- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, The Affiliated Huizhou Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Huizhou, China
- 2School of Public Health, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
- 4Department of Radiotherapy, Southern Medical University Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 5People’s Hospital of Shaodong, Shaoyang, China
- 6Nanjing Tongrentang Chinese Medicine, Huizhou, China
- 7Department of Radiation Oncology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Objective: To evaluate the feasibility and dosimetric benefits of Halcyon-based coplanar dual-arc volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiotherapy (HA-WBRT).
Methods: Twenty-one HA-WBRT patients were replanned using dual-arc VMAT (collimator 23°/293°) on Halcyon and Truebeam. The planning target volume (PTV) was segmented into three substructures and optimized with different weight parameters. Dosimetric parameters of PTV, monitor units (MUs), does to organs-at-risk(OARs), hippocampal normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) and gamma passing rate were recorded.
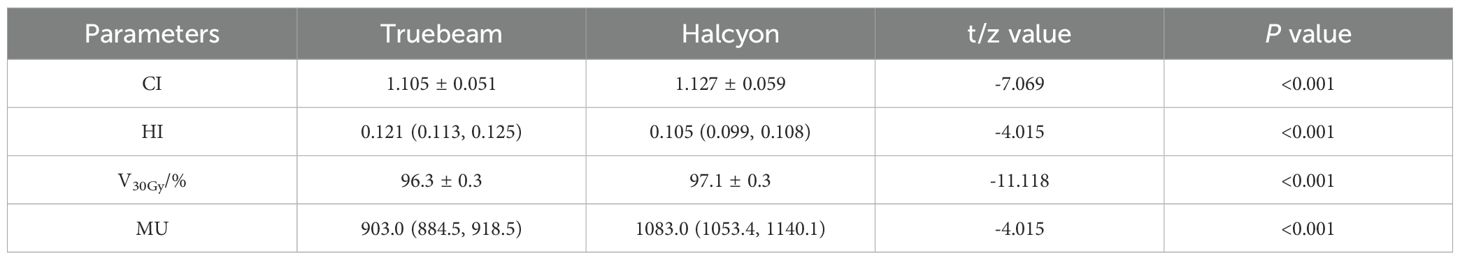
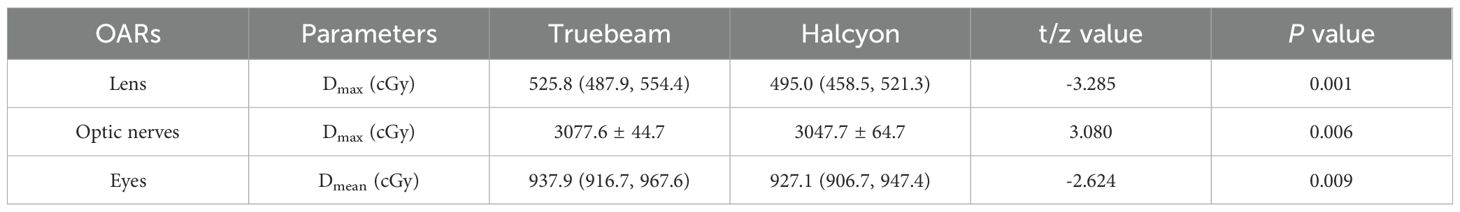
Results: All plans met RTOG 0933 criteria. The Halcyon plans demonstrated significantly better homogeneity index (HI) and V30Gy of the PTV (HI: 0.105 vs. 0.121, P<0.001; V30Gy: 97.1% vs. 96.3%, P<0.001), alongside reduced hippocampal dose (D100%: 626.8 vs. 695.0cGy; Dmean: 850.0 vs. 898.4cGy; Dmax: 1348.1 vs. 1399.8 cGy; NTCP: 34.16% vs. 31.67%, P ≤ 0.001), OARs sparing improved for Lens Dmax (495.0 vs. 525.8cGy, P = 0.001), Optic nerves Dmax(3047.7 vs. 3077.6cGy, P = 0.006), and eyes Dmean(927.1 vs. 937.9cGy, P = 0.009). The average gamma passing rates were higher for Halcyon than Truebeam (3%/2mm: 99.96% vs. 99.85; 2%/2mm: 99.83% vs. 99.49%).
Conclusions: Under the innovative planning approach, redefined hippocampal-sparing radiotherapy using Halcyon system, providing superior prescription dose coverage, improved OAR sparing, and reduced hippocampal NTCP.
Introduction
The incidence of brain metastases has been steadily increasing in recent years (1, 2). Despite advances in systemic therapies, the efficacy of chemotherapy in controlling brain metastases remains limited due to the restrictive nature of the blood-brain barrier (3). Whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) has demonstrated efficacy in improving local control and extending overall survival in patients with brain metastases (4). However, the neurotoxic effects of WBRT on the central nervous system have become a growing concern (5). Studies have demonstrated that radiation-induced hippocampal damage significantly impairs neurocognitive functions, particularly those related to learning, memory, and spatial processing (6). A multicenter phase II clinical trial (RTOG 0933) revealed that hippocampal-avoidance WBRT (HA-WBRT) effectively preserves patients’ neurocognitive functions and improves their quality of life (7).
