse events showed no statistical difference between SBRT and RFA (RR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.53–1.01, P = 0.05).
Conclusion: SBRT and RFA exhibit comparable efficacy and safety profiles in managing HCC within the Milan criteria.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a primary liver malignancy ranking sixth in global incidence and third in cancer-related mortality, imposes a substantial disease burden (1). Its pathogenesis predominantly arises in the context of chronic liver diseases, with major etiological factors including chronic hepatitis B/C virus infections, alcoholic cirrhosis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (2). Surgical resection and liver transplantation remain the gold-standard curative therapies for early-stage HCC (3, 4), particularly in patients meeting Milan criteria (5). These interventions achieve 5-year survival rates ranging from 60% to 80% (6), earning them first-line recommendations in guidelines from the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL,2024) (4) and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD, 2023) (7).
However, 30–40% of patients are precluded from these radical surgical options due to clinical constraints (8) such as inadequate hepatic functional reserve (9), complex tumor anatomy such as proximity to major vasculature or hepatic hilum (10), tumor diameter exceeding eligibility thresholds (11), or donor organ shortages (12). For intermediate-stage patients ineligible for surgery, the BCLC guidelines recommend transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as standard of care (13), while radioembolization using yttrium-90 microspheres is recommended for preserving liver function in advanced cases (14). Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) serves as a principal locoregional therapy for early-stage tumors not amenable to surgery, achieving local control rates of 70–90% (15). Nevertheless, its efficacy exhibits significant dependence on cirrhosis severity, tumor size (particularly lesions >3 cm), and anatomical location (4). Technical limitations include incomplete ablation and procedure-related complications such as needle tract seeding metastasis, intrahepatic hemorrhage, and thermal injury to adjacent organs (16, 17).
Notably, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) as an emerging local treatment modality in recent years, has demonstrated the ability to effectively control tumor growth while minimizing damage to surrounding normal tissues (18), owing to its submillimeter positioning accuracy and steep dose gradient characteristics (19). Recent clinical observations have highlighted its potential for HCC, particularly for lesions abutting ablation-sensitive organs such as the gastrointestinal tract and diaphragm (20). Research conducted by Fu et al. (21) and Maher et al. (22) have both demonstrated that for patients meeting the Milan criteria, the overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) of SBRT are comparable to those of RFA. Conversely, a propensity score matching study conducted by Berger et al. (23) revealed median survival times of 22 months for the SBRT group and 32 months for the RFA group, with the OS in the SBRT cohort being significantly lower than that in the RFA cohort.
Existing studies comparing SBRT and RFA are largely defined by single-center retrospective designs, limited sample sizes, and heterogeneous inclusion criteria, resulting in a scarcity of high-quality evidence for survival outcomes and treatment-related adverse events in HCC patients meeting Milan criteria. This meta-analysis specifically focuses on patients within Milan criteria because both RFA and SBRT are validated treatment options for this subgroup in EASL/AASLD guidelines (4, 7). By systematically evaluating OS, PFS, and adverse event profiles, this study aims to provide high-quality evidence to guide precise selection of curative local treatment protocols in clinical practice.
Methods
Search strategy
This study adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines (24), employing a systematic literature search strategy. Computerized searches were conducted in databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, and Web of Science, spanning from the inception of each database to May 1, 2025. A comprehensive search strategy combining Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free-text keywords was utilized to enhance retrieval precision. Boolean operators (AND/OR) were used for logical term combination, with adaptations made to align with the subject indexing rules of each database. For example, the PubMed search strategy employed the following syntax: ((“Hepatocellular Carcinoma”[Mesh] OR hepatocellular carcinoma OR HCC) AND (“Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy”[Mesh] OR stereotactic body radiotherapy OR SBRT) AND (“Radiofrequency Ablation”[Mesh] OR radiofrequency ablation OR RFA)). To minimize the risk of potentially eligible studies being overlooked, a manual search of the reference lists of included studies was conducted as a supplementary search strategy.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria for studies:
1. Study Population: Adult patients with pathologically or radiologically confirmed HCC meeting the Milan criteria (single tumor ≤5 cm in diameter, or ≤3 tumors with the largest diameter ≤3 cm, without vascular invasion or extrahepatic metastasis).
2. Interventions: Experimental group receiving SBRT as the primary treatment modality, with the control group undergoing RFA.
3. Study Design: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or prospective/retrospective cohort studies that directly compare the outcomes of SBRT and RFA.
4. Outcome Measures: At least one of the following prognostic data reported: OS, PFS, or incidence of adverse events.
5. Data Completeness: Extractable survival analysis data (e.g., hazard ratios [HR], 95% confidence intervals [CI], or Kaplan-Meier curves) provided.
Exclusion Criteria for Studies:
1. Non-comparative studies, case reports, conference abstracts, review articles, or animal studies.
2. Studies involving mixed HCC stages or treatment modalities that preclude separate extraction of SBRT and RFA data.
3. Duplicate publications or studies with overlapping data (only the study with the largest sample size or longest follow-up duration was retained).
4. Non-English publications or studies with available only as abstracts without full texts.
5. Studies with a sample size <20 cases or follow-up duration <12 months.
Data extraction and research quality evaluation
Literature screening and data extraction were independently performed by two investigators (J.X.J and F.R.Z) trained in systematic review methodology. Literature was managed by use Zotero 6.0 software. Discrepancies were resolved through cross-checking and discussion, with a third investigator (G.S.L) invited for arbitration when necessary. Data extraction included basic characteristics such as first author, publication year, study type, country, number of samples, gender, age, tumor diameter and Child-Pugh grading; intervention parameters including SBRT total dose and fractionation scheme; and outcome data comprising OS, PFS, and incidence of treatment-related adverse events. Retrospective studies using propensity score matching (PSM) and RCTs were both considered to have a high level of research quality evidence.
