- 1Oral Disease Research Key Laboratory of Guizhou Tertiary Institution,School of Life Science, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
- 2Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
- 3Department of General Surgery, Digestive Disease Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
Infantile hemangioma (IH), the most prevalent benign vascular tumor in neonates, typically appears several weeks after birth, undergoes rapid proliferation, and subsequently enters a prolonged phase of spontaneous involution. Recent advancements in molecular and cellular biology have revealed increasing evidence that the etiology and progression of IH arise from complex, multi-level interactions involving various factors. In this review, we examine the categorization of IH cells, analyze the pivotal roles of key molecular signaling pathways (e.g., VEGF, HIF, Notch), and elucidate the contributions of immune cells, hypoxia, the extracellular matrix, and exosome-mediated signaling within the tumor microenvironment to the angiogenic processes and regression of IH. These insights will enhance our understanding of IH pathogenesis, thereby laying the groundwork for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
1 Introduction
Infantile hemangioma (IH) is a common benign vascular tumor composed mainly of proliferating endothelial cells. It typically appears as red, sometimes raised, lesions on the skin or subcutaneous tissues. Although IH most often affects the head, neck, and limbs, it can also occur in the viscera or airways (1, 2). IH is not present at birth; it usually emerges within a few weeks after birth, undergoes rapid proliferation during infancy, stabilizes, and then gradually involutes (Figure 1). The etiology of IH remains unclear but may involve abnormal fetal blood vessel formation, hypoxia, genetic factors, and environmental influences, with a prevalence of approximately 2%–10% (3–5). IH is more common in premature and low-birth-weight infants, has a female-to-male ratio of about 3:1 (6), and is more prevalent in Caucasians than in Asian or African-American populations (7–9). Although most IH lesions regress naturally, some require aggressive treatment due to ulceration, infection, or impairment of vital organ functions (8). Effective management of IH depends on a thorough understanding of its pathophysiology to develop individualized treatment plans.
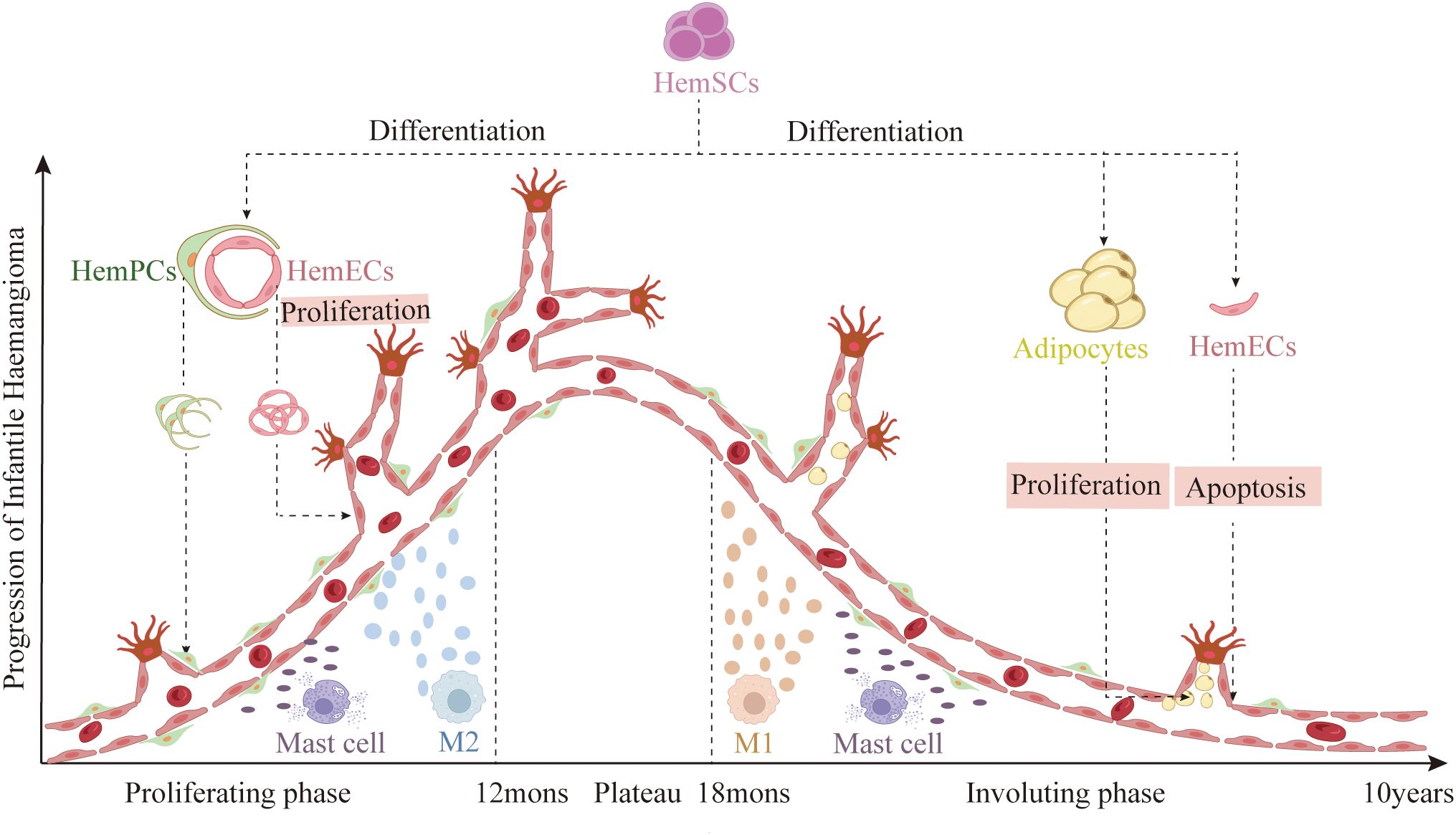
Figure 1. Disease stages of IH: First, a rapid proliferative phase during the first year of life, characterized by abundant endothelial cells forming syncytial masses without a defined vascular architecture. This is followed by a plateau phase of approximately six months, during which growth stabilizes. Next, a gradual involution phase that can last up to ten years, marked by apoptosis of HemECs and differentiation of HemSCs into adipocytes. (Created with BioRender.com).
IH is typically diagnosed based on its clinical appearance; however, imaging (e.g., ultrasound, MRI) or biopsy may be necessary to exclude other conditions such as lymphangiomas, vascular malformations, or malignant tumors (10–16). Observation is an option for small, non-functional IH, while rapidly growing, ulcerated, or functionally impairing lesions may require early intervention using oral propranolol, topical agents (glucocorticoids or interferon), laser therapy, or surgery (8, 15, 17). Patient-specific, timely decisions are critical to minimize complications and improve outcomes.
A thorough understanding of the cellular, molecular, and microenvironmental mechanisms underlying IH is essential for the development of effective therapeutic strategies. Despite significant advances, the pathogenesis of IH remains incompletely understood. This review integrates current findings to elucidate these interactions from a multidimensional perspective, providing a theoretical foundation for precision treatments, the development of novel therapies, and further research on IH.
2 Cell components of IH
The development of IH involves dynamic interactions among various cell types (Figure 2). Recent research has highlighted the roles of several cellular components in tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, and spontaneous involution (18–20).
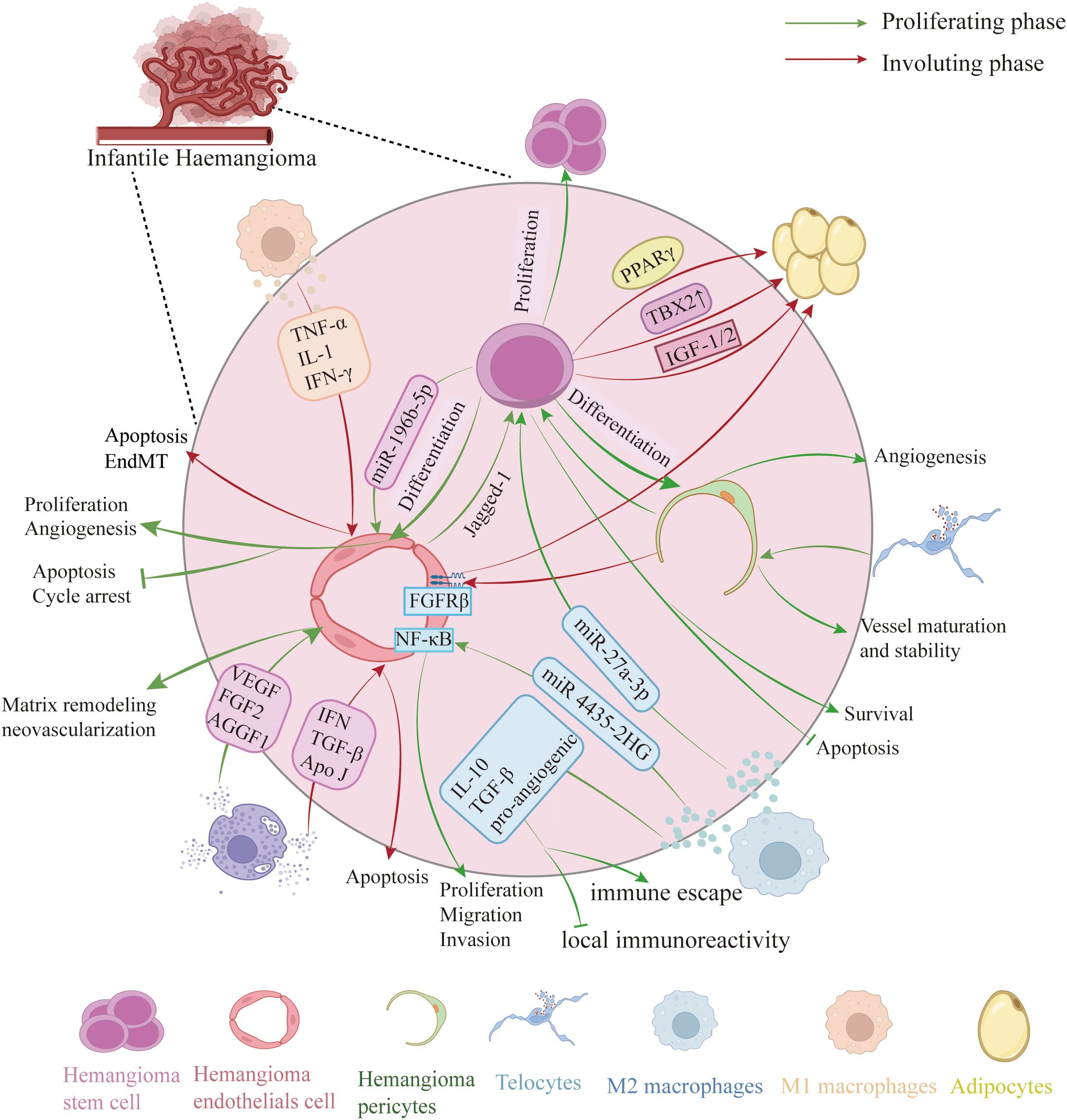
Figure 2. Cellular composition of IH. Proliferative phase: HemSCs differentiate into HemECs, which display enhanced proliferation and migration, reduced apoptosis, and—via Notch–Jagged-1 signaling—further differentiate into HemPCs. M2-polarized macrophages secrete IL-10, TGF-β, pro-angiogenic factors and exosomes that modulate HemSCs and HemECs behavior. Mast cells release VEGF, FGF2, AGGF1 and matrix-degrading enzymes (chymotrypsin, trypsin, MMPs) to remodel the extracellular matrix and drive neovascularization. Involuting phase: HemSCs predominantly become adipocytes. M1 macrophages increase and release TNF-α, IL-1β and IFN-γ to induce HemECs apoptosis or endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), promoting regression. Mast cells produce anti-angiogenic factors (interferon, TGF-β) and apolipoprotein J to trigger early endothelial apoptosis. Telocytes envelop pericytes to support vessel stability and maturation. (Created with BioRender.com).
