- The Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, West China Second University Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Introduction: Vulvar Paget’s disease (VPD) is a rare vulvar malignant tumor commonly observed in postmenopausal females. VPD cases are mainly treated by surgery, and the postoperative recurrence rate is high. Owing to the absence of any specific clinical manifestations, VPD is often misdiagnosed as eczematous skin lesions, which leads to diagnostic delay.
Case presentation: A 63-year-old woman experienced vulvar itching for over 4 months after 15 years of menopause. Computed tomography scans revealed a slightly friable vulva. Gynecological examination detected that the bilateral labia majora, especially the right labia majora, were exposed to light skin pigmentation; a red spot with a diameter of 5cm was observed outside the right labia majora, with visible scratch marks. The pathological results of the vulvar biopsy indicated Paget’s disease. The patient received local vulvectomy, vulvar skin flap transplantation, and vulvar plastic surgery. Routine gynecological examination and radiological examination indicated negative results 3 years after the surgery. Moreover, neither local recurrence nor distant metastasis was recorded.
Conclusion: VPD is commonly misdiagnosed as its clinical manifestations are nonspecific, mimicking other dermatological diseases. The diagnosis of VPD relies on pathological examination. Surgical treatment is preferred for its treatment, but the recurrence rate is high. Hence, early diagnosis and postoperative follow-up are critical in VPD treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the survival and quality of life of VPD patients.
1 Introduction
Extramammary Paget’s disease (EMPD) is a rare intraepithelial adenocarcinoma, accounting for approximately 6.5% of all Paget’s disease cases (1–4). EMPD predominantly occurs in areas with abundant apocrine glands, with the vulva being the most common site, followed by the perianal region, scrotum, penis, and axilla (5–7). Vulvar Paget’s disease (VPD), which accounts for over 50% of EMPD cases (8), primarily affects postmenopausal women (9, 10). Clinically, VPD presents as red vulvar plaques with well-demarcated borders, often accompanied by pruritus, localized pain, or a burning sensation (11). Due to its resemblance to eczematous lesions, it is frequently misdiagnosed (12). Approximately 15% of patients are asymptomatic (13). A vulvar skin biopsy is the diagnostic gold standard. Surgical excision remains the primary treatment. In most cases, the disease remains confined to the epithelium, resulting in a favorable prognosis, with a five-year survival rate exceeding 90% (14). However, dermal invasion significantly worsens the prognosis, as it increases the risk of malignancy and distant metastasis (15). The recurrence rate of VPD is relatively high after surgery, so long-term follow-up is crucial. Here, we report our experience in treating a patient with VPD who underwent surgery and did not experience recurrence or metastasis during a three-year follow-up.
2 Case report
A 63-year-old postmenopausal woman presented with vulvar pruritus persisting for over four months. She had been menopausal for 15 years, with a history of hypertension for five years. She had not experienced childbirth. A computed tomography scan revealed mild roughness of the vulva. Gynecological examination showed light pigmentation of the bilateral labia majora, particularly on the right side, where a 5-cm red lesion with visible scratch marks was observed (Figure 1A). Histopathological section indicated dysplastic stratified squamous epithelium with basal acantholysis (Figures 1B, C). The patient underwent local vulvectomy with skin flap transplantation and vulvar reconstruction (Figures 2A, B). Postoperative pathology confirmed VPD with positive IHC markers for GCDFP-15, CEA, CAM5.2, and GATA3 (Figures 3A–D). Follow-up included regular gynecological and radiological assessments. After three years, there was no evidence of local recurrence or distant metastasis.