The Risk of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool (25) was employed to evaluate the risk of bias in the included non-randomized controlled studies. Two investigators independently conducted these assessments, focusing on seven specific domains: confounding, selection of participants, exposure assessment, misclassification during follow-up, missing data, measurement of the outcome, and selective reporting of the results. The risk of bias was categorized as “low risk,” “moderate risk,” “high risk,” or “uncertain risk” based on the strength of the evidence. For RCTs, the Cochrane-recommended Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2) tool (26) was utilized, addressing the following domains: the randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing data; outcome measurement, and selective reporting. Ratings were classified as “low risk,” “some concerns,” or “high risk” according to evidence strength. Inter-rater agreement was quantified using the weighted Cohen’s kappa coefficient, and discrepancies were resolved through consultation with a third investigator to reach consensus.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 software. For dichotomous outcomes, risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were employed as effect measures. Survival endpoints (OS and PFS) were analyzed using hazard ratios (HR). In studies where HRs were not explicitly reported, values were derived from Kaplan-Meier survival curves through digitization and calibration of coordinate points using Engauge Digitizer 4.1 software, following the methodology proposed by Tierney et al. (27). Heterogeneity was quantified using the χ² test (Cochran’s Q statistic) and I² statistic. A fixed-effect model (Mantel-Haenszel method) was applied when heterogeneity was low (P > 0.1 for χ² test and I² < 50%). For high heterogeneity (P ≤ 0.1 or I² ≥ 50%), subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses were conducted to explore heterogeneity sources. If unresolved, a random-effects model (DerSimonian-Laird method) was adopted. Subgroup investigations stratified studies by tumor diameter (≤3 cm vs. 3–5 cm), tumor origin types (primary vs. recurrent), and study design (RCT/PSM study vs. retrospective study). Sensitivity analyses were conducted using a leave-one-out approach to determine if the pooled effect sizes were significantly affected by individual studies. Publication bias was assessed through a visual examination of the funnel plot symmetry. All statistical tests were two-sided, with a significance level set at α=0.05.
Result
Literature retrieval results
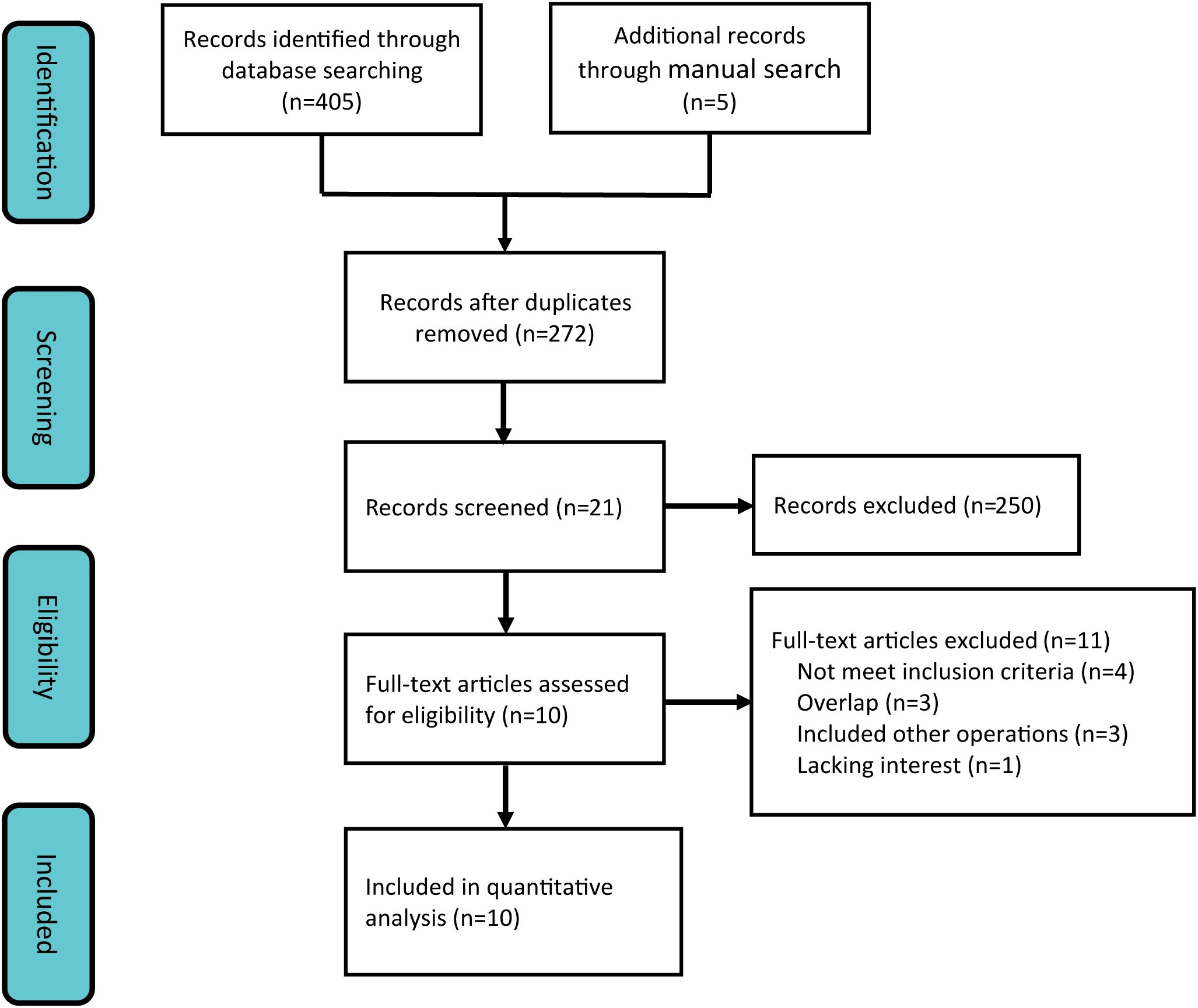
Employing a systematic search strategy, we initially identified 410 potentially pertinent studies. Through a stepwise screening process, which involved the exclusion of duplicate publications, review articles, case reports, single-arm studies, and animal experiments, 21 studies satisfied the preliminary inclusion criteria. Subsequent to a comprehensive full-text review, 11 additional studies were excluded due to non-compliance with the predefined outcome indicators. Consequently, 10 clinical studies (21, 22, 28–35) were incorporated into the meta-analysis (Figure 1), consisting of 1 RCT and 9 retrospective studies.
