- 1Department of Chest Medicine, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 2School of Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 3Department of Haematology-Oncology, National University Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
- 4Department of Clinical Oncology, Faculty of Medicine, State Key Laboratory in Oncology in South China, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- 5Department of Radiotherapy and Oncology, Sarawak General Hospital, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia
- 6Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
- 7Jilin Cancer Hospital, Changchun, China
- 8Department of Thoracic Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
- 9Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 10Amgen, Inc., Singapore, Singapore
- 11Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive neuroendocrine carcinoma with a poor prognosis and accounts for approximately 11% of all lung cancers. Owing to the complex and aggressive nature of the disease, clinical management of SCLC is challenging. Many SCLC regional guidelines, including those from East Asia, have been developed in light of potential regional variations in socioeconomic conditions and healthcare infrastructure. However, less is known about the potential implications of the inherent population/regional differences in clinical management and the emerging treatment landscape in SCLC. Here, we review variations in the real-world patient characteristics and in diagnosis and treatment guidelines in SCLC between East Asia and Europe/North America. We also consider similarities and differences in real-world treatment patterns, as well as clinical outcomes between regions, to explore the need to adapt clinical management in SCLC.
Introduction
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive neuroendocrine (NE) carcinoma, characterized by rapid proliferation, a predisposition for early metastasis, and poor prognosis (1). SCLC accounts for approximately 11% of all lung cancers, and the survival rate is poor (2–4). Early diagnosis is crucial, yet challenging owing to the aggressive nature of the disease, which limits options for curative treatment (1, 5). SCLC is linked with tobacco smoking, and its prevalence often follows the trend in smoking prevalence, with a lag period of approximately 30 years (5).
SCLC carcinogenesis involves multiple pathways, including those disrupting normal DNA repair mechanisms, leading to genomic instability (6). Patients with a history of smoking are likely to have a high tumor mutational burden (TMB) in SCLC (7, 8). Genomic analyses have shown that the most frequent mutations and chromosomal aberrations in patients with SCLC involve inactivation of the tumor protein 53 (TP53) and/or loss of retinoblastoma 1 (RB1) genes (9, 10). Deregulation of the Notch pathway has also been shown to contribute to the clinical behavior of SCLC, including drug resistance and relapse (11, 12). Notch-1 receptor-mediated processes such as NE differentiation, proliferation, cell adhesion, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition play a key role in SCLC development and tumorigenesis (11).
Although SCLC is considered a single disease entity, there are biologically distinct subtypes due to complex pathophysiology and tumor heterogeneity. Complex associations between NE expression and transcription factors warrant further investigation owing to potential subtype-specific therapeutic vulnerabilities (13, 14). A key area that has been poorly understood in SCLC is the influence of ethnic or regional variations in patient characteristics, in the diagnosis and treatment of SCLC, including real-world treatment patterns, and in clinical outcomes. Owing to potential regional variations in socioeconomic conditions and healthcare infrastructure, different regional guidelines for the treatment of SCLC have been developed (15). Although these guidelines are primarily based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Tumor, Node, Metastasis (TNM) classification (stages 0–IV), most have adopted a pragmatic approach of combining the TNM staging system and the previous Veterans Administration (VA) two-stage classification scheme (i.e., limited-stage [LS] disease and extensive-stage [ES] disease) (15).
Unlike in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), there are no pan-Asian guidelines developed for SCLC diagnosis and management (16). Additionally, publications comparing SCLC guidelines from across the globe are limited. In this narrative review, we focused on comparing East Asia with Europe and/or North America (Europe/North America). We provide a comparison of real-world patient characteristics and diagnosis and treatment guidelines between East Asia and Europe/North America. We further explore similarities and differences in real-world treatment patterns, as well as clinical outcomes in SCLC, to shed some light on the potential implications of the inherent population/regional differences in clinical management and the emerging treatment landscape.
Real-world patient characteristics in SCLC: East Asia versus Europe/North America
Smoking is associated with SCLC, with most patients being former or current smokers (6, 17). Besides smoking history, patient characteristics such as sex and age are potential risk factors associated with SCLC (Table 1). Studies from East Asia indicated continued increased prevalence of SCLC in men compared with women (18–20). In contrast, recent reports from Europe and the United States (US) suggest a shift from the initial male predominance of SCLC to an equal prevalence in men and women (12, 15, 21). There is also an increased prevalence of SCLC in elderly populations (>70 years of age) compared with younger age groups, a trend similar in East Asia and Europe/North America (18, 22).
Among the global smoking population, the prevalence of smoking in men was highest in East and South-East Asia and East Europe, and the highest prevalence in women was noted in European countries (23). Given the link between smoking and SCLC, the prevalence of SCLC seems to mirror the prevalence of smoking (5). The proportion of smokers with SCLC ranged from 48.3 to 97.6% (year of publication, range: 2015–2023) in East Asia versus 38.7–98.2% in Europe/North America (year of publication, range: 2012–2023) (17, 24–46) (Table 1). Although the relative incidence of SCLC has declined over the past few decades, reflecting a decrease in smoking prevalence, studies suggest that the risk of developing SCLC in young smoking populations is on the rise (6, 12, 17). It should be noted that there is a lag time of approximately 30 years between smoking and occurrence of SCLC; hence, any variations in the prevalence of SCLC are likely attributable to the differences in smoking over time (5, 23, 47).
Although SCLC is linked to smoking, SCLC can occur in never-smokers (43, 48, 49). There are regional- and sex-based differences in the prevalence of SCLC in never-smokers. The East Asian population has a higher incidence of SCLC among never-smokers compared with the European/North American population. Based on available data, the proportion of never-smokers with SCLC ranged from 1.9 to 44.6% in East Asia (year of publication, range: 2015–2023) versus 1.5–4.5% in Europe/North America (year of publication, range: 2009–2023) (17, 24–30, 32, 34–46, 48, 50, 51) (Table 1). The higher incidence of SCLC among never-smokers in East Asia versus Europe/North America may be attributed to ethnic differences, second-hand smoking, and increased exposure to occupational and environmental carcinogens in East Asia (52). Regardless of these regional differences, women account for a high proportion of never-smoking patients with SCLC in both East Asia and Europe/North America (17, 32, 49, 52). Although data indicate the presence of distinct molecular profiles in never-smokers with SCLC compared with those with a smoking history, less is known about any regional differences in the prevalence of molecular subtypes of SCLC in East Asia versus in Europe/North America (28). Although the Achaete-scute homolog 1 NE subtype seems to be the most prevalent subtype of SCLC, on the basis of studies from East Asia and Europe/North America, further comparative analyses are needed to reveal the existence of any distinct mutational signatures in these regional populations (9, 53–59). A study by Lin et al. indicated potential disparities in mutational signatures in East Asian patients with SCLC versus White patients (60). The observation that the East Asian study population had high mutation counts of DNA-damage response signaling pathways and TMB compared with the White study population (P<0.05) may have important therapeutic implications (60).
Diagnosis and staging of SCLC in East Asia versus Europe/North America
SCLC is typically diagnosed when patients present with symptoms indicative of locally advanced or metastatic-stage disease (61, 62). There is no effective screening test available to detect early-stage SCLC (61, 62). Low-dose computed tomography (CT) screening has been shown to reduce lung cancer mortality in asymptomatic high-risk patients (63). However, this screening test is not an effective approach for SCLC detection, because of the symptomatic development of the disease between annual CT scans, owing to its aggressive nature (21, 62).
Guidelines regarding the diagnosis of SCLC are generally similar across East Asia and Europe/North America, and recommend a combination of imaging and pathological examination (21, 62, 64–66). These guidelines primarily follow the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system for lung tumors, which is based on the characteristic histology on hematoxylin and eosin staining when good-quality histologic samples are available (67). Mitotic cell counting is essential for differential diagnosis, and the WHO suggests immunohistochemistry (IHC) as a supportive tool in SCLC definitive diagnosis (67). Although international guidelines are in general agreement regarding diagnostic approaches, there is limited concordance among pathologists on ideal diagnostic criteria (68).
In Europe, histological examination of a biopsy is recommended for SCLC diagnosis by the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) (21). Although the ESMO Guidelines note the use of NE markers such as synaptophysin, chromogranin A, neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM/CD56), and the nuclear protein Ki-67, a recommendation for the use of specific markers is lacking (21, 69). There is no established role for the use of molecular testing in Europe, and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and TMB testing are not recommended in routine clinical practice (21).
In North America, diagnosis can be based on biopsy or cytology of a primary or metastatic site (62, 70). Based on the guidelines developed by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®), if a sample is limited, IHC is recommended for SCLC diagnosis and for distinguishing from NSCLC or other NE tumors (62). Markers for IHC, such as insulinoma-associated protein 1 (INSM1), chromogranin A, NCAM/CD56, and synaptophysin, are suggested, although these alone are not recommended for SCLC diagnosis (62). The NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) suggest molecular profiling via blood, tissue or both in rare cases of SCLC, particularly for patients with ES-SCLC or relapsed SCLC who are never-smokers, light-smokers, or who have a remote smoking history (62). Similarly, the Canadian consensus report on SCLC management suggests molecular testing for driver mutations when combined SCLC (defined as a combination of SCLC and non–small cell carcinoma of any histological type) is suspected or in nonsmokers with a new diagnosis of SCLC (5, 70).
Most East Asian countries generally follow the ESMO and/or NCCN Guidelines® for SCLC diagnosis. In Taiwan and Thailand, for example, SCLC diagnosis is based predominantly on NCCN Guidelines, whereas in China and Korea, recommendations around diagnosis are broadly based on the NCCN and ESMO Guidelines. In China, histopathology- and cytology-based diagnosis is recommended to detect the presence and type of tumor (66). Japan follows a similar diagnostic pathway to other countries, which involves imaging and pathological examination (64). On the basis of the Japan Lung Cancer Society Guidelines, pathological diagnosis using NE markers such as chromogranin A, synaptophysin, and NCAM/CD56 are currently used to distinguish SCLC from other lung NE tumors in Japan (64).
Once SCLC is diagnosed, staging of the disease is an important factor when considering the appropriate treatment. The guidelines reported in this article have adopted a combined approach for staging SCLC using both the AJCC TNM staging system and the VA two-stage classification scheme (21, 62, 64–66, 71). However, there seems to be a lack of consensus for the classification of LS- and ES-SCLC (15). Descriptions used for defining LS and ES disease either lack clarity or are inconsistent among these guidelines. Of note, in their definition of LS-SCLC, NCCN Guidelines exclude T3–T4 owing to multiple lung nodules that either are too extensive or have tumor/nodal volume that is too large to use a tolerable radiation plan, unlike ESMO, Chinese, and Taiwanese guidelines (21, 62, 65, 66). The Japanese guidelines have primarily adopted the VA two-stage, classification-based definitions of “localized SCLC and extensive SCLC,” especially when considering treatment choice (64). The rationale for this is based on applicability of this staging criteria in treatment choice and the widespread usage of these terms in clinical trials (64).
Current treatment of SCLC in East Asia versus Europe/North America
Comparison of treatment guidance across regions and key differences in recommended therapies in LS- and ES-SCLC
A comparison of treatment recommendations in LS- and ES-SCLC highlights some differences between regional guidelines. As with SCLC diagnosis guidance, Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand follow the NCCN Guidelines for SCLC treatment, whereas China follows the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Guidelines (66). As noted earlier, differences between these guidelines largely lie within how each country or region defines a clinical stage eligible for the recommended treatment algorithm (21, 62, 64–66). A summary of treatment guidance across East Asia and Europe/North America in LS-SCLC is provided in Figure 1. Treatment guidelines on ES-SCLC largely align across regions.