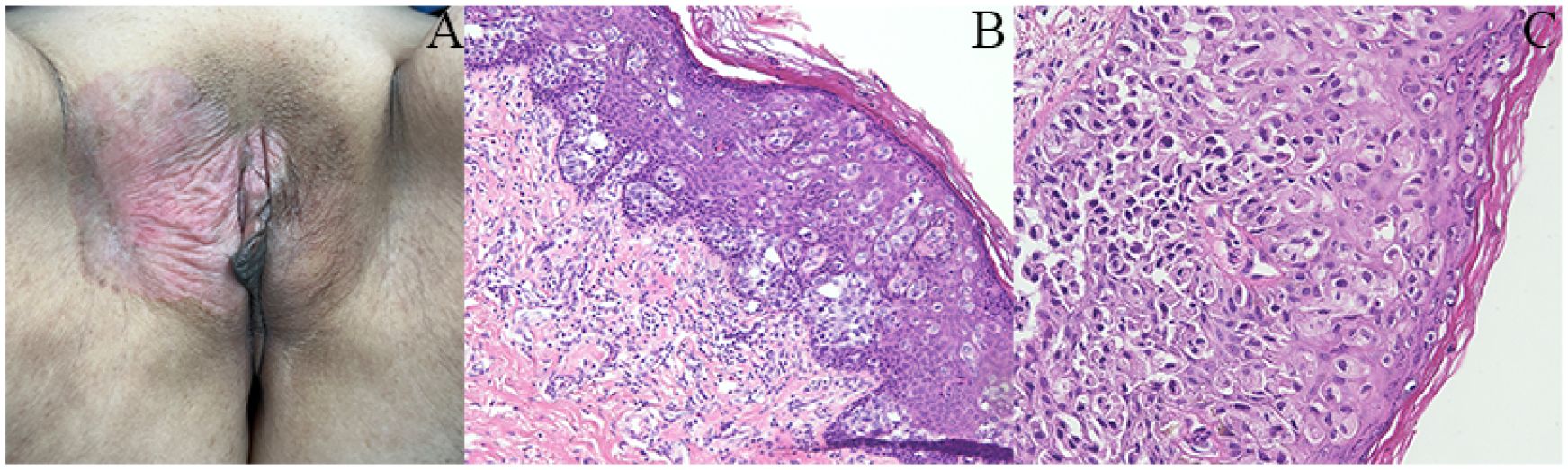
Figure 1. Clinical and histopathological features of the patient. (A) Gynecological examination revealed a 5-cm red lesion with visible scratch marks in the right-side labia majora. (B, C) Histopathological section indicated dysplastic stratified squamous epithelium showing basal acantholysis.
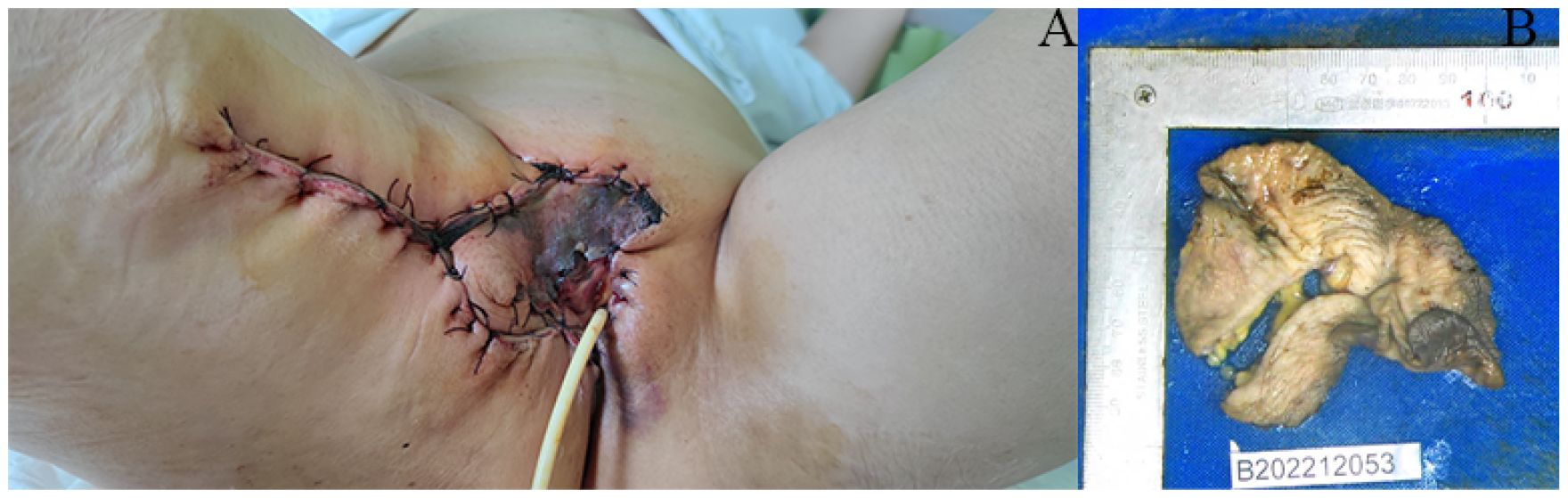
Figure 2. Surgery specimen of the patient. (A, B) Surgery was performed on the lesion, which involved local vulvectomy with skin flap transplantation and vulvar reconstruction.
