- 1Department of Urology, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
- 2Department of Urology, Deyang Hospital Affiliated to Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Deyang, China
- 3Department of Urology, Dazhou Dachuan District People's Hospital China (Dazhou Third People’s Hospital), Dazhou, China
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and safety of three drugs—Apalutamide, Abiraterone, and Bicalutamide—combined with Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC).
Methods: We retrospectively collected survival data of patients treated at our hospital from January 2019 to March 2024. Patients who received three different treatment regimens—Apalutamide (240 mg/day) combined with ADT, Abiraterone (1000 mg/day) plus Prednisone (5 mg/day) combined with ADT, and Bicalutamide (50 mg/day) combined with ADT.
Results: This study analyzed 146 mHSPC patients. The results are displayed that Apalutamide and Abiraterone significantly prolonged PFS and PSA-PFS compared to Bicalutamide. Univariate and multivariate COX regression analyses suggested that factors such as age <75 years, absence of lymph node metastasis, use of Apalutamide or Abiraterone, and a low ECOG score were associated with longer PFS. Moreover, Apalutamide and Abiraterone showed superior efficacy in improving PSA response compared to Bicalutamide. Importantly, no life-threatening adverse events were reported in any of the three treatment groups.
Conclusion: Compared to Bicalutamide, the novel endocrine therapies Apalutamide and Abiraterone both significantly prolong PFS, PSA-PFS, and improve PSA response rates.
1 Introduction
Metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) refers to prostate cancer (PCa) that responds to endocrine therapy and is associated with bone or other organ metastases. In 1941, Huggins and colleagues first discovered the androgen dependency of PCa and proposed androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which focuses on blocking androgen signaling as a core treatment strategy for PCa (1). Currently, androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is widely regarded as the cornerstone of systemic therapy for mHSPC (2). ADT involves reducing serum testosterone levels to ≤50 ng/dl (castration level) through pharmacological or surgical methods, thereby diminishing the effects of androgens in the serum to block androgen action (3). ADT combined with endocrine therapy has been proven to effectively slow tumor growth, thereby improving patients’ survival outcomes and quality of life. Early ADT treatment can provide good disease control, but over time, the diminishing therapeutic effect is common, leading to the metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) stage.
Early-stage prostate cancer often lacks obvious clinical symptoms, and in China, the vast majority of patients are already in the middle or late stages at diagnosis (4). Subgroup analysis of the TITAN trial in East Asia also showed that, compared to Western populations, the incidence of prostate cancer is lower in East Asian countries, but East Asian populations tend to present at more advanced stages at initial diagnosis (5). Maximizing the time from mHSPC progression to mCRPC and improving patient survival and prognosis are the current focal points of discussion among clinicians. In recent years, in addition to traditional non-steroidal anti-androgen drugs (e.g., bicalutamide), the emergence of new endocrine drugs (e.g., abiraterone acetate, apalutamide, darolutamide, enzalutamide) has significantly transformed the treatment landscape of mHSPC.
Abiraterone acetate is a novel endocrine drug that selectively inhibits the cytochrome P450 isoform 17 (CYP17). By inhibiting CYP17A1, abiraterone effectively reduces androgen levels in the body. In recent years, with the successive results of large randomized controlled trials (RCTs) such as LATITUDE and STAMPEDE (6–8), studies have shown that abiraterone significantly prolongs the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of mHSPC patients. Apalutamide, like bicalutamide, is an androgen receptor (AR) antagonist, but it has a stronger binding affinity for AR, inhibiting its activity and suppressing the growth and spread of prostate cancer cells. Recent high-quality studies on apalutamide have demonstrated that, in patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, apalutamide combined with standard first-line therapy can significantly prolong PFS and OS (5, 9, 10). Japanese researchers have also reported studies comparing the efficacy and prognosis of abiraterone versus bicalutamide and apalutamide versus bicalutamide in high-risk mHSPC patients. The results consistently show that both abiraterone and apalutamide provide advantages in extending progression-free survival over bicalutamide, to varying degrees (11–14).
We conducted this retrospective study to compare the efficacy and adverse events of apalutamide, abiraterone, and bicalutamide in mHSPC patients. This study aims to provide valuable reference for clinicians and offer insights into further exploration of the treatment effects of novel endocrine therapies for mHSPC.
