- 1Student Research Committee, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
- 2Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
- 3Student Research Committee, MMS.C., Islamic Azad University, Mashhad, Iran
- 4Neuropathology Unit, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States
Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) is a dual-substrate enzyme that hydrolyzes both cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), playing a critical role in regulating intracellular signaling pathways. While its function has been extensively studied in the central nervous system, emerging evidence highlights its broader physiological and pathological relevance, including its involvement in cancer. Functionally, it modulates key signaling pathways such as cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) and cGMP/protein kinase G (PKG), influencing cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. In cancer, PDE10A exhibits a context-dependent role. It functions as an oncogene in cancers such as colorectal, ovarian, gastric, and non-small cell lung cancers through overexpression and downstream activation of the Wnt/β-catenin, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways. Pharmacological inhibition of PDE10A using selective inhibitors has demonstrated potent anti-tumor effects in preclinical models by restoring cyclic nucleotide levels and suppressing oncogenic signaling. Conversely, in glioblastoma (GBM), PDE10A acts as a tumor suppressor, and its knockdown promotes tumor progression via activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. These findings showed the ability of PDE10A to be considered as a promising biomarker and therapeutic target in oncology; however, it is suggested to examine the tissue-specific expression of PDE10A, baseline cyclic nucleotide levels, cross-talk with other pathways, differences in the degree and duration of PDE10A suppression, and the interplay between PDE10A-mediated cyclic nucleotide signaling and compensatory oncogenic pathways for an effective therapy as observed in other PDEs family reviewed in this manuscript.
1 Introduction
Phosphodiesterase (PDE) 10A belongs to a family of at least eleven phosphodiesterase isoenzymes responsible for the hydrolytic degradation of the second messengers, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and/or cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). PDE10A, the sole gene product of this family, exhibits dual substrate specificity. Although it demonstrates a higher binding affinity for cAMP, it more efficiently hydrolyzes cGMP. Three protein-coding isoforms of PDE10A have been identified, including PDE10A1 and PDE10A19 that localize to the cytosol, and membrane-associated PDE10A2 (1–3).
The pharmacological inhibition of PDE10A has garnered increasing interest in both academic and industrial research due to its potential to elevate intracellular cAMP and/or cGMP levels. Such modulation holds therapeutic promise across a range of disorders involving both the central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as in various malignancies (4). By modulating intracellular levels of cyclic nucleotides, such as cAMP and cGMP, PDE10A can influence key processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis. Recent studies suggest that PDE10A is overexpressed in specific cancer types and may contribute to tumor progression, making it a potential biomarker and therapeutic target (5–12).
Despite the growing evidence linking PDE10A to cancer biology, most existing reviews focus primarily on its role in neurological disorders, and only limited literature addresses its function in oncogenesis (13, 14). Given the recent studies highlighting PDEs involvement in tumor growth, this review aimed to explore the structure, signaling, and significant roles of the Phosphodiesterase family in cancer with a focus on the dual role activity of PDE10A in various cancers and its potential to be used as a biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, or as a therapeutic target.
2 Phosphodiesterase family: structure, signaling, and roles in cancer
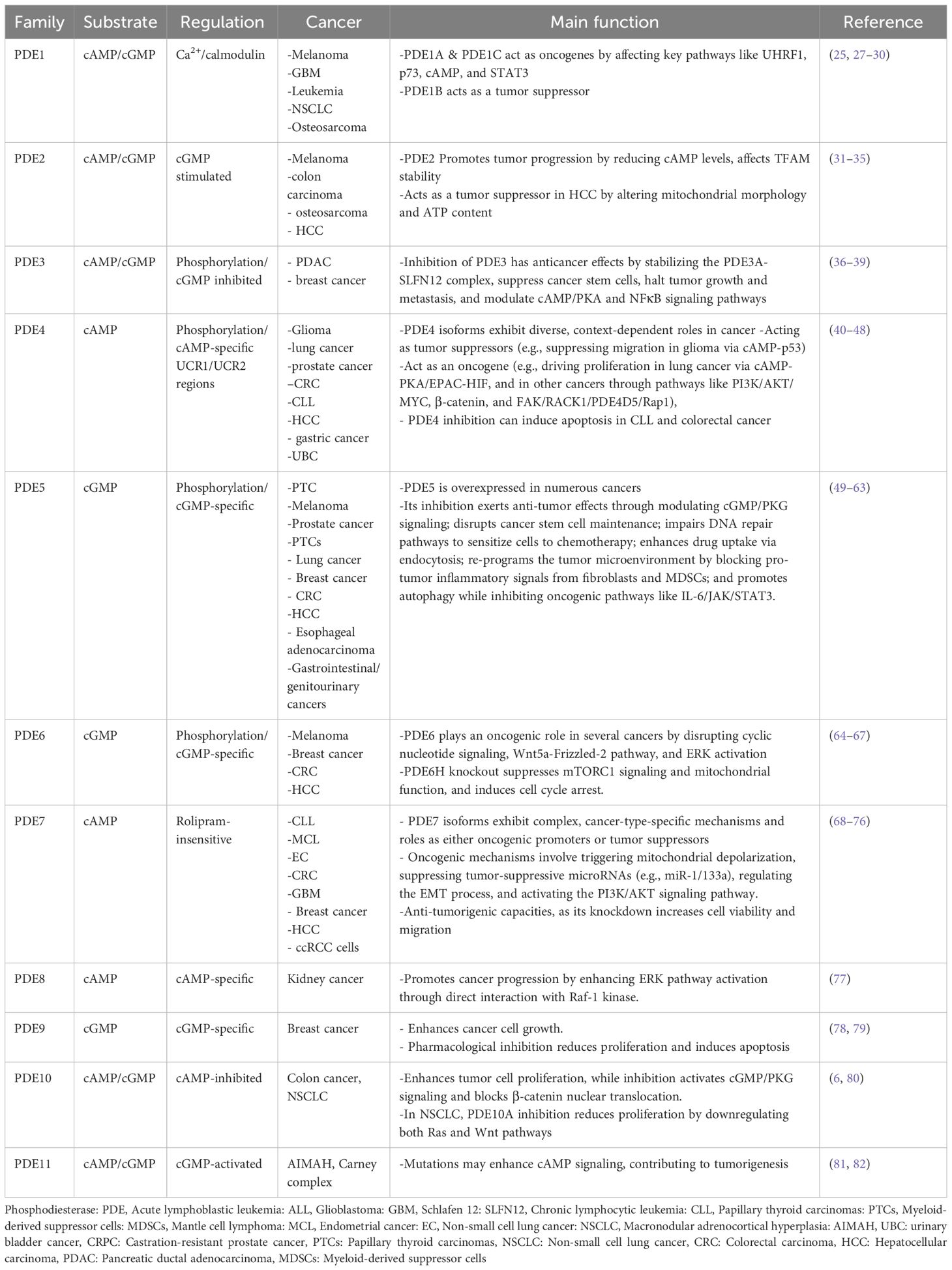
The PDEs constitute a superfamily of enzymes that regulate intracellular levels of cAMP and cGMP by catalyzing their hydrolysis to 5′ AMP and 5′ GMP, respectively (15, 16). Mammalian PDEs are classified into 11 subfamilies encoded by 21 distinct genes, many of which produce multiple splice variants with unique subcellular localizations and regulatory roles (15, 17). These enzymes are categorized based on substrate specificity, including cAMP-specific (PDE4, PDE7, PDE8), cGMP-specific (PDE5, PDE6, PDE9), and dual-specificity PDEs that hydrolyze both cyclic nucleotides (PDE1, PDE2, PDE3, PDE10, and PDE11), though individual members often display a higher affinity for one nucleotide (15, 17). Substrate recognition is modulated by a conserved glutamine switch, which regulates purine ring binding within the catalytic domain (18). While their catalytic and regulatory domains are conserved, isoform-specific differences, particularly in the N- and C-terminal regions, define the subcellular targeting and functional specificity of each PDE (17, 19). The expression of PDEs is variable and widely distributed across tissues, including the brain, where each isoform shows distinct spatiotemporal expression patterns, emphasizing their role in fine-tuning cyclic nucleotide signaling (20, 21). Although the primary aim of this review is to explore PDE10A as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in cancer, we first provide a brief overview of the structural characteristics and oncological relevance of other PDE isoforms to show and compare the dual role and expression of PDE10A in cancers.
2.1 Phosphodiesterase 1
Phosphodiesterase 1 (PDE1) is a calmodulin- and Ca²-dependent enzyme family comprising three subtypes, including PDE1A, PDE1B, and PDE1C. PDE1A, PDE1B, and PDE1C are encoded by genes located on chromosomes 2q32.1, 12q13, and 7p14.3, respectively. Alternative splicing generates multiple isoforms, including ten for PDE1A, two for PDE1B, and five for PDE1C. PDE1 isoforms are broadly expressed in various tissues, including the heart, brain, lung, and smooth muscle, with distinct distribution patterns and physiological roles (17). Uniquely, PDE1 enzymes are regulated by two Ca²+/calmodulin binding domains and two phosphorylation sites at the N-terminus (22). These enzymes hydrolyze both cAMP and cGMP with isoform-specific nucleotide affinities. PDE1A and PDE1B exhibit higher affinity for cGMP. However, PDE1C hydrolyzes cAMP and cGMP with comparable efficiency (23).
Functionally, PDE1 has been implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation in various malignancies. It is a specific pharmacological target of differentiation-inducing factor 1, which inhibits cancer cell proliferation by competitively blocking cAMP binding to PDE1 in a dose-dependent manner (24). In melanoma cells, PDE1C is overexpressed, and its inhibition by vinpocetine significantly reduces tumor growth (25). Natural compounds such as curcumin and thymoquinone have been shown to target PDE1, leading to apoptosis and growth inhibition in melanoma and leukemia cells, respectively, through modulation of epigenetic and cell cycle-related markers (26, 27). Specifically, thymoquinone suppresses PDE1A expression and inhibits UHRF1 via a p73-dependent mechanism, suggesting potential application in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) therapy (Table 1) (27). Another study by Zhang et al. showed the importance of PDE1A as a significant promoter of Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastasis through regulating exosome release and activating the STAT3 pathway by interacting with YTHDF2, suggesting PDE1A as a potential therapeutic target for metastatic disease (28).
In IDH-wildtype GBM, elevated PDE1C expression correlates with poor prognosis (83). Genetic silencing of PDE1C using siRNAs significantly disrupts GBM cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target (Table 1) (29). Collectively, these findings highlight the therapeutic promise of targeting PDE1 in cancer treatment. However, the development of highly selective and potent PDE1 inhibitors remains a significant unresolved challenge (84).
In contrast to most PDE1 subtypes, a study by Chen et al. investigates the role of PDE1B in osteosarcoma, suggesting that PDE1B is a tumor suppressor gene that prevents osteosarcoma from escaping the immune system (30). This study highlighted the importance of considering dual role activity of PDE1 in cancers, requiring further study.
2.2 Phosphodiesterase 2
The Phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2) is a dual-substrate enzyme that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP, with half-maximal velocities (Km) of approximately 30 µM and 10 µM, respectively (85, 86). It is uniquely stimulated by cGMP, which enhances cAMP hydrolysis by up to six-fold, earning it the designation cGMP-stimulated PDE (85, 86). PDE2 is encoded by a single gene, PDE2A, which gives rise to three isoforms, including PDE2A1, PDE2A2, and PDE2A3 (87). It is broadly expressed in human tissues such as the adrenal gland, heart, lung, liver, platelets, and endothelial cells (88). Several selective inhibitors have been developed, including EHNA, BAY 60-7550, oxindole derivatives, IC933, PDP, and ND7001; however, these have not yet been evaluated in clinical cancer therapy (89–91).
In the context of cancer biology, PDE2 has been implicated in tumor progression. Notably, specific tumor cells, such as malignant melanoma and colon carcinoma, exhibit reduced cAMP levels, where cAMP serves as a negative regulator of proliferation (31). Zhao et al. showed that mitochondrial calcium (Ca2+) could activate PDE2, acting as an inhibitor of PKA, which affects mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) stability and increases CRC growth (32).
In malignant melanoma cells, inhibition of PDE2 using EHNA or PDE2A-targeted siRNAs suppressed both cell growth and invasion, suggesting a functional role for PDE2 in tumor aggressiveness (92). It has also been observed that topical application of erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl) adenine hydrochloride (EHNA hydrochloride) on a mouse model of ultraviolet light B (UVB)-induced skin carcinogenesis, a PDE2 inhibitor increases apoptosis and attenuates tumor formation (33). The exclusive expression of mutant PDE2A2 isoforms in these cells indicates that PDE2A2 may serve as a novel therapeutic target in malignant melanoma (Table 1) (93). In addition to skin cancer, Murata et al. reported that EHNA and 8-bromo-cAMP PDE2 inhibitors could decrease proliferation and migration of HOSM-1 osteosarcoma cells (34).
In contrast to these findings, Chen et al. report that PDE2A has an inverse correlation with AFP level, immune function, vascular invasion, grade, and stage of HCC patients. In addition, overexpression of PDE2A in two HCC cell lines (HLF and SNU-368) caused inhibition of invasion, colony formation, migration, and proliferation, possibly via a change in mitochondrial morphology and ATP content (35). This inconsistency has been reported to be likely related to the variation in predominant PDE isoforms across different tissues, as well as unidentified mechanisms through which of these isoforms regulate cellular behavior (35).
2.3 Phosphodiesterase 3
Phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) is a dual-specificity enzyme that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP, with a higher affinity for cGMP. Consequently, cGMP acts as a potent competitive inhibitor of cAMP hydrolysis (94). The PDE3 family consists of two genes, PDE3A and PDE3B. PDE3A is expressed in three splice variants, including PDE3A1 (136 kDa), PDE3A2 (118 kDa), and PDE3A3 (94 kDa), whereas no splice variants have been identified for PDE3B (95). Structurally, PDE3 enzymes contain N-terminal hydrophobic membrane-association regions and a unique 44-amino acid insertion within the catalytic domain (96). Multiple phosphorylation sites in the N-terminal region confer diverse regulatory functions (97).
PDE3 is widely expressed in cardiac and vascular myocytes, brain, liver, adipose tissue, pancreatic β-cells, endothelium, epithelium, oocytes, and platelets (98). Functionally, PDE3A regulates cardiac contractility, platelet aggregation, smooth muscle contraction, oocyte maturation, and renin secretion, whereas PDE3B is more involved in insulin signaling and cell proliferation (99, 100). Several potent and selective PDE3 inhibitors, including cilostamide, cilostazol, and olprinone, have been developed (101).
Recent studies have highlighted PDE3A as both a biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in cancer. A novel mechanism has been described for the small molecule DNMDP (6-(4-(diethylamino)-3-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-one), which acts through a gain-of-function allosteric mechanism. DNMDP stabilizes the interaction between PDE3A and Schlafen 12 (SLFN12), inducing cytotoxicity in cancer cells with elevated expression of both proteins (Table 1) (36, 37). Another study on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) showed that combining the epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate with a PDE3 inhibitor dramatically suppressed cancer stem cells (CSCs) and halted tumor growth and metastasis in vivo (38). In addition, PDE3A was shown to be able to suppress cAMP/PKA and induce NFκB signaling pathway, causing expression of the stem cell marker OCT4 and cancer stemness in breast cancer. Inhibition of PDE3A with cilostazol could reduce metastasis and suppress tumor growth in xenograft breast cancer models (39).
2.4 Phosphodiesterase 4
The Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) represents the largest and one of the earliest identified PDE families, characterized by its specificity for cAMP hydrolysis, with a Km ranging between 2–4 µM (102). It comprises four genes including PDE4A, PDE4B, PDE4C, and PDE4D that located on chromosomes 19p13.2, 1p31, 19p13.11, and 5q12, respectively (103). Alternative splicing of the N-terminal region results in the generation of multiple isoforms in long, short, and super-short forms, based on the presence or absence of upstream conserved regions (UCR1 and UCR2). These UCRs regulate isoform activity through phosphorylation by PKA and ERK, and influence PDE4 dimerization (104).
PDE4 is broadly expressed in various tissues, including the brain, liver, heart, lungs, smooth muscle, endothelial cells, and immune cells. Functionally, it modulates critical physiological and pathological processes, including neural function, immune cell activation, vascular remodeling, fertility, and cardiac activity (104). Notably, PDE4 demonstrates the highest cAMP-hydrolyzing activity in 41 out of 60 examined tumor cell lines (105). It has been implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous brain tumors, including glioblastoma, medulloblastoma, and ependymoma, and may serve as a therapeutic target in these malignancies (106).
