- 1Clinical Medical College, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 2First Clinical Medical College, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
Resistance to chemotherapy, targeted agents, and particularly immunotherapy remains the principal challenge in the management of gastrointestinal malignancies. This review aims to comprehensively delineate the molecular and microenvironmental drivers of resistance, with emphasis on mechanisms impacting immunotherapy response, and evaluate emerging, mechanism−guided interventions (including immunotherapeutic combinations) for precision therapy. We first examine intrinsic mechanisms—including drug−target alterations, dysregulated drug metabolism and efflux, hyperactivation of DNA damage repair pathways, and epigenetic remodeling—and extrinsic influences stemming from the tumor microenvironment and extracellular matrix remodeling. We then highlight epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) as a critical nexus that integrates stromal cues with cell−intrinsic survival programs, thereby promoting drug efflux and immune evasion. Next, we discuss how single−cell and spatial omics, liquid biopsy, patient−derived organoids, and AI−enabled analytics facilitate subclone−level mapping of resistance networks and real−time tracking of clonal evolution. Finally, we review mechanism−based strategies—including KRAS G12C inhibitors, efflux−pump antagonists, apoptosis reactivators, and epigenetic/autophagy modulators—and propose an integrated, multimodal regimen leveraging immunotherapy where appropriate, informed by real-time drug sensitivity data (e.g., from liquid biopsy), dynamic biomarkers and AI−driven optimization to overcome resistance and improve patient outcomes.
1 Introduction
Gastrointestinal (GI) tumors comprise malignant neoplasms arising within the digestive system, including gastric carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic carcinoma, and gallbladder carcinoma (1). Their high incidence and mortality rates impose an escalating global public health burden (2, 3). Despite significant advances in surgical resection, chemotherapy, molecularly targeted therapies, and immunotherapy, drug resistance remains the principal obstacle to durable treatment response (4). Drug resistance—defined as a marked diminution in tumor sensitivity following therapy, leading to treatment failure and poorer prognosis—can be classified into primary (pre-existing) resistance and acquired resistance that emerges during the course of treatment; these forms often co-exist and interact to drive disease relapse and progression (5–7). Consequently, delineating resistance mechanisms in the gastrointestinal tract, particularly those constraining immunotherapeutic efficacy, is crucial. This study examines how integrating molecular profiling, immunotherapeutic data, and functional drug sensitivity assays can inform the design of enhanced treatment regimens to improve clinical outcomes. Critically, translating molecular insights into clinical action requires bridging two key gaps: predicting immunotherapy resistance driven by dynamic tumor-immune interactions, and quantifying drug sensitivity at the individual patient level. This review therefore emphasizes functional drug sensitivity profiling—using ex vivo models and liquid biopsy—as a linchpin for integrating molecular mechanisms with immunotherapeutic strategies to design adaptive treatment regimens.
2 Overview of anti−tumor drug resistance mechanisms in gastrointestinal tumors
Acquired resistance develops when primary resistance is a measure of tumor cell insensitivity inherent to the tumor that occurs before any form of therapy, which causes suboptimal responses to initial chemotherapy or targeted therapies. Acquired resistance develops when once−sensitive cells, under sustained drug pressure, gain resistance through genetic mutations or adaptive reprogramming (8, 9). The emergence of resistance is a multifactorial process involving both cell−intrinsic and microenvironmental factors. Intrinsic mechanisms comprise drug target alterations, drug metabolism and efflux dysregulation, hyperactivation of DNA damage repair pathways, and epigenetic alterations (9–12). Extrinsic mechanisms are derived from the tumor microenvironment and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, which together generate physical and biochemical barriers to drug delivery efficiency (13, 14). In addition, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the induction of cancer stem cell (CSC) features have been established as underlying determinants of drug resistance. EMT−associated transcription factors not only promote invasion and migration but also confer anti−apoptotic capacity, while CSC populations inherently tolerate drugs and regenerate the tumor mass after therapy, acting as reservoirs of resistant cells (15–18). These interconnected mechanisms synergize to establish the refractory phenotype of gastrointestinal tumors. Critically, these mechanisms also orchestrate immune evasion, constituting a major barrier to the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy, which has emerged as a pivotal therapeutic modality alongside chemotherapy and targeted agents (19) (Figure 1).
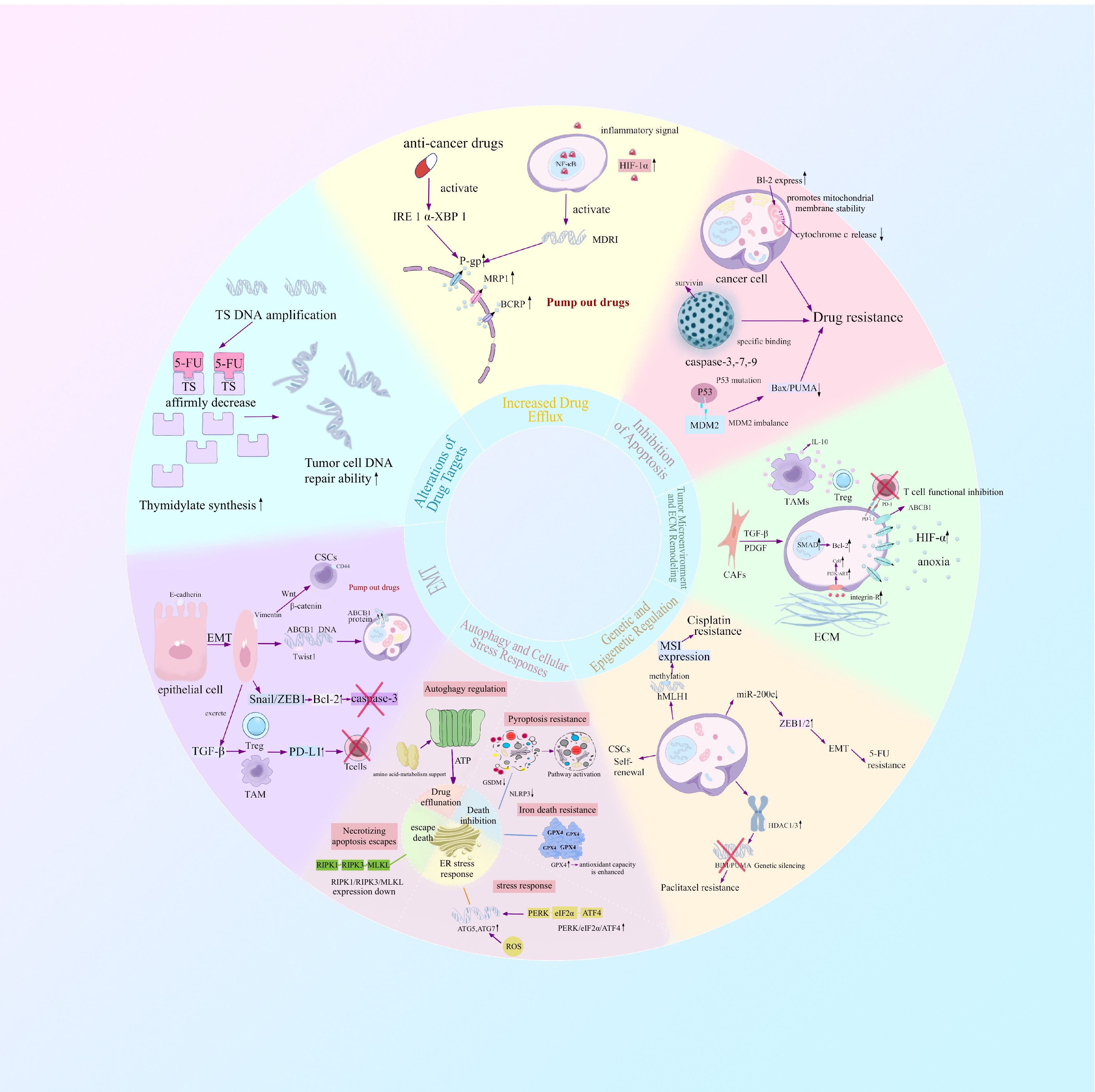
Figure 1. The development of therapeutic resistance in gastrointestinal cancers is a multifactorial phenomenon driven by both tumor cell–intrinsic programs and extrinsic influences from the surrounding microenvironment. Intrinsic mechanisms include alterations in drug targets, dysregulation of drug metabolism and efflux systems, overactivation of DNA damage repair pathways, and widespread epigenetic reprogramming. In parallel, extrinsic mechanisms arise from dynamic remodeling of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and extracellular matrix (ECM), which together establish physical and biochemical barriers that impede effective drug delivery. Moreover, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the acquisition of cancer stem cell (CSC)-like properties have emerged as central determinants of resistance phenotypes. EMT-associated transcription factors not only drive tumor cell invasiveness and migratory capacity but also endow cells with enhanced resistance to apoptosis. Simultaneously, CSC populations exhibit innate tolerance to chemotherapy and possess the ability to repopulate tumors post-treatment, thereby serving as a persistent reservoir of drug-refractory cells.