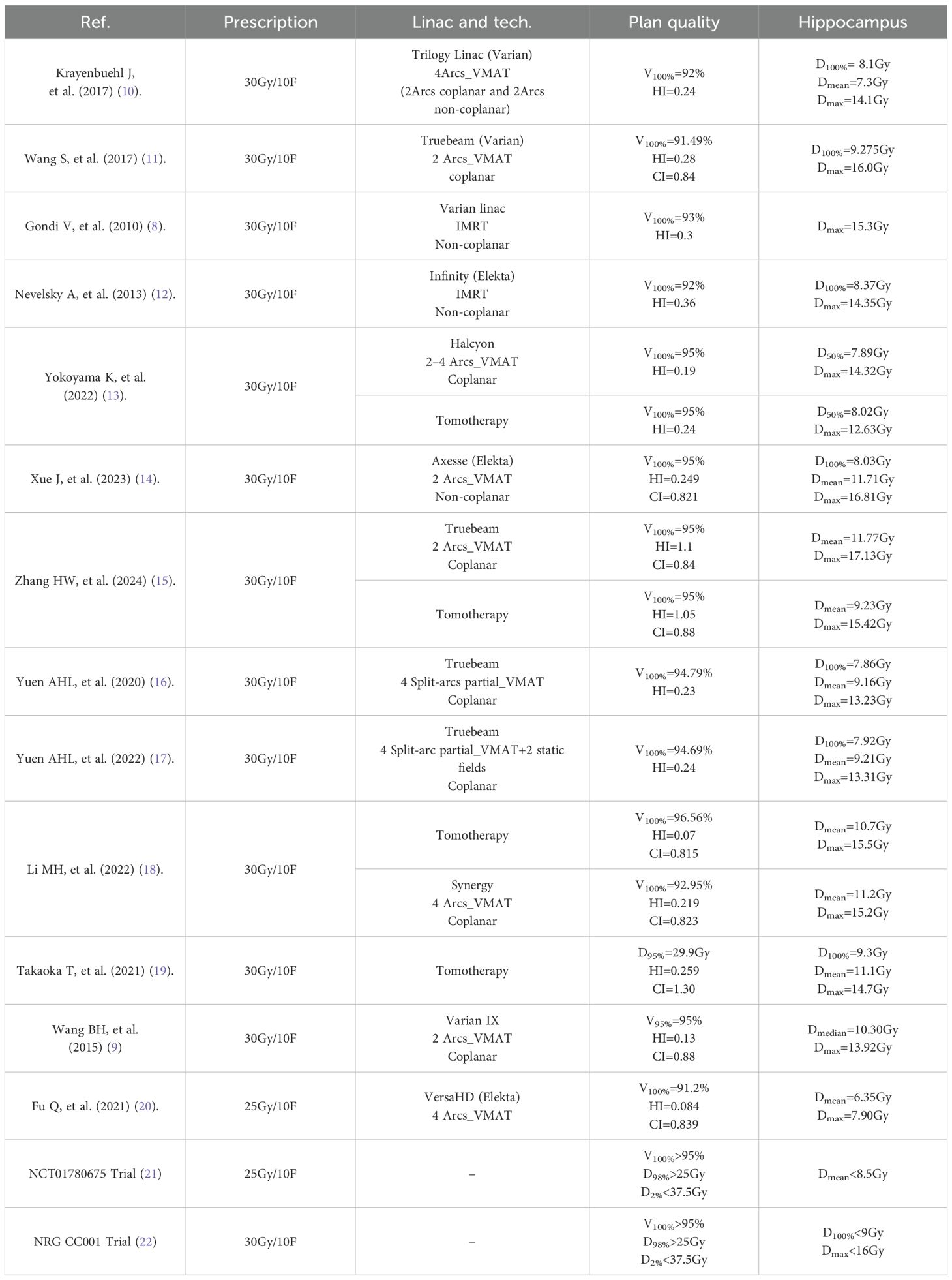
Over the past decades, HA-WBRT have been developed to use intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT), and tomotherapy (TOMO) techniques as listed in Table 1 (8–22). Gondi et al. (8) found that TOMO technology offers more advantages in HA-WBRT. However, the high cost of TOMO equipment makes it unaffordable for many small-scale hospitals. Wang et al. (9) have reported that HA-WBRT based IMRT techniques takes a long time for patients on the couch, which may cause patients discomposure. Dosimetric performance of conventional VMAT for HA-WBRT has been reported in previous studies following RTOG 0933 criteria, suggesting that VMAT irradiations use non-coplanar multi-arc irradiation. However, non-coplanar VMAT techniques increase the risk of tumor movement and extend treatment time.
In recent years, the Halcyon has gained widespread adoption in clinical practice due to its innovative design features. Unlike conventional C-arm accelerators, the Halcyon employs a circular ring gantry structure, eliminating the need for fixed jaws and enabling a ring rotation speed of 24°/s/eedi times that of C-arm LINACs. Additionally, the Halcyon is equipped with a dual-layer multi-leaf collimator (MLC) featuring 29 proximal and 28 distal leaves, which effectively minimizes leakage and transmission. The Halcyon exclusively utilizes a 6 MV flattening filter-free (FFF) photon beam, further enhancing its efficiency and precision in delivering high-quality radiotherapy. To the best of our knowledge, only a few studies have been reports of HA-WBRT using Halcyon. The results from Yokoyama et al. (13) demonstrated that three-arc Halcyon treatment plan was effective in handling hippocampus sparing whole-brain radiotherapy. However, the three-arc design prolonged prolong treatment time and increase costs. Here, we propose a novel coplanar dual-arc VMAT technique on the Halcyon platform that incorporates both target segmentation and collimator angle optimization, and systematically evaluate the dosimetric characteristics of HA-WBRT using coplanar dual-arc VMAT on Halcyon and Truebeam platforms.
Materials and methods
Patient selection
We retrospectively studied twenty-one patients who underwent HA-WBRT from June 2024 to December 2024. The cohort consisted of six males and four females, with a median age of 49 years (range: 33 – 70 years). All patients were diagnosed with non-hematologic malignancies confirmed through histopathological or cytological examination, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing brain metastases located at least 5 mm away from the hippocampus. Local approval was granted, and written informed consent was obtained.
