- 1Department of Hospital Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Background: The interpretation of PD-L1 expression in advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) has recently emerged as a component of companion diagnostics, essential in identifying candidates for immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). However, evaluating PD-L1 expression using the combined positive score (CPS) and tumor proportion score (TPS) has posed challenges, particularly in selecting appropriate specimens and determining hotspots for measurement.
Methods: This study included 68 HNSCC cases from the oropharynx and tongue, collecting complete sets of preoperative biopsy, surgical resection, and metastatic lymph node samples. PD-L1 22C3 staining was performed on each 204 samples to assess PD-L1 expression. The CPS and TPS were measured in all samples using QuPath, an open-source bioimage analysis tool. Statistical comparisons of CPS and TPS among the three specimen types were conducted using Kruskal-Wallis test.
Results: Significant discrepancies were observed in both CPS and TPS between biopsy and surgical resection (p <0.01, respectively), as well as in both CPS and TPS between resection and metastatic lymph node (p <0.01, respectively). However, no significant statistical differences were observed between the biopsy and metastatic lymph node.
Conclusions: Our analysis highlights the heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression across different specimen types. Significant variability exists between the preoperative biopsy and surgical resection, and between surgical resection and metastatic lymph node in patients with HNSCC. These findings suggest that PD-L1 expression varies in response to tumor microenvironment across various tumor areas and time frames. Therefore, individualized PD-L1 assessment for each specimen type is crucial for accurately determining eligibility for ICIs.
1 Introduction
Head and neck cancer is the seventh most common type of malignancy, with approximately 890,000 new cases diagnosed worldwide annually (1). Over 90% of these cases are classified as squamous cell carcinoma. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) significantly impairs a patient’s quality of life, with a high risk of metastasis or recurrence, often leading to poor clinical outcomes despite multimodal treatment strategies.
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is an immune checkpoint protein expressed on tumor cells. Its interaction with PD-L1 receptors on T cells results in immune tolerance, allowing tumor cells to evade immune surveillance. Several studies that have reported an association between PD-L1 expression and clinical factors in HNSCC, with some suggesting that the presence of human papilloma virus (HPV) is associated with higher PD-L1 expression likely due to immune activation (2).
The introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has revolutionized cancer treatment by restoring T cell-mediated immune responses against tumor cells. ICIs, such as pembrolizumab, has been approved as both a first-line and second-line treatment options for advanced HNSCC. Accurate pathological assessment of PD-L1 expression, using the combined positive score (CPS) and tumor proportion score (TPS), remains critical for guiding patient selection.
Based on the KEYNOTE-689 trial, current guidelines recommend pembrolizumab for patients with resectable, locally advanced HNSCC (stage III–IVA) when CPS is ≥1 in the first-line setting and TPS is ≥50% in the second-line setting (3). In addition, the CHECKMATE-141 trial demonstrated that nivolumab is effective in recurrent HNSCC irrespective of PD-L1 expression or p16 status (4).
Many studies have examined PD-L1 expression levels in cohorts of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Some have demonstrated intra-tumoral heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression (4), as well as inter-site heterogeneity within individual tumors (5, 6), raising the question of whether PD-L1 expression changes during tumor metastasis.
In the HNSCC, some contradictory reports suggest that a single specimen may adequately represent the PD-L1 expression of the entire tumor, regardless of the degree of intra-tumoral heterogeneity (7), while others indicate that recurrent or metastatic tumors may show distinct PD-L1 expression patterns compared to primary tumors (8).
Despite the clinical significance of PD-L1 expression, its consistency across different specimen types—including preoperative biopsy, surgical resection, and metastatic lymph nodes—remains controversial. However, there are no standardized guidelines for PD-L1 interpretation across different specimen types. There is no consensus on which tissue should best be used for PD-L1 immunohistochemical testing to avoid misclassification of PD-L1 status (9).
This study aims to investigate the heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression across different specimen types in HNSCC and to analyze the comparative relationships between CPS and TPS measurements.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patient and material
Between 2014 and 2023, histologically confirmed cases of HNSCC were retrieved from the pathology archives of the Department of Hospital Pathology, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital. A total of 68 cases were retrospectively selected, comprising tumors of the oropharynx (palatine tonsil and base of tongue) and oral cavity (tongue proper and floor of mouth). These anatomical sites were selected for their accessibility and rising incidence, while tumors of the hypopharynx, maxilla, larynx were excluded due to limited case numbers and suboptimal PD-L1 staining following decalcification.
Within the oropharyngeal group (39 cases), 14 were stage I, 19 were stage II, five were stage III, and one was stage IV at diagnosis. In the oral cavity group (29 cases), 20 were stage III and nine were stage IV. For each case, complete sets of preoperative biopsy, surgical resection, and lymph node metastasis samples were collected. In most cases (66/68), lymph node metastases were resected during the same surgical procedure as the primary tumor. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained slides were reviewed to confirm the presence of carcinoma.
2.2 Immunohistochemistry procedures
Initial HPV status screening was performed using p16 IHC. Confirmation was then conducted with the PANA RealTyper HPV kit (Panagene, Daejeon, Korea), a multiplex real-time PCR assay performed on DNA extracted from the tumor tissue. In parallel, PD-L1 IHC was performed using the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx assay (Agilent/Dako, CA, USA).
Both p16 and PD-L1 22C3 IHC were conducted on 4-µm-thick sections prepared from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks. The entire process for the 204 tissue sections (representing complete sets of specimens from 68 patients) were automated on the Ventana BenchMark ULTRA automated staining platform (Ventana Medical Systems, AZ, USA).
