- 1Department of Pathology, Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Pathology, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China
Introduction: Since the release of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumours-Digestive System Tumours in 2019, the pathology of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) has entered an era of integrated diagnosis, encompassing gross classification, histological subtyping, as well as drug molecular target screening. Substantial evidence indicates that the histological subtypes of iCCA are significantly associated with the detection frequency of molecular targets relevant to the targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Through rational immunohistochemistry profiling, patients with iCCA can be precisely diagnosed and individually managed.
Methods: A thorough literature search was conducted using terms pertinent to the pathological diagnosis, histological subtyping, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy of iCCA. The content related to immunohistochemistry was summarized.
Results: In the first part, we summarize the immunohistochemical markers for the histological subtype of iCCA (e.g., large duct type iCCA, small duct type iCCA), with a particular emphasis on their percentage of positive cases, expression location, and association with prognosis. Subsequently, a summary of the immunohistochemical markers for targeted therapy and immunotherapy of iCCA is performed, focusing on the consistency between immunohistochemistry and molecular detection, optimal clone, and prognostic significance.
Conclusions: This review summarizes the critical role of immunohistochemistry in the pathological diagnosis of iCCA. It is noted that any diagnosis must be made by integrating comprehensive information. A pathological diagnosis merely based on immunohistochemical results is unreasonable. The development of subtype-specific and drug-targeted antibodies holds promise for refining iCCA precise diagnosis and therapeutic stratification.
1 Introduction
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is a malignant intrahepatic epithelial neoplasm with biliary differentiation, which may originate from the lining epithelium of the intrahepatic bile duct, peritubular gland, and liver progenitor cell, accounting for approximately 10%~15% of primary liver cancers (1, 2). The 5th edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumours-Digestive System Tumours recommends classifying iCCA into large duct type, small duct type and other less common histological subtypes (2). Histological subtyping has become an essential component of the standardized diagnosis of iCCA, and the use of appropriate immunohistochemical markers significantly enhances classification accuracy, particularly in tumors with overlapping or heterogeneous pathologic features (3).
With the success of clinical trials involving small-molecule inhibitors targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 2 rearrangements (4), isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 mutations (5) and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors (6, 7), it is now recommended that patients with advanced-stage iCCA undergo precise drug-related profiling to develop personalized treatments (8). Many studies have indicated that there are considerable differences in molecular alterations between large and small duct type iCCA, which facilitates the integration of histological subtyping with pharmacological options (9). Most molecular targets are recommended to be identified through next-generation sequencing (NGS). Considering the high cost and relatively complex procedures of NGS detection and analysis, several studies have attempted to use immunohistochemistry to screen suitable candidates for target therapy and immunotherapy.
Focusing on these concerns, we aim to summarize existing studies about the immunohistochemical practice for histological subtyping and drug selection in iCCA, providing a practical reference for pathologists and clinicians.
2 Histological subtypes of iCCA
The histological subtype of iCCA was first characterized in the 20th century. In 1977, Okuda et al. categorized iCCA into ‘‘hilar type’’ and ‘‘peripheral type’’ based on autopsy findings, proposing that the former resembled extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, while the latter shared similarities with hepatocellular carcinoma (10). Subsequent research examined the biological behavior and prognosis of iCCA within this classification and validated its rationale (11, 12). However, as hilar cholangiocarcinoma was a distinct tumor entity, this classification required a more suitable term, Nakanuma Y. et al. introduced the classification of ‘‘large duct type’’ and ‘‘small duct type’’ corresponding to ‘‘hilar type’’ and ‘‘peripheral type’’ in 2010 (13). This classification was incorporated into the 5th edition of the WHO Classification of Tumours-Digestive System Tumours (2). Currently, multiple guidelines and consensuses recommend this histological concept of iCCA (1, 8). Although most subtypes of iCCA can be identified through morphological assessment, the application of immunohistochemical markers is vital for subtype clarification and regional delineation when morphological characteristics are ambiguous, overlapping, or coexistent (3, 14). We aim to review the percentage of positive cases, localizations of expression, and prognostic implications of these markers. It should be noted that although some studies did not use the terms ‘‘large duct type’’ and ‘‘small duct type’’, the descriptions of the classification criteria in these studies were consistent with the corresponding concepts. we have also included these studies in our review (Table 1).
2.1 Large duct type iCCA
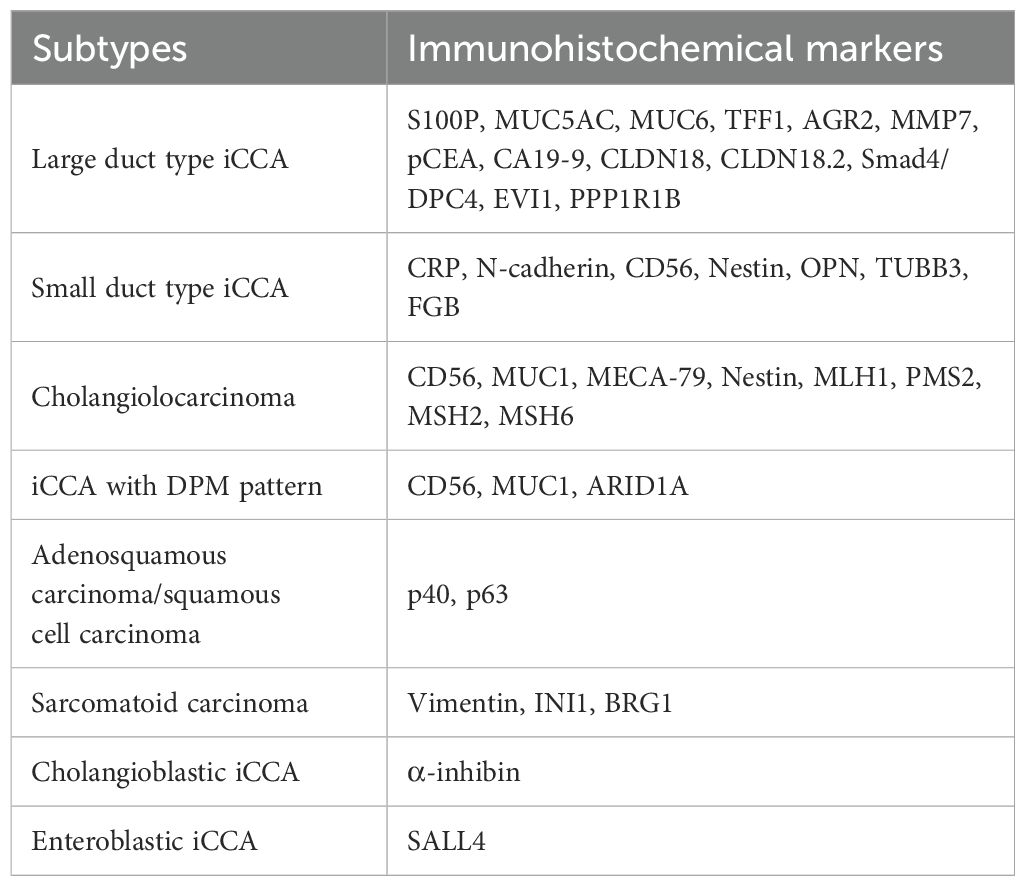
Large duct type iCCA generally manifests as periductal infiltrating type or periductal infiltrating type + mass-forming type grossly and is histologically characterized by a ductal or tubular pattern with columnar to cuboidal epithelium rich in mucus. The WHO Classification lists the following markers for large duct type iCCA: S100 calcium-binding protein P (S100P), mucin (MUC) 5AC, MUC6, trefoil factor 1 (TFF1), anterior gradient protein (AGR) 2, and matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7).
S100P, a member of the S100 family containing 95 amino acids, was initially identified in the placenta. It is associated with the growth, invasion, and metastasis of various tumors (15). S100P is the most widely recognized marker for large duct type iCCA. The percentage of positive cases of S100P in large duct type iCCA was reported to range from 68.5% to 100.0%, whereas in small duct type iCCA, it ranged from 0.0% to 57.6%, demonstrating a significant difference (16–28). Another study reported a percentage of positive cases of only 9.1% (1/11) for S100P in large duct type iCCA (29), possibly due to small sample size, antigen degradation during prolonged archival of tissue (some blocks archived >10 years), limited tumor area in tissue microarrays, and stringent evaluation criteria (>20% strong tumor cell labeling). Different clones of S100P antibody showed varying sensitivity and specificity (22). S100P typically shows cytoplasmic and/or nuclear expression in tumor cells, with nuclear staining being more diagnostically significant. Notably, neutrophils exhibit positive S100P staining, which may cause potential misinterpretation (12). Many studies concluded that S100P expression was significantly associated with poor prognosis in iCCA (12, 30), suggesting that large duct type iCCA has a worse survival compared to small duct type iCCA (18).
As a member of the MUC family characterized by foveolar-type mucin, MUC5AC demonstrates superior diagnostic value in distinguishing large duct type iCCA from small duct type iCCA. The reported percentage of positive cases of MUC5AC in large duct type iCCA ranges from 50.0% to 96.7%, whereas in small duct type iCCA, this percentage was significantly lower, at 1.8% to 25.0% (23, 25, 31–34). MUC5AC expression localizes in the cytoplasm of tumor cells, sometimes restricted to the apical cytoplasm, and is also observed in the mucus secreted into the glandular lumen. While rare small duct type iCCAs show focal expression of MUC5AC, such expression is strictly limited to apical cytoplasm of tumor cells and mucus within the glandular lumen. Positive expression of MUC5AC is associated with poor prognosis in iCCA (35), which is similar to S100P (18).
MUC6 is another representative of the MUC family of gastric pyloric gland-type mucin. Large duct type iCCA (13.7%~33.3%) exhibited a marginal but not significant higher percentage of positive cases of MUC6 expression than that of small duct type iCCA (3.8%~20.0%) (25, 31, 33, 34). The localization of MUC6 expression parallels that of MUC5AC. In terms of prognosis, MUC6 has an opposite trend to MUC5AC, with its high expression being positively correlated with a favorable prognosis in patients with iCCA (31, 36–38). However, no studies have elucidated the underlying mechanisms responsible for this correlation.
TFF1 plays a crucial role in the mucosal defense and repair of the gastrointestinal tract, being secreted with mucus onto the epithelial surface (39). TFF1 predominantly localizes in large bile ducts and diseased liver tissues, probably representing a feedback response to biliary injury (40). The percentage of positive cases of TFF1 in large duct type iCCA ranges from 54.9% to 91.8%, while in small duct type iCCA, it ranges from 12.0% to 48.1% (17, 19, 28, 32, 41). TFF1 staining is confined to the cytoplasm of tumor cells and the luminal surface of tumor glands (42). Some scholars have found that high expression of TFF1 indicates more invasive and metastatic potential in patients with liver fluke-related cholangiocarcinoma, which mainly were large duct type iCCA (32, 43).
The AGR family consists of three members: AGR1, AGR2, and AGR3, which are involved in the regulation of the redox reactions. AGR2 is an atypical member of this family, and its physiological function remains poorly understood. However, AGR2 is connected with the tumor progression of various cancers (44, 45). AGR2 was initially found positive expression in fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma, while classic hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatocellular adenoma exhibited negative expression (46). Subsequent studies found that AGR2 was expressed in the columnar epithelial cell covering the intrahepatic and hilum large bile duct, as well as the peribiliary gland, gallbladder epithelial cell, and large duct type iCCA (47). Two studies reported that the percentage of positive cases of AGR2 in large duct type iCCA varied between 58.9% and 86.7%, while in small duct type iCCA, it varied between 19.5% and 33.3% (17, 41). AGR2 staining is concentrated in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. To date, no studies have investigated the prognostic significance of AGR2 in iCCA.
MMP7 is one of the gene products of the MMP family, involved in the proteolytic processing of extracellular matrix components, including collagen, proteoglycans, laminin, and fibronectin. MMP7 overexpression in iCCA was demonstrated to be strongly associated with poor outcomes (48, 49). Itatsu K et al. further demonstrated the significance of MMP7 in large duct type iCCA, with a percentage of positive cases of 91.2% (31/34), while noting absent expression in normal bile ducts (50). However, data on the positivity percentage of MMP7 in small duct type iCCA patient remain limited. MMP7 expression is circumscribed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells.
Additionally, some scholars have suggested other potential immunohistochemical markers of large duct type iCCA, including polyclonal carcinoembryonic antigen (pCEA), carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), claudin (CLDN) 18/CLDN18.2, SMAD family member 4 (Smad4/DPC4), ecotropic virus integration site 1 protein homolog (EVI1), and protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 1B (PPP1R1B).
CEA is among the most frequently utilized serum tumor markers in clinical practice. Antibodies against CEA have been employed in the histopathological diagnosis of various tumors (51). Notably, pCEA has been found to be useful in liver tumors. A recent study indicated that pCEA can effectively differentiate between large duct type (12/18, 66.7%) and small duct type iCCA (1/11, 9.1%), with a significantly higher percentage of positive cases observed in the former. The staining pattern for pCEA is characterized by diffuse cell membrane expression (52). To date, no studies have been published investigating the relationship between its expression and the prognosis of iCCA.
CA19–9 is another common serum tumor marker, frequently positive in pancreatic cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, and gastric cancer (53). Most immunohistochemical studies on CA19–9 have focused on distinguishing iCCA from hepatocellular carcinoma. The percentage of positive cases of CA19–9 in iCCA ranges from 45.5% to 100.0%, which is significantly higher than that observed in hepatocellular carcinoma (54–58). Studies demonstrated that staining of CA19–9 could aid in differentiating subtypes of iCCA, with a percentage of positive cases of 72.7% (8/14) in large duct type iCCA and 8.4% (13/155) in small duct type iCCA (29); the corresponding percentages of strongly positive expression were 50.0% (50/100) and 35.0% (35/100), respectively (59). CA19–9 positive staining is shown in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. No study has focused on the relationship between CA19–9 expression and the prognosis of iCCA.
CLDN18 was initially identified as a new downstream target gene of the thyroid-specific enhancer-binding protein/NK2 homeobox 1 homologous domain transcription factor. CLDN18 is spliced into two specific isoforms expressed in lung and gastric tissues, with selective splicing of exons 1a and 1b forming CLDN18.1 and CLDN18.2, respectively. CLDN18.1 is mainly expressed in normal lung tissue and lung cancer cells, while CLDN18.2 is restricted to gastric tissue under normal conditions and appears on the cell membrane in cancerous tissues, including iCCA (60, 61). Tanaka M et al. demonstrated that the percentage of positive cases of CLDN18 was higher in large duct type iCCA (69.0%, 29/42) compared with that in small duct type iCCA (12.7%, 7/55) (34). CLDN18.2 was also reported to have value in distinguishing subtypes of iCCA, with a percentage of positive cases of 41.2% (42/102) and 10.0% (2/20) in large and small duct type iCCA, respectively (19). Their positive staining localizes to the cell membrane of tumor cells. Although their prognostic and treatment significance in iCCA remains unconfirmed, Zolbetuximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CLDN18.2, has shown efficacy in patients with CLDN18.2-positive gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (62). Potential studies in associated iCCA patients are well worth exploring.
Smad4/DPC4 belongs to a family of signal transduction proteins that are phosphorylated and activated by transmembrane serine/threonine receptor kinases in response to transforming growth factor beta signaling through multiple pathways. This gene functions as a tumor suppressor, and the inactivation of Smad4/DPC4 is most prominently observed in pancreatic cancer (63). In iCCA, loss of expression of Smad4/DPC4 occurs more frequently in large duct type iCCA patients than in small duct type iCCA patients (33.3%, 7/21 vs. 3.8%, 1/26) (33), and is considerably associated with a poorer histological grade, advanced clinical stage, as well as metastasis (64, 65).
EVI1, a recognized oncogenic transcription factor in hematopoietic cells, enhances the oncogenic potential of pancreatic cancer by upregulating Kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) expression. According to a study by Tanaka M et al., large duct type iCCA exhibited a higher percentage of positive cases of EVI1 positivity (33 out of 42, 78.6%) compared to small duct type iCCA (18 out of 55, 32.7%). In iCCA, EVI1 is primarily expressed in the nuclei of tumor cells. In contrast, non-neoplastic intrahepatic biliary epithelium shows either no or minimal EVI1 expression. Hepatocytes show no or only very weak EVI1 positivity. Vascular endothelial cells do not show any immunoreactivity for EVI1. Patients with EVI1-positive iCCA had significantly poorer overall survival and recurrence-free survival rates (34).
PPP1R1B inhibits protein phosphatase-1 and protein kinase A, with demonstrated prognostic relevance in breast cancer and pancreatic cancer (66, 67). Recently, PPP1R1B was identified as a potential immunohistochemical marker for histosubtyping of iCCA, with a percentage of positive cases of 90.9% (40/44) in large duct type and 4.0% (2/50) in small duct type iCCA. PPP1R1B is expressed in the common bile duct but not in intrahepatic bile duct. The positive staining of PPP1R1B localizes in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. The expression of PPP1R1B promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and indicated a worse prognosis of iCCA (28).
In summary, the immunohistochemical markers of large duct type iCCA are frequently expressed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells and are closely associated with secreted mucus (Figure 1). Consequently, numerous studies utilized Alcian Blue staining or Alcian Blue-Periodic Acid-Schiff staining to differentiate subtypes of iCCA. Positive staining is indicative of large duct type iCCA (percentage of positive cases of mucus staining in large duct type iCCA vs. small duct type iCCA: 82.0%~100% vs. 10.7%~45%) (18, 19, 21, 23, 52, 59, 68). However, since adenocarcinomas from other organs can produce similar mucus and metastasize to the liver, these markers are primarily used to distinguish large duct type iCCA from small duct type iCCA and should be cautiously employed when differentiating large duct type iCCA from other liver-metastatic adenocarcinomas. Organ-specific markers for large duct type iCCA remain undefined. Due to the same embryonic origins, adenocarcinomas arising from the pancreas, ampulla, stomach, extrahepatic bile ducts, and gallbladder exhibit highly similar immunohistochemical profiles to large duct type iCCA. In such cases, histological evidence of premalignant lesions is essential, such as biliary intraepithelial neoplasia or intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile ducts. Furthermore, large duct type iCCA typically demonstrates abundant fibrous stroma and dilated mucin-rich tumor glands compared to metastatic adenocarcinomas to the liver, though this is not absolute. Additionally, imaging findings and clinical information should be emphasized. Metastatic adenocarcinomas often manifest as multiple subcapsular lesions accompanied by tumors in other organs and corresponding clinical symptoms, whereas large duct type iCCA predominantly shows infiltrative growth along the intrahepatic bile ducts near the porta hepatis. When the diagnosis is uncertain despite these considerations, pathological reports should employ cautious terminology and recommend multidisciplinary treatment. Given the significant differences in treatment, organ-specific immunohistochemical markers for adenocarcinomas originating from the upper gastrointestinal tract, large bile ducts, and pancreas are critically needed.
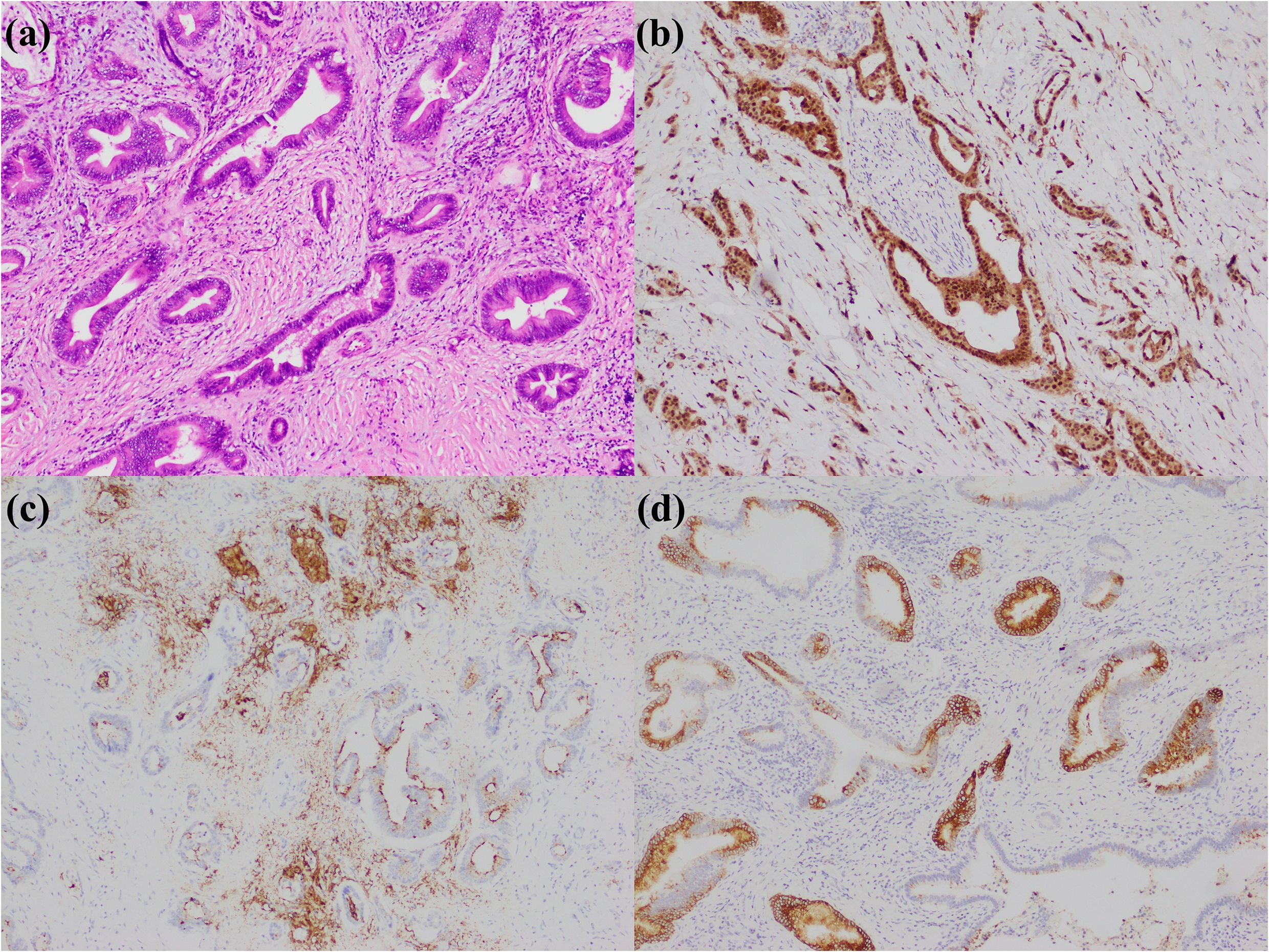
Figure 1. Large duct type iCCA. (a) histological morphology; (b) S100P positive; (c) MUC5AC positive; (d) MUC6 positive (magnification: 100×).