2 Materials and methods
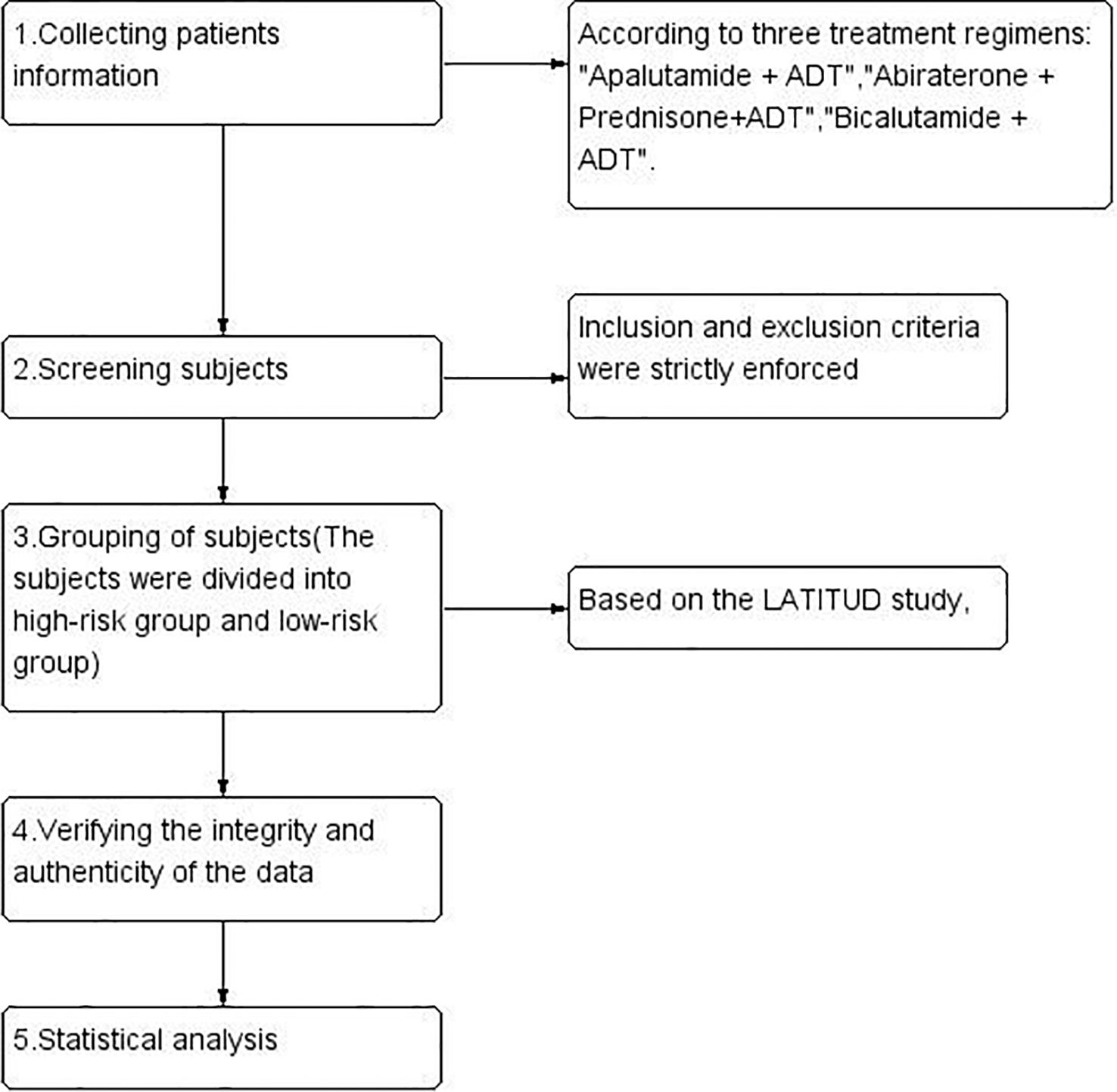
We retrospectively collected data from our hospital between January 2019 and March 2024 on patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) who received apalutamide (240 mg/day) combined with ADT (Group A), abiraterone (1000 mg/day) plus prednisone (5 mg/day) combined with ADT (Group B), or bicalutamide (50 mg/day) combined with ADT (Group C). All patients were required to continue using ADT (except for those who underwent bilateral orchiectomy), with ADT mainly involving LHRH agonists (such as goserelin acetate, triptorelin acetate, leuprorelin acetate) to maintain serum testosterone levels below 50 ng/dL (<1.7 nmol/L). The study design and flowchart are referenced in (Figure 1).
After strictly applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria (Supplementary File 1), we ultimately screened 146 patients. Based on the risk stratification from the LATITUDE study (6), patients were categorized into high-risk and low-risk disease groups for subgroup analysis (hereafter referred to as the high-risk/low-risk groups). This study aims to focus on disease progression(PSA progression/Imaging progression) (15, 16), PSA response at three months after treatment (nPSA: the lowest serum PSA level reached by patients after endocrine therapy, defined in this study as <0.2 ng/mL; PSA50: PSA decline ≥50%; PSA90: PSA decline ≥90%), and the incidence of adverse events. The effective follow-up period is from the initiation of treatment until disease progression or death; once disease progression or death occurs, follow-up ends. Adverse events were assessed using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (Approval No: 2024ER130-1). In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, this study is classified as a retrospective study and the institutional review board waived the requirement for individual written informed consent.
We used IBM SPSS Statistics 26 software for statistical analysis and finished survival curves. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to assess differences in PFS among the three treatment regimens, and Cox univariate and multivariate regression analyses were performed to identify factors affecting PFS. The forest diagram was drawn in R (version 4.3.0) software. The chi-square test and Wilcoxon rank-sum test were appropriately used to compare the three groups. All results were considered statistically significant at P<0.05.