In glioma, PDE4C suppressed migration and induced apoptosis through the cAMP-p53 axis, and its expression could be epigenetically silenced by promoter hypermethylation, suggesting a role as a glioma biomarker (40). Additionally, PDE4 is upregulated in lung cancer and contributes to tumor progression via the cAMP–PKA/EPAC–HIF pathway, while its inhibition attenuates tumor cell proliferation (41). TGF-β1-mediated PDE4 upregulation promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in lung epithelial cells, identifying PDE4 as a target for mitigating EMT-related lung pathologies (Table 1) (107). EMT was also enhanced in hepatocellular carcinoma following ectopic expression of PDE4a (42).
In prostate cancer, PKA-mediated phosphorylation of PDE4 may enhance tumor growth (43). In addition, the PDE4B/PKA pathway plays a key role in the progression of androgen-dependent prostate cancer to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), which is non-responsive to docetaxel and has a poor prognosis (44). Furthermore, PDE4B is upregulated by oncogenic KRAS in CRC, and its inhibition by rolipram or shRNA induces apoptosis and restores epithelial polarity, underscoring its value as both a therapeutic and prognostic marker (45). PDE4B is reported to be able to promote immune infiltration of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and increase the clonal formation, proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer via the PI3K/AKT/MYC pathway (46). PDE4B is also able to promote proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of urinary bladder cancer (UBC) via the β-catenin pathway, while its inhibition by rolipram reverses these effects (47).
Moreover, the higher expression of PDE4, along with exchange protein 1 directly activated by cAMP (Epac1), has been reported in rectal carcinoma (108). The FAK/RACK1/PDE4D5/Rap1 axis facilitates tumor cell adhesion and migration through localized cAMP degradation (109). In chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), PDE4 inhibition promotes apoptosis via activation of PP2A and dephosphorylation of Bcl-2 family members (48). Another study on advanced B-cell malignancies reported the efficacy of roflumilast as a PDE4 inhibitor in combination with prednisone in the treatment of patients with B-cell malignancies (110).
Another study by Mukherjee et al. reported a higher level of PDE4 in breast CSCs compared to normal stem cells. Inhibition of PDE4 by rolipram in breast CSCs caused cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via antagonizing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and noncanonical activation of mTOR. Moreover, this study showed that the combination of Rolipram with paclitaxel caused a synergistic effect and eradicated breast CSCs (111). An increased expression of PDE4D in MCF-7 and T47D resistant cells to tamoxifen, a crucial hormonal therapy for ER-positive breast cancer, has been reported to be related to worse survival in tamoxifen-treated patients with breast cancer. Inhibition of PDE4D by dipyridamole and Gebr-7b or siRNAs could have restored tamoxifen sensitivity via activating cAMP/ER stress/p38-JNK signaling and induction of apoptosis (112). Upregulation of PDE4D was also seen in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tumors with higher clinical progression and poor prognosis (113). Another study by Cao et al. also reported the involvement of PDE4D in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). They showed that targeting PDE4D with roflumilast or its knockout using CRISPR/Cas9 reduces the progression of ccRCC cells and enhances the apoptotic effect of sorafenib via attenuating MAPK/ERK signaling in a CRAF-dependent manner (114). Overall, PDE4 has been implicated in a wide range of cancers, including melanoma, DLBCL, liver, and colon cancers, positioning it as a promising target for novel anti-tumor strategies (Table 1) (84).
2.5 Phosphodiesterase 5
The Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) is a cGMP-specific hydrolase encoded by a single gene, PDE5A, located on chromosome 4q27. In humans, it produces three N-terminal splice variants, including PDE5A1, PDE5A2, and PDE5A3 (115). The N-terminal domain harbors two GAF domains, comprising GAF-A, which mediates allosteric binding of cGMP, and GAF-B, which modulates the affinity of GAF-A for cGMP (116). PDE5 is predominantly expressed in platelets, vascular smooth muscle, brain, lung, heart, kidney, and skeletal muscle, with PDE5A1 and PDE5A2 widely distributed across tissues, while PDE5A3 is confined to vascular smooth muscle (117). Functionally, PDE5 is a critical regulator of vascular tone, particularly in penile and pulmonary tissues, modulates NO-cGMP signaling in platelets, and may influence cGMP signaling in the brain (118).
Dysregulated PDE5 expression has been reported in several malignancies, including bladder, prostate, breast, brain, colorectal, oral, and NSCLC, as well as in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (49, 118, 119). Intriguingly, oncogenic BRAF V600E downregulates PDE5A in melanoma, leading to elevated cGMP levels and increased invasiveness (50). Moreover, the PDE/cGMP/PKG axis is essential for maintaining the stemness of PC3-derived cancer stem cells, and combining PDE5 inhibitors with chemotherapeutics effectively impedes prostate cancer progression and metastasis (Table 1) (51).
The scientists investigated the association between PDE5 inhibitor and prostate cancer risk in the Reduction by Dutasteride of Prostate Cancer Events (REDUCE) trial. They found PDE 5 inhibitor use was not associated with decreased prostate cancer diagnoses on post-hoc analysis of REDUCE. Notably, they revealed that in North American men, who had much higher baseline use of PDE5 inhibitors, this treatment was associated with an inverse trend of prostate cancer diagnosis, but did not reach statistical significance (120). Another study on prostate cancer revealed that PDE5 inhibitors sildenafil and vardenafil, but not tadalafil, sensitize CRPC cells to doxorubicin and other topoisomerase II inhibitors. This combination treatment enhances apoptosis in a PDE5-independent mechanism by impairing two key DNA repair pathways, including homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining (52).
PDE5 is also reported in human papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs), especially in those with a BRAF mutation. The PDE5 inhibitors sildenafil and tadalafil were found to reduce the proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells in vitro, suggesting that targeting PDE5 may be a potential treatment strategy for PTCs (49). PDE5 inhibitors dipyridamole, vardenafil, and/or sildenafil could also increase the uptake of anti-cancer drugs in lung cancer cells by enhancing endocytosis both in vitro and in vivo. This effect significantly improved the anti-tumor efficacy of trastuzumab in a lung cancer xenograft nude mice model (53).
It has also been reported that mRNA and protein expression of PDE5 increased in human breast cancer patients, enhancing the tumor-stimulatory activities of fibroblasts and decreasing the survival of patients. Expression of PDE5 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) also increases cell proliferation, motility, and invasion, making it a potential target for cancer (54). Another study used Tadalafil as a potent PDE-5 inhibitor against N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary gland carcinogenesis and found that a PDE-5 inhibitor could restore all biological markers to normal through blockade of DuCLOX signaling and attenuation of mitochondrial-oxidative stress (55). Catalano et al. also reported that elevated PDE5 expression is linked to more aggressive breast cancer subtypes and shorter patient survival, and PDE5 overexpression enhances cancer cell invasion and motility by activating Rho GTPase signaling (56).
PDE5 inhibitors were reported to be able to decrease the risk of CRC in patients diagnosed with benign colorectal neoplasm (57). PDE5 inhibitors also could prohibit the development and progression of aflatoxin-induced Hepatocellular carcinoma in rats (58). PDE5 is also expressed in myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), where it contributes to immune evasion by promoting cytokine secretion, ROS production, and upregulation of nitric oxide synthase and arginase. Inhibiting PDE5 with sildenafil reduced MDSC infiltration and suppressed inflammation-driven colon tumorigenesis in preclinical models (59, 60). Additionally, cGMP signaling via PKG2 promotes expression of antioxidant genes through activation of FOXO transcription factors, particularly in the colonic epithelium. It highlights the therapeutic potential of PDE5 inhibitors in targeting redox and immune pathways (Table 1) (121). Moreover, P. Sharpe et al. reported that PDE5 inhibitors could inhibit the tumor-promoting function of cancer-associated fibroblasts and increase the efficacy of chemotherapy in esophageal adenocarcinoma (61). Using PDE5 inhibitors is also reported to be useful in improving the effect of chemotherapy agents against gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancers by promoting autophagy and inducing DNA damage (62). Another type of study found that the PDE5 inhibitor sildenafil suppresses gastric tumor growth by activating PKG, which leads to the degradation of c-MYC and the suppression of the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway (63). Collectively, these findings position PDE5 as a promising prognostic marker and a novel therapeutic target in various cancers.
2.6 Phosphodiesterase 6
The Phosphodiesterase 6 (PDE6), primarily known as the photoreceptor PDE, consists of several subunits encoded by distinct genes comprising PDE6A (5q31.2–34), PDE6B (4p16.3), and PDE6C (10q24), along with regulatory or accessory subunits PDE6D (2q35-q36), PDE6G (17q25), and PDE6H (12p13) (122). PDE6 is abundantly expressed in the photoreceptor outer segments of the mammalian retina and the pineal gland (123). In rod cells, the active enzyme is a heterodimer of PDE6A (α subunit) and PDE6B (β subunit), while in cone cells, the enzyme forms a homodimer of PDE6C (α′ subunit) (122). Each subunit contains two N-terminal GAF domains, including GAF-A and GAF-B, and a C-terminal catalytic domain. The GAF-A domain serves as a high-affinity cGMP-binding site and is likely critical for dimerization (124). While PDE6 exhibits high specificity for cGMP at low concentrations, it can also hydrolyze cAMP at elevated levels (123).
PDE6 was the first PDE family associated with genetic diseases, with mutations in the α and β subunits implicated in stationary night blindness and various forms of retinitis pigmentosa (125). Beyond the retina, PDE6 has been involved in cancer biology. In melanoma cells, deregulated activation of PDE6 occurs through a Wnt5a-Frizzled-2 signaling cascade, which reduces cGMP levels and increases intracellular calcium mobilization, thereby influencing cellular homeostasis (64). Furthermore, PDE6 may have oncogenic relevance in breast cancer. Epidemiological data indicate a link between artificial light at night and increased breast cancer risk (Table 1) (65). Microarray analyses of breast cancer cell lines and patient tissues revealed significant expression of PDE6B, PDE6C, and PDE6D, with minimal to no expression of PDE6A, PDE6G, and PDE6H. Immunohistochemistry confirmed PDE6B protein presence in multiple patient samples and MCF-7 breast cancer cells (126). Moreover, PDE6H, the inhibitory (or gamma) subunit of the cone-specific cGMP phosphodiesterase, has been identified as a key controller of cancer cell growth. Knockout of PDE6H increased cGMP levels, reduced mTORC1 signaling, induced cell cycle arrest, suppressed mitochondrial function, and slowed tumor growth in a xenograft model. This study also reported that treatment with the PDE5/6 inhibitor sildenafil decreases CRC tumor growth and improves survival (66). Moreover, PDE6D, as the delta subunit of rod-specific photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase, is significantly overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with advanced tumor stages and ERK activation. PDE6D expression was also induced by TGF-β1 and was overexpressed in sorafenib-resistant cells. Functionally, PDE6D depletion reduced cancer cell proliferation and migration, and conferred resistance to the chemotherapy drug sorafenib (67). These findings establish PDE6D as a key contributor to tumor progression and chemoresistance, marking it as a promising new therapeutic target for cancer.
2.7 Phosphodiesterase 7
The Phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) is a cAMP-specific enzyme with high affinity for its substrate, particularly at low concentrations (127). It comprises two genes, including PDE7A, located on chromosome 8q13, and PDE7B, on chromosome 6q23–24. PDE7A encodes three splice variants, including PDE7A1, PDE7A2, and PDE7A3, while PDE7B encodes four variants. Notably, the N-terminal region of PDE7 lacks a known regulatory domain, although it contains consensus sites for PKA phosphorylation. PDE7 is widely expressed at both mRNA and protein levels in various immune cells, implicating a possible role in T-lymphocyte activation (128).
In the nervous system, PDE7B1 is activated via the cAMP/PKA/cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling axis in striatal neurons and may be involved in memory regulation. It is suggested to have potential as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases (129). In oncology, PDE7 expression levels serve as a prognostic indicator in hematologic malignancies. For example, PDE7B is upregulated 23-fold in CLL and 21-fold in mantle cell lymphoma compared to normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells, indicating its value as a molecular target for therapy (68, 69). Additionally, overexpression of PDE7A in endometrial cancer (EC) cells facilitates cancer cell migration and invasion through the suppression of the miR-1/133a microRNA cluster (Table 1) (70). Lowering PDE7A expression with miR-23b or silencing PDE7A could also reduce the migration and invasion abilities of colon cancer cells (SW620 and SW480 cells) (71). Pharmacological inhibition of PDE7 using BRL-50481 enhances cAMP-PKA-dependent apoptosis in CLL cells, further supporting its therapeutic relevance (69). Elevated PDE7B expression has been reported in GBM cases, negatively impacts patient survival, and promotes the expansion of stem-like cancer cells and increased tumor aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo (72). Zhang et al. also discovered that suppressing PDE7B using miR-200c could inhibit the proliferation and progression of triple-negative breast cancer cells (73). In addition, inhibiting PDE7 using BRL-50481, IR-202, and IR-284, increasing intracellular cAMP levels, which triggers mitochondrial depolarization and the release of cytochrome c, caused apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (74). These findings demonstrate that PDE7B acts as an oncogene, increasing the progression of tumors, and pharmacological inhibition of PDE7B could be beneficial.
In contrast, Du et al. reported that PDE7B is significantly hypermethylated and downregulated in Hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. PDE7B expression has been reported to be correlated with poor prognosis and recurrence in HCC patients. Restoring PDE7B expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines inhibited tumor proliferation and metastasis by regulating the EMT process and inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (75). Similarly, Sun et al. showed that PDE7B was downregulated in ccRCC cells, and knockdown of PDE7B could increase cell viability and migration, suggesting PDE7B has anti-tumorigenic capacity (76). This controversy may be related to the method used in these studies, which employed acute (pharmacological inhibition) or chronic (using stable overexpression or stable knockout) approaches, yielding different results. However, investigating the genetic and expression profiles of patients seems necessary before any intervention on PDE7 expression, bringing to us the importance of personalized medicine.
2.8 Phosphodiesterase 8
The Phosphodiesterase 8 (PDE8) is a cAMP-specific enzyme characterized by exceptionally high substrate affinity compared to other PDE isoforms. It comprises two homologous genes, PDE8A (chromosome 15q25.3) and PDE8B (chromosome 5q13.3), with PDE8A generating five splice variants (PDE8A1-PDE8A5) (130). PDE8A is broadly expressed, with predominant localization in the testis and T lymphocytes, whereas PDE8B is mainly found in the brain and thyroid (131). PDE8 plays essential roles in diverse physiological processes, including T-cell activation, Leydig cell steroidogenesis, spermatogenesis, thyroid hormone synthesis, and cardiac regulation (132). Although its N-terminal region contains REC and PAS domains, the precise regulatory mechanisms remain poorly understood (133).
Clinically, two PDE8B mutations (H391A and P660L) have been associated with ACTH-independent macronodular adrenocortical hyperplasia (AIMAH) and non-secreting adrenocortical carcinomas (ACCs). These associations suggest a potential role for PDE8B in tumorigenesis and increased susceptibility to ACCs (134). Furthermore, PDE8A interacts with Raf-1 kinase with high picomolar affinity via amino acids 454-465, thereby promoting Raf-1 phosphorylation and enhancing ERK pathway activation. Disruption of the PDE8A/Raf-1 interaction using a synthetic peptide suppressed ERK signaling and the cellular response to EGF. Overexpression of a dominant-negative, catalytically inactive PDE8A1 mutant resulted in elevated Raf-1 phosphorylation at the inhibitory S259 site (77). Additionally, genetic deletion of PDE8 in Drosophila melanogaster decreased basal ERK activity and increased susceptibility to stress-induced mortality. These findings highlight the PDE8A/Raf-1 signaling complex as a promising therapeutic target in cancer (Table 1) (77).
2.9 Phosphodiesterase 9
The Phosphodiesterase 9 (PDE9) is a cGMP-specific enzyme with the highest affinity for cGMP among all PDE isoforms. The human PDE9A gene, located on chromosome 21q22.3, gives rise to 21 known splice variants (135). Unlike other PDEs, PDE9A lacks GAF domains or other defined regulatory motifs in its N-terminal region. PDE9A is predominantly expressed in the spleen, intestine, and brain, with particularly high levels in Purkinje neurons and the cerebellum (136). Functionally, selective inhibition of PDE9A by BAY 73–6691 has been shown to enhance cognitive performance, improving learning and memory in rodent models (137, 138).
In oncological contexts, elevated PDE9A expression has been observed in malignant breast tumors compared to normal tissues (78). Treatment of MCF-7 and MDA-MB468 breast cancer cells with BAY 73–6691 led to a dose- and time-dependent reduction in cell proliferation and an increase in apoptosis, highlighting PDE9A as a promising therapeutic target in breast cancer (Table 1) (79).
