- 1Department of Oncology, Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang, Sichuan, China
- 2School of Public Health, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Radiology, Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang, Sichuan, China
Background: Although antiangiogenic agents and HIFU (High-intensity focused ultrasound) are extensively used in the systematic treatment of advanced primary and secondary liver cancer, respectively, the efficacy and safety of their combination remain unclear. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the efficacy, safety, and synergistic effect of the combination of antiangiogenic drugs with HIFU in the treatment of advanced liver cancer.
Methods: Advanced liver cancer patients undergoing HIFU were included and matched 1:1 to two groups based on admission criteria: patients who received HIFU combined with antiangiogenic agents were assigned to the Combined HIFU group, whereas those who received HIFU but not antiangiogenic agents were assigned to the Only HIFU group. Then, therapeutic parameters, short-term efficacy, long-term survival, and safety of HIFU were analyzed and compared in this study.
Results: There were 25 cases in both the Combined HIFU and Only HIFU groups. A significant difference was noted in the median ultrasound grayscale (hyperechoic region) occurrence time between the two groups (p=0.04). The coagulative necrosis rate, ORR, and DCR of liver lesions were numerically higher in the Combined HIFU group (60%, 64%, and 96%) than those in the Only HIFU group (44%, 36%, and 84%). Contrastingly, mOS did not differ significantly between the two groups. (HR,0.91; 95% CI, 0.45 to 1.82; p = 0.79). Finally, Acute adverse events (AEs) primarily included skin-burning pain, fever, and impaired liver function, and the incidence of infectious fever and impaired liver function was lower in the combined HIFU group.
Conclusion: Antiangiogenic agents combined with HIFU are effective and safe in the treatment of advanced primary and secondary liver cancer.
1 Introduction
According to epidemiological studies (1), the mortality rate of liver cancer ranks the third in the world, and the incidence rate is increasing year by year. In China, 78.6% of liver cancer cases are diagnosed at the advanced stage (2), with the liver being the most common metastatic site for malignant solid tumors. At present, anti-angiogenic agents have been widely used in the systemic treatment of advanced primary liver cancer and secondary liver cancer. When local lesions are poorly controlled, intensive treatment combined with local interventions is often required. Primary therapeutic approaches for liver cancer encompass surgery, Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE), radiofrequency ablation, and radiotherapy. However, the first three methods are invasive, and antiangiogenic agents must be discontinued for at least 4 weeks prior to treatment. This may lead to tumor progression and missing the optimal window for local treatment (3). While radiation therapy is non-invasive, it is associated with prolonged treatment duration, high costs, and substantial variability in treatment equipment and technology across different centers. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is a completely non-invasive local thermal ablation therapy that offers numerous advantages, including high real-time guidance accuracy, short treatment time, fast recovery, and low cost. Theoretically, it can be simultaneously performed with antiangiogenic agents, eliminating the need for discontinuation of antiangiogenic agents before treatment. Notwithstanding, the efficacy and safety of this combination remain elusive. At the same time, liver cancer tumor cells are characterized by a rich blood supply that dissipates heat and complicates HIFU treatment. Considering that anti-angiogenic agents can inhibit tumor neovascularization, as well as reduce vascular permeability and blood supply, their combination with HIFU may potentially enhance treatment efficiency and concurrently shorten operation time. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the efficacy, safety, and synergistic efficiency of the combination of antiangiogenic agents with HIFU in the treatment of advanced liver cancer.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design
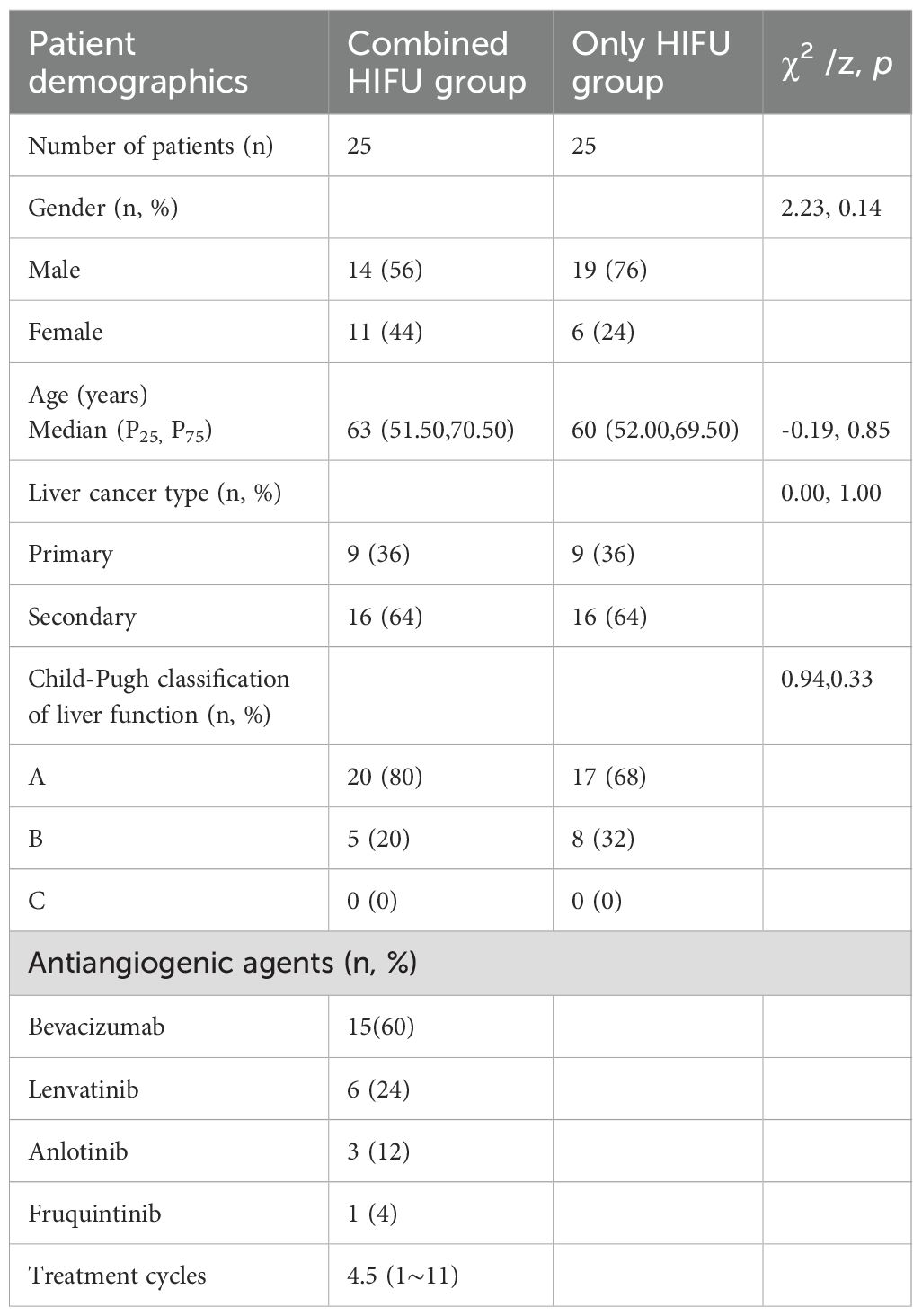
This study employed a case-control design. The experimental cohort comprised 25 patients with advanced liver cancer who underwent HIFU therapy subsequent to antiangiogenic targeted therapy at Mianyang Central Hospital, China, between January 5, 2022, and June 19, 2024. Using SPSS 22.0 (IBM Corp.), matched controls were selected for each case from the pool of advanced liver cancer patients who did not receive antiangiogenic targeted therapy. Matching was performed based on three key variables: liver cancer subtype, liver function status, and size of the target lesion with a 1:1 matching ratio. Ultimately, 25 eligible matched controls were successfully enrolled for subsequent analyses.