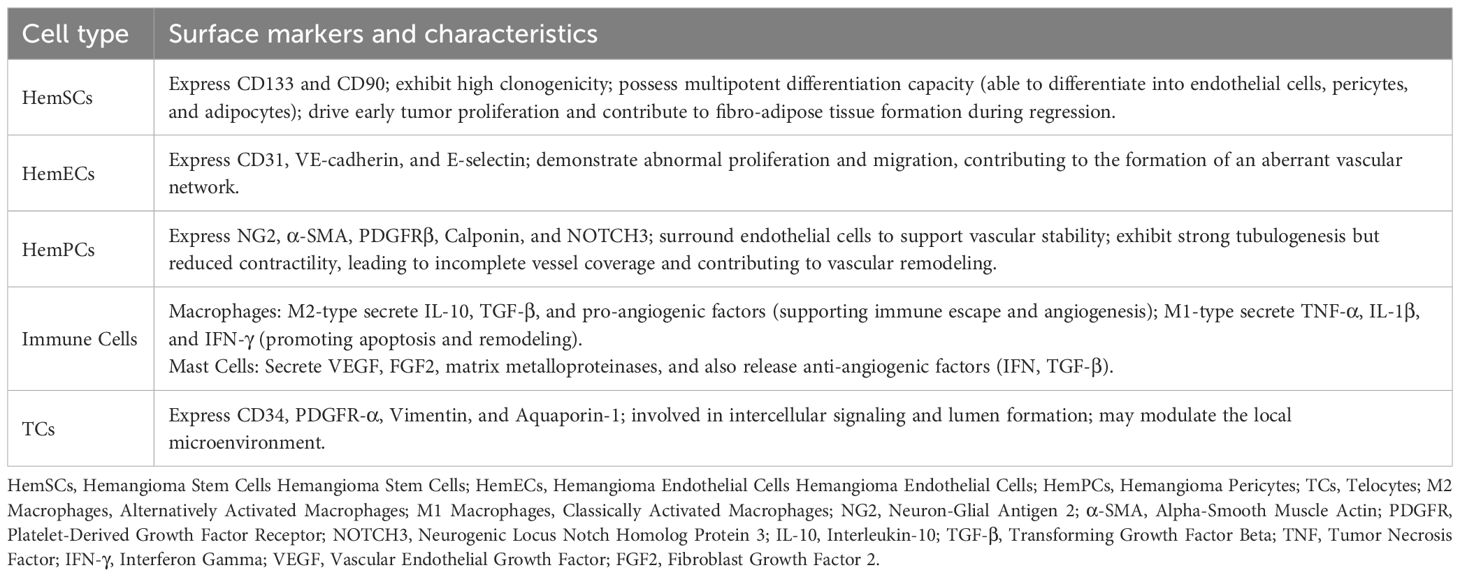
2.1 Hemangioma stem cells
Hemangioma stem cells (HemSCs) account for approximately 1% of the total cell population (21) and were isolated from IH tissues by Khan et al. Considered the seed cells of IH, they possess multidirectional differentiation potential, enabling them to become hemangioma endothelial cells (HemECs), hemangioma pericytes (HemPCs), or adipocytes in response to microenvironmental cues. This capability underlies rapid neovascularization during the proliferative phase and the formation of residual fibro-adipose tissue during regression (22–25). Isolated from proliferative IH specimens, HemSCs display a mesenchymal morphology in vitro, express stem cell markers, e.g., CD133 and CD90, and exhibit high clonogenicity and self-renewal (26, 27). In vivo, HemSCs implantation in immunodeficient mice reproduces human IH features, including the formation of Glucose Transporter 1 (GLUT1)-positive vessels and subsequent adipose tissue development (26, 28). As IH regresses, HemSC differentiation toward adipocytes increases, reducing vascular density and generating fibro-fatty tissue—a cellular basis for IH self-limitation (18, 29).
2.2 HemECs and HemPCs
HemECs, the most visually apparent component, exhibit typical endothelial morphology, are densely packed, and display irregular arrangements (22). They express markers such as CD31, VE-cadherin, and E-selectin, which aid in diagnosis and indicate similarities to normal endothelial cells. However, HemECs show abnormal proliferation and migration, likely due to low vascular endothelial growth factor 1(VEGFR1) and high VEGFR2 expression (30–33). HemECs can be classified intoGLUT1-positive and GLUT1-negative subtypes. GLUT1-positive HemECs possess stem cell properties and can revert to a mesenchymal phenotype in culture, potentially contributing to IH recurrence (34). In contrast, GLUT1-negative HemECs require supportive cells to establish perfused vessels in vivo (35), suggesting that their function depends on both intrinsic gene expression and the surrounding microenvironment.
HemPCs support vascular stability by surrounding endothelial cells (17), and express markers such as Neuron-Glial Antigen 2 (NG-2), Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin (αSMA), Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Subunit Beta (PDGFRβ), calponin, and Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3 (NOTCH3). Notch signaling is upregulated in proliferative IH, promoting HemSC differentiation into pericytes via Notch/Jagged-1 interactions (20, 36, 37). Compared to normal pericytes, HemPCs exhibit enhanced pro-angiogenic properties and reduced contractility, which may contribute to incomplete vessel coverage and increased permeability, thereby facilitating abnormal vessel formation (38). During involution, pericytes mature and stabilize the vasculature while supporting endothelial transformation into adipocytes (17, 39–41).
2.3 Additional cellular players
Macrophages in IH are mainly classified into two subtypes. In proliferative IH, M2-polarized macrophages secrete pro-angiogenic factors and exosomes that regulate HemSC and HemEC behavior. During the involution phase, M1-polarized macrophages increase to promote hemangioma regression (42, 43). Mast cells, though fewer during proliferation and more active during early regression, secrete both pro- and anti-angiogenic factors (e.g., VEGF, Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2/bFGF), Interferon (IFN), Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β)) that modulate angiogenesis and regression, with their activity influenced by the local environment (19, 44). Telocytes (TCs), a distinctive type of interstitial cells, have garnered significant interest because of their distinct morphology and diverse functions. In IH, TCs exhibit overexpression of CD34, PDGFR-α, Vimentin, and Aquaporin-1 (AQP-1), with AQP-1 and PDGFR-α being the most reliable markers for identifying TCs in IH (45). TCs, which closely interact with endothelial cells and pericytes, may regulate intercellular communication and lumen formation (45, 46).
3 Molecular mechanisms of IH
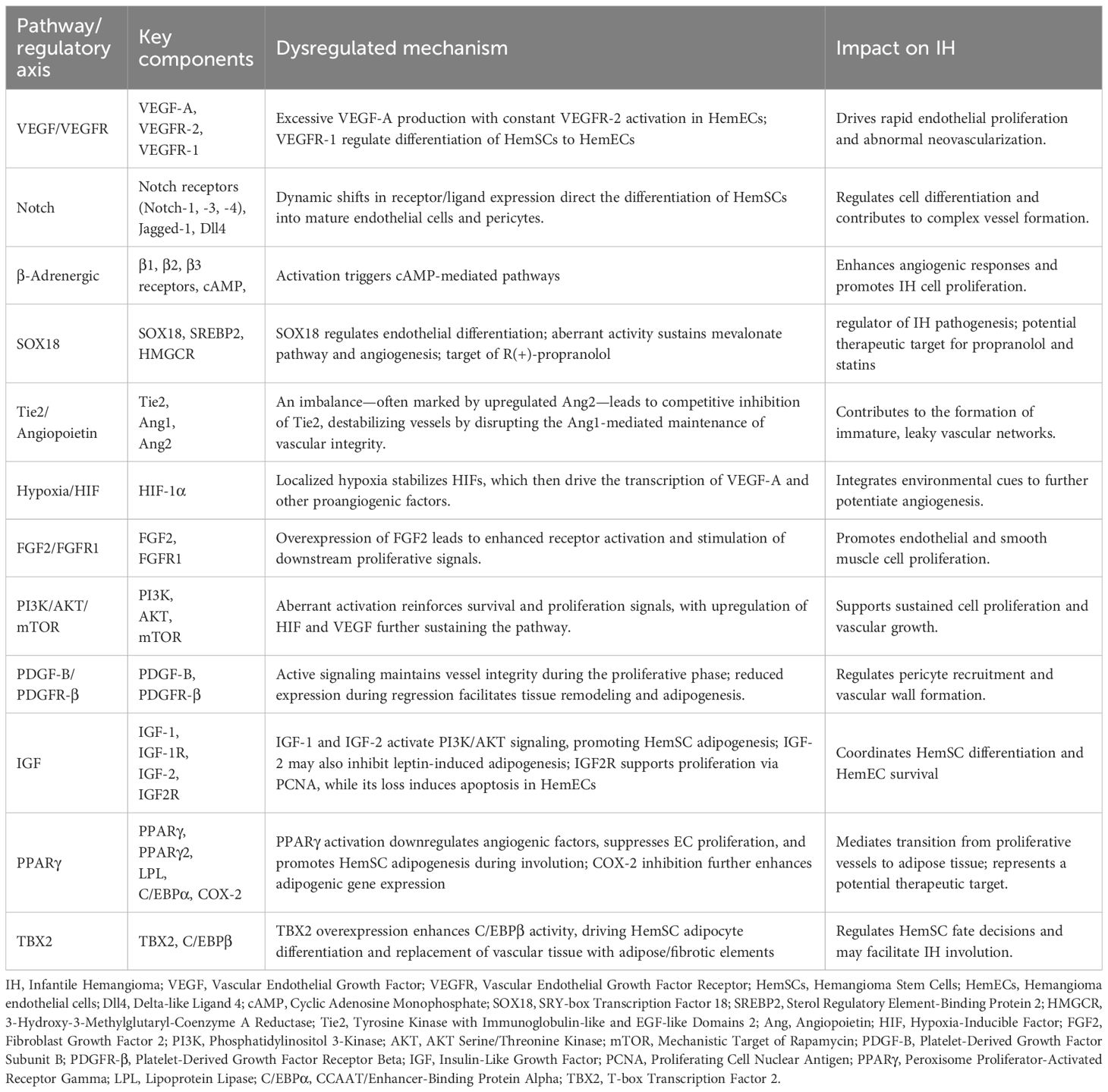
The development of IH involves a complex interplay of molecular mechanisms, dysregulated signaling pathways, and cell fate decisions, as summarized in Table 1; Figure 3.
