- 1Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 2Institute of Urology, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 3Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 4Anhui Public Health Clinical Center, Hefei, Anhui, China
Primary bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma (BMA) is an exceedingly rare and aggressive malignancy. We report a case of a 72-year-old male presenting with hematuria and dysuria. Imaging revealed a bladder mass, and histopathological examination following biopsy demonstrated characteristic extracellular mucin pools and signet-ring cells. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was crucial for diagnosis, showing a negative profile for GATA binding protein 3 (GATA3) and Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2), along with membrane nuclear positivity for β-catenin. Endoscopic examination confirmed the absence of a primary gastrointestinal malignancy. The patient underwent robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystoprostatectomy followed by three cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy with the FOLFOX regimen (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin). No recurrence was observed during the 6-month follow-up. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges of BMA and emphasizes the importance of a multimodal diagnostic approach incorporating histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and endoscopy. The potential efficacy of adjuvant FOLFOX regimen is worth further exploration given the lack of standard therapeutic guidelines for this rare entity.
Introduction
Mucinous adenocarcinoma predominantly arise in the gastrointestinal tract such as the stomach, appendix, or colon, or in the ovaries, while primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the bladder is exceptionally rare, accounting for merely 2% of bladder malignancies. Distinguishing Primary bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma (BMA) from metastatic adenocarcinoma is often challenging due to overlapping histological features. Moreover, BMA is highly aggressive and often progresses rapidly. More than 50% of BMA cases are diagnosed at stage T3 or higher, and approximately 10% already show lymph node involvement or distant metastases at diagnosis. Therefore, early and accurate diagnosis is crucial. Herein, we present a representative BMA case to illustrate the value of multimodal diagnostic integration, including imaging, endoscopy, and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) evaluations. Concurrently, we review clinical outcomes of various therapeutic regimens reported in BMA management, aiming to enhance recognition of this rare aggressive entity and advance optimization of treatment strategies.
Case report
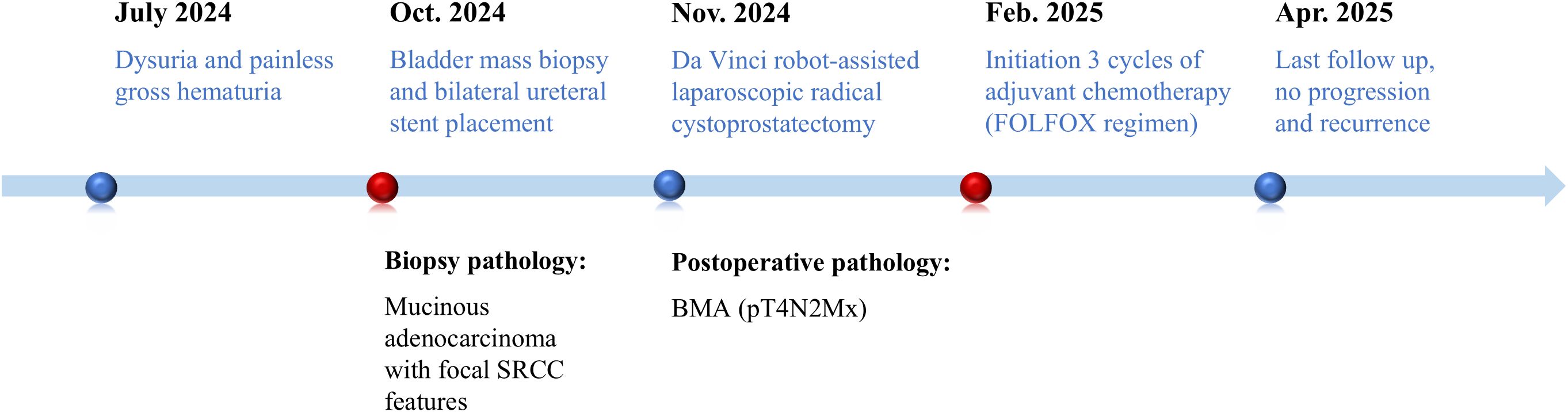
A 72-year-old male presented to a local hospital with a 3-month history of dysuria and painless gross hematuria. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a heterodense lesion within the bladder cavity and left hydronephrosis. The patient underwent ureteroscopy with biopsy of the bladder lesion and bilateral ureteral stent placement to maintain upper urinary tract patency. The biopsy showed mucinous adenocarcinoma with focal signet-ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) features, raising the possibility of a metastatic adenocarcinoma. The patient was subsequently referred to our department for definitive diagnosis and treatment planning.