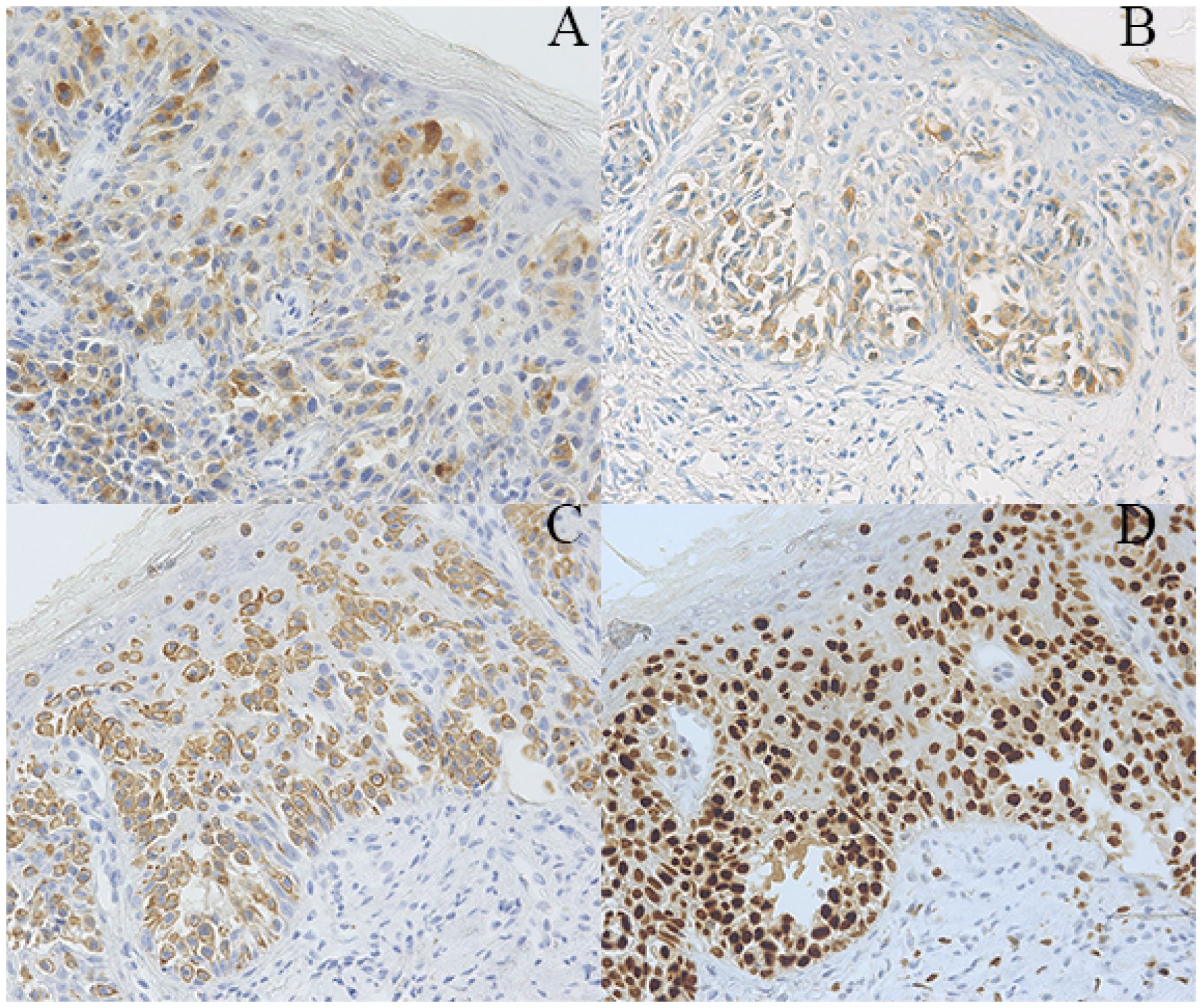
Figure 3. Pathological findings of the patient. (A–D) Immunohistochemical staining showing tumor cells positive for GCDFP-15 (A), CEA (B), CAM5.2 (C), and GATA3 (magnification x200).
3 Discussion
VPD is the most common form of EMPD, accounting for 1-2% of all vulvar tumors (16). First described by Dubreuilh in 1901, VPD typically originates in the labia majora and can extend to the pubic region, inguinal folds, perineum, medial thighs, labia minora, and vagina. VPD is classified as either primary or secondary based on its histocytological origin (17). Primary VPD arises from basal epithelial cells, often involving adjacent skin appendages. In some cases, it originates from skin appendages or sweat glands, which may give rise to adenocarcinomas. Secondary VPD results from epidermal metastasis or direct invasion by adenocarcinomas of the anal, rectal, or urogenital epithelium. VPD predominantly affects postmenopausal women over the age of 60, and its non-specific symptoms often delay diagnosis, contributing to disease progression.