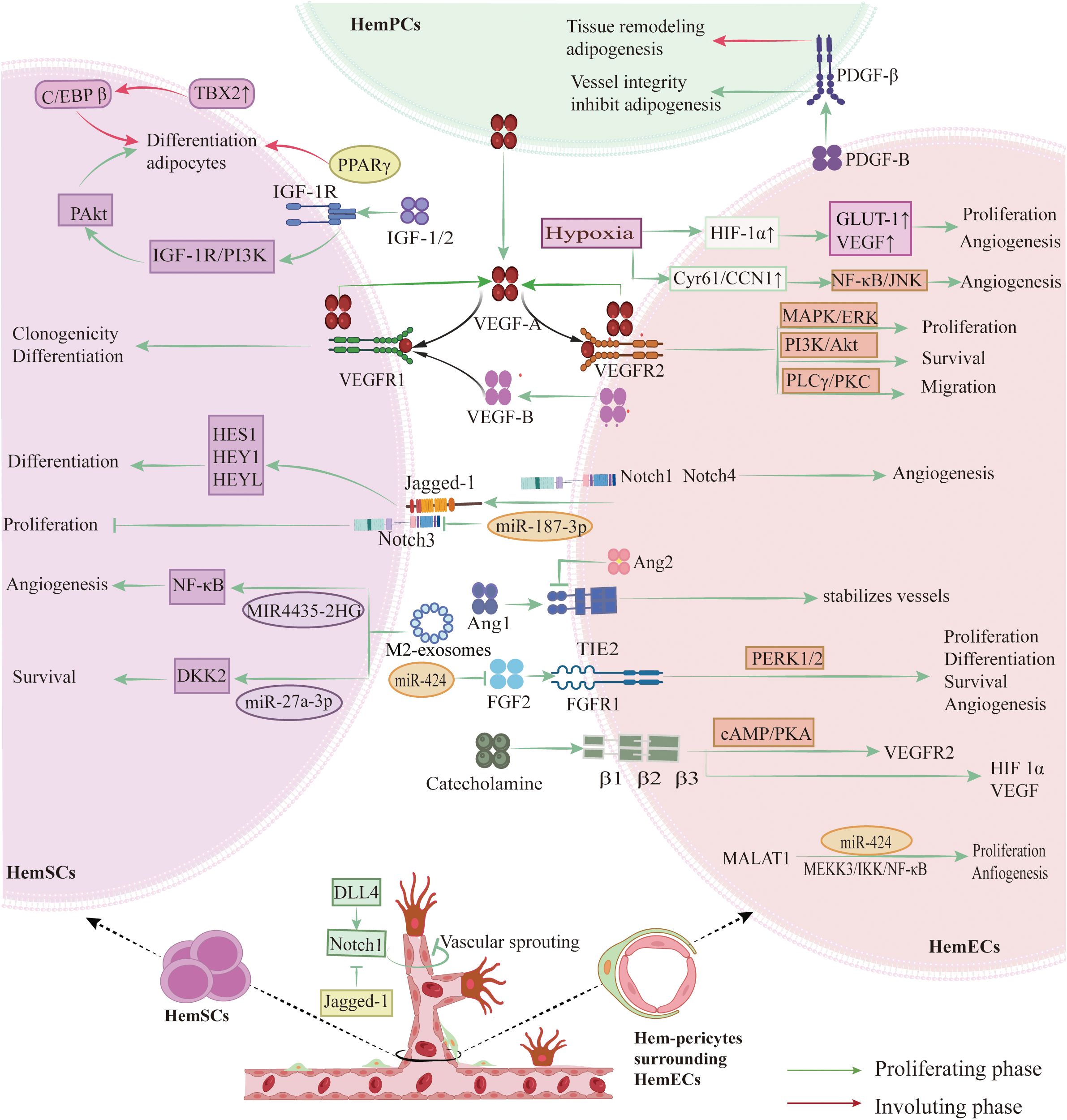
Figure 3. Key signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms in IH pathogenesis. HemECs overexpress VEGFR-2, activating the PI3K/AKT, MEK/ERK, and PLCγ/PKC pathways to drive proliferation, migration, and tube formation. An autocrine VEGFA–VEGFR-2 loop, potentiated by low VEGFR-1 levels, sustains HemECs growth, while paracrine VEGFR-1 signaling directs HemSCs differentiation. Notch signaling—via Notch1/3/4 receptors and Dll4/Jagged1 ligands—controls tip versus stalk cell fate, branching, and pericyte recruitment. β-Adrenergic signaling through β1/2/3 receptors elevates cAMP/PKA and EPAC, upregulating VEGFR-2. The Tie2–Ang1 axis stabilizes vessels via PI3K/EPAC, whereas Ang2 and hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/2α destabilize vessels and enhance VEGFA expression. FGF (bFGF) binding FGFR1 activates ERK1/2 to promote proliferation. Concurrently, IGF-1, IGF-2, PPARγ (including PPARγ2), and TBX2 drive HemSCs adipogenic differentiation, while declining PDGF-B/PDGFR-β signaling permits adipogenesis. (Created with BioRender.com).
3.1 VEGF/VEGFR pathway
The VEGF/VEGFR pathway is essential for IH (33). In IH, abnormal vascular growth arises from both angiogenesis—the sprouting of new vessels from existing ones—and vasculogenesis, where endothelial progenitor cells differentiate and form primitive vessels; central to both processes is the aberrant activation of the VEGF/VEGFR pathway (47). VEGF-A is highly expressed during the proliferative phase of IH and declines during involution, underscoring its role in sustaining lesion growth (48–50). In proliferative IH, HemECs highly express VEGFR‐2. When VEGF-A binds to VEGFR-2, it activates the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B (PI3K/AKT), Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Kinas (MEK/ERK), and Phospholipase C gamma/Protein Kinase C (PLCγ/PKC) cascades, promoting endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and lumen formation, which leads to a dense vascular network (25, 37). HemECs frequently activate autocrine VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 signaling, which stimulates downstream pathway that drive proliferation, migration, and survival (33). Low VEGFR-1 expression in HemECs further amplifies VEGFR-2 signaling, exacerbating abnormal angiogenesis (32, 51). In contrast, HemSCs predominantly express VEGFR-1, which binds VEGF-A to regulate their differentiation into endothelial cells (52). VEGF-B—a VEGFR-1 ligand—is highly expressed in HemECs and similarly promotes HemSC differentiation (53). Together, these paracrine and autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-1 signals synergistically enhance angiogenesis in IH (53). Aberrant VEGF/VEGFR activation not only accelerates endothelial expansion but also stabilizes diseased cells through anti-apoptotic signaling, presenting a clear target for clinical treatment (54–56).
3.2 Notch signaling
Notch signaling, which depends on direct cell-to-cell contact, is essential for cell differentiation and vascular maturation; this evolutionarily conserved system governs cell fate decisions and balances proliferation with differentiation (57). In IH, Notch receptors (Notch‐1, Notch‐3, Notch‐4) and ligands (primarily Jagged‐1 and Delta‐like ligand 4 (Dll4)) are abnormally expressed. Upon ligand binding, the Notch intracellular domain is cleaved and translocates to the nucleus to activate transcriptional repressors such as Hairy and Enhancer of Split (HES) and Hairy/Enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif (HEY), leading to cell cycle exit and maturation (33, 57, 58). In IH tissues, regional variations in Notch expression reflect the differing roles of endothelial and supporting cells. HemSCs are enriched in Notch-3 and downstream targets like HES1, HEY1, and HEYL, priming them for differentiation into both endothelial and mural cells and contributing to the formation of the complex vascular structures typical of IH. In contrast, mature HemECs exhibit higher levels of Notch-1, Notch-4, and Jagged-1 (59). Disruption of Notch receptor–ligand interactions markedly inhibits neovascularization, highlighting its key role in vessel formation and branching (60). Additionally, endothelial-derived Jagged-1 can induce tumor stem cells to acquire a pericyte-like phenotype, which is essential for maintaining vascular wall integrity (37). The balance between Dll4 and Jagged-1 is critical; while Dll4–Notch interactions restrict excessive sprouting by limiting tip cell formation, Jagged-1 promotes vascular branching (61). Experimental evidence shows that blocking Notch signaling leads to significant defects in vessel formation and maturation (60, 62).
3.3 β‐adrenergic signaling
The clinical success of propranolol has redirected attention to β‐adrenergic signaling in IH. HemECs express several β‐adrenergic receptor subtypes (β1, β2, and β3), and activation of these receptors by catecholamines triggers the classical Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP) signaling cascade, leading to the activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA) and Exchange Protein Activated by cAMP and an increase in proangiogenic factors such as VEGFR‐2 (63–65). In experimental models, β‐receptor agonists enhance endothelial cell sensitivity to growth factors, while β‐blockers mitigate this effect (66–71). Moreover, β‐adrenergic stimulation may exacerbate angiogenesis in hypoxic conditions by indirectly upregulating Hypoxia‐Inducible Factors-1α (HIF-1α) and VEGF (72, 73). Interestingly, propranolol’s therapeutic effects are not solely due to β‐blockade. Its S(–) enantiomer strongly blocks β‐adrenergic receptors, while the R(+) enantiomer targets the endothelial transcription factor SRY-box transcription factor 18 (SOX18), a master regulator of endothelial differentiation that is aberrantly upregulated in proliferative IH lesions (74–76). Inhibition of SOX18 disrupts transcriptional programs necessary for vessel formation, thereby reducing vascular proliferation. Recent studies indicate that SOX18 also regulates genes in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis and membrane prenylation—key processes for endothelial growth. The R(+) enantiomer selectively inhibits SOX18 independently of β‐adrenergic antagonism, downregulating angiogenic signaling and suggesting potential for drug repurposing (77).