Simulation
Patients were immobilized in the supine position using a thermoplastic mask. CT images were acquired using a Brilliance Big Bore CT scanner (Philips, Netherlands) with a slice thickness of 2.5 mm, covering the region from the scalp to the upper edge of the second cervical vertebra. Additionally, contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI scans with a slice thickness of 1 mm were performed within two weeks before radiotherapy. CT and MRI images were fused in the Eclipse v16.1 treatment planning system to facilitate precise hippocampal delineation by radiation oncologists.
Target and organs at risk delineation
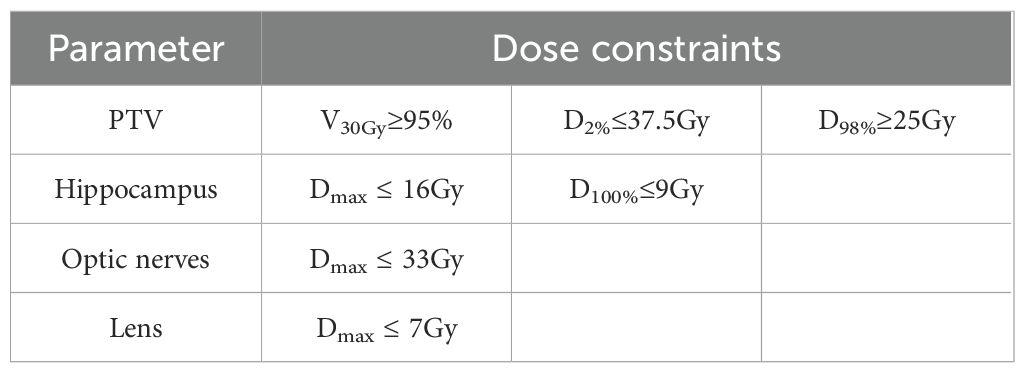
Following the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) atlas, the hippocampus was manually delineated using fused CT and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI images. A 5-mm three-dimensional margin around the hippocampus was designated as the hippocampal avoidance region (HA). The clinical target volume (CTV) was defined as the whole brain excluding the HA region. The planning target volume (PTV) was created by expanding the CTV by 3 mm while excluding the HA region. The prescription dose for the PTV was 30Gy in 10 fractions, with at least 95% of the PTV volume receiving the prescribed dose. Dose constraints for the PTV, hippocampus, and other organs at risk (OARs) are listed in Table 2.
Equipment parameters
The Halcyon designed with a ring gantry from Varian Corporation in the United States was employed, equipped with dual-layer MLCs (29 proximal and 28 distal leaves with a 5-mm resolution) and a 6 MV FFF photon beam with a maximum dose rate of 800 MU/min. For comparison, the Truebeam linac featured a single-layer MLC with 60 leaves (40 central leaves at 5-mm width and 20 peripheral leaves at 10-mm width), a dynamic jaw tracking system, and a maximum dose rate of 1400MU/min. All treatment plans were designed using the Eclipse v16.1 treatment planning system.
Plan design
To optimize PTV coverage while sparing the hippocampus, the PTV was segmented into three sub-structures: zPTV_up (from the upper PTV boundary to the superior edge of the HA region), zPTV_mid (the PTV portion overlapping the HA region), and zPTV_down (from the inferior edge of the HA region to the lower PTV boundary). This segmentation strategy enhanced modulation efficiency during treatment planning optimization (Figure 1A).
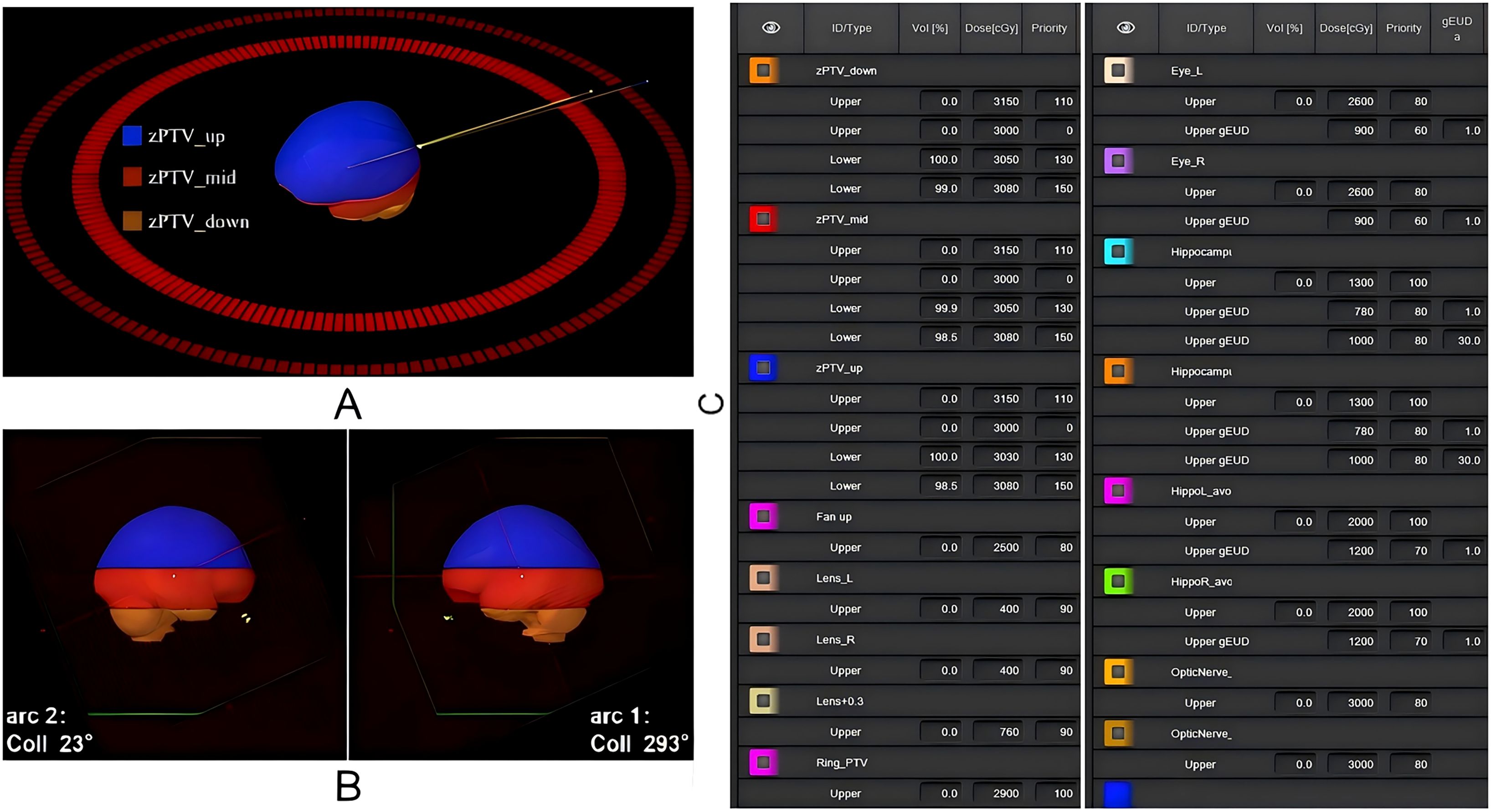
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the radiotherapy plan design and key target structure optimization parameters. (A) Logical segmentation of the PTV structure; (B) Gantry angle settings for dual-arc VMAT; (C) Key optimization parameters for target structures in the treatment plan.
As illustrated in Figure 1B, to ensure a consistent and unbiased comparative evaluation between the selected machine models under identical clinical conditions, all treatment plans utilized coplanar dual-arc VMAT with collimator angles set at 23° and 293°. Optimization was performed using the photon optimization (PO) algorithm, and dose calculations were conducted with the Acuros XB algorithm at a grid resolution of 2.5 mm. Identical dose constraints and optimization parameters were applied to both Halcyon and Truebeam plans to ensure comparability (Figure 1C).
Plan evaluation