2.10 Phosphodiesterase 10
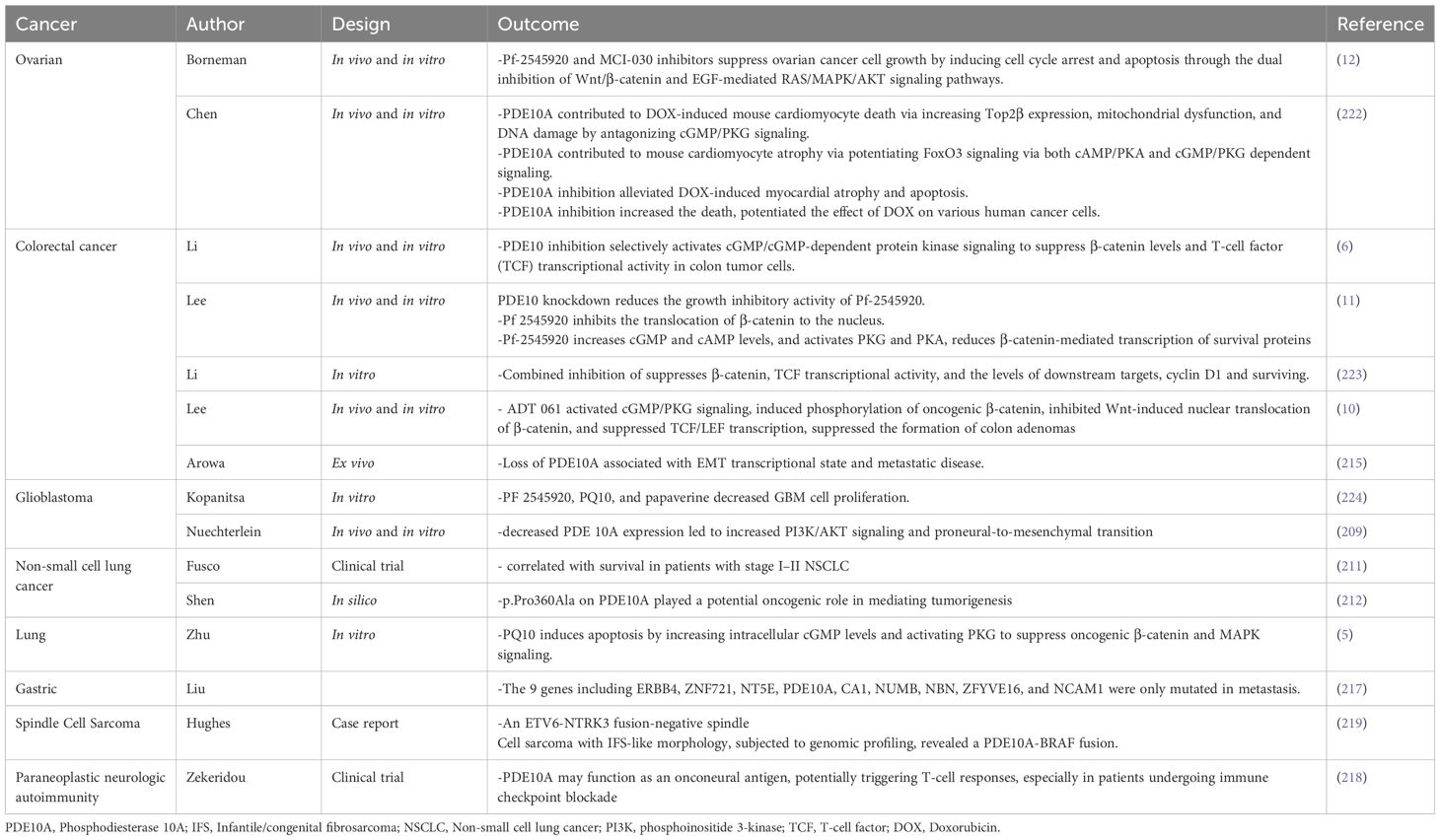
The PDE10 is encoded by the PDE10A gene located on chromosome 6q26 and exists in multiple isoforms, with PDE10A1 and PDE10A2 being the most prominent variants in humans (139, 140). PDE10 isoforms contain two GAF domains and hydrolyze both cAMP and cGMP, although they exhibit a higher affinity for cAMP; notably, cAMP binds specifically to the GAF-B domain (141). PDE10A expression is predominantly localized in the brain, particularly in the striatum, as well as in the thyroid and pituitary glands, suggesting a role in modulating cGMP signaling involved in learning and memory processes (142).
PDE10A has also been implicated in several malignancies, including lung, breast, and colon cancers (80, 143, 144). Elevated expression of PDE10A has been detected in colon tumor cells compared to normal colonocytes, and siRNA-mediated knockdown of PDE10A significantly inhibited tumor cell proliferation (144, 145). Additionally, pharmacological inhibition of PDE10A suppressed colon tumor growth by activating cGMP/PKG signaling, which in turn blocked nuclear translocation of β-catenin (6). In NSCLC, PDE10A is overexpressed, and its inhibition via siRNA or selective inhibitors suppressed cell proliferation by simultaneously downregulating Ras and Wnt signaling pathways (Table 1) (80). These findings support PDE10A as a potential therapeutic target in certain cancer types.
2.11 Phosphodiesterase 11
The Phosphodiesterase 11 (PDE11) is a dual-substrate enzyme capable of hydrolyzing both cAMP and cGMP with comparable affinities (146). It is encoded by a single gene, PDE11A, located on chromosome 2q31.2, and gives rise to four splice variants (PDE11A1–PDE11A4) that differ in their N-terminal regions due to distinct transcriptional start sites (147). PDE11A expression has been detected in various human tissues, including skeletal muscle, prostate, testis, salivary and thyroid glands, and liver (148). Functional studies in knockout mice suggest a role for PDE11A in sperm development and function, as well as in the pathogenesis of testicular and adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing disease, and certain psychiatric conditions (149, 150).
PDE11A has also emerged as a potential target in oncology. It is notably expressed in several malignancies, including renal, prostate, colon, lung, and breast cancers (151). In prostate cancer, inactivating mutations in PDE11A correlate with reduced protein expression, although the contribution of these mutations to cancer susceptibility remains unclear (152). The PDE11A4 isoform has been implicated as a predisposing genetic factor in AIMAH by activating the cAMP signaling pathway (81). Furthermore, a high frequency of PDE11A variants has been identified in patients with Carney complex (CNC), especially in those with PRKAR1A mutations. This observation suggests that PDE11A may act as a genetic modifier in the pathogenesis of adrenal and testicular tumors (82). Additionally, inactivating PDE11A variants have been associated with familial and bilateral testicular germ cell tumors, underscoring its relevance as a genetic risk factor (Table 1) (149, 153).
3 Structure and function of PDE10A
3.1 Structure
The human PDE10A gene (HSPDE10A1) is located on chromosome 6q26 and encodes a dual-substrate phosphodiesterase that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP (2, 154). PDE10A was first identified in 1999 via bioinformatics approaches. Its expression is predominantly restricted to the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in the medium spiny neurons (MSNs) of the dorsal and ventral striatum, which are integral parts of the basal ganglia (20, 155, 156). Within these neurons, PDE10A is localized in both the cell bodies and dendritic arbors. Low levels of expression have also been reported in other brain regions, including the cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum (14, 20, 155).
The highest PDE10A expression has been found in the striatum, that have a key role in regulating cAMP/cGMP signaling downstream of dopamine receptor signaling and is critically involved in the changes to gene expression caused by drugs (157). For example, inhibition of PDE10A could be significant in striatal activation and behavioral suppression, representing PDE10A inhibitors useful as antipsychotic agents. The presence of PDE10A in post-synaptic membranes of the medium spiny neurons also enables it to regulate intracellular signaling from glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs (158). In addition, Birjandi et al. showed that the high expression of PDE10A in the basal ganglia/striatum but not in the prefrontal cortex could be helpful to recover from the striatum using a PDE10A inhibitor (TAK-063), but not cortical stroke, consistent with its brain localization (159). PDE10A inhibitors also could mimic D2 antagonist effects by preferentially activating indirect pathway MSNs, offering potential therapeutic benefits for psychosis, schizophrenia, Tourette syndrome, and other movement disorders (160, 161). Moreover, it has been found that PDE10A integrates into a large protein complex at synaptic membranes, associating with AKAP150, PKA, and NMDA receptors upon PDE10A phosphorylation (162). Low levels of PDE10A expression have been observed in the hippocampus (20); however, Giralt et al. showed that inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) with the drug papaverine improved spatial and recognition memories in mouse models of Huntington’s disease, possibly via increasing cAMP levels and activating the hippocampal PKA signaling (163). This minimal expression of PDE10A in the hippocampus could, however, counteract its potential benefits in other neurological disorders that should be considered. The PDE10A inhibitor PF-2545920 has been shown to have a pro-epileptic effect by enhancing hippocampal excitability and seizure activity by promoting the trafficking of glutamate receptors (GluA1 and NR2A) to the post-synaptic density and increasing the phosphorylation of GluA1, which strengthens excitatory synapses, leading to synchronized synaptic transmission that can cause seizures (164).
Structurally, like all members of the PDE family, PDE10A contains a catalytic domain at the C-terminus, which is linked to regulatory domains located at the N-terminus. The N-terminal region is essential for dimerization, which is necessary for enzymatic activity, and also provides a platform for alternative splicing (165). At least 18 splice variants of PDE10A have been identified, primarily differing in their N- and C-terminal regions. In humans, PDE10A1 and PDE10A2 are the two primary isoforms, while rodents predominantly express PDE10A2 and PDE10A3. Of these, PDE10A2 is the major isoform expressed in the brain of both species (166).
A unique feature of PDE10A is the presence of GAF domains, which act as regulatory modules capable of binding small molecules, such as cyclic nucleotides (141, 167). In PDE10A, the GAF-B domain adopts a structure consisting of six anti-parallel β-sheets flanked by α-helices, forming a characteristic fold (168). This domain binds cAMP, which allosterically activates the enzyme, making PDE10A the only known mammalian PDE with this function (141).
The amino acid sequence of PDE10A1 and PDE10A2 is identical except for the N-terminus. PDE10A2 contains 789 amino acids, whereas PDE10A1 is 10 residues shorter. This difference results in distinct subcellular localization, with PDE10A2 being associated with the membrane and PDE10A1 residing in the cytosol (166). The catalytic domains of human, rat, and mouse PDE10A are 98% identical in sequence, and the overall amino acid identity is 95% (2, 166).
The crystal structure of the PDE10A2 catalytic domain, comprising 340 amino acids, was published in 2007. The structure contains 15 α-helices, forming a compact topology consistent with other PDEs (169). The active site comprises 11 conserved amino acid residues, including Val678, Thr685, Ala689, Ile692, Tyr693, Met713, Gly725, Gln726, Phe729, Tyr730, and Trp762 (166, 170). This active site is organized into four sub-pockets (171), each playing a critical role in substrate recognition and catalysis. The metal-binding pocket (M) coordinates Zn²+ and Mg²+ ions, which are essential for catalysis; Zn²+ forms strong interactions with histidine and aspartate residues, while Mg²+ forms weaker bonds, together activating a water molecule that mediates nucleophilic attack on the phosphodiester bond of the substrate (165, 170). The core pocket (Q) contains an invariant glutamine residue that forms hydrogen bonds with the purine ring of the substrate, providing specificity and stabilizing its orientation for efficient hydrolysis. Adjacent to this, the hydrophobic clamp (H) creates a rigid, hydrophobic environment that accommodates the planar ring structures of substrates or inhibitors, with aromatic residues such as Phe and Ile contributing to binding affinity and selectivity through hydrophobic interactions. Finally, the lid region (L) modulates substrate accessibility and binding by forming a structural lid over the active site, influencing the entry, orientation, and positioning of ligands. Collectively, these sub-pockets act cooperatively, ensuring high substrate specificity and catalytic efficiency while also providing distinct structural features that can be exploited in the design of selective PDE10A inhibitors (166).
Notably, PDE10A also features a unique lipophilic binding pocket not typically found in other PDEs. Within this region, Tyr693 plays a critical role by anchoring ligands via hydrogen bonding, further establishing PDE10A as a druggable target (172). The hydroxyl group of Tyr-693 forms a hydrogen bond with ligands, such as triarylimidazole and pyrazole derivatives, stabilizing their orientation within the pocket (173). This interaction is further reinforced by the structural positioning of the conserved Gln-726, which forms an additional hydrogen bond network with Tyr-693, anchoring the inhibitor effectively. Importantly, this lipophilic pocket is unique to PDE10A due to the presence of Gly-725, which allows access to the pocket, and the deeper M-loop structure, which is longer in PDE10A than in most other PDE isoforms (172). The presence of Tyr-693 in this context provides a structural handle that is not available in other PDEs, except PDE2, where access to the pocket is sterically blocked by a leucine residue (170). Consequently, designing inhibitors that form hydrogen bonds with Tyr-693 while occupying this lipophilic pocket allows for highly selective targeting of PDE10A over other PDE family members. This strategy has been successfully applied in the development of pyrazole and triarylimidazole compounds, which show nanomolar to subnanomolar IC50 values and >100–1000-fold selectivity against other PDEs (172).
3.2 Function and cellular signaling
The PDE10A is a dual-substrate enzyme that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP, with approximately 20-fold greater affinity for cAMP, making it an ideal target for disorders involving the fronto-striatal circuits (17, 155, 174). This higher affinity enhances phosphorylation of downstream targets such as DARPP-32 and CREB, modulating neuronal excitability, synaptic transmission, and dopaminergic signaling in direct and indirect pathway MSNs, influencing pathway-specific signaling, behavioral outcomes, and therapeutic applications. This makes PDE10A a critical regulator of cAMP-dependent signaling pathways, making PDE10A targeting under the control of cAMP/PKA activity, particularly those involving PKA, which influences other signaling proteins and downstream targets like dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP-32) (162, 175). In addition, the mechanism of action of current antipsychotics is reported to be related to activation of the indirect pathway of MSNs in the striatum by the blockade of dopamine D2 receptors, concomitant upregulation of cAMP level, making it essential for monitoring antipsychotic efficacy. PDE10A inhibitors that also cause overactivation of the PDE10A direct pathway could cancel its pharmacological effect (176). In addition, the level of occupancy by PDE10A inhibitors in the striatum has been reported to be directly correlated to an increase in activated cAMP response elements (pCREB), as a marker of neuronal activation (177). Thus, secondary messengers, cAMP and cGMP play critical roles in intracellular signaling, particularly in neuronal pathways involving dopamine and glutamate (178, 179). PDE10A regulates the intracellular concentrations of these nucleotides by catalyzing their hydrolysis to inactive 5’-nucleotides, thereby terminating their downstream signaling cascades (179, 180).
As discussed in the previous section, PDE10A is predominantly expressed in MSNs of the striatum, which are integral to both direct and indirect pathways of the basal ganglia (181, 182). In these neurons, PDE10A critically modulates cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling, which is essential for synaptic plasticity and cognitive function (158, 183). The inhibition of PDE10A results in elevated intracellular cAMP levels, leading to the activation of PKA through its regulatory subunits (184). PKA, in turn, phosphorylates several downstream substrates, including CREB and dopamine- and cAMP-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein 32 kDa (DARPP-32) (185, 186). Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 at threonine-34 (Thr34) converts it into a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 (PP1), whereas phosphorylation at Thr75 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) attenuates PKA signaling (187, 188). In line with these mechanisms, further insights from genetic and pharmacological studies have clarified how specific phosphorylation states of DARPP-32, particularly at Thr34 and Thr75, dictate the differential responses of MSNs to PDE10A inhibition. The phosphorylation of DARPP-32 at Thr75 by Cdk5 converts it into an endogenous PKA inhibitor, dampening cAMP-mediated signaling (183, 188). However, studies in Thr75Ala mutant mice, as well as experiments using Cdk5 inhibition with roscovitine, revealed no significant changes in the D1/D2 imbalance of PDE10A inhibition responses (189). These findings indicate that Thr75 phosphorylation does not critically determine the differential MSN responses to PDE10A inhibition. Taken together, these results highlight that PDE10A inhibition primarily alters neuronal signaling homeostasis through Thr34 phosphorylation of DARPP-32, leading to enhanced PKA signaling and PP1 inhibition in D2 MSNs. This mechanism explains the selective responsiveness of indirect pathway MSNs and supports the role of DARPP-32 as a key molecular switch integrating PDE10A-dependent cAMP/PKA signals in the striatum (175, 190–193). The experimental evidence, including studies using the PDE10A inhibitor papaverine, indicates that these functional outcomes are predominantly mediated by cAMP/PKA signaling, with minimal effects on cGMP/PKG pathways (17, 183). Thus, the higher affinity of PDE10A for cAMP shifts the intracellular signaling balance in MSNs toward cAMP-dependent pathways, providing a mechanistic basis for its effects on striatal function. Through these mechanisms, PDE10A inhibition alters the phosphorylation state of ion channels such as AMPA and GABA-A receptors, thus influencing neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission (194, 195).