3.4 (Tie2)/Angiopoietin signaling
Tie2/Angiopoietin signaling is another key regulator of IH vascular dynamics. The Tie2 receptor on endothelial cells interacts with angiopoietin‐1 (Ang1) and angiopoietin‐2 (Ang2) to control vessel maturation and stability (78, 79). Under normal conditions, Ang1 binding to Tie2 activates pathways such as PI3K/AKT and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), promoting endothelial survival, pericyte recruitment, and vessel quiescence (80, 81). In contrast, Ang2—often upregulated during the proliferative phase of IH—acts as a context‐dependent antagonist by competitively inhibiting Tie2 activation, which destabilizes vessels, impairs pericyte recruitment, and leads to the formation of immature, leaky vascular networks (82).
3.5 HIFs
HIFs are critical mediators of the cellular response to low oxygen tension and trigger many proangiogenic signals in IH. Rapid hemangioma proliferation often results in localized hypoxia, which stabilizes HIF‐1α and HIF‐2α by preventing their degradation under normoxic conditions (83, 84). Stabilized HIFs translocate to the nucleus, where they induce the transcription of genes such as VEGF‐A and GLUT1 (49, 85, 86) The hypoxia-induced upregulation of VEGF‐A further amplifies autocrine and paracrine signaling loops, driving HemEC proliferation and survival. Additionally, HIFs modulate other key signaling molecules, integrating with pathways such as Notch and Tie2/Angiopoietin to coordinate rapid vascular expansion during the proliferative phase and subsequent vessel maturation and involution as oxygenation improves (87).
3.6 bFGF
bFGF is a potent angiogenic factor that stimulates the proliferation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells as well as fibroblast migration (88–90). Its effects are mediated by binding to FGFR1, which triggers receptor autophosphorylation and activates signaling pathways that control cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and angiogenesis (91, 92). Overexpression of bFGF parallels proliferative hemangioma growth, linking the bFGF/FGFR1 pathway to hemangioma formation, proliferation, and involution (93, 94). Additionally, miR-424 may reduce FGFR1 expression and inhibit the bFGF/FGFR1 pathway, suppressing ERK1/2 phosphorylation and ultimately decreasing cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation (95).
3.7 PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway plays a central role in regulating cell growth, survival, and autophagy (96–98). In IH cells, aberrant activation of this pathway upregulates HIF-1α and VEGF, increasing cellular tolerance to stress (96, 97). Recent studies have shown that SOX4 binds to the promoter of endothelial cell–specific molecule 1 (ESM1), activating the PI3K/AKT pathway and amplifying angiogenic signaling[ (99). Consistently, ex vivo experiments demonstrate that pharmacologic inhibition of this pathway, including the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin, reduces IH cell proliferation and angiogenesis, underscoring its therapeutic potential (100).
3.8 Insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling pathway plays a central role in cell proliferation and insulin sensitivity. IGF-1 binds to its receptor (IGF-1R), a tetramer of two extracellular α-subunits and two transmembrane β-subunits with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity (101) This interaction activates the PI3K/AKT pathway, increases AKT phosphorylation, and drives HemSCs to differentiate into adipocytes (102). Similarly, IGF-2 promotes HemSCs adipogenesis via the same mechanism. However, one study reported that IGF-2 can inhibit leptin-induced adipogenesis in HemSCs, indicating a context-dependent modulatory role that warrants further investigation (103, 104). In parallel, IGF-2 signaling through IGF2R enhances proliferation by upregulating proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Loss of IGF2R, by contrast, weakens PI3K/AKT signaling, reduces PCNA and Bcl-2 expression, and induces apoptosis in HemECs, underscoring IGF2R’s dual role in growth and survival (105).
3.9 Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) signaling has gained increasing attention in angiogenesis research. Activation of PPARγ exerts anti-angiogenic effects by downregulating angiogenic factors and suppressing endothelial cell migration and proliferation (106, 107). PPARγ agonists, such as thiazolidinediones (TZDs), inhibit angiogenesis by reducing chemotaxis and promoting apoptosis through Erk5 activation (106). In tumor cells, PPARγ ligands also induce growth arrest and apoptosis via the p63 and p73 pathways (108). During involution of IH, PPARγ and its isoform PPARγ2 orchestrate HemSCs differentiation into adipocytes (109). The involuting phase is marked by coordinated upregulation of PPARγ2, lipoprotein lipase (LPL), CCAAT Enhancer-Binding Protein α (C/EBPα), and apolipoprotein A (110). Moreover, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibition may further enhance adipogenic gene expression via the PPARγ/C/EBP axis (111). Collectively, these findings highlight PPARγ as a potential therapeutic target in IH.
3.10 T-box transcription factor 2
T-box transcription factor 2 (TBX2), highly expressed in HemSCs, has been proposed as a critical regulator of cell fate decisions (112). TBX2 overexpression augments C/EBPβ activity, promoting adipocyte differentiation of HemSCs, and facilitates the gradual replacement of proliferative vascular tissue with mature adipose and fibrous elements (113).However, current evidence is largely based on in vitro studies, with limited in vivo validation. It also remains unclear whether TBX2 acts independently or as part of a broader transcriptional network, underscoring gaps in mechanistic understanding.
3.11 PDGF-B/PDGFR-β
PDGF family consists of four ligands—PDGF-A, -B, -C, and -D—that bind to the tyrosine kinase receptors PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β (114). The PDGF-B/PDGFR-β system mediates communication between endothelial cells and pericytes, regulating pericyte recruitment and vascular wall formation (115). In proliferative IH, active PDGF signaling maintains vessel integrity by inhibiting adipose differentiation, while reduced PDGFR-β expression during regression facilitates tissue remodeling and adipogenesis (51). Overall, receptor-mediated PDGF signaling appears to constrain involution, but further research is needed to clarify the mechanisms underlying altered PDGF-B expression.
4 Role of the microenvironment
4.1 Immune and inflammatory mechanisms
Inflammatory cytokines and immune cells play pivotal roles in both the progression and regression of IH. In the proliferative phase, high local concentrations of cytokines such as IL-6, Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and IL-1β stimulate the proliferation of HemECs and HemSCs, while enhancing VEGF expression via activation of pathways like Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK/STAT) and Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) (116, 117). Allograft inflammatory factor-1(AIF-1) is highly expressed in endothelial cells in most IH samples, which may recruit myeloid cells to the lesion, although the exact source of these cells remains unclear (118). TNF-α exhibits dual effects: it inhibits vascular expansion in regions with insufficient pericytes, whereas in areas with an adequate pericyte population, TNF-α promotes neovascularization, highlighting the modulatory role of pericytes in inflammatory signaling (119).
During the proliferative phase, immune cells in IH are predominantly M2-type macrophages. These cells secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, in addition to pro-angiogenic factors, thereby reducing local immunoreactivity and supporting tumor cell immune escape (117, 120). Conversely, in the degenerative phase, the proportion of M1-type macrophages increases; these cells release pro-apoptotic factors such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFN-γ, which induce endothelial apoptosis or trigger endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EndMT), thus facilitating tumor regression (117). Moreover, exosomes secreted by M2-type macrophages contain specific non-coding RNAs (e.g., lncRNA mir 4435-2HG) that further enhance HemEC proliferation, migration, and invasion via NF-κB activation (121). Mast cells also exhibit dynamic changes during IH progression. Their numbers are low during the proliferative phase but their enzymatic activity peaks during early regression. Activated mast cells secrete pro-angiogenic factors (e.g., VEGF, FGF2) along with matrix-degrading enzymes (including chymotrypsin, trypsin, and matrix metalloproteinases [MMPs]) to facilitate extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and neovascularization (19, 122–126). Additionally, mast cells release anti-angiogenic factors like IFN and TGF-β and produce Apo J, which promotes endothelial apoptosis during the early stages of regression, thereby initiating tumor involution (127).
4.2 Hypoxia
A hypoxic microenvironment is a key driver of IH development. During the proliferative phase, rapid tumor cell growth coupled with immature neovascularization results in significant local hypoxia. This low-oxygen state upregulates HIF-1α, which in turn activates downstream genes such as GLUT-1 and VEGF to accelerate HemEC proliferation and neovascularization (49, 85, 86). Furthermore, the protein AIBP, which regulates cholesterol metabolism, promotes cholesterol efflux, destabilizes HIF-1α, reduces VEGF expression, and ultimately inhibits IH growth (128). Cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 (Cyr61/CCN1) is markedly upregulated under hypoxic conditions and localizes primarily to immature microvessels. CCN1 further promotes VEGF-A production through activation of NF-κB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways, creating a positive feedback loop that sustains angiogenesis (129). In addition to promoting angiogenesis, hypoxia relates to metabolic reprogramming in hemangioma cells.
Elevated levels of lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 enhance glycolysis by increasing glucose uptake and lactate production, thereby providing the energy necessary for rapid cell proliferation. This glycolytic enhancement can be partially reversed by inhibiting HIF-1α, underscoring its role in energy metabolism regulation (130).
4.3 ECM
ECM is vital for supporting the vascular endothelium in IH by providing a structural scaffold and regulating angiogenesis. It supports blood vessel formation through adhesive interactions with integrins on endothelial cells, thus maintaining the vascular network (131). Composed of collagen, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins, the ECM is dynamically regulated by its synthesis and degradation, allowing precise control over neovessel formation and maturation. Interactions between the ECM and cells deliver essential signals that govern adhesion, migration, and receptor activation. Alterations in adhesion, increased cell migration, and protease secretion can change vascular permeability, enabling plasma-derived matrix molecules to modify the local ECM composition. Such variations are evident between sites of vessel formation and regions of active angiogenesis. Several studies have shown that changes in the ECM environment correlate with IH progression. For example, differences in ECM composition between the proliferative and involuting phases suggest a causal link between ECM remodeling and angiogenic growth (132). The ECM also influences endothelial responses to angiogenic factors by modulating integrin expression. Adhesion between ECM components and integrins—such as α2β1, α1β1, αvβ3, and α5β1, which bind collagen, fibronectin, and tenascin—is crucial for endothelial tube formation and downstream receptor activation (133–137). In IH, laminin (LN), fibronectin (FN), and vitronectin (VN) are the most frequently studied ECM components (23, 138). For example, LN has been detected in the thickened basement membranes of hemangiomas (139), and the α6-integrin subunit is associated with tumor angiogenesis and cellular invasiveness (140). Despite these insights, further research is needed to clarify other ECM-related factors in IH.
4.4 Exosome-mediated signaling
Exosomes, which are extracellular vesicles ranging from 30 to 150 nm in diameter, play crucial roles in intercellular communication within the IH microenvironment. Secreted by HemSCs, HemECs, and immune cells, exosomes carry a variety of bioactive molecules, including miRNAs, lncRNAs, and proteins, which participate in the regulation of IH development.