2.3 Whole slide image preparation
Whole-slide images of the PD-L1-stained slides were digitalized using the Philips Intellisite Pathology Solution platform. The images were then exported as high-resolution TIFF files for further bioimage analysis.
2.4 Bioimage analysis
QuPath, an open-source bioimage analysis platform, was used for the manual annotation of four distinct cell populations: tumor cells, immune cells, PD-L1-expressing tumor cells, and PD-L1-expressing immune cells (10) (Figure 1).
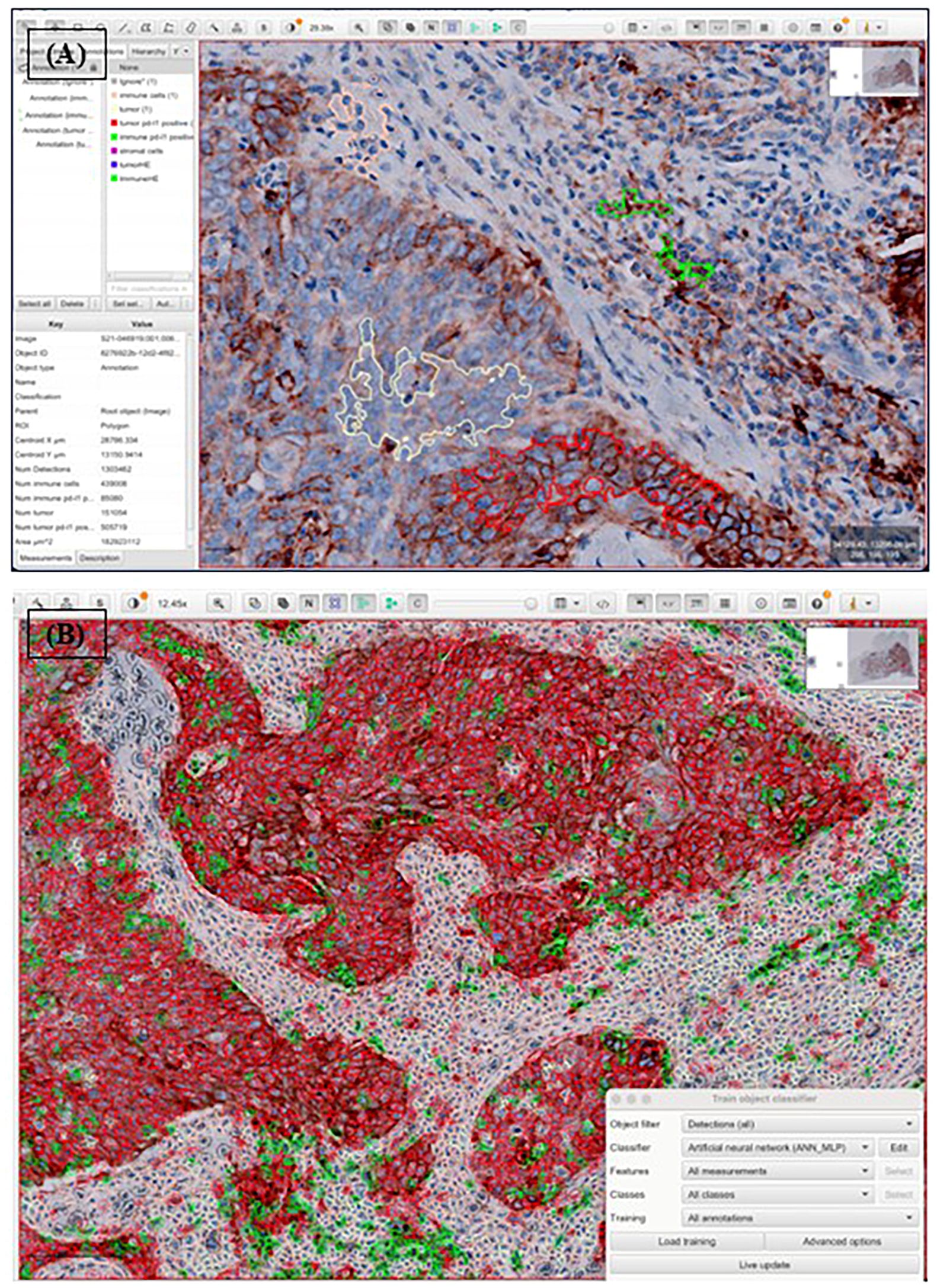
Figure 1. Procedure of automated analysis of PD-L1 22C3 expression using QuPath. Each PD-L1 22C3 pharmDx-stained slide was digitally scanned and exported into Qupath, followed by whole cell detection. Annotation was conducted to classify four different cell populations: tumor cells (light yellow), immune cells (pink), PD-L1 stained tumor cells (red), PD-L1 stained immune cells (green), non-relevant cells (black, not shown) (A). The annotated classification was then applied across the entire slide using an object classifier (B). CPS and TPS were subsequently calculated based on numerical outputs derived from the analysis.
2.5 PD-L1 scoring and classification
PD-L1 expression was evaluated using two standardized scoring systems for each specimen. The combined proportion score (CPS) was calculated as the number of PD-L1–positive cells, including tumor cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages, divided by the total number of viable tumor cells and multiplied by 100. The tumor proportion score (TPS) was calculated as the percentage of PD-L1–positive tumor cells among at least 100 viable tumor cells. Necrotic areas and non-neoplastic cellular components were excluded from the analysis. Based on these scores, specimens were classified into three expression categories: negative (CPS <1; TPS <1%), low expression (CPS 1–19; TPS 1–49%), and high expression (CPS ≥20; TPS ≥50%) (Figure 2).