Characteristics and methodological quality assessment of included studies
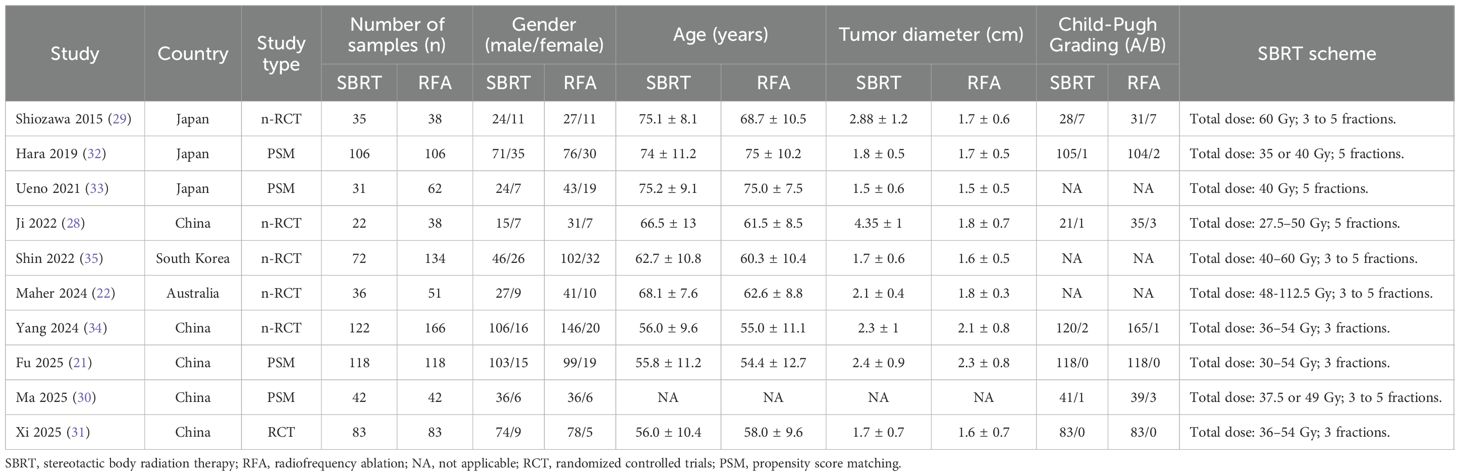
The studies incorporated in this meta-analysis were published between 2015 and 2024, encompassing five studies from China (21, 28, 30, 31, 34), three from Japan (29, 32, 33), one from South Korea (35), and one from Australia (29). Collectively, these studies included a total of 1505 patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma who met the Milan criteria. Of these patients, 667 were assigned to the SBRT group, while 838 were assigned to the RFA group. Baseline characteristic analyses revealed no statistically significant differences between SBRT and RFA cohorts across demographic parameters including gender distribution, patient age, and pre-treatment liver function status. Notably, in two comparative studies (28, 29), the SBRT groups exhibited significantly larger tumor diameters compared to their RFA counterparts, suggesting potential treatment selection bias (Table 1). With regard to SBRT protocols, the administered biologically effective doses varied between participating institutions, ranging from 27.5 to 112.5 Gy, with fractionation schedules typically delivered over 3 to 5 consecutive treatment sessions.
The methodological quality of the single randomized controlled trial (RCT) was assessed using the RoB 2 tool. The evaluation revealed “some concerns” in the domain of deviations from intended interventions, attributed to incomplete reporting of blinding implementation details, while all other domains were rated as “low risk.” Consequently, the overall assessment classified this RCT as having “some concerns” regarding methodological quality (Supplementary Figure 1). For the nine non-RCTs, the risk of bias was evaluated using the ROBINS-I tool. Specifically, three studies were rated as having a “moderate risk” for confounding bias control, and three for outcome measurement bias. In the domain of selection bias, one study was deemed to have a “moderate risk” due to unclear inclusion criteria. Regarding bias due to missing data, two studies failed to report follow-up loss. Importantly, no studies were rated as “high risk” in the overall rating. The consistency between the two evaluators was relatively high (Cohen’s kappa=0.759), and the main differences focused on the determination of bias in exposure assessment and measurement of the outcome (Supplementary Table 1). Finally, a consensus was reached after third-party arbitration.
Overall survival
Nine of the included studies (21, 22, 28, 30–35) compared OS between SBRT and RFA for HCC patients meeting the Milan criteria, with 632 patients in the SBRT group and 800 in the RFA group. Heterogeneity testing indicated low inter-study heterogeneity (I² = 0%). A fixed-effect model was selected for meta-analysis, which demonstrated no significant difference in OS between the two groups (HR = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.72–1.32, P = 0.87) (Figure 2).