M2-polarized macrophage-derived exosomes (M2-exos) have been shown to deliver lncRNA MIR4435-2HG to HemECs. This delivery activates the NF-κB signaling pathway via modulation of the HNRNPA1 protein, thereby enhancing cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and ultimately exacerbating angiogenesis (121). Additionally, M2-exos may transfer miR-27a-3p to HemSCs, leading to the downregulation of Dickkopf-related protein 2 (DKK2). The resulting decrease in DKK2 expression reduces propranolol sensitivity, promotes cell survival, and diminishes apoptosis, offering a potential explanation for treatment resistance in some IH patients (141). Engineered exosomes carrying miR-187-3p have demonstrated the ability to inhibit Notch signaling in HemSCs, resulting in reduced cell proliferation and diminished lumen formation (142). Moreover, Exos derived from IH stem cells are enriched with miR-196b-5p, a molecule that not only promotes HemEC proliferation and angiogenesis but also reduces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by targeting the CDKN1B gene (143). Targeting exosomal signaling pathways could thus provide a molecular foundation for novel therapies that inhibit pathological angiogenesis and induce tumor regression.
Exosomes act not only as pro-angiogenic mediators but also as potential therapeutic targets. Their molecular cargos may serve as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers, while Engineered exosomes could be developed as precision drug-delivery systems. Future research should focus on source-specific features, cargo profiles, and translational applications to advance exosome-based therapies for IH.
5 Unresolved issues in infantile hemangioma research
5.1 Genetic mechanisms
Although familial aggregation and cases in monozygotic twins have been reported (144), most IH cases are sporadic. This suggests that genetic susceptibility, epigenetic regulation, and gene-environment interactions warrant further investigation (145). Early studies suggested a familial basis, with Walter et al. mapping IH to chromosome 5q31–33, which includes genes FGFR4, PDGFRB, and VEGFR-3; variants in these genes were linked to reduced disease risk (146). Somatic mutations in VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 have also been identified in some patients (147), implicating VEGF signaling in IH pathogenesis. However, these findings lack consistent validation in larger cohorts, and their functional significance remains unclear. Single nucleotide polymorphism analyses have suggested a possible association between the VEGF-A rs2010963 G allele and IH susceptibility, but overall evidence remains inconclusive (148).
Increasingly, epigenetic mechanisms—such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNA regulation—are thought to contribute to IH initiation and regression (149). The transcription factor SOX18 and its downstream targets, which regulate vascular development and differentiation, may also influence IH progression via epigenetic pathways and represent promising therapeutic targets (150).
In summary, genetic studies have identified several candidate genes and pathways in IH but no consistent pathogenic mutations. Future investigations should employ multicenter genomic studies, single-cell sequencing, and integrative epigenomic analyses to define the genetic and epigenetic landscape of IH and identify novel susceptibility genes and clinically relevant biomarkers.
5.2 Estrogen
IH exhibits a clear female predilection, sparking interest in the role of estrogen and its receptors in its pathogenesis (6). Elevated serum estrogen levels and increased expression of estrogen receptors in IH tissues suggest that estrogen may promote tumor progression through stimulation of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis (6, 19, 151). 17β-estradiol has been shown to bind ER-α in HemSCs, upregulating VEGF-A and enhancing angiogenesis and tumor growth (151). Estrogen also modulates the secretion of multiple angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors, including FGF-2, IFN-α/β/γ, and TGF-β, which may exert stage-dependent effects during the proliferative and involuting phases of IH (19). Nevertheless, the mechanisms by which estrogen influences IH remain unclear, and its impact on intracellular signaling pathways is debated. Future studies should systematically investigate estrogen’s role at different stages of IH and assess its potential as a therapeutic target.
5.3 Safety of propranolol
Propranolol, the primary treatment for IH, has shown substantial efficacy, yet concerns remain regarding its long-term safety, side effects, and potential for recurrence (152). Despite numerous safety studies, there is a lack of multicenter follow-up studies reporting long-term outcomes (153, 154). Some patients experience relapses after treatment cessation, suggesting that propranolol may temporarily impede lesion progression without providing a definitive cure (155, 156). Future large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed to assess propranolol’s long-term safety and efficacy. Additionally, exploring combination therapies with other targeted approaches may help reduce recurrence risk.
5.4 Mechanism of IH regression
Most hemangiomas gradually degenerate into fibrous adipose tissue after proliferation and stabilization. This regression involves endothelial cell apoptosis, stem cell differentiation into adipocytes, and changes in the local microenvironment (157, 158). However, the precise molecular pathways, regulatory networks, and mechanisms of cell fate determination remain incompletely understood.
5.5 Ideal IH model
Current in vitro and animal models do not fully mimic the growth and regression of human IH. There is an urgent need to develop comprehensive models that closely reflect human pathology to advance the study of IH mechanisms and therapeutic strategies (159, 160).
5.6 Intercellular communication
Intercellular communication in IH involves not only the abnormal behavior of individual cell types but also complex signaling among hemangioma stem cells, endothelial cells, pericytes, and immune cells through cytokines, exosomes, and direct cell-cell interactions (38, 121, 141, 143). The precise mechanisms underlying these interactions remain incompletely elucidated, and further research using techniques such as single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomics is needed to fully understand these signaling networks and identify potential molecular targets for therapy.
6 Conclusion
Current research indicates that the development of IH is driven by the synergistic effects of multiple cellular (Table 2) and molecular factors within a dynamic microenvironment. Abnormally proliferating HemECs and multipotent HemSCs serve as the primary cellular sources of IH formation, while environmental factors such as hypoxia, inflammation, ECM, and exosome-mediated intercellular communication critically regulate tumor growth, angiogenesis, and eventual regression (3, 17, 18, 84, 161).
With growing insight into IH biology, several molecules have emerged as promising therapeutic targets. SOX18, a key transcription factor in vascular development and endothelial differentiation, has been implicated in abnormal endothelial proliferation in IH. Pharmacologic inhibition of SOX18, including the non–β-adrenergic effects of R(+)-propranolol and repurposing of statins via the SOX18–mevalonate pathway axis, highlights its translational potential (74, 77, 150). Exosomes, as central mediators of intercellular communication and angiogenesis, represent potential intervention points through modulation of their release or function. HIF-1α, a major driver of VEGF expression in hypoxic niches, may provide an opportunity for early control of IH proliferation (87). In addition, hormonal signaling and immune microenvironmental regulation may enable more individualized treatment strategies.
In conclusion, IH is a complex vascular anomaly regulated by a dynamic network of cellular and molecular mechanisms. Continued exploration of its genetic, metabolic, and immunologic drivers will provide a foundation for future innovation in vascular biology and therapy. Progress will require multidisciplinary approaches combining advanced molecular technologies with rigorous clinical research. Such efforts will be critical to resolving existing controversies, validating emerging therapeutic targets, and accelerating the translation of mechanistic discoveries into precision treatments for IH.
Author contributions
ZZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. FW: Writing – review & editing. LZ: Writing – review & editing. QS: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Zunyi United Fund: Innovative Team in Oral and Maxillofacial Plastic Surgery (Code: Zunyi Science Cooperation HZ No. (2020) 294).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Krowchuk DP, Frieden IJ, Mancini AJ, Darrow DH, Blei F, Greene AK, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the management of infantile hemangiomas. Pediatrics. (2019) 143:. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3475
2. Gong X, Li Y, Yang K, Chen S, and Ji Y. Infantile hepatic hemangiomas: looking backwards and forwards. Precis Clin Med. (2022) 5:pbac006. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbac006
3. Holm A, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Infantile hemangioma: the common and enigmatic vascular tumor. J Clin Invest. (2024) 134(8):e172836. doi: 10.1172/JCI172836
4. Anderson KR, Schoch JJ, Lohse CM, Hand JL, Davis DM, and Tollefson MM. Increasing incidence of infantile hemangiomas (IH) over the past 35 years: Correlation with decreasing gestational age at birth and birth weight. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2016) 74:120–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2015.08.024
5. Seiffert A, Schneider M, Roessler J, Larisch K, and Pfeiffer DA-OX. Incidence, treatment patterns, and health care costs of infantile hemangioma: results of a retrospective German database analysis. Pediatr Dermatol. (2017) 34:450–7. doi: 10.1111/pde.13187
6. Rodriguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF, Wargon O, and Wong LF. Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2021) 85:1379–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.019
7. Chiller KG, Passaro D, and Frieden IJ. Hemangiomas of infancy: clinical characteristics, morphologic subtypes, and their relationship to race, ethnicity, and sex. Arch Dermatol. (2002) 138:1567–76. doi: 10.1001/archderm.138.12.1567
8. Leaute-Labreze C, Harper JI, and Hoeger PH. Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. (2017) 390:85–94. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00645-0
9. Ding Y, Zhang JZ, Yu SR, Xiang F, and Kang XA-O. Risk factors for infantile hemangioma: a meta-analysis. World J Pediatr. (2020) 16:377–84. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00327-2
10. Frieden IJ, Rogers M, and Garzon MC. Conditions masquerading as infantile haemangioma: Part 1. Australas J Dermatol. (2009) 50(2):77–97; quiz 98. doi: 10.1111/j.440-0960.2009.00514_1.x
11. Hassanein AH, Alomari Ai, Schmidt Ba, and Greene AK. Pilomatrixoma imitating infantile hemangioma. J Craniofac Surg. (2011) 22:734–6. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318207f29f
12. Han JS, Lee MW, Choi JH, and Moon KC. Congenital myofibroma mimicking an infantile hemangioma in an infant. Indian J Dermatol. (2014) 59:317. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.131472
13. Friedman BJ, Shah Kn, Taylor Ja, and Rubin AI. Congenital myofibroma masquerading as an ulcerated infantile hemangioma in a neonate. Pediatr Dermatol. (2013) 30:e248–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01678.x
14. Chiloeches Fernández CA-O, Feito Rodríguez MA-O, Rodríguez Bandera AA-O, Quintana Castanedo LA-OX, Ruiz Bravo E, and de Lucas Laguna R. Metastatic neuroblastoma mimicking an infantile hemangioma. Pediatr Dermatol. (2021) 38:316–7. doi: 10.1111/pde.14421
15. Sebaratnam DF, Rodriguez Bandera AL, Wong LF, and Wargon O. Infantile hemangioma. Part 2: management. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2021) 85:1395–404. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.020
16. Inarejos Clemente EJ, Diaz Leyva J, Karakas SP, Duarte AM, Mas TR, and Restrepo R. Radiologic and clinical features of infantile hemangioma: potential pitfalls and differential diagnosis. Radiographics. (2023) 43:e230064. doi: 10.1148/rg.230064
17. Xiang S, Gong X, Qiu T, Zhou J, Yang K, Lan Y, et al. Insights into the mechanisms of angiogenesis in infantile hemangioma. BioMed Pharmacother. (2024) 178:117181. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117181
18. Sun Y, Qiu F, Hu C, Guo Y, and Lei S. Hemangioma endothelial cells and hemangioma stem cells in infantile hemangioma. Ann Plast Surg. (2022) 88:244–9. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002835
19. Hou F, Dai Y, Fan CY, Suen JY, and Richter GT. Estrogen is involved in hemangioma regression associated with mast cells. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2018) 13:181. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0928-x
20. Ji Y, Chen S, Xiang B, Li Y, Li L, and Wang Q. Jagged1/Notch3 signaling modulates hemangioma-derived pericyte proliferation and maturation. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2016) 40:895–907. doi: 10.1159/000453148