The plan quality was assessed using dose-volume histograms (DVHs). PTV evaluation metrics included V30Gy (%), conformity index (CI), and homogeneity index (HI), calculated using the following Equation 1 (23):
In the formulas, represents the volume receiving the prescription dose, is the target volume, and is the volume of the prescription dose within the target volume. , and represent the doses received by 2%, 98%, and 50% of the target volume, respectively. The CIcloser to 1 indicates better dose conformity to the target, while the HI closer to 0 reflects more uniform dose distribution within the target.
The evaluation parameters of OARs include D100%, Dmean, and Dmax for the hippocampus; Dmax for the lens and optic nerves; and Dmean for the eyeball. Additionally, the total monitor units (MUs) for all plans were recorded.
Normal tissue complication probability
The normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) is a quantitative measurement of the probability that a dose of radiation will have an undesirable effect on an organ. The following mechanistic of formula is used to calculate the NTCP, as shown in Equations 2, 3 (24):
was received by 40% of bilateral hippocampal volume, was the valuecorresponding to a 50% probability of neurocognitive decline, and m represented the slope of the dose-response curve. Moreover, and m were estimated to be 14.88 Gy and 0.54 by Gondi et al (24).
Biologically equivalent dose in 2-Gy fraction () to 40% of the bilateral hippocampi was evaluated according to the following Equation 4 (25):
Where D represented the total dose and d represented the dose per fraction. An ratio for the hippocampus was assumed to be 2 (25).
Dose verification
3D gamma passing rate analysis on dose images of all treatments was performed using the Portal Dosimetry module in Varian Eclipse. Halcyon plans were verified using its built-in digital megavolt imager, with a pixel resolution of 1280 × 1280 (0.336 mm per pixel) and an active detection area of 43 cm × 43 cm. Truebeam plans were verified using the a-Si1000 electronic portal imaging device, with a pixel resolution of 1024 × 768 (0.39 mm per pixel) and an active detection area of 40 cm × 30 cm. The gamma analysis criteria were set as follows: a dose threshold of 10%, dose tolerance/distance to agreement of 3%/2 mm and 2%/2 mm, respectively. The passing rates for all treatment plans were recorded and analyzed.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS v25.0 and Origin 2022. The Shapiro-Wilk test was employed to assess data normality. Normally distributed data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using paired t-test, while non-normally distributed data were expressed as median (interquartile range) and analyzed using Wilcoxon test. A two-tailed α-level of 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Dose distribution and DVH comparison
The Halcyon plan demonstrated superior PTV coverage and hippocampal sparing compared to the Truebeam plan, as illustrated in Figure 2. The DVHs for the same patient, shown in Figure 3, indicate that both plans met clinical requirements. Notably, the Halcyon plan achieved OAR doses well below tolerance limits and demonstrated a more favorable DVH profile compared to the Truebeam plan.

Figure 2. The dose distribution of Truebeam and Halcyon applying double arc coplanar VMAT for a representative patient. (A-C) Dose distribution at the axial, sagittal and coronal views. The top and bottom figures are the Truebeam and Halcyon plans, respectively.