2.2 Small duct type iCCA
Small duct type iCCA typically shows as a mass-forming type and is morphologically characterized by a tubular pattern with low columnar to cuboidal cells lacking mucus. According to the 5th edition of the WHO Classification, immunohistochemical markers for small duct type iCCA include C-reactive protein (CRP), N-cadherin, and CD56.
CRP is an acute inflammatory protein primarily produced by the liver (69). It is one of the most sensitive and specific markers for small duct type iCCA with its percentage of positive cases in small duct type iCCA ranging from 65.0% to 100.0%, while in large duct type iCCA it ranges from 5.3% to 71.7% (19, 22, 25, 52, 59, 70). Furthermore, two studies found that CRP was the most markedly differentially expressed gene between small and large duct type iCCA (19, 71). Positive staining of CRP is observed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. Notably, as CRP is a secreted protein, it often appears as diffuse strong positive staining in tumor stroma in cases with pronounced inflammation, which can affect the interpretation of tumor cell staining intensity and extent. Moreover, CRP may present simple membrane staining in tumor cells, which has no clear diagnostic significance for small duct type iCCA. Additionally, granular cytoplasmic staining of CRP in the mucosal epithelium of intrahepatic large bile ducts and the periductal glands intermixed within the lesions of large duct type iCCA may result in misdiagnosis. These three scenarios may be potential reasons for the higher percentage of positive cases of CRP observed in large duct type iCCA in some studies (59, 70). Therefore, it is essential to clarify the expression position of CRP to make an accurate diagnosis. A high expression of CRP in iCCA indicated a favorable prognosis (72), suggesting that the prognosis of small duct type iCCA is better than that of large duct type iCCA (19, 25, 68).
N-cadherin, the expression product of cadherin 2 (CDH2), is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mediates tumor cell migration (73). It is another one of the most classic markers for small duct type iCCA. The noted percentage of positive cases of N-cadherin in small duct type iCCA varied between 55.0% and 95.5%, whereas in large duct type iCCA, it varied between 5.6% and 49.1% (17–19, 22, 23, 25, 28, 41, 52, 59, 74). N-cadherin staining appears on the membrane of tumor cells. Although the sensitivity and specificity of N-cadherin for small duct type iCCA may be slightly lower than those of CRP, N-cadherin does not manifest strong background staining, making it easier to interpret than CRP and suitable for use in conjunction with CRP. The impact of N-cadherin on the prognosis of iCCA remains controversial. A study by a Thai team suggested that high expression of N-cadherin was indicative of a poor prognosis for iCCA (75), while a study by a Taiwanese team suggested that N-cadherin expression did not represent a different prognosis (72). These discrepancies may be attributed to the different etiological factors and proportions of histological subtypes in the studied populations.
CD56 serves as a marker of liver progenitor cells (76) and is expressed in canals of Hering, bile ductules, and interlobular bile ducts, as well as ductular reactions, bile duct adenomas, and biliary hamartomas (77–79). Consequently, it is recognized as an immunohistochemical marker for small duct type iCCA, particularly its specific subtypes: cholangiolocarcinoma and iCCA with ductal plate malformation (DPM) pattern (80). The percentage of positive cases of CD56 in small duct type iCCA (16.2% to 82.1%) was higher than that in large duct type iCCA (0.0% to 25.5%) (18, 20, 22, 23, 25, 28, 29, 59). CD56 staining is localized in the cell membrane and cytoplasm of tumor cells and is frequently focally positive in small duct type iCCA. Its positivity correlates with the morphological features of cholangiolocarcinoma, although this association is not absolute. To date, there have been no studies focusing on the prognostic significance of CD56 expression in iCCA. Given that CD56 is often expressed in cholangiolocarcinoma, which generally has a better prognosis (20, 81–83), it is reasonable to infer that patients with CD56 expression in iCCA have a more favorable prognosis.
In addition to the aforementioned immunohistochemical markers, several other valuable markers for small duct type iCCA were identified, including nestin, osteopontin (OPN), class III β-tubulin (TUBB3), and fibrinopeptide B (FGB).
Nestin is commonly utilized for the diagnosis of nervous system disorders. Subsequently, a multicenter study discovered its specificity in combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and its association with poor prognosis of this tumor entity. This study also involved 204 iCCAs and found that Nestin staining was positive in 120 patients (positive percentage: 58.8%) (84). Consequently, Sasaki M et al. published two papers discussing the diagnostic significance of Nestin in iCCA, reporting that percentage of positive cases ranged from 40.9% to 47.2% in small duct type iCCA and 3.3%~5.0% in large duct type iCCA (85, 86), suggesting its potential as a marker for differentiating subtypes of iCCA. However, some scholars argued that Nestin-positive tumors should be directly classified as cholangiolocarcinoma, whereas classic small duct type iCCA did not express Nestin (80). Nestin-positive staining localizes in the cytoplasm of tumor cells and is not expressed in the non-tumorous small bile duct, large bile duct, or hepatocyte, while the vessel of liver show Nestin-positive expression. It also should be noted that given the comparable expression status of Nestin observed in combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and iCCA (84), careful consideration should be given to the possibility of the intermediate cell carcinoma component within combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma when diagnosing small duct type iCCA (87). This is crucial since morphological differentiation can be challenging between intermediate cell carcinoma and small duct type iCCA. Additionally, the potential diagnosis of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma should be considered when encountering small duct type iCCA lacking expression of Nestin in needle biopsy specimens (87).
OPN is a multifunctional protein that plays important roles in various conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, cancers, diabetes, and kidney stones, and in the processes of inflammation, biomineralization, cell viability, and wound healing (88). Song G et al. conducted single-cell sequencing for 14 patients with iCCA, identifying two molecular subtypes: S100P-secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1)+ iCCA and S100P+SPP1- iCCA, with the gene-derived substance of SPP1 being OPN. Immunohistochemical staining of a tissue microarray comprising 201 iCCAs revealed that OPN was positive in 92.0% (82/88) of small duct type iCCA patients and 3.4% (2/59) of large duct type iCCA patients (24). Yoshizawa T et al. further validated the utility of OPN in distinguishing iCCA subtypes using whole-section staining, demonstrating that OPN was positive in 100.0% (32/32) of small duct type iCCA patients and 12.2% (5/41) of large duct type iCCA patients, with all positive cases in the latter group being weakly positive (27). OPN is localized in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. The viewpoints on the significance of OPN in the biological behavior of iCCA are inconsistent. Terashi T et al. reported that low expression of OPN correlated with enhanced tumor invasiveness and poor prognosis (89), but Zheng Y et al. found that elevated OPN expression was associated with shorter overall survival and higher recurrence rates of iCCA by facilitating the growth and metastasis of iCCA (90). Laohaviroj M et al. noted that OPN expression in the tumor stroma was positively correlated with the malignant biological behavior of iCCA (91). These discrepancies may be attributed to differences in the subtypes of iCCA included in these studies.
TUBB3 is a microtubule protein that shares similarities with Nestin, which is typically expressed in neuron-derived cells. It is expressed in various types of tumors, including lung cancer, ovarian cancer, and esophageal cancer (92). For iCCA, two studies indicated that TUBB3 had potential value in differentiating the histological subtypes. Zen Y et al. found that TUBB3 was expressed in 50.0% (14/28) of small duct type iCCA patients, while the percentage of positive cases was conspicuously lower in the large duct type cases (15.0%, 6/40) (93). Another study conducted by Akita M et al. reported that the percentage of positive cases of TUBB3 in small duct type iCCA was 64.5% (20/31), compared to 31.6% (6/19) in the large duct type patients (22). TUBB3 staining is located in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. To date, no studies have focused on the prognostic significance of TUBB3 in iCCA.
Fibrinogen is primarily synthesized in the liver and is converted into fibrin through thrombin. During this process, fibrinogen releases FGB. FGB is recognized as an inflammation marker (94) and possesses similar functions to CRP. A study by Rhee H et al. found that FGB could serve as a valuable marker for small duct type iCCA, with a percentage of positive cases of 50.0% (10/20) in the small duct type iCCAs and 17.6% (18/102) in the large duct type iCCAs (19). Another study by Chung T et al. also indicated that the overall percentages of positive cases of FGB and CRP were significantly higher in small duct type iCCA (68). FGB is expressed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells, and its prognostic significance in iCCA remains unclear.
In summary, the expression of immunohistochemical markers in small duct type iCCA is primarily observed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells and shows organ specificity, particularly for CRP and N-cadherin (Figure 2). This enables the application of these markers to extend from subtype diagnosis to differential diagnosis. Furthermore, the liver specifically synthesizes albumin, so albumin in situ hybridization has been increasingly performed for the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of liver tumors in recent years. Numerous studies showed that the percentage of positive cases of albumin in situ hybridization in small duct type iCCA is significantly higher than in large duct type iCCA, and both are higher than in metastatic adenocarcinoma. Consequently, albumin in situ hybridization can serve as a novel method for the histological subtype diagnosis and differential diagnosis of iCCA, supplementing immunohistochemistry (29, 52, 70, 95–98).
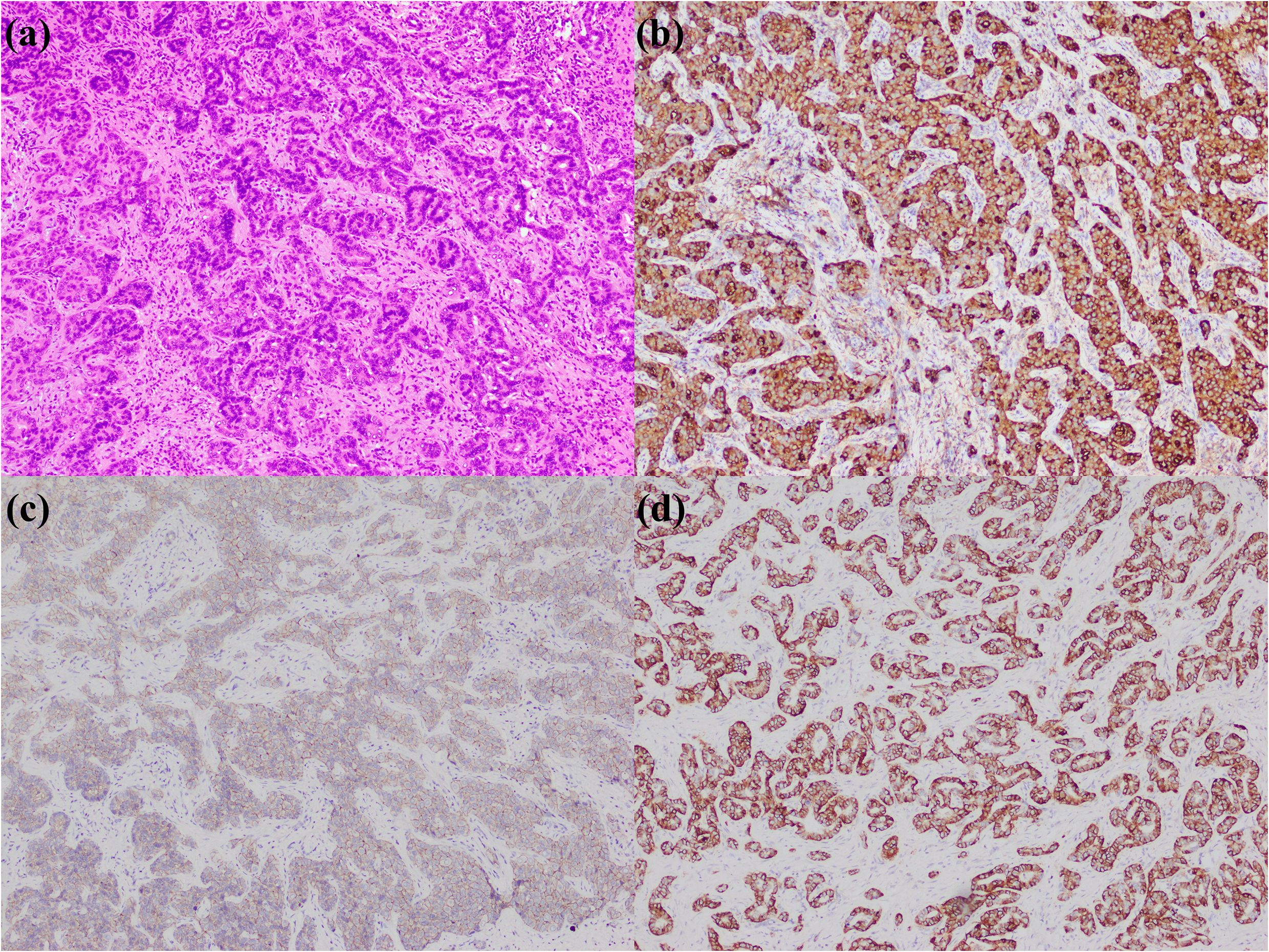
Figure 2. Small duct type iCCA. (a) histological morphology; (b) CRP positive; (c) N-cadherin positive; (d) CD56 positive (magnification: 100×).
2.3 Cholangiolocarcinoma
Cholangiolocarcinoma is composed by a well-differentiated ductular or cord-like structure resembling reactive bile ductules. The term “cholangiolocarcinoma” was first put forward in 1959 (99), and this entity was initially classified as a subtype of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (100). Nevertheless, multiple studies demonstrated that its morphological, immunohistochemical, and molecular characteristics are more akin to the small duct type iCCA (101–103). Therefore, in the 5th edition of the WHO Classification, cholangiolocarcinoma is reclassified as a distinct subtype of small duct type iCCA (2). To date, no specific immunohistochemical markers have been identified for cholangiolocarcinoma. A few studies with small sample sizes indicated that cholangiolocarcinoma frequently expressed CD56, with a percentage of positive cases ranging from 40.0% to 100.0% (20, 101, 102, 104, 105), while some researchers argued that the percentage of positive cases of CD56 in cholangiolocarcinoma did not remarkably differ from that in classical small duct type iCCA (101). The luminal expression pattern of MUC1 was another useful marker, although it was proved not to be specific (Figure 3) (16, 80, 101, 106, 107), similarly, the luminal expression of the L-selectin ligand MECA-79 mirrored MUC1 patterns and provided diagnostic utility (107). Nestin was another immunohistochemical marker that could assist in the diagnosis (85). One study even suggested that Nestin could serve as a differential marker between cholangiolocarcinoma and small duct type iCCA (80), although this view has not yet been widely accepted. Additionally, a recent study indicated that cholangiolocarcinoma had molecular alterations highly comparable to those of small duct type iCCA, and they found that cholangiolocarcinoma was notably characterized by mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR), leading to the loss of expression of MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, and MSH6, which could assist in differentiation (108).
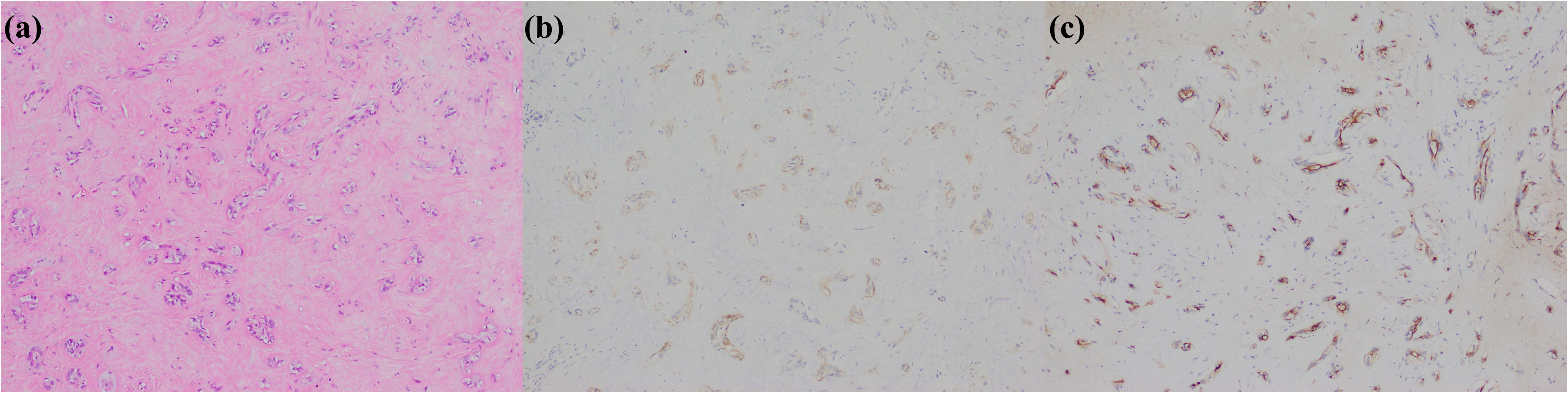
Figure 3. Cholangiolocarcinoma. (a) histological morphology; (b) CD56 positive; (c) MUC1 positive (magnification: 100×).
2.4 iCCA with DPM pattern
Nakanuma Y et al. first introduced the term “iCCA with DPM pattern” in 2012 and classified it as a distinct subtype of small duct type iCCA. Histopathologically, this entity is characterized by irregularly dilated neoplastic bile ducts, resembling DPMs, and composed of single-layered columnar or low cuboidal cells with minimal cytoplasm and small nuclei lacking mitosis (109). This entity possesses some features of the hepatic progenitor cells, including the expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), cytokeratin (CK) 19, and CD56 (109, 110), leading some researchers to speculate that iCCA with DPM pattern shares commonness with cholangiolocarcinoma, both probably originating from the canals of Hering and bile ductules (80, 111). Pathological diagnosis of iCCA with DPM pattern primarily relies on morphological characteristics. The expression of CD56 (with a reported 100.0% percentage of positive cases in some small sample size studies) (80, 112, 113) and the luminal expression pattern of MUC1 (80) were valuable but not specific (Figure 4). Additionally, two studies found that AT-rich interactive domain 1A (ARID1A) mutation was closely associated with iCCA with DPM pattern. The immunohistochemical staining revealed that the percentage of absence or abnormal expression of ARID1A ranged from 40.0% to 57.9% (111, 113). It is important to emphasize that ARID1A mutations are not specific to this subtype and also occur in other histological subtypes of iCCA and even extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (114). Therefore, ARID1A mutations cannot be considered a specific gene variation for iCCA with DPM pattern.
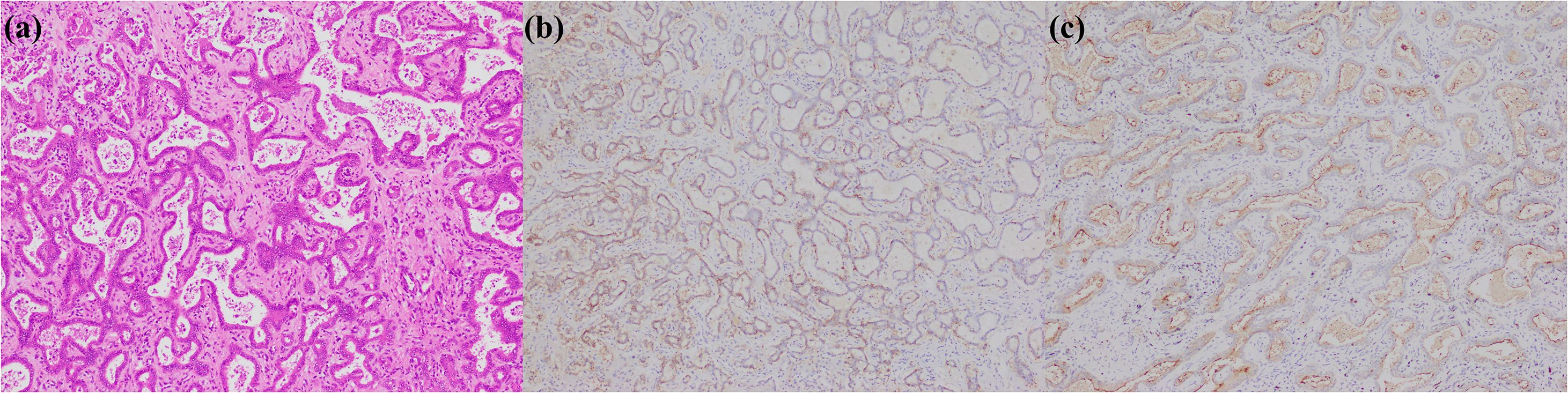
Figure 4. iCCA with DPM pattern. (a) histological morphology; (b) CD56 positive; (c) MUC1 positive (magnification: 100×).
2.5 Other rare subtypes of iCCA
The rare subtypes of iCCA were collected in the WHO Classification including adenosquamous and squamous cell carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, signet ring cell carcinoma, clear cell carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma, and sarcomatous iCCA (Figure 5) (2). Moreover, some new provisional subtypes of iCCA, such as cholangioblastic iCCA, enteroblastic iCCA, and acinar cell carcinoma, are also notable. There exist several useful immunohistochemical markers for identifying these iCCA entities. For instance, adenosquamous carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma can be confirmed by p40 and p63. Sarcomatoid carcinoma can be identified by vimentin (115) and integrase interactor 1 (INI1), brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1), and other members of the switch defective/sucrose non-fermentable complex (23, 116). Cholangioblastic iCCA can be assessed using α-inhibin (117). Enteroblastic iCCA is characterized by the expression of spalt-like transcription factor 4 (SALL4) (118). Lymphoepithelial-like carcinoma requires confirmation by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small ribonucleic acid (RNA) in situ hybridization. Immunohistochemical detection of latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is unreliable for ascertaining Epstein-Barr virus infection in iCCA (119).