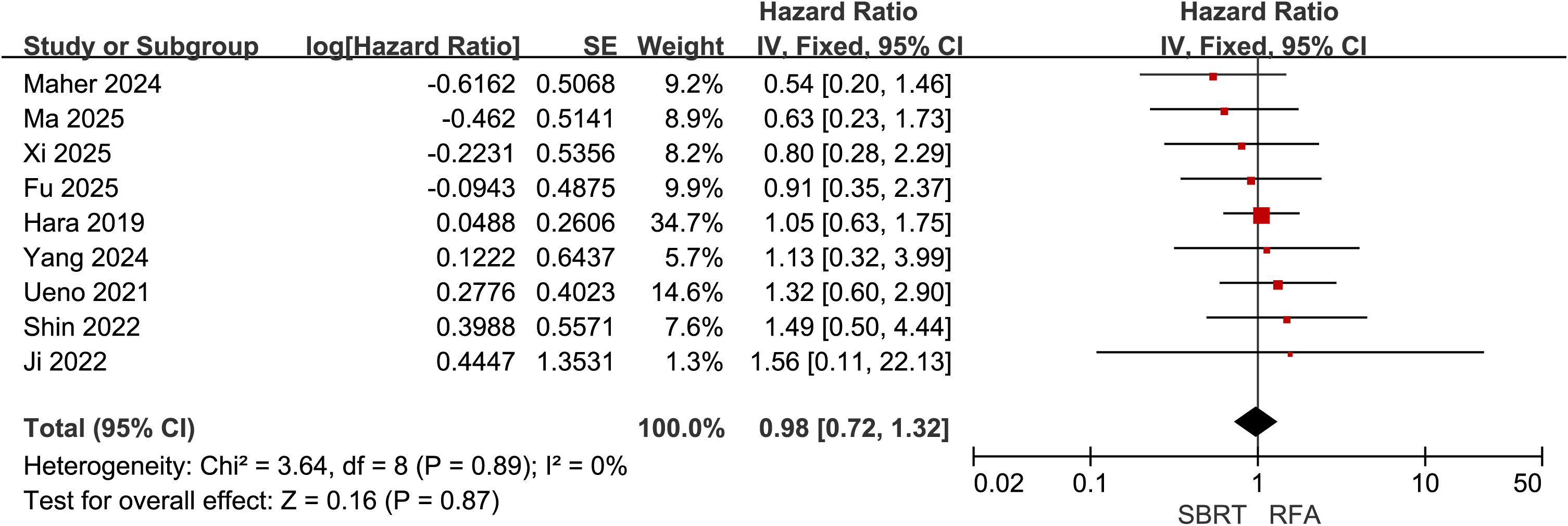
Figure 2. Forest plot of hazard ratios (HR) for overall survival (OS) comparing the Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) and Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) groups in patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) within Milan criteria.
Disease free survival
Eight of the included studies (21, 22, 28–31, 34, 35) compared PFS between SBRT and RFA for HCC patients meeting the Milan criteria, with 530 patients in the SBRT group and 670 in the RFA group. Heterogeneity testing revealed low inter-study heterogeneity (I² = 0%). A fixed-effect model was selected for meta-analysis, which demonstrated no significant difference in PFS between the two groups (HR = 0.84, 95% CI = 0.67–1.06, P = 0.14) (Figure 3).
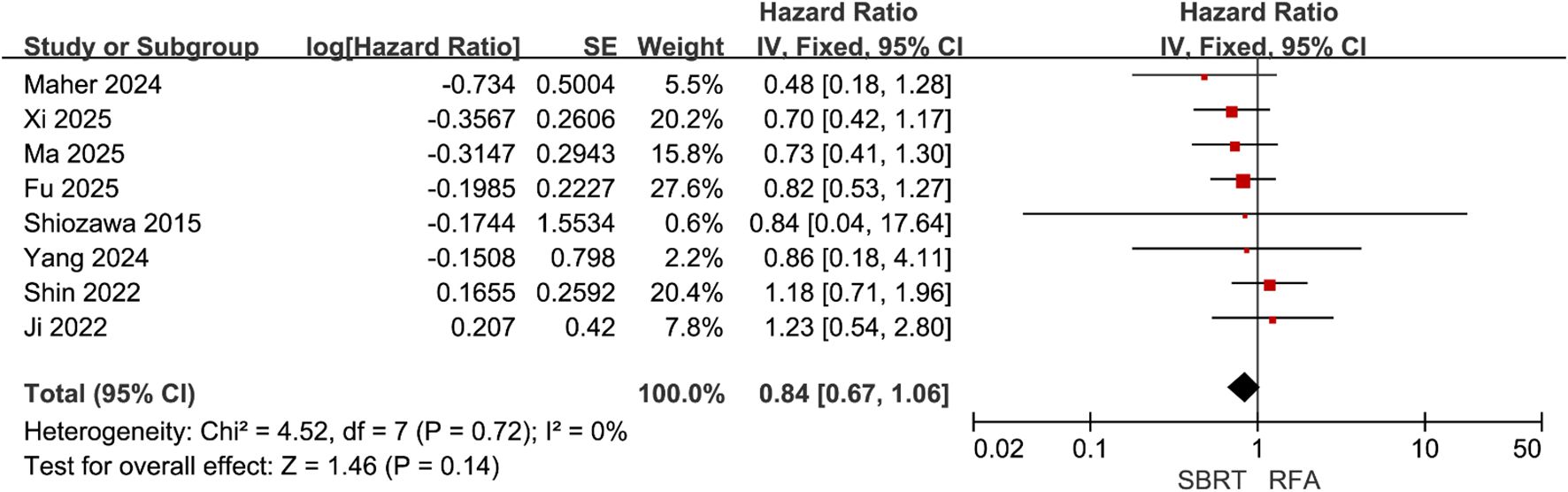
Figure 3. Forest plot of hazard ratios (HR) for progression-free survival (PFS) comparing the Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) and Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) groups in patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) within Milan criteria.