3 Resistance mechanisms
3.1 Intrinsic factors
3.1.1 Functional drug sensitivity profiling platforms
Beyond mechanistic insights, patient-derived organoids (PDOs) serve as ex vivo micro-tumors for high-throughput drug screening. By exposing PDOs to chemotherapy, targeted agents, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1), researchers quantify tumor-specific sensitivity and identify synergistic combinations (20). For instance, gastric cancer PDOs co-cultured with autologous T cells revealed that TGF-β blockade enhanced pembrolizumab efficacy in immunologically “cold” tumors (21). This functional approach complements genomic and immune profiling to prioritize clinically actionable regimens.
3.1.2 Alterations of drug targets
Structural or expression modification of drug targets dramatically lowers drug–target affinity, hence, driving drug resistance. For instance, 5-fluouracil (5-FU) and raltitrexed are thymidylate synthase (TS) inhibitors that inhibit thymidine synthesis and DNA replication and repair, yet amplification or point mutations of the TS gene within gastrointestinal tumor cells generate TS overexpression or conformational changes which lower inhibitor affinity and induce drug resistance (22, 23). In a similar manner, resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (cetuximab, panitumumab) is largely caused by acquired mutations of the EGFR extracellular domain (ECD). S492R substitution abolishes cetuximab binding without impacting upon panitumumab affinity, with further ECD mutations (R451C, K467T, S464L, G465R, I491M) being present within clinical samples and cell−line models of resistance; it is these variants that modify antibody epitope conformation, allowing for continued EGFR (24–27). Moreover, mutations or amplifications of downstream effectors—KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA—can activate the MAPK and PI3K−AKT pathways independently of EGFR, thus mediating both primary and acquired resistance to EGFR blockade (28, 29).
3.1.3 Increased drug efflux
Overexpression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters is a key driver of drug resistance in gastrointestinal tumors. P-glycoprotein (P-gp; ABCB1), MRP1 (ABCC1), and BCRP (ABCG2) utilize ATP hydrolysis to actively extrude chemotherapeutic agents from the cytosol, markedly reducing intracellular drug accumulation and promoting resistance (30–34). Chemotherapy-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress has been shown to activate the IRE1α–XBP1 axis, leading to upregulation of ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG2 expression (35). In the gastric tumor microenvironment, inflammatory cues activate NF-κB and HIF-1α, which cooperatively bind the MDR1 promoter and drive P-gp overexpression, thereby conferring resistance to paclitaxel and doxorubicin. Overexpression of MRP1 is associated with reduced sensitivity to irinotecan and cisplatin (36, 37). Small molecule inhibitors of ABC transporters or upstream regulators are therefore potential options for reversing drug resistance and reestablishing chemosensitivity.
3.1.4 Inhibition of apoptosis
Antineoplastic agents induce tumor cell death primarily via two canonical apoptotic cascades: the intrinsic, mitochondria-mediated pathway and the extrinsic, death receptor-mediated pathway. The intrinsic pathway involves Bax/Bak oligomerization, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, cytochrome c release, and sequential activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3. The extrinsic pathway is initiated when ligands such as FasL or TRAIL bind their cognate death receptors, triggering caspase-8 and downstream caspase-3 activation.
Gastrointestinal tumor cells commonly evade both cascades through multiple mechanisms. First, anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Mcl-1) are frequently overexpressed in gastric and colorectal cancers; by antagonizing Bax/Bak oligomerization and preserving mitochondrial integrity, they prevent cytochrome c release and caspase activation, thereby conferring resistance to 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin (38–40). Second, inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), notably XIAP and Survivin, bind directly to caspase-3, -7, and -9, blocking their protease activity. Survivin expression is markedly elevated in gastric and colorectal tumors and correlates with resistance to cisplatin and irinotecan (41–46). Finally, dysfunction of the p53 pathway—via MDM2 overexpression or TP53 mutation—impairs transcriptional induction of pro-apoptotic targets such as Bax and PUMA, substantially reducing tumor cell sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents (47–54).
3.1.5 Genetic and epigenetic regulation
Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms regulate gene expression through reversible chemical modifications and non-coding RNAs without altering the underlying DNA sequence, playing a pivotal role in the development of drug resistance in gastrointestinal (GI) tumors. DNA methylation, particularly hypermethylation of gene promoters, leads to the silencing of tumor suppressor genes and drug-metabolizing enzymes, both of which contribute to resistance. For example, promoter hypermethylation of the mismatch repair gene MLH1 in gastric cancer results in microsatellite instability (MSI), thereby reducing the efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapeutics (55, 56).
Histone modifications such as acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation exert their action by modifying chromatin structure to thereby control the expression of resistance-associated genes (57). In gastric cancer, overexpression of HDAC1/3 contributes to deacetylation, silencing pro-apoptotic genes such as BIM and PUMA, which is a key mechanism in taxane resistance (58). Additionally, noncoding RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs), and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), regulate drug susceptibility by targeting mRNA or affecting signaling pathways of vital importance and drug-resistant clone expansion in the case of therapeutic pressure (59). For example, downregulation of the miR−200 family, particularly miR-200c, upregulates ZEB1/2 and promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process that enhances resistance to 5−fluorouracil (5−FU) in colorectal cancer (60–64). The epigenetic network also plays a critical role in maintaining the self-renewal and multi−lineage differentiation potential of cancer stem cells (CSCs), thereby supporting the persistence and expansion of drug-resistant clones under therapeutic stress. The network is a dynamic and adaptive system both promoting resistance and tumor growth and is thus of particular importance as a target in GI oncology (61, 65–67).
3.1.6 Autophagy and cellular stress responses
Tumor cells orchestrate multiple modes of cell death regulation to collectively contribute to therapeutic resistance. Autophagy, a lysosome-mediated degradation pathway, maintains cellular homeostasis under nutrient deprivation, hypoxia, or drug-induced stress. In gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, autophagy acts in concert with stress responses—such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and oxidative stress—to promote survival and resistance under chemotherapy or targeted therapy pressure (68). The autophagic degradation of macromolecules generates ATP, which fuels drug efflux mediated by ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, while the recycled amino acids and fatty acids fulfill the metabolic demands of tumor cells under treatment, thereby reinforcing chemoresistance. Conversely, defective autophagy leads to the accumulation of p62/SQSTM1, which activates NF-κB signaling and upregulates pro-survival and pro-inflammatory genes, exacerbating cisplatin resistance (69–71).