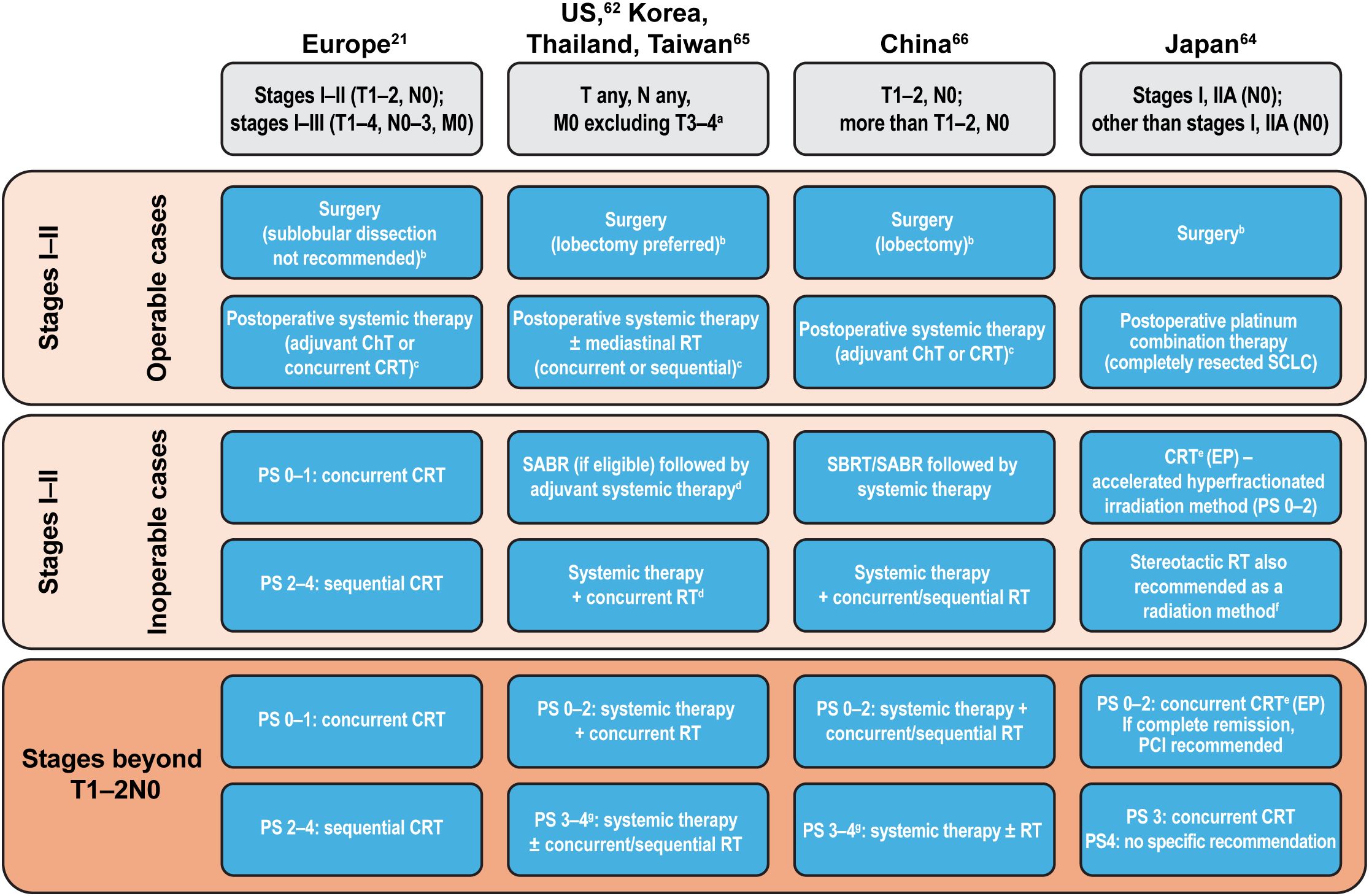
Figure 1. Summary of treatment guidance in LS-SCLC across East Asia and Europe/North America. aDue to multiple lung nodules that are either too extensive or have tumor/nodal volume that is too large to use a tolerable radiation plan; bPathological mediastinal staging recommended; cDepending on postoperative clinical stage; dSABR not included in management consensus for Taiwan; eRecommended method; if ineligible for EP, then sequential therapy with EC followed by RT; fIn stages I–IIA (TNM 9th edition) without lymph node metastases (weak recommendation); gDue to SCLC. ChT, chemotherapy; CRT, chemoradiotherapy; EC, etoposide + carboplatin; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; EP, etoposide + cisplatin; (LS-)SCLC, (limited-stage) small cell lung cancer; PS, ECOG performance status; RT, radiotherapy; SABR, stereotactic ablative radiotherapy; SBRT, stereotactic body radiation therapy; TNM, Tumor, Node, Metastasis; US, United States.
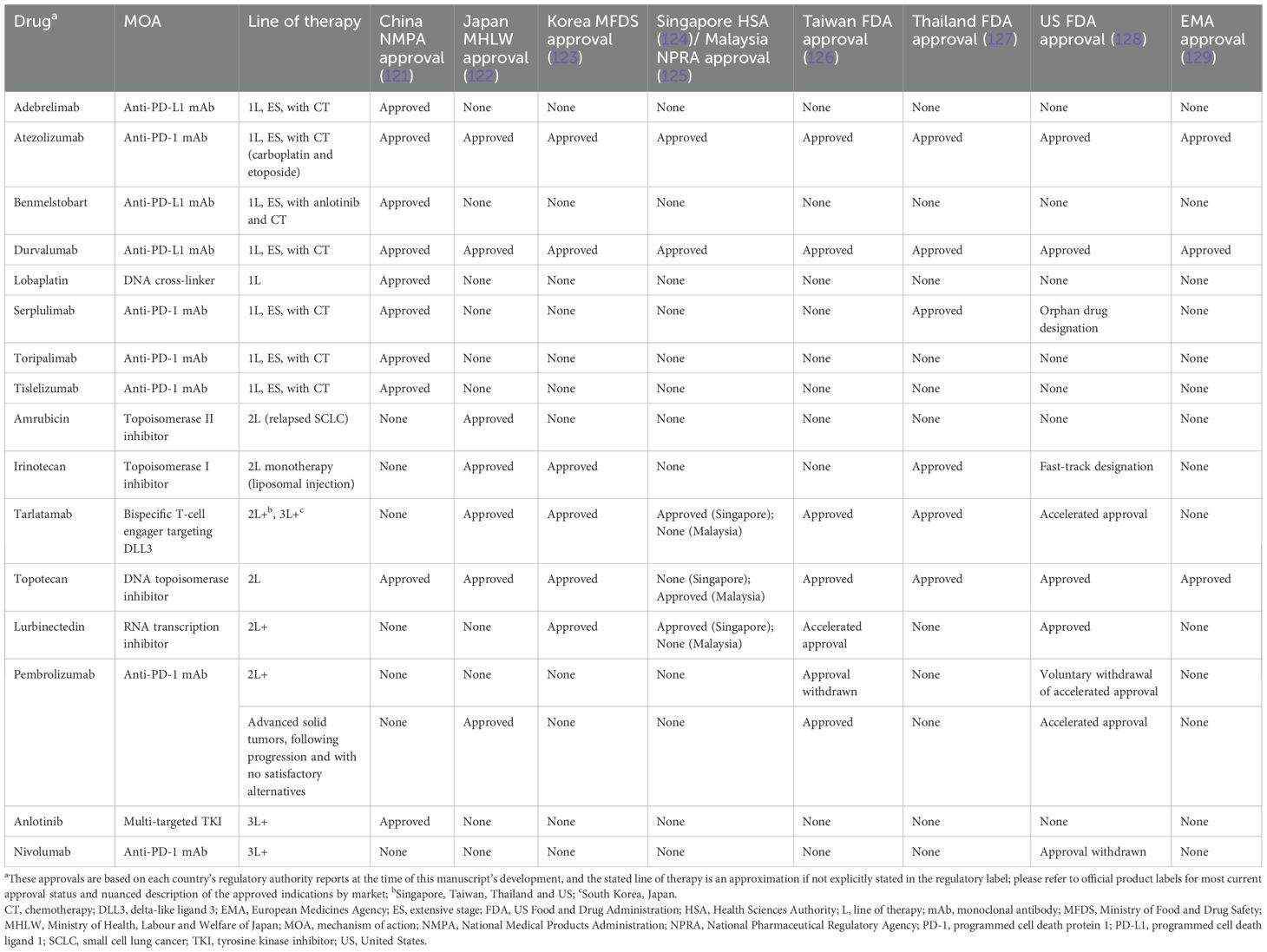
Globally, there is a general consensus in the overall approach to treating SCLC. Chemoradiotherapy is recommended for LS-SCLC treatment, especially for patients who cannot undergo surgery, and systemic therapy using a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy is generally recommended for the treatment of ES-SCLC (21, 62, 64–66). However, there are some differences in the choice of drugs used across East Asia and Europe/North America in LS- and ES-SCLC (Table 2). It must be also noted that any recent approvals of indications in SCLC might not have been updated in the guidelines during the development of this report.
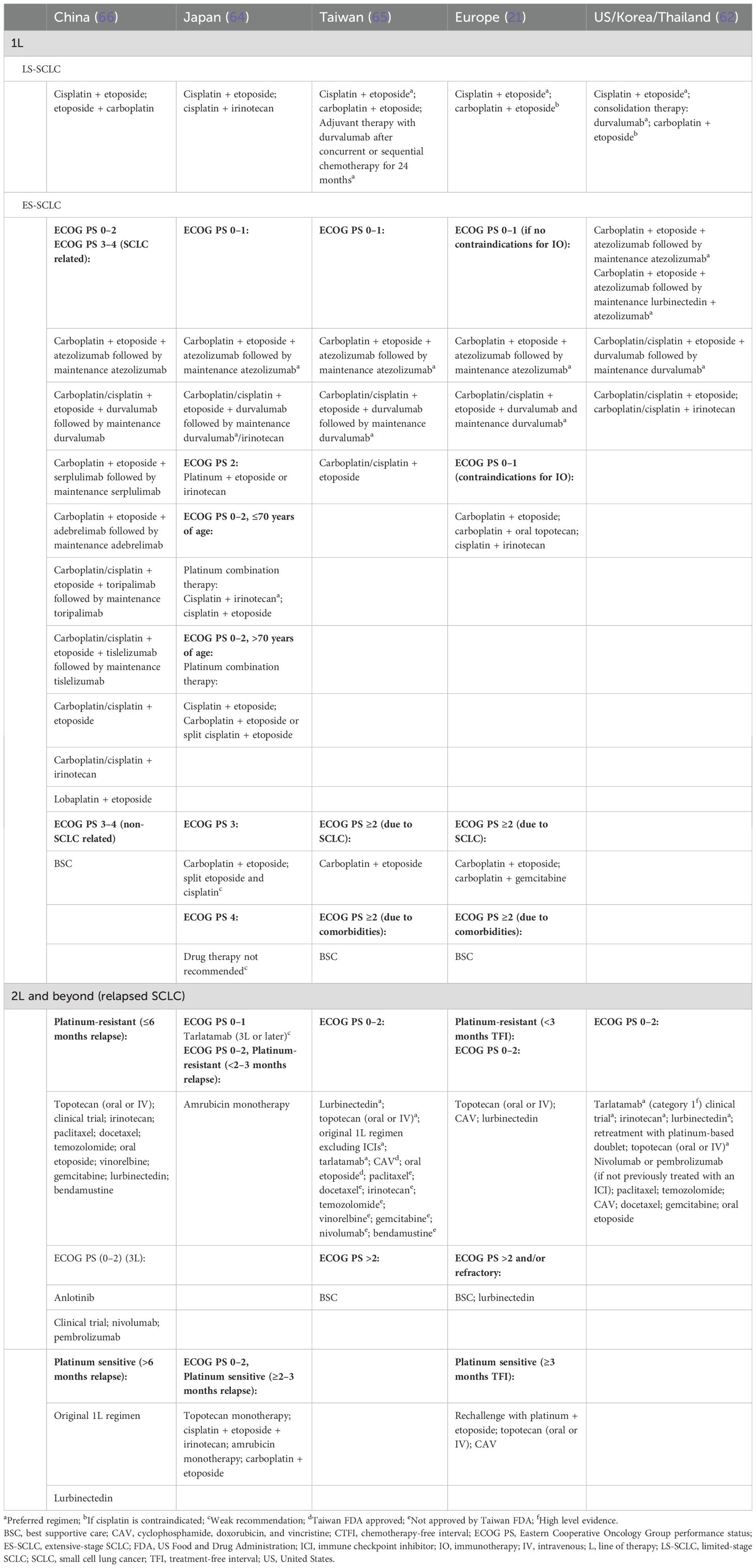
Table 2. Comparison of first-line and second-line guideline-recommended systemic treatments for LS- and ES-SCLC: East Asia versus Europe/North America.