On admission, physical examination showed a soft abdomen without tenderness or palpable masses. The urine drained via the indwelling catheter was pale-red and contained blood clots. Digital rectal examination revealed a grade II enlarged prostate with firm consistency and no nodules.
Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count, hepatic and renal function panels, coagulation profile, and electrolyte levels, were unremarkable. Urinalysis demonstrated a red blood cell count of 2,849/μL and a white blood cell count of 531/μL. Serum tumor markers for gastrointestinal malignancy (carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA], alpha-fetoprotein [AFP], carbohydrate antigen [CA]125, CA19-9) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) were within normal limits.
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of bladder with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) identified an irregular focal thickening in the left posterior bladder wall, forming an intraluminal protrusion extending into the prostate (Figures 1A–C). Bilateral enlarged lymph nodes adjacent to the iliac vessels were detected. These findings were corroborated by contrast-enhanced CT urography, which additionally revealed irregular hypodense areas within the lesion, resembling mucin-filled cystic cavities (Figure 1D). To exclude gastrointestinal metastasis, combined esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy were performed, demonstrating no evidence of primary gastrointestinal malignancy.

Figure 1. Preoperative and postoperative imaging of bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma. (A–C) T2-weighted pelvic MRI demonstrate an intravesical lesion (arrows) arising from the left posterior bladder wall in the coronal (A) axial (B) and sagittal (C) planes. The asterisk (*) in (C) indicates tumor invasion into the prostate. (D) CT urography reveals a posterior bladder wall mass with heterogeneous hypodensity (arrowheads), suggesting mucin deposition. (E) Postoperative CT at 6 months after radical cystectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy demonstrates no pelvic fluid, bowel obstruction, or metastatic recurrence. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Based on these findings, we performed additional IHC staining on the biopsy tissue sections obtained from the external hospital (Figure 2). IHC revealed negative expression of cytokeratin 7 (CK7), cytokeratin 20 (CK20), GATA binding protein 3 (GATA3), Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2), and Villin, with scattered positivity for caudal type homeobox 2 (CDX2). β-catenin showed membrane positivity without nuclear staining, and the Ki-67 proliferation index was 60%. These collective features strongly suggested the possibility of primary bladder adenocarcinoma (PBA).

Figure 2. Histopathological and immunohistochemical features of primary bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma. (A, B) H&E staining (×40) shows extracellular mucin pools with floating tumor cell clusters. (C) High-power view (×200) reveals signet-ring cells (arrows) exhibiting cytoplasmic mucin accumulation and crescent-shaped nuclei. (D–H) IHC profile: (D) Ki-67 (+, ~57% proliferation index); (E) GATA3 (−); (F) β-catenin (membranous +); (G) CDX2(+); (H) SATB2 (−).H&E staining, Hematoxylin-eosin staining, IHC, Immunohistochemistry; GATA3, GATA binding protein 3; CDX2, caudal type homeobox 2; SATB2, Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2.
The patient subsequently underwent Da Vinci robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystoprostatectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection, appendectomy, and urinary diversion via Wallace ureteroileal anastomosis. Intraoperative frozen sections of both ureteral margins were negative for tumor involvement.
Postoperative histological examination revealed tumor cells with glandular differentiation invading the full thickness of the bladder wall and involving the prostate. Abundant extracellular mucin formed extensive mucinous lakes, with some cells demonstrating intracellular mucin accumulation and signet-ring morphology. Metastatic adenocarcinoma was identified in bilateral pelvic lymph nodes. The final pathological diagnosis confirmed advanced primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the bladder, staged as pT4N2Mx.
The operation was successful, and the patient subsequently received 3 cycles of the FOLFOX regimen. Grade 2 myelosuppression occurred during treatment cycles, which was successfully managed with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) support. At the 6-month follow-up, the patient remained clinically stable, with no signs of recurrence on abdominopelvic CT (Figure 1E). Clinical evaluations every 3 months and annual CT scans were recommended for surveillance. The key events and corresponding timelines in this case are summarized in Figure 3.