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent, lipid peroxidation–driven form of cell death. GI tumor cells commonly resist ferroptosis inducers (e.g., erastin, RSL3) and certain chemotherapeutics by upregulating glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), thereby enhancing antioxidant capacity (72–74). In addition, tumor cells evade necroptosis, a RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL-dependent death pathway, through downregulation of RIPK3 or MLKL expression, or by exploiting molecular chaperones to suppress pathway activation, enabling escape from TNFα family cytokines or certain chemotherapy-induced cell death (75, 76). Pyroptosis, defined as gasdermin-mediated inflammatory lytic death, is also suppressed by tumor cells through downregulation of GSDM proteins (e.g., GSDMD, GSDME) or inhibition of upstream inflammasome activation (e.g., NLRP3), conferring resistance to immunotherapy- or chemotherapy-induced pyroptosis (77, 78).
Stress responses are pervasive during chemotherapy. Chemotherapy-induced ER stress activates the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 axis, upregulating core autophagy genes (ATG5, ATG7), thereby enhancing autophagic flux, alleviating protein-folding stress, and supporting cell survival. Meanwhile, chemotherapy-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) further activate the transcription factor Nrf2, driving the expression of antioxidants (HO-1, NQO1) and autophagy-related genes, ultimately increasing tolerance to oxidative and drug-induced damage.
3.2 Extrinsic factors
3.2.1 Tumor microenvironment and ECM remodeling
The tumor microenvironment (TME) comprises cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), immune and endothelial cells, along with extracellular matrix (ECM) components, cytokines, and metabolites; its dynamic network profoundly influences therapeutic response in gastrointestinal tumors (79–82). CAF-derived factors such as TGF-β and PDGF activate SMAD, PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling, leading to upregulation of anti−apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Survivin) and enhanced resistance to 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer (83–86). Hypoxia within the TME stabilizes HIF-1α, which drives expression of ABC transporters (ABCB1, ABCG2), promoting drug efflux and metabolic reprogramming that confer a survival advantage under treatment pressure (87–90). Concurrently, immunosuppressive populations—including regulatory T cells (Tregs) and tumor−associated macrophages (TAMs)—together with upregulated immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, inhibit cytotoxic T-cell activity, thereby contributing significantly to resistance against both chemotherapy and immunotherapy (91). Remodeling of the ECM—characterized by deposition of hyaluronan and laminin—increases interstitial fluid pressure, impedes drug penetration, and engages integrin/FAK signaling to promote tumor cell adhesion, survival, and migration, thereby exacerbating resistance phenotypes (92–94).
3.2.2 Metabolomics analysis
Metabolomics, through the systematic profiling of dynamic changes in small-molecule metabolites, offers a unique lens for deciphering the mechanisms underlying drug resistance in gastrointestinal (GI) cancers. Accumulating evidence indicates that resistant tumor cells reprogram key metabolic pathways—including energy metabolism, redox homeostasis, and nucleotide biosynthesis—or engage metabolite-mediated epigenetic regulation to evade chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity. For instance, in oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells, the expression of hexokinase 2 (HK2) and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) is markedly upregulated, thereby enhancing glycolytic flux and reducing intracellular drug accumulation (95–97). In gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer models, increased expression of glutamate–cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), the rate-limiting enzyme in glutathione (GSH) synthesis, promotes the clearance of chemotherapy-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) and preserves redox homeostasis, ultimately protecting tumor cells (98, 99). Moreover, resistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in colorectal cancer has been linked to the overexpression of thymidylate synthase (TYMS) and increased dUTPase activity, which together drive competitive inhibition of the drug’s molecular target (100, 101).
3.3 Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition is a cellular reprogramming process in which epithelial tumor cells lose polarity and cell-cell adhesion while acquiring mesenchymal characteristics; hallmarks include downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of Vimentin, accompanied by enhanced migratory and invasive capacities that confer resistance to anticancer agents (102–106). EMT also promotes a cancer stem cell phenotype through activation of Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, and related pathways, enabling cells to evade chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity (14, 107). Furthermore, EMT transcription factors upregulate ABC transporter genes such as ABCB1 and ABCC1, increasing drug efflux; for example, Twist1 binds the ABCB1 promoter in colorectal cancer, driving irinotecan export and resistance (108, 109). By modulating the expression of apoptotic regulators, EMT factors further inhibit drug-induced cell death (110). In addition, EMT promotes an immunosuppressive TME recruiting regulatory immune cells and upregulating checkpoint molecules (e.g., PD-L1), creating a feed-forward loop that sustains resistance to both cytotoxic agents and immunotherapy (111, 112).
3.4 The role of the gut microbiota
In gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, the gut microbiota profoundly modulates the metabolism of chemotherapeutic agents, thereby influencing therapeutic efficacy. For example, bacterial β-glucuronidase (GUS) can hydrolyze the inactive metabolite SN-38G into the toxic compound SN-38, leading to severe diarrhea (113). Fusobacterium nucleatum has been shown to activate the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway, induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and attenuate DNA damage, thereby promoting chemoresistance (114). Conversely, certain microbes enhance responses to immunotherapy: Akkermansia muciniphila increases CCL5+CD8+ T-cell infiltration, thereby potentiating the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade and improving clinical outcomes (115). Moreover, microbial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids and tryptophan-derived catabolites exert potent immunomodulatory effects (116, 117). Collectively, these findings highlight the gut microbiota as a dynamic and therapeutically targetable regulator of treatment responses in GI cancers. Interventions such as fecal microbiota transplantation or engineered bacteria–based delivery strategies hold promise for reshaping the immune microenvironment and effectively reversing tumor drug resistance (118–120).
3.5 Emerging technologies reveal new mechanisms
The introduction of single-cell sequencing, liquid biopsy with circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), patient-derived organoid models, and artificial intelligence has brought about a multi-dimensional era for gastrointestinal tumor resistance research (121, 122). In colorectal cancer, single−cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has revealed a pronounced expansion of LGR5+ cancer stem cells following oxaliplatin treatment, with resistance maintained via Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling. Single-cell DNA sequencing (scDNA-seq) permits dynamic monitoring of clonal composition pre- and post-treatment for gastric cancer, with selection for TP53 and APC mutant upon chemotherapeutic challenge—offering a genetic explanation for acquired drug resistance (123–127). Liquid biopsy, analyzing ctDNA, enables non-invasive detection of resistance-driving alterations (genetic, epigenetic) and dynamic monitoring of clonal evolution, serving as a crucial tool for real-time drug sensitivity assessment and early intervention (128). Detection of KRAS/NRAS mutations in colorectal cancer ctDNA, often emerging months before radiographic progression, provides actionable insights into evolving drug sensitivity and resistance, enabling timely therapeutic adjustments. The combination of patient-derived organoid (PDO) models with in vitro immune cell co-culture systems establishes a powerful functional platform for validating tumor sensitivity to immunotherapy. These systems faithfully recapitulate key components of the tumor-immune microenvironment—such as tumor-associated fibroblasts, dendritic cells, macrophages, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes—and enable direct testing of how interventions targeting TGF-β, IDO1, or CSF1R can reverse immune suppression and restore anti−tumor cytotoxicity. Furthermore, generative or graph-based AI modeling approaches can simulate evolutionary trajectories of resistant subclones under immunotherapy pressure, enabling dynamic, adaptive planning of combination regimens (e.g. ICB + HDAC inhibitors or ICB + autophagy blockers) tailored to expected resistance mechanism.