LS-SCLC
Surgical resection of SCLC (stage I–II) as part of multimodality treatment remains controversial, with only a minority of patients being eligible (21). When permitted, guidelines across East Asia and Europe/North America suggest a similar approach, with extensive pathological mediastinal staging as a first step prior to surgery, followed by postoperative systemic therapy. Japanese guidelines strongly recommend surgical resection in stages I–IIA without lymph node metastases; for nonsurgical patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) of 0–2, accelerated hyperfractionated irradiation is recommended, with stereotactic irradiation weakly recommended for inoperable stages I–IIA without lymph node metastases (64). In the US, Korea, and Thailand, concurrent chemoradiation or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) followed by systemic therapy is recommended for LS-SCLC (stage I–II, T1–2, N0, M0) in selected patients whose SCLC is medically inoperable or for whom a decision was made against performing surgery (62). As per NCCN Guidelines, advanced technologies, such as volumetric modulated arc therapy, are appropriate to use for delivering adequate tumor doses (62). In China, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)/SABR followed by chemotherapy, or chemotherapy with concurrent/sequential radiotherapy, is recommended for patients in LS-SCLC (stages I–IIA) who are unwilling to undergo surgery, and in inoperable LS-SCLC (stages I–IIA) (66).
In LS-SCLC (stages I–II), postoperative therapy using chemotherapy or definitive chemoradiotherapy is recommended across East Asia and Europe/North America, although the timing and choice of drugs varies between the regional guidelines (Figure 1, Table 2). Although most of the East Asian and European/North American guidelines recommend an etoposide-based platinum combination therapy in LS-SCLC, the Japanese guidelines recommend an etoposide- or irinotecan-based cisplatin combination therapy (Table 2). Consolidation therapy with durvalumab has also shown significant overall survival and progression-free survival benefits for patients with LS-SCLC (72) and is now included in guidelines (62, 73).
ES-SCLC
In ES-SCLC, the first-line therapy recommended by all guidelines is systemic treatment with a combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy (21, 62, 64–66). For patients with ES-SCLC and ECOG PS 0–1, all guidelines recommend carboplatin/cisplatin-etoposide in combination with atezolizumab or durvalumab as the preferred first-line therapy (Table 2). However, if immunotherapy is contraindicated or patients have a poor ECOG PS (≥2), the preferred treatment across most guidelines is chemotherapy. Although there are similarities, guidelines across East Asia and Europe/North America differ in recommendations based on ECOG PS (Table 2).
Prophylactic cranial irradiation in LS- and ES-SCLC
Japanese guidelines strongly recommend prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in patients who achieve complete remission after initial treatment of localized tumors in LS-SCLC (GRADE IB; i.e., strong positive recommendation with moderate confidence) (64). In China, PCI is recommended in LS-SCLC (T1–2, N0) for patients with operable disease, and in those with inoperable disease with complete/partial responses after SBTR/SABR or chemoradiotherapy (level III [weak] recommendation) (66). For patients beyond T1–2, N0, PCI is recommended (level II) for those with complete/partial responses (66). As per ESMO and NCCN Guidelines, the role of PCI is not well defined in patients with stage I–II disease; therefore, PCI is not recommended in patients with a poor ECOG PS, in those who are at risk of neurocognitive decline, in frail patients, or in those who are ≥70 years of age (21, 62). NCCN Guidelines indicate that PCI can be considered in ES-SCLC, with the caveats indicated above (62). In Europe, ESMO Guidelines indicate that, for ES-SCLC, PCI is the standard treatment for patients with stage IV disease (<75 years of age with ECOG PS 0–2) without progression after first-line chemotherapy (level II recommendation [i.e., generally recommended treatment]) (21). In China, although PCI has been recommended, this is not a preferred treatment option for patients with ES-SCLC and PS 0–2 or PS3–4 (66).
Recommended 2L therapy and beyond in relapsed SCLC
Across treatment guidelines, recommendations following relapse include rechallenge with platinum-based chemotherapy as well as the use of topotecan, irinotecan, lurbinectedin, or tarlatamab (21, 62). In relapsed SCLC, there is a lack of consensus on how to define sensitivity to platinum-based therapies across the guidelines. The Japanese guidelines define platinum sensitivity/resistance using a disease progression cutoff of 60–90 days (approximately 2–3 months) after the end of first-line platinum-based chemotherapy (64). The NCCN Guidelines no longer use platinum sensitivity/resistance to distinguish 2L+ treatment choices whereas the ESMO guidelines still define it with a 3-month cutoff (21, 62). Chinese guidelines use a cutoff of >6 months after the end of first-line platinum-based chemotherapy to define platinum-sensitive relapse and ≤6 months to define platinum-resistant relapse (66). A study from Japan reassessed the cutoff values in the post–immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) era and found that a 75-day cutoff after the end of first-line treatment was the most suitable for the prognostic classification of relapsed SCLC compared with traditional cutoffs (39).
Guidelines also differ in their recommendations for optimal treatment in relapsed SCLC (Table 2); several therapies are approved for second-line use, as summarized in Table 3. Tarlatamab is now included in the NCCN Guidelines as the only category 1 recommended preferred option for 2L+ SCLC; topotecan is recommended in platinum-resistant and platinum-sensitive SCLC by ESMO and NCCN; in contrast, the Japanese guidelines recommend the use of topotecan only in platinum-sensitive SCLC (21, 62, 64). In China, platinum rechallenge is recommended in platinum-sensitive SCLC and topotecan is recommended in platinum-resistant SCLC; other recommendations include irinotecan, taxanes (paclitaxel and docetaxel), gemcitabine, oral etoposide, vinorelbine, temozolomide, bendamustine, and lurbinectedin (66). Taxanes are also potential treatment options recommended by ESMO and NCCN Guidelines (21, 62, 74). Other NCCN-recommended therapies in platinum-resistant and platinum-sensitive SCLC include irinotecan and ICIs (Table 2).
China is currently the only country to have a third-line therapy, anlotinib, approved for the treatment of SCLC (66). Although amrubicin monotherapy is recommended in platinum-resistant SCLC in Japan, other guidelines do not recommend its use (Table 2). Globally, despite guidelines recommending optimal treatment options, as well as approvals of new treatment options such as immunotherapy, disparities in cancer treatment availability, accessibility, and affordability among Asian countries have set a major drawback in tackling disease burden in this region (75).
Real-world treatment patterns in East Asia versus Europe/North America
Data from real-world studies provide a glimpse into the variability of treatment usage in East Asia versus Europe/North America (Table 4). Prior to the approval of immunotherapy in SCLC, platinum-etoposide therapy was the most frequent first-line treatment across East Asia and Europe/North America (25, 30, 35, 41, 44, 76–80). In Korea and Thailand, platinum-etoposide use ranged from 61.3 to 81.4% between 2007 and 2016 in patients with LS- and ES-SCLC (41, 44, 77). Between 2014 and 2016, the use of platinum-etoposide was significantly more common in the US (87.0%) than in Europe (82.1%) and Japan (73.3%, P<0.05) in patients with ES-SCLC (76). Carboplatin-etoposide was the most common first-line regimen in Japan, Europe, and the US from 2014 to 2016, though the highest usage was in the US (60.4% vs 41.3% in Europe and 49.6% in Japan) (76). In comparison, cisplatin-etoposide was more frequently used in Europe (40.8%) than in the US (26.6%) or Japan (23.7%) (P<0.05) from 2014 to 2016 (76). In Korea and Taiwan, the cisplatin-etoposide combination was the most commonly used first-line platinum therapy from 2011 to 2016 (41, 81).
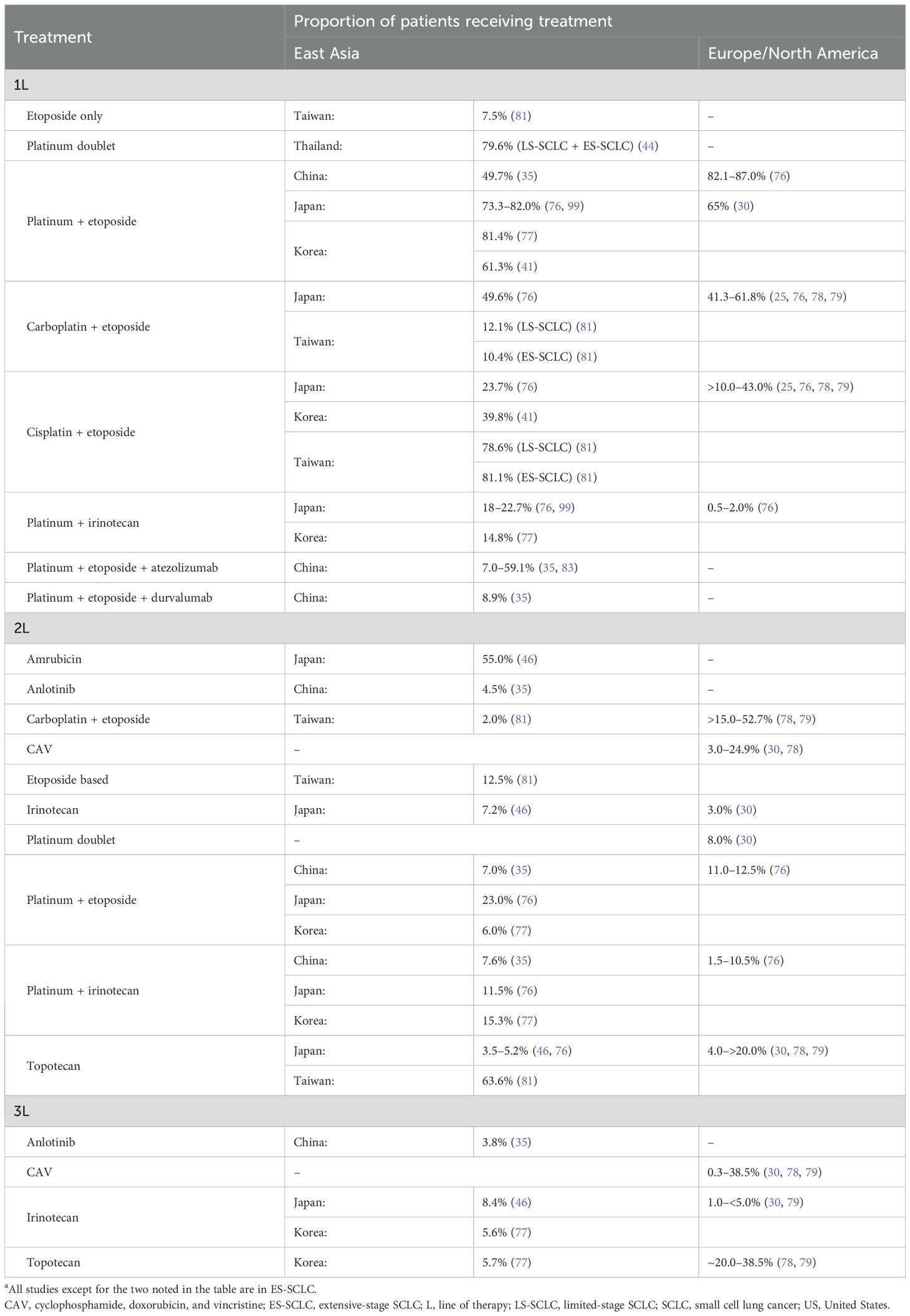
Table 4. Overview of real-world treatment patterns in SCLCa: East Asia versus Europe/North America.