As highlighted in recent studies, phosphorylation of DARPP-32 at Thr34 by PKA enhances its ability to inhibit PP1, thereby sustaining PKA-mediated phosphorylation of multiple downstream substrates, including ion channels and receptor subunits (196). This modulation has direct functional implications for receptor sensitivity and neuronal excitability. For example, disruption of DARPP-32 significantly attenuates the phosphorylation of GABAA_AA receptor β1/β3 subunits following D1 receptor stimulation, leading to reduced efficacy of D1 receptor coupling to GABAA_AA receptor currents (197). Functional assays in DARPP-32 knockout mice demonstrated that at low levels of D1 receptor stimulation, the absence of phospho-DARPP-32 markedly diminishes the ability of D1 agonists (e.g., SKF 81297) to modulate GABA-evoked currents. In contrast, at higher agonist concentrations, this deficit can be partially overcome (197). These findings indicate that phospho-DARPP-32 inhibition of PP1 is particularly critical under conditions of submaximal dopaminergic input, where it amplifies the signal-to-noise ratio of D1 receptor signaling to GABAA_AA receptors.
Beyond GABAA receptors, the phosphorylation state of DARPP-32 may also influence other PKA-regulated ion channels such as AMPA receptors, L-type Ca2+ channels, and NMDA receptors, thereby modulating synaptic plasticity and excitability (194, 198, 199). These effects underscore the role of DARPP-32 as a central integrator of dopaminergic and glutamatergic signaling, with PDE10A inhibition indirectly affecting ion channel phosphorylation states through the DARPP-32/PP1 regulatory axis (200).
Given its regulatory role in critical signaling pathways, PDE10A is implicated in the pathophysiology of multiple neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders, including schizophrenia, HD, PD, and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (201, 202). In schizophrenia, PDE10A is implicated due to its high expression in dopaminoceptive MSNs and its role in modulating both dopaminergic and glutamatergic signaling. PDE10A inhibition increases cAMP levels, activating D1-like signaling in the direct pathway and mimicking D2 receptor antagonism in the indirect pathway (185, 190–193). These effects support its therapeutic potential in mitigating both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia (185, 193, 201). In PD, PDE10A expression is downregulated in dopaminergic-depleted regions such as the striatum, correlating with motor dysfunction severity (4, 201, 203, 204). Interestingly, PDE10A levels are upregulated in the nucleus accumbens following dopamine loss, potentially contributing to disease progression [53]. In AD, downregulation of the adenylyl cyclase/cAMP/PKA pathway and inhibition of CREB by β-amyloid plaques contribute to cognitive deficits (201, 205). In HD, a neurodegenerative disorder marked by loss of striatal GABAergic MSNs, PDE10A expression is significantly reduced in advanced stages (142). Despite this, acute inhibition of PDE10A in HD mouse models enhanced corticostriatal input and increased phosphorylation of CREB, suggesting a compensatory therapeutic mechanism (206, 207).
PDE10A is not only involved in CNS disorders but also plays a role in peripheral cancers. It is highly expressed in NSCLC and CRC compared to normal tissues (5, 6). Therefore, inhibiting PDE10A activates the cGMP/PKG pathway, downregulates β-catenin, and promotes apoptosis through caspase and PARP activation (5, 6, 11, 208). It also suppresses MEK/ERK and RAF/MAPK signaling, highlighting its tumor-suppressive potential (5, 11). In the subsequent sections, we will examine the effect of PDE10A in various malignancies.
4 PDE10A as a cancer biomarker
PDE10A has emerged as a context-dependent modulator of tumorigenesis. PDE10A appears to act as either a tumor suppressor or an oncogene based on tissue type and the surrounding tumor microenvironment. This dual role highlights its potential as a valuable biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, and targeted therapy in various cancers (6).
In GBM, PDE10A has been identified as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor located at chromosomal locus 6q27. Combined CRISPR/Cas9 data, human spatial transcriptomic data, and human and mouse RNA sequencing data led to the nomination of PDE10A as a potential haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in the 6q27 region. Loss of PDE10A in GBM correlates with poor prognosis and aggressive tumor phenotypes across multiple GBM cohorts. Mechanistically, the RCAS/tv-a mouse model demonstrates that PDE10A depletion enhances tumorigenicity by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway independent of PTEN. It has been shown that PDE10A suppression leads to increased phosphorylation of AKT (pAKT) and PI3K (p-PI3K) without altering total AKT and PI3K levels, indicating activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. However, PTEN levels were not different between the PDE10A knockdowns and control, showing that PDE10A suppression activates the PI3K/AKT pathway independent of PTEN (209). This is accompanied by a phenotypic shift from proneural to mesenchymal transcriptional state, a hallmark of treatment-resistant GBM (209, 210).
In contrast to GBM, epithelial ovarian cancer, CRC, and NSCLC, showed to have a higher PDE10A expression that contributes to tumor progression, therapy resistance, and reduced patient survival (6, 12, 211). In ovarian cancer, while PDE10A mRNA may be downregulated, elevated protein levels in tumor tissues and cell lines (such as OVCAR8, SKOV3) indicate post-transcriptional regulation (12). High PDE10A expression was also reported to be related to a significant poor overall survival (12).
In NSCLC, elevated PDE10A expression has been observed at both mRNA and protein levels, particularly in lung adenocarcinoma. Its predominant cytoplasmic and membranous localization reflects a tumor-specific pattern (212). Pharmacologic inhibition using selective inhibitors such as Pf-2545920 activates the cGMP/PKG axis, suppresses β-catenin, and inhibits MAPK signaling, leading to decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis (5, 212).
Consistent with these findings, the antitumor activity of PDE10A inhibition in colorectal cancer appears to be primarily mediated through activation of the cGMP/PKG signaling axis rather than the cAMP/PKA pathway. Mechanistically, PKG exerts a dual repressive influence on oncogenic β-catenin signaling. First, it suppresses transcription of the CTNNB1 gene, thereby reducing both β-catenin mRNA expression and protein abundance. Second, PKG promotes the nuclear retention of FOXO4, which sequesters β-catenin and consequently diminishes its availability for TCF-dependent transcriptional activation. Notably, these effects occur independently of proteasome-mediated β-catenin degradation via canonical phosphorylation at Ser33/37/Thr41 (213). By contrast, PKA signaling has been shown to stabilize β-catenin through phosphorylation at Ser552 and Ser675, which enhances its nuclear localization and transcriptional activity (214). These observations indicate that the growth-suppressive effects of PDE10A inhibition in colorectal cancer cells are critically dependent on PKG-mediated downregulation of β-catenin signaling, a mechanism not effectively reproduced by PKA activation.
The PDE10A rs12660420 variant is associated with a higher risk of developing tobacco-related NSCLC. Interestingly, elevated PDE10A expression is linked to better clinical outcomes in patients with early-stage NSCLC (211). In CRC, PDE10A is variably regulated across the neoplastic continuum from precancerous lesions to advanced metastatic stages (6, 215). In vitro, inhibition of PDE10A reduces CRC cell viability, induces G2/M cell cycle arrest, activates caspase-3, and promotes apoptosis (6, 11). Notably, PDE10A is also overexpressed in histologically normal mucosa of CRC patients, suggesting potential as an early detection biomarker (6, 156). Furthermore, decreased PDE10A expression is associated with an EMT phenotype and metastatic disease in colon adenocarcinoma (215). In prostate cancer (PCa), somatic mutations in PDE10A are restricted to tumor tissues and have lower expression in regular counterparts. Upregulation of PDE10A disrupts the cAMP/cGMP balance, elevating pCREB/CREB ratios and activating CREB-dependent oncogenic transcription programs (216). In metastatic gastric cancer, deleterious mutations in PDE10A have been identified exclusively in peritoneal metastases, implicating this gene in metastatic transition and phenotypic plasticity (217).
Beyond solid tumors, paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (PNS) have been associated with anti-PDE10A IgG antibodies. These have been detected in patients presenting with movement disorders and concurrent malignancies such as lung and renal cancers. PDE10A may function as an onconeural antigen, potentially triggering T-cell responses, especially in patients undergoing immune checkpoint blockade (218). Additionally, PDE10A::BRAF fusions have been reported in rare pediatric sarcomas. These fusion drives the aberrant activation of the MAPK pathway, promoting tumorigenesis. Such alterations underscore the therapeutic relevance of PDE10A in precision oncology for pediatric mesenchymal tumors (219, 220).
In summary, PDE10A demonstrates context-specific roles across various cancer types. The differential expression of PDE10A and its regulatory influence on oncogenic pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT, MAPK, and β-catenin pathways, underscores its role in cancer progression. In addition, overexpression of PDE10A in cancer cells and tumors compared to normal cells and normal tissues has been observed (221). Loss of the PDE10A gene locus (6q27) could be considered an independent poor prognostic indicator in IDH wild-type glioblastoma, showing lower overall survival (209). Similarly, PDE10A overexpression in ovarian cancer has been reported to be in association with worse overall survival and upregulation of oncogenic pathways (Wnt/β-catenin, RAS/MAPK) (12). In addition, a study by Zekeridou et al. introduces a novel autoantibody, PDE10A IgG, as a biomarker for a rare paraneoplastic neurological syndrome that affects older adults with cancer (particularly lung, renal, and pancreatic carcinomas) and is characterized by hyperkinetic movement disorders (218). These associations with prognosis and treatment response support its potential as a biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, and targeted therapy in oncology for different tumors (Table 2).
5 PDE10A inhibition in cancer
Elevated PDE10A expression has been documented in multiple cancer types, including colorectal cancer (CRC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (5, 6). Notably, selective PDE10AIs significantly attenuate cell proliferation in several CRC cell lines (HT29, SW480, and HCT116). This antiproliferative effect is reported to be mediated via the cGMP/PKG signaling axis, leading to phosphorylation and functional suppression of β-catenin. Consequently, PDE10AIs offer a novel molecular strategy to inhibit β-catenin-driven transcriptional activity in tumor cells (225). Therefore, Pharmacological inhibition of PDE10A has emerged as a promising strategy in cancer therapeutics due to its selective overexpression in malignant tissues and minimal expression in corresponding normal cells (6–12,). Multiple small-molecule inhibitors have been developed to target PDE10A, including papaverine, PQ-10, PF-2545920 (MP-10), TP-10, ADT-061, and MCI-030. These agents have shown potent anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of such as ovarian, colorectal, lung, and breast cancers. These inhibitors function by elevating intracellular levels of cyclic nucleotides (cAMP and cGMP), leading to activation of the downstream effectors PKA and PKG. The consequent modulation of signaling cascades results in the suppression of key oncogenic pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin, RAS/MAPK, and PI3K/AKT pathways (7, 9, 10, 12, 226). In this context, a study conducted by Kopanitsa et al. examines the effects of 28 PDE inhibitors, including PF-2545920, PQ10, and papaverine, as PDE10A inhibitors on human U87MG, A172, and T98G GBM cells. The results demonstrated that pharmacological inhibition of PDE10A using PF-2545920, particularly in combination with the PDE5 inhibitor MY-5445 and multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 inhibitor reversan, leads to synergistic suppression of GBM cell proliferation in vitro, suggesting a promising low-toxicity therapeutic strategy (224).
Moreover, PF-2545920 and MCI-030 significantly inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cell lines (SKOV3, OV-90, and OVCAR3). These effects were associated with increased phosphorylation of VASP at Ser157 and Ser239, indicating activation of PKA and PKG pathways. These treatments also led to decreased nuclear localization of β-catenin and reduced expression of β-catenin target genes, including c-MYC, survivin, and cyclin D1 (Table 2) (7, 226). MCI-030, a sulindac derivative, demonstrated high potency with an IC50 of ~0.5 µM and achieved stable plasma and ovarian tissue concentrations (~2 µM) after oral administration in murine models, with an excellent safety profile (7). Similarly, ADT-061, another sulindac-derived non-COX-inhibitory compound, selectively targeted colon tumor cells (IC50 = 0.3–0.5 µM), sparing normal colonocytes. It enhanced intracellular cGMP levels, activated PKG, and inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signaling by reducing nuclear β-catenin translocation (9). ADT-061 demonstrated chemopreventive efficacy in Apc^+/Min-FCCC mice by significantly reducing colorectal adenoma burden without observable toxicity (Table 2) (8, 10).
In colon cancer models, PDE10 inhibitors comprising PF-2545920, papaverine, and PQ-10, induced G1-phase cell cycle arrest, inhibited proliferation, and promoted apoptosis, with reduced cytotoxic effects on normal epithelial cells. Similar findings were reported in colon cancer cell lines (HCT116, HT29), where siRNA-mediated PDE10A knockdown mimicked pharmacological inhibition, resulting in decreased cell viability, caspase-dependent apoptosis, and reduced DNA synthesis (6). Notably, both pharmacological inhibition and siRNA approaches selectively activated the cGMP/PKG signaling pathway in cancer cells. This was evidenced by increased phosphorylation of VASP at Ser239, with minimal effect on cAMP/PKA signaling. This functional specificity likely reflects a tumor-context preference for cGMP regulation mediated by PDE10A. It may be attributed to the kinetic properties of the enzyme or the compensatory degradation of cAMP by other PDE isoforms in normal tissues (10). Moreover, stable knockdown of PDE10A using lentiviral shRNA vectors impaired the anchorage-independent growth and colony formation of colon tumor cell lines such as HT-29, SW-480, and HCT-116, reinforcing the critical role of PDE10A in sustaining malignancy (11). At the molecular level, PDE10A inhibition resulted in transcriptional repression of β-catenin target genes, including cyclin D1 and survivin. This effect was likely mediated by nuclear PKG interfering with TCF/LEF transcriptional activity and downregulating CTNNB1 gene expression (Table 2) (10). Collectively, these findings highlight the therapeutic potential of PDE10A inhibition in specific cancer types. The development and preclinical evaluation of selective inhibitors, such as ADT-061 and MCI-030, underscore their efficacy in suppressing tumor growth and promoting apoptosis, while exhibiting minimal toxicity (Figure 1).