Although such tools offer unmatched resolution for mapping multi-dimensional mechanisms of resistance, issues with data standardization, cost, and data complexity arise. Data sharing and harmonization are needed future initiatives, which must be targeted toward translating laboratory data into clinical applications more rapidly.
4 Clinical implications and mechanism-based therapeutic strategies
4.1 Mechanism-driven intervention approaches
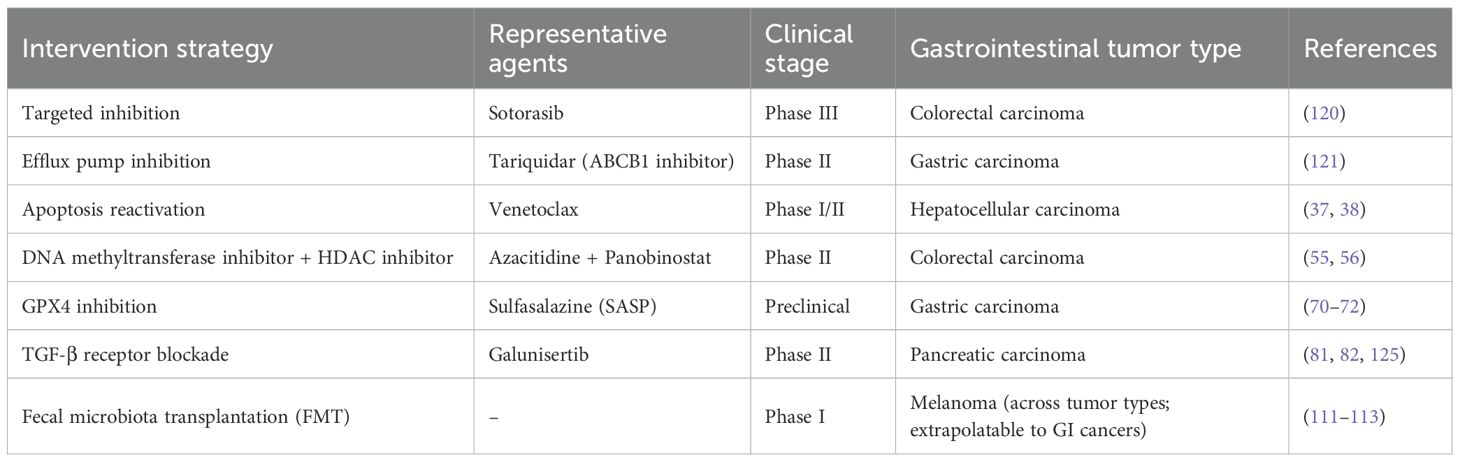
Deeper insights into molecular and immunological drivers of resistance are spurring the development of targeted and immunotherapeutic interventions, evaluated both preclinically and clinically. (Table 1) One promising example is the KRAS G12C inhibitor sotorasib, which covalently binds the mutant cysteine in a hidden pocket of KRAS, traps the protein in its inactive GDP-bound state, and effectively quenches aberrant MAPK signaling in G12C-mutant colorectal tumors (129). To overcome efflux mediated by transporters, tariquidar, a drug inhibitor of P-gp, has been combined with nanoparticle-encapsulated paclitaxel. In gastric cancer models, it is shown to significantly increase intracellular paclitaxel concentration and restore sensitivity to taxane therapy (130–132). Concomitant efforts toward restoration of apoptosis pathways are Smac mimetics, which neutralize inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins (IAPs) for reactivation of caspase-dependent cell death, and Bcl-2 antagonist venetoclax, which disassembles mitochondrial prosurvival defenses—both with efficacies shown in preclinical models of reversal of apoptosis blockade (38, 39, 133). Targeting the tumor stroma, TGF-β receptor blockade (e.g., galunisertib) dampens CAF activation, reduces collagen deposition, and softens the ECM. This not only enhances chemotherapy delivery and efficacy but also alleviates immunosuppression within the TME, potentially improving response to immunotherapy (85, 86, 134, 135). Reversing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) represents another avenue: the small−molecule reversine inhibits Twist1 nuclear translocation, reestablishing 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by restoring epithelial characteristics (109, 136, 137). Epigenetic resistance can be addressed by combining the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor azacitidine with the HDAC inhibitor panobinostat, which together reverse MGMT promoter hypermethylation, reactivate pro-apoptotic gene expression, and augment chemotherapy response in colorectal models (55, 56, 138). Lastly, simultaneous targeting of autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress—using hydroxychloroquine to block autophagosome–lysosome fusion and GSK2606414 to inhibit the PERK/eIF2α axis—has been shown to synergistically overcome autophagy-dependent resistance phenotypes (67, 110, 111).
4.2 Prospects for personalized precision therapy
Drug resistance in gastrointestinal tumors reflects a heterogeneous and adaptive network of molecular and microenvironmental alterations. Personalized precision medicine aims to “tailor” therapeutic strategies to each patient’s unique resistance landscape. Integrating single−cell transcriptomics with spatial metabolomics enables precise mapping of resistant clones and their metabolic niches—for example, co−localization of KRAS−mutant subpopulations with cancer−associated fibroblasts in colorectal cancer suggests focal FAK inhibition, whereas lactate−rich microdomains in gastric cancer may be targeted via MCT1 blockade. Liquid biopsy (ctDNA, exosomes) provides real-time monitoring of drug sensitivity and resistance dynamics, enabling early detection of recurrence and data-driven treatment adaptation (139).Mechanism-based combinatorial strategies integrating immunotherapy are emerging: e.g.,triplet therapies combining KRAS inhibitors, immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), and epigenetic modulators (like HDAC inhibitors that enhance tumor antigen presentation) show synergistic efficacy. In recent years, multiple trials, including the KRYSTAL-1 trial (NCT03785249), have demonstrated that triplet therapy can effectively reverse acquired resistance in gastrointestinal tumors (140–143). Dual targeting of epithelial mesenchymal transition and autophagy (e.g., Twist1 inhibitors plus hydroxychloroquine) can dismantle the survival networks of cancer stem like cells and re-sensitize tumors to conventional chemotherapy.AI-driven sensitivity prediction is a key strategy to overcome drug resistance. For instance, multimodal AI platforms integrate genomic features (such as IFN-γ response genes), digital pathology images, and ex vivo organoid drug screening data (144, 145), generating patient-specific immunotherapy sensitivity scores with predictive accuracy superior to single biomarkers like PD-L1 IHC. Studies have shown that such AI-based prediction models exhibit immense potential in oncology (146, 147), providing powerful tools for personalized treatment decisions. Rigorous clinical validation of these approaches, with attention to safety, feasibility, and cost-effectiveness, will be essential. Ultimately, the goal of personalized precision therapy is not only to surmount therapeutic resistance but also to preserve patient dignity and hope throughout the treatment journey.
5 Conclusion and future perspectives
Drug resistance in GI malignancies represents a complex “survival race,” driven by tumor cell-intrinsic mechanisms (genetic, epigenetic) and extrinsic factors (microenvironmental crosstalk, immune evasion) to evade cytotoxic, targeted, and immunotherapies. These mechanisms operate not in isolation but as a dynamic, interconnected network, collectively enabling tumor persistence and progression under therapeutic pressure.
Interdisciplinary technologies (spatial/single-cell omics, liquid biopsy, organoids, AI) are deciphering this complexity, enabling more precise mapping of resistance mechanisms (including immune evasion) and facilitating drug sensitivity profiling for improved clinical decisions. Nevertheless, there are substantial issues, including integration of data, standardization, cost, and translation into everyday practice.