Subgroup analysis
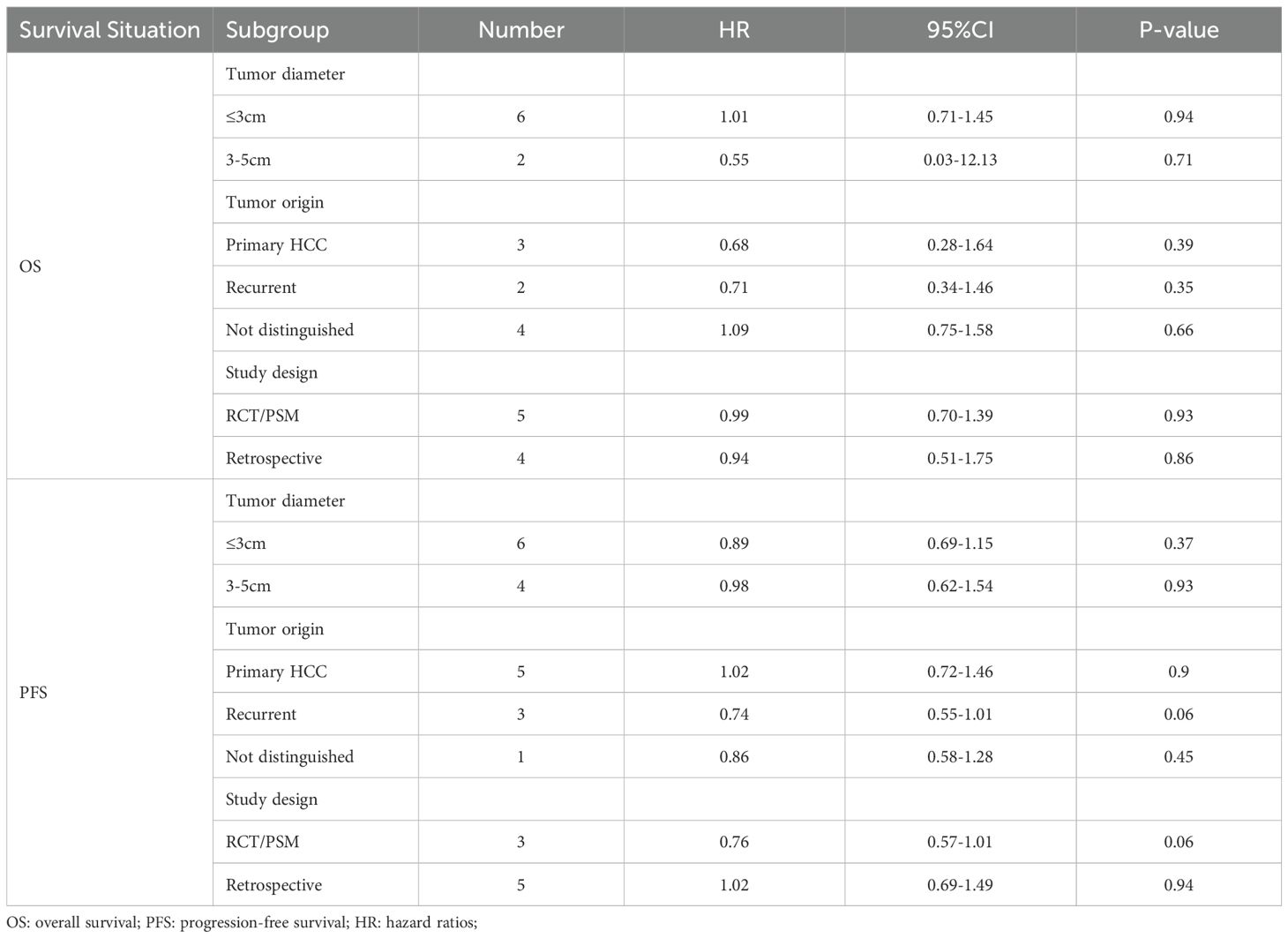
The subgroup analysis results indicated that across various stratifications of tumor diameter (≤3 cm and 3–5 cm), tumor origin types (primary HCC, recurrent HCC, and not distinguished), and study design types (RCT/PSM study or retrospective study), there were no statistically significant differences in the HR for OS and PFS between the SBRT and RFA groups (all P values > 0.05) (Table 2).
Adverse event
Five studies (22, 28–31) documented adverse event outcomes, identifying 96 adverse events among 218 patients in the SBRT group and 155 adverse events among 252 patients in the RFA group. The meta-analysis indicated no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the groups (RR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.53–1.01, P = 0.05) (Figure 4A). Furthermore, six studies (22, 28–31, 34) reported serious adverse events (CTCAE grade ≥3), with 27 events occurring in 320 patients in the SBRT group and 22 events in 418 patients in the RFA group. The meta-analytic findings revealed no significant difference between the groups in the incidence of serious adverse events (RR = 1.48, 95% CI = 0.88–2.49, P = 0.14) (Figure 4B).
![Forest plots depicting risk ratios comparing SBRT (Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy) and RFA (Radiofrequency Ablation). Panel A shows studies with various events, totals, and risk ratios, with an overall risk ratio of 0.73 [0.53, 1.01] and significant heterogeneity. Panel B represents similar data, with an overall risk ratio of 1.21 [0.24, 5.97], also showing substantial heterogeneity. Both panels include individual study results and overall effects, indicated by diamonds on a logarithmic scale.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1644001/fonc-15-1644001-HTML/image_m/fonc-15-1644001-g004.jpg)
Figure 4. Forest plot of RR of any adverse events (A) and serious adverse events (B) comparing the SBRT and RFA groups in patients with HCC within Milan criteria.
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
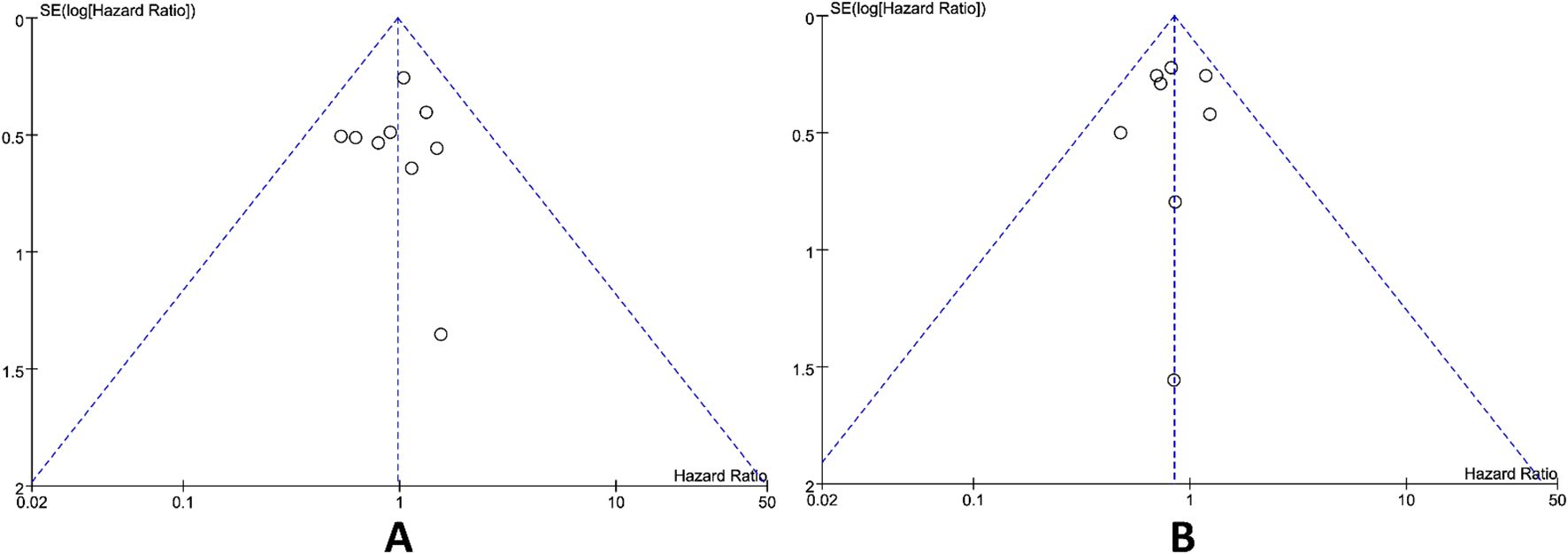
Publication bias was assessed utilizing the funnel plot method. Upon visual inspection, the funnel plots for the primary outcomes OS and PFS was appeared approximately symmetrical (Figure 5), suggesting that publication bias exerted a minimal influence on the results. Sensitivity analysis conducted by leave-one-out method demonstrated that excluding any single study did not significantly alter the pooled effect sizes, indicating the meta-analysis results were highly robust and unaffected by individual studies.