Use of irinotecan in combination with platinum was a common first-line treatment in Japan (22.7%) but not in the US (2.0%) or in Europe (0.5%, P<0.0001) during 2014–2016 (76). The high usage of irinotecan in Japan is reflective of the Japanese treatment guideline recommendation (64). Irinotecan in combination with platinum is also used as a first-line and second-line chemotherapy in Korea (77). Amrubicin was the most commonly used second-line (55.0%) or later (22.0%) therapy compared with other chemotherapy regimens in Japan (46). Due to failure in achieving survival benefit in European/North American studies, amrubicin is currently not available in these regions (21, 61, 62).
Although limited data are available on the real-world usage of immunotherapy in SCLC owing to its approval only in the recent years, studies from Europe and China indicate an increased use of immunotherapy combination as first-line therapy in ES-SCLC in the post-approval era (82, 83). A pan-European study reported that, among patients with ES-SCLC receiving a first-line treatment (N = 1176), the use of platinum-based chemotherapy (platinum-etoposide) decreased from 91.8% in 2018 to 42.3% in 2021 (82). This decline was associated with an increased use of immunotherapy combination during the study period: the use of platinum-etoposide in combination with atezolizumab increased from 0% in 2018, reflecting the approval of atezolizumab only in late 2019 in Europe, to 41.2% in 2021 (82). A multicenter Chinese study in patients with ES-SCLC (N = 225) reported a higher proportion of patients receiving first-line platinum-etoposide in combination with atezolizumab (59.1%) versus platinum-etoposide alone (40.9%) during 2019–2022 (83).
Prognosis and clinical outcomes in East Asia versus Europe/North America
Differentiating key prognostic factors in SCLC: East Asia versus Europe/North America
Given SCLC has been viewed as a smoker’s disease, studies have looked at whether smoking could be a potential prognostic factor for poor survival outcomes. Studies from East Asia and Europe/North America report conflicting results for survival outcomes based on smoking history (28, 32, 41, 50). Most of the studies noted that there was no significant correlation between smoking status and overall survival (OS) in SCLC (LS- and ES-SCLC) (28, 32, 41). However, of note, the study by Liu et al. from China reported that, in LS- and ES-SCLC, smoking is an independent prognostic factor for poor progression-free survival (PFS) but not for OS in SCLC: in never-smokers versus smokers, median PFS was 8.37 versus 7.10 months (hazard ratio [HR], 0.753; P = 0.047), and median OS was 19.73 versus 14.40 months (HR, 0.780; P = 0.236), respectively (32). In the US study by Ou et al., a positive history of smoking was noted as a significant prognostic factor for poor OS in ES-SCLC (HR, 1.31; P = 0.0125; vs never-smokers) (50).
Studies have reported differences in OS and toxicity between East Asian and European/North American populations (84, 85). Ethnicity is a prognostic factor in SCLC, with studies indicating that better survival outcomes in SCLC are seen in patients of Asian ethnicity than in those of White ethnicity (86, 87). In LS-SCLC (stage III), Asian patients have a reduced risk of death compared with White patients (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.77–0.91; P<0.001) (86). In ES-SCLC, Asian ethnicity is a favorable prognostic factor (HR, 0.785; P = 0.0076) (50). Other differentiating prognostic factors of note are high neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio, which have been associated with poor prognosis for survival outcomes in an East Asian population but not in a White population (88). Inherent differences due to genetic polymorphisms could also affect drug metabolism, transport, and receptor-binding (85).
Survival outcomes by region/ethnicity in clinical trials
Ethnicity-related differences were noted in response to chemotherapy in two large phase 3 trials from Japan (JCOG 9511) and North America (SWOG 0124), despite similar eligibility criteria and treatment regimens (89). The two studies compared the survival benefit of cisplatin-etoposide with that of cisplatin-irinotecan in ES-SCLC, with the Japanese study showing a survival benefit for cisplatin-irinotecan (90, 91). On the contrary, the North American trial, consisting of more than 90.0% White patients, did not report any difference in survival outcomes for cisplatin-irinotecan versus cisplatin-etoposide (91).
A pooled comparative outcomes analysis of these two studies noted significantly higher response rates in the Japanese study population compared with the North American study population: 68.0% versus 57.0% (P = 0.02) in the cisplatin-etoposide group, and 87.0% versus 60.0% (P<0.001) in the cisplatin-irinotecan group, respectively (89). OS and PFS were similar across the two studies in the cisplatin-etoposide group. However, OS was significantly higher in the cisplatin-irinotecan group in the Japanese patients versus North American patients (12.8 vs 9.9 months; P<0.001, adjusted for age, sex, and ECOG PS). Differences in toxicity were also noted across the two studies, with Japanese study patients experiencing increased hematologic toxicity versus US study patients (89). However, it is crucial to consider that, besides pharmacogenomic variability among various ethnicities, differences between clinical trials investigating similar or identical therapies could also be a result of many other factors, including differences in study design, eligibility criteria, patient selection, demographics, and treatment regimens (91).
Results from phase 3 trials that evaluated immunotherapy plus chemotherapy, such as CASPIAN and IMpower133, demonstrated similar efficacy outcomes in their global trials and corresponding Asian subgroup analyses (92–96). CASPIAN and IMpower133 studies evaluated the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitors durvalumab and atezolizumab, respectively, in a first-line treatment setting for ES-SCLC. In the CASPIAN global trial, durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide significantly improved OS compared with platinum-etoposide alone (median, 12.9 vs 10.5 months; HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62–0.91; nominal P = 0.0032) (92). Results from a preplanned subgroup analysis of Japanese patients, as well as an exploratory analysis of a subgroup of Asian patients (Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, or China), were similar to the global data (93, 94). In both of these studies, durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide numerically improved OS versus platinum-etoposide alone: median not reached versus 15.2 months (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.26–2.26) in Japanese patients (93), and 14.8 versus 11.9 months (HR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.45–1.64) in the Asia subgroup, respectively (94). Based on interim results from the ongoing phase 3 ADRIATIC trial, adjuvant therapy with durvalumab in patients with LS-SCLC was shown to significantly improve OS (median, 55.9 vs 33.4 months; HR, 0.73; 98.321% CI, 0.54–0.98; P = 0.01) and PFS (median, 16.6 vs 9.2 months; HR, 0.76; 97.195% CI, 0.59–0.98; P = 0.02) compared with placebo (72). Of note, nearly half of the study population in the ADRIATIC trial are Asian (72). In the global IMpower133 trial, atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin-etoposide significantly improved OS (median, 12.3 vs 10.3 months; HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.54–0.91; P = 0.007) and PFS (median 5.2 vs 4.3 months; HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62–0.96; P = 0.02) compared with chemotherapy alone (95). Results from a subgroup analysis in Japanese patients were consistent with the global trial (96).
Survival outcomes in real-world studies: East Asia versus Europe/North America
Real-world cancer registry data from Japan reported a 5-year survival rate of approximately 20.0% for patients with localized SCLC and 2.0% for those at an advanced stage of the disease (97). Five-year relative survival rates from US-based registry data also demonstrate a similar trend, ranging from 30.0% for those with localized SCLC to 3.0% for those with metastatic disease (98). It remains unclear if these outcomes are impacted by differences in the usage of treatments between regions due to a lack of treatment utility data.
OS data from real-world studies across East Asia and Europe/North America, stratified by line of therapy and treatment, are provided in Table 5. For patients with LS-SCLC, OS ranged from 9.3 to 22.2 months in East Asia; data for Europe/North America were limited (Table 5). The ranges for OS in patients with ES-SCLC were 4.2–15.8 months in East Asia and 2.9–12.8 months in Europe/North America.
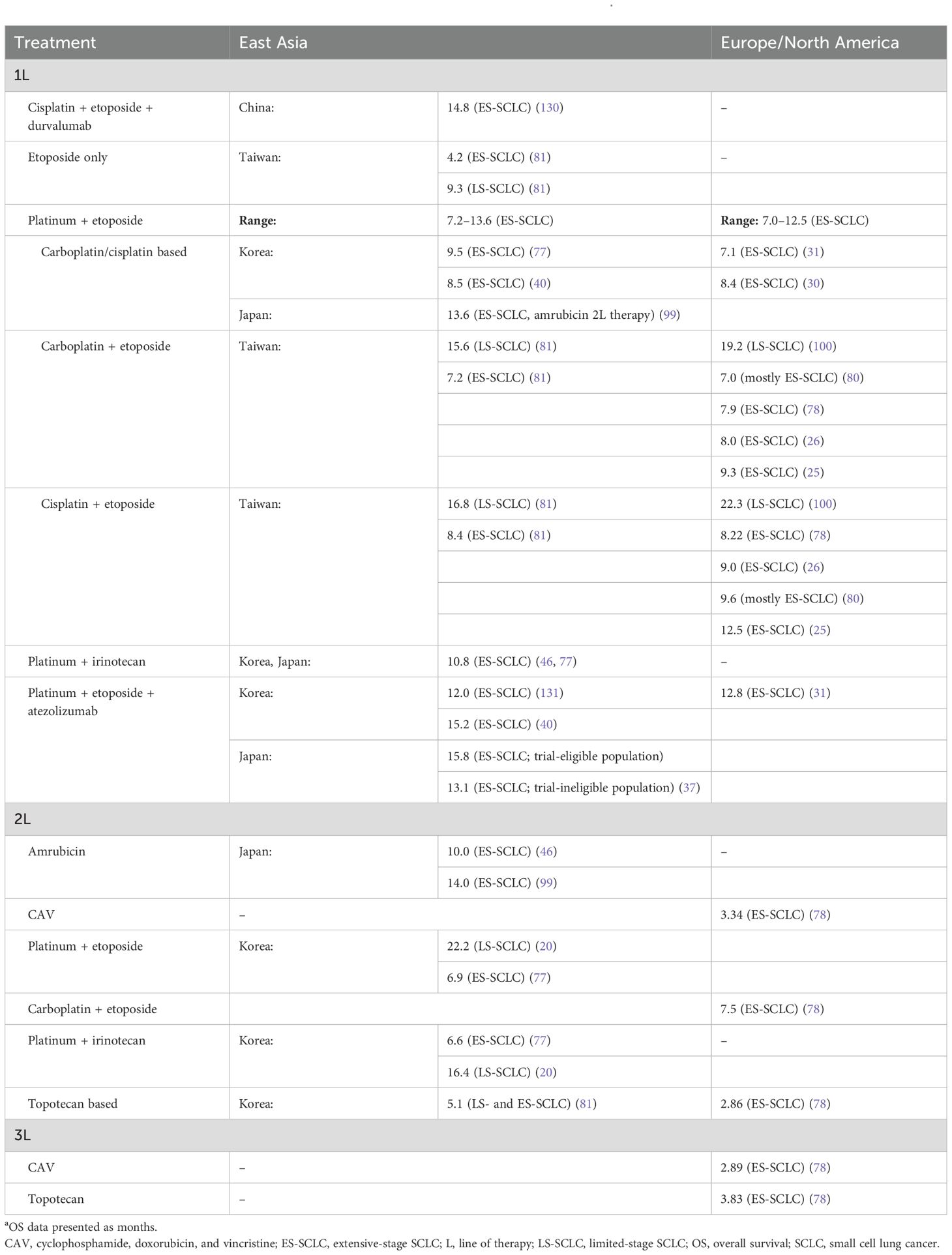
Table 5. OS outcomes from real-world studies in SCLC: East Asia versus Europe/North Americaa.