Prospects for future research include high-resolution, spatiotemporal mapping of resistance niches; deep learning platforms predicting adaptive responses and optimizing real-time treatment regimens; proactive intervention approaches that preempt and countermand resistance; and rational reengineering of the tumor microenvironment for dismantling protective niches. Leveraging these intelligent tools and patient-centric strategies-particularly those integrating immunotherapy insights and drug sensitivity analysis-holds promise for transforming drug resistance into a navigable challenge, leading to sustained remission and enhanced patient outcomes.
Author contributions
HX: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – original draft. KZ: Writing – original draft. JF: Writing – original draft. ZG: Writing – original draft. XCZ: Writing – original draft. ZZ: Writing – original draft. XLZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Sichuan Medical Science and Technology Innovation Research Association (SCMSIA) Launches “Top of Medical Innovation” Specialized Research Project (No.YCH-KY-YCZD2024-298).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kyaruzi VM, Mduma E, Abdelhammed A, Suvvari TK, de Dieu TMJ, Davis B, et al. Methodologies, Epigenetics and field cancerization as the caveats of carcinogenesis and recurrence of gastrointestinal Malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. J Surg Prot Res Methodol. (2023) 2023(2):snad005. doi: 10.1093/jsprm/snad005
2. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, and Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2015) 65:87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262
3. Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska K, Longacre M, Snyder N, et al. Drug resistance in cancer: an overview. Cancers (Basel).. (2014) 6:1769–92. doi: 10.3390/cancers6031769
4. Siegel RL, Miller KD, and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. A cancer journal for clinicians. (2015) 65(1):5–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21254
5. White NJ. Delaying antimalarial drug resistance with combination chemotherapy. Parassitologia. (1999) 41:301–8.
6. Thomas H and Coley HM. Overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: an update on the clinical strategy of inhibiting p-glycoprotein. Cancer control: J Moffitt Cancer Center. (2003) 10:159–65. doi: 10.1177/107327480301000207
7. Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, and Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nature Rev Cancer. (2013) 13:714–26. doi: 10.1038/nrc3599
8. Longley D and Johnston PG. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. J Pathol. (2005) 205:275–92. doi: 10.1002/path.1706
9. Gottesman MM, Fojo T, and Bates S. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP–dependent transporters. Nature Rev Cancer. (2002) 2:48–58. doi: 10.1038/nrc706
10. Borst P and Elferink RO. Mammalian ABC transporters in health and disease. Annual review of biochemistry. (2002) 71:537–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.102301.093055
11. Fojo T and Bates SJO. Strategies for reversing drug resistance. Oncogene. (2003) 22:7512–23. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206951
12. Maier S, Dahlstroem C, Haefliger C, Plum A, and Piepenbrock C. Identifying DNA methylation biomarkers of cancer drug response. Am J Pharmacogenom : Genomics-related Res Drug Develop Clin Practice. (2005) 5:223–32. doi: 10.2165/00129785-200505040-00003
13. Taylor ST, Hickman JA, and Dive C. Epigenetic determinants of resistance to etoposide regulation of Bcl-XL and Bax by tumor microenvironmental factors. The EMBO Journal 20. (2000) 92:18–23. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.1.18
14. Shang Y, Cai X, and Fan D. Roles of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer drug resistance. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2013) 13:915–29. doi: 10.2174/15680096113136660097
15. Xia H and Hui KM. Mechanism of cancer drug resistance and the involvement of noncoding RNAs. Curr Med Chem. (2014) 21:3029–41. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140414101939
16. Mitra A, Mishra L, and Li SJO. EMT, CTCs and CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:10697. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4037
17. Prieto-Vila M, Takahashi R-u, Usuba W, Kohama I, and Ochiya T. Drug resistance driven by cancer stem cells and their niche. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:2574. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122574
18. Papamichael D. The use of thymidylate synthase inhibitors in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: current status. Oncologist. (1999) 4:478–87. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.4-6-478
19. Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med. (2018) 24:541–50. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x
20. Vlachogiannis G, Hedayat S, Vatsiou A, Jamin Y, Fernández-Mateos J, Khan K, et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science. (2018) 359:920–6. doi: 10.1126/science.aao2774
21. Barker CA and Riaz N. A macrophage-activated abscopal effect. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:1282–3. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00464-0
22. Rustum YM, Harstrick A, Cao S, Vanhoefer U, Yin M-B, Wilke H, et al. Thymidylate synthase inhibitors in cancer therapy: direct and indirect inhibitors. J Clin Oncol: Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (1997) 15:389–400. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.1.389
23. Montagut C, Dalmases A, Bellosillo B, Crespo M, Pairet S, Iglesias M, et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nature Med. (2012) 18:221–3. doi: 10.1038/nm.2609
24. Arena S, Bellosillo B, Siravegna G, Martínez A, Canadas I, Lazzari L, et al. Emergence of multiple EGFR extracellular mutations during cetuximab treatment in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res : Official J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2015) 21:2157–66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2821
25. Morelli M, Overman M, Dasari A, Kazmi S, Mazard T, Vilar E, et al. Characterizing the patterns of clonal selection in circulating tumor DNA from patients with colorectal cancer refractory to anti-EGFR treatment. Annal Oncol : Official J Eur Soc Med Oncol. (2015) 26:731–6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv005
26. Newhall K, Price T, Peeters M, Kim T, Li J, Cascinu S, et al. Frequency of S492R mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor: analysis of plasma DNA from metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with panitumumab or cetuximab monotherapy. Lancet Oncol. (2014) 25:ii109. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu193.11
27. Hong DS, Fakih MG, Strickler JH, Desai J, Durm GA, Shapiro GI, et al. KRASG12C inhibition with sotorasib in advanced solid tumors. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1207–17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1917239
28. Cicenas J, Tamosaitis L, Kvederaviciute K, Tarvydas R, Staniute G, Kalyan K, et al. KRAS, NRAS and BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer and melanoma. Medical Oncol (Northwood, London, England). (2017) 34:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0879-9
29. Alketbi L, Al-Ali A, Talaat IM, Hamid Q, and Bajbouj K. The role of ATP-binding cassette subfamily A in colorectal cancer progression and resistance. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1344. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021344
30. Andersen V, Svenningsen K, Knudsen LA, Hansen AK, Holmskov U, Stensballe A, et al. Novel understanding of ABC transporters ABCB1/MDR/P-glycoprotein, ABCC2/MRP2, and ABCG2/BCRP in colorectal pathophysiology. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:11862–76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11862
31. Qutub RM, Al-Ghafari AB, Al Doghaither HA, Omar UM, and Ghulam JM. Increased expressions of cellular ATP-binding cassette transporters may be a promising diagnostic marker for colorectal cancer. Saudi Med J. (2020) 41:834–40. doi: 10.15537/smj.2020.8.25187
32. Modi A, Roy D, Sharma S, Vishnoi JR, Pareek P, Elhence P, et al. ABC transporters in breast cancer: their roles in multidrug resistance and beyond. J Drug Targeting. (2022) 30:927–47. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2022.2091578
33. Domenichini A, Adamska A, and Falasca M. ABC transporters as cancer drivers: Potential functions in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. (2019) 1863:52–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.09.019
34. Gao Q, Li XX, Xu YM, Zhang JZ, Rong SD, Qin YQ, et al. IRE1α-targeting downregulates ABC transporters and overcomes drug resistance of colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. (2020) 476:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.007
35. Pilotto Heming C, Muriithi W, Wanjiku Macharia L, Niemeyer Filho P, Moura-Neto V, and Aran V. P-glycoprotein and cancer: what do we currently know? Heliyon. (2022) 8:e11171. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11171
36. Seelig A. P-glycoprotein: one mechanism, many tasks and the consequences for pharmacotherapy of cancers. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:576559. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.576559
37. Jin L, Chen Y, Cheng D, He Z, Shi X, Du B, et al. YAP inhibits autophagy and promotes progression of colorectal cancer via upregulating Bcl-2 expression. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:457. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03722-8
38. McDonnell TJ, Beham A, Sarkiss M, Andersen MM, and Lo P. Importance of the Bcl-2 family in cell death regulation. Experientia. (1996) 52:1008–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01920110
39. Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N, et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell. (2005) 122:927–39. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.002
40. Gyrd-Hansen M and Meier P. IAPs: from caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2010) 10:561–74. doi: 10.1038/nrc2889
41. LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG, and MacKenzie AE. The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene. (1998) 17:3247–59. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202569
42. Kim WJ, Kim W, Bae JM, Gim J, and Kim SJ. Dehydroabietic acid is a novel survivin inhibitor for gastric cancer. Plants (Basel Switzerland). (2021) 10:1047. doi: 10.3390/plants10061047
43. Lu CD, Altieri DC, and Tanigawa N. Expression of a novel antiapoptosis gene, survivin, correlated with tumor cell apoptosis and p53 accumulation in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. (1998) 58:1808–12.