3 Results
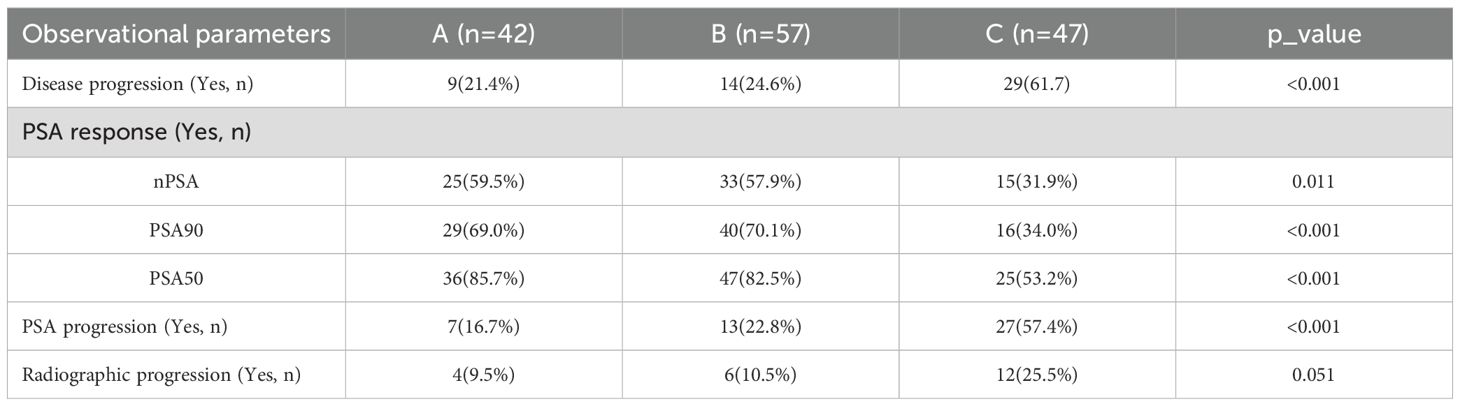
A total of 146 patients were included in this retrospective study and there were no significant statistical differences in the baseline characteristics of the patients(patient characteristics are provided in the Supplementary File 2: Table 1); 42 patients in Group A, 57 in Group B, and 47 in Group C. We conducted a statistical analysis of the observed parameters in these patients. Both the treatment regimens in Group A and Group B significantly improved disease progression, PSA progression, and PSA response compared to Group C, with no significant differences observed between Group A and Group B. Additionally, the incidence of radiographic progression was lower in Groups A and B compared to Group C, though the difference was not statistically significant (Table 1).