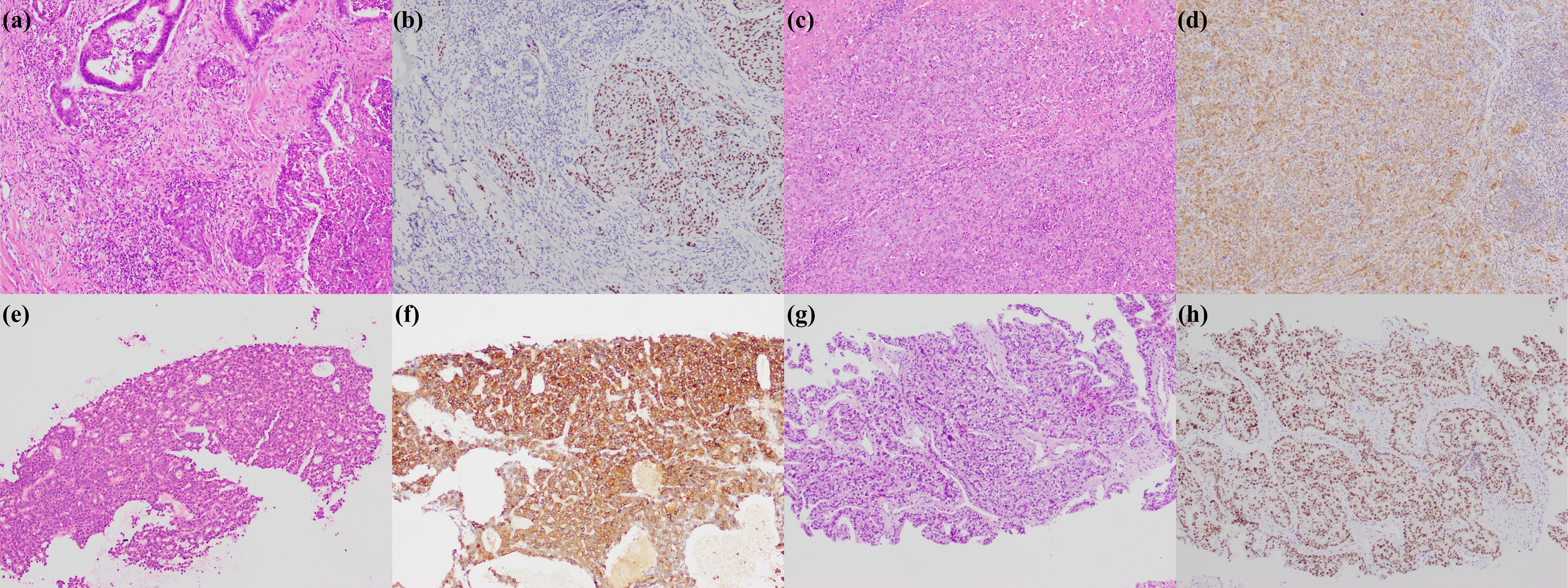
Figure 5. Rare subtypes of iCCA. (a) adenosquamous carcinoma; (b) p40 positive in squamous cell carcinoma region; (c) sarcomatous iCCA; (d) Vimentin positive in sarcomatous iCCA; (e) cholangioblastic iCCA; (f) α-inhibin positive in cholangioblastic iCCA; (g) enteroblastic iCCA; (h) SALL4 positive in enteroblastic iCCA (magnification: 100×).
2.6 Summary
The preceding sections summarize the current landscape of immunohistochemical markers used for histological subtyping of iCCA. Because of the different morphological interpretation criteria, antibody clones, positivity thresholds, and the preservation status of tumor tissues, the results across studies varied slightly, but few contradictory conclusions were reported. However, some established and emerging markers (e.g., MMP7, pCEA, CA19-9, CLDN18, CLDN18.2, Smad4/DPC4, EVI1, PPP1R1B, FGB), which were validated in a single study, still require more evidence through larger datasets. Based on WHO recommendations, reported discriminatory effectiveness, and our experience, we give our recommendations about immunohistochemical markers used in differentiating large duct type iCCA and small duct type iCCA (Table 2). Among the preferred markers, S100P, MUC5AC, CRP, and N-cadherin are also prioritized in the “Expert Consensus on Pathological Diagnosis of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (2022 version)”. Additionally, OPN has been demonstrated with strong discriminatory performance and is supported by dual validation through molecular and immunohistochemical testing, making it a promising emerging marker for small duct type iCCA. Overall, small duct type iCCA markers demonstrate superior disease specificity compared to large duct type iCCA markers. The markers of large duct type iCCA are mainly used in the differential diagnosis with small duct type iCCA.
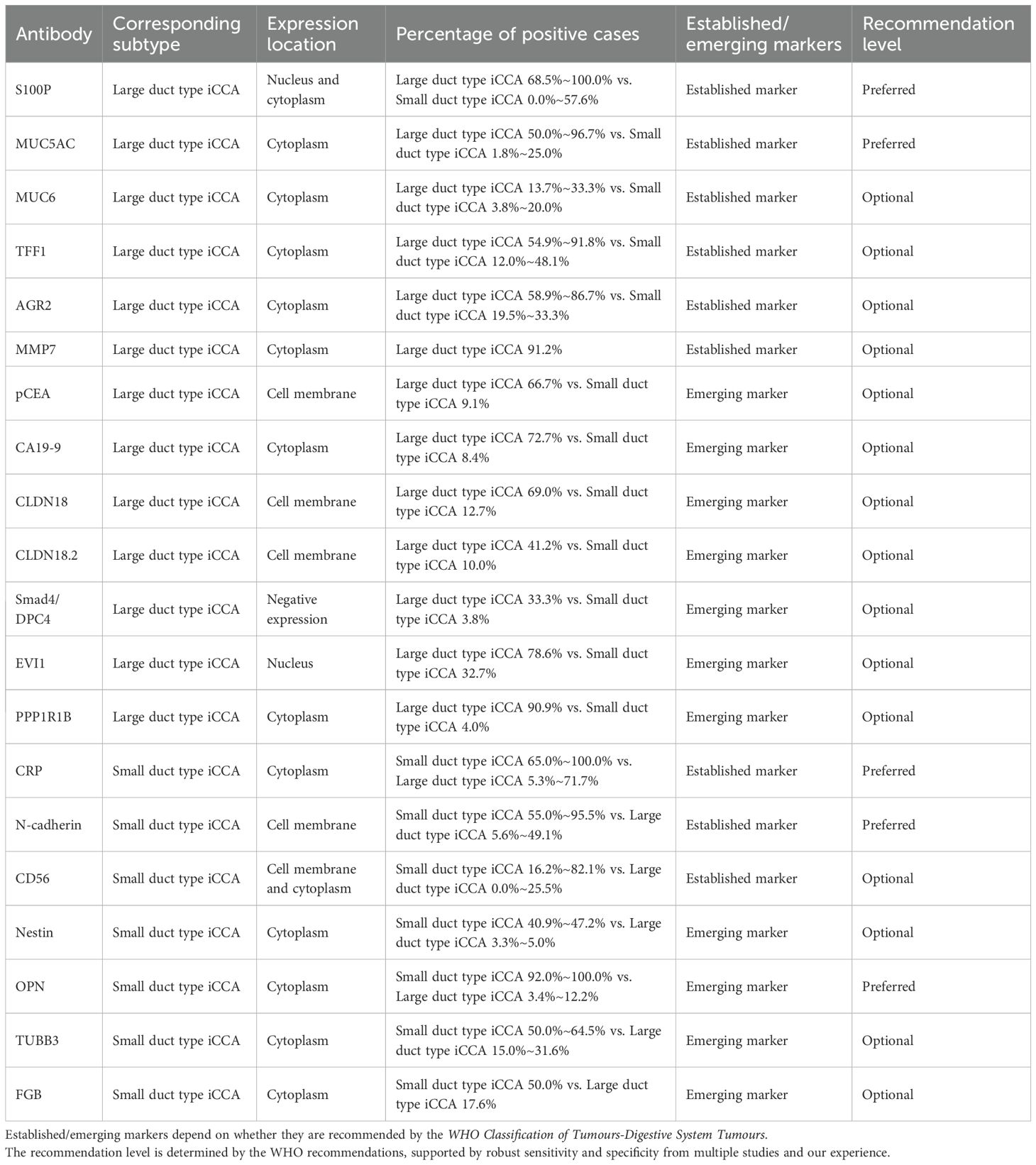
Table 2. Characterization of immunohistochemical markers of large duct type and small duct type iCCA.
In some cases, co-expression of markers of different subtypes may occur, which may be attributed to several reasons. First, careful assessment of localization and extent of expression is essential; for instance, CRP-positive small glands in large duct type iCCA may represent residual peribiliary glands; although S100P is not uncommonly expressed in small duct type iCCA, the staining is usually weak, focal, and cytoplasmic. The published studies often employed semi-quantitative scoring systems based on both staining intensity and distribution. According to our experience and the methodologies reported in the literature, at least 10% of aggregated tumor cells exhibiting moderate-to-strong staining is considered meaningful, and the localization of staining should be accurate. Second, iCCAs originating at the junction between septal and area bile ducts may exhibit overlapping immunophenotypic and morphological features of both subtypes. In such cases, classification as hybrid/mixed subtypes is recommended. Pathologists should interpret immunohistochemical findings in the context of histological morphology and clinical data. When definitive subtyping is challenging, detailed documentation of expression patterns of markers—including distribution, intensity, and localization—should be included in the pathology report.
Currently, there is still a lack of immunohistochemical markers with high sensitivity and specificity for cholangiolocarcinoma and iCCA with DPM pattern. As for the former, there is morphological overlap with typical small duct type iCCA. It is recommended to apply a panel reflecting stem cell features in cases of well-differentiated iCCA with prominent sclerotic stroma to assist in the diagnosis of cholangiolocarcinoma. As for the latter, its morphological features are generally distinctive, and misdiagnosis is uncommon. Recent studies have proposed a subtype of cholangiocarcinoma associated with biliary adenofibroma, termed tubulocystic carcinoma of bile ducts (120). According to the histopathological images and molecular data presented in the literature, this entity exhibits a high similarity with iCCA with DPM pattern and may represent different terms of the same disease. This opinion has gained recognition among some researchers (121).
The subtyping of iCCA has gained increasing acceptance and application in China. This trend is not only influenced by the WHO recommendations, but also supported by extensive studies demonstrating that different iCCA subtypes have different genetic profiles, particularly in their drug-related molecular signatures, thereby generating significant clinical demand. At present, the identification of these genetic alterations mainly relies on molecular pathology techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Sanger sequencing, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and NGS. Due to the high costs and technical complexity of these methods, several studies have explored immunohistochemistry for screening and achieved satisfactory sensitivity and specificity. This will be reviewed in the next part.
3 Targeted therapy and immunotherapy of iCCA
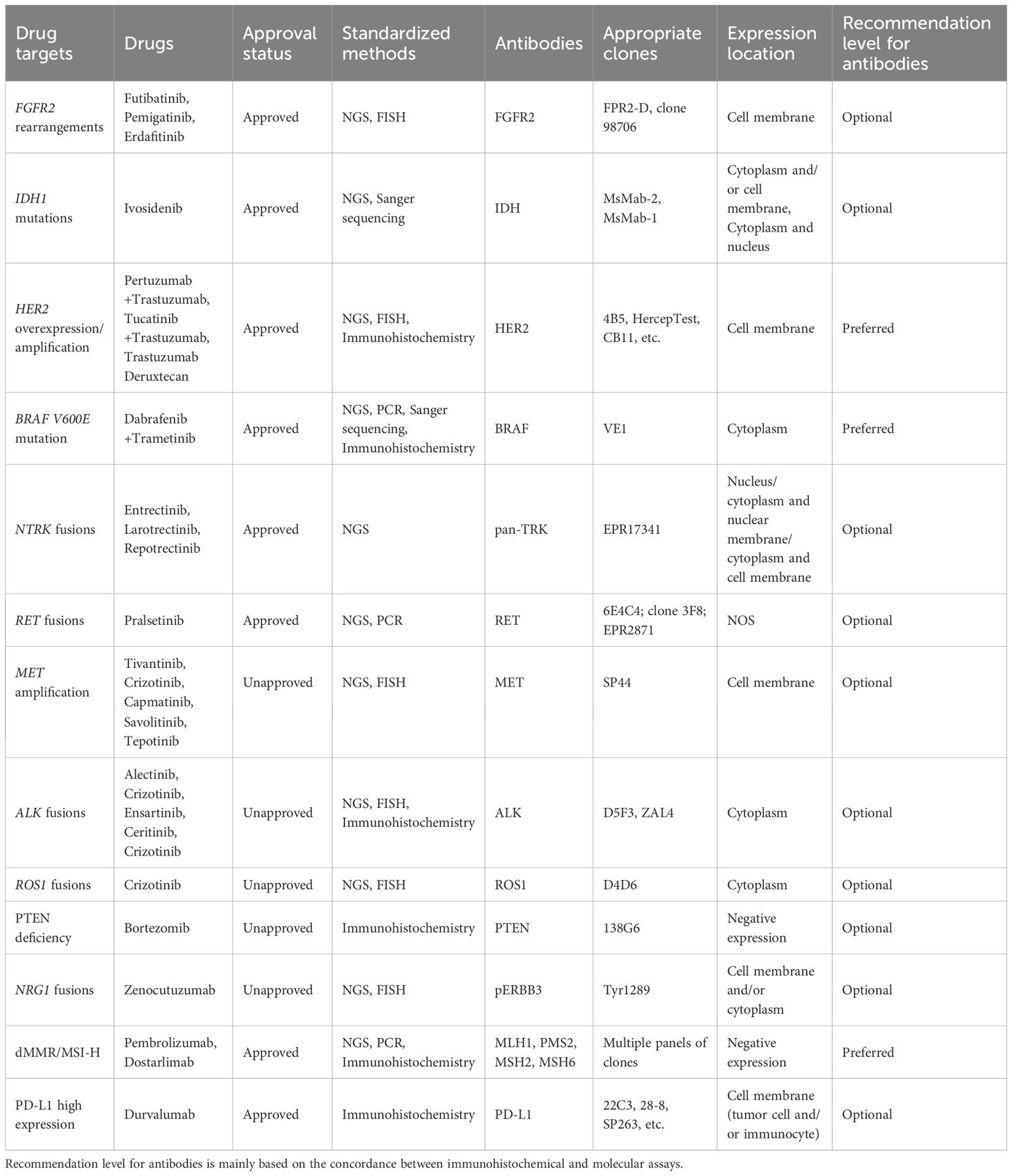
Following the latest guidelines and consensus, multiple drug-related targets were identified for iCCA, which can be utilized for primary/subsequent-line therapies of unresectable or metastatic biliary tract cancer (8, 122–126). These targets include FGFR2 rearrangements, IDH1 mutations, human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 2 overexpression/amplification, v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1 (BRAF) V600E mutation, neurotrophin receptor kinase (NTRK) fusions, rearranged during transfection (RET) fusions, KRAS G12C mutation, mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) amplification, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusions, ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase (ROS1) fusions, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) deficiency, neuregulin 1 (NRG1) fusions, pathogenic breast cancer susceptibility gene (BRCA) variation, microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or dMMR, high tumor mutational burden (TMB-H), and PD-L1 high expression. There is currently a paucity of immunohistochemistry-related studies on KRAS G12C mutation and pathogenic BRCA variation. Moreover, TMB-H, derived from NGS, cannot be assessed via immunohistochemistry, and thus are not discussed herein.
3.1 FGFR2 rearrangements
The FGFR family comprises four tyrosine kinase receptors—FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4. Upon binding to specific growth factors, these receptors undergo dimerization, thereby activating downstream signalling pathways that regulate key processes such as cell proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis (127). FGFR2 rearrangements mainly result in gene fusions and the incidence of FGFR2 rearrangements in iCCA is approximately 10% to 15%, predominantly occurring in small duct type iCCA patients (3, 128, 129). Futibatinib, Pemigatinib, and Erdafitinib were validated effective for patients with biliary tract cancer with these molecular alterations (4, 130, 131) and were recommended by National Comprehensive Cancer Network as subsequent-line treatment regimen for unresectable and metastatic disease. The standardized methods for detecting FGFR2 rearrangements include FISH and NGS (132), with RNA-NGS being particularly advantageous for identifying its partner genes. Several studies explored immunohistochemistry as a screening tool for FGFR2 alterations in biliary tract cancer. Uson Junior PLS et al. initially used two FGFR2 antibodies (clone: FPR2-D and clone 98706) to stain 99 patients of biliary tract cancer. The first antibody identified 20 tumors with positive staining, while the second identified 10 tumors. The following verification using FISH or NGS confirmed that 14 of these tumors carried FGFR2 alterations (13 fusions and 1 mutation). The immunohistochemical method demonstrated high accuracy (91.9% and 78.7%) and specificity (97.7% and 82.9%), along with moderate sensitivity (57.1% and 53.9%) (133). Additionally, Sasaki M et al. found that the percentage of positive cases of FGFR2 (clone: D4L2V) was significantly higher in small duct type iCCAs (25.7%, 9/35) than large duct type iCCAs (3.3%, 1/30) and hepatocellular carcinomas (0.0%, 0/35). They also noted that the 5’/3’ (E5/E18) imbalance in FGFR2 (E5/E18 ratio > 2) was frequently observed in FGFR2-positive small duct type iCCAs, but less so in FGFR2-negative tumors (134). However, Zou Y et al. denied the screening value of the clone D4L2V of FGFR2. They analysed 167 iCCAs and found that 80 (47.9%) cases were positive for FGFR2, and 87 cases (52.1%) were negative. However, the immunohistochemical results showed inconsistency test for both FISH (κ = 0.048) and NGS (κ = 0.125) (135). Consistent with the findings of Zou Y et al., Cao Z et al. conducted an NGS analysis to identify FGFR2 rearrangements in 9 out of 76 patients of iCCA. However, there was a relatively low consistency (κ = 0.464) between the results of NGS and immunohistochemistry of FGFR2 (clone: D4L2V) (136). These findings suggest that FGFR2 immunohistochemistry can serve as an available screening method for FGFR2 rearrangements, but the clone of the antibody needs to be strictly selected. Regarding the prognostic significance, Uson Junior PLS et al. reported no statistically significant differences in overall survival, progression-free survival, and time to tumor recurrence between FGFR2-positive and FGFR2-negative patients (clone: FPR2-D and clone 98706) (133). However, another study involving 92 iCCA patients indicated that those expressing FGFR2 (clone: D4L2V) had worse recurrence-free survival (137). The discrepancies in these results may be attributed to different clones, highlighting the need for the development of more sensitive and specific FGFR2 antibodies (Figure 6).
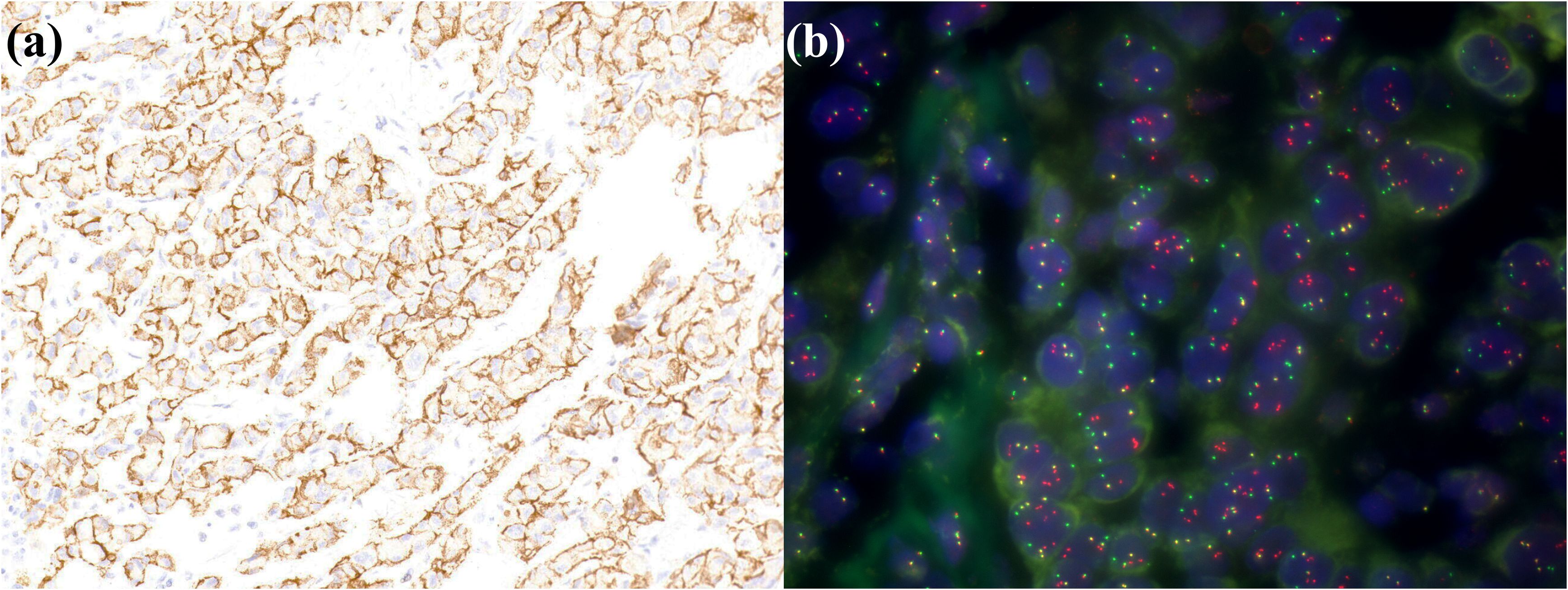
Figure 6. A small duct type iCCA patient with FGFR2 rearrangements. (a) FGFR2 is positively expressed in tumor cells; (b) FISH demonstrates FGFR2 breakage.
