- 1Department of Head Neck and Thyroid Surgery, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Department of Pathology, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- 4Department of Anatomy, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
A Correction on
Heterotypic neutrophil-in-tumor structure: a novel pathological feature first discovered in the tissues of OPSCC
By Fan J, Li P, Fang Q, Yang Y, Zhang H, Du W, Liu S and Luo R (2022). Front. Oncol. 12:807597. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.807597
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5B as published. In the original Figure 5, the fluorescent staining images of Figure 5B was vague, and the third image from the left in the first row of Figure 5B was mistakenly used in the work of another colleague in my lab, so I decided to delete Figure 5B.
The updated Figure 5 appear below.
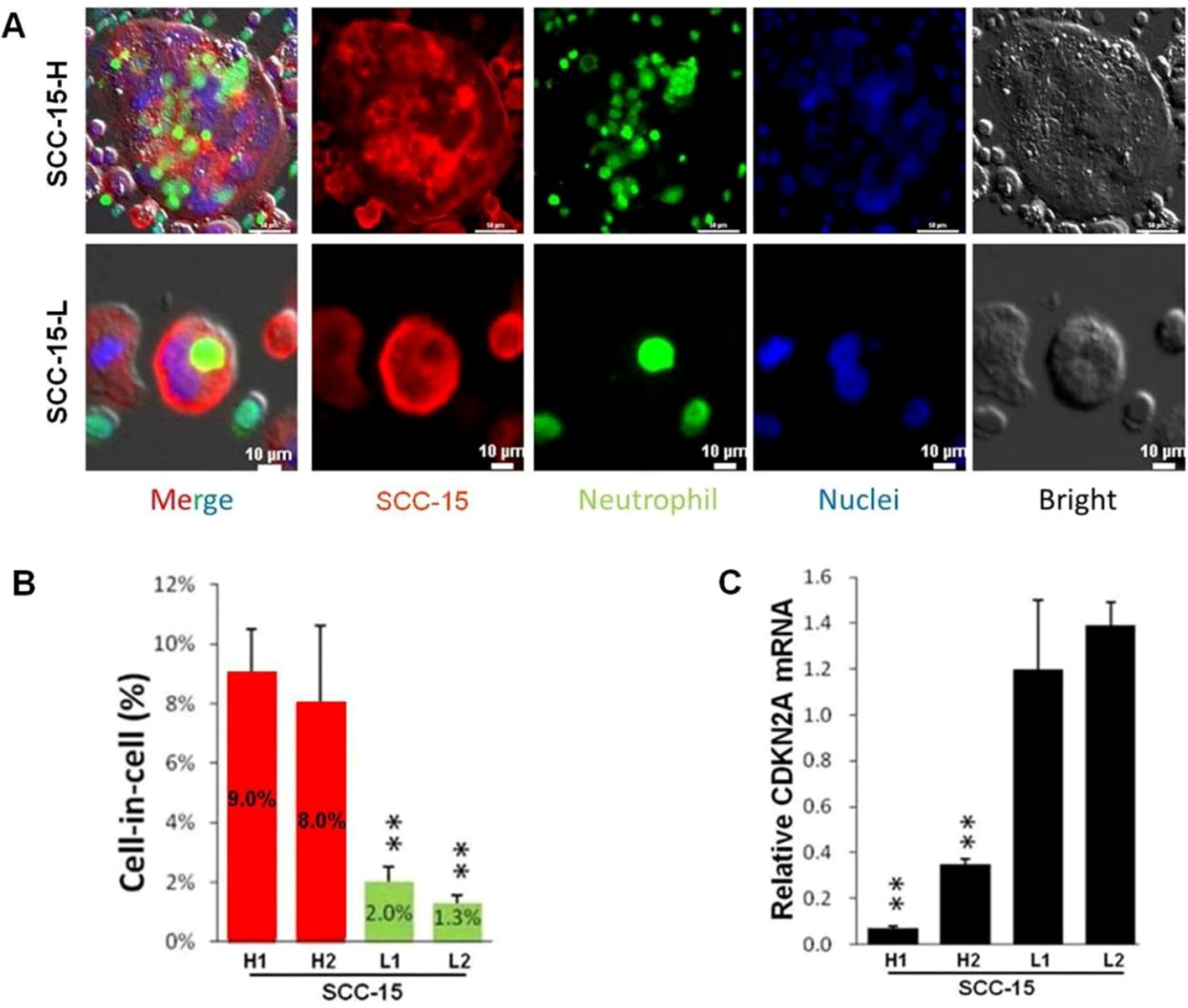
Figure 5. Fluorescent staining result of typical hNiT structures formed between SCC-15 and HL-60 cells which negatively correlate with CDKN2A expression. (A) Fluorescent staining images of typical hNiT structures formed between SCC-15-H or SCC-15-L and HL-60 cells (SCC-15-H: subpopulation of SCC-15 with the high ability to internalize more HL-60 cells to form hNiT; SCC-15-L: subpopulation of SCC-15 with the low ability to internalize less HL-60 cells to form hNiT). Scale bars: 10μm. (B) The hNiT formation in H1, H2, L1 and L2 subpopulations of SCC-15 cells. (C) The CDKN2A expression in H1, H2, L1 and L2 subpopulations of SCC-15 cells (H1 and H2: subpopulations of SCC-15 with the high ability to internalize more HL-60 cells to form hNiT; L1 and L2: subpopulations of SCC-15 with the low ability to internalize less HL-60 cells to form hNiT).
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 5 as published. Because original Figure 5B was decided to be deleted, the relevant legend for original Figure 5B was to be deleted accordingly. The original legend numbers “(C) and (D)” for Figure 5C and 5D were changed to “(B) and (C)”, respectively.
The corrected legend appears below.
“Fluorescent staining result of typical hNiT structures formed between SCC-15 and HL-60 cells which negatively correlate with CDKN2A expression. (A) Fluorescent staining images of typical hNiT structures formed between SCC-15-H or SCC-15-L and HL-60 cells(SCC-15-H: subpopulation of SCC-15 with the high ability to internalize more HL-60 cells to form hNiT; SCC-15-L: subpopulation of SCC-15 with the low ability to internalize less HL-60 cells to form hNiT). Scale bars: 10μm. (B) The hNiT formation in H1, H2, L1 and L2 subpopulations of SCC-15 cells. (C) The CDKN2A expression in H1, H2, L1 and L2 subpopulations of SCC-15 cells (H1 and H2: subpopulations of SCC-15 with the high ability to internalize more HL-60 cells to form hNiT; L1 and L2: subpopulations of SCC-15 with the low ability to internalize less HL-60 cells to form hNiT)”.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: heterotypic neutrophil-in-tumor structure, oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, p16, disease-specific survival, pathological feature
Citation: Fan J, Li P, Fang Q, Yang Y, Zhang H, Du W, Liu S and Luo R (2025) Correction: Heterotypic neutrophil-in-tumor structure: a novel pathological feature first discovered in the tissues of OPSCC. Front. Oncol. 15:1651340. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1651340
Received: 21 June 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 15 July 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Avraham Eisbruch, University of Michigan, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Fan, Li, Fang, Yang, Zhang, Du, Liu and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Fan, amllZmFuMTk4OUAxMjYuY29t; Shanting Liu, bGl1c2hhbnRpbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ruihua Luo, NjY2bHJoQHNpbmEuY29t
 Jie Fan
Jie Fan Peng Li1
Peng Li1 Qigen Fang
Qigen Fang Shanting Liu
Shanting Liu