44. Kawasaki H, Altieri DC, Lu CD, Toyoda M, Tenjo T, and Tanigawa N. Inhibition of apoptosis by survivin predicts shorter survival rates in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. (1998) 58:5071–4.
45. Chen Y, Ye B, Wang C, Nie Y, Qin J, and Shen Z. PLOD3 contributes to HER-2 therapy resistance in gastric cancer through FoxO3/Survivin pathway. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:321. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01103-4
46. Di Y, Jing X, Hu K, Wen X, Ye L, Zhang X, et al. The c-MYC-WDR43 signalling axis promotes chemoresistance and tumour growth in colorectal cancer by inhibiting p53 activity. Drug resistance updates: Rev commentaries antimicrobial Anticancer chemotherapy. (2023) 66:100909. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100909
47. Li XL, Zhou J, Chen ZR, and Chng WJ. P53 mutations in colorectal cancer - molecular pathogenesis and pharmacological reactivation. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:84–93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.84
48. Kastenhuber ER and Lowe SW. Putting p53 in context. Cell. (2017) 170:1062–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.028
49. Sabapathy K and Lane DP. Therapeutic targeting of p53: all mutants are equal, but some mutants are more equal than others. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:13–30. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.151
50. Zhou X, Hao Q, and Lu H. Mutant p53 in cancer therapy-the barrier or the path. J Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 11:293–305. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy072
51. Stiewe T and Haran TE. How mutations shape p53 interactions with the genome to promote tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Drug resistance updates: Rev commentaries antimicrobial Anticancer chemotherapy. (2018) 38:27–43. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2018.05.001
52. Hientz K, Mohr A, Bhakta-Guha D, and Efferth T. The role of p53 in cancer drug resistance and targeted chemotherapy. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:8921–46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13475
53. Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Sci (New York N.Y.). (2004) 303:844–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1092472
54. Bejarano L, Jordāo MJC, and Joyce JA. Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. (2021) 11:933–59. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1808
55. Kim H, Kim YH, Kim SE, Kim NG, Noh SH, and Kim H. Concerted promoter hypermethylation of hMLH1, p16INK4A, and E-cadherin in gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability. J Pathol. (2003) 200:23–31. doi: 10.1002/path.1325
56. Li Y and Seto E. HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2016) 6:a026831. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026831
57. Oehme I, Linke JP, Böck BC, Milde T, Lodrini M, Hartenstein B, et al. Histone deacetylase 10 promotes autophagy-mediated cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2013) 110:E2592–601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300113110
58. Yang SM, Huang C, Li XF, Yu MZ, He Y, and Li J. miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells by regulating PTEN. Toxicology. (2013) 306:162–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.02.014
59. Chi H, Huang J, Yan Y, Jiang C, Zhang S, Chen H, et al. Unraveling the role of disulfidptosis-related LncRNAs in colon cancer: a prognostic indicator for immunotherapy response, chemotherapy sensitivity, and insights into cell death mechanisms. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1254232. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1254232
60. Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Balaguer F, Nagasaka T, Koike J, et al. MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. (2013) 62:1315–26. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301846
61. Ji D, Chen Z, Li M, Zhan T, Yao Y, Zhang Z, et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor suppressor WIF-1. Mol Cancer. (2014) 13:86. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-86
62. Yang J, Qi M, Fei X, Wang X, and Wang K. LncRNA H19: A novel oncogene in multiple cancers. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:3188–208. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62573
63. Cui M, Chen M, Shen Z, Wang R, Fang X, and Song B. LncRNA-UCA1 modulates progression of colon cancer through regulating the miR-28-5p/HOXB3 axis. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:6926–36. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27630
64. Novak D, Hüser L, Elton JJ, Umansky V, Altevogt P, and Utikal J. SOX2 in development and cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 67:74–82. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.007
65. Liu K, Lin B, Zhao M, Yang X, Chen M, Gao A, et al. The multiple roles for Sox2 in stem cell maintenance and tumorigenesis. Cell signalling. (2013) 25:1264–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.02.013
66. Debnath J, Gammoh N, and Ryan KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:560–75. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00585-z
67. Rai SK, Gong T, Gao Z, Qin Y, Huo M, Nakastu K, et al. Abstract 7075: Global epitranscriptomic and transcriptomic footprint revealed upregulation of methylated single minded 2-small variant (meSIM2-SV) in colorectal cancer (CRC) by NTMT1(METTL11A) via m6A-YTHDF1-dependent manner. Cancer Res. (2024) 84:7075–5. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2024-7075
68. Manzoor S, Muhammad JS, Maghazachi AA, and Hamid Q. Autophagy: A versatile player in the progression of colorectal cancer and drug resistance. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:924290. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.924290
69. Zhou H, Yuan M, Yu Q, Zhou X, Min W, and Gao D. Autophagy regulation and its role in gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Cancer biomarkers: section A Dis Markers. (2016) 17:1–10. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160613
70. Cao Y, Luo Y, Zou J, Ouyang J, Cai Z, Zeng X, et al. Autophagy and its role in gastric cancer. Clinica chimica acta; Int J Clin Chem. (2019) 489:10–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.11.028
71. Rozpedek W, Pytel D, Mucha B, Leszczynska H, Diehl JA, and Majsterek I. The role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr Mol Med. (2016) 16:533–44. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937
72. Zhou Q, Meng Y, Li D, Yao L, Le J, Liu Y, et al. Ferroptosis in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:55. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01769-5
73. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
74. Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, Sakamoto T, and Koumura T. Lipid peroxidation-dependent cell death regulated by GPx4 and ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. (2017) 403:143–70. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_508
75. Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, and Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2010) 11:700–14. doi: 10.1038/nrm2970
76. Hu S, Chang X, Zhu H, Wang D, and Chen G. PI3K mediates tumor necrosis factor induced-necroptosis through initiating RIP1-RIP3-MLKL signaling pathway activation. Cytokine. (2020) 129:155046. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155046
77. Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Huang H, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. (2015) 526:660–5. doi: 10.1038/nature15514
78. Shen Y, Chi H, Xu K, Li Y, Yin X, Chen S, et al. A novel classification model for lower-grade glioma patients based on pyroptosis-related genes. Brain Sci. (2022) 12:700. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12060700