3.2 IDH1/2 mutations
The IDH family consists of three isoforms (IDH1, IDH2, and IDH3) that facilitate metabolic exchange and electron transfer between mitochondria and the cytosol. IDH1/2 serve as the primary source of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate in most tissues. As a critical reducing agent, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate regulates antioxidant defense systems by neutralizing reactive oxygen species. Compromised IDH1/2 activity in cancer cells may disrupt these detoxification processes, thereby inducing genomic instability through accumulated deoxyribonucleic acid lesions (138). IDH mutations, particularly IDH1 mutations in iCCA patients, can benefit from Ivosidenib (recommended by National Comprehensive Cancer Network as subsequent-line treatment regimen for unresectable and metastatic biliary tract cancer) (5, 139). A small number of patients with iCCA also present with IDH2 mutations. IDH mutations frequently occurr in small duct type iCCA patients. The common mutated sites for IDH1 are at codon 132, and for IDH2, at codon 172. The incidence of IDH1/2 mutations in iCCA is approximately 15% to 20% (140–143). Detection of IDH mutations can be accomplished through Sanger sequencing or NGS. The selection of suitable antibodies is of utmost importance because of the multiplicity of IDH-mutated sites. For instance, in a study employing the IDH1 antibody with clone OTI24A2, it was found that 92.9% (105/113) of iCCAs showed positive expression, failing to screen for related gene mutations (144). So far, two studies yielded encouraging results. In one study involving 95 iCCAs, IDH1 R132 mutations were observed in 19 cases (20.0%), encompassing 5 cases of IDH1 R132L, 11 cases of IDH1 R132C, and 3 cases of IDH1 R132G. IDH2 R172 mutations were confirmed in 2 cases (2.1%), including 1 case of IDH2 R172M and 1 case of IDH2 R172K. All IDH1 R132L mutation cases exhibited positive staining of IDH (clone: MsMab-2), while other IDH1 R132 mutations, IDH2 mutations, and wild-type samples were negative (145). In another study, Ma B et al. conducted sequencing of 130 patients with iCCA and revealed that 21 patients (16.1%) carried IDH1/2 mutations, including 6 cases of IDH1 R132C, 5 cases of IDH1 R132G, 4 cases of IDH1 R132H, 2 cases of IDH1 R132L, 2 cases of IDH2 R172K, and 2 cases of IDH2 R172W. Positive expression of IDH (clone: MsMab-1) was detected in 14 patients (10.8%) of iCCA, which was specific for IDH1 R132G, IDH1 R132H, and IDH2 R172W. The sensitivity and specificity of this antibody for detecting the above three types of IDH1/2 mutations were 81.8% (9/11) and 95.8% (114/119) (κ = 0.691) (21). The above two studies used different clones of IDH antibodies, and their combination may further enhance the detection efficacy. Unfortunately, these two studies did not show the prognostic significance of the expression of IDH. Moreover, the most prevalent IDH1 R132C mutation in iCCA (143) cannot be accurately detected by these antibodies. Further research is still necessary as the existing IDH antibodies are incapable of covering all types of IDH mutations.
3.3 HER2 overexpression/amplification
The HER/erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog (ERBB) family proteins are type I transmembrane growth factor receptors that function to activate intracellular signaling pathways in response to extracellular signals. The members of HER family of kinases were shown to form both homodimers and heterodimers with each other, resulting in the activation of crucial cell signaling pathways, including the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway. HER3 interacts directly with PI3K, and HER2 indirectly activates this pathway through its interaction with HER3. The overexpression/amplification of HER2 is implicated in multiple cancers (146). HER2 detection can be achieved through immunohistochemistry, FISH, and NGS. HER2 immunohistochemistry has been widely employed in various cancer types such as breast cancer, gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma, and bladder cancer, and their standardized approaches are highly thorough. The commonly employed clone of HER2 includes 4B5, HercepTest, CB11, and so on. For biliary tract cancer, the high-grade evidence of approved HER2-targeted drugs is based on four clinical studies. The first one is the MyPathway study, where Pertuzumab combined with Trastuzumab was performed to treat metastatic biliary tract cancer patients with immunohistochemistry 3+ HER2, HER2 amplification indicated by FISH or chromogenic in situ hybridization (HER2:CEP17 ratio > 2.0, or HER2 copy number > 6.0), or HER2 amplification detected by NGS (HER2 copy number gain) (147). The second is the SGNTUC-019 study, in which Tucatinib and Trastuzumab were used to treat metastatic biliary tract cancer patients with the same inclusion criteria as the MyPathway study (148). The third is Trastuzumab Deruxtecan for the treatment of advanced solid tumor patients with immunohistochemistry 3+ HER2 (149). The fourth study is HERIZON-BTC-01 which validated that Zanidatamab could improve the prognosis of the unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer patients with HER2 2+ and 3+, especially for the latter population (150). Regarding the percentage of positive cases of HER2 expression in iCCA, a meta-analysis including 40 studies showed that when the moderate/strong positive expression of HER2 was defined as positive, the percentage of positive cases of HER2 expression in iCCA was 4.8% (151). Another study incorporating 110 iCCAs suggested that when evaluated based on the guideline from the College of American Pathologists, American Society for Clinical Pathology, and the American Society of Clinical Oncology for gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma (152), the detection percentage of 2+ and 3+ HER2 expression in iCCA was 3.7% (153). One more study including 27 cases of iCCA indicated that when HER2 scoring was performed under the 2018 version of the American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline (154), the detection percentage of 2+ and 3+ HER2 expression in iCCAs was also 3.7% (155). In terms of prognosis, a meta-analysis including 31 studies revealed that the overall survival of biliary tract cancer patients with HER2 overexpression was poorer, but when specified to the patients of iCCA, the conclusion still need further verification (156). Currently, there is no evidence for an independent HER2 immunohistochemical interpretation standard for iCCA, mainly referring to the methods of gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma and breast cancer. Considering that clear clinical evidence has been obtained through these methods, it is feasible from an empirical perspective (Figure 7). Additionally, although the majority of HER2 alterations are gene overexpression or amplification, activating missense mutations have also been proven to be an important subset of HER2 alterations, which cannot be detected by immunohistochemistry.
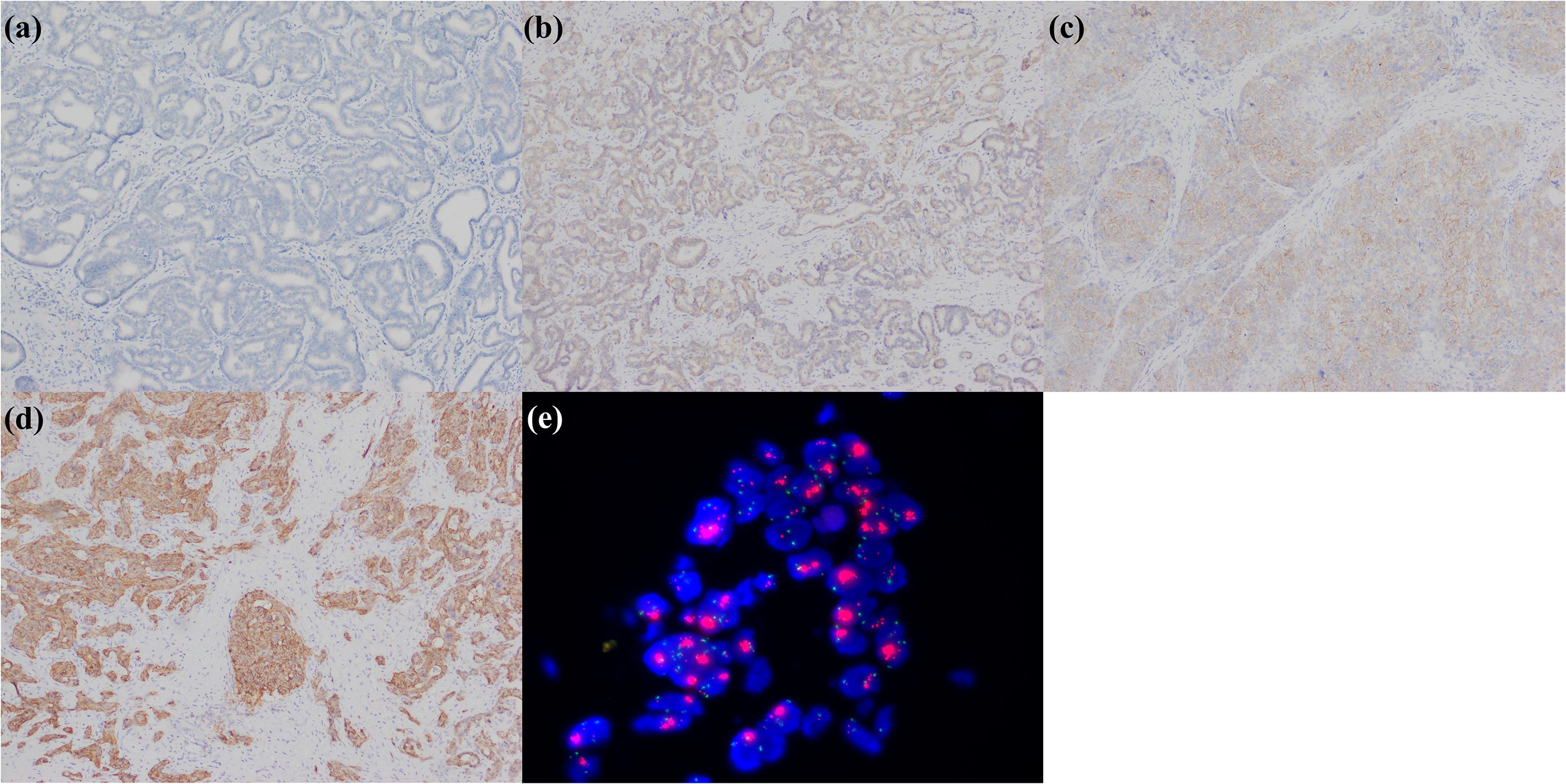
Figure 7. iCCA with heterogeneous HER2 status. (a) HER2 0; (b) HER2 1+; (c) HER2 2+; (d) HER2 3+; (e) FISH demonstrates HER2 amplification.
3.4 BRAF V600E mutation
BRAF is a serine/threonine kinase and a critical node in the canonical mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Activated BRAF phosphorylates mitogen activated protein kinase 1/2, which, once activated, subsequently phosphorylate extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. The activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 then phosphorylate downstream effectors that regulate cell proliferation, survival, and various other cellular processes. When BRAF undergoes mutation, it leads to constitutive activation of this pathway, thereby promoting tumorigenesis (157). In 2020, the results of Dabrafenib combined with Trametinib for the treatment of BRAF V600E mutant biliary tract cancer publised, reporting an approximately 50% objective response rate, and the vast majority of the enrolled patients were iCCA (39/43, 90.7%) (158). Therefore, it was approved by National Comprehensive Cancer Network for the treatment of advanced biliary tract cancer patients as a subsequent-line regimen. The mutation rate of BRAF V600E in iCCA is approximately 1.1% to 3.0% (159–161). PCR, Sanger sequencing, and NGS are currently the standard approaches for detecting this mutation. The immunohistochemical detection of BRAF V600E mutation yielded excellent results in non-small cell lung cancer, thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, and melanoma (162–165), which spurred an exploration in biliary tract cancer. Sasaki M et al. utilized its specific antibody VE1 staining in 17 patients with small duct type iCCA and found no positive expression, and no BRAF V600E mutation was identified through PCR detection (166). Goeppert B et al. also employed VE1 to detect 159 patients of iCCA, 149 patients of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, and 69 patients of carcinoma of the gallbladder, and discovered 5 patients with positive expression, all of whom were iCCAs (5/159, 3.1%). Further PCR for BRAF V600E mutation was highly consistent with the immunohistochemical results (167). Regarding prognosis, Goeppert B et al. asserted that BRAF V600E mutation was not correlated with the prognosis of biliary tract cancer (167), while Wu S et al. suggested that BRAF V600E (clone: RM8) was positively expressed in 10.0% of iCCA patients (11/110), and the prognosis of BRAF V600E positive iCCA patients was better, but they did not verify the consistency between positive expression and molecular mutation (38). To sum up, immunohistochemical detection using the BRAF V600E antibody holds potential as an effective means for the selection of related targeted therapies for patients with iCCA (Figure 8).
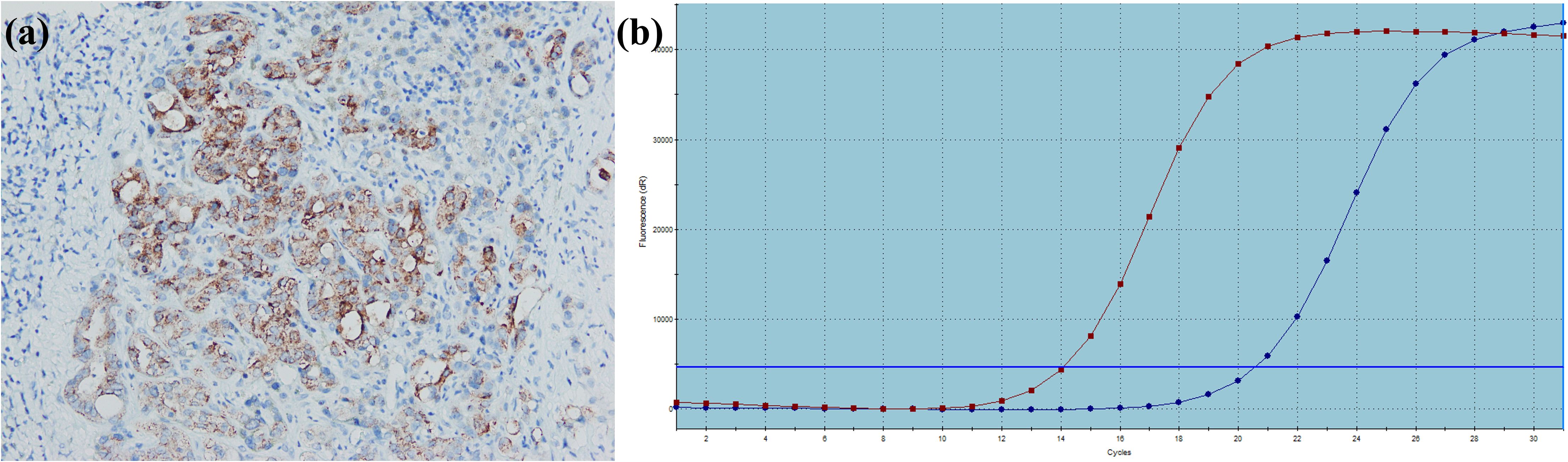
Figure 8. A large duct type iCCA patient with BRAF V600E mutation. (a) BRAF is positively expressed in tumor cells; (b) PCR demonstrates BRAF V600E mutation.
3.5 NTRK fusions
The TRK receptor family include TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC (encoded by NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3, respectively), all of which share a highly homologous sequences with conserved structural organization. TRK receptors bind neurotrophin family ligands, a group of highly homologous dimeric growth factors involved in the development and maintenance of the nervous system (168). NTRK fusions were initially discovered in colon cancer and subsequently identified in various tumor types (169). Entrectinib (170), Larotrectinib (171), and Repotrectinib (172) were recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network for the primary/subsequent-line therapies of biliary tract cancer with NTRK fusions. Considering that the occurrence rate of NTRK fusions in biliary tract cancer is less than 1%, rational testing is required to screen for relevant patients. The recommended testing method is NGS, especially RNA-NGS, and the related immunohistochemical antibody pan-TRK (clone: EPR17341) is also applied in practice. In the initial studies, it was thought that pan-TRK immunohistochemistry could effectively recognize solid tumors with NTRK fusions and could present three staining patterns: nuclear staining, cytoplasmic and nuclear membrane staining, or cytoplasmic and cytoplasmic membrane staining (173, 174). However, with the increased exploitation, it was found that its sensitivity to NTRK3 fusions was limited, and there were a considerable number of false-positive cases (175). For biliary tract cancer, a study involving 351 Caucasian patients revealed that no pan-TRK-positive staining was detected (clone: EPR17341) (176). In another study encompassing 85 Asian patients (42 patients of iCCA), pan-TRK positive expression was observed in 26 patients (13 patients with iCCA) with 25 weakly positive (clone: EPR17341) (177). The above two studies imply that pan-TRK expression may vary by ethnicity. Zhang D et al. conducted pan-TRK testing on 69 patients of iCCA and 110 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. The former group showed no positive expression and 12 patients of hepatocellular carcinoma showed weak expression of tumor cells in the cytoplasm, but no NTRK fusions were detected through molecular testing (clone: EPR17341) (178). Demols A et al. tested 140 samples of biliary tract cancer and indicated that 17 cases showed positive expression, among which 11 were iCCA. However, only 1 case of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma was found to have NTRK fusions through NGS testing, and its immunohistochemical staining was weakly positive (clone: EPR17341) (179). The above results suggest that pan-TRK immunohistochemical staining can currently only function as a rough screening approach. Given its notable false-positive rate, any intensity and pattern of staining should not be overlooked, and further NGS testing for positive expression cases is necessary.
3.6 RET fusions
RET encodes for a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase with proto-oncogene properties. RET binds to the ligand-co-receptor complex of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family ligands. RET signaling is vital for renal morphogenesis, neural and neuroendocrine tissue development, and spermatogonial stem cell maintenance. RET fusions are a type of somatic mutation leading to the formation of distinct RET oncoproteins. The Phase I/II ARROW clinical trial gauged the effectiveness of Pralsetinib for patients having RET fusions-positive solid tumors. Out of the 28 assessable patients, three had biliary tract cancer, and two obtained a verified response (180). The Phase I/II LIBRETTO-001 study appraised the efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET fusions-positive solid tumors and included one patient with biliary tract cancer (181). Both Pralsetinib and Selpercatinib were integrated into the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines as primary/subsequent-line treatment alternatives for advanced biliary tract cancer featuring RET fusions (8). The “Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of RET fusion non-small cell lung cancer in China” (182) and the “Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of advanced RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (2023 edition)” (183) suggested detecting RET fusions through NGS, PCR, FISH, and immunohistochemistry. They recommended that NGS and PCR were favored due to greater sensitivity and specificity. As of now, no studies have evaluated RET immunohistochemistry in iCCA. Immunohistochemistry screening for RET fusions showed passable sensitivity and specificity in the studies of non-small cell lung cancer (clone: 6E4C4; clone 3F8; EPR2871) (184–187). Another study based on 41,869 tumors indicated that the specificity of RET immunohistochemistry (clone: EPR2871) was 82.0% (73/89). The detection sensitivity varied by fusion partner: KIF5B had the highest sensitivity (100.0%, 31/31), followed by CCDC6 (88.9%, 16/18) and NCOA4 (50.0%, 6/12) (188). These results highlight the potential of immunohistochemistry in the detection of RET-fusions for iCCA patients.
3.7 MET amplification
The MET proto-oncogene encodes the tyrosine kinase receptor of the hepatocyte growth factor and modulates critical biological processes including embryonic development, tissue repair, hepatic regeneration, vascular remodeling, and immune regulation. In cancer, dysregulated MET signaling drives tumor progression through its ability to enhance invasive potential, stimulate blood vessel formation, and facilitate metastatic dissemination (189). MET amplifications, mutations, and fusions are drivers of oncogenesis. Although no clinical trials have affirmatively demonstrated that iCCA with MET amplification can gain benefits from MET inhibitors, many preclinical studies and case reports pointed out its potential (190–200). MET variations are not scarce in iCCA. An NGS analysis of 28 iCCAs showed that the rate of MET variations was 7.1% (201). Another study on 349 advanced iCCAs indicated that the rate of MET amplification was 4.6% (202). One more study covering 6,130 iCCAs suggested that the proportion of MET amplification was 2.0% (142). Existing studies explored the MET expression in iCCA and its connection with tumor biological behavior, prognosis, and molecular alterations. Regarding tumor biological behavior, two studies performed MET immunohistochemical staining in iCCAs and documented that the expression was stronger in well-differentiated tumors than in poorly differentiated ones (203, 204). However, Joo HH et al. held that MET expression was directly related to tumor invasiveness in biliary tract cancer (205). Heo MH et al. believed MET expression was not associated with the clinicopathological characteristics of biliary tract cancer (206). In terms of prognosis, three studies discovered that the percentage of high expression of MET in iCCA ranged from 6.8% to 51.5% and was significantly related to the poor prognoses (207–209). Regarding the consistency of MET expression and MET amplification, a study involving 133 iCCAs revealed that 21 cases (15.8%), 41 cases (30.8%), and 71 cases (53.4%) had high-frequency MET amplification, low-frequency MET amplification, and normal MET, respectively. Among the high-frequency MET amplification cases, 3 tumors had cluster amplification, and they all showed strong MET expression. Strong staining was not observed in tumors with other genetic alterations. The proportion of MET positive expression in high-frequency MET amplification patients was higher than that in low-frequency MET amplification and normal MET patients (52.4% vs. 22.0% vs. 8.5%) (210). Another exploration of 27 iCCAs showed that 4 had MET amplification, 6 showed MET positive expression to varying degrees, and 1 had MET amplification when MET staining was negative (155). Overall, immunohistochemical detection of MET expression can provide a preliminary reference for patients with MET amplification to some extent. Recently, the “Chinese expert consensus on clinical practice of MET detection in non-small cell lung cancer” was issued, recommending FISH and NGS as the standardized methods to validate MET amplification and proposing a scoring approach for MET immunohistochemical evaluation integrating expression range and intensity, and preferentially using the SP44 clone MET antibody (211), which can be referred to (Figure 9).