Discussion
This meta-analysis systematically evaluated the therapeutic efficacy and safety of SBRT versus RFA in HCC patients meeting Milan criteria. The findings demonstrated comparable efficacy between the two modalities in OS (HR = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.72–1.32, P = 0.87) and PFS (HR = 0.84, 95% CI = 0.67–1.06, P = 0.14), with SBRT showing no statistically significant increase in treatment-related adverse events (RR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.53–1.01, P = 0.05). These results provide critical clinical decision-making insights for non-surgical candidates with Milan criteria-compliant HCC, positioning SBRT as an alternative treatment option that is non-inferior to RFA. This conclusion significantly broadens the spectrum of local therapeutic options available for HCC management, particularly in scenarios where ablation may be contraindicated or technically challenging.
As an established curative-intent local therapy for HCC, RFA has definite therapeutic effects on HCC that meets the Milan criteria (36). However, its clinical application encounters significant challenges when tumors are located in subcapsular regions, adjacent to the diaphragmatic dome, or in proximity to major vascular structures (17). In such challenging anatomical contexts, RFA frequently encounters technical limitations including heat sink effects (37) and restricted maneuverability, resulting in incomplete ablation rates ranging from 7.2% to 34.7% (38). These suboptimal outcomes often necessitate salvage interventions such as transarterial chemoembolization or repeat ablation procedures (39). Historically, conventional external beam radiotherapy has been limited in patients with cirrhosis due to the risk of radiation-induced liver disease and inadequate dose conformity (40, 41). In contrast, SBRT addresses these technical challenges by utilizing four-dimensional computed tomography simulation with respiratory gating (32), which allows for precise control of liver motion within a 3 mm displacement (42). Advanced inverse planning intensity-modulated techniques facilitate steep dose gradients of 10% per millimeter (43), thereby restricting radiation exposure to ≤15 Gy in normal hepatic parenchyma within 2 cm of the target volume (44). This precise dosimetry significantly reduces the likelihood of radiation-induced liver injury while ensuring therapeutic doses are delivered to tumor targets (29). Consequently, these technological advancements render SBRT a viable alternative for patients with lesions contraindicated for radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or those facing elevated procedural risks (28, 30), particularly in anatomically challenging situations where thermal ablation is less effective.
RFA achieves tumor control primarily through direct thermal effects that induce coagulative necrosis (36), whereas SBRT relies on high-dose radiation to provoke tumor vascular damage and DNA double-strand breaks (18). Despite their divergent mechanisms of action, the equivalent survival outcomes observed in this study suggest that for patients meeting the Milan criteria, treatment selection should prioritize individualized considerations—such as tumor anatomical location, hepatic functional reserve, and procedural feasibility—rather than pursuing marginal survival differences (4). Subgroup analyses demonstrated internal consistency in the study findings. No significant heterogeneity in HRs was observed between tumor diameter stratifications (≤3 cm vs. 3–5 cm), indicating comparable tumor burden control efficacy between the two modalities. This contrasts with prior reports by Xi et al. (31), which suggested superior local control with SBRT for smaller tumors (≤3 cm). However, our analysis incorporated additional RCTs and PSM studies, thereby mitigating selection bias and providing a more objective reflection of real-world efficacy. Notably, consistent outcomes were observed in both primary and recurrent HCC subgroups, implying that prior treatment history may not influence the relative efficacy of these modalities. This finding holds significant clinical implications for patients with post-transplant recurrence or disease progression after prior locoregional therapies.
In this study, no significant difference in treatment-related adverse event rates was observed between the SBRT and RFA groups, which contrasts with previous reports suggesting a potential link between SBRT and increased risks of radiation-induced liver disease (45). Notably, however, the comparative analysis of adverse events revealed borderline statistical significance (RR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.53-1.01, P = 0.05), a finding that warrants careful consideration. This borderline result hints at a subtle trend toward potentially increased toxicity with SBRT, though the narrow confidence interval (spanning close to 1.0) indicates that the absolute difference in clinical risk between the two modalities remains limited and may not reach meaningful clinical relevance. Several factors may contribute to this nuanced observation. First, contemporary advancements in radiotherapy techniques have likely played a pivotal role in mitigating excessive toxicity risks. Innovations such as image-guided radiotherapy (46), respiratory gating (47), and dose sculpting algorithms (19) have significantly improved the precision of radiation delivery, thereby minimizing inadvertent exposure to healthy hepatic parenchyma. Second, the included studies in our analysis consistently applied stringent dosimetric constraints, which are known to reduce the likelihood of radiation-induced liver injury. These technical refinements and standardized safety protocols may explain why the observed trend toward increased toxicity with SBRT remains borderline and clinically modest, rather than reaching the more pronounced risk levels suggested in earlier literature.