The exact etiology of VPD remains unclear, with potential associations with seborrheic dermatitis, superficial fungal infections, Bowen’s disease, and superficial basal cell carcinoma (18). Some studies suggest a link between VPD and EMPD, proposing that EMPD may originate from ectopic mammary glands in the vulva (19). HER2/neu overexpression or amplification is related to the pathogenesis of VPD (20). It has been demonstrated to be a basic pathogenic pathway of VPD. Garganese et al. reported that 21% of non-invasive VPD cases and up to 45.5% of invasive VPD cases were exposed to HER2/neu re-expression or amplification (21). Moreover, HER2/neu overexpression or amplification is associated with a poor prognosis, considering that it involves tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis, and recurrence (22–25). Ogawa et al. reported that 19.4% of metastatic VPD cases were exposed to HER2 overexpression, which was achieved via CISH (26).
Clinically, VPD typically presents as a well-defined red or brown plaque, a few centimeters in size, with a smooth surface. Patients often experience pruritus, pain, or a burning sensation (27). In advanced stages, lesions may ulcerate, bleed, or exhibit edema, crusting, and nodularity, with potential regional lymph node enlargement (28). Lesions can be solitary or multiple, and unilateral or bilateral. The VPD demonstrated non-specific clinical manifestations, leading to confusion with eczema, malignant melanoma, vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions, vulvar squamous cell carcinoma, chronic simple lichen, and atrophic sclerosing lichen. As a result, corticosteroids and/or antifungal drugs are used, resulting in lesion deterioration. Therefore, biopsy is considered when the local drug efficacy is poor or the development of vulvar lesions is highly likely. The gold standard for diagnosing VPD is a pathological examination, including skin biopsy and cytologic analysis of vulvar lesion scrapings. Gross examination often reveals epidermal thickening with occasional fibroepitheliomatous changes (29). Microscopically, VPD is characterized by solid, nested, or glandular structures composed of large, oval, or polygonal Paget cells, which have abundant cytoplasm, transparent vacuoles, and prominent nucleoli (30). Paget cells are dispersed or clustered within the epithelium; they are typically located near the basal layer. After HE staining, the cytoplasm appears grey-blue. Special staining can facilitate the identification of Paget cells. For instance, the cytoplasm of Paget cells, which contains neutral and acidic mucus, is stained positively after periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining, which significantly helps distinguish VPD from other vulvar diseases (31, 32). Immunohistochemistry is crucial for the diagnosis of VPD, and VPD cells typically express GCDFP-15, CEA, CK7, and Ca15–3 instead of CK20 or HMB-45. Melanoma cells are highly similar to Paget’s cells, whereas melanoma cells display overexpression of Mel-A, HMB45, and S-100 instead of GCDFP-15, CEA, and CK7 after IHC staining (33). Hence, Ca15–3 can serve as a biomarker for the differentiation of VPD from Bowen’s disease (34). Moreover, both HPV typing test and liquid-based cytology of papillomavirus-induced high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia were positive, although no etiological studies have demonstrated the relationship of VPD with HPV infection (35).
The incidence of VPD is rare, and large-scale studies are lacking, resulting in no standardized treatment approach. Currently, surgery is the primary treatment option. However, due to the extensive infiltration of Paget cells into the epidermis, complete removal is challenging, leading to high recurrence rates (36, 37). Postoperative recurrence rates for radical vulvectomy, radical semi-vulvectomy, and wide excision are reported at 15%, 20%, and 43%, respectively (16). Murata et al. have recommended a surgical margin of 2cm to reduce recurrence (38, 39). If interstitial infiltration exceeds 1mm or there is concern for adenocarcinoma, the surgical depth should extend to the fascial layer, with unilateral or bilateral inguinal lymph node dissection based on lesion location (40, 41). Additionally, Mohs micrographic surgery has shown promise in reducing recurrence rates (42). Bae et al. analyzed 90 cases treated with Mohs surgery and reported a 12.2% recurrence rate and an 83.6% five-year tumor-free survival rate (43). Similarly, Bruce et al. found a three-year recurrence rate of 6.7% for Mohs surgery, compared to 34.1% for traditional excision (44). Achieving complete negative margins with Mohs surgery often requires excising more than 5cm beyond the visible lesion in 97% of cases (45). In cases with large lesions, reconstructive surgery, such as skin grafts, local flaps, or muscle flap grafts, is often necessary. The complication rate for skin grafts after vulvectomy is approximately 6.8%, including sexual dysfunction and mobility issues (46). In this case, pathological examination confirmed VPD with positive immunohistochemical markers for GCDFP-15 and CEA. The patient underwent local vulvectomy, vulvar skin flap transplantation, and vulvar reconstruction. Intraoperative frozen section biopsy ensured negative margins. After three years of follow-up, regular gynecological exams and radiological assessments showed no recurrence or distant metastasis. Therefore, for women with VPD, local excision with negative margins provides favorable outcomes, and intraoperative frozen section biopsy is recommended to confirm margin status.