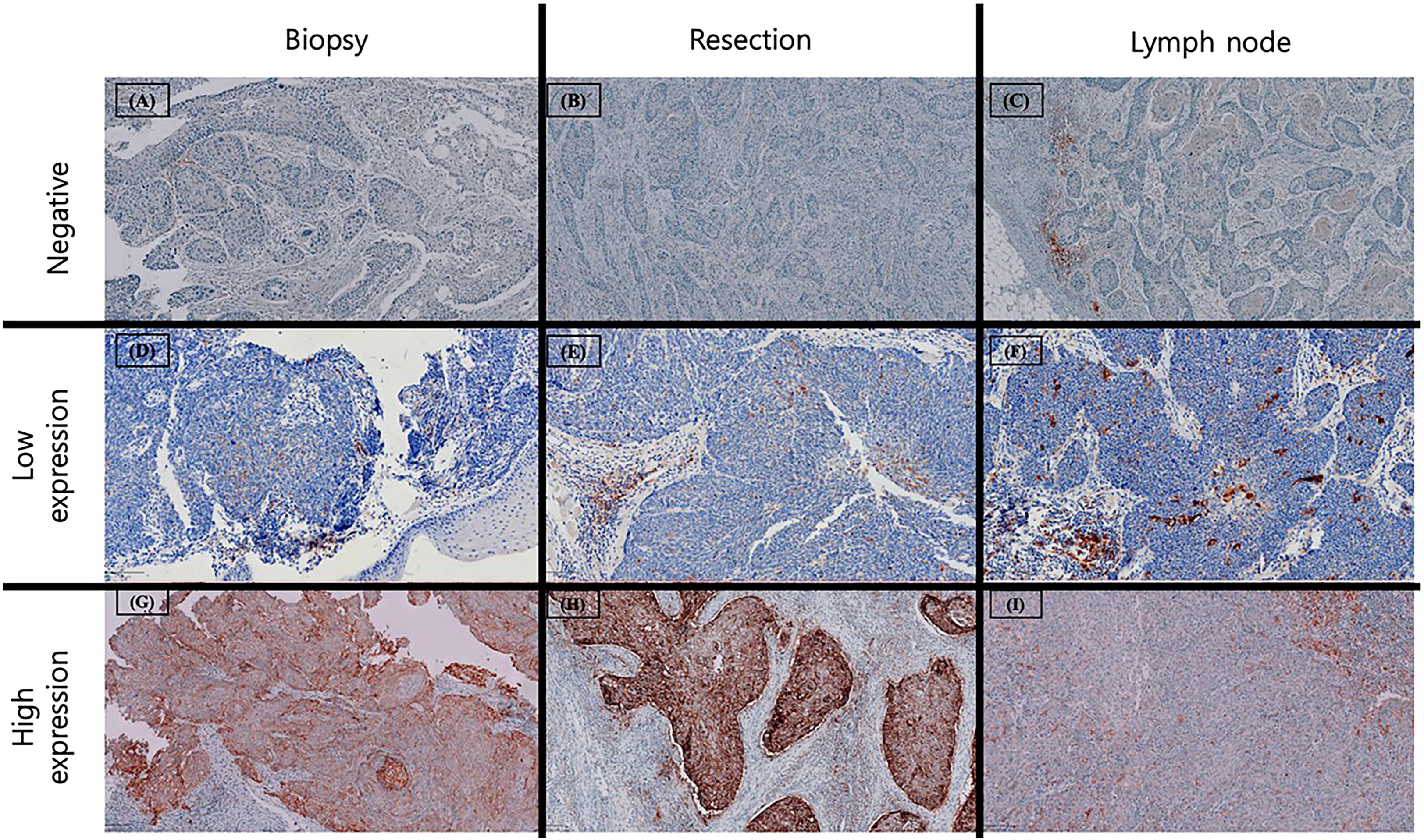
Figure 2. Examples of PD-L1 expression across different specimens. Negative PD-L1 expression (CPS < 1 or TPS < 1%) in preoperative biopsy (A), surgical resection (B) and metastatic lymph node (C). Low PD-L1 expression (CPS 1–20 or TPS 1- 50%) in preoperative biopsy (D), surgical resection (E) and metastatic lymph node (F), characterized by scarce staining in tumor cells with occasional PD-L1 stained mononuclear immune cells. High PD-L1 expression (CPS ≥ 20 or TPS ≥ 50%) in preoperative biopsy (G), surgical resection (H) and metastatic lymph node (I) with strong staining in tumor cells and accompanying immune cells adjacent to tumor nests.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed to investigate the relationships between different variables. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to analyze the association between HPV status (determined by p16 IHC and PCR) and PD-L1 expression, as well as the association between PD-L1 expression and the stage of oropharyngeal cancer. The Kruskal-Wallis test was applied to compare CPS and TPS values across different specimen types (biopsy, resection, and metastasis). A two-tailed significance level of p<0.05 was used to determine statistical significance.
3 Results
3.1 Clinicopathological features
Among the 68 HNSCC cases, primary tumors originated from the oropharynx (57.3%, 39/68) and the oral cavity (42.7%, 29/68). The mean age at diagnosis was 59.1 years, with a male predominance (male 71%, female 29%). In oropharyngeal HNSCCs, HPV positivity was confirmed in 89.7% of cases (35/39) and was significantly associated with p16 IHC (p <0.05). CPS was significantly higher in HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers in both biopsy and resection specimens (p < 0.05). Notably, CPS scores differed significantly between early-stage (I-II) and advanced-stage (III-IV) oropharyngeal cancers in resection specimens (p <0.05). No oral cavity HNSCCs were HPV-associated (0/29). Other clinicopathological aspects and PD-L1 scores are summarized in Table 1.