These findings collectively highlight the evolving role of technological advancements in reducing toxicity risks associated with SBRT (48), thereby challenging historical concerns regarding its safety compared to RFA in specific patient populations.
Several limitations warrant attention. First, difficulties in accessing raw data hindered the performance of subgroup analyses for critical variables, such as the number of liver tumors, cirrhosis status, RFA margin width, and SBRT biologically effective dose, as well as specific data on subsequent targeted or immunotherapy regimens. This limitation may impede the ability to identify context-specific survival benefits associated with each technique, particularly within high-risk subgroups. Secondly, most studies lack detailed data on tumor location, a factor that may significantly influence local recurrence rates and the risk of complications. Lastly, our meta-analysis did not address cost-effectiveness analyses and quality-of-life assessments, both of which are essential for a comprehensive and objective comparison of the clinical value of the two techniques.
Conclusion
This study addresses the lack of direct comparative evidence between stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in treating hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) under the Milan criteria. Using a systematic meta-analysis, it evaluated the clinical efficacy and safety of both treatments. The results indicate that SBRT and RFA are statistically equivalent in key efficacy measures like overall and disease-free survival rates, as well as in safety indicators such as complication rates. The study suggests SBRT as a viable alternative to RFA, particularly for patients with tumors in challenging locations, and highlights its potential in HCC treatment. This supports SBRT as a reliable option for personalized HCC diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JJ: Formal Analysis, Validation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Methodology, Data curation, Supervision, Investigation, Conceptualization, Software. FZ: Software, Writing – original draft, Data curation. HZ: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. GL: Validation, Investigation, Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Software. ZD: Funding acquisition, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Visualization, Project administration, Supervision, Software, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1644001/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | Risk of bias for the included the nine non-RCTs, based on the ROBINS-I tool. ROBINS-I: risk of bias in non-randomized studies of interventions; NA=not applicable
Supplementary Figure 1 | Risk of bias for the included the one RCT, based on the RoB 2 tool.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:6. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3
3. Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, Saikam V, and Singh R. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2020) 1873:188314. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188314
4. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2025) 82:315–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.08.028
5. Tsilimigras DI, Bagante F, Moris D, Merath K, Paredes AZ, Sahara K, et al. Defining the chance of cure after resection for hepatocellular carcinoma within and beyond the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer guidelines: A multi-institutional analysis of 1,010 patients. Surgery. (2019) 166:967–74. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.08.010
6. Yu X-C, Liu J-B, Tang Q-H, Diao X, Fan Q-Y, Huang Z-Y, et al. Recent trends in the incidence and survival of stage I liver cancer: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. Ann Med. (2022) 54:2785–95. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2131328
7. Singal AG, Llovet JM, Yarchoan M, Mehta N, Heimbach JK, Dawson LA, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. (2023) 78:1922–65. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000466
8. Dimick JB, Cowan JA, Knol JA, and Upchurch GR. Hepatic resection in the United States: indications, outcomes, and hospital procedural volumes from a nationally representative database. Arch Surg. (2003) 138:185–91. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.138.2.185
9. Gazzaniga GM, Cappato S, Belli FE, Bagarolo C, and Filauro M. Assessment of hepatic reserve for the indication of hepatic resection: how I do it. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. (2005) 12:27–30. doi: 10.1007/s00534-004-0946-z
10. Aubé C, Oberti F, Lonjon J, Pageaux G, Seror O, N’Kontchou G, et al. EASL and AASLD recommendations for the diagnosis of HCC to the test of daily practice. Liver Int. (2017) 37:1515–25. doi: 10.1111/liv.13429
11. Wu F, Wei C, Zhang S, Jia S, and Zhang J. The efficacy of surgical resection versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma: A SEER-based study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2023) 2023:1269504. doi: 10.1155/2023/1269504
12. Wang D, Xiao M, Wan Z-M, Lin X, Li Q-Y, and Zheng S-S. Surgical treatment for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and challenges. World J Gastrointest Surg. (2023) 15:544–52. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.544
13. Kim J, Kim J-H, Ko E, Kim J-Y, Im BS, Kim GH, et al. Model predicting survival in intermediate-stage HCC patients reclassified for TACE based on the 2022 BCLC criteria. Cancers (Basel). (2025) 17:894. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050894
14. Vilgrain V, Pereira H, Assenat E, Guiu B, Ilonca AD, Pageaux G-P, et al. Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres compared with sorafenib in locally advanced and inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (SARAH): an open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:1624–36. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30683-6
15. Deng Q, He M, Fu C, Feng K, Ma K, and Zhang L. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Hyperthermia. (2022) 39:1052–63. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2059581
16. Francica G. Needle track seeding after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: prevalence, impact, and management challenge. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. (2017) 4:23–7. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S106558
17. Ahmad SA. Limitations of radiofrequency ablation in treating liver metastases: a lesson in geometry. Ann Surg Oncol. (2004) 11:358–9. doi: 10.1245/ASO.2004.10.929
18. Matsuo Y. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A brief overview. Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:2493–500. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30020190
19. Duan Y, Lin Y, Wang H, Kang B, Feng A, Ma K, et al. How does the gradient measure of the lung SBRT treatment plan depend on the tumor volume and shape? Front Oncol. (2021) 11:781302. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.781302
20. Baumann BC, Wei J, Plastaras JP, Lukens JN, Damjanov N, Hoteit M, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for hepatocellular carcinoma: high rates of local control with low toxicity. Am J Clin Oncol. (2018) 41:1118–24. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000435