Imiquimod, a topical immune response modulator, has emerged as an alternative therapy for treating VPD (47). As a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist, it activates T cells and Langerhans cells, enhancing the immune response. Imiquimod exhibits direct anti-tumor activity by inhibiting cancer cell proliferation through the induction of autophagy and apoptosis (48, 49). Compared to extensive lesion excision, imiquimod may offer a more effective cure for VPD (50). In 2003, Wang et al. (51) was the first to report complete remission in recurrent VPD following topical imiquimod treatment. In a retrospective study by Machida et al. involving 63 patients with VPD, 73% achieved complete remission with no disease progression (52). The cumulative complete remission rates at 2, 4, and 6 months were 9.8%, 31.1%, and 71.6%, respectively. Despite these promising results, larger studies with long-term follow-up are needed to confirm the efficacy of imiquimod in VPD treatment.
Non-surgical treatments, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, are viable options for advanced-stage patients, particularly those unable to tolerate surgery. Radiation therapy is often used as an adjuvant treatment for patients with positive surgical margins, postoperative recurrence, or those who cannot undergo surgery (53, 54). A systematic review by Tagliaferri et al. of 195 patients treated with radiation therapy reported a complete remission rate of 92.6% and a recurrence rate of 33% (55). Iacoponi also found that postoperative radiotherapy in advanced cases reduced metastasis risk and extended survival (56). Chemotherapeutic agents such as 5-fluorouracil and bleomycin are sometimes used in VPD (57–59), though their efficacy remains unclear (60–62), and chemotherapy is not recommended as a primary treatment (63, 64). For advanced patients with VPD with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positivity and distant metastasis, immunotherapy with trastuzumab combined with paclitaxel may be considered. Kimura et al. reported that one HER2-positive VPD patient with pulmonary lymph node metastases showed no malignant progression for 36 months following immunotherapy (59).
Recently, novel therapies such as CO2 laser treatment and photodynamic therapy have been explored for VPD management. However, CO2 laser treatment has limited effectiveness as a primary therapy, with recurrence rates of 31–67% for superficial lesions (65, 66). Photodynamic therapy, while innovative, can cause severe pain at the treatment site, making it challenging for some patients to complete the regimen, and is less effective in areas that are difficult to expose to light (67, 68).
4 Conclusions
VPD, although rare, predominantly affects postmenopausal women and presents with atypical symptoms, often resembling eczematous skin lesions. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and disease progression. Clinicians should carefully consider the patient’s history and clinical signs when VPD is suspected and perform a biopsy promptly for accurate diagnosis. Based on the pathological findings, individualized treatment plans should be developed. Given the high postoperative recurrence rate, long-term follow-up is essential for monitoring disease recurrence and ensuring timely intervention. In case of suspected recurrence, invasion, or metastasis, thorough gynecological examinations (including vulvar, vaginal, and digital rectal examinations) and complete radiological examinations (such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) should be conducted during the follow-up period to evaluate the overall condition of the patients.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
GW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171625).
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kanitakis J. Mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2007) 21:581–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02154.x
2. Chagpar AB, Heim K, Carron KR, and Sewell C. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the axilla: an unusual case. Breast J. (2007) 13:291–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2007.00424.x
3. Fardal RW, Kierland RR, Clagett OT, and Woolner LB. Prognosis in cutaneous Paget’s disease. Postgrad Med. (1964) 36:584–93. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1964.11695362
4. Lam C and Funaro D. Extramammary Paget’s disease: Summary of current knowledge. Dermatol Clin. (2010) 28:807–26. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2010.08.002
5. Urabe A, Matsukuma A, Shimizu N, Nishimura M, Wada H, Hori Y, et al. Extramammary Paget’s disease: comparative histopathologic studies of intraductal carcinoma of the breast and apocrine adenocarcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. (1990) 17:257–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1990.tb00099.x
6. Oliveira A, Sanches M, and Selores M. Axillary Paget’s disease associated with breast carcinoma in an elderly patient. Eur J Dermatol. (2011) 21:102–3. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2011.1161
7. Lloyd J and Flanagan AM. Mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. J Clin Pathol. (2000) 53:742–9. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.10.742