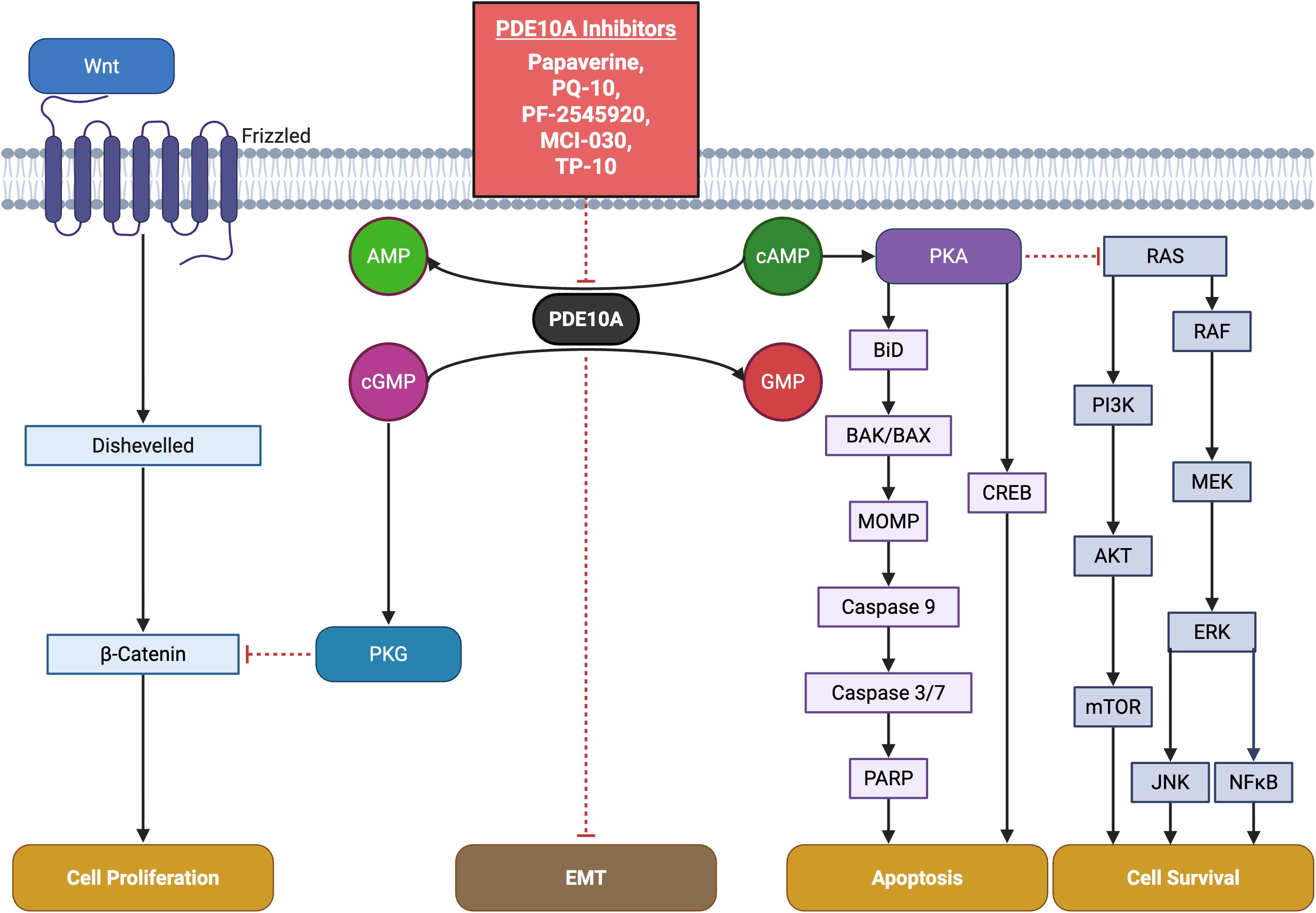
Figure 1. Key pathways involving PDE10A in cancer and pharmacological targeting by small-molecule inhibitors. The schematic highlights critical PDE10A-mediated signaling nodes including cAMP/cGMP, PKA, PKG, and cross-talk with CREB, MAPK, PI3K or Wnt/β-catenin pathways implicated in tumor proliferation, survival, and apoptosis. Known PDE10A inhibitors including TP-10, MCI-030, papaverine, PQ-10, and PF-2545920 and their chemical structures are shown, emphasizing their potential therapeutic for cancer.
However, this finding appears to contrast with the results of Nuechterlein et al, who introduce PDE10A as a potential haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in the 6q27 region. Moreover, they developed a PDE10A-suppressed GBM model using the RCAS/tv-a system in mice, which caused an aggressive glioma phenotype, promoted a proneural-to-mesenchymal transition, and increased resistance to chemo- and radiotherapy. Cell culture analysis also showed that reduced expression of PDE10A activates the PI3K/AKT pathway, contributing to glioma progression and temozolomide resistance (209). This discrepancy may be attributed to differences in experimental models (pharmacologic inhibition vs. genetic knockout), the degree and duration of PDE10A suppression. This suggest that in contrast to acute drug inhibition using small molecules and inhibitors that decrease proliferation of GBM cells, the long-term knockdown may allow for compensatory PI3K/AKT signaling that promotes tumor growth, make it vulnerable to PI3K inhibition (209). Critically, the anti-tumor efficacy of PDE10A inhibitors like PF-2545920 and MCI-030 occurs at concentrations that significantly elevate cyclic nucleotides without immediately activating PI3K/AKT feedback loops in responsive tumors. In addition, combination strategies with PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors may help mitigate compensatory activation, as seen in GBM models where PI3K inhibitors blocked AKT activation induced by PDE10A suppression (209). Accordingly, it also increases the importance of existence and establishing a therapeutic window, describing the dose and period of time of treatment, which may be based on tumor PDE10A expression and PI3K/PTEN status, to maximize efficacy while minimizing the risks of compensatory signaling.
Moreover, pharmacological inhibitors, such as PF-2545920, ADT-061, and MCI-030, selectively elevate intracellular cAMP and/or cGMP, activating PKA or PKG pathways, in ovarian, colorectal, and other cancer models suggesting a tumor-specific preference for cyclic nucleotide regulation, possibly due to kinetic properties of the enzyme or compensatory cAMP degradation by other PDE isoforms. This could be related to the context-dependent manner of PDE10A inhibition, which modulates cAMP and cGMP levels accordingly, leading to differential activation of PKA and PKG across various cancer models. Moreover, this contrast finding may be due to tissue-specific expression of PDE10A isoforms (higher level of cAMP in ovary) (182, 227), baseline cyclic nucleotide levels, and cross-talk with other pathways.
Therefore, while PDE10A inhibition shows promise as a therapeutic strategy under controlled pharmacologic conditions, these divergent outcomes emphasize the need for tumor-specific molecular profiling and careful consideration of potential pro-tumorigenic consequences when translating PDE10A-targeted therapies to the clinic (Figure 2).
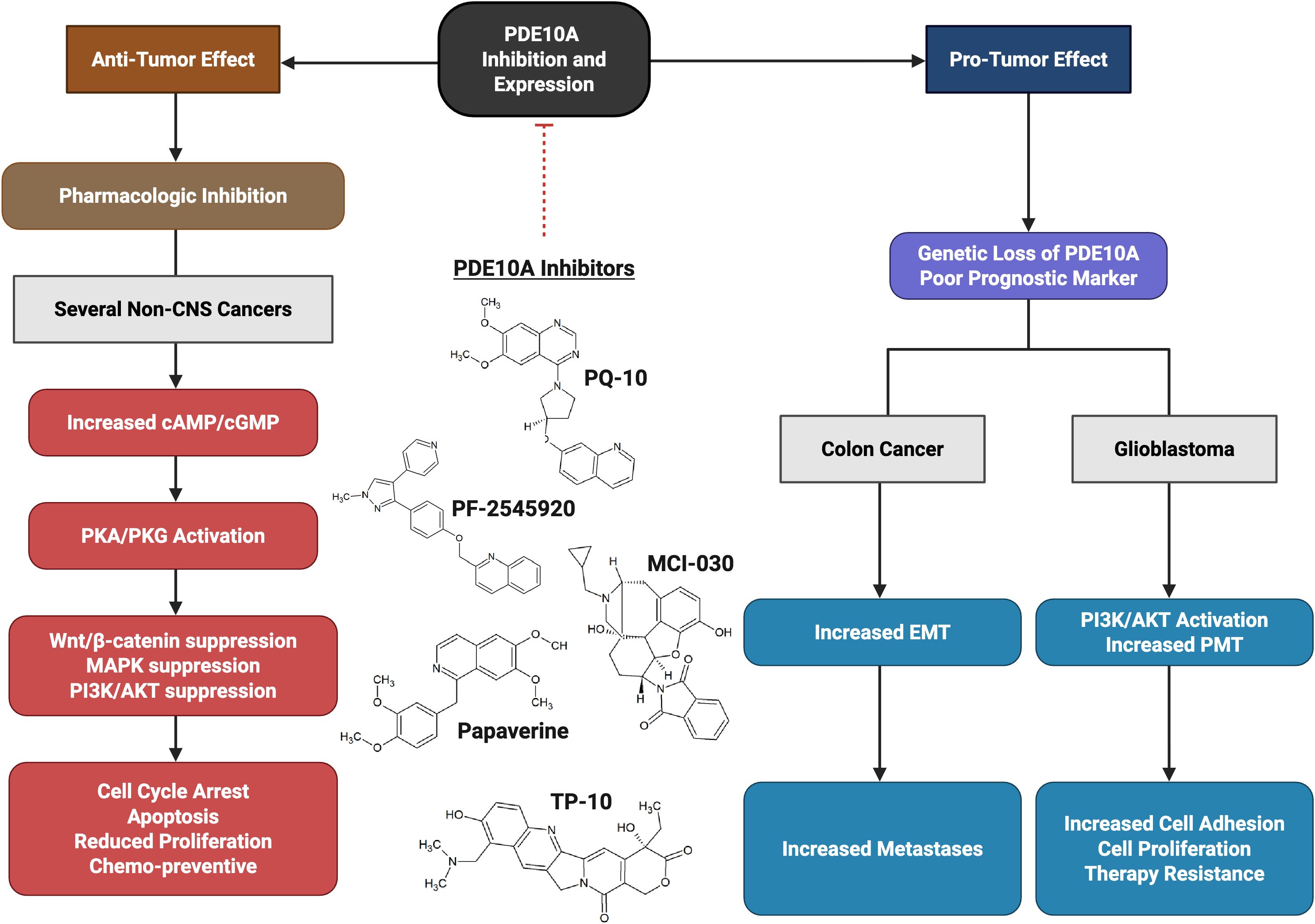
Figure 2. The dual role activity of PDE10A. Tumor promoting role in glioblastoma (GBM) via activation of PI3K/AKT pathway and enhancing proneural–mesenchymal transition (PMT). Anti-tumor activity (most cancers) after inhibition with PDE10A Inhibitors (such as TP-10, MCI-030, papaverine, PQ-10, and PF-2545920) via increase in Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), and suppressing Wnt/β-catenin, RAS/MAPK, and PI3K/AKT.
6 Future direction
Preclinical studies have consistently demonstrated the antitumor efficacy of PDE10A inhibitors across various cancer models. However, clinical translation remains limited. Several PDE10A inhibitors have entered Phase I and II clinical trials for non-oncologic indications, such as schizophrenia (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers: NCT00570063, NCT02477020, NCT02019329, NCT01568203), and have shown favorable safety profiles (228). Despite this, robust data on pharmacokinetics, optimal dosing strategies, and long-term effects in clinical trials of oncology are lacking. Further clinical studies are necessary to determine the therapeutic viability of these approaches in cancer settings. In addition, PDE10A exhibits context-dependent roles within tumor biology. In GBM, it may function as a tumor suppressor (209), whereas in CRC, NSCLC, and ovarian cancers, it contributes to tumor progression (6, 12, 211). The same dual role has been observed and reported in this review article in other PDEs including PDE1, PDE2, PDE4, and PDE7 that could complicate therapeutic development and underscores the need for molecular studies to elucidate tumor-specific signaling contexts and microenvironmental factors that modulate PDE10A activity. Precision targeting requires a clear understanding of these context-dependent mechanisms.
Resistance to PDE10A-targeted monotherapy also presents another significant challenge. Adaptive signaling through compensatory pathways may limit long-term efficacy. Rational combination therapies that co-target synergistic pathways, such as the MAPK pathway, could enhance treatment outcomes (5, 212). Multi-omics integration and computational modeling provide strategic tools for predicting effective drug combinations and resistance mechanisms. Non-invasive imaging and molecular diagnostics should be developed to guide clinical decision-making and improve precision medicine approaches.
Beyond oncology, PDE10A inhibition holds promise in reducing unintended toxicities. Preclinical evidence suggests protective effects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, indicating potential value in cardio-oncology. A broader exploration of PDE10A inhibitors in other disease domains may expand their therapeutic utility (229).
7 Conclusion
PDE10A plays a multifaceted role in both physiological and pathological contexts. Its dual function, as an oncogene in certain cancers, such as CRC, and a tumor suppressor in GBM, highlights the complexity of its molecular regulation and context-dependent activity as seen in other PDEs including PDE1, PDE2, PDE4, and PDE7. Structural insights into its GAF and catalytic domains have expanded our understanding of its unique enzymatic profile. The emerging data position PDE10A as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target, especially in CNS disorders and various malignancies, including GBM, NSCLC, and CRC. Selective PDE10A inhibitors demonstrate promise in preclinical studies, although clinical translation remains in its infancy. Further investigation is warranted to elucidate tissue-specific mechanisms and to develop targeted therapies that utilize the biological functions of PDE10A. In addition, it’s suggested to examine the tissue-specific expression of PDE10A, baseline cyclic nucleotide levels, cross-talk with other pathways, differences in the degree and duration of PDE10A suppression, and the interplay between PDE10A-mediated cyclic nucleotide signaling and compensatory oncogenic pathways for an effective therapy. Additionally, studying the protein expression along with mRNA expression in necessary to consider post-transcriptional regulation. Moreover, it seems a lack of study comparing acute and chronic PDE10A inhibition with genetic tools or pharmacological inhibition with both toxic and non-toxic functional dose to make sure these contrast results are not related to dose, method or duration of suppression. In addition, investigating and considering all these factors seems necessary before any intervention on PDEs, bringing to us the importance of personalized medicine for patients suffering from cancer.
Author contributions
SG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FA: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MJ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke at the National Institutes of Health (PJC).
Acknowledgments
The figures were prepared using Biorender.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kotera J, Fujishige K, Yuasa K, and Omori K. Characterization and phosphorylation of PDE10A2, a novel alternative splice variant of human phosphodiesterase that hydrolyzes cAMP and cGMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (1999) 261:551–7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1013
2. Fujishige K, Kotera J, Michibata H, Yuasa K, Takebayashi S-I, Okumura K, et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel human phosphodiesterase that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP (PDE10A). J Biol Chem. (1999) 274:18438–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.26.18438
3. MacMullen CM, Fallahi M, and Davis RL. Novel PDE10A transcript diversity in the human striatum: Insights into gene complexity, conservation and regulation. Gene. (2017) 606:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.12.033
4. Zagórska A. Phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10) inhibitors: An updated patent review (2014-present). Expert Opin Ther Patents. (2020) 30:147–57. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1709444
5. Zhu B, Lindsey A, Li N, Lee K, Ramirez-Alcantara V, Canzoneri JC, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A is overexpressed in lung tumor cells and inhibitors selectively suppress growth by blocking β-catenin and MAPK signaling. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:69264. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20566
6. Li N, Lee K, Xi Y, Zhu B, Gary BD, Ramírez-Alcántara V, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A: a novel target for selective inhibition of colon tumor cell growth and β-catenin-dependent TCF transcriptional activity. Oncogene. (2015) 34:1499–509. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.94
7. Silva LMD, Gavin E, Lee K, Aragon I, Ramírez-Alcántara V, Scalici J, et al. Abstract A76: Targeting phosphodiesterase 10A for chemoprevention and treatment of ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:A76–A. doi: 10.1158/1557-3265.OVCA15-A76
8. Lee KJ, Chen X, Valiyaveettil J, Lindsey AS, Andrews J, Ramirez-Alcantara V, et al eds. Novel non-COX inhibitory sulindac derivative with PDE10 inhibitory activity reduces incidence and multiplicity of colorectal adenomas in the APC plus/min-FCCC mouse model. 615 Chestnut St, 17th Floor, Philadelphia, PA: Amer Assoc Cancer Research (2017). Cancer Research.
9. Silva LMD, Gavin E, Lee KJ, Ramírez-Alcántara V, Berry KL, Taylor HT, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A inhibition as a novel approach to suppress β-catenin signaling in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:5174. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2017-5174
10. Lee KJ, Chang W-CL, Chen X, Valiyaveettil J, Ramirez-Alcantara V, Gavin E, et al. Suppression of colon tumorigenesis in mutant Apc mice by a novel PDE10 inhibitor that reduces oncogenic β-Catenin. Cancer Prev Res. (2021) 14:995–1008. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-21-0208
11. Lee K, Lindsey AS, Li N, Gary B, Andrews J, Keeton AB, et al. β-catenin nuclear translocation in colorectal cancer cells is suppressed by PDE10A inhibition, cGMP elevation, and activation of PKG. Oncotarget. (2015) 7:5353. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6705
12. Borneman RM, Gavin E, Musiyenko A, Richter W, Lee KJ, Crossman DK, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) as a novel target to suppress β-catenin and RAS signaling in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. (2022) 15:120. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01050-9
13. Jankowska A, Świerczek A, Wyska E, Gawalska A, Bucki A, Pawłowski M, et al. Advances in discovery of PDE10A inhibitors for CNS-related disorders. Part 1: overview of the chemical and biological research. Curr Drug Targets. (2019) 20:122–43. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666180808105056
14. Siuciak JA and Strick CA. Treating neuropsychiatric disorders with PDE10A inhibitors. Drug Discov Today. (2006) 3:527–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ddstr.2006.10.012
15. Azevedo MF, Faucz FR, Bimpaki E, Horvath A, Levy I, de Alexandre RB, et al. Clinical and molecular genetics of the phosphodiesterases (PDEs). Endocrine Rev. (2014) 35:195–233. doi: 10.1210/er.2013-1053
16. Delhaye S and Bardoni B. Role of phosphodiesterases in the pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mol Psychiatry. (2021) 26:4570–82. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00997-9
17. Bender AT and Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev. (2006) 58:488–520. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.5
18. Zhang KY, Card GL, Suzuki Y, Artis DR, Fong D, Gillette S, et al. A glutamine switch mechanism for nucleotide selectivity by phosphodiesterases. Mol Cell. (2004) 15:279–86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.07.005
19. Thul PJ, Åkesson L, Wiking M, Mahdessian D, Geladaki A, Ait Blal H, et al. A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science. (2017) 356:eaal3321. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3321
20. Lakics V, Karran EH, and Boess FG. Quantitative comparison of phosphodiesterase mRNA distribution in human brain and peripheral tissues. Neuropharmacology. (2010) 59:367–74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.05.004
21. Zeisel A, Hochgerner H, Lönnerberg P, Johnsson A, Memic F, van der Zwan J, et al. Molecular architecture of the mouse nervous system. Cell. (2018) 174:999–1014.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.021
22. Goraya TA and Cooper DM. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase (PDE1): current perspectives. Cell signalling. (2005) 17:789–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.12.017
23. Francis SH, Turko IV, and Corbin JD. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: relating structure and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol (2000) 66:241–277. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6603(00)65001-8
24. Shimizu K, Murata T, Tagawa T, Takahashi K, Ishikawa R, Abe Y, et al. Calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE1) is a pharmacological target of differentiation-inducing factor-1, an antitumor agent isolated from Dictyostelium. Cancer Res. (2004) 64:2568–71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3551
25. Shimizu K, Murata T, Watanabe Y, Sato C, Morita H, and Tagawa T. Characterization of phosphodiesterase 1 in human Malignant melanoma cell lines. Anticancer Res. (2009) 29:1119–22.