Figure 3. DVHs comparison for PTV and OARs between Truebeam and Halcyon applying VMAT. The yellow, green and red line represents the physical dose exposure to the lens, hippocampus and PTV, respectively.
Dosimetric parameters and monitor unit comparison
All plans achieved ≥ 95% PTV coverage at the prescription dose. The Halcyon plan demonstrated superior coverage at 97.1%, compared to 96.3% for the Truebeam plan (P< 0.001). In terms of dose homogeneity, the Halcyon plan achieved a significantly lower median HI value than the Truebeam plan (0.105 vs. 0.121, P< 0.001). Conversely, the CI was marginally better in the Truebeam plan compared to the Halcyon plan (1.105 vs. 1.127, P< 0.001). However, the Halcyon plan required significantly more MUs than the Truebeam plan (1083.0 vs. 903.0, P< 0.001), as shown in Table 3.
Dosimetric comparison for OARs
The average volume of the hippocampal avoidance region and PTV were 5.4 cm3 (1.5 - 8.1 cm3) and 1542.4 cm3 (1298.3 - 1872.3 cm3), respectively. The volume of hippocampal avoidance region was accounted for 0.35% of PTV. The Halcyon plan showed superior dosimetric performance for hippocampal protection, achieving significantly lower D100%, Dmean, Dmax and NTCP than the Truebeam plan: 626.8 ± 35.8cGyvs. 695.0 ± 31.5cGy (P<0.001), 850.0(837.4, 883.9)cGyvs. 898.4 (880.1, 924.7) cGy (P = 0.001), 1348.1 ± 62.2cGyvs. 1399.8 ± 74.4cGy (P<0.001), and 34.16 ± 2.02% vs. 31.67 ± 1.57% (p<0.001), as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Comparison of hippocampus dosimetric parameters. The results are shown for the (A) D100%, (B) Dmean, (C) Dmax and (D) NTCP of hippocampus, respectively.
Additionally, the Halcyon plan achieved a significantly lower Dmax for the lens and optic nerves and lower Dmean for the eyes compared to the Truebeam plan, as shown in Table 4.
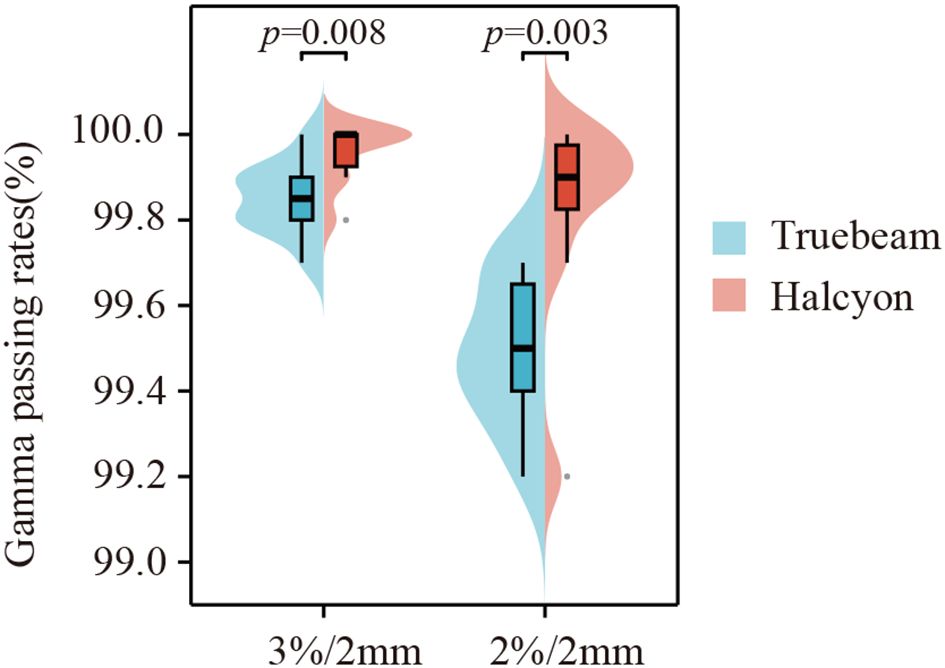
Gamma passing rate comparison
All plans successfully passed the quality assurance test under the 3%/2 mm and 2%/2 mm gamma criteria, with passing rates exceeding 97%. As shown in Figure 5, the Halcyon plan demonstrated superior gamma passing rates compared to the Truebeam plan under both criteria: 99.96% ± 0.07% vs. 99.85% ± 0.08% for 3%/2 mm (z=16.5, P = 0.008) and 99.83% ± 0.24% vs. 99.49% ± 0.17% for 2%/2 mm (z=11, P = 0.003).
Comparison with other studies in hippocampal-avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy
Compared to previous studies, the Halcyon plan achieved notable milestones in HA-WBRT. The Halcyon plan delivered higher prescription dose coverage (D98%, 29.5 Gy; D2%, 32.8 Gy; V95%, 98.7%; V100%, 97.1%), superior dose homogeneity (HI, 0.105), and excellent hippocampal protection (D100%, 6.27Gy; Dmean, 8.50Gy; Dmax, 13.48Gy). These results are comparable or superior to outcomes reported for Tomotherapy and non-coplanar VMAT techniques.