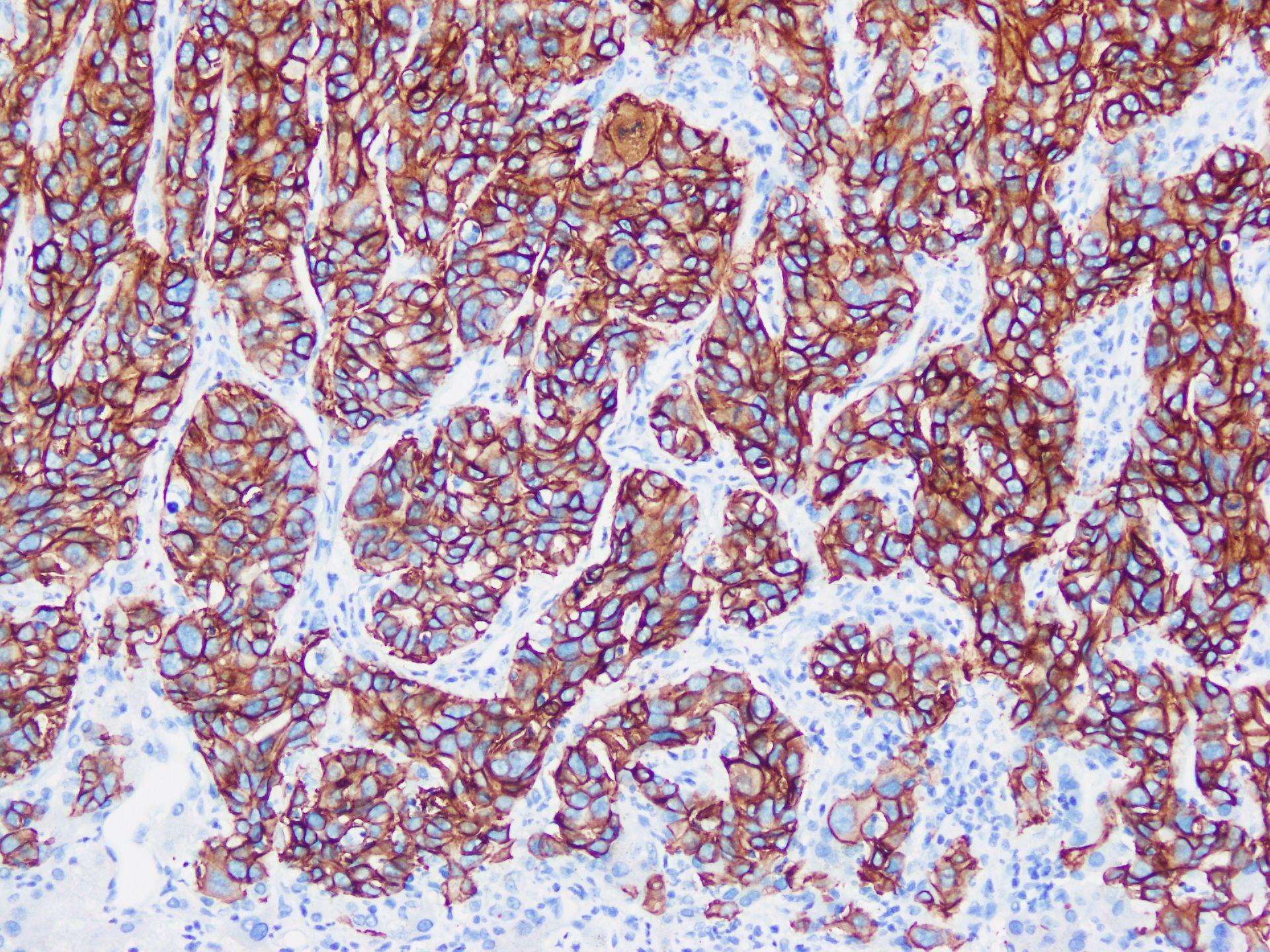
Figure 9. A small duct type iCCA patient with MET amplification harbored by NGS exhibits strong MET expression in tumor cells.
3.8 ALK fusions
ALK encodes a highly conserved receptor tyrosine kinase in the insulin receptor superfamily and leads to the activation of downstream signaling pathways critical for cellular proliferation, survival, and differentiation. In several cancers, ALK fusions have been identified as key oncogenic drivers (212). ALK inhibitors have made significant progress in non-small cell lung cancer and can be accurately identified through immunohistochemical detection (213). Even though ALK-related molecular alterations are seldom seen in iCCA (214–217), preclinical studies and case reports verified the existence of ALK fusions in this tumor entity and the possible benefit from ALK inhibitors (197, 218–220). The reported gene fusions in iCCA included EML4::ALK and STRN::ALK (197, 218, 219, 221). Among them, two papers provided ALK immunohistochemical results, both of which were positive (clone: D5F3) (219, 221). Another study included 80 iCCAs for ALK immunohistochemical staining (clone: ZAL4) with 55 cases showing positive expression, but only 5 cases showed strong expression. Further FISH detection revealed that one of them had ALK rearrangement, but no detailed fusion gene data were provided (209). Based on these studies, immunohistochemistry for screening patients with iCCA with ALK fusions has potential value, but it needs to be clarified by FISH or NGS.
3.9 ROS1 fusions
ROS1 is located at 6q22 and encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase in the subclass of the insulin receptor family. The function of ROS1 in human physiology remains unclear. Genetic fusions in ROS1 result in constitutive activation of the tyrosine kinase, serving as a driver for tumor proliferation (222). ROS1 fusions are rare in iCCA (223). Reported fusion genes in iCCA include TMEM106B::ROS1, FIG::ROS1, and RDX::ROS1 (224–227). Preclinical studies and case reports suggested the targeted therapeutic significance of ROS1 fusions (197, 226). The expression of ROS1 in iCCA and its connection with molecular alterations were documented in three literatures. The immunohistochemical staining of ROS1 (clone: D4D6) in 194 iCCAs by Lee KH et al. disclosed positive expression in 72 cases. Positive expression of ROS1 was associated with well-differentiated tumors and great disease-free survival, but no ROS1 fusion was detected through FISH (228). The immunohistochemical staining of ROS1 in 85 cases of iCCA by Chiang NJ et al. indicated positive expression in 57 cases (67.1%) and strong positive expression in 9 cases (10.6%). However, they thought positive expression of ROS1 was positively correlated with the unfavorable prognosis, and no ROS1 fusion cases were detected by FISH either (209). The immunohistochemical staining of ROS1 (clone: D4D6) in 198 cases of iCCA by Lim SM et al. manifested positive expression in 38 cases and identified that 3 cases had ROS1 rearrangement, but one of them was ROS1 negative (229). Given this, both the recognition capability of ROS1 immunohistochemical staining and its correlation with prognosis remain unclear, and its utilization should be prudent.
3.10 PTEN deficiency
PTEN regulates many cellular processes, including proliferation, survival, energy metabolism, cellular architecture, and motility. The tumor-suppressor activity of PTEN depends largely on its lipid phosphatase activity, which inhibits PI3K/AKT activation (230). For the genesis of malignant tumors, PTEN stands as one of the most common genes. The absence of PTEN expression is not a rare occurrence in iCCA. Lee D et al. demonstrated that 67 cases showed the loss of PTEN expression among 101 iCCAs, and the prognosis of such cases was unfavorable (clone: 138G6) (231). Jiang TY et al. identified that 30 patients had loss of expression of PTEN (clone: 138G6) among 98 advanced iCCAs (232). For patients with advanced iCCA with the loss of PTEN expression, they further probed into the therapeutic value of Bortezomib. Among the 130 included patients, 38 patients (29.2%) were affirmed to have the absent or low expression of PTEN (clone: 138G6). The objective response rate and disease control rate of the 13 patients who eventually received Bortezomib treatment were 23.1% and 53.9%, respectively. The median progression-free survival was 3.6 months, and the median overall survival was 9.6 months, which surpassed the prognosis of patients with high PTEN expression. The three patients with notable tumor shrinkage were all with complete loss of PTEN expression (233). Currently, the study on PTEN and iCCA remains limited, and immunohistochemical testing of PTEN has yet to be widely used in routine clinicopathological practice for iCCA. Based on our experience, PTEN frequently exhibits weakly positive staining with ambiguous localization in tumors, leading some pathologists to interpret such cases as negative. This risks significant false-negative interpretation. We propose that strict criteria should be established to distinguish patients with PTEN deficiency, and further validation should be conducted in larger cohorts of iCCA.
3.11 NRG1 fusions
NRG1 is critical for cell differentiation and organogenesis (234). NRG1 fusions act as driver gene in solid tumors. The connection between NRG1 and HER3 boosts heterodimerization with other kinases of the HER/ERBB family, thus strengthening downstream signaling pathways and tumorigenesis. As a result, focusing on the ERBB pathway becomes a hopeful therapeutic approach for cancers with NRG1 fusions (235). Zenocutuzumab, an antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-enhanced anti-HER2 and HER3 bispecific antibody, proved effective in treating solid tumors harboring NRG1 fusions and received endorsement from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network in the treatment of pancreatic cancer (236). A phase II clinical trial evaluating its safety and efficacy in NRG1 fusions-positive advanced solid tumors indicated a partial response in one of three cholangiocarcinoma patients (237). Although NRG1 fusions are seldom seen in iCCA (238), there has been case reports noting successful treatments in related patients (239). In 2024, Chinese scholars issued the “Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of NRG1/2 fusion solid tumors” proposing RNA-NGS and pERBB3 immunohistochemistry as efficient methods for detecting NRG fusions (240). Notably, pERBB3 immunohistochemistry showed high sensitivity and specificity in lung adenocarcinoma (clone: Tyr1289) (241, 242). Comparable studies in iCCA are currently absent.
3.12 MSI-H/dMMR
The DNA MMR system is responsible for the identification, excision, and repair of base-pair mismatches or indel loops in the genome. Loss of expression of any of the MMR proteins involved in this process will disrupt genomic stability, leading to MSI and is associated with a higher risk for tumorgenesis (243). The success and approval of Pembrolizumab (244) and Dostarlimab (245) in the treatment of solid tumors with MSI-H or dMMR prompted many academic societies to formulate guidelines for the detection of dMMR tumors (246–248). These guidelines unanimously propose three methods: PCR for MSI, immunohistochemistry for MMR (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2), and NGS. Among them, immunohistochemistry is regarded as the most convenient method with the complete absence of expression of any one or more of the four proteins in tumor cells indicating dMMR (Figure 10). The prevalence of dMMR in biliary tract cancers is approximated to be 2% to 3% (249). Nevertheless, large-scale investigations specifically focusing on the incidence of dMMR in iCCA are scarce. A study encompassing 584 iCCAs reported an MSI-H rate of 6.0% (n=35), with patients demonstrating enhanced prognosis after immunotherapy (250). An NGS-based study discovered an MSI-H rate of 1.3% (75/5,885) in iCCAs (142). From the aspect of immunohistochemistry, Winkelmann R et al. did not find dMMR among 35 iCCA patients (251). Yu J et al. identified dMMR in 2.7% (n=2) of 73 iCCAs (252). A study of 71 iCCAs determined that 9.9% (n=7) had at least one MMR protein lacking, which correlated with a histology of mucinous adenocarcinoma and a poor prognosis (253). Khuntikeo N et al. discovered that 27.3% (n=21) of 77 liver fluke-related iCCAs were with dMMR, suggesting a favorable prognosis for these patients (254). This detection rate of dMMR was not in line with the MSI-H rate in another group of liver fluke-related iCCA patients (255), but the prognostic implications were consistent with the findings of Cloyd JM et al. (256). The actual incidence of dMMR in iCCA remains to be fully clarified. Existing evidence substantiated the clinical advantage of immunotherapy for dMMR-positive patients (250, 257–260). Hence, routine detection for MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 in iCCA patients is highly significant. Although the three detection methods demonstrate substantial concordance, studies in other tumor types have revealed a discordance rate of <15% between MMR and MSI testing results (261–263). The main reasons for the inconsistency include: functional redundancy among MMR proteins (e.g., MSH3 can compensate for isolated MSH6 loss, preserving partial MMR activity and MSS status), missense mutations and false-positive of MLH1, suboptimal immunohistochemical staining quality, and the low tumor cellularity (264). Given these potential differences, the simultaneous use of immunohistochemistry and PCR, or even NGS, might offer more reliable data (265).
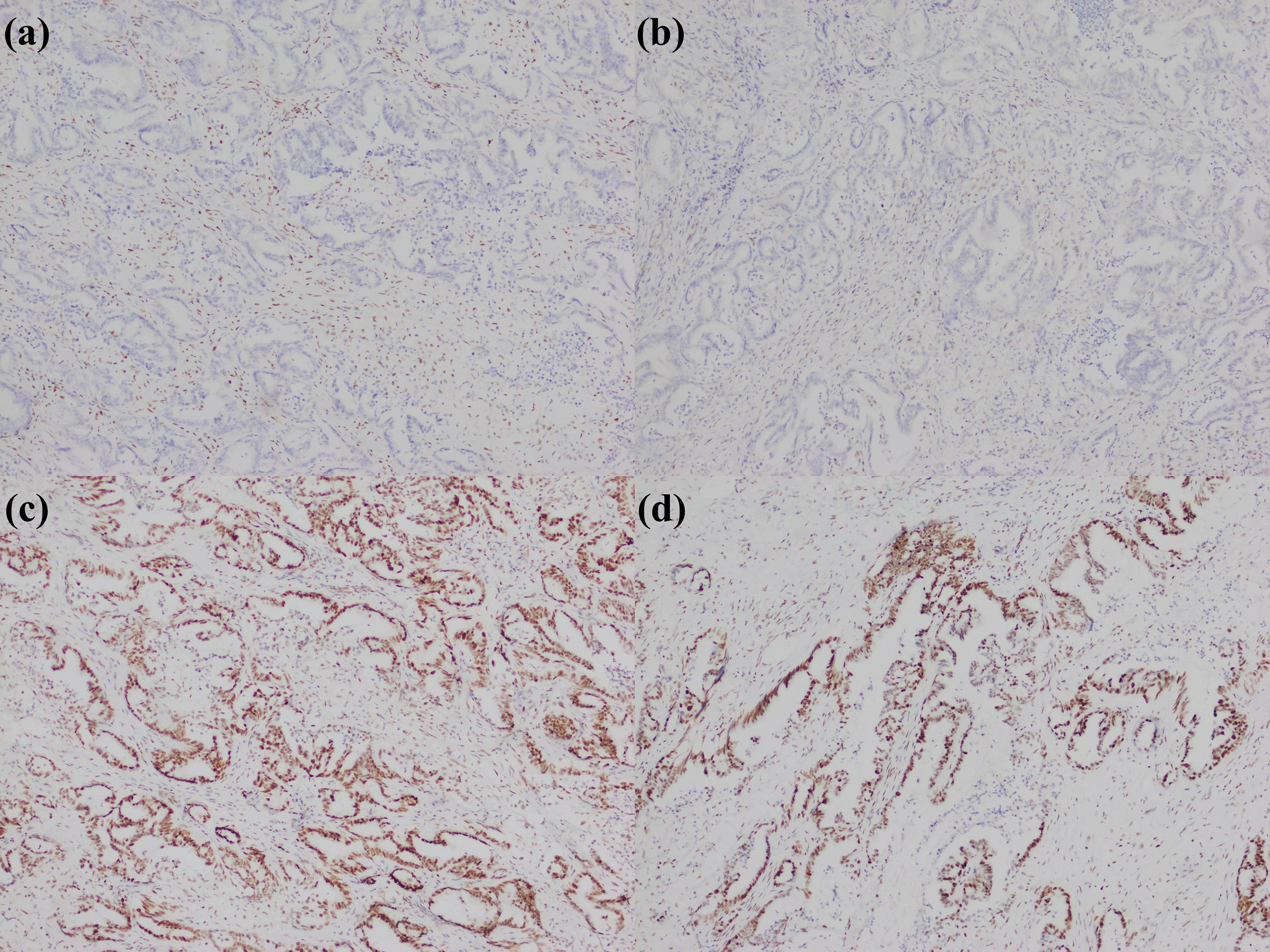
Figure 10. A large duct type iCCA patient with dMMR. (a) loss of MLH1 expression; (b) loss of PMS2 expression; (c) MSH2 expression; (d) MSH6 expression.
3.13 PD-L1 high expression
PD-L1 is notably expressed across tumor-associated cell populations, including neoplastic cells, stromal components, and myeloid lineages (Figure 11). Through dual ligand interactions with programmed death-1 receptors on T cells and CD80 co-stimulatory molecules on antigen-presenting cells, PD-L1 inhibits T cell proliferation, cytokine production, and cytolytic activity driving T cells toward a dysfunctional exhausted state (266). Although PD-L1 inhibitor Durvalumab has been approved for primary preferred treatment of biliary tract cancer, the connection between elevated PD-L1 expression and the therapeutic outcome of immunotherapy for iCCA remains uncertain but this relationship warrants attention. A study manifested that PD-L1 expression in biliary tract cancer could serve as a potential predictor for the therapeutic efficacy of Pembrolizumab. The objective response rate and disease control rate were higher in the high PD-L1 expression group [tumor-positive score (TPS) ≥ 50%] (267). In a single-arm phase II clinical trial of Camrelizumab combined with Gemcitabine and Oxaliplatin for the treatment of patients with advanced biliary tract cancer, the objective response rate of patients with PD-L1 TPS ≥ 1% was 80.0%, outperforming that of 53.8% of patients with PD-L1 TPS < 1% (268). A meta-analysis encompassing 30 studies investigated the predictive value of PD-L1 expression for the response to immunotherapy in biliary tract cancer and suggested that there was no significant distinction in the objective response rate and disease control rate between PD-L1+ and PD-L1- patients. Nevertheless, the progression-free survival and overall survival were enhanced in the former group. Within the included studies, the determination of PD-L1 positivity was mainly based on TPS ≥ 1% or combined positive score (CPS) ≥ 1 (269). Another meta-analysis incorporating 10 studies revealed that high PD-L1 expression was positively correlated with poorer overall survival and recurrence-free survival in iCCA (270). Hence, it is rationally supposed that although the prognosis of iCCA with high PD-L1 expression is unfavorable, immunotherapy may improve the prognosis of this subgroup. There were some proposed interpretation standards and validated clones for PD-L1 immunohistochemistry in recent years (271–273), which are used to assess PD-L1 evaluation in iCCA.
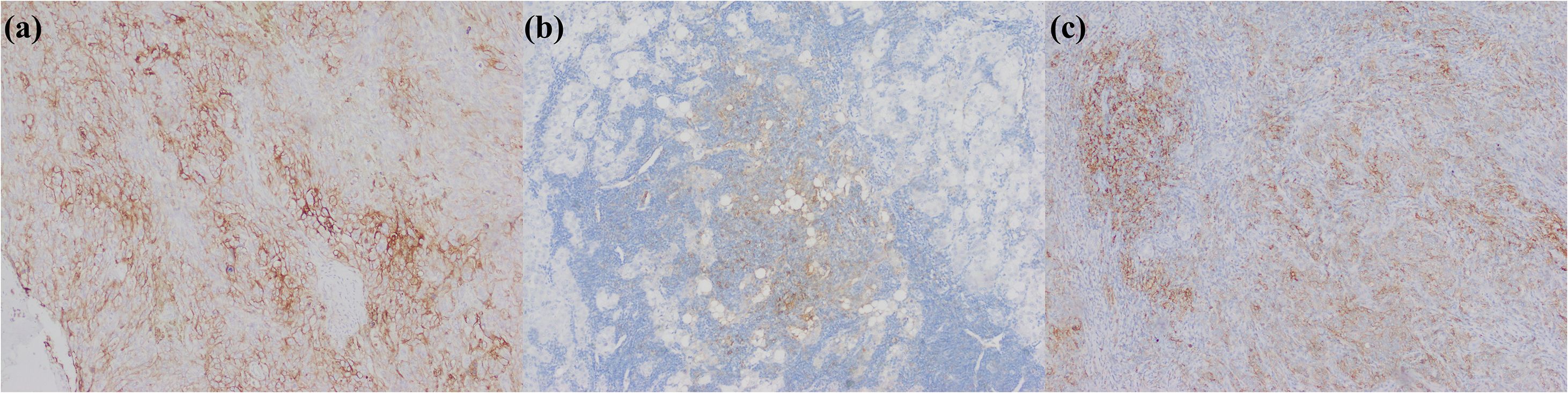
Figure 11. iCCA with heterogeneous PD-L1 expression. (a) PD-L1 is positively expressed in tumor cells; (b) PD-L1 is positively expressed in immunocytes; (c) PD-L1 is positively expressed in tumor cells and immunocytes.
3.14 Summary
The screening of drug-related molecular targets by immunohistochemistry in iCCA remains nascent. Among the aforementioned immunohistochemical markers, HER2, BRAF, and MMR proteins have demonstrated great concordance with molecular testing in iCCA. Diffuse and strong HER2 membranous staining, diffuse BRAF cytoplasmic staining, and absence of MMR proteins expression are indicative of potential survival benefits from corresponding targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
Furthermore, the correlation between PD-L1 expression levels and the clinical efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in iCCA has not yet been definitively established. This may be attributed to several factors, including heterogeneous PD-L1 expression across tumor cells, variability in detection platforms and scoring criteria, as well as complex interactions with other molecules within the tumor microenvironment. It is therefore recommended that, when feasible, PD-L1 testing be performed on multiple paraffin blocks representing different regions from the same case, in order to obtain a more comprehensive profile and provide clinicians with enhanced insights.
For immunohistochemical markers of other molecular alterations, their current utility remains limited. There are still many conflicting reports for the same marker, which might be attributed to discrepancies in antibody clones (leading to variations in sensitivity and specificity), differences in histological subtypes of study populations, and variations in interpretation methodologies. It is recommended that definite staining with any intensity, localization, and distribution warrant further confirmation through molecular testing, and detailed information regarding expression should be documented. In cases which immunohistochemical findings are discordant with molecular testing, appropriate explanations should be provided to both patients and clinicians, with molecular testing serving as the optimal standard currently. In addition to the continuous optimization of existing antibody clones to more precisely correspond with the associated molecular alterations, for gene alternations lacking antibodies, such as KRAS G12C mutation, the development of effective immunohistochemical detections is meaningful. Moreover, standardizing interpretation methods and implementing rigorous quality control standards are essential to ensure consistency in microscopic assessments for pathologists.If immunohistochemistry can be effectively aligned with molecular testing in the future, it will fundamentally transform the economic costs, execution efficiency, and clinical trial enrollment criteria for selecting targeted therapies and immunotherapies in patients with iCCA. A comprehensive summary of drug-related immunohistochemical antibodies is provided in Table 3.
4 Conclusions
Immunohistochemistry, serving as a practical and cost-effective method, is indispensable for the contemporary pathological management of iCCA. We summarize distinct immunohistochemical profiles that are significantly related to the identification of histological subtyping. However, based on current findings, there is still a lack of highly specific immunohistochemical markers for large duct type iCCA, cholangiolocarcinoma, and iCCA with DPM pattern. This warrants further exploration in future studies. Since the histological subtyping of iCCA is closely correlated with the frequency of molecular alterations, accurate histological subtyping can provide more valuable clues and facilitate the screening of drug-related molecular targets. While molecular pathological techniques remain essential for definitively detecting of many genetic alterations, the immunohistochemical markers summarized herein offer an alternative approach for drug-target identification, especially in resource-limited settings. However, many immunohistochemical antibodies targeting drug-associated targets continue to demonstrate only poor correlations with molecular findings. It is necessary to focus on developing highly specific antibodies for emerging therapeutic targets to assist in the treatment selection of iCCA. Pathologists and clinicians should be aware that histological morphology and clinical information are essential prerequisites for any pathological diagnosis when utilizing immunohistochemistry for diagnosis. The positive range, localization, intensity, and appropriate controls of immunohistochemical staining are all indispensable considerations to ensure accurate interpretation.