Discussion
PBA is a rare malignancy, accounting for only 0.5-2% of all bladder malignancies (1). The peak incidence occurs in the sixth decade of life, with a male predominance (2). The pathogenesis of PBA is predominantly linked to chronic irritation, such as urinary retention, bladder calculi, or chronic cystitis. This persistent insult triggers a metaplastic process in the bladder mucosa, which evolves through a series of stages including urothelial hyperplasia, cystitis glandularis, and cystitis cystica, eventually culminating in the development of adenocarcinoma (3, 4).
PBA encompasses several histological subtypes, including signet-ring cell, clear cell, enteric, hepatoid, mucinous, and adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified (NOS) (5, 6). BMA, a relatively rare and highly aggressive subtype, accounts for 15% of all primary bladder adenocarcinomas (7). Histologically, BMA is characterized by tumor cells arranged in nests floating within extensive extracellular mucin pools. In some cases, tumor cells contain intracellular mucin, which displaces the nucleus and cytoplasm to the periphery, resulting in a signet-ring cell appearance (8). Consequently, BMA is frequently observed to harbor a signet-ring cell component (9). When signet-ring cells predominate within a mucinous background, the tumor is classified as a signet-ring cell mucinous adenocarcinoma (SRCMA) (2, 10).
As a non-urachal origin bladder adenocarcinoma, BMA predominantly arises in the posterior wall and trigone of the bladder rather than the dome (11). Although a minority of patients exhibit pathognomonic mucus in urine, the vast majority of BMA cases present with nonspecific symptoms analogous to conventional urothelial carcinoma (UC), including hematuria, urinary frequency, dysuria, and pelvic pain (9). The lack of specific symptoms often leads to a delayed diagnosis. Approximately 50% of BMA patients are diagnosed at stage T3 or T4. Moreover, nearly 10% present with lymph node or distant metastases at initial diagnosis (12).
In terms of supporting examinations, BMA typically demonstrates no abnormalities in serologic tumor markers (13). While CT and MRI scans can help understand the tumor size, anatomical location, depth of invasion, and metastatic spread, they exhibit limited specificity in differentiating BMA from UC. Therefore, cystoscopy with histopathological biopsy is necessary for establishing a definitive diagnosis. Furthermore, it is essential to distinguish BMA from other adenocarcinomas that secondarily involve the bladder, either through metastasis or direct invasion, such as colorectal, prostatic, or endometrial adenocarcinomas. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy can help to exclude potential primary malignancies in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, a comprehensive IHC analysis was critical. It ruled out metastatic adenocarcinoma and confirmed the primary bladder adenocarcinoma diagnosis (14). Urothelial-specific markers such as GATA3, p63, and uroplakin II/III are typically negative in BMA. β-catenin usually shows nuclear positivity in colorectal adenocarcinoma but demonstrates membranous and cytoplasmic staining in primary bladder adenocarcinoma, serving as an important diagnostic marker (9, 15). Classic colorectal adenocarcinomas are typically positive for CDX2, SATB2, and villin, whereas BMA often exhibits negative or weakly positive expression of these markers (16–18). Notably, recent studies have indicated that CK7 and CK20 immunostaining lacks specificity in distinguishing primary from secondary adenocarcinomas, as 29% of primary bladder adenocarcinomas exhibit an IHC profile overlapping with colorectal adenocarcinoma, characterized by CK7 negativity and CK20 positivity (19). As a novel diagnostic approach, molecular testing remains under investigation for its potential role in diagnosing BMA and guiding therapeutic strategies. Pires-Luis et al. performed next-generation sequencing and identified KRAS, GRIN2A, and AURKB as the most frequent genetic alterations in BMA (20).
Regarding therapeutic management, no consensus exists on clinical strategies for BMA due to its rarity, aggressive behavior, and frequent delayed diagnosis. Radical cystectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy is generally considered the primary treatment option for surgically resectable BMA (21). However, a retrospective analysis of 426 BMA patients revealed no survival advantage for muscle-invasive cases treated with radical surgery versus partial or local resection. This finding indicates that bladder-preserving approaches may be feasible (22).