Discussion
HA-WBRT has been shown to be superior to standard WBRT in preserving neurocognitive function and improving patients’ quality of life (26), and it has gradually become a widely adopted therapy for brain metastases. In medical centers equipped with both conventional linear accelerators and Halcyon platforms, selecting the optimal radiotherapy device is a critical step in treatment planning. In this study, HA-WBRT plans were generated for both Halcyon and Truebeam accelerators, and differences in dose distributions for target volumes and OARs were analyzed. Both plans met the RTOG 0933 protocol and clinical requirements. The Halcyon plans demonstrated significant advantages in HI and V30Gyfor the PTV, as well as hippocampal, lens, optic nerves, and eyes. Conversely, Truebeam plans showed a slight advantage in PTV CI, with a marginal 2.0% difference. The Halcyon plans achieved a 15.2% improvement in HI, reflecting superior dose uniformity. Although the Halcyon plans required 16.6% more MUs than Truebeam, the Halcyon’s gantry rotation speed is four times faster, significantly reducing treatment delivery time (27). It should be noted that the higher MU requirements of Halcyon systems may exacerbate several potential problems: (i) increased scatter dose, (ii) accelerated machine wear, and (iii) higher treatment costs.
In terms of hippocampal protection, the Halcyon plans demonstrated a significant reduction in D100% (626.8cGy), achieving a 10.9% decrease compared to the Truebeam plans. The reductions in Dmean (850.0cGy vs. 898.4cGy) and Dmax (1348.1cGy vs. 1399.8cGy) were more modest, at approximately 4.8%. While statistically significant differences were observed in plan comparisons, the clinical implications of these variations warrant further investigation. To address this issue to some extent, we employed NTCP modeling - a validated quantitative measure for assessing radiation-induced tissue damage severity. Our analysis revealed that Halcyon treatment plans demonstrated the most favorable neurocognitive protection profile, as evidenced by significantly lower NTCP values (p<0.001).These findings suggests that the Halcyon system offers superior protection for normal tissues surrounding by the target volume, particularly in low-dose regions. Several factors may account for this advantage:
1. Jawless Design:
The Halcyon accelerator’s jawless configuration positions the MLC leaves closer to the source. Although the leaf tips are rounded, their longer radius and straighter edges minimize the dosimetric leaf gap (DLG) to just 0.1mm (28), significantly reducing the penumbra compared to the 1.8mm DLG observed with Truebeam’s MLC design.
2. Dual-Layer MLC:
Halcyon utilizes a dual-layer, staggered MLC configuration with a transmission factor of only 0.47% (29), markedly lower than Truebeam’s average transmission of 1.5% for 6 MV beams (30). This design effectively reduces dose leakage and improves the protection of surrounding tissues.
3. Faster Leaf Motion:
The MLC leaves on the Halcyon achieve a maximum speed of 5cm/s, double Truebeam’s maximum leaf speed of 2.5cm/s. Previous studies have demonstrated that faster leaf motion enhances the sparing of OARs outside the target region (31), consistent with the findings of this study.
4. Enhanced Modulation Capabilities:
In traditional accelerators, achieving optimal modulation often requires fixing the jaw position due to the limitations of MLC movement when dealing with large target diameters and fields (32). In contrast, the Halcyon’s MLC design eliminates this restriction, allowing full extension of the leaves without carriages and enabling seamless modulation across the entire field. Truebeam, by comparison, is limited by a maximum leaf extension of 15 cm beyond the central carriage, which restricts modulation in VMAT plans for larger fields. To address these challenges, techniques such as partial arcs and smaller field sizes have been employed on Truebeam, as reported by Yuen et al. (16), achieving a target HI of 0.23 and a hippocampal Dmean of 9.16 Gy. However, the Halcyon platform inherently overcomes these limitations due to its innovative MLC design and superior modulation capabilities.
Rong et al. (33) compared IMRT, VMAT, and TOMO for HA-WBRT, concluding that TOMO provides superior dosimetric distribution, particularly in terms of dose uniformity. In studies conducted by Takaoka et al. (19) and Li et al. (18), TOMO achieved 95% PTV coverage with V30Gy, CI values of 1.3 and 0.815, and hippocampal Dmax and Dmean of 14.7 Gy/11.1 Gy and 15.5 Gy/10.7 Gy, respectively. Hippocampal volume had a large effect on the planning parameters, as shown in Table 4. The treatment planning with the small hippocampal volume resulted in the better dose distribution of target and lower Dmax values of hippocampus. For instance, the volume of hippocampi was 5.4 cm3 in our study, whereas the value was 3.95 cm3 described by Takaoka et al. (19). In our study, Halcyon plans demonstrated better hippocampal sparing (Dmax of 13.48 Gy, Dmean of 8.50 Gy) and achieved exceptional PTV coverage and homogeneity. These findings underscore Halcyon’s competitive performance in HA-WBRT and its potential as an effective alternative to TOMO. Yokoyama et al. (13) investigated the impact of arc number (2 – 4 arcs) in Halcyon-based VMAT plans, and recommended 3 arcs for HA-WBRT, reporting a hippocampal Dmax of 14.32 Gy. In our study, the dual-arc VMAT plan achieved a lower hippocampal Dmax (13.48 Gy vs. 14.32 Gy). We attribute this improvement to two innovations in our coplanar dual-arc technique: (i) Target structure segmentation with differential weighting during optimization, enhancing the plan’s modulation capability. (ii) The orthogonal collimator angle design facilitates more conformal subfield shapes and better protection of OARs, particularly in complex spatial relationships between the target and OARs.
Non-coplanar IMRT and VMAT techniques have been explored to improve hippocampal sparing. For example, Nevelsky et al. (12) achieved hippocampal Dmax and Dmean of 14.1 Gy and 7.3 Gy, respectively, using nine-field non-coplanar IMRT, though the PTV coverage (92% for V30Gy) was suboptimal. Subsequently, Xue et al. (14) employed a non-coplanar VMAT approach improving the V30Gy coverage to 95%. and achieving a HI and CI values of 0.249 and 0.821, respectively, with hippocampal D100%, Dmax, and Dmean values of 8.03 Gy, 16.81 Gy, and 11.71 Gy. Although Halcyon does not currently support non-coplanar delivery, its HA-WBRT plan quality in our study remains competitive with these reported techniques, demonstrating comparable hippocampal sparing and robust target coverage.