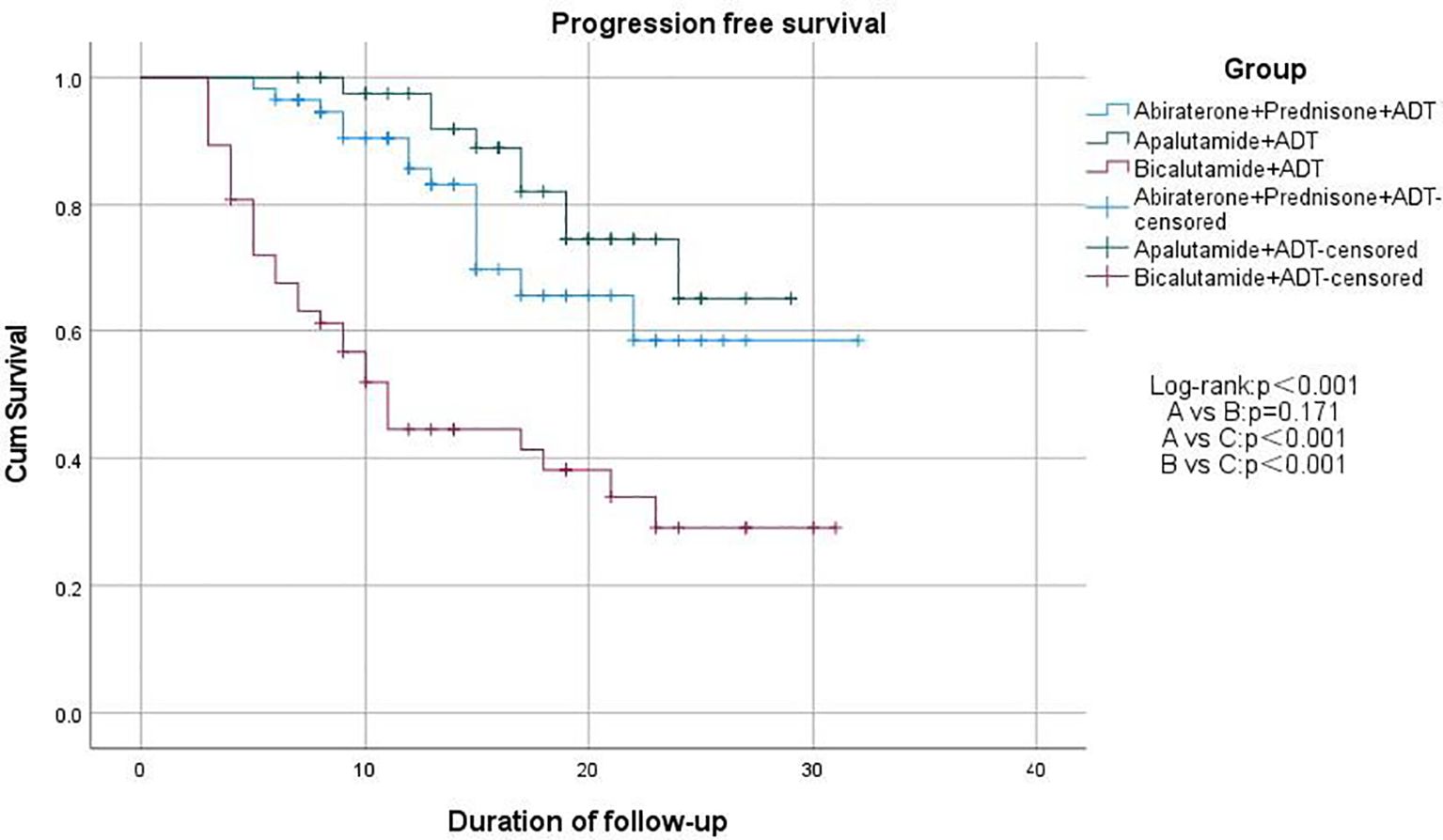
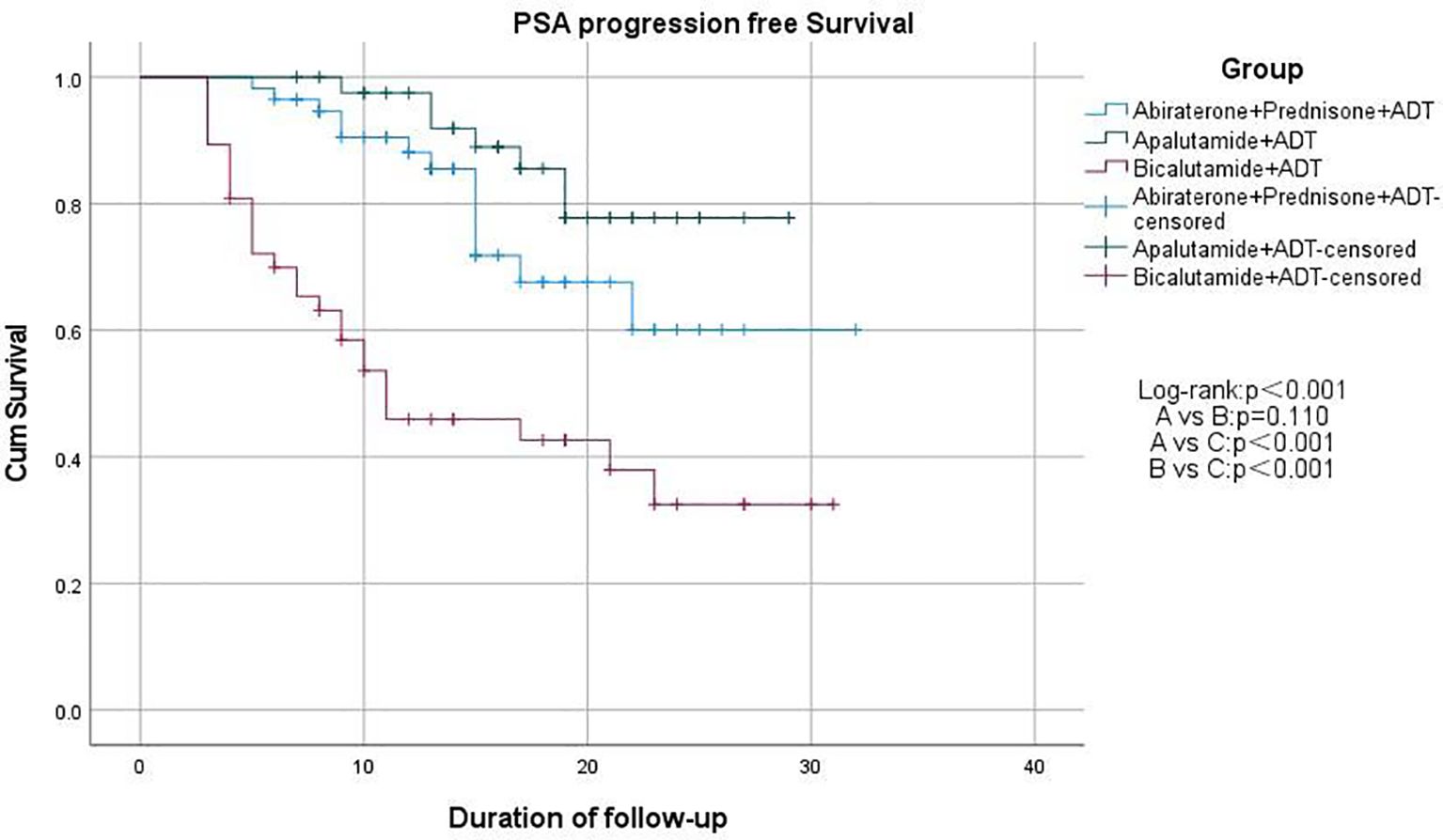
We used Kaplan-Meier survival curves to evaluate patients’ progression-free survival (PFS) and performed statistical analysis using the log-rank test. We found that treatment regimens A and B significantly prolonged PFS compared to regimen C (p < 0.001), but there was no significant difference between regimens A and B (p = 0.171; Figure 2). Additionally, we compared PSA-PFS among the three groups, and the results were similar to those for PFS (Figure 3). The median PFS and PSA-PFS in Group C were both 11 months, while neither was reached in Groups A and B.