3.2 PD-L1 expression in general
The average CPS and TPS was 42.8 (0.3-100) and 27.8% (0-92.1) in preoperative biopsies, 62.2 (4.1 -100) and 40.7% (0.04-100) in surgical resections, and 47.4 (0.1-100) and 27.9% (0-9-2.7) in metastatic lymph nodes.
In preoperative biopsies, CPS was negative in 3/68 (4.4%), low in 21/68 (30.9%), and high in 44/68 (64.7%). TPS was negative in 9/68 (13.2%), low in 44/68 (64.7%), and high in 15/68 (22.1%). In surgical resections, CPS was negative in 0/68 (0%), low in 9/68 (13.2%), and high in 59/68 (86.8%). TPS was negative in 1/68 (1.5%), low in 42/68 (61.7%), and high in 25/68 (36.8%). In metastatic lymph nodes, CPS was negative in 2/68 (2.9%), low in 20/68 (29.4%), and high in 46/68 (67.7%). TPS was negative in 11/68 (16.2%), low in 40/68 (58.8%), and high in 17/68 (25.0%).
Among PD-L1–positive cases (low and high expression), CPS consistently showed higher expression in oropharyngeal cancers across all specimen types, whereas TPS displayed variable patterns between oropharyngeal and oral cavity tumors.
In preoperative biopsies, CPS positivity was observed in 26/37 (70.3%) oropharyngeal cancers and 18/28 (64.3%) oral cavity cancers, while TPS positivity was found in 8/34 (23.5%) and 7/25 (28.0%), respectively. In surgical resections, CPS positivity was seen in 34/39 (87.2%) oropharyngeal cancers and 25/29 (86.2%) oral cavity cancers, with TPS positivity in 13/39 (33.3%) and 12/28 (42.9%), respectively. In metastatic lymph nodes, CPS positivity was present in 27/38 (71.1%) oropharyngeal cancers and 19/28 (67.9%) oral cavity cancers, while TPS positivity was seen in 12/33 (36.4%) and 5/24 (20.8%), respectively. Comparison bar graphs for oropharyngeal and oral cavity tumors across specimen types are shown in Figure 3.
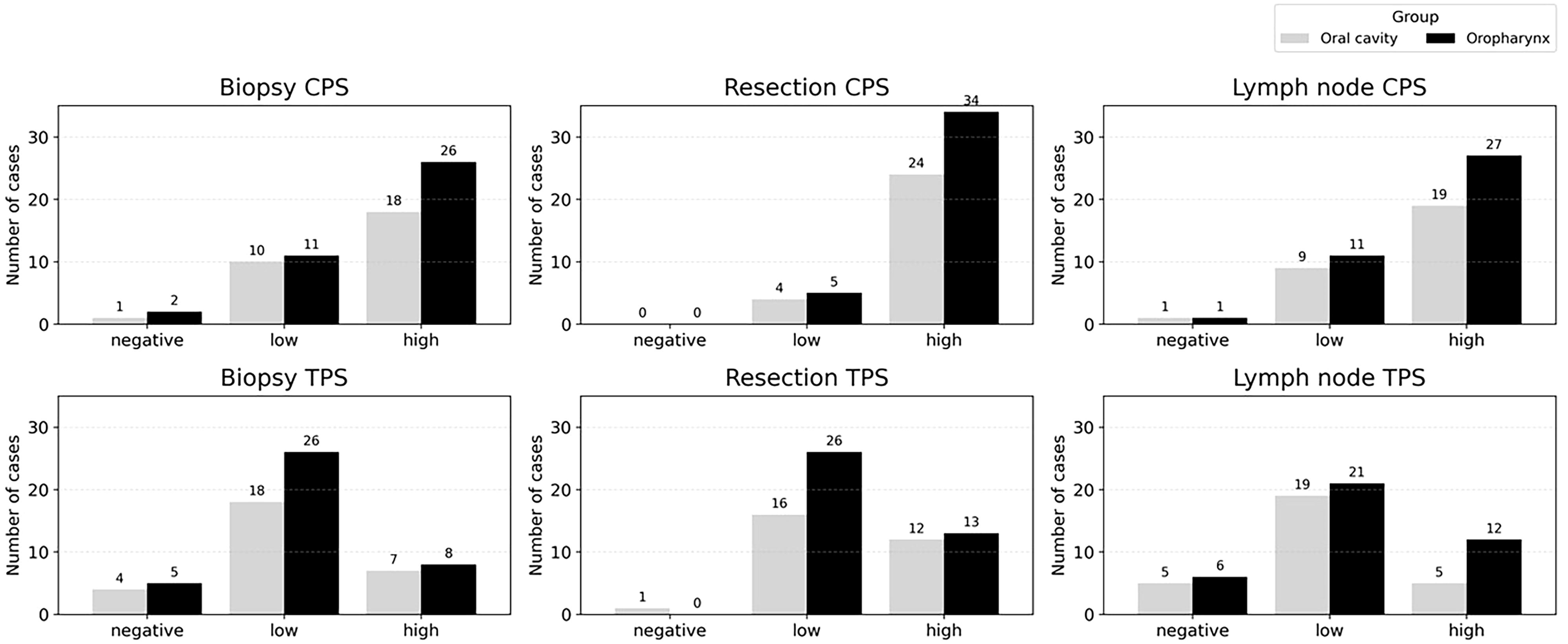
Figure 3. PD-L1 expression by CPS (top) and TPS (bottom) in oropharyngeal and oral cavity carcinomas across biopsy, resection, and lymph node specimens. CPS and TPS were categorized as negative (CPS < 1, TPS < 1%), low (CPS 1–19, TPS 1–49%), and high (CPS ≥ 20, TPS ≥ 50%).