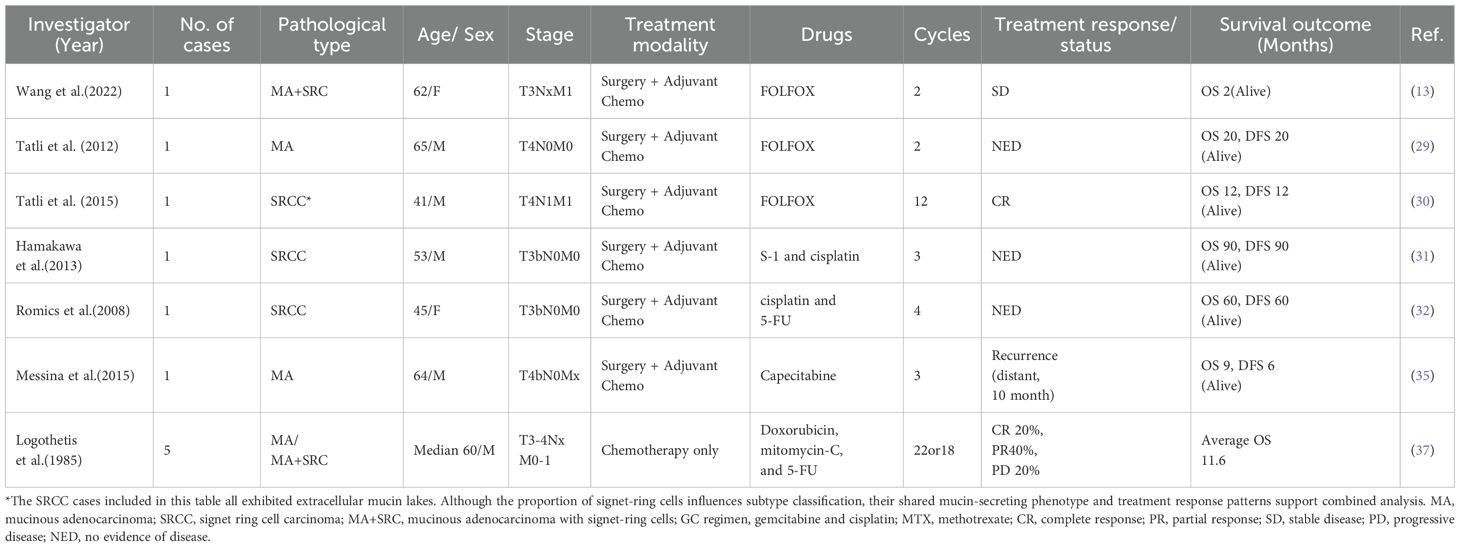
According to the US National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, postoperative adjuvant chemoradiotherapy may be considered for advanced or unresectable bladder adenocarcinoma (23). However, due to limited clinical trial evidence, no consensus exists regarding the optimal chemotherapy regimens or their efficacy. Initially, chemotherapy protocols commonly used for UC have been empirically applied to BMA (Table 1). Wajpeyi et al. and Di Maida et al. reported two cases of BMA with signet-ring cell components. In both cases, adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and paclitaxel was administered after radical cystectomy but yielded suboptimal outcomes. Both patients developed inguinal lymph node recurrence within 8 and 10 months postoperatively, respectively, and succumbed to the disease shortly thereafter (10, 24). In contrast, Ball et al. described a successful case treated with carboplatin, gemcitabine, and paclitaxel, where the patient remained recurrence- and metastasis-free for 90 months after radical cystectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy (25). Additionally, the gemcitabine plus cisplatin (GC) regimen has been sporadically reported in BMA management (26–28). Subsequently, given the adenocarcinoma characteristics of BMA, chemotherapy regimens typically used for gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas have also been implemented, achieving sporadically successful outcomes (Table 2). Notably, given the established efficacy of FOLFOX in gastrointestinal-derived mucinous adenocarcinomas, some researchers have explored its application in BMA. Tatil et al. reported a case of a BMA patient who experienced disease progression after four cycles of the GC regimen; subsequent switch to FOLFOX resulted in a 10-month clinical remission, suggesting potential efficacy in this setting (29). Another patient diagnosed with SRCC accompanied by multiple pulmonary metastases achieved a complete response following FOLFOX chemotherapy (30). In recent cases, the FOLFOX regimen has increasingly been adopted as a first-line option (9, 13). Similarly, combinations of cisplatin with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or tegafur-gimeracil-oteracil (S-1), which are commonly used in gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas, have also demonstrated efficacy in BMA management (31, 32).