26. Abusnina A, Alhosin M, Keravis T, Muller CD, Fuhrmann G, Bronner C, et al. Down-regulation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE1A is the key event of p73 and UHRF1 deregulation in thymoquinone-induced acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell apoptosis. Cell signalling. (2011) 23:152–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.08.015
27. Gali-Muhtasib H, Roessner A, and Schneider-Stock R. Thymoquinone: a promising anti-cancer drug from natural sources. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2006) 38:1249–53. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.10.009
28. Zhang C, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Wu Y, Cheng J, Luo K, et al. Phosphodiesterase 1A physically interacts with YTHDF2 and reinforces the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. eLife. (2025) 13:RP98903. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98903
29. Rowther FB, Wei W, Dawson TP, Ashton K, Singh A, Madiesse-Timchou MP, et al. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase-1C (PDE1C) drives cell proliferation, migration and invasion in glioblastoma multiforme cells in vitro. Mol carcinogenesis. (2016) 55:268–79. doi: 10.1002/mc.22276
30. Chen Q, Xing C, Zhang Q, Du Z, Kong J, and Qian Z. PDE1B, a potential biomarker associated with tumor microenvironment and clinical prognostic significance in osteosarcoma. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:13790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64627-y
31. Boynton A JFW. The role of cyclic AMP in cell proliferation: a critical assessment of the evidence. Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research (1983) 15:193–223.
32. Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Jin M, Zhou F, et al. PDE2 inhibits PKA-mediated phosphorylation of TFAM to promote mitochondrial ca(2+)-induced colorectal cancer growth. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:663778. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.663778
33. Bernard JJ, Lou YR, Peng QY, Li T, and Lu YP. PDE2 is a novel target for attenuating tumor formation in a mouse model of UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e109862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109862
34. Murata T, Shimizu K, Kurohara K, Tomeoku A, Koizumi G, and Arai N. Role of phosphodiesterase2A in proliferation and migration of human osteosarcoma cells. Anticancer Res. (2019) 39:6057–62. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13812
35. Chen L, Zhou J, Zhao Z, Zhu Y, Xing J, An J, et al. Low expression of phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2A) promotes the progression by regulating mitochondrial morphology and ATP content and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells. (2023) 12:68. doi: 10.3390/cells12010068
36. De Waal L, Lewis TA, Rees MG, Tsherniak A, Wu X, Choi PS, et al. Identification of cancer-cytotoxic modulators of PDE3A by predictive chemogenomics. Nat Chem Biol. (2016) 12:102–8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1984
37. Nazir M, Senkowski W, Nyberg F, Blom K, Edqvist P-H, Jarvius M, et al. Targeting tumor cells based on Phosphodiesterase 3A expression. Exp Cell Res. (2017) 361:308–15. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.10.032
38. Kumazoe M, Takai M, Hiroi S, Takeuchi C, Yamanouchi M, Nojiri T, et al. PDE3 inhibitor and EGCG combination treatment suppress cancer stem cell properties in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1917. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02162-9
39. Hao N, Shen W, Du R, Jiang S, Zhu J, Chen Y, et al. Phosphodiesterase 3A represents a therapeutic target that drives stem cell–like property and metastasis in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. (2020) 19:868–81. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-1233
40. Bao Z, Feng Y, Wang H, Zhang C, Sun L, Yan Z, et al. Integrated analysis using methylation and gene expression microarrays reveals PDE4C as a prognostic biomarker in human glioma. Oncol Rep. (2014) 32:250–60. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3176
41. Pullamsetti S, Banat G, Schmall A, Szibor M, Pomagruk D, Hänze J, et al. Phosphodiesterase-4 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis of lung cancer by crosstalk with HIF. Oncogene. (2013) 32:1121–34. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.136
42. Peng Y, Li Y, Tian Y, and Ao G. PDE4a predicts poor prognosis and promotes metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. (2018) 9:2389–96. doi: 10.7150/jca.24079
43. Byrne AM, Elliott C, Hoffmann R, and Baillie GS. The activity of cAMP-phosphodiesterase 4D7 (PDE4D7) is regulated by protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation within its unique N-terminus. FEBS letters. (2015) 589:750–5. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.02.004
44. Kashiwagi E, Shiota M, Yokomizo A, Itsumi M, Inokuchi J, Uchiumi T, et al. Downregulation of phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) activates protein kinase A and contributes to the progression of prostate cancer. Prostate. (2012) 72:741–51. doi: 10.1002/pros.21478
45. Tsunoda T, Ota T, Fujimoto T, Doi K, Tanaka Y, Yoshida Y, et al. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) activity triggers luminal apoptosis and AKT dephosphorylation in a 3-D colonic-crypt model. Mol cancer. (2012) 11:1–12. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-46
46. Su R, Narenmandula, Qiao X, and Hu Q. PDE4B promotes the progression of gastric cancer via the PI3K/AKT/MYC pathway and immune infiltration. Am J Cancer Res. (2024) 14:3451–67. doi: 10.62347/TYOS8160
47. Huang Z, Liu J, Yang J, Yan Y, Yang C, He X, et al. PDE4B induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer cells and is transcriptionally suppressed by CBX7. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.783050
48. Moon E-Y and Lerner A. PDE4 inhibitors activate a mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells that is regulated by protein phosphatase 2A. Blood J Am Soc Hematology. (2003) 101:4122–30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3208
49. Sponziello M, Verrienti A, Rosignolo F, De Rose RF, Pecce V, Maggisano V, et al. PDE5 expression in human thyroid tumors and effects of PDE5 inhibitors on growth and migration of cancer cells. Endocrine. (2015) 50:434–41. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0586-x
50. Houslay MD. Hard times for oncogenic BRAF-expressing melanoma cells. Cancer Cell. (2011) 19:3–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.004
51. Liu N, Mei L, Fan X, Tang C, Ji X, Hu X, et al. Phosphodiesterase 5/protein kinase G signal governs stemness of prostate cancer stem cells through Hippo pathway. Cancer Letters. (2016) 378:38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.05.010
52. Chang J-F, Hsu J-L, Sheng Y-H, Leu W-J, Yu C-C, Chan S-H, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors sensitize topoisomerase II inhibitors in killing prostate cancer through PDE5-independent impairment of HR and NHEJ DNA repair systems. Front Oncol. (2019) 8. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00681
53. Li Q and Shu Y. Pharmacological modulation of cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of anti-cancer drugs by PDE5 inhibitors in lung cancer cells. Pharm Res. (2014) 31:86–96. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1134-0
54. Barone I, Panza S, Giordano C, Gyorffy B, Augimeri G, Gelsomino L, et al. Role of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in breast cancer stroma: implications for targeted therapy. FASEB J. (2019) 33:496.1–.1. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2019.33.1_supplement.496.1
55. Singh M, Kasna S, Roy S, Aldosary S, Saeedan AS, Ansari MN, et al. Repurposing mechanistic insight of PDE-5 inhibitor in cancer chemoprevention through mitochondrial-oxidative stress intervention and blockade of DuCLOX signalling. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:996. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6152-9
56. Catalano S, Campana A, Giordano C, Győrffy B, Tarallo R, Rinaldi A, et al. Expression and function of phosphodiesterase type 5 in human breast cancer cell lines and tissues: implications for targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:2271–82. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1900
57. Huang W, Sundquist J, Sundquist K, and Ji J. Use of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors is associated with lower risk of colorectal cancer in men with benign colorectal neoplasms. Gastroenterology. (2019) 157:672–81.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.012
58. Chhonker SK, Rawat D, and Koiri RK. Repurposing PDE5 inhibitor tadalafil and sildenafil as anticancer agent against hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting key events of glucose metabolism and multidrug resistance. J Biochem Mol Toxicology. (2022) 36:e23100. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23100
59. Wesolowski R, Markowitz J, and Carson WE. Myeloid derived suppressor cells–a new therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. J immunotherapy cancer. (2013) 1:1–11. doi: 10.1186/2051-1426-1-10
60. Lin S, Wang J, Wang L, Wen J, Guo Y, Qiao W, et al. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition suppresses colonic inflammation-induced tumorigenesis via blocking the recruitment of MDSC. Am J Cancer Res. (2017) 7:41.
61. Sharpe BP, Hayden A, Manousopoulou A, Cowie A, Walker RC, Harrington J, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors enhance chemotherapy in preclinical models of esophageal adenocarcinoma by targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3:100541. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100541
62. Booth L, Roberts JL, Cruickshanks N, Conley A, Durrant DE, Das A, et al. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors enhance chemotherapy killing in gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. (2014) 85:408–19. doi: 10.1124/mol.113.090043
63. Zhang Z, Huang W, Huang D, Xu Z, Xie Q, Tan X, et al. Repurposing of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil as a therapeutic agent to prevent gastric cancer growth through suppressing c-MYC stability for IL-6 transcription. Commun Biol. (2025) 8:85. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07519-9
64. Lagman D, Franzén IE, Eggert J, Larhammar D, and Abalo XM. Evolution and expression of the phosphodiesterase 6 genes unveils vertebrate novelty to control photosensitivity. BMC Evolutionary Biol. (2016) 16:1–20. doi: 10.1186/s12862-016-0695-z
65. Stevens RG. Testing the light-at-night (LAN) theory for breast cancer causation. Chronobiology Int. (2011) 28:653–6. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2011.606945
66. Yalaz C, Bridges E, Alham NK, Zois CE, Chen J, Bensaad K, et al. Cone photoreceptor phosphodiesterase PDE6H inhibition regulates cancer cell growth and metabolism, replicating the dark retina response. Cancer Metab. (2024) 12:5. doi: 10.1186/s40170-023-00326-y
67. Dietrich P, Hellerbrand C, and Bosserhoff A. The delta subunit of rod-specific photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE6D) contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancers. (2019) 11:398. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030398
68. Fang C, Dong H-J, Zou Z-J, Fan L, Wang L, Zhang R, et al. High expression of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 7B mRNA predicts poor prognosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Leukemia Res. (2013) 37:536–40. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2013.02.006
69. Zhang L, Murray F, Zahno A, Kanter JR, Chou D, Suda R, et al. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase profiling reveals increased expression of phosphodiesterase 7B in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2008) 105:19532–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806152105
70. Yamamoto N, Nishikawa R, Chiyomaru T, Goto Y, Fukumoto I, Usui H, et al. The tumor-suppressive microRNA-1/133a cluster targets PDE7A and inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in endometrial cancer. Int J Oncol. (2015) 47:325–34. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2986
71. Hao L and Yu H. MiR-23b inhibits cell migration and invasion through targeting PDE7A in colon cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2017) 10:9436–43.
72. Brooks MD, Jackson E, Warrington NM, Luo J, Forys JT, Taylor S, et al. PDE7B is a novel, prognostically significant mediator of glioblastoma growth whose expression is regulated by endothelial cells. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e107397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107397
73. Zhang DD, Li Y, Xu Y, Kim J, and Huang S. Phosphodiesterase 7B/microRNA-200c relationship regulates triple-negative breast cancer cell growth. Oncogene. (2019) 38:1106–20. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0499-2
74. Zahno AC, Murray F, Zhang L, Rassenti L, Cottam H, Kipps T, et al. Phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) and PDE4/7 inhibitors kill chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells via a cAMP-mitochondrial-dependent pathway. FASEB J. (2009) 23:761.10–.10. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.23.1_supplement.761.10
75. Du Y, Xu Y, Guo X, Tan C, Zhu X, Liu G, et al. Methylation-regulated tumor suppressor gene PDE7B promotes HCC invasion and metastasis through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. BMC Cancer. (2024) 24:624. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12364-w
76. Sun Y, Zou J, Ouyang W, and Chen K. Identification of PDE7B as a potential core gene involved in the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. (2020) 12:5701–12. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S259192
77. Brown KM, Day JP, Huston E, Zimmermann B, Hampel K, Christian F, et al. Phosphodiesterase-8A binds to and regulates Raf-1 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:E1533–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303004110
78. Karami-Tehrani F, Moeinifard M, Aghaei M, and Atri M. Evaluation of PDE5 and PDE9 expression in benign and Malignant breast tumors. Arch Med Res. (2012) 43:470–5. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.08.006
79. Saravani R, Karami-Tehrani F, Hashemi M, Aghaei M, and Edalat R. Inhibition of phosphodiestrase 9 induces c GMP accumulation and apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468. Cell proliferation. (2012) 45:199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2012.00819.x
80. Zhu B, Lee K, Canzoneri J, Ramirez-Alcantara V, Sigler S, Gary B, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A inhibition suppresses lung tumor cell growth by activating PKG to inhibit ras and Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:4372. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2015-4372
81. Vezzosi D, Libé R, Baudry C, Rizk-Rabin M, Horvath A, Levy I, et al. Phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A) gene defects in patients with ACTH-independent macronodular adrenal hyperplasia (AIMAH): functional variants may contribute to genetic susceptibility of bilateral adrenal tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:E2063–E9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2275
82. Libé R, Horvath A, Vezzosi D, Fratticci A, Coste J, Perlemoine K, et al. Frequent phosphodiesterase 11A gene (PDE11A) defects in patients with Carney complex (CNC) caused by PRKAR1A mutations: PDE11A may contribute to adrenal and testicular tumors in CNC as a modifier of the phenotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 96:E208–E14. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1704
83. Engström PG, Tommei D, Stricker SH, Ender C, Pollard SM, and Bertone P. Digital transcriptome profiling of normal and glioblastoma-derived neural stem cells identifies genes associated with patient survival. Genome Med. (2012) 4:1–20. doi: 10.1186/gm377
84. Peng T, Gong J, Jin Y, Zhou Y, Tong R, Wei X, et al. Inhibitors of phosphodiesterase as cancer therapeutics. Eur J medicinal Chem. (2018) 150:742–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.046
85. Martins TJ, Mumby M, and Beavo J. Purification and characterization of a cyclic GMP-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from bovine tissues. J Biol Chem. (1982) 257:1973–9. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)68134-2
86. Sadek MS, Cachorro E, El-Armouche A, and Kämmerer S. Therapeutic implications for PDE2 and cGMP/cAMP mediated crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7462. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207462
87. Rosman GJ, Martins TJ, Sonnenburg WK, Beavo JA, Ferguson K, and Loughney K. Isolation and characterization of human cDNAs encoding a cGMP-stimulated 3′, 5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Gene. (1997) 191:89–95. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00046-2
88. Norris RP, Ratzan WJ, Freudzon M, Mehlmann LM, Krall J, Movsesian MA, et al. Cyclic GMP from the surrounding somatic cells regulates cyclic AMP and meiosis in the mouse oocyte. Development (2009) 136:186–1878. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.05.115
89. Keravis T, Silva AP, Favot L, and Lugnier C. Role of PDEs in vascular health and disease: endothelial PDEs and angiogenesis. In: Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases in health and disease. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA (2006). p. 417–39.