8. Goldblum JR and Hart WR. Vulvar Paget’s disease: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 19 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. (1997) 21:1178–87. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199710000-00008
9. McCarter MD, Quan SH, Busam K, Paty PP, Wong D, Guillem JG, et al. Long-term outcome of perianal Paget’s disease. Dis Colon Rectum. (2003) 46:612–6. doi: 10.1007/s10350-004-6618-x
10. Salamanca J, Benito A, García-Peñalver C, Azorín D, Ballestín C, Rodríguez-Peralto JL, et al. Paget’s disease of the glans penis secondary to transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: a report of two cases and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. (2004) 31:341–5. doi: 10.1111/j.0303-6987.2004.0184.x
11. Baker GM, Selim MA, and Hoang MP. Vulvar adnexal lesions: a 32-year, single-institution review from Massachusetts General Hospital. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2013) 137:1237–46. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0434-OA
12. Inui S, Fukuhara S, Asada H, Tadokoro T, Yoshikawa K, Itami S, et al. Double involvement of extramammary Paget’s disease in the genitalia and axilla. J Dermatol. (2000) 27:409–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2000.tb02194.x
13. Parashurama R, Nama V, and Hutson R. Paget’s disease of the vulva: A review of 20 years’ Experience. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2017) 27:791–3. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000901
14. van der Linden M, Oonk MHM, van Doorn HC, Bulten J, van Dorst EBL, Fons G, et al. Vulvar Paget disease: A national retrospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2019) 81:956–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.016
15. Johnson J and O’Laughlin D. Paget disease of the vulva. JAAPA. (2019) 32:33–4. doi: 10.1097/01.JAA.0000550285.65463.a9
16. Delport ES. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the vulva: An annotated review of the current literature. Australas J Dermatol. (2013) 54:9–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2012.00898.x
17. Wilkinson EJ and Brown HM. Vulvar Paget disease of urothelial origin: a report of three cases and a proposed classification of vulvar Paget disease. Hum Pathol. (2002) 33:549–54. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2002.124788
18. Ishizawa T, Mitsuhashi Y, Sugiki H, Hashimoto H, and Kondo S. Basal cell carcinoma within vulvar Paget’s disease. Dermatology. (1998) 197:388–90. doi: 10.1159/000018039
19. Popiolek DA, Hajdu SI, and Gal D. Synchronous Paget’s disease of the vulva and breast. Gynecol Oncol. (1998) 71:137–40. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1998.5136
20. Karam A, Berek JS, Stenson A, Rao J, and Dorigo O. HER-2/neu targeting for recurrent vulvar Paget’s disease A case report and literature review. Gynecol Oncol. (2008) 111:568–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.12.014
21. Garganese G, Inzani F, Mantovani G, Santoro A, Valente M, Babini G, et al. The vulvar immunohistochemical panel (VIP) project: molecular profiles of vulvar Paget’s disease. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2019) 145:2211–25. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02975-3
22. Plaza JA, Torres-Cabala C, Ivan D, and Prieto VG. HER-2/neu expression in extramammary Paget disease: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemistry study of 47 cases with and without underlying Malignancy. J Cutan Pathol. (2009) 36:729–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2008.01148.x
23. Reich O, Liegl B, Tamussino K, and Regauer S. p185HER2 overexpression and HER2 oncogene amplification in recurrent vulvar Paget’s disease. Mod Pathol. (2005) 18:354–7. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800243
24. Richter CE, Hui P, Buza N, Silasi DA, Azodi M, Santin AD, et al. HER-2/NEU overexpression in vulvar Paget disease: the Yale experience. J Clin Pathol. (2010) 63:544–7. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2010.077446
25. Sekiguchi N, Kubota S, Noguchi T, Fukushima T, Kobayashi T, Kanda S, et al. Experiences of trastuzumab plus paclitaxel combination therapy in metastatic human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive extramammary Paget’s disease: Four cases and a review. J Dermatol. (2020) 47:1276–9. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15515
26. Ogawa T, Nagashima Y, Wada H, Akimoto K, Chiba Y, Nagatani T, et al. Extramammary Paget’s disease: analysis of growth signal pathway from the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 protein. Hum Pathol. (2005) 36:1273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2005.09.009
27. Morris CR and Hurst EA. Extramammary Paget disease: A review of the literature-part I: history, epidemiology, pathogenesis, presentation, histopathology, and diagnostic work-up. Dermatol Surg. (2020) 46:151–8. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000002064
28. Wagner G and Sachse MM. Extramammary Paget disease - clinical appearance, pathogenesis, management. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. (2011) 9:448–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2010.07581.x