Finally, we used Cox univariate and multivariate regression analyses to explore the impact of various factors on PFS. Regression analysis revealed that factors such as age < 75 years, absence of lymph node metastasis, treatment with regimens A or B, and ECOG performance status were associated with longer PFS. Notably, patients with an ECOG performance status score of 1 had significantly longer PFS compared to those with a score of ≥2 (Figure 4).
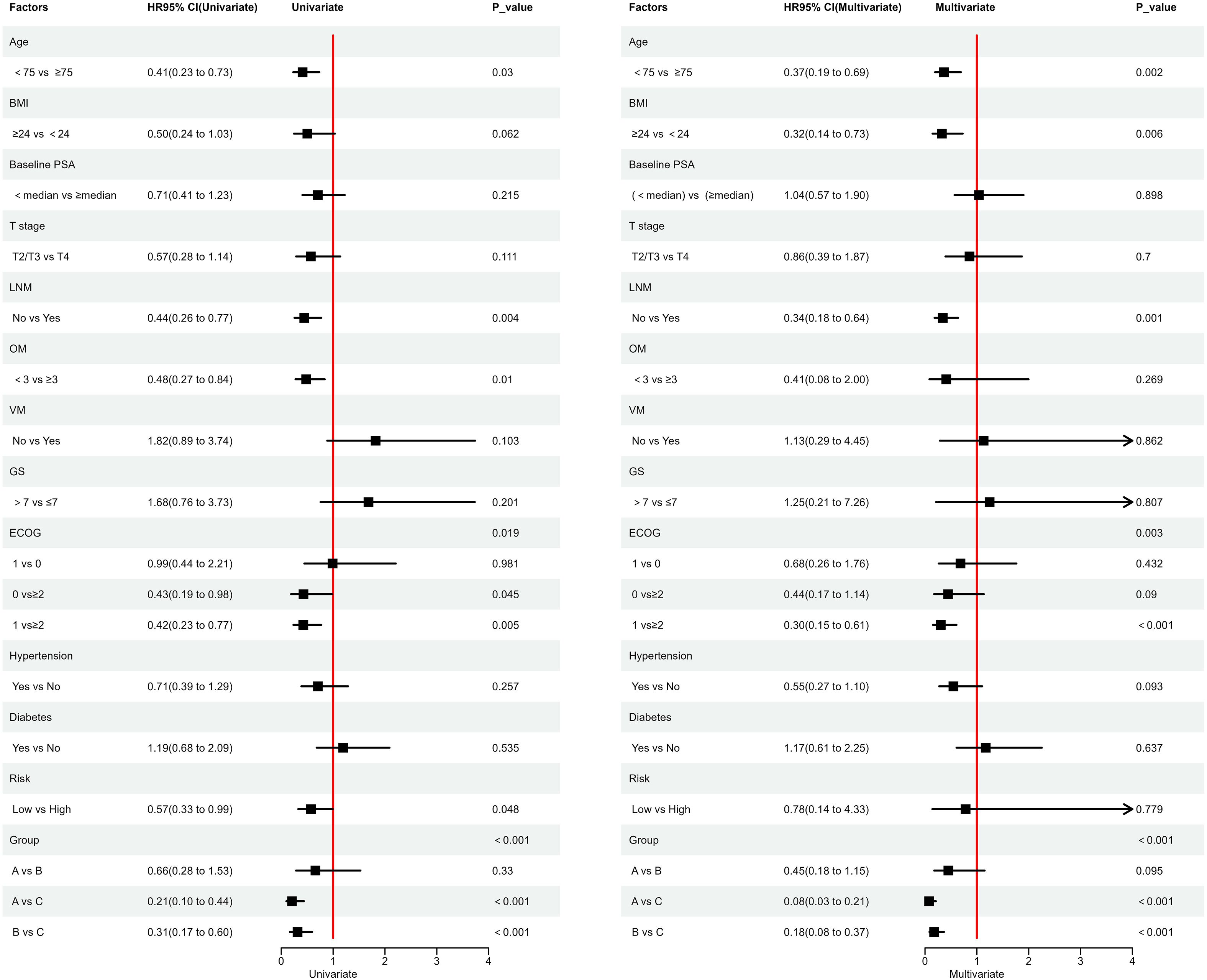
Figure 4. Cox Univariate and Multivariate Regression Analysis; ECOG: Represents the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status.