Table 1. Reported outcomes of urothelial carcinoma-based chemotherapy regimens in bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma.
The efficacy of postoperative radiotherapy in BMA remains poorly documented. However, a retrospective study from Egypt demonstrated that adjuvant radiotherapy following cystectomy provided favorable survival rates and local control for PBA patients, though with limited efficacy in controlling distant metastases, particularly in BMA and SRCC (33).
Due to frequent delays in detection and diagnosis, BMA is generally associated with a poor prognosis. Retrospective studies indicate a 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate of 36% for BMA and 7% for SRCC, both significantly lower than those of UC or other adenocarcinoma subtypes (33). Song et al. analyzed 426 BMA patients from the SEER database, reporting a median overall survival (OS) of 47 months (22). Notably, this analysis revealed no significant survival difference between muscle-invasive and non-muscle-invasive BMA patients, suggesting limited prognostic value of T-stage classification in BMA. It has been reported that postoperative elevation of CEA levels may assist in assessing SRCC malignancy and monitoring disease progression (34), with similar patterns observed in BMA cases (35). However, whether these CEA level changes are associated with distant metastasis remains undetermined.
In summary, the diagnosis and management of BMA remain challenging. Due to its rarity, current understanding is largely based on isolated case reports, which lack long-term follow-up data and dedicated clinical studies. Therefore, future efforts should focus on establishing multi-institutional registries and promoting collaborative research to improve diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
XC: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Investigation. WW: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LY: Data curation, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ST: Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft. JT: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Supervision. YF: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – original draft. JZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Health Committee Project of Anhui Province in China (No. AHWJ2023BAc10007) and Outstanding Scientific Research and Innovation Team for Male Genitourinary Diseases in Anhui Provincial Universities (No.2022AH010071).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
BMA: primary bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma
IHC: immunohistochemistry
CT: computed tomography
SRCC: signet-ring cell carcinoma
CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen
AFP: alpha-fetoprotein
CA125: carbohydrate antigen 125
CA19-9: carbohydrate antigen 19-9
PSA: prostate-specific antigen
MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
DWI: diffusion-weighted imaging
CK7: cytokeratin 7
CK20: cytokeratin 20
SATB2: special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2
GATA3: GATA binding protein 3
CDX2: caudal type homeobox 2
PBA: primary bladder adenocarcinoma
G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
NOS: not otherwise specified
SRCMA: signet-ring cell mucinous adenocarcinoma
p63: tumor protein p63
UC: urothelial carcinoma
NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network
5-FU: 5-fluorouracil
S-1: tegafur-gimeracil-oteracil
NCCN: US National Comprehensive Cancer Network
DFS: disease-free survival
OS: overall survival.
References
1. Bates AW and Baithun SI. Secondary neoplasms of the bladder are histological mimics of nontransitional cell primary tumours: clinicopathological and histological features of 282 cases. Histopathology. (2000) 36:32–40. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2000.00797.x
2. Board WCoTE. Who Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Urinary and Male Genital Tumours. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC (2022).