Author contributions
HW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. We have received funding from the Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2023ZD0500100), Municipal Hospital Clinical Technology Promotion and Management Optimization Project by Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center (No. SHDC22023208), and Take-off Project Talent Program of EHBH (No. TF2024XSJJ02).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the kind contribution of Yu-Yao Zhu (Department of Pathology, Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Naval Medical University) and Xin Zhang (Department of Pathology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University), who generously shared some of the images used in this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
AGR: Anterior gradient protein
AKT: Protein kinase B
ALK: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase
ARID1A: AT-rich interactive domain 1A
BRAF: V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1
BRCA: Breast cancer susceptibility gene
BRG1: Brahma-related gene 1
CA19-9: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9
CDH2: Cadherin 2
CK: Cytokeratin
CLDN: Claudin
CPS: Combined positive score
CRP: C-reactive protein
dMMR: MMR-deficient
DPM: Ductal plate malformation
EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule
ERBB: Erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog
EVI1: Ecotropic virus integration site 1 protein homolog
FGB: Fibrinopeptide B
FGFR: Fibroblast growth factor receptor
FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridization
HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor
iCCA: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
IDH: Isocitrate dehydrogenase
INI1: Integrase interactor 1
KRAS: Kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene homolog
LMP1: Latent membrane protein 1
MET: Mesenchymal-epithelial transition
MMP7: Matrix metalloproteinase 7
MSI-H: Microsatellite instability-high
MUC: Mucin
NGS: Next-generation sequencing
NRG1: Neuregulin 1
NTRK: Neurotrophin receptor kinase
OPN: Osteopontin
pCEA: Polyclonal carcinoembryonic antigen
PCR: Polymerase chain reaction
PD-L1: Programmed cell death ligand 1
PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase
PPP1R1B: Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 1B
PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog
RET: Rearranged during transfection
RNA: Ribonucleic acid
ROS1: ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase
S100P: S100 calcium-binding protein P
SALL4: Spalt-like transcription factor 4
Smad4/DPC4: SMAD family member 4
SPP1: Secreted phosphoprotein 1
TFF1: Trefoil factor 1
TMB-H: Tumor mutational burden
TPS: Tumor-positive score
TUBB3: Class III β-tubulin
WHO: World Health Organization
References
1. Wang H, Chen J, Zhang X, Sheng X, Chang XY, Chen J, et al. Expert consensus on pathological diagnosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (2022 version). J Clin Trans hepatol. (2023) 11:1553–64. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00118
2. Board WCoTE. WHO Classification of Tumours, Digestive System Tumours. 5th edition. Lyon: IARC Press (2019).
3. Zen Y. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: typical features, uncommon variants, and controversial related entities. Hum pathol. (2023) 132:197–207. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2022.06.001
4. Abou-Alfa GK, Sahai V, Hollebecque A, Vaccaro G, Melisi D, Al-Rajabi R, et al. Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:671–84. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30109-1
5. Zhu AX, Macarulla T, Javle MM, Kelley RK, Lubner SJ, Adeva J, et al. Final overall survival efficacy results of ivosidenib for patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma with IDH1 mutation: the phase 3 randomized clinical ClarIDHy trial. JAMA Oncol. (2021) 7:1669–77. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.3836
6. Oh DY, He AR, Bouattour M, Okusaka T, Qin S, Chen LT, et al. Durvalumab or placebo plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in participants with advanced biliary tract cancer (TOPAZ-1): updated overall survival from a randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 9:694–704. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00095-5
7. Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, Finn RS, Furuse J, Ren Z, et al. Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2023) 401:1853–65. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00727-4
8. Benson AB, D'Angelica MI, Abrams T, Ahmed A, Akce M, Anaya DA, et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, Biliary Tract Cancers (Version 5.2024). Plymouth Meeting: National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2024).
9. Choi JH and Thung SN. Recent advances in pathology of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers. (2024) 16:1537. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081537
10. Okuda K, Kubo Y, Okazaki N, Arishima T, and Hashimoto M. Clinical aspects of intrahepatic bile duct carcinoma including hilar carcinoma: a study of 57 autopsy-proven cases. Cancer. (1977) 39:232–46. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197701)39:1<232::AID-CNCR2820390137>3.0.CO;2-Y
11. Aishima S, Kuroda Y, Nishihara Y, Iguchi T, Taguchi K, Taketomi A, et al. Proposal of progression model for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: clinicopathologic differences between hilar type and peripheral type. Am J Surg Pathol. (2007) 31:1059–67. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802b34b6
12. Aishima S, Fujita N, Mano Y, Kubo Y, Tanaka Y, Taketomi A, et al. Different roles of S100P overexpression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: carcinogenesis of perihilar type and aggressive behavior of peripheral type. Am J Surg pathol. (2011) 35:590–8. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31820ffdf1
13. Nakanuma Y, Sato Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Xu J, and Ikeda H. Pathological classification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma based on a new concept. World J Hepatol. (2010) 2:419–27. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.419
14. Kinzler MN, Schulze F, Jeroch J, Schmitt C, Ebner S, Gretser S, et al. Heterogeneity of small duct- and large duct-type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Histopathology. (2024) 84:1061–7. doi: 10.1111/his.15162
15. Jiang H, Hu H, Tong X, Jiang Q, Zhu H, and Zhang S. Calcium-binding protein S100P and cancer: mechanisms and clinical relevance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2012) 138:1–9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1062-5
16. Komuta M, Govaere O, Vandecaveye V, Akiba J, Van Steenbergen W, Verslype C, et al. Histological diversity in cholangiocellular carcinoma reflects the different cholangiocyte phenotypes. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2012) 55:1876–88. doi: 10.1002/hep.25595
17. Liau JY, Tsai JH, Yuan RH, Chang CN, Lee HJ, and Jeng YM. Morphological subclassification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: etiological, clinicopathological, and molecular features. Modern Pathol. (2014) 27:1163–73. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.241
18. Hayashi A, Misumi K, Shibahara J, Arita J, Sakamoto Y, Hasegawa K, et al. Distinct clinicopathologic and genetic features of 2 histologic subtypes of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Surg pathol. (2016) 40:1021–30. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000670
19. Rhee H, Ko JE, Chung T, Jee BA, Kwon SM, Nahm JH, et al. Transcriptomic and histopathological analysis of cholangiolocellular differentiation trait in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. (2018) 38:113–24. doi: 10.1111/liv.13492
20. Yamada M, Yamamoto Y, Sugiura T, Kakuda Y, Ashida R, Tamura S, et al. Comparison of the clinicopathological features in small bile duct and bile ductular type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39:2121–7. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13325
21. Ma B, Meng H, Tian Y, Wang Y, Song T, Zhang T, et al. Distinct clinical and prognostic implication of IDH1/2 mutation and other most frequent mutations in large duct and small duct subtypes of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC cancer. (2020) 20:318. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06804-6
22. Akita M, Sawada R, Komatsu M, Suleman N, Itoh T, Ajiki T, et al. An immunostaining panel of C-reactive protein, N-cadherin, and S100 calcium binding protein P is useful for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma subtyping. Hum pathol. (2021) 109:45–52. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.12.005
23. Wagner BJ, Plum PS, Apel K, Scherer M, Buchner D, Brinkmann S, et al. Protein-loss of SWI/SNF-complex core subunits influences prognosis dependent on histological subtypes of intra- and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. (2021) 21:349. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12610
24. Song G, Shi Y, Meng L, Ma J, Huang S, Zhang J, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis suggests two molecularly subtypes of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:1642. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29164-0
25. Li Z, Huang N, Du Q, Huang W, Wang B, Wang B, et al. Role of immunophenotypic characterisation in prognostic subtyping of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Pathology. (2023) 55:979–88. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2023.07.008
26. Chen Y, Liu X, Huang L, Chen L, and Wang B. Clinicopathological, etiological and molecular characteristics of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma subtypes classified by mucin production and immunohistochemical features. Expert Rev Mol diagnostics. (2023) 23:445–56. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2023.2205588
27. Yoshizawa T, Uehara T, Iwaya M, Nakajima T, Shimizu A, Kubota K, et al. An immunohistochemical analysis of osteopontin and S100 calcium-binding protein P is useful for subclassifying large- and small-duct type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Am J Surg pathol. (2024) 48:751–60. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002224
28. Chen Z, Gao J, Li Z, Ma D, Wang Y, Cheng Q, et al. Integrative analysis reveals different feature of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma subtypes. Liver Int. (2024) 44:2477–93. doi: 10.1111/liv.16015
29. Sigel CS, Drill E, Zhou Y, Basturk O, Askan G, Pak LM, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas have histologically and immunophenotypically distinct small and large duct patterns. Am J Surg pathol. (2018) 42:1334–45. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001118
30. Sarcognato S, Gringeri E, Fassan M, Di Giunta M, Maffeis V, Guzzardo V, et al. Prognostic role of BAP-1 and PBRM-1 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Virchows Archiv: an Int J pathol. (2019) 474:29–37. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2478-y
31. Aishima S, Kuroda Y, Nishihara Y, Taguchi K, Taketomi A, Maehara Y, et al. Gastric mucin phenotype defines tumour progression and prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: gastric foveolar type is associated with aggressive tumour behaviour. Histopathology. (2006) 49:35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02414.x
32. Thuwajit P, Chawengrattanachot W, Thuwajit C, Sripa B, May FE, Westley BR, et al. Increased TFF1 trefoil protein expression in Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma is important for invasive promotion. Hepatol Res. (2007) 37:295–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00045.x
33. Akita M, Fujikura K, Ajiki T, Fukumoto T, Otani K, Azuma T, et al. Dichotomy in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas based on histologic similarities to hilar cholangiocarcinomas. Modern Pathol. (2017) 30:986–97. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.22
34. Tanaka M, Shibahara J, Ishikawa S, Ushiku T, Morikawa T, Shinozaki-Ushiku A, et al. EVI1 expression is associated with aggressive behavior in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Virchows Arch. (2019) 474:39–46. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2476-0
35. Abe T, Amano H, Shimamoto F, Hattori M, Kuroda S, Kobayashi T, et al. Prognostic evaluation of mucin-5AC expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, mass-forming type, following hepatectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2015) 41:1515–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2015.07.006
36. Thuwajit P, Chawengrattanachot W, Thuwajit C, Sripa B, Paupairoj A, and Chau-In S. Enhanced expression of mucin 6 glycoprotein in cholangiocarcinoma tissue from patients in Thailand as a prognostic marker for survival. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2008) 23:771–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05332.x
37. Park SY, Roh SJ, Kim YN, Kim SZ, Park HS, Jang KY, et al. Expression of MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6 in cholangiocarcinoma: prognostic impact. Oncol Rep. (2009) 22:649–57. doi: 10.3892/or_00000485
38. Wu S, Wang M, Zhou Q, Tang H, and Wang Z. The expression and clinicopathological significance of BRAF V600E and mucin 6 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A retrospective study. Int J Surg Pathol. (2024) 33:399–407. doi: 10.1177/10668969241266930
39. Aihara E, Engevik KA, and Montrose MH. Trefoil factor peptides and gastrointestinal function. Annu Rev Physiol. (2017) 79:357–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105447
40. Srivatsa G, Giraud AS, Ulaganathan M, Yeomans ND, Dow C, and Nicoll AJ. Biliary epithelial trefoil peptide expression is increased in biliary diseases. Histopathology. (2002) 40:261–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2002.01347.x
41. Kinzler MN, Schulze F, Bankov K, Gretser S, Becker N, Leichner R, et al. Impact of small duct- and large duct type on survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Results from a German tertiary center. Pathol Res Pract. (2022) 238:154126. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154126
42. Kosriwong K, Menheniott TR, Giraud AS, Jearanaikoon P, Sripa B, and Limpaiboon T. Trefoil factors: tumor progression markers and mitogens via EGFR/MAPK activation in cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. (2011) 17:1631–41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i12.1631
43. Muenphon K, Limpaiboon T, Jearanaikoon P, Pairojkul C, Sripa B, and Bhudhisawasdi V. Amplification of chromosome 21q22.3 harboring trefoil factor family genes in liver fluke related cholangiocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis. World J Gastroenterol. (2006) 12:4143–8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i26.4143
44. Brychtova V, Vojtesek B, and Hrstka R. Anterior gradient 2: a novel player in tumor cell biology. Cancer Lett. (2011) 304:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.12.023
45. Brychtova V, Mohtar A, Vojtesek B, and Hupp TR. Mechanisms of anterior gradient-2 regulation and function in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2015) 33:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.04.005
46. Vivekanandan P, Micchelli ST, and Torbenson M. Anterior gradient-2 is overexpressed by fibrolamellar carcinomas. Hum Pathol. (2009) 40:293–9. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2008.08.003
47. Lepreux S, Bioulac-Sage P, and Chevet E. Differential expression of the anterior gradient protein-2 is a conserved feature during morphogenesis and carcinogenesis of the biliary tree. Liver Int. (2011) 31:322–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02438.x
48. Miwa S, Miyagawa S, Soeda J, and Kawasaki S. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression and biologic aggressiveness of cholangiocellular carcinoma. Cancer. (2002) 94:428–34. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10235
49. Hirashita T, Iwashita Y, Ohta M, Komori Y, Eguchi H, Yada K, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 is an unfavorable prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. (2012) 16:842–8. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1813-2
50. Itatsu K, Zen Y, Yamaguchi J, Ohira S, Ishikawa A, Ikeda H, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 is an unfavorable postoperative prognostic factor in cholangiocarcinoma of the perihilar, hilar, and extrahepatic bile ducts. Hum Pathol. (2008) 39:710–9. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.09.016
51. Wittekind C. Carcinoembryonic antigen family members as diagnostic tools in immunohistopathology. Tumour Biol. (1995) 16:42–7. doi: 10.1159/000217927
52. Gong R, Chen ZE, and Matsukuma K. Morphologic and immunohistochemical characterization of small and large duct cholangiocarcinomas in a Western cohort: A panel of pCEA, CRP, N-cadherin, and albumin in situ hybridization aids in subclassification. Ann Diagn pathol. (2025) 75:152437. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2025.152437
53. Lee T, Teng TZJ, and Shelat VG. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 - tumor marker: Past, present, and future. World J gastrointestinal surg. (2020) 12:468–90. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v12.i12.468
54. Tsuji M, Kashihara T, Terada N, and Mori H. An immunohistochemical study of hepatic atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, hepatocellular carcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma with alpha-fetoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen, CA19-9, epithelial membrane antigen, and cytokeratins 18 and 19. Pathol Int. (1999) 49:310–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.1999.00865.x
55. Hurlimann J and Gardiol D. Immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of liver carcinomas. Am J Surg pathol. (1991) 15:280–8. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199103000-00008
56. Nakajima T and Kondo Y. Well-differentiated cholangiocarcinoma: diagnostic significance of morphologic and immunohistochemical parameters. Am J Surg pathol. (1989) 13:569–73. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198907000-00004
57. Haglund C, Lindgren J, Roberts PJ, and Nordling S. Difference in tissue expression of tumour markers CA 19–9 and CA 50 in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Br J cancer. (1991) 63:386–9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.90
58. Mocan LP, Rusu I, Melincovici CS, Boșca BA, Mocan T, Crăciun R, et al. The role of immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis between intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastasis, as well as its prognostic value. Diagnostics (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 13:1542. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13091542
59. Gerber TS, Müller L, Bartsch F, Gröger LK, Schindeldecker M, Ridder DA, et al. Integrative analysis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma subtypes for improved patient stratification: clinical, pathological, and radiological considerations. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:3156. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133156
60. Tojjari A, Idrissi YA, and Saeed A. Emerging targets in gastric and pancreatic cancer: Focus on claudin 18. 2 Cancer Lett. (2024) 611:217362. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217362
61. Wang C, Wu N, Pei B, Ma X, and Yang W. Claudin and pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1136227. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1136227
62. Shitara K, Shah MA, Lordick F, Van Cutsem E, Ilson DH, Klempner SJ, et al. Zolbetuximab in gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2024) 391:1159–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2409512
63. McCarthy AJ and Chetty R. Smad4/DPC4. J Clin Pathol. (2018) 71:661–4. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2018-205095
64. Kang YK, Kim WH, and Jang JJ. Expression of G1-S modulators (p53, p16, p27, cyclin D1, Rb) and Smad4/Dpc4 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hum pathol. (2002) 33:877–83. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2002.127444
65. Yan XQ, Zhang W, Zhang BX, Liang HF, Zhang WG, and Chen XP. Inactivation of Smad4 is a prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Chin Med J (Engl). (2013) 126:3039–43. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.20121235
66. Kotecha S, Lebot MN, Sukkarn B, Ball G, Moseley PM, Chan SY, et al. Dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 32 kDa (DARPP-32) and survival in breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of protein and mRNA expression. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:16987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53529-z
67. Tiwari A, Tashiro K, Dixit A, Soni A, Vogel K, Hall B, et al. Loss of HIF1A from pancreatic cancer cells increases expression of PPP1R1B and degradation of p53 to promote invasion and metastasis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 159:1882–97.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.046
68. Chung T, Rhee H, Nahm JH, Jeon Y, Yoo JE, Kim YJ, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma according to gross morphologic type: cholangiolocellular differentiation traits and inflammation- and proliferation-phenotypes. HPB. (2020) 22:864–73. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.10.009
69. Plebani M. Why C-reactive protein is one of the most requested tests in clinical laboratories? Clin Chem Lab Med. (2023) 61:1540–5. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2023-0086
70. Albrecht T, Rossberg A, Rose F, Breuhahn K, Baumann EM, Tóth M, et al. Combined analysis of albumin in situ hybridisation and C reactive protein immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: towards a molecular classification paradigm. J Clin Pathol. (2025) 78:307–16. doi: 10.1136/jcp-2024-209429
71. Bernatz S, Schulze F, Bein J, Bankov K, Mahmoudi S, Grünewald LD, et al. Small duct and large duct type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveal distinct patterns of immune signatures. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150:357. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05888-y
72. Yeh YC, Lei HJ, Chen MH, Ho HL, Chiu LY, Li CP, et al. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a promising diagnostic immunohistochemical marker for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and is associated with better prognosis. Am J Surg pathol. (2017) 41:1630–41. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000957
73. Radice GL. N-cadherin-mediated adhesion and signaling from development to disease: lessons from mice. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. (2013) 116:263–89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394311-8.00012-1
74. Yu TH, Yuan RH, Chen YL, Yang WC, Hsu HC, and Jeng YM. Viral hepatitis is associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with cholangiolar differentiation and N-cadherin expression. Mod Pathol. (2011) 24:810–9. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011.41
75. Janthamala S, Jusakul A, Kongpetch S, Kimawaha P, Klanrit P, Loilome W, et al. Arctigenin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma progression by regulating cell migration and cell viability via the N-cadherin and apoptosis pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2021) 394:2049–59. doi: 10.1007/s00210-021-02123-0
76. Xu J, Tan Y, Shao X, Zhang C, He Y, Wang J, et al. Evaluation of NCAM and c-Kit as hepatic progenitor cell markers for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Pathol Res Pract. (2018) 214:2011–7. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.09.005
77. Dezso K, Paku S, Papp V, Turányi E, and Nagy P. Architectural and immunohistochemical characterization of biliary ductules in normal human liver. Stem Cells Dev. (2009) 18:1417–22. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0110
78. Turányi E, Dezsö K, Csomor J, Schaff Z, Paku S, and Nagy P. Immunohistochemical classification of ductular reactions in human liver. Histopathology. (2010) 57:607–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03668.x
79. Aishima S, Tanaka Y, Kubo Y, Shirabe K, Maehara Y, and Oda Y. Bile duct adenoma and von Meyenburg complex-like duct arising in hepatitis and cirrhosis: pathogenesis and histological characteristics. Pathol Int. (2014) 64:551–9. doi: 10.1111/pin.12209
80. Nguyen Canh H, Takahashi K, Yamamura M, Li Z, Sato Y, Yoshimura K, et al. Diversity in cell differentiation, histology, phenotype and vasculature of mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Histopathology. (2021) 79:731–50. doi: 10.1111/his.14417
81. Chen J, He J, Deng M, Wu HY, Shi J, Mao L, et al. Clinicopathological, radiologic, and molecular study of 23 combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinomas with stem cell features, cholangiolocellular type. Hum pathol. (2017) 64:118–27. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.01.016
82. Takamura H, Gabata R, Obatake Y, Nakanuma S, Hayashi H, Kozaka K, et al. Clinical features and diagnostic imaging of cholangiolocellular carcinoma compared with other primary liver cancers: a surgical perspective. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2020) 19:1533033820948141. doi: 10.1177/1533033820948141
83. Sugita H, Nakanuma S, Gabata R, Tokoro T, Takei R, Okazaki M, et al. Clinicopathological features of cholangiolocarcinoma and impact of tumor heterogeneity on prognosis: A single institution retrospective study. Oncol Lett. (2024) 27:213. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14346
84. Calderaro J, Di Tommaso L, Maillé P, Beaufrère A, Nguyen CT, Heij L, et al. Nestin as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. (2022) 77:1586–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.019
85. Sasaki M, Sato Y, and Nakanuma Y. Is nestin a diagnostic marker for combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma? Histopathology. (2022) 80:859–68. doi: 10.1111/his.14622
86. Sasaki M, Sato Y, and Nakanuma Y. Nestin may be a candidate marker for differential diagnosis between small duct type and large duct type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Pathol Res practice. (2024) 253:155061. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.155061
87. Malvi D, de Biase D, Fittipaldi S, Grillini M, Visani M, Pession A, et al. Immunomorphology and molecular biology of mixed primary liver cancers: is Nestin a marker of intermediate-cell carcinoma? Histopathology. (2020) 76:265–74. doi: 10.1111/his.13966
88. Icer MA and Gezmen-Karadag M. The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin. Clin Biochem. (2018) 59:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.07.003
89. Terashi T, Aishima S, Taguchi K, Asayama Y, Sugimachi K, Matsuura S, et al. Decreased expression of osteopontin is related to tumor aggressiveness and clinical outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. (2004) 24:38–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.00886.x
90. Zheng Y, Zhou C, Yu XX, Wu C, Jia HL, Gao XM, et al. Osteopontin promotes metastasis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through recruiting MAPK1 and mediating Ser675 phosphorylation of β-Catenin. Cell Death disease. (2018) 9:179. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0226-x
91. Laohaviroj M, Chamgramol Y, Pairojkul C, Mulvenna J, and Sripa B. Clinicopathological significance of osteopontin in cholangiocarcinoma cases. Asian Pacific J Cancer prevention: APJCP. (2016) 17:201–5. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.1.201
92. Person F, Wilczak W, Hube-Magg C, Burdelski C, Möller-Koop C, Simon R, et al. Prevalence of βIII-tubulin (TUBB3) expression in human normal tissues and cancers. Tumour Biol. (2017) 39:1010428317712166. doi: 10.1177/1010428317712166
93. Zen Y, Britton D, Mitra V, Pike I, Sarker D, Itoh T, et al. Tubulin β-III: a novel immunohistochemical marker for intrahepatic peripheral cholangiocarcinoma. Histopathology. (2014) 65:784–92. doi: 10.1111/his.12497
94. Jennewein C, Tran N, Paulus P, Ellinghaus P, Eble JA, and Zacharowski K. Novel aspects of fibrin(ogen) fragments during inflammation. Mol Med (Cambridge Mass). (2011) 17:568–73. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00146
95. D’Errico A, Baccarini P, Fiorentino M, Ceccarelli C, Bonazzi C, Ponzetto A, et al. Histogenesis of primary liver carcinomas: strengths and weaknesses of cytokeratin profile and albumin mRNA detection. Hum pathol. (1996) 27:599–604. doi: 10.1016/S0046-8177(96)90169-0
96. Avadhani V, Cohen C, Siddiqui MT, and Krasinskas A. A subset of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas express albumin RNA as detected by in situ hybridization. Appl immunohistochemistry Mol morphology: AIMM. (2021) 29:175–9. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000882
97. Chung YS, Jeon Y, Yoo JE, Chung T, Ryu HJ, Kim H, et al. Albumin, filamin-A and cytokeratin 19 help distinguish intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from extrahepatic adenocarcinoma. Hepatol Int. (2023) 17:77–85. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10428-2
98. Albertini E, Chillotti S, Monti G, Malvi D, Deserti M, Degiovanni A, et al. Decreasing Albumin mRNA Expression in Cholangiocarcinomas along the Bile Duct Tree. Pathobiology. (2024) 91:338–44. doi: 10.1159/000538706