2.2 Subjects
Patients with advanced liver cancer (defined as stage III-IV primary liver cancer and secondary liver cancer) undergoing HIFU between January 5,2022 and June 19,2024were eligible for inclusion. All patients were staged according to AJCC eighth edition TNM staging criteria (4), and the diagnosis was confirmed by pathological examination. The inclusion criteria were as follows: patients with liver lesions who are not eligible or unwilling to undergo surgery, radiotherapy, TACE, and radiofrequency ablation with well-controlled non-liver lesions. The exclusion criteria were as follows: having previously received HIFU, other local treatment, or less than one treatment cycle of antiangiogenic agent targeted therapy, incomplete or unavailable HIFU treatment parameters and follow-up data, including but not limited to postoperative monitoring of signs and symptoms, laboratory test results, and liver contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI) before and within 1 month after surgery. Patients in the experimental group who were administered antiangiogenic agents at the time of HIFU treatment were assigned to the Combined HIFU group, whereas the Only HIFU (control) group comprised patients who did not receive antiangiogenic agents before HIFU treatment.
2.3 HIFU therapeutic procedure
Patients were treated using a high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment system (Model: HIFU-JC200, Chongqing Haifu Medical Technology, Chongqing, China) equipped with a real-time ultrasound guidance device. The detailed information about the HIFU treatment is as follows.
2.3.1 Patients preparation
All patients signed an informed consent prior to HIFU and consumed a diet low in liquid residue for 3 days before treatment. Patients were kept under fasting conditions 12 hours before surgery, and compound polyethylene glycol electrolyte powder was orally administered to induce diarrhea. Additionally, an enema was performed before surgery. Under general anesthesia, the patient’s skin was degassed and degreased after tracheal intubation, and a catheter was inserted to minimize patient discomfort. For patients with lesions in the left liver, a nasogastric tube was inserted to decompress the stomach, improve visualization of liver lesions, and minimize the risk of gastric heat damage.
2.3.2 Treatment position
the lesions in the right lobe of the liver were treated in the right lateral position, while the lesions in the left lobe of the liver were treated in the prone position.
2.3.3 Selection of ultrasound path
there should be no gas, scar, bone, or calcification lesions in the ultrasound path that had strong reflection effects on ultrasound.
2.3.4 Pre-scan
the treatment range was determined based on the target lesion and its proximity to important organs. The layer spacing was generally set at 3mm or 5mm.
2.3.5 The treatment probe was generally selected at 0.8 MHz
Transducers with focal lengths of 115mm and 165mm were often used based on the depth of tumor treatment. The scanning mode was mainly linear scanning; the scanning direction was usually longitudinal scanning, and “θ” was set to 90 degrees. The treatment approach was carried out from the deeper layer to the superficial layer of the target lesion.
2.4 Outcome
2.4.1 Primary endpoint
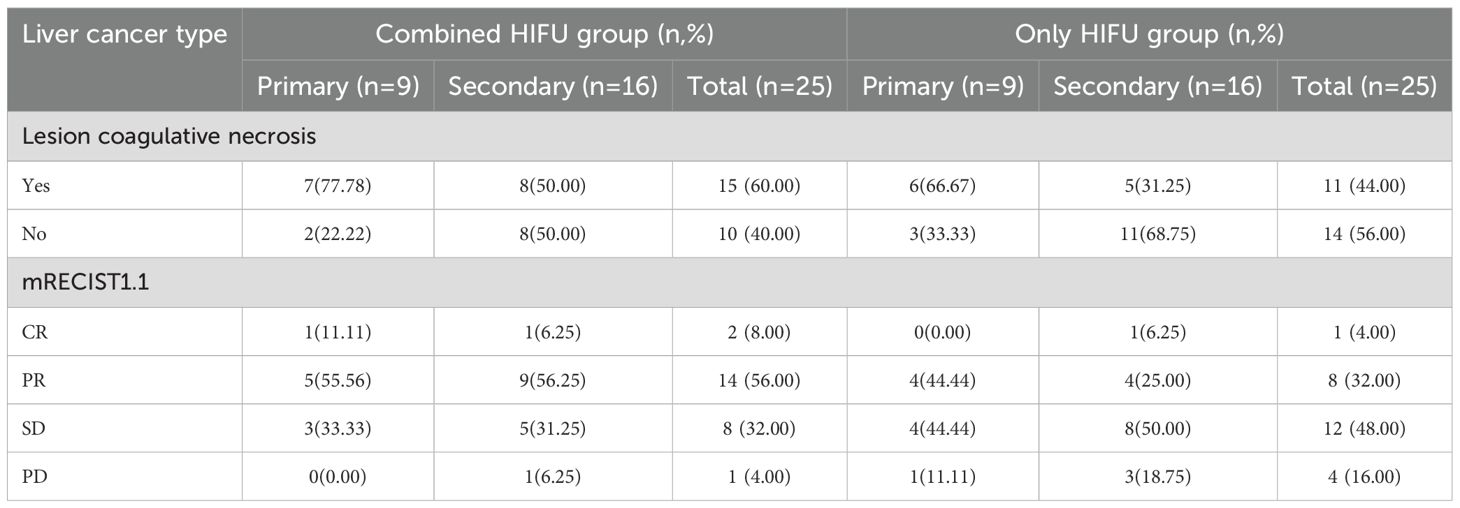
the objective response rate (ORR), as assessed by the investigators, was determined in accordance with the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1 (mRECIST 1.1). ORR was defined as the composite of complete remission (CR) and partial remission (PR) of the tumor following treatment. The details were as follows: complete response (CR): complete coagulative necrosis of the target lesion; partial response (PR): the longest diameter of the coagulated necrosis area of the target lesion was ≥ 30% of the baseline; stable disease (SD): no PR and no PD; disease progression (PD): no coagulative necrosis of the target lesion and at least a 20% increase in the longest diameter.
In coagulative necrotic lesions, intracellular proteins undergo denaturation, organelles are disrupted, and the integrity of cell membranes is lost-resulting in irreversible cellular inactivation and the complete absence of tumor cell viability. Clinically, this therapeutic effect is equivalent to lesion regression. Therefore, the inclusion of “coagulative necrosis” in the RECIST 1.1 criteria was scientifically justified.
2.4.2 Secondary endpoint
I. Ultrasound grayscale occurrence time: defined as the time point at which the hyperechoic region first appears on grayscale images during real-time ultrasound monitoring of HIFU therapy.
The temporal dynamics of grayscale changes, including the onset speed, expansion rate, and temporal stability of hyperechoic regions, can effectively reflect the efficiency of thermal energy deposition and the tissue response to HIFU. Thus, this parameter served as a valuable reference indicator for dynamically assessing therapeutic efficacy and guiding the adjustment of treatment intensity intraoperatively.
II. Investigator-assessed disease control rate (DCR): defined as the sum of tumor responses achieving remission CR and PR and SD following treatment.
III. Overall survival (OS): defined as the time from the initiation of planned HIFU treatment to death of the patient from any cause.
IV. Acute adverse events (AEs): it was examined based on patients’ symptoms and signs within 3 days post-treatment and liver function 24 h after surgery. Pain was evaluated using the numeric rating scale (NRS), whilst liver function was evaluated using the Common Adverse Reactions Scale 5.0 (CTCAE5.0).