3.3 HPV status and PD-L1 expression
In oropharyngeal cancers (n=39), HPV-positive tumors were associated with significantly higher PD-L1 expressions than HPV-negative cases for CPS for biopsy and resection specimens, and for TPS in resection specimens (p <0.05) (Figure 4).
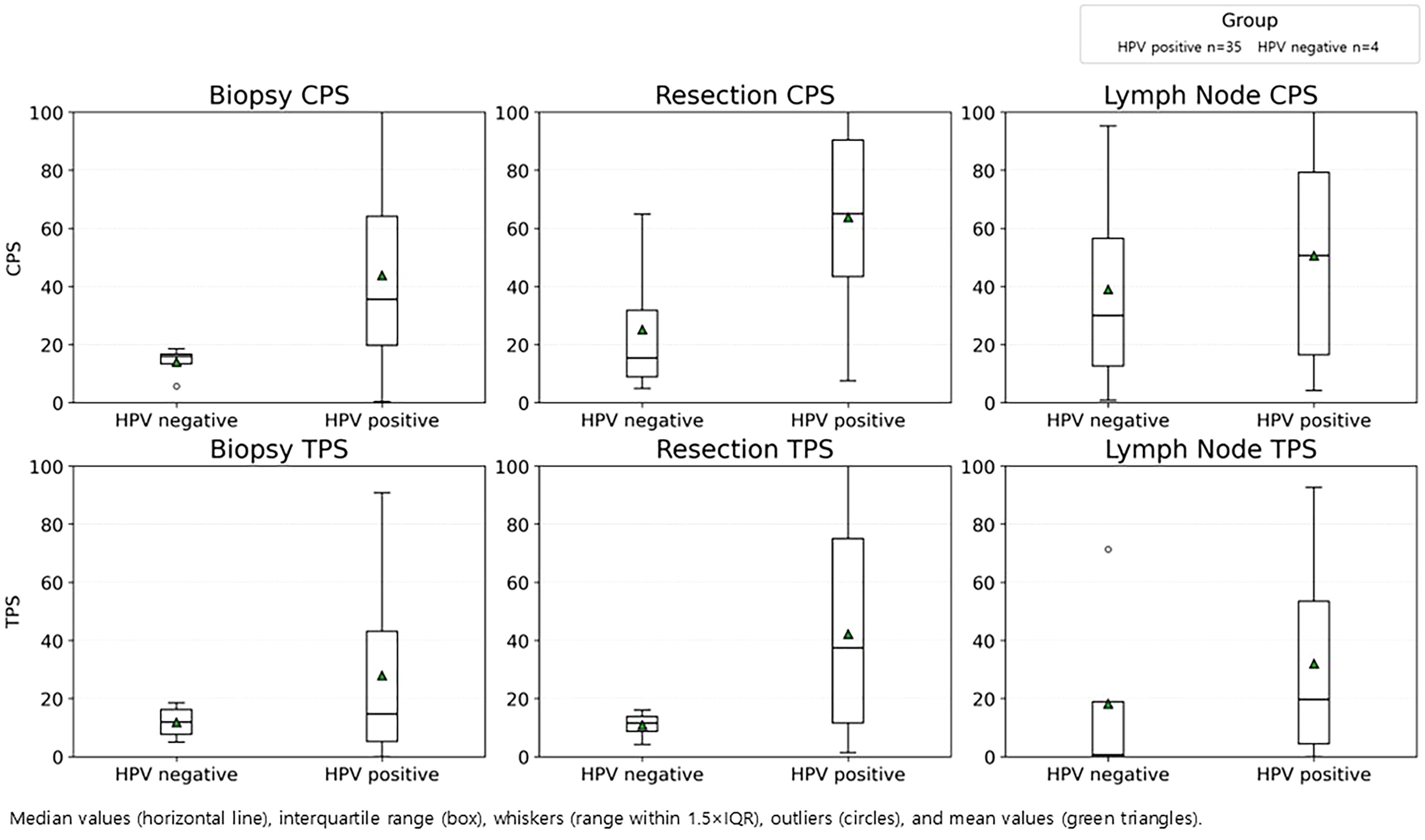
Figure 4. PD-L1 expression by HPV status in oropharyngeal cancer. CPS (top) and TPS (bottom) in biopsy, resection, and lymph node specimen, stratified by HPV-positive (n=35) and HPV-negative (n=4) groups.
3.4 Paired statistical analysis of PD-L1 expression across specimens
The Kruskal-Wallis test revealed significant differences in both CPS and TPS when comparing preoperative biopsies with surgical resections (p<0.05 for both). Similarly, significant differences were found between surgical resections and metastatic lymph nodes (p<0.05 for both). No statistically significant differences were observed for CPS and TPS between preoperative biopsies and metastatic lymph nodes.
3.5 Categorical comparison of PD-L1 expression between primary and metastatic specimens
When comparing paired primary tumors (resection specimens) and metastatic lymph nodes, the overall categorical concordance rate for CPS was 72.1% (49/68). Higher CPS values were observed in the primary tumor in 25.0% (17/68) of cases, while higher CPS was found in the lymph node in 2.9% (2/68) of cases. For TPS, the overall concordance rate was 47.1% (32/68), with higher values in the primary tumor and lymph node in 38.2% (26/68) and 14.7% (10/68) of cases, respectively (Table 2).