3. Huang Y, Wang H, Li H, Liu J, and Wang J. Primary bladder adenocarcinoma: A case report. Cancer Plus. (2022) 4:41–4. doi: 10.18063/cp.v4i1.242
4. Palmero Martí JAQZ JL, Bonillo García MA, Budía Alba A, and Jiménez Cruz JF. F.J. Vera sempere. Adenocarcinoma mucinoso de vejiga. Actas Urologicas Espanolas. (2003) 27:274–80. doi: 10.1016/S0210-4806(03)72920-9
5. Zhong M, Gersbach E, Rohan SM, and Yang XJ. Primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: differential diagnosis and clinical relevance. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2013) 137:371–81. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0076-RA
6. Grignon DJ, Ro JY, Ayala AG, Johnson DE, and Ordonez NG. Primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. A clinicopathologic analysis of 72 cases. Cancer. (1991) 67:2165–72. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910415)67:8<2165::aid-cncr2820670827>3.0.co;2-m
7. Wang J, Wang FW, and Kessinger A. The impact of signet-ring cell carcinoma histology on bladder cancer outcome. World J Urol. (2011) 30:777–83. doi: 10.1007/s00345-011-0718-8
8. Marques ML DAG, Chade DC, Lanzoni VP, Saiovici S, and Almeida CJ. Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the bladder with signet-ring cells: case report. Sao Paulo Med J. (2007) 125:297–9. doi: 10.1016/S0210-4806(03)72920-9
9. Winarti NW, Kristiana T, Sriwidyani NP, and Sumadi IWJ. Mucinous adenocarcinoma (Signet ring cell carcinoma) of the urinary bladder in young male: A case report. Gaceta Médica Caracas. (2022) 130:49–55. doi: 10.47307/GMC.2022.130.s1.10
10. Wajpeyi K, Hiwale K, and Vagha S. Primary signet ring cell mucinous adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: A rare case report. Int J Life Sci Pharma Res. (2023) 13:15–20. doi: 10.22376/ijlpr.2023.13.4.L15-L20
11. Roy S and Parwani AV. Adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2011) 135:1601–5. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2009-0713-RS
12. Akamatsu S, Takahashi A, Ito M, and Ogura K. Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Urology. (2010) 75:615–8. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2009.06.065
13. Wang D, Zhang K, Guan L, and Wen N. Imaging features of primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of bladder outlet and urethra: A case report and literature review. Transl Cancer Res. (2022) 11:2416–24. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-1547
14. Ghewade P, Shukla S, Vagha S, Kalode SS, and Gadkari P. Primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: A case report on a rare Malignancy. Cureus. (2024) 16:e66269. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66269
15. Thomas AA, Stephenson AJ, Campbell SC, Jones JS, and Hansel DE. Clinicopathologic features and utility of immunohistochemical markers in signet-ring cell adenocarcinoma of the bladder. Hum Pathol. (2009) 40:108–16. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2008.06.022
16. Benerjee N, Parmar K, and Vaiphei K. Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Autops Case Rep. (2021) 11:e2021264. doi: 10.4322/acr.2021.264
17. Rao Q, Williamson SR, Lopez-Beltran A, Montironi R, Huang W, Eble JN, et al. Distinguishing primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder from secondary involvement by colorectal adenocarcinoma: extended immunohistochemical profiles emphasizing novel markers. Mod Pathol. (2013) 26:725–32. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.229
18. Suh N, Yang XJ, Tretiakova MS, Humphrey PA, and Wang HL. Value of cdx2, villin, and alpha-methylacyl coenzyme a racemase immunostains in the distinction between primary adenocarcinoma of the bladder and secondary colorectal adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. (2005) 18:1217–22. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800407
19. Roy S, Smith MA, Cieply KM, Acquafondata MB, and Parwani AV. Primary bladder adenocarcinoma versus metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma: A persisting diagnostic challenge. Diagn Pathol. (2012) 7:151. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-151
20. Pires-Luis AS, Martinek P, Alaghehbandan R, Trpkov K, Comperat EM, Perez Montiel DM, et al. Molecular genetic features of primary nonurachal enteric-type adenocarcinoma, urachal adenocarcinoma, mucinous adenocarcinoma, and intestinal metaplasia/adenoma: review of the literature and next-generation sequencing study. Adv Anat Pathol. (2020) 27:303–10. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000268
21. Witjes JA, Babjuk M, Bellmunt J, Bruins HM, De Reijke TM, De Santis M, et al. Eau-esmo consensus statements on the management of advanced and variant bladder cancer-an international collaborative multistakeholder effort(Dagger): under the auspices of the eau-esmo guidelines committees. Eur Urol. (2020) 77:223–50. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.09.035
22. Song W, Pan J, Li Y-R, Lei Q-F, Wang F, Dai R-X, et al. Nomograms for predicting survival outcomes in patients with bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma: A large population-based investigation. Research Square [Preprint] (2022). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1525937/v1
23. Flaig TW, Spiess PE, Abern M, Agarwal N, Bangs R, Buyyounouski MK, et al. Nccn guidelines(R) insights: bladder cancer, version 3.2024. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2024) 22:216–25. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2024.0024
24. Di Maida F, Amorim Aita G, and Amorim Aita D. Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder with signet-ring cells: description of an uncommon case and critical points in its management. Case Rep Urol. (2016) 2016:6080859. doi: 10.1155/2016/6080859
25. Ball MW, Nathan R, and Gerayli F. Long-term response after surgery and adjuvant chemoradiation for T4 mucinous adenocarcinoma of the bladder: A case report and review of the literature. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2016) 14:e225–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2015.12.025
26. Cobo-Dols JA M, Gutiérrez V, Gil S, Alés I, Villar E, Montesa A, et al. Primary signet ring cell adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. Oncología. (2006) 29:177–80.
27. Shringarpure SS, Thachil JV, Raja T, and Mani R. A case of signet ring cell adenocarcinoma of the bladder with spontaneous urinary extravasation. Indian J Urol. (2011) 27:401–3. doi: 10.4103/0970-1591.85449
28. Lendorf ME, Dohn LH, Á Dunga B, Loya AC, and Pappot H. An updated review on primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder and report of a case. Scand J Urol. (2018) 52:87–93. doi: 10.1080/21681805.2017.1418020
29. Tatli AM, Uysal M, Goksu SS, Gunduz S, Arslan D, and Ozdogan M. Complete response of primary bladder adenocarcinoma with the folfox4 regimen. Urol Int. (2015) 94:363–5. doi: 10.1159/000354332
30. Tatli AM, Uysal M, Goksu SS, Arslan D, Gunduz S, Ozdogan M, et al. Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the bladder: complete response with folfox-4 regimen. Med Oncol. (2012) 29:1935–7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-0090-y
31. Hamakawa T, Kojima Y, Naiki T, Kubota Y, Yasui T, Tozawa K, et al. Long-term survival of a patient with invasive signet-ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder managed by combined S-1 and cisplatin adjuvant chemotherapy. Case Rep Urol. (2013) 2013:915874. doi: 10.1155/2013/915874
32. Romics I, Szekely E, and Szendroi A. Signet-ring cell carcinoma arising from the urinary bladder. Can J Urol. (2008) 15:4266–8.
33. Zaghloul MS, Nouh A, Nazmy M, Ramzy S, Zaghloul AS, Sedira MA, et al. Long-term results of primary adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder: A report on 192 patients. Urol Oncol. (2006) 24:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2005.05.027
34. Yamamoto S, Ito T, Akiyama A, Miki M, Tachibana M, Takase M, et al. Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder inducing renal failure. Int J Urol. (2001) 8:190–3. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-2042.2001.00280.x
35. Messina C, Dellepiane C, Caroti C, Sarocchi F, Ravetti GL, Boccardo F, et al. A case of advanced mucinous adenocarcinoma of bladder in an adult patient treated with capecitabine-based chemotherapy and review of literature. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2015) 13:e365–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2015.04.002
36. Ota TS T, Hinotsu S, Akaza H, Koiso K, Noro M, and Ogata T. Primary signet ring cell carcinoma of the bladder effectively treated with intra-arterial chemotherapy and radiation therapy: A case report. Nishinihon J Urol. (1995) 57:1019–23.
Keywords: primary bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma, signet-ring cell carcinoma, immunohistochemistry, chemotherapy, FOLFOX
Citation: Cheng X, Wang W, Yang L, Tai S, Tao J, Fu Y and Zhou J (2025) Diagnosis and therapeutic strategies for primary bladder mucinous adenocarcinoma: a case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 15:1652375. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1652375
Received: 23 June 2025; Accepted: 26 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Dean Markić, University of Rijeka, CroatiaReviewed by:
Rajesh Kumar, Kerala University of Health Sciences, IndiaAnte Jaksic, Clinical Hospital Center Rijeka, Croatia
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Wang, Yang, Tai, Tao, Fu and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Zhou, dXJvZG9jdG9yemhvdUAxNjMuY29t; Yao Fu, eWFvX2Z1QGFsaXl1bi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xi Cheng
Xi Cheng Weibo Wang1,2†
Weibo Wang1,2† Junyue Tao
Junyue Tao Jun Zhou
Jun Zhou