21. Hali F, Moubine I, Berrami H, Serhier Z, Othmani MB, and Chiheb S. Predictors of poor response to oral propranolol in infantile hemangiomas. Arch Pediatr. (2023) 30:455–7. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2023.06.004
22. Boscolo E and Bischoff J. Vasculogenesis in infantile hemangioma. Angiogenesis. (2009) 12:197–207. doi: 10.1007/s10456-009-9148-2
23. Khan ZA, Boscolo E, Picard A, Psutka S, Melero-Martin JM, Bartch TC, et al. Multipotential stem cells recapitulate human infantile hemangioma in immunodeficient mice. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:2592–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI33493
24. Xu W and Zhao H. Management of infantile hemangiomas: Recent advances. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:1064048. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1064048
25. Harbi S, Wang R, Gregory M, Hanson N, Kobylarz K, Ryan K, et al. Infantile hemangioma originates from A dysregulated but not fully transformed multipotent stem cell. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:35811. doi: 10.1038/srep35811
26. Xu D, TM O, Shartava A, Fowles TC, Yang J, Fink LM, et al. Isolation, characterization, and in vitro propagation of infantile hemangioma stem cells and an in vivo mouse model. J Hematol Oncol. (2011) 4:54. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-4-54
27. Mai HM, Zheng Jw, Wang Y-a, Yang X-j, Zhou Q, Qin Z-p, et al. CD133 selected stem cells from proliferating infantile hemangioma and establishment of an in vivo mice model of hemangioma. Chin Med J (Engl). (2013) 126:88–94. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.20121141
28. Edwards AK, Glithero K, Grzesik P, Kitajewski AA, Munabi NC, Hardy K, et al. NOTCH3 regulates stem-to-mural cell differentiation in infantile hemangioma. JCI Insight. (2017) 2(21):e93764. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.93764
29. Yu Y, Fuhr J, Boye E, Gyorffy S, Soker S, Atala A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and adipogenesis in hemangioma involution. Stem Cells. (2006) 24:1605–12. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0298
30. Boye E, Yu Y, Paranya G, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR, and Bischoff J. Clonality and altered behavior of endothelial cells from hemangiomas. J Clin Invest. (2001) 107:745–52. doi: 10.1172/JCI11432
31. Khan ZA, Melero-Martin JM, Wu X, Paruchuri S, Boscolo E, Mulliken JB, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells from infantile hemangioma and umbilical cord blood display unique cellular responses to endostatin. Blood. (2006) 108:915–21. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-006478
32. Jinnin M, Medici D, Park L, Limaye N, Liu Y, Boscolo E, et al. Suppressed NFAT-dependent VEGFR1 expression and constitutive VEGFR2 signaling in infantile hemangioma. Nat Med. (2008) 14:1236–46. doi: 10.1038/nm.1877
33. Ji Y, Chen S, Li K, Li L, Xu C, and Xiang B. Signaling pathways in the development of infantile hemangioma. J Hematol Oncol. (2014) 7:13. doi: 10.1186/756-8722-7-13
34. Huang L, Nakayama H, Klagsbrun M, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Glucose transporter 1-positive endothelial cells in infantile hemangioma exhibit features of facultative stem cells. Stem Cells. (2015) 33:133–45. doi: 10.1002/stem.1841
35. Lee D, Boscolo E, Durham JT, Mulliken JB, Herman IM, and Bischoff J. Propranolol targets the contractility of infantile haemangioma-derived pericytes. Br J Dermatol. (2014) 171:1129–37. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13048
36. Zhang H, Wei T, Johnson A, Sun R, Richter G, and Strub GM. NOTCH pathway activation in infantile hemangiomas. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2021) 9:489–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.07.010
37. Boscolo E, Stewart Cl, Greenberger S, Wu JK, Durham JT, Herman Im, et al. JAGGED1 signaling regulates hemangioma stem cell-to-pericyte/vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2011) 31:181–92. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.232934
38. Boscolo E, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Pericytes from infantile hemangioma display proangiogenic properties and dysregulated angiopoietin-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2013) 33:501–9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300929
39. Cristancho AG and Lazar MA. Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2011) 12:722–34. doi: 10.1038/nrm3198
40. Corselli M, Chen CW, Crisan M, Lazzari L, and Peault B. Perivascular ancestors of adult multipotent stem cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2010) 30:1104–9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.191643
41. Vishvanath L, MacPherson KA, Hepler C, Wang QA, Shao M, Spurgin SB, et al. Pdgfrbeta+ Mural preadipocytes contribute to adipocyte hyperplasia induced by high-fat-diet feeding and prolonged cold exposure in adult mice. Cell Metab. (2016) 23:350–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.018
42. Wang FQ, Chen G, Zhu JY, Zhang W, Ren JG, Liu H, et al. M2-polarised macrophages in infantile haemangiomas: correlation with promoted angiogenesis. J Clin Pathol. (2013) 66:1058–64. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201286
43. Zhang W, Chen G, Wang FQ, Ren JG, Zhu JY, Cai Y, et al. Macrophages contribute to the progression of infantile hemangioma by regulating the proliferation and differentiation of hemangioma stem cells. J Invest Dermatol. (2015) 135:3163–72. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.321
44. Sun ZJ, Zhao YF, and Zhao JH. Mast cells in hemangioma: a double-edged sword. Med Hypotheses. (2007) 68:805–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2006.09.012
45. Ding HW, Wang Q, Wang M, Chen Y, and Yuan SM. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural identification of telocytes in the infantile hemangioma. Ultrastruct Pathol. (2024) 48:563–74. doi: 10.1080/01913123.2024.2415608
46. Moisan F, Oucherif S, Kaulanjan-Checkmodine P, Prey S, Rousseau B, Bonneu M, et al. Critical role of Aquaporin-1 and telocytes in infantile hemangioma response to propranolol beta blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2021) 118(7):e2018690118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2018690118
47. Wildgruber M, Sadick M, Muller-Wille R, and Wohlgemuth WA. Vascular tumors in infants and adolescents. Insights Imaging. (2019) 10:30. doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0718-6
48. Przewratil P, Sitkiewicz A, and Andrzejewska E. Local serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in infantile hemangioma: intriguing mechanism of endothelial growth. Cytokine. (2010) 49:141–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.11.012
49. Greenberger S, Boscolo E, Adini I, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Corticosteroid suppression of VEGF-A in infantile hemangioma-derived stem cells. N Engl J Med. (2010) 362:1005–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0903036
50. Zhang L, Lin X, Wang W, Zhuang X, Dong J, Qi Z, et al. Circulating level of vascular endothelial growth factor in differentiating hemangioma from vascular malformation patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2005) 116:200–4. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000170804.80834.5f
51. Calicchio ML, Collins T, and Kozakewich HP. Identification of signaling systems in proliferating and involuting phase infantile hemangiomas by genome-wide transcriptional profiling. Am J Pathol. (2009) 174:1638–49. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080517
52. Anspach L, Tsaryk R, Seidmann L, Unger RE, Jayasinghe C, Simiantonaki N, et al. Function and mutual interaction of BiP-, PERK-, and IRE1alpha-dependent signalling pathways in vascular tumours. J Pathol. (2020) 251:123–34. doi: 10.1002/path.5423
53. Boscolo E, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. VEGFR-1 mediates endothelial differentiation and formation of blood vessels in a murine model of infantile hemangioma. Am J Pathol. (2011) 179:2266–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.040
54. Lee J Jr., Chen Ch, Chen Y-H, Huang M-J, Huang J, Hung J-S, et al. COSMC is overexpressed in proliferating infantile hemangioma and enhances endothelial cell growth via VEGFR2. PLoS One. (2013) 8:. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056211
55. Lichtenberger BM, Tan PK, Niederleithner H, Ferrara N, Petzelbauer P, and Sibilia M. Autocrine VEGF signaling synergizes with EGFR in tumor cells to promote epithelial cancer development. Cell. (2010) 140:268–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.046
56. Ji Y, Chen S, Li K, Xiao X, Xu T, and Zheng S. Upregulated autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor-2 loop prevents apoptosis in haemangioma-derived endothelial cells. Br J Dermatol. (2014) 170:78–86. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12592
57. Iso T, Hamamori Y Fau - Kedes L, and Kedes L. Notch signaling in vascular development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2003) 23:543–53. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000060892.81529.8F
58. Gridley T. Notch signaling during vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2001) 98:5377–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.101138098
59. Wu JK, Adepoju O, De Silva D, Baribault K, Boscolo E, Bischoff J, et al. A switch in Notch gene expression parallels stem cell to endothelial transition in infantile hemangioma. Angiogenesis. (2010) 13:15–23. doi: 10.1007/s10456-009-9161-5
60. Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, Shutter JR, Maguire M, Sundberg JP, et al. Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes Dev. (2000) 14:1343–52. doi: 10.1101/gad.14.11.1343
61. Kume T. Ligand-dependent Notch signaling in vascular formation. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2012) 727:210–22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0899-4_16
62. Xue Y, Gao X, Lindsell CE, Norton CR, Chang B, Hicks C, et al. Embryonic lethality and vascular defects in mice lacking the Notch ligand Jagged1. Hum Mol Genet. (1999) 8:723–30. doi: 10.093/hmg/8.5.723
63. Zhang X, Odom Dt, Koo S-H, Conkright MD, Canettieri G, Best J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of cAMP-response element binding protein occupancy, phosphorylation, and target gene activation in human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2005) 102:4459–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501076102
64. Luttrell LM, Ferguson Ss, Daaka Y, Miller WE, Maudsley S, Della Rocca GJ, et al. Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science. (1999) 283:655–61. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5402.655
65. Ji Y, Chen S, Xiao X, Zheng S, and Li K. β-blockers: a novel class of antitumor agents. Onco Targets Ther. (2012) 5:391–401. doi: 10.147/OTT.S38403
66. Shahzad MM, Arevalo Jm, Armaiz-Pena GN, Lu C, Stone RL, Moreno-Smith M, et al. Stress effects on FosB- and interleukin-8 (IL8)-driven ovarian cancer growth and metastasis. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:35462–70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.109579
67. Bernabé DG, Tamae Ac, Biasoli ÉR, and Oliveira SH. Stress hormones increase cell proliferation and regulates interleukin-6 secretion in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Brain Behav Immun. (2011) 25:574–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.012
68. Cole SW, Arevalo Jm, Takahashi R, Sloan EK, Lutgendorf SK, Sood AK, et al. Computational identification of gene-social environment interaction at the human IL6 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2010) 107:5681–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911515107
69. Chakroborty D, Sarkar C, Basu B, Dasgupta PS, and Basu S. Catecholamines regulate tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. (2009) 69:3727–30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4289
70. Pasquier E, Street J, Pouchy C, Carre M, Gifford AJ, Murray J, et al. β-blockers increase response to chemotherapy via direct antitumour and anti-angiogenic mechanisms in neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer. (2013) 108:485–94. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.205
71. Ji Y and Chen S. Comment on ‘Beta-blockers increase response to chemotherapy via direct anti-tumour and anti-angiogenic mechanisms in neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer. (2013) 109:22–3. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.497
72. Hara MR, Kovacs Jj, Whalen EJ, Rajagopal S, Strachan RT, Grant W, et al. A stress response pathway regulates DNA damage through β2-adrenoreceptors and β-arrestin-1. Nature. (2011) 477:349–53. doi: 10.1038/nature10368
73. Glaser R and Kiecolt-Glaser JK. Stress-induced immune dysfunction: implications for health. Nat Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:243–51. doi: 10.1038/nri571
74. Schrenk S and Boscolo E. A transcription factor is the target of propranolol treatment in infantile hemangioma. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132(3):e156863. doi: 10.1172/JCI156863
75. Mehvar R and Brocks DR. Stereospecific pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of beta-adrenergic blockers in humans. J Pharm Pharm Sci. (2001) 4:185–200.