3.6 Case-wise PD-L1 expression trends
Figure 5 illustrates case-wise PD-L1 expression trends in CPS and TPS. Average CPS scores in surgical specimens were approximately 20 points higher than corresponding TPS values. One case showed consistently low PD-L1 expression (TPS <1%) across all specimens. Inverse expression patterns, where surgical specimens had lower PD-L1 expression than biopsies or lymph nodes, were observed in a subset of cases (highlighted in orange and blue in Figure 5).
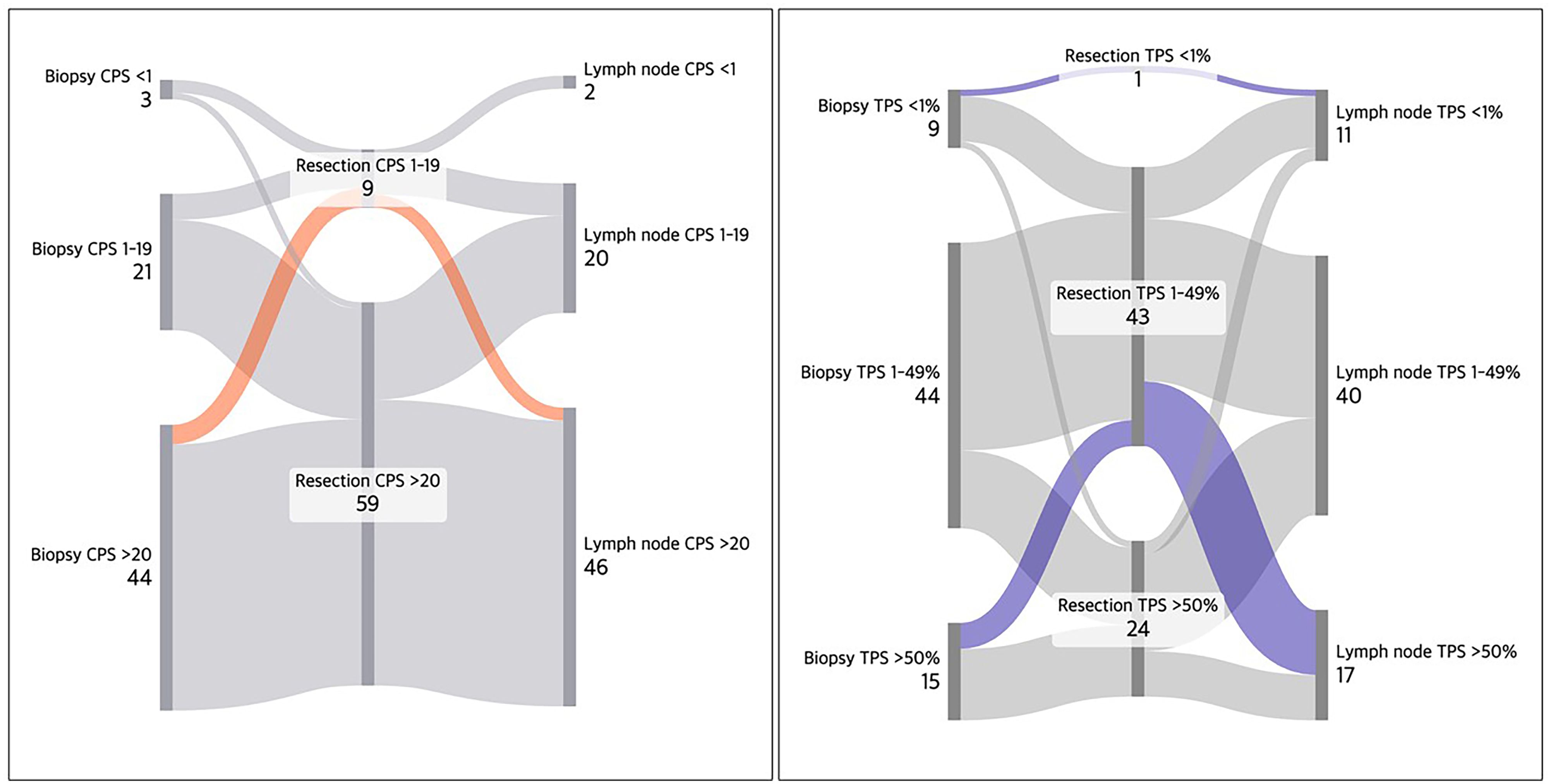
Figure 5. Sankey diagrams showing PD-L1 expression trends (CPS and TPS) across 68 HNSCC cases. Surgical specimens generally exhibited higher CPS (~20 scale) compared to TPS, likely due to PD-L1-positive immune cells. A case demonstrated uniformly low PD-L1 expression (TPS <1%) across all specimens (depicted in top blue). Several cases with inverse PD-L1 expression pattern (lower expression in resection) are also depicted in red orange and blue.
4 Discussion
This study explores PD-L1 expression patterns in Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma across preoperative biopsies, surgical resections and metastatic lymph nodes, using CPS and TPS categorized into three groups. Oropharyngeal tumors demonstrated clinicopathological features distinct from oral cavity cancers, in part due to their strong association with HPV infection and its correlation with p16 IHC (2). Also, CPS scores from resection specimens were significantly lower in advanced-stage disease compared with early-stage cancer (median value 37.8 vs.67.7, p < 0.05).