90. Podzuweit T, Nennstiel P, and Müller A. Isozyme selective inhibition of cGMP-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases by erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl) adenine. Cell signalling. (1995) 7:733–8. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(95)00042-N
91. Masood A, Huang Y, Hajjhussein H, Xiao L, Li H, Wang W, et al. Anxiolytic effects of phosphodiesterase-2 inhibitors associated with increased cGMP signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2009) 331:690–9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.156729
92. Hiramoto K, Murata T, Shimizu K, Morita H, Inui M, Manganiello VC, et al. Role of phosphodiesterase 2 in growth and invasion of human Malignant melanoma cells. Cell signalling. (2014) 26:1807–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.03.031
93. Morita H, Murata T, Shimizu K, Okumura K, Inui M, and Tagawa T. Characterization of phosphodiesterase 2A in human Malignant melanoma PMP cells. Oncol Rep. (2013) 29:1275–84. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2260
94. Beavo JA. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: functional implications of multiple isoforms. Physiol Rev. (1995) 75:725–48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.4.725
95. Wechsler J, Choi Y-H, Krall J, Ahmad F, Manganiello VC, and Movsesian MA. Isoforms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE3A in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:38072–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203647200
96. Keravis T and Lugnier C. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDE) and peptide motifs. Curr Pharm design. (2010) 16:1114–25. doi: 10.2174/138161210790963760
97. Omori K and Kotera J. Overview of PDEs and their regulation. Circ Res. (2007) 100:309–27. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000256354.95791.f1
98. Shakur Y, Holst LS, Landstrom TR, Movsesian M, Degerman E, and Manganiello V. Regulation and function of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3) gene family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol (2000) 66:241–277. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6603(00)66031-2
99. Beca S, Ahmad F, Shen W, Liu J, Makary S, Polidovitch N, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 3A regulates basal myocardial contractility through interacting with sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase type 2a signaling complexes in mouse heart. Circ Res. (2013) 112:289–97. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.300003
100. Ahmad F, Degerman E, and Manganiello V. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3 signaling complexes. Hormone Metab Res. (2012) 44:776–85. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1312646
101. Lanfear DE, Hasan R, Gupta RC, Williams C, Czerska B, Tita C, et al. Short term effects of milrinone on biomarkers of necrosis, apoptosis, and inflammation in patients with severe heart failure. J Trans Med. (2009) 7:1–6. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-67
102. Bolger G, Michaeli T, Martins T, St John T, Steiner B, Rodgers L, et al. A family of human phosphodiesterases homologous to the dunce learning and memory gene product of Drosophila melanogaster are potential targets for antidepressant drugs. Mol Cell Biol. (1993) 13:6558–71. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6558-6571
103. Houslay MD, Schafer P, and Zhang KY. Keynote review: phosphodiesterase-4 as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov Today. (2005) 10:1503–19. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03622-6
104. Eskandari N, Mirmosayyeb O, Bordbari G, Bastan R, Yousefi Z, and Andalib A. A short review on structure and role of cyclic-3’, 5’-adenosine monophosphate-specific phosphodiesterase 4 as a treatment tool. J Res Pharm practice. (2015) 4:175–81. doi: 10.4103/2279-042X.167043
105. Marko D, Pahlke G, Merz K-H, and Eisenbrand G. Cyclic 3 ‘, 5 ‘-nucleotide phosphodiesterases: potential targets for anticancer therapy. Chem Res toxicology. (2000) 13:944–8. doi: 10.1021/tx000090l
106. Sengupta R, Sun T, Warrington NM, and Rubin JB. Treating brain tumors with PDE4 inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2011) 32:337–44. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.02.015
107. Kolosionek E, Savai R, Ghofrani HA, Weissmann N, Guenther A, Grimminger F, et al. Expression and activity of phosphodiesterase isoforms during epithelial mesenchymal transition: the role of phosphodiesterase 4. Mol Biol Cell. (2009) 20:4751–65. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0019
108. Kong X, Ai G, Wang D, Chen R, Guo D, Yao Y, et al. PDE4 and Epac1 Synergistically Promote Rectal Carcinoma via the cAMP Pathway. Analytical Cell Pathology. (2019) 2019:7145198. doi: 10.1155/2019/7145198
109. Serrels B, Sandilands E, and Frame MC. Signaling of the direction-sensing FAK/RACK1/PDE4D5 complex to the small GTPase Rap1. Small GTPases. (2011) 2:1086–92. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.2.1.15137
110. Kelly K, Mejia A, Suhasini AN, Lin A-P, Kuhn J, Karnad AB, et al. Safety and pharmacodynamics of the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in advanced B-cell Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:1186–92. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1207
111. Mukherjee P, Bagchi A, Banerjee A, Roy H, Bhattacharya A, Biswas A, et al. PDE4 inhibitor eliminates breast cancer stem cells via noncanonical activation of mTOR. J Cell Biochem. (2022) 123:1980–96. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30325
112. Mishra RR, Belder N, Ansari SA, Kayhan M, Bal H, Raza U, et al. Reactivation of cAMP pathway by PDE4D inhibition represents a novel druggable axis for overcoming tamoxifen resistance in ER-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 24:1987–2001. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2776
113. Liu F, Ma J, Wang K, Li Z, Jiang Q, Chen H, et al. High expression of PDE4D correlates with poor prognosis and clinical progression in pancreaticductal adenocarcinoma. J Cancer. (2019) 10:6252–60. doi: 10.7150/jca.35443
114. Cao M, Nawalaniec K, Ajay AK, Luo Y, Moench R, Jin Y, et al. PDE4D targeting enhances anti-tumor effects of sorafenib in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and attenuates MAPK/ERK signaling in a CRAF-dependent manner. Trans Oncol. (2022) 19:101377. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101377
115. Kotera J, Fujishige K, Imai Y, Kawai E, Michibata H, Akatsuka H, et al. Genomic origin and transcriptional regulation of two variants of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterases. Eur J Biochem. (1999) 262:866–73. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00450.x
116. Wang H, Robinson H, and Ke H. Conformation changes, N-terminal involvement, and cGMP signal relay in the phosphodiesterase-5 GAF domain. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:38149–56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.141614
117. Giordano D, De Stefano ME, Citro G, Modica A, and Giorgi M. Expression of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) in mouse tissues and cell lines using an antibody against the enzyme amino-terminal domain. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res. (2001) 1539:16–27. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4889(01)00086-6
118. Barone I, Giordano C, Bonofiglio D, Catalano S, and Andò S. Phosphodiesterase type 5 as a candidate therapeutic target in cancers. Curr pathobiology Rep. (2015) 3:193–201. doi: 10.1007/s40139-015-0083-1
119. Cesarini V, Martini M, Vitiani LR, Gravina GL, Di Agostino S, Graziani G, et al. Type 5 phosphodiesterase regulates glioblastoma multiforme aggressiveness and clinical outcome. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:13223. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14656
120. Jamnagerwalla J, Howard LE, Vidal AC, Moreira DM, Castro-Santamaria R, Andriole GL, et al. The association between phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors and prostate cancer: results from the REDUCE study. J Urol. (2016) 196:715–20. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.03.172
121. Wang R, Islam BN, Bridges A, Sharman SK, Hu M, Hou Y, et al. cGMP signaling increases antioxidant gene expression by activating forkhead box O3A in the colon epithelium. Am J Pathology. (2017) 187:377–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.10.016
122. Cote RH. Characteristics of photoreceptor PDE (PDE6): similarities and differences to PDE5. Int J impotence Res. (2004) 16:S28–33. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901212
123. Tcheudji JFK, Lebeau L, Virmaux N, Maftei CG, Cote RH, Lugnier C, et al. Molecular organization of bovine rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase 6. J Mol Biol. (2001) 310:781–91. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4813
124. Muradov H, Boyd KK, and Artemyev NO. Structural determinants of the PDE6 GAF A domain for binding the inhibitory γ-subunit and noncatalytic cGMP. Vision Res. (2004) 44:2437–44. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2004.05.013
125. Qureshi BM, Behrmann E, Schöneberg J, Loerke J, Bürger J, Mielke T, et al. Asymmetric properties of rod cGMP Phosphodiesterase 6 (PDE6): structural and functional analysis. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. (2015) 16:1–2. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-16-S1-A76
126. Dong H, Claffey KP, Brocke S, and Epstein PM. Expression of phosphodiesterase 6 (PDE6) in human breast cancer cells. Springerplus. (2013) 2:1–10. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-680
127. Michaeli T, Bloom T, Martins T, Loughney K, Ferguson K, Riggs M, et al. Isolation and characterization of a previously undetected human cAMP phosphodiesterase by complementation of cAMP phosphodiesterase-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. (1993) 268:12925–32. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)31474-1
128. Han P, Sonati P, Rubin C, and Michaeli T. PDE7A1, a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase, inhibits cAMP-dependent protein kinase by a direct interaction with C. J Biol Chem. (2006) 281:15050–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601333200
129. Morales-Garcia JA, Aguilar-Morante D, Hernandez-Encinas E, Alonso-Gil S, Gil C, Martinez A, et al. Silencing phosphodiesterase 7B gene by lentiviral-shRNA interference attenuates neurodegeneration and motor deficits in hemiparkinsonian mice. Neurobiol aging. (2015) 36:1160–73. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.10.008
130. Gamanuma M, Yuasa K, Sasaki T, Sakurai N, Kotera J, and Omori K. Comparison of enzymatic characterization and gene organization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 8 family in humans. Cell signalling. (2003) 15:565–74. doi: 10.1016/S0898-6568(02)00146-8
131. Jorde R, Schirmer H, Wilsgaard T, Joakimsen RM, Mathiesen EB, Njølstad I, et al. The phosphodiesterase 8B gene rs4704397 is associated with thyroid function, risk of myocardial infarction, and body height: the Tromsø study. Thyroid. (2014) 24:215–22. doi: 10.1089/thy.2013.0177
132. Patrucco E, Albergine MS, Santana LF, and Beavo JA. Phosphodiesterase 8A (PDE8A) regulates excitation–contraction coupling in ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2010) 49:330–3. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.03.016
133. Gilles-Gonzalez M-A and Gonzalez G. Signal transduction by heme-containing PAS-domain proteins. J Appl Physiol. (2004) 96:774–83. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00941.2003
134. Rothenbuhler A, Horvath A, Libé R, Faucz FR, Fratticci A, Raffin Sanson ML, et al. Identification of novel genetic variants in phosphodiesterase 8B (PDE8B), a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase highly expressed in the adrenal cortex, in a cohort of patients with adrenal tumours. Clin endocrinology. (2012) 77:195–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2012.04366.x
135. Singh N and Patra S. Phosphodiesterase 9: insights from protein structure and role in therapeutics. Life Sci. (2014) 106:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.04.007
136. Huang M, Shao Y, Hou J, Cui W, Liang B, Huang Y, et al. Structural asymmetry of phosphodiesterase-9A and a unique pocket for selective binding of a potent enantiomeric inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol. (2015) 88:836–45. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.099747
137. van der Staay FJ, Rutten K, Bärfacker L, DeVry J, Erb C, Heckroth H, et al. The novel selective PDE9 inhibitor BAY 73–6691 improves learning and memory in rodents. Neuropharmacology. (2008) 55:908–18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.07.005
138. Schmidt CJ. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors as potential cognition enhancing agents. Curr topics medicinal Chem. (2010) 10:222–30. doi: 10.2174/156802610790411009
139. Loughney K, Snyder P, Uher L, Rosman G, Ferguson K, and Florio V. Isolation and characterization of PDE10A, a novel human 3′, 5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Gene. (1999) 234:109–17. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00171-7
140. Kehler J, Ritzén A, and Greve DR. The potential therapeutic use of phosphodiesterase 10 inhibitors. Expert Opin Ther Patents. (2007) 17:147–58. doi: 10.1517/13543776.17.2.147
141. Gross-Langenhoff M, Hofbauer K, Weber J, Schultz A, and Schultz JE. cAMP is a ligand for the tandem GAF domain of human phosphodiesterase 10 and cGMP for the tandem GAF domain of phosphodiesterase 11. J Biol Chem. (2006) 281:2841–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511468200
142. Hebb A, Robertson H, and Denovan-Wright E. Striatal phosphodiesterase mRNA and protein levels are reduced in Huntington′ s disease transgenic mice prior to the onset of motor symptoms. Neuroscience. (2004) 123:967–81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.11.009
143. Lindsey AS, Lee K, Zhu B, Arora R, Otali D, Ramirez-Alacantara V, et al. PDE10A overexpression in cancer cells and tumors as compared to normal cells and tissues. Cancer Res. (2016) 76:4736. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2016-4736
144. Russo S, Li N, Lee K, Xi Y, Zhu B, Gary B, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10, a novel target in colon cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:503. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.32.3_suppl.503
145. Lee KJ, Li N, Chen X, Zhu B, Yet L, and Piazza G. Phosphodiesterase 10, a novel target for colorectal cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:1762. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2014-1762
146. Fawcett L, Baxendale R, Stacey P, McGrouther C, Harrow I, Soderling S, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct human phosphodiesterase gene family: PDE11A. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2000) 97:3702–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.7.3702
147. Makhlouf A, Kshirsagar A, and Niederberger C. Phosphodiesterase 11: a brief review of structure, expression and function. Int J impotence Res. (2006) 18:501–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901441
148. Yuasa K, Kanoh Y, Okumura K, and Omori K. Genomic organization of the human phosphodiesterase PDE11A gene: evolutionary relatedness with other PDEs containing GAF domains. Eur J Biochem. (2001) 268:168–78. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2001.01866.x
149. Horvath A, Korde L, Greene MH, Libe R, Osorio P, Faucz FR, et al. Functional phosphodiesterase 11A mutations may modify the risk of familial and bilateral testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer Res. (2009) 69:5301–6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0884
150. Kaneda T, Kido Y, Tajima T, Urakawa N, and Shimizu K. PDE4 and PDE5 regulate cyclic nucleotide contents and relaxing effects on carbachol-induced contraction in the bovine abomasum. J Veterinary Med Science. (2015) 77:15–9. doi: 10.1292/jvms.14-0248
151. D’Andrea MR, Qiu Y, Haynes-Johnson D, Bhattacharjee S, Kraft P, and Lundeen S. Expression of PDE11A in normal and Malignant human tissues. J Histochem Cytochemistry. (2005) 53:895–903. doi: 10.1369/jhc.5A6625.2005
152. Faucz FR, Horvath A, Rothenbuhler A, Almeida MQ, Libe R, Raffin-Sanson M-L, et al. Phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A) genetic variants may increase susceptibility to prostatic cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 96:E135–E40. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1655
153. Horvath A, Giatzakis C, Robinson-White A, Boikos S, Levine E, Griffin K, et al. Adrenal hyperplasia and adenomas are associated with inhibition of phosphodiesterase 11A in carriers of PDE11A sequence variants that are frequent in the population. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:11571–5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2914
154. MacMullen C, Vick K, Pacifico R, Fallahi-Sichani M, and Davis R. Novel, primate-specific PDE10A isoform highlights gene expression complexity in human striatum with implications on the molecular pathology of bipolar disorder. Trans Psychiatry. (2016) 6:e742–e. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.3
155. Seeger TF, Bartlett B, Coskran TM, Culp JS, James LC, Krull DL, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of PDE10A in the rat brain. Brain Res. (2003) 985:113–26. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(03)02754-9
156. Coskran TM, Morton D, Menniti FS, Adamowicz WO, Kleiman RJ, Ryan AM, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of phosphodiesterase 10A in multiple mammalian species. J Histochem Cytochem. (2006) 54:1205–13. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A6930.2006
157. Bonate R, Kurek G, Hrabak M, Patterson S, Padovan-Neto F, West AR, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A): regulator of dopamine agonist-induced gene expression in the striatum. Cells. (2022) 11:597–607. doi: 10.3390/cells11142214
158. Xie Z, Adamowicz WO, Eldred WD, Jakowski AB, Kleiman RJ, Morton DG, et al. Cellular and subcellular localization of PDE10A, a striatum-enriched phosphodiesterase. Neuroscience. (2006) 139:597–607. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.12.042
159. Birjandi SZ, Abduljawad N, Nair S, Dehghani M, Suzuki K, Kimura H, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A inhibition leads to brain region-specific recovery based on stroke type. Transl Stroke Res. (2021) 12:303–15. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00819-8
160. Marshall RD and Menniti FS. Tepper MA. A novel PDE10A inhibitor for tourette syndrome and other movement disorders. Cells. (2024) 13:1230. doi: 10.3390/cells13141230
161. Menniti FS, Chappie TA, and Schmidt CJ. PDE10A inhibitors-clinical failure or window into antipsychotic drug action? Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:600178. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.600178
162. Russwurm C, Koesling D, and Russwurm M. Phosphodiesterase 10A is tethered to a synaptic signaling complex in striatum. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290:11936–47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595769
163. Giralt A, Saavedra A, Carretón O, Arumí H, Tyebji S, Alberch J, et al. PDE10 inhibition increases GluA1 and CREB phosphorylation and improves spatial and recognition memories in a Huntington’s disease mouse model. Hippocampus. (2013) 23:684–95. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22128
164. Zhang Y, Gao B, Zheng F, Lu S, Li Y, Xiong Y, et al. The phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor PF-2545920 enhances hippocampal excitability and seizure activity involving the upregulation of gluA1 and NR2A in post-synaptic densities. Front Mol Neurosci. (2017) 10. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00100
165. Conti M and Beavo J. Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu Rev Biochem. (2007) 76:481–511. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.060305.150444
166. Kehler J and Nielsen J. PDE10A inhibitors: novel therapeutic drugs for schizophrenia. Curr Pharm design. (2011) 17:137–50. doi: 10.2174/138161211795049624
167. Zoraghi R, Corbin JD, and Francis SH. Properties and functions of GAF domains in cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and other proteins. Mol Pharmacol. (2004) 65:267–78. doi: 10.1124/mol.65.2.267
168. Handa N, Mizohata E, Kishishita S, Toyama M, Morita S, Uchikubo-Kamo T, et al. Crystal structure of the GAF-B domain from human phosphodiesterase 10A complexed with its ligand, cAMP. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:19657–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800595200
169. Wang H, Liu Y, Hou J, Zheng M, Robinson H, and Ke H. Structural insight into substrate specificity of phosphodiesterase 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2007) 104:5782–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700279104
170. Card GL, England BP, Suzuki Y, Fong D, Powell B, Lee B, et al. Structural basis for the activity of drugs that inhibit phosphodiesterases. Structure. (2004) 12:2233–47. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.10.004
171. Manallack DT, Hughes RA, and Thompson PE. The next generation of phosphodiesterase inhibitors: structural clues to ligand and substrate selectivity of phosphodiesterases. J medicinal Chem. (2005) 48:3449–62. doi: 10.1021/jm040217u
172. Verhoest PR, Chapin DS, Corman M, Fonseca K, Harms JF, Hou X, et al. Discovery of a novel class of phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitors and identification of clinical candidate 2-[4-(1-methyl-4-pyridin-4-yl-1 H-pyrazol-3-yl)-phenoxymethyl]-quinoline (PF-2545920) for the treatment of schizophrenia. J medicinal Chem. (2009) 52:5188–96. doi: 10.1021/jm900521k
173. Seko N, Yoshino K, Yokota K, and Tsukamoto G. Synthesis and platelet aggregation inhibitory activity of diphenylazole derivatives. I. Thiazole and imidazole derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). (1991) 39:651–7. doi: 10.1248/cpb.39.651
174. Heckman PR, Van Duinen MA, Bollen EP, Nishi A, Wennogle LP, Blokland A, et al. Phosphodiesterase inhibition and regulation of dopaminergic frontal and striatal functioning: clinical implications. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2016) 19:pyw030. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw030
175. Polito M, Guiot E, Gangarossa G, Longueville S, Doulazmi M, Valjent E, et al. Selective effects of PDE10A inhibitors on striatopallidal neurons require phosphatase inhibition by DARPP-32. eNeuro. (2015) 2:ENEURO.0060–15. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0060-15.2015
176. Suzuki K, Harada A, Suzuki H, Miyamoto M, and Kimura H. TAK-063, a PDE10A inhibitor with balanced activation of direct and indirect pathways, provides potent antipsychotic-like effects in multiple paradigms. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2016) 41:2252–62. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.20
177. Li Y-W, Seager MA, Wojcik T, Heman K, Molski TF, Fernandes A, et al. Biochemical and behavioral effects of PDE10A inhibitors: Relationship to target site occupancy. Neuropharmacology. (2016) 102:121–35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.10.037
178. Beavo JA and Brunton LL. Cyclic nucleotide research—still expanding after half a century. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2002) 3:710–7. doi: 10.1038/nrm911
179. Snyder GL and Vanover KE. PDE inhibitors for the treatment of schizophrenia. In: Phosphodiesterases: CNS Functions and Diseases. Springer: London (2017).