76. Stoschitzky K, Lindner W, and Kiowski W. Stereoselective vascular effects of the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of propranolol and atenolol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (1995) 25:268–72. doi: 10.097/00005344-199502000-00012
77. Tan JWH, Wylie-Sears J, Seebauer CT, Mulliken JB, Francois M, Holm A, et al. R(+) propranolol decreases lipid accumulation in haemangioma-derived stem cells. Br J Dermatol. (2025) 192:757–9. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae452
78. Jones N, Master Z, Jones J, Bouchard D, Gunji Y, Sasaki H, et al. Identification of Tek/Tie2 binding partners. Binding to a multifunctional docking site mediates cell survival and migration. J Biol Chem. (1999) 274:30896–905. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.43
79. Jones N, Chen Sh, Sturk C, Master Z, Tran J, Kerbel RS, et al. A unique autophosphorylation site on Tie2/Tek mediates Dok-R phosphotyrosine binding domain binding and function. Mol Cell Biol. (2003) 23:658–68. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.8.2658-68.003
80. Jeansson M, Gawlik A, Anderson G, Li C, Kerjaschki D, Henkelman M, et al. Angiopoietin-1 is essential in mouse vasculature during development and in response to injury. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:278–89. doi: 10.1172/JCI46322
81. Koh GY. Orchestral actions of angiopoietin-1 in vascular regeneration. Trends Mol Med. (2013) 19:31–9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.10.010
82. Yu Y, Varughese J, Brown LF, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Increased Tie2 expression, enhanced response to angiopoietin-1, and dysregulated angiopoietin-2 expression in hemangioma-derived endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. (2001) 159:271–80. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63077-5
83. Semenza GL. Hydroxylation of HIF-1: oxygen sensing at the molecular level. Physiology (Bethesda). (2004) 19:176–82. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00001.2004
84. de Jong S, Itinteang T, Withers AH, Davis PF, and Tan ST. Does hypoxia play a role in infantile hemangioma?. Arch Dermatol Res. (2016) 308:219–27. doi: 10.1007/s00403-016-1635-x
85. Kleinman ME, Greives Mr, Churgin SS, Blechman KM, Chang EI, Ceradini DJ, et al. Hypoxia-induced mediators of stem/progenitor cell trafficking are increased in children with hemangioma. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2007) 27(12):2664–70 doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.150284
86. Gomez-Acevedo H, Dai Y, Strub G, Shawber C, Wu JK, and Richter GT. Identification of putative biomarkers for Infantile Hemangiomas and Propranolol treatment via data integration. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:3261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60025-2
87. Jiang X, Tian W, Tu AB, Pasupneti S, Shuffle E, Dahms P, et al. Endothelial hypoxia-inducible factor-2α Is required for the maintenance of airway microvasculature. Circulation. (2019) 139:502–17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036157
88. Walsh DA. Pathophysiological mechanisms of angiogenesis. Adv Clin Chem. (2007) 44:187–221. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(07)44006-9
89. Bikfalvi A, Klein S, Pintucci G, and Rifkin DB. Biological roles of fibroblast growth factor-2. Endocr Rev. (1997) 18:26–45. doi: 10.210/edrv.18.1.0292
90. Sahni A, Khorana Aa, Baggs RB, Peng H, and Francis CW. FGF-2 binding to fibrin(ogen) is required for augmented angiogenesis. Blood. (2006) 107:126–31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-460
91. Okada-Ban M, Thiery Jp, and Jouanneau J. Fibroblast growth factor-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2000) 32:263–7. doi: 10.1016/s357-2725(99)00133-8
92. Turner N and Grose R. Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2010) 10:116–29. doi: 10.1038/nrc2780
93. Frieden IJ, Haggstrom An, Drolet BA, Mancini AJ, Friedlander SF, Boon L, et al. Infantile hemangiomas: current knowledge, future directions. Proceedings of a research workshop on infantile hemangiomas, April 7-9, 2005, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. Pediatr Dermatol. (2005) 22:383–406. doi: 10.1111/j.525-470.2005.00102.x
94. Frischer JS, Huang J, Serur A, Kadenhe A, Yamashiro DJ, and Kandel JJ. Biomolecular markers and involution of hemangiomas. J Pediatr Surg. (2004) 39:400–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2003.11.043
95. Yang L, Dai J, Li F, Cheng H, Yan D, and Ruan Q. The expression and function of miR-424 in infantile skin hemangioma and its mechanism. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:11846. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10674-7
96. Lamming DW, Ye L, Sabatini DM, and Baur JA. Rapalogs and mTOR inhibitors as anti-aging therapeutics. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:980–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI64099
97. Benjamin D, Colombi M, Moroni C, and Hall MN. Rapamycin passes the torch: a new generation of mTOR inhibitors. (2011) 10:868–80. doi: 10.1038/nrd3531
98. Slomovitz BM and Coleman RL. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:5856–64. doi: 10.1158/078-0432.CCR-12-662
99. Li Y, Kong M, Qiu T, and Ji Y. Targeting ESM1 via SOX4 promotes the progression of infantile hemangioma through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Precis Clin Med. (2024) 7:pbae026. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbae026
100. Greenberger S, Yuan S, Walsh LA, Boscolo E, Kang K-T, Matthews B, et al. Rapamycin suppresses self-renewal and vasculogenic potential of stem cells isolated from infantile hemangioma. J Invest Dermatol. (2011) 131:467–76. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.300
101. Laviola L, Natalicchio A, and Giorgino F. The IGF-I signaling pathway. Curr Pharm Des. (2007) 13:663–9. doi: 10.174/138161207780249146
102. Wang F, Li H, Lou Y, Xie J, Cao D, and Huang X. Insulin−like growth factor I promotes adipogenesis in hemangioma stem cells from infantile hemang. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:825–30. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9895
103. Zhang K, Wang F, Huang J, Lou Y, Xie J, Li H, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 2 promotes the adipogenesis of hemangioma-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 17:1663–9. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7132
104. Kleiman A, Keats Ec, Chan NG, and Khan ZA. Elevated IGF2 prevents leptin induction and terminal adipocyte differentiation in hemangioma stem cells. Exp Mol Pathol. (2013) 94:126–36. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.09.023
105. Ou JM, Lian WS, Qiu MK, Dai YX, Dong Q, Shen J, et al. Knockdown of IGF2R suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in hemangioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. (2014) 45:1241–9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.512
106. Biyashev D, Veliceasa D, Kwiatek A, Sutanto MM, Cohen RN, and Volpert OV. Natural angiogenesis inhibitor signals through Erk5 activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma). J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:13517–24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.117374
107. Sun K, Huang R, Wu S, Chen Z, Deng S, Zhou J, et al. The pleiotropic effects of PPARs on vascular cells and angiogenesis: implications for tissue engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. (2016) 11:265–73. doi: 10.174/1574888x1103160303181155
108. Kim S, Lee Jj, and Heo DS. PPARγ ligands induce growth inhibition and apoptosis through p63 and p73 in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 406:389–95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.052
109. Mitra R, Fitzsimons HL, Hale T, Tan ST, Gray C, and White MPJ. Recent advances in understanding the molecular basis of infantile haemangioma development. Br J Dermatol. (2024) 191:661–9. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae241
110. Yuan SM, Guo Y, Wang Q, Xu Y, Wang M, Chen HN, et al. Over-expression of PPAR-γ2 gene enhances the adipogenic differentiation of hemangioma-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:115817–28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23705
111. Wang F, Li H, Lou Y, Xie J, Cao D, and Huang X. Insulin−like growth factor I promotes adipogenesis in hemangioma stem cells from infantile hemangiomas. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19(4):2825–30.doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9895
112. Abrahams A, Parker Mi, and Prince S. The T-box transcription factor Tbx2: its role in development and possible implication in cancer. IUBMB Life. (2010) 62:92–102. doi: 10.1002/iub.275
113. Todorovich SM and Khan ZA. Elevated T-box 2 in infantile hemangioma stem cells maintains an adipogenic differentiation-competent state. Dermatoendocrinol. (2013) 5:352–7. doi: 10.4161/derm.26739
114. Roach EE, Chakrabarti R, Park NI, Keats EC, Yip J, Chan NG, et al. Intrinsic regulation of hemangioma involution by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell Death Dis. (2012) 3:. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.58
115. Bjarnegård M, Enge M, Norlin J, Gustafsdottir S, Fredriksson S, Abramsson A, et al. Endothelium-specific ablation of PDGFB leads to pericyte loss and glomerular, cardiac and placental abnormalities. Development. (2004) 131:1847–57. doi: 10.242/dev.01080
116. Greenberger S, Adini I, Boscolo E, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Targeting NF-κB in infantile hemangioma-derived stem cells reduces VEGF-A expression. Angiogenesis. (2010) 13:327–35. doi: 10.1007/s10456-010-9189-6
117. Wu KQ, Muratore CS, So EY, Sun C, Dubielecka PM, Reginato AM, et al. M1 macrophage-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition promotes infantile hemangioma regression. Am J Pathol. (2017) 187:102–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.05.014
118. Jia J, Bai Y, Fu K, Sun ZJ, Chen XM, and Zhao YF. Expression of allograft inflammatory factor-1 and CD68 in haemangioma: implication in the progression of haemangioma. Br J Dermatol. (2008) 159:811–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08744.x
119. Kang TY, Bocci F, Jolly MK, Levine H, Onuchic JN, and Levchenko A. Pericytes enable effective angiogenesis in the presence of proinflammatory signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2019) 116:23551–61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913373116
120. Zheng P, Luo Q, Wang W, Li J, Wang T, Wang P, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages-derived exosomes promote the migration of gastric cancer cells by transfer of functional Apolipoprotein E. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:434. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0465-5