4.1 CPS versus TPS
Across all specimen types, CPS consistently exceeded TPS, with an average difference of approximately 20 units. This discrepancy reflects the contribution of PD-L1-positive immune cells incorporated into CPS but excluded from TPS. Prior studies have similarly suggested that CPS better represents the tumor microenvironment (11), particularly in surgically resected specimens where immune infiltrates are more comprehensively sampled (12). Notably, inter-specimen concordance was higher for CPS than for TPS (72.1% vs. 48.5%), supporting the notion that CPS provides a more stable and reproducible measure across tumor compartments (13, 14), even though intratumoral heterogeneity remains.
4.2 Evaluation of variability of PD-L1 expression
Several studies have highlighted the challenges in evaluating PD-L1 expression in HNSCCs, including variability in expression levels and the difficulty of selecting representative samples (13, 14). Karpathiou et al. reported that PD-L1 expression may decline in archival specimens, potentially compounding heterogeneity in reported results (15). Furthermore, PD-L1 assessment after chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy has yielded conflicting outcomes across studies (16–18).
In other malignancies, such as lung cancer, the consistency of PD-L1 expression between primary tumors and metastases has also been examined. Gradecki et al. observed high concordance between core biopsies and resections in NSCLC, particularly in specimens with diffuse staining involving >50% of tumor cells (19). In contrast, more recent investigations have underscored significant variability in PD-L1 expression across specimen types in both early and advanced NSCLC (6, 20).
4.3 Pairwise specimen comparisons of PD-L1 expression
4.3.1 Preoperative biopsy vs. surgical resection
Both CPS and TPS were significantly higher in surgical resections (p < 0.05), consistent with spatial heterogeneity where biopsies may underestimate PD-L1-rich areas. This suggests that interpretations should be done in biopsy and surgical resection parallelly for optimal clinical decision-making, a pattern consistent with precious reports (9).
4.3.2 Surgical resection vs. metastatic lymph node
Significant differences (p < 0.05) were also observed, with lower CPS and TPS in lymph nodes, possibly reflecting temporal heterogeneity arising during the interval of metastasis or recurrence, and/or clonal selection with lower PD-L1 expression. In contrast, Paolino et al. reported higher degree of positivity in metastatic lymph nodes (14). A potential source of discrepancy includes overestimation of PD-L1 expressing cells, which may not truly represent tumor-immune interactions. Taken together, these observations highlight the need for prospective studies comparing primary tumors and matched metastases.
4.3.3 Preoperative biopsy vs. metastatic lymph node
No significant statistical difference was observed overall, though presence of difference at a group level.
4.3.4 Categorical reclassification across specimen types
For CPS, three negative and 21 low-expression preoperative biopsy cases were largely reclassified into the high-expression category in surgical resections. However, in metastatic lymph nodes, 20 cases reverted to low expression, with only 46 maintaining high expression. For TPS, high expression was identified in 15 preoperative biopsies, increasing to 25 surgical resections. In contrast, only 17 metastatic lymph nodes retained this status, while 40 cases shifted to low-expression category. Notably, a category-skipping phenomenon (negative preoperative biopsy to high expressing surgical resection) was observed both in CPS and TPS, including transitions from negative biopsies to high-expression resections, and, conversely, a decline from high-expression resections to negative lymph nodes. These threshold-crossing events underscore the substantial heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression across specimens.
4.3.5 Oropharyngeal cancers vs. oral cavity cancers
When analyzed by anatomical site, high CPS and low TPS groups were the most frequent categories across all specimens from oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancers. Separate Kruskal-Wallis tests revealed that oropharyngeal tumors showed a CPS difference only between preoperative biopsy and surgical resection, while oral cavity tumors demonstrated differences in both CPS and TPS between biopsy and resection, and resection and metastatic lymph node. These findings suggest site-specific biological differences, potentially influenced by HPV status or other tumor–microenvironmental factors, despite their shared squamous histology.
4.4 Outliers
Several unique cases were identified. One tongue tumor demonstrated uniformly negative PD-L1 expression across all specimens, suggesting an inherently PD-L1-negative phenotype. Of note, a few cases (oropharynx n=1, oral cavity n=2) displayed inverse patterns, with negative surgical resections but corresponding biopsies or lymph nodes strongly positive. This may reflect heterogeneity of tumors, or clonal selection capable of immune evasion in metastatic sites. These unusual patterns underscore the need for further investigation into the biological behavior of such tumor and their potential clinical implications.
Despite these insights, this study has several limitations. First, it is a retrospective, single-institution study with a relatively small sample size, and the inclusion of a few older archival samples, which may limit generalizability of findings. Second, interobserver variability in PD-L1 scoring, especially for immune cell staining, was not assessed. Third, lymph node specimens collected after resection were not separately analyzed but included as a pooled group, without distinction between normal and metastatic lymph nodes, that could have provided further insight for metastatic potential of tumors. Fourth, we did not correlate PD-L1 expression with clinical outcomes, such as response to immune checkpoint inhibitors, which would be necessary to validate the predictive value of these findings.