79. Zhang H, Yue X, Chen Z, Liu C, Wu W, Zhang N, et al. Define cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the tumor microenvironment: new opportunities in cancer immunotherapy and advances in clinical trials. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:159. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01860-5
80. Li H, Fan X, and Houghton J. Tumor microenvironment: the role of the tumor stroma in cancer. J Cell Biochem. (2007) 101:805–15. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21159
81. Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu J, et al. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:131. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01428-1
82. Guo Z, Saw PE, and Jon S. Non-invasive physical stimulation to modulate the tumor microenvironment: unveiling a new frontier in cancer therapy. Bio Integration. (2024) 5:1–14. doi: 10.15212/bioi-2024-0012
83. Giraldo NA, Sanchez-Salas R, Peske JD, Vano Y, Becht E, Petitprez F, et al. The clinical role of the TME in solid cancer. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:45–53. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0327-z
84. Matsuoka T and Yashiro M. The role of the transforming growth factor-β Signaling pathway in gastrointestinal cancers. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:1551. doi: 10.3390/biom13101551
85. Achyut BR and Yang L. Transforming growth factor-β in the gastrointestinal and hepatic tumor microenvironment. Gastroenterology. (2011) 141:1167–78. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.048
86. Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen H, et al. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:157. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1089-9
87. Bai R, Li Y, Jian L, Yang Y, Zhao L, and Wei M. The hypoxia-driven crosstalk between tumor and tumor-associated macrophages: mechanisms and clinical treatment strategies. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:177. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01645-2
88. Chou CW, Wang CC, Wu CP, Lin YJ, Lee YC, Cheng YW, et al. Tumor cycling hypoxia induces chemoresistance in glioblastoma multiforme by upregulating the expression and function of ABCB1. Neuro-oncology. (2012) 14:1227–38. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos195
89. Nicolini A and Ferrari P. Involvement of tumor immune microenvironment metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer progression, immune escape, and response to immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1353787. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1353787
90. Misra S, Heldin P, Hascall VC, Karamanos NK, Skandalis SS, Markwald RR, et al. Hyaluronan-CD44 interactions as potential targets for cancer therapy. FEBS J. (2011) 278:1429–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08071.x
91. Luo Z, Mei J, Wang X, Wang R, He Z, Geffen Y, et al. Voluntary exercise sensitizes cancer immunotherapy via the collagen inhibition-orchestrated inflammatory tumor immune microenvironment. Cell Rep. (2024) 43:114697. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114697
92. To KK, Poon DC, Wei Y, Wang F, Lin G, and Fu LW. Vatalanib sensitizes ABCB1 and ABCG2-overexpressing multidrug resistant colon cancer cells to chemotherapy under hypoxia. Biochem Pharmacol. (2015) 97:27–37. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.034
93. Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, and Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. (2010) 141:52–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.015
94. Katoh M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer (Review). Int J Oncol. (2005) 27:1677–83. doi: 10.3892/ijo.27.6.1677
95. Qin R, Fan X, Huang Y, Chen S, Ding R, Yao Y, et al. Role of glucose metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer progression and drug resistance. Transl Oncol. (2024) 50:102156. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102156
96. Shi T, Ma Y, Cao L, Zhan S, Xu Y, Fu F, et al. B7-H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells by regulating HK2. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:308. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1549-6
97. Hu L, Huang S, Chen G, Li B, Li T, Lin M, et al. Nanodrugs Incorporating LDHA siRNA Inhibit M2-like Polarization of TAMs and Amplify Autophagy to Assist Oxaliplatin Chemotherapy against Colorectal Cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2022) 14:31625–33. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c05841
98. Vaziri-Gohar A, Hue JJ, Abbas A, Graor HJ, Hajihassani O, Zarei M, et al. Increased glucose availability sensitizes pancreatic cancer to chemotherapy. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:3823. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38921-8
99. Jagust P, Alcalá S, Sainz B Jr., Heeschen C, and Sancho P. Glutathione metabolism is essential for self-renewal and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer stem cells. World J Stem Cells. (2020) 12:1410–28. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i11.1410
100. Longley DB, Boyer J, Allen WL, Latif T, Ferguson PR, Maxwell PJ, et al. The role of thymidylate synthase induction in modulating p53-regulated gene expression in response to 5-fluorouracil and antifolates. Cancer Res. (2002) 62:2644–9.
101. Sharma R, Hoskins JM, Rivory LP, Zucknick M, London R, Liddle C, et al. Thymidylate synthase and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms and toxicity to capecitabine in advanced colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. (2008) 14:817–25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0425
102. Du B and Shim JS. Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to overcome drug resistance in cancer. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2016) 21:965. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070965
103. Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X, and Zhou BP. The role of snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2013) 13:963–72. doi: 10.2174/15680096113136660102
104. Saxena M, Stephens MA, Pathak H, and Rangarajan A. Transcription factors that mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition lead to multidrug resistance by upregulating ABC transporters. Cell Death Dis. (2011) 2:e179. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.61
105. Wang J, Lu Y, Zhang R, Cai Z, Fan Z, Xu Y, et al. Modulating and imaging macrophage reprogramming for cancer immunotherapy. Phenomics. (2024) 4:401–14. doi: 10.1007/s43657-023-00154-6
106. Guo Q, Zhou Y, Xie T, Yuan Y, Li H, Shi W, et al. Tumor microenvironment of cancer stem cells: Perspectives on cancer stem cell targeting. Genes Dis. (2024) 11:101043. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.05.024
107. Lamouille S, Xu J, and Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2014) 15:178–96. doi: 10.1038/nrm3758
108. Jiang ZS, Sun YZ, Wang SM, and Ruan JS. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: potential regulator of ABC transporters in tumor progression. J Cancer. (2017) 8:2319–27. doi: 10.7150/jca.19079
109. Saitoh M. Transcriptional regulation of EMT transcription factors in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2023) 97:21–9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.10.001
110. Taki M, Abiko K, Ukita M, Murakami R, Yamanoi K, Yamaguchi K, et al. Tumor immune microenvironment during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer research: an Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2021) 27:4669–79. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4459
111. Li H, Xu F, Li S, Zhong A, Meng X, and Lai M. The tumor microenvironment: An irreplaceable element of tumor budding and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediated cancer metastasis. Cell adhesion migration. (2016) 10:434–46. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2015.1129481
112. Leung SY, Yuen ST, Chung LP, Chu KM, Chan AS, and Ho JC. hMLH1 promoter methylation and lack of hMLH1 expression in sporadic gastric carcinomas with high-frequency microsatellite instability. Cancer Res. (1999) 59:159–64.