21. Fu Y, Yang Z, Liu S, Guan R, Wang X, Chen J, et al. Comparison of resection, ablation, and stereotactic body radiation therapy in treating solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm: a retrospective, multicenter, cohort study. Int J Surg. (2025) 111:1535–40. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001977
22. Maher AM, Shanker M, Liu HYH, Lee Y, Leggett D, Hodgkinson P, et al. Comparison of outcomes following surgical resection, percutaneous ablation or stereotactic body radiation therapy in early-stage, solitary and small (≤3 cm) treatment-naïve hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2024) 13:e6978. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6978
23. Berger NG, Tanious MN, Hammad AY, Miura JT, Mogal H, Clarke CN, et al. External radiation or ablation for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: A survival analysis of the SEER database. J Surg Oncol. (2017) 116:307–12. doi: 10.1002/jso.24661
24. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
25. Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. (2016) 355:i4919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4919
26. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
27. Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, and Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. (2007) 8:16. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-8-16
28. Ji R, Ng KK, Chen W, Yang W, Zhu H, Cheung T-T, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome between stereotactic body radiotherapy and radiofrequency ablation for unresecta ble hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine. (2022) 101:e28545. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028545
29. Shiozawa K. Comparison of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and CyberKnife® for initial solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study. WJG. (2015) 21:13490. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13490
30. Ma Z-H, Lin X-L, Liu F-H, Zhang J-L, Yan M-L, Song X-C, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter, propensity score matching analysis. BMC Cancer. (2025) 25:424. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13800-1
31. Xi M, Yang Z, Hu L, Fu Y, Hu D, Zhou Z, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial. JCO. (2025) 43:1073–82. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-01532
32. Hara K, Takeda A, Tsurugai Y, Saigusa Y, Sanuki N, Eriguchi T, et al. Radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma results in comparable survival to radiofrequency ablation: A propensity score analysis. Hepatology. (2019) 69:2533–45. doi: 10.1002/hep.30591
33. Ueno M, Takabatake H, Itasaka S, Kayahara T, Morimoto Y, Yamamoto H, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy versus radiofrequency ablation for single small hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity-score matching analysis of their impact on liver function and clinical outcomes. J Gastrointest Oncol. (2021) 12:2334–44. doi: 10.21037/jgo-21-356
34. Yang Z, Liu S, Hu L, Chen J, Wang J, Pan Y, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy is an alternative to radiofrequency ablation for single HCC ≤5. 0 cm. JHEP Rep. (2024) 6:101151. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101151
35. Shin HS, Hwan Lee S, Jun BG, Kim HS, Kang SH, Park JY, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy versus radiofrequency ablation as initial treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 34:1187–94. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002442
36. Seror O, N’Kontchou G, Nault J-C, Rabahi Y, Nahon P, Ganne-Carrié N, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma within milan criteria: no-touch multibipolar radiofrequency ablation for treatment-long-term results. Radiology. (2016) 280:611–21. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016150743
37. Boregowda G and Mariappan P. Effect of high blood flow on heat distribution and ablation zone during microwave ablation-numerical approach. Int J Numer Method BioMed Eng. (2024) 40:e3835. doi: 10.1002/cnm.3835
38. Lu H, Xie X, Zeng Y, Xia X, Dong X, Bu F, et al. Prognostic comparison of complete vs. Incomplete radiofrequency ablation for colorectal liver metastases: A multicenter prospective study. Cancer Med. (2025) 14:e70735. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70735
39. Hirooka M, Hiraoka A, Ochi H, Kisaka Y, Joko K, Michitaka K, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with or without radiofrequency ablation: outcomes in patients with barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2018) 210:891–8. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18177
40. Scher N, Janoray G, Riet F-G, Le Bayon A-G, Debbi K, Lévy S, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from a retrospective multicentre study. Cancer Radiother. (2019) 23:104–15. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2018.07.138
41. Liang S-X, Huang X-B, Zhu X-D, Zhang W-D, Cai L, Huang H-Z, et al. Dosimetric predictor identification for radiation-induced liver disease after hypofractionated conformal radiotherapy for primary liver carcinoma patients with Child-Pugh Grade A cirrhosis. Radiother Oncol. (2011) 98:265–9. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.10.014
42. Kruis MF, van de Kamer JB, Sonke J-J, Jansen EPM, and van Herk M. Registration accuracy and image quality of time averaged mid-position CT scans for liver SBRT. Radiother Oncol. (2013) 109:404–8. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.08.047
43. Henry J, Moreno C, Crownover RL, Baacke D, Papanikolaou N, Gutierrez AN, et al. (2016) 4:145–51.
44. Apisarnthanarax S, Barry A, Cao M, Czito B, DeMatteo R, Drinane M, et al. External beam radiation therapy for primary liver cancers: an ASTRO clinical practice guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. (2022) 12:28–51. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2021.09.004
45. Sawrie SM, Fiveash JB, and Caudell JJ. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases and primary hepatocellular carcinoma: normal tissue tolerances and toxicity. Cancer Control (2010) 17:111–9. doi: 10.1177/107327481001700206
46. Koay EJ, Owen D, and Das P. Radiation-induced liver disease and modern radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. (2018) 28:321–31. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.06.007
47. Toesca DAS, Ibragimov B, Koong AJ, Xing L, Koong AC, and Chang DT. Strategies for prediction and mitigation of radiation-induced liver toxicity. J Radiat Res. (2018) 59:i40–9. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrx104
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, Milan criteria, stereotactic body radiation therapy, radiofrequency ablation, meta-analysis
Citation: Jing J, Zhong F, Zhang H, Luo G and Du Z (2025) Comparative outcomes of stereotactic body radiotherapy versus radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 15:1644001. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1644001
Received: 09 June 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 02 September 2025.
Edited by:
Kaya Kuru, University of Central Lancashire, United KingdomReviewed by:
Robert Damm, University Hospital Magdeburg, GermanyMuhamad Serhal, Northwestern University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Jing, Zhong, Zhang, Luo and Du. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zongzhi Du, ZHV6b25nemhpbmJAb3V0bG9vay5jb20=; Guosong Luo, Z3Vvc29uZ2x1b3piYkAxNjMuY29t
 Jianxiong Jing1
Jianxiong Jing1 Furui Zhong
Furui Zhong Hao Zhang
Hao Zhang Zongzhi Du
Zongzhi Du