The median OS of patients with ES-SCLC who received a platinum-etoposide first-line therapy ranged from 7.2 to 13.6 months in East Asia, and from 7.0 to 12.5 months in Europe/North America (25, 26, 30, 31, 40, 77, 78, 80, 81, 99). Some of the studies from East Asia and Europe/North America indicated a favorable survival outcome with first-line cisplatin-etoposide therapy in ES-SCLC (25, 81). Based on a multicenter Spanish observational study in ES-SCLC, cisplatin-etoposide therapy (first line) significantly increased median OS compared with carboplatin-etoposide therapy (12.5 vs 9.3 months, P<0.001) (25). Similarly, a Taiwanese study noted significantly improved OS in patients with ES-SCLC receiving first-line cisplatin-etoposide versus in those receiving carboplatin-etoposide (8.4 vs 7.2 months; P = 0.002) (81). A real-world Korean study in LS-SCLC showed that cisplatin-etoposide second-line therapy significantly improved OS compared with irinotecan-platinum therapy (22.2 vs 16.4 months, P<0.0001) (20). In the US, a real-world study in LS-SCLC demonstrated that OS was significantly improved in patients receiving first-line cisplatin-etoposide versus carboplatin-etoposide (22.3 vs 19.2 months, P = 0.017) (100).
Real-world data on immunotherapy in ES-SCLC remain scarce (40). On the basis of limited data available from East Asia and Europe/North America, there is a favorable survival trend for first-line immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy in ES-SCLC when compared with chemotherapy alone (31, 40). In a Canadian study (N = 67), platinum-etoposide plus atezolizumab (first line) significantly prolonged OS compared with platinum-etoposide alone (12.8 vs 7.1 months; P = 0.01) (31). Similarly, a Korean study (N = 89) reported that first-line platinum-etoposide plus atezolizumab significantly improved OS compared with platinum-etoposide alone (15.2 vs 8.5 months; P = 0.047) (40).
Implications and future perspectives
Implications
Harmonization of SCLC guideline practices across Asian countries would require unified pan-Asian guideline recommendations for SCLC diagnosis and treatment that purposefully take into account the impact of ethnic, geographical, and socioeconomic factors (including differences in reimbursement policies) on clinical outcomes. Considering the complexity and diversity of these factors within Asia, the substantial regional collaboration and standardization efforts needed to create such guidance would present many challenges.
Ethnicity and smoking status are key patient characteristics that could potentially impact SCLC clinical outcomes across regions (12, 86). However, despite the differences in clinical outcomes observed between East Asia and Europe/North America, the outcomes themselves remain dismal across all regions. Although some studies indicate the potential impact of inter- and intra-population pharmacogenomic variability in treatment outcomes and/or toxicity, race- or ethnicity-based recommendations are under scrutiny, primarily because of “race” and “ethnicity” arguably being sociopolitical constructs rather than reflecting the true genotypic variations (89–91, 101, 102).
It is imperative, therefore, that researchers gain a better understanding of the impact genetic variations may have and what this may mean for the differential clinical management needed in SCLC. Many studies noted in this review do not report the ethnicity of the study population, and studies from some of the regions, particularly the US, have a mixed ethnicity-based population. Additionally, many regional studies were based on data from a single center or had small sample sizes, including subgroup analyses of clinical trials. Hence, it was challenging to draw any conclusive interpretations on the implications of ethnicity on SCLC clinical management. Moreover, data for East Asia might not be generalizable to the whole region, owing to scarce or no data from some of the East Asian countries, such as Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia. Our review also highlights a lack of prevalence and incidence data specific to SCLC across various regions, as most registries only provide overall data on lung cancer, and data for SCLC are often reported on the basis of estimations. Moreover, most of the real-world evidence studies noted in this review were conducted prior to the approval of immunotherapy in SCLC. The impact of immunotherapy-based treatments on survival outcomes in patients with SCLC remains to be robustly evaluated.
Emerging treatment options
A major challenge in the management of SCLC is the limited efficacy of existing treatments and the development of therapeutic resistance (103). Worldwide trends in SCLC survival analyses indicate that the prognosis of SCLC is still unsatisfactory, with no significant improvements in OS noted either in East Asia or in Europe/North America, thus highlighting the unmet need for the development of novel treatments (27, 97, 104, 105). Increased profiling of molecular subtypes in SCLC may be a promising avenue for the development of targeted therapies; however, further evidence is needed to support this personalized approach to treatment (57).
Delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3) has emerged as a promising candidate for targeted therapy in SCLC. As downregulation of major histocompatibility complex molecules, failure of antigen presentation, and tumor heterogeneity contribute to ICI resistance in SCLC, targeting alternative cell surface proteins provides a strategy for bypassing canonical antigen presentation pathways (1, 106, 107). DLL3-targeting therapeutic molecules currently in development include: T-cell engagers such as tarlatamab (half-life extended bispecific engager; phase 1–3 studies), Obrixtamig (BI764532; bispecific antibody; phase 1 study), and MK 6070 (HPN328; tri-specific recombinant protein; phase 1/2 study); and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) therapies such as DLL3-CAR-NK cells (anti-DLL3–transduced natural killer cells; phase 1 study) (1). Of note, the US Food and Drug Administration recently granted tarlatamab accelerated approval for ES-SCLC with disease progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy, following results of the DeLLphi-301 trial, which demonstrated objective response rates of 40% and OS of 14.3 months in the 10-mg dose group (108, 109). Based on a long-term follow-up of a median of 13.6 months, efficacy outcomes continued to be favorable in the 10-mg tarlatamab dose group (objective response rate, 40.4%; OS, 15.2 months) (110).
Other potential candidates for targeted therapy in SCLC are B7-H3, a member of the B7 ligand family, and seizure-related 6 homolog (SEZ6): both overexpressed in tumor cells with limited heterogeneity (111, 112). Examples of drugs currently in development include antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) such as ifinatamab deruxtecan (anti-B7-H3 ADC; NCT04145622) (111, 113). Additionally, data from East Asian populations, mostly from China, are emerging, including the ETER701 study (NCT04234607) investigating the combination of benmelstobart (a PD-L1 inhibitor) and anlotinib plus etoposide/carboplatin and the ASTRUM-005 trial (NCT04063163), investigating serplulimab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment in ES-SCLC (114–117).
Summary
International guidelines for SCLC are rooted in similar approaches, but with some East Asian guidelines falling short of reflecting the inherent regional/population-based variability. It must be noted that most clinical trials in oncology are still largely conducted in Europe/North America, with the vast majority of patient populations being White (118). Given the low representation of non-White ethnic populations in clinical trials, there is a need to move away from the “one-size-fits-all” approach often used in clinical trial design, to conduct more studies that represent diverse populations. Potential differences in the molecular profiles of patients with SCLC in East Asia and Europe/North America also warrant further study on novel therapeutic approaches (60). A realistic approach to this end might be for clinical trial designs to include umbrella trials based on molecular subtypes in SCLC. Other key areas of exploration include differences in the underlying pathophysiology in never-smokers versus smokers with SCLC to help guide optimal clinical management.
Finally, given that clinical trials are conducted in highly selective populations in a controlled environment, reported outcomes might not be sufficiently representative of those seen in routine clinical practice (119). Therefore, it is imperative to also gather real-world outcomes data. Differences noted in the real-world treatment patterns and survival outcomes in SCLC in this review may not yet be substantial enough to advocate changes in SCLC clinical management in East Asia versus Europe/North America. Socioeconomic factors are certainly critical components that decide the course of clinical management in SCLC; however, further studies are needed to gauge and improve medicine availability and affordability disparities, as well as treatment accessibility issues, noted in many East Asian countries (75).
Author contributions
C-LC: Resources, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RS: Validation, Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing. TM: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Conceptualization. PV: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Validation, Conceptualization. LT: Conceptualization, Validation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. CY: Resources, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HH: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Conceptualization. BC: Resources, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation. KX: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Validation. M-JA: Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Amgen Asia Holding Ltd (Hong Kong). The study sponsor played a role in the study design, preparation of the manuscript and decision to publish. Funding for medical writing support for this article was also provided by the study sponsor.
Acknowledgments
Medical writing support, including development of a draft outline and subsequent drafts in consultation with the authors, assembling tables and figures, collating author comments, copyediting, fact-checking, and referencing, was provided by Sreerekha Pillai, PhD, of Aspire Scientific Limited (Bollington, UK).
Conflict of interest
XK is an employee of Amgen, Inc., Singapore.