3.1 Subgroup analysis
We conducted subgroup analyses by stratifying patients into high-risk and low-risk groups based on the risk stratification from the LATITUDE study. In the high-risk group, the median PFS for Group C was 7 months, and the median PSA-PFS was 8 months, while in the low-risk group, both the median PFS and PSA-PFS for Group C were 11 months. Neither Group A nor Group B reached the median PFS or PSA-PFS, and the differences were statistically significant. In the high-risk group, we also found that patients in Groups A and B had significantly better outcomes in terms of disease progression, PSA response, and PSA progression compared to Group C. The incidence of radiographic progression in Groups A and B was lower than that in Group C; however, the difference was not statistically significant. In the low-risk group, both Groups A and B significantly alleviated disease progression and PSA progression compared to Group C, achieving an increase in PSA90. Although Groups A and B were superior to Group C in nPSA, PSA50, and radiographic progression, these differences were not statistically significant (Supplementary File 2: Tables 2, 3). We also employed Kaplan-Meier survival curves to evaluate PFS and PSA-PFS for both groups, using the log-rank test for statistical analysis. We found that treatment regimens A and B significantly prolonged both PFS and PSA-PFS compared to regimen C, with no significant difference between regimens A and B (Supplementary File: Figures 1-4).
3.2 Adverse events
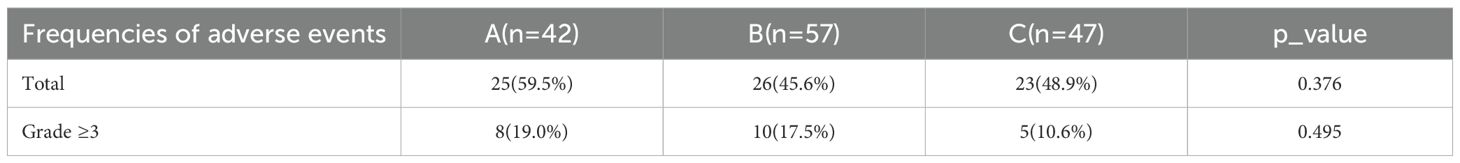
During the treatment with the three drugs, we summarized the types and frequencies of adverse events experienced by patients, as well as those classified as grade ≥3 (Supplementary File: Table 4). The main adverse events in Group A included pain, fatigue, and hot flashes. Group B primarily reported edema, pain, and fatigue. Group C mainly included pain, gastrointestinal reactions, and sleep disturbances. No life-threatening serious adverse events occurred with any of the three drugs. We conducted a summary analysis of the results (Table 2); the incidence of adverse events in Group A was 59.5%, which was higher than that in Group B (45.6%) and Group C (48.9%), but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.376). The incidence of grade ≥3 adverse events in Group A (19.0%) was slightly higher than that in Group B (17.5%) and Group C (10.6%), but overall, the results also showed no statistical differences (p = 0.495).
4 Discussion
In this retrospective study, we found that apalutamide and abiraterone significantly prolonged both PFS and PSA-PFS, with consistent results observed in the subgroup analyses. According to Cox regression analysis, factors such as age < 75 years, absence of lymph node metastasis, treatment with apalutamide or abiraterone, and ECOG performance status (patients with a score of 1 showed significantly longer PFS compared to those with a score ≥2) were associated with prolonged PFS. Both apalutamide and abiraterone were significantly more effective than bicalutamide in improving disease progression, PSA progression, and PSA response. The incidence of radiographic progression was lower for both drugs compared to bicalutamide, although this difference was not statistically significant. Similar results were observed in the high-risk group. In the low-risk group, patients treated with apalutamide and abiraterone showed better nPSA and PSA50 outcomes compared to bicalutamide, though the differences were not statistically significant. Other indicators followed similar trends as previously described. In terms of adverse events, the incidence was higher with apalutamide than with abiraterone, and slightly higher with abiraterone compared to bicalutamide. The incidence of grade ≥3 adverse events was similar across all three groups, with no statistically significant differences.
Currently, androgen receptor axis-targeted agent (ARAT) therapy has become a standard treatment for patients with mHSPC. Several studies comparing apalutamide with bicalutamide, and abiraterone with bicalutamide, have shown that apalutamide combined with ADT is superior to bicalutamide in terms of overall survival (OS) and PSA-PFS. Compared to bicalutamide, abiraterone acetate can prolong the time to mCRPC in high-risk mHSPC patients. Additionally, abiraterone significantly reduces the incidence of castration resistance compared to bicalutamide (50.6% vs. 25.2%, P<0.001) (12–14, 17). These findings are consistent with the results of our study. However, in those studies, the dose of bicalutamide was 80 mg/day, while in our study, the dose was 50 mg/day. The difference in dosage may have influenced the therapeutic benefits observed in patients. Overall, the emergence of new endocrine agents such as apalutamide and abiraterone has demonstrated significantly superior clinical benefits compared to bicalutamide.
In our study, we found that patients aged >75 years were at higher risk for shorter PFS, possibly due to the increased risk of being diagnosed with Gleason score ≥7 cancer as age increases, which may affect PFS (18). However, our study found no significant association between Gleason score (>7 vs ≤7) and PFS, which may be attributed to the small sample size. On the other hand, related studies have shown that lymph node metastasis is a prognostic factor for recurrence-free survival, metastasis-free survival, and overall survival in prostate cancer patients (19), which may partially explain our findings. Additionally, our study found that a higher ECOG performance status was a risk factor for shorter PFS. This may be partly because a higher proportion of patients with ECOG score ≥2 in our data were over 75 years old. Older patients tend to have a higher likelihood of being diagnosed with high-risk disease and exhibit lower tolerance to tumors.