29. Ishida-Yamamoto A, Sato K, Wada T, Takahashi H, Toyota N, Shibaki T, et al. Fibroepithelioma-like changes occurring in perianal Paget’s disease with rectal mucinous carcinoma: case report and review of 49 cases of extramammary Paget’s disease. J Cutan Pathol. (2002) 29:185–9. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0560.2002.290311.x
30. Reddy SV, Menaa C, Singer FR, Demulder A, and Roodman GD. Cell biology of Paget’s disease. J Bone Miner Res. (1999) 14 Suppl 2:3–8. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650140203
31. Morbeck D, Tregnago AC, Baiocchi G, Sacomani C, Peresi PM, Osório CT, et al. GATA3 expression in primary vulvar Paget disease: a potential pitfall leading to misdiagnosis of pagetoid urothelial intraepithelial neoplasia. Histopathology. (2017) 70:435–41. doi: 10.1111/his.13086
32. Gonçalves AA, Batista FMB, Neves FR, and Chambô FA. Paget disease of the vulva: diagnosis by immunohistochemistry. Case Rep Dermatol Med. (2015) 2015:162483. doi: 10.1155/2015/162483
33. Gadducci A, Carinelli S, Guerrieri ME, and Aletti GD. Melanoma of the lower genital tract: Prognostic factors and treatment modalities. Gynecol Oncol. (2018) 150:180–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.04.562
34. Gomez LD, Chavez-Rojas AJ, Gomez FEJ, Miranda I, Ancona CC, Suro SY, et al. Primary extramammary Paget’s disease in a male patient exhibiting genital involvement mimicking clinical and histopathological features of Bowen’s disease: A case report. Cureus. (2025) 17:e78242. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78242
35. Al-Obaidy KI, Kao CS, and Idrees MT. P16 expression in extramammary Paget’s disease of the vulva and scrotum is not human papillomavirus related. Int J Surg Pathol. (2018) 26:617–20. doi: 10.1177/1066896918775513
36. Zollo JD and Zeitouni NC. The Roswell Park Cancer Institute experience with extramammary Paget’s disease. Br J Dermatol. (2000) 142:59–65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03242.x
37. Shim PJ and Zeitouni NC. Photodynamic therapy for extramammary Paget’s disease: A systematic review of the literature. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2020) 31:101911. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101911
38. Murata Y and Kumano K. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the genitalia with clinically clear margins can be adequately resected with 1cm margin. Eur J Dermatol. (2005) 15:168–70.
39. Fanning J, Lambert HC, Hale TM, Morris PC, and Schuerch C. Paget’s disease of the vulva: prevalence of associated vulvar adenocarcinoma, invasive Paget’s disease, and recurrence after surgical excision. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (1999) 180:24–7. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70143-2
40. Saito A, Sawaizumi M, Matsumoto S, and Takizawa K. Stepladder V-Y advancement medial thigh flap for the reconstruction of vulvoperineal region. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2009) 62:e196–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2009.01.090
41. Terlou A, Blok LJ, Helmerhorst TJ, and van Beurden M. Premalignant epithelial disorders of the vulva: squamous vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, vulvar Paget’s disease and melanoma in situ. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2010) 89:741–8. doi: 10.3109/00016341003739575
42. Damavandy AA, Terushkin V, Zitelli JA, Brodland DG, Miller CJ, Etzkorn JR, et al. Intraoperative immunostaining for cytokeratin-7 during mohs micrographic surgery demonstrates low local recurrence rates in extramammary Paget’s disease. Dermatol Surg. (2018) 44:354–64. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001355
43. Bae JM, Choi YY, Kim H, Oh BH, Roh MR, Nam K, et al. Mohs micrographic surgery for extramammary Paget disease: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2013) 68:632–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2012.12.960
44. Bruce KH, Kilts TP, Lohman ME, Vidal NY, Fought AJ, McGree ME, et al. Mohs surgery for female genital Paget’s disease: a prospective observational trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2023) 229:660.e1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.08.018
45. Hendi A, Brodland DG, and Zitelli JA. Extramammary Paget’s disease: surgical treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2004) 51:767–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2004.07.004
46. Lavoue V, Lemarrec A, Bertheuil N, Henno S, Mesbah H, Watier E, et al. Quality of life and female sexual function after skinning vulvectomy with split-thickness skin graft in women with vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia or vulvar Paget disease. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2013) 39:1444–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.09.014
47. Cohen PR, Schulze KE, Tschen JA, Hetherington GW, and Nelson BR. Treatment of extramammary Paget disease with topical imiquimod cream: case report and literature review. South Med J. (2006) 99:396–402. doi: 10.1097/01.smj.0000209223.68763.b1
48. Dogan A, Hilal Z, Krentel H, Cetin C, Hefler LA, Grimm C, et al. Paget’s disease of the vulva treated with imiquimod: case report and systematic review of the literature. Gynecol Obstet Invest. (2017) 82:1–7. doi: 10.1159/000449158