C-LC has received honoraria for lectures from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, Merck, MSD, Pfizer Roche and Takeda. RS has received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Pfizer; consulting fees for advisory board participation from AbbVie, Amgen, AnHeart, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, GSK, J INTS BIO, Janssen, Lily, Merck, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Puma, Roche, Sanofi, Taiho, Takeda, Thermo Fisher and Yuhan; and honoraria from Chugai. PV has received consulting fees for advisory board participation from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen-Cilag, Johnson & Johnson, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis and Pfizer; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Janssen-Cilag, Johnson & Johnson, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis and Pfizer; and clinical trial contracts personal/institution from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen-Cilag, Johnson & Johnson, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis, Revolutionary Medicine, Roche and Viracta Therapeutics. HH has received honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Chugai, Lilly, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical and Roche; and research funding from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical and Roche; and reports advisory board participation for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Chugai, ONO Pharmaceutical and Roche. M-JA has received consulting fees from Alpha Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Genexine, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, Voronoi and Yuhan; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck, MSD, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Roche, Takeda, and Yuhan. BC has received consulting fees from ABION, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, CJ, CureLogen, Cyrus Therapeutics, GI Cell, Guardant Health, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, HK inno.N, Imnewrun Biosciences, Janssen, Lilly, MedPacto, MSD, Novartis, Onegene Biotechnology, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, RandBio, Roche, Takeda and Yuhan; payment or honoraria for presentations from ASCO, AstraZeneca, ESMO, Guardant Health, IASLC, Korean Cancer Association, Korean Cancer Study Group, Korean Society of Medical Onoclogy, Korean Society of Thyroid-Head and Neck Surgery, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and The Chinese Thoracic Oncology Society; and research funding from AbbVie, ABION, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, BridgeBio, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Champions Oncology, CJ Bioscience, CJ Blossom Park, Cyrus Therapeutics, Dizal Pharma, Dong-A ST, Genexine, GI Cell, GI Innovation, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, Illumina, ImmuneOncia, Interpark Bio Convergence Corp., Janssen, J INTS BIO, Kanaph Therapeutics, LG Chem, Lilly, MOGAM Institute, MSD, Novartis, Nuvalent, Oncternal Therapeutics, Ono Pharmaceutical, Oscotec, Regeneron, Therapex, Vertical Bio AG and Yuhan Corporation; owns royalties in Champions Oncology, Crown Bioscience, Imagen and PearlRiver Bio GmbH; owns stock in BridgeBio, Cyrus Therapeutics, Gencurix, Interpark Bio Convergence Corp., J INTS BIO, Kanaph Therapeutics and TheraCanVac; is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board for Amgen, BridgeBio, Cyrus Therapeutics, Gilead, Guardant Health, Kanaph Therapeutics, Oscotec, J INTS BIO and Therapex; is a member of the board of directors at J INTS BIO; is an employee of Yonsei University Health System; and is a founder of DAAN Biotherapeutics. LT has received consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca and Roche; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eisai, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Roche and Takeda; and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eisai, MSD and Roche. TM has received grants or contracts from AstraZeneca, BMS, G1 Therapeutics, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, SFJ Pharmaceuticals, Takeda and XCovery all paid to institution; consulting fees from AbbVie; ACEA Pharma, Adagene, Alentis Therapeutics AG, Alpha Biopharma, Amgen, Amoy Diagnostics, AnHeart Therapeutics, AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals Ltd, BeiGene, BerGenBio ASA, Berry Oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Blueprint Medicines, BridgeBio, BMS, Bowtie Life Insurance, BridgeBio, Covidien, C4 Therapeutics, Cirina, CStone Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, D3 Bio, Da Volterra, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Elevation Oncology, Erasca, Fishawack Facilitate Ltd, G1 Therapeutics, geneDecode Co., Ltd, Gilead, GLG, Gritstone Oncology, Guardant Health, Hengrui Therapeutics, HiberCell, HUTCHMED, Ignyta, Illumina, Imagene AI, Incyte, Inivata Ltd, InxMed Hong Kong Ltd, IQVIA, Janssen, LakeShore Biotech Ltd, Lilly, Lunit USA, Loxo Oncology, Lucence, Medscape LLC/WebMD, Medtronic, Merck Serono, MSD, Mirati Therapeutics, MiRXES, MoreHealth, Novartis, Novocure GmbH, Ningbo NewBay Technology Development Co., Ltd, Omega Therapeutics, OrigiMed, OSE Immunotherapeutics, PeerVoice, Phanes Therapeutics, Pfizer, prIME Oncology, Prenetics, Puma Biotechnology, Qiming Development HK Ltd, Regen Medtech Ltd, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Roche/Genentech, Roche Pharmaceuticals/Diagnostics/Foundation One, Sanofi-Aventis, Schrödinger, Inc., Seagen International GmbH, SFJ Pharmaceuticals, Simcere, Synergy Research, Summit Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceuticals Hong Kong Ltd, Tigermed, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Virtus Medical Group, Xencor, Yuhan; has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from ACEA Pharma, Alpha Biopharma, Amgen, Amoy Diagnostics, AstraZeneca before 1/1/19, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Daz Group, Fishawack Facilitate Ltd, inMed Communications, Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, Jiahui Holdings Co. Ltd, LiangYiHui Healthcare, Lilly, Lucence, MD Health Brazil, Medscape LLC, Merck Pharmaceutical HK Ltd, MiRXES, MSD, Novartis, OrigiMed, Permanyer, PeerVoice, Physicians’ Education Resource, Pfizer, prIME Oncology, Research to Practice, Roche Pharmaceuticals/Diagnostics/Foundation One, Sanofi-Aventis, Shanghai BeBirds Translation & Consulting, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Takeda Oncology and Touch Independent Medical Education; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel (personal or paid to institution) from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Liangyihui, MiRXES, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Zai Lab; reports participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for AbbVie, ACEA Pharma, Alentis Therapeutics AG, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BerGenBio ASA, Berry Oncology, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bowtie Life Insurance, C4 Therapeutics, Covidien, CStone Pharmaceuticals, Curio Science, D3 Bio, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Erasca, Fishawack Facilitate Ltd., G1 Therapeutics, Gilead, Gritstone Oncology, Guardant Health, geneDecode Co. Ltd. unpaid, Hengrui Therapeutics, HutchMed, Ignyta, Incyte, Imagene AI., Inivata, IQVIA, Janssen, Lakeshore Biotech, Lily, Loxo-Oncology, Lunit, Merck Serono, MSD, Mirati Therapeutics., MiRXES, Novartis, OrigiMed, Phanes Therapeutics, Pfizer, Prenetics, Puma Biotechnology, Roche/Genentech, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi-Aventis R&D, SFJ Pharmaceutical, Simcere of America, Simcere Zaiming, Takeda, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Virtus Medical Group, Xencor, Yuhan; owns stock or stock options in Alentis Therapeutics AG, AstraZeneca, Aurora Tele-Oncology Ltd, Biolidics Ltd, Bowtie Life Insurance, D3 Bio, HutchMed, Insighta, LakeShore Biotech Ltd, Loxo Oncology, Lunit, Phanes Therapeutics, Prenetics, Virtus Medical Group and Yinson Production Capital Pte. Ltd; and a leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group, paid or unpaid, for AstraZeneca, Aurora, HutchMed, Epoch Biosciences unpaid and Insighta XK is an employee of Amgen, Inc., Singapore.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Amgen Asia Holding Ltd (Hong Kong). The study sponsor played a role in the study design, preparation of the manuscript and decision to publish. Funding for medical writing support for this article was also provided by the study sponsor.
The handling editor AA declared a past co-authorship with the authors RS, BC.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
ADC: antibody–drug conjugate
AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer
ASCL1: Achaete-scute homolog 1
CAR: chimeric antigen receptor
CT: computed tomography
DLL3: delta-like ligand 3
ECOG PS: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status
ES: extensive-stage
ESMO: European Society for Medical Oncology
HR: hazard ratio
ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor
IHC: immunohistochemistry
INSM1: insulinoma-associated protein 1
LS: limited-stage
NCAM/CD56: neural cell adhesion molecule
NCCN®: National Comprehensive Cancer Network®
NE: neuroendocrine
NK: natural killer
NSCLC: non–small cell lung cancer
OS: overall survival
PCI: prophylactic cranial irradiation
PD-1: programmed cell death protein 1
PD-L1: programmed cell death ligand 1
PFS: progression-free survival
RB1: retinoblastoma 1
SABR: stereotactic ablative radiotherapy
SBRT: stereotactic body radiation therapy
SCLC: small cell lung cancer
SEZ6: seizure-related 6 homolog
TMB: tumor mutational burden
TNM: Tumor, Node, Metastasis
TP53: tumor protein 53
US: United States
VA: Veterans Administration
WHO: World Health Organization.
References
1. Rudin CM, Reck M, Johnson ML, Blackhall F, Hann CL, Yang JC, et al. Emerging therapies targeting the delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3) in small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:66. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01464-y
2. Wells LE, Cohen S, Brennan B, Banerjee M, and Kalemkerian GP. Epidemiology of SCLC in the United States from 2000 to 2019: A study utilizing the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results registry. JTO Clin Res Rep. (2025) 6:100799. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2025.100799
3. Uprety D, Seaton R, Niroula A, Hadid T, Parikh K, and Ruterbusch JJ. Trends in the incidence and survival outcomes in patients with small cell lung cancer in the United States: An analysis of the SEER database. Cancer Med. (2025) 14:e70608. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70608
4. Zhang Y, Vaccarella S, Morgan E, Li M, Etxeberria J, Chokunonga E, et al. Global variations in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype in 2020: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. (2023) 24:1206–18. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00444-8
5. Rudin CM, Brambilla E, Faivre-Finn C, and Sage J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:3. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00235-0
6. Basumallik N and Agarwal M. Small cell lung cancer. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL (2023).
7. Pleasance ED, Stephens PJ, O’Meara S, McBride DJ, Meynert A, Jones D, et al. A small-cell lung cancer genome with complex signatures of tobacco exposure. Nature. (2010) 463:184–90. doi: 10.1038/nature08629
8. Alexandrov LB, Ju YS, Haase K, Van Loo P, Martincorena I, Nik-Zainal S, et al. Mutational signatures associated with tobacco smoking in human cancer. Science. (2016) 354:618–22. doi: 10.1126/science.aag0299
9. George J, Lim JS, Jang SJ, Cun Y, Ozretić L, Kong G, et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature. (2015) 524:47–53. doi: 10.1038/nature14664
10. Sivakumar S, Moore JA, Montesion M, Sharaf R, Lin DI, Colón CI, et al. Integrative analysis of a large real-world cohort of small cell lung cancer identifies distinct genetic subtypes and insights into histologic transformation. Cancer Discov. (2023) 13:1572–91. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-22-0620
11. Marignol L. Notch signalling: the true driver of small cell lung cancer? Transl Cancer Res. (2017) 6:S1191–6. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2017.09.22
12. Wang Q, Gümüş ZH, Colarossi C, Memeo L, Wang X, Kong CY, et al. SCLC: epidemiology, risk factors, genetic susceptibility, molecular pathology, screening, and early detection. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:31–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.10.002
13. Rudin CM, Poirier JT, Byers LA, Dive C, Dowlati A, George J, et al. Molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer: a synthesis of human and mouse model data. Nat Rev Cancer. (2019) 19:289–97. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0133-9
14. Schwendenwein A, Megyesfalvi Z, Barany N, Valko Z, Bugyik E, Lang C, et al. Molecular profiles of small cell lung cancer subtypes: therapeutic implications. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2021) 20:470–83. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.02.004
15. Zhao H, Ren D, Liu H, and Chen J. Comparison and discussion of the treatment guidelines for small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. (2018) 9:769–74. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12765
16. Wu YL, Planchard D, Lu S, Sun H, Yamamoto N, Kim DW, et al. Pan-Asian adapted Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a CSCO-ESMO initiative endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS.Ann oncol. (2019) 30:171–210. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy554