99. Steiner PE and Higginson J. Cholangiolocellular carcinoma of the liver. Cancer. (1959) 12:753–9. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195907/08)12:4<753::AID-CNCR2820120420>3.0.CO;2-L
100. Sciarra A, Park YN, and Sempoux C. Updates in the diagnosis of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. (2020) 96:48–55. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2019.11.001
101. Balitzer D, Joseph NM, Ferrell L, Shafizadeh N, Jain D, Zhang X, et al. Immunohistochemical and molecular features of cholangiolocellular carcinoma are similar to well-differentiated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. (2019) 32:1486–94. doi: 10.1038/s41379-019-0290-0
102. Moeini A, Sia D, Zhang Z, Camprecios G, Stueck A, Dong H, et al. Mixed hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma tumors: Cholangiolocellular carcinoma is a distinct molecular entity. J hepatol. (2017) 66:952–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.01.010
103. Kusano H, Naito Y, Mihara Y, Kondo R, Ogasawara S, Akiba J, et al. Distinctive clinicopathological features and KRAS and IDH1/2 mutation status of cholangiolocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. (2020) 50:84–91. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13428
104. Kozaka K, Sasaki M, Fujii T, Harada K, Zen Y, Sato Y, et al. A subgroup of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with an infiltrating replacement growth pattern and a resemblance to reactive proliferating bile ductules: ‘bile ductular carcinoma’. Histopathology. (2007) 51:390–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02735.x
105. Xu J, Zhang C, Qiao A, and Xi Y. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (cholangiolocellular type) with stem-cell features: a clinicopathologic analysis of 26 cases. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. (2016) 45:175–9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2016.03.007
106. Maeno S, Kondo F, Sano K, Takada T, and Asano T. Morphometric and immunohistochemical study of cholangiolocellular carcinoma: comparison with non-neoplastic cholangiole, interlobular duct and septal duct. J hepato-biliary-pancreatic Sci. (2012) 19:289–96. doi: 10.1007/s00534-011-0483-5
107. Hoshino H, Ohta M, Ito M, Uchimura K, Sakai Y, Uehara T, et al. Apical membrane expression of distinct sulfated glycans represents a novel marker of cholangiolocellular carcinoma. Lab investigation; J Tech Methods pathol. (2016) 96:1246–55. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.104
108. Makino K, Ishii T, Takeda H, Saito Y, Fujiwara Y, Fujimoto M, et al. Integrated analyses of the genetic and clinicopathological features of cholangiolocarcinoma: cholangiolocarcinoma may be characterized by mismatch-repair deficiency. J Pathol. (2024) 263:32–46. doi: 10.1002/path.6257
109. Nakanuma Y, Sato Y, Ikeda H, Harada K, Kobayashi M, Sano K, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with predominant “ductal plate malformation” pattern: a new subtype. Am J Surg pathol. (2012) 36:1629–35. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31826e0249
110. Choe JY and Kim H. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with predominant ductal plate malformation pattern. Clin Mol hepatol. (2014) 20:214–7. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2014.20.2.214
111. Sasaki M, Sato Y, and Nakanuma Y. Cholangiolocellular carcinoma with “Ductal plate malformation” Pattern may be characterized by ARID1A genetic alterations. Am J Surg pathol. (2019) 43:352–60. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001201
112. Wang Q, Xu Y, Wang SM, Hu AY, Pan YC, and Zhang SH. Histopathological evidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma occurring in ductal plate malformation: A clinicopathologic study of 5 cases. Ann Diagn pathol. (2021) 55:151828. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2021.151828
113. Chung T, Rhee H, Shim HS, Yoo JE, Choi GH, Kim H, et al. Genetic, clinicopathological, and radiological features of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with ductal plate malformation pattern. Gut liver. (2022) 16:613–24. doi: 10.5009/gnl210174
114. Zhao S, Xu Y, Wu W, Wang P, Wang Y, Jiang H, et al. ARID1A variations in cholangiocarcinoma: clinical significances and molecular mechanisms. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:693295. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.693295
115. Sintra S, Costa R, Filipe C, and Simão A. Intrahepatic sarcomatoid cholangiocarcinoma. BMJ Case Rep. (2018) 2018:bcr2018225017. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225017
116. Minato H, Yoshikawa A, Katayanagi K, Kurumaya H, Kato K, and Kitamura H. An intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with focal rhabdoid features and SMARCA4-deficiency. Int J Surg Pathol. (2022) 30:581–5. doi: 10.1177/10668969211070169
117. Hissong E, Al Assaad M, Bal M, Reed KA, Fornelli A, Levine MF, et al. NIPBL::NACC1 fusion hepatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. (2024) 48:183–93. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002159
118. Chun J, Moore M, Kelly P, Kanzawa M, Itoh T, Hong SM, et al. Enteroblastic cholangiocarcinoma: An uncommon, underrecognized subtype of bile duct cancer. Hum Pathol. (2024) 144:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2024.01.011
119. Huang YH, Zhang CZ, Huang QS, Yeong J, Wang F, Yang X, et al. Clinicopathologic features, tumor immune microenvironment and genomic landscape of Epstein-Barr virus-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J hepatol. (2021) 74:838–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.10.037
120. Masetto F, Mafficini A, Saka B, Armutlu A, Chatterjee D, Jang KT, et al. Tubulocystic carcinoma of bile ducts: A distinct type of cholangiocarcinoma associated with adenofibroma-type lesions. Am J Surg pathol. (2024) 48:1082–92. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002278
121. Liao X, Agostini-Vulaj D, Li RX, and Zhang X. Characterization of cholangiocarcinomas with tubulocystic morphology associated with biliary adenofibroma or biliary adenofibroma-like lesions. Mod Pathol. (2025) 38:100815. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2025.100815
122. Rushbrook SM, Kendall TJ, Zen Y, Albazaz R, Manoharan P, Pereira SP, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines for the diagnosis and management of cholangiocarcinoma. Gut. (2023) 73:16–46. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330029
123. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL-ILCA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:181–208. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.010
124. Vogel A, Bridgewater J, Edeline J, Kelley RK, Klümpen HJ, Malka D, et al. Biliary tract cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2023) 34:127–40. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.506
125. Neuzillet C, Decraecker M, Larrue H, Ntanda-Nwandji LC, Barbier L, Barge S, et al. Management of intrahepatic and perihilar cholangiocarcinomas: Guidelines of the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF). Liver Int. (2024) 44:2517–37. doi: 10.1111/liv.15948
126. Society for Molecular Diagnosis, Chinese Research Hospital Association and Translational Medicine Branch of China Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics. Expert consensus for clinical application of molecular diagnosis on hepatobiliary tumors (2024 edition). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2024) 32:872–82. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20240407-00177
127. Angerilli V, Fornaro L, Pepe F, Rossi SM, Perrone G, Malapelle U, et al. FGFR2 testing in cholangiocarcinoma: translating molecular studies into clinical practice. Pathologica. (2023) 115:71–82. doi: 10.32074/1591-951X-859
128. Arai Y, Totoki Y, Hosoda F, Shirota T, Hama N, Nakamura H, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 tyrosine kinase fusions define a unique molecular subtype of cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. (2014) 59:1427–34. doi: 10.1002/hep.26890
129. Goyal L, Kongpetch S, Crolley VE, and Bridgewater J. Targeting FGFR inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. (2021) 95:102170. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102170
130. Goyal L, Meric-Bernstam F, Hollebecque A, Valle JW, Morizane C, Karasic TB, et al. Futibatinib for FGFR2-rearranged intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:228–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206834
131. Pant S, Schuler M, Iyer G, Witt O, Doi T, Qin S, et al. Erdafitinib in patients with advanced solid tumours with FGFR alterations (RAGNAR): an international, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. (2023) 24:925–35. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00275-9
132. Zhang X, Bai Q, Wang Y, Jiang Z, Han J, Xue C, et al. FGFR2 fusion/rearrangement analysis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using DNA/RNA-based NGS and FISH. Virchows Arch. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00428-025-04067-9
133. Uson Junior PLS, DeLeon TT, Bogenberger JM, Pai RK, Kosiorek HE, Yin J, et al. FGFR2-IIIb expression by immunohistochemistry has high specificity in cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 genomic alterations. Dig Dis Sci. (2022) 67:3797–805. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-07303-9
134. Sasaki M, Sato Y, and Nakanuma Y. Expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) in combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: clinicopathological study. Virchows Arch. (2024) 484:915–23. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03792-x
135. Zou Y, Zhu K, Pang Y, Han J, Zhang X, Jiang Z, et al. Molecular detection of FGFR2 rearrangements in resected intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas: FISH could be an ideal method in patients with histological small duct subtype. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2023) 11:1355–67. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00060S
136. Cao Z, Yang Y, Liu S, Sun L, Liu Y, Luo Y, et al. FGFR2 fusions assessed by NGS, FISH, and immunohistochemistry in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol. (2025) 60:235–46. doi: 10.1007/s00535-024-02175-y
137. Toshida K, Itoh S, Yugawa K, Kosai Y, Tomino T, Yoshiya S, et al. Prognostic significance for recurrence of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients undergoing curative hepatic resection. Hepatol Res. (2023) 53:432–9. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13875
138. Dang L, Yen K, and Attar EC. IDH mutations in cancer and progress toward development of targeted therapeutics. Ann Oncol. (2016) 27:599–608. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw013
139. Abou-Alfa GK, Macarulla T, Javle MM, Kelley RK, Lubner SJ, Adeva J, et al. Ivosidenib in IDH1-mutant, chemotherapy-refractory cholangiocarcinoma (ClarIDHy): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:796–807. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30157-1
140. Grassian AR, Pagliarini R, and Chiang DY. Mutations of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. (2014) 30:295–302. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000050
141. Wang XY, Zhu WW, Wang Z, Huang JB, Wang SH, Bai FM, et al. Driver mutations of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma shape clinically relevant genomic clusters with distinct molecular features and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Theranostics. (2022) 12:260–76. doi: 10.7150/thno.63417
142. Kendre G, Murugesan K, Brummer T, Segatto O, Saborowski A, and Vogel A. Charting co-mutation patterns associated with actionable drivers in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J hepatol. (2023) 78:614–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.11.030
143. Makawita S, Lee S, Kong E, Kwong LN, Abouelfetouh Z, Danner De Armas A, et al. Comprehensive immunogenomic profiling of IDH1-/2-altered cholangiocarcinoma. JCO Precis Oncol. (2024) 8:e2300544. doi: 10.1200/PO.23.00544
144. Bi C, Liu M, Rong W, Wu F, Zhang Y, Lin S, et al. High Beclin-1 and ARID1A expression corelates with poor survival and high recurrence in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a histopathological retrospective study. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:213. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5429-3
145. Hayashi A, Misumi K, Shibahara J, Kokudo N, Kato Y, and Fukayama M. Immunohistochemistry using monoclonal antibody MsMab-2 is useful to detect IDH1 R132L in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol Int. (2016) 66:578–82. doi: 10.1111/pin.12459
146. Moasser MM. The oncogene HER2: its signaling and transforming functions and its role in human cancer pathogenesis. Oncogene. (2007) 26:6469–87. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210477
147. Javle M, Borad MJ, Azad NS, Kurzrock R, Abou-Alfa GK, George B, et al. Pertuzumab and trastuzumab for HER2-positive, metastatic biliary tract cancer (MyPathway): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2a, multiple basket study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1290–300. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00336-3
148. Nakamura Y, Mizuno N, Sunakawa Y, Canon JL, Galsky MD, Hamilton E, et al. Tucatinib and trastuzumab for previously treated human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic biliary tract cancer (SGNTUC-019): A phase II basket study. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:5569–78. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00606
149. Meric-Bernstam F, Makker V, Oaknin A, Oh DY, Banerjee S, González-Martín A, et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-expressing solid tumors: primary results from the DESTINY-panTumor02 phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:47–58. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02005
150. Harding JJ, Fan J, Oh DY, Choi HJ, Kim JW, Chang HM, et al. Zanidatamab for HER2-amplified, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer (HERIZON-BTC-01): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2b study. Lancet Oncol. (2023) 24:772–82. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00242-5
151. Galdy S, Lamarca A, McNamara MG, Hubner RA, Cella CA, Fazio N, et al. HER2/HER3 pathway in biliary tract Malignancies; systematic review and meta-analysis: a potential therapeutic target? Cancer Metastasis Rev. (2017) 36:141–57. doi: 10.1007/s10555-016-9645-x
152. Bartley AN, Washington MK, Colasacco C, Ventura CB, Ismaila N, Benson AB 3rd, et al. HER2 testing and clinical decision making in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: guideline from the college of american pathologists, american society for clinical pathology, and the American society of clinical oncology. J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:446–64. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.4836
153. Hiraoka N, Nitta H, Ohba A, Yoshida H, Morizane C, Okusaka T, et al. Details of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in 454 cases of biliary tract cancer. Hum Pathol. (2020) 105:9–19. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.08.006
154. Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey BE, Mangu PB, Bartlett JMS, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of American pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:2105–22. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.8738
155. Kim Y, Jee S, Kim H, Paik SS, Choi D, Yoo SH, et al. EGFR, HER2, and MET gene amplification and protein expression profiles in biliary tract cancer and their prognostic significance. oncologist. (2024) 29:e1051–e60. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae181.009
156. Zhou W, Jiang C, Zhan N, Lv X, Fan L, and Ninu M. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, epidermal growth factor receptor, and c-MET overexpression and survival in biliary tract cancer: A meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Ther. (2018) 14:S28–s35. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.206864
157. Hanrahan AJ, Chen Z, Rosen N, and Solit DB. BRAF - a tumour-agnostic drug target with lineage-specific dependencies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2024) 21:224–47. doi: 10.1038/s41571-023-00852-0
158. Subbiah V, Lassen U, Élez E, Italiano A, Curigliano G, Javle M, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAF(V600E)-mutated biliary tract cancer (ROAR): a phase 2, open-label, single-arm, multicentre basket trial. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:1234–43. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30321-1
159. Xin HY, Sun RQ, Zou JX, Wang PC, Wang JY, Ye YH, et al. Association of BRAF variants with disease characteristics, prognosis, and targeted therapy response in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e231476. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1476
160. Voss JS, Holtegaard LM, Kerr SE, Fritcher EG, Roberts LR, Gores GJ, et al. Molecular profiling of cholangiocarcinoma shows potential for targeted therapy treatment decisions. Hum Pathol. (2013) 44:1216–22. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2012.11.006
161. Sia D, Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Roayaie S, Ferrer J, Tabak B, et al. Integrative molecular analysis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveals 2 classes that have different outcomes. Gastroenterology. (2013) 144:829–40. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.001
162. Ilie M, Long E, Hofman V, Dadone B, Marquette CH, Mouroux J, et al. Diagnostic value of immunohistochemistry for the detection of the BRAFV600E mutation in primary lung adenocarcinoma Caucasian patients. Ann Oncol. (2013) 24:742–8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds534
163. Abd Elmageed ZY, Sholl AB, Tsumagari K, Al-Qurayshi Z, Basolo F, Moroz K, et al. Immunohistochemistry as an accurate tool for evaluating BRAF-V600E mutation in 130 samples of papillary thyroid cancer. Surgery. (2017) 161:1122–8. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.06.081
164. Reagh J, Clarkson A, Bullock M, Shepherd P, and Gill AJ. Real world experience of BRAFV600E mutation specific immunohistochemistry in colorectal carcinoma. Pathology. (2018) 50:342–4. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2017.09.025
165. Anwar MA, Murad F, Dawson E, Abd Elmageed ZY, Tsumagari K, and Kandil E. Immunohistochemistry as a reliable method for detection of BRAF-V600E mutation in melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of current published literature. J Surg Res. (2016) 203:407–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.04.029
166. Sasaki M, Sato Y, and Nakanuma Y. Bile duct adenoma and small-sized small duct type intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma show distinct differences in genetic alterations, expression of IMP3 and EZH2 and stromal and inflammatory components. Histopathology. (2023) 83:298–309. doi: 10.1111/his.14932
167. Goeppert B, Frauenschuh L, Renner M, Roessler S, Stenzinger A, Klauschen F, et al. BRAF V600E-specific immunohistochemistry reveals low mutation rates in biliary tract cancer and restriction to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. (2014) 27:1028–34. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.206
168. Hechtman JF. NTRK insights: best practices for pathologists. Mod Pathol. (2022) 35:298–305. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00913-8
169. Cocco E, Scaltriti M, and Drilon A. NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:731–47. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0113-0
170. Doebele RC, Drilon A, Paz-Ares L, Siena S, Shaw AT, Farago AF, et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:271–82. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30691-6
171. Drilon A, Laetsch TW, Kummar S, DuBois SG, Lassen UN, Demetri GD, et al. Efficacy of larotrectinib in TRK fusion-positive cancers in adults and children. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:731–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1714448
172. Dhillon S. Repotrectinib: first approval. Drugs. (2024) 84:239–46. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01990-6
173. Hechtman JF, Benayed R, Hyman DM, Drilon A, Zehir A, Frosina D, et al. Pan-trk immunohistochemistry is an efficient and reliable screen for the detection of NTRK fusions. Am J Surg Pathol. (2017) 41:1547–51. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000911
174. Rudzinski ER, Lockwood CM, Stohr BA, Vargas SO, Sheridan R, Black JO, et al. Pan-trk immunohistochemistry identifies NTRK rearrangements in pediatric mesenchymal tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. (2018) 42:927–35. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001062
175. Koehne de González A, Mansukhani MM, Fernandes H, and Hsiao SJ. Pan-tumor screening for NTRK gene fusions using pan-TRK immunohistochemistry and RNA NGS fusion panel testing. Cancer Genet. (2022) 262-263:47–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2021.12.010
176. Westphalen CB, Preinfalk A, Kruger S, Haas M, Renz BW, Riener MO, et al. Neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) and nerve growth factor (NGF) are not expressed in Caucasian patients with biliary tract cancers: pooled data from three independent cohorts. Clin Trans Oncol. (2019) 21:1108–11. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-02030-6
177. Leepisuth P, Watcharadetwittaya S, and Sa-Ngiamwibool P. Tropomyosin receptor kinase protein expression in Thai cholangiocarcinoma: Clinicopathological correlation, expression pattern, and prognosis. Ann Diagn pathol. (2022) 60:151996. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2022.151996
178. Zhang D and Liao X. Pan-TRK immunohistochemistry and NTRK gene fusions in primary carcinomas of the liver. Appl immunohistochemistry Mol morphology: AIMM. (2022) 30:435–40. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000001032
179. Demols A, Rocq L, Perez-Casanova L, Charry M, De Nève N, Ramadhan A, et al. A two-step diagnostic approach for NTRK gene fusion detection in biliary tract and pancreatic adenocarcinomas. oncologist. (2023) 28:e520–e5. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad075
180. Subbiah V, Cassier PA, Siena S, Garralda E, Paz-Ares L, Garrido P, et al. Pan-cancer efficacy of pralsetinib in patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumors from the phase 1/2 ARROW trial. Nat Med. (2022) 28:1640–5. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01931-y
181. Subbiah V, Wolf J, Konda B, Kang H, Spira A, Weiss J, et al. Tumour-agnostic efficacy and safety of selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumours other than lung or thyroid tumours (LIBRETTO-001): a phase 1/2, open-label, basket trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:1261–73. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00541-1
182. Pu X, Xu C, Wang Q, Wang W, Wu F, Cai X, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of RET gene fusion non-small cell lung cancer in China. Thorac cancer. (2023) 14:3166–77. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15105
183. Society of Cancer Precision of Chinese Anti-Cancer Association, Lung Cancer Expert Group of Chinese Medical Journal, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology, and Expert Committee on Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of advanced RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (2023 edition). Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi. (2023) 45:991–1002. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20230711-00290
184. Wang R, Hu H, Pan Y, Li Y, Ye T, Li C, et al. RET fusions define a unique molecular and clinicopathologic subtype of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:4352–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.1477
185. Go H, Jung YJ, Kang HW, Park IK, Kang CH, Lee JW, et al. Diagnostic method for the detection of KIF5B-RET transformation in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam Netherlands). (2013) 82:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.07.009
186. Tsuta K, Kohno T, Yoshida A, Shimada Y, Asamura H, Furuta K, et al. RET-rearranged non-small-cell lung carcinoma: a clinicopathological and molecular analysis. Br J cancer. (2014) 110:1571–8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.36
187. Platt A, Morten J, Ji Q, Elvin P, Womack C, Su X, et al. A retrospective analysis of RET translocation, gene copy number gain and expression in NSCLC patients treated with vandetanib in four randomized Phase III studies. BMC cancer. (2015) 15:171. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1146-8
188. Yang SR, Aypar U, Rosen EY, Mata DA, Benayed R, Mullaney K, et al. A performance comparison of commonly used assays to detect RET fusions. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:1316–28. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3208
189. Recondo G, Che J, Jänne PA, and Awad MM. Targeting MET dysregulation in cancer. Cancer Discov. (2020) 10:922–34. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1446
190. Barat S, Bozko P, Chen X, Scholta T, Hanert F, Götze J, et al. Targeting c-MET by LY2801653 for treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Mol carcinogenesis. (2016) 55:2037–50. doi: 10.1002/mc.22449
191. Cheng CT, Chen YY, Wu RC, Tsai CY, Chiang KC, Yeh TS, et al. MET−RON dual inhibitor, BMS−777607, suppresses cholangiocarcinoma cell growth, and MET−RON upregulation indicates worse prognosis for intra−hepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients. Oncol Rep. (2018) 40:1411–21. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6543
192. Wei K, Li M, Zöller M, Wang M, Mehrabi A, and Hoffmann K. Targeting c-MET by Tivantinib through synergistic activation of JNK/c-jun pathway in cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:231. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1460-1
193. Yu Y, Liu Q, Li W, Qu Y, Zhang Y, and Liu T. Identification of a novel EHBP1-MET fusion in an intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma responding to crizotinib. oncologist. (2020) 25:1005–8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2020-0535
194. Lefler DS, Tierno MB, and Bashir B. Partial treatment response to capmatinib in MET-amplified metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: case report & review of literature. Cancer Biol Ther. (2022) 23:112–6. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2022.2029128
195. Zhou K, Liu Y, and Zhu H. Dramatic response and acquired resistance to savolitinib in advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with MET amplification: a case report and literature review. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1254026. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1254026
196. Turpin A, Descarpentries C, Grégoire V, Farchi O, Cortot AB, and Jamme P. Response to capmatinib in a MET fusion-positive cholangiocarcinoma. oncologist. (2023) 28:80–3. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyac194
197. Myint KZ, Sueca-Comes M, Collier P, Balasubramanian B, Venkatraman S, Gordan J, et al. Preclinical evidence for anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors as novel therapeutic treatments for cholangiocarcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1184900. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1184900
198. Ueta A, Yamada A, Yoshioka M, Kanai M, Muto M, and Okita N. Remarkable response to capmatinib in a patient with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma harboring TFG-MET fusion. Int Cancer Conf J. (2024) 13:199–203. doi: 10.1007/s13691-024-00664-8
199. Reichinger A, Essl L, Kerschner P, Burghofer J, Webersinke G, Rumpold H, et al. Exceptional sustained long-term complete response to Tepotinib in a MET-amplified advanced intrahepatic biliary tract cancer failing Durvalumab plus Cisplatin and Gemcitabine. oncologist. (2024) 29:1090–94. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyae265
200. Wu JH, Fan YZ, Sun J, and Duan XZ. Response to crizotinib in advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with ZKSCAN1-MET fusion and MET amplification: case reports and literature review. Discov Oncol. (2025) 16:1107. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02930-4
201. Ross JS, Wang K, Gay L, Al-Rohil R, Rand JV, Jones DM, et al. New routes to targeted therapy of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas revealed by next-generation sequencing. oncologist. (2014) 19:235–42. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0352
202. Spencer K, Pappas L, Baiev I, Maurer J, Bocobo AG, Zhang K, et al. Molecular profiling and treatment pattern differences between intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Institute. (2023) 115:870–80. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djad046
203. Terada T, Nakanuma Y, and Sirica AE. Immunohistochemical demonstration of MET overexpression in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and in hepatolithiasis. Hum pathol. (1998) 29:175–80. doi: 10.1016/S0046-8177(98)90229-5
204. Aishima SI, Taguchi KI, Sugimachi K, Shimada M, Sugimachi K, and Tsuneyoshi M. c-erbB-2 and c-Met expression relates to cholangiocarcinogenesis and progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Histopathology. (2002) 40:269–78. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2002.00353.x
205. Joo HH, Song EY, Jin SH, Oh SH, and Choi YK. Expressions and clinical significances of c-met, c-erbB-2, COX-2, and IL-6 in the biliary tract cancers. Korean J Gastroenterol = Taehan Sohwagi Hakhoe chi. (2007) 50:370–8.