It is worth noting that due to the complexity of HA-WBRT, plan quality is of paramount importance, and selecting appropriate collimator angles is a critical factor for achieving an optimal dose distribution. In this study, the collimator angles for Arc 1 (293°) and Arc 2 (23°) were set with an inter-arc angle of 90°, consistent with previous studies (34). To address the high complexity of the target structure, the zPTV_mid module, which posed greater challenges in meeting planning objectives, was assigned higher optimization weights. This segmentation and weighting strategy improved modulation efficiency during plan optimization, aligning with the modified VMAT techniques reported by Fu et al. (20). Compared to previously published data (as shown in Table 1), the HA-WBRT plans only using coplanar dual-arc technology in our study demonstrated superior prescription dose coverage and dose uniformity. The PTV coverage reached 97.1%, with hotspots (D2%) controlled within 108% of the prescription dose. In terms of hippocampal sparing, the plans achieved groundbreaking results, maintaining an average hippocampal dose below 9 Gy and reducing the lens Dmax to less than 5 Gy.
Several limitations should be acknowledged in this study. First, this is a retrospective single-center study that lacks validation of long-term clinical outcomes. Second, although our study demonstrated favorable clinical outcomes, the small sample size (n=21) may limit the extrapolation of the results. Third, the potential impact of brain metastasis locations on plan quality was not evaluated. Future longitudinal, multicenter prospective studies will evaluate both cognitive outcomes and survival endpoints in patients with HA-WBRT.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the Halcyon accelerator is a viable and efficient platform for HA-WBRT, with excellent PTV dose coverage, superior dose homogeneity, and effective hippocampal sparing while reducing treatment times. These findings provide a robust basis for further exploration and clinical adoption of the Halcyon platform in hippocampal-avoidance radiotherapy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Review Committee of Huizhou Third People’s Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
RT: Methodology, Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. ML: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition. XS: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing. AG: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. QL: Investigation, Writing – original draft. YJL: Writing – original draft, Software, Formal analysis. GY: Validation, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZP: Resources, Writing – review & editing. GD: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Medical Science and Technology Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. A2023250), Huizhou Science and Technology Innovation Team Project (Grant No. 2023EQ050012), and Huizhou Outstanding Youth Science and Technology Talent Project (Grant No. 2025EQ050018).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Arvold ND, Lee EQ, Mehta MP, Margolin K, Alexander BM, Lin NU, et al. Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro Oncol. (2016) 18:1043–65. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now127
2. Schimmel WCM, Gehring K, Eekers DBP, Hanssens PEJ, and Sitskoorn MM. Cognitive effects of stereotactic radiosurgery in adult patients with brain metastases: A systematic review. Adv Radiat Oncol. (2018) 3:568–81. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.06.003
3. Seute T, Leffers P, Wilmink JT, ten Velde GP, and Twijnstra A. Response of asymptomatic brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer to systemic first-line chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. (2006) 24:2079–83. doi: 10.1200/jco.2005.03.2946
4. Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, et al. Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2012) 82:2111–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.027
5. Gore EM, Bae K, Wong SJ, Sun A, Bonner JA, Schild SE, et al. Phase iii comparison of prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: primary analysis of radiation therapy oncology group study Rtog 0214. J Clin Oncol. (2011) 29:272–8. doi: 10.1200/jco.2010.29.1609
6. Tallet AV, Azria D, Barlesi F, Spano JP, Carpentier AF, Gonçalves A, et al. Neurocognitive function impairment after whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: actual assessment. Radiat Oncol. (2012) 7:77. doi: 10.1186/1748-717x-7-77
7. Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, Caine C, Corn B, Kanner A, et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (Rtog 0933): A phase ii multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:3810–6. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.57.2909
8. Gondi V, Tolakanahalli R, Mehta MP, Tewatia D, Rowley H, Kuo JS, et al. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy: A “How-to” Technique using helical tomotherapy and linear accelerator-based intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2010) 78:1244–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.01.039
9. Wang BH, Hua W, Gu X, Wang XL, Li J, Liu LQ, et al. Dosimetric study of different radiotherapy planning approaches for hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiation therapy (Ha-Wbrt) based on fused Ct and mri imaging. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. (2015) 38:767–75. doi: 10.1007/s13246-015-0397-7
10. Krayenbuehl J, Di Martino M, Guckenberger M, and Andratschke N. Improved plan quality with automated radiotherapy planning for whole brain with hippocampus sparing: A comparison to the Rtog 0933 trial. Radiat Oncol. (2017) 12:161. doi: 10.1186/s13014-017-0896-7
11. Wang S, Zheng D, Zhang C, Ma R, Bennion NR, Lei Y, et al. Automatic planning on hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy. Med Dosim. (2017) 42:63–8. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2016.12.002
12. Nevelsky A, Ieumwananonthachai N, Kaidar-Person O, Bar-Deroma R, Nasrallah H, Ben-Yosef R, et al. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy using elekta equipment. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2013) 14:4205. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v14i3.4205
13. Yokoyama K, Kurosaki H, Oyoshi H, Miura K, and Utsumi N. Plan quality comparison between hippocampus-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy treated with halcyon and tomotherapy intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 21:15330338221108529. doi: 10.1177/15330338221108529