17. Pesch B, Kendzia B, Gustavsson P, Jöckel KH, Johnen G, Pohlabeln H, et al. Cigarette smoking and lung cancer–relative risk estimates for the major histological types from a pooled analysis of case-control studies. Int J Cancer. (2012) 131:1210–9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27339
18. Li D, Xu X, Liu J, Liang D, Shi J, Li S, et al. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) incidence and trends vary by gender, geography, age, and subcategory based on population and hospital cancer registries in Hebei, China (2008-2017). Thorac Cancer. (2020) 11:2087–93. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13412
19. Toh CK, Hee SW, Lim WT, Leong SS, Fong KW, Yap SP, et al. Survival of small-cell lung cancer and its determinants of outcome in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singap. (2007) 36:181–8. doi: 10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.V36N3p181
20. Kim SR, Hong JH, Sung S-Y, Kim YH, Chun SH, Lee HW, et al. Efficacy of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for patients with limited-disease small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:340. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08082-2
21. Dingemans A-MC, Früh M, Ardizzoni A, Besse B, Faivre-Finn C, Hendriks LE, et al. Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up☆. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:839–53. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.03.207
22. Abdel-Rahman O. Changing epidemiology of elderly small cell lung cancer patients over the last 40 years; a SEER database analysis. Clin Respir J. (2018) 12:1093–9. doi: 10.1111/crj.12632
23. Islami F, Torre LA, and Jemal A. Global trends of lung cancer mortality and smoking prevalence. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2015) 4:327–38. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.08.04
24. Chen J, Qi Y, Wampfler JA, Jatoi A, Garces YI, Busta AJ, et al. Effect of cigarette smoking on quality of life in small cell lung cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. (2012) 48:1593–601. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.002
25. Franco F, Carcereny E, Guirado M, Ortega AL, López-Castro R, Rodríguez-Abreu D, et al. Epidemiology, treatment, and survival in small cell lung cancer in Spain: data from the Thoracic Tumor Registry. PloS One. (2021) 16:e0251761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251761
26. Longo V, Pizzutilo P, Catino A, Montrone M, Pesola F, Marerch I, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: an Italian real-world retrospective analysis of 244 patients treated over the last decade. Thorac Cancer. (2022) 13:3486–95. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14712
27. Blackhall F, Girard N, Livartowski A, McDonald LA-O, Roset MA-O, Lara N, et al. Treatment patterns and outcomes among patients with small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) in Europe: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e052556. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052556
28. Thomas A, Mian I, Tlemsani C, Pongor L, Takahashi N, Maignan K, et al. Clinical and genomic characteristics of small cell lung cancer in never smokers: results from a retrospective multicenter cohort study. Chest. (2020) 158:1723–33. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.068
29. Stratmann JA, Timalsina R, Atmaca A, Rosery V, Frost N, Alt J, et al. Clinical predictors of survival in patients with relapsed/refractory small-cell lung cancer treated with checkpoint inhibitors: a German multicentric real-world analysis. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2022) 14:17588359221097191. doi: 10.1177/17588359221097191
30. Rittberg R, Leung B, Al-Hashami Z, and Ho C. Real-world eligibility for platinum doublet plus immune checkpoint inhibitors in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1002385. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1002385
31. Elegbede AA, Gibson AJ, Fung AS, Cheung WY, Dean ML, Bebb DG, et al. A real-world evaluation of atezolizumab plus platinum-etoposide chemotherapy in patients with extensive-stage SCLC in Canada. JTO Clin Res Rep. (2021) 2:100249. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100249
32. Liu X, Jiang T, Li W, Li X, Zhao C, Shi J, et al. Characterization of never-smoking and its association with clinical outcomes in Chinese patients with small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2018) 115:109–15. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.11.022
33. Shi Y, Xing P, Fan Y, Zhang X, Hu C, Wang C, et al. Current small cell lung cancer treatment in China. Thorac Cancer. (2015) 6:233–8. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12218
34. Guo J, Shen L, Ren Z, Liu Y, and Liang C. Long-term results of postoperative unsuspected small cell lung cancer on real-world data. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:1256. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10341-9
35. Zheng Y, Tan K, Wang A, Lu X, Dong H, Li J, et al. Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes in 157 patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: real-world evidence from a single-center retrospective study. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1287628. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1287628
36. Liu L, Wei J, Teng F, Zhu Y, Xing P, Zhang J, et al. Clinicopathological features and prognostic analysis of 247 small cell lung cancer with limited-stage after surgery. Hum Pathol. (2021) 108:84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.11.007
37. Fujimoto D, Morimoto T, Tamiya M, Hata A, Matsumoto H, Nakamura A, et al. Outcomes of chemoimmunotherapy among patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer according to potential clinical trial eligibility. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e230698. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.0698
38. Sonehara K, Tateishi K, Fukushima T, Komatsu M, Yamamoto H, Koizumi T, et al. The efficacy of amrubicin third-line chemotherapy in patients with relapsed extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective and historical study in a single institute. Thorac Cancer. (2019) 10:1805–11. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13150
39. Torasawa M, Horinouchi H, Nomura S, Igawa S, Asai M, Ishii H, et al. Reconsidering the cutoff value for sensitive and refractory relapses in extensive-stage SCLC in the era of immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. (2024) 19:325–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.09.1446
40. Kim SH, Jo EJ, Mok J, Lee K, Kim KU, Park HK, et al. Real-world evaluation of atezolizumab and etoposide-carboplatin as a first-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Korean J Intern Med. (2023) 38:218–25. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2022.361
41. Kang HS, Lim JU, Yeo CD, Park CK, Lee SH, and Kim SJ. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients with nonsmoking small cell lung cancer in Korea. BMC Pulm Med. (2022) 22:200. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01989-x
42. Choi CM, Kim HC, Jung CY, Cho DG, Jeon JH, Lee JE, et al. Report of the korean Association of Lung Cancer Registry (KALC-R), 2014. Cancer Res Treat. (2019) 51:1400–10. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.704
43. Tseng J-S, Chiang C-J, Chen K-C, Zheng Z-R, Yang T-Y, Lee W-C, et al. Association of smoking with patient characteristics and outcomes in small cell lung carcinoma, 2011-2018. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e224830. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.4830
44. Sukauichai S, Tovanabutra C, Tangchewinsirikul T, Wanglikitkoon S, Chomprasert K, Namkanitsorn T, et al. Survival of patients with small-cell lung cancer treated at tertiary hospitals in the east of Thailand, 2007-2016: a retrospective study. Adv Lung Cancer. (2019) 8:1–14. doi: 10.4236/alc.2019.81001
45. Huang L and Shi Y. Prognostic value of pretreatment smoking status for small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Thorac Cancer. (2020) 11:3252–9. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13661
46. Okuma HS, Horinouchi H, Kitahara S, Asao T, Sunami K, Goto Y, et al. Comparison of amrubicin and weekly cisplatin/etoposide/irinotecan in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. (2017) 18:234–40.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2016.09.005
47. Huang R, Wei Y, Hung RJ, Liu G, Su L, Zhang R, et al. Associated links among smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and small cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium. EBioMedicine. (2015) 2:1677–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.09.031
48. Pelosof L, Ahn C, Gao A, Horn L, Madrigales A, Cox J, et al. Proportion of never-smoker non-small cell lung cancer patients at three diverse institutions. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2017) 109:djw295. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw295
49. Sun JM, Choi YL, Ji JH, Ahn JS, Kim KM, Han J, et al. Small-cell lung cancer detection in never-smokers: clinical characteristics and multigene mutation profiling using targeted next-generation sequencing. Ann Oncol. (2015) 26:161–6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu504
50. Ou SH, Ziogas A, and Zell JA. Prognostic factors for survival in extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC): the importance of smoking history, socioeconomic and marital statuses, and ethnicity. J Thorac Oncol. (2009) 4:37–43. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31819140fb
51. Varghese AM, Zakowski MF, Yu HA, Won HH, Riely GJ, Krug LM, et al. Small-cell lung cancers in patients who never smoked cigarettes. J Thorac Oncol. (2014) 9:892–6. doi: 10.1097/jto.0000000000000142
52. Zhou F and Zhou C. Lung cancer in never smokers-the East Asian experience. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2018) 7:450–63. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2018.05.14
53. Baine MK, Hsieh MS, Lai WV, Egger JV, Jungbluth AA, Daneshbod Y, et al. SCLC subtypes defined by ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3, and YAP1: a comprehensive immunohistochemical and histopathologic characterization. J Thorac Oncol. (2020) 15:1823–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.09.009
54. Hwang S, Hong TH, Kim HK, Choi YS, Zo JI, Shim YM, et al. Whole-section landscape analysis of molecular subtypes in curatively resected small cell lung cancer: clinicopathologic features and prognostic significance. Mod Pathol. (2023) 36:100184. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2023.100184
55. Chiang CL, Huang HC, Luo YH, Shen CI, Chao HS, Tseng YH, et al. Clinical utility of immunohistochemical subtyping in patients with small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2024) 188:107473. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.107473
56. Qi J, Zhang J, Liu N, Zhao L, and Xu B. Prognostic implications of molecular subtypes in primary small cell lung cancer and their correlation with cancer immunity. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:779276. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.779276
57. Park S, Hong TH, Hwang S, Heeke S, Gay CM, Kim J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of transcription factor-based molecular subtypes and their correlation to clinical outcomes in small-cell lung cancer. EBioMedicine. (2024) 102:105062. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105062
58. Ding XL, Su YG, Yu L, Bai ZL, Bai XH, Chen XZ, et al. Clinical characteristics and patient outcomes of molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). World J Surg Oncol. (2022) 20:54. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02528-y
59. Shirasawa M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi K, Takigami A, Takayanagi D, Imabayashi T, et al. Identification of inflamed-phenotype of small cell lung cancer leading to the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 antibody and chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. (2023) 179:107183. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107183
60. Lin A, Zhou N, Zhu W, Zhang J, Wei T, Guo L, et al. Genomic and immunological profiles of small-cell lung cancer between East Asians and Caucasian. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:173. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02588-w
61. Ganti AKP, Loo BW, Bassetti M, Blakely C, Chiang A, D’Amico TA, et al. Small cell lung cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2021) 19:1441–64. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0058
62. Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Small Cell Lung Cancer V.2.2026 © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org, in: NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way (2025).
63. The National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. (2011) 365:395–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
64. The Japan Lung Cancer Society. Lung Cancer Treatment Guidelines – including Malignant pleural mesothelioma and thymic tumors (2024 edition) . Available online at: https://www.haigan.gr.jp/guideline/2024/index.html (Accessed September 26, 2025).
65. Taiwan Society of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine. Consensus on drug treatment for advanced lung cancer in Taiwan . Available online at: https://www.tspccm.org.tw/media/12666?fbclid=IwAR1FsToHyMpGruyGwupfwIqnaDfDJdI-QZmiB_RrfmRUHPMOzWTjzCK_D1M (Accessed April 23, 2025).
66. Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Guidelines of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology: small-cell lung cancer. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House (2024).
67. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol. (2015) 10:1243–60. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630
68. Ericson Lindquist K, Ciornei C, Westbom-Fremer S, Gudinaviciene I, Ehinger A, Mylona N, et al. Difficulties in diagnostics of lung tumours in biopsies: an interpathologist concordance study evaluating the international diagnostic guidelines. J Clin Pathol. (2022) 75:302–9. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-207257
69. Campana D, Nori F, Piscitelli L, Morselli-Labate AM, Pezzilli R, Corinaldesi R, et al. Chromogranin A: is it a useful marker of neuroendocrine tumors? J Clin Oncol. (2007) 25:1967–73. doi: 10.1200/jco.2006.10.1535
70. Melosky BL, Leighl NB, Dawe D, Blais N, Wheatley-Price PF, Chu QS, et al. Canadian consensus recommendations on the management of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:6289–315. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30070465
71. Oncology Society of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Medical Association Publishing House. Chinese Medical Association Guideline for clinical diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer (2023 edition). Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. (2023) 45:539–74. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20230510-00200
72. Cheng Y, Spigel David R, Cho Byoung C, Laktionov Konstantin K, Fang J, Chen Y, et al. Durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2024) 391:1313–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2404873
73. Kalemkerian GP, Khurshid H, and Ismaila N. Systemic Therapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Guideline Expert Panel. Systemic therapy for small cell lung cancer: ASCO guideline rapid recommendation update. J Clin Oncol. (2025) 43:101–5. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-02245
74. Meriggi F. Second-line treatment options for small-cell lung cancer: a light at the end of the tunnel. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16:255. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020255
75. Eniu A, Cherny NI, Bertram M, Thongprasert S, Douillard JY, Bricalli G, et al. Cancer medicines in Asia and Asia-Pacific: what is available, and is it effective enough? ESMO Open. (2019) 4:e000483. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2018-000483
76. DiBonaventura MD, Shah-Manek B, Higginbottom K, Penrod JR, and Yuan Y. Adherence to recommended clinical guidelines in extensive disease small-cell lung cancer across the US, Europe, and Japan. Ther Clin Risk Manage. (2019) 15:355–66. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.S183216
77. Lee JS, Kim S, Sung SY, Kim YH, Lee HW, Hong JH, et al. Treatment outcomes of 9,994 patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer from a retrospective nationwide population-based cohort in the Korean HIRA database. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:546672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.546672
78. O’Sullivan DE, Cheung WY, Syed IA, Moldaver D, Shanahan MK, Bebb DG, et al. Real-world treatment patterns, clinical outcomes, and health care resource utilization in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in Canada. Curr Oncol. (2021) 28:3091–103. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28040270
79. Karve SJ, Price GL, Davis KL, Pohl GM, Smyth EN, and Bowman L. Comparison of demographics, treatment patterns, health care utilization, and costs among elderly patients with extensive-stage small cell and metastatic non-small cell lung cancers. BMC Health Serv Res. (2014) 14:555. doi: 10.1186/s12913-014-0555-8
80. Debieuvre D, Dayen C, Dixmier A, Pau D, Sibley-Revelat A, Greenwood W, et al. FRESC: French Real world Extensive stage SCLC Cohorts: a retrospective study on patient characteristics and treatment strategy based on KBP-2010. Lung Cancer. (2022) 164:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.11.013
81. Chiang CL, Hsieh WT, Tang CH, Sheu ML, and Chen YM. Treatment patterns and survival in patients with small cell lung cancer in Taiwan. J Chin Med Assoc. (2021) 84:772–7. doi: 10.1097/jcma.0000000000000576
82. Reguart N, Pérol M, Cortinovis D, Puntis S, Öhrling K, Archangelidi O, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of treatment patterns in small-cell lung cancer in five European countries. Future Oncol. (2024) 20:1151–64. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-1315
83. Chen H, Ma X, Liu J, Yang Y, Fang Y, Wang L, et al. Clinical outcomes of atezolizumab in combination with etoposide/platinum for treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a real-world, multicenter, retrospective, controlled study in China. Chin J Cancer Res. (2022) 34:353–64. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2022.04.04
84. Soo RA, Kawaguchi T, Loh M, Ou SH, Shieh MP, Cho BC, et al. Differences in outcome and toxicity between Asian and caucasian patients with lung cancer treated with systemic therapy. Future Oncol. (2012) 8:451–62. doi: 10.2217/fon.12.25
85. Li LJ, Chong Q, Wang L, Cher GB, and Soo RA. Different treatment efficacies and side effects of cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Thorac Dis. (2020) 12:3785–95. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.08.63
86. Zhou K, Shi H, Chen R, Cochuyt JJ, Hodge DO, Manochakian R, et al. Association of race, socioeconomic factors, and treatment characteristics with overall survival in patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e2032276. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32276
87. Roof L, Wei W, Tullio K, Pennell NA, and Stevenson JP. Impact of socioeconomic factors on overall survival in SCLC. JTO Clin Res Rep. (2022) 3:100360. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100360
88. Lohinai Z, Bonanno L, Aksarin A, Pavan A, Megyesfalvi Z, Santa B, et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is prognostic in early stage resected small-cell lung cancer. PeerJ. (2019) 7:e7232. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7232
89. Lara PN Jr., Chansky K, Shibata T, Fukuda H, Tamura T, Crowley J, et al. Common arm comparative outcomes analysis of phase 3 trials of cisplatin + irinotecan versus cisplatin + etoposide in extensive stage small cell lung cancer: final patient-level results from Japan Clinical Oncology Group 9511 and Southwest Oncology Group 0124. Cancer. (2010) 116:5710–5. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25532
90. Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, Negoro S, Sugiura T, Yokoyama A, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2002) 346:85–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa003034
91. Lara PN Jr., Natale R, Crowley J, Lenz HJ, Redman MW, Carleton JE, et al. Phase III trial of irinotecan/cisplatin compared with etoposide/cisplatin in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: clinical and pharmacogenomic results from SWOG S0124. J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:2530–5. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.1061
92. Goldman JW, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:51–65. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30539-8
93. Hotta K, Nishio M, Saito H, Okamoto I, Nakahara Y, Hayashi H, et al. First-line durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: CASPIAN Japan subgroup analysis. Int J Clin Oncol. (2021) 26:1073–82. doi: 10.1007/s10147-021-01899-8
94. Nishio M, Ji JH, Hotta K, Chiu C, Lee J, Azuma K, et al. (2019). Overall survival with first-line durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide in patients with ES-SCLC in CASPIAN: subgroup findings from Asia, in: ESMO Asia, Singapore. Annals of Oncology. 30.
95. Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczęsna A, Havel L, Krzakowski M, Hochmair MJ, et al. First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:2220–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809064
96. Nishio M, Sugawara S, Atagi S, Akamatsu H, Sakai H, Okamoto I, et al. Subgroup analysis of Japanese patients in a phase III study of atezolizumab in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (IMpower133). Clin Lung Cancer. (2019) 20:469–76.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.07.005
97. Oze IA-O, Ito HA-O, Nishino Y, Hattori M, Nakayama T, Miyashiro I, et al. Trends in small-cell lung cancer survival in 1993–2006 based on population-based cancer registry data in Japan. J Epidemiol. (2019) 29:347–53. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20180112
98. Cancer.org and Lung Cancer Survival Rates. Available online at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html (Accessed October 18, 2024).
99. Uda S, Yamada T, Yoshimura A, Goto Y, Yoshimine K, Nakamura Y, et al. Clinical impact of amrubicin monotherapy in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer: a multicenter retrospective study. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2022) 11:1847–57. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-160
100. Sama S, Kerrigan K, Sinnott JA, Puri S, Akerley W, Haaland B, et al. Real-world comparison of survival outcomes with cisplatin versus carboplatin in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Res Commun. (2023) 35:100686. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2023.100686
101. Goodman CW and Brett AS. Race and pharmacogenomics—personalized medicine or misguided practice? JAMA. (2021) 325:625–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.25473
102. Mersha TB and Beck AF. The social, economic, political, and genetic value of race and ethnicity in 2020. Hum Genomics. (2020) 14:37. doi: 10.1186/s40246-020-00284-2
103. Moliner L, Zhang B, Lamberti G, Ardizzoni A, Byers LA, and Califano R. Novel therapeutic strategies for recurrent SCLC. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2023) 186:104017. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104017
104. Khakwani A, Rich AL, Tata LJ, Powell HA, Stanley RA, Baldwin DR, et al. Small-cell lung cancer in England: trends in survival and chemotherapy using the National Lung Cancer Audit. PloS One. (2014) 9:e89426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089426
105. Wang S, Tang J, Sun T, Zheng X, Li J, Sun H, et al. Survival changes in patients with small cell lung cancer and disparities between different sexes, socioeconomic statuses and ages. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1339. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01571-0
106. Tendler S and Rudin CM. Tarlatamab: new star on the horizon for small-cell lung cancer? J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:2877–80. doi: 10.1200/jco.23.00148
107. Furuta M, Kikuchi H, Shoji T, Takashima Y, Kikuchi E, Kikuchi J, et al. DLL3 regulates the migration and invasion of small cell lung cancer by modulating Snail. Cancer Sci. (2019) 110:1599–608. doi: 10.1111/cas.13997
108. Ahn MJ, Cho BC, Felip E, Korantzis I, Ohashi K, Majem M, et al. Tarlatamab for patients with previously treated small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389:2063–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2307980
109. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to tarlatamab-dlle for extensive stage small cell lung cancer. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-tarlatamab-dlle-extensive-stage-small-cell-lung-cancer (Accessed October 18, 2024).
110. Sands J, Cho BC, Ahn MJ, Reck M, Bustamante-Alvarez J, Hummel HD, et al. OA10.03 tarlatamab sustained clinical benefit and safety in previously treated SCLC: DeLLphi-301 phase 2 extended follow-up. J Thorac Oncol. (2024) 19:S30–1. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2024.09.057
111. Patel SR and Das M. Small cell lung cancer: emerging targets and strategies for precision therapy. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:4016. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164016
112. Kontos F, Michelakos T, Kurokawa T, Sadagopan A, Schwab JH, Ferrone CR, et al. B7-H3: an attractive target for antibody-based immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:1227–35. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-2584
113. ClinicalTrials.gov. Study of ifinatamab deruxtecan (DS-7300a, I-DXd) in participants with advanced solid malignant tumors. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04145622 (Accessed October 18, 2024).
114. Cheng Y, Chen J, Zhang W, Xie C, Hu Q, Zhou N, et al. Benmelstobart, anlotinib and chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2967–76. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03132-1
115. Cheng Y, Han L, Wu L, Chen J, Sun H, Wen G, et al. Effect of first-line serplulimab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: the ASTRUM-005 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2022) 328:1223–32. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.16464
116. ClinicalTrials.gov. A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled phase iii study to investigate efficacy and safety of HLX10 + chemotherapy (carboplatin- etoposide) in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04063163 (Accessed October 18, 2024).
117. ClinicalTrials.gov. A study of TQB2450 or placebo combined with anlotinib, etoposide and carboplatin versus etoposide and carboplatin in subjects with extensive small cell lung cancer (ETER701). Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04234607 (Accessed October 18, 2024).
118. Camidge DR, Park H, Smoyer KE, Jacobs I, Lee LJ, Askerova Z, et al. Race and ethnicity representation in clinical trials: findings from a literature review of phase I oncology trials. Future Oncol. (2021) 17:3271–80. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-1262
119. Kim HS, Lee S, and Kim JH. Real-world evidence versus randomized controlled trial: clinical research based on electronic medical records. J Korean Med Sci. (2018) 33:e213. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e213
120. Torres-Durán M, Curiel-García MT, Ruano-Ravina A, Provencio M, Parente-Lamelas I, Hernández-Hernández J, et al. Small-cell lung cancer in never-smokers. ESMO Open. (2021) 6:100059. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100059
121. National Medical Products Administration, China. Available online at: https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/drugs.html (Accessed May 15, 2024).
122. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Available online at: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/ (Accessed May 15, 2024).
123. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, Republic of Korea. Available online at: https://www.mfds.go.kr/eng/index.do (Accessed May 15, 2024).
124. Health Sciences Authority, Singapore. Available online at: https://www.hsa.gov.sg/. (Accessed May 15, 2024).
125. National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency, Ministry of Health Malaysia. Available online at: https://www.npra.gov.my/index.php/en/ (Accessed May 15, 2024).
126. Taiwan Food and Drug Administration. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov.tw/eng/ (Accessed May 15, 2024).
127. Thailand Food and Drug Administration. Available online at: https://en.fda.moph.go.th/ (Accessed May 15, 2024).
128. US Food and Drug Administration. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/ (Accessed May 15, 2024).
129. European Medicines Agency. Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/homepage (Accessed May 15, 2024).
130. Cheng Y, Wang J, Yao W, Yu Y, Zang A, Cao L, et al. 519P Final results and subgroup analysis of ORIENTAL: a phase IIIB study of durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of Chinese patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:S1673. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.598
131. Lee S, Shim HS, Ahn BC, Lim SM, Kim HR, Cho BC, et al. Efficacy and safety of atezolizumab, in combination with etoposide and carboplatin regimen, in the first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: a single-center experience. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:1093–101. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03052-w
Keywords: Asian countries, East Asia, diagnosis, small cell lung cancer, survival outcomes, treatment guidelines, treatment patterns
Citation: Chiang C-L, Soo RA, Mok T, Voon PJ, Thamlikitkul L, Cheng Y, Horinouchi H, Cho BC, Xu KL and Ahn M-J (2025) A comparison of clinical guidelines, treatment characteristics and outcomes in small cell lung cancer between East Asia and Europe/North America. Front. Oncol. 15:1646608. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1646608
Received: 31 July 2025; Accepted: 08 October 2025;
Published: 27 October 2025.
Edited by:
Alfredo Addeo, Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève (HUG), SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Jun Hyeok Lim, Inha University, Republic of KoreaGyörgy – Losonczy, Semmelweis University, Hungary
Copyright © 2025 Chiang, Soo, Mok, Voon, Thamlikitkul, Cheng, Horinouchi, Cho, Xu and Ahn. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Myung-Ju Ahn, c2lsa2FobkBza2t1LmVkdQ==
†ORCID: Myung-Ju Ahn, orcid.org/0000-0002-5740-9654
 Chi-Lu Chiang
Chi-Lu Chiang Ross Andrew Soo3
Ross Andrew Soo3 Pei Jye Voon
Pei Jye Voon Ying Cheng
Ying Cheng Hidehito Horinouchi
Hidehito Horinouchi Byong Chul Cho
Byong Chul Cho Myung-Ju Ahn
Myung-Ju Ahn