180. Francis SH, Blount MA, and Corbin JD. Mammalian cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular mechanisms and physiological functions. Physiol Rev. (2011) 91:651–90. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2010
181. Fujishige K, Kotera J, and Omori K. Striatum-and testis-specific phosphodiesterase PDE10A: Isolation and characterization of a rat PDE10A. Eur J Biochem. (1999) 266:1118–27. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00963.x
182. Soderling SH, Bayuga SJ, and Beavo JA. Isolation and characterization of a dual-substrate phosphodiesterase gene family: PDE10A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1999) 96:7071–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.7071
183. Nishi A, Kuroiwa M, Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP, Bateup HS, Shuto T, et al. Distinct roles of PDE4 and PDE10A in the regulation of cAMP/PKA signaling in the striatum. J Neurosci. (2008) 28:10460–71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2518-08.2008
184. Kim C, Vigil D, Anand G, and Taylor SS. Structure and dynamics of PKA signaling proteins. Eur J Cell Biol. (2006) 85:651–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.02.004
185. Siuciak JA, Chapin DS, Harms JF, Lebel LA, McCarthy SA, Chambers L, et al. Inhibition of the striatum-enriched phosphodiesterase PDE10A: a novel approach to the treatment of psychosis. Neuropharmacology. (2006) 51:386–96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.04.013
186. Rajput PS, Kharmate G, Somvanshi RK, and Kumar U. Colocalization of dopamine receptor subtypes with dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP-32) in rat brain. Neurosci Res. (2009) 65:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.05.005
187. Bateup HS, Svenningsson P, Kuroiwa M, Gong S, Nishi A, Heintz N, et al. Cell type–specific regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation by psychostimulant and antipsychotic drugs. Nat Neurosci. (2008) 11:932–9. doi: 10.1038/nn.2153
188. Bibb JA, Snyder GL, Nishi A, Yan Z, Meijer L, Fienberg AA, et al. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signalling in neurons. Nature. (1999) 402:669–71. doi: 10.1038/45251
189. Svenningsson P, Nishi A, Fisone G, Girault JA, Nairn AC, and Greengard P. DARPP-32: an integrator of neurotransmission. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2004) 44:269–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802.121415
190. Megens AA, Hendrickx HM, Hens KA, Fonteyn I, Langlois X, Lenaerts I, et al. Pharmacology of JNJ-42314415, a centrally active phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) inhibitor: a comparison of PDE10A inhibitors with D2 receptor blockers as potential antipsychotic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2014) 349:138–54. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.211904
191. Nishi A and Snyder GL. Advanced research on dopamine signaling to develop drugs for the treatment of mental disorders: biochemical and behavioral profiles of phosphodiesterase inhibition in dopaminergic neurotransmission. J Pharmacol Sci. (2010) 114:6–16. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10R01FM
192. Rodefer JS, Murphy ER, and Baxter MG. PDE10A inhibition reverses subchronic PCP-induced deficits in attentional set-shifting in rats. Eur J Neurosci. (2005) 21:1070–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03937.x
193. Grauer SM, Pulito VL, Navarra RL, Kelly MP, Kelley C, Graf R, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor activity in preclinical models of the positive, cognitive, and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2009) 331:574–90. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.155994
194. Surmeier DJ, Bargas J, Hemmings HC Jr., Nairn AC, and Greengard P. Modulation of calcium currents by a D1 dopaminergic protein kinase/phosphatase cascade in rat neostriatal neurons. Neuron. (1995) 14:385–97. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90294-5
195. Roche KW, O’Brien RJ, Mammen AL, Bernhardt J, and Huganir RL. Characterization of multiple phosphorylation sites on the AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit. Neuron. (1996) 16:1179–88. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80144-0
196. Greengard P, Allen PB, and Nairn AC. Beyond the dopamine receptor: the DARPP-32/protein phosphatase-1 cascade. Neuron. (1999) 23:435–47. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80798-9
197. Fienberg AA, Hiroi N, Mermelstein PG, Song W, Snyder GL, Nishi A, et al. DARPP-32: regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science. (1998) 281:838–42. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5378.838
198. Yan Z, Hsieh-Wilson L, Feng J, Tomizawa K, Allen PB, Fienberg AA, et al. Protein phosphatase 1 modulation of neostriatal AMPA channels: regulation by DARPP-32 and spinophilin. Nat Neurosci. (1999) 2:13–7. doi: 10.1038/4516
199. Snyder GL, Fienberg AA, Huganir RL, and Greengard P. A dopamine/D1 receptor/protein kinase A/dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (Mr 32 kDa)/protein phosphatase-1 pathway regulates dephosphorylation of the NMDA receptor. J Neurosci. (1998) 18:10297–303. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-24-10297.1998
200. Flores-Hernandez J, Hernandez S, Snyder GL, Yan Z, Fienberg AA, Moss SJ, et al. D(1) dopamine receptor activation reduces GABA(A) receptor currents in neostriatal neurons through a PKA/DARPP-32/PP1 signaling cascade. J Neurophysiol. (2000) 83:2996–3004. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.83.5.2996
201. Zagorska A, Partyka A, Bucki A, Gawalskax A, Czopek A, and Pawlowski M. Phosphodiesterase 10 inhibitors-novel perspectives for psychiatric and neurodegenerative drug discovery. Curr medicinal Chem. (2018) 25:3455–81. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180309110629
202. Ring H and Serra-Mestres J. Neuropsychiatry of the basal ganglia. J Neurology Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2002) 72:12–21. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.72.1.12
203. Jellinger KA. Pathology of Parkinson’s disease: changes other than the nigrostriatal pathway. Mol Chem neuropathology. (1991) 14:153–97. doi: 10.1007/BF03159935
204. Duty S and Jenner P. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: a source of novel treatments and clues to the cause of the disease. Br J Pharmacol. (2011) 164:1357–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01426.x
205. Liang Z, Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, and Gong CX. Down-regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by over-activated calpain in Alzheimer disease brain. J neurochemistry. (2007) 103:2462–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04942.x
206. Giampà C, Laurenti D, Anzilotti S, Bernardi G, Menniti FS, and Fusco FR. Inhibition of the striatal specific phosphodiesterase PDE10A ameliorates striatal and cortical pathology in R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. PLoS One. (2010) 5:e13417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013417
207. Beaumont V, Zhong S, Lin H, Xu W, Bradaia A, Steidl E, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A inhibition improves cortico-basal ganglia function in Huntington’s disease models. Neuron. (2016) 92:1220–37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.064
208. Tinsley HN, Gary BD, Keeton AB, Lu W, Li Y, and Piazza GA. Inhibition of PDE5 by sulindac sulfide selectively induces apoptosis and attenuates oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin–mediated transcription in human breast tumor cells. Cancer Prev Res. (2011) 4:1275–84. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0095
209. Nuechterlein N, Shelbourn A, Szulzewsky F, Arora S, Casad M, Pattwell S, et al. Haploinsufficiency of phosphodiesterase 10A activates PI3K/AKT signaling independent of PTEN to induce an aggressive glioma phenotype. Genes Dev. (2024) 38:273–88. doi: 10.1101/gad.351350.123
210. Wilson LS and Brandon NJ. Emerging biology of PDE10A. Curr Pharm Des. (2015) 21:378–88. doi: 10.2174/1381612820666140826114744
211. Fusco JP, Pita G, Pajares MJ, Andueza MP, Patiño-García A, de-Torres JP, et al. Genomic characterization of individuals presenting extreme phenotypes of high and low risk to develop tobacco-induced lung cancer. Cancer Med. (2018) 7:3474–83. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1500
212. Shen Q, Cheng F, Song H, Lu W, Zhao J, An X, et al. Proteome-scale investigation of protein allosteric regulation perturbed by somatic mutations in 7,000 cancer genomes. Am J Hum Genet. (2017) 100:5–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.09.020
213. Kwon IK, Wang R, Thangaraju M, Shuang H, Liu K, Dashwood R, et al. PKG inhibits TCF signaling in colon cancer cells by blocking beta-catenin expression and activating FOXO4. Oncogene. (2010) 29:3423–34. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.91
214. Shah K and Kazi JU. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of WNT/beta-catenin signaling. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:858782. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.858782
215. Arowa S, Nuechterlein N, Ha V, Shelbourn A, Chowdhury A, Banasavadi-Siddegowda YK, et al. Loss of PDE10A is associated with metastasis of colon adenocarcinoma. Histol Histopathol. (2025), 18951. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-951
216. de Alexandre RB, Horvath A, Szarek E, Manning AD, Leal LF, Kardauke F, et al. Phosphodiesterase sequence variants may predispose to prostate cancer. Endocrine-related cancer. (2015) 22:519. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0134
217. Liu H, Li F, Zhu Y, Li T, Huang H, Lin T, et al. Whole-exome sequencing to identify somatic mutations in peritoneal metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma: a preliminary study. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:43894. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9707
218. Zekeridou A, Kryzer T, Guo Y, Hassan A, Lennon V, Lucchinetti CF, et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A IgG: a novel biomarker of paraneoplastic neurologic autoimmunity. Neurology. (2019) 93:e815–e22. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007971
219. Hughes CE, Correa H, Benedetti DJ, Smith B, Sumegi J, and Bridge J. Second report of PDE10A-BRAF fusion in pediatric spindle cell sarcoma with infantile fibrosarcoma-like morphology suggesting PDE10A-BRAF fusion is a recurrent event. Pediatr Dev Pathology. (2021) 24:554–8. doi: 10.1177/10935266211012186
220. Vairy S, Jouan L, Bilodeau M, Dormoy-Raclet V, Gendron P, Couture F, et al. Novel PDE10A-BRAF fusion with concomitant NF1 mutation identified in an undifferentiated sarcoma of infancy with sustained response to trametinib. JCO Precis Oncol. (2018) 2:1–13. doi: 10.1200/PO.18.00007
221. Lindsey AS, Lee K, Zhu B, Arora R, Otali D, Ramirez-Alacantara V, et al. Abstract 4736: PDE10A overexpression in cancer cells and tumors as compared to normal cells and tissues. Cancer Res. (2016) 76:4736. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2016-4736
222. Chen S, Chen J, Du W, Mickelsen DM, Shi H, Yu H, et al. PDE10A inactivation prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and tumor growth. Circ Res. (2023) 133:138–57. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.322264
223. Li N, Chen X, Zhu B, Ramírez-Alcántara V, Canzoneri JC, Lee K, et al. Suppression of β-catenin/TCF transcriptional activity and colon tumor cell growth by dual inhibition of PDE5 and 10. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:27403–15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4741
224. Kopanitsa L, Kopanitsa MV, Safitri D, Ladds G, and Bailey DS. Suppression of proliferation of human glioblastoma cells by combined phosphodiesterase and multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 inhibition. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:9665. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189665
225. Mehta A and Patel BM. Therapeutic opportunities in colon cancer: Focus on phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Life Sci. (2019) 230:150–61. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.043
226. Barber RM, Gavin E, Musiyenko A, Richter W, Lee KJ, Wilhite A, et al. PDE10A as a novel target to suppress Wnt/β-catenin signaling and other oncogenic pathways in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. (2021) 81:1213. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2021-1213
227. Hubbard CJ. Ovarian cAMP and cGMP fluctuations in the hamster during the oestrous cycle. J Reprod Fertil. (1980) 59:351–5. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0590351
228. Macek TA, McCue M, Dong X, Hanson E, Goldsmith P, Affinito J, et al. A phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of TAK-063 in subjects with an acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. (2019) 204:289–94. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2018.08.028
Keywords: phosphodiesterase 10A, PDE10A, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cancer
Citation: Ghoflchi S, Nakhaei A, Abbasinezhad-Moud F, Jalili-Nik M and Cimino PJ (2025) PDE10A as a novel diagnostic and therapeutic target in cancer: insights and challenges. Front. Oncol. 15:1669157. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1669157
Received: 19 July 2025; Accepted: 03 October 2025;
Published: 16 October 2025.
Edited by:
Bekir Cinar, Clark Atlanta University, United StatesReviewed by:
Arunima Biswas, University of Kalyani, IndiaMohammad Uzzal Hossain, National Institute of Biotechnology (NIB), Bangladesh
Arka Bagchi, All India Institute of Medical Sciences Kalyani, India
Copyright © 2025 Ghoflchi, Nakhaei, Abbasinezhad-Moud, Jalili-Nik and Cimino. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohammad Jalili-Nik, bW9oYW1tYWQuamFsaWxpbmlrQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Patrick J. Cimino, cGouY2ltaW5vQG5paC5nb3Y=
†These authors share senior authorship
 Sahar Ghoflchi
Sahar Ghoflchi Ali Nakhaei3
Ali Nakhaei3 Mohammad Jalili-Nik
Mohammad Jalili-Nik Patrick J. Cimino
Patrick J. Cimino