14. Xue J, Jin S, Zhang H, Zou K, Sheng J, Tang J, et al. A simplified non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy for the whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampus avoidance. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1143564. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1143564
15. Zhang HW, Hu B, and Pang HW. Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy in hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2024) 25:e14218. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14218
16. Yuen AHL, Wu PM, Li AKL, and Mak PCY. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (Vmat) for hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiation therapy: planning comparison with dual-arc and split-arc partial-field techniques. Radiat Oncol. (2020) 15:42. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01488-5
17. Yuen AHL, Wu PM, Li AKL, and Mak PCY. Hybrid split-arc partial-field volumetric modulated arc therapy: an improved beam arrangement for linear accelerator-based hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiation therapy. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. (2022) 27:352–9. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2022.0022
18. Li MH, Chen LJ, Chang CC, Tsai JT, and Lin JC. Effect of the simulated half leaf width of a multileaf collimator on volumetric modulated arc therapy plan quality in hippocampal avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2022) 23:e13575. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13575
19. Takaoka T, Tomita N, Mizuno T, Hashimoto S, Tsuchiya T, Tomida M, et al. Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy and intensity-modulated proton therapy in hippocampus- and scalp-sparing whole brain radiotherapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2021) 20:15330338211060170. doi: 10.1177/15330338211060170
20. Fu Q, Chen D, Yan H, Chen J, Zhu J, Yan L, et al. Treatment planning of volumetric modulated arc therapy and positioning optimization for hippocampal-avoidance prophylactic cranial irradiation. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2021) 22:15–23. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13217
21. Candiff O, Belderbos J, Wolf AL, Damen E, van Haaren P, Crijns W, et al. Quality assurance and safety of hippocampal avoidance prophylactic cranial irradiation in the multicenter randomized phase iii trial (Nct01780675). J Natl Cancer Cent. (2023) 3:135–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2023.05.004
22. Brown PD, Gondi V, Pugh S, Tome WA, Wefel JS, Armstrong TS, et al. Hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy plus memantine for patients with brain metastases: phase III trial Nrg oncology Cc001. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:1019–29. doi: 10.1200/jco.19.02767
23. Tang R, Li A, Li Y, Deng G, Wang Y, Xiao Q, et al. Dosimetric comparison of two dose expansion methods in intensity modulated radiotherapy for breast cancer. Radiat Oncol. (2023) 18:23. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02217-4
24. Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, and Tomé WA. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2012) 83:e487–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.10.021
25. Prokic V, Wiedenmann N, Fels F, Schmucker M, Nieder C, and Grosu AL. Whole brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on multiple brain metastases: A planning study on treatment concepts. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2013) 85:264–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.02.036
26. Oskan F, Ganswindt U, Schwarz SB, Manapov F, Belka C, and Niyazi M. Hippocampus sparing in whole-brain radiotherapy. A Review. Strahlenther Onkol. (2014) 190:337–41. doi: 10.1007/s00066-013-0518-8
27. Sun T, Lin X, Li K, Qiu Q, Duan J, Zhang G, et al. Volumetric modulated arc therapy for hippocampal-sparing prophylactic cranial irradiation: planning comparison of halcyon and C-arm accelerators. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:993809. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.993809
28. Hernandez V, Saez J, Angerud A, Cayez R, Khamphan C, Nguyen D, et al. Dosimetric leaf gap and leaf trailing effect in a double-stacked multileaf collimator. Med Phys. (2021) 48:3413–24. doi: 10.1002/mp.14914
29. Lim TY, Dragojević I, Hoffman D, Flores-Martinez E, and Kim GY. Characterization of the halcyon(Tm) multileaf collimator system. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2019) 20:106–14. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12568
30. Li Y, Chen L, Zhu J, Wang B, and Liu X. A quantitative method to the analysis of Mlc leaf position and speed based on epid and Ebt3 film for dynamic imrt treatment with different types of Mlc. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2017) 18:106–15. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12102
31. Vorwerk H, Wagner D, and Hess CF. Impact of different leaf velocities and dose rates on the number of monitor units and the dose-volume-histograms using intensity modulated radiotherapy with sliding-window technique. Radiat Oncol. (2008) 3:31. doi: 10.1186/1748-717x-3-31
32. Rossi M, Boman E, Skyttä T, and Kapanen M. A novel arc geometry setting for pelvic radiotherapy with extensive nodal involvement. J Appl Clin Med Phys. (2016) 17:73–85. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.6028
33. Rong Y, Evans J, Xu-Welliver M, Pickett C, Jia G, Chen Q, et al. Dosimetric evaluation of intensity-modulated radiotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and helical tomotherapy for hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiotherapy. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0126222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126222
Keywords: Halcyon, hippocampus, whole brain radiotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, treatment planning
Citation: Tang R, Lan M, Sun X, Luo Y, Gu A, Liu Q, Li Y, Yang G, Pan Z and Deng G (2025) An innovative hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy planning approach via the Halcyon system: achieving lower hippocampal doses. Front. Oncol. 15:1652684. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1652684
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 20 August 2025;
Published: 02 September 2025.
Edited by:
Poonam Yadav, Northwestern University, United StatesReviewed by:
Peta Lonski, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, AustraliaRenxian Xie, Shantou University, China
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Lan, Sun, Luo, Gu, Liu, Li, Yang, Pan and Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guanhua Deng, Z2guZGVuZ0Bmb3htYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ran Tang
Ran Tang Maoying Lan3†
Maoying Lan3† Xingru Sun
Xingru Sun Yue Luo
Yue Luo Guozi Yang
Guozi Yang Zhenyu Pan
Zhenyu Pan Guanhua Deng
Guanhua Deng