206. Heo MH, Kim HK, Lee H, Kim KM, Lee J, Park SH, et al. The clinical impact of c-MET over-expression in advanced biliary tract cancer (BTC). J Cancer. (2017) 8:1395–9. doi: 10.7150/jca.17898
207. Miyamoto M, Ojima H, Iwasaki M, Shimizu H, Kokubu A, Hiraoka N, et al. Prognostic significance of overexpression of c-Met oncoprotein in cholangiocarcinoma. Br J cancer. (2011) 105:131–8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.199
208. Mao ZY, Zhu GQ, Ren L, Guo XC, Su D, and Bai L. Prognostic value of C-met expression in cholangiocarcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat. (2016) 15:227–33. doi: 10.1177/1533034615578959
209. Chiang NJ, Hsu C, Chen JS, Tsou HH, Shen YY, Chao Y, et al. Expression levels of ROS1/ALK/c-MET and therapeutic efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in advanced biliary tract cancer. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:25369. doi: 10.1038/srep25369
210. Pu XH, Yue S, Wu HY, Yang J, Fan XS, Fu Y, et al. C-MET in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: High-Frequency amplification predicts protein expression and a unique molecular subtype. Pathol Res practice. (2020) 216:152857. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.152857
211. Chinese Society of Pathology, Pathology Quality Control Center, Lung Cancer Group of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Oncology, China Anti-cancer Association, Chinese Society of Lung Cancer, et al. Chinese expert consensus on clinical practice of MET detection in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi = Chin J Pathol. (2022) 51:1094–103. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20220606-00491
212. Poei D, Ali S, Ye S, and Hsu R. ALK inhibitors in cancer: mechanisms of resistance and therapeutic management strategies. Cancer Drug Resist. (2024) 7:20. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.25
213. Li L, Li W, Wu C, Xi Y, Guo L, Ji Y, et al. Real-world data on ALK rearrangement test in Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer (RATICAL): a nationwide multicenter retrospective study. Cancer Commun (London England). (2024) 44:992–1004. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12593
214. Ruzzenente A, Fassan M, Conci S, Simbolo M, Lawlor RT, Pedrazzani C, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma heterogeneity revealed by multigene mutational profiling: clinical and prognostic relevance in surgically resected patients. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:1699–707. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-5046-6
215. Trachu N, Sirachainan E, Larbcharoensub N, Rattanadech W, Detarkom S, Monnamo N, et al. Molecular alterations and clinical prognostic factors for cholangiocarcinoma in Thai population. OncoTargets Ther. (2017) 10:4955–68. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S143982
216. Augustin J, Gabignon C, Scriva A, Menu L, Calmel C, Scatton O, et al. Testing for ROS1, ALK, MET, and HER2 rearrangements and amplifications in a large series of biliary tract adenocarcinomas. Virchows Archiv. (2020) 477:33–45. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02822-8
217. Mitiushkina NV, Tiurin VI, Anuskina AA, Bordovskaya NA, Shestakova AD, Martianov AS, et al. Molecular analysis of biliary tract cancers with the custom 3’ RACE-based NGS panel. Diagnostics (Basel Switzerland). (2023) 13:3168. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203168
218. Valery M, Facchinetti F, Malka D, Ducreux M, Friboulet L, and Hollebecque A. Cholangiocarcinoma with STRN-ALK translocation treated with ALK inhibitors. Digestive liver Dis. (2021) 53:1664–5. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.09.001
219. Huang S, Li D, Huang Y, Lu G, Tian Y, Zhong X, et al. An unresectable and metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with EML4-ALK rearrangement achieving partial response after first-line treatment with ensartinib: a case report. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1191646. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1191646
220. Myint KZ, Balasubramanian B, Venkatraman S, Phimsen S, Sripramote S, Jantra J, et al. Therapeutic implications of ceritinib in cholangiocarcinoma beyond ALK expression and mutation. Pharm (Basel). (2024) 17:197. doi: 10.3390/ph17020197
221. Favre L, Pujals A, Maille P, Poullot E, and Calderaro J. Identification of an EML4-ALK rearrangement in an intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol Int. (2021) 71:630–2. doi: 10.1111/pin.13138
222. Azelby CM, Sakamoto MR, and Bowles DW. ROS1 targeted therapies: current status. Curr Oncol Rep. (2021) 23:94. doi: 10.1007/s11912-021-01078-y
223. Liu P, Wu Y, Sun L, Zuo Q, and Shi M. ROS kinase fusions are not common in Chinese patients with cholangiocarcinoma. Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = J South Med University. (2013) 33:474–8.
224. Saborowski A, Saborowski M, Davare MA, Druker BJ, Klimstra DS, and Lowe SW. Mouse model of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma validates FIG-ROS as a potent fusion oncogene and therapeutic target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:19513–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311707110
225. Gu TL, Deng X, Huang F, Tucker M, Crosby K, Rimkunas V, et al. Survey of tyrosine kinase signaling reveals ROS kinase fusions in human cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e15640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015640
226. Jakubowski CD, Mohan AA, Kamel IR, and Yarchoan M. Response to crizotinib in ROS1 fusion-positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. JCO Precis Oncol. (2020) 4:825–8. doi: 10.1200/PO.20.00116
227. Plum PS, Hess T, Bertrand D, Morgenstern I, Velazquez Camacho O, Jonas C, et al. Integrative genomic analyses of European intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Novel ROS1 fusion gene and PBX1 as prognostic marker. Clin Trans Med. (2024) 14:e1723. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1723
228. Lee KH, Lee KB, Kim TY, Han SW, Oh DY, Im SA, et al. Clinical and pathological significance of ROS1 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC cancer. (2015) 15:721. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1737-4
229. Lim SM, Yoo JE, Lim KH, Meng Tai DW, Cho BC, and Park YN. Rare incidence of ROS1 rearrangement in cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. (2017) 49:185–92. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.497
230. Worby CA and Dixon JE. PTEN. Annu Rev Biochem. (2014) 83:641–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-082411-113907
231. Lee D, Do IG, Choi K, Sung CO, Jang KT, Choi D, et al. The expression of phospho-AKT1 and phospho-MTOR is associated with a favorable prognosis independent of PTEN expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Modern Pathol. (2012) 25:131–9. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011.133
232. Jiang TY, Cui XW, Zeng TM, Pan YF, Lin YK, Feng XF, et al. PTEN deficiency facilitates gemcitabine efficacy in cancer by modulating the phosphorylation of PP2Ac and DCK. Sci Trans Med. (2023) 15:eadd7464. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.add7464
233. Zeng TM, Jiang TY, Yang G, Cheng Z, Lou C, Wei W, et al. Bortezomib in previously treated phosphatase and tension homology-deficient patients with advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: An open-label, prospective and single-centre phase II trial. Clin Trans Med. (2024) 14:e1675. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1675
234. Gupta B, Borghaei L, and Liu SV. NRG1 fusions: the new kid on the block. Curr Oncol Rep. (2025) 27:190–4. doi: 10.1007/s11912-025-01640-y
235. Schram AM, Odintsov I, Espinosa-Cotton M, Khodos I, Sisso WJ, Mattar MS, et al. Zenocutuzumab, a HER2xHER3 bispecific antibody, is effective therapy for tumors driven by NRG1 gene rearrangements. Cancer discov. (2022) 12:1233–47. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1119
236. Zenocutuzumab shines in PDAC. Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:1864. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2021-0356
237. Schram AM, Goto K, Kim D-W, Martin-Romano P, Ou S-HI, O’Kane GM, et al. Efficacy and safety of zenocutuzumab, a HER2 x HER3 bispecific antibody, across advanced NRG1 fusion (NRG1+) cancers. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:105–. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.105
238. Jonna S, Feldman RA, Swensen J, Gatalica Z, Korn WM, Borghaei H, et al. Detection of NRG1 gene fusions in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:4966–72. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0160
239. Jones MR, Lim H, Shen Y, Pleasance E, Ch’ng C, Reisle C, et al. Successful targeting of the NRG1 pathway indicates novel treatment strategy for metastatic cancer. Ann Oncol. (2017) 28:3092–7. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx523
240. Xu C, Wang Q, Wang D, Wang W, Fang W, Li Z, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of NRG1/2 gene fusion solid tumors. Global Med Genet. (2024) 11:86–99. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1781457
241. Fernandez-Cuesta L, Plenker D, Osada H, Sun R, Menon R, Leenders F, et al. CD74-NRG1 fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer discov. (2014) 4:415–22. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0633
242. Trombetta D, Graziano P, Scarpa A, Sparaneo A, Rossi G, Rossi A, et al. Frequent NRG1 fusions in Caucasian pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma predicted by Phospho-ErbB3 expression. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:9661–71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23800
243. Brooksbank K and Martin SA. DNA mismatch repair deficient cancer - Emerging biomarkers of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibition. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2023) 164:106477. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2023.106477
244. Marabelle A, Le DT, Ascierto PA, Di Giacomo AM, De Jesus-Acosta A, Delord JP, et al. Efficacy of pembrolizumab in patients with noncolorectal high microsatellite instability/mismatch repair-deficient cancer: results from the phase II KEYNOTE-158 study. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:1–10. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02105
245. André T, Berton D, Curigliano G, Sabatier R, Tinker AV, Oaknin A, et al. Antitumor activity and safety of dostarlimab monotherapy in patients with mismatch repair deficient solid tumors: A nonrandomized controlled trial. JAMA network Open. (2023) 6:e2341165. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.41165
246. Vikas P, Messersmith H, Compton C, Sholl L, Broaddus RR, Davis A, et al. Mismatch repair and microsatellite instability testing for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: ASCO endorsement of college of American pathologists guideline. J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:1943–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02462
247. Luchini C, Bibeau F, Ligtenberg MJL, Singh N, Nottegar A, Bosse T, et al. ESMO recommendations on microsatellite instability testing for immunotherapy in cancer, and its relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumour mutational burden: a systematic review-based approach. Ann Oncol. (2019) 30:1232–43. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz116
248. Mishima S, Naito Y, Akagi K, Hayashi N, Hirasawa A, Hishiki T, et al. Japanese Society of Medical Oncology/Japan Society of Clinical Oncology/Japanese Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology-led clinical recommendations on the diagnosis and use of immunotherapy in patients with DNA mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) tumors, third edition. Int J Clin Oncol. (2023) 28:1237–58. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02397-9
249. Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Sci (New York NY). (2017) 357:409–13. doi: 10.1126/science.aan6733
250. Yang X, Lian B, Zhang N, Long J, Li Y, Xue J, et al. Genomic characterization and immunotherapy for microsatellite instability-high in cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Med. (2024) 22:42. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03257-7
251. Winkelmann R, Schneider M, Hartmann S, Schnitzbauer AA, Zeuzem S, Peveling-Oberhag J, et al. Microsatellite instability occurs rarely in patients with cholangiocarcinoma: A retrospective study from a German tertiary care hospital. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1421. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051421
252. Yu J, Zhang X, Huang Q, Tan S, Xiong X, and Gou H. Rare DNA mismatch repair-related protein loss in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and their response to immunotherapy. Cancer Manage Res. (2021) 13:4283–90. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S304281
253. Vivaldi C, Genovesi V, Ugolini C, Bernardini L, Casadei-Gardini A, Formica V, et al. Mismatch repair deficiency in biliary tract cancer: prognostic implications and correlation with histology. Oncology. (2024) 102:157–67. doi: 10.1159/000533406
254. Khuntikeo N, Padthaisong S, Loilome W, Klanrit P, Ratchatapusit S, Techasen A, et al. Mismatch Repair Deficiency Is a Prognostic Factor Predicting Good Survival of Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Cholangiocarcinoma at Early Cancer Stage. Cancers. (2023) 15:4831. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194831
255. Liengswangwong U, Nitta T, Kashiwagi H, Kikukawa H, Kawamoto T, Todoroki T, et al. Infrequent microsatellite instability in liver fluke infection-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas from Thailand. Int J cancer. (2003) 107:375–80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11380
256. Cloyd JM, Chun YS, Ikoma N, Vauthey JN, Aloia TA, Cuddy A, et al. Clinical and genetic implications of DNA mismatch repair deficiency in biliary tract cancers associated with lynch syndrome. J gastrointestinal cancer. (2018) 49:93–6. doi: 10.1007/s12029-017-0040-9
257. Nakamura M, Ueno M, Hayami S, Kawai M, Miyamoto A, Suzaki N, et al. Effective response of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma to pembrolizumab: A case report. Anticancer Res. (2020) 40:4123–9. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14411
258. Toshida K, Itoh S, Yoshizumi T, Shimagaki T, Wang H, Kurihara T, et al. Efficacy of pembrolizumab in microsatellite instability-high locally advanced cholangiocarcinoma: a case report. Clin J gastroenterol. (2021) 14:1459–63. doi: 10.1007/s12328-021-01458-8
259. Matsushita S, Ueo T, Minami R, Ozawa T, Matsumoto A, Kimura Y, et al. A case of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma receiving sustainable pembrolizumab therapy. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai zasshi = Japanese J gastro-enterol. (2022) 119:360–7. doi: 10.11405/nisshoshi.119.360
260. Polyakov IS, Kovalenko AL, Petrovsky AN, Akobyan AV, and Porhanov VA. The rare thoracic complication: perforation of gastric fundus ulcer: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2022) 16:472. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03684-1
261. Li X, Zhang S, Zeng J, Song SS, Liu X, Kang W, et al. Heterogeneous expression of mismatch repair proteins and interpretation of immunohistochemical results in colorectal cancer and endometrial cancer. Pathol Res practice. (2023) 248:154647. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154647
262. Riedinger CJ, Esnakula A, Haight PJ, Suarez AA, Chen W, Gillespie J, et al. Characterization of mismatch-repair/microsatellite instability-discordant endometrial cancers. Cancer. (2024) 130:385–99. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35030
263. Gu YJ, Xu HM, Li QY, Yuan F, Dong L, and Wang CF. Analysis of discordant results between multiplex fluorescence PCR-capillary electrophoresis for microsatellite instability (MSI) detection and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for mismatch repair (MMR) protein expression in gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi [Chinese J oncology]. (2025) 47:715–25. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20241031-00469
264. Evrard C, Tachon G, Randrian V, Karayan-Tapon L, and Tougeron D. Microsatellite instability: diagnosis, heterogeneity, discordance, and clinical impact in colorectal cancer. Cancers. (2019) 11:1567. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101567
265. Yang RK, Chen H, Roy-Chowdhuri S, Rashid A, Alvarez H, Routbort M, et al. Clinical testing for mismatch repair in neoplasms using multiple laboratory methods. Cancers. (2022) 14:4550. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194550
266. Wang H, Qian YW, Dong H, and Cong WM. Pathologic assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of immunotherapy: a narrative review. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2024) 13:472–93. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-22-527
267. Ahn S, Lee JC, Shin DW, Kim J, and Hwang JH. High PD-L1 expression is associated with therapeutic response to pembrolizumab in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:12348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69366-4
268. Chen X, Wu X, Wu H, Gu Y, Shao Y, Shao Q, et al. Camrelizumab plus gemcitabine and oxaliplatin (GEMOX) in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer: a single-arm, open-label, phase II trial. J immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e001240. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001240
269. Yoon SB, Woo SM, Chun JW, Kim DU, Kim J, Park JK, et al. The predictive value of PD-L1 expression in response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for biliary tract cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1321813. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1321813
270. Xian F, Ren D, Bie J, and Xu G. Prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1119168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1119168
271. Cheung CC, Barnes P, Bigras G, Boerner S, Butany J, Calabrese F, et al. Fit-for-purpose PD-L1 biomarker testing for patient selection in immuno-oncology: guidelines for clinical laboratories from the Canadian association of pathologists-association canadienne des pathologistes (CAP-ACP). Appl immunohistochemistry Mol morphology: AIMM. (2019) 27:699–714. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000800
272. Paver EC, Cooper WA, Colebatch AJ, Ferguson PM, Hill SK, Lum T, et al. Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) as a predictive marker for immunotherapy in solid tumours: a guide to immunohistochemistry implementation and interpretation. Pathology. (2021) 53:141–56. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2020.10.007
273. Pathology Quality Control Center, Chinese Society of Pathology, and Pathology Committee of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Consensus on the immunohistochemical tests of PD-L1 in solid tumors (2021 version). Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi = Chin J Pathol. (2021) 50:710–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20210228-00172
Keywords: large duct type, small duct type, cholangiolocarcinoma, iCCA with ductal plate malformation pattern, target therapy, immunotherapy, molecular pathology, IHC
Citation: Wang H, He M-X, Cong W-M and Dong H (2025) Immunohistochemistry in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: histological subtyping and drug selection. Front. Oncol. 15:1653534. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1653534
Received: 25 June 2025; Accepted: 19 September 2025;
Published: 06 October 2025.
Edited by:
Zhaohui Tang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shilpi Minocha, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, IndiaLuigi Tornillo, University of Basel, Switzerland
Copyright © 2025 Wang, He, Cong and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Dong, aHVpZG9uZ3doQDEyNi5jb20=; Wen-Ming Cong, d21jb25nQHNtbXUuZWR1LmNu; Miao-Xia He, aG1tMjZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Han Wang
Han Wang Miao-Xia He
Miao-Xia He Wen-Ming Cong
Wen-Ming Cong Hui Dong
Hui Dong