Regarding PSA response, Boegemann M et al.’s latest study demonstrated that in mHSPC patients treated with apalutamide combined with ADT, 94.4% achieved PSA50, 70.8% achieved PSA90, and 42.2% achieved uPSA (uPSA is defined similarly to nPSA in this article) after 3 months of treatment. These findings are consistent with the results of this study. Additionally, both Boegemann M and Encarnación Navarro JA highlighted in their published research that in subgroup analyses of M1a metastatic patients, apalutamide combined with ADT still provided significant clinical benefits (20, 21). This discovery supplements the findings of the TITAN study. The study by Benjamin Lowentritt, M.D., et al. found that at 6 months of follow-up, a higher proportion of patients receiving apalutamide achieved PSA90 compared to those receiving abiraterone (66.2% vs. 43.4%) (22). By 9 months, the proportion of patients in the apalutamide group who achieved PSA90 remained higher (68.1% vs. 47.4%). The results for apalutamide in that study are similar to our findings. However, the results for abiraterone acetate differ somewhat from our data. The results from Benjamin Lowentritt, M.D., et al.’s study are significantly lower than those of our study. Additionally, our study reports a slightly lower PSA90 response compared to the LATITUDE post-hoc analysis (79.3% at the end of follow-up) (23). We hypothesize that this may be due to some patients not adhering to follow-up schedules and the relatively small sample size. In addition, some current studies have proposed that the implementation of metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) for mHSPC patients through stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) combined with androgen receptor signaling inhibitors (ARSI) can significantly improve the PSA response rate. This strategy helps delay further systemic treatment for patients and may also postpone the onset of castration resistance (24, 25).
There are several limitations to this study, primarily that it is a retrospective analysis, and all participants were drawn from a single institution, which may introduce selection bias. Additionally, the follow-up period was not long enough to fully reveal overall survival differences. Furthermore, the generalizability of the findings may be limited due to the small sample size. Based on these factors, we hope that future studies with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up durations will be conducted to further validate these preliminary findings.
5 Conclusions
In patients with mHSPC, both novel endocrine agents apalutamide and abiraterone were shown to prolong PFS and PSA-PFS compared to bicalutamide. Apalutamide and abiraterone also reduced the risk of disease progression and improved PSA response rates, with no life-threatening or rare adverse events observed.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (Approval No: 2024ER130-1). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, this study is classified as a retrospective study and the institutional review board waived the requirement for individual written informed consent.
Author contributions
JBZ: Visualization, Validation, Formal Analysis, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology. QW: Validation, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. JJZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. HG: Software, Visualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing. PH: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. TW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by: Health Commission of Sichuan Province Medical Science and Technology Program(24LCYJPT15); Medical Research Project of Sichuan Medical Association(S2024066); The Primary Health Development Research Center of Sichuan Province Program(SWFZ21-C-98).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1656216/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Silberstein JL, Poon SA, Sjoberg DD, Maschino AC, Vickers AJ, Bernie A, et al. Long-term oncological outcomes of a phase II trial of neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy followed by radical prostatectomy for patients with clinically localised, high-risk prostate cancer. BJU Int. (2015) 116:50–6. doi: 10.1111/bju.12676
2. Crawford ED, Schellhammer PF, McLeod DG, Moul JW, Higano CS, Shore N, et al. Androgen receptor targeted treatments of prostate cancer: 35 years of progress with antiandrogens. J Urol. (2018) 200:956–66. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.04.083
3. Schaeffer EM, Srinivas S, Adra N, An Y, Barocas D, Bitting R, et al. Prostate cancer, version 4.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2023) 21:1067–96. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.0050
4. Yano A, Kagawa M, Takeshita H, Okada Y, Morozumi M, and Kawakami S. Improved survival of men with metastatic prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy plus radiotherapy to the prostate. Int J urol: Off J Japanese Urological Assoc. (2017) 24:863–5. doi: 10.1111/iju.13479
5. Chung BH, Huang J, Ye ZQ, He DL, Uemura H, Arai G, et al. Apalutamide for patients with metastatic castrationsensitive prostate cancer in East Asia: a subgroup analysis of the TITAN trial. Asian J Androl. (2022) 24(2):161–6. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_64_21
6. Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, Matsubara N, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Alekseev BY, et al. Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:352–60. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1704174
7. Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, Matsubara N, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Alekseev BY, et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in patients with newly diagnosed high-risk metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (LATITUDE): final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2019) 20:686–700. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30082-8
8. Sydes MR, Spears MR, Mason MD, Clarke NW, Dearnaley DP, de Bono JS, et al. Adding abiraterone or docetaxel to long-term hormone therapy for prostate cancer: directly randomised data from the STAMPEDE multi-arm, multi-stage platform protocol. Ann Oncol. (2018) 29:1235–48. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy072
9. Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, Chung BH, Pereira de Santana Gomes AJ, Given R, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. New Engl J Med. (2019) 381:13–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
10. Chi KN, Chowdhury S, Bjartell A, Chung BH, Pereira de Santana Gomes AJ, Given R, et al. Apalutamide in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer: final survival analysis of the randomized, double-blind, phase III TITAN study. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:2294–303. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03488
11. Ueda T, Shiraishi T, Ito S, Ohashi M, Matsugasumi T, Yamada Y, et al. Abiraterone acetate versus bicalutamide in combination with gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist therapy for high risk metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:10094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89609-2
12. Naiki T, Takahara K, Ito T, Nakane K, Sugiyama Y, Koie T, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes between androgen deprivation therapy with up-front abiraterone and bicalutamide for Japanese patients with LATITUDE high-risk prostate cancer in a real-world retrospective analysis. Int J Clin Oncol. (2022) 27:592–601. doi: 10.1007/s10147-021-02071-y
13. Ueda T, Shiraishi T, Miyashita M, Kayukawa N, Gabata Y, Sako S, et al. Apalutamide versus bicalutamide in combination with androgen deprivation therapy for metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:705. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51389-w
14. Yanagisawa T, Kimura T, Mori K, Suzuki H, Sano T, Otsuka T, et al. Abiraterone acetate versus nonsteroidal antiandrogen with androgen deprivation therapy for high-risk metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Prostate. (2022) 82:3–12. doi: 10.1002/pros.24243
15. Scher HI, Halabi S, Tannock I, Morris M, Sternberg CN, Carducci MA, et al. Design and end points of clinical trials for patients with progressive prostate cancer and castrate levels of testosterone: recommendations of the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group. J Clin Oncol. (2008) 26:1148–59. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.4487
16. Watanabe H, Okada M, Kaji Y, Satouchi M, Sato Y, Yamabe Y, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours-revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2009) 36:2495–501.
17. Ueda T, Fujita K, Nishimoto M, Shiraishi T, Miyashita M, Kayukawa N, et al. Predictive factors for the efficacy of abiraterone acetate therapy in high-risk metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer patients. World J Urol. (2022) 40:2939–46. doi: 10.1007/s00345-022-04200-2
18. Godtman RA, Kollberg KS, Pihl CG, Månsson M, and Hugosson J. The association between age, prostate cancer risk, and higher gleason score in a long-term screening program: results from the göteborg-1 prostate cancer screening trial. Eur Urol. (2022) 82:311–7. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.01.018
19. Grivas N, Wit E, Pos F, de Jong J, Vegt E, Bex A, et al. Sentinel lymph node dissection to select clinically node negative prostate cancer patients for pelvic radiation therapy: effect on biochemical recurrence and systemic progression. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2017) 97:347–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.10.016
20. Boegemann M, Bennamoun M, Dourthe LM, Encarnacion JA, Hegele A, Hellmis E, et al. Final analysis of ArtemisR, a European real-world retrospective study of apalutamide for the treatment of patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. BMC Cancer. (2025) 25:1119. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14294-7
21. Encarnación Navarro JA, Morillo Macías V, Borrás Calbo M, de la Fuente Muñoz I, Lozano Martínez A, García Martínez V, et al. Multicenter real-world study: 432 patients with apalutamide in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Curr Oncol. (2025) 32:119. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32030119
22. Lowentritt B, Pilon D, Waters D, Rossi C, Muser E, Kurteva S, et al. Comparison of prostate-specific antigen response in patients with metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer initiated on apalutamide or abiraterone acetate: A retrospective cohort study. Urologic Oncol. (2023) 41:252.e19–.e27. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2023.03.013
23. Matsubara N, Chi KN, Özgüroğlu M, Rodriguez-Antolin A, Feyerabend S, Fein L, et al. Correlation of prostate-specific antigen kinetics with overall survival and radiological progression-free survival in metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer treated with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone or placebos added to androgen deprivation therapy: post hoc analysis of phase 3 LATITUDE study. Eur Urol. (2020) 77:494–500. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.11.021
24. Encarnación JA, Morillo Macías V, de la Fuente Muñoz I, Soria VD, Fernández Fornos L, Antequera MA, et al. Apalutamide and stereotactic body radiotherapy in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: multicenter real-world study. Cancers (Basel). (2025) 17:2216. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132216
Keywords: apalutamide, abiraterone acetate, bicalutamide, prostate cancer, endocrine therapy, androgen deprivation therapy
Citation: Zhang J, Wang Q, Zhou J, Gao H, Hao P and Wu T (2025) Efficacy and safety of apalutamide, abiraterone acetate, and bicalutamide in the treatment of metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1656216. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1656216
Received: 29 June 2025; Accepted: 25 September 2025;
Published: 13 October 2025.
Edited by:
Megan Ludwig, University of Minnesota Twin Cities, United StatesReviewed by:
Juan Antonio Encarnacion, Virgen de la Arrixaca University Hospital, SpainAnthony Serritella, University of Wisconsin-Madison, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Zhou, Gao, Hao and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Wu, YWxoYXdraW5nQG5zbWMuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jiabin Zhang1†
Jiabin Zhang1† Tao Wu
Tao Wu