121. Li Z, Cao Z, Li N, Wang L, Fu C, Huo R, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA MIR4435-2HG promotes progression of infantile hemangiomas by targeting HNRNPA1. Int J Nanomed. (2023) 18:5943–60. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S435132
122. Ranieri G, Passantino L, Patruno R, Passantino G, Jirillo F, Catino A, et al. The dog mast cell tumour as a model to study the relationship between angiogenesis, mast cell density and tumour Malignancy. Oncol Rep. (2003) 10:1189–93. doi: 10.3892/or.10.5.1189
123. Zhan M, Hori Y, Wada N, Ikeda J, Hata Y, Osuga K, et al. Angiogenic factor with G-patch and FHA domain 1 (AGGF1) expression in human vascular lesions. Acta Histochem Cytochem. (2016) 49:75–81. doi: 10.1267/ahc.15035
124. Hiromatsu Y and Toda S. Mast cells and angiogenesis. Microsc Res Tech. (2003) 60:64–9. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10244
125. Marler JJ, Fishman Sj, Kilroy SM, Fang J, Upton J, Mulliken JB, et al. Increased expression of urinary matrix metalloproteinases parallels the extent and activity of vascular anomalies. Pediatrics. (2005) 116:38–45. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1518
126. Komi DEA and Redegeld FA. Role of mast cells in shaping the tumor microenvironment. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2020) 58:313–25. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08753-w
127. Hasan Q, Rüger Bm, Tan ST, Gush J, and Davis PF. Clusterin/apoJ expression during the development of hemangioma. Hum Pathol. (2000) 31:691–7. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2000.7638
128. Jiang Y, Li X, Liu Q, Lei G, Wu C, Chen L, et al. Apolipoprotein A-I binding protein inhibits the formation of infantile hemangioma through cholesterol-regulated hypoxia-inducible factor 1α Activation. J Invest Dermatol. (2024) 144:645–58.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.07.030
129. Wu P, Xu H, Li N, Huo R, Shen B, Lin X, et al. Hypoxia-induced cyr61/CCN1 production in infantile hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2021) 147:412e–23e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007672
130. Mei H, Xian H, and Ke J. LncRNA-MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the progression of infantile hemangiomas by increasing miR-138-5p/HIF-1alpha axis-regulated glycolysis. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:753218. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.753218
131. Davis GE and Senger DR. Endothelial extracellular matrix: biosynthesis, remodeling, and functions during vascular morphogenesis and neovessel stabilization. Circ Res. (2005) 97:1093–107. doi: 10.161/01.RES.0000191547.64391.e3
132. Jang YC, Arumugam S, Ferguson M, Gibran NS, and Isik FF. Changes in matrix composition during the growth and regression of human hemangiomas. J Surg Res. (1998) 80:9–15. doi: 10.006/jsre.5355
133. Park H, Park H, Chung HY, TM O, and Waner M. Comparative analysis of the extracellular matrix composition in proliferating and involuted infantile hemangiomas. Arch Plast Surg. (2015) 42:544–51. doi: 10.5999/aps.2015.42.5.544
134. Whelan MC and Senger DR. Collagen I initiates endothelial cell morphogenesis by inducing actin polymerization through suppression of cyclic AMP and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:327–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207554200
135. Liu Y and Senger DR. Matrix-specific activation of Src and Rho initiates capillary morphogenesis of endothelial cells. FASEB J. (2004) 18:457–68. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0948com
136. Davis GE and Bayless KJ. An integrin and Rho GTPase-dependent pinocytic vacuole mechanism controls capillary lumen formation in collagen and fibrin matrices. Microcirculation. (2003) 10:27–44. doi: 10.1038/sj.mn.7800175
137. Senger DR. Molecular framework for angiogenesis: a complex web of interactions between extravasated plasma proteins and endothelial cell proteins induced by angiogenic cytokines. Am J Pathol. (1996) 149:1–7.
138. Zhu LA-O, Xie J, Liu Z, Huang Z, Huang M, Yin H, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor/vascular endothelial growth factor ratio plays a crucial role in the spontaneous regression of infant hemangioma and in the therapeutic effect of propranolol. doi: 10.1111/cas.13611
139. Tan ST, Velickovic M, Ruger BM, and Davis PF. Cellular and extracellular markers of hemangioma. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2000) 106:529–38. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200009030-00001
140. Primo L, Seano G, Roca C, Maione F, Gagliardi PA, Sessa R, et al. Increased expression of alpha6 integrin in endothelial cells unveils a proangiogenic role for basement membrane. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:5759–69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0507
141. Liu C, Zhao Z, Guo S, Zhang L, Fan X, and Zheng J. Exosomal miR-27a-3p derived from tumor-associated macrophage suppresses propranolol sensitivity in infantile hemangioma. Cell Immunol. (2021) 370:104442. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104442
142. Zhao ZL, Liu C, Wang QZ, Wu HW, and Zheng JW. Engineered exosomes for targeted delivery of miR-187-3p suppress the viability of hemangioma stem cells by targeting Notch signaling. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:621. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4138
143. Wang QZ, Zhao ZL, Liu C, and Zheng JW. Exosome-derived miR-196b-5p facilitates intercellular interaction in infantile hemangioma via down-regulating CDKN1B. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:394. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-6456
144. Castren E, Salminen P, Vikkula M, Pitkaranta A, and Klockars T. Inheritance patterns of infantile hemangioma. Pediatrics. (2016) 138(5):e20161623. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-1623
145. Cheung DS, Warman Ml, and Mulliken JB. Hemangioma in twins. Ann Plast Surg. (1997) 38:269–74. doi: 10.097/00000637-199703000-00014
146. Walter JW, Blei F, Anderson JL, Orlow SJ, Speer MC, and Marchuk DA. Genetic mapping of a novel familial form of infantile hemangioma. Am J Med Genet. (1999) 82:77–83. doi: 10.002/(sici)096-8628(19990101)82:1<77::aid-ajmg15>3.0.co;2-a
147. Walter JW, North Pe, Waner M, Mizeracki A, Blei F, Walker JWT, et al. Somatic mutation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in juvenile hemangioma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. (2002) 33:295–303. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10028
148. Oszajca K, Szemraj J, Wyrzykowski D, Chrzanowska B, Salamon A, and Przewratil P. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 genes and risk of infantile hemangioma. Int J Dermatol. (2018) 57:1201–7. doi: 10.111/ijd.14127
149. Wang L, Zou Y, Huang Z, Wang W, Li J, Bi J, et al. KIAA1429 promotes infantile hemangioma regression by facilitating the stemness of hemangioma endothelial cells. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:1569–81. doi: 10.1111/cas.15708
150. Holm A, Graus MS, Wylie-Sears J, Tan JWH, Alvarez-Harmon M, Borgelt L, et al. An endothelial SOX18-mevalonate pathway axis enables repurposing of statins for infantile hemangioma. J Clin Invest. (2025) 135(7):e179782. doi: 10.1172/JCI179782
151. Zhang L, Wu HW, Yuan W, and Zheng JW. Estrogen-mediated hemangioma-derived stem cells through estrogen receptor-alpha for infantile hemangioma. Cancer Manag Res. (2017) 9:279–86. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S138687
152. Xerfan EMS, Andersen ML, Facina AS, Tufik S, and Tomimori J. Sleep disturbances as an adverse effect of propranolol use in children with infantile hemangioma. World J Pediatr. (2020) 16:537–8. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00335-2
153. Yu L, Wei L, Xu Z, Zhang B, Han X, Sun Y, et al. Safety assessment of propranolol for infantile hemangioma: a study in an Asian population. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. (2022) 15:237–42. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2020638
154. Su R, Qian H, Hu C, Li W, Li J, Wu B, et al. Oral propranolol for the treatment of hemangiomas in high-risk infants: safety and cost analysis of outpatient-initiated therapy. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1439449. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1439449
155. Yang E, Wang X, Huang S, Li M, Li Y, Geng Y, et al. Shikonin reverses pyruvate kinase isoform M2-mediated propranolol resistance in infantile hemangioma through reactive oxygen species-induced autophagic dysfunction. Cancer Sci. (2023) 114:806–21. doi: 10.1111/cas.15649
156. Frongia GA-O, Byeon JO, Mehrabi A, and Günther P. Recurrence rate of infantile hemangioma after oral propranolol therapy. Eur J Pediatr. (2021) 180(2):585–90. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03872-5
157. Razon MJ, KrÄLing BM, Mulliken JB, and Bischoff J. Increased apoptosis coincides with onset of involution in infantile hemangioma. Microcirculation. (2010) 5:189–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.1998.tb00068.x
158. Li HH, Lou Y, Zhang RR, Xie J, and Cao DS. Propranolol accelerats hemangioma stem cell transformation into adipocyte. Ann Plast Surg. (2019) 83:e5–e13. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002104
159. Kong M, Li Y, Wang K, Zhang S, and Ji Y. Infantile hemangioma models: is the needle in a haystack? J Transl Med. (2023) 21:308. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04144-0
160. Li Y, Zhu X, Kong M, Chen S, Bao J, and Ji Y. Three-dimensional microtumor formation of infantile hemangioma-derived endothelial cells for mechanistic exploration and drug screening. Pharm (Basel). (2022) 15(11):1393. doi: 10.3390/ph15111393
Keywords: infantile hemangioma, cell subpopulations, angiogenesis, extracellular matrix, immune microenvironment
Citation: Zhu Z, Jiang X, Wang F, Zhao L and Song Q (2025) Decoding infantile hemangioma: cellular dynamics, molecular signals, and microenvironmental influences. Front. Oncol. 15:1675194. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1675194
Received: 29 July 2025; Accepted: 10 September 2025;
Published: 25 September 2025.
Edited by:
Elisa Boscolo, University of Cincinnati, United StatesReviewed by:
Meng Kong, Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, ChinaManuel Flores-Sáenz, University of Alcalá, Spain
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Jiang, Wang, Zhao and Song. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qinggao Song, c29uZ3FpbmdnYW9Aem11LmVkdS5jbg==
 Zongdong Zhu1
Zongdong Zhu1 Lijin Zhao
Lijin Zhao Qinggao Song
Qinggao Song