113. Jariwala PB, Pellock SJ, Goldfarb D, Cloer EW, Artola M, Simpson JB, et al. Discovering the microbial enzymes driving drug toxicity with activity-based protein profiling. ACS Chem Biol. (2020) 15:217–25. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00788
114. Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by modulating autophagy. Cell. (2017) 170:548–563.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.008
115. Xu Y, Tan X, Yang Q, Fang Z, and Chen W. Akkermansia muciniphila outer membrane protein regulates recruitment of CD8(+) T cells in lung adenocarcinoma and through JAK-STAT signalling pathway. Microb Biotechnol. (2024) 17:e14522. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14522
116. Luu M and Visekruna A. Short-chain fatty acids: Bacterial messengers modulating the immunometabolism of T cells. Eur J Immunol. (2019) 49:842–8. doi: 10.1002/eji.201848009
117. Tintelnot J, Xu Y, Lesker TR, Schönlein M, Konczalla L, Giannou AD, et al. Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. Nature. (2023) 615:168–74. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05728-y
118. Zhu C, Wang Y, Zhu R, Wang S, Xue J, Zhang D, et al. Gut microbiota and metabolites signatures of clinical response in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 based immunotherapy of biliary tract cancer. biomark Res. (2024) 12:56. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00607-8
119. Simpson RC, Shanahan ER, Scolyer RA, and Long GV. Towards modulating the gut microbiota to enhance the efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:697–715. doi: 10.1038/s41571-023-00803-9
120. Wang Y, Dong A, Man J, Chen H, Shen W, Wang L, et al. TREM2 scFv-Engineering Escherichia coli Displaying Modulation of Macrophages to Boost Cancer Radio-Immunotherapy. Adv Mater. (2025) 37:e2417920. doi: 10.1002/adma.202417920
121. Musyuni P, Bai J, Sheikh A, Vasanthan KS, Jain GK, Abourehab MAS, et al. Precision medicine: Ray of hope in overcoming cancer multidrug resistance. Drug resistance updates: Rev commentaries antimicrobial Anticancer chemotherapy. (2022) 65:100889. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100889
122. Li R, Liu X, Huang X, Zhang D, Chen Z, Zhang J, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis deciphers heterogenous cancer stem-like cells in colorectal cancer and their organ-specific metastasis. Gut. (2024) 73:470–84. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330243
123. Pan Y, Lu F, Fei Q, Yu X, Xiong P, Yu X, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals compartmental remodeling of tumor-infiltrating immune cells induced by anti-CD47 targeting in pancreatic cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2019) 12:124. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0822-6
124. Melnekoff DT and Laganà A. Single-cell sequencing technologies in precision oncology. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2022) 1361:269–82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-91836-1_15
125. Li X, Li M, Huang M, Lin Q, Fang Q, Liu J, et al. The multi-molecular mechanisms of tumor-targeted drug resistance in precision medicine. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2022) 150:113064. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113064
126. Pessoa LS, Heringer M, and Ferrer VP. ctDNA as a cancer biomarker: A broad overview. Crit Rev oncology/hematology. (2020) 155:103109. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103109
127. Fan S-B, Xie X-F, Wei W, and Hua T. Senescence-related lncRNAs: pioneering indicators for ovarian cancer outcomes. Phenomics. (2024) 4:379–93. doi: 10.1007/s43657-024-00163-z
128. Kuboki Y, Fakih M, Strickler J, Yaeger R, Masuishi T, Kim EJ, et al. Sotorasib with panitumumab in chemotherapy-refractory KRAS(G12C)-mutated colorectal cancer: a phase 1b trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:265–70. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02717-6
129. Patil Y, Sadhukha T, Ma L, and Panyam J. Nanoparticle-mediated simultaneous and targeted delivery of paclitaxel and tariquidar overcomes tumor drug resistance. J Control Release. (2009) 136:21–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.01.021
130. Chavanpatil MD, Patil Y, and Panyam J. Susceptibility of nanoparticle-encapsulated paclitaxel to P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux. Int J pharmaceutics. (2006) 320:150–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.03.045
131. Fulda S. Promises and challenges of smac mimetics as cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer research: an Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2015) 21:5030–6. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0365
132. Rojas-Cessa MA. Recent plant-synthesized gold nanoparticle advancements for gastric cancer therapy. Nano TransMed. (2024) 3:100050. doi: 10.1016/j.ntm.2024.100050
133. Huang CY, Chung CL, Hu TH, Chen JJ, Liu PF, and Chen CL. Recent progress in TGF-β inhibitors for cancer therapy. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2021) 134:111046. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111046
134. Herbertz S, Sawyer JS, Stauber AJ, Gueorguieva I, Driscoll KE, Estrem ST, et al. Clinical development of galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate), a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway. Drug design Dev Ther. (2015) 9:4479–99. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S86621
135. Park YL, Ha SY, Park SY, Choi JH, Jung MW, Myung DS, et al. Reversine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via upregulation of the Fas and DR5 signaling pathways in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. (2019) 54:1875–83. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4746
136. Piccoli M, Ghiroldi A, Monasky MM, Cirillo F, Ciconte G, Pappone C, et al. Reversine: A synthetic purine with a dual activity as a cell dedifferentiating agent and a selective anticancer drug. Curr medicinal Chem. (2020) 27:3448–62. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190103120725
137. Ramaiah MJ, Tangutur AD, and Manyam RR. Epigenetic modulation and understanding of HDAC inhibitors in cancer therapy. Life Sci. (2021) 277:119504. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119504
138. Onorati AV, Dyczynski M, Ojha R, and Amaravadi RK. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Cancer. (2018) 124:3307–18. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31335
139. Wang DS, Liu ZX, Lu YX, Bao H, Wu X, Zeng ZL, et al. Liquid biopsies to track trastuzumab resistance in metastatic HER2-positive gastric cancer. Gut. (2019) 68:1152–61. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316522
140. Ou SI, Jänne PA, Leal TA, Rybkin II, Sabari JK, Barve MA, et al. First-in-human phase I/IB dose-finding study of adagrasib (MRTX849) in patients with advanced KRAS(G12C) solid tumors (KRYSTAL-1). J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2530–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02752
141. Takiuchi H, Goto M, Imamura H, Furukawa H, Imano M, Imamoto H, et al. Multi-center phase II study for combination therapy with paclitaxel/doxifluridine to treat advanced/recurrent gastric cancer showing resistance to S-1 (OGSG 0302). Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2008) 38:176–81. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyn003
142. Kopetz S, Grothey A, Yaeger R, Van Cutsem E, Desai J, Yoshino T, et al. Encorafenib, binimetinib, and cetuximab in BRAF V600E-mutated colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:1632–43. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908075
143. Van Cutsem E, Huijberts S, Grothey A, Yaeger R, Cuyle PJ, Elez E, et al. Binimetinib, encorafenib, and cetuximab triplet therapy for patients with BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: safety lead-in results from the phase III BEACON colorectal cancer study. J Clin Oncol. (2019) 37:1460–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.02459
144. Hoang DT, Dinstag G, Shulman ED, Hermida LC, Ben-Zvi DS, Elis E, et al. A deep-learning framework to predict cancer treatment response from histopathology images through imputed transcriptomics. Nat Cancer. (2024) 5:1305–17. doi: 10.1038/s43018-024-00793-2
145. Chen RJ, Lu MY, Williamson DFK, Chen TY, Lipkova J, Noor Z, et al. Pan-cancer integrative histology-genomic analysis via multimodal deep learning. Cancer Cell. (2022) 40:865–878.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.07.004
146. Chu G, Ji X, Wang Y, and Niu H. Integrated multiomics analysis and machine learning refine molecular subtypes and prognosis for muscle-invasive urothelial cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2023) 33:110–26. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.06.001
Keywords: cancer, drug resistance, tumor microenvironment (TME), molecular mechanisms, artificial intelligence (AI), precision oncology, drug sensitivity profiling, therapeutic strategies
Citation: Xu H, Lu J, Wu J, Zhang K, Zhou X, Gao Z, Feng J, Zhuang Z and Zhong X (2025) Integrated molecular and microenvironmental drivers of drug resistance in gastrointestinal cancers: mechanisms, immunotherapy challenges, and precision strategies. Front. Oncol. 15:1675745. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1675745
Received: 29 July 2025; Accepted: 14 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Zhiwen Luo, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yong Zhang, Zhengzhou University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Xu, Lu, Wu, Zhang, Zhou, Gao, Feng, Zhuang and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiaan Lu, THVqaWFhbjEzMDEzMEAxNjMuY29t; Xiaolin Zhong, eGlhb2xpbnpob25nQHN3bXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Heng Xu
Heng Xu Jiaan Lu
Jiaan Lu Jiangying Wu
Jiangying Wu Kangling Zhang1
Kangling Zhang1 Xuancheng Zhou
Xuancheng Zhou Ziye Zhuang
Ziye Zhuang Xiaolin Zhong
Xiaolin Zhong