5 Conclusions
Our study demonstrates that PD-L1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is heterogeneous across specimen types. Oropharyngeal tumors generally exhibited overall higher PD-L1 levels, whereas oral cavity tumors showed greater variability in score-based classification across specimens, with statistically significant differences in measured values for both tumor sites. These indicate that no single specimen can reliably represent tumor’s overall PD-L1 status, despite moderate concordance in scoring. Therefore, assessment of multiple specimen types should be considered when determining PD-L1 status for immunotherapy eligibility.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Catholic Medical Center. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by- product of routine care or industry. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
HS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MK: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. S-YK: Resources, Writing – original draft. D-IS: Resources, Writing – original draft. YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Software, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: RS-2021-KH113146).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank MK, S-YK, and D-IS for their assistance and provision of clinical resources.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
2. Kim HS, Lee JY, Lim SH, Park K, Sun JM, Ko YH, et al. Association between PD-L1 and HPV status and the prognostic value of PD-L1 in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. (2016) 48:527–36. doi: 10.4143/crt.2015.249
3. Uppaluri R, Haddad RI, Tao Y, Lee NY, Even C, Garcia J, et al. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant pembrolizumab in locally advanced head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2025) 393:37–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2415434
4. Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J, Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, et al. Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:1856–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602252
5. Haragan A, Field JK, Davies MPA, Escriu C, Gruver A, and Gosney JR. Heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: implications for specimen sampling in predicting treatment response. Lung Cancer. (2019) 134:79–84. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.06.005
6. Josephides EC, Smith D, Bille A, Patel A, Rush HL, Dunn R, et al. A retrospective evaluation of PD-L1 expression and heterogeneity in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (REPLICA). Clin Lung Cancer. (2025) 26:e223–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2025.01.008
7. Ambrosini-Spaltro A, Limarzi F, Gaudio M, Calpona S, and Meccariello G. PD-L1 expression in head and neck carcinoma by combined positive score: a comparison among preoperative biopsy, tumor resection, and lymph node metastasis. Virchows Arch. (2022) 481:93–9. doi: 10.1007/s00428-022-03306-w
8. Karabajakian A, Bouaoud J, Michon L, Kamal M, Crozes C, Zrounba P, et al. Longitudinal assessment of PD-L1 expression and gene expression profiles in patients with head and neck cancer reveals temporal heterogeneity. Oral Oncol. (2021) 119:105368. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105368
9. Bill R, Faquin WC, and Pai SI. Assessing PD-L1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: trials and tribulations [Review. Head Neck Pathol. (2023) 17:969–75. doi: 10.1007/s12105-023-01590-6
10. Bankhead P, Loughrey MB, Fernández JA, Dombrowski Y, McArt DG, Dunne PD, et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17204-5
11. Hirshoren N, Al-Kharouf I, Weinberger JM, Eliashar R, Popovtzer A, Knaanie A, et al. Spatial intratumoral heterogeneity expression of PD-L1 antigen in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology. (2021) 99:464–70. doi: 10.1159/000515441
12. Ilie M, Long-Mira E, Bence C, Butori C, Lassalle S, Bouhlel L, et al. Comparative study of the PD-L1 status between surgically resected specimens and matched biopsies of NSCLC patients reveals major discrepancies depending on IHC protocols. Ann Oncol. (2016) 27:147–53. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv489
13. Girolami I, Pantanowitz L, Barberis M, Paolino G, Brunelli M, Vigliar E, et al. Challenges facing pathologists evaluating PD-L1 in head & neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. (2021) 50:864–73. doi: 10.1111/jop.13220
14. Paolino G, Donati M, Didona D, Mercuri SR, Cantisani C, Moliterni E, et al. PD-L1 evaluation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: insights regarding specimens, heterogeneity and therapy. Pathol Res Pract. (2021) 227:153605. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153605
15. Karpathiou G, Froudarakis M, Forest F, Casteillo F, Marcoux M, Venet M, et al. PD-L1 expression in head and neck cancer tissue specimens decreases with time. Pathol Res Pract. (2022) 233:154042. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154042
16. Ock CY, Kim S, Keam B, Kim M, Kim TM, Kim JH, et al. Changes in programmed death-ligand 1 expression during cisplatin treatment in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:83755–65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18542
17. Leduc C, Adam J, Louvet E, Sourisseau T, Dorvault N, Bernard M, et al. TPF induction chemotherapy increases PD-L1 expression in tumour cells and immune cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. ESMO Open. (2018) 3:e000257. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000257
18. Girolami I, Marletta S, Fiorentino V, Battocchio S, Cerbelli B, Fiamengo B, et al. Effect of radio-chemotherapy on PD-L1 immunohistochemical expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pers Med. (2023) 13:363. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020363
19. Gradecki SE, Grange JS, and Stelow EB. Concordance of PD-L1 expression between core biopsy and resection specimens of non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. (2018) 42:1090–4. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001100
Keywords: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, PD-L1, combined positive score, tumor proportion score, heterogeneity
Citation: Sohn H, Kim M, Kim S-Y, Sun D-I and Lee YS (2025) Comparison of PD-L1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma among preoperative biopsy, surgical resection and metastatic lymph node. Front. Oncol. 15:1666078. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1666078
Received: 15 July 2025; Accepted: 01 October 2025;
Published: 15 October 2025.
Edited by:
Raffaele Addeo, ASLNAPOLI2NORD ONCOLOGIA, ItalyReviewed by:
Mario Pirozzi, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, ItalyHaolei Tan, Hunan Cancer Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Sohn, Kim, Kim, Sun and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Youn Soo Lee, bHlzOTkwOEBjYXRob2xpYy5hYy5rcg==
†ORCID: Heeseung Sohn, orcid.org/0009-0009-9967-8009
Meejeong Kim, orcid.org/0000-0002-1232-8439
Sang-Yeon Kim, orcid.org/0000-0003-3745-5124
Dong-Il Sun, orcid.org/0000-0001-9950-568X
Youn Soo Lee, orcid.org/0000-0002-1653-6315
 Heeseung Sohn
Heeseung Sohn Meejeong Kim1†
Meejeong Kim1†