2.5 Statistical analysis
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistical test was performed to determine the normality of the data. Non-normally distributed data were presented as medians (P25, P75) and compared using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The chi-square test was used to compare gender, liver cancer type, and liver function grade. The median follow-up time was calculated using the Reverse Kaplan-Meier method. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed to plot patient survival curves and calculate the median survival period. COX regression analysis was utilized to calculate the risk ratio (HR) for survival outcomes. IBM SPSS 22.0 statistical software was used for statistical analysis and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
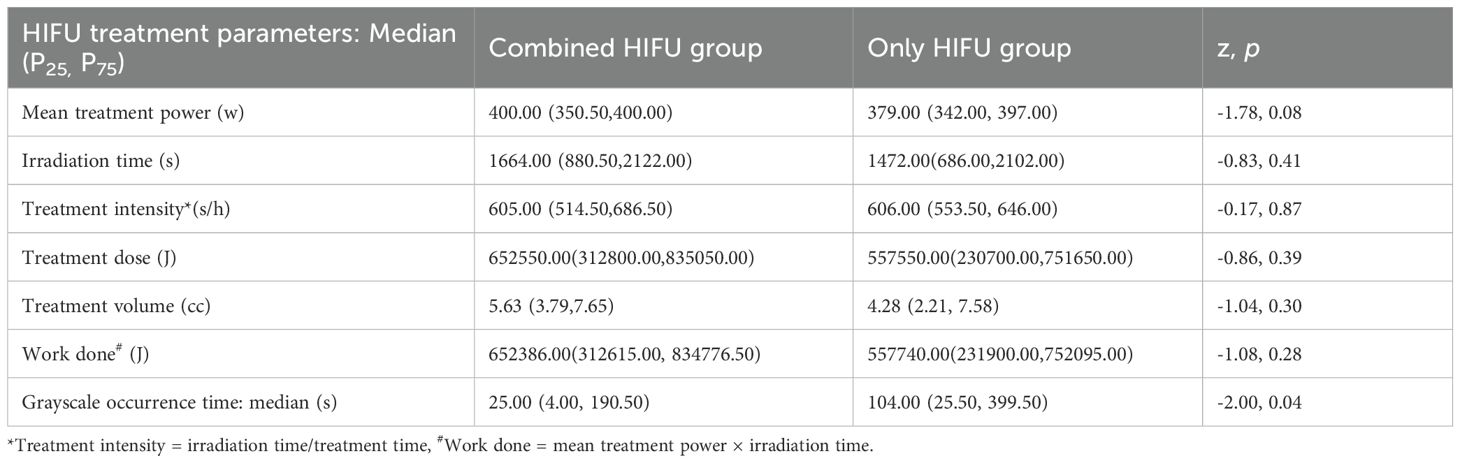
In the Combined HIFU group, there were 12 male and 11 female patients with a median age of 63 years. In the Only HIFU group, there were 19 male and 6 female patients with a median age of 60 years. With respect to the type of liver cancer, each group included 9 cases of primary liver cancer and 16 cases of secondary liver cancer. Among the primary liver cancer cases, two-thirds were at stage III and one-third at stage IV; all secondary liver cancer cases were at stage IV. No patients in either group had Child-Pugh class C liver function. There were no statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics between the two groups (p>0.05), indicating that they were comparable. In the Combined HIFU group, the mean number of cycles of antiangiogenic targeted therapy administered prior to HIFU treatment was 4.5 (range:1–11). Specifically, 60% of the patients received bevacizumab, 24% lenvatinib, 12% anlotinib, and 4% fruquintinib (Table 1). HIFU treatment parameters of the two groups are presented in Table 2. During HIFU treatment, changes in ultrasound grayscale images can reflect real-time treatment efficacy, corresponding to the degree of coagulated necrosis in target lesions (5–7). As illustrated in Figure 1, the intraoperative ultrasound image displayed significant alterations in grayscale in a lesion in the left lobe of the liver after HIFU treatment, with the echo intensity being significantly higher than the initial treatment image. In the current study, the median grayscale occurrence time was 25s in the Combined HIFU group and 104s in the Only HIFU group, and the difference was statistically different (z=-2.00, p=0.04). This finding suggests that the combination treatment achieved faster and more sensitive treatment responses. Under the guidance of a senior radiologist, CE-MRI images were analyzed, and changes in lesions before and after HIFU treatment were compared, measuring lesion size and coagulated necrosis area to determine treatment efficacy according to mRECIST1.1. 60% (15/25) of patients in the Combined HIFU group had a higher degree of coagulative necrosis compared to the Only HIFU group, and the 1-month disease control rate (DCR) was 96% and 84%, respectively. Despite some lesions not displaying evidence of coagulative necrosis, follow-up revealed that they benefited from HIFU treatment in controlling short-term lesion progression, and the likelihood of local lesion progression after treatment was only 1/4 of compared to the control group (Figure 2, Table 3). Furthermore, this study also demonstrated that the efficacy of HIFU therapy varied across different subtypes of advanced carcinoma. Both the coagulative necrosis rate and DCR were higher in patients with primary liver cancer than in those with secondary liver cancer, with this difference being more pronounced in the combined therapy group (Table 3). However, due to the small sample size of each subgroup, statistical analysis could not be performed. Therefore, studies with a larger sample size will be required to further validate this finding.
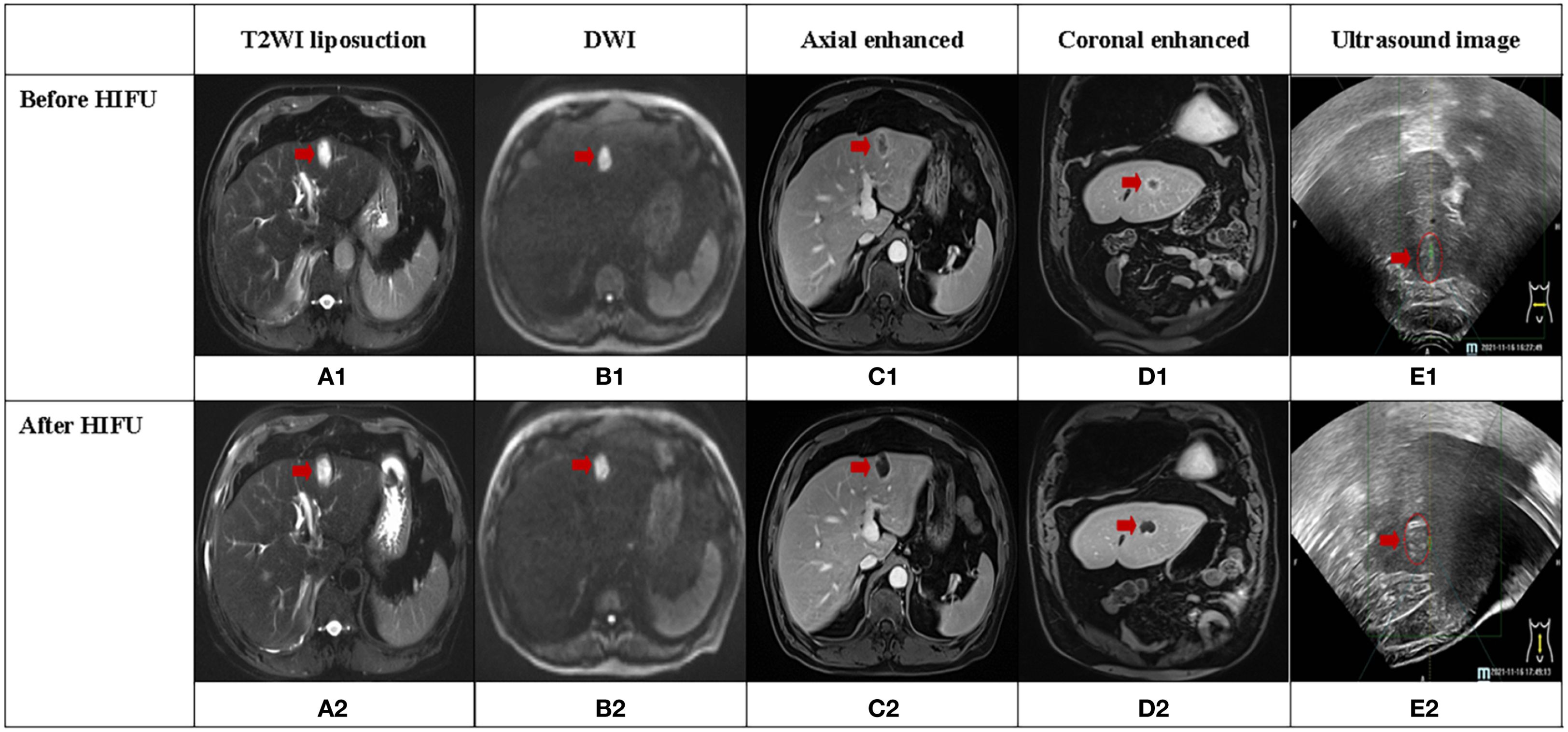
Figure 1. A case of secondary liver cancer achieved complete response (CR) after HIFU treatment, and the lesion was located in the left lobe of the liver (red arrow). (A1-D1, A2-D2) illustrate MRI sequences before and after HIFU treatment, respectively. (E1, E2) display ultrasound images before and after HIFU treatment, respectively. (E2) depicts significant grayscale changes in the lesion.