49. Baiocchi G, Begnami MD, Fukazawa EM, Surima WS, Badiglian-Filho L, Costa FD, et al. Conservative management of extramammary paget disease with imiquimod. J Low Genit Tract Dis. (2012) 16:59–63. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0b013e31822d2484
50. Pang J, Assaad D, Breen D, Fialkov J, Antonyshyn O, Balogh J, et al. Extramammary Paget disease: review of patients seen in a non-melanoma skin cancer clinic. Curr Oncol. (2010) 17:43–5. doi: 10.3747/co.v17i5.588
51. Wang LC, Blanchard A, Judge DE, Lorincz AA, Medenica MM, Busbey S, et al. Successful treatment of recurrent extramammary Paget’s disease of the vulva with topical imiquimod 5% cream. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2003) 49:769–72. doi: 10.1067/s0190-9622(03)02107-8
52. Machida H, Moeini A, Roman LD, and Matsuo K. Effects of imiquimod on vulvar Paget’s disease: a systematic review of literature. Gynecol Oncol. (2015) 139:165–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.07.097
53. Shepherd V, Davidson EJ, and Davies-Humphreys J. Extramammary Paget’s disease. BJOG. (2005) 112:273–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00438.x
54. Hashimoto H and Ito T. Current management and treatment of extramammary Paget’s disease. Curr Treat Options Oncol. (2022) 23:818–30. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00923-3
55. Tagliaferri L, Casa C, Macchia G, Pesce A, Garganese G, Gui B, et al. The role of radiotherapy in extramammary Paget disease: A systematic review. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2018) 28:829–39. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001237
56. Iacoponi S, Zalewski K, Fruscio R, Diaz-De la Noval B, De Iaco P, Ceccaroni M, et al. Prognostic factors for recurrence and survival among patients with invasive vulvar Paget disease included in the VULCAN study. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. (2016) 133:76–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2015.08.018
57. Dilme-Carreras E, Iglesias-Sancho M, Marquez-Balbas G, Sola-Ortigosa J, and Umbert-Millet P. Radiotherapy for extramammary Paget disease of the anogenital region. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2011) 65:192–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.689
58. Brown RS, McCormack M, Lankester KJ, and Spittle MF. Spontaneous apparent clinical resolution with histologic persistence of a case of extramammary Paget’s disease: response to topical 5-fluorouracil. Cutis. (2000) 66:454–5.
59. Kimura T, Akamatsu Y, Kajihara I, Fukushima S, and Ihn H. Case of metastatic extramammary Paget’s disease treated with trastuzumab-biosimilar monotherapy after S-1 and docetaxel combination chemotherapy. J Dermatol. (2020) 47:e1–2. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15096
60. Merritt BG, Degesys CA, and Brodland DG. Extramammary Paget disease. Dermatol Clin. (2019) 37:261–7. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2019.02.002
61. Fujisawa Y, Umebayashi Y, and Otsuka F. Metastatic extramammary Paget’s disease successfully controlled with tumour dormancy therapy using docetaxel. Br J Dermatol. (2006) 154:375–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.07046.x
62. Mochitomi Y, Sakamoto R, Gushi A, Hashiguchi T, Mera K, Matsushita S, et al. Extramammary Paget’s disease/carcinoma successfully treated with a combination chemotherapy: report of two cases. J Dermatol. (2005) 32:632–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00812.x
63. Niikura H, Yoshida H, Ito K, Takano T, Watanabe H, Aiba S, et al. Paget’s disease of the vulva: clinicopathologic study of type 1 cases treated at a single institution. Int J Gynecol Cancer. (2006) 16:1212–5. doi: 10.1136/ijgc-00009577-200605000-00040
64. Parker LP, Parker JR, Bodurka-Bevers D, Deavers M, Bevers MW, Shen-Gunther J, et al. Paget’s disease of the vulva: pathology, pattern of involvement, and prognosis. Gynecol Oncol. (2000) 77:183–9. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2000.5741
65. Louis-Sylvestre C, Haddad B, and Paniel BJ. Paget’s disease of the vulva: results of different conservative treatments. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2001) 99:253–5. doi: 10.1016/S0301-2115(01)00394-3
66. Ewing TL. Paget’s disease of the vulva treated by combined surgery and laser. Gynecol Oncol. (1991) 43:137–40. doi: 10.1016/0090-8258(91)90059-E
67. Li Q, Gao T, Jiao B, Qi X, Long HA, Qiao H, et al. Long-term follow-up of in situ extramammary Paget’s disease in Asian skin types IV/V treated with photodynamic therapy. Acta Derm Venereol. (2010) 90:159–64. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0818
Keywords: Vulvar Paget’s disease, pathologic characteristic, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis
Citation: Wang G (2025) Case Report: A case of Vulvar Paget’s disease and literature review. Front. Oncol. 15:1648891. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1648891
Received: 17 June 2025; Accepted: 25 September 2025;
Published: 31 October 2025.
Edited by:
Stefano Restaino, Ospedale Santa Maria della Misericordia di Udine, ItalyReviewed by:
Giuseppe Angelico, Kore University of Enna, ItalyHelamã Santos, Federal University of the Southern Frontier, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guojie Wang, Z3Vvamlld2FuZzEwMjVAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Guojie Wang
Guojie Wang