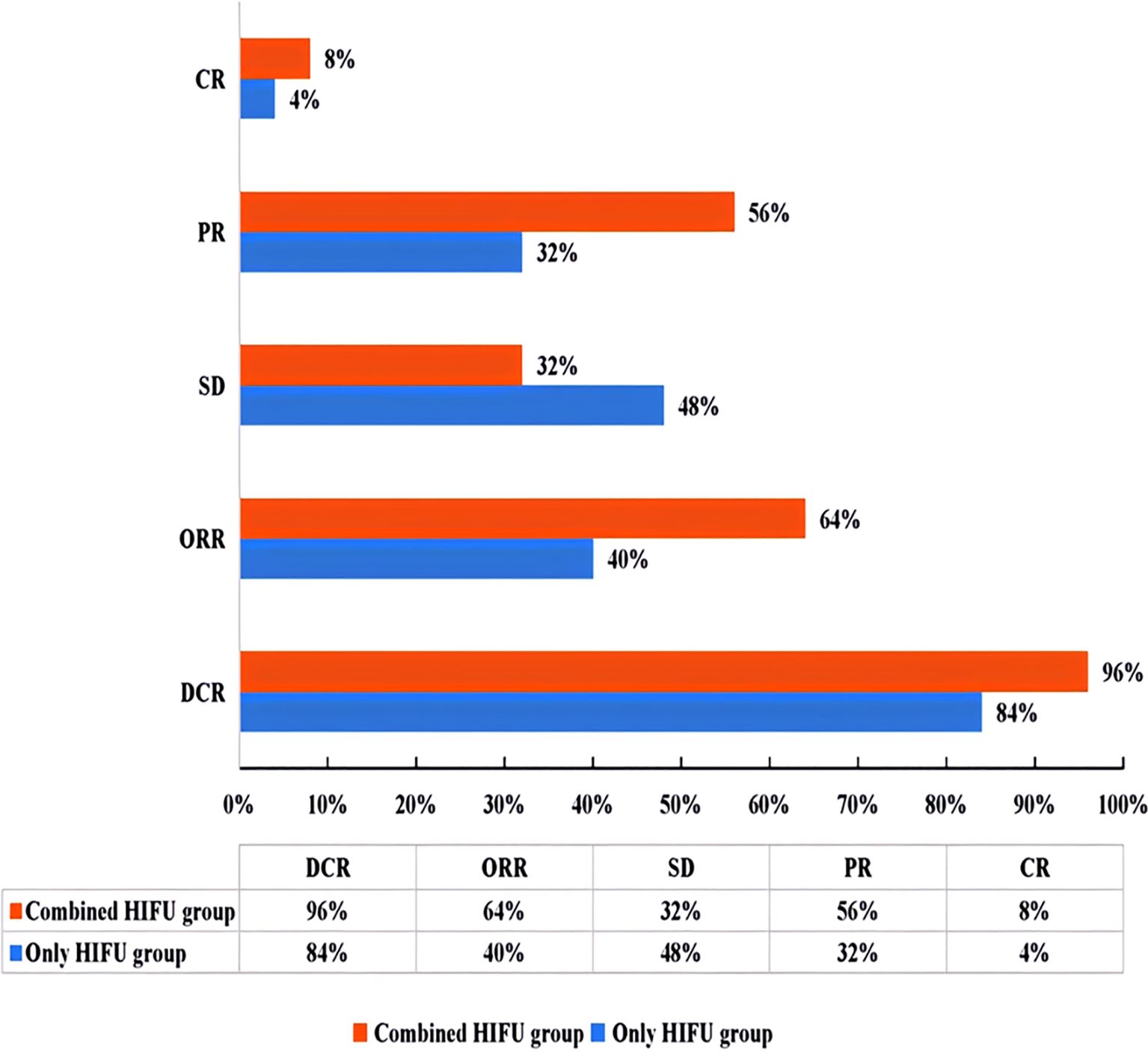
Figure 2. Efficacy evaluation chart according to mRECIST1.1 criteria (ORR=CR+PR; DCR=CR+PR+SD). ORR, objective response rate; DCR, disease control rate; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease.
Figure 1 depicts CE-MRI and intraoperative ultrasound images of a CR secondary liver cancer before and after HIFU treatment. The lesion was located in the left outer lobe of the liver and measured approximately 3cm×2cm. Pre-treatment revealed a low signal on T1WI, a high signal on T2WI, a high signal on DWI, and uneven enhancement on contrast-enhanced scan, predominantly with marginal ring enhancement. Post-treatment imaging showed a low signal on T1WI, a high signal on T2WI, and a high signal on DWI. There was no evidence of enhancement areas on enhanced scan, only marginal linear enhancement. Before and after treatment, coagulative necrosis (non-enhanced area) completely covered the original lesion. Ultrasound images displayed hyperechoic grayscale change (hyperechoic region) after treatment, which was consistent with the coagulated necrosis area observed on CE-MRI images.
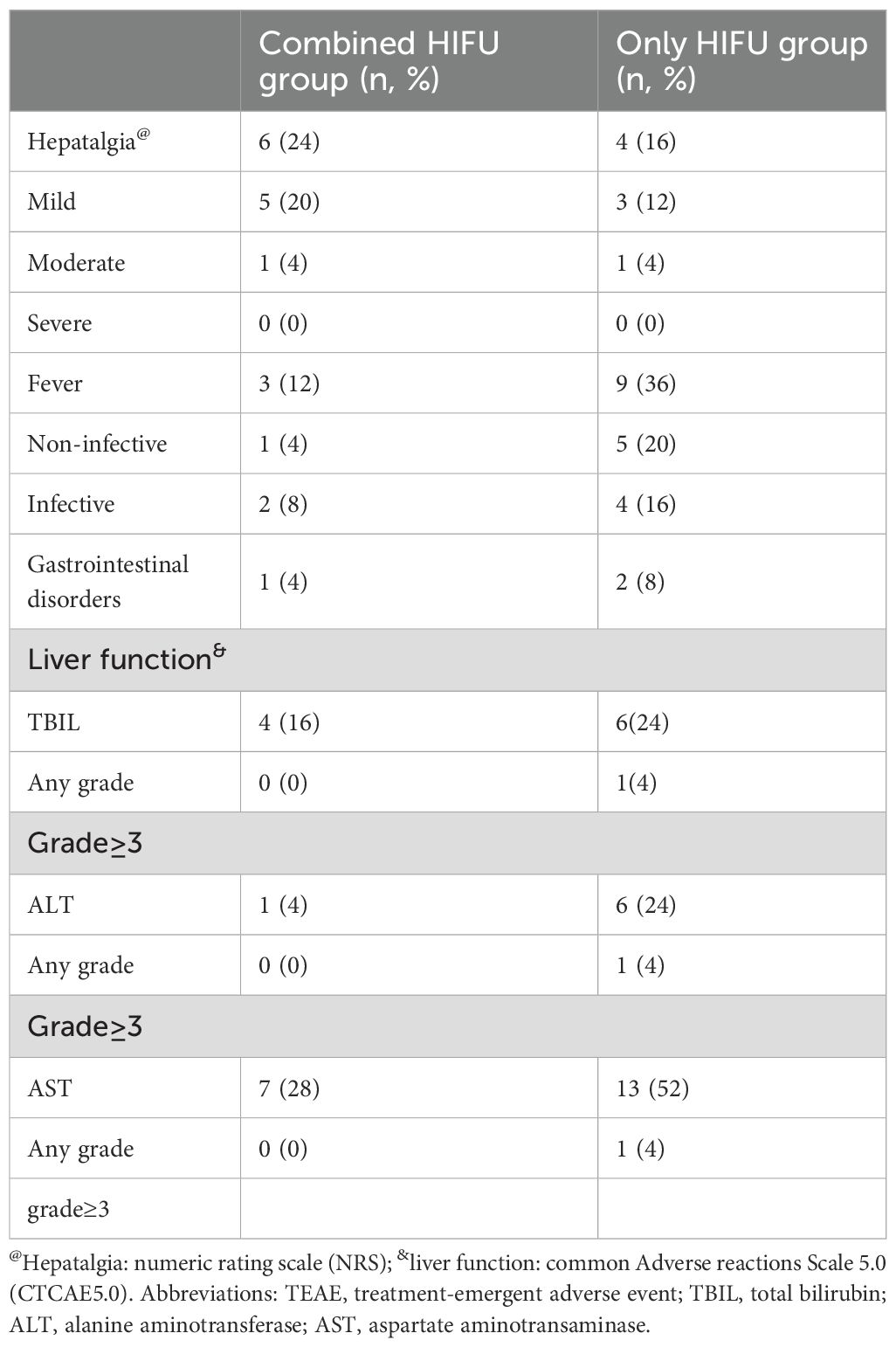
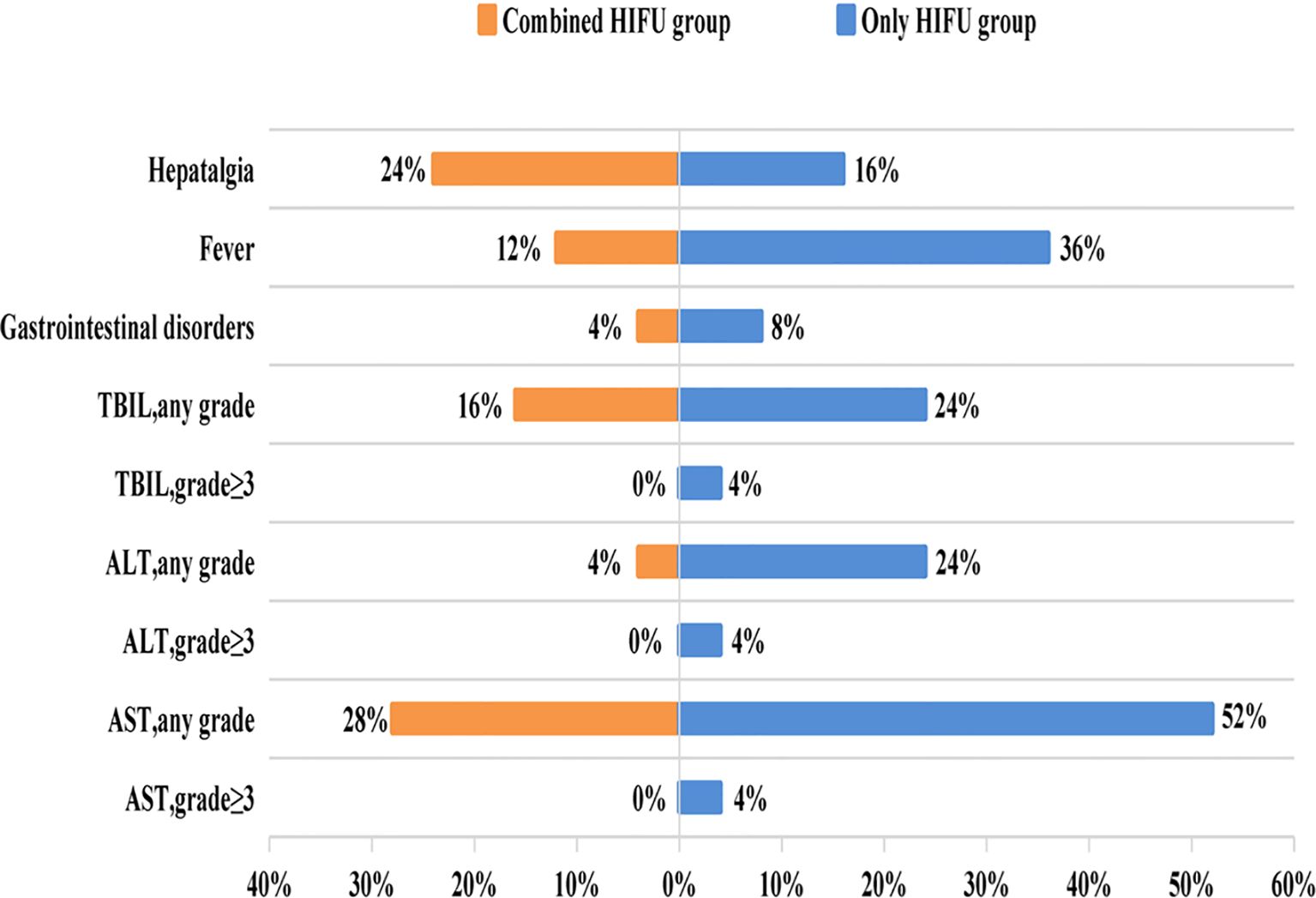
No skin infection, tumor rupture, hemorrhage, or organ perforation occurred in either group. 20% (10/50) of patients developed hepatalgia and mild to moderate burning pain on the skin, with no patients experiencing severe pain. Mild pain was relieved after treatment with ice and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and moderate pain in two patients was alleviated after treatment with weak opioid painkillers and ice. 24% (12/50) of patients were febrile within 3 days after the operation, largely due to bile duct infection and sepsis, with the incidence of fever being 3 times in the Only HIFU group compared with the Combined HIFU group. All liver function injuries occurred within 24h after HIFU, with most of them being transient and resolving without treatment. Notably, no patients developed grade 3 or higher liver damage in the Combined HIFU group, whereas 12% developed grade 3 or higher liver damage in the Only HIFU group (Table 4, Figure 3).
The median follow-up was 16.9 months (95% CI 12.1-21.7). Until the end of the follow-up period, 11 patients (44%) in the Combined HIFU group survived, with a 12 months survival rate of 48% and median overall survival (mOS) of 10.7 months (95% CI 1.3-20.1). On the other hand, six patients (24%) in the Only HIFU group survived, with a 12-month survival rate of 44% and an mOS of 11.8 months (95% CI 10.3-13.3). There was no significant difference in mOS between the two groups (HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.45 to 1.82; p = 0.79) (Figure 4). All deaths were cancer-related.
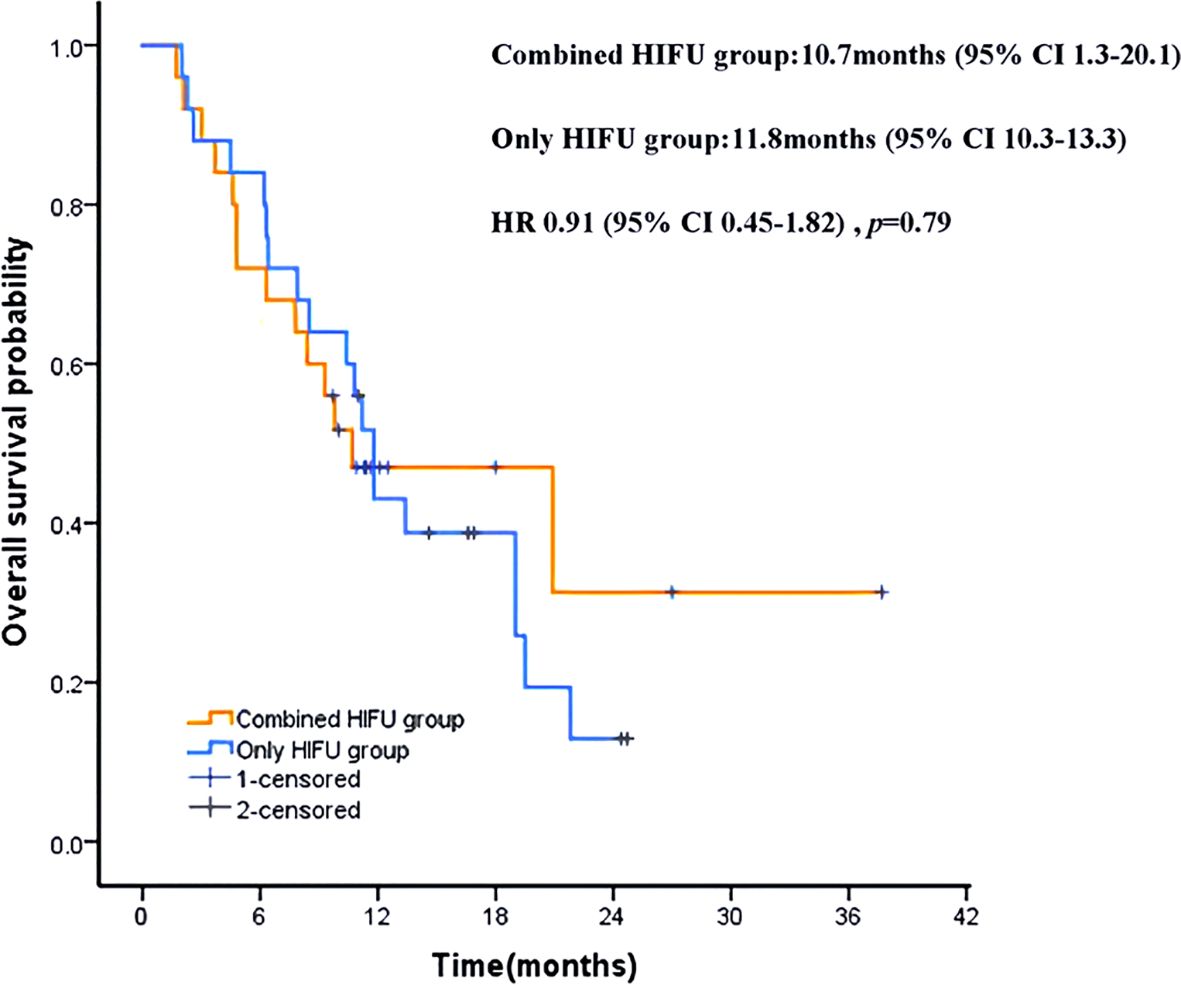
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier patient survival curves. HRs were derived from stratified Cox proportional hazards models. HR, hazard ratio.
4 Discussion
As is well documented, the liver is one of the organs with the most common incidence of malignant tumor (8). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the main pathological type of primary liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75% to 85%, which is one of the malignant tumors with the highest morbidity and mortality globally (9). China ranks fourth in liver cancer morbidity and second in mortality. Moreover, patients are often diagnosed at advanced stages, contributing to the poor prognosis of liver cancer patients (10). In addition, HCC is highly malignant and prone to recurrence and metastasis, which brings challenges to treatment (1, 11–13). Secondary liver cancer is also referred to as metastatic liver cancer. The dual blood supply of the liver results in an abnormally rich blood flow. Consequently, upon entering the bloodstream, cancer cells can move to the liver to form metastases. The actual incidence rate of liver cancer is currently not precisely known, but for most common malignant tumors, such as those in the digestive tract, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, the liver is the most frequently affected organ, metastatic liver cancer is more common than primary liver cancer (14).This is largely consistent with what has been reported in this study. Among patients with advanced liver cancer, 64% are diagnosed with metastatic liver cancer, and 53.1% of these metastatic cases originate from the colorectum. The median survival time of patients with untreated liver metastases is merely 6.9 months (15), making it the leading cause of death in patients with CRC (16, 17). Therefore, active treatment of liver metastases is an effective strategy for delaying disease progression and improving survival outcomes.
Tumor pathogenesis is intricately related to vascular diseases, with the ligand and receptor families of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) playing a decisive role. By actively targeting VEGF, antiangiogenic agents inhibit tumor neovascularization and promote the normalization of abnormal blood vessels to eventually inhibit tumor proliferation. The FDA has approved over a dozen drugs targeting the VEGF/VEGFR pathway, including bevacizumab, lenvatinib, fuquitinib, and anlotinib, which have been used for the treatment of a range of cancers (18), encompassing primary liver cancer (19, 20), CRC (21, 22), lung cancer (23, 24), ovarian cancer (25), and soft tissue sarcoma (26). Rajabi et al. (27) pointed out that effective anti-angiogenic therapy prevents tumor growth. Nonetheless, under specific conditions, they cannot eradicate tumors with single-agent therapies due to compensatory mechanisms, necessitating combination therapies to enhance efficacy. Of note, local treatment can achieve optimal anti-tumorigenic effects in patients with poor local lesion control.
HIFU is a non-invasive technique that employs focused high-energy ultrasound (0.8-3.5MHz) directed at local lesions, thereby instantaneously increasing the temperature at the focal point within seconds and causing irreversible coagulative necrosis of tumor lesions without damaging surrounding tissues (28–30). HIFU can also use (boiling) tissue fragmentation to generate non-thermal effects and destroy focal tissues (31). Compared with surgical interventions and other ablative procedures, the primary advantage of HIFU is its non-invasive nature, which mitigates the risk of tumor spread and metastasis caused by invasive procedures. Furthermore, HIFU allows for the use of antiangiogenic agents without the need for discontinuation before invasive treatment, ensuring that patients do not miss the optimal treatment window and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. HIFU has been widely used in the treatment of both benign and malignant tumors (30, 32, 33–36). Prachee et al. (37) concluded that, to date, HIFU remains the only completely non-invasive local treatment for liver malignant tumors. Herein, no severe adverse events such as skin infection and necrosis, tumor rupture and bleeding, organ perforation, fistula formation, or death were recorded after HIFU treatment for advanced primary liver cancer or secondary liver cancer, validating its non-invasive nature and safety profile. At the same time, HIFU is not limited by the size of the lesion. Wu et al. (38) documented that HIFU can safely and effectively be used for the treatment of large liver cancers with diameters exceeding 4–14 cm. In the present study, 54% (27/50) of lesions had a longest straight length greater than 5 cm. Although other ablation techniques (e.g., radiofrequency ablation, laser ablation, microwave ablation, and cryoablation) are also minimally invasive, they cannot effectively ablate liver cancer with a diameter exceeding 5 cm, limiting their applicability in cases of advanced liver cancers.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound imaging (US) are currently the two mainstream modalities for guiding and monitoring clinical HIFU surgery, providing integrated treatment planning, real-time control (spatial and temperature), and evaluation (39, 40). Although MRI is highly sensitive to temperature and soft tissue contrast, it does not meet real-time imaging requirements during treatment and is costly, especially due to a lack of specialized MRI-HIFU equipment for liver cancer (41, 42). Ultrasound image-guided HIFU (US-HIFU) is the most widely used technique in the clinical setting owing to its low cost, favorable compatibility, and real-time performance (43). Thus, US-HIFU was used in this study. According to the HIFU treatment parameters in this study, a statistical difference was identified in the occurrence time of grayscale between the combined HIFU treatment group and the single HIFU group (p=0.04). The median grayscale occurrence time of the former was significantly shorter than that of the latter, signaling that advanced liver cancer treated with antiangiogenic agents was more sensitive to lesions and had a faster onset of effect during HIFU surgery. The grayscale of an ultrasound image is determined by the ultrasonic reflection coefficient of tissues (i.e., the intensity of reflected signals). In normal tissues, the cellular structure, density, and water content are relatively uniform, resulting in a stable reflection coefficient. Accordingly, the grayscale presents as uniform “isoechoic” (echo intensity matching the surrounding normal tissue) or “hypoechoic” (echo intensity lower than the surrounding normal tissue).After HIFU treatment, however, the proteins in the target lesion undergo denaturation. This process leads to the disruption of cellular structures, an increase in tissue density, and the formation of irregular “coagulative necrosis foci”. The density difference between the treated lesion and the surrounding normal tissue is thereby significantly enlarged, which enhances the ultrasonic reflection signals—causing the treated area to appear “hyperechoic” (echo intensity higher than the surrounding normal tissue) on ultrasound images. Therefore, the real-time monitoring of HIFU treatment efficacy can be achieved by tracking changes in ultrasonic grayscale (44).Although the irradiation time was not statistically different between the two groups, the median treatment volume in the combined HIFU group was 1 cc larger than that in the control group. Larger volumes are typically correlated with longer irradiation times. Therefore, while the total operation time was similar, larger lesions were simultaneously treated, which partially enhanced treatment efficiency, accelerated procedural workflow, and lowered the risk of intraoperative anesthesia. HIFU enables the selective destruction of tumor blood vessels with a diameter of ≤ 2 mm, while sparing major blood vessels. This mechanism blocks the nutritional supply to tumor cells, leading to their ischemic necrosis, without inducing the dissemination or metastasis of tumor cells (45).Additional studies have demonstrated that tumor vascular structure components including elastic fiber, endothelial cells all were destroyed by HIFU. After ultrasonic ablation, gray-scale of tumor nodules enhanced in ultrasonography, tumor peripheral and internal blood flow signals disappeared or significantly reduced in color Doppler flow imaging (46). In advanced liver cancer, tumors exhibit abundant blood flow and high perfusion. The heat generated by HIFU is easily dissipated by the bloodstream, leading to insufficient temperature elevation in the tumor target region. As a result, the critical threshold of an instantaneous high temperature (over 60 °C),which is required to achieve one-time coagulative necrosis, and cannot be reached rapidly. This ultimately results in limited therapeutic efficacy and prolonged treatment duration. In the present study, antiangiogenic targeted drugs are administered prior to HIFU therapy to inhibit tumor blood supply and reduce blood flow. This intervention transforms the target lesion from a hypervascular state to a hypovascular state, thereby enhancing treatment efficiency and achieving a synergistic anti-tumor effect. Currently, Some studies on HIFU combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) or radiotherapy also hinges on this fundamental principle (47, 48).It is worth recognizing that this study failed to demonstrate statistical differences due to the small sample size. In the future, large randomized clinical trials are warranted to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of the combination of antiangiogenic agents with HIFU for patients with advanced liver cancer.
CE-MRI can be used to visualize coagulated necrosis of liver cancer and evaluate the effectiveness of HIFU treatment. Although coagulative necrosis was not detected in some lesions, the absent or significantly reduced tumor blood supply resulted in lesion shrinkage, which was also effective according to the RECIST1.1 criteria. At present, there is no universal HIFU standard that takes into account both types of efficacy evaluation. Therefore, this study formulated mRECIST1.1 combined with RECIST1.1, which is a tailored approach for clinical HIFU efficacy evaluation. This study exposed that despite most lesions showing varying degrees of coagulative necrosis after HIFU treatment, the remaining ones were stable or reduced in size, achieving a disease control rate of 90% at one month. Besides, the coagulative necrosis rate, DCR, and ORR were all higher in the Combined HIFU group compared with the Only HIFU group. In short, short-term efficacy was higher in the Combined HIFU group. Previous studies have established that the complete ablation rate of HIFU for HCC after a single treatment ranges between 28.5%-68% (33, 38, 49, 50). However, it was less than 10% in this study, ascribed to all subjects having advanced liver cancer, among which 64% (32/50) of cases were diagnosed with secondary liver cancer, and 54% (27/50) had lesions over 5 cm in diameter. Treatment goals were mainly palliative, potentially restraining treatment intensity. After a long-term follow-up period of 16.9 months, the median survival of patients with advanced liver cancer in this study was over 10 months, which was significantly higher than that of patients with untreated liver metastases (15). The marginally lower mOS in the Combined HIFU group compared to the Only HIFU group could be attributed to secondary liver cancer originating from different sites and multiple factors influencing long-term survival. A recent study indicates that HIFU significantly improves OS in CRC liver metastasis patients, but the number of metastases treated with HIFU and systemic treatment lines significantly influenced survival (51).
In terms of safety, Acute adverse events in this study consistent with the findings of earlier studies. No new or fatal adverse events occurred in the Combined HIFU group, the incidence of infectious fever and liver function impairment was significantly lower than that in the only HIFU group, which may be associated with antiangiogenic agents inhibiting tumor neovascularization and inflammatory factor release, normalizing abnormal blood vessels, minimizing focal blood supply, regulate the immune microenvironment, thereby reducing tissue damage and inflammatory responses (52, 53).
This study has drawn several preliminary conclusions of clinical value, but it also has its limitations. Specifically, the study was designed as a single-center, small-sample retrospective study and did not include key biological markers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). In this study, over 70% of the patients received other anti-tumor treatments after HIFU. The adverse events might be influenced by other factors and it was difficult to attribute them solely to HIFU. Therefore, only the analysis of acute adverse reactions was conducted, which might result in the omission of risks associated with late toxicity. Furthermore, the follow-up for long-term survival outcomes remains inadequate-for instance, specific subsequent treatment regimens were not incorporated into the study. In future research, a prospective large-sample stratified cohorts study will be conducted to address these limitations. This research approach is expected to provide more accurate conclusions for clinical practice, thereby offering evidence-based guidance for clinical decision-making and ultimately benefiting a larger patient population.
5 Conclusion
Antiangiogenic agents combined with HIFU are effective and safe in the treatment of advanced liver cancer and enhance the efficiency of HIFU treatment. Nonetheless, their efficacy and safety should be evaluated in large-scale prospective randomized clinical studies.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because privacy restrictions. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis. QS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YL: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – original draft. FS: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YH: Data curation, Writing – original draft. PM: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. LF: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. YB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. GF: Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Ethics statement
Studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the medical ethics committee of the Mianyang Central Hospital (File No.:S20230217-02). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the State Key Laboratory of Ultrasound in Medicine and Engineering (No.:2023KFKT020).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, and Soerjomataram I. Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Wang CY and Li S. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of 2887 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A single center 14 years experience from China. Medicine. (2019) 98:e14070. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014070
3. Translational therapy Collaboration Group, Liver Cancer Professional Committee, and Chinese Anticancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on transformation and perioperative treatment of primary liver cancer (2024 edition). Chin J Of Digestive Surg. (2024) 23:492–513. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20240228-00135
4. Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York: Springer (2017).
5. Fukuda H, Numata K, Nozaki A, Kondo M, Morimoto M, Tanaka K, et al. Hyperecho in ultrasound images during high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas. Eur J Radiol. (2011) 80:e571–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.09.001
6. Wu F, Wang ZB, Wang ZL, Zou JZ, Chen WZ, and Liu C. Changes in ultrasonic image of tissue damaged by high intensity focused ultrasound in vivo. J Acoust Soc Am. (1998) 103:2869. doi: 10.1121/1.421636
7. Wu F, Wang ZB, Chen WZ, Zou JZ, Bai J, Zhu H, et al. Extracorporeal focused ultrasound surgery for treatment of human solid carcinomas: early Chinese clinical experience. Ultrasound Med Biol. (2004) 30:245–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.10.010
8. Cranston D. A review of high intensity focused ultrasound in relation to the treatment of renal tumours and other Malignancies. Ultrason Sonochem. (2015) 27:654–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.05.035
9. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, and Jemal A. Global cancer statistic. Ca-Cancer J Clin. (2015) 65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262
10. Kanwal F and Singal AG. Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: current best practice and future direction. Gastroenterology. (2019) 157:54–64. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.049
11. Siegel RL, Miller KD, and Jemal A. Cancer statistic. CA Cancer J Clin. (2022) 72:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
12. Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, Yin P, Zhu J, Chen W, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in Chinaand its provinces 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of DiseaseStudy 2017. Lancet. (2019) 394:1145–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1
13. Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Baade PD, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Jemal A, et al. Cancer statistics in Chin. CA Cancer J Clin. (2016) 66:115–32. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
14. Rumgay H, Ferlay J, de Martel C, Georges D, Ibrahim AS, Zheng R, et al. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur J Cancer. (2022) 161:108–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.11.023
15. Stewart CL, Warner S, Ito K, Raoof M, Wu GX, Kessler J, et al. Cytoreduction for colorectal metastases: liver, lung, peritoneum, lymph nodes, bone, brain. When does it palliate, prolong survival, and potentially cure? Curr Probl Surg. (2018) 55:330–79. doi: 10.1067/j.cpsurg.2018.08.004
16. Gastrointestinal Surgery Group and Surgical Society of Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and comprehensive Treatment of liver metastases in Colorectal Cancer (2023 Ed.). Chin J Digestive Surg. (2023) 22:1–28. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221228-00762
17. Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, and Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistic. Ca-Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:233–54. doi: 10.3322/caac.21772
18. Li SJ, Chen JX, and Sun ZJ. Improving antitumor immunity using antiangiogenic agents: Mechanistic insights, current progress, and clinical challenges. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2021) 41:830–50. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12183
19. Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. (2018) 391:1163–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1
20. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. New Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1894–905. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
21. Cremolini C, Antoniotti C, Lonardi S, Rossini D, Pietrantonio F, Cordio S, et al. Updated results of TRIBE2, a phase III, randomized strategy study by GONO in the first- and second-line treatment of unresectable mCRC. J Clin Oncol. (2019) 37:3508–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.3508
22. Dasari A, Sobrero A, Yao J, Yoshino T, Schelman WR, Nanda S, et al. FRESCO-2: a global Phase III study investigating the efficacy and safety of fruquintinib in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Future Oncol. (2021) 17:3151–62. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0202
23. Han G, Li C, and Yi P. The efficacy of bevacizumab combined with platinum-containing chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1293039. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1293039
24. Cheng Y, Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Zhang L, Shi JH, et al. Effect of anlotinib as a third- or further-line therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with different histologic types: Subgroup analysis in the ALTER0303 trial. Cancer Med. (2020) 9:2621–30. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2913
25. Farooq MZ, Rehman UO, Fatima E, Imran H, Akram U, Ahmad AB, et al. Bevacizumab combination therapy versus standard chemotherapy for ovarian cancer in shorter and longer followup duration: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:e23296. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.16_suppl.e23296
26. Li T, Ye Z, Wei Y, Wang S, Liu Y, and Chen J. A phase II study of anlotinib in the first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma: Updated results. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:e23559. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.e23559
27. Rajabi M and Mousa SA. The role of angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Biomedicines. (2017) 5:34. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines5020034
28. Cheung TT, Ma KW, and She WH. A review on radiofrequency, microwave and high-intensity focused ultrasound ablations for hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2021) 10:193–209. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2020.03.11
29. Wang J and Zhang L. High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for liver cancer. J North Sichuan Med Coll. (2023) 38:1451–1454+1474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2023.11.003
30. Wu F. High intensity focused ultrasound ablation and antitumor immune response. J Acoust Soc Am. (2013) 134:1695–701. doi: 10.1121/1.4812893
31. Khokhlova VA, Fowlkes JB, Roberts WW, SChade GR, Xu Z, Khokhlova TD, et al. Cain CA:Histotripsy methods in mechanical disintegration of tissue: towards clinical applications. Int J Hyperther. (2015) 31:145–62. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2015.1007538
32. Huang SQ, Mei CW, Chen SY, and Jiang XY. High intensity focused ultrasound combined with chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Chin J Clin Oncol Rehabil. (2011) 18:71–3. doi: 10.13455/j.cnki.cjcor.2011.01.021
33. Wu F, Wang ZB, Chen WZ, Wang W, Gui Y, Zhang M, et al. Extracorporeal high intensity focused ultrasound ablation in the treatment of 1038 patients with solid carcinomas in China: an overview. Ultrason Sonochem. (2004) 11:149–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2004.01.011
34. Lei T, Guo X, Gong C, Chen X, Ran F, He Y, et al. High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation in the treatment of recurrent ovary cancer and metastatic pelvic tumors: a feasibility study. Int J Hyperther. (2021) 38:282–7. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2021.1889698
35. Zhong Q, Tang F, Ni TT, Chen YP, Liu YC, Wu J, et al. Salvage high intensity focused ultrasound for residual or recurrent cervical cancer after definitive chemoradiotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:995930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.995930
36. Chok KS, Cheung TT, Lo RC, Chu FS, Tsang SH, Chan AC, et al. Pilot study of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation as a bridging therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients wait-listed for liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. (2014) 20:912–21. doi: 10.1002/lt.23892
37. Prachee I, Wu F, and Cranston D. Oxford's clinical experience in the development of high intensity focused ultrasound therapy. Int J Hyperther. (2021) 38:81–8. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2021.1899311
38. Wu F, Wang ZB, Chen WZ, Zhu H, Bai J, Zou JZ, et al. Extracorporeal high intensity focused ultrasound ablation in the treatment of patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2004) 11:1061–9. doi: 10.1245/ASO.2004.02.026
39. Han Y, Hou GY, Wang S, and Konofagou E. High intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) focal spot localization using harmonic motion imaging (HMI). Phys Med Biol. (2015) 60:5911–24. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/15/5911
40. Siedek F, Yeo SY, Heijman E, Grinstein O, Bratke G, Heneweer C, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (MR-HIFU): technical background and overview of current clinical applications (Part 1). Rofo-Fortschr Rontg. (2019) 191:522–30. doi: 10.1055/a-0817-5645
41. Kim YS. Advances in MR image-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy. Int J Hyperther. (2014) 31:225–32. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2014.976773
42. De Senneville BD, Moonen C, and Ries M. MRI-guided HIFU methods for the ablation of liver and renal cancers. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2016) 880:43–63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22536-4_3
43. Ebbini ES and ter Haar G. Ultrasound-guided therapeutic focused ultrasound: current status and future directions. Int J Hyperther. (2015) 31:77–89. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2014.995238
44. Sha WH, Li YY, Nie YQ, Wang ZB, Li FQ, Li CY, et al. focal region of high intensi ty focused ultrasound combined with ultrasound contrast agent on rabbi t liver. Chin J Ultrasonography. (2004) 4:58–61.
45. Lan JT, Liao FT, and He WY. Clinical progress of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in the treatment of renal tumors. J Modern Urologic Genitourinary Oncol. (2025) 17:65–7. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1674-4624.2025.01.018
46. Guan L and Xu G. Destructive effect of HIFU on rabbit embedded endometrial carcinoma tissues and their vascularities. Oncotarget. (2017) 2:8. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14751
47. Luo Y and Jiang Y. Comparison of Efficiency of TACE plus HIFU and TACE alone on Patients with Primary Liver Cancer. Jcpsp-J Coll Physici. (2019) 4:29. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2019.05.414
48. Xu T, Jing HX, Li LJ, Zhang J, Yu JY, Cheng XF, et al. Clinical research of IMRT combined with HIFU for inoperable recurrent primary hepatocarcinoma after operation and TACE. Chongqing Med. (2016) 36:5088–5090+5094. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.36.015
49. Zhang L, Zhu H, Jin C, Zhou K, Li K, Su K, et al. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU):effective and safe therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to major hepatic veins. Eur Radiol. (2009) 19:437–45. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-1137-0
50. Tsang SH, Ma KW, She WH, Chu F, Lau V, Lam SW, et al. High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of liver tumors in difficult locations. Int J Hyperther. (2021) 38:56–64. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2021.1933217
51. Wang S, Zhang Z, Sun L, Li J, Liu H, Huang X, et al. Clinical observation and immune effect of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatment on patients with colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Int J Hyperthermia. (2025) 11:42. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2025.2519344
52. Swamy K. Vascular-immuno-phenotypic (VIP) model for locally advanced and oligo-metastatic cancer: A hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. (2021) 152:110618. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2021.110618
Keywords: liver cancer, antiangiogenic agents, high-intensity focused ultrasound, ultrasound grayscale, coagulative necrosis
Citation: Wu R, Shi Q, Liao D, Liao Y, Sun F, He Y, Mao P, Fan L, Bai Y and Feng G (2025) Efficacy and safety of antiangiogenic agents combined with HIFU in the treatment of advanced liver cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1652434. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1652434
Received: 23 June 2025; Accepted: 04 September 2025;
Published: 26 September 2025.
Edited by:
Antonio Giovanni Solimando, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyReviewed by:
Antonella Argentiero, National Cancer Institute Foundation (IRCCS), ItalyFabrizio Pappagallo, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Consorziale Policlinico di Bari, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Shi, Liao, Liao, Sun, He, Mao, Fan, Bai and Feng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rong Wu, c2hpeXVuaml1eWVAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Gang Feng, ZmVuZ2dhbmdteWNoQHNpbmEuY29t
 Rong Wu
Rong Wu Qiuling Shi
Qiuling Shi Dongbiao Liao